Page 1

3Com 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge
User Guide
Model: WL-560
3CRWE675075
http://www.3com.com/
Part No. DUA6750-75AAA01
Published November 2004
Version 1.0.2
Page 2

3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive
Marlborough
MA USA 01752-3064
Copyright © 2004, 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced
in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or
adaptation) without written permission from 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in content from time
to time without obligation on the part of 3Com Corporation to provide notification of such revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or condition of any kind, either
implied or expressed, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties, terms or conditions of
merchantability, satisfactory quality, and fitness for a particular purpose. 3Com may make improvements or
changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this documentation at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it is furnished under a license
agreement included with the product as a separate document, in the hard copy documentation, or on the
removable media in a directory file named LICENSE.TXT or !LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to locate a copy,
please contact 3Com and a copy will be provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the software described herein are
provided to you subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and developed solely at private expense.
Software is delivered as “Commercial Computer Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014 (June 1995) or
as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR 2.101(a) and as such is provided with only such rights as are
provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the Software. Technical data is provided with limited
rights only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015 (Nov 1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987), whichever is
applicable. You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any licensed program or
documentation contained in, or delivered to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the United States and may or may not
be registered in other countries.
3Com and the 3Com logo are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation.
Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows
NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Novell and NetWare are registered trademarks of
Novell, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively
through X/Open Company, Ltd.
IEEE and 802 are registered trademarks of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are
associated.
ENVIRONMENTAL STATEMENT
It is the policy of 3Com Corporation to be environmentally-friendly in all operations. To uphold our policy, we
are committed to:
Establishing environmental performance standards that comply with national legislation and regulations.
Conserving energy, materials and natural resources in all operations.
Reducing the waste generated by all operations. Ensuring that all waste conforms to recognized
environmental standards. Maximizing the recyclable and reusable content of all products.
Ensuring that all products can be recycled, reused and disposed of safely.
Ensuring that all products are labelled according to recognized environmental standards.
Improving our environmental record on a continual basis.
End of Life Statement
3Com processes allow for the recovery, reclamation and safe disposal of all end-of-life electronic components.
Regulated Materials Statement
3Com products do not contain any hazardous or ozone-depleting material.
Environmental Statement about the Documentation
The documentation for this product is printed on paper that comes from sustainable, managed forests; it is
fully biodegradable and recyclable, and is completely chlorine-free. The varnish is environmentally-friendly, and
the inks are vegetable-based with a low heavy-metal content.
Page 3

CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions 2
Related Documentation 2
Accessing Online Documentation 3
Product Registration and Support 4
1 INTRODUCTION
Product Features 5
Security 5
Wireless Network Standards 6
Network Configuration and Planning 7
Example Configurations 8
2 INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
Unpacking the Bridge 9
Observing Safety Precautions 10
Deciding Where to Place the Bridge 11
Wall-Mounting the Bridge 11
Installing the Locking Bar 12
Placing the Bridge on a Flat Surface 13
Connecting the Bridge 14
Connecting to a Serial Device 14
Connecting to an Ethernet Device 15
About the Client List 15
Connecting to a Hub 15
Connecting to a Network Printer 16
Connecting to a Computer 16
Checking the LED Indicators 17
Attaching An External Antenna 18
Determining if you Need to Configure the Bridge 18
Using the 3Com Installation CD 21
Page 4

3 CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Using Secure Web Server Connection 23
Using the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager 24
Using the Configuration Management System 27
Clearing and Applying System Configuration Settings 28
Changing System Properties 29
Setting IP Network Properties 30
Setting Wireless Network Properties 31
Manually Select Radio Channels 33
Setting Up an Ad-Hoc Network 34
Changing Wireless Security Settings 35
Changing RADIUS Settings 37
Changing SNMP Settings 38
Using the Access Control List 39
Serial Port 40
Resetting the Bridge 42
Restoring the Bridge to Factory Defaults 43
Upgrading the System 44
Changing the Administration Login Name and Password 45
Backing up a Configuration 45
Restoring a Configuration 46
Logging Out 46
Clearing the Ethernet Client List 46
Viewing Connection Status 47
Viewing System Summary 47
4 TROUBLESHOOTING
Diagnosing Problems 49
Disconnecting the Bridge 51
Uninstalling Software and Documentation 51
Upgrading Bridge Firmware 52
Page 5

A OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR 3COM PRODUCT
Register Your Product to Gain Service Benefits 53
Solve Problems Online 53
Purchase Extended Warranty and Professional Services 54
Access Software Downloads 54
Contact Us 54
Telephone Technical Support and Repair 55
END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
REGULATORY INFORMATION
Page 6

Page 7
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide provides all the information you need to install and use the
3Com 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge in its default state.
The guide is intended for use by IT managers and experienced network
installation and administration professionals who have a basic knowledge
of current networking concepts.
If the information in the release notes that are shipped with your product
differ from the information in this guide, follow the instructions in the
release notes.
Most user guides and release notes are available in Adobe Acrobat
Reader Portable Document Format (PDF) or HTML on the 3Com
World Wide Web site:
http://www.3com.com/
Page 8
2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions Table 1 and Table 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Tab le 1 Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Description
Information note Information that describes important features or
instructions.
Caution Information that alerts you to potential loss of data or
potential damage to an application, system, or device.
Warning Information that alerts you to potential personal
injury.
Tab le 2 Text Conventions
Convention Description
Screen displays This typeface represents information as it appears on the
Syntax The word “syntax” means that you must evaluate the syntax
The words “enter”
and “type”
Keyboard key names If you must press two or more keys simultaneously, the key
Words in italics Italics are used to:
screen.
provided and then supply the appropriate values for the
placeholders that appear in angle brackets. Example:
To change your password, use the following syntax:
system password <password>
In this example, you must supply a password for <password>.
When you see the word “enter” in this guide, you must type
something, and then press Return or Enter. Do not press
Return or Enter when an instruction simply says “type.”
names are linked with a plus sign (+). Example:
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del
■ Emphasize a point.
■ Denote a new term at the place where it is defined in the
text.
■ Identify menu names, menu commands, and software
button names. Examples:
From the Help menu, select Contents.
Click OK.
Related
Documentation
In addition to this guide, each Bridge documentation set includes the
following:
Page 9

Accessing Online Documentation 3
■ Quick Start Guide—printed guide that describes basic installation.
■ Online Help—product help systems that describe how to use the
Configuration Management System and 3Com Wireless Infrastructure
Device Manager.
■ Release Note—printed note that describes important product
information.
■ README.TXT file—text file located on the 3Com Installation CD that
describes last-minute product information.
Accessing Online
Documentation
The CD supplied with your Bridge contains the following online
documentation:
■ 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge User Guide
■ 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager Online Help
■ 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge Configuration
Management System Online Help
To access the online documentation from the CD:
1 Insert the 3Com Installation CD supplied with your Bridge in the CD-ROM
drive.
The setup menu appears. If it does not appear, you can start the setup
menu from the Windows Start menu. For example: Start > Run >
d:setup.exe.
2 In the menu, click View the Documentation to view the Bridge User
Guide.
To view the online help, install and launch the Wireless Infrastructure
Device Manager or Configuration Management System. See Chapter 3
for instructions.
Page 10

4 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Product
Registration and
Support
To register your product with 3Com, go to the following Web page:
http://esupport.3com.com
For support information, see “Obtaining Support for your 3Com
Product” on page 53 or log on to the 3Com Web site at
http://www.3com.com and navigate to the product support page.
Page 11

INTRODUCTION
1
3Com wireless technology has all of the benefits of a local area network
(LAN) without the constraints and expense of network wiring.
3Com 11a/b/g Wireless LAN products provide easy, affordable, flexible
ways to extend wireless networks to more users. This guide shows how
you can use the 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge in your office
or classroom to connect groups of wired Ethernet client devices to your
wireless LAN.
Product Features The 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge includes a robust suite of
standards-based security features, and supports wireless network
standards including 802.11a and 802.11g.
Security To protect sensitive data broadcast over the radio, 3Com supports
Wireless Equivalent Privacy (WEP) RC4 64-bit, 128-bit and 152-bit
shared-key encryption. 3Com strengthens this basic security mechanism
with additional security features, including:
■ MAC address access control lists
■ IEEE 802.1x per-port user authentication with RADIUS server
authentication support
■ Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
■ Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
■ WiFi Protected Access (WPA)
■ Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) support: EAP-TTLS and PEAP
Page 12

6 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Wireless Network
Standards
Understanding the characteristics of the 802.11a and 802.11g standards
can help you
make the best choice for your wireless implementation plans.
802.11a
Ratified in 2002, 802.11a is IEEE’s more recent wireless standard. It
operates at the 5
GHz band and supports data rates at up to 54 Mbps.
Because there are fewer devices in the 5 GHz band, there’s less potential for
RF interference. However, because it is at an entirely different radio
spectrum, it is not compatible with 802.11g.
The higher spectrum provides about 50 m (164 ft) of coverage—about
what 802.11g offers.
half
Consider 802.11a when you need high throughput in a confined space
and you are:
■ Running high-bandwidth applications like voice, video, or multimedia
over a wireless network that can benefit from a five-fold increase in
data throughput.
■ Transferring large files like computer-aided design files, preprint
publishing documents or graphics files, such as MRI scans for medical
applications, that demand additional bandwidth.
■ Supporting a dense user base confined to a small coverage area.
Because 802.11a has a greater number of non-overlapping channels,
you can pack more wireless devices in a tighter space.
802.11g
802.11g operates in the 2.4 GHz band at up to 54 Mbps. Ratified in
2003, it supports
the widest coverage—up to 100 m (328 ft). However, is
subject to a greater risk of radio interference because it operates in the more
popular 2.4 GHz band.
802.11b operates at up to 11 Mbps and supports coverage up to 100 m
(328 ft).
Page 13

