Page 1

Bio-Plex Pro
™
Human
Chemokine Assays
Instruction Manual
For technical support, call your local Bio-Rad office, or in the U.S., call 1-800-424-6723.
For research use only. Not for diagnostic procedures.
Page 2

Table of Contents
Introduction 1
Principle 2
Kit Contents and Storage 4
Recommended Materials 5
Assay Workflow 6
lmportant Considerations 7
Detailed Instructions 7
1. Plan Plate Layout 8
2. Prepare Instrument 9
3. Prepare Wash Method 10
4. Prepare Wash Buffer 11
5. Prepare Standards and Controls 11
6. Prepare Samples 14
7. Prepare Coupled Beads 16
8. Run Assay 18
9. Read Plate 22
Troubleshooting Guide 29
Appendix: Non-Human Primate (NHP) Cross-Reactivity 34
Plate Layout Template 35
Calculation Worksheet 36
Safety Considerations 38
Legal Notices 38
Ordering Information 39
Page 3

Introduction
Chemokines are small molecular weight (8–10 kD) cytokines secreted by
various eukaryotic cell types, including those of the immune system. Their
main function is to promote and regulate cell migration in both normal
and pathological conditions, including immune surveillance, inflammation,
angiogenesis, microbial infection, autoimmune diseases, tumor growth,
vascular diseases, and transplant rejection (Locati et al. 2005, Slettenaar
and Wilson 2006). The regulatory functions of chemokines are exerted
via binding and signaling through specific G protein–coupled receptors
expressed on the surface of chemokine-responsive cells.
Chemokines are classified into four subfamilies (C, CC, CXC, and CX3C)
based on the number and spacing of cysteine residues within the protein
sequence. The C chemokines are known as lymphotactins, and are
found at high levels in spleen, thymus, intestine, and peripheral blood
leukocytes. The CC chemokines have the first two cysteines in adjacent
positions and are known to attract granulocytes and lymphocytes,
including NK cells. The CXC chemokines have the first two of four
cysteines separated by a single amino acid, denoted X. Most CXC
chemokines are chemo-attractants for neutrophils and lymphocytes. The
CX3C chemokines have three amino acids inserted between the first two
cysteines. The only CX3C chemokine discovered to date is fractalkine,
which is both a chemo-attractant and adhesion molecule.
Multiplexing with Bio-Plex Pro Chemokine Assays
Bio-Plex Pro chemokine assays enable researchers to quantify multiple
protein biomarkers in a single well of a 96-well plate in just 3–4 hours.
These robust immunoassays require as little as 12.5 l of serum or
plasma or 50 l of other biological fluid. The use of magnetic (MagPlex)
beads allows researchers to automate wash steps on a Bio-Plex Pro
(or similar) wash station. Magnetic separation offers greater convenience
and reproducibility compared to vacuum filtration.
For more information please visit www.bio-rad.com/bio-plex.
1
Page 4

Principle
Technology
The Bio-Plex® multiplex system is built upon the three core elements of
xMAP technology:
n
Fluorescently dyed magnetic microspheres (also called beads), each
with a distinct color code or spectral address to permit discrimination of
individual tests within a multiplex suspension. This allows simultaneous
detection of up to 500 different molecules in a single well of a 96-well
microplate on the Bio-Plex
on the Bio-Plex
Bio-Plex
n
A dedicated plate reader. The Bio-Plex 200 and Bio-Plex 3D systems
®
®
200 system, and up to 50 different molecules on the
MAGPIX™ system
are flow cytometry–based instruments with two lasers and associated
optics to measure the different molecules bound to the surface of the
beads. In the Bio-Plex MAGPIX system, the sample is injected into a
chamber where the beads are imaged using LED and CCD technology
n
A high-speed digital signal processor that efficiently manages the
fluorescence data
Assay Format
Bio-Plex Pro™ assays are essentially immunoassays formatted on
magnetic beads. The assay principle is similar to that of a sandwich
ELISA (Figure 1). Capture antibodies directed against the desired
biomarker are covalently coupled to the beads. Coupled beads react
with the sample containing the biomarker of interest. After a series of
washes to remove unbound protein, a biotinylated detection antibody
is added to create a sandwich complex. The final detection complex is
formed with the addition of streptavidin-phycoerythrin (SA-PE) conjugate.
Phycoerythrin serves as a fluorescent indicator, or reporter.
®
3D system, up to 100 different molecules
2
Page 5
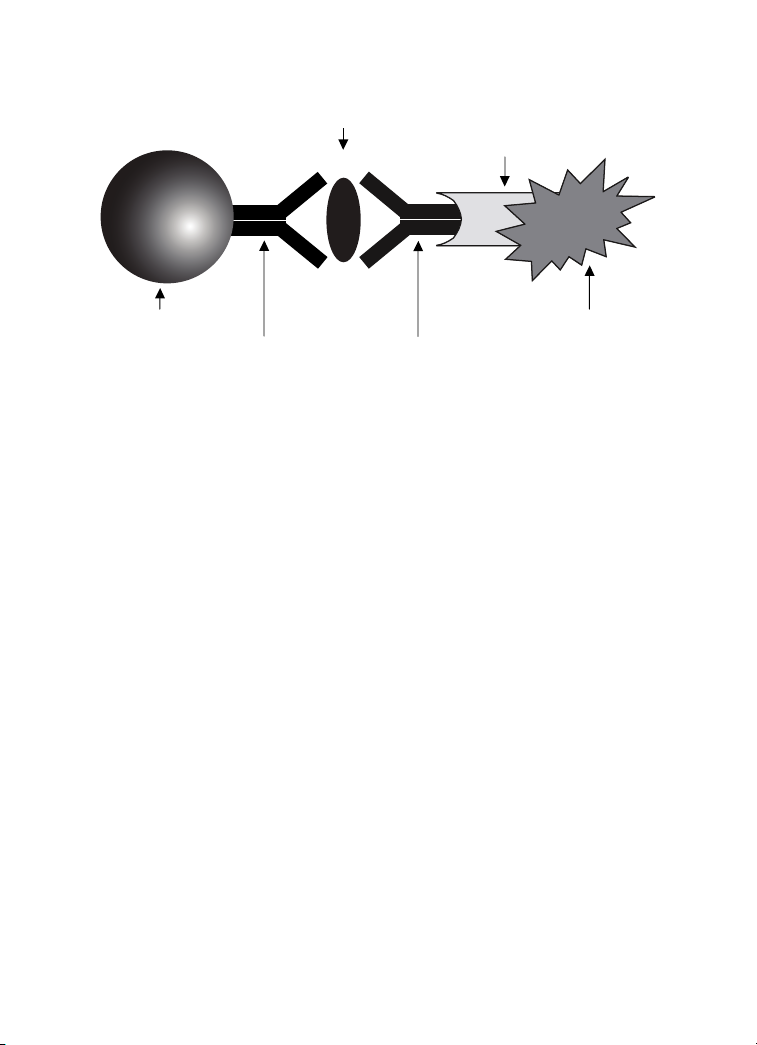
Biomarker
of Interest
Streptavidin
Magnetic Bead
Capture
Antibody
Fig. 1. Bio-Plex sandwich immunoassay.
Biotinylated
Detection
Antibody
Phycoerythrin
Fluorescent
Reporter
Data Acquisition and Analysis
Data from the reactions are acquired using a Bio-Plex system or similar
Luminex-based reader. When a multiplex assay suspension is drawn into
the Bio-Plex 200 reader, for example, a red (635 nm) laser illuminates
the fluorescent dyes within each bead to provide bead classification and
thus assay identification. At the same time, a green (532 nm) laser excites
PE to generate a reporter signal, which is detected by a photomultiplier
tube (PMT). A high-speed digital processor manages data output, and
Bio-Plex Manager
intensity (MFI) as well as concentration (pg/ml). The concentration of
analyte bound to each bead is proportional to the MFI of reporter signal.
Using Bio-Plex Data Pro
can be combined into a single project for easy data management, quick
visualization of results, and simple statistical analysis.
™
software presents data as median fluorescence
™
software, data from multiple instrument runs
3
Page 6

