Page 1

Contents
General guide .................................................. E - 2
Power supply ......................................................................... E - 2
The keyboard ......................................................................... E - 2
Display symbols .................................................................... E - 3
Display formats ..................................................................... E - 3
Order of operations................................................................ E - 4
Correction .............................................................................. E - 5
Accuracy and Capacity.......................................................... E - 5
Overflow / Error conditions.................................................... E - 7
Basic calculation ............................................. E - 8
Mixed arithmetic calculation ................................................. E - 8
Parentheses calculations ...................................................... E - 8
Constant calculation .............................................................. E - 8
Percentage calculation .......................................................... E - 9
Memory calculation ............................................................... E - 9
Scientific calculation ..................................... E - 10
Reciprocal, Factorial ........................................................... E - 10
Square, Square / Cubic Root, Power, Root ........................ E - 10
Logarithms and Antilogarithms ........................................... E - 10
Fraction calculation ............................................................. E - 10
Angular units conversion..................................................... E - 11
Trigonometric / Inverse trigonometric functions ................. E - 11
Hyperbolic / Inverse hyperbolic functions ........................... E - 12
Rectangular / Polar coordinates.......................................... E - 12
Permutations, Combinations ..............................................E - 12
Sexagesimal ↔ Decimal form conversion ......................... E - 13
Base-n mode calculation ....................................................E - 13
Complex numbers calculation ............................................E - 14
Random numbers and Exchange key................................. E - 14
Unit conversion.................................................................... E - 15
Statistics calculation ..................................... E - 15
Computing single variable statistics ................................... E - 15
Viewing statistics data ........................................................ E - 16
Adding a data entry ............................................................. E - 17
Editing statistics data .......................................................... E - 17
Delete error .......................................................................... E - 18
Weighted data entry method............................................... E - 18
E-1
Page 2

General guide
Power supply
On or Off :
T o turn the calculator on, press [ON/C]; to turn the calculator off, press
[2ndF] [OFF].
Auto power-off function :
This calculator automatically turns off it when not operated for
a pproximately 9 minutes. Power ca n be restored by pressing the [ON/C]
key again. Memory contents and the previous mode setting (ST A T, DEG,
CPLX, Base-n,…) are retained even when power is turned off or auto
power-off.
Battery replacement :
The calculator uses two alkaline button batteries GP76A(LR44) for
power. If the display becomes dim and difficult to read, the batteries should
be replaced as soon as possible.
T o re place batteries :
1) Remove the screws that hold the back cover.
2) Remove the back cover.
3) Replace the old batteries and install new ones with polarity in correct
directions.
4) Secure the screws in place, then press [ON/C] to turn the power on.
The keyboard
Many of the calculator’s keys are used to perform more than one function.
The functions marked on the keyboard are printed differently to help you find
the one you need quickly and easily.
–1
2nd functions
1st functions
1st functions
Those are the functions that are normally executed when you press the key.
2nd functions
The second function is printed above or to the right of the key . T o execute
2nd functions key, please press [ 2ndF ] then the corresponding key. When
you press [ 2ndF ], the “ 2ndF ” indicator shown in the display is to tell you
that you will be selecting the second function of the next key you press. If you
press [ 2ndF ] by mistake, simply press [ 2ndF ] again to remove the “ 2ndF
” indicator.
sin
sin
E-2
Page 3

(Note) : [ A ], [ B ], [ C ], [ D ], [ E ], [ F ] are 1st functions in HEX mode.
Display symbols
Indicators shown on the display is to indicate you the current status
of the calculator.
DEG or RAD or GRAD : angular unit
M : Independent memory CPLX :Complex number mode
E : Overflow / Error ST A T : Statistical mode
– : minus 2ndF : [2ndF] key pressed
( ) : Parenthesis calculation CP : Precision capability
BIN : Binary mode CPK : Process capability
OCT : Octal mode : Deviation
HEX : Hexadecimal mode USL : Setting upper limit
ED : Edit mode LSL : Setting lower limit
HYP : Hyperbolic mode
Display formats
The calculator can display numbers in four formats : floating point, fixed
point, scientific, and engineering.
Floating point display format
The floating point format displays numbers in decimal form, using up
to 10 digits. Any trailing zeros are truncated.
If the result of a calculation is too large to be represented in 10 digits,
the display automatically switches to scientific format. If the result of later
calculations is small enough to be displayed in 10 digits, the calculator
returns to floating point format.
(Ex.) : Set the display in floating display format.
Step : Press [ 2ndF ] [ TAB ] [ • ]
Fixed point display format
The fixed point, scientific, and engineering formats use a fixed number
of decimal places to display numbers. If more than the selected number of
decimal places is keyed, it will be rounded to the correct number of decimal
places.
DEG
0.
(Ex.) : Fix the display at 2 decimal places, then key in 3.256
Step 1 : press [ 2ndF ] [ TAB ] 2
Step 2 : key in 3.256 [ = ]
DEG
DEG
E-3
0.00
3.26
Page 4

