Page 1
K
Service Source
Power Macintosh 8200 and
8500 Series/WS 8550
Power Macintosh 8200 Series (Europe Only), 8500
Series, and WS 8550 Series
Page 2
K
Service Source
Basics
Power Macintosh 8200 and 8500
Series/WS 8550 Series
Page 3

Basics Overview - 1
Overview
This manual covers the Power Macintosh 8200 Series
(available only in Europe), the Power Macintosh 8500
Series, and the WorkGroup Server 8550 Series computers.
These computers all share the same form factor as the
earlier Power Macintosh 8100.
Power Macintosh 8200 Series
The Power Macintosh 8200 Series computers are available
only in Europe. There are two versions of the Power
Macintosh 8200, the Power Macintosh 8200/100 and the
8200/120. Features of the Power Macintosh 8200 Series
include
• A 100 or 120 MHz PowerPC™ 601 microprocessor on
the logic board with built-in FPU and 32K on-chip cache
Page 4

Basics Overview - 2
• 256K level 2 cache
• 16 MB of DRAM, expandable to 256 MB
• Three PCI expansion slots
• SCSI DMA bus that supports up to four external and
three internal SCSI devices
• Built-in AAUI and 10BASE-T Ethernet support
• Support for AppleTalk and TCP/IP networking protocols
• Two GeoPort serial ports
• AppleCD™ 600i 4x CD-ROM drive
• 16-bit stereo sound input/output
• 1 MB of soldered VRAM
• Mac™ OS system software 7.5.3
Page 5

Basics Overview - 3
Power Macintosh 8500/WS 8550
The Power Macintosh 8500 and Workgroup Server 8550
feature three PCI expansion slots, a removable 604
microprocessor card, and, in addition, the Power Macintosh
8500 features video in and out functionality standard.
The list of features for the Power Macintosh 8500 includes
• A 120, 132, 150, or 180 MHz PowerPC™ 604
microprocessor card with built-in FPU and 32K onchip cache
• Three PCI expansion slots
• One Digital Audio Video (DAV) slot
• 10 MB per second internal SCSI channel, 5 MB per
second external SCSI channel
• 256 K Level 2 cache
• DRAM expansion up to 512 MB using 168-pin, 70 ns,
64-bit DIMMs
Page 6

Basics Overview - 4
• 2 MB of VRAM, expandable to 4 MB
• 24-bit composite and S-video input and output
• Built-in AAUI and 10BASE-T Ethernet
• Two GeoPort serial ports
• AppleCD™ 600i 4x CD-ROM drive or 1200i 8x CD-ROM
drive (8500/150 8x CD and 8500/180)
• 1.4 MB floppy drive
• CD-quality stereo sound in/out
• Mac™ OS system software 7.5.2 (8500/120) or 7.5.3
(8500/132 and 8500/150) or 7.5.3 Revision 2
(8500/150 8x-CD and 8500/180)
The list of features for the Workgroup Server 8550 Series
computers includes
• A 132 MHz or 200 MHz PowerPC™ 604 microprocessor
card with built-in FPU and 32K on-chip cache
• 512K Level 2 cache
Page 7

Basics Overview - 5
• 24 MB of DRAM, expandable to 512 MB using 168-pin,
70 ns, 64-bit DIMMs
• Two SCSI DMA buses supporting up to eight SCSI devices
and transfers up to 10 MB/s (internal bus only)
• Three PCI expansion slots
• Built-in AAUI and 10BASE-T Ethernet
• Two GeoPort serial ports
• AppleCD™ 600i or 1200i CD-ROM drive
• 2 GB hard drive, with bracket and cable for a second
drive (support for array drives)
• DDS-2 DAT drive (optional)
• 1.4 MB floppy drive
• CD-quality stereo sound in/out
• Built-in 2 MB VRAM display support
• Support for TCP/IP networking software with Apple
Open Transport
• Mac™ OS system software 7.5.3 (8550/132) or 7.5.3
Revision 2 (8550/200)
Page 8

Basics Configurations - 6
Configurations
The Power Macintosh 8500/120 comes standard with
• 120 MHz PowerPC 604 microprocessor card
• 16 MB of DRAM
• 256K Level 2 cache DIMM
• 1 GB or 2 GB hard drive
• AppleCD 600i CD-ROM drive
• 2 MB of VRAM
The Power Macintosh 8500/132, 8500/150, and
8500/180 come standard with
• 132, 150, or 180 MHz PowerPC 604 microprocessor
card
• 16 MB of DRAM (8500/132) and 16 or 32 MB of DRAM
(8500/150 and 8500/180)
• 256K Level 2 cache DIMM
Page 9

Basics Configurations - 7
• 1.2 GB or 2 GB hard drive
• AppleCD 600i 4x CD-ROM drive (8500/120, 8500/
132, and 8500/150) or 1200i 8x CD-ROM drive
(8500/150 8x-CD and 8500/180)
• 2 MB of VRAM
The WS 8550/132 and 8550/200 come standard with
• 132 MHz (8550/132) or 200 MHz (8550/200)
PowerPC 604 microprocessor card
• 24 MB of DRAM
• 512K Level 2 cache DIMM
• 2 GB hard drive
• AppleCD 600i (8550/132) or 1200i (8550/200)
CD-ROM drive
• 2 MB of VRAM
Page 10

Basics PowerPC 601 Microprocessor - 8
PowerPC 601 Microprocessor
The Power Macintosh 8200 Series computers feature the
PowerPC 601 RISC microprocessor built onto the logic
board. Features of this microprocessor include
• Full RISC processor architecture
• 32-bit addressing
• 64-bit data bus
• Built-in FPU
• 32K cache for data and instructions
• Internal Memory Management Unit (MMU)
• Advanced branching techniques for improved throughput
Page 11

Basics PowerPC 604 Microprocessor - 9
PowerPC 604 Microprocessor
The Power Macintosh 8500 and WS 8550 computers feature
the PowerPC 604 RISC microprocessor. The PowerPC 604
microprocessor is installed via a card that plugs into the
logic board, allowing for maximum flexibility with future
upgrades.
Features of this microprocessor include
• Full RISC processing architecture
• Parallel processing units: one load-store unit, two
integer units, one complex integer unit, and one floating
point unit
• Separate built-in caches for data and instructions, 16
KB each, four-way set associative
• Advanced branching techniques for improved throughput
Page 12

