4-Channel, 104 MSPS Digital
a
FEATURES
Pin Compatible to the AD6622
18-Bit Parallel Digital IF Output
Real or Interleaved Complex
18-Bit Bidirectional Parallel Digital IF Input/Output
Allows Cascade of Chips for Additional Channels
Clipped or Wrapped Over Range
Two’s Complement or Offset Binary Output
Four Independent Digital Transmitters in Single Package
RAM Coefficient Filter (RCF)
Programmable IF and Modulation for Each Channel
Programmable Interpolating RAM Coefficient Filter
/4-DQPSK Differential Phase Encoder
3/8-PSK Linear Encoder
8-PSK Linear Encoder
Programmable GMSK Look-Up Table
Programmable QPSK Look-Up Table
All-Pass Phase Equalizer
Programmable Fine Scaler
Programmable Power Ramp Unit
High Speed CIC Interpolating Filter
Transmit Signal Processor (TSP)
AD6623
Digital Resampling for Noninteger Interpolation Rates
NCO Frequency Translation
Carrier Output from DC to 52 MHz
Spurious Performance Better than –100 dBc
Separate 3-Wire Serial Data Input for Each Channel
Bidirectional Serial Clocks and Frames
Microprocessor Control
2.5 V CMOS Core, 3.3 V Outputs, 5 V Inputs
JTAG Boundary Scan
APPLICATIONS
Cellular/PCS Base Stations
Micro/Pico Cell Base Stations
Wireless Local Loop Base Stations
Multicarrier, Multimode Digital Transmit
GSM, EDGE, IS136, PHS, IS95, TDS CDMA, UMTS,
CDMA2000
Phased Array Beam Forming Antennas
Software Defined Radio
Tuning Resolution Better than 0.025 Hz
Real or Complex Outputs
SDINA
SDFIA
SDFOA
SCLKA
SDINB
SDFIB
SDFOB
SCLKB
SDINC
SDFIC
SDFOC
SCLKC
SDIND
SDFID
SDFOD
SCLKD
SP
SP
SP
SP
ORT
ORT
ORT
ORT
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
RAM
COEFFICIENT
FILTER
RAM
COEFFICIENT
FILTER
RAM
COEFFICIENT
FILTER
RAM
COEFFICIENT
FILTER
JTAG
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
I
Q
I
Q
I
Q
I
Q
SCALER
SCALER
SCALER
SCALER
AND
POWER
RAMP
AND
POWER
RAMP
AND
POWER
RAMP
AND
POWER
RAMP
I
Q
I
Q
I
Q
I
Q
CIC5
FILTER
CIC5
FILTER
CIC5
FILTER
CIC5
FILTER
I
rCIC2
Q
FILTER
I
rCIC2
Q
FILTER
I
rCIC2
Q
FILTER
I
rCIC2
Q
FILTER
MICROPORT
I
Q
I
Q
I
Q
I
Q
NCO = NUMERICALLY CONTROLLED
OSCILLATOR/TUNER
CHAN A
NCO
CHAN B
NCO
SUMMATION
CHAN C
NCO
CHAN D
NCO
SYNC
4
QIN
IN
[17–0]
OEN
QOUT
OUT
[17:0]
TDL TMS TCK
TDO
TRST
D[7:0]
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
A[2:0]MODERW
DTACKDS
CS
CLK
RESET
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002

AD6623
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
APPLICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
LOGIC INPUTS (5 V TOLERANT) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
LOGIC OUTPUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
IDD SUPPLY CURRENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
POWER DISSIPATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
GENERAL TIMING CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
MICROPROCESSOR PORT TIMING CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
MICROPROCESSOR PORT, MODE INM (MODE = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
MICROPROCESSOR PORT, MOTOROLA (MODE = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
TIMING DIAGRAMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
PIN CONFIGURATION – 128-Lead MQFP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
128-PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
PIN CONFIGURATION – 196-Lead CSPBGA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
196-PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
POWER SUPPLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
INPUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
MICROPORT CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
OUTPUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
JTAG AND BIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
CONTROL REGISTER ADDRESS NOTATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
SERIAL DATA PORT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Serial Master Mode (SCS = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Serial Slave Mode (SCS = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Serial Data Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Self-Framing Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
External Framing Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Serial Port Cascade Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Serial Data Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
PROGRAMMABLE RAM COEFFICIENT FILTER (RCF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
OVERVIEW OF THE RCF BLOCKS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
INTERPOLATING FIR FILTER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Channel A RCF Control Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
PSK MODULATOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
/4-DQSPK Modulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8-PSK Modulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3/8-8-PSK Modulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
MSK Look-Up Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
GMSK Look-Up Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
QPSK Look-Up Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
PHASE EQUALIZER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
FINE SCALE AND RAMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
FINE SCALING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
RCF POWER RAMPING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Ramp Triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Special Handling for SYNC0 Pin-Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
CASCADED INTERGRATOR COMB (CIC)
INTERPOLATING FILTERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
CIC Scaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
CIC5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
The rCIC2 RESAMPLING INTERPOLATION FILTER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Permissible Values of L
Frequency Response for rCIC2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Programming Guidelines for AD6623 CIC Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
NUMERICALLY CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR/TUNER (NCO) . . . . . 27
Phase Dither . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Amplitude Dither . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Phase Offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
NCO Frequency Update and Phase Offset
Update Hold-Off Counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
NCO Control Scale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
SUMMATION BLOCK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Dual 18-Bit Output Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Output Data Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Output Clip Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Cascading Multiple AD6623s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Selection of Real and Complex Data Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
SYNCHRONIZATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Hold-Off Counters and Shadow Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Start with No Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
rCIC2
and M
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
rCIC2
Start with SoftSync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Start with Pin Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Hop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Set Frequency No Hop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Hop with SoftSync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Hop with Pin Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Beam . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Set Phase No Beam . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Beam with SoftSync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Beam with Pin Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Time Slot (Ramp) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Set Output Power, No Ramp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Time Slot (Ramp) with SoftSync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Time Slot with Pin Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
JTAG INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
SCALING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Multicarrier Scaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Single Carrier Scaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
MICROPORT INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Microport Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
EXTERNAL MEMORY MAP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Intel Nonmultiplexed Mode (INM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Motorola Nonmultiplexed Mode (MNM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
External Address 7 Upper Address Register (UAR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
External Address 6 Lower Address Register (LAR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
External Address 5 SoftSync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
External Address 4 Sleep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
External Address 3:0 (Data Bytes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
INTERNAL CONTROL REGISTERS AND ON-CHIP RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
AD6623 and AD6622 Compatibility
Common Function Registers (not associated with a particular channel) . . . . . . 36
Channel Function Registers (0x1xx = Ch. A,
0x2xx = Ch. B, 0x3xx = Ch. C, 0x4xx = Ch. D) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
(0x000) Summation Mode Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
(0x001) Sync Mode Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
(0x002) BIST Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
(0x003) BIST Result . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
(0xn00) Start Update Hold-Off Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn01) NCO Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn02) NCO Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn03) NCO Frequency Update Hold-Off Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn04) NCO Phase Offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn05) NCO Phase Offset Update Hold-Off Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn06) CIC Scale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn07) CIC2 Decimation – 1 (M
(0xn08) CIC2 Interpolation – 1 (L
(0xn09) CIC5 Interpolation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn0A) Number of RCF Coefficients – 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn0B) RCF Coefficient Offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn0C) Channel Mode Control 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
(0xn0D) Channel Mode Control 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn0E) Fine Scale Factor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn0F) RCF Time Slot Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn10–0xn11) RCF Phase Equalizer Coefficients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn12–0xn15) FIR-PSK Magnitudes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn16) Serial Port Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn17) Power Ramp Length 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn18) Power Ramp Length 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn19) Power Ramp Rest Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn20–0xn1F) Unused . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn20–0xn3F) Data Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn40–0xn17F) Power Ramp Coefficient Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
(0xn80–0xnFF) Coefficient Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
PSEUDOCODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Write Pseudocode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Read Pseudocode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
AD6623 EVALUATION PCB AND SOFTWARE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
APPLICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Using the AD6623 to Process UMTS Carriers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Multiple TSP Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Determining the Number of TSPs to Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Programming Multiple TSPs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Driving Multiple TSP Serial Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
USING THE AD6623 TO PROCESS TWO UMTS CARRIERS
WITH 24⫻ OUTPUT RATE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Configuring the AD6623 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
AD6623 Register Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
THERMAL MANAGEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
– 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
CIC2
– 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
CIC2
–2–
REV. A

AD6623
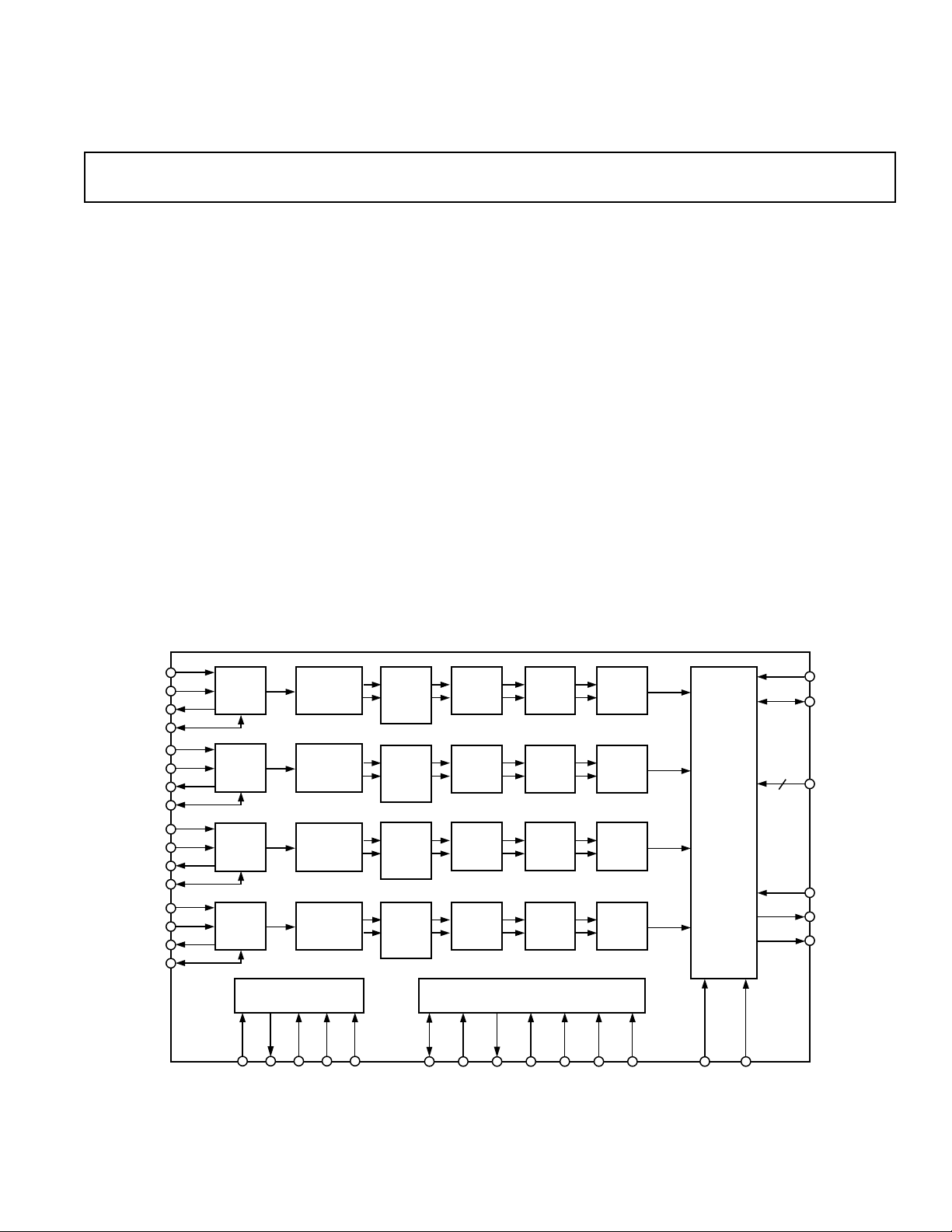
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD6623 is a 4-channel Transmit Signal Processor (TSP)
that creates high bandwidth data for Transmit Digital-to-Analog
Converters (TxDACs) from baseband data provided by a Digital Signal Processor (DSP). Modern TxDACs have achieved
sufficiently high sampling rates, analog bandwidth, and dynamic
range to create the first Intermediate Frequency (IF) directly.
