Page 1

Experion™
Pro260 Analysis Kit
Instruction Manual
Catalog #700-7101
Page 2

Bio-Rad Technical Support
For help and advice regarding products from the Experion™ automated electrophoresis system, please contact the Bio-Rad
Technical Support department, which in the United States is open Monday–Friday, 5:00 AM–5:00 PM, Pacific Time.
Phone: 1-800-4BIORAD (1-800-424-6723)
Fax: 1-510-741-5802
Email: LSG_TechServ_US@bio-rad.com (for U.S. and international customers)
Online technical support and worldwide contact information are available at www.consult.bio-rad.com.
Legal Notices
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including
photocopy, recording, or any information storage or retrieval system, without permission in writing from Bio-Rad Laboratories.
Bio-Rad reserves the right to modify its products and services at any time. This user guide is subject to change without notice.
Although prepared to ensure accuracy, Bio-Rad assumes no liability for errors, or for any damages resulting from the application
or use of this information.
Bio-Lyte, Criterion, Experion, Precision Plus Protein, and ReadyPrep are trademarks of Bio-Rad Laboratories. B-PER is a
trademark of Pierce. BugBuster is a trademark of Novagen. Coomassie and Pluronic are trademarks of BASF Aktiengesellschaft.
Excel is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Triton is a trademark of Union Carbide. Tween is a trademark of ICI Americas, Inc.
Zwittergent is a trademark of EMD Chemicals Inc.
The dyes in Experion kits are manufactured by Molecular Probes, Inc. and are licensed for research use only.
LabChip and the LabChip logo are trademarks of Caliper Life Sciences, Inc. Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. is
licensed by Caliper Life Sciences, Inc. to sell products using the LabChip technology for research use only.
These products are licensed under U.S. patents 5,863,753; 5,658,751; 5,436,134; and 5,582,977, and pending
patent applications, and related foreign patents, for internal research and development use only in detecting,
quantitating, and sizing macromolecules, in combination with microfluidics, where internal research and development use
expressly excludes the use of this product for providing medical, diagnostic, or any other testing, analysis, or screening services,
or providing clinical information or clinical analysis, in any event in return for compensation by an unrelated party.
Copyright © 2010 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: Experion™ Pro260 Analysis Kit ............................................. 1
1.1 Product Description .......................................................... 2
1.2 Kit Components ............................................................. 3
1.3 Storage Conditions ........................................................... 3
1.4 Specifications ............................................................... 3
1.5 Additional Requirements ....................................................... 4
Chapter 2: Essential Practices ...................................................... 5
2.1 Storing and Preparing Samples and Reagents ...................................... 6
2.2 Priming and Loading the Chip................................................... 6
2.3 Running the Analysis.......................................................... 7
2.4 General Maintenance ......................................................... 7
2.5 Experion Video Tutorials ....................................................... 7
Chapter 3: Experion Pro260 Assay Procedure ......................................... 9
3.1 Set Up the Electrophoresis Station .............................................. 10
3.2 Equilibrate the Kit Reagents ................................................... 10
3.3 Filter the Gel and Prepare the Gel-Stain Solution ................................... 10
3.4 Prepare the Sample Buffers ................................................... 11
3.4.1 Reducing Conditions ..................................................... 11
3.4.2 Nonreducing Conditions .................................................. 11
3.5 Prepare the Samples and the Pro260 Ladder ...................................... 11
3.6 Prime the Chip ............................................................. 12
3.7 Load the Chip .............................................................. 13
3.8 Run the Pro260 Analysis...................................................... 14
3.9 Clean the Electrodes......................................................... 15
3.10 Evaluate the Run........................................................... 16
Chapter 4: Data Analysis ......................................................... 17
4.1 Viewing Data............................................................... 18
4.1.1 Managing Run Files and Project Folders in the Tree View.......................... 18
4.1.2 General Display Controls .................................................. 19
4.1.3 Electropherogram View.................................................... 19
4.1.4 Gel View ............................................................... 23
4.1.5 Results and Settings ..................................................... 23
Page 4

4.2 Changing the Fluorescence Intensity Scale ........................................ 24
4.3 Using Results and Settings to View and Annotate Data .............................. 25
4.4 Comparing Data from Different Runs ............................................ 26
4.5 Saving, Exporting, and Printing Data............................................. 27
4.5.1 Saving Data Files ........................................................ 27
4.5.2 Exporting Data Files to Other Applications ..................................... 27
4.5.3 Printing Data Files ........................................................ 27
Chapter 5: Protein Quantitation Methods ............................................ 29
5.1 Protein Quantitation Methods .................................................. 30
5.2 Performing Percentage Determination............................................ 30
5.3 Performing Relative Quantitation ................................................ 31
5.4 Performing Absolute Quantitation ............................................... 32
5.4.1 Absolute Quantitation Using the Upper Marker as Standard ........................ 32
5.4.2 Absolute Quantitation Using a User-Defined Internal Standard ...................... 34
Chapter 6: Changing Analysis Settings and Parameters ................................ 35
6.1 Designating and Searching for Specific Proteins .................................... 36
6.2 Changing Protein Quantitation Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6.3 Manually Setting a Marker..................................................... 36
6.4 Excluding a Peak from Analysis ................................................ 36
6.5 Changing Peak Finding Parameters ............................................. 37
6.6 Changing General Settings .................................................... 37
6.7 Baseline Modification ........................................................ 38
6.8 Turning Analysis Off ......................................................... 39
6.9 Manual Peak Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Chapter 7: Troubleshooting ....................................................... 41
7.1 Electrophoresis and Priming Stations ............................................ 42
7.2 Experion Pro260 Analysis ..................................................... 42
7.3 Contacting Technical Support.................................................. 46
Appendices .................................................................... 47
Appendix A: How the Experion System Works ........................................ 48
Appendix B: Deep Cleaning Procedure .............................................. 53
Appendix C: Chemical Compatibility ................................................ 54
Appendix D: Glossary............................................................ 58
Appendix E: Bibliography ......................................................... 60
Appendix F Ordering Information................................................... 61
Page 5

1
Experion™ Pro260
Analysis Kit
1
Page 6

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
1.1 Product Description
The Experion Pro260 analysis kit is used for protein analysis with the Experion automated
electrophoresis system (Figure 1.1). The Experion system employs LabChip microfluidic technology
to automate protein and nucleic acid electrophoresis by integrating separation, detection, and data
analysis within a single platform. The Experion automated electrophoresis system uses smaller sample
and reagent quantities than standard analysis methods, and it accomplishes analysis in a single
30-minute, automated step.
The Experion Pro260 analysis kit supplies the microfluidic chips, reagents, and instructions required to
separate and analyze 10–260 kD proteins under denaturing conditions. The sensitivity of the Experion
Pro260 analysis kit is comparable to (though sometimes more sensitive than) colloidal Coomassie Blue
staining of SDS-PAGE gels. Each Experion Pro260 chip can analyze up to 10 samples.
For details about how the Experion Pro260 kit analyzes proteins, refer to Appendix A in this manual.
Register your Experion system in order to ensure you receive important updates on software,
tech notes, and manuals. Upon installation, a dialog will provide registration instructions.
4
1
2
5a
Fig. 1.1. The Experion system. The system includes the following components: 1) automated electrophoresis
station, 2) priming station, 3) vortex station used for nucleic acid analysis only, 4) system operation and data analysis
tools (software), and 5) analysis kits, which include the (a) chips and (b) reagents for protein (Pro260 kit), standardsensitivity RNA (StdSens kit), high-sensitivity RNA (HighSens kit), and DNA (DNA 1K and 12K kits) analyses.
3
5b
2 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 7

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
1.2 Kit Components
Table 1.1. Components of the Experion Pro260 analysis kit.
Item Description Volume (per Vial) 10-Chip Kit
Pro260 chip Microfluidic chips used for protein separation 10 chips
Cleaning chip Chip used for cleaning electrodes 1 chip
Pro260 gel Proprietary polymeric sieving matrix 520 µl 3 vials
Pro260 stain Proprietary fluorescent dye 45 µl 1 vial
Sample buffer Buffer for protein sample preparation; contains a 1.2 kD 400 µl 1 vial
lower marker and 260 kD upper marker for alignment of
samples to the Pro260 ladder
Pro260 ladder Protein standard containing 9 purified recombinant proteins 60 µl 1 vial
of 10–260 kD and optimized for automated electrophoresis
on the Experion system
Spin filters Used for filtering reagents during sample preparation 3 filters
1.3 Storage Conditions
Table 1.2. Storage conditions.
Item Storage Shelf Life
Experion Pro260 reagents 4ºC See expiration date on packaging
Experion Pro260 chips Ambient See expiration date on packaging
Gel-stain solution (GS, prepared) 4ºC 1 month from filtration (can be refiltered once)
Gel (G, prepared) 4ºC 1 month from filtration (can be refiltered once)
1.4 Specifications
Number of sample wells per chip 10
Sample volume required 4 µl
Total run time ~30 min per chip
Protein sizing range 10–260 kD
Limit of detection 2.5 ng/µl carbonic anhydrase (10 ng total) in 1x PBS; similar to
colloidal Coomassie Blue G-250 stain
Linear dynamic range 5–2,000 ng/µl (bovine serum albumin in 1x PBS)
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 3
Page 8

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
1.5 Additional Requirements
Experion automated electrophoresis station
Experion priming station
Microcentrifuge (1,000–10,000 x g)
Heating block or water bath set at 95–100°C
Benchtop vortexer
Aluminum foil
Calibrated pipets and narrow-bore tips (for example, VWR #87001-688 or Rainin #L-10F)
Microcentrifuge tubes, 0.5 or 1.5 ml
Deionized water, 0.2 µm-filtered (ReadyPrep™ proteomics grade water, catalog #163-2091)
β-Mercaptoethanol (catalog #161-0710)
Benchtop centrifuge (optional, catalog #166-0612)
Extra spin filter for additional filtration steps (as needed, catalog #700-7254)
Experion electrode cleaner (catalog #700-7252)
4 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 9

2
Essential Practices
5
Page 10

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
2.1 Storing and Preparing Samples and Reagents
Store all Experion™ Pro260 reagents at 4°C when not in use. Do not store reagents at room temperature
for >2 hr, as this will shorten their shelf life.
Before use, allow all kit reagents to equilibrate to room temperature (~15–20 min). Once thawed, gently
vortex all kit reagents before use. Before opening the tubes, quickly centrifuge them to collect solution
to the bottoms of tubes.
If the Pro260 gel has frozen, discard it.
Protect the stain, sample buffer, and gel-stain solution (GS) from light: store these solutions in a dark
place and keep them covered with foil when using them.
The Pro260 stain contains DMSO, which is hygroscopic. Cap tightly.
Use GS and filtered gel (G) for up to 1 month. After that, GS and G can be refiltered once again.
Prepare samples in either reducing or nonreducing sample buffer, but always prepare Pro260 ladder in
reducing sample buffer.
Do not use coated or treated pipet tips or microcentrifuge tubes (for example, siliconized polypropylene)
for preparation of kit reagents or samples. Use of treated tips or tubes may cause separation artifacts.
Use 0.2 μm-filtered or ReadyPrep™ proteomics grade water. Do not use autoclaved water for sample
or reagent preparation.
If possible, use sample protein concentrations (before preparation with the Pro260 sample buffer) that
are near the middle of the linear dynamic range.
2.2 Priming and Loading the Chip
To avoid contamination, wear gloves and handle chips by the edges. Never touch the glass portions of
the chip.
Load the chip on a benchtop or in the priming station. Never load a chip in the electrophoresis station.
Avoid sources of dust and other contaminants when preparing samples and loading the chip. Foreign
particles in reagents, samples, or the wells of the chip interfere with separation. Remove chips from their
packaging immediately before use.
It may be easier to load the chip on a white background. Tilt the chip to look for bubbles.
Use narrow-bore pipet tips for loading the chip (for example, VWR #87001-688 or Rainin #L-10F).
To avoid introducing air bubbles, do the following (for more help with chip loading, refer to the Experion
Training Video in the Experion software Help section under Contents and Index > Contents >
Appendices > Technical Videos):
n
Insert the pipet tip all the way to the bottom of the chip well when dispensing liquids
(this reduces the possibility of trapping air)
n
Hold the tip vertically, perpendicular to the chip surface. Holding the tip at an angle
may trap air bubbles at the bottom of the well
n
When expelling liquid, dispense slowly and only to the first stop on the pipet. Using the
second stop introduces air and bubbles into the liquid. Reverse pipetting is acceptable
6 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 11

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Dislodge bubbles at the bottom of a well with a clean pipet tip, or remove the solution and load it again.
Use a primed and loaded chip within 5 min of loading. When chips are not used within this time,
reagents may evaporate, leading to poor results or a chip performance error.
Fill all the chip wells when running an analysis. Use blank samples (prepared with water instead of
sample) or replicates if necessary. All 16 electrode pins must be in contact with liquid; otherwise, an IV
(current voltage) check failure error will occur.
2.3 Running the Analysis
Place the electrophoresis station on a stable surface, where it will not be subjected to vibrations or other
movement, and away from direct sunlight and all other potential sources of extreme heat.
Power on the electrophoresis station before launching Experion software.
The first time that the Experion electrophoresis station is used, confirm that communication has been
established between the software and electrophoresis station before preparing the reagents.
Do not open the lid of the electrophoresis station during a run. The run will abort if the lid is opened.
2.4 General Maintenance
For recommendations on general instrument maintenance, refer to the Experion system manual
(bulletin 10001312).
Clean the electrodes after each run (routine cleaning). Cleaning maintains the instrument in optimum
condition and prevents buildup and cross-contamination of reagents and samples.
Perform the deep cleaning procedure described in Appendix B to clean the electrodes:
n
Prior to first use of the Experion electrophoresis station
n
Whenever contamination is suspected or visible (for example, salt deposits or other
precipitates) on the electrodes
n
Whenever a chip has been left in the electrophoresis station for an extended period of time
(for example, overnight)
Never store the cleaning chip inside the electrophoresis station. Store the empty cleaning chip covered
to keep the wells clean. A new cleaning chip is included with every box of chips.
2.5 Experion Video Tutorials
For additional information, view the video tutorials available online at www.bio-rad.com:
North America: Home > Life Science Research > Support > Tutorials > Electrophoresis and Blotting >
Experion System Training
Other: Home > Life Science Research > Electrophoresis > Automated Electrophoresis >
Experion Training Videos
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 7
Page 12