On the contrary, if fewer than the selected number of decimal places
is keyed, it will be padded with trailing zero.
(Ex.) : Fix the display at 4 decimal places, then key in 4.23
Step 1 : press [ 2ndF ] [ TAB ] 4
Step 2 : key in 4.23 [ = ]
DEG
DEG
0.0000
4.2300
Scientific display format
In Scientific display format, the number 891500 can be shown in scientific
format as 8.915 x 10 05, where 8.915 is called the mantissa and 5 is as the
exponent of 10.
(Ex.) : 7132 x 125 is displayed in scientific display format.
Step 1 : key in 7132 [ x ] 125 [ = ]
Step 2 : press [ F↔E ]
DEG
DEG
891500.
8.915
05
(in floating point format)
Besides, entry can be made in scientific notation by using the [EXP]
key after entering the mantissa.
(Ex.) : Key the number 4.82296 x 10
Step : key in 4.82296 [ EXP ] 5
5
DEG
4.82296
05
(in floating point format)
Engineering display format
The format is similar to the scientific format, expect the mantissa can
have up to three digits left of the decimal, instead of only one, and the
exponent is always a multiple of three. It is useful for engineers to convert
units based on multiples of 10 3.
(Ex.) : Convert 15V into 15000mV (V : Volt)
Step 1 : key in 15
Step 2 : press [ ENG ] twice
DEG
DEG
15.
15000.
– 03
(Ex.) : Convert 15V into 0. 015KV (V : Volt)
Step 1 : key in 15
Step 2 : press [ 2ndF ] [ ] twice
DEG
DEG
15.
0.015
03
Order of operations
Each calculation is performed in the following order of precedence :
1) Operation in parenthesis
2) Functions required pressing the function key before entering, for
exa mple, [ DA T A ] in ST A T mode a nd [ EXP ] key .
3) Functions required inputing values before pressing the function key,
for example, cos, sin, tan, cos–1, sin–1, tan–1, log, ln, X 2, 1/x, , ,
, X!, %, RND, ENG,
4) Fractions
, ,,,, ,,
, and 6 units conversion.
E-4
Page 5
5) +/–
6) X y,
y
X
7) nPr, nCr
8) x , ÷
9) +, –
Correction
If you have made a mistake when entering a number (but you have not yet
pressed an arithmetic operator key), just press [ CE ] to clear the last entry
then input it again, or delete individual digits by using the backspace key
[ 00
by pressing [ON/C] to clear the calculation completely (expect clearing
memory, see page 9).
0 ]
(Ex.) : Correct 12385 as 789
Step : press [ CE ] 789
DEG
789.
(Ex.) : Correct 12385 as 123
Step : press [ 00
0 ] twice
DEG
123.
In a series of calculations, you can correct errors in immediate results
If you press the wrong arithmetic operation key, just press [ CE ] key
before entering anything else.
Accuracy and Capacity
Accuracy : 1 in 10th digit.
Capacity :
In general, every reasonable calculation is displayed up to 10 digit
mantissa, or 10-digit mantissa plus 2-digit exponent up to 10 99or integers
between – 9999999999 and 9999999999.
Numbers used as input must be within the range of the given
function. The range for each of the calculator’s functions is given in the
following pages.
Functions Input range
sin x, cos x, tan x Deg X 4.5 x 1010deg
Rad X 2.5 x 10 8rad
Grad X 5 x 10 10grad
however, for tan x
Deg X 90 (2n+1)
Rad X (2n+1)
π
2
Grad X 100 (2n+1)
(n is an integer)
E-5
Page 6
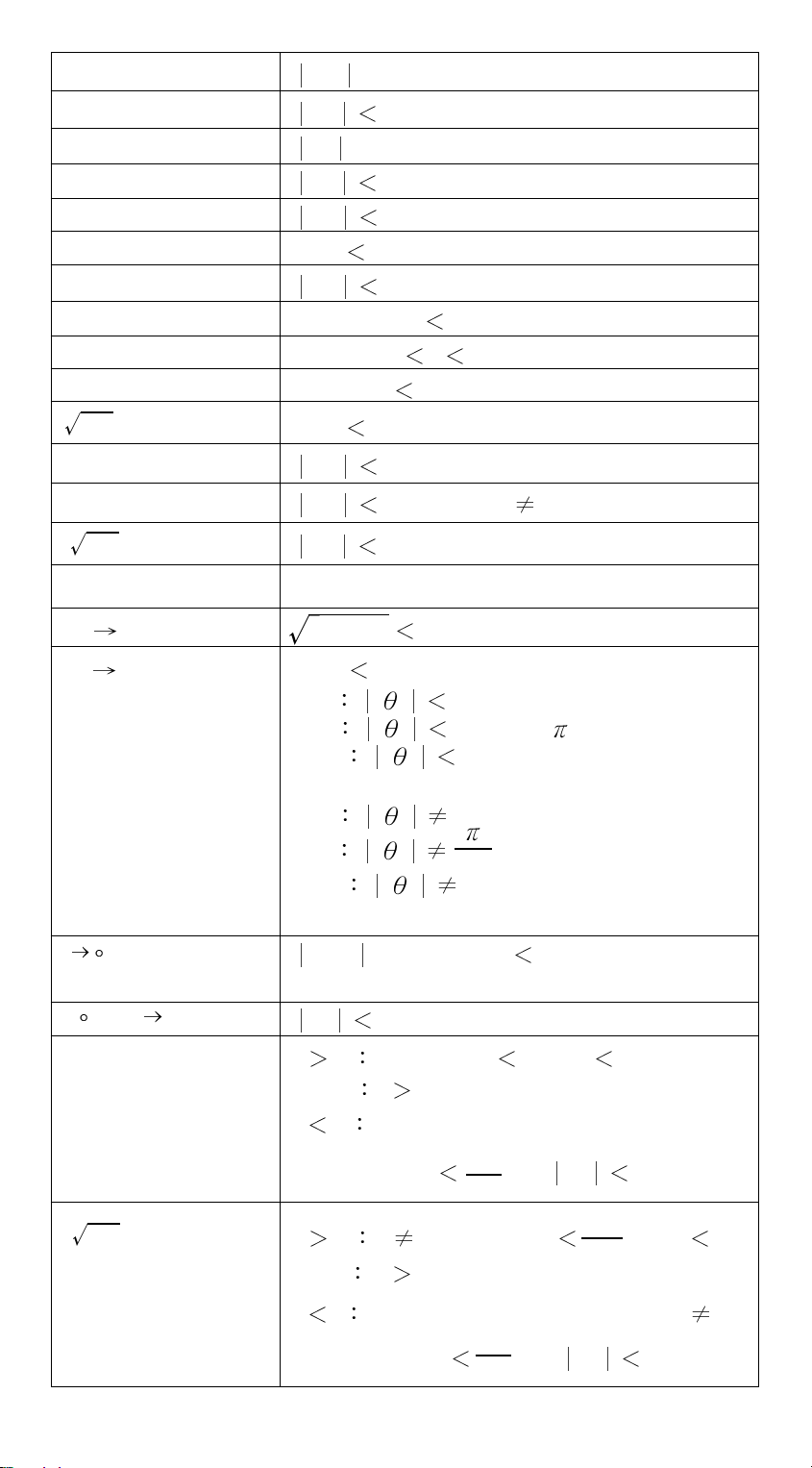
sin –1 x, cos –1 x X ≤ 1
tan–1 x X 1 x 10
100
sinh x, cosh x X ≤ 230.2585092
tanh x X 1 x 10
sinh–1 x X 5 x 10
cosh–1 x1 ≤ X 5 x 10
100
99
99
tanh–1 x x 1
log x, ln x 1 x 10
x
10
e
x
x
X
2
–1 x 10
–1 x 10
0 ≤ X 1 x 10
–99
≤ X 1 x 10
100
X 100
100
X≤ 230.2585092
X 1 x 10
1 / X X 1 x 10
3
X
X 1 x 10
100
50
100
100
100
, X 0
X ! 0 ≤ X ≤ 69 , X is an integer.
R P 1 x 10
X2 +Y
P R0≤ r 1 x 10
2
100
Deg 4.5 x 10 10deg
Rad 2.5 x 10 8rad
Grad 5 x 10 10grad
however, for tan x
Deg 90 (2n+1)
Rad (2n+1)
2
Grad 100 (2n+1)
(n is an integer)
, ,,
DD , MM, SS.SS 1 x 10
0 ≤ MM, SS.SS
, ,,
y
X
x 1 x 10
X 0 –1 x 10
100
100
X = 0 y 0
X 0 y = n , 1/(2n+1), n is an integer .
but -1 x 10
100
1
log X 100
100
y log X 100
y
100
,
y
X
X 0 y 0, –1 x 10
100
1
log X 100
y
X = 0 y 0
X 0 y = 2n+1, I/n, n is an integer.(n 0)
but – 1 x 10
100
1
log X 100
y
E-6
Page 7