The AD6623 synthesizes multicarrier and multistandard digital
signals to drive these TxDACs. The RAM-based architecture
allows easy reconfiguration for multimode applications. Modulation, pulse-shaping and anti-imaging filters, static equalization,
and tuning functions are combined in a single, cost-effective
device. Digital IF signal processing provides repeatable manufacturing, higher accuracy, and more flexibility than comparable
high dynamic range analog designs.
The AD6623 has four identical digital TSPs complete with
synchronization circuitry and cascadable wideband channel
summation. AD6623 is pin compatible to AD6622 and can
operate in AD6622-compatible control register mode.
The AD6623 utilizes a 3.3 V I/O power supply and a 2.5 V core
power supply. All I/O pins are 5 V tolerant. All control registers
and coefficient values are programmed through a generic microprocessor interface. Intel and Motorola microprocessor bus
modes are supported. All inputs and outputs are LVCMOS
compatible.
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Each TSP has five cascaded signal processing elements: a
programmable interpolating RAM Coefficient Filter (RCF), a
programmable Scale and Power Ramp, a programmable fifth
order Cascaded Integrator Comb (CIC5) interpolating filter,
a flexible second order Resampling Cascaded Integrator Comb
filter (rCIC2), and a Numerically Controlled Oscillator/Tuner
(NCO).
The outputs of the four TSPs are summed and scaled on-chip. In
multicarrier wideband transmitters, a bidirectional bus allows the
Parallel (wideband) IF Input/Output to drive a second DAC. In
this operational mode two AD6623 channels drive one DAC and
the other two AD6623 channels drive a second DAC. Multiple
AD6623s may be combined by driving the INOUT[17:0] of the
succeeding with the OUT[17:0] of the preceding chip. The
INOUT[17:0] can alternatively be masked off by software to
allow preceding AD6623’s outputs to be ignored.
Each channel accepts input data from independent serial ports
that may be connected directly to the serial port of Digital Signal Processor (DSP) chips.
The RCF implements any one of the following functions: Interpolating Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter, /4-DQPSK
modulator, 8-PSK modulator, or 3/8-8-PSK modulator, GMSK
modulator, and QPSK modulator. Each AD6623 channel can
be dynamically switched between the GMSK modulation mode
and the 3/8-8-PSK modulation mode in order to support the
GSM/EDGE standard. The RCF also implements an Allpass
Phase Equalizer (APE) which meets the requirements of IS-95-A/B
standard (CDMA transmission).
The programmable Scale and Power Ramp block allows power
ramping on a time-slot basis as specified for some air-interface
standards (e.g., GSM, EDGE). A fine scaling unit at the programmable FIR filter output allows an easy signal amplitude
level adjustment on time slot basis.
The CIC5 provides integer rate interpolation from 1 to 32 and
coarse anti-image filtering. The rCIC2 provides fractional rate
interpolation from 1 to 4096 in steps of 1/512. The wide range
of interpolation factors in each CIC filter stage and a highly
flexible resampler incorporated into rCIC2 makes the AD6623
useful for creating both narrowband and wideband carriers in a
high-speed sample stream.
The high resolution 32-bit NCO allows flexibility in frequency
planning and supports both digital and analog air interface
standards. The high speed NCO tunes the interpolated complex
signal from the rCIC2 to an IF channel. The result may be real
or complex. Multicarrier phase synchronization pins and phase
offset registers allow intelligent management of the relative
phase of independent RF channels. This capability supports the
requirements for phased array antenna architectures and management of the wideband peak/power ratio to minimize clipping
at the DAC.
The wideband Output Ports can deliver real or complex data.
Complex words are interleaved into real (I) and imaginary (Q)
parts at half the master clock rate.
REV. A
–3–
AD6623
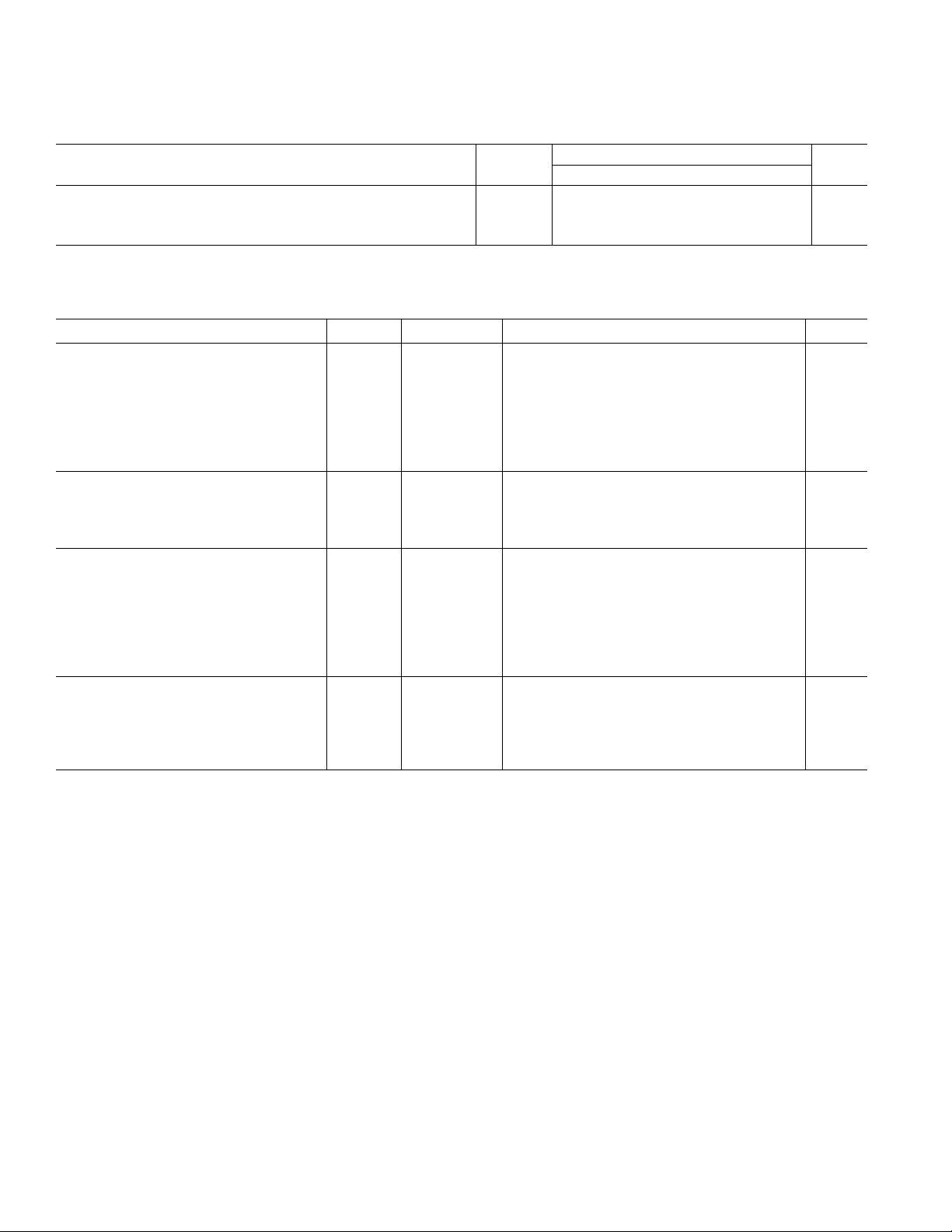
AD6623–SPECIFICATIONS
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Test AD6623
Parameter Level Min Typ Max Unit
VDD IV 2.25 2.5 2.75 V
VDDIO IV 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
T
AMBIENT
IV –40 +25 +85 °C
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Parameter (Conditions) Temp Test Level Min Typ Max Unit
LOGIC INPUTS (5 V TOLERANT)
Logic Compatibility Full 3.3 V CMOS
Logic “1” Voltage Full IV 2.0 5.0 V
Logic “0” Voltage Full IV –0.3 +0.8 V
Logic “1” Current Full IV 1 10 µA
Logic “0” Current Full IV 0 10 µA
Input Capacitance 25°CV 4 pF
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Logic Compatibility Full 3.3 V CMOS/TTL
Logic “1” Voltage (I
Logic “0” Voltage (IOL = 0.25 mA) Full IV 0.2 0.4 V
IDD SUPPLY CURRENT
GSM Example: CORE V 232 mA
I/O 56 mA
IS-136 Example: CORE V 207 mA
I/O 55 mA
WBCDMA Example V TBD mA
Sleep Mode Full IV TBD mA
POWER DISSIPATION
GSM Example V 740 mW
IS-136 Example V 700 mW
WBCDMA Example V TBD mW
Sleep Mode Full IV TBD mW
See the Thermal Management section of the data sheet for further details.