Network Configuration and Planning 7
Consider 802.11g when you need wider coverage and vendor
compatibility and you are:
■ Maintaining support for existing 802.11b users and the existing
wireless investment while providing for expansion into 802.11g.
■ Implementing a complete wireless LAN solution, including bridges,
gateways, access points and clients; Wi-Fi certification guarantees
compatibility among vendors.
■ Providing access to hot spots in public spaces such as coffee shops or
university cafeterias.
Network Configuration and Planning
The Bridge can operate in either infrastructure or ad-hoc mode, and can
support a stand-alone wireless network configuration or an integrated
configuration with 10/100 Mbps Ethernet LANs.
Operating in infrastructure mode and connected to an Ethernet hub, a
single Bridge can combine up to 16 client devices—such as computers
with network adapters and printers—into a multiclient workgroup. The
workgroup associates with the wired network through a wireless LAN
access point such as the 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless LAN Access Point.
Infrastructure configurations extend your wireless LAN to devices that
would otherwise have to be connected to the wired network.
Operating in ad-hoc mode, two or more Bridges can associate among
themselves and communicate with one another at close range without an
access point. You may wish to set up an ad-hoc network, for example, if
a group is working away from the office, or if a group in the office needs
to share files apart from the wired LAN.
Page 14

8 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
POWER
ETHERN
ET
W
I
RELESS
PO
W
ER
ETHERN
ET
W
IRE
LE
SS
Example Configurations
The following examples illustrate ways you can use the Bridge to
configure Ethernet client devices into workgroups. (Details for setting up
specific configurations are in “Installing the Bridge” on page 9.)
Wireless Infrastructure Network
You can connect several computers, including those with non-Windows
operating systems, and network printers, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Wireless Infrastructure Network
H
oup
irele
B
ub
ss
r
idg
e
a
1
1
.
g
1
1
.
0
0
1
.
0
1
.
A
ccess
P
oint
11a/b/g W
ET
ET
N
N
R
R
E
E
S
S
R
R
H
H
E
E
LES
LES
ET
ET
W
W
E
E
O
O
R
I
IR
P
P
W
W
W
orkgr
Workgroup Ad-Hoc Network
You can provide flexible wireless network association for small groups in
areas that cannot be wired, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Workgroup Ad-Hoc Network
H
ub
11a/b/g W
W
11a/b/g W
W
orkgr
orkgr
oup
oup
irele
irele
ss
B
r
id g
e
a
1
1
.
g
1
1
.
00
1
.
0
1
.
ss
B
r
id g
e
a
1
1
.
g
1
1
.
0
0
1
.
0
1
.
H
ub
Page 15

2
INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
This chapter contains the information you need to install and set up the
Bridge. It covers the following topics:
■ Unpacking the Bridge
■ Observing Safety Precautions
■ Deciding Where to Place the Bridge
■ Connecting the Bridge
■ Checking the LED Indicators
■ Attaching An External Antenna
■ Determining if you Need to Configure the Bridge
■ Using the 3Com Installation CD
Unpacking the Bridge
Make sure that you have the following items, which are included with the
Bridge:
■ Power adapter and power cord.
■ Standard Category 5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) Ethernet cable.
■ Locking bar (used for securing a wall-mounted installation).
■ Rubber feet (four; used for a flat-surface installation).
■ 3Com Installation CD.
For wall-mounting installations, you need the following items, which
are not included with the Bridge:
■ Mounting screws.
■ Plastic anchors (for drywall mounting).
To secure the Bridge using the locking bar, you need a lock (not
supplied).
Page 16
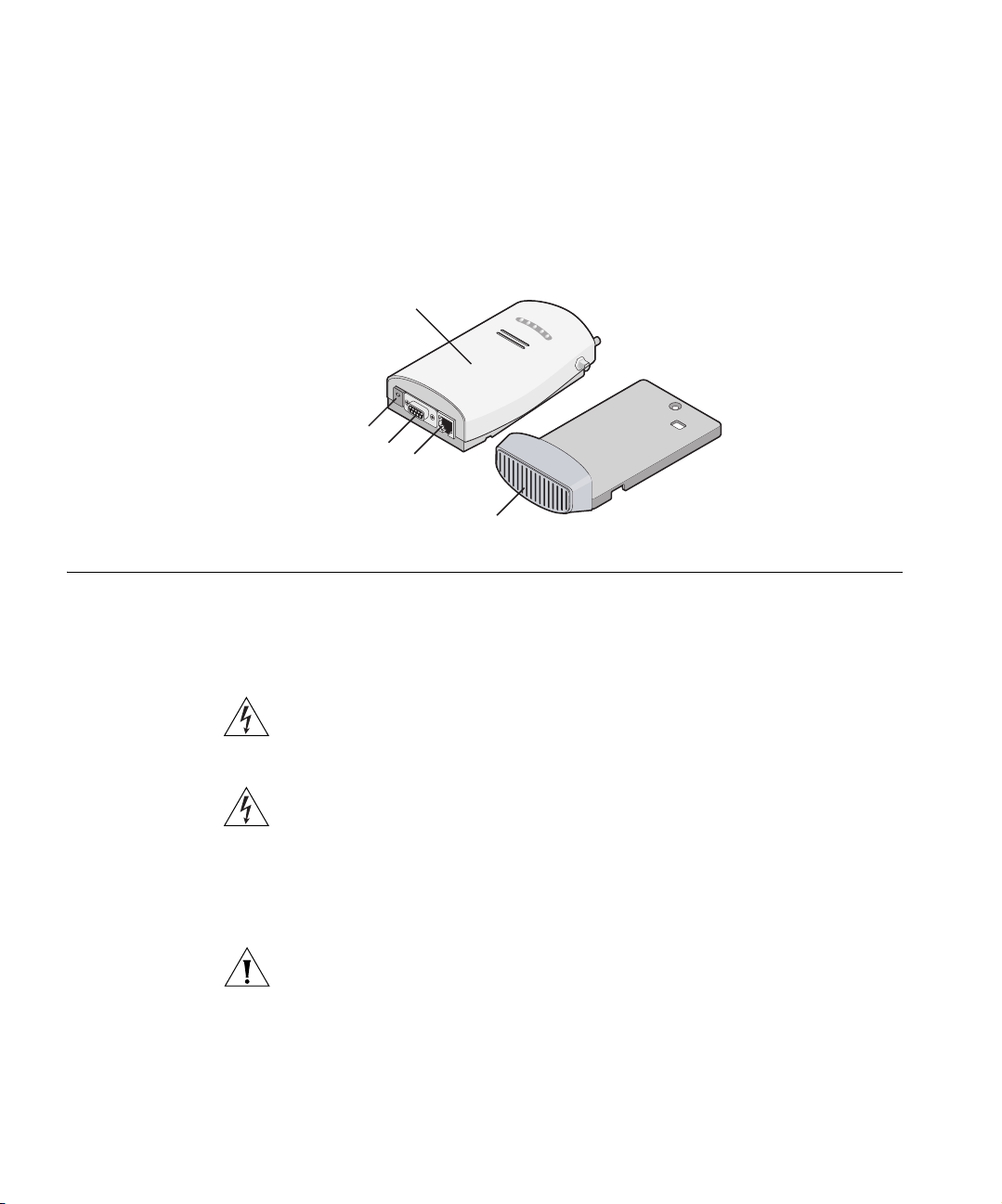
10 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
Figure 3 shows the front view of the Bridge, including the LEDs and
connecting ports. It also shows the cradle, which is used to mount the
Bridge to a wall or to install the Bridge on a flat surface.
Figure 3 Bridge
Observing Safety Precautions
11a/b/g W
W
orkgr
P
ower
S
erial
E
oup
P
ort
therne
irele
ss
B
r
idg
e
P
ort
t
P
ort
C
radl
e
This equipment must be installed in compliance with local and national
building codes,
regulatory restrictions, and FCC rules. For the safety of
people and equipment, only professional network personnel should
install the Bridge.
WARNING: To comply with FCC radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, a
minimum body-to-antenna distance of 20 cm (8 in.) must be maintained
when the Bridge is operational.
WARNING: To avoid possible injury or damage to equipment, you must
use either the provided power supply or power supply equipment that is
safety certified according to UL, CSA, IEC, or other applicable national or
international safety requirements for the country of use. All references to
power supply in this document refer to equipment meeting these
requirements.
CAUTION: The 3Com power supply (part number 61-0107-000) input
relies on a 16A rated building fuse or circuit protector for short circuit
protection of the line to neutral conductors.
Page 17
Deciding Where to Place the Bridge 11
Deciding Where to Place the Bridge
Wall-Mounting the
Bridge
Place the Bridge in a dry, clean location near the hub, computer, or
printer that will be connected to the Bridge. The location must have a
power source and be within the following distance of a Wi-Fi compliant
wireless LAN access point or ad-hoc wireless station:
■ For 802.11a compatibility, place the Bridge within 50 m (164 ft) of a
Wi-Fi compliant wireless LAN access point.
■ For 802.11b/g compatibility, place the Bridge within 100 m (328 ft) of
a Wi-Fi compliant wireless LAN access point.
The location should be away from transformers, heavy-duty motors,
fluorescent lights, microwave ovens, refrigerators, or other equipment
that could cause radio signal interference.
The Bridge comes with a cradle for mounting on a wall. For additional
security, the Bridge also comes with a locking bar, which can be used
with a security lock (not provided) to lock the Bridge to the cradle after
the Bridge is mounted to a wall.
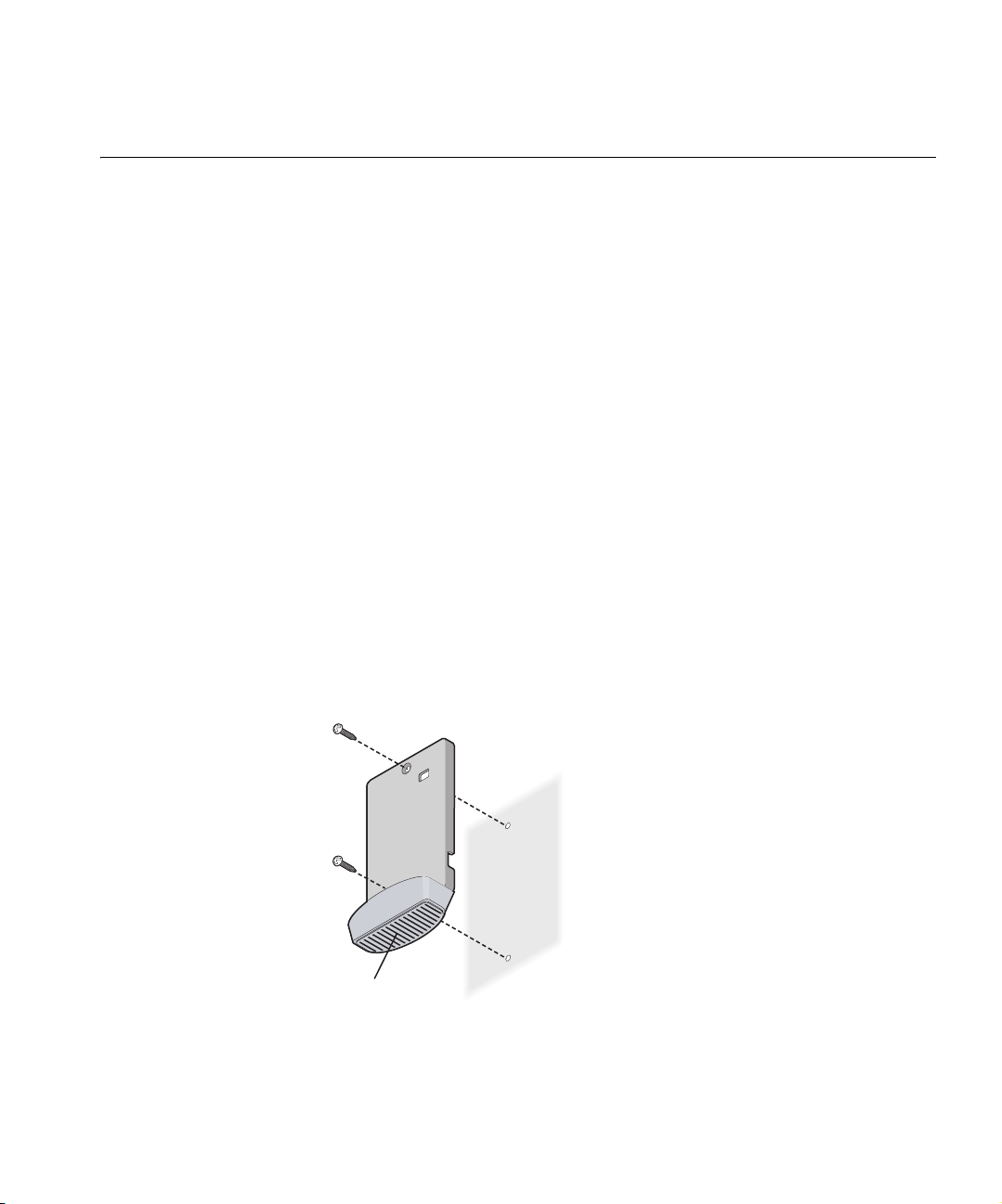
To wall-mount the bridge:
1 Screw the cradle to a wall,
Figure 4 Wall-Mounting the Bridge
as shown in Figure 4.
C
radl
e
Page 18
12 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
2 Route the power and Ethernet cables through the large opening in the cradle.
Figure 5 shows a cable being routed under the cradle.
Figure 5 Routing Cable Under the Cradle
3 Connect the power and Ethernet cables to the ports on the Bridge.
4 Snap the Bridge onto the cradle.
Installing the
Locking Bar
For additional security, install the locking bar in the cradle after the Bridge
is mounted to the wall. Use your own lock to secure it in place.
To install the locking bar:
1 Insert the locking bar through the opening in the side of the cradle, as
shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Inserting the Locking Bar
.11a
.11g
.100
.10
Page 19