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
8 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 13

Experion™ Pro260 Assay
3
Procedure
For an abbreviated version of this protocol, refer to the Quick Guide provided with the kit.
9
Page 14

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
3.1 Set Up the Electrophoresis Station
1. If needed, perform a deep cleaning of the electrodes (see Appendix B for instructions).
2. Power on the computer and then power on the Experion electrophoresis station by pushing the
green button in the center of the front panel. The steady green LED above the button indicates that
the unit is on.
3. Launch Experion software. If the instrument and computer are communicating properly:
n
A green dot and the last 4 digits of the instrument serial number appear in the lower right corner
of the software screen
n
The electrophoresis station icon appears in the upper left corner
When there is no connection, these indicators are absent and a grayed-out instrument icon appears
in the upper left corner of the software screen.
3.2 Equilibrate the Kit Reagents
1. Set a heating block or water bath to 95–100°C. You will use this heating block to denature the
samples and Pro260 ladder later in the protocol.
2. Equilibrate the following kit reagents to room temperature for ~15–20 min:
n
Pro260 stain (blue cap)
n
Pro260 sample buffer (yellow cap)
n
Pro260 ladder (red cap)
n
2 tubes Pro260 gel (green cap)
3. Vortex the contents of each tube and briefly centrifuge the solutions to the bottoms of the tubes.
Make sure the Pro260 stain solution (blue cap) is thawed before proceeding.
If the gel-stain solution (GS) and filtered gel (G) were prepared previously, equilibrate them to room
temperature. Use the GS and G within 1 month of preparation. After 1 month, refilter them before
use. Keep both the G and GS at room temperature and covered until ready for use.
3.3 Filter the Gel and Prepare the Gel-Stain Solution
1. Prepare the GS by adding 20 µl Pro260 stain (blue cap) to a tube of Pro260 gel (green cap, 520 µl).
Vortex the GS for 10 sec at the highest setting and then spin it down briefly in a microcentrifuge.
2. Transfer the GS to a spin filter, and transfer the contents of the other Pro260 gel (green cap) into
another spin filter. Label and date the tubes.
3. Centrifuge both spin filters for 5 min at 10,000 × g. Inspect the tubes to ensure all of the gel passed
through the filters, and then discard the filters. Cover the GS with foil.
10 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 15
Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
3.4 Prepare the Sample Buffers
Separate protein samples under either reducing or nonreducing conditions, but always use reducing
conditions for separation of the Pro260 ladder. Reduced and nonreduced samples can be run on the
same chip. Prepare fresh sample buffer daily.
3.4.1 Reducing Conditions
For each chip, combine 1 µl β-mercaptoethanol and 30 µl sample buffer (yellow cap). Vortex and spin
down briefly. Protect the sample buffer from light.
At pH <7, reducing agents such as β-mercaptoethanol and DTT are less effective; use 5–7.5 mM
tributylphosphine (TBP) or tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) instead. Otherwise, neutralize the
buffer or use buffers of higher pH before preparing samples for Experion runs.
3.4.2 Nonreducing Conditions
Prepare two stocks of sample buffer: one reducing (for the Pro260 ladder) and one nonreducing
(for the protein samples).
1. For each chip, transfer 30 µl sample buffer (yellow cap) to 2 microcentrifuge tubes.
2. Add 1 µl β-mercaptoethanol to one tube (reducing sample buffer) and 1 µl deionized water to the
other (nonreducing sample buffer). This generates enough nonreducing sample buffer for
10 samples. Vortex the tubes and cover them with foil to protect them from light.
3.5 Prepare the Samples and the Pro260 Ladder
Each chip can analyze up to 10 protein samples. All wells of a chip must be filled for the
electrophoresis station to operate properly.
The total protein concentration, including any added user-defined internal standards, in all starting
samples should be toward the middle of the linear dynamic range of the assay, if possible.
1. Prepare the Pro260 ladder by combining 4 µl Pro260 ladder (red cap) and 2 µl sample buffer with
β-mercaptoethanol (reducing sample buffer) in a microcentrifuge tube.
2. Prepare the samples by combining 4 µl sample and 2 µl sample buffer (Section 3.4) in a
microcentrifuge tube.
3. Vortex all tubes briefly and spin down in a microcentrifuge for a few sec.
4. Heat the samples and Pro260 ladder at 95–100°C for 3–5 min. Spin down the tubes in a
microcentrifuge for a few sec.
5. Add 84 µl deionized water to each tube and vortex briefly to mix. Do not modify this step to adjust
sample concentration.
Both the diluted samples and the Pro260 ladder are stable for several hours when stored at room
temperature and protected from light.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 11
Page 16

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
3.6 Prime the Chip
Start the run within 5 min of priming and loading the chip. For help with chip loading, refer to the
Experion Training Video: Chip Loading, available in the Experion software Help section under
Contents and Index > Contents > Appendices > Technical Videos.
1. Pipet 12 µl GS into the top right well of the chip (highlighted and labeled GS, gel priming well)
(Figure 3.1). Insert the pipet tip vertically and to the bottom of the well when dispensing. Dispense
slowly to the first stop on the pipet, and do not expel air at the end of the pipetting step.
2. On the priming station, set the pressure setting to B and the time setting to 3, as specified by the
alphanumeric code on the chip (Figure 3.1).
Gel priming well
Priming code
Fig. 3.1. Experion Pro260 chip. The locations of the gel priming
well (GS, highlighted) and alphanumeric priming code are indicated.
3. Open the Experion priming station and place the chip on the chip platform, matching the arrow on
the chip with the alignment arrow on the chip platform. A post on the chip prevents insertion in the
wrong position. Do not force the chip into position.
4. Close the priming station by pressing down on the lid. The lid should snap closed.
5. Press Start. A “Priming” message appears on the screen of the priming station, and the timer counts
down. Priming requires approximately 60 sec. Do not open the priming station during countdown.
6. An audible signal and “Ready” message indicate that priming is complete. Open the priming station
and remove the chip. If the lid sticks, press down on it while pressing down on the release lever.
7. Turn the chip over and inspect the microchannels for bubbles or evidence of incomplete priming. If
the chip is primed properly, the microchannels will be difficult to see (it may be helpful to compare a
primed chip to a new, unused chip). If you detect a problem, such as a bubble or incomplete priming,
prime a new chip.
8. Place the chip on a clean surface for loading.
Bubbles forced into microchannels during priming take the shape of the microchannel and are
elongated, not round.
12 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 17

