Page 1

Mini Trans-Blot®
Electrophoretic
Transfer Cell
Instruction Manual
Catalog numbers
170-3930
170-3935
170-3989
170-3836
Page 2

Page 3

Assembly and Disassembly
To insure best performance from the Mini Trans-Blot®
electrophoretic transfer cell, become fully acquainted
with these operating instructions before using the cell
to transfer samples. Bio-Rad recommends that you first
read these instructions carefully. Then assemble and
disassemble the cell completely. After these preliminary
steps, you should be ready to transfer a sample.
Wash Cell Before Use
Bio-Rad also recommends that all Mini Trans-Blot
electrophoretic transfer cell components and accessories
be cleaned with a suitable laboratory cleaner (such as
Bio-Rad Cleaning Concentrate, catalog #161-0722) and
rinsed thoroughly with distilled water before use.
Warranty
Bio-Rad Laboratories warrants the Mini Trans-Blot
electrophoretic transfer cell against defects in materials
and workmanship for 1 year. If any defects occur in
the instrument during this warranty period, Bio-Rad
Laboratories will repair or replace the defective parts free.
The following defects, however, are specifically excluded:
1. Defects caused by improper operation.
2. Repair or modification done by anyone other than
Bio-Rad Laboratories or an authorized agent.
3. Use of fittings or other spare parts supplied by anyone
other than Bio-Rad Laboratories.
4. Damage caused by accident or misuse.
5. Damage caused by disaster.
6. Corrosion due to use of improper solvent or sample.
For any inquiry or request for repair service, contact
Bio-Rad Laboratories after confirming the model and serial
number of your instrument.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell i
Page 4

Page 5

Table of Contents
Assembly and Disassembly .......................................... i
Wash Cell Before Use ................................................... i
Warranty ........................................................................ i
Section 1 Introduction .................................................. 1
1.1 Specifications ................................................. 3
1.2 Safety Instructions .......................................... 4
Section 2 Mini Trans-Blot Cell Assembly and
Preparation for Transfer ............................................... 5
2.1 Mini Trans-Blot Cell Description and
Assembly of Parts .......................................... 5
2.2 Preparation for Blotting .................................. 6
2.3 Acidic Transfers ............................................. 9
Section 3 Transfer Conditions ....................................10
3.1 General Guide to Transfer Buffers and
Running Conditions.......................................10
3.2 Notes on Electrophoretic Transfer
Conditions ....................................................11
3.3 Buffer Formulation ........................................13
Section 4 Strategies for Optimizing
Electrophoretic Transfer ............................................. 15
4.1 Optimizing Protein Transfer ...........................15
4.2 Optimizing DNA and RNA Transfer................ 18
Section 5 Choice of Blotting Membranes.................. 19
5.1 Protein Blotting ............................................ 19
5.2 DNA and RNA Blotting Membranes ............. 20
Section 6 Troubleshooting Guide .............................. 22
6.1 Electrophoretic Transfer ............................... 22
Section 7 References ................................................. 27
Section 8 Product Information .................................. 29
Page 6

Page 7

Section 1
Introduction
Blotting was first performed by Southern in 1975 with
the transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nitrocellulose
membranes.1 Since that time, blotting has been applied to
2-4
RNA
and proteins
gels. To circumvent the inefficiencies observed in
various capillary transfers, electric current has been
adopted for eluting proteins from polyacrylamide gels,
as first described by Towbin et al. in 1979.7 The use of
electrophoretic transfer has also been applied to DNA and
RNA blotting.
the topic of protein electrophoretic transfer techniques.
There have also been reviews summarizing the expanding
literature being generated on electrophoretic blotting
methodology.
The Mini Trans-Blot® tank is part of Bio-Rad’s modular
Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra system. The unique feature of this
electrophoresis system is that the electrode modules
are interchangeable. After finishing gel electrophoresis,
remove the electrode module from the buffer tank, insert
a new electrode module, add new buffer, and the next
electrophoresis application can be performed.
The Mini Trans-Blot module accommodates two cassettes
for electrophoretic transfer. The Mini Trans-Blot module is
useful for blotting either protein or nucleic acid from both
agarose and acrylamide gels. It is also capable of blotting
isoelectric focusing gels from horizontal electrophoresis
cells, or DNA and RNA gels from the Mini-Sub® submarine
electrophoresis cell. For applications where the gel is
larger than 7.5 x 10 cm, or when there are more than two
mini gels to be transferred, the larger standard Trans-Blot®
cell (catalog #170-3910 or 170-3946), Criterion™ Blotter
(catalog #170-4070, 170-4071) or the Trans-Blot® SD
semi-dry cell (catalog #170-3940) should be used.
The heart of the Mini Trans-Blot cell is its electrode
module. This module has the capacity to hold two gel
cassettes between parallel electrodes only 4 cm apart.
The driving force for blotting applications is the voltage
applied over the distance between the electrodes.
5, 6
in both agarose and polyacrylamide
8–14
Numerous publications have dealt with
27–29
15–26
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 1
Page 8