= 0.25 mA) Full IV 2.0 VDD – 0.2 V
OH
–4–
REV. A
AD6623
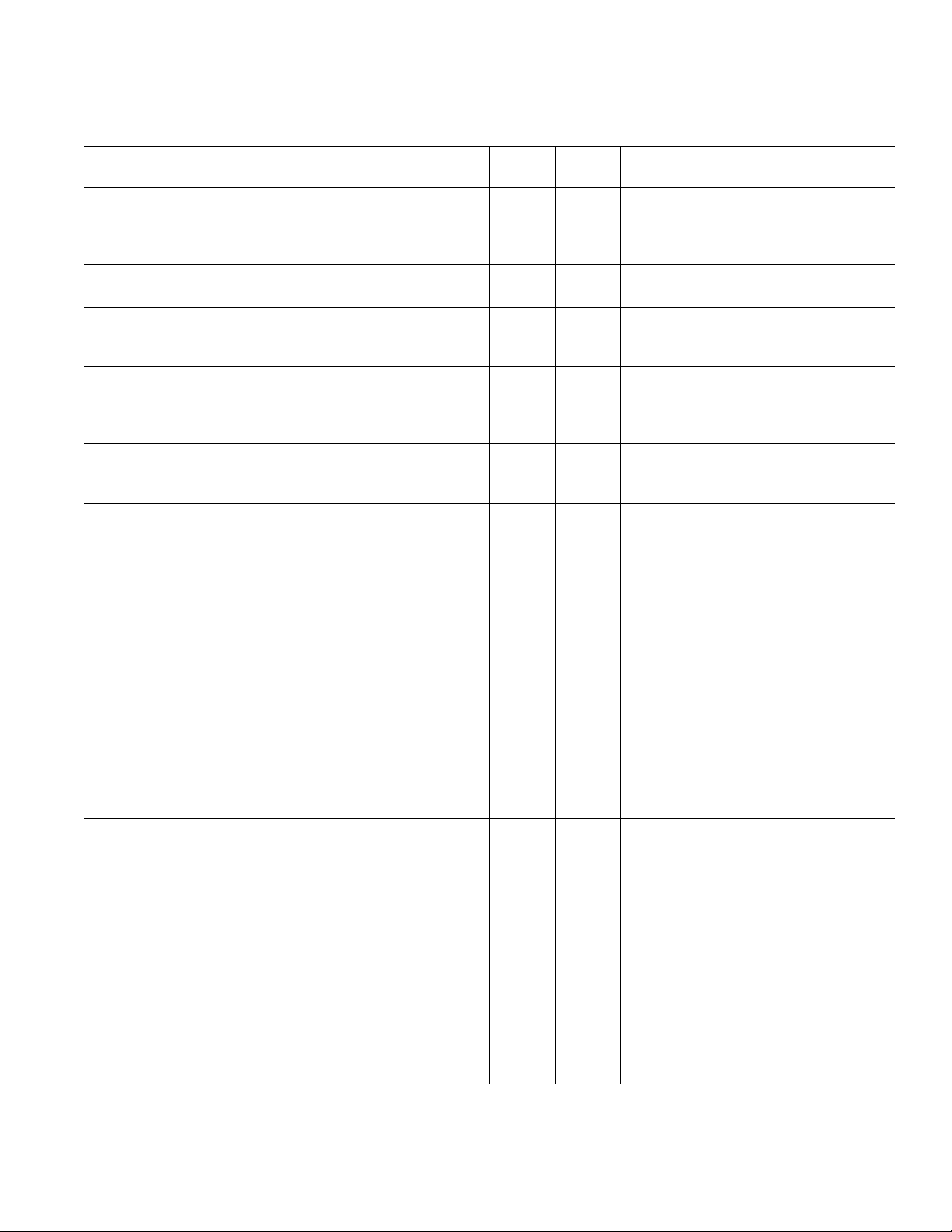
GENERAL TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
1, 2
Test AD6623AS
Parameter (Conditions) Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
CLK Timing Requirements:
t
CLK
t
CLKL
t
CLKH
CLK Period Full I 9.6 ns
CLK Width Low Full IV 3 ns
CLK Width High Full IV 3 0.5 × t
CLK
ns
RESET Timing Requirement:
t
RESL
RESET Width Low Full I 30.0 ns
Input Data Timing Requirements:
t
SI
t
HI
INOUT[17:0], QIN to ↑CLK Setup Time Full IV 1 ns
INOUT[17:0], QIN to ↑CLK Hold Time Full IV 2 ns
Output Data Timing Characteristics:
t
DO
↑CLK to OUT[17:0], INOUT[17:0],
QOUT Output Delay Time Full IV 2 6 ns
t
DZO
OEN HIGH to OUT[17:0] Active Full IV 3 7.5 ns
SYNC Timing Requirements:
t
SS
t
HS
Master Mode Serial Port Timing Requirements (SCS = 0):
Switching Characteristics
t
DSCLK1
t
DSCLKH
t
DSCLKL
SYNC(0, 1, 2, 3) to ↑CLK Setup Time Full IV 1 ns
SYNC(0, 1, 2, 3) to ↑CLK Hold Time Full IV 2 ns
3
↑CLK to ↑SCLK Delay (divide by 1) Full IV 4 10.5 ns
↑CLK to ↑SCLK Delay (for any other divisor) Full IV 5 13 ns
↑CLK to ↓SCLK Delay
(divide by 2 or even number) Full IV 3.5 9 ns
t
DSCLKLL
↓CLK to ↓SCLK Delay
(divide by 3 or odd number) Full IV 4 10 ns
Channel is Self-Framing
t
SSDI0
t
HSDI0
t
DSFO0A
SDIN to ↑SCLK Setup Time Full IV 1.7 ns
SDIN to ↑SCLK Hold Time Full IV 0 ns
↑SCLK to SDFO Delay Full IV 0.5 3.5 ns
Channel is External-Framing
t
SSFI0
t
HSFI0
t
SSDI0
t
HSDI0
t
DSFO0B
Slave Mode Serial Port Timing Requirements (SCS = 1):
Switching Characteristics
t
SCLK
t
SCLKL
t
SCLKH
SDFI to ↑SCLK Setup Time Full IV 2 ns
SDFI to ↑SCLK Hold Time Full IV 0 ns
SDIN to ↑SCLK Setup Time Full IV 2 ns
SDIN to ↑SCLK Hold Time Full IV 0 ns
↑SCLK to SDFO Delay Full IV 0.5 3 ns
3
SCLK Period Full IV 2 t
CLK
ns
SCLK Low Time Full IV 3.5 ns
SCLK High Time Full IV 3.5 ns
Channel is Self-Framing
t
SSDH
t
HSDH
t
DSFO1
SDIN to ↑SCLK Setup Time Full IV 1 ns
SDIN to ↑SCLK Hold Time Full IV 2.5 ns
↑SCLK to SDFO Delay Full IV 4 10 ns
Channel is External-Framing
t
SSFI1
t
HSFI1
t
SSDI1
t
HSDI1
t
DSFO1
NOTES
1
All Timing Specifications valid over VDD range of 2.375 V to 2.675 V and VDDIO range of 3.0 V to 3.6 V.
2
C
= 40 pF on all outputs (unless otherwise specified).
LOAD
3
The timing parameters for SCLK, SDIN, SDFI, SDFO, and SYNC apply to all four channels (A, B, C, and D).
Specifications subject to change without notice.