Deciding Where to Place the Bridge 13
2 Push the locking bar through the opening until the hole on the locking
bar is exposed.
3 Insert a lock through the hole on the locking bar, and then close the lock
to secure it in place, as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 Securing the Locking Bar
.10
.100
.11g
.11a
Placing the Bridge on
a Flat Surface
The Bridge comes with four rubber feet that can be used to install the
Bridge on a flat surface such as a table or desktop.
CAUTION: Do not place the Bridge on any type of metal surface. Select a
location that is clear of obstructions and provides good reception.
Remove the backing from the rubber feet and attach them to the bottom
of the cradle. After the rubber feet are installed, place the Bridge on a flat
surface.
Page 20
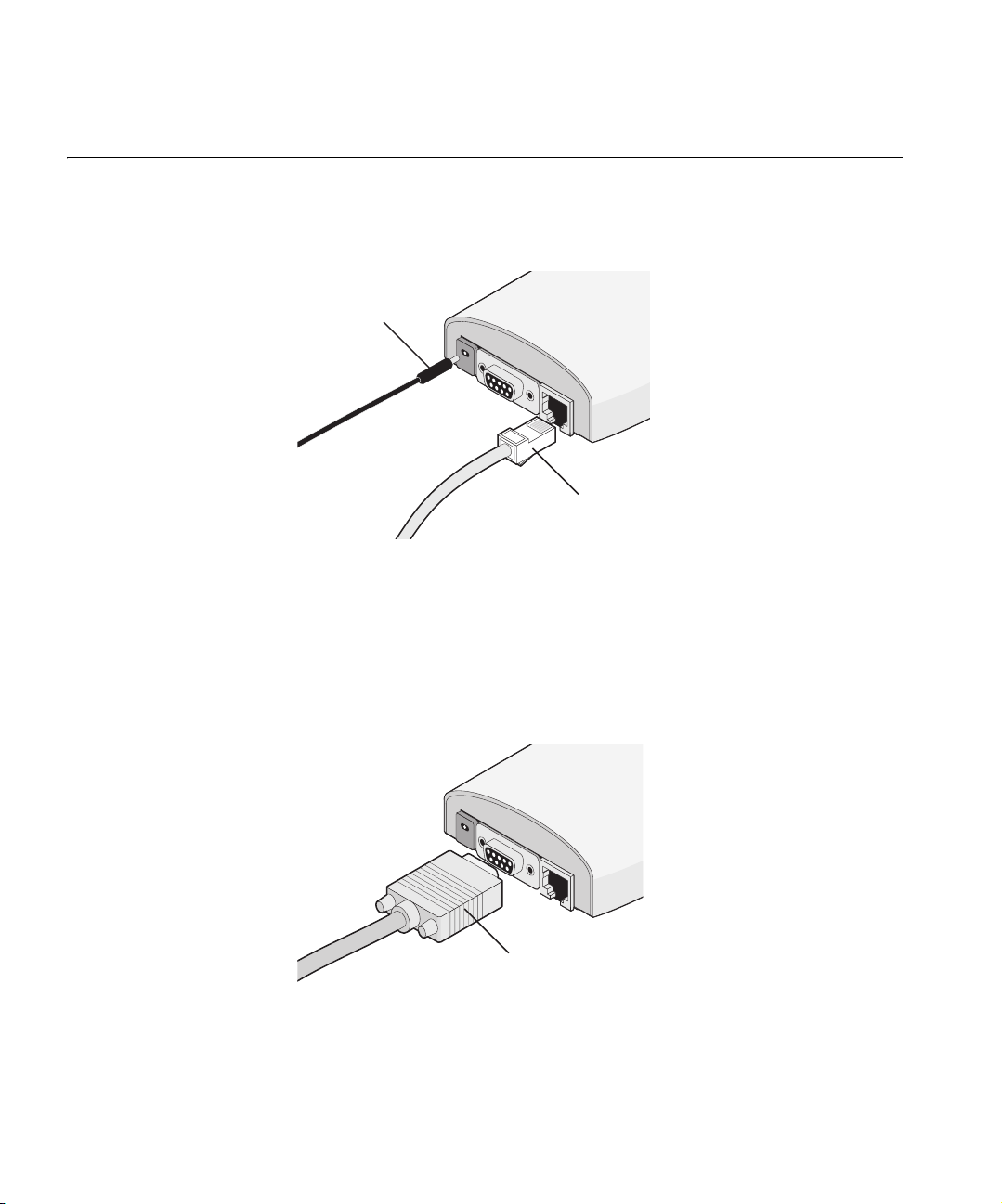
14 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
Connecting the Bridge
Connecting to a
Serial Device
The Bridge has power, Ethernet, and serial ports, as shown in Figure 8.
Before connecting the Bridge to an Ethernet device, connect the power.
Figure 8 Connecting the Power
P
ower
C
able
E
therne
t
C
able
The Bridge can also be connected to a serial device, as shown in Figure 9.
Serial cables come with a variety of connector sizes. If your connector is
large and prevents the cradle from being attached to the Bridge, remove
the end cap on the cradle. This allows the connector to extend through
the cradle.
Figure 9 Connecting a Serial Cable
S
erial
C
able
Page 21
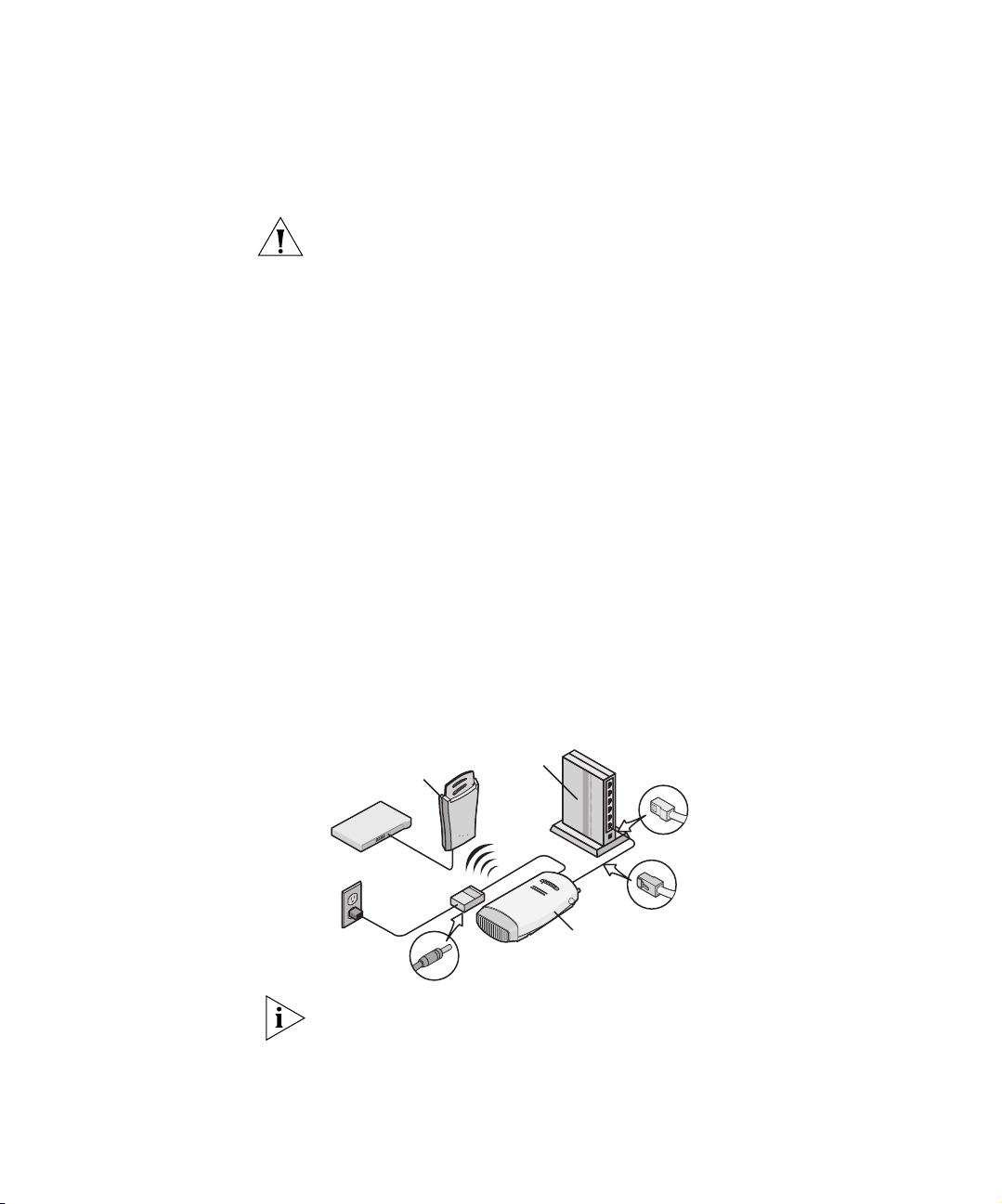
Connecting the Bridge 15
POWER
ETHERNET
WIRE
LE
SS
Connecting to an
Ethernet Device
The Bridge is designed to be connected to an Ethernet client device such
as a hub, computer, or printer.
CAUTION:
To avoid the possibility of a transmission loop situation between
the Bridge and an access point, which could disrupt network operation, do
not connect a Bridge that is set in Wireless Client (Infrastructure) mode
directly to the LAN (for example, through a wall port or through a hub that is
connected directly to the LAN).
About the Client List The Bridge supports up to 16 specific Ethernet client devices. It uses a
client list of MAC addresses to keep track of specific devices that have
been connected.
After 16 different devices have been connected, the client list is full, and
you must clear it before the next new device can associate with the
network through the Bridge.
To clear the list, you must access the Bridge’s Configuration Management
System. Details are in “Clearing the Ethernet Client List” on page 46.
Connecting to a Hub You can supply network connections for up to 16 devices, such as
computers and network printers, by connecting the Bridge to an Ethernet
hub, as shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10 Connecting to a Hub
H
A
ccess
P
oint
NET
R
E
S
R
S
H
E
LE
ET
W
E
O
P
WIR
ub
a
1
1
.
g
1
1
.
0
0
1
.
0
1
.
11a/b/g W
W
orkgr
oup
U
plin
irele
B
r
k
ss
id g
P
ort
e
You can directly connect the Bridge to a hub that does not have an uplink
(MDIX) port, without the need of an Ethernet crossover cable.
Page 22