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
3.7 Load the Chip
1. Using a pipet, remove and discard any remaining GS from the gel priming well. Pipet 12 µl GS into all
4 wells labeled GS (including the gel priming well, Figure 3.2).
2. Pipet 12 µl filtered gel (G) into the well labeled G (Figure 3.2).
3. Pipet 6 µl of each diluted sample into sample wells 1–10.
4. Pipet 6 µl diluted Pro260 ladder into the ladder well labeled L (Figure 3.2). Use the Pro260 ladder
within 8 hr of preparation. Every chip must have Pro260 ladder loaded into the ladder well labeled L.
Load 6 µl sample into wells 1–10
Load 6 µl ladder into well
labeled L
Fig. 3.2. Experion Pro26 0 chip. Wells for loading GS, G, samples, and ladder are indicated.
Load 12 µl GS into all 4 wells labeled GS
Load 12 µl G into well labeled G
5. Inspect all wells for bubbles by holding the chip above a light-colored background and looking
through the wells (Figure 3.3). Dislodge any bubbles at the bottom of a well with a clean pipet tip or
by removing and reloading the solution.
6. Place the loaded chip into the Experion electrophoresis station and start the run within 5 min.
Fig. 3.3. Bubble formation during loading of Experion Pro260 chips. Surface bubbles do not generally cause
problems during a run, but bubbles at the bot toms of wells must be removed. Lef t, bubbles trapped at the bottom of
wells. The GS and G wells and sample wells 1, 3, and 4– 6 contain no solution. Wells 8, 10, and L are filled properly and
have no bubbles, but large bubbles have formed at the bot toms of wells 7 and 9 (note the difference in the diameter of
the light-colored circles in wells 8 and 9). Right, bubbles have formed at the surface of the three GS wells on the right
side of the chip; the rest of the wells have no bubbles.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 13
Page 18
Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
3.8 Run the Pro260 Analysis
1. Open the lid of the electrophoresis station by pulling the release latch. Place the primed and loaded
chip on the chip platform and close the lid.
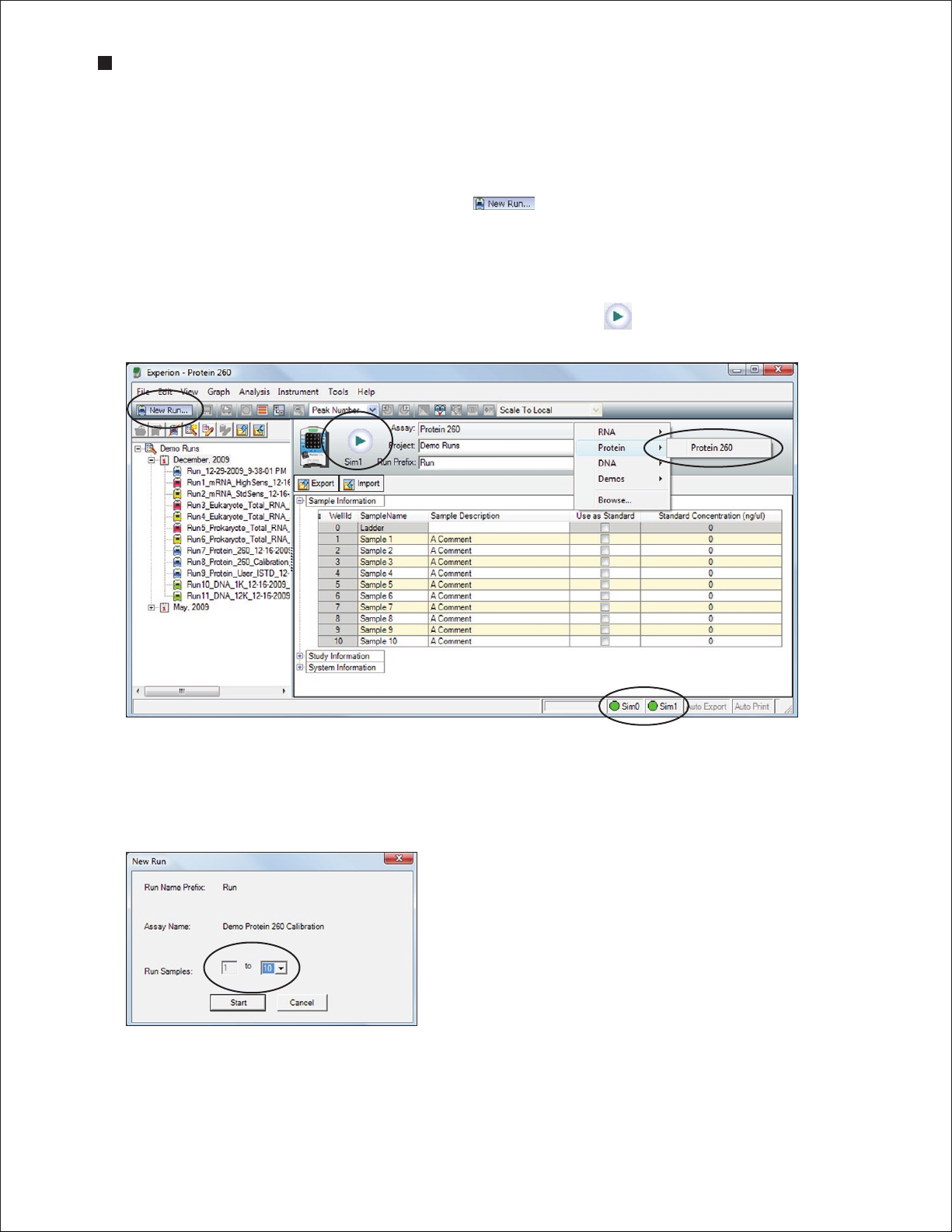
2. In the Experion software toolbar, click New Run . In the New Run screen (Figure 3.4), from
the Assay pull-down list, select Protein > Protein 260.
3. Either select a project folder for the run from the Project pull-down list or create a new project folder
by entering a name in the Project field or by selecting File > Project > New. The project folder
appears in the project tree.
4. Enter a name for the run in the Run Prefix field and click Start Run .
Fig. 3.4. Details of the N ew Run screen. The green dot in the lower right corner indicates that communication
between the ele ctrophoresis station and Experion software has been established.
5. In the New Run dialog (Figure 3.5), select the number of samples to be analyzed. Though all wells
are filled, the Experion system stops the analysis when it reaches the number of samples entered.
Fig. 3.5. New Run dialog. The Experion system stops analysis when it
reaches the number of samples entered.
14 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 19
Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
6. Click Start. The green LED in the center of the front panel on the electrophoresis station blinks, and
the system performs a number of checks: it confirms that a chip has been inserted, that all wells
contain liquid, that electrical connections are made, etc. A calibration counter marks the progress of
these calibrations at the upper right of the screen.
Do not open the lid of the Experion electrophoresis station until the run is complete. The lid does
not lock. Opening the lid aborts the run.
An “IV Check Error” message indicates the system cannot make electrical contact in one of the
wells. This often means there is a bubble at the bottom of the well. Abort the run, and check the
chip for bubbles or empty wells. Refill the affected well(s), and start the run again.
7. During separation, the sample name is highlighted in the project tree and the electropherogram
trace, and virtual gel bands appear in real time:
n
The electropherogram of the sample being separated appears in the electropherogram
view
n
The lane corresponding to that sample is outlined in pink and has a dark background
To display the electropherogram of another sample, click on either the sample name in the project
tree or on a lane in the virtual gel.
8. When analysis is complete (after ~30 min), the instrument beeps and a window opens indicating the
end of the run. Select OK and remove the chip from the chip platform.
9. Clean the electrodes using deionized water within 30 min of each Pro260 chip run.
3.9 Clean the Electrodes
1. Fill a cleaning chip with 800 µl deionized water (0.2 µm-filtered). Gently tap the side of the cleaning
chip to remove any trapped bubbles from the wells.
2. Place the cleaning chip on the chip platform in the electrophoresis station, close the lid, and leave it
closed for 1 min.
Never store the cleaning chip inside the electrophoresis station. Store the empty cleaning chip
covered to keep the wells clean. A cleaning chip is included with each box of chips.
3. Open the lid, remove the cleaning chip, and allow the electrodes to dry for 1 min. Close the lid.
4. Replace the water in the cleaning chip after use to avoid contamination. For storage, remove the
water from the cleaning chip and store the chip in a clean location.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 15
Page 20
Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
3.10 Evaluate the Run
When a run is complete, evaluate the run and the analysis of the data by Experion software.
1. Ensure all lanes (ladder and samples) are visible in the virtual gel. The markers (indicated by pink
triangles) should be visible in and aligned across all lanes. If the marker peaks are not properly
assigned, you may need to include or exclude peaks, or manually set the marker (see Section 6.3).
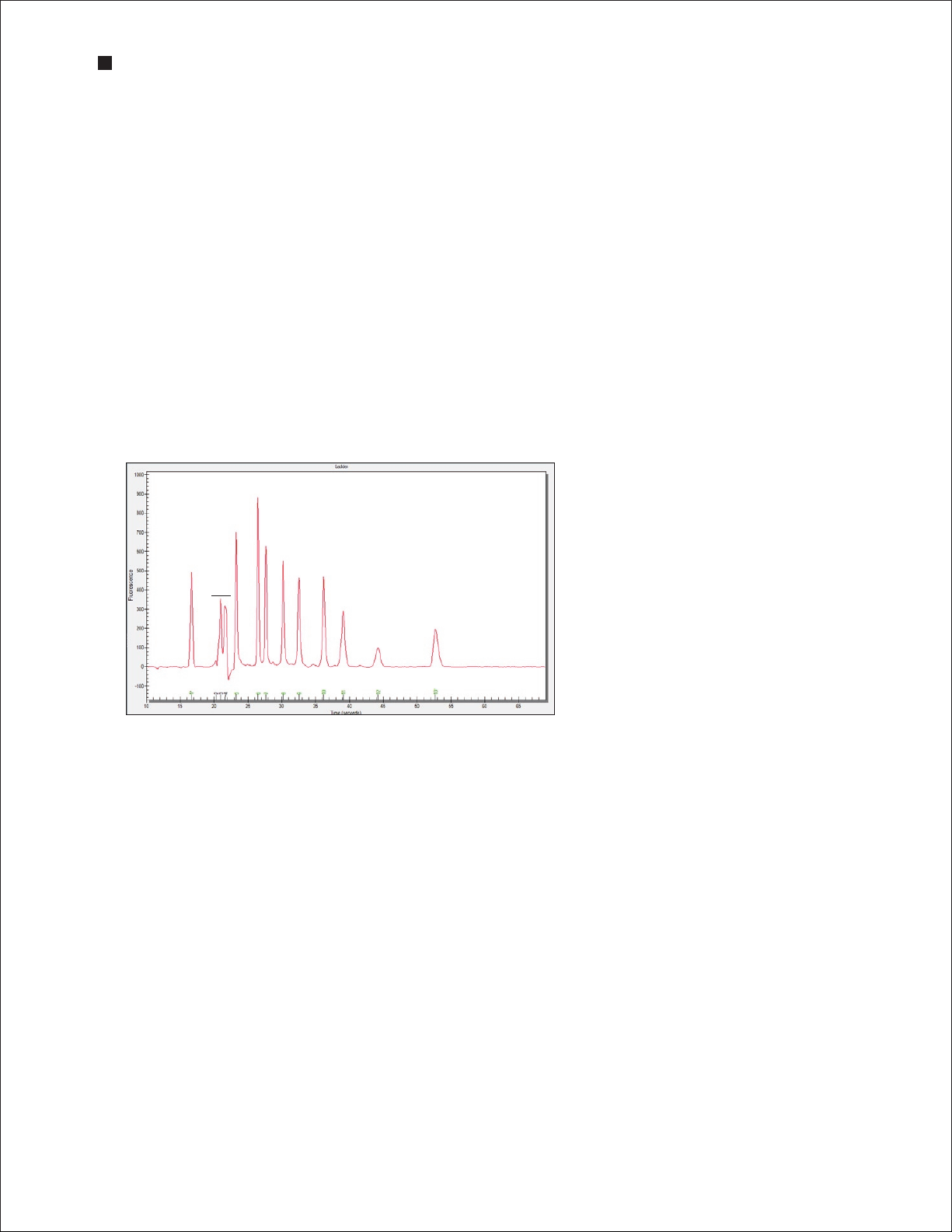
2. Evaluate the separation of the Pro260 ladder. To display the ladder electropherogram, click the
ladder well in the project tree, or click on the lane labeled L in the virtual gel. The electropherogram
should resemble the one shown in Figure 3.6 and should have the following features (if your ladder
does not have these features, see Chapter 7, Troubleshooting for more information):
n
Two marker peaks and a set of system peaks
n
Eight Pro260 ladder peaks between the system peaks and upper marker
n
Flat baseline
n
Marker peaks at least 20 fluorescence units above the baseline
Pro260 lad der pe aks
Lower marker
System p eaks
Upper m arker
Baseline
Fig. 3.6. Separation of the Pro260 ladder. Note
the flat baseline and well-resolved peaks. All
identified peaks are numbered, and the lower and
upper markers are indicated by green asterisks (*).
The 260 kD protein in the Pro260 ladder is labeled
as the upper marker in the Results table.
3. Examine the separation of at least one sample. Click on the sample name in the project tree or on
the lane in the virtual gel to view the electropherogram, which should have the following features:
n
Two well-resolved marker peaks and a set of system peaks
n
Sample peaks located between the system peaks and upper marker
n
Flat baseline
If the upper and lower marker peaks are not properly assigned, you may need to include or exclude
peaks, or manually set the marker (see Section 6.3).
4. Evaluate the data analysis performed by Experion software (see Chapter 4, Data Analysis). If
necessary, change the analysis settings and parameters — including protein quantitation methods
— by following the instructions in Chapters 5 and 6.
16 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 21

4
This chapter outlines the basic steps and software features used to view and analyze data. For a
more detailed description of Experion™ software and its various functions, refer to the software Help
menu. For information on how to customize analysis parameters, refer to Chapter 6, Changing Analysis
Settings and Parameters.
Data Analysis
17
Page 22

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
4.1 Viewing Data
The main window of the Experion software user interface contains menus and toolbars, a tree view, and
three data views: the electropherogram view, gel view, and results and settings tabs. (Figure 4.1).
Menu ba r
Main sc reen too lbar
Electr opher ogram v iew
Displ ay toolba r
Tree view
Fig. 4.1. Main window of Experion software. The toolbars, menus, and data views are indicated.
Gel vie w
Resul ts and set tings
tabs
4.1.1 Managing Run Files and Project Folders in the Tree View
The tree view (Figure 4.2) displays the project tree, a hierarchical tree of all projects and the data files
they contain. Use the project tree and the toolbar above it to:
n
Open run files and select samples for viewing
n
Create project folders
n
Export and import one or more run files
n
Edit names of run files and project folders
n
Move runs into project folders
n
Delete run files and project folders
Toolbar
Projec t folde r
Run file
Sample
Fig. 4.2. Tree view details. The project folder name, sample well
label, and run file prefix can be customized.
18 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 23

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
To open a run file, double-click on it. The run file opens, displaying the electropherogram and Results
tab for the Pro260 ladder, and the virtual gel for the entire run.
To view the data from a sample, click on the sample name or select the corresponding lane in the
gel view.
To edit a run file or project folder name, right-click on it and select Rename Project or Rename Run.
Type in the new name.
To import, export, move, or delete files and folders, click the ocons in the toolbar or use the context
menu accessed by right-clicking on the items in the tree view. For more details, refer to the Experion
software Help file.
4.1.2 General Display Controls
Data in the electropherogram view, gel view, and results and settings tabs are linked. Selecting a
sample or peak in one area automatically opens or highlights that sample/peak in the other two areas.
To adjust the relative sizes of the three data views and the tree view, click on and drag the border of the
view to its new location.
To hide or show one of the three data views, click on the corresponding icon in the display toolbar
(located in the upper-right corner of the display, just above the gel view (Figure 4.1).
To zoom in on (expand the view of) a portion of an electropherogram or virtual gel, click on the corner of
the area that you would like to enlarge and mouse over to the opposite corner. Double-click anywhere in
the electropherogram view to return to the previous view.
4.1.3 Electropherogram View
Experion software plots fluorescence intensity versus migration time to generate an electropherogram
for each sample. In the electropherogram, peaks identified by Experion software are numbered (Figure
4.3). Peaks generated by the markers and used for normalization (for example, the lower and upper
markers) are numbered in green and labeled with an asterisk.
To view the calculated size of a peak or other area of an electropherogram, place the cursor over the
peak/area (Figure 4.3). To display the sizes of all the peaks in the electropherogram, select Molecular
Weight in the Select Peak Information pull-down list (main screen toolbar).
Fig. 4.3 . Example of an electropherogr am. All identified peaks are numbered, and the lower and upper markers are
indicated by a green asterisk (*). Place the cursor over a peak to reveal its size.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 19
Page 24

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Double- or right-click on a peak to select it. An inverted black arrow appears above the peak in the
electropherogram, and a pink arrow appears above the corresponding band in the virtual gel. The peak
number and corresponding data also appear highlighted in the Results table.
Display electropherograms in three different ways:
n
One at a time (single-well view)
n
All at once in separate windows (all-wells view)
n
As superimposed images (overlays)
Single-Well View
This is the default view, which shows the electropherogram data from a single well (Figure 4.4). To return
to this display:
1. Click on the sample in the project tree or on the corresponding lane in the virtual gel.
2. In the main screen toolbar, click View Single Well or select View > Single Well.
3. The electropherogram appears. The corresponding lane in the virtual gel is outlined in pink.
Fig. 4.4. Single-well view. As indicated by the arrows, a single electropherogram appears, the name of the sample is highlighted in the project
tree, and the corresponding lane in the vir tual gel is outlined.
All-Wells View
To display all electropherograms simultaneously (Figure 4.5):
1. In the main screen toolbar, click View All Wells or select View > All Wells.
2. Electropherograms for each sample populate the electropherogram view (Figure 4.5). Use the
scroll bar to scroll through the electropherograms, or minimize the results and settings table to
accommodate the multiple electropherograms.
3. To select and expand a particular electropherogram, double-click on it. The data appear in a
single-well view.
20 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 25

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Scroll b ar
Fig. 4.5. All-wells view.
All electropherograms
are shown in the
electropherogram view.
Use the scroll bar to view
electropherograms.
Electropherogram Overlays
Superimpose (overlay) multiple electropherograms to facilitate direct comparison among profiles.
To overlay a subset of electropherograms (Figure 4.6), use one of the following options:
n
Move into the single-well view and, in the main screen toolbar, click Start Overlay .
Select wells (lanes) in the virtual gel. Each gel lane that is displayed in the electropherogram
is outlined. To end the overlay, click End Overlay
n
Select the lanes in the virtual gel while holding the Ctrl key (for noncontiguous, individual
lanes) or the Shift key (for lanes next to the original lane selected). To exit, click on a lane in
the virtual gel or on a sample name in the project tree
n
Select Analysis > Start Overlay. Select the lanes to overlay. To end the overlay, select
Analysis > End Overlay
Electropherograms appear superimposed in a single window, each in a different color. (The colors
cannot be changed.) The sample name appears at the top of the electropherogram, in a color that
corresponds to the trace. The fluorescence scale of the overlay electropherogram is based on the
sample that is selected first; therefore, select the sample with the highest peaks first.
Fig. 4.6. Electropherogr am
overlay. Electropherograms are
shown in different colors, and the
corresponding lanes in the virtual gel
are outlined. In this example, lanes 2,
5, and 7 are superimposed using the
overlay feature.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 21
Page 26

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Peak Labels
Experion software automatically labels detected peaks with numbers for easy identification, and the
upper and lower markers used for normalization are indicated in green and with an asterisk (*).
To change the type of label displayed, select Graph > Peak Info (or use the pull-down list in the main
screen toolbar) and select one of the following options:
n
No Peak Info — displays no peak information
n
Peak Number — uses sequential numbers for peak identification (default selection)
n
Peak Time — uses peak migration time (min:sec) for peak labels
n
Peak Height — uses peak height in units of fluorescence intensity for peak labels
n
Peak Cor. Area — uses calculated (corrected) peak area for peak labels
n
Molecular Weight — uses calculated mass (molecular weight, kD) for peak labels
n
Peak Concentration — uses calculated relative concentration (ng/μl) for peak labels
Electropherogram Tags (Annotations)
To annotate a peak in the electropherogram, right-click on the peak and select Add Tag (Figure 4.7).
A tag is automatically generated with the peak information selected (for example, peak number).
To edit a tag, right-click on it, select Edit Tag, and change the information. Click OK.
To annotate a region in the electropherogram, right-click in the region and select Add Tag. In the
Edit Tag dialog, enter the annotation and click OK.
To move a tag, click and drag the label to the desired place in the electropherogram.
Fig. 4.7. Example of tagged
(annotated) peaks in an
electropherogram.
22 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 27