SDFI to ↑ SCLK Setup Time Full IV 2 ns
SDFI to ↑SCLK Hold Time Full IV 1 ns
SDIN to ↑SCLK Setup Time Full IV 1 ns
SDIN to ↑SCLK Hold Time Full IV 2.5 ns
↓SCLK to SDFO Delay Full IV 10 ns
REV. A
–5–
AD6623
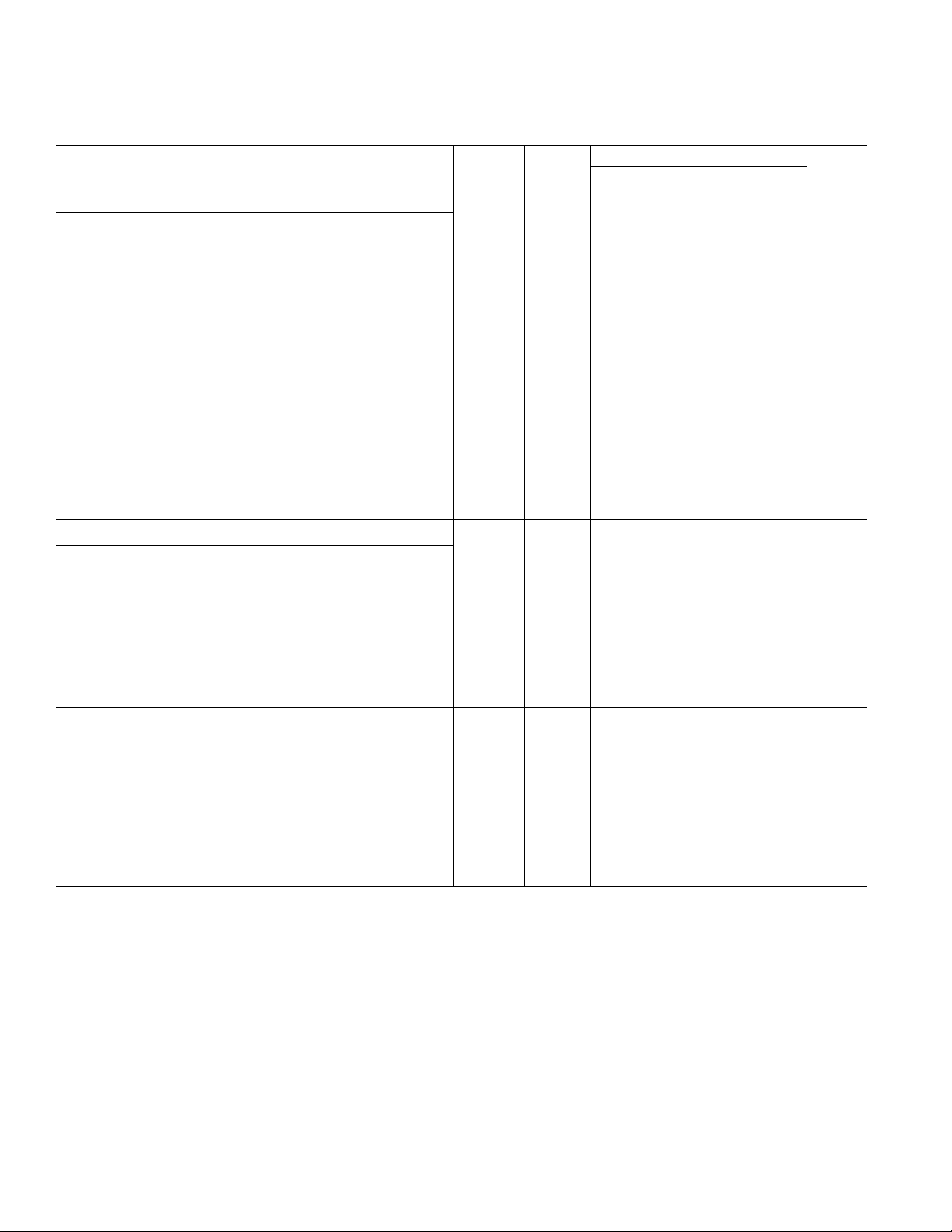
MICROPROCESSOR PORT TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
1, 2
Test AD6623AS
Parameter (Conditions) Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
MICROPROCESSOR PORT, MODE INM (MODE = 0)
MODE INM Write Timing:
t
SC
t
HC
t
HWR
t
SAM
t
HAM
t
DRDY
t
ACC
Control3 to ↑CLK Setup Time Full IV 4.5 ns
Control3 to ↑CLK Hold Time Full IV 2.0 ns
WR(RW) to RDY(DTACK) Hold Time Full IV 8.0 ns
Address/Data to WR(RW) Setup Time Full IV 3.0 ns
Address/Data to RDY(DTACK) Hold Time Full IV 2.0 ns
WR(RW) to RDY(DTACK) Delay Full IV 4.0 ns
WR(RW) to RDY(DTACK) High Delay Full IV 4 × t
CLK
5 × t
CLK
9 × t
CLK
ns
MODE INM Read Timing:
t
SC
t
HC
t
SAM
t
HAM
t
ZOZ
t
DD
t
DRDY
t
ACC
Control3 to ↑CLK Setup Time Full IV 4.5 ns
Control3 to ↑CLK Hold Time Full IV 2.0 ns
Address to RD(DS) Setup Time Full IV 3.0 ns
Address to Data Hold Time Full IV 2.0 ns
Data Three-State Delay Full IV ns
RDY(DTACK) to Data Delay Full IV ns
RD(DS) to RDY(DTACK) Delay Full IV 4.0 ns
RD(DS) to RDY(DTACK) High Delay Full IV 8 × t
CLK
10 × t
CLK
13 × t
CLK
ns
MICROPROCESSOR PORT, MOTOROLA (MODE = 1)
MODE MNM Write Timing:
t
SC
t
HC
t
HDS
t
HRW
t
SAM
t
HAM
t
DDTACK
t
ACC
Control3 to ↑CLK Setup Time Full IV 4.5 ns
Control3 to ↑CLK Hold Time Full IV 2.0 ns
DS(RD) to DTACK(RDY) Hold Time Full IV 8.0 ns
RW(WR) to DTACK(RDY) Hold Time Full IV 8.0 ns
Address/Data to RW(WR) Setup Time Full IV 3.0 ns
Address/Data to RW(WR) Hold Time Full IV 2.0 ns
DS(RD) to DTACK(RDY) Delay ns
RW(WR) to DTACK(RDY) Low Delay Full IV 4 × t
CLK
5 × t
CLK
9 × t
CLK
ns
MODE MNM Read Timing:
t
SC
t
HC
t
HDS
t
SAM
t
HAM
t
ZD
t
DD
t
DDTACK
t
ACC
NOTES
1
All Timing Specifications valid over VDD range of 2.375 V to 2.675 V and VDDIO range of 3.0 V to 3.6 V.
2
C
= 40 pF on all outputs (unless otherwise specified).
LOAD
3
Specification pertains to control signals: RW, (WR), DS, (RD), CS.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
Control3 to ↑CLK Setup Time Full IV 4.0 ns
Control3 to ↑CLK Hold Time Full IV 2.0 ns
DS(RD) to DTACK(RDY) Hold Time Full IV 8.0 ns
Address to DS(RD) Setup Time Full IV 3.0 ns
Address to Data Hold Time Full IV 2.0 ns
Data Three-State Delay Full IV ns
DTACK(RDY) to Data Delay Full IV ns
DS(RD) to DTACK(RDY) Delay Full IV ns
DS(RD) to DTACK(RDY) Low Delay Full IV 8 × t
CLK
10 × t
CLK
13 × t
CLK
ns
–6–
REV. A
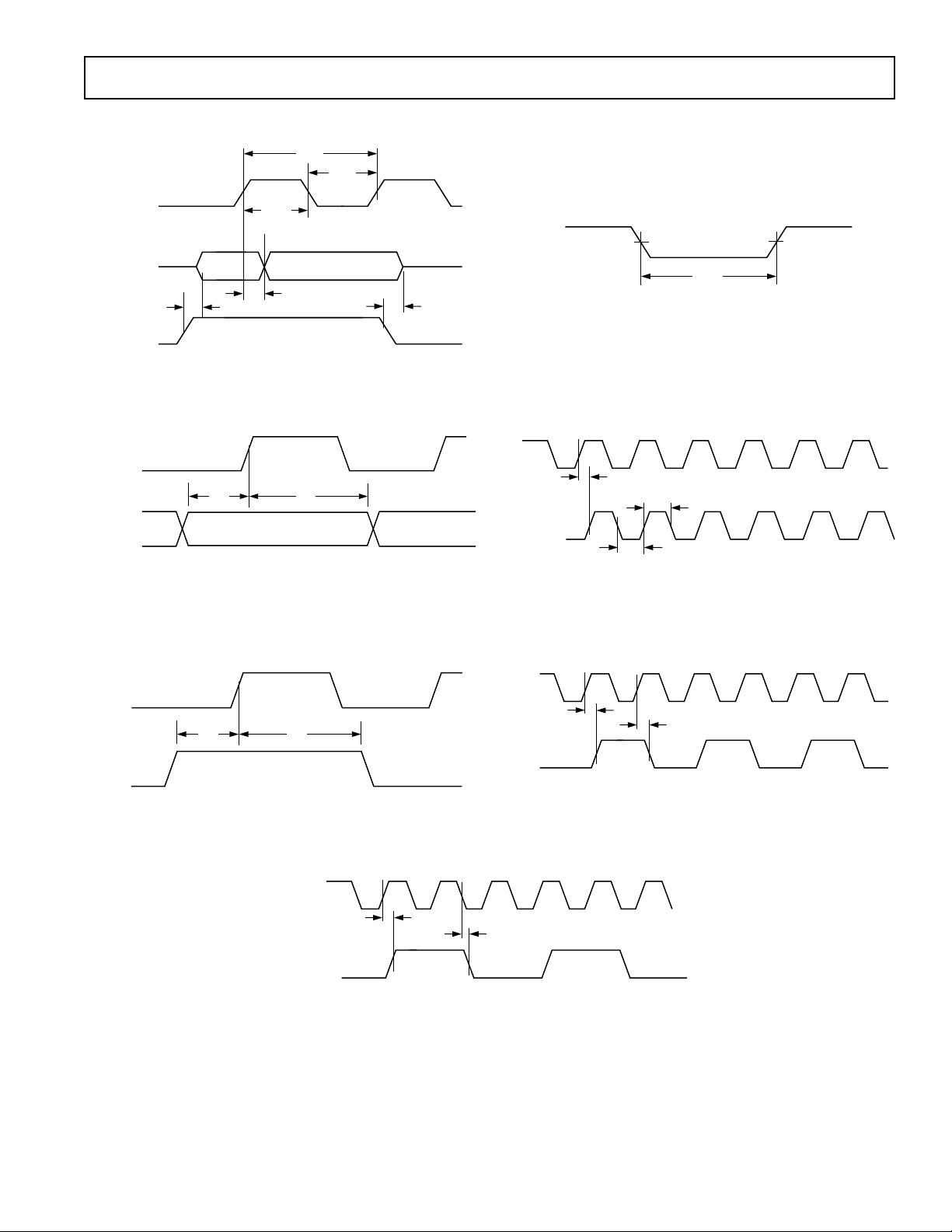
TIMING DIAGRAMS
R
CLK
INOUT[17:0]
OUT[17:0]
QOUT
t
ZO
OEN
AD6623
t
CLK
t
CLKL
t
CLKH
ESET
t
t
DO
t
ZO
RESL
Figure 1. Parallel Output Switching Characteristics
CLK
INOUT[17:0]
QIN
t
SI
t
HI
Figure 2. Wideband Input Timing
CLK
SYNC
t
SS
t
HS
Figure 3. SYNC Timing Inputs
Figure 4.