Basics Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) - 10
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
The Power Macintosh 8200 Series, Power Macintosh 8500
Series, and WS 8550 computers offer a Peripheral
Component Interconnect (PCI) expansion bus. Because the
PCI bus is an industry standard, most existing PCI 2.0compliant cards (with the addition of a Mac OS-specific
software driver) will work in these computers.
PCI offers significantly higher performance than the NuBus
architecture used in previous Macintosh models. Running at
33 MHz, the PCI bus is up to three times faster than NuBus,
offering overall enhanced system performance, particularly
in the areas of video and networking.
Page 13

Basics Dual In-Line Memory Modules (DIMMs) - 11
Dual In-Line Memory Modules (DIMMs)
The Power Macintosh 8200 Series, Power Macintosh 8500
Series, and WS 8550 computers use DRAM Dual In-Line
Memory Modules (DIMMs) instead of DRAM SIMMs.
Whereas SIMMs have 72 pins, DIMMs have 168 pins. The
extra pins provide a 64-bit data path, compared to a 32-bit
data path for SIMMs. In addition, DIMMs do not have to be
installed in pairs like the SIMMs on earlier Macintosh
models. (However, to take advantage of memory
interleaving, the DIMMs should be installed in paired slots.
See "Memory Configurations" in Basics for more
information.)
Important:
used in previous Macintosh models are
these computers.
The Single In-Line Memory Modules (SIMMs)
not
compatible with
Page 14

Basics Memory Configurations - 12
Important
pin 70 ns or faster) instead of VRAM SIMMs. The VRAM
SIMMs used in earlier Power Macintosh models are
compatible.
: These computers also use VRAM DIMMs (112-
not
Memory Configurations
Following is the memory configuration information for the
computers covered in this manual.
Power Macintosh 8200 Series
The Power Macintosh 8200 Series logic boards have four
DRAM DIMM slots, each with a 64-bit data bus. You can
increase the computer’s DRAM to a total of 256 MB using 5volt, 64-bit-wide, 168-pin fast-paged mode, 70 ns
DIMMs.
Page 15
Basics Memory Configurations - 13
Note:
These computers do not have any main memory
soldered to the logic board. At least one DRAM DIMM must be
present for the computer to operate.
DRAM DIMMs can be installed individually or in pairs. These
computers support linear memory only; therefore, no
memory gains are seen when two DIMMs of the same size are
installed (that is, memory interleaving is not supported on
the Power Macintosh 8200 Series computers).
Note: DIMMs purchased from different manufacturers can
be paired; However, Apple recommends that you use DIMMs
of the same size and speed.
The drawing on the next page illustrates where the DRAM
slots are located on the Power Macintosh 8200 Series logic
boards and how they are numbered. DRAM can be installed in
any order.
Page 16
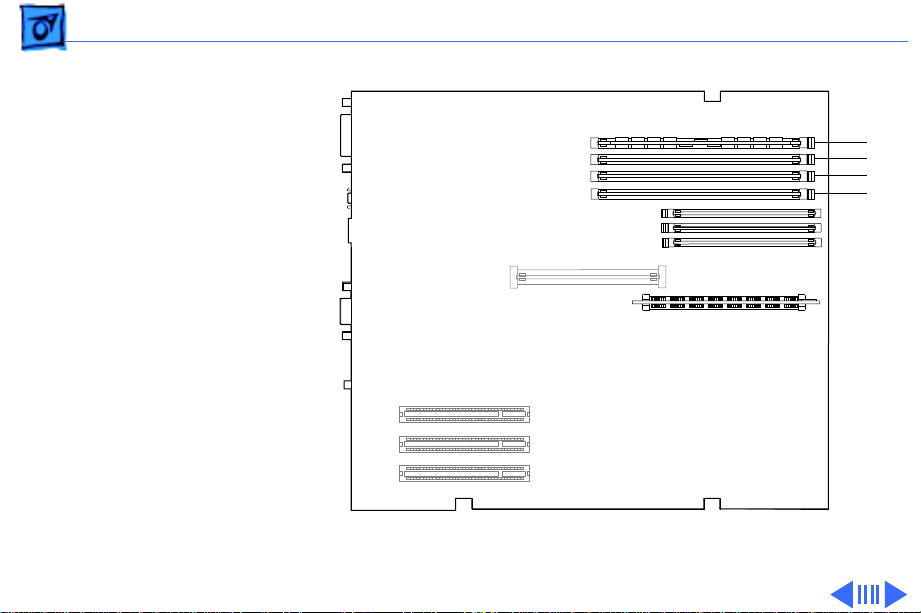
Basics Memory Configurations - 14
4
3
2
1
Figure: PM 8200 Series DRAM DIMM Slots
Page 17

Basics Memory Configurations - 15
Power Macintosh 8500 Series/WS 8550
The Power Macintosh 8500 and WS 8550 logic boards have
eight DRAM DIMM slots, each with a 64-bit data bus. You
can increase the DRAM to a total of 512 MB using 5-volt,
64-bit-wide, 168-pin fast-paged mode, 70 ns DIMMs.
Note:
These computers do not have any main memory
soldered to the logic board. At least one RAM DIMM must be
present for the computers to operate. DRAM DIMMs can be
installed individually; however, if you wish to take
advantage of the computer’s interleaving* capability, which
provides maximum performance, you must install the
DIMMs in matching pairs and in paired slots (A4 and B4, A3
and B3, and so on).
* Memory interleaving allows the computer to read or write
to its memory while other memory reads or writes are
occurring, thus providing for faster performance.
Page 18

Basics Memory Configurations - 16
For a pair of DIMMs to function as a single 128-bit wide
pair, they must be the same type and size.
Note:
DIMMs purchased from different manufacturers can
be paired as long as they are the same size and speed.
The drawing on the next page illustrates where the DRAM
slots are located on the Power Macintosh 8500 and WS
8500 logic boards and how they are numbered.
Page 19
Basics Memory Configurations - 17
B4 slot
B3 slot
B2 slot
B1 slot
A4 slot
A3 slot
A2 slot
A1 slot
(front of computer)
Figure: PM 8500 and WS 8550 DRAM DIMM Slots
Page 20

Basics Ethernet Support - 18
Ethernet Support
There are two Ethernet ports on the Power Macintosh 8200,
Power Macintosh 8500, and WS 8550 logic boards: an AAUI
port and a 10BASE-T port. You can use only one Ethernet
port at one time, however. If you have cables plugged into
both Ethernet ports, the computer uses the 10BASE-T port
by default.
AV Support
The Power Macintosh 8500 comes standard with an AV
module that provides support for: composite video input and
output, S-video input and output, audio input (left and
right), and audio output (left and right).
Page 21