This short 4 cm electrode distance allows generation of
higher driving forces to produce efficient protein transfers.
A second feature of the electrode module is that it is
offset to accommodate a blue cooling unit. The cooling
unit, which is completely contained within the Mini
Trans-Blot cell, absorbs the Joule heat generated during
rapid electrophoretic transfers. The advantages of having
an internal cooling unit include elimination of an expensive
external cooling bath and avoidance of cumbersome
cooling tubing. Other features of the Mini Trans-Blot cell
include gel holder cassette latches for easy handling, color
coordinated cassettes and electrodes to insure proper
orientation of the gel during transfer, and an efficient
design which simplifies insertion and removal of the
cassettes from the electrode assembly. These features
result in an electrophoretic transfer system which is easy
to use and produces excellent blotting results.
2 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 9

1.1 Specifications
Construction
Electrode module Molded polysulfone
Gel holder cassettes Molded polycarbonate
Electrodes Platinum wire 0.254 mm
diameter
Buffer chamber and lid Molded polycarbonate
Cooling unit Polyethylene
Overall dimensions
Mini Trans-Blot cell 16 (L) x 12 (W) x 18 (H) cm
Gel holder dimensions 10 x 11 cm
Maximum gel size 7.5 x 10 cm
Buffer capacity
With cooling unit 950 ml
Without cooling unit 1,150 ml
Cleaning Use mild soap and warm
water to clean the electrodes,
cassettes, and buffer tank.
Use special care when
cleaning the electrode cards.
Avoid stretching or breaking
the platinum wires. Do not
use abrasives or strong
detergents. Rinse the fiber
pads under hot water and
then in distilled, deionized
water.
Chemical compatibility The Mini Trans-Blot cell
components are not
compatible with chlorinated
hydrocarbons (e.g.,
chloroform), aromatic
hydrocarbons (e.g., toluene,
benzene), or acetone. Use of
organic solvents voids all
warranties.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 3
Page 10
1.2 Safety Instructions
!
Power to the Mini Trans-Blot cell is supplied by
an external DC voltage power supply. This power
supply must be ground isolated in such a way that
the DC voltage output floats with respect to ground.
All of Bio-Rad’s power supplies meet this important
safety requirement. Regardless of which power
supply is used, the maximum specified operating
parameters for the cell are:
400 VDC Maximum voltage limit
500 W Maximum power limit
40°C Maximum ambient temperature limit
Current to the cell, provided from the external power
supply, enters the unit through the lid assembly,
providing a safety interlock to the user. Current to
the cell is broken when the lid is removed. Do not
attempt to circumvent this safety interlock, and
always turn the power supply off before removing
the lid, or when working with the cell in any way.
Important: This Bio-Rad instrument is designed and certified to
meet IEC61010-1 and EN61010-1* safety standards. Certified
products are safe to use when operated in accordance with the
instruction manual. This instrument should not be modified or
altered in any way. Alteration of this instrument will:
• Void the manufacturer’s warranty
• Void the IEC61010-1 and EN61010-1 safety certification
• Create a potential safety hazard
Bio-Rad is not responsible for any injury or damage caused by
the use of this instrument for purposes other than for which it is
intended or by modifications of the instrument not performed by
Bio-Rad or an authorized agent.
* IEC61010-1 and EN61010-1 are internationally accepted electrical safety standard
for laboratory instruments.
4 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 11
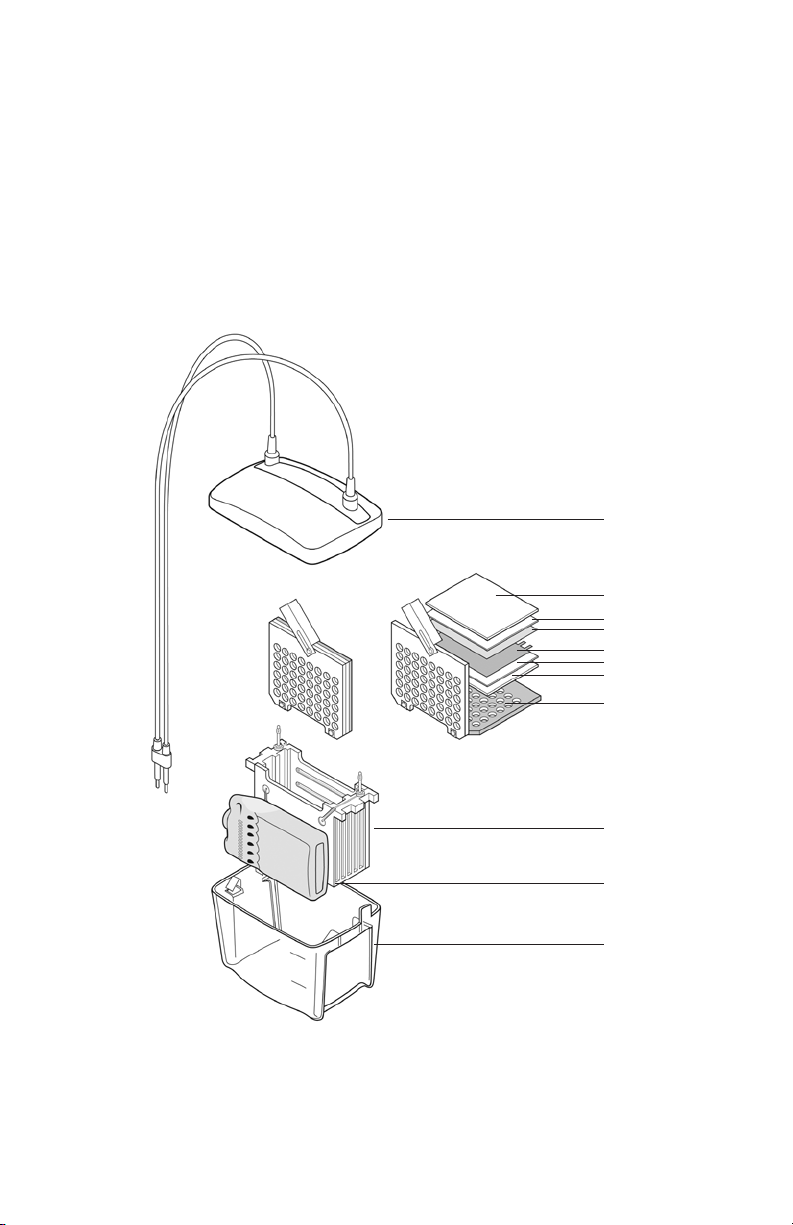
Section 2
Mini Trans-Blot® Cell Assembly and
Preparation for Transfer
2.1 Mini Trans-Blot Cell Description and Assembly of
Parts
Lid
Fiber pad
Filter paper
Membrane
Gel
Filter paper
Fiber pad
Gel holder
cassette
Electrode
module
Blue cooling
(keep frozen at
–20°C)
Buffer tank
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 5
Page 12
2.2 Preparation for Blotting
Store the blue cooling unit in your laboratory freezer at
–20°C until ready to use. After use, rinse the outside
container with water and return the cooling unit to the
freezer for storage.
1. Prepare the transfer buffer. (See Section 3.3 for buffer
formulation. Using buffer chilled to 4°C will improve
heat dissipation.)
2. Cut the membrane and the filter paper to the
dimensions of the gel or use precut membranes
and filter paper. Always wear gloves when handling
membranes to prevent contamination. Equilibrate the
gel and soak the membrane, filter paper, and fiber
pads in transfer buffer (15–20 min depending on gel
thickness).
3. Prepare the gel sandwich.
a. Place the cassette, with the gray side down,
on a clean surface.
b. Place one prewetted fiber pad on the gray
side of the cassette.
c. Place a sheet of filter paper on the fiber pad.
d. Place the equilibrated gel on the filter paper.*
e. Place the prewetted membrane on the gel.*
f. Complete the sandwich by placing a piece of
filter paper on the membrane.*
g. Add the last fiber pad.
6 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 13