Kit Contents and Storage
Reagents Supplied
Bio-Plex Pro™ human chemokine assays are available in a convenient
all-in-one kit format that includes assay, reagent, and diluent
components in a single box.
Table 1. Contents of 1 x 96-well kits.
Component
Coupled magnetic beads (20x)
Detection antibodies (20x)
Standards
Quality control*
Sample diluent HB
Detection antibody diluent HB
Standard diluent HB
Assay buffer
Wash buffer (10x)
Streptavidin-PE (100x)
Assay plate (96-well flat bottom plate)**
Sealing tape
Assay quick guide
Product data sheet
* Provided with the 40-plex fixed panel only.
** Filter plate option available with custom x-Plex
*** Volumes shown are approximate.
Quantity
1 bottle (8 ml)
1 bottle (3.5 ml)
1 bottle (10 ml)
1 bottle (50 ml)
1 bottle (60 ml)
1 pack of 4
™
and Express kits.
***
1 tube
1 tube
1 vial
1 vial
1 tube
1 plate
1 booklet
1 sheet
Storage and Stability
Kit contents should be stored at 4°C and never frozen. Coupled magnetic
beads and streptavidin-PE should be stored in the dark. All components
are guaranteed for a minimum of six months from the date of purchase
when stored as specified.
4
Page 7

Table 2. Recommended materials.
Item
Bio-Plex Pro Chemokine Assays Quick Guide
Ordering Information
Bulletin #10031991 (download
at www.bio-rad.com/bio-plex)
®
Bio-Plex
Bio-Plex validation kit
200 system or Luminex system with HTF
Bio-Rad catalog #171-000205
Bio-Rad catalog #171-203001
Note: Run the validation kit monthly to ensure optimal
performance of fluidics and optics systems
Bio-Plex calibration kit
Bio-Rad catalog #171-203060
Note: Run the calibration kit daily to standardize
fluorescence signal
Bio-Plex Pro wash station
Bio-Rad catalog #300-34376
For use with magnetic bead-based assays only
Bio-Plex Pro II wash station
Bio-Rad catalog #300-34377
For use with both nonmagnetic and magnetic
bead-based assays
Bio-Plex handheld magnetic washer
Bio-Rad catalog #170-20100
For use with magnetic bead–based assays only
Bio-Plex Pro flat bottom plates (40 x 96-well)
Bio-Rad catalog #171-025001
For magnetic separation on the Bio-Plex Pro wash station
Titertube
®
micro test tubes
Bio-Rad catalog #223-9390
For preparing replicate standards, samples, and controls
prior to loading the plate
Microtiter plate shaker
IKA MTS 2/4 shaker for 2 or 4 microplates
or
Barnstead/Lab-Line Model 4625 plate
IKA catalog #320-8000
VWR catalog #57019-600
shaker (or equivalent capable of 300–1,100 rpm)
™
vacuum manifold
Aurum
Bio-Rad catalog #732-6470
For vacuum filtration
BR-2000 vortexer
Reagent reservoirs, 25 ml
For capture beads and detection antibodies
Reagent reservoir, 50 ml (for reagents and buffers)
Pall Life Science Acrodisc: 25 mm PF syringe filter
(0.8/0.2 µm Supor membrane)
Filter plate, 1 x 96 with clear plastic lid and tray
Bio-Rad catalog #166-0610
VistaLab catalog #3054-1002
or
VistaLab catalog #3054-1004
VistaLab catalog #3054-1006
Pall Life Sciences
catalog #4187
Bio-Rad catalog #171-304502
Other: 15 ml polypropylene tubes for reagent dilutions, calibrated pipets, pipet tips, sterile
distilled water, aluminum foil, absorbent paper towels, 1.5 or 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes, and
standard flat bottom microplate (for calibrating vacuum manifold).
5
Page 8
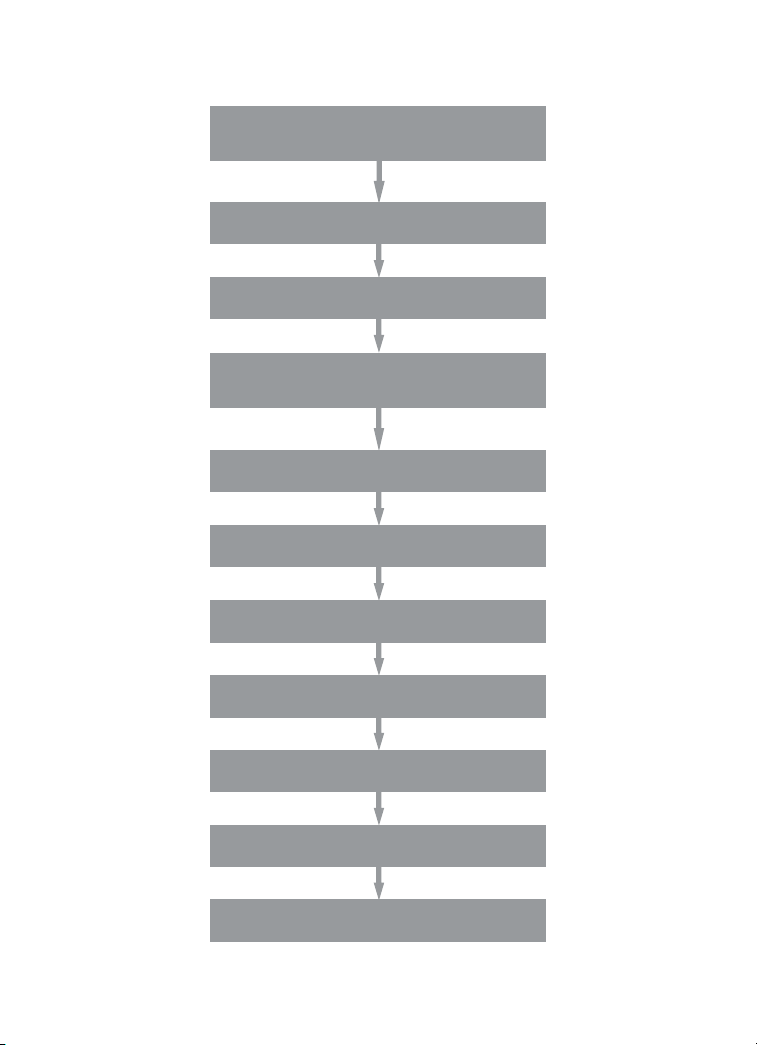
Assay Workflow
Prewet wells
(for lter plate only)
Add 50 μl 1x beads to wells
Wash 2 x 100 μl
Add 50 μl standards, samples, controls;
incubate on shaker at 850 rpm for 1 hr at RT
Wash 3 x 100 μl
Add 25 μl 1x detection antibody; incubate
on shaker at 850 rpm for 30 min at RT
Wash 3 x 100 μl
Add 50 μl 1x streptavidin-PE; incubate
on shaker at 850 rpm for 10 min at RT
Wash 3 x 100 μl
Resuspend in 125 μl assay buffer,
shake at 850 rpm for 30 sec
Acquire data on Bio-Plex system
6
Page 9

