Page 1

Nuvia™ cPrime
™
Hydrophobic
Cation
Exchange Media
Instruction
Catalog
156-3401 156-3404
156-3402 156-3405
156-3403 156-3406
numbers
Manual
Please read the instructions in this manual prior to using
Nuvia cPrime hydrophobic cation exchange media. If you
have any questions or require any further assistance, please
contact your Bio-Rad Laboratories representative.
Page 2

Page 3

Table of Contents
Section
Section
Section
Section
Packing Small
Packing Process Scale
Flow Properties
Buffers
Section
Section
Section
Section
Section
Section
1:
Introduction 1
2 :
Technical Description 2
3 :
Preparation
4 :
Column
Columns
5 :
Column Packing Evaluation 7
6 :
Method Development
7 :
Sanitization
8 :
Storage 11
9:
Regulatory Support 11
10: Ordering
Packing
Information
Columns
and
8
Regeneration 10
11
3
3
3
4
5
6
Page 4

Section
1
Introduction
Nuvia™ cPrime™ hydrophobic cation exchange media are
designed for the process scale purification of a wide variety of
therapeutic proteins. Nuvia cPrime media’s unique selectivity
allows method developers to use hydrophobic and cation
exchange interaction modes to achieve effective purification. More
importantly, the media have a wide design space for binding and
elution, allowing for the development of highly robust methods in
a commercial manufacturing setting. Nuvia cPrime media are built
on a rigid, mechanically and chemically stable macroporus base
matrix with a particle size optimized to deliver exceptional flow
properties, fast mass transfer, and stability. See the Nuvia cPrime
media product information sheet for more product details.
If you have questions or require methods development assistance
with Nuvia cPrime media, contact your local Bio-Rad process
chromatography representative or the Bio-Rad chromatography
technical support group for assistance at 1-510-741-6563.
1
Page 5
Section
2
Technical
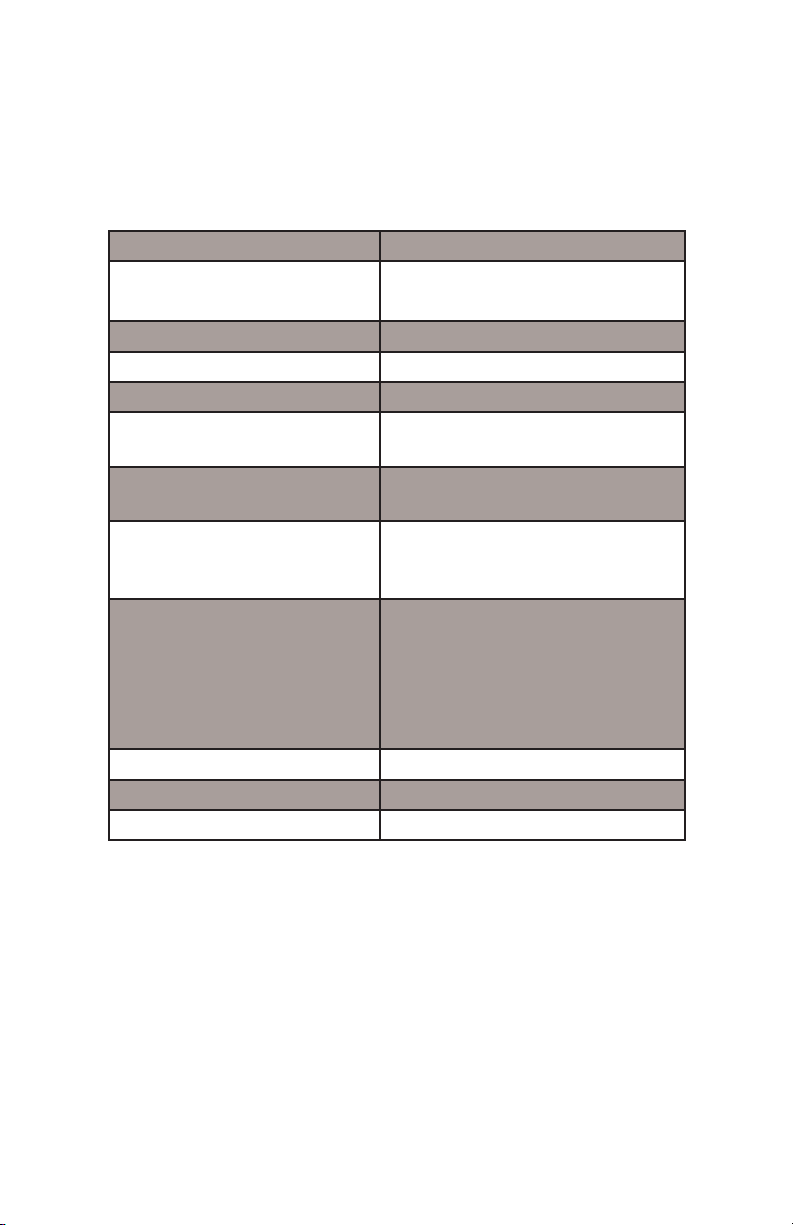
Table 1. Nuvia™ cPrime™ media technical description.
Functional group Hydrophobic cation exchanger
Base matrix composition Macroporous highly crosslinked
Particle size 70 µm ± 10 µm
Dynamic binding capacity* ≥ 40 mg/ml
Ligand density 55–75 µeq/ml
Recommended linear flow
rate range
Pressure vs. flow
performance**
pH stability 2–14 short term
Chemical stability 1.0 N NaOH, 1.0 N HCl, 25%
Shipping solution 20% ethanol
Storage conditions 20% ethanol
Shelf life*** 5 yrs
Description
hydrophilic polymer
50–600 cm/hr
Under 2 bar @ a flow rate of 600
cm/hr
3–13 long term
HOAc, 8 M Urea, 6 M Gu-HCl,
6 M KSCN, 3 M NaCl, 1% Triton
X-100, 2% SDS + 0.25 M NaCl,
20% ethanol, 70% ethanol, 30%
isopropanol
* at 10% breakthrough hIgG.
** 20 cm X 20 cm packed bed (1.17 compression factor).
*** Stored at room temperature in 20% ethanol under accelarated
conditions.
2
Page 6