* Removing any air bubbles which may have formed is very important for good
results. Use a glass tube or roller to gently roll out air bubbles.
Fiber pad
Filter paper
Membrane
Gel
Filter paper
Fiber pad
4. Close the cassette firmly, being careful not to move
the gel and filter paper sandwich. Lock the cassette
closed with the white latch.
5. Place the cassette in module. Repeat for the other
cassette.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 7
Page 14

6. Add the frozen blue cooling unit. Place in tank and fill
to the “blotting” mark on the tank.
7. Add a standard stir bar to help maintain even buffer
temperature and ion distribution in the tank. Set the
speed as fast as possible to keep ion distribution
even.
8 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 15

8. Put on the lid, plug the cables into the power supply,
and run the blot. Refer to Section 3 for run times and
voltage settings with various buffers.
9. Upon completion of the run, disassemble the
blotting sandwich and remove the membrane for
development. Clean the cell, fiber pads, and cassettes
with laboratory detergent and rinse well with deionized
water.
2.3 Acidic Transfers
If transferring under acidic conditions, switch the gel and
membrane in the set up instructions. This will place the
membrane on the cathode side of the gel. Under acidic
conditions, proteins will transfer in the opposite direction
going toward the negative cathode.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 9
Page 16

Section 3
Transfer Conditions
3.1 General Guide to Transfer Buffers and Running
Conditions
Table 3.1 provides guidelines for power conditions using
different buffers. Power conditions are provided for various
run times. Where multiple conditions are displayed, the
higher the voltage, the less time required for the run.
Always use the blue cooling unit.
Table 3.1. Guide to Buffers and Running Conditions.
Buffer Standard Field High
SDS-PAGE Gels Buffer A or B or C Buffer A or B or C
A: 25 mM Tris, pH 8.3, 192
mM glycine, with or without
20% MeOH and .025%–0.1%
SDS
B: 48 mM Tris, pH 9.2, 39 mM
glycine, with or without 20%
MeOH and .025%–0.1% SDS
C: 10 mM NaHCO3, 3 mM
NaCO3, pH 9.9, with or
without 20% MeOH and
.025%–0.1% SDS
DNA and RNA
TAE : 20 mM Tris, pH 7.8,
10 mM
TBE: 50 mM Tris, pH 8.3,
50 mM sodium borate, 1.0
mM EDTA
Native Gels
25 mM Tris, pH 8.3,
92 mM glycine. No methanol.
Isoelectric Focusing, Native
Gels, Basic Proteins, Acid
Urea Gels*
0.7% acetic acid 30 V, constant
*Please refer to Section 2.3 before transferring.
Intensity Field
Buffer Overnight
Transfer
30 V, constant
90 mA
30 V, constant
100 mA
30 V, constant
90 mA
100 mA
High Intensity Field
1 Hour Transfer
100 V, constant
350 mA
80 V, constant
500 mA
100 V, constant
350 mA
100 V, constant
350 mA
10 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 17