CLK
SCLK
t
DSCLKH
t
SCLKL
RESET
Timing Requirements
t
SCLKH
Figure 5. SCLK Switching Characteristics (Divide by 1)
CLK
t
DSCLKH
SCLK
t
DSCLKL
Figure 6. SCLK Switching Characteristic (Divide by 2 or
EVEN Integer)
CLK
t
DSCLKH
SCLK
t
DSCLKLL
Figure 7. SCLK Switching Characteristic (Divide by 3 or ODD Integer)
REV. A
–7–
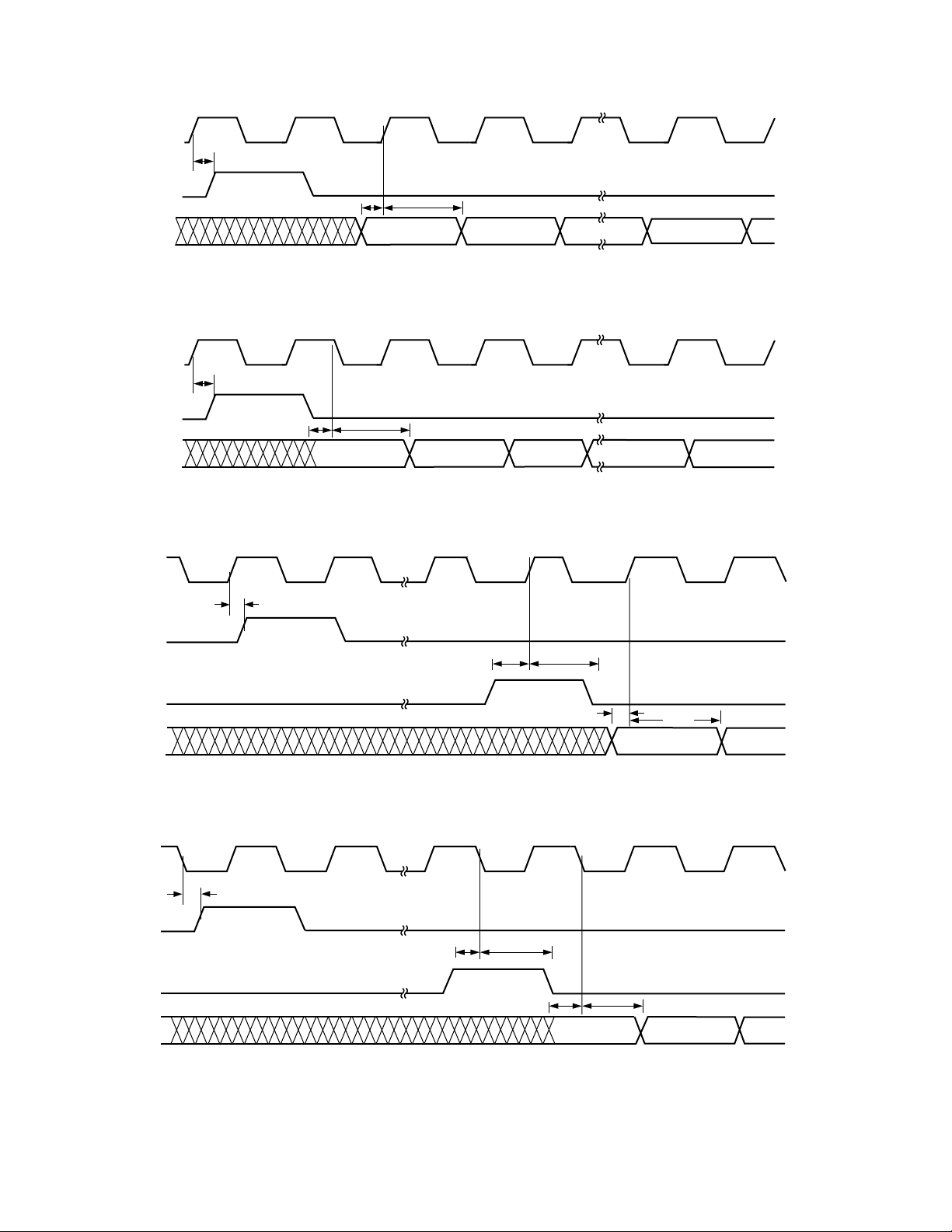
AD6623
SCLK
SDFO
SDIN
SCLK
SDFO
SDIN
t
DSFO0A
t
SSDI0
DATA n
t
HSDI0
Figure 8. Serial Port Timing, Master Mode (SCS = 0), Channel is Self-Framing
t
DSFO1
t
SSDI1
DATA n
t
HSDI1
Figure 9. Serial Port Timing, Slave Mode (SCS = 1), Channel is Self-Framing
SCLK
SDFO
SDFI
SDIN
SCLK
SDFO
SDFI
SDIN
nCLKs
t
DSFO0B
t
SSDI0
t
HSFI0
t
DATA n
HSDI0
t
SSFI0
Figure 10. Serial Port Timing, Master Mode (SCS = 0), Channel is External-Framing
nCLKs
t
DSFO1
t
SSDI1
t
HSFI1
DATA n
t
HSDI1
t
SSFI1
Figure 11. Serial Port Timing, Slave Mode (SCS = 1), Channel is External-Framing
–8–
REV. A
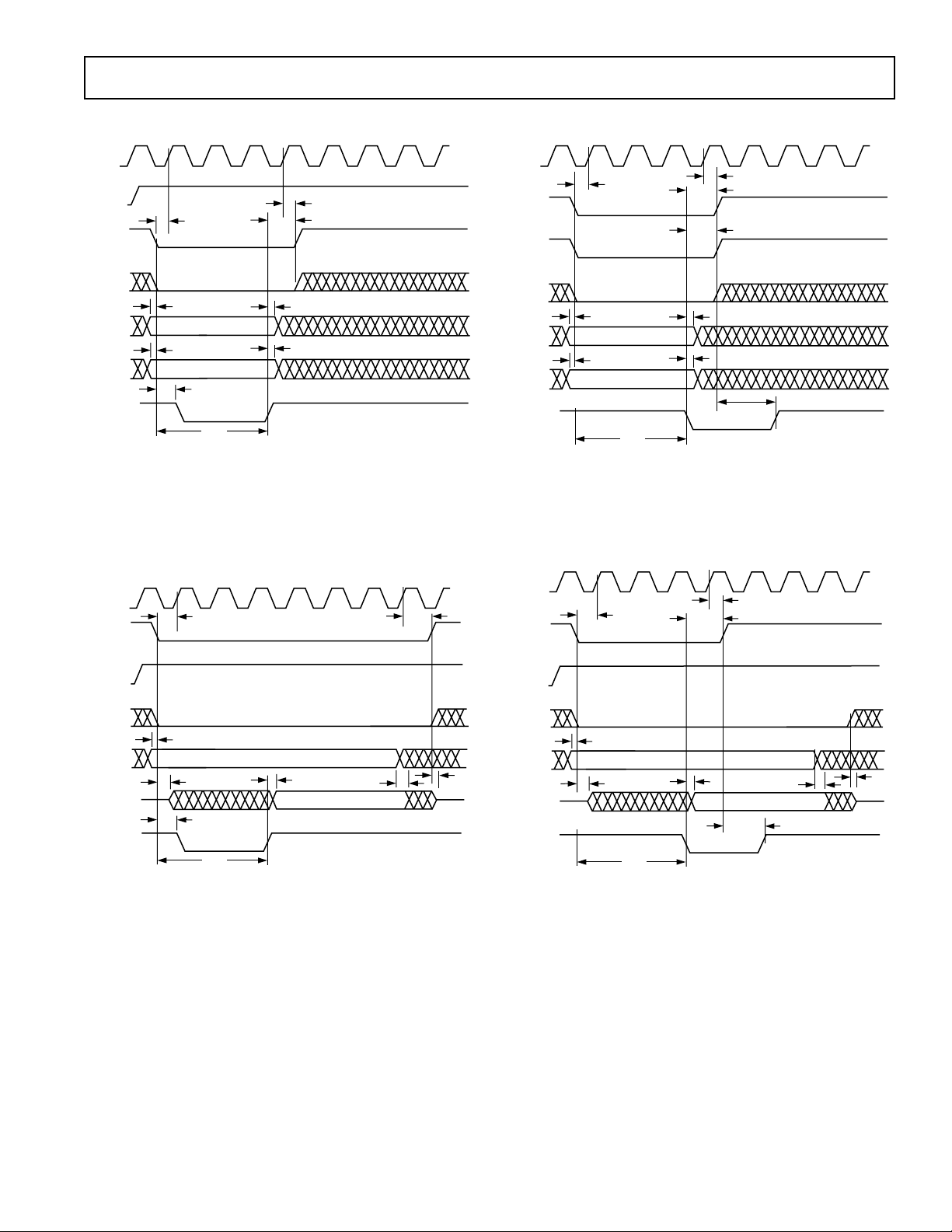
AD6623
[
CLK
DS (RD)
RW (WR)
A[2:0]
D[7:0]
DTACK
(RDY)
t
SC
t
SAM
t
ZD
VA LID DATA
VA LID ADDRESS
t
ACC
t
HC
CS
t
ZD
t
HAM
t
DD
t
DDTACK
t
HDS
NOTES
1.
t
ACC
ACCESS TIME DEPENDS ON THE ADDRESS ACCESSED. ACCESS TIME IS
MEASURED FROM FE OF DS TO THE FE OF DTACK.
2.
t
ACC
REQUIRES A MAXIMUM 13 CLK PERIODS.
TIMING DIAGRAMS—INM MICROPORT MODE
CLK
RD (DS)
t
WR (RW)
CS
A[2:0]
D[7:0]
RDY
(DTACK)
NOTES
t
ACCESS TIME DEPENDS ON THE ADDRESS ACCESSED. ACCESS TIME IS
1.
ACC
MEASURED FROM FE OF WR TO TH E R E OF RDY.
t
REQUIRES A MAXIMUM 9 CLK PERIODS.
2.
ACC
SC
VALI D D ATA
t
DRDY
t
ACC
t
t
HAM
HAM
t
SAM
VA LID ADDRESS
t
SAM
t
HC
t
HWR
Figure 12. INM Microport Write Timing Requirements
TIMING DIAGRAMS—MNM MICROPORT MODE
CLK
t
t
SC
t
VALI D D ATA
t
ACC
t
t
HDS
HAM
HAM
DS (RD)
RW (WR)
CS
t
SAM
A[2:0]
D[7:0]
DTACK
(RDY)
NOTES
t
1.
ACC
MEASURED FROM FE OF DS TO THE FE OF DTACK.
t
2.
ACC
VA LID ADDRESS
t
SAM
ACCESS TIME DEPENDS ON THE ADDRESS ACCESSED. ACCESS TIME IS
REQUIRES A MAXIMUM 9 CLK PERIODS.
HC
t
HRW
t
DDTACK
Figure 14. MNM Microport Write Timing Requirements
CLK
t
t
SAM
SC
t
ZD
t
DRDY
t
ACC
RD (DS)
WR (RW)
CS
A[2:0]
D[7:0]
RDY
(DTACK)
NOTES
t
ACCESS TIME DEPENDS ON THE ADDRESS ACCESSED. ACCESS
1.
ACC
TIME IS MEASURED FROM FE OF WR TO T HE RE OF RDY.
t
REQUIRES A MAXIMUM OF 13 CLK PERIODS AND APPLIES TO
2.
ACC
2:0] = 7, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1
A
Figure 13. INM Microport Read Timing Requirements
REV. A
VA LID ADDRESS
t
DD
VA LID DATA
t
HAM
t
HC
t
ZD
Figure 15. MNM Microport Read Timing Requirements
–9–
AD6623
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
VDDIO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +3.6 V
VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +2.75 V
Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +5 V (5 V Tolerant)
Output Voltage Swing . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to VDDIO + 0.3 V
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
128-Lead MQFP with Internal Heat Spreader:
= 28.1°C/W, no airflow
JA
= 22.6°C/W, 200 lfpm airflow
JA
= 20.5°C/W, 400 lfpm airflow
JA
Load Capacitance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200 pF
Junction Temperature Under Bias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125°C
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C (Ambient)
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (5 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280°C
*Stresses greater than those listed above may cause permanent damage to the
device. These are stress ratings only; functional operation of the devices at these
or any other conditions greater than those indicated in the operational sections of
this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions
for extended periods may affect device reliability.