Basics GeoPort - 19
GeoPort
Geoport is a hardware and software communications
architecture that has been optimized for computertelephony integration. It has three main attributes:
• It lets any computer connect to any telephone (analog or
digital, public or private) anywhere in the world.
• Once connected, it supports an arbitrary number of
independent data streams up to a total bandwidth of
2 MB/second.
• Unlike traditional asynchronous data communications
(such as AppleTalk), GeoPort also supports isochronous
data streams (such as real-time voice and video) and
provides the real-time Application Program Interfaces
(APIs) necessary to hide the implementation details
from both the recipient and the sender.
Page 22

Basics PC Compatibility Cards - 20
By attaching an Apple GeoPort Telecom Adapter to these
computers, you can enjoy all the features of a 14.4 modem,
including data, fax, send and receive, and voice capabilities.
The GeoPort Telecom Adapter serves as a line interface to
standard (analog) telephone lines. The adapter is capable of
sending or receiving data at up to 14.4 kbps and faxes at up
to 9600 bps using the GeoPort Telecom Adapter software.
PC Compatibility Cards
Apple computer offers two PC Compatibility Card upgrade
kits that bring full DOS functionality to the Macintosh
computer. Two versions of the PC Compatibility card are
available: a 7" card and a 12" card. The cards plug into any
available PCI slot on the logic board. Refer to the Upgrades
chapter in this manual for installation instructions.
Page 23

Basics The Cuda Chip - 21
The Cuda Chip
The Cuda is a microcontroller chip. Its function is to
• Turn system power on and off
• Manage system resets from various commands
• Maintain parameter RAM (PRAM)
• Manage the Apple Desktop Bus (ADB)
• Manage the real-time clock
Many system problems can be resolved by resetting the Cuda
chip (see Symptom Charts for examples). Press the Cuda
reset button on the logic board to reset the Cuda chip. (See
"Logic Board Diagram" later in this chapter to locate the
Cuda reset button.) If you continue to experience system
problems, refer to "Resetting the Logic Board" later in this
Basics chapter.
Page 24

Basics Resetting the Logic Board - 22
Resetting the Logic Board
Resetting the logic board can resolve many system problems
(refer to "Symptom Charts" for examples). Whenever you
have a unit that fails to power up, you should follow this
procedure before replacing any modules.
1 Unplug the computer.
2 Remove the logic board. (Refer to the Take Apart chapter
for instructions on how to remove the logic board.)
3 Using a small flat-blade screwdriver, pry open the latch
at the end of the battery holder and lift off the battery
holder cover.
4 Remove the battery from its holder.
Page 25

Basics Resetting the Logic Board - 23
5 Verify the power supply cable is disconnected from the
logic board and then press the Power On button. (See
"Logic Board Diagram" later in this chapter to locate the
Power On button.)
6 Wait at least 10 minutes before replacing the battery.
Make sure the battery is installed in the correct +/direction.
7 Reassemble the computer and test the unit.
Note:
This procedure resets the computer’s PRAM. Be sure
to check the computer’s time/date and other system
parameter settings afterwards.
Note:
If this procedure resolves the problem, claim an
adjustment on an SRO. If not, replace the defective
component and DO NOT claim the adjustment procedure.
Page 26

Basics Fast SCSI - 24
Fast SCSI
The Power Macintosh 8500 and WS 8550 computers offer
Fast SCSI support on the internal SCSI connector, which
provides for significantly enhanced data throughput. The
internal SCSI bus on these computers supports transfer
rates up to 10 MB/sec.
Page 27

Basics Rear View Diagram - 25
Rear View Diagram
The Power Macintosh 8200 and WS 8550 computers offer
the following external ports: SCSI, AAUI and 10BASE-T
Ethernet, serial printer (GeoPort compatible), serial
modem (GeoPort compatible), DB-15 video, ADB, sound
input, and sound output.
The drawing on the following page illustrates the back panel
of the Power Macintosh 8200 and WS 8550 computers.
Page 28
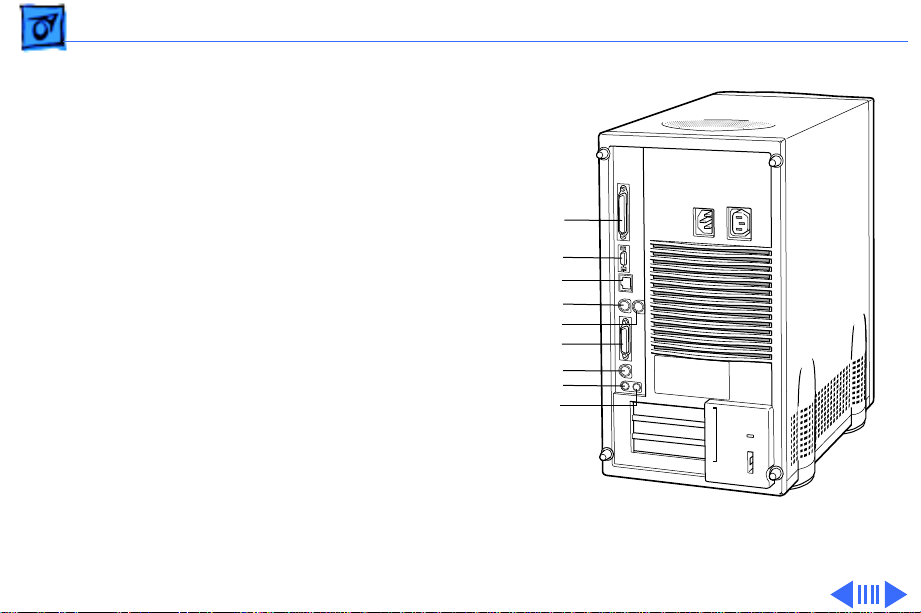
Basics Rear View Diagram - 26
SCSI
AAUI Ethernet
10 BASE-T Ethernet
Printer
Modem
Monitor
ADB
Sound in
Sound out
Figure: Power Macintosh 8200 and WS 8550 Rear Panel
Page 29