3.2 Notes on Electrophoretic Transfer Conditions
These variables will change total resistance and thus
the current readings:
• Alterations in buffer make-up, i.e., addition of SDS, or
changes in ion concentration due to addition of acid
or base to adjust the pH of the buffers
• Gel pH, ionic strength, and percentage of acrylamide,
especially if the gel has not been properly equilibrated
• Number of gels; current increases slightly as the
number of gels increases
• Volume of buffer; current increases when volume
increases
• Platinum mass; current increases when mass
increases
• Transfer temperature; current increases when
temperature increases
• Time in transfer at which reading was taken;
current normally increases as the buffering capacity
diminishes with progress of the run
Pre-equilibration of gels (15–20 min)
All electrophoresis gels should be pre-equilibrated in
transfer buffer prior to electrophoretic transfer.
Pre-equilibration will facilitate the removal of contaminating
electrophoresis buffer salts and neutralization salts (salts
resulting from the denaturation of nucleic acids prior to
transfer). If the salts are not removed, they will increase the
conductivity of the transfer buffer and the amount of heat
generated during the transfer. Also, low percentage gels
will shrink in methanol buffers. Equilibration allows the gel
to adjust to its final size prior to electrophoretic transfer.
Current limits
The PowerPac™ Basic power supply is capable of a
75 W output. Unless a current limit is set, uncontrolled
conductivity changes may result in full power being
delivered to the Mini Trans-Blot® cell.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 11
Page 18

The gel holders may warp, and the transfer buffer may boil
and evaporate (further increasing conductivity). This would
result in a potential safety hazard. Refer to the PowerPac
Basic power supply instruction manual for setting current
limits and run times. The Mini Trans-Blot cell is also
compatible with the PowerPac HC power supply.
Use of a stir bar during transfer
For all blotting applications a stir bar must be placed
inside the Mini Trans-Blot cell and the entire unit be
placed on a stir bar mixer, so that the transfer buffer
is stirred during the course of the experiment. This will
help to maintain uniform conductivity and temperature
during electrophoretic transfer. Failure to properly control
transfer buffer temperature results in poor transfer of
macromolecules and poses a potential safety hazard.
Transfer buffer pH
Do not adjust the pH of transfer buffers unless specifically
indicated. Adjustments of the transfer buffers pH, when
not indicated, will result in increased buffer conductivity.
This is manifested by a higher than expected initial current
output and a decreased resistance. It is recommended
that the buffer conductivity and resistance be checked
with the PowerPac Basic power supply before starting
each transfer.
Transfer buffer recommendations
Use only high quality, reagent grade methanol.
Contaminated methanol can result in increased
transfer buffer conductivity, as well as poor transfer of
macromolecules. Do not reuse transfer buffers or dilute
transfer buffers below recommended levels. Reuse of
transfer buffers is not advised, since these buffers have
most likely lost their ability to maintain a stable solution
pH during transfer. Dilution of transfer buffers below their
recommended levels is also not advised, since this will
decrease buffering capacity.
12 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 19

Voltage limits
Do not increase voltage settings beyond those indicated
in Table 3.1. If overnight transfers at low voltages are
ineffective for your application, and higher voltages are
necessary, transfer times must also be decreased. Failure
to do so may result in a potential safety hazard.
3.3 Buffer Formulation
All formulas provided below are for a total volume of 1 L of
buffer. Approximately 950 ml of buffer are required for the
Mini Trans-Blot cell with cooling unit. Ethanol can be used
in place of methanol in all buffer formulations.
Do not add acid or base to adjust pH of the following
buffers. Methanol should be analytical reagent grade, as
metallic contaminants in low grade methanol will plate on
the electrodes.
Note: Some pH electrodes will not perform a proper measurement for
the pH of Tris buffers. If the pH of the buffer is off, check to make sure
the electrode is designed to work with Tris buffers. If the pH electrode
functions properly for Tris buffers and the pH is below 8.0, remake the
buffer.
25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, 20% v/v methanol, pH 8.3
Mix 3.03 g Tris, 14.4 g glycine, and 200 ml of methanol;
add distilled deionized water (ddH2O) to 1 L.
25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, pH 8.3
Mix 3.03 g Tris and 14.4 g glycine; add ddH2O to 1 L.
48 mM Tris, 39 mM glycine, 20% v/v methanol, pH 9.2
Mix 5.82 g Tris and 2.93 g glycine in ddH2O, add 200 ml
methanol.
Add to 1 L with ddH2O.
48 mM Tris, 39 mM glycine, pH 9.2
Mix 5.82 g Tris and 2.93 g glycine.
Add ddH2O to 1 L.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 13
Page 20

10 mM NaHCO3, 3 mM NaCO3, 20% methanol, pH 9.9
Mix 0.84 g NaHCO3 and 0.318 g NaCO3 in ddH2O, add
200 ml methanol.
Add to 1 L with ddH2O.
1.0x TBE (Tris-Borate EDTA), pH 8.3
90 mM Tris-Borate, 1 mM EDTA
5x stock solution
54 g Tris base
27.5 boric acid
20 ml 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0)
Add 200 ml 5x stock solution to 800 ml ddH2O to make
1x working solution.
1x TAE (Tris-Acetate EDTA)
40 mM Tris-Acetate, 1 mM EDTA
50x stock solution
242 g Tris base
57.1 ml glacial acetic acid
100 ml 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0)
Add 20 ml 50x stock solution to 980 ml ddH2O to make
1x working solution.
14 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 21