16 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
POWER
ETHER
N
ET
W
I
RE
L
ESS
POWER
ETHER
N
ET
WI
REL
ESS
Connecting to a
Network Printer
You can connect a network printer directly to the Bridge or to a hub that
is connected to the Bridge. Used this way, the Bridge allows you to place
network printers in areas that are not wired for Ethernet.
1 Configure the network printer as you would for connecting it to the wired
LAN. For details on configuring the printer, see your printer documentation.
2 If necessary, configure the Bridge to associate with your access point.
3 Connect the Bridge to the power supply in its permanent location.
4 Connect the network printer directly to the Bridge as shown in Figure 11,
or to a hub that is connected to the Bridge as shown in “Connecting to a
Hub” on page 15.
Figure 11 Connecting to a Network Printer
A
ccess
P
oint
S
R
E
ES
L
W
E
O
R
I
P
W
ET
N
R
E
H
ET
11a/b/g W
W
orkgr
oup
a
1
1
.
g
1
1
.
0
1
.
0
10
.
irele
B
r
id g
ss
e
Connecting to a
Computer
You can connect the Bridge directly to a computer through Ethernet as
shown in Figure 12. Used this way, the Bridge can convert a desktop
computer to a wireless computer. This connection also allows you to
configure a Bridge before connecting it to another device.
Figure 12 Connecting to a Computer
A
ccess
P
oint
ET
N
R
E
S
R
H
E
ES
L
ET
W
E
O
P
WIR
a
1
1
.
g
1
1
.
0
10
.
10
.
W
11a/b/
W
irele
orkgr
B
g
ss
oup
r
idg
e
Page 23

Checking the LED Indicators 17
Checking the LED Indicators
When the Bridge is connected to power, LEDs indicate activity as follows:
Figure 13 LED Indicators
.11b/g
.100
.11a
Tab le 3 LED Descriptions
LED Color Indicates
Power Green
The Bridge is powered up and operating
normally.
Off
The Bridge is not receiving power or there is a
fault with the power supply.
11a Green (solid)
The Bridge has an 802.11a 5 GHz radio band
connection.
Green (blinking)
The Bridge has WLAN frame transmission over
the 802.11a 5 GHz radio band.
.10
Off
11b/g Green (solid)
Green (blinking)
Off
100 Green (solid)
Green (blinking)
Off
10 Green (solid)
Green (blinking)
Off
No link is present.
The Bridge has an 802.11g 2.4 GHz radio band
connection.
The Bridge has WLAN frame transmission over
the 802.11g 2.4 GHz radio band.
No link is present.
The Bridge has a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet
connection.
The Bridge has 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet activity.
No link is present.
The Bridge has a 10 Mbps Ethernet connection.
The Bridge has 10 Mbps Ethernet activity.
No link is present.
Page 24

18 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
Attaching An External Antenna
Determining if you Need to Configure the Bridge
The Bridge has two internal diversity dual-band antennas.
If you want to increase the range of the Bridge, an external antenna can
be attached to the external antenna connector on the Bridge.
The 3Com-approved external antenna for this Bridge is the
3Com 2.4/5 GHz Omnidirectional Workgroup Bridge Antenna
(3CWE501). For more information, go to www.3Com.com
If your network has a DHCP server and no special security requirements,
you can most likely use the Bridge just as it is shipped from the factory.
It takes approximately one to two minutes for the Bridge to determine if
there is a DHCP server on the network.
View the Bridge’s default settings on page 20 to determine whether or
not you need to configure the Bridge for your network. If the factory
defaults meet your requirements, you can connect the Bridge as
described in “Connecting the Bridge” on page 14.
If your network does not have a DHCP server or is more complex, you
may have to configure the Bridge and organize devices so that you can
manage the wireless LAN easily and keep it secure. You can use the
3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager (Widman) included on the
3Com Installation CD.
For non-U.S. versions of the Bridge, you need to set the Country mode. This is
done when you first open the Bridge’s Configuration Management System. See
“Using the Configuration Management System” on page 27 for instructions.
Networks with a DHCP Server
If your network has a DHCP server, an IP address is automatically assigned
to the Bridge. It takes approximately one to two minutes for the Bridge to
determine if there is a DHCP server on the network. Use the 3Com Wireless
Infrastructure Device Manager (Widman) included on the 3Com Installation
CD to locate the Bridge on the network and view its IP address.
Alternatively, you can enter the Bridge’s IP address into a web browser on
a computer on the same subnet to view the Bridge’s system status or
change its configuration. See “Configuring the Bridge” on page 23 for
instructions.
Page 25