Basics Rear View Diagram - 27
In addition to the ports shown on the previous page, the
Power Macintosh 8500 offers composite video input and
output, S-video input and output, audio input (left and
right), and audio output (left and right) ports.
The drawing on the following page illustrates the back panel
of the Power Macintosh 8500 computer.
Page 30
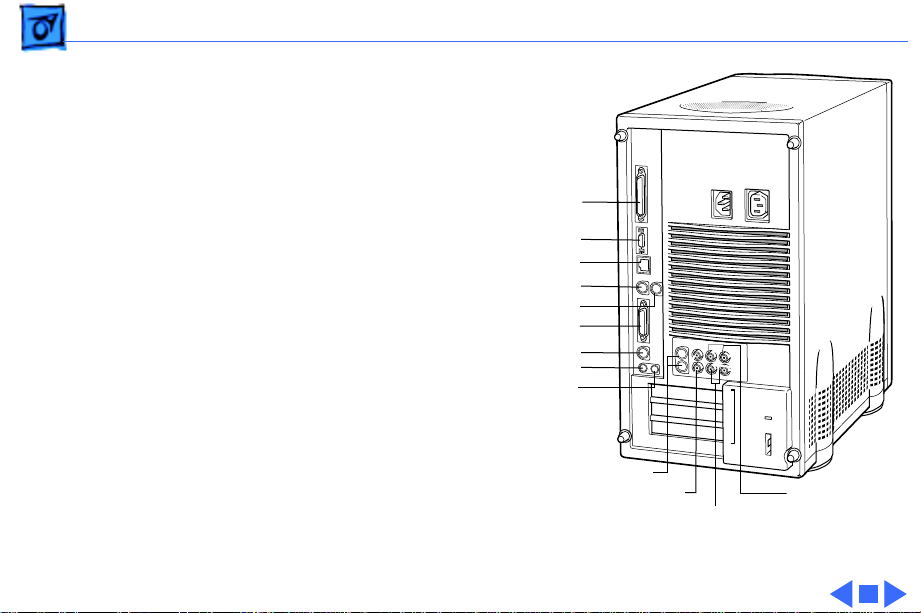
Basics Rear View Diagram - 28
SCSI
AAUI Ethernet
10 BASE-T Ethernet
Printer
Modem
Monitor
ADB
Sound in
Sound out
S-video
Composite video
Audio output
(left &right)
Audio input
(left & right)
Figure: Power Macintosh 8500 Rear Panel
Page 31

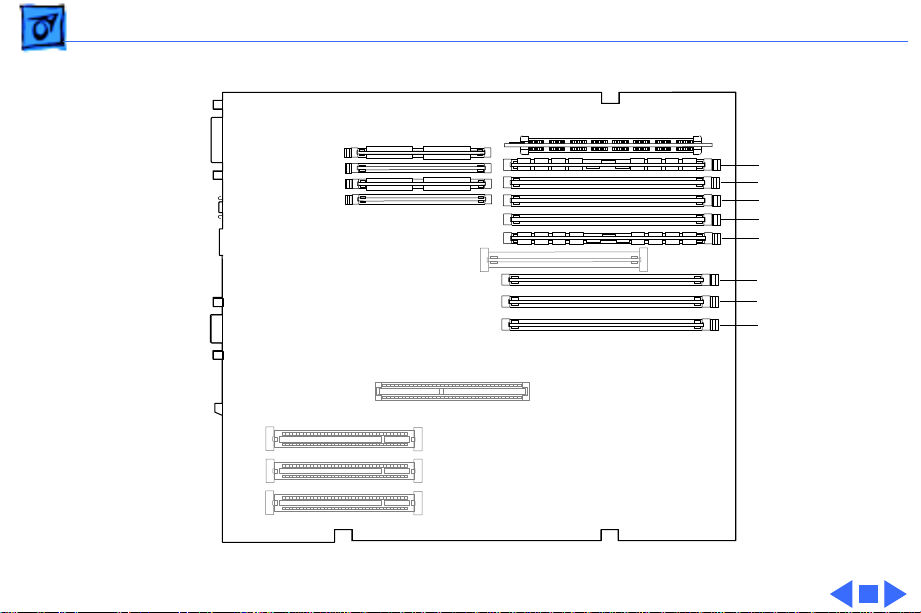
Basics Logic Board Diagram - 29
Logic Board Diagram
The following graphics illustrate the connectors on the
Power Macintosh 8500, WS 8550, and Power Macintosh
8200 logic boards.
Note:
Some versions of the logic board have a ROM SIMM
while other versions have the ROM soldered on the logic
board.
Page 32

Basics Logic Board Diagram - 30
External SCSI
VRAM Slots
AAUI Ethernet
10BASE-T
Ethernet
Modem (top)/
Printer (bottom)
Video
ADB
Cuda Reset
Sound Out (top)/
Sound In (bottom)
PCI Slots
Internal
SCSI
Power
Supply
AV Module
Speaker
Processor
Card Slot
CD
Audio
DAV
Floppy
Drive
Figure: Power Macintosh 8500 Logic Board
3.3V Power
Supply
ROM
SIMM
DRAM
Slots
Cache
DIMM
DRAM
Slots
Battery
Power
LED
Power
On/Off
Page 33

Basics Logic Board Diagram - 31
External SCSI
VRAM Slots
AAUI Ethernet
10BASE-T
Ethernet
Modem (top)/
Printer (bottom)
Video
ADB
Cuda Reset
Sound Out (top)/
Sound In (bottom)
PCI Slots
Figure: Workgroup Server 8550 Logic Board
Internal
SCSI
Power
Supply
Speaker
Processor
Card Slot
CD
Audio
DAV
Floppy
Drive
3.3V Power
Supply
ROM
SIMM
DRAM
Slots
Cache
DIMM
DRAM
Slots
Battery
Power
LED
Power
On/Off
Page 34

Basics Logic Board Diagram - 32
External SCSI
AAUI Ethernet
10BASE-T
Ethernet
Modem (bottom)
Printer (top)
Video
ADB
Sound Out (top)
Sound In (bottom)
PCI Slots
Cuda Reset
Figure: Power Macintosh 8200 Logic Board
Internal
SCSI
Power
Supply
CD
Audio
Floppy
Drive
3.3V Power
Supply
4
3
2
1
3
2
1
PowerPC 601 Processor Speaker
Battery
DRAM Slots
VRAM Slots
Cache DIMM
ROM SIMM
Power LED
Power
On/Off
Page 35

Basics Repair Strategy - 33
Repair Strategy
Service the Power Macintosh 8500 and WS 8550 computers
through module exchange and parts replacement. Customers
can request on-site service from an Apple Authorized
Service Provider Plus (AASP+) or Apple Assurance. They
can also choose carry-in service from an AASP.
Ordering
Apple Service Providers planning to support the Power
Macintosh 8500 and WS 8550 computers may purchase
Service modules and parts to develop servicing capability.
To order parts, use the AppleOrder system and refer to the
Power Macintosh 8500 or Workgroup Server 8550
"Service Price Pages."
Page 36

