Anritsu MG3696A, MG3695A, MG3694A, MG3693A, MG3692A Service Manual
...
SERIES
MG369XA
SYNTHESIZED SIGNAL GENERATORS
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
490 JARVIS DRIVE
MORGAN HILL, CA 95037-2809
P/N: 10370-10355
REVISION: D
PRINTED: FEBRUARY 2005
COPYRIGHT 2005 ANRITSU CO.
WARRANTY
The Anritsu product(s) listed on the title page is (are) warranted against defects in materials and
workmanship for three years from the date of shipment.
Anritsu's obligation covers repairing or replacing products which prove to be defective during the
warranty period. Buyers shall prepay transportation charges for equipment returned to Anritsu for
warranty repairs.Obligation is limited to the original purchaser.Anritsuis not liable for consequen
tial damages.
LIMITATION OF WARRANTY
The foregoing warranty does not apply to Anritsu connectors that have failed due to normal wear.
Also,the warranty does not apply to defects resulting from improper or inadequate maintenance by
the Buyer,unauthorized modification or misuse, or operation outside of the environmental specifications of the product. No other warranty is expressed or implied, and the remedies provided herein
are the Buyer's sole and exclusive remedies.
TRADEMARK ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Adobe Acrobat is a registered trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
MS-DOS and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
-
NOTICE
Anritsu Company has prepared this manual for use by Anritsu Company personnel and customers
as a guide for the proper installation, operation, and maintenance of Anritsu Company equipment
and computer programs. The drawings, specifications, and information contained herein are the
property of Anritsu Company, and any unauthorized use or disclosure of these drawings, specifica
tions,and information is prohibited; they shall not be reproduced, copied, or used in whole or in part
-



Safety Symbols
To prevent the risk of personal injury or loss related to equipment malfunction, ANRITSU Company uses the
following symbols to indicate safety-related information.For your own safety,please read this information
carefully BEFORE operating the equipment.
Symbols used in manuals
DANGER
Indicates a very dangerous procedure that could result in serious in
jury or death if not performed properly.
WARNING Indicates a hazardous procedure that could result in serious injury or
death if not performed properly.
CAUTION Indicates a hazardous procedure or danger that could result in light-
to-severe injury,or loss related to equipment malfunction, if proper
precautions are not taken.
Safety Symbols Used on Equipment and in Manuals
(Some or all of the following five symbols may or may not be used on all ANRITSU equipment. In addition,
there may be other labels attached to products that are not shown in the diagrams in this manual.)
The following safety symbols are used inside or on the equipment near operation locations to provide information about safety items and operation precautions. Ensure that you clearly understand the meanings of
the symbols and take the necessary precautions BEFORE operating the equipment.
This symbol indicates a prohibited operation.The prohibited operation
is indicated symbolically in or near the barred circle.
-
This symbol indicates a compulsory safety precaution. The required
operation is indicated symbolically in or near the circle.
This symbol indicates warning or caution. The contents are indicated
symbolically in or near the triangle.
This symbol indicates a note. The contents are described in the box.
These symbols indicate that the marked part should be recycled.
MG369XA MM Safety-1
For Safety
WARNING
Always refer to the operation manual when working near locations
where the alert mark, shown on the left, is attached. If theoperation,
etc.,is performed without heeding the advice in the operation manual,
there is a risk of personal injury. In addition, the equipment perfor
mance may be reduced.
-
Repair
Moreover,this alert mark is sometimes used with other marks and de
scriptions indicating other dangers.
WARNING
When supplying AC power to this equipment, connect the accessory
3-pin power cord to a 3-pin grounded power outlet.If a grounded 3-pin
outlet is not available, use a conversion adapter and ground the green
wire,orconnect theframegroundon therearpanel of theequipmentto
ground.Ifpoweris suppliedwithoutgroundingthe equipment,there is
a risk of receiving a severe or fatal electric shock.
WARNING
Thisequipment cannot berepairedbythe operator.DONOTattempt to
remove the equipment covers or to disassemble internal components.
Only qualified service technicians with a knowledge of electrical fire
andshock hazards should service this equipment.Thereare high-volt
age parts in this equipment presenting a risk of severe injury or fatal
electric shock to untrained personnel. In addition, there is a risk of
damage to precision components.
-
-
WARNING
If this equipment is used in a manner not specified by the manufac
turer, the protection provided by the equipment may be impaired.
Safety-2 MG369XA MM
-

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 General Information
1-1 Scope of Manual ............................1-3
1-2 Introduction ..............................1-3
1-3 Description ...............................1-3
1-4 Identification Number .........................1-5
1-5 Online Manual .............................1-5
1-6 Related Manuals ............................1-5
Operation Manual ······················1-5
GPIB Programming Manual ·················1-5
1-7 Options .................................1-5
1-8 Level of Maintenance .........................1-6
Troubleshooting ·······················1-6
Repair ····························1-6
Calibration··························1-6
Preventive Maintenance ···················1-6
1-9 Component Handling .........................1-6
1-10 Preventive Maintenance........................1-8
1-11 Startup Configurations ........................1-9
1-12 Recommended Test Equipment ...................1-10
MG369XA MM i

Table of Contents (Continued)
Chapter 2 Functional Description
2-1 Introduction ..............................2-3
2-2 Major Subsystems ...........................2-3
Digital Control ························2-3
Front Panel Assembly ····················2-4
Frequency Synthesis ·····················2-4
A9 YIG Assembly·······················2-5
ALC/AM/Pulse Modulator···················2-5
RFDeck···························2-5
Power Supply ························2-5
Inputs/ Outputs ·······················2-6
Motherboard/ Interconnections ················2-6
2-3 Frequency Synthesis ..........................2-9
Phase Lock Loops ······················2-9
Overall Operation ······················2-10
RF Outputs 0.01 MHz to 65 GHz ··············2-14
Frequency Modulation····················2-15
Phase Modulation ······················2-15
Analog Sweep Mode ·····················2-16
Step Sweep Mode ······················2-16
2-4 ALC/AM/Pulse Modulation......................2-17
ALC Loop Operation ····················2-17
Pulse Generator Operation ·················2-19
2-5 RF Deck Assemblies .........................2-20
RF Deck Configurations ···················2-20
YIG-tuned Oscillator ····················2-21
RF Signal Filtering ·····················2-22
0.01 to 2 GHz Down Converter (Option 5) ··········2-23
0.01 to 2.2 GHz Digital Down Converter (Option 4) ·····2-23
Switched Doubler Module ··················2-24
Source Quadrupler Module ·················2-25
Step Attenuators ······················2-26
ii MG369XA MM