Determining if you Need to Configure the Bridge 19
Networks without a DHCP Server
If your network does not have a DHCP server, the Bridge uses a default
IP address (169.254.2.2) that is assigned at the factory. You can use that
IP address to configure the Bridge, or you can assign a new IP address to
the Bridge.
To verify that the Bridge is using the default IP address assigned at the
factory:
1 Connect a computer directly to the Bridge using the supplied standard
Category 5 UTP Ethernet cable.
See Figure 12 on page 16 for a connection diagram.
2 Enter the Bridge’s default IP address (169.254.2.2) into the computer’s
web browser.
■ If the Configuration Management System starts, the Bridge is using
the factory assigned IP address. You can configure the Bridge with the
following login information:
■ Login name: admin
■ Password: none (blank)
See “Configuring the Bridge” on page 23 for detailed instructions.
■ If the Configuration Management System does not start, the Bridge is
on a different subnet than the computer. Install and start the 3Com
Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager to discover the Bridge’s IP
address. See “Using the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device
Manager” on page 24 for instructions.
Page 26

20 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
Bridge Default Settings
Table 4 shows the Bridge configuration factory defaults.
Tab le 4 Factory Default Settings
Property Default Setting
Device Name 3Com WWB
Device Location None (blank)
Country For U.S. version, United States and Canada
Client Mode Support multiple wired Ethernet clients
IP Network Setting Obtain IP address automatically
IP Address Obtained automatically (with a DHCP server)
Subnet Mask Obtained automatically (with a DHCP server)
Gateway IP Address Obtained automatically (with a DHCP server)
Network Mode Wireless Client (Infrastructure)
Radio Mode Auto Select
Wireless LAN Service Area Attach to any WLAN Service Area (ESSID) automatically
Channel Selection Automatic Best Channel (uses access point setting)
Transmit Power 100%
Antenna Selection Internal
Data Preamble Long (if Network Mode is set to Ad-Hoc)
Security Setting Open System (no security)
802.1x Authentication State Disabled
SNMP Enabled
Access Control List Disabled
Administration Login Name admin
Administration Password None (blank)
TFTP Server IP Address None
FTP Server IP Address None
For non-U.S. version, set by the user
169.254.2.2 (without a DHCP server)
255.255.0.0 (without a DHCP server)
0.0.0.0 (without a DHCP server)
Same as access point setting (if Network Mode is set
to Wireless Client [Infrastructure])
Page 27

Using the 3Com Installation CD 21
Using the 3Com Installation CD
The 3Com Installation CD contains the following tools and utilities:
■ 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager—an administration
tool that helps you select 3Com wireless LAN devices and launch their
configurations in your Web browser.
■ 3Com 3CDaemon Server Tool—a firmware upgrade tool that can
act in four different capacities:
■ As a TFTP Server, used for firmware upgrades as well as backup
and restore functions.
■ As a SysLog Server, which is necessary to view SysLog messages.
■ As an optional TFTP Client.
■ As an optional FTP Server.
To use the 3Com Installation CD, you need a computer running one of the
operating systems and browser listed in
Tab le 5 Supported Operating Systems and Browser
Operating Systems Windows XP
Windows 2000
Windows NT 4.0
Windows Me
Windows 98
Browser Internet Explorer (latest version is recommended)
Ta bl e 5 .
Page 28

22 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE BRIDGE
To install one of the tools on your computer:
1 Turn on the computer.
2 Insert the 3Com Installation CD in the CD-ROM drive.
The setup menu appears. If it does not appear, you can start the setup
menu from the Windows Start menu. For example: Start > Run >
d:setup.exe.
3 In the menu, click Tools and Utilities.
4 In the next screen, click the tool you want to install.
5 Follow the instructions on the screens to complete the installation.
Reboot the computer if prompted to do so.
6 Launch the tool from the Windows Start menu.
For details on using the Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager, see
“Using the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager” on page 24.
For instructions on using the 3CDaemon Server Tool, see the application’s
online help.
Page 29

3
CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
If the Bridge configuration that was set at the factory does not meet your
network requirements, or if you want to customize the settings, you can
use these tools to change the configuration:
Tab le 6 Configuration Tools
Configuration Tool Description
3Com Wireless
Infrastructure Device
Manager (Widman)
3Com 11a/b/g Wireless
Workgroup Bridge
Configuration
Management System
Helps you locate 3Com wireless LAN devices on the
network, select a device and view its properties, and
launch the device’s configuration in your Web browser.
See “Using the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device
Manager” on page 24 for details.
Resides on the Bridge and lets you configure the Bridge
through your web browser. The latest version of
Internet Explorer is recommended.
See “Using the Configuration Management System” on
page 27 for details.
Using Secure Web Server Connection
The Bridge can be configured using Secure Socket Layer (SSL) technology,
which is used to encrypt data exchanged between the computer and the
Bridge during a configuration session.
Without SSL enabled, data is exchanged in the form of plain text and can
be intercepted during the configuration session.
You must enable the HTTPS option to establish a secure session.
See “Web GUI Protocol” in Table 9 on page 30 for instructions.
Page 30

24 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Using the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager
The 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager (Widman) helps you
locate 3Com wireless LAN devices on the network, select a device and
view its properties, and launch the Configuration Management System in
your Web browser.
The Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager must be installed on a
computer that:
■ Has a working Ethernet adapter.
■ Is running Internet Explorer and one of the Windows operating
systems listed in “Using the 3Com Installation CD” on page 21.
■ Is on the same subnet as the Bridge.
See “Using the 3Com Installation CD” on page 21 for installation
instructions.
The device to be configured using the Wireless Infrastructure Device
Manager must be:
■ Connected to power.
■ Wired to the network, associating with the wireless network, or, in
some cases with the Bridge, connected directly to the computer.
If there is more than one device with the same name in the network (for
example, 3Com WWB), make a note of the MAC address of the device
you want to select so that you can identify it in the device manager.
If you do not have a DHCP server on your network, it can take up to one
minute for a device to become discovered after it has been powered up.
To use the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager:
1 Launch the device manager by selecting Start > Programs >
3Com Wireless > Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager.
If you have more than one network adapter installed on your computer,
you may be prompted to choose a network adapter. Choose the
appropriate adapter and click OK.
The Wireless Network Tree appears in the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure
Device Manager window, as shown in Figure 14.
The tree lists all WLAN service areas on the network and expands to show
the 3Com wireless LAN devices that are associated to each service area.
Page 31

Using the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager 25
Devices in a different subnet than your computer are identified with
exclamation points (!). You can refresh this display by clicking Refresh. You
should refresh the display, for example, after you change a device IP address.
Figure 14 Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager Wireless Network Tree
2 In the Wireless Network Tree, select the device you want to configure.
If more than one wireless LAN device appears in the tree and you are not
sure that you have selected the right one, click Properties and check the
MAC address to verify that it is the one you want.
3 Click Configure.
■ If the selected device is on the same subnet as your computer, the
Configuration Management System main page appears in your Web
browser. See “Using the Configuration Management System” on
page 27, for details.
■ If the selected device is on a different subnet, the device manager
helps you to assign an IP address on the same subnet as your
computer, as shown in Figure 15. You may accept the address offered
or enter an address and click Next.
Page 32

26 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Figure 15 Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager Pre-IP Configuration
4 The next window prompts for an administrative password to allow the
new IP address to be set. If this is the first time the device is being
configured, leave the password field blank and click Next.
The configuration main page appears in your Web browser. See “Using
the Configuration Management System” on page 27 for details.
Table 7 describes the functions of the buttons in the 3Com Wireless
Infrastructure Device Manager window.
Tab le 7 Infrastructure Device Manager Options
Button Description
Properties Displays the following properties of the selected device:
Device Name, Device Type, Wireless LAN Service Area (ESSID),
IP Address, Subnet Mask, and MAC Address.
Configure Launches the Configuration Management System for the
selected device. If the selected device is on a different subnet,
you are prompted to assign an address on the same subnet as
your computer.
Refresh Scans the network and displays the connected 3Com 11a/b/g
Wireless LAN devices.
Choose NIC If your computer has more than one network interface card
installed, allows you to choose which card to use.
Close Closes the device manager window and ends the session.
Help Launches the device manager help page in your browser.
Page 33