lmportant Considerations
Instruments and Software
The Bio-Plex Pro™ assays described in this manual are compatible with
all currently available Luminex-based life science research instruments.
Assays can be read and analyzed with either Bio-Plex Manager
or Luminex xPONENT software (see the Run Assay section).
Assay Procedures
Please pay close attention to vortexing, shaking, and incubation times
and to Bio-Plex
specifically for each assay panel.
®
reader PMT (RP1) setting, as these have been optimized
Assay Quick Guide
Each assay kit comes complete with a printed Bio-Plex Pro™ Assay Quick Guide
(bulletin #10031991), which can be used to prepare and run a full 1 x 96-well
assay plate. Users can also download a copy at www.bio-rad.com/bio-plex.
Bead Regions and Multiplexing Compatibility
n
Bead regions for all analytes are listed in the Read Plate section
n
Do not mix analytes between different Bio-Plex panels or reagent kits.
Resulting standard curves and sample values may be inaccurate
™
software
Detailed Instructions
The following pages provide detailed instructions for each step of the
assay procedure, including preparation, running the assay, and reading the
plate with Bio-Plex Manager
7
™
and Luminex xPONENT software.
Page 10
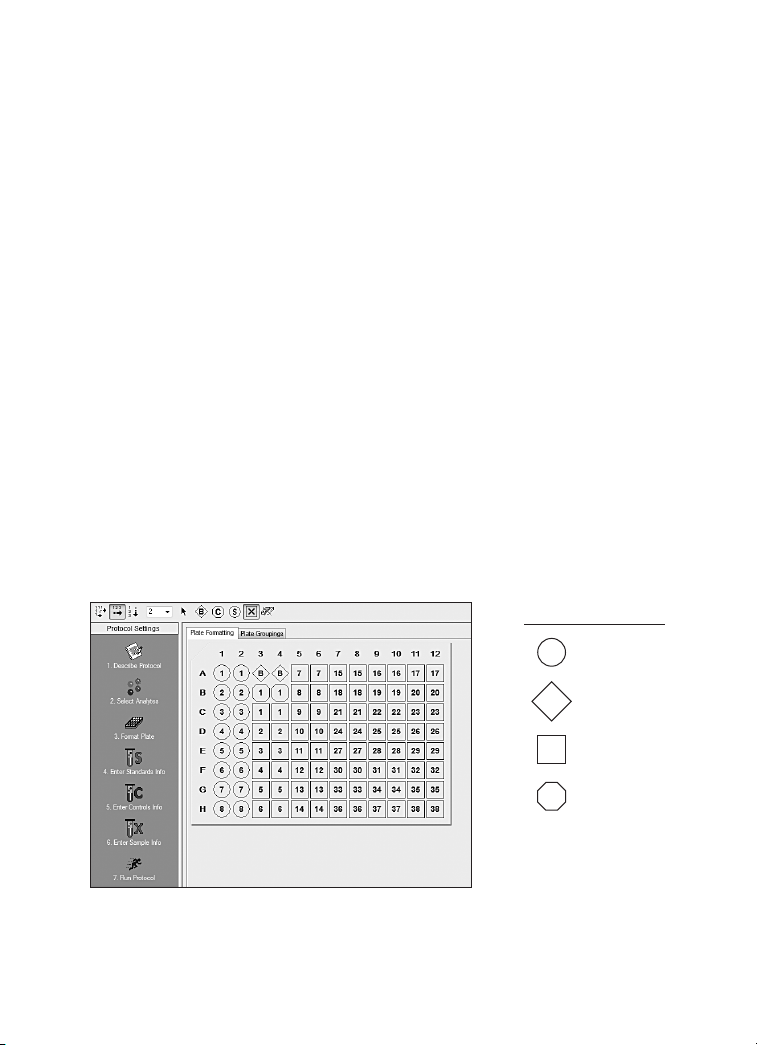
1. Plan Plate Layout
Determine the total number of wells in the experiment using the Plate
Layout Template on page 35 or the Plate Formatting tab in
Bio-Plex Manager
with all conditions in duplicate.
1. Assign standards to columns 1 and 2, with the highest concentration
in row A and the lowest concentration in row H.
2. Assign the blank to wells A3 and A4. The blank should consist of your
chosen standard diluent. Note that Bio-Plex Manager automatically
subtracts the blank (B) MFI value from all other assay wells.
3. User-specified controls, as well as the quality controls supplied in
premixed kits, are assigned to wells in columns 3 and 4.
4. The remainder of the plate is available for samples.
5. Once the total number of wells is known, you can calculate the
required volumes of beads, detection antibody, and streptavidin-PE.
Use Tables 6–7, 9–10, and 11, respectively, or the Calculation
Worksheet on pages 36–37.
Legend
S Standard
™
. A suggested plate layout is shown in Figure 2,
B Blank
X Samples
C Controls
Fig. 2. Suggested plate layout. For detailed instructions on plate
formatting in Bio-Plex Manager, see the Read Plate section.
8
Page 11

2. Prepare Instrument
These directions are specific for the Bio-Plex® 100/200 reader. To prepare
either a Bio-Plex 3D or Bio-Plex
user manuals.
Note: While the instrument is warming up, bring the 10x wash buffer,
assay buffer, and diluents to room temperature. Keep other items on ice
until needed. Also, begin to thaw frozen samples.
Start up and calibrate the Bio-Plex system with Bio-Plex Manager
software prior to setting up the assay. The calibration kit should be run
daily or before each use of the instrument to standardize the fluorescent
signal. For instructions on using other xMAP system software packages,
contact Bio-Rad Technical Support.
The validation kit should be run monthly to ensure optimal performance of
fluidics and optics systems. Refer to either the software manual or online
Help for directions on how to conduct validation.
®
MAGPIX™ reader, consult their respective
™
Start Up System (Bio-Plex 100, 200, or similar)
1. Empty the waste bottle and fill the sheath fluid bottle before starting
if high throughput fluidics (HTF) are not present. This will prevent
fluidic system backup and potential data loss.
2. Turn on the reader, XY platform, and HTF (if included). Allow the
system to warm up for 30 min (if not already done).
3. Select Start up
for 4 hr without acquiring data, the lasers will automatically turn off.
To reset the 4-hr countdown, select Warm up
lasers/optics to reach operational temperature.
and follow the instructions. If the system is idle
and wait for the
Calibrate System
1. Select Calibrate and confirm that the default values for CAL1
and CAL2 are the same as the values printed on the bottle of Bio-Plex
calibration beads. Use the Bio-Plex system low RP1 target value.
9
Page 12

2. Select OK and follow the software prompts for step-by-step
instructions for CAL1 and CAL2 calibration.
Note: In Bio-Plex Manager version 6.1 and higher, startup, warm up,
and calibration can be performed together by selecting the Start up and
calibrate icon.
3. Prepare Wash Method
Bio-Plex Pro™ assays are compatible with both magnetic separation and
vacuum filtration methods. However, for best results, we recommend
performing the assays in a flat bottom plate with magnetic separation.
Table 3. Summary of compatible wash stations and plate types.
Wash Method Wash Station Assay Plate
Magnetic separation Bio-Plex Pro Flat bottom plate
Bio-Plex Pro II (use MAG programs)
Bio-Plex
Vacuum filtration Bio-Plex Pro II (use VAC programs) Filter plate
Vacuum manifold (manual)
Setting up the Bio-Plex Pro or Bio-Plex Pro II
Wash Station
The wash station should be primed before use. For more information, refer
to the Bio-Plex Pro Wash Stations Quick Guide (bulletin #5826).
1. Install the appropriate plate carrier on the wash station.
2. Use the Prime procedure to prime channel 1 with 1x wash buffer.
®
handheld magnetic washer
Setting up the Bio-Plex Handheld Magnetic Washer
Place an empty flat bottom plate on the magnetic washer by sliding
it under the retaining clips. Push the clips inward to secure the plate.
Make sure the plate is held securely. If needed, the clips can be adjusted
for height and tension. For detailed instructions, refer to the user guide
(bulletin #10023087).
10
Page 13

Setting up a Vacuum Manifold
Calibrate the vacuum manifold by placing a standard 96-well flat bottom
plate on the unit and adjusting the pressure to –1 to –3" Hg. In general,
100 µl liquid should take 3–4 sec to clear the well. For more detailed
instructions, refer to bulletin #10005042.
4. Prepare Wash Buffer
1. Bring the 10x stock solution to room temperature.
2. If crystals exist, ensure that they are completely dissolved. Mix the
10x stock solution by inversion before preparing the 1x wash buffer.
3. To prepare 1x wash buffer, dilute 1 part of 10x stock solution with
9 parts of deionized water.
5. Prepare Standards and Controls
General Instructions
n
It is essential to prepare standards and quality controls (if included)
exactly as described in this section. Incorrect preparation may lead to
low signal or variable measurements from plate to plate
n
The product data sheet provided with the standards lists the most
concentrated point on the standard curve (S1). Enter this information
into Bio-Plex Manager
™
software as instructed in section 9
Using the Quality Controls (optional)
A single vial of quality controls is provided with the 40-plex fixed panel only.
Their use is intended for monitoring the day-to-day quality of assay results.
11
Page 14