Table of Contents (Continued)
Chapter 3 Performance Verification
3-1 Introduction ..............................3-3
3-2 Test Records ..............................3-3
3-3 Connector and Key Notation......................3-4
3-4 Recommended Test Equipment ....................3-4
3-5 Measurement Uncertainty.......................3-4
3-6 Internal Time Base Aging Rate Test .................3-6
3-7 Spurious Signals Test .........................3-9
3-8 Single Sideband Phase Noise Test ..................3-11
3-9 Power Level Accuracy and Flatness Tests ..............3-19
Power Level Log Conformity·················3-20
Power Level Accuracy (³ –60 dBm) ·············3-22
Power Level Accuracy (< –60 dBm) ·············3-23
Power Level Flatness ····················3-26
Maximum Leveled Power ··················3-27
3-10 Residual FM Tests ..........................3-28
Locked FM Mode Off ····················3-29
Locked FM Mode On ····················3-30
Unlocked Narrow FM Mode On ···············3-30
Unlocked Wide FM Mode On ················3-31
3-11 Frequency Modulation Tests .....................3-32
FM Attenuator ·······················3-33
Locked FM Accuracy ····················3-41
FM Accuracy ························3-50
Unlocked Narrow FM Accuracy ···············3-59
FM/FM Flatness ······················3-61
FM/FM Bandwidth ·····················3-68
Alternate FM and FM Accuracy Tests ············3-75
MG369XA MM iii

Table of Contents (Continued)
3-12 Amplitude Modulation Tests .....................3-83
External AM Accuracy ···················3-84
Internal AM Accuracy ····················3-86
AM Roll Off ·························3-88
AM Flatness ························3-90
3-13 Pulse Modulation Tests........................3-92
Rise Time, Fall Time and Overshoot ·············3-94
Pulse Power Accuracy ····················3-97
Pulse On/Off Ratio ·····················3-100
Chapter 4 Calibration
4-1 Introduction ..............................4-3
4-2 Recommended Test Equipment ....................4-3
4-3 Test Records ..............................4-3
4-4 Subassembly Replacement.......................4-4
4-5 Connector and Key Notation......................4-4
4-6 Initial Setup ..............................4-6
Interconnection························4-6
PC Setup···························4-7
4-7 Preliminary Calibration .......................4-10
Equipment Setup ······················4-10
Calibration Steps ······················4-11
Alternate 10 MHz
Reference Oscillator Calibration ··············4-14
4-8 Frequency Synthesis Tests ......................4-16
Coarse Loop/ YIG Loop ···················4-16
Fine Loop ··························4-17
4-9 Switched F ilter Shaper ........................4-18
Equipment Setup ······················4-18
Log Amplifier Zero Calibration ···············4-19
Limiter DAC Adjustment ··················4-19
Shaper DAC Adjustment ··················4-21
iv MG369XA MM

Table of Contents (Continued)
4-10 RF Level Calibration .........................4-22
4-11 ALC Bandwidth Calibration .....................4-25
Equipment Setup ······················4-25
Bandwidth Calibration ···················4-26
4-12 ALC Slope Calibration ........................4-27
Equipment Setup ······················4-27
ALC Slope DAC Adjustment·················4-28
4-13 AM Calibration ............................4-31
Equipment Setup ······················4-31
AM Calibration Procedure··················4-32
4-14 FM Calibration ............................4-34
Equipment Setup ······················4-34
FM Calibration Procedure ··················4-35
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting
5-1 Introduction ..............................5-3
5-2 Recommended Test Equipment ....................5-3
5-3 Error Messages.............................5-3
Self-Test Error Messages ···················5-3
Normal Operation Error and Warning/Status Messages ····5-7
5-4 No Error Message...........................5-10
5-5 Troubleshooting Tables........................5-10
Chapter 6 Removal and Replacement Procedures
6-1 Introduction ..............................6-3
6-2 Exchange Assembly Program .....................6-3
6-3 Chassis Covers ............................6-10
6-4 Front Panel Assembly ........................6-12
6-5 A2 Microprocessor PCB Board ....................6-13
6-6 A3 Reference/Fine Loop PCB.....................6-14
6-7 A4 Coarse Loop PCB .........................6-15
MG369XA MM v

Table of Contents (Continued)
6-8 A5—A9 PCB Removal ........................6-17
Card Cage Cover ······················6-17
A5 Auxiliary PCB ·····················6-18
A6ALCPCB························6-18
A7YIGLockPCB······················6-19
A8DDSPCB························6-19
A9 YIG Assembly ······················6-19
6-9 Power Supply Assembly .......................6-20
Power Supply Top Assembly·················6-20
12 Volt Power Supply PCB ·················6-21
Power Supply Regulator PCB ················6-22
6-10 Anritsu Customer Service Centers..................6-24
Appendix A Test Records
A-1 Introduction ..............................A-1
A-2 Uncertainty Specifications ......................A-1
A-3 Test Records ..............................A-1
Appendix B Performance Specifications
B-1 MG369XA Technical Data Sheet ...................B-1
vi MG369XA MM

Table of Contents
1-1 Scope of Manual ............................1-3
1-2 Introduction ..............................1-3
1-3 Description ...............................1-3
1-4 Identification Number .........................1-5
1-5 Online Manual .............................1-5
1-6 Related Manuals ............................1-5
Operation Manual ······················1-5
GPIB Programming Manual ·················1-5
1-7 Options .................................1-5
Chapter 1
General Information
1-8 Level of Maintenance .........................1-6
Troubleshooting ·······················1-6
Repair ····························1-6
Calibration··························1-6
Preventive Maintenance ···················1-6
1-9 Component Handling .........................1-6
1-10 Preventive Maintenance........................1-8
1-11 Startup Configurations ........................1-9
1-12 Recommended Test Equipment ...................1-10