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
4.1.4 Gel View
Experion software converts electropherogram data into densitometric bands, which appear in the virtual
gel (Figure 4.8). Each lane of the virtual gel corresponds to a different sample, and all samples from a
chip are shown in a single gel view. When a sample is selected for view as an electropherogram, the
corresponding lane in the virtual gel is outlined in pink.
Place the cursor over an area in the virtual gel to view its estimated size in kilodaltons (“kDa”). If a band
corresponds to a peak identified by Experion software, view the peak number and calculated size,
concentration, and percentage of total protein by placing the cursor over the band (Figure 4.8).
Right-click on a band to select it. A pink arrow appears above the selected band in the virtual gel, and
an inverted black arrow appears above the corresponding peak in the electropherogram. The peak
number and corresponding data also appear highlighted in the Results table. Only one peak can be
selected at a time.
To select a different color scheme, choose View > Gel Color and select a color from the list. By default,
the gel view displays bands as black signals on a white background.
To change the contrast of the bands, use the sliding cursor (Figure 4.8). Changing the contrast does not
change the data, but it may improve visualization of faint bands in the virtual gel.
Sliding cursor
Fig. 4.8 . Gel view. Place the cursor over a band in the gel view to display the peak number, size,
concentration, and % of total protein. Move the sliding cursor to adjust band intensity.
4.1.5 Results and Settings
The six results and settings tabs (Figure 4.9) present options for viewing, customizing, and analyzing the
separation data (see Section 4.3, Using Results and Settings to View and Annotate Data).
Fig. 4.9. Results and settings. Shown is the Results table for a single sample.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 23
Page 28

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
4.2 Changing the Fluorescence Intensity Scale
To display more or less detail in the electropherogram traces and lanes in the virtual gel, use the options
available under the Graph menu, which determine the scale used for the y-axis (fluorescence intensity)
of electropherograms and define the relative scale intensity of the lanes in the virtual gel (Figure 4.10):
n
Scale To Selected — uses the fluorescence value of the tallest peak in a selected
electropherogram to set the scale of the y-axis for all the other samples. Use this option
when comparing (overlaying) a sample with a high-intensity peak and one with a less
intense peak
n
Scale To Global — uses the fluorescence value of the tallest peak from all samples to set
the scale of the y-axis for all the samples. Use this option to adjust the virtual gel to be most
similar to an SDS-PAGE separation
n
Scale To Local (default) — uses the fluorescence value of the tallest peak in each
electropherogram to set the scale of the y-axis for that electropherogram: each sample
is scaled separately. This is the best way to view protein electropherograms and sample
details
n
Scale To Selected Peak — uses the fluorescence value of the selected peak to set the
scale of the y-axis for all samples
Scale To Sel ected
Fig. 4.10. Options for modifying the fluorescence intensity scale. Examples of how each option affects the display of a vir tual gel are shown.
Scale To Glo bal
Scale To Loca l
Scale To Sel ected Pe ak (Lane 11)
24 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 29

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
4.3 Using Results and Settings to View and Annotate Data
The following options appear under the results and settings tabs:
n
Results — summarizes analysis data for all detected peaks. The data in this table can be
exported (see Section 4.5.2, Exporting Data Files to Other Applications). To view the results
of a particular sample, click the electropherogram in the all-wells view or lane in the gel
view, or select that sample from the project tree. Alternatively, use the arrows in the main
screen toolbar to navigate through the samples. See below for instructions on how to
customize the types of data shown under this tab
n
Run Summary — displays a run summary for all wells; right-click to export the data
n
Protein Search Result — summarizes user-defined known proteins: lists the samples
that contain a peak that fits with the search of size, or molecular mass as defined
under the Protein Search Criteria tab and performs statistical calculations for the size,
concentration, and percentage of total protein for each peak identified
n
Protein Search Criteria — used to compare statistics for specific proteins in the samples
(see Section 6.1, Designating and Searching for Specific Proteins for information on how to
designate and then search for known proteins)
n
Run Info — used to enter sample names and comments after a run is finished (see below
for instructions)
n
Settings — used mostly for troubleshooting, but can be used to edit the parameters used
to identify peaks (see Section 6.5, Changing Peak Finding Parameters, or the Experion
software Help file for more details about these settings)
To customize the types of data shown under the Results tab:
1. Right-click on any of the column headers in the Results tab (or click the arrow to the left of the
column header). The Column Selector dialog opens.
2. Use the arrow keys to show, hide, or change the order of display of any of the available headers.
For detailed explanations of each setting, refer to the software Help file.
3. Click OK to save the changes, or click Cancel to close the dialog without saving the changes.
Under the Results tab, total concentration data appear at the bottom of the table. This calculation
represents the total protein concentration of the original sample. See Bio-Rad bulletins 5299, 5784,
and 5423 to learn more about comparing these calculations to data gathered by other methods.
To enter sample names and descriptions:
1. Click the Run Info tab and then click on the plus sign (+) next to Sample Information.
2. Click on any active cell, enter the sample names and descriptions, and click Apply. Click
File/Save to save the changes. The sample name appears above its electropherogram.
To enter other information about the experiment:
1. In the Run Info tab, click the plus sign (+) next to the Study Information and/or System
Information area(s).
2. Double-click in any blank field, enter the information, and click Apply. Click File/Save.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 25
Page 30

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
4.4 Comparing Data from Different Runs
Experion software allows you to overlay runs from different chips (same assay type), enabling direct
comparison of electropherograms and virtual gels from multiple chips. You can save and edit this new
virtual chip, but you will not be able to make any new calculations. All calculations in the Results table
carry over from the original runs.
In security mode, all run comparisons are saved and cannot be deleted.
1. Click Create a New Compare Run or select Analysis > New Compare Run. In the Compare
Runs Setting dialog, enter a name for the comparison in the Compare Name field.
2. Select the project in which you wish to store the comparison from the Target Project pull-down list.
3. Select the assay from the Assay Type pull-down list and click Next. The Compare Runs dialog
opens, displaying only runs of the same assay type.
4. Double-click to expand the run files you want to compare, or select a run file and click List Samples.
5. Click the run file or sample(s) and use the arrows to move them to and from the Compare field.
To select several lanes at a time, click the sample names while holding the Ctrl or Shift key.
To open a window displaying the selected samples in a gel view, click Show Gel Lanes.
Experion software accepts up to 40 samples for comparison (the default is 30). To change the
number of wells used, select Tools > Options. Under the Advanced tab, change the number
under Visible Compare Runs Gel lanes.
Only one ladder can be used per comparison. If a ladder is not selected, the ladder used in the first
run file is used as the ladder for the entire virtual chip. If an additional ladder is inserted in the virtual
chip, it is treated as a sample.
6. Select Realign Data to align the results of all the runs and click OK. The separations appear
together in one window as a single experiment. In the Results table, the sizes and concentrations for
proteins in each sample are unchanged; the original sizes and concentrations are shown.
7. To change the lanes used in the run comparison:
a. Open a run comparison by double-clicking the file name in the tree view and then clicking Edit
Compare Run or selecting Analysis > Edit Compare Run.
b. Select the samples you want to add or delete, and use the arrows to add or remove them from
the comparison.
c. To view the samples within a run, double-click the run file or select it and click List Samples.
8. Click OK to process the changes and view the results.
26 Tech Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 31

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
4.5 Saving, Exporting, and Printing Data
4.5.1 Saving Data Files
Data are automatically saved to a run file. Names for run files are given according to the selection made
in the Run Files tab of the Options dialog.
To designate a new name for a file, select File > Save As and enter the desired name.
To view the selections or make changes in the automatic naming of files, select Tools > Options >
Run Files. The following options appear:
n
Create Run name by combining — select the options to be added to the file name.
Options include the prefix (enter the desired characters), assay class (adds the assay type
to the file name), instrument name, date, and time
n
Run file folder — choose between default (saves files to the directory C:\Program Files\
BioRad Laboratories\Experion Software\Data) and custom (enables navigation and
selection of another folder)
n
Create daily folders — select to enable creation of daily subfolders by date. When this
option is selected, the software stores all run files from the same date in a single folder
4.5.2 Exporting Data Files to Other Applications
To export data to another program (for example, Excel software), select File > Export Data. In the
Export dialog, select the desired options. For a complete description of all export options, refer to the
Experion software Help file.
To export files automatically after a run is completed:
1. Select Tools > Options and click the Advanced tab.
2. Select Auto Export and then click Settings.
3. Select the options for Auto Export and click Apply.
To quickly copy and paste electropherograms, virtual gels or lanes in the gels, or data tables into
another application, use the options under the Edit pull-down list.
4.5.3 Printing Data Files
You can print both graphic and tabulated data from a run.
To choose the print options, select File > Print and select the desired options in the Print dialog.
For a complete description of all printing options, refer to the Experion software Help file (search term
“printing data”).
To print files automatically after a run is completed:
1. Select Tools > Options and click the Advanced tab.
2. Select Auto Print and then click Settings.
3. Choose the desired options in the Experion Print dialog and click Apply.
To save or print the data as a PDF file, select File > Print and select Print PDF.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 27
Page 32

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
28 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 33

5
Protein Quantitation Methods
29
Page 34

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
5.1 Protein Quantitation Methods
Experion™ software enables protein quantitation by several approaches. The selection of approaches
depends on the type of experiment and desired level of accuracy (Table 5.1). Refer to Appendix A and
bulletin 5784 for details about the different quantitation methods.
Table 5.1. Protein quantitation methods used by Experion software. Absolute quantitation methods provide greater
accuracy than relative quantitation methods. The accuracy of percentage determination is protein dependent.
Calibration Method and Internal Standard Used
Single-Point Calibration Curve
Quantitation Method Output Upper Marker User-Defined Upper Marker User-Defined
Percentage Determination % Total No internal standard required
Concentration Determination
Relative quantitation ng/µl l — — —
— l — —
Absolute quantitation ng/µl — — l —
— — —
l
5.2 Performing Percentage Determination
Experion software automatically calculates a percentage of total protein (% total) value for each detected
peak and lists the results in the % Total column of the Results table (Figure 5.1). Click on the peak of
interest in the electropherogram to highlight the data for that peak.
Fig. 5.1. Results table showing quantitation data for peaks in a sample. Experion software automatically
performs % total and relative concentration determinations for each peak identified in every sample.
To exclude a peak from the % total calculation, right-click on the peak (in either the single-well
electropherogram view or Results table) and select Exclude Peak in the context menu. The new
calculations for the remaining peaks appear in the Results table.
This change affects a selected sample. To exclude multiple peaks from multiple samples, use the
Settings tab and the Peak Find Settings options in the All Wells Settings dialog (see Section
6.4, Excluding a Peak From Analysis and 6.5, Changing Peak Finding Parameters) and adjust the
peak detection criteria.
30 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 35

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
5.3 Performing Relative Quantitation
Experion software also automatically performs quantitation of all peaks in a sample by a single-point
calibration to the 260 kD upper marker and presents these data in the Concentration (ng/µl) column of
the Results table.
To view these default relative quantitation results, click on the peak of interest in the electropherogram to
highlight the data for that peak.
To perform relative quantitation against a different, user-defined internal standard:
n
Add the standard to the samples at a single concentration, and
n
Change some of the analysis settings in the software
Selection of the user-defined standard in the software may be done after the run is complete. This
enables easy comparison of the relative quantitation results derived by using both the upper marker and
the user-defined standard.
To perform relative quantitation with a single concentration of a user-defined internal standard:
1. Prepare the protein samples and reagents as outlined in Section 3.5, except add a known
concentration of the internal standard (for example, 500 ng/µl) to each sample. For example, replace
half the volume of sample with the internal standard (combine 2 µl sample, 2 µl internal standard, and
2 µl sample buffer).
Do not add the internal standard to the Pro260 ladder.
2. Run the Pro260 analysis.
3. After evaluating the run as described in Section 3.10, select Analysis > Internal Std. and Std
Protein Calibration Curve.
4. In the Internal Std. and Std. Protein Calibration Curve window (Figure 5.2), select Use User
Internal Standard and enter the name, concentration, and molecular weight (MW) of the internal
standard. Click Apply and then Close. The new concentrations appear in the Results table under
the Concentration (ng/µl) column (Figure 5.3).
Fig. 5.2. Internal Std. and Std. Protein
Calibration Curve window.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 31
Page 36

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Fig. 5.3. Results from
relative quantitation.
5.4 Performing Absolute Quantitation
Experion software also allows quantitation using a calibration curve generated by a range of known
concentrations of that protein (absolute quantitation). In this method:
n
Different concentrations of the protein are separated in different sample wells
n
The peak areas of the different concentrations are compared to the peak area of an internal
standard. As with relative quantitation, either the upper marker or a user-defined protein
can be used as the internal standard
n
The protein concentrations in the samples are then determined from this calibration curve
Experion software displays the results for both relative and absolute quantitation, enabling easy
comparison of the accuracy achieved by these different approaches.
5.4.1 Absolute Quantitation Using the Upper Marker as Standard
1. Prepare a dilution series of 3–6 different concentrations of the protein used for calibration. The total
protein concentration in each sample must be within the linear dynamic range of the assay. Prepare
these samples with the other samples for Pro260 analysis as described in Section 3.5.
2. In the Run Info tab under Sample Information, designate the wells that contain the proteins for
the calibration curve by selecting them in the Use as Standard column (Figure 5.4). Enter their
concentrations in the Standard Concentration column and click Apply.
3. Run the Pro260 analysis.
Fig. 5.4. Run Info tab illustrating the creation of a 5-point calib ration cur ve with wells 1–5 .
32 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 37