ab/c
denominator must be within 10 digits
(includes division marks)
Result Result displayed as fraction for
integer when integer, numerator and
Input T otal of integer , numerator and
denominator are less than 1 x 10
10
nPr, nCr 0 r n, n 9999999999, n,r are integers.
STAT x 1x10
0 ≤ x
2
50
1 x 10
x 1 x 10
100
, n, r are integer
100
_
n 0 S n 1 n 0
x
Range = 1 ~ r, 1 ≤ n ≤ r, 80 ≤ r ≤ 20400
DEC 0 ≤ X ≤ 9999999999 (for zero or positive )
– 9999999999
≤ X ≤ – 1 (for negative)
BIN 0 ≤ X ≤ 01 1 1 1 1 11 11 (for zero, positive)
1000000000 ≤ X≤ 1111111111
(for negative)
OCT 0 ≤ X ≤ 3777777777 (for zero or positive)
4000000000 ≤ X ≤ 7777777777
(for negative)
HEX 0≤ X≤ 2540BE3FF( for zero or positive)
FDABF41C01 ≤ X ≤ FFFFFFFFFF
(for negative)
Overflow / Error conditions
A symbol “ E ” are indicated on the display when any of the following
conditions occur and further calculation becomes impossible. Just press
[ ON/C ] to release those overflow or error indicator and the subsequent
calculation can then be performed.
1) When function calculations are performed with a number exceeding
the input range.
2) When a number is divided by 0.
3) When the [ ( ] key is used more than 15 times in a single expression.
4) When a result (whether intermediate or final) or accumulated total in
memory exceeds the limit. ( 9.999999999 x 10 99)
5) When more than six pending operations.
Basic calculation
Before performing the following calculation, check to see that your
calculator is in decimal base and floating point display.
E-7
Page 8