Figure 1-1.
Typical Series MG369XA Synthesized Signal Generator (Model MG3692A Shown)
1-2 MG369XA MM

Chapter 1 General Information
1-1 Scope of Manual This manual provides service information for the Model MG369XA
Signal Generators. The service information includes replaceable parts
information, troubleshooting, performance verification tests, calibra
tion procedures, functional circuit descriptions and block diagrams,
and assembly/subassembly removal and replacement. Throughout this
manual, the terms MG369XA or synthesizer are used to refer to the in
strument. Manual organization is shown in the table of contents.
-
-
1-2 Introduction This chapter provides a general description of the MG369XA identifi
cation numbers, related manuals, and options. Information is included
concerning level of maintenance, replaceable subassemblies and RF
components, exchange assembly program, and preventive maintenance. Static-sensitive component handling precautions and lists of
exchangeable subassemblies and recommended test equipment are
also provided.
1-3 Description The series MG369XA is a microprocessor-based, synthesized signal
source with high resolution phase-lock capability. It generates both
discrete CW frequencies and broad (full range) and narrow band step
sweeps across the frequency range of 2 GHz to 65 GHz. Options are
available to extend the low end of the frequency range to 0.1 Hz. All
functions of the CW generator are fully controllable locally from the
front panel or remotely (except for power on/standby) via the
IEEE-488 General Purpose Interface Bus (GPIB).Table 1-1 on
page 1-4 lists models, frequency ranges, and maximum leveled output
power.
-
MG369XA MM 1-3

Description General Information
Table 1-1. Series MG369XA Models
Max Leveled
Model
Number Configuration
Frequency
Range
Max Leveled
Output Power
Max Leveled
Output Power
w/Step Attenuator
Output Power
w/Electronic
Step Attenuator
MG3691A
MG3692A
MG3693A
MG3694A
MG3695A
MG3696A
w/opt 4
w/opt 5
Standard
w/opt 4
w/opt 5
Standard
Standard
w/opt 4
w/opt 5
Standard
Standard
w/opt 4
w/opt 5
Standard
Standard
w/opt 4
w/opt 5
Standard
Standard
w/opt 4
w/opt 5
Standard
Standard
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £8.4 GHz
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £8.4 GHz
>8.4 – £20.0 GHz
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £20.0 GHz
>20.0 – £30.0 GHz
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £20.0 GHz
>20.0 – £40.0 GHz
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £20.0 GHz
>20.0 – £50.0 GHz
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £20.0 GHz
>20.0 – £65.0 GHz
With Option 15 (High Power) Installed
+17.0 dBm
+17.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+17.0 dBm
+17.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+9.0 dBm
+6.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+9.0 dBm
+6.0 dBm
+12.0 dBm
+12.0 dBm
+10.0 dBm
+3.0 dBm
+12.0 dBm
+12.0 dBm
+10.0 dBm
+3.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+11.0dBm
+15.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+11.0dBm
+11.0dBm
+11.0dBm
+11.0dBm
+7.0 dBm
+3.0 dBm
+11.0dBm
+11.0dBm
+7.0 dBm
+3.0 dBm
+10.0 dBm
+10.0 dBm
+8.0 dBm
+0.0 dBm
+10.0 dBm
+10.0 dBm
+8.0 dBm
+0.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+9.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+9.0 dBm
+3.0 dBm
Not Available
Not Available
Not Available
Not Available
*
w/opt 4
MG3691A
MG3692A
MG3693A
MG3694A
Note: In models with Option 22, rated output power is reduced by 2 dB.
* Typical 60 - 65 GHz.
w/opt 5
Standard
w/opt 4
w/opt 5
Standard
Standard
w/opt 4
w/opt 5
Standard
Standard
Standard
Option 4
Option 5
Standard
Standard
Standard
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £8.4 GHz
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £10.0 GHz
>10.0 – £20.0 GHz
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £10.0 GHz
>10.0 – £20.0 GHz
>20.0 – £30.0 GHz
³0.01 – £2.2 GHz
³0.01 – £2.0 GHz
³2.0 – £10.0 GHz
>10.0 – £20.0 GHz
>20.0 – £40.0 GHz
+19.0 dBm
+19.0 dBm
+19.0 dBm
+19.0 dBm
+19.0 dBm
+19.0 dBm
+17.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+12.0 dBm
+14.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+12.0 dBm
+14.0 dBm
+18.0 dBm
+18.0 dBm
+18.0 dBm
+18.0 dBm
+18.0 dBm
+18.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+14.0 dBm
+14.0 dBm
+14.0 dBm
+10.0 dBm
+12.0 dBm
+14.0 dBm
+14.0 dBm
+14.0 dBm
+10.0 dBm
+12.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+15.0 dBm
+13.0 dBm
+7.0 dBm
Not Available
Not Available
1-4 MG369XA MM

General Information Identification Number
1-4 Identification Number All Anritsu instruments are assigned a unique six-digit ID number,
such as “875012.” The ID number is imprinted on a decal that is af
fixed to the rear panel of the unit. Special-order instrument configura
tions also have an additional special number tag attached to the rear
panel of the unit, such as SM1234.
When ordering parts or corresponding with Anritsu customer service,
please use the correct serial number with reference to the specific in
strument's model number (i.e., Model MG3692A CW Signal Generator,
Serial No. 875012, and the special's number, if appropriate).
-
-
1-5 Online Manual This manual is available on CD ROM as an Adobe Acrobat Portable
Document Format (*.pdf) file. The file can be viewed using Acrobat
Reader, a free program that is also included on the CD ROM. The file
is “linked” such that the viewer can choose a topic to view from the dis
played “bookmark” list and “jump” to the manual page on which the
topic resides. The text can also be word-searched. Contact Anritsu customer service for price and availability.
-
-
1-6 Related Manuals This is one of a three manual set that consists of an operation manual,
a GPIB programming manual, and a maintenance manual.
Operation
Manual
GPIB
Programming
Manual
1-7 Options The options available for the Anritsu MG369XA series signal genera
tors are described in the product data sheet (p/n 11410-00327). A copy
of this data sheet is located in Appendix B.
The operation manual provides instructions for operating the MG369XA using the front panel controls.
It also includes general information, performance
specifications, installation instructions, and operation verification procedures. The Anritsu part num
ber for the Model MG369XA Operation Manual is
10370-10353.
The GPIB programming manual provides informa
tion for remotely operating the MG369XA using
product specific commands sent from an external
controller via the IEEE 488 General Purpose Inter
face Bus (GPIB). It contains a complete listing and
description of all MG369XA GPIB product specific
commands and several programming examples. The
Anritsu part number for the Model MG369XA GPIB
Programming Manual is 10370-10354.
-
-
-
-
MG369XA MM 1-5