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
4. After evaluating the run as described in Section 3.10, select Analysis > Internal Std. and Std
Protein Calibration Curve.
5. In the Internal Std. and Std. Protein Calibration Curve window (Figure 5.5), do the following:
a. Under Standard Information, next to Standard Protein Molecular Weight, enter the MW
corresponding to the region where the software searches for a peak, for both the calibrants
and the samples. The software checks for a peak in the sample wells that has the entered
value (± 5%). If necessary, modify the concentrations of the calibrants by double-clicking on the
concentration value and typing in a new value.
b. Ensure that Use User Internal Standard is not selected.
c. Under Calibration Curve Settings, if the protein used for calibration (calibrant) is different or
has a different mass than the protein being quantitated, select Quantitate All Proteins and click
Apply. If you do not do this, the software only reports absolute concentrations for peaks that are
the same size as the calibrant.
d. Under Calibration Curve Settings, select the Linear Regression to be used.
e. Click Apply to update the calculation. The calibration curve appears and displays the equation
for the linear regression (Figure 5.5). The table below the graphic displays data for the wells
containing the standards. Click Close.
6. In the Results tab, the concentration for each protein identified by Experion software is derived
by relative quantitation against the 260 kD upper marker and automatically appears in the
Concentration column; the calibrated concentrations of proteins found in the specified region
appear in the Calib. Conc. column.
Fig. 5.5. Internal Std. and Std Protein Calibration Curve window. In this example, a 100 kD protein is used to build a
5-point calibration curve for quantitating a 100 kD sample protein.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 33
Page 38

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
5.4.2 Absolute Quantitation Using a User-Defined Internal Standard
This is the most stringent method of quantitation. It combines two of the approaches described above:
n
A calibration curve is generated using known concentrations of a protein, and
n
A user-defined protein is used as the internal standard
1. Prepare a dilution series of 3–6 concentrations of the protein that you will use for calibration.
2. Add a known concentration of the internal standard to each sample (except the Pro260 ladder),
including those that will be used for calibration. Prepare these samples and other samples as
described in Section 3.5.
3. Under the Run Info tab, designate the wells that contain the proteins for the calibration curve and
enter their concentrations (Figure 5.5). Click Apply and run the Pro260 analysis.
4. After evaluating the run as described in Section 3.10, select Analysis > Internal Std. and Std
Protein Calibration Curve.
5. In the Internal Std. and Std. Protein Calibration Curve window (Figure 5.5), do the following:
a. Under Standard Information, next to Standard Protein Molecular Weight, enter the MW
corresponding to the region where the software searches for a peak, for both the calibrants
(standards) and the samples. The software checks for a peak in the sample wells that has the
entered value (± 5%). If necessary, modify the standard concentrations by double-clicking on the
concentration and entering a new value.
b. Select Use User Internal Standard and enter the name, concentration, and size of the internal
standard. Click Apply.
c. Under Calibration Curve Settings, if the protein used for calibration (calibrant) is different or
has a different mass than the protein being quantitated, select Quantitate All Proteins and click
Apply. If you do not do this, the software only reports absolute concentrations for peaks that are
the same size as the calibrant.
d. Under Calibration Curve Settings, select the Linear Regression to be used. Click Apply to
update the calculation.
6. The calibration curve appears, displaying the equation for the linear regression. The table below the
graphic displays the data for the protein standard samples. Click Close.
7. In the Results table, the concentration for each protein derived by relative quantitation against
the user-defined internal standard appears in the Concentration column, and the calibrated
concentration (using the calibration curve in conjunction with the user-defined standard) appears in
the Calib. Conc. column.
34 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 39

Changing Analysis
6
Settings and Parameters
Once an Experion™ analysis is complete and you have examined the quality of the run and of the
data, you can reanalyze the data by changing some of the settings. Most of the steps outlined in
this chapter are used for troubleshooting purposes or are optional; they are not required in most
analyses.
35
Page 40

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
6.1 Designating and Searching for Specific Proteins
1. Designate and search for specific proteins in your samples:
a. In the Protein Search Criteria tab, click Add Protein Name , or in the electropherogram,
right-click on a peak and select Add to Protein Search Criteria. The Protein Search Criteria
tab opens and contains the mass and tolerance range for that entry.
b. Click in the field under Protein Name and enter the protein name.
c. Click in the field under Mol Wt and enter the size of the protein in kD.
d. Click in the field under the ±s mass column to enter the new value for the tolerance in kD and
exclude wells that are not relevant to the search.
2. A list of all the peaks that fit the criteria appears in the Protein Search Result tab. Separate tables
appear for each protein designated in the search criteria list. To exclude a peak, right-click on the
peak name in the table and select Exclude Peak.
3. To delete designated proteins (“protein names”) from a search, click Delete Protein Name in
the toolbar of the Protein Search Criteria tab.
6.2 Changing Protein Quantitation Parameters
Experion software uses relative quantitation against the upper marker to calculate the concentrations of
all the peaks detected in a sample. The calculated concentrations appear in the Results table, under the
Concentration (ng/µl) column.
For more information about protein quantitation, including about how to perform relative quantitation
against a user-defined standard or to perform absolute quantitation using a calibration curve, refer to
Appendix A and the instructions provided in Chapter 5, Protein Quantitation Methods.
6.3 Manually Setting a Marker
To designate a peak as a marker (and change the alignment of a sample), right-click on the peak in
either the electropherogram (single-well view) or the Results table and select Manually Set Lower
Marker or Manually Set Upper Marker to define the peak as the new lower or upper marker. Do this if
no or incorrect peaks have been selected as the lower or upper marker.
Pink triangles in the virtual gel indicate markers. The markers should be aligned across all lanes.
6.4 Excluding a Peak from Analysis
To exclude one or more peaks from analysis of a single sample, right-click on the peak in either the
electropherogram (single-well view) or Results table and select Exclude Peak from the context menu.
This change affects only a selected sample.
To exclude multiple peaks from multiple samples, open the Settings tab and use the Peak Find
Settings options in the All Wells Settings dialog (see Section 6.5, Changing Peak Finding Parameters)
to adjust the criteria by which peaks are detected.
Excluded peaks are not included in total protein calculations. Therefore, excluding a peak from analysis
affects percentage determination (% total calculations) for the other peaks in a sample.
36 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 41

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
6.5 Changing Peak Finding Parameters
The parameters entered tell the peak-find algorithm whether a peak is significant.
To edit the parameters used by Experion software for finding peaks in a selected sample/well:
1. Select the sample by clicking on the lane in the virtual gel (or on the sample name in the tree view).
2. Under the Settings tab, edit the parameters under Peak Find Settings:
n
Slope Threshold — represents the variation in fluorescence units over time required to
detect a peak (accepted values are 0.2–1,000, with lower values yielding more peaks)
n
Min. Peak Height — minimum height required for a peak to be integrated (accepted values
are 0.1–1,000). Determine the appropriate value for this parameter by zooming in on a small
peak in an electropherogram and reading its fluorescence value on the y-axis
n
Min. Peak Width — minimum amount of time that must elapse before a peak is
recognized (accepted values are 0.1–10, with lower values yielding more peaks)
3. Click Apply to apply the changes and reanalyze the data. Click Save in the main screen toolbar to
save the new conditions or click Reset to Default to recover the default settings.
To modify the peak-find settings for all sample wells:
1. Under the Settings tab, click the All Well Settings tab or select Analysis > All Wells Settings.
2. In the All Wells Settings dialog, expand Peak Find Settings and select the type of modification you
would like to apply (see above for descriptions).
3. Click OK to apply changes and Ye s to overwrite the settings. Click Save in the main screen toolbar
to save the new conditions. To reset to default settings, click Reset to Default.
Do not adjust the Peak Find Settings values so that the markers are eliminated from analysis.
6.6 Changing General Settings
These settings appear in the Settings tab, in the All Wells Settings dialog under General Settings
(Figure 6.1). They apply to all samples in a run.
n
Data Frequency — displays the rate of data collection in Hz
n
Display Start Time — displays the time Experion software begins displaying peaks
n
Display End Time — displays the time Experion software stops displaying peaks
n
Upper Marker Concentration — displays the concentration of the upper marker
n
Use Time Corrected Areas — corrects for peaks of different sizes that pass the detector
at different rates
n
Calibrate All Valid Peaks — select this option if you are running a calibration curve and
want Experion software to calibrate all peaks (this is the same as selecting Quantitate All
Proteins in the Internal Std. Protein Calibration Curve window)
n
Filter Width — determines the width of the polynomial (in sec) to be applied to the data for
filtering (noise reduction). Set this variable to less than twice the width of peaks. Valid values
are 0.3–10
n
Polynomial Order — defines the power series applied to fit the raw data. Valid values are
1–10, with lower values yielding smoother curves
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 37
Page 42

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Fig. 6.1. General Set tings options.
6.7 Baseline Modification
To change the method used by Experion software for adjusting the baseline in a selected
electropherogram (single sample):
1. Under the Settings tab, select one of the following two options under Algorithm Inclusion Settings
(Figure 6.2):
n
Baseline Correction — (default) subtracts the baseline from the signal. The baseline
represents a slow, rolling component in the signal. Generally, this method affects the
original shape of the curve and subsequent calculations. The more complex the baseline,
the greater impact subtraction might have on the signal. However, for well-resolved peaks
with a slow rolling component, this method can normalize calculations across the chip.
If peaks are poorly resolved, baseline correction can cause considerable artifacts
n
Zero Baseline — subtracts the average baseline value from the signal. This method
does not affect the shape of the curve; it shifts the baseline down to zero. If the Baseline
Correction option results in undesirable artifacts (small peaks do not appear, or too many
peaks appear), change this setting to see if it remedies the problem
Deselecting both options makes the original signal(s) appear. Sometimes it is important to see the
difference between the signals across the chip if no correction is applied.
2. Click Apply to apply the changes and reanalyze the data, and click Save in the main screen toolbar
to save the new conditions or choose Reset to Default to recover the default settings.
To edit the parameters used by Experion software for adjusting the baseline for all samples:
1. Either open the Settings tab or select Analysis > All Wells Settings.
2. In the All Well Settings dialog, expand Algorithm Inclusion Settings and select the type of
modification you would like to apply (see above for descriptions or Figure 6.2). Click OK.
3. In the Experion Application dialog, click OK and Yes to to overwrite the sample settings. Click
Save in the main screen toolbar to save the new conditions. To reset to default settings, click
Reset to Default in the Settings tab under All Well Settings.
38 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 43

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Fig. 6.2. Algorithm Inclusion Settings window.
6.8 Turning Analysis Off
To turn analysis off, select Analysis > Turn Analysis Off. Analysis remains off for all runs until it is
turned back on.
Turning analysis off displays the raw data from a run; it deactivates alignment, shifting the positions of
the upper and lower markers in each sample. In addition, the pink arrows (in the virtual gel) indicating
the positions of the markers appear only in the ladder lane. With analysis off, the migration of the
markers may not be perfectly aligned and the position of the upper marker may drift (Figure 6.3). Turning
analysis off can help reveal if a problem is isolated (one or a few wells have markers out of alignment) or
is general (alignment problems across the entire chip).
Analy sis on Analysis of f Analy sis on A nalysis off
Fig. 6.3. Effects of turning analysis of f for two samples.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 39
Page 44

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
6.9 Manual Peak Integration
This function enables definition or refinement of peak areas for the ladder and all sample lanes.
1. Select a sample and click or select Analysis > Manual Integration to start manual integration.
2. Adjust the baseline by clicking and dragging the dots at the ends of the peaks (Figure 6.4).
If a peak in the electropherogram is not detected by the software, right-click on that peak and select
Add Peak. Zoom in on the peak for a better view of the baseline.
3. Save any changes by selecting File > Save Run As (use a new file name), or revert to the original
baseline and integration by clicking .
Manual integration applies to individual sample wells. Moving back to automated integration loses
changes made during manual integration unless those changes are saved.
Fig. 6.4. Manua l integration mode indicates the beginning and end of peak baselines
with blue dots.
40 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 45

7
Troubleshooting
41
Page 46

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
7.1 Electrophoresis and Priming Stations
Error Probable Cause Recommended Action
IV Check Failure
(Experion™ software)
Check Seal
(Priming station)
One or more wells are not filled correctly, and
the electrodes are not immersed
Air bubbles are interfering with the electrical
contact in one or more of the wells
An electrode is loose or disconnected Perform a conductivit y test with the cleaning chip or
Lid is not closed Close the lid
The chip is not primed properly Repeat the analysis using a new chip
The priming seal is worn, torn, or clogged Replace the priming seal (catalog #700-7031)
The chip is not positioned correctly in the
priming station
The gel-stain solution (GS) was added to the
wrong well for priming
Fill all sample wells of the chip with blank or replicate samples
Ensure pipets are properly calibrated
Stop the run, remove the chip, and use a clean pipet tip to
remove the sample and apply a new aliquot
When pipetting, inser t the tip vertically and to the bottom of
the well. Dispense the liquid slowly. Do not expel air at the end
of the pipetting step. Dispense only to the first stop on the
pipet. Positive (reverse) pipetting may also be used
conductivit y chip from the Experion validation kit (catalog
#700-7051). Add 850 µl water to the chip, place the chip in
the electrophoresis station, and close the lid. In Experion
software, select Tools > Diagnose Instrument and select
Conductivity in the Instrument Diagnostics dialog
If the test passes, focus on the sources of error above. If it
fails, contact technical support with the results
Align the arrow on the chip with the arrow on the platform
The priming well is highlighted on the chip. Se e Section 3.6,
Prime the Chip
No chip detected Chip not positioned properly, empty wells,
Run aborts before all wells
are analyzed
or incor rect reagents
The computer power saver options are
causing the runs to abort (this is only a
problem with Experion software prior to
version 3.0)
Make sure chip is positioned prope rly and correct reage nts
used
Upgrade to the newest software version
Confirm that all power saver and/or power options are turned
off before star ting the assay. Do not let the computer “sleep”
during a run. If the computer goes to sleep, the run will abort
7.2 Experion Pro260 Analysis
Error Probable Cause Recommended Action
Concentrations are not
reproducible (CV > 20%)
Peaks were not detected in
the Pro260 ladder
Sample preparation procedures are
inconsistent
An air bubble is at the bottom of the ladde r
well or microchannels due to poor priming or
sample loading; air bubbles can interfere with
the contact between the electrode and the
liquid
Use the same reagents and follow the same procedures
for each sample and each r un. Do not modify the
protocol outlined in Chapter 3 to compensate for protein
concentration or sample variabilit y
Check the chip for air bubbles after priming and sample
loading:
n
After priming: turn the chip over and make sure the
microchannels are filled with gel-stain solution (GS). If
the chip is primed correctly, the wells should be hard to
see. Compare the primed chip to an unprimed chip if
necessary. Do not touch the glass
n
After sample loading: tilt the chip and view it from different
angles against a light background
42 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 47