Basics Ordering - 34
Large businesses, universities, and K-12 accounts must
provide a purchase order on all transactions, including
orders placed through the AppleOrder system. Service
providers not enrolled in AppleOrder may fax their orders
to Service Provider Support (512-908-8125) or mail
them to
Apple Computer, Inc.
Service Provider Support
MS 212-SPS
Austin, TX 78714-9125
If you have further questions, please call Service Provider
Support at 800-919-2775 and select option #1.
Page 37

Basics Warranty and AppleCare - 35
Warranty and AppleCare
The Power Macintosh 8500 and WS 8550 computers are
covered under the Apple One-Year Limited Warranty. The
AppleCare Service Plan is also available for these products.
Service Providers are reimbursed for warranty and
AppleCare repairs made to these computers. For pricing
information, refer to "Service Price Pages."
Page 38

K
Service Source
Specifications
Power Macintosh 8200 and 8500
Series/WS 8550 Series
Page 39

Specifications Processor - 1
Processor
CPU
PM 8200
PM 8500
PowerPC 601 RISC microprocessor running at 100 or 120 MHz
Built-in FPU and 32K cache
Requires system software version 7.5.3 or later with appropriate
System Enabler
PowerPC 604 RISC microprocessor running at 120, 132, 150 or
180 MHz
Built-in FPU and 32K cache
Requires system software version 7.5.2 or later (8500/120),
7.5.3 or later (8500/132 and 8500/150) with appropriate
System Enabler, and 7.5.3 Revision 2 (8500/150 8x-CD and
8500/180)
Page 40

Specifications Processor - 2
WS 8550
PowerPC 604 RISC microprocessor running at 132 or 200 MHz
Built-in FPU and 32K cache
Requires system software version 7.5.3 or later with appropriate
System Enabler (8550/132) or 7.5.3 Revision 2 or later
(8550/200)
Page 41

Specifications Memory - 3
Memory
DRAM
PM 8200/100 and 8200/120
PM 8500/120 and 8500/132
PM 8500/150 and
8500/180
WS 8550
8 MB or 16 MB standard; expandable to 256 MB
Uses 168-pin, 64-bit, 70 ns or faster DRAM DIMMs
16 MB standard; expandable to 512 MB
Uses 168-pin, 64-bit, 70 ns or faster DRAM DIMMs
16 or 32 MB standard; expandable to 512 MB
Uses 168-pin, 64-bit, 70 ns or faster DRAM DIMMs
24 MB standard; expandable to 512 MB
Uses 168-pin, 64-bit, 70 ns or faster DRAM DIMMs
Page 42

Specifications Memory - 4
ROM
Cache
PM 8200
PM 8500
WS 8550
Clock/Calendar
4 MB ROM (may be installed in ROM SIMM slot, or soldered on the
logic board)
256K Level 2 cache DIMM
256K Level 2 cache
512K Level 2 cache
CMOS custom circuitry with long-life battery
Page 43

Specifications I/O Interfaces - 5
I/O Interfaces
SCSI
PM 8500 and
WS 8550
Serial
ADB
Ethernet
Dual-channel asynchronous SCSI interface; external channel
supports up to seven SCSI devices
Internal channel supports a hard disk array
Two RS-232/RS-422 serial ports compatible with LocalTalk and
GeoPort cables; mini DIN-8 connectors
One Apple Desktop Bus port for a keyboard, mouse, etc.
One AAUI and one 10BASE-T Ethernet port (if cables are plugged
into both ports, system defaults to 10BASE-T)
Page 44

Specifications I/O Interfaces - 6
Expansion
Sound
Video
PM 8500
Three PCI expansion slots, compatible with all PCI 2.0
specification-compliant cards with the addition of Mac OS-
specific software driver (not NuBus compatible)
16-bit stereo sound input and output ports
Built-in DB-15 video connector on logic board
24-bit video input and output connectors on AV module
Page 45

Specifications I/O Devices - 7
I/O Devices
Keyboard
Mouse
Microphone
Standard, extended, or adjustable keyboard; keyboard draws
25-80 mA, depending on model type
ADB Mouse II; mouse draws up to 10 mA
Apple PlainTalk microphone standard
Page 46

Specifications Video Support - 8
Video Support
Table 1: PM8500 and WS 8550 Video Support
PIXEL DEPTHS
MONITOR DISPLAY SIZE 2 MB VRAM 4 MB VRAM
512 by 384 8, 16, 32 8, 16, 32
640 by 480 8, 16, 32 8, 16, 32
768 by 576 8, 16, 32 8, 16, 32
800 by 600 8, 16, 32 8, 16, 32
832 by 624 8, 16, 32 8, 16, 32
1024 by 768 8, 16 8, 16, 32
1152 by 870 8, 16 8, 16
Page 47

Specifications Video Support - 9
Table 1: PM8500 and WS 8550 Video Support
PIXEL DEPTHS
MONITOR DISPLAY SIZE 2 MB VRAM 4 MB VRAM
1280 by 960 8 8, 16
1280 by 1024 8 8, 16
Page 48

Specifications Disk Storage - 10
Disk Storage
Hard Drive
PM 8500
WS 8550
Floppy Drive
CD-ROM Drive
1, 1.2, or 2 GB fast internal SCSI hard drive
2 GB fast internal SCSI hard drive
Supports drive array with dual hard drive bracket
One Apple SuperDrive 1.4 MB floppy drive
One internal AppleCD 600i 4x CD-ROM drive or
1200i 8x CD-ROM drive
Page 49

Specifications Electrical - 11
Electrical
Line V oltage
Frequency
Maximum Power
100—240 VAC, RMS single phase, automatically configured
50—60 Hz, single phase
DC Power: 225 W, not including monitor
AC Power: 340 W maximum continuous; 520 W peak input
Page 50

Specifications Physical - 12
Physical
Dimensions
Weight
Height: 14 in. (35.6 cm)
Width: 7.7 in. (19.6 cm)
Depth: 15.75 in. (40.0 cm)
25 lb. (11.3 kg); weight varies depending on devices installed
Page 51

Specifications Environmental - 13
Environmental
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Relative Humidity
Maximum Altitude
50 to 104° F (10 to 40° C)
—40 to 116° F (—40 to 47° C)
5% to 95% noncondensing
10,000 ft. (3,048 m)
Page 52