Using the Configuration Management System 27
Using the Configuration Management System
The 3Com11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge Configuration
Management System resides on the Bridge and lets you configure the
Bridge through your Web browser.
To use the Configuration Management System, the computer you are
using to connect to the Bridge must be located on the same subnet as
the Bridge.
There are two ways to access the Configuration Management System:
■ Enter the IP address of the Bridge in your computer’s web browser.
■ Start the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager, locate the
Bridge, and then click Configure.
For non-U.S. versions of the Bridge, when you first open the
Configuration Management System you are prompted to select the
country in which the Bridge is operating. Select the country in which the
Bridge is installed to ensure compliance with local regulations, and then
click Apply.
When you first open the Configuration Management System, you are
prompted for a user name and password:
■ User name — admin
■ Password — blank (press enter)
The Configuration Management System displays the Connection Status
page, as detailed in Table 8.
Tab le 8 Connection Status Page
Property Description Default Value
Connection The MAC address of the associated
access point.
Network Type The type of network for which the
Bridge is configured: Wireless
Client (Infrastructure) or Ad-hoc
(Peer-to-Peer).
SSID The Service Set ID. Varies
Radio Mode The way in which the Bridge selects
a radio band.
N/A
Wireless Client
(Infrastructure)
Auto-Select
Page 34

28 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Tab le 8 Connection Status Page (continued)
Current Channel The channel over which the Bridge
Security The type of security for which the
Rx Data Rate (Mbps) The most recent data reception
Tx Data Rate (Mbps) The most recent data transmission
Link Quality The normalized transmitted data
Received Signal
Strength
Activity (Packets Rx) The number of packets the Bridge
Activity (Packets Tx) The number of packets the Bridge
IP Address The IP address of the Bridge. Varies
is communicating with clients.
Bridge is configured.
rate.
rate.
rate (that is, the current data rate
over the maximum data rate).
Note: Link Quality is shown in
Infrastructure mode only.
The strength of the radio signal
that the Bridge detects.
Note: Received Signal Strength is
shown in Infrastructure mode only.
has received.
has transmitted.
Varies
Open System
(no security)
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Clearing and
Applying System
Configuration
Settings
The pages in the Configuration Management System have two buttons:
Clear and Apply.
■ Clear returns the settings to the values they were when you last
clicked Apply.
■ Apply stores the settings permanently in the nonvolatile flash memory.
After you click Apply, the new settings take effect and you can see the
changes on the System Summary page.
CAUTION: Your changes are lost if you forget to
click Apply before
moving to a new configuration page.
Page 35

Using the Configuration Management System 29
Changing System
Properties
Under System Configuration, click System Properties. The System
Properties page displays the properties of the selected Bridge. You can
change properties by entering a value in a field (see Table 9). When you are
finished, click Apply. Table 9 describes the properties.
Tab le 9 System Properties Page
Property Description Default Value
Device Name This name appears in the System
Summary window. You can change the
default name to one of your choice.
Device Location If you use the default device name,
entering the location is optional.
Client Mode This setting allows the Bridge to support
single or multiple Ethernet clients
attached to the Bridge.
Support Single Wired Ethernet Client is
used only when the Bridge is used for
replacement of a 3Com Ethernet Client
Bridge. Select a MAC option:
■ Capture: Each time the Bridge is
powered on, it captures its MAC
address from the first packet it
receives on the Ethernet port. The
Bridge detects and uses the same
MAC address as the device plugged
into the Ethernet port.
The Bridge uses the previously
captured MAC address upon
power-on until the first packet is
received on the Ethernet port.
■ Dynamic: The Bridge changes its
MAC address each time the device
plugged into the Ethernet port
changes.
The Bridge detects the MAC address
of the device plugged into the
Ethernet port and uses that as its
own. The Bridge uses the built-in
MAC address upon power-on until a
packet is received on the Ethernet
port.
■ Built-in: The Bridge uses the
manufacturing radio MAC address
as default.
3Com WWB
None
Support multiple wired
Ethernet clients
Page 36

30 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Tab le 9 System Properties Page (continued)
Setting IP Network
Properties
Web GUI
Protocol
This setting allows users to enable the
secure data exchange scheme over SSL
during a configuration session.
■ HTTPS — enables SSL technology.
■ HTTP — disables SSL technology.
HTTP
Under System Configuration, click IP Network. The IP Network Properties
page appears, where you can change the settings shown in Table 10.
If you change the IP address and click Apply, you cannot continue to
configure the device using the old IP address. Therefore, you must do the
following steps after changing the IP address:
1 Close your browser.
2 Return to the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager and click
Refresh.
3 Select the device and click Configure to start a new configuration session.
Table 10 describes the IP Network properties.
Table 10 IP Network Properties Page
Setting Description
IP Network Setting This setting allows you to change the IP address of the device.
To let the device get an IP address automatically from a DHCP
server, select Obtain an IP address automatically and click
Apply.
To specify an IP address, select Specify an IP address, enter the
IP address parameters in the spaces provided, and click Apply.
IP Address When Specify an IP address is selected, enter the IP address in
the space provided, and click Apply.
Subnet Mask When Specify an IP address is selected, enter the Subnet Mask
Gateway IP
Address
in the space provided, and click Apply.
When Specify an IP address is selected, enter the Gateway IP
Address in the space provided, and click Apply.
Page 37

Using the Configuration Management System 31
Setting Wireless
Network Properties
Under System Configuration, click Wireless Network. The Wireless
Network Properties page appears, where you can select different wireless
settings, as described in Table 11. When you are finished, click Apply.
The Bridge supports Dynamic and Static Turbo modes and boosts
throughput up to 108 Mbps.
The Dynamic Turbo mode allows automatic switching between normal and
turbo modes without modification by the user. The feature increases
throughput when bandwidth demands are high. When bandwidth demands
are low and at regular intervals, normal mode allows legacy connectivity and
new associations. The Dynamic Turbo mode connection between the Bridge
and the access point may turn to normal mode connection if another station
associates with the access point in normal mode.
The Static Turbo mode operates by using two radio channels and does
not switch to normal mode. Static Turbo mode must be configured by
the user on both the access point and the station.
Table 11 Wireless Network Page
Setting Description
Network Mode Select Wireless Client (Infrastructure) to associate with an
access point.
Select Ad-hoc (Peer-to-Peer) to join or form an ad-hoc network.
Radio Mode See “Network Configuration and Planning” on page 7 for
information on selecting the best Radio Mode for your network.
■ Select Auto Select to have the Bridge select the best
Radio Mode automatically.
■ Select 802.11a to set the Bridge to operate with either
802.11a mode or 802.11a Dynamic Turbo mode. Dynamic
Turbo mode is entered only when the channel is set to 40,
48, 56, 153, or 161 for 802.11a networks.
■ Select 802.11a Turbo to set the Bridge to operate with
802.11a Static Turbo mode. Do not select this mode unless
the access point you intend to associate with is running in
802.11a Static Mode.
■ Select 802.11b/802.11g to set the Bridge to operate with
either 802.11b/g mode or 802.11g Dynamic Turbo mode.
Dynamic Turbo mode is entered only when the channel is
set to 6 for 802.11g networks.
■ Select 802.11g Turbo to set the Bridge to operate with
802.11g Static Turbo mode. Do not select this mode unless
the access point you intend to associate with is running in
802.11g Static mode.
Page 38

32 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Table 11 Wireless Network Page (continued)
Wireless LAN
Service Area
Select Attach to any WLAN Service Area (ESSID) automatically
to allow the Bridge to associate with any access point without
specifying the ESSID. In this mode, the Bridge uses the ESSID of
the access point with the best signal strength. This mode is not
available when the network mode is Ad-hoc (Peer-to-Peer).
Select Specify the Wireless LAN Service Area to allow the
Bridge to associate only with access points with the same
service area. You may enter the WLAN service area name or
select it from the list. You must specify the WLAN service area
when the network mode is Ad-hoc (Peer-to-Peer).
To maintain a wireless association, the WLAN service area on a
Bridge and the access point with which it is associated must
match exactly. Therefore, if the Bridge is set to Specify the
WLAN Service Area and you change the access point WLAN
service area, make sure to also change the Bridge WLAN
service area.
Channel Selection If Radio Mode is set to Auto Select, you do not have the
following options to choose from.
When the network mode is Wireless Client (Infrastructure), a
user may have the Bridge automatically select an appropriate
channel by using Automatic Best Channel or specify the
channels by using Specify Channel.
When the network mode is Ad-hoc (Peer-to-Peer) you may
specify channel selection as follows:
■ Automatic Best Channel—When this option is enabled, the
Bridge scans the primary channels. If the Bridge is
establishing a new ad-hoc network, it chooses the channel
with the least number of packets. If the Bridge is joining an
existing ad-hoc network, it selects the channel in use.
■ Specify Channel—Click the button preceding this option
and enter the Advanced Wireless Network page. On this
page, you can choose channels from the Channel list.
Transmit Power This option specifies the level of transmission power. Select
one of the values (100%, 50%, 25%, 12%, min) from the
drop-down menu.
Decrease the Transmit Power setting if more than one Bridge is
using the same channel frequency.
Page 39

Using the Configuration Management System 33
Table 11 Wireless Network Page (continued)
Antenna Selection Select an antenna for the radio signal:
■ Internal — this default setting should be used in most
circumstances.
■ External and one internal antenna — this setting
automatically determines which antenna is best for sending
packets to individually attached clients. Choose this setting
if the Bridge is located in a place that is surrounded or
hindered by metal paths or walls.
Data Preamble To increase performance, click Short (Enhanced performance).
When equipment that does not support short preamble is also
being used, click Long (Wi-Fi Interoperable).
Note: The Data Preamble option is available in ad-hoc mode
only. However, the Short Data Preamble option is not available
for 802.11a and 802.11a Turbo modes in ad-hoc mode.
Manually Select
Radio Channels
On the Advanced Wireless Network page, you can manually select the
radio channels and radio modes. The Bridge only looks for a best SSID
that matches the specified radio mode on the specified channels.
Page 40