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Error Probable Cause Recommended Action
No peaks were detected
in some samples
No peaks detected in any
samples
There is not enough sample in the wells Ensure that pipets are calibrated and that 6 µl solution has
Samples were not prepared properly Review the sample preparation procedure detailed in
Pro260 stain was photobleached Protect the Pro260 stain, gel-stain solution (GS), sample
Particulates are clogging the microchannels Use only high-quality, 0.2 µm-filtered water (such as
Gel-stain solution (GS) is old or has been
photobleached
Chip was not primed with the correct pressure
and time settings
Particulates are clogging the microchannels Use only high-quality, 0.2 µm-filtered water (such as
been added to the wells
Chapter 3. The Pro260 ladder must be prepared with
reducing sample buf fer even when samples are to be
separated under nonreducing conditions
buffer, and prepared and diluted samples from light
Prepare new GS; use a new tube of Pro260 stain if
necessary
ReadyPrep™ proteomics grade water, not autoclaved water)
Verify that the gel (G) and GS were properly filtered
If using samples that contain particulates, perform a quick
microcentrif uge spin of the prepared sample to pellet
particulates before loading
Prepare fresh GS
Check settings on the priming station and repeat the
analysis with a new chip
ReadyPrep proteomics grade water, not autoclaved water)
Verify that the gel (G) and gel-stain solution (GS) were
properly filtered
If using samples, such as cell lysates, that contain
particulates, perform a quick microcentrifuge spin of the
prepared sample to pellet particulates before loading
Lower and/or upper marker
is missing
Electropherogram peaks are
much smaller than expected
(peaks are <50% of what is
expected)
Samples do not contain sample bu ffer or were
not prepared properly (if both are missing)
Late migration If only the upper marker is missing, refer to the
Too much stain in the gel-stain solution (GS);
sample cannot destain completely, and the
background is high; too much stain can
contribute to high background (>1,000 RFU)
and low sample and ladder peaks
Not enough sample was added Ensure pipets are calibrated
Too much salt in the sample; salt ions compete
with the sample ions during injection
One or more components in the sample is
beyond the concentration range listed in the
compatibilit y table (Appendix C)
Gel-stain solution (GS) is old or has been
photobleached
Review the sample preparation procedure in Chapter 3
trouble shooting tips for late migration (below)
Prepare new GS using a new tube of stain. Ensure stain is
thawed completely before preparation
Use pipets that accurately deliver volumes of 10 µl or less
Analy ze a dilution series of the sample in water on
another chip. If the peak heights and calculated protein
concentrations of the diluted sample increase, the salt is too
high in the original sample. Determine the proper dilution to
minimize the salt effect
Analy ze a dilution series of the sample in water on another
chip. Adjust your sample preparation procedure as
necessary
Prepare fresh GS
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 43
Page 48

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Error Probable Cause Recommended Action
Reagents, specifically the Pro260 stain, were
not brought to room temperature prior to use; if
stain is not equilibrated to room temperature, it
will be more concentrated when it is added to
the gel, which may result in signific antly lower
protein peaks and areas
Repeat the analysis with a new chip, new tube of stain, and
properly equilibrated reagents
Peaks are small, broad, or
missing in some samples,
but present in other samples
on the chip
Late migration (peaks
broaden and are de layed
over the course of the r un)
Gel (G) and gel-stain solution (GS) were
mislabeled or used improperly. The Pro260
chip contains specific wells for G and GS:
GS wells carry the sample through the
microchannels and supply the dye for analysis,
and the G well is used for destaining prior
to detection. If G and GS are added to the
incorrect wells, peaks can be small, crowded,
or missing in ele ctropherograms
Pro260 ladder and samples were not
completely denatured
Contaminants are prese nt Che ck chemical compatibility char ts (Appendix C) and
Sample pH is lower than 5 Adjust pH of the sample to 5 or above
Air bubbles are interfering with electrical
contact in one or more of the wells
Ensure chip was primed with GS
Ensure G was used in the G well and GS was used in all
wells marked GS
Heat samples and Pro260 ladder for 3 –5 min at 95–100°C
before loading
prepare samples in a dif ferent extraction buffer or dilute
them in water, if necessary
Do not use autoclaved water for diluting protein samples or
ladder. Use only high-quality, 0.2 µm-filtered water (such as
ReadyPrep proteomics grade water)
Turn analysis off (see Section 6.8, Turning Analysis Off, for
more information). Late migration is indicated if there is a
drift in the migration of the lower marker across the chip and
the upper marker migrates later and runs off the top of the
gel view. Refer to the troubleshooting tips that follow
Stop the run, remove the chip, and use a clean pipet tip to
remove or dislodge the bubbles, or re move and replace the
solution in affected wells
When pipetting, inser t the tip vertically and to the bottom of
the well. Dispense liquids slowly. Do not expel air at the end
of the pipetting step. Dispense only to the first stop
Peaks migrating faster than
usual; electropherogram
appears compressed
Molecular mass (sizing) is
incorrect
Electrophoresis station temperature is
inappropriate or fluctuating during the run
(should be 30– 35°C); there is no cooling
unit in the electrophore sis station, so if the
temperature changes during the course of a
run, the samples will exhibit different separation
characteristics
Pro260 ladder peaks and upper and lower
markers were improperly assigned by the
software
Ensure that the temperature of the room is appropriate and
stable, and place the electrophoresis station away from all
heat sources, such as windows or ovens
Exclude peaks (follow the instructions in Section 6.4,
Excluding a Peak From Analysis) or ma nually assign markers
(follow the instructions in Section 6.3, Manually Setting a
Marker), if necessary
Sizing should be within 10% of the size seen by SDS-PAGE,
except for proteins with high levels of posttranslational
modification, or highly acidic or basic proteins
44 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 49

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Error Probable Cause Recommended Action
Protein quantitation is
incorrect
Upper and lower markers were not properly
assigned by the software
Pipetting and/or dilution errors occurred during
sample preparation or chip loading
Samples are old or have not been stored
properly, and the proteins degraded
Samples were not denatured prope rly;
regardless of whether re ducing or nonreducing
conditions are used, the Pro260 ladder and
samples must be heat-denatured for the assay
to run properly
Samples do not have the same staining
proper ties as the upper marker
Check that both markers were properly assigned. Manually
select the marker(s), if necessar y (follow the instr uctions in
Section 6.3, Manually Set ting a Marker)
Ensure your calculations and dilutions are corre ct
Ensure that pipets a re calibrated, and use pipets that
accurately deliver volumes of 10 µl or less
Do not modify the sample preparation and loading protocols
described in this manual
Ensure that the total protein concentration of your samples
(including any user-defined internal standards that may be
added) is within the linear dynamic range before procee ding
with the sample preparation instructions described in
Section 3.4; if total protein concentration is unknown, run a
Pro260 analysis of a dilution series of your sample
Review the essential practices described in Chapter 2
before initiating another analysis with a new chip
Prepare fresh samples and try the analysis again
Heat the samples and the Pro260 ladder for 3–5 min at
95–100°C before loading them into the chip. Keep the
caps of the s ample and ladder tubes closed during heating
to prevent loss of vapor and subsequent changes in
concentration. Briefly centrifuge the samples before opening
Use a dif ferent internal standard or a calibration curve
(see Chapter 5, Protein Quantitation Methods, for more
information)
Ghost peaks or
contaminants appear in
electropherograms
Upper or lower marker is
incorrectly identified
Portion of the
electropherogram is
incorrectly identified as a
peak
Virtual gel does not
resemble an SDS-PAGE
separation of the same
samples
Glycoproteins are not
separating as expected
Electrodes are contaminated Follow the deep cleaning procedure described in Appendix
Sometimes Experion soft ware selects the
incorrect peak to correspond to the upper or
lower marker. Such an error affects alignment
and sizing
Default integration settings are inapporpriate
for the sample
The gel view is a direct interpretation of
the electropherogram data. By default, the
fluorescence intensity of the bands in each
lane is sc aled to the intensity/peak height
of the highest peak in that sample (scale to
local). Consequently, each gel lane may have
a different scale of fluorescence intensity. In
addition, Experion Pro260 analysis differs from
SDS-PAGE in several ways that may impact
separations
Large and complex glycosolated proteins may
not migrate as expected with the Experion
Pro260 assay; however, their separation
characteristics will be reproducible
B and the sof tware Help section (se arch term “electrodes”)
Use only 0.2 µm-filtered water (such as ReadyPrep
proteomics grade water) for diluting the protein s amples and
Pro260 ladder; do not use autoclaved water
Manually select the upper and lower mar kers by following
the instructions in Section 6.3
Manually exclude a peak (see Section 6.4) or change the
peak finding parameters (see Section 6.5)
Adjust scaling of the vir tual gel to Scale To Global
(see Section 4.2). This also adjusts the scale on all the
electropherograms. Adjust the intensity bar to the right of
the virtual gel as needed
In an Experion Pro260 analysis, the separation of the 10 kD
and 260 kD markers is almost linear, whereas in SDS-PAGE
it is logarithmic. To mimic the appearance of an SDS-PAGE
separation, select Tools > Options > Advanced and select
the Gel Mobilit y Correction option
For more information, refer to Bio-Rad bulletin 5453 or
contact Technical Suppor t
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 45
Page 50

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Error Probable Cause Recommended Action
Baseline is fluctuating (for
example into very negative
and positive values)
Air bubbles are interfering with electrical
contact in one or more of the wells
Chip is not completely primed Prime and load a new chip
Samples are too concentrated; protein levels
are out of the range of the assay
Stop the run, remove the chip, and remove and replace
solution in affected wells
Dilute the samples and repeat the analysis
7.3 Contacting Technical Support
If you are having problems with a run and would like the Bio-Rad Technical Support team to review your
data, please submit the following files to LSG_TechServ_US@bio-rad.com for analysis:
n
Run file (C:\Program Files\Bio-Rad Laboratories\Experion Software\Data\<daily folder
name>\<run name>.bdf)
n
Run log (C:\Program Files\Bio-Rad Laboratories\Experion Software\Data\<daily folder
name>\<run name>.log)
n
Packet file (C:\Program Files\Bio-Rad Laboratories\Experion Software\Data\<daily folder
name>\Packet\<run name>.txt)
n
System log (C:\Program Files\Bio-Rad Laboratories\Experion Software\Backup\Version X\
Experion_System.log or .txt)
n
Lot numbers of the Pro260 chips and the Experion Pro260 analysis kit
To export the run file, log file, and packet file, select the run(s) in the tree view and click Export Selected
Runs. The software exports the files into folders with the corresponding project name(s).
46 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 51

A
Appendices
47
Page 52

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Appendix A: How the Experion™ System Works
The Experion automated electrophoresis system performs electrophoresis of samples within a
microfluidic chip. Within each chip, a series of microchannels connects the sample wells to a separation
channel and buffer wells. A set of electrodes in the electrophoresis station applies a voltage across
the microchannels, causing charged molecules in the samples to migrate into and through the
separation channel. Samples are run sequentially, with a sufficient lag between them to prevent crosscontamination. For separation, the microchannels are filled with a proprietary gel-stain solution (GS)
that acts as a sieving matrix, and under denaturing conditions in the presence of lithium dodecyl sulfate
(LDS), the sample proteins migrate through the separation channel at a rate based on their size. Finally,
proteins interact with a fluorescent dye during separation and are detected as they pass a laser and
photodiode detector (laser-induced fluorescence).
Protein analysis is accomplished with the Experion Pro260 analysis kit and involves the following steps:
n
Preparing the chip (priming and loading) — Priming fills the microchannels of the
microfluidic chip with GS, which contains both the sieving matrix and fluorescent dye.
Protein samples are then prepared in Pro260 sample buffer, which contains LDS, heatdenatured, and added to the sample wells
n
Running the chip — The chip is inserted into the electrophoresis station, and as the
instrument lid is closed, electrodes come into contact with the solution in the wells. Voltage
is applied to the sample wells of the chip, causing the charged, LDS-coated protein ions
to migrate into the separation channel. In the separation channel, the different proteins
separate as they move at different rates through the gel matrix, depending on their size.
During separation, the fluorescent dye associates with the LDS micelles coating the
proteins and with free micelles1
n
Detecting the fragments — As the molecules migrate toward the end of the separation
channel, destaining occurs. Pro260 gel (G), which does not contain dye or LDS, flows
alongside the separation channel. Diffusion of free LDS into this detergent-free zone
reduces the concentration of LDS below its critical micellar concentration, releasing dye
molecules from unbound micelles. When it is free of the hydrophobic interior of the LDS
micelle, the dye fluoresces weakly; the background signal is thus reduced. Dye-micelle
complexes are more stable to the destaining process when they are bound to proteins.
Downstream a laser excites the dye, causing it to fluoresce if it is bound to the LDS micelleprotein complexes. A photodiode detects the fluorescence, and Experion software plots the
fluorescence intensity vs. time to produce an electropherogram and a virtual gel image
n
Analyzing the data — Following separation, Experion software subtracts background noise,
removes spikes, identifies and integrates peaks, and assigns their sizes and concentrations.
Following analysis, parameters may be changed and the data reanalyzed
1
An important difference between the Experion system and traditional sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) lies in how sample fragments are detected: in SDS-PAGE, samples are generally stained in the gel
once separation is completed, while in the Experion system proteins are stained with a fluorescent dye during separation.
48 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 53