K
Service Source
Troubleshooting
Power Macintosh 8200 and 8500
Series/WS 8550 Series
Page 53

Troubleshooting General - 1
General
The Symptom Charts included in this chapter will help you
diagnose specific symptoms related to your product. Because cures
are listed on the charts in the order of most likely solution, try
the first cure first. Verify whether or not the product continues to
exhibit the symptom. If the symptom persists, try the next cure.
(Note: If you have replaced a module, reinstall the original module
before you proceed to the next cure.)
If you are not sure what the problem is, or if the Symptom Charts
do not resolve the problem, refer to the Flowchart for the product
family.
For additional assistance, contact Apple Technical Support.
Page 54

Troubleshooting Cleaning Procedure for Card Connectors - 2
Cleaning Procedure for Card Connectors
It is possible for residue to build up on the gold edge connector
pins on some PCI cards, which could cause a variety of symptoms.
If you are having problems with a PCI card, inspect the connector
pins with a magnifying glass. If you find residue, use a pencil
eraser to gently clean the pins.
Page 55

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Power Supply - 3
Symptom Charts
Power Supply
System doesn’t power up1 Reseat processor card and ROM SIMM (if present).
2 Reset Cuda chip. (Refer to The Cuda Chip in Basics for
instructions.)
3 Reset logic board. (Refer to Resetting the Logic Board in
Basics for instructions.)
4 Replace power supply.
5 Replace processor card.
6 Replace logic board.
Page 56

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Error Chords - 4
Error Chords
One-part error
chord sounds during
startup sequence
1 Disconnect SCSI data cable from hard drive and reboot
system. If startup sequence is normal, initialize hard drive.
Test unit again with SCSI data cable connected. If error chord
still sounds, replace hard drive.
2 Disconnect floppy drive cable from floppy drive and reboot
system. If startup sequence is normal, replace floppy drive.
3 Reseat processor card.
4 Replace processor card.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
Page 57

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Error Chords
(Continued)
- 5
Eight-part error
chord (death chimes)
sounds during
startup sequence
Error Chords
1 Replace DRAM DIMMs one at a time to test DRAM. Replace
any faulty DIMMs.
2 Replace logic board.
(Continued)
Page 58

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/System - 6
System
Does not power on,
screen is black, fan is
not running and LED
is not lit
1 Check power cables.
2 Plug monitor directly into wall socket, and verify that
monitor has power.
3 Reseat ROM SIMM (if present) and processor card. The logic
board must have a processor card installed to operate.
4 Reset Cuda chip. (Refer to The Cuda Chip in Basics for
instructions.)
5 Reset logic board. (Refer to Resetting the Logic Board in
Basics for instructions.)
6 Replace power cord.
7 Replace power supply.
8 Replace processor card.
9 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
Page 59

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/System
(Continued)
- 7
Clicking, chirping,
or thumping
System
1 Remove all PCI cards and test the unit. If problem does not
2 Remove hard drive. If problem no longer occurs, replace
3 Replace power supply.
4 Replace processor card.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
6 Replace floppy drive cable.
7 Replace floppy drive.
(Continued)
occur with cards removed, begin replacing them one at a
time to determine which card is causing the problem.
Replace problem card with known-good card.
hard drive with a known-good drive.
Page 60

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/System
(Continued)
- 8
System shuts down
intermittently
System
1 Make sure air vents are clear. Thermal protection
2 Make sure power cord is firmly plugged in.
3 Replace power cord.
4 Check battery.
5 Reset Cuda chip. (Refer to The Cuda Chip in Basics for
6 Reset logic board. (Refer to Resetting the Logic Board in
7 Replace power supply.
8 Replace processor card.
9 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
(Continued)
circuitry may shut down system. After 30 to 40 minutes,
system should be OK.
instructions.)
Basics for instructions.)
Page 61

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/System
(Continued)
- 9
System
intermittently
crashes or hangs
System
1 Verify system software is version 7.5.2 or later (PM8500/
2 Verify DIMMs are noncomposite.
3 Verify software is known-good. Do a clean install of the
4 Verify software is Power Macintosh 8500 compatible
5 Clear parameter RAM. Hold down <Command> <Option> <P>
6 Remove all DRAM DIMMs and try replacing them one at a
7 Replace processor card.
8 Replace logic board. Retain DIMMs.
(Continued)
120) or 7.5.3 or later (PM 8500/132, PM 8500/150,
and WS 8550).
system software.
(contact developer). Also, try booting with extensions off to
determine if there are system init problems.
<R> during startup but before "Welcome to Macintosh"
appears.
time to test. Replace any bad DIMMs.
Page 62

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/System
(Continued)
- 10
During startup,
following message is
displayed, "This
startup disk will not
work on this
Macintosh model...."
PM 8200 can’t be
powered off unless
external 1.2 GB hard
drive is off
remains lit when
system is powered off
and attached 1.2 GB
hard drive is left
powered on
or
LED
System
1 Verify that startup disk is good.
2 Verify system software is version 7.5.2 or later (PM8500/
3 Do a clean install of the system software.
This problem only affects PM 8200 machines with serial
numbers in the following ranges:
(Continued)
120) or 7.5.3 or later (PM 8500/132, PM 8500/150,
and WS 8550).
• CK634xxxxxx to CK637xxxxxx
• XB634xxxxxx to XB637xxxxxx
• SG634xxxxxx to SG637xxxxxx
• FC634xxxxxxx to FC637xxxxxx
•
If system falls into one of these serial number ranges, execute
the following instructions:
Page 63

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/System
1) Unplug system and remove top cover.
2) Disconnect hard drive SCSI cable and power cable.
3) Remove hard drive from chassis.
4) Turn drive over and examine part number label on 50-pin
SCSI connector (removing drive carrier if necessary). If
label reads “1280S p/n TM12S012”
replace drive.
Note
: Only Revision “02” drives cause this problem; therefore, make sure bar code label includes the words “REV 02B” before replacing hard drive.
and
“REV 02-B”,
(Continued)
- 11
Page 64

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Video - 12
Video
Screen is black, boot
tone is present, drive
operates, fan is
running, and LED is
lit
1 Adjust brightness on monitor.
2 Clear parameter RAM. Hold down <Command> <Option> <P>
<R> during startup but before "Welcome to Macintosh"
appears.
3 Reset Cuda chip. (Refer to The Cuda Chip in Basics.)
4 Reset logic board. (Refer to Resetting the Logic Board in
Basics.)
5 Replace monitor cable.
6 Remove all DRAM DIMMs and try replacing them one at a
time to test. Replace any bad DIMMs.
7 Test with known-good monitor. Replace monitor if
necessary. Refer to appropriate monitor manual to
troubleshoot defective monitor.
8 Replace processor card.
9 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
Page 65