Section
3
Preparation
Nuvia™ cPrime™ media are supplied fully hydrated in 20% ethanol
as a 50% (v/v) slurry. For column packing, removal of the shipping
buffer is recommended. Small volumes of Nuvia cPrime media are
easily washed in a Büchner funnel with 4–5 volumes of packing
buffer. For large volume preparation, cycle through 3–4 settling and
decanting steps using the column packing buffer in the shipping
container.
Removal of fines from Nuvia cPrime media is not required. If, however,
particle fines have been generated during handling, resuspend the settled
media and remove any opaque or cloudy supernatant before resettling is
complete. Repeat several times until supernatant is clear.
Section
Column
Nuvia™ cPrime™ media can be packed using standard column
packing methods. To pack columns for optimal operation, a
20–50% slurry volume is recommended.
Packing Small Columns
This slurry packing method was designed to pack Nuvia cPrime
media in a conventional laboratory scale column with an internal
diameter of 5–50 mm. All buffers should be degassed. Since a
relatively large volume of slurry is required, a packing reservoir
should be used.
1. Prepare degassed 1.0 M NaCl, 20–50 mM buffer salt (see
2. Decant the shipping solution away from the resin bed as
3. After thorough buffer exchange, prepare an aliquot of Nuvia
4. Seal the cylinder and rotate it to suspend the resin. Caution:
4
Packing
Table 2) referred to herein as the packing buffer.
outlined in Section 3, maintaining an approximate slurry
percentage of 50%.
cPrime media in a graduated cylinder to determine the slurry
percentage.
do not mix with a magnetic stir bar as damage may occur.
Larger amounts of slurry may be mixed with a low-shear
impeller at low to moderate speed.
3
Page 7

5. Using a compression factor of 1.17, calculate the volume of
slurry required for the intended bed height.
a. For example, for a 20 cm bed height using a 50% slurry, the
volume would be:
1.17 (20/0.5) * πr
6. Add a small amount of packing buffer to the column to wet the
bottom frit, then pour in calculated amount of resin slurry.
7. Insert the column flow adaptor and flow pack at a linear velocity of
300–600 cm/hr with packing buffer for at least 10 min. Note the
compressed bed height, stop the flow, and adjust the flow adaptor to
compress the bed to the intended bed height.
8. Equilibrate with at least 3 column volumes (CV) of equilibration
buffer and evaluate column efficiency using your standard operating
procedures or the procedure described in Section 5.
2
Packing Process Scale Columns
After removing the storage buffer (Section 3), prepare a 20–50%
slurry (v/v) with packing buffer (see Table 2). For most process
columns, follow the manufacturer’s recommendations with one
major exception: do not recirculate the Nuvia cPrime media slurry
through the packing pump. Use a low-shear impeller for automatic
mixing or a plastic paddle for manual mixing to avoid damaging the
media. The best overall performance of Nuvia cPrime media will
be obtained with a compression ratio of 1.15–1.20. Compression
factor is defined as settled bed height divided by packed bed
height.
After achieving the desired compression ratio, it is recommended
to condition the column by flowing fresh packing or equilibration
buffer for 3 CV followed by 3 CV in downflow at the chosen
process flow rate. After this flow conditioning step, evaluate
column efficiency using your standard operating procedures or the
procedure described in Section 5.
4
Page 8