Level of Maintenance General Information
1-8 Level of Maintenance Maintenance of the MG369XA consists of:
Troubleshooting the instrument to a replaceable subassembly or
q
RF component
Repair by replacing the failed subassembly or RF component.
q
Calibration
q
Preventive maintenance
q
Trouble
shooting
Repair Most instrument failures are field repairable by re-
Calibration The MG369XA may require calibration after repair.
Preventive
Maintenance
-
The MG369XA firmware includes internal diagnos
tics that self-test most of the internal assemblies.
When the MG369XA fails self-test, one or more error
messages appear to aid in troubleshooting the fail
ure to a replaceable subassembly or RF component.
Chapter 5—Troubleshooting lists and describes the
self-test error messages and provides procedures for
isolating MG369XA failures to a replaceable subas
sembly or RF component.
placing the failed subassembly or RF component.
Detailed instructions for removing and replacing
failed subassemblies and components are provided
in Chapter 6—Removal and Replacement Procedures.
Refer to Chapter 4—Calibration for a listing of requirements and procedures.
Preventive maintenance on the MG369XA consists
of cleaning the fan honeycomb filter, described in
Section 1-10.
-
-
-
1-9 Component Handling The MG369XA contains components that can be damaged by static
electricity.Figure 1-2 illustrates the precautions that should be fol
lowed when handling static-sensitive subassemblies and components.
If followed, these precautions will minimize the possibilities of
static-shock damage to these items.
NOTE
Use of an grounded wrist strap when handling subassem
blies or components is strongly recommended.
1-6 MG369XA MM
-
-
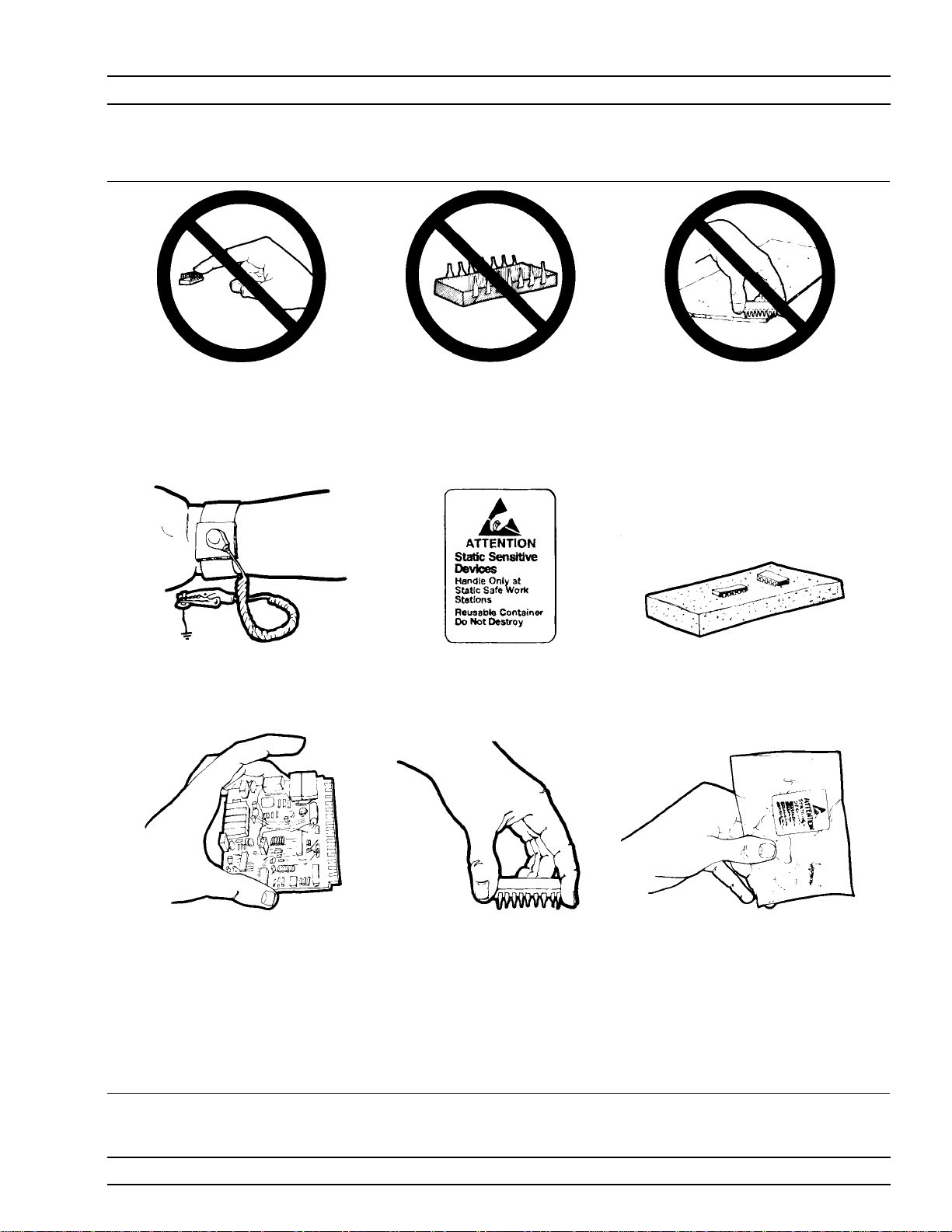
General Information Component Handling
1. Do not touch exposed contacts
on any static sensitive
component.
4. Wear a static-discharge
wristband when working with
static sensitive components.
2. Do not slide static sensitive
component across any surface.
5. Label all static sensitive
devices.
3. Do not handle static sensitive
components in areas where the
floor or work surface covering
is capable of generating a
static charge.
6. Keep component leads shorted
together whenever possible.
7. Handle PCBs only by their
edges. Do not handle by the
edge connectors.
10. Additional Precautions:
Keep work spaces clean and free of any objects capable of holding or storing a static charge.
Connect soldering tools to an earth ground.
Use only special anti-static suction or wick-type desoldering tools.
Figure 1-2. Static-Sensitive Component Handling Precautions
8. Lift & handle solid state de
vices by their bodies – never
by their leads.
-
9. Transport and store PCBs and
other static sensitive devices
in static-shielded containers.
MG369XA MM 1-7
Preventive Maintenance General Information
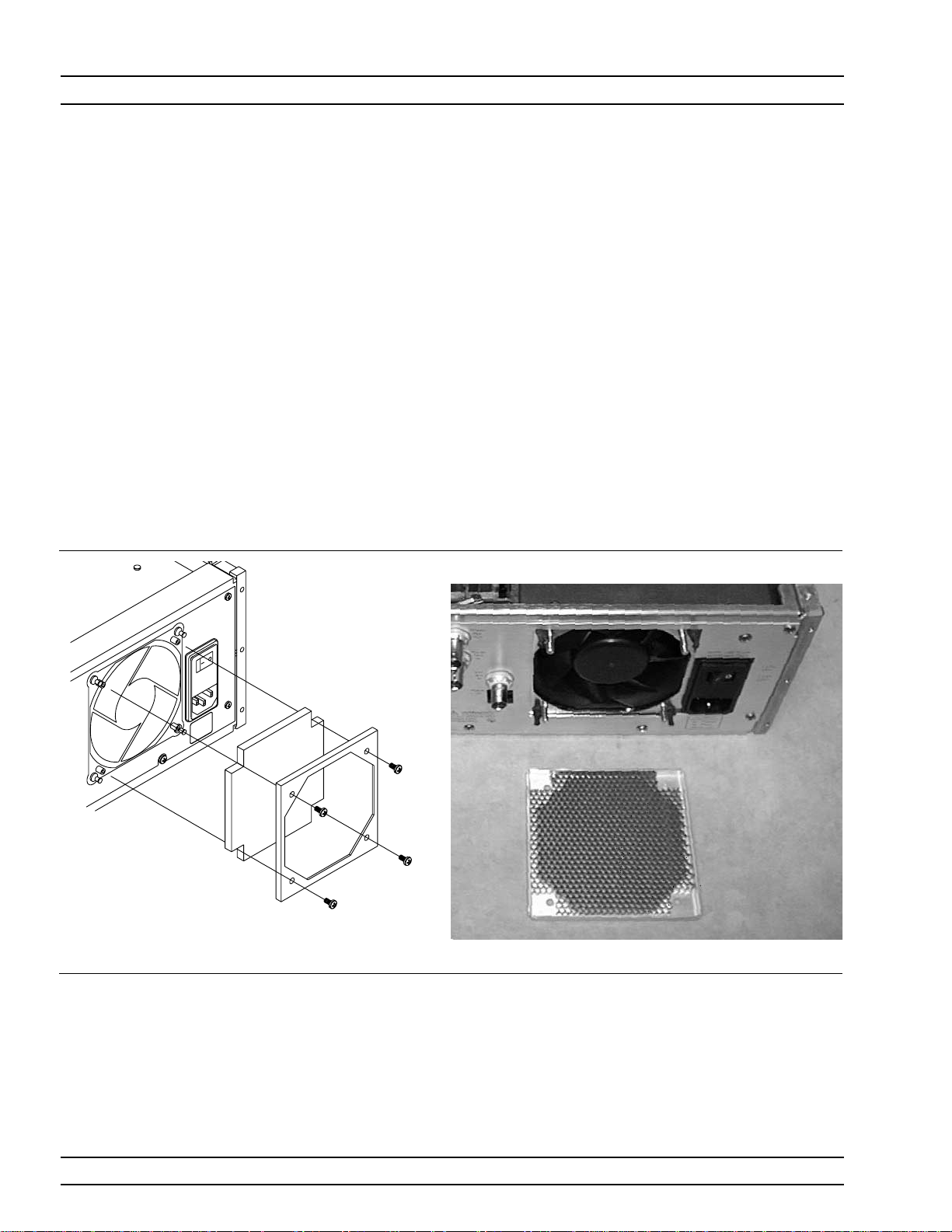
1-10 Preventive
Maintenance
The MG369XA must always receive adequate ventilation.A blocked
fan filter can cause the instrument to overheat and shut down. Check
and clean the rear panel fan honeycomb filter periodically.Clean the
fan honeycomb filter more frequently in dusty environments. Clean
the filter as follows.
Step 1. Use a #3 screwdriver to remove the four screws that
fasten the filter guard to the rear panel (see
Figure 1-3). Retain the screws for reassembly.
Step 2. Vacuum the honeycomb filter to clean it.
Step 3. Reinstall the filter guard.
Step 4. Fasten the filter guard to the rear panel using the
four screws that were removed in Step 1.
Figure 1-3. Removing/Replacing the Fan Filter Guard
1-8 MG369XA MM
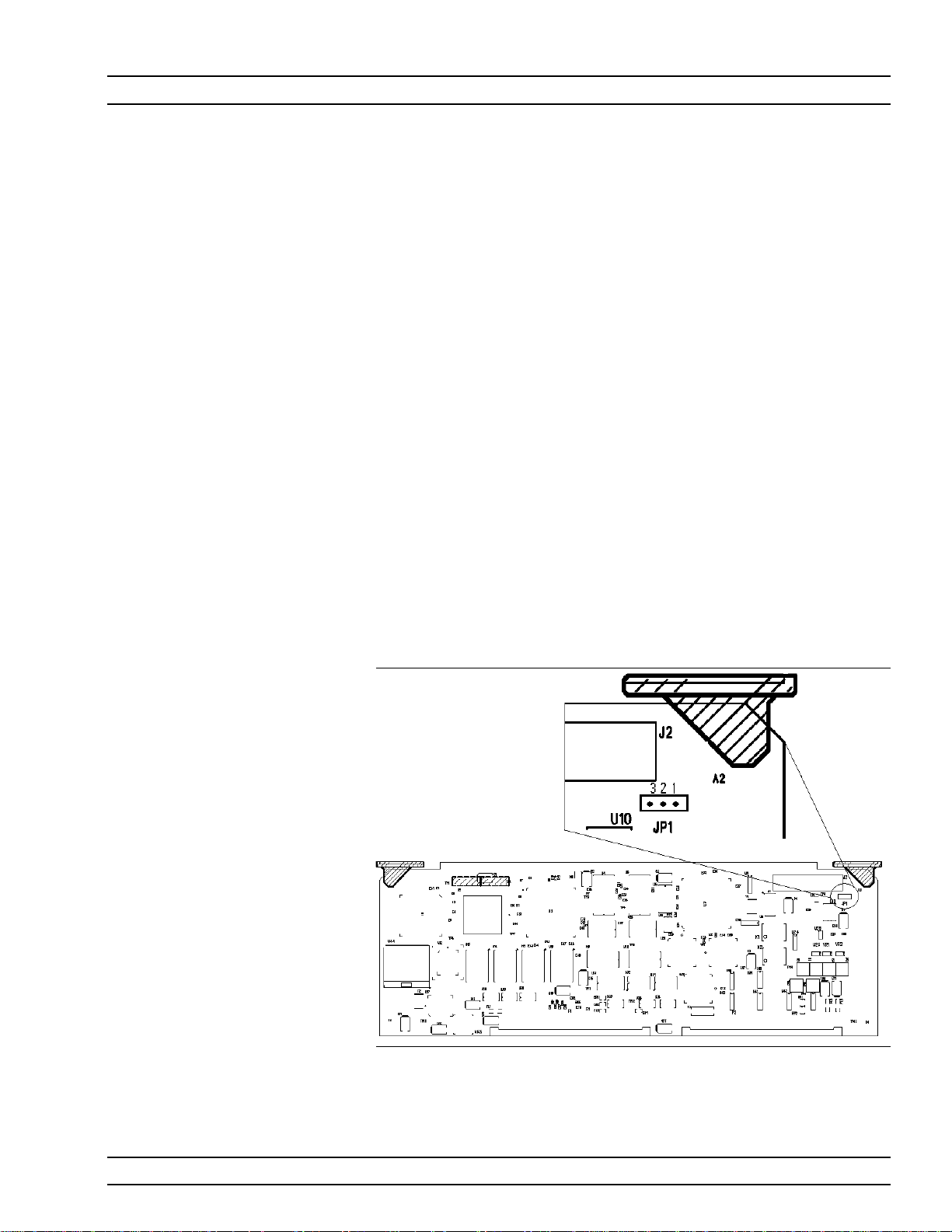
General Information Startup Configurations
1-11 Startup
Configurations
The MG369XA comes from the factory with a jumper across pins 2 and
3 of the A2 microprocessor PCB connector JP1 (Figure 1-4). In this
configuration, connecting the instrument to line power automatically
places it in operate mode (front panel OPERATE LED on).
The startup configuration can be changed so that the signal generator
comes up in standby mode (front panel STANDBY LED on) when it is
connected to line power.Change the startup configuration as follows:
Step 1. Disconnect the instrument from line power.
Step 2. Remove the top cover from the MG369XA and A2