Section 4
Strategies for Optimizing Electrophoretic
Transfer
4.1 Optimizing Protein Transfer
Generally, quantitative elution of denatured high molecular
weight proteins is difficult. The following tactics, alone or in
combination, will increase transfer efficiency.
Vary gel composition
Gradient gels are often more effective than single gel
concentrations for elution of a wide range of molecular
weight proteins.
Lower the total monomer to create a more porous gel.
Increase or decrease the percentage of crosslinker. A
5.26% C gel will contain the smallest pore size of all gels
no matter what the concentration of acrylamide. Decrease
in %C will make gels more porous with little loss in
resolution.
grams bis
%C = x 100
grams bis + grams acrylamide
Increase transfer time
An initial control should be performed to determine the
time required for complete transfer.
18, 25
Times may vary
from as little as 30 minutes to as long as overnight.
Remember all overnight applications should be performed
at 30 volts to minimize heating problems.
Increase the power
Initial controls should be performed to evaluate the
efficiency of increasing the V/cm as well as its effects on
the temperature of transfer. The temperature increase may
change buffer resistance and subsequent power delivered,
as well as the state of protein denaturation, thus affecting
transfer efficiency.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 15
Page 22

Reduce buffer strength
Dilution of transfer buffer results in lower current at any
given voltage. This will allow the use of higher voltages
without excessive heating. However, be aware not to dilute
the buffer below its buffering capacity.
Vary buffer type and pH
Maximize charge-to-mass ratio. It appears that alcohols
present in SDS transfer buffer strip SDS from proteins.
Basic proteins in Tris, glycine, methanol buffer at pH
8.3 may assume a state near isoelectric neutrality and
thus transfer poorly. For example, lysozyme exhibits this
behavior. Buffers with pH of 9.5–10.0 have shown much
better elution and binding characteristics for basic proteins
such as lysozyme and histones.
41
Different buffer types at similar V/cm may yield different
efficiencies. Generally, Tris buffers allow more efficient
transfer than acetate or phosphate buffers.
Add detergent
Addition of 0.1% SDS detergent to Tris, glycine, methanol
buffer has been reported to increase transfer efficiency.25
SDS, however, increases relative current, power, and
heating. Also, temperatures below 10°C may precipitate
the SDS so the starting buffer temperature will be higher.
SDS may also affect the antigenicity of some proteins.
SDS will aid in eluting the proteins from the gel, but it
may reduce the binding efficiency of those proteins to the
membrane.
Eliminate alcohol from the transfer buffer
Alcohol in the transfer buffer improves binding of proteins
to nitrocellulose only. Elimination of alcohol results in
increased transfer efficiency but diminishes binding to
nitrocellulose. Transfer efficiency is increased because
alcohol causes gel pores to contract resulting in capture of
large molecular weight proteins within the gel matrix.
16 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 23

Use of PVDF membrane for protein transfers eliminates
the alcohol requirement, and constitutes a logical
strategy for analysis of high molecular weight or difficultto-transfer proteins.
27, 28
PVDF must be wetted in 100%
methanol but may then be used in buffer without
methanol.
Limited protease treatment
A protocol for protease digestion of protein during transfer
has been published.23 Efficient transfer without loss of
immunological reactivity was reported.
Alter membrane type
Both nitrocellulose and PVDF can be used for protein
transfer.
Alter gel system
If possible, use nondenaturing gradient pore gels for
separation of proteins. Isoelectric focusing gels, or native
gels, may be considered if separation by molecular weight
is not mandatory.
Enhance gel-membrane contact
Failure of molecules to bind efficiently to the membrane,
caused by poor gel-membrane contact, is often confused
with inefficient elution. Poor contact is usually due to
excess moisture in the gel-membrane interface. Proper
technique and the use of a test tube or glass pipet as a
“rolling pin” should assure good contact. Proper selection
of filter paper spacers will help assure good compression.
Gel and membrane equilibration in transfer buffer for 15–
20 min prior to transfer will help prevent shrinking of either
component during transfer, and will eliminate reactants
such as urea or SDS from the gel.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 17
Page 24

4.2 Optimizing DNA and RNA Transfer
Problems with elution of nucleic acids can be solved by
altering the gel percentage. It may be somewhat more
difficult to quantitatively transfer large amounts of DNA
used in genomic blots. Agarose gels over 6 mm thick are
not compatible with the Mini Trans-Blot. The following
tactics should be considered for optimizing elution in such
transfers.
Alter gel composition
Lower % total monomer or % crosslinker for
polyacrylamide gels.
Lower % agarose. This allows better elution of high
molecular weight DNA.
Alter DNA denaturants
It has been found that glyoxal denaturation allows more
efficient elution of DNA than NaOH. Boiling polyacrylamide
gels to denature DNA has also been found to give
excellent results.12 Base denaturation often causes
polyacrylamide gels to weaken and stick to blotting
membranes.
18 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 25