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
How Experion Software Analyzes Proteins
Data Presentation
As the photodiode detects fluorescent signals from the dye-LDS micelle-protein complexes, Experion
software converts the signal into an electropherogram (a plot of fluorescence vs. time). Experion Pro260
electropherograms generally have the following features (Figure A.1):
n
Sample peak(s) — signal(s) generated by the sample protein(s)
n
System peaks — cluster of signals generated by small molecules that interact with LDS
micelles. The system peaks are not considered in the concentration determination
n
Upper and lower markers — signals generated by the internal upper (260 kD) and lower
(1.2 kD) markers, which are included in the sample buffer to normalize the separation of
proteins across all wells in a chip. The upper marker is also used as an internal standard for
relative quantitation (see below). For each lane, comparison of the area of this peak with the
area of every detected peak allows estimation of relative concentration
IgG
Lower marker
System p eaks
Upper m arker
Fig. A.1. Electropherogram generated by Experion Pro260 analysis of immunoglobulin (IgG) under nonreducing conditions.
The relative positions of the lower marker, system peaks, sample peak (IGG), and upper marker are shown.
Once separation occurs, the data are converted into a densitometric gel-like image, or virtual gel
(Figure A.2). Each lane in the virtual gel corresponds to a different sample. The sample and system
peaks and upper and lower markers seen in the electropherogram also appear in the virtual gel.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 49
Page 54

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Upper m arker
System p eaks
Lower marker
Fig. A.2. Virtual gel generated by Experion Pro26 0 analysis. Shown are separations
of the Pro260 ladder (L) and 10 samples on a single chip.
Once separation is complete, the software subtracts background noise, removes spikes, identifies and
integrates peaks, and assigns their sizes and concentrations. The results of data analysis are tabulated
and presented in a Results table at the end of analysis (Figure A.3). The types of data available include
the following:
n
Protein size (or mass, in kD)
n
Protein concentration (in ng/μl): relative concentration under Concentration (ng/µl) and
absolute concentration under Calib. Conc. (ng/ µl)
n
% Total sample (percentage determination)
Fig. A.3. Results table generated by Experion Pro26 0 analysis.
50 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 55

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Data Analysis: Normalization, Sizing, and Quantitation
Following separation, Experion software analyses proteins using one or more of the following:
n
Internal markers for normalizing the migration times of samples in the different wells
n
Pro260 ladder for determining fragment size (sizing)
n
Internal markers or calibrants for determining concentration (quantitation)
Normalization: Aligning the Protein Peak Migration Times
To compensate for small variations in each separation, Experion Pro260 analysis uses internal markers
to normalize the migration times among samples. The two internal markers, an upper marker (260 kD)
and lower marker (1.2 kD), are included in the Experion Pro260 sample buffer. Therefore, both of these
markers are added to each sample and the Pro260 ladder (Figure A.1). Inclusion of these markers and
the normalization process ensure that the software accurately identifies and sizes peaks.
Protein Sizing: Determining Molecular Mass
The first sample analyzed is the Pro260 ladder, a modified version of the Precision Plus Protein™
standards that has been optimized for automated electrophoresis on the Experion system. The Pro260
ladder contains nine purified recombinant proteins of 10–260 kD. Experion software constructs a
standard curve of migration time as a function of size from the ladder separation. It then calculates the
size of the proteins from the sample wells by comparing their migration times to the curve.
Protein Quantitation: Determining Protein Amount
Experion software offers two different types of protein quantitation methods: percentage determination
and concentration determination. All measurements are based on the time-corrected peak area
(corrected area) of each peak identified in an electropherogram. The corrected area of a peak is
proportional to the amount of the protein it represents in a mixture. For more details of the protein
quantitation methods used by Experion software, refer to bulletin 5784.
Percentage determination — measures the percentage of each protein in a mixture (% total). This
method is commonly used for determining protein content, protein purity, and protein stability. The
accuracy of this method depends on the dye binding efficiency of each component in the protein
mixture. As with other dye-based assays or other methods of quantitation using SDS-PAGE, differences
in the amino acid sequences or structures of proteins result in their unique interaction with the Pro260
stain-LDS micelle complexes, which in turn affects peak intensity. As a result, the % total value may not
always reflect the actual percentage in mass for each protein in a mixture. If the component is wellcharacterized, this method of quantitation can be an efficient method for processes requiring routine
monitoring of protein samples, such as protein manufacturing and purification
Concentration determination — provides the amount of the protein(s) in a mixture rather than just
a percentage of the total. There are several different ways that concentration determination can be
performed, and these methods provide more or less accuracy depending on the type of internal
standard used and the extent to which a calibration curve is used:
n
Relative quantitation — Experion software uses an internal standard to estimate the
concentrations of sample proteins. Estimates are calculated by comparing the corrected
peak area of the sample peak to that of the internal standard in each sample well. The
internal standard can be either the upper marker (260 kD) or a user-defined internal
standard (between 10 and 260 kD) added to each sample at a known concentration
n
Absolute quantitation — Experion software can also create a calibration curve to use for
quantitation. To create the calibration curve, a protein calibrant at different concentrations is
separated in different sample wells. The corrected areas of the different sample peaks are
compared to that of an internal standard (as with relative quantitation, the upper marker or a
user-defined protein can be used). Experion software plots the resulting ratios as a function
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 51
Page 56

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
of protein concentration, and the sample protein concentration is then determined from this
calibration curve and reported in the the Calib. Conc. column of the Results tab. Absolute
quantitation methods are often more accurate than relative concentration methods
How Experion Pro260 Analysis Differs from SDS-PAGE
Though the Experion Pro260 analysis kit and SDS-PAGE both use a gel-based matrix and voltage
difference to separate proteins according their size, there are a number of fundamental differences
between the two methods that may affect how specific proteins are separated and how data are
interpreted (see Table A1 below or refer to bulletins 5299, 5423, and 5453).
Table A.1. Comparison of Experion Pro260 analysis and SDS-PAGE.
Aspect SDS-PAGE Experion Pro260 Analysis
Sieving polymer (matrix) Formulation can be changed to affect resolution Fixed formulation
Crosslinked polymer Polymer (not crosslinked)
Protein stain Multiple available Single, proprietary stain
Binds proteins Binds LDS micelle-protein complexes
Detection Separate staining step, proteins stained af ter
separation
Separate destaining step Integrated destaining; proteins destained after
Requires photography or other imaging
equipment for documentation, analysis
Types of separation Denaturing and native; reducing and
nonreducing conditions
Downstream applications Separated proteins available for excision,
electroelution, blotting applications
Reagent and sample usage Moderate to ex tensive (ml to L) Minimal (µl)
Waste generation Moderate to extensive (ml to L) Minimal (µl)
Overall analysis time Hours (depends on gel size, staining method,
and methods of documentation and analysis)
Data analysis Manual; requires additional equipment and
software
Integrated separation step; proteins stained
during separation
separation
Laser excites the stain, detection using a
photodiode, both incorporated
Denaturing; reducing and nonreducing conditions
Proteins not available for further analysis
30 min/chip (10 samples per chip)
Automated (with flexibilit y of manual adjustments)
52 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 57

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Appendix B: Deep Cleaning Procedure
This manual procedure applies Experion™ electrode cleaner directly to the 16 platinum pins in the
electrode manifold. It is the most stringent method of cleaning the Experion electrode pins and helps
ensure RNase-free operation of the system.
The need for this deep cleaning will vary from lab to lab and depends on the frequency of use of the
Experion system and on the types of assays (protein, RNA, or DNA analysis) that are performed.
Perform deep cleaning:
n
Prior to first use of the Experion electrophoresis station
n
Between a protein and DNA or RNA analysis (an Experion electrophoresis station used to
analyze protein samples will become contaminated with RNases and should be cleaned
prior to any RNA analysis), or between a DNA and RNA analysis
n
Whenever RNase contamination is suspected or other contamination (for example, salt
deposits or other precipitates) is visible on the electrodes
n
Whenever a chip has been left in the electrophoresis station for an extended period of time
(for example, overnight)
Perform this procedure with the electrode manifold in place (installed in the electrophoresis station).
It requires the following supplies:
n
Experion electrode cleaner (catalog #700-7252)
n
Experion DEPC-treated water (catalog #700-7253)
n
Foam cleaning swabs (catalog #700-7264)
Warning: Keep the chip platform dry during this procedure. Either cover the chip platform using
plastic wrap and a paper towel or foil or place a cleaning chip on the chip platform.
1. Shut off power to the electrophoresis station.
2. Add 0.5–1 ml Experion electrode cleaner to a microcentrifuge tube. Insert a swab into the solution
until it is saturated with the electrode cleaner.
3. Use the swab to gently scrub each electrode pin one at a time, on all four sides. Do not press too
hard on the pins, as they may bend. Finally, clean the tip of each pin. Add more electrode cleaner to
the swab as necessary.
-Or-
Move the swab up and down, and side to side, 2–3 times along the columns and rows of pins.
Finally, clean the tip of each of pin. Add more electrode cleaner to the swab as necessary.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 twice, each time with a fresh swab soaked in DEPC-treated water.
5. Fill a cleaning chip with 800 μl DEPC-treated water, place it in the electrophoresis station, and close
the lid for 5 min.
6. Remove the chip and allow the pins to dry completely by leaving the lid open for 5–10 min.
Refer to the Experion system manual for more details and images.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 53
Page 58

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Appendix C: Chemical Compatibility
For best results, the starting protein sample (undiluted) should contain components at concentrations
less than or equal to the values indicated in the tables below. If concentrations are above these values,
dilute the samples accordingly.
Buffers
Table C.1. Buffers with no observable effect on Experion™ Pro26 0 separation or analysis at or below the
concentrations listed.
Buffer Concentration
B-PER (Pierce) 0.5x
BugBuster (Novagen) 1x: BugBuster and benzonase nuclease
CPEB (ReadyPrep™ protein extraction 0.5x
kit, cytoplasmic/nuclear)
GST binding/wash buffer (Novagen) 0.5x
His elution buffer (Pierce) 0.5x
His wash buffer 1 (Pierce) 0.5x
His wash buffer 2 (Pierce) 0.5x
IEF cathode buffer 1.5x: 30 mM Lysine, 30 mM arginine
IMAC elution buffer 1x: 50 mM KH2PO4, 150 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole, pH 8.0
IMAC lysis buffer 1x: 25 mM KH2PO4, 150 mM NaCl, pH 8.0
IMAC wash buf fer 1 1x: 100 mM KH2PO4, 600 mM KCl, 10 mM imidazole, pH 8.0
IMAC wash buf fer 2 1x: 100 mM KH2PO4, 600 mM KCl, 20 mM imidazole, pH 8.0
LB medium 0.5x: 1% Tryptone, 0.5% yeast extract, 1% NaCl
M1 (ReadyPrep protein extraction kit, 0.5x
membrane I)
M2 (ReadyPrep protein extraction kit, 0.5x
membrane I)
M-PER 0.5x
PBS 1.5x: 15 mM Sodium phosphate, 225 mM NaCl, pH 7.5
PBS-Tween 1x: 10 mM Sodium phosphate, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween, pH 7.2
S1 (ReadyPrep protein extraction kit, 0.5x
signal)
Tricine sample buffer 0.5x: 100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 1% SDS, 20% glycerol, 0.02% Coomassie Brilliant Blue
Tris-borate-EDTA (TBE) 1.5x: 133 mM Tris, 133 mM boric acid, 3 mM EDTA, pH 8.3
Tris/CAPS 1.5x: 90 mM Tris, 60 mM CAPS, 0.15% SDS pH 9.6
Tris/glycine 1.5x: 37.5 mM Tris, 288 mM glycine, pH 8.3
Tris/glycine/SDS 1.5x: 37.5 mM Tris, 288 mM glycine, 0.15% SDS, pH 8.3
Tris/Tricine/SDS 1.5x: 150 mM Tris, 150 mM Tricine, 0.15% SDS, pH 8.3
Urea/phosphate/NaCl buffer 0.5x: 4 M Urea, 25 mM sodium phosphate, 150 mM NaCl, pH 8
Criterion™ XT MOPS buffer 1.5x
Criterion XT sample buffer 1.5x
Criterion XT Tricine buffer 1.5x
Zymogram sample buffer 0.5x: 31.3 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 2% SDS, 12.5% glycerol, 0.005% bromophenol blue
54 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 59