PCB.Refer to Section 6-5 for instructions.
Step 3. Locate the connector JP1 and remove the jumper
from across pins 2 and 3.Refer to Figure 1-4 below.
Step 4. Install the jumper across pins 1 and 2 of the connec-
tor JP1.
Step 5. Install the top covers and connect the signal genera-
tor to line power.The instrument should come up in
standby mode.
Figure 1-4. Startup Configuration of A2 Connector JP1
MG369XA MM 1-9
Recommended Test Equipment General Information
1-12 Recommended Test
Equipment
Table 1-2 provides a list of recommended test equipment needed for
the performance verification, calibration, and troubleshooting proce
dures presented in this manual.
Table 1-2. Recommended Test Equipment
INSTRUMENT
Spectrum Analyzer
Phase Noise Measure
ment System
Modulation Analyzer
Frequency Counter
Power Meter with
Power Sensor
Power Supply Output: +1V DC Agilent E3631A P
Digital Multimeter
Function Generator DDS, 0.01 to 10 MHz Agilent 33120A C, P
Digital Sampling
Oscilloscope
Measuring Receiver Noise Floor: <–140 dBm @ 500 MHz Anritsu Model ML2530A C, P
Frequency Reference
Local Oscillator Frequency: 0.01 to 40 GHz
Local Oscillator
(Level Calibration)
Scalar
Network Analyzer with
RF Detector
Diplex Switch Assembly
Mixer
* P = Performance Verification Tests; C = Calibration; T = Troubleshooting
Frequency: 0.01 to 50 GHz
Resolution Bandwidth: 10 Hz
Frequency Range: 5 MHz to 26.5 GHz
See Table 3-2 on page 3-11
AM and FM Measurement Capability to
>500 MHz and –20 dBm
Frequency Range: 0.01 to 40 GHz
Input Impedance: 50W
Resolution: 1 Hz
Other: External Time Base Input
Frequency: 0.01 to 65 GHz
Power Range: –70 to +20 dBm
Minimum 1% RMS ACV Accuracy at
100 kHz
Frequency: 50 GHz
Frequency: 10 MHz
Accuracy:5x10
Frequency: 0.01 to 40 GHz
Frequency: 0.01 to 60 GHz
Frequency Range: 0.1 Hz to 10 MHz
Frequency Range: 0.01 to 40 GHz
Frequency Range: 500 MHz to 40 GHz
Conversion Loss: 10 dB (typical)
CRITICAL
SPECIFICATION
–12
(1 of 2)
parts/day
RECOMMENDED
MANUFACTURER/MODEL
HP8565E C, P
Aeroflex/Comstron PN9000 with:
PN9060-00 Status Module
PN9470-00 Noise Output Module
PN9450-00 Lock Control Module
PN9342-00 Phase Detector Module
PN9530-00 Crystal Oscillator Module
HP8901A P
Anritsu Model MF2414B C, P
Anritsu Model ML2437A/38A with Power Sensor:
MA2421A (100 kHz to 18 GHz)
MA2474A (0.01 to 40 GHz)
SC6230 (0.01 to 65 GHz)
Fluke 8840A C, P
Agilent 86100A with:
83484A 50 GHz Module
Absolute Time Corp., Model 300 C, P
Anritsu Model MG3694A with:
Options 3, 4 and 15
Anritsu Model 69067B with:
Option 14 and SM5709
Anritsu Model 56100A with RF Detector:
560-7K50 (0.01 to 40 GHz)
560-7VA50(0.01 to 50 GHz)
SC5198 (0.01 to 60 GHz)
Anritsu P/N: 46504
Anritsu P/N: 29850
Anritsu P/N: 60-114 C, P
USAGE*
C, P
C, T
-
P
P
P
C
C
1-10 MG369XA MM
General Information Recommended Test Equipment
Table 1-2.
INSTRUMENT
Attenuator
Attenuator
Adapter
2.4 mm (m) to K (f)
Adapter
3.5 mm (m) to BNC (f)
Feed Through
Termination
Tee Connectors: 50W BNC Any common source P
Cables
AUX I/O Interface Cable
Special AUX I/O
Cable Assembly
Serial Interface
Assembly
Personal Computer
Level Calibration
Software
* P = Performance Verification Tests; C = Calibration; T = Troubleshooting
Recommended Test Equipment (2 of 2)
CRITICAL
SPECIFICATION
Frequency Range: DC to 40 GHz
Max Input Power: >+20 dBm
Attenuation: 3, 6, 10, and 20 dB
Frequency Range: DC to 60 GHz
Max Input Power: >+20 dBm
Attenuation: 10 dB
Frequency Range: 0.01 to 40 GHz
50W Any common source P
50W BNC Any common source P
Connectors: 50W BNC
RF Connections: K-Cables
Provides interface between the
MG369XA and the
56100A Scalar Network Analyzer
Provides interface between the
MG369XA and the Power Meter
Provides serial interface between the
PC and the MG369XA
IBM AT or compatible with
GPIB interface
Provides automated power level cali
bration of the MG369XA
RECOMMENDED
MANUFACTURER/MODEL
Anritsu, Model 41KC-3
Anritsu, Model 41KC-6
Anritsu, Model 41KC-10
Anritsu, Model 41KC-20
Anritsu, Model 41V-10 C
Any common source
(Agilent P/N: 11904-60003)
Any common source C, P
Anritsu P/N:806-7 C
Anritsu P/N: 806-97 P
Anritsu P/N: T1678 C
PC: Any common source
GPIB Interface: National Instruments P/N:
PCI-GPIB (Desktop)
PCMCIA-GPIB (Notebook)
Anritsu P/N: 2300-497 C
USAGE*
C, P
P
C
MG369XA MM 1-11/1-12