Mixed arithmetic calculation
1 + 2 x 3 = ? 1 [ + ] 2 [ x ] 3 [ = ]
– 3.5 + 8 ÷ 2 = ? 3.5 [ +/– ] [ + ] 8 [ ÷ ] 2 [ = ]
DEG
DEG
7.
0.5
Parentheses calculations
Operation inside parentheses are always executed first. Y ou can use up
to 15 levels of parentheses in a single calculation. When the first parenthesis
is opened, the “ ( ) ” indicator appears and remains in the display until the
last parenthesis is closed.
( 5 – 2 x 1.5 ) x 3 [ ( ] 5 [ – ] 2 [ x ] 1.5 [ ) ] [ x ]
DEG
2.8
+ 0.8 x ( – 4 ) = ? 3 [ + ] 0.8 [ x ] 4 [ +/– ] [ = ]
2 x { 7 + 6 x ( 5 + 4 ) } 2 [ x ] [ ( ] 7 [ + ] 6 [ x ]
DEG
122.
= ? [ ( ] 5 [ + ] 4 [ = ]
(Note) : It is unnecessary to press the [ ) ] key before the [ = ] key.
Constant calculation
The calculator enables you to repeat the last number entered or the
last operation executed by pressing [ = ] key.
Repeating the last number
3 x 3 = ? 3 [ x ] [ = ]
3 x 3 x 3 = ? [ = ]
3 x 3 x 3 x 3 = ? [ = ]
Repeating the arithmetic operation
321 + 357 = ? 321 [ + ] 357 [ = ]
654 + 357 = ? 654 [ = ]
579 – 159 = ? 579 [ – ] 159 [ = ]
456 – 159 = ? 456 [ = ]
18 x 45 = ? 3 [ x ] 6 [ x ] 45 [ = ]
18 x 23 = ? 23 [ = ]
18 x (0.5 x 10 2) = ? 0.5 [ EXP ] 2 [ = ]
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
9.
27.
81.
678.
101 1.
420.
297.
810.
414.
900.
E-8
Page 9