Section 5
Choice of Blotting Membranes
5.1 Protein Blotting Membranes
Nitrocellulose Membrane
Nitrocellulose membranes have been used extensively
for protein binding and detection.
easily stained for total protein by a dye stain (Amido
Black, Coomassie Blue, Ponceau S, Fast Green FCF,
etc.),28 or the more sensitive Colloidal Gold Total Protein
Stain, and also allow either RIA, FIA, or EIA.8 Nitrocellulose
has a high binding capacity of 80–100 μg/cm2 Nonspecific
protein binding sites are easily and rapidly blocked,
avoiding subsequent background problems. No preactivation is required. Low molecular weight proteins
(especially <15,000 daltons) may be lost during
post transfer washes, thus limiting detection sensitivity.20
Smaller pore size nitrocellulose membrane (0.2 μm),
has been shown to be effective in eliminating this loss.
Large proteins (>100,000 daltons) denatured by SDS
may transfer poorly due to the addition of alcohol to the
transfer buffer. Alcohol increases binding of SDS-proteins
to nitrocellulose, but decreases pore sizes in the gel.
Elimination of alcohol from SDS-protein transfers results in
considerably diminished binding. Adding SDS (up to 0.1%)
to the transfer buffer increases the transfer efficiency
of proteins, but reduces the amount of binding to the
membrane.18 Also, SDS increases the conductivity of the
buffer and the heat generated during transfer.
8, 21, 24, 25, 28
They can be
30
PVDF Membrane
Polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane is an ideal
support for amino-terminal sequencing, amino acid
analysis and immunoassays of blotted proteins. PVDF
retains proteins under extreme conditions of exposure to
acidic or basic conditions, and in the presence of organic
solvents.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 19
Page 26

Greater retention during sequencing manipulations
enhances the likelihood of obtaining information from
rare, low abundance proteins, by increased initial coupling
and higher repetitive yields. In addition, PVDF membrane
exhibits better binding efficiency of blotted material in the
presence of SDS in the transfer buffer. PVDF must first
be wetted in 100% MeOH but can then be used in buffer,
which does not contain MeOH.
5.2 DNA and RNA Blotting Membranes
Zeta-Probe® Nylon Membrane
Nitrocellulose is not a suitable medium for electrophoretic
transfer of nucleic acids, as high concentrations of salt
(>10x SSC) are required for efficient binding.13 Molecules
≤500 bp are not bound at all, even at high salt. Low
resistance results when an electric current is passed
through a solution of high salt. This causes potentially
damaging high currents (and power) even at very low
voltages. Since V/cm is the eluting force, inefficient
transfer occurs under conditions required for proper
binding. Zeta-Probe membrane allows efficient binding of
all sizes of single stranded DNA and RNA in the presence
of low ionic strength buffers.13 Zeta-Probe membrane
is an ideal alternative to nitrocellulose for the transfer of
nucleic acids. Binding is more stable through post transfer
washes, and reprobing may be performed as many as 10
times.
A variety of blotting membranes is available for
immunoblotting, each with particular advantages
depending on the needs of the experiment. The
physical properties and performance characteristics of a
membrane should be evaluated when selecting the
appropriate transfer conditions.
20 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 27

Table 5.1 Guide to Protein Blotting Membranes
Membrane Pore Size Binding
Notes
Capacity
2
(μg/cm
)
Nitrocellulose 0.45 μm
0.2 μm
Supported
Nitrocellulose
0.45 μm
0.2 μm
80–100 General purpose protein blotting
membrane.
80–100 Pure nitrocellulose cast on an
inert synthetic support; increased
strength for easier handling and
for reprobing.
PVDF 0.2 μm 170–200 High mechanical strength and
chemical stability, used for protein
sequencing and western blotting;
enhanced binding in the presence
of SDS. Must be wet in alcohol
before equilibration in buffer.
Nylon 0.2 μm 170 Recommended for nucleic acids.
Note: Nucleic acids cannot be transferred to nitrocellulose by electrophoretic
blotting. Use Zeta-Probe membrane.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 21
Page 28

Section 6
Troubleshooting Guide
6.1 Electrophoretic Transfer
Poor electrophoretic transfer (as detected by staining
the gel)—proteins
1. Transfer time is too short.
• Increase the transfer time
2. Power is too low.
• Always check the current at the beginning
of the run. The current may be too low for a
particular voltage setting. If the buffer is prepared
improperly, the conductivity may be too low, and
not enough power will be delivered to the cell.
See the power guidelines for specific applications
in Section 3
• Remake the buffer or increase the voltage
• Try the high intensity blotting option
3. Power supply circuit is inoperative, or an inappropriate
power supply was used.
• Check the fuse. Be sure the voltage and current
output of the power supply match the needs of
the blotting instrument
4. Transfer apparatus is assembled incorrectly, and the
proteins are moving in the wrong direction.
• The gel/membrane sandwich may be assembled
in the wrong order or the cassette is inserted in
the tank facing the opposite orientation. Check
the polarity of the connections to the power supply
• Use a pre-stained protein standard to assess
transfer efficiency after blotting
22 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 29