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Video
(Continued)
- 13
Screen is black, no
boot tone and drive
does not operate, but
fan is running and
LED is lit
Video
1 Reset Cuda chip. (Refer to The Cuda Chip in Basics for
2 Reset logic board. (Refer to Resetting the Logic Board in
3 Remove all DRAM DIMMs and try replacing them one at a
4 Replace processor card.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
6 Replace power supply.
(Continued)
instructions.)
Basics for instructions.)
time to test. Replace any bad DIMMs.
Page 66

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Video
(Continued)
- 14
Boot tone is present
and screen lights up,
but nothing is
displayed on screen
Video
1 Reset Cuda chip. (Refer to The Cuda Chip in Basics for
2 Reset logic board. (Refer to Resetting the Logic Board in
3 Replace monitor cable.
4 Test with known-good monitor. Replace monitor if
5 Replace processor card.
6 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
(Continued)
instructions.)
Basics for instructions.)
necessary. Refer to appropriate monitor manual to
troubleshoot defective monitor.
Page 67

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Video
(Continued)
- 15
Video display
distorted on Power
Macintosh 8500 with
DAV card installed
Video
Symptom occurs when an add-in card attached to the DAV
connector requires a mode configuration under which the add-in
card controls most of the signal lines (Mode 2). Verify that the
logic board installed supports DAV cards; if not, replace the logic
board.
If the logic board in question meets
then it DOES support DAV cards and you need not replace the board:
(Continued)
either
of the following criteria,
• Part number 820-0752 is silk-screened on the logic
board.
• The Logic board has the wiring scenario shown on the next
page.
Page 68

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Video
NOTE: The dotted
line indicates that
the jumper wire is
running underneath
the logic board.
(Continued)
- 16
Jumper Wire
PCB Part Number
Power Macintosh 8500 Logic Board with DAV Fix
U18
820-0564-XX
Page 69

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Floppy Drive - 17
Floppy Drive
Internal floppy drive
does not operate
During system
startup, disk ejects;
display shows icon
with blinking "X"
1 Replace floppy disk with known-good disk.
2 Replace floppy drive cable.
3 Replace floppy drive.
4 Replace processor card.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
1 Replace disk with known-good system disk.
2 Replace floppy drive cable.
3 Replace floppy drive.
4 Replace processor card.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
Page 70

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Floppy Drive
(Continued)
- 18
Floppy Drive
Does not eject disk 1 Switch off computer. Hold mouse button down while you
switch computer on.
2 Replace floppy drive cable.
3 Replace floppy drive.
4 Replace processor card.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
Attempts to eject
disk, but doesn’t
1 Reseat floppy drive bezel and drive so bezel slot aligns
correctly with drive.
2 Replace floppy drive.
(Continued)
Page 71

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Floppy Drive
(Continued)
- 19
Internal floppy drive
runs continuously
MS-DOS drive does
not recognize a disk
formatted on a 1.4 MB
drive
Floppy Drive
1 Replace disk with known-good floppy disk.
2 Replace floppy drive cable.
3 Replace floppy drive.
4 Replace processor card.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
To read and write files with either MS-DOS or 1.4 MB drive,
format all disks with MS-DOS drive first.
(Continued)
Page 72

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Hard Drive - 20
Hard Drive
Single internal hard
drive does not
operate; drive
doesn’t spin
No internal SCSI
drives operate
1 Replace hard drive power cable.
2 Replace hard drive. If problem resolved, reinstall SCSI
device driver and system software.
3 Replace power supply.
1 Verify there are no duplicate SCSI device addresses.
2 Disconnect external SCSI devices and check for proper
termination. Only last device in SCSI chain should be
terminated.
3 Replace SCSI data cable.
4 Replace power supply.
5 Replace processor card.
6 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
Page 73

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Hard Drive
(Continued)
- 21
Drive does not appear
on the desktop
Hard Drive
1 Verify there are no duplicate SCSI device addresses.
2 Update the SCSI device driver using Drive Setup. Run Disk
First Aid to verify the condition of the drive's directory
structure.
3 Replace the SCSI hard drive cable.
4 If drive is not initialized, use Drive Setup to initialize.
5 Replace with known-good hard drive.
6 If the hard drive still doesn't work, switch back to the
original hard drive and replace the logic board.
(Continued)
Page 74

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Hard Drive
(Continued)
- 22
Works with internal
or external SCSI
devices but not with
both
Hard Drive
1 Verify there are no duplicate SCSI device addresses.
2 Replace terminator on external SCSI device.
3 Verify that SCSI device at end of internal SCSI data cable is
only device terminated.
4 Refer to appropriate manual to troubleshoot defective
external device.
(Continued)
Page 75

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Peripherals - 23
Peripherals
Cursor does not move 1 Check mouse connection.
2 Inspect inside of mouse for buildup of dirt or other
contaminants. Clean mouse if necessary.
3 If mouse was connected to keyboard, connect mouse to
computer ADB port instead. If mouse works, replace
keyboard.
4 Replace ADB cable.
5 If mouse does not work in any ADB port on computer, replace
mouse.
6 Replace processor card.
7 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
Page 76

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Peripherals
(Continued)
- 24
Cursor moves, but
clicking mouse
button has no effect
Double-click doesn’t
open application,
disk, or server
Peripherals
1 Boot from floppy or bootable CD.
2 Replace mouse.
3 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
1 Remove duplicate system folders.
2 Clear parameter RAM. Hold down <Command> <Option> <P>
<R> during startup but before "Welcome to Macintosh"
appears.
3 If mouse was connected to keyboard, connect mouse to
computer ADB port instead. If mouse works, replace
keyboard.
4 If mouse does not work in any ADB port on computer, replace
mouse.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
(Continued)
Page 77

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Peripherals
(Continued)
- 25
No response to any
key on keyboard
Known-good serial
printer does not work
Peripherals
1 Check keyboard connection to ADB port.
2 Replace keyboard cable.
3 Replace keyboard.
4 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
1 Verify you have correct version of system software.
2 Verify that Chooser is set correctly.
3 Reinstall correct printer drivers.
4 Do clean install of system software.
5 Replace printer interface cable.
6 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
(Continued)
Page 78