96 ÷ 8 = ? 96 [ ÷ ] 8 [ = ]
75 ÷ 8 = ? 75 [ = ]
(1.2 x 10 2) ÷ 8 = ? 1.2 [ EXP ] 2 [ = ]
Percentage calculation
DEG
DEG
DEG
12.
9.375
15.
30% of 120 = ? 120 [ x ] 30 [ 2ndF ] [ % ]
DEG
[ = ]
70% of 120 = ? 70 [ 2ndF ] [ % ] [ = ]
88 is 55% of 88 [ ÷ ] 55 [ 2ndF ] [ % ]
DEG
DEG
what number = ? [ = ]
30% add-on of 120 120 [ + ] 30 [ 2ndF ] [ % ]
DEG
= ? [ = ]
30% discount of 120 120 [ – ] 30 [ 2ndF ] [ % ]
DEG
= ? [ = ]
Memory calculation
Y ou should keep the f ollowing rules in mind when performing memory
calculations.
1) The “ M ” indicator appears when a number is stored in the memory.
2) Recalling from a memory by pressing [ MR ] key does not affect its
contents .
3) All memories are unavaila ble under STA T mode.
4) In order to exchange the content of the memory for the
displayed number, please press [X M] key.
5) The contents of the memories can be cleared by pressing [ 0 ]
[X M] or [ CE ] [X M] in sequence.
36.
84.
160.
156.
84.
[ CE ] [X M]
3 x 5 3 [ x ] 5 [ M+ ] M
+) 56 ÷ 7 56 [ ÷ ] 7 [ M+ ] M
+) 74 – 8 x 7 74 [ – ] 8 [ x ] 7 [ M+ ] M
Total = ? [ MR ] M
0 [X M]
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
Scientific calculation
Before performing the following calculation, check to see that your
calculator is fixed at 2 decimal places display format.
E-9
0.
15.
8.
18.
41.
0.
Page 10

Reciprocal, Factorial
1
= ? 1.25 [ 2ndF ] [1/X] [ = ]
1.25
5! = ?
5 [ 2ndF ] [ X! ] [ = ]
DEG
DEG
120.00
Square, Square / Cubic Root, Power, Root
22+ 3 4= ? 2 [ X 2] [ + ] 3 [ X y] 4 [ = ]
3
5 x + 5 [ x ] 27 [ 2ndF ] [
27
34
3
]
= ? [ + ] 34 [ ] [ = ]
9
= ? 72 [ 2ndF ] [ ] 9 [ = ]
72
y
X
DEG
DEG
DEG
85.00
20.83
Logarithms and Antilogarithms
ln7 + log100 = ? 7 [ ln ] [ + ] 100 [ log ] [ = ]
102= ? 2 [ 2ndF ] [ 10 x] [ = ]
e5– e
– 2
= ? 5 [ 2ndF ] [ e x] [ – ]
2 [ +/– ] [ 2ndF ] [ e x] [ = ]
DEG
DEG
DEG
100.00
148.28
Fraction calculation
0.80
1.61
3.95
Fraction value display is as follow :
5 12 Display of
56 5 12 Display of 56
5
12
5
12
(Note) : Total of integer, numerator a nd denominator must be within 10
digits, or the fractional value couldn’t be shown completely.
By pressing [ 2ndF ] [d/e ], the displayed value will be converted to the
improper fraction.
2
+ 7 2 [a b/c ] 3 [ + ]
3
4
= 8 7 [a b/c ] 3 [a b/c ] 5 [ = ]
3
5
DEG
8 4 15
15
124
= [ 2ndF ] [d/e ]
15
DEG
124 15
When a press of [a b/c ] key after the [ = ] key or a fraction performed
with a decimal, the a n swer is display ed a s a decimal.
4
5 + 3 5 [a b/c ] 4 [a b/c ] 9
9
7
= 9 [+] 3 [a b/c ] 3 [a b/c ] 4 [ = ]
36
3
4
= 9.19 [a b/c ]
E-10
DEG
9 7 36
DEG
9.19
Page 11

4
8 + 3.75 8 [a b/c ] 4 [a b/c ] 9
9
DEG
12.19
= 12.19 [ + ] 3.75 [ = ]
During a fraction calculation, if the figure is reducible, a figure is
reduced to the lowest terms after pressing a function command key ([ + ],
[ – ], [ x ] or [ ÷ ]) or the [ = ] key.
119
3 = 8 3 [a b/c ] 1 19 [a b/c ] 21
21
2
3
DEG
8 2 3
[ = ]
If total of integer, numerator and denominator exceeds 10 digits
(including division marks), t he result answer will be displayed as a decimal.
12345 + 5 12345 [ a b/c ] 5 [a b/c ] 16
5
16
6
13
DEG
12350.77
= 12350.77 [+] 5 [a b/c ] 6 [a b/c ] 13 [=]
Angular units conversion
The calculator enables you to convert a angular unit among degrees
(DEG), radians(RAD ), a nd grad(GR AD).
The relatio n among the t hree angle uni ts is :
180 ° = rad = 200 gra d
1) T o change the default setting to another setting, press [ DRG ] key
repeatedly until the angular unit you want is indicated in the display.
2) After entering an angle, press [ 2ndF ] [ DRG ] repeatedly until the
converted value is displayed.
90 °(deg) 90
= ? (rad) [ 2ndF ] [ DRG ]
= ? (grad) [ 2ndF ] [ DRG ]
DEG
RAD
GRAD
1.57
100.00
T rigonometric / Inverse trigonometric functio ns
When using those key, make sure the calculator is set for the angular
unit you want.
3 sin 85 ° = ? 3 [ x ] 85 [ sin ] [ = ]
cos ( rad) = ?
4
[ 2ndF ] [ ] [ ÷ ] 4 [ = ]
[ cos ]
tan 150grad = ? 150 [ ta n ]
sin–10.5 = ? deg 0.5 [ 2ndF ] [ si n
–1
E-11
]
DEG
RAD
GRAD
DEG
2.99
0.71
–1.00
30.00
90
Page 12