Selecting a Diluent for Standards and Controls
Refer to Table 4 for recommended diluents based on different sample types.
In order to meet the lot-specific control ranges provided on the product data
sheet, both the standards and controls should be reconstituted in Bio-Plex
®
standard diluent HB. If reconstituting in a different diluent, users will need to
establish/validate their own control ranges or acceptance criteria.
Table 4. Summary of recommended diluents for standards and controls.
Diluent for Standards
Sample Type and Controls* Add BSA
Serum and plasma Standard diluent HB None
Culture media, with serum Culture medium None
Culture media, serum-free Culture medium To 0.5% final**
Lavage, sputum, other fluids Sample diluent HB To 0.5% final**
Lysate Sample diluent HB To 0.5% final**
* If using diluents other than standard diluent HB, users must establish their own control ranges.
** At least 0.5% final BSA is recommended to stabilize analytes and reduce adsorption to labware.
Reconstitute Standards and Quality Controls
This procedure prepares enough standard to run each dilution in duplicate.
Note: The appearance of the lyophilized standards or controls may vary
from a white pellet to clear crystals. Regardless of appearance, the vials
have passed QC specifications and perform accordingly.
1. Gently tap the vial containing the lyophilized standards on a solid
surface to ensure the pellet is at the bottom of the vial.
2. Reconstitute a single vial of standards with 781 µl of the appropriate
diluent. Optional: at the same time, reconstitute the controls vial with
250 µl of the appropriate diluent as summarized in Table 4. Controls
do not require further dilution.
3. Vortex the reconstituted standards and controls at medium speed
for 5 sec, then incubate on ice for 30 min. It is important that
reconstitution of standards and controls is started and ended at the
same time. Be consistent with this incubation time to ensure optimal
assay performance and reproducibility.
12
Page 15

4. During the incubation period, prepare the samples as instructed in
the Prepare Samples section.
Prepare the Standard Dilution Series
The following procedure produces an eight-point standard curve with a
fourfold dilution between each point. Pipet carefully using calibrated pipets
and use a new pipet tip for every volume transfer.
1. Label eight 1.5 ml polypropylene tubes S2 through S8 and Blank.
Alternatively, using Titertube
convenient if a multichannel pipet will be used to load the plate.
2. Add 150 µl of the appropriate diluent to tubes S2–S8 (Figure 3).
3. Vortex reconstituted standards at medium speed for 5 sec before
removing any volume. Transfer 50 µl to the S2 tube containing the
chosen standard diluent. Vortex for 5 sec.
4. Use a new pipet tip to transfer 50 µl from the S2 tube to the S3 tube.
Vortex for 5 sec.
5. Continue with 1:4 (fourfold) serial dilutions as shown in Figure 3.
6. Use reconstituted and diluted standards and controls immediately.
Do not freeze for future use.
®
micro test tubes may prove to be more
50 50 50 50 50 50 50
Reconstituted
Standard
150 150 150 150 150 150 150 150
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 Blank
Fig. 3. Preparing a fourfold dilution series with a single reconstituted standard.
Transfer Volume, µl
13
Diluent, µl
Page 16

6. Prepare Samples
General guidelines for preparing different sample types are provided
here. For more information, consult publications listed in Bio-Rad bulletin
#5297, available for download at www.bio-rad.com, or contact Bio-Rad
Technical Support.
n
Once thawed, keep samples on ice. Prepare dilutions just prior to the
start of the assay and equilibrate to room temperature before use
n
Prepare sample dilutions in microcentrifuge tubes. Alternatively, if a
multichannel pipet will be used to load the plate, then aliquot the required
volumes into Titertube
n
Do not freeze diluted samples
Table 5. Summary of recommended sample diluents and dilution factors.
Sample Type Diluent Add BSA Sample Dilution*
Serum and plasma Sample diluent HB None Fourfold (1:4)
Culture media,
with serum Culture media None User optimized (neat to 1:10)
Culture media,
serum-free Culture media To 0.5% final* User optimized (neat to 1:10)
Lavage, sputum,
other fluids Sample diluent HB To 0.5% final* User optimized (neat to 1:10)
User optimized (at least 1:2 for
Lysate Sample diluent HB To 0.5% final* 200–900 µg/ml final protein)
* At least 0.5% final BSA is recommended to stabilize analytes and reduce adsorption to labware.
®
micro test tubes
Serum and Plasma
Note: If using plasma, EDTA or citrate is preferred as an anticoagulant.
Heparin-treated plasma, while compatible with Bio-Plex Pro
may absorb certain soluble proteins of interest. Avoid using hemolyzed
samples as this may lead to false positive results.
1. Draw whole blood into collection tubes containing anticoagulant.
Invert tubes several times to mix.
2. For serum, allow blood to clot at room temperature for 30 to 45 min.
For plasma, proceed directly to the centrifugation steps.
14
™
assays,
Page 17

3. Perform centrifugation at 1,000 x g for 15 min at 4°C and transfer the
serum or plasma to a clean polypropylene tube.
4. To completely remove platelets and precipitates, centrifuge again at
10,000 x g for 10 min at 4°C. Alternatively, filter the samples with a
0.8/0.2 m dual filter to prevent clogging.
5. Dilute samples fourfold (1:4) by adding 1 volume of sample to
3 volumes of Bio-Plex
sample + 120 µl sample diluent HB).
6. Assay samples immediately or aliquot into single-use tubes and store
at –70°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
®
sample diluent HB (for example, 40 µl
Cell Culture Supernatant
1. Collect supernatants and centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 15 min at 4°C.
For cell lines cultured in serum-free culture media, collect samples and
add BSA as a carrier protein to a final concentration of at least 0.5%
to stabilize protein analytes and to prevent adsorption to labware.
2. Transfer to a clean polypropylene tube. If cellular debris or precipitates
are present, centrifuge again at 10,000 x g for 10 min at 4°C.
3. We recommend testing undiluted samples first. If high levels of
analyte are expected, samples can be further diluted in culture
medium. Rarely would samples need to be diluted greater than 1:10.
4. Assay immediately or store samples in single-use aliquots at –70°C.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Lavage, Sputum, and Other Biological Fluid Samples
Keep all samples on ice until ready for use. The appropriate sample
dilution factor should be optimized by the user.
1. If required, dilute the sample in Bio-Plex sample diluent with BSA
added to a final concentration of 0.5%.
2. Centrifugation at 10,000 x g for 10 min at 4°C may be required to
clarify the sample.
15
Page 18

Lysates
The Bio-Plex cell lysis kit is required for lysate preparation (available
separately, catalog #171-304011 and #171-304012). Refer to bulletin #5297
for a list of published articles on cytokine analysis in tissue samples.
1. Prepare the cell or tissue lysates according to the instructions
provided with the Bio-Plex cell lysis kit. The protease inhibitors
factor I and factor II are included in the kit. PMSF needs to be added
to lysis buffer at a final concentration of 2 mM. The lysates should be
free of particulate matter.
2. Determine the total protein concentration of the lysate. It may be
necessary to test lyse your samples with different volumes of lysing
solution to obtain the specified protein concentration range.
3. Dilute at least 1:2 in sample diluent + 0.5% BSA, to a final protein
concentration of 200–900 g/ml. For analytes with high expression, a
lysate protein concentration as low as 50 g/ml may be sufficient.
Note: For optimum antibody binding during sample incubation, it is
important to dilute lysates as much as possible to reduce the detergent
concentration.
4. If the lysate is not tested immediately, store at –20°C to –70°C. Avoid
repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
7. Prepare Coupled Beads
1. Use Tables 6–7 or the Calculation Worksheet on page 36 to calculate
the volume of coupled beads and assay buffer needed to prepare a
1x stock.
2. Add the required volume of Bio-Plex
polypropylene tube.
16
®
assay buffer to a 15 ml
Page 19

3. Vortex the 20x stock of coupled beads at medium speed for
30 sec. Carefully open the cap and pipet any liquid trapped in the
cap back into the tube. This is important to ensure maximum bead
recovery. Do not centrifuge the vial; doing so will cause the
beads to pellet.
4. Dilute coupled beads to 1x by pipetting the required volume into the
15 ml tube. Vortex.
Each well of the assay requires 2.5 l of the 20x stock adjusted to a
final volume of 50 l in assay buffer.
5. Protect the beads from light with aluminum foil. Equilibrate to room
temperature prior to use.
Note: To minimize volume loss, use a 200–300 l capacity pipet to remove
beads from the 20x stock tube. If necessary, perform the volume transfer in
two steps. Do not use a 1,000 l capacity pipet and/or wide bore pipet tip.
Preparing 1x coupled beads from 20x stock (includes 20% excess volume)
Table 6. Premixed panel or one singleplex assay.
# of Wells 20x Beads, µl Assay Buffer, µl Total Volume, µl
96 288 5,472 5,760
48 144 2,736 2,880
Table 7. Mixing singleplex assays.
20x Beads, µl 20x Beads, µl
# of Wells Singleplex #1 Singleplex #2 Assay Buffer, µl Total Volume, µl
96
48
288 288 5,184 5,760
144 144 2,592 2,880
17
Page 20