Table of Contents
2-1 Introduction ..............................2-3
2-2 Major Subsystems ...........................2-3
Digital Control ························2-3
Front Panel Assembly ····················2-4
Frequency Synthesis ·····················2-4
A9 YIG Assembly·······················2-5
ALC/AM/Pulse Modulator···················2-5
RFDeck···························2-5
Power Supply ························2-5
Inputs/ Outputs ·······················2-6
Chapter 2
Functional Description
Motherboard/ Interconnections ················2-6
2-3 Frequency Synthesis ..........................2-9
Phase Lock Loops ······················2-9
Overall Operation ······················2-10
RF Outputs 0.01 MHz to 65 GHz ··············2-14
Frequency Modulation····················2-15
Phase Modulation ······················2-15
Analog Sweep Mode ·····················2-16
Step Sweep Mode ······················2-16
2-4 ALC/AM/Pulse Modulation......................2-17
ALC Loop Operation ····················2-17
Pulse Generator Operation ·················2-19

Table of Contents (Continued)
2-5 RF Deck Assemblies .........................2-20
RF Deck Configurations ···················2-20
YIG-tuned Oscillator ····················2-21
RF Signal Filtering ·····················2-22
0.01 to 2 GHz Down Converter (Option 5) ··········2-23
0.01 to 2.2 GHz Digital Down Converter (Option 4) ·····2-23
Switched Doubler Module ··················2-24
Source Quadrupler Module ·················2-25
Step Attenuators ······················2-26
2-2 MG369XA MM