5. Charge-to-mass ratio is incorrect.
• Try a more basic or acidic transfer buffer to
increase protein mobility.
6. Protein is precipitating in the gel.
• Try using SDS in the transfer buffer. SDS can
increase transfer efficiency, but can also reduce
binding efficiency to nitrocellulose and affect
reactivity of some proteins with antibodies
• An excess of methanol will lead to protein
precipitation. Try decreasing methanol content
7. Methanol in the transfer buffer is restricting elution.
• Reduction of methanol results in increased
transfer efficiency of proteins from the gel, but it
also diminishes binding to nitrocellulose
8. Gel percentage too high.
• Reduce %T (total monomer) or %C (crosslinker).
A 5.26% C (with bis as the crosslinker) will
produce the smallest pore size gel. Decreasing
from this concentration will increase the pore size
and increase transfer efficiency
Poor transfer—nucleic acid
1. Gel percentage is too high.
• Reduce the %T or %C in the acrylamide gel or
reduce % agarose in an agarose gel
• Prior to transfer, cleave DNA in 0.25 M HCl or
RNA in dilute NaOH
2. Transfer time is too short or power conditions are too
low.
• Increase the transfer time, or try high intensity
transfer
3. DNA or RNA cannot be transferred electrophoretically
to nitrocellulose, since high salt concentrations are
required for efficient binding.
• Use Zeta-Probe membrane instead of
nitrocellulose
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 23
Page 30

Swirls or missing bands; diffuse transfers
1. Poor contact between the membrane and the gel. Air
bubbles or excess buffer remain between the blot and
gel.
• Use a test tube or pipet as a rolling pin, and roll
over the membrane carefully in both directions
until air bubbles and excess buffer are removed
from between gel and membrane, and complete
contact is established
• Use thicker filter paper in the gel/membrane
sandwich
• Replace the fiber pads. Pads will compress with
time, and will not hold the membrane to the gel
2. Power conditions are too high.
• Always check the current at the beginning
of the run. The current may be too high for a
particular voltage setting. If the buffer is prepared
improperly, the conductivity may be too high,
resulting in excessive power delivered to the cell.
See the power guidelines for specific applications
in Section 3
3. The membrane is not properly wet or has dried out.
• White spots on the nitrocellulose membrane
indicate dry areas where protein will not bind. If
wetting does not occur immediately by immersion
of the sheet in transfer buffer, heat distilled water
until just under the boiling point, and soak the
membrane until completely wet. Equilibrate in
transfer buffer until ready for use
• Because of the hydrophobic nature of PVDF, the
membrane must be prewet in methanol prior to
equilibration in aqueous transfer buffer. Do not let
membrane dry after wetting. Rewet in methanol if
necessary
24 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 31

4. The gel electrophoresis may be at fault.
• Artifacts of electrophoresis may be produced
by poor polymerization, inappropriate running
conditions, contaminated buffers, sample
overload, etc
Gel cassette pattern transferred to blot
1. Contaminated or thin fiber pads are used.
• Replace the fiber pads, or thoroughly clean the
contaminated pads
2. Excessive amounts of protein were loaded on the
gel, or too much SDS was used in the transfer buffer.
Proteins can pass through the membrane without
binding, and recirculate through the tank blotting
system.
• Reduce the amount of protein on the gel, and
SDS in the transfer buffer. Reduce transfer
duration or add a second sheet of membrane to
bind excess protein
3. The transfer buffer is contaminated.
• Make fresh solutions. Transfer buffer solution
cannot be reused
Poor binding to the membrane—nitrocellulose
1. Nitrocellulose requires 20% methanol in the transfer
buffer for optimal protein binding.
• Make sure the buffer contains the proper amount
of methanol
2. Proteins may be transferring through the nitrocellulose.
• Use PVDF (higher binding capacities) or 0.2 μm
nitrocellulose (smaller pore size). Decrease the
voltage if using the high intensity option
3. Mixed ester celluloses bind proteins poorly.
• Use pure nitrocellulose
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 25
Page 32

4. Proteins <15,000 daltons may show diminished
binding to 0.45 μm nitrocellulose, or may be washed
from the membrane during assays.
• To increase stability of binding, proteins can be
crosslinked to nitrocellulose with glutaraldehyde
• Use PVDF membrane, which has higher binding
capacities
• Use Tween-20 detergent in the wash and
antibody incubation steps. Reduce or eliminate
the more stringent washing conditions
5. SDS in the transfer buffer will reduce binding efficiency
of proteins.
• Reduce or eliminate the SDS from the transfer
buffer
6. The membrane may not be completely wet.
• White spots on the membrane indicate dry areas
where protein will not bind. If wetting does not
occur immediately by immersion of the sheet in
transfer buffer, heat distilled water until just under
the boiling point, and soak the membrane until
completely wet. Equilibrate in transfer buffer until
ready for use
Poor binding to the membrane—PVDF
1. The membrane may not be completely wet.
• Because of the hydrophobic nature of PVDF, the
membrane must be prewet in alcohol prior to
equilibration in aqueous transfer buffer. Follow the
directions in the product insert
2. The membrane may have been allowed to dry during
handling.
• A completely wet membrane has a gray,
translucent appearance. White spots will form
on the surface of the membrane, indicating that
it has been allowed to dry. Since proteins will not
bind to the dry spots, rewet the membrane with
methanol and re-equilibrate in transfer buffer
26 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 33