8. Run Assay
Considerations
n
Bring all assay components and samples to room temperature
before use
n
Use calibrated pipets and pipet carefully, avoiding bubbles
n
Pay close attention to vortexing, shaking, and incubation instructions.
Deviation from the protocol may result in low assay signal and
assay variability
n
Assay incubations are carried out on a shaker at 850 ± 50 rpm at room
temperature (RT). Cover the plate with sealing tape and protect from
light with aluminum foil
Table 8. Summary of wash options and protocols. After each assay step, select the
appropriate Bio-Plex Pro
step as summarized below.
Bio-Plex Pro or Bio-Plex Pro II Handheld Magnet or
Pro II Wash Station Wash Station Vacuum Manifold
Assay Step Magnetic Program Vacuum Program Manual Wash Steps
Add beads to plate MAG x2 VAC x2 2 x 100 l
Sample incubation
Detection Ab incubation MAG x3 VAC x3 3 x 100 l
SA-PE incubation
™
wash station program or perform the appropriate manual wash
Considerations When Using a Vacuum Manifold
n
After each incubation, place the filter plate on a calibrated vacuum
apparatus and remove the liquid by vacuum filtration
n
To wash, add 100 l wash buffer to each well and remove the liquid as
before. Ensure that all wells are exposed to the vacuum
n
Thoroughly blot the bottom of the filter plate with a clean paper towel
between each vacuum step to prevent cross contamination
n
Place the assay plate on the plastic plate holder/tray as needed
n
Before each incubation, gently cover the plate with a new sheet of
sealing tape. Avoid pressing down on the wells to prevent leaking from
the bottom
18
Page 21

Add Coupled Beads, Samples, Standards, Blank,
and Controls
1. Cover unused wells of the assay plate with sealing tape.
2. Prewet the filter plate. Skip this step if using a flat bottom plate.
Prewet the wells with 100 µl assay buffer and remove the liquid by
vacuum filtration. Dry the bottom of the filter plate thoroughly by
blotting on a clean paper towel.
3. Vortex the diluted (1x) beads for 30 sec at medium speed. Pour into
a reagent reservoir and transfer 50 µl to each well of the assay plate.
Tip: A multichannel pipet is highly recommended for ease of use
and efficiency.
4. Wash the plate two times with 100 µl Bio-Plex
well, using the wash method of choice.
5. Vortex the diluted samples, standards, blank, and controls at medium
speed for 5 sec. Transfer 50 µl of each to the appropriate well of the
assay plate, changing the pipet tip after every volume transfer.
6. Cover plate with a new sheet of sealing tape and protect from light
with aluminum foil. Incubate on shaker at 850 ± 50 rpm for 1 hr at RT.
Note: Be consistent with this incubation time and shaker setting for
optimal assay performance and reproducibility.
®
wash buffer per
Prepare and Add Detection Antibodies
1. While the samples are incubating use Tables 9 and 10 or the
Calculation Worksheet on page 36 to calculate the volume of
detection antibodies and Bio-Plex detection antibody diluent HB
needed to prepare a 1x stock. Detection antibodies should be
prepared 10 min before use.
2. Add the required volume of Bio-Plex detection antibody diluent HB to
a 15 ml polypropylene tube.
3. Vortex the 20x stock of detection antibodies for 15–20 sec at
medium speed, then perform a 30 sec spin to collect the entire
volume at the bottom of the tube.
19
Page 22

4. Dilute detection antibodies to 1x by pipetting the required volume into
the 15 ml tube. Vortex.
Each well of the assay requires 1.25 l of the 20x stock adjusted to a
final volume of 25 l in detection antibody diluent.
Preparing 1x detection antibodies from 20x stock (includes 25% excess volume)
Table 9. Premixed panel or one singleplex assay.
20x Detection Detection Antibody
# of Wells Antibodies, µl Diluent, µl Total Volume, µl
96 150 2,850 3,000
48 75 1,425 1,500
Table 10. Mixing singleplex assays.
20x Detection 20x Detection Detection
Antibodies, µl Antibodies, µl Antibody
# of Wells Singleplex #1 Singleplex #2 Diluent, µl Total Volume, µl
96
48
150 150 2,700 3,000
75 75 1,500 1,500
5. After incubating the beads, samples, standards, blank, and controls,
slowly remove and discard the sealing tape.
6. Wash the plate three times with 100 µl wash buffer per well.
7. Vortex the diluted (1x) detection antibodies at medium speed for
5 sec. Pour into a reagent reservoir and transfer 25 µl to each well
of the assay plate using a multichannel pipet.
8. Cover plate with a new sheet of sealing tape and protect from light with
aluminum foil. Incubate on shaker at 850 ± 50 rpm for 30 min at RT.
Prepare and Add Streptavidin-PE (SA-PE)
1. While detection antibodies are incubating, use Table 11 or the
Calculation Worksheet on page 36 to calculate the volume of SA-PE
and assay buffer needed to prepare a 1x stock. SA-PE should be
prepared 10 min before use.
20
Page 23

2. Add the required volume of assay buffer to a 15 ml polypropylene tube.
3. Vortex the 100x stock of SA-PE for 5 sec at medium speed. Perform
a 30 sec spin to collect the entire volume at the bottom of the tube.
4. Dilute SA-PE to 1x by pipetting the required volume into the 15 ml
tube. Vortex and protect from light until ready to use.
Each well of the assay requires 0.5 l of the 100x stock adjusted to a
final volume of 50 l in assay buffer.
Table 11. Preparing 1x SA-PE from 100x stock (includes 25% excess volume).
# of Wells 100x SA-PE, µl Assay Buffer, µl Total Volume, µl
96 60 5,940 6,000
48 30 2,970 3,000
5. After detection antibody incubation, slowly remove and discard
the sealing tape.
6. Wash the plate three times with 100 µl of wash buffer per well.
7. Vortex the diluted (1x) SA-PE at medium speed for 5 sec. Pour
into a reagent reservoir and transfer 50 µl to each well using a
multichannel pipet.
8. Cover plate with a new sheet of sealing tape and protect from light with
aluminum foil. Incubate on shaker at 850 ± 50 rpm for 10 min at RT.
9. After the streptavidin-PE incubation step, slowly remove and discard
the sealing tape.
10. Wash the plate three times with 100 µl of wash buffer per well.
11. To resuspend beads for plate reading, add 125 µl assay buffer to
each well. Cover the plate with a new sheet of sealing tape. Shake
at room temperature at 850 ± 50 rpm for 30 sec, and slowly remove
the sealing tape. Ensure that the plate cover has been removed
before placing the plate on the reader.
21
Page 24