Flow Properties
Nuvia cPrime Media vs. Pressure Flow
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200
Linea r flow ra te , cm/hr
Pressure, bar
Nuvia cPrime Media DBC (Lactoferrin) vs. Flow Rate
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
150 300 450 600
Flow rate, cm/h
10% BT DBC, mg/ml
Fig. 1. Nuvia cPrime media pressure vs. flow performance for a
20 cm diameter column and a 20 cm bed height; compression ratio
1.17. Nuvia cPrime media have fast mass transfer properties allowing
users to achieve high productivity at fast flow rates. The media should
be run at the highest linear velocities that allow good separation and are
allowed by the column and chromatography system specifications. A
linear flow rate of 300 cm/hr and a 20 cm bed is a recommended starting
point.
Fig. 2. Effect of flow rate on Nuvia cPrime media binding capacity for
lactoferrin.
Column dimension: 1.1 x 9.6 cm
Sample: 5.25 mg/ml lactoferrin
5
Page 9

Buffers
All buffers commonly used for ion exchange chromatography can
be used with Nuvia cPrime media.
Table 2. Common buffers for cation exchange
chromatography. A buffer concentration of 60 mM is
recommended for most buffers.
Buffer Buffering Range
Acetic acid 4.8–5.2
Citric acid 4.2–5.2
HEPES 6.8–8.2
Lactic acid 3.6–4.3
MES 5.5–6.7
Phosphate 6.5–8.0
Tris 7.5–9.0
6
Page 10

Section
5
Column Packing
After column packing is complete, equilibrate the column with up
to 5 CV equilibration buffer. To test the efficiency of the column
packing operation, inject a sample of a low molecular weight,
unretained compound (for example, acetone or 1 M NaCl) to
determine height equivalent to a theoretical plate (HETP). If acetone
is used as the test marker (use a UV absorbance monitor set at
280 nm), the equilibration buffer must have a salt concentration
<100 mM. If 1 M NaCl is the test marker (use a conductivity
monitor), then the equilibration buffer salt concentration should be
100–200 mM. The sample volume should be 1–3% of the total
column volume. Column testing should be operated using the
same linear velocity used to load and/or elute the sample.
To obtain comparable HETP values among columns, the same
conditions must be applied. Minimum theoretical plate values
should be 1,000–3,000 plates/m for linear velocities of 50–500 cm/
hr.
HETP = L/N
N =
5.54(Ve/W½h)
L = Bed height (cm)
N = Number of
Ve =
Peak elution volume
W
=
Peak
½h
Ve and W
theoretical
width at peak
should
½h
Evaluation
2
plates
or time
always
half
height in
be in the same units
volume
or time
Peaks should be
possible
Peak asymmetry factor calculation:
As =
a = Front section of peak width at 10% of peak
denoting
b = Latter section of peak width at 10% of peak height bisected by line
denoting
As = 0.8–1.8 is acceptable
to 1.
b/a
V
V
symmetrical
Values
of 0.8–1.8 are acceptable.
e
e
and the
7
asymmetry
factor as close as
height
bisected by line
Page 11

Section
6
Method Development
Developing an effective and robust method with Nuvia™ cPrime™
media is straightforward. Below is general information on the
binding and elution mechanism and an approach to guide method
development; results will vary depending on protein of interest and
feed composition.
The binding and elution mechanisms of Nuvia cPrime media
are determined chiefly by pH and salt. The high salt tolerance of
the media often allows for direct loading at high conductivity. An
increase in pH will in most cases achieve elution. Conductivity
is another way to achieve and/or optimize elution and the final
method is often a combination of an increase in pH and/or an
increase/decrease in salt concentration. In some cases, the use of
an elution buffer modifier or a different salt in the elution buffer may
be required for optimal elution, recovery, and resolution.
The schematic below outlines a general method development
rational. In most cases, conducting a few simple DOE experiments
to identify optimal binding and elution conditions will yield an
effective, robust, and scalable method.
8
Page 12