cos–1( ) = ? rad
1
2
2 [ ] [ 2ndF ] [ 1/X ]
[ 2ndF ] [ cos
– 1
tan–1 1 = ? grad 1 [ 2ndF ] [ tan –1]
]
RAD
GRAD
50.00
Hyperbolic / Inverse hyperbolic functions
0.79
cosh1.5+sinh1.5 = 1.5 [ HYP ] [ cos ] [ + ]
DEG
1.5 [ HYP ] [ sin ] [ = ]
sinh–17 = 7 [ HYP ] [ 2ndF ] [ sin –1]
tanh 1 = 1 [ HYP ] [ tan ]
DEG
DEG
Rectangular / Polar coordinates
Rectangular Coordinates Polar Coordinates
Y
• P( x, y )
y
0
x
X
a + b i= r (cos + i sin )
(Note) :When using those key, make sure the calculator is set for the
angular unit you want.
Y
• P( r, )
r
0
X
4.48
2.64
0.76
Converting from Rectangular to Polar
If a = 5 and b = 6 5 [ a ] 6 [ b ]
, what are r and ? [ 2ndF ] [ R P]
[ b ]
Converting from Polar to Rectangular
If r = 25 and = 56° 25 [ a ] 56 [ b ]
, what are a and b? [ 2ndF ] [ P R]
[ b ]
Permutations, Combinations
nPr = nCr =
n !
(n – r) !
How many 7 [ 2ndF ] [ nPr ] 4 [ = ]
permutations of 4
items can you select
out of a set of
numbers of 7 items?
n !
r ! (n – r) !
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
7.81
50.19
13.98
20.73
840.00
E-12
Page 13

How many 7 [ 2ndF ] [ nCr ] 4 [ = ]
combinations of 4
items can you select
out of a set of
numbers of 7 items?
DEG
35.00
Sexagesimal
The calculator enables you to converts the sexagesimal figure
(degree, minute and second) to decimal notation by pressing [
and converts the de cimal notation to the sexagesimal not ation by [2ndF]
, ,,
[
Sexagesim al figure val ue display is as follow :
12 45 30 5
(Note) :The total of DD, MM and SS.SS must be within 8 dig its, or
Converting from Sexagesimal to Decimal
12 deg., 45 min., 12 [
30.5 sec.=? 30.5 [
Converting from Decimal to Sexagesimal
2.12345 = ? 2.12345 [ 2ndF ] [
].
the sexagesimal couldn’t be shown complet ely.
↔↔
↔ Decimal form conversion
↔↔
, ,,
Represent 12 degrees,
45 minutes, 30.27 seconds
, ,,
, ,,
] 45 [
]
, ,,
, ,,
DEG
]
]27 24 42
12.76
]
Base-n mode calculation
Converting between bases
The unit enables you to calculate in number base other than decimal.
The calculator can add, subtract, multiply, and divide binary, octal, and
hexadecimal numbers. Select the number base you want by the [ BIN],
[ OCT], [ HEX], [ DEC] keys. The BIN, OCT, and HEX indicators
show you which base you are using.(if none of the indicators appears in the
appear in the display, you are in decimal base.)
The keys active in each base is described as follows :
Binary base : [ 0 ] [ 1 ]
Octal base : [ 0 ] ~ [ 7 ]
Decimal base : [ 0 ] ~ [ 9 ]
Hexadecimal base : [ 0 ] ~ [ 9 ], [ A ] ~ [ F ]
31 (base 10) [ 2ndF ] [ DEC ] 31
= ? (base 2) [ 2ndF ] [ BIN ]
= ? (base 8) [ 2ndF ] [ OCT ]
= ? (base 16) [ 2ndF ] [ HEX ]
DEG
DEG BIN
DEG O CT
DEG HEX
31.
11111.
37.
1F.
E-13
Page 14