196-Lead BGA:
= 26.3°C/W, no airflow
JA
= 22°C/W, 200 lfpm airflow
JA
Thermal measurements made in the horizontal position on a
4-layer board.
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
I. 100% Production Tested
II. 100% Production Tested at 25°C, and Sample Tested at
Specified Temperatures
III. Sample Tested Only
IV. Parameter Guaranteed by Design and Analysis
V. Parameter is Typical Value Only
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD6623AS –40°C to +85°C (Ambient) 128-Lead MQFP (Plastic Quad Flatpack) S-128
AD6623ABC –40°C to +85°C (Ambient) 196-Lead CSPBGA (Chip Scale Package Ball Grid Array) BC-196
AD6623S/PCB MQFP Evaluation Board with AD6623 and Software
AD6623BC/PCB CSPBGA Evaluation Board with AD6623 and Software
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD6623 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
–10–
REV. A
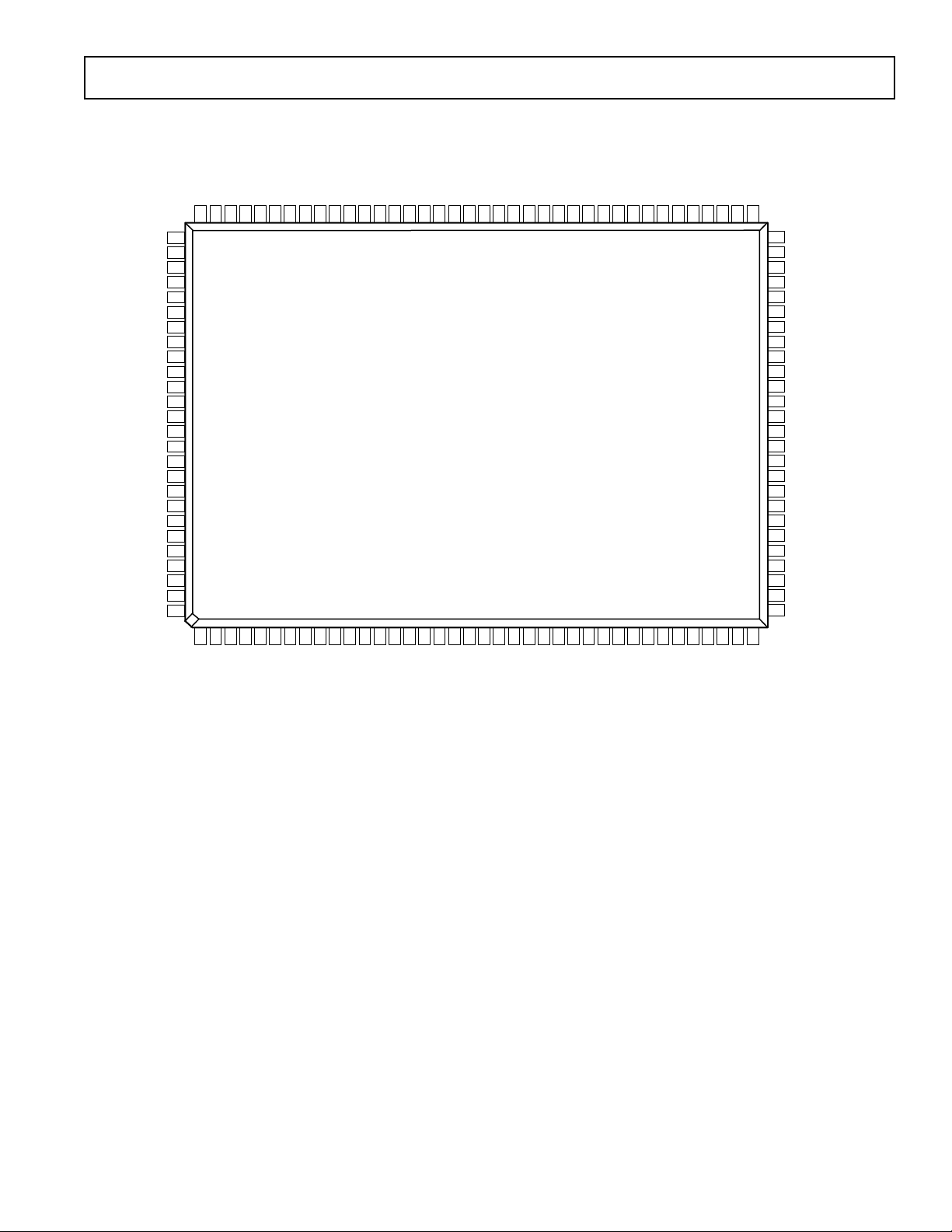
GND
VDD
SDFIA
TMS
TDO
TDI
SCLKA
VDDIO
SDFOA
SDINA
SCLKB
SDFOB
SDFIB
GND
SDFIC
SDINB
SCLKC
SDFOC
SDINC
VDDIO
SCLKD
SDFOD
SDIND
SDFID
VDD
GND
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
GND
102
1
GND
TCK
101
2
OEN
TRST
100
3
GND
GND
99
4
GND
GND
98
5
GND
INOUT0
GND
97
769
OUT0
OUT1
GND
95
8
OUT2
INOUT1
INOUT2
93
94
10
GND
OUT3
INOUT3
INOUT4
92
12
11
OUT4
OUT5
PIN CONFIGURATION
128-Lead MQFP
VDDIO
INOUT5
INOUT6
INOUT7
INOUT8
GND
GND
GND
INOUT9
90918889879686
83
82
84
AD6623
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
16
15
13
OUT6
14
VDDIO
OUT7
OUT8
1817201922
GND
OUT9
OUT10
GND
21
GND
INOUT11
INOUT12
VDDIO
INOUT10
78
81
79
80
24232625282730
OUT11
OUT12
OUT13
OUT14
INOUT13
INOUT14
INOUT15
INOUT16
SYNC3
GND
INOUT17
QIN
SYNC2
76
7785757374717269706768
343336
31
32
D7
GND
GND
VDDIO
OUT15
29
OUT16
OUT17
GND
QOUT
GND
CLK
353837
GND
GND
VDD
66
D6
GND
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
GND
AD6623
GND
SYNC1
SYNC0
RESET
CS
VDD
A0
A1
A2
MODE
GND
GND
GND
RW(WR)
DTACK(RDY)
DS(RD)
D0
VDD
D1
D2
D3
D4
GND
VDDIO
D5
GND
REV. A
–11–
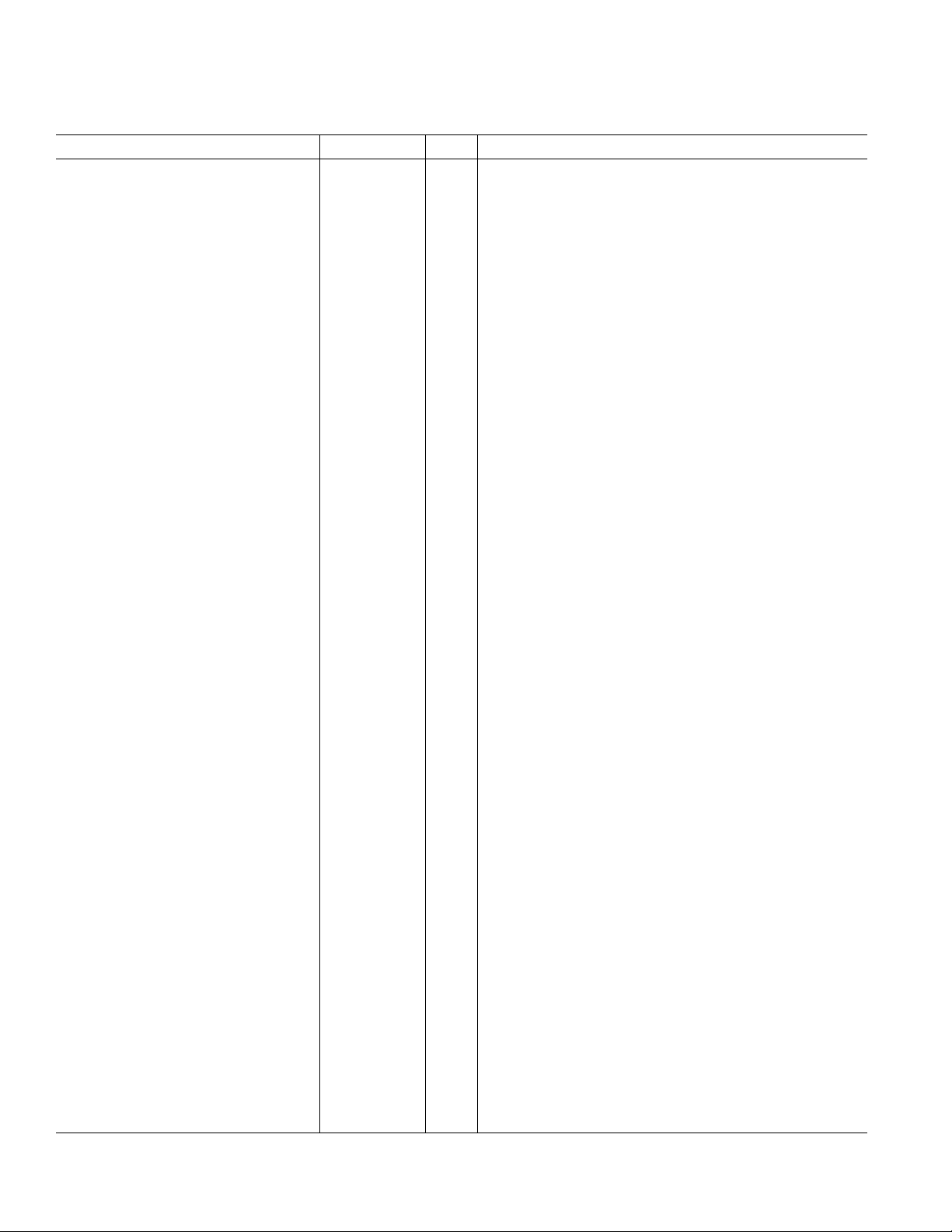
AD6623
128-LEAD FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Number Mnemonic Type Description
1, 3–5, 9, 19–21, 31, 32, 34–36, 38, 39, GND P Ground Connection
42, 52–54, 64–65, 68, 72, 83–85, 95, 96,
98, 99, 102, 103, 116, 128
2 OEN
29, 28, 27, 25, 24, 23, 22, 18, 17, 16, 15, OUT[17:0] O/T Parallel Output Data
13, 12, 11, 10, 8, 7, 6
47, 59, 66, 104, 127 VDD P 2.5 V Supply
14, 26, 41, 78, 90, 110, 122 VDDIO P 3.3 V Supply
30 QOUT O/T When HIGH indicates Q Output Data (Complex Output Mode)
33, 37, 40, 43, 44, 45, 46, 48 D[7:0] I/O/T Bidirectional Microport Data
49 DS (RD)IINM Mode: Read Signal, MNM Mode: Data Strobe Signal
50 DTACK (RDY) O Acknowledgment of a Completed Transaction (Signals when
51 RW (WR)IActive HIGH Read, Active Low Write
55 MODE I
56, 57, 58 A[2:0] I Microport Address Bus
60 CS IChip Select, Active low enable for µP Access
61 RESET
62 SYNC0
63 SYNC1
67 CLK
69 SYNC2
70 QIN
71, 74–77, 79–82, 86–89, 91–94, 97 INOUT[17:0]1I/O Wideband Input/Output Data (Allows Cascade of Multiple
73 SYNC3
100 TRST
101 TCK
105 SDFIA I Serial Data Frame Input—Channel A
106 TMS
107 TDO O Test Data Output
108 TDI
109 SCLKA I/O Bidirectional Serial Clock—Channel A
111 SDFOA O Serial Data Frame Sync Output—Channel A
112 SDINA
113 SCLKB I/O Bidirectional Serial Clock—Channel B
114 SDFOB O Serial Data Frame Sync Output—Channel B
115 SDFIB I Serial Data Frame Input —Channel B
117 SDFIC I Serial Data Frame Input—Channel C
118 SDINB
119 SCLKC I/O Bidirectional Serial Clock—Channel C
120 SDFOC O Serial Data Frame Sync Output—Channel C
121 SDINC
123 SCLKD I/O Bidirectional Serial Clock—Channel D
124 SDFOD O Serial Data Frame Sync Output—Channel D
125 SDIND
126 SDFID I Serial Data Frame Input—Channel D
NOTES
1
Pins with a Pull-Down resistor of nominal 70 kΩ.