34 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Setting Up an Ad-Hoc
Network
Operating in ad-hoc mode, two or more Bridges can associate among
themselves to form an ad-hoc network without the intervention of an
access point. You may wish to set up an ad-hoc network, for example, if
a group is working away from the office, or if a group in the office needs
to share files apart from the wired LAN.
CAUTION:
must match exactly.
while you are configuring, 3Com recommends
directly to the computer.
To ensure correct operation, the settings on the two Bridges
To avoid the possibility of losing wireless association
that you connect the Bridge
1 Connect the first Bridge to power and use the Ethernet cable to connect
it to the computer.
2 Use the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager to select the
Bridge and launch the Configuration Management System.
3 Under System Configuration, click Wireless Network.
4 In the Wireless Network page:
a Locate the Network Mode field and select Ad-hoc (Peer-to-Peer).
b Specify the Wireless LAN Service Area and the Channel Selection as
described in “Setting Wireless Network Properties” on page 31.
c Set the Data Preamble.
To increase performance, select Short (Enhanced performance). When
equipment that does not support short preamble is also being used,
select Long (Wi-Fi Interoperable). When you are finished, click Apply.
Security settings default to Open System (no security). Optionally, you can
set different WEP settings as described in “Changing Wireless Security
Settings” on page 35.
5 When you are finished, click Apply.
6 End the browser session.
7 Repeat steps 1–6 with the second Bridge. Make sure you configure
Bridge settings to match exactly. When you are finished, click Apply and
end the browser session.
8 Connect the Ethernet devices to the Bridges. If you use hubs, make sure
that the Bridges are connected through the hub uplink ports.
Page 41

Using the Configuration Management System 35
Changing Wireless
Security Settings
Under System Configuration, click Wireless Security. The Wireless Security
Settings page appears, where you can select the type of security to be
used on the Bridge.
The Bridge can be configured to support three types of data encryption:
WEP, TKIP, and AES. After selecting a data encryption type, you can
select an authentication type.
The following sections describe the settings. To maintain wireless
association, the settings on clients and the access points they associate
with (or other members of an ad-hoc network) must match exactly.
No Security (Open System)
No encryption is used. The network communications could be intercepted
by unintended recipients.
40/64-bit Shared Key (WEP)
This option encrypts the wireless transmissions to protect data, but still
allows communication among compatible wireless LAN clients and access
points from third-party manufacturers that are Wi-Fi certified.
This type of security requires you to set up encryption in one of the
following ways:
■ String—For use only with other 3Com 11a/b/g wireless devices, an
encryption string is a case-sensitive string of characters between 6 and
30 characters long. To enter the string, select Enter a string to
generate shared keys. Then type any combination of letters and
numbers in the space provided and select Apply.
■ Shared keys—Hexadecimal keys are sequences of hexadecimal digits
arranged into four keys. A hexadecimal digit may be a letter from
A to F or a number from 0 to 9. This type of encryption is compatible
with equipment from other manufacturers that use Wi-Fi certified
40-bit encryption. To enter the keys, select Specify shared keys and
which to use. In the shared keys window, enter all the keys in the
provided spaces, then select a radio button in the Selected Key
column to specify which key to use and select Apply.
Page 42

36 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
104/128-bit Shared Key
This option can be used with other 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless LAN devices
and with equipment from certain manufacturers that also support 128-bit
shared key encryption. It provides a higher level of security than the 40-bit
Shared Key (Wi-Fi) option and uses a more complicated type of encryption.
This type of security requires you to set up encryption using a string or
shared keys as described in “40/64-bit Shared Key (WEP)” on page 35.
128/152-bit Shared Key
This option can be used with other 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless LAN devices
and with equipment from certain manufacturers that also support 152-bit
shared key encryption. It provides a higher level of security than the 128-bit
Shared Key option and uses a more complicated type of encryption. This
type of security requires you to set up encryption using a string or shared
keys as described in “40/64-bit Shared Key (WEP)” on page 35.
Click the button preceding Specify Shared Keys and Which Key to Use to
create or modify WEP keys.
TKIP
The Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) option improves data
encryption over WEP scheme by dynamically updating the encryption
keys every 10,000 packets. TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a
message integrity check, and a re-keying mechanism.
To use TKIP:
1 On the Wireless Security page, select TKIP.
2 Select WPA-PSK for home network or WPA for the scenarios where
RADIUS servers are employed:
■ WPA-PSK: Enter a pass-phrase key or hexidecimal key. The key can be
generated based on a pass-phrase or a sequence of manually entered
64 hexidecimals. The 64 hexidecimals can be automatically generated
by selecting Generate a Random Key.
■ WPA: Select an authentication scheme (TTLS or PEAP) and a relevant
authentication type, and enter a user name and a password.
3 Select Apply.
Click the button of TKIP to set TKIP relevant parameters.
Page 43

Using the Configuration Management System 37
AES
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) option uses the highest security
cipher for data encryption.
To u se AES :
1 On the Wireless Security page, select AES.
2 Select WPA-PSK for home network or WPA for the scenarios where
RADIUS servers are employed:
■ WPA-PSK: Enter a pass-phrase key or hexidecimal key. The key can be
generated based on a pass-phrase or a sequence of manually entered
64 hexidecimals. The 64 hexidecimals can be automatically generated
by selecting Generate a Random Key.
■ WPA: Select an authentication scheme (TTLS or PEAP) and a relevant
authentication type, and enter a user name and a password.
3 Select Apply.
Click the button of AES to set or modify AES relevant parameters.
Changing RADIUS
Settings
Under System Configuration, click RADIUS. The RADIUS page appears,
where you can set the primary and secondary RADIUS Server settings.
This page allows for configuration of a Remote Access Dial-in User Service
(RADIUS) server for authentication purposes in 802.1x networks. You can
change the settings by entering values in the fields as described in
Table 12. When you are finished, select Apply.
Table 12 RADIUS Authentication Server Settings
Setting Description
802.1x Authenticator
State
Primary RADIUS
Server
Primary RADIUS Port Enter the port number of the primary RADIUS Authentication
Primary RADIUS
Secret
Enable or disable RADIUS authentication by selecting Enable
or Disable.
Enter the IP address of the primary RADIUS Authentication
Server. Make sure this address matches the address set in the
RADIUS Authentication software.
Server. Make sure this number matches the number set in the
RADIUS Authentication software. The default port is 1812.
Enter the password of the primary RADIUS Authentication
Server. Make sure this password matches the password set in
the RADIUS Authentication software.
Page 44
38 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Table 12 RADIUS Authentication Server Settings (continued)
Changing SNMP
Settings
Secondary RADIUS
Server
Secondary RADIUS
Port
Secondary RADIUS
Secret
Enter the IP address of the secondary RADIUS Authentication
Server. Make sure this address matches the address set in the
RADIUS Authentication software.
Enter the port number of the secondary RADIUS
Authentication Server. Make sure this number matches the
number set in the RADIUS Authentication software. The
default port is 1812.
Enter the password of the secondary RADIUS Authentication
Server. Make sure this password matches the password set in
the RADIUS Authentication software.
Under System Configuration, click SNMP to display and change settings
for the Simple Network Management Protocol.
To communicate with the Bridge, the SNMP agent must first be enabled
and the Network Management Station must submit a valid community
string for authentication. Select SNMP Enable and enter data into the
fields as described below. When you are finished, click Apply.
Table 13 SNMP Settings
Setting Description
SNMP Enables or disables SNMP.
Contact Sets the location string that describes the system location.
Community Name
(Read Only)
Community Name
(Read/Write)
Trap Destination
IP Address
Trap Destination
Community Name
Maximum length: 255 characters.
Specifies a community string with read-only access.
Authorized management stations are able to retrieve MIB
objects. Maximum length: 23 characters.
Specifies a community string with read-write access.
Authorized management stations are able to both retrieve
and modify MIB objects. Maximum length: 23 characters.
Enter the IP address of the trap manager that will receive
these messages.
Enter the community name of the trap manager that will
receive these messages.
Page 45

Using the Configuration Management System 39
Using the Access
Control List
You can use the Access Control List to allow or prohibit access to the
wireless network from Ethernet clients.
Follow these steps to build the Access Control List:
1 Under System Configuration, click Access Control List.
2 On the Access Control List page, click Add.
The Access Control List New ACL page appears.
3 On the New ACL page, enter the MAC address of the client you want to
add to the Access Control List, select the permission type, and click the
Add button to substantially add it.
4 Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each client.
5 Select the System Default Mode:
■ Allow—allows the client to access the Bridge.
■ Deny—prohibits the client from accessing the Bridge.
CAUTION: With the Allow option of the System Default Mode selected,
the Bridge allows all Ethernet frames except those carrying the
MAC addresses that are specified in the Access Control List and have the
permission type Deny. Similarly, with the Deny option of the System
Default Mode selected, the Bridge denies all Ethernet frames except
those carrying the MAC addresses that are specified in the Access Control
List and have the permission type Allow.
Make sure that the MAC address of the computer through which you are
configuring the Bridge is not specified in the Access Control List with the
permission type Deny if you want to set the access control type to Allow.
If you want to set the Access Control Type to Deny, make sure that the
MAC address of the computer is included in the Access Control List with
the permission type Allow. Failure to do so results in access to the Bridge
being blocked; the Bridge will no longer be configurable through the
computer.
6 Click Apply.
To delete one or more than one client(s) from the Access Control List,
select the client(s) and then click Delete.
Page 46