Table 12. Read the plate using the appropriate instrument settings.
Instrument RP1 (PMT) DD Gates Bead Events
Bio-Plex 100, 200* Low 5,000 (low), 25,000 (high) 50
Bio-Plex 3D* Standard Select MagPlex beads 50
®
Bio-Plex
* Or similar Luminex-based system.
MAGPIX™ N/A, use default instrument settings
9. Read Plate
Bio-Plex Manager™ software is recommended for all Bio-Plex Pro™ assay
data acquisition and analysis. Instructions for Luminex xPONENT software
are also included. For instructions using other xMAP system software
packages, contact Bio-Rad Technical Support or your regional Bio-Rad
field applications specialist.
Prepare Protocol in Bio-Plex Manager Software
Version 6.0 and Higher
The protocol should be prepared in advance so that the plate is read as
soon as the experiment is complete.
A protocol file specifies the analytes in the assay, the plate wells to be
read, sample information, the values of standards and controls, and
instrument settings.
Bio-Plex Manager software versions 6.0 and higher contain protocols for
most Bio-Plex
protocol. To create a new protocol, select File, then New from the main
menu. Locate and follow the steps under Protocol Settings.
1. Click Describe Protocol and enter information about the assay
(optional).
2. Click Select Analytes and create a new panel. Visually confirm the
selected analytes and proceed to step 3.
®
assays. Choose from available protocols or create a new
22
Page 25

a. Click Add Panel
in the Select Analytes toolbar. Enter a new
panel name. Select Bio-Plex Pro Assay Magnetic from the
assay dropdown list. If using Bio-Plex Manager version 5.0 or lower,
select MagPlex from the assay dropdown list.
b. Click Add. Enter the bead region number and name for the first
analyte. Click Add Continue to repeat for each analyte in the
assay. Refer to the bead regions in parentheses ( ) listed on the
peel-off label provided with the standards.
For reference, bead regions are shown in Table 13.
c. Click Add when the last analyte has been added and click OK to
save the new panel.
d. Highlight analytes from the Available list (left) and move to the
Selected list (right) using the Add button. To move all analytes at
once, simply click Add All.
e. If some of the analytes need to be removed from the Selected
list, highlight them and select Remove. If desired, it is possible to
rename the panel by clicking Rename Panel and entering a new
panel name.
Table 13. Bead regions for the human chemokine panel.
Analyte Bead Region Analyte Bead Region Analyte Bead Region
6Ckine/CCL21 12 IL-1b 39 MDC/CCL22 29
BCA-1/CXCL13 74 IL-2 38 MIF 35
CTACK/CCL27 72 IL-4 52 MIG/CXCL9 14
ENA-78/CXCL5 73 IL-6 19 MIP-1a/CCL3 55
Eotaxin/CCL11 43 IL-8/CXCL8 54 MIP-1δ/CCL15 66
Eotaxin-2/CCL24 30 IL-10 56 MIP-3a/CCL20 62
Eotaxin-3/CCL26 65 IL-16 27 MIP-3b/CCL19 76
Fractalkine/CX3CL1 77 IP-10/CXCL10 48 MPIF-1/CCL23 37
GCP-2/CXCL6 15 I-TAC/CXCL11 25 SCYB16/CXCL16 64
GM-CSF 34 MCP-1/CCL2 53 SDF-1a+b/CXCL12 22
Gro-a/CXCL1 61 MCP-2/CCL8 57 TARC/CCL17 67
Gro-b/CXCL2 78 MCP-3/CCL7 26 TECK/CCL25 46
I-309/CCL1 20 MCP-4/CCL13 28 TNF-a 36
IFN-g 21
23
Page 26

Note: Do not use preset panels found in Bio-Plex Manager software
version 5.0 or earlier, as the bead regions are not up to date.
3. Click Format Plate and format the plate according to the plate layout
created in section 1 (Plan Plate Layout). To modify the plate layout,
follow the steps below (see Figure 4).
a. Select the Plate Formatting tab.
b. Select the standards icon
S
and drag the cursor over all the
wells that contain standards. Repeat this process for
Blanks
B
, Controls C, and Samples X. Note that
Bio-Plex Manager automatically subtracts the blank MFI
value from all other assay wells.
4. Click Enter Standards Info in the Protocol Settings bar.
a. Enter the highest concentration of each analyte in the top row
(labeled S1) of the table. S1 concentration information is included
with each vial of standards.
Fig. 4. Plate formatting.
24
Page 27

b. Enter a dilution factor of 4 and click Calculate. The concentrations
for each standard point will be populated for all analytes in the table.
c. Optional: enter the lot number of the vial of standards into the
Standard Lot box and click Save.
5. Click Enter Controls Info.
a. For user-specified controls, select an analyte from the dropdown
menu, then enter a description and concentration. Repeat for
each additional analyte in the assay.
b. For the quality controls supplied with the 40-plex fixed panel
only, format the appropriate wells as controls, enter descriptions,
but leave the concentrations blank. Alternatively, the quality
controls can be formatted as samples with clear descriptions
such as “quality control high” and “quality control low.” In any
case, the expected control ranges provided are not entered
into Bio-Plex Manager software version 6.1 and earlier.
6. Click Enter Sample Info and enter sample information and the
appropriate dilution factor.
7. Click Run Protocol and confirm that the assay settings are correct.
a. Refer to Table 12 for the recommended RP1 (PMT) setting.
Protocols using alternative PMT settings should be validated by
the end user.
b. Confirm that data acquisition is set to 50 beads per region.
In Advanced Settings, confirm that the bead map is set to
100 region, the sample size is set to 50 µl, and the doublet
discriminator (DD) gates are set to 5,000 (Low) and 25,000 (High).
In Bio-Plex Manager software versions 4.0, 4.1, 4.1.1, and 5.0,
check Override Gates and set the DD gate values as indicated.
Select Start, name and save the .rbx file, and begin data
acquisition. The Run Protocol pop-up screen will appear. Click
Eject/Retract to eject the plate carrier.
25
Page 28

Acquire Data
1. Shake the assay plate at 850 ± 50 rpm for 30 sec, and visually
inspect the plate to ensure that the assay wells are filled with buffer.
Slowly remove the sealing tape and any plate cover before placing
the plate on the plate carrier.
2. Click Run Protocol and on the pop-up screen, select Load Plate
and click OK to start acquiring data.
3. Use the Wash Between Plates
to reduce the possibility of clogging the instrument.
4. If acquiring data from more than one plate, empty the waste bottle and
refill the sheath bottle after each plate (if HTF are not present). Select
Wash Between Plates and follow the instructions. Then repeat the
Prepare Protocol and Acquire Data instructions.
5. When data acquisition is complete, select Shut Down
follow the instructions.
command after every plate run
and
Reacquire Data
It is possible to acquire data from a well or plate a second time using the
Rerun/Recovery mode located below Start in the Run Protocol step.
Any previous data will be overwritten.
1. Check the wells from which data will be reacquired.
2. Aspirate the buffer with the wash method of choice, but do not
perform the wash step.
3. Add 100 µl of assay buffer to each well. Cover the plate with a new
sheet of sealing tape. Shake the plate at 850 ± 50 rpm for 30 sec.
Slowly remove the sealing tape before placing the plate on the
plate reader.
4. Repeat the Acquire Data steps to reacquire data. The data acquired
should be similar to those acquired initially; however, the acquisition
time will be extended because the wells have fewer beads.
26
Page 29

Data Analysis
Quality Controls
If the quality controls were run in the assay plate, open the results (.rbx) file,
click on Report Table, and locate the control wells. Visually compare the
observed concentrations of the high and low controls in the Report Table
against the lot-specific control ranges shown in the product data sheet.
Note: Expected control ranges are provided for reference and should be
used as general guidelines. Actual results may vary for some operators.
If the controls do not fall within the expected ranges, please refer to the
troubleshooting section for possible causes and solutions.
Removing Outliers
Outliers are identified as standard data points that do not meet accuracy
or precision requirements and should be considered invalid when
performing curve fitting. As such, they should be removed to generate a
more realistic and accurate standard curve. This may result in an extended
assay working range and allow quantitation of samples that might
otherwise be considered out of range.
In Bio-Plex Manager software version 6.0 and higher, outliers can be
automatically removed by selecting the Optimize button in the Standard
Curve window. In Bio-Plex Manager software 5.0 and earlier versions,
outliers also can be manually selected in the Report Table. Visit online Help
to learn more about the standard curve optimizer feature and how outliers
are determined.
Previous Versions of Bio-Plex Manager Software
For instructions on using previous versions of Bio-Plex Manager software,
please contact Bio-Rad Technical Support.
27
Page 30

Luminex xPONENT Software
Although guidelines are provided here, consult the xPONENT software
manual for more details. Perform a system initialization with Luminex’s
calibration and performance verification kit, as directed by Luminex. Select
Batches to set up the protocol and follow the information under Settings.
Note: The instrument settings described below apply to Luminex
100/200 and FLEXMAP 3D or Bio-Plex
Bio-Plex
®
MAGPIX™ reader, use the default instrument settings.
®
3D instruments. For the
1. Select MagPlex as the bead type for magnetic beads, which
automatically sets the DD gates.
2. Volume = 50 µl.
3. Refer to Table 12 to select the appropriate PMT setting for
your instrument.
4. Plate name: 96-well plate.
5. Analysis type: Quantitative, 5PL Curve Fit.
6. Number of standards: 8.
Select Analytes to set up the panel.
1. Enter pg/ml in the Units field.
2. Enter 50 in the Count field.
3. Select the bead region and enter the analyte name.
4. Click Apply all for Units and Count.
Select Stds and Ctrls.
1. Enter standard concentrations, lot number, dilution factor, and other
information as applicable.
After the assay is complete, select Results, then select Saved Batches.
28
Page 31