Chapter 2 Functional Description
2-1 Introduction This chapter provides brief functional descriptions of the major sub
systems that are contained in each model of the MG369XA.In addi
tion, the operation of the frequency synthesis, automatic level control
(ALC), and RF deck subsystems is described so that the reader may
better understand the overall operation of the instrument. Block dia
grams are included to supplement the written descriptions.
2-2 Major Subsystems The MG369XA circuitry consists of various distinct subsystems that
are contained on one or more printed circuit board (PCB) assemblies
or in microwave components located on the RF deck. The following
paragraphs identify the subsystems that make up the instrument and
provide a brief description of each.Figure 2-1 (page 2-7) is an overall
block diagram of a typical MG369XA.
Digital
Control
This circuit subsystem consists of the A2 Microprocessor PCB. The central processor unit (CPU) located on this PCB is the main controller for the
MG369XA. This controller directly or indirectly controls all functions of the instrument.The CPU contains memory that stores the main operating system
components and instrument firmware, instrument
calibration data, and front panel setup data during
the power-off condition. It has a GPIB interface that
allows it to communicate with external devices over
the GPIB and a serial interface to a serial terminal
port on the rear panel. The CPU is directly linked
via a dedicated data and address bus to the front
panel assembly,the A5 Auxiliary/Analog Instruction
PCB,the A6 ALC PCB, the A7 Yig-lock PCB, the
A9 YIG assembly, the optional A8 DDS PCB of the
CW Generator or Function Generator of the Signal
Generator, and the A13 Pulse Generator PCB.
-
-
-
Interface circuits on the A2 PCB indirectly link the
CPU to the A3 reference/fine loop PCB, and the A4
coarse loop PCB. The A2 PCB contains circuits that
perform parallel-to-serial and serial-to-parallel data
conversion. The A2 also contains circuitry for many
of the rear panel signals and a 13-bit resolution digi
tal volt meter (DVM).
MG369XA MM 2-3
-