2
Pins with a Pull-Up resistor of nominal 70 kΩ.
1
IActive High Output Enable Pin
µP Port Is Ready for an Access) Open Drain, Must Be
Pulled Up Externally
Sets Microport Mode: MODE = 1, MNM Mode;
MODE = 0,
2
1
1
1
1
1
IActive Low Reset Pin
ISYNC Signal for Synchronizing Multiple AD6623s
ISYNC Signal for Synchronizing Multiple AD6623s
I Input Clock
ISYNC Signal for Synchronizing Multiple AD6623s
I
When HIGH indicates Q input data (Complex Input Mode)
INM Mode
AD6623 Chips In a System)
1
2
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
ISYNC Signal for Synchronizing Multiple AD6623s
ITest Reset Pin
ITest Clock Input
ITest Mode Select
ITest Data Input
I Serial Data Input—Channel A
I Serial Data Input—Channel B
I Serial Data Input—Channel C
I Serial Data Input—Channel D
–12–
REV. A
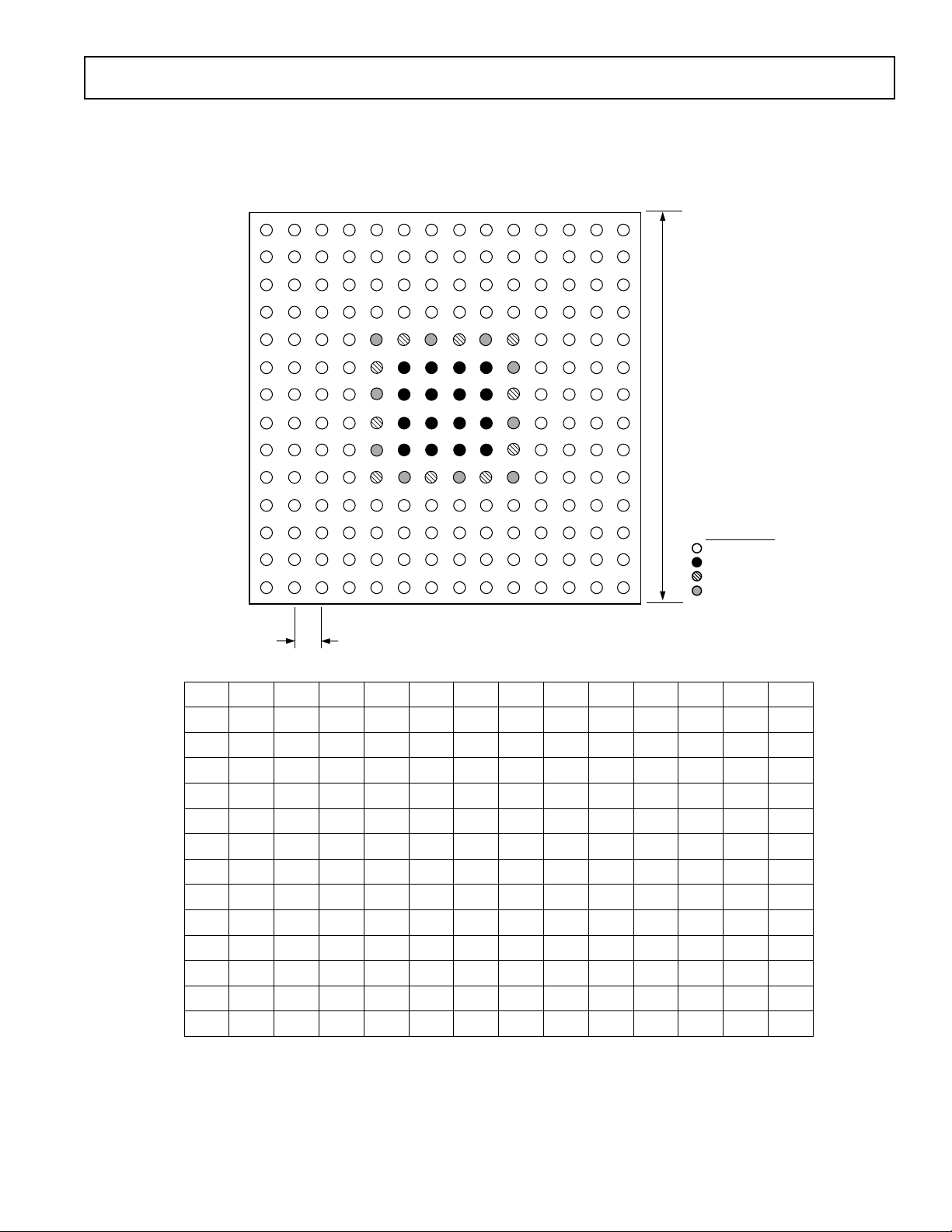
PIN CONFIGURATION
196-Lead CSPBGA
AD6623
1234567891011 12 13 14
TOP VIEW
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
15mm sq.
BALL LEGEND
I/O
GROUND
CORE POWER
RING POWER
1
NC
A
B
C
OUT2
D
E
OUT5
F
OUT8
G
OUT9
H
OUT11
J
OUT14
K
OUT16
L
QOUT
M
N
NC
P
NC = NO CONNECT
2
OUT1
OUT4
OUT7
OUT10
OUT13
D6
3
OUT0
OUT3
OUT6
OUT12
OUT17
OUT15
D7
1.0mm
4
SDFID
OEN
SDFOD
D4
D5
D2
5
SDINC
SDIND
VDDIO
VDD
VDDIO
VDD
VDDIO
VDD
D1
D3
6
SDINB
SDFOC
SCLKD
VDD
GND
GND
GND
GND
VDDIO
DTACK
(RDY)
D0
DS(RD)
7
SDFOB
SDFIC
SCLKC
VDDIO
GND
GND
GND
GND
VDD
MODE
(ALE)
RW (WR)
8
SCLKB
SDINA
SDFIB
VDD
GND
GND
GND
GND
VDDIO
A1
9
SCLKA
TDI
SDFOA
VDDIO
GND
GND
GND
GND
VDD
RESET
A0
A2
10
TDO
TMS
VDD
VDDIO
VDD
VDDIO
VDD
VDDIO
SYNC0
CS
11
SDFIA
TRST
SYNC1
12
TCK
IN2
IN3
IN6
IN12
IN16
QIN
13
IN5
IN8
IN11
IN14
IN17
CLK
14
NC
IN0
IN1
IN4
IN7
IN9
IN10
IN13
IN15
SYNC3
SYNC2
NC
REV. A
–13–
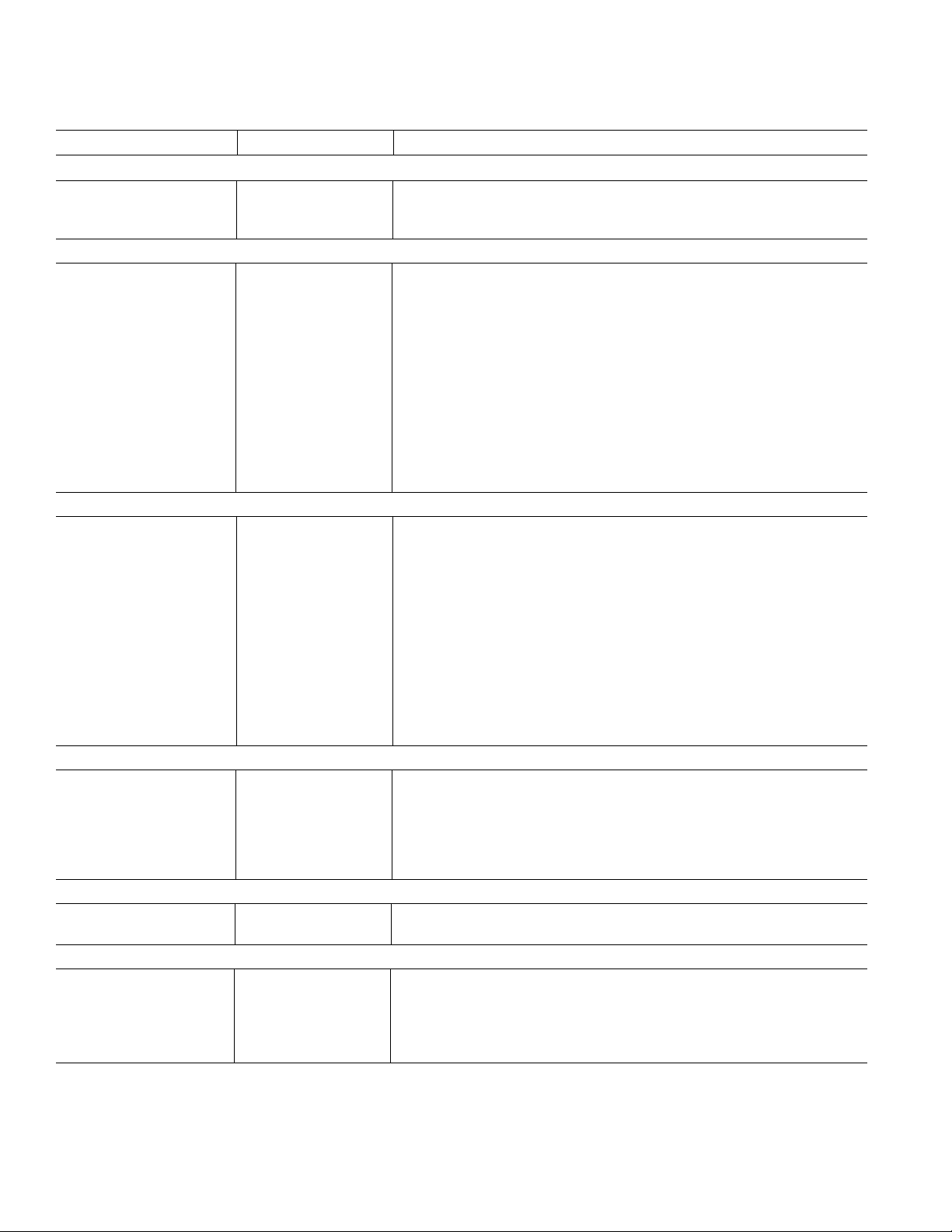
AD6623
196-LEAD FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Mnemonic Type Function
POWER SUPPLY
VDD P 2.5 V Supply
VDDIO P 3.3 V IO Supply
GND G Ground
INPUTS
INOUT[17:0]
1
QIN
RESET
1
CLK
SYNC0
SYNC1
SYNC2
SYNC3
SDINA
SDINB
SDINC
SDIND
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
CS IActive LOW Chip Select
CONTROL
SCLKA I/O Bidirectional Serial Clock—Channel A
SCLKB I/O Bidirectional Serial Clock—Channel B
SCLKC I/O Bidirectional Serial Clock—Channel C
SCLKD I/O Bidirectional Serial Clock—Channel D
SDFOA O Serial Data Frame Sync Output—Channel A
SDFOB O Serial Data Frame Sync Output—Channel B
SDFOC O Serial Data Frame Sync Output—Channel C
SDFOD O Serial Data Frame Sync Output—Channel D
SDFIA I Serial Data Frame Input—Channel A
SDFIB I Serial Data Frame Input—Channel B
SDFIC I Serial Data Frame Input—Channel C
SDFID I Serial Data Frame Input—Channel D
1
OEN
MICROPORT CONTROL
D[7:0] I/O/T Bidirectional Microport Data
A[2:0] I Microport Address Bus
DS (RD)IActive Low Data Strobe (Active Low Read)
DTACK (RDY)
2
RW (WR)IRead Write (Active Low Write)
MODE I Intel or Motorola Mode Select
OUTPUTS
OUT[17:0] O Wideband Output Data
QOUT O When HIGH Indicates Q Output Data (Complex Output Mode)
JTAG AND BIST
2
TRST
1
TCK
2
TMS
TDO O/T Test Data Output
1
TDI
NOTES
1
Pins with a Pull-Down resistor of nominal 70 kΩ.
2
Pins with a Pull-Up resistors of nominal 70 kΩ.
I/O A Input Data (Mantissa)
IWhen HIGH Indicates Q Input Data (Complex Input Mode)
IActive LOW Reset Pin
I Input Clock
IAll Sync Pins Go to All Four Output Channels
IAll Sync Pins Go to All Four Output Channels
IAll Sync Pins Go to All Four Output Channels
IAll Sync Pins Go to All Four Output Channels
I Serial Data Input—Channel A
I Serial Data Input—Channel B
I Serial Data Input—Channel C
I Serial Data Input—Channel D
IActive High Output Enable Pin
O/T Active Low Data Acknowledge (Microport Status Bit)
ITest Reset Pin (Active Low)
ITest Clock Input
ITest Mode Select Input
ITest Data Input
–14–
REV. A

AD6623
CONTROL REGISTER ADDRESS NOTATION
Register address notation and bit assignment referred to throughout
this data sheet are as follows: There are eight, one-digit “External”
register addresses in decimal format. “Internal” address notation
(read from left to right) begins with “0x”, meaning the address
that follows is hexadecimal. The next three characters represent
the address. The first number or character is the MSB of the
address. If an “n” is present, its value can be 1, 2, 3, or 4 and it
depends upon the channel that is being addressed (A, B, C, or D).
The remaining two digits preceding the colon (if present) are the
LSBs of the address. If a colon follows the address, then the
succeeding digits tell the user what bit number(s) is/are involved
in decimal format. For example, 0xn24:7-0.
SERIAL DATA PORT
The AD6623 has four independent Serial Ports (A, B, C, and D),
and each accepts data to its own channel (A, B, C, or D) of the
device. Each Serial Port has four pins: SCLK (Serial CLocK),
SDFO (Serial Data Frame Out), SDFI (Serial Data Frame In),