Troubleshooting Guide
This troubleshooting guide addresses problems that may be encountered
with Bio-Plex Pro
™
assays. If you experience any of the problems listed
below, review the possible causes and solutions provided. Poor assay
performance may also be due to the Bio-Plex
®
suspension array reader.
To eliminate this possibility, use the validation kit to assist in determining if
the array reader is functioning properly.
Possible Causes
High Inter-Assay CV
Standards and controls were not
reconstituted consistently between
assays
Possible Solutions
Incubate the reconstituted
standards for 30 min on ice. Always
be consistent with the incubation
time and temperature.
Reconstituted standards, controls,
and diluted samples were not
stored properly
Reconstituted standards and diluted
samples should be prepared on ice
as instructed. Prior to plating, the
reconstituted standards and diluted
samples should be equilibrated to
room temperature.
Bottom of filter plate not dry
Dry the bottom of the filter plate with
absorbent paper towel (preferably
lint-free) to prevent cross-well
contamination.
29
Page 32

Possible Causes
High Intra-Assay CV
Improper pipetting technique
Possible Solutions
Pipet carefully when adding
standards, controls, samples,
detection antibodies, and
streptavidin-PE, especially when
using a multichannel pipet. Use a
calibrated pipet. Change pipet tip
after every volume transfer.
Reagents and assay components
not equilibrated to room
temperature prior to pipetting
Contamination with wash buffer
during wash steps
Slow pipetting of samples and
reagents across the plate
Bio-Plex wash station:
insufficient washing due to
clogged pins
30
All reagents and assay components
should be equilibrated to room
temperature prior to pipetting.
During the wash steps, be careful
not to splash wash buffer from one
well to another. Be sure that the
wells are filtered completely and that
no residual volume remains. Ensure
that the microplate shaker setting is
not too high. Reduce the microplate
shaker speed to minimize splashing
Sample pipetting across the entire
plate should take less than 4 min.
Reagent pipetting across the entire
plate should take less than 1 min.
Clean dispensing pins with the thicker
of the two cleaning needles provided
with washer. Perform regular rinses to
minimize salt buildup.
Page 33

Possible Causes
Low Bead Count
Miscalculation of bead dilution
Possible Solutions
Check your calculations and be
careful to add the correct volumes.
Beads clumped in multiplex
bead stock tube
Vacuum on for too long when
aspirating buffer from wells
Assay plate not shaken enough
during incubation steps and prior
to reading
Reader is clogged
Incorrect needle height of the
reader
Low Signal or Poor Sensitivity
Standards reconstituted incorrectly
Vortex for 30 sec at medium speed
before aliquoting beads.
Do not apply vacuum to the filter
plate for longer than 10 sec after the
buffer is completely drained from
each well.
Shake the plate at 850 ± 50 rpm
during incubation steps and for
30 sec immediately before reading
the plate.
Refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the Bio-Plex System Hardware
Instruction Manual (bulletin
#10005042).
Adjust the needle height to coincide
with the plate type provided in the kit.
Follow the standard preparation
instructions carefully.
Detection antibody or
streptavidin-PE diluted incorrectly
31
Check your calculations and be
careful to add the correct volumes.
Page 34

Possible Causes
High Background Signal
Incorrect buffer was used
for (example, assay buffer
used to dilute standards)
Possible Solutions
Use standard diluent or diluent similar to
final sample matrix to dilute standards.
Accidentally spiked blank
wells
Detection antibodies or
streptavidin-PE incubated
too long
Poor Recovery
Expired Bio-Plex reagents
were used
Incorrect amounts of
components were added
Microplate shaker set to an
incorrect speed
High end saturation of the
standard curve
Do not add any antigens to the
blank wells.
Follow the procedure incubation
time precisely.
Check that reagents have not expired. Use
new or nonexpired components.
Check your calculations and be careful to
add the correct volumes.
Check the microplate shaker speed and
use the recommended setting. Setting the
speed too high may cause splashing and
contamination. Use the recommended
plate shaker. Setting the speed too low may
cause low assay signal and false plateau or
high end saturation of standard curves.
Make sure that correct shaker speed and
incubation times are used. Remove S1 for
data analysis if needed.
Quality controls do not fall
within expected ranges
Make sure that the controls are
reconstituted at the same time as standards
and in the same diuent (standard diluent
HB). Incubate for precisely 30 min.
32
Page 35

Possible Causes
Poor Recovery
Improper pipetting
technique
Impact of Sample Matrix
Negative MFI values in
samples or standards
Possible Solutions
Pipet carefully when adding standards, samples,
detection antibodies, and streptavidin-PE, especially
when using a multichannel pipet. Use a calibrated
pipet. Change pipet tip after every volume transfer.
If samples contain little or no analyte, negative
values observed may be due to statistical variation.
If assay drift is suspected, retest the samples
by positioning them next to the standards. If
contamination of standards is suspected, check
the standard replicate value and be careful when
adding samples to the wells. Matrix effects could
also produce negative sample values.
Bio-Plex Manager
subtracts the Blank (B) MFI value from all
other assay wells. While this has no impact on
observed concentrations of samples within the
assay working range, it may result in a negative
MFI value if the Blank’s MFI value is greater than
either the standard or the sample value. If this
is undesirable, then reformat the blank wells
as Sample (X) or Control (C) in the protocol or
results file.
Poor precision in
serum and
plasma sample
measurements
Check if any interfering components, additives,
or gel from separators were introduced into the
samples. Avoid using hemolyzed and heavily
lipemic samples. Remove visible particulate in
samples by centrifugation. Avoid multiple freezethaw cycles of samples.
33
™
software automatically
Page 36

Appendix: Non-Human Primate (NHP) Cross-Reactivity
The human chemokine assays were found to be cross-reactive with
two common NHP species, cynomolgus (Cyno) macaque and rhesus
macaque. Other NHP species were not tested. The degree of crossreactivity was determined based on the ability of each assay to detect
native analyte in serum, plasma and/or culture media from mitogen
stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC).
Assay signal (MFI) for the most highly cross-reactive samples were compared
against the human standard curve and scored as shown in the Table 14.
Table 14. NHP cross-reactivity of the human chemokine assays.
Analyte Cyno Rhesus Analyte Cyno Rhesus
6Ckine/CCL21 – – IL-8
BCA-1/CXCL13
CTACK/CCL27 – – I-TAC/CXCL11
ENA-78/CXCL5
Eotaxin/CCL11
Eotaxin-2/CCL24 – – MCP-3/CCL7 – –
Eotaxin-3/CCL-26 – – MCP-4/CCL13
Fractalkine/CX3CL1
GCP-2/CXCL6 – – MIF
GM-CSF
Gro-a/CXCL1 – – MIP-1a/CCL3
Gro-b/CXCL2
I-309/CCL1 – – MIP-3a/CCL20 – –
IFN-g – – MIP-3b/CCL19
IL-10
IL-16
IL-1b
IL-2 – – TARC/CCL17 – –
IL-4
IL-6
– No NHP cross-reactivity observed. Assay signal below S6 on the standard curve.
+
Some NHP cross-reactivity observed. Assay signal above S6.
++
Moderate NHP cross-reactivity observed. Assay signal above S5.
+++
Strong NHP cross-reactivity observed. Assay signal above S3.
+++ +++
+
+
+++ +
+++ +++
+
+++ +++
+
+++ +++
++
+++ +++
+
MCP-1/CCL2
+
MCP-2/CCL8
MDC/CCL22
+
MIP-1δ/CCL15 –
+
SCYB16/CXCL16 –
+
TECK/CCL25
IP-10/CXCL10
MIG/CXCL9 – –
MPIF-1/CCL23 – –
SDF-1a+b/CXCL12 +
TNF-a
+++ +++
+++ +++
+++ +++
+++ +++
++
+++ +++
+
+++ +++
+++ +++
++
+
+
–
–
++
+
++
+
+
+
34
Page 37