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Peripherals
(Continued)
- 26
Known-good network
printer does not print
Peripherals
1 Check network connections.
2 Verify you have correct version of system software.
3 Verify that Chooser is set correctly.
4 Does printer show up in Chooser? If so, do clean install of
system software and/or network and printer software.
5 Replace logic board. Retain customer's DIMMs.
(Continued)
Page 79

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/CD-ROM Drive - 27
CD-ROM Drive
CD-ROM drive does
not work
Macintosh does not
display CD-ROM icon
once CD is inserted in
drive
Computer with 600i
CD-ROM drive makes
stuttering sounds
when playing CD+ or
CD-R formatted
discs or CD-ROM disc
won’t mount
1 Try using known-good compact disc.
2 Replace CD-ROM drive mechanism.
1 Verify that CD-ROM software is installed.
2 Replace CD-ROM drive mechanism.
3 Replace SCSI data cable.
Replace CD-ROM drive.
Page 80

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Miscellaneous - 28
Miscellaneous
No sound from
speaker
1 Verify that volume setting in Control Panel is 1 or above.
2 Clear parameter RAM. Hold down <Command> <Option> <P>
<R> during startup but before "Welcome to Macintosh"
appears. Verify speaker is plugged into logic board.
3 Replace speaker.
4 Replace logic board. Retain customer’s DIMMs.
Page 81

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Miscellaneous - 29
Errors occur when
initializing or erasing
floppy disks and/or
1.4 MB disks show
only 1 MB available
after initialization
This problem only occurs on systems using a 180 MHz or faster
processor card. Upgrade to system software version 7.5.4 to
resolve this problem (the Apple recommended solution) or,
alternatively, install the Power Mac Format Patch, which can be
found on the original system disks that shipped with the computer.
To install the patch:
• While holding down the Option key, drag the Power Mac
Format Patch icon onto the System Folder’s icon.
• Click OK to automatically place the patch in the Extensions
folder.
• Restart the computer by choosing Restart from the Special
menu.
Page 82

K
Service Source
T ak e Apart
Power Macintosh 8500 Series/WS
8550 Series
Page 83

Take Apart Top Housing - 1
Top Housing
Top Housing
No preliminary steps are
required before you begin
this procedure.
Note:
The top housing covers
the top, front, and left and
right sides of the computer.
IMPORTANT
the computer with the top
housing removed. Failure to
comply may result in
irreparable damage to
internal components.
: Never operate
Page 84

Take Apart Top Housing - 2
1 Loosen the four captive
cover screws on the rear
panel and slide the top
housing forward about
1
3
2
4
one inch.
Page 85

Take Apart Top Housing - 3
2 Lift the top housing
Top Housing
straight up to remove it
from the computer.
Page 86

Take Apart CD-ROM Drive - 4
CD-ROM
Drive
CD-ROM Drive
Before you begin, remove
the top housing.
Note:
The CD-ROM drive is
located in the top drive bay.
Page 87

Take Apart CD-ROM Drive - 5
CD-Rom Audio Cable
CD-Rom Drive
Power CableSCSI Data Cable
1 Disconnect the SCSI data
cable, audio cable, and
power cable from the
back of the CD-ROM
drive.
Page 88

Take Apart CD-ROM Drive - 6
Retaining ClipCD-ROM Drive
2 Pull up the retaining
clip beneath the front of
the CD-ROM drive and
slide the drive forward
to remove it from the
computer.
Note:
Be sure to remove the
CD-ROM drive from its
carrier before returning the
drive to Apple.
Page 89

Take Apart Floppy Drive - 7
Floppy
Floppy
Drive
Drive
Floppy Drive
Before you begin, remove
the following:
• Top Housing
• CD-ROM Drive
Note:
The floppy drive is
located in the second drive
bay from the top.
Page 90

Take Apart Floppy Drive - 8
Floppy Drive
Plastic Guides
Floppy Drive Cable
1 Disconnect the floppy
drive cable from the
logic board and remove
the cable from the
plastic guides.
Page 91

Take Apart Floppy Drive - 9
Floppy Drive Retaining Clip
2 Press down the retaining
clip beneath the front of
the floppy drive and
slide the floppy drive
forward about two
inches.
3 Disconnect the floppy
drive cable from the
back of the floppy drive
and remove the floppy
drive from the
computer.
Replacement Note:
Be sure
to remove the floppy drive
from its carrier before
returning the drive to Apple.
Page 92

Take Apart DAT Tape Drive-WS 8550 - 10
DAT Tape DriveWS 8550
Before you begin, remove
the top housing.
Note:
The DAT tape drive is
located in third drive bay
from the top. The tape drive
is optional on the WS 8550.
Page 93

Take Apart DAT Tape Drive-WS 8550 - 11
1 Disconnect the SCSI
cable and power cable
from the back of the tape
drive.
Page 94

Take Apart DAT Tape Drive-WS 8550 - 12
2 Remove the four screws
securing the carrier to
the tape drive. Remove
the carrier before
returning the tape drive
to Apple.
Page 95

Take Apart Hard Drive-Power Macintosh 8500 - 13
Hard Drive-Power Macintosh 8500
Before you begin, remove
the top housing.
Note:
The hard drive is
located in the bottom drive
Hard
Drive
bay.
Page 96

Take Apart Hard Drive-Power Macintosh 8500 - 14
1 Disconnect the SCSI data
cable and hard drive
power cable from the
hard drive.
Power CableSCSI Cable
Page 97

Take Apart Hard Drive-Power Macintosh 8500 - 15
2 Press down the retaining
clip beneath the front of
the hard drive and slide
the hard drive forward
to remove it from the
computer.
Note:
For information on
removing the hard drive
from its carrier and
returning drives, cables,
and carriers to Apple, refer
to Additional Procedures in
the Hard Drives manual.
Hard Drive Retaining Clip
Page 98

Take Apart Hard Drive-WS 8550 - 16
Hard Drive-WS 8550
Before you begin, remove
the top housing.
Note:
The Workgroup
Server 8550 can hold up to
two hard drives, which
install in a metal drive
bracket as opposed to the
plastic drive carrier used in
the Power Macintosh 8500.
Page 99

Take Apart Hard Drive-WS 8550 - 17
1 Press down the retaining
clip beneath the front of
the hard drive bracket
and gently slide the hard
drive bracket forward as
far as it will reach.
Page 100

Take Apart Hard Drive-WS 8550 - 18
2 Disconnect the SCSI
cable from the back of
the hard drive.
 Loading...
Loading...