4 X 1B (base 16) [ 2ndF ] [ HEX ]
DEG HEX
6C.
4 [ x ] 1B [ = ]
= ? (base 2) [ 2ndF ] [ BIN ]
= ? (base 10) [ 2ndF ] [ DEC ]
= ? (base 8) [ 2ndF ] [ OCT ]
DEG BIN
DEG
DEG O CT
1 101 100.
108.00
154.
Negative and Complements
In binary, octal, and hexadecimal bases, the calculator represents
negative numbers using complement notation. The complement is the
result of subtracting that number from 10000000000 in that number’s
base by pressing [ +/– ] key in non-decimal bases.
Calculate the [ 2ndF ] [ BIN ] 1101 1
DEG BIN
complement of binary [ +/– ] 1 1 1 1 100101.
number 11011
Complex numbers calculation
Select the complex numbers mode by pressing [ CPLX ] key and
make sure “ CPLX ” indicator appears on the display. The calculator
enables you to add, subtract, multiply, and divide complex numbers.
Complex numbers are generally represented as a + b i, where a is a
real and b is imaginary.
[ 2ndF ] [ CPLX ]
DEG CPLX
( 7– 9 i ) 7 [ a ] 9 [ +/– ] [ b ] 22.00
+ (15 + 10 i) = ? [ + ] 15 [ a ] 10 [ b ] [ = ]
[ b ]
DEG CPLX
1.00
(Note) : Memory calculation is available in complex number mode.
Random numbers and Exchange key
Random key
Pressing [ RND ] key enables the display to generate random
numbers between 0.000 and 0.999.
Step : press [ 2ndF ] [ RND ]
Exchange key
Pressing [ 2ndF ] [ X↔ Y ] enables the displayed value to exchange
as the previous value.
123 + 456 = ? 123 [ + ] 456 [ = ]
[ 2ndF ] [ X↔Y ]
[ 2ndF ] [ X↔Y ]
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
0.231
579.00
456.00
579.00
E-14
Page 15

Unit conversion
↔↔
in
↔cm
↔↔
12 in = ? cm 12 [ A B ] [ 2ndF ]
DEG
[ in↔cm ]
98 cm = ? in 98 [ 2ndF ] [ A B ]
DEG
[ 2ndF ] [ in↔cm ]
(Note) : The operating procedure for unit conversion key, [ ↔ ],
[ mmHg↔Kpa ], [ gal↔l ], [ lb↔kg ], [ OZ↔g ], is similar to the
above example.
Statistics calculation
Computing single variable statistics
Select the mode by pressing [ STAT ] key and make sure “ STAT ”
indictor appears on the display.
The ST A T mode enables you to calculate the f ollowing single variable
statistics :
30.48
38.58
n number of all data
x sum of all data
2
x
sum of the squares
_
x
s Sample Standard deviation
mean value
x2– x)2/ n
n – 1
x2– x)2/ n
Population standard deviation
n
USL – LSL
CP Precision capability
6
CPK Process capability Min(CPU, CPL)
where CPU = CPL =
USL –
x
3
– LSLx
3
(Note) : In ST AT mode, all function key are available, except base-n
calculation.
_
(Ex. 1) : Enter the following data to calculate x, x2, n,
, S, CP,
x
and CPK , where data 1 = 2, data 2~5 = 5, data 6-8 = 9, USL
value : 12, LSL value : 2
In ST AT mode [ 2ndF ] [ STAT ]
Enter all data [ DATA ] 2
[ DA TA ] 5
E-15
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
0.00
2.
5.
Page 16

[ DA TA ] 5
[ DA TA ] 5
[ DA TA ] 5
[ DA TA ] 9
[ DA TA ] 9
[ DA TA ] 9
[ = ]
_
= ? [
x
_
]
x
n = ? [ n ]
S = ? [ S ]
x = ? [ 2ndF] [ x ]
x2= ? [ 2ndF ] [ x2]
= ? [ 2ndF ] [ ]
CP = ? [ 2ndF ] [ CP ] 12
[ = ] 2
[ = ]
CPK = ? [ 2ndF ] [ CPK ]
[ = ]
[ = ]
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
5.
5.
5.
9.
9.
9.
0.00
6.13
8.00
2.59
49.00
347.00
2.42
12.
2.
0.69
12.00
2.00
0.57
CP
USL
CP
LSL
CP
CPK
USL
CPK
LSL
CPK
(Note) : The calculator keeps a record of all the entries you make and
these entries are retained even if auto power-off or turning off,
unless exiting ST A T mode.
Viewing statistics data
Pressing [ DAT A ] or [ = ] key under ED mode can view the statistics data
you have entered. The difference between [ DA T A ] a nd [ = ] is the item of
the data entry a ppears 1.5 sec. before the value by [ DATA ], the value
appears immediately without the item by [ = ].
(Ex.2) : View the statistics data based on Ex. 1.
Step 0 : Press [ 2ndF ] [ EDIT ] to enter ED mode.
(Method 1) :
Step 1 : Press [ DA T A ] once to view the f irst data.
DEG ED STAT
1.5 sec.
dAtA 1 2.00
Step 2 : Continue pressing [ DATA ] once f or ea ch data, it
will display data 2, 5.00, data 3, 5.00, data 4,
5.00, data 5, 5.00, data 6, 9.00, data 7, 9.00, data 8,
9.00 in sequence.
DEG ED STAT
E-16
Page 17