Plate Layout Template
35
Page 38

Calculation Worksheet
If using either a premixed panel or one singleplex assay, follow
these directions.
Plan the plate layout and enter the number of wells to be used in the assay:_______
1
1. Determine the volume of 1x coupled beads needed.
a. Each well requires 50 µl of coupled beads (1x): _______ x 50 µl = _______ µl
b. Include 20% excess to ensure enough volume: _______ µl x 0.20 = _______ µl
c. Total volume of 1x coupled beads: _______ µl + _______ µl = _______ µl
d. Volume of 20x coupled beads required: _______ µl/20 = _______ µl
e. Volume of assay buffer required: _______ µl – _______ µl = _______ µl
2 3 4
4 5 6
2. Determine the volume of 1x detection antibody needed.
a. Each well requires 25 µl detection antibodies (1x): ______ x 25 µl = _______ µl
b. Include 25% excess to ensure enough volume: _______ µl x 0.25 = _______ µl
c. Total volume of 1x detection antibodies: _______ µl + _______ µl = _______ µl
d. Volume of 20x detection antibodies required: _______ µl/20 = _______ µl
e. Volume of detection antibody diluent required: _____ µl – _____ µl = _____ µl
3. Determine the volume of 1x streptavidin-PE needed.
a. Each well requires 50 µl streptavidin-PE (1x): _______ x 50 µl = _______ µl
b. Include 25% excess to ensure enough volume: _______ µl x 0.25 = _______ µl
c. Total volume of 1x streptavidin-PE: ______ µl + ______ µl = ______ µl
d. Volume of 100x streptavidin-PE required: _______ µl/100 = _______ µl
e. Volume of assay buffer required: _______ µl – _______ µl = _______ µl
12 13 14
14 15 16
1 2
2 3
4 5
1 7
7 8
7 8 9
9 10
9 10 11
1 12
12 13
14 15
36
Page 39

If mixing singleplex assays, follow these directions.
Enter the number of wells to be used in the assay:_______
1
1. Determine the volume of 1x coupled beads needed.
a. Each well requires 50 µl coupled beads (1x): _______ x 50 µl = _______ µl
b. Include 20% excess to ensure enough volume: _______ µl x 0.20 = _______ µl
c. Total volume of 1x coupled beads: _______ µl + _______ µl = _______ µl
d. Enter the number of singleplex sets (or analytes) that will be multiplexed: _______
2 3 4
1 2
2 3
5
e. Volume of 20x coupled beads required from each stock tube:
_______ µl/20 = _______ µl
4 6
f. Total volume of combined bead stocks: _______ x _______ µl = _______ µl
g. Volume of assay buffer required: _______ µl – _______ µl = _______ µl
5 6 7
4 7 8
2. Determine the volume of 1x detection antibody needed.
a. Each well requires 25 µl detection antibodies (1x): _______ x 25 µl = _______ µl
b. Include 25% excess to ensure enough volume: _______ µl x 0.25 = _______ µl
c. Total volume of 1x detection antibodies: _______ µl + _______ µl = _______ µl
d. Enter the number of singleplex sets (or analytes) that will be multiplexed: _______
9 10 11
1 9
9 10
5
e. Volume of 20x detection antibodies required from each stock tube:
_______ µl/20 = _______ µl
11 12
f. Total volume of combined detection antibody stock: _____ µl x _____ = _____ µl
g. Volume of detection antibody diluent required: ____ µl – ____ µl = ____µl
12 5 13
11 13 14
3. Determine the volume of 1x streptavidin-PE needed.
a. Each well requires 50 µl streptavidin-PE (1x): _______ x 50 µl = _______ µl
b. Include 25% excess to ensure enough volume: _______ µl x 0.25 = _______ µl
c. Total volume of 1x streptavidin-PE: ______ µl + ______ µl = _______ µl
d. Volume of 100x streptavidin-PE required: _______ µl/100 = _______ µl
e. Volume of assay buffer required: _______ µl – _______ µl = _______ µl
15 16 17
17 18 19
1 15
15 16
17 18
37
Page 40

Safety Considerations
Eye protection and gloves are recommended when using these products.
Consult the MSDS for additional information. The Bio-Plex Pro
contain components of animal origin. This material should be handled as
if capable of transmitting infectious agents. Use universal precautions.
These components should be handled at Biosafety Level 2 containment
as defined by U.S. government publication, Biosafety in Microbiological
and Biomedical Laboratories (Centers for Disease Control 1999).
™
assays
Legal Notices
Acrodisc and Supor are trademarks of Pall Corporation. MagPlex,
xMAP, xPONENT, FLEXMAP 3D, and Luminex are trademarks of
Luminex Corporation.
The Bio-Plex
microspheres and instrumentation licensed to Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
by the Luminex Corporation.
References
Page 1, Introduction:
Locati M et al. (2005). Chemokines and their receptors: Roles in specific
clinical conditions and measurement in the clinical laboratory. Am J Clin
Pathol 123, S82–S95.
Slettenaar VIF and Wilson JL (2006). The chemokine network: A target in
cancer biology? Adv Drug Deliv Rev 58, 962–974.
®
suspension array system includes fluorescently labeled
38
Page 41

Ordering Information
Detailed ordering information can be found at www.bio-rad.com/bio-plex.
Catalog # Premixed Multiplex Assay Panel
171-AK99MR2 Bio-Plex Pro Human Chemokine Panel 40-Plex, 1 x 96-well
Singleplex Set
Various Bio-Plex Pro Human Chemokine Singleplex Sets, 1 x 96-well
Individual Components and Accessories
171-304090 Bio-Plex Pro Reagent Kit III with Filter Plate, 1 x 96-well
171-304090M Bio-Plex Pro Reagent Kit III with Flat Bottom Plate, 1 x 96-well
171-DK0001 Bio-Plex Pro Human Chemokine Standard, pkg of 1 vial
171-DK0050 Bio-Plex Pro Human Chemokine Standard, pkg of 50 vials
171-304502 Filter Plate, 1 x 96-well with clear plastic lid and tray
(requires reagent kit III and chemokine standards to run an assay)
Bio-Plex
®
x-Plex™ Assays (We Mix)
Premium custom assay service using the Bio-Plex Assay Builder
(www.bio-rad.com/bio-plex/assaybuilder) to select analytes and
plate type of interest. Assays are supplied as premixed coupled beads
and detection antibodies in the all-in-one kit format. Quality controls
are not included in chemokine x-Plex kits.
Bio-Plex Express Assays (You Mix)
Fast and economical custom assay service using the Bio-Plex Assay
Builder (www.bio-rad.com/bio-plex/assaybuilder) to select analytes
and plate type of interest. Assays are supplied as individual sets of
coupled beads and detection antibodies in the all-in-one kit format.
Quality controls are not included in chemokine Express kits.
Other Components and Accessories
Bio-Plex software, wash buffer, Bio-Plex Pro flat bottom plates, and
streptavidin-PE are also available individually. For more information, go to
www.bio-rad.com/bio-plex.
39
Page 42

Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.
Life Science
Group
Web site ww w.bio-rad.com USA 800 424 6723 Australia 61 2 9914 2800
Austria 01 877 89 01 Belgium 09 385 55 11 Brazi l 55 11 5044 5699
Canada 905 364 3435 China 86 21 6169 8500
Czech R epubli c 420 241 430 532 Den mark 44 52 10 00
Finland 09 804 22 00 France 01 47 95 69 65 Ger many 089 31 88 4 0
Greece 30 210 9532 220 Hon g Kong 852 2789 33 00
Hungary 36 1 459 6100 India 91 124 4029300 Israel 03 963 6050
Italy 39 02 216091 Japan 03 6361 7000 Korea 82 2 3473 4460
Mexico 52 5 55 488 7670 The Netherlands 0318 540666
New Zealand 64 9 415 2280 No rway 23 38 41 30
Poland 48 22 331 99 99 Portugal 351 21 472 7700
Russia 7 495 721 14 04 Singapore 65 6415 3188
South Africa 27 861 246 723 Spain 3 4 91 590 5200
Sweden 08 555 1270 0 Switzerland 026 674 55 05
Taiwan 886 2 2578 7189 Thailand 800 88 22 88
United Kingdom 020 8328 200 0
Sig 121210031990 Rev A
 Loading...
Loading...