and SDIN (Serial Data INput). SDFI and SDIN are inputs, SDFO
is an output, and SCLK is either input or output depending on
the state of SCS (Serial Clock Slave: 0xn16, Bit 4). Each channel
can be operated either as a Master or Slave channel depending
upon SCS. The Serial Port can be self-framing or accept external
framing from the SFDI pin or from the previous adjacent channel
(0xn16, Bits 7 and 6).
Serial Master Mode (SCS = 0)
In master mode, SCLK is created by a programmable internal
counter that divides CLK. When the channel is “sleeping,” SCLK
held low. SCLK becomes active on the first rising edge of CLK
is
after Channel
address 4). Once
the CLK frequency
sleep is removed (D0 through D3 of external
active, the SCLK frequency is determined by
and the SCLK divider, according to the
equations below.
AD6623 mode:
f
CLK
SCLKdivider
+1
(1)
f
SCLK
=
AD6622 mode:
f
CLK
SCLKdivider
(2)
f
SCLK
=
×+21()
The SCLK divider is a 5-bit unsigned value located at Internal
Channel Address 0xn0D (Bits 4–0), where “n” is 1, 2, 3, or 4 for
the chosen channel A, B, C, or D, respectively. The user must
select the SCLK divider to insure that SCLK is fast enough to
accept full input sample words at the input sample rate. See the
design example at the end of this section. The maximum SCLK
frequency is equal to the CLK when operating in AD6623 mode
serial clock master. When operating in AD6622 compatible mode,
the maximum SCLK frequency is one-half the CLK. The minimum
SCLK frequency is 1/32 of the CLK frequency in AD6623
mode or 1/64 of the CLK frequency when in AD6622 mode.
SDFO changes on the positive edge of SCLK when in master mode.
SDIN is captured on positive edge when SCLK is in master mode.
Serial Slave Mode (SCS = 1)
Any of the AD6623 serial ports may be operated in the serial slave
mode. In this mode, the selected AD6623 channel requires that
an external device such as a DSP to supply the SCLK. This is
done to synchronize the serial port to meet an external timing
requirement. SDIN is captured on negative edge of SCLK when
in slave mode.
Serial Data Framing
The SDIN input pin of each transmit channel of the AD6623
receives data from an external DSP to be digitally filtered, inter-
polated, and then modulated by the NCO-generated carrier.
Serial data from the DSP to the AD6623 is sent as a series of
blocks or frames. The length of each block is a function of the
desired output format that is supported by the AD6623. Block
length may range from 1 bit (MSK) to 32 bits of I and Q data.
The flow of data to the SDIN input is regulated either by the
AD6623 (in Self-Framing Mode) or by the external DSP (using
AD6623 External Framing Mode). This is accomplished by
generating a pulse, SDFO or SDFI, to indicate that the next
frame or serial data block is ready to be input or sent to the
AD6623. Functions of the two pins, SDFO and SDFI, are fully
described in the framing modes that follow.
Self-Framing Mode
In this mode Bit 7 of register 0xn16 is set low. The serial data
frame output, SDFO, generates a self-framing data request and
is pulsed high for one SCLK cycle at the input sample rate. In
this mode, the SDFI pin is not used, and the SDFO signal would
be programmed to be a serial data frame request (0xn16, Bit 5 = 0).
SDFO is used to provide a sync signal to the host. The input
sample rate
lation
is determined by the CLK divided by channel interpo-
factor. If the SCLK rate is not an integer multiple of the
input sample rate, then the SDFO will continually adjust the
by one SCLK cycle to keep the average SDFO rate equal
period
to the input sample rate. When the channel is in sleep mode, SDFO
is held low. The first SDFO is delayed by the channel reset latency
after the Channel Reset is removed. The channel reset latency
varies dependent on channel configuration.
External Framing Mode
In this mode Bit 7 of register 0xn16 is set high. The external
framing can come from either the SDFI pin (0xn16, Bit 6 = 0) or
the previous adjacent channel (0xn16, Bit 6 = 1). In the case of
external framing from a previous channel, it uses the internal frame
end signal for serial data frame synchronizing. When in master
mode, SDFO and SDFI transition on the positive edge of SCLK,
and SDIN is captured on the positive edge of SCLK. When in
slave mode, SDFO and SDFI transition on the negative edge of
SCLK, and SDIN is captured on the negative edge of SCLK.
Serial Port Cascade Configuration
In this case the SDFO signal from the last channel of the first
chip would be programmed to be a serial data frame end
(SFE:0xn16, Bit 5 = 1). This SDFO signal would then be fed as
an input for the second cascaded chip’s SDFI pin input. The
second chip would be programmed to accept external framing
from the SDFI pin (0xn16, Bit 7 = 1, Bit 6 = 0).
REV. A
–15–
 Loading...
Loading...