(Method 2) :
Step 1 : Press [ = ] once to view the first data
Step 2 : Continue pressing [ = ] once for each data, it will
display 5.00, 5.00, 5.00, 5.00, 9.00, 9.00, 9.00 in
sequence.
Adding a data entry
(Ex.3) : Add data 9 = 10 to Ex.1
Step 1 : Press [ DATA ] 10
Step 2 : The calculator updates the statistics as you enter
data. You can then recall all varia ble statistics to
get the following result : = 6.56, n = 9.00, S = 2.
74, x = 59.00, x2= 447.00, = 2.59, where
data 1 = 2.00, data 2~5 = 5.00, data 6~8 = 9.00,
data 9 = 10.00
Editing statistics data
DEG ED STAT
DEG ED STAT
2.00
10.
x
(Ex.4) : Based on Ex.1, correct data 1 = 2 as data 1 = 3
Method 1 :
Press 2 [ 2ndF ] [ DEL ] 3 to overwrite.
Method 2 :
Step 1 : Press [ 2ndF ] [ EDIT ]
Step 2 : Find out 2 by [ DAT A ] or [ = ]
Step 3 : Enter 3 to overwrite 2
DEG ED STAT
DEG ED STAT
DEG ED STAT
Step 4 : Press [ = ] and [ 2ndF ] [ EDIT ] to exit ED mode,
where those data are changed as data 1 = 3.00,
data 2~5 = 5.00, data 6~8 = 9.00.
(Ex.5) : Based on Ex.1, delete data 1 = 2 .
Method 1 :
Press 2 [ 2ndF ] [ DEL ] to delete 2.
Method 2 :
Step 1 : Press [ 2ndF ] [ EDIT ]
Step 2 : Find out 2 by [ DAT A ] or [ = ]
Step 3 : Press [ 2ndF ] [ DEL ]
DEG ED STAT
DEG ED STAT
DEG ED STAT
0.00
2.00
3.
0.00
2.00
5.00
Step 4 : Press [ 2ndF ] [ EDIT ] to exit ED mode, where
those data are changed as data 1~4 = 5.00, data
5~7 = 9.00.
E-17
Page 18

Delete error
(Ex.6) : If you enter and delete a value that isn’t included in the stored
data by mistake, “dEL Error ” appears, but the previous data are still
retained, for example, delete 7 based on Ex.1.
Step 1 : Press 7 [ 2ndF ] [ DEL ]
Step 2 : Press any key to clear it
Step 3 : Enter ED mode, then view data by [ DATA ] or [ = ],
where those data are still data 1 = 2.00, data 2~5 = 5.
00, data 6~8 = 9.00.
(Ex.7) : Ba sed on Ex.1, enter 5 x 5 and delete it.
Step 1 : Press 5 [ x ] 5 [ 2ndF ] [ DEL ]
Step 2 : Press any key to clear it
Step 3 : Enter ED mode, then view data by [ DATA ] or [ = ],
where those data are changed as data 1 = 2.00, data
2~4 = 9.00.
DEG STAT
dEL Error
DEG STAT
DEG STAT
dEL Error
DEG STAT
0.00
0.00
Weighted data entry method
Instead of entering directly each data, when often several item of data
have the same value, you can enter the value and the number of occurrences up to 255. The data based on Ex.1 can be rewritten and entered as
follow :
V alue Number of occurrences Alternative method
21 [ DATA ] 2
5 4 [ DA TA ] 5 [ x ] 4
9 3 [ DA TA ] 9 [ x ] 3
, where data 1 = 2, data 2~5 = 5, data 6~8 = 9.
Under ED mode, when you continue choosing a value from data 2~5 and
correcting it as 33, the permutation among those data will be changed as
data 1 = 2, data 2~4 = 5, data 5 = 33, data 6~8 = 9, where the new value 33
is inserted after data 4 = 5.
(Note) : A “FULL” is indicated when any of the following conditions occur
and further data entry becomes impossible. Just pressing any
key can clear the indicator. The previous data entries are still
retained unless exiting ST A T mode.
1) If the times of data entry by [ DA T A ] is more tha n 80
2) The number of occurrences is more than 255
3) n 20400 (n = 20400 appears when the times of data entry by
[ DA TA ] are up to 80 a nd the number of occurrences for e a ch
value are all 255, i.e. 20400 = 80 x 255.)
E-18
 Loading...
Loading...