Section 7
References
1. Southern, E. M., J. Mol. Biol., 98, 503 (1975).
2. Alwine, J. C., Kemp, D. J., Parker, B. A., Reiser, J.,
Renart J., Stark, G. R. and Wahl, G. W., Methods
Enzymol., 68, 220 (1979).
3. Thomas, P. S., Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci., 77, 5201 (1980).
4. Seed, B., Nuc. Acids Res., 10, 1799 (1982).
5. Renart. J., Reiser, J. and Stark, G. R., Proc. Nat.
Acad. Sci., 76, 3116 (1979).
6. Bowen, P., Steinberg, J., Laemmli, U. K. and
Weintraub, H., Nuc. Acids Res., 8, 1 (1980).
7. Towbin, H., Staehelin, T. and Gordon, J., Proc. Nat.
Acad. Sci., 76, 4350 (1970).
8. Bittner, M., Kupferer, P. and Morris, C. R., Anal.
Biochem., 102, 459 (1980).
9. Stellwag, E. J. and Dahlberg, A. E., Nuc. Acids Res.,
8, 299 (1980)
10. Kutateladze, T. V., Axelrod, B. D., Gorbulev, V. G.,
Belzhelarshaya, S. N. and Vartikyan, R. M., Anal.
Biochem., 100, 129 (1979).
11. Peudelhuber, T. L., Ball, D. J., Davis, A. H. and
Garrard, W. J., Nuc. Acids Res., 10, 1311 (1982).
12. Danner, D. B., Anal. Biochem., 125, 139 (1982).
13. Bio-Rad Technical Bulletin 1110 “Zeta-Probe Blotting
Membranes” (1982).
14. Beisiegel, V., Electrophoresis, 7, 1 (1986).
15. Holland, L. J. and Wangh, L. H., Nuc. Acids Res., 10,
3283 (1983).
16. Syminton, J., Green, M. and Brackmann, K., Proc.
Nat. Acad. Sci., 78, 177 (1981).
17. Reiser, J. and Wardale, J., Eur. J. Biochem., 114, 569
(1981).
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 27
Page 34

18. Burnette, W. N., Anal. Biochem., 112, 195 (1981).
19. Legocki, R. P. and Verma, D. P. S., Anal. Biochem.,
111, 385 (1981).
20. Lin, W. and Kasamatsu, H., Anal. Biochem., 128, 302
(1983).
21. Anderson, N. L., Nance, S. L., Pearson, T. W. and
Anderson, N. G., Electrophoresis, 3, 135 (1982).
22. McLellan, T. and Pamshaw, J. A. M., Biochem.
Genetics, 19, 647 (1981).
23. Gibson, W., Anal. Biochem., 118, 1 (1981).
24. Howe, J. G. and Hershey, J. W. B., J. Biol. Chem.,
2566, 12836 (1981).
25. Erickson, P. G., Minier, L. N. and Lasher, P. S., J.
Immun. Meth., 51, 241 (1982).
26. Tsang, V. C. W., Peralta, J. M. and Simons, A. R.,
Meth. Enzymol., 92, 377 (1983).
27. Gershoni, J. M. and Palade, G. E., Anal. Biochem.,
124, 396 (1982).
28. Gershoni, J. M. and Palade, G. E., Anal. Biochem.,
131, 1 (1983).
29. Bio-Rad Laboratories, unpublished.
30. Polvino, W. J., Saravis, C. A., Sampson, C. E. and
Cook, R. B., Electrophoresis, 4, 368 (1983).
28 Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell
Page 35

Section 7
Product Information
Catalog
Number Product Description
Mini Trans-Blot® Cell
170-3930 Mini Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell, includes 2 gel
170-3935 Mini Trans-Blot Module, same as 170-3930 without lower
170-3989 Mini Trans-Blot Cell and PowerPac Basic Power Supply
170-3836 Mini Trans-Blot Cell and PowerPac HC Power Supply
Mini Trans-Blot Cell Accessories
170-3931 Mini Gel Holder Cassette
170-3932 Filter Paper, 7.5 x 10.5 cm, 50
170-3933 Fiber Pads, 8 x 11 cm, 4
170-3934 Bio-Ice
holder
cassettes, 4 fiber pads, modular electrode assembly, blue
cooling unit, lower buffer chamber,
and lid with cables
buffer chamber and lid
™
Cooling Unit
Tween is a trademark of ICI Americas Inc.
Coomassie is a trademark of BASF Aktienquesellschaft.
Mini-Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell 29
Page 36

Page 37

Page 38

Page 39

Page 40

Sig 1213M1703930 Rev K US/EG
Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.
Life Science
Group
Web site www.bio-rad.com USA 800 424 6723
Australia 61 2 9914 2800 Austria 01 877 89 01 Belgium 09 385 55 11
Brazil 55 11 306 5 7550 Canada 905 364 3435 China 86 21 6169 8500
Czech Republic 420 241 430 532 Denmar k 44 52 10 00
Finland 09 804 22 00 France 01 47 95 69 65 Germ any 089 31 884 0
Greece 30 210 9532 220 Hong Ko ng 852 2789 3300
Hungary 36 1 459 6100 India 91 124 4029300 Israel 03 963 6050
Italy 39 02 2160 91 Japan 81 3 6361 7000 Korea 82 2 3473 4460
Mexico 52 555 4 88 7670 The Netherlands 0318 540666
New Zealand 64 9 415 2280 Norway 23 38 41 30
Poland 48 22 331 99 99 Portugal 351 21 472 7700
Russia 7 495 721 14 04 Singapore 65 6415 3188
South Africa 27 861 246 723 Spain 34 91 59 0 5200
Sweden 08 555 1270 0 Switzerland 026 674 55 05
Taiwan 886 2 2578 7189 Thailand 1800 88 22 88
United Kingdom 020 8328 2000
 Loading...
Loading...