1. Load feed or eluate from previous step directly without
dilution onto the Nuvia cPrime media column. To elute, use an
increasing pH gradient. If satisfactory elution and recovery are
achieved, refine and/or make a step gradient to complete the
step (range pH 4–8, depending on protein).
2. If elution is not satisfactory after step 1, run a salt gradient to
disrupt electrostatic or hydrophobic interactions that may be
preventing elution or broadening the peak. Use the pH where
there was best elution (from step 1). The direction of this salt
gradient (increasing or decreasing) can be easily assessed
and will depend on the relative contributions of ionic vs.
hydrophobic interactions involved in binding.
3. If elution is still unsatisfactory after step 2 of this process,
consider using a modifier such as propylene glycol, urea, or
arginine to disrupt any remaining interactions. Other modifiers
may also be used; in some cases changing to another salt
may also be required.
For further assistance or to discuss method development,
contact Bio-Rad chromatography technical support group
at 1-510-741-6563.
9
Page 13

Section
7
Sanitization
After each chromatography run, the packed media bed should
be washed to remove reversibly bound material and prepare the
column for the subsequent run. This cleaning process is achieved
by washing the column with 2–6 column volumes of 1–2 M
NaCl followed by 2–6 column volumes of 0.1 N NaOH to remove
remaining proteinaceous impurities. Washing should be conducted
until absorbance returns to baseline. The column is now ready to
be sanitized in 1.0 N NaOH.
After sanitization, to equilibrate the column we recommend
applying 4–6 column volumes of a solution such as 60 mM NaOAC
(sodium acetate)
Note: if the column no longer yields reproducible results, the
media may require additional cleaning to remove strongly bound
contaminants. Acceptable cleaning agents include 25% acetic
acid, 8 M urea, 1% Triton X-100, 6 M potassium thiocyanate,
70% ethanol, 30% isopropyl alcohol, 1 N NaOH, or 6 M guanidine
hydrochloride.
and Regeneration
10
Page 14

Section 8
Storage
For long-term storage, Nuvia™ cPrime™ media should be with 0.1 N
NaOH or 20% ethanol.
Section 9
Regulatory Support
A regulatory support file is available for Nuvia™ cPrime™ media. If
you need assistance validating the use of Nuvia cPrime media in a
production process, contact your local Bio-Rad representative.
Section 10
Ordering Information
Catalog numbers Description
156-3401 Nuvia™ cPrime™ Media, 25 ml
156-3402 Nuvia cPrime Media, 100 ml
156-3403 Nuvia cPrime Media, 500 ml
156-3404 Nuvia cPrime Media, 1 L
156-3405 Nuvia cPrime Media, 5 L
156-3406 Nuvia cPrime Media, 10 L
Larger volumes
available
Triton is a
upon request.
trademark
and
special packaging
of
Union Carbide
for
Corporation.
11
industrial applications
are
Page 15

Page 16

Life Science
Group
Sig 121110023853 Rev B US/EG
Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.
Web site ww w.bio-rad.com USA 800 424 6723
Australia 61 2 9914 2800 Austria 01 877 89 01
Belgium 09 385 55 11 Braz il 55 11 5044 5699
Canada 905 364 3435 China 86 21 6169 8500
Czech R epublic 420 241 430 5 32 Denmark 44 52 10 00
Finland 09 804 22 00 France 01 47 95 69 65
Germany 089 31 884 0 Greece 30 210 9532 220
Hong Kong 8 52 2789 3300 Hungary 36 1 459 6100
India 91 124 4029300 Israel 03 963 6050 Italy 39 02 216 091
Japan 03 6361 7000 Korea 82 2 3473 4460
Mexico 52 5 55 488 7670 The Netherlands 0318 540666
New Zealand 64 9 415 228 0 Norway 23 38 41 30
Poland 48 22 331 99 99 Portugal 351 21 472 7700
Russia 7 495 721 14 04 Singapore 65 6415 3188
South Africa 27 861 246 723 Spain 3 4 91 590 5200
Sweden 08 555 1270 0 Switzerland 061 717 95 55
Taiwan 88 6 2 2578 7189 Thailand 800 88 22 88
United Kingdom 020 8328 200 0
 Loading...
Loading...