Major Subsystems Functional Description
Front Panel
Assembly
Frequency
Synthesis
This circuit subsystem consists of the front panel,
the front panel rotary data knob,the front panel
control PCB, and the liquid crystal display (LCD).
The subsystem interfaces the front panel LCD, light
emitting diodes (LEDs), and keys to the CPU via the
dedicated data and address bus. The front panel ro
tary data knob is also linked to the CPU via the data
and address bus.
The front panel PCB contains the keyboard matrix
conductive rubber switches. It has circuits to control
the LCD dot-matrix display, turn the front panel
LEDs on and off, and convert keyboard switch ma
trix signals to parallel key code.It also contains the
standby/operate line switch and the optical encoder
for the rotary data knob.
The frequency synthesis subsystem consists of the
A3 reference/fine loop PCB, the A4 coarse loop PCB,
the A7 YIG lock PCB, and the A9 YIG assembly. It
provides the reference frequencies and phase lock
circuits for precise control of the YIG-tuned oscillator frequencies, as follows:
q
The reference loop circuitry located on the A3
PCB supplies the stable 10 MHz and 500 MHz
reference frequency signals for the rest of the
frequency synthesis system
q
The A4 coarse loop PCB generates coarse tun
ing frequencies of 219.5 to 245 MHz for use by
the YIG lock PCB
q
The fine loop circuitry located on the A3 PCB
provides fine tuning frequencies of 21.5 to
40 MHz for use by the YIG lock PCB
q
The A7 YIG lock PCB performs phase detec
tion of the YIG-tuned oscillator's output fre
-
quency and provides a YIG loop error voltage
signal. This error signal is further conditioned,
producing a correction signal that is used to
fine tune and phase lock the YIG-tuned
oscillator
The CPU sends control data to the A3 reference/ fine
loop PCB and the A4 coarse loop PCB as serial data
words. Refer to Section 2-3 for a functional overview
of the frequency synthesis subsystem.
2-4 MG369XA MM

Functional Description Major Subsystems
A9 YIG
Assembly
ALC/AM/Pulse
Modulator
The A9 YIG assembly contains the YIG-tuned oscil
lator and associated PCB assembly.The PCB assem
bly contains the driver circuitry that provides the
tuning current and bias voltages for the YIG-tuned
oscillator. The CPU controls the A9 YIG assembly
via the dedicated data and address bus.
This ALC circuit subsystem consists of the A6 ALC
PCB,the A6A1 AM module, and part of the A9 YIG
PCB assembly.It provides the following:
Level control of the RF output power
q
Current drive signals to the PIN switches lo
q
cated in the A10 switched filter assembly
(SWF), the A12 switched doubler module
(SDM), and the source quadrupler module
(SQM)
Drive signals for the step attenuator (Option 2)
q
and the diplexers (used with Option 22)
The CPU controls the A6 ALC PCB (and the A6A1
AM module via the A6 PCB) and the A9 YIG PCB
assembly via the dedicated data and address bus. It
sends control data to the A13 Pulse Generator PCB
via the A1 Motherboard as serial data words. Refer
to Section 2-4 for a functional overview of the ALC
subsystem.
-
-
RF Deck This subsystem contains those elements related to
the generation, modulation, and control of the
sweep- and CW-frequency RF signals. These ele
ments include the A9 YIG-tuned oscillator/PCB as
sembly,the 0.01 to 2 GHz down converter assembly
(A11), the A10 switched filter assembly, the A12
switched doubler module, the source quadrupler
module, the directional coupler/level detector, and
the optional step attenuator.Refer to Section 2-5 for
a functional overview of the RF deck subsystem.
Power Supply The power supply subsystem consists of the power
input connector/filter module, the regulator PCB, the
power supply PCB, the standby power supply PCB,
and the power module fan unit.It supplies all the
regulated DC voltages used by the MG369XA cir
cuits. The voltages are routed throughout the instru
ment via the motherboard PCB.
-
-
MG369XA MM 2-5

Major Subsystems Functional Description
Inputs/
Outputs
The A21 rear panel PCB and the A2 microprocessor
PCB contain the interface circuits for the majority of
the rear panel input and output connectors, includ
ing the AUX I/O connector.
The A5 Auxiliary PCB (or the optional A5 Analog In
struction PCB) provides a 0V to +10V ramp signal to
the rear panel HORIZ OUT connector,a V/GHz signal
to the rear panel AUX I/O connector,and a SLOPE
signal to the A6 ALC PCB for slope-vs-frequency cor
rection of the RF output power.
The rear panel EXT ALC IN, AM IN, and AM OUTare
routed through the A21 rear panel PCB, and then
through the motherboard PCB to the A6 ALC PCB.
The rear panel connectors, 10 MHz REF OUT and
10 MHz REF IN, are routed through the A21 PCB
and coupled to the A3 Reference/Fine Loop PCB via
coaxial cables.
The rear panel FM/FMINandFM/FM OUT connec-
tors are routed through the A21 rear panel PCB and
then through the Motherboard PCB to the A7
YIG-lock PCB. The rear panel PULSE TRIG IN connector is routed through the A21 rear panel PCB
and then to the A6 ALC PCB (or optional A13 Pulse
Generator PCB for units with Option 24 installed).
The rear panel PULSE SYNC OUT and PULSE
VIDEO OUT connectors are routed through the A21
rear panel PCB, and then to the optional A13 Pulse
Generator PCB via coaxial cables. The rear panel
EFC IN connector is routed to the A3 Reference/Fine
Loop PCB via coaxial cables.
-
-
-
-
Motherboard/
Interconnections
The rear panel IEEE-488 GPIB and SERIAL I/O con
nectors are routed through the A21 rear panel PCB
and then through the motherboard to the A2 micro
processor PCB.
The motherboard PCB and associated cables provide
the interconnections for the flow of data, signals, and
DC voltages between all internal components and
assemblies throughout the MG369XA.
2-6 MG369XA MM
-
 Loading...
Loading...