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Table C.2 . Buf fers with mild effects on Experion Pro260 separation or analysis.
Buffer Concentration Effect(s)
IEF anode buffer 1.5x: 10.5 mM phosphoric acid Quantitation
Laemmli buffer 0.5x: 31.3 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 1% SDS, Quantitation
12.5% glycerol, 0.005% bromophenol blue,
2.5% b-mercapotethanol
PSB (ReadyPrep protein extraction kit, 0.5x Quantitation
membrane I)
RIPA buffer 1x: 150 mM NaCl, 1.0% NP40, 0.5%
sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 50 mM Tris Enlarged system peak shifts to
right; 10 kD sizing affected
TBS 1.5x: 30 mM Tris, 750 mM NaCl pH 7.4 Quantitation
Table C.3. Buffers with severe effects on Experion Pro260 separation or analysis.
Buffer Effect(s)
Rehydration buffer (ReadyPrep 2-D star ter kit) Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing, sizing af fected
S2 (ReadyPrep protein extraction kit, signal) Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing, sizing affected
Reagent 2 (ReadyPrep sequential extraction kit) Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing, sizing affected
Reagent 3 (ReadyPrep sequential extraction kit) Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing, sizing affected
Total protein extraction buffer Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing, sizing af fected
Criterion XT MES buffer (1.5x) 10 kD peak is missing
Chemicals
Table C.4. Chemicals with no obser vable effects on Experion Pro260 separation or analysis at or below the
concentrations listed.
Chemical Concentration Chemical Concentration
Acetonitrile 30% MeOH 15%
Ammonium sulfate 250 mM Na3VO4 5 mM
Arginine 500 mM NaCl 250 mM
DMSO 15% NaF 50 mM
EDTA 10 mM NaHCO3 50 mM, pH 8
EGTA 150 mM NaN3 0.75%
Ethanol 30% NaOAc 50 mM, pH 4
Glucose 0.5 M NaOH 150 mM
Glycerol 35% NDSB201 1%
Glycine 1 M Sodium carbonate 150 mM, pH 11.5
Guanidine isothiocyanate 25 mM Succinic acid 100 mM
HEPES 50 mM, pH 7 Tetramethylammonium chloride 1 M
Imidazole 0.5 M, pH 7 Trehalose 5%
KCl 250 mM Tris base 1.5 M
MgCl2 150 mM Urea 4.5 M
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 55
Page 60

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Table C.5. Chemicals with mild ef fects on Experion Pro260 separation or analysis.
Chemical Concentration Effect(s)
Acetone 15% Quantitation affected
Bio-Lyte® 3/10 0.75% Quantitation affected
Guanidine HCl 25 mM Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
KCl 1.5 M Quantitation affected
MES 50 mM, pH 6.0 Quantitation affected
MOPS 100 mM, pH 7.2 Quantitation af fected
PEG 0.50% Quantitation affected
Propylene glycol 50% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
Sucrose 200 mM Quantitation af fected
Table C.6. Chemicals with severe ef fects on Experion Pro260 separation or analysis.
Chemical Concentration Effect(s)
Ammonium sulfate 1.5 M Protein precipitation
Guanidine isothiocyanate 1 M Protein precipitation; no markers appear
Guanidine HCl 1 M Protein precipitation; no markers appear
HCl 150 mM Protein precipitation; markers missing
Pluronic F-68 0.1% Protein smears
Detergents and Reductants
Table C.7. Detergents and reductants with no observable ef fects on Experion Pro260 separation or analysis.
Detergent/Reductant Concentration
ASB-14 0.10%
CHAPS 0.50%
CHAPSO 0.10%
Deoxycholate 1.0%
Octyl-thioglucopyranoside 0.50%
Tributylphosphine (TBP) 7.5 mM
Triton X-100 0.40%
Tween-20 0.50%
Table C.8. Detergents and reductants with mild effects on Experion Pro260 separation or analysis.
Detergent/Reductant Concentration Effect(s)
ASB-14 0.5% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
CHAPS 1% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
CHAPSO 0.2% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
Deoxycholate 2% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
LDS 3% Enlarged system peak shif ts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
NP40 0.5% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
SB3-10 0.1% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing and quantitation
affected
SDS 1% Quantitation affected
Tween-20 0.75% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
Zwittergent 3-14 0.10% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
β-Mercaptoethanol 1.5 M Quantitation affected
DTT 150 mM Quantitation affected
56 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 61

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Table C.9. Detergents and reductants with severe effects on Experion Pro260 separation or analysis.
Detergent/Reductant Concentration Ef fect(s)
ASB-14 2% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing
n-Dodecyl-b-D-maltoside 1% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing
NP40 2% Enlarged system peak shif ts to right; 10 kD peak is missing
SB3-10 2% Enlarged system peak shif ts to right; 10 kD sizing affected
Triton X-100 1% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing
Tween-20 1% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing
Tween-80 1% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing
Zwittergent 3-14 1% Enlarged system peak shifts to right; 10 kD peak is missing
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 57
Page 62

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Appendix D: Glossary
% Total
Calculation performed by Experion™ software to
show the percent of the total protein comprised by
a particular peak; used in purity assessments
Absolute quantitation
Method of quantitation of a defined protein in
which concentrations are determined against a
calibration curve, which is usually generated using
the same protein
All-wells view
Mode of display within the electropherogram view
wherein electropherograms of all wells are shown
Baseline
Line of initial data that serves as the control, or
signal representing no fluorescence
Calibration curve
Curve of fluorescence intensity (signal) as a
function of protein concentration; generated using
various known concentrations of a specific protein
and used for calculating the protein concentration
of samples
Chip
Microfluidic device used to perform separation
using the Experion system
Electropherogram
Trace recording of signal (fluorescence
intensity) as a function of time; displayed in the
electropherogram view
Electropherogram view
Portion of the Experion software user interface
dedicated to display of electropherogram data
Electrophoresis station
Instrument that houses all the electrical, optical,
and hardware components necessary to perform
separation, staining, destaining, band detection,
and imaging of samples; equipped with a universal
power supply to operate at 100–240 V, 50–60 Hz
Gel priming well
Well of the microfluidics chip used to fill the
microchannels of the chip with gel-stain solution
(GS) during priming
Gel-stain solution (GS)
A mixture of gel matrix and stain; used for sample
separation and detection
Gel view
Portion of the Experion software user interface
dedicated to display of virtual gel data
Internal standard
Protein added to the sample for quantitation; can
be either the upper marker (260 kD), which is
included in the Pro260 sample buffer, or a userdefined protein (that is baseline resolved from the
sample peak being quantitated) added to each
sample at a known concentration
LabChip
Microfluidic “lab-on-a-chip” technology developed
by Caliper Life Sciences; the Experion automated
electrophoresis system was built on LabChip
technology
LDS micelle-protein complex
Micelle of the detergent lithium dodecyl sulfate
(LDS) bound with protein(s)
Lithium dodecyl sulfate (LDS)
Anionic detergent that may be used in place
of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) for denaturing
electrophoresis
Lower marker
1.2 kD marker included in the Experion Pro260
sample buffer and used to normalize the
separation of proteins across all wells in the chips
Microchannels
Fine channels approximately the diameter of a
human hair are used for samples separation in
Experion microfluidic chips
Microfluidic technology (microfluidics)
Multidisciplinary field comprising physics,
chemistry, engineering, and biotechnology that
deals with the behavior, precise control, and
manipulation of microliter and nanoliter volumes
of fluids
Nonreducing
Sample condition that does not include reducing
agents for the reduction of disulfide bonds
58 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 63

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Normalization
Alignment of protein peak migration times across
different sample wells of the same chip; the lower
and upper markers are used by Experion software
for this purpose
Overlay
Function of Experion software that allows different
electropherograms to be superimposed for easier
comparison
Peak
Signal in an electropherogram generated
and identified by the peak-find settings to be
significantly different from the baseline
Priming
Filling the microchannels of the microfluidic chip
with gel-stain solution in preparation for analysis
Priming station
Instrument used to prepare chips for sample
analysis; applies pressure to the priming well
of the microfluidic chip and fills the network of
microchannels with the gel-stain solution
Pro260 ladder
Modified version of the Precision Plus Protein™
standards that has been optimized for automated
electrophoresis on the Experion system; contains
9 purified recombinant proteins of 10–260 kD
Project folder
User-defined folder containing multiple run files
comprising a particular project
Project tree
Hierarchical tree of all saved projects and the data
files they contain
Quantitation
Determination of the concentration of a protein in
a sample
Reducing
Sample condition that includes reducing agents
for the reduction of disulfide bonds
Relative quantitation
Method of quantitation in which concentrations
are determined against a single-point internal
standard
Results and settings
Portion of the Experion software user interface
dedicated to display of tabulated analysis results
and analysis settings and parameters
Run file
File containing data for a single run
Single-well view
Function of Experion software that allows an
electropherogram from a single well to be viewed
Sizing
Determination of the molecular mass of a protein
Spin filter
Polypropylene spin tubes with filter membranes
used to remove particulate matter from the
gel-stain (GS) and gel (G) by centrifugation
System peaks
Cluster of signals generated by small molecules
that interact with fluorescent detergent micelles;
not considered in the concentration estimation
Tree view
Portion of the Experion software user interface
dedicated to display of the project tree; used to
locate and manipulate data files and organize runs
into projects
Upper marker
260 kD protein included in the Experion Pro260
sample buffer and used to normalize the
separation of proteins across all wells in the chips;
also used as an internal standard for relative
quantitation by default
User-defined standard
Protein (10–260 kD) added to each sample at a
known concentration and used for quantitation
Virtual gel
Densitometric, gel-like image generated from
electropherogram data and displaying peaks as
bands; displayed in the gel view
Vortex station
Instrument used to mix RNA or DNA samples and
loading buffers (supplied in the kits) in the chip
wells; used for nucleic acid applications only
Results table
Tab that displays analysis results, settings, and
parameters
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 59
Page 64

Experion Automated Electrophoresis System
Appendix E: Bibliography
Visit us on the Web at www.bio-rad.com (search term “Experion”) for a list of technical literature and to
download copies of all current documents.
Bulletin Title
3176 Monitoring the Expression, Purification, and Processing of GST-Tagged Proteins Using the
Experion™ Automated Electrophoresis System
5283 Bio-Rad Applies Microfluidics to Automate Gel Electrophoresis
5299 Performance Comparison of the Experion Automated Electrophoresis System and
SDS-PAGE for Protein Analysis
5302 Performance Comparison of the Experion Automated Electrophoresis System and a
Competing Automated System for Protein Analysis
5328 Experion Automated Electrophoresis System and the Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit:
Accurate and Reproducible Protein Sizing and Quantitation in the Presence of High
Salt Concentrations
5423 Protein Quantitation: A Comparative Analysis Using the Experion Automated
Electrophoresis System, Bradford and Modified Lowry Assays, and SDS-PAGE
5453 Application of the Experion Automated Electrophoresis System to Glycoprotein Visualization
and Analysis
5501 Rapid, Efficient Purification and Evaluation of His-Tagged Proteins
5506 Monitoring Development of Chromatographic Methods With the Experion Automated
Electrophoresis System
5784 Comparison of Protein Quantitation Methods Using the Experion Automated
Electrophoresis System
60 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Page 65

Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit
Appendix F: Ordering Information
Catalog # Description
700-7000 Experion™ System, 100–240 V, for protein analysis, includes electrophoresis station,
priming station, software, USB2 cable
701-7000 Experion System, 100–240 V, for protein analysis, includes electrophoresis station,
priming station, software, USB2 cable, Experion Pro260 starter kit
700-7101 Experion Pro260 Analysis Kit for 10 Chips, includes 10 Pro260 chips, 1 cleaning chip,
3 x 520 µl Pro260 gel, 45 µl Pro260 stain, 60 µl Pro260 ladder (10–260 kD), 400 µl
Pro260 sample buffer, 3 spin filters
700-7110 Experion Pro260 Starter Kit, includes 3 Experion chips, 1 cleaning chip, Experion
reagents, spin filters, IgG protein standard, DTT, cleaning swabs (lint free), electrode
cleaner, narrow bore polypropylene pipet tips, polypropylene 0.5 ml microcentrifuge
tubes, DEPC-treated water (0.2 μm filtered)
700-7151 Experion Pro260 Chips, 10, plus 1 cleaning chip
700-7152 Experion Pro260 Reagents and Supplies, for 10 chips, includes 3 x 520 µl Pro260 gel,
45 µl Pro260 stain, 60 µl Pro260 ladder (10–260 kD), 400 µl Pro260 sample buffer,
3 spin filters
700-7256 Experion Protein Ladder, 60 µl
700-7251 Experion Cleaning Chips, 10
700-7254 Experion Spin Filters, 10
700-7252 Experion Electrode Cleaner, 250 ml
163-2091 ReadyPrep™ Proteomics Grade Water, 500 ml
161-0710 2-Mercaptoethanol, 25 ml
700-7051 Experion Validation Kit, 3 test chips, qualification procedures, dongle
700-7264 Cleaning Swabs, lint free, for electrode deep cleaning, 25
700-7031 Experion Priming Seals, 2
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com 61
Page 66

Page 67

Page 68

Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.
Life Science
Group
Bulle tin 10000975 Rev C US/EG 1010 Sig 1109
Web site www.bio-rad.com USA 800 424 6723 Australia 61 2 9914 2800 Austria 01 877 89 01 Belgium 09 385 55 11 Brazil 55 31 3689 6600
Canada 905 364 3435 China 86 20 8732 2339 Czech Republic 420 241 430 532 Denmark 44 52 10 00 Finland 09 804 22 00 France 01 47 95 69 65
Germany 089 31 884 0 Greece 30 210 777 4396 Hong Kong 852 2789 3300 Hungary 36 1 459 6100 India 91 124 4029300 Israel 03 963 6050
Italy 39 02 216091 Japan 03 6361 7000 Korea 82 2 3473 4460 Mexico 52 555 488 7670 The Netherlands 0318 540666 New Zealand 0508 805 500
Norway 23 38 41 30 Poland 48 22 331 99 99 Portugal 351 21 472 7700 Russia 7 495 721 14 04 Singapore 65 6415 3188 South Africa 27 861 246 723
Spain 34 91 590 5200 Sweden 08 555 12700 Switzerland 061 717 95 55 Taiwan 886 2 2578 7189 United Kingdom 020 8328 2000
 Loading...
Loading...