40 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Serial Port Under System Configuration, click Serial Port to set up network serial port
operation.
About UART
A Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) is the
fundamental hardware for serial communication, controlling the speed
and method of data transfer of the serial port.
Applications utilizing a network serial port between an RS-232 interface
and a wireless device use a TCP/IP socket connection. Any program that
uses standard TCP/IP network sockets may be used to communicate with
the serial port of the Bridge. Once a socket is established to the Bridge,
any data written to the socket is sent out the serial port of the Bridge. At
the same time, any data received by the serial port of the Bridge is
returned via the socket connection.
The Bridge network serial port may be used in two modes:
■ Server Mode — TCP Listen Port
■ Client Mode — TCP Connect Port
In Server Mode, the Bridge waits for a TCP/IP socket connection to be
made by the network program with which it will communicate.
Server Mode should be used if you have a central server that expects to
open a TCP/IP socket connection to the Bridge.
In Client Mode, the Bridge establishes a socket connection to the
IP address and port number specified in the configuration. Client Mode
should be used if your system expects the Bridge to open a TCP/IP socket
connection to a central server.
Configuring Operation Mode
Attach your computer to the serial port on the Bridge, and then configure
the Bridge through the computer.
■ Select Enable to establish a TCP/IP socket with a remote computer in
either infrastructure or ad-hoc mode. This allows you to do data
communication with the remote computer.
■ Select Disable to disable the Network Serial Port.
Page 47

Using the Configuration Management System 41
Configuring UART Settings
For proper operation, it is imperative that these settings always match the
settings of the device to which the bridge is connected via the RS-232
port. There are two groups of parameters that need to be configured to
accomplish this task: UART Settings and Flow Control Settings.
Flow control is the process of adjusting the flow of data from one device
to another to ensure that the receiving device can handle all of the
incoming data.
To configure the UART settings:
1 Select the baud rate of your device.
The baud rate indicates the data transfer rate of the serial port.
2 Determine the data bits setting of the device you are connecting to the
Bridge, then set the Data Bits setting for the bridge that matches the data
bits setting of that device.
The Data Bits setting determines the number of bits used to transmit
data. The possible values are 7 and 8.
3 Determine the stop bits setting of the device you are connecting to the
Bridge, then set the Stop Bits setting on the Bridge that matches the stop bits
setting of that device.
The Stop Bits setting determines the number of bits used to represent an
end of a character. The value can be 1 or 2.
4 Determine the parity bit setting of the device you are connecting to the
Bridge, then set the Parity Bit setting on the Bridge that matches the parity
bit setting of that device.
The Parity Bit setting is used to check for correct data transmission.
Options are: none, even, and odd.
Configuring Network Serial Port Settings
For Server Mode, click Server Mode and enter the port number to which
the Bridge connects in the List on port field. The default port number is
4000.
For Client Mode, select Client Mode and enter the IP address and port
number to which the Bridge connects. The default port number is 4000.
Page 48

42 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Applying Settings
After you set the UART settings, network serial port settings, and
operation mode, select Apply to make the settings take effect.
The socket can be substantially established between a client and server;
that is, a Bridge in server mode and the other in client mode. The Bridge
with the Network Serial Port option set cannot work alone. Generally, a
Bridge is set to server mode first, which listens to a designated port. The
other Bridge is then set to client mode, which connects to the designated
port on the IP address of the Bridge set to server mode.
Resetting the Bridge If the Bridge stops responding correctly, you can perform a reset, which
disrupts the network association temporarily, but does not affect Bridge
configuration settings that have already been applied with Apply.
To reset the Bridge, under Tools, click Reset Wireless Workgroup Bridge.
In the next page, click Reset.
The Bridge can also be reset using the Wireless Infrastructure Device
Manager (Widman). Right-click the Bridge in Widman, and then select
Reset.
Page 49

Using the Configuration Management System 43
Restoring the Bridge
to Factory Defaults
You can restore Bridge settings to the defaults that were set at the
factory either manually or through software.
To restore the settings manually, insert a pointed object (such as the end
of a straightened paper clip) into the reset hole on the back of the Bridge,
and hold for five seconds.
The reset hole is accessible with the Bridge in the cradle, as shown in
Figure 16, or with the Bridge out of the cradle.
Figure 16 Manually Resetting the Bridge in the Cradle
Reset Hole
RESET
RESET
To restore the settings through software:
1 Under Tools, click Restore Factory Defaults.
2 Click Restore.
If the Bridge was using an IP address setting other than the default,
restoring the factory defaults will change the IP address. If you want to
continue configuring the Bridge, do the following:
1 Close your browser.
2 Return to the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager and click Refresh.
3 Select the device and click Configure to start a new configuration session.
Page 50

44 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Upgrading the
System
You can download firmware updates or updates of the Configuration
Management System from the 3Com Web site and install those updates
on the Bridge.
Options for upgrading the system include using a Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP) server or File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server. The Bridge acts
as a TFTP or FTP client to receive the download. Alternatively, you an use
the HTTP option and upload the firmware from a downloaded file placed
on your computer.
Using FTP (default)
The general instructions for installing the upgrade using FTP are:
1 Launch the Configuration Management System.
2 Under Tools, click Upgrade System.
3 Select FTP.
4 Enter the IP address of the FTP server where the upgrade files are located.
5 Enter the user name, password, path and filename in the appropriate
fields.
6 Click Upgrade.
Using TFTP
The general instructions for installing the upgrade using TFTP are:
1 Launch the Configuration Management System.
2 Under Tools, click Upgrade System.
3 Select TFTP.
4 Enter the file name for the firmware.
5 Enter the IP address of the TFTP server where the upgrade files are located.
6 Click Upgrade.
Page 51

Using the Configuration Management System 45
Using HTTP
The general instructions for installing the upgrade using HTTP are:
1 Launch the Configuration Management System.
2 Under Tools, click Upgrade System.
3 Select HTTP.
4 Click Browse to locate the downloaded firmware file.
5 Click Upgrade to start the upgrade process.
The upgrade takes place through the HTTP protocol from the local
computer.
Changing the
Administration Login
Name and Password
Backing up a
Configuration
3Com recommends that you set a password to protect against
unauthorized access. After you set the password, you must enter it each
time you launch the configuration for the device.
Under Tools, click Change Administration Password. The Change
Administration Password page appears, where you can change the login
name and administration password for the device. Enter the current
password and new password in the spaces provided and click Save.
As part of system maintenance, you should save and back up the
configurations of individual Bridges in case you need to reload them in
the future. The backup saves all the parameters of the selected Bridge in
a file on your computer. The file can be used later to restore the
configuration on this or another bridge.
1 Set the Bridge parameters in the System Configuration pages.
2 Under Tools, click Backup Wireless Workgroup Bridge.
3 In the next page, click Backup Now.
4 Specify a name and location for the backup, and click OK.
Page 52

46 CHAPTER 3: CONFIGURING THE BRIDGE
Restoring a
Configuration
Logging Out To log out of the Configuration Management System, click Logout under
Clearing the Ethernet
Client List
If you have stored a backup configuration on your computer, you can
restore the configuration as follows:
1 Under Tools, click Restore Wireless Workgroup Bridge.
2 In the next page, click Browse and select the backup file to upload.
3 Click Restore.
The configuration is restored and activated on the Bridge. This operation
may cause the Bridge to reboot.
If the Bridge was using an IP address setting other than the backup,
restoring the configuration will change the IP address. If you want to
continue configuring the Bridge, do the following:
1 Close your browser.
2 Return to the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager and click Refresh.
3 Select the device and click Configure to start a new configuration session.
Tools.
The Bridge supports up to 16 specific clients (for example, computers and
printers) and keeps track of the clients with a list of their MAC addresses.
After the client limit is reached, you must clear the client list to allow a
new client to associate with the network. For example, in a hub
configuration with 16 clients connected, if you disconnect a desktop
computer and connect a new laptop in its place, you must clear the client
list to establish network association for the laptop.
To clear the Ethernet Client List:
1 Disconnect a client by unplugging its Ethernet cable from the hub or the
Bridge.
2 Launch the Configuration Management System.
3 Under System Status, click Ethernet Client List.
4 In the Ethernet Client List page, click Clear Client List.
The Bridge erases the client list. Clients that remain connected to the Bridge
are added to the list automatically when they next interact with the network.
5 Connect the new client by plugging its Ethernet cable into the hub or the
Bridge.
Page 53

Using the Configuration Management System 47
Viewing Connection
Status
Viewing System
Summary
Under System Summary, click Connection Status to view a summary of the
Bridge’s current connection information. See Table 8 on page 27 for details.
Under System Summary, you can view the following information:
Table 14 System Summary Page
Property Description Default Value
Device Name The name assigned to the Bridge. You can
change the default name to one of your
choice by clicking System Properties under
System Configuration.
Device Location If you use the default device name, entering
the location is optional.
Country Code The Country Code determines the available
channels and transmission power level
based on regulatory restrictions in the
county where the Bridge is installed.
Transmit Power The level of transmission power (100%,
50%, 25%, 12%, or Min).
You can change this setting by clicking
Wireless Network under System Configuration.
MAC Address The MAC address of the Bridge. N/A
Serial Number The serial number of the Bridge. N/A
Firmware Version The version of firmware the Bridge is
currently using.
DHCP Client Determines if the Bridge obtains its
IP address from the DHCP server on the
network.
IP Address The IP address of the Bridge. You can
change this address by clicking IP Network
under System Configuration.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask address of the Bridge.
You can change this address by clicking IP
Network under System Configuration.
Data Preamble The data preamble setting (Short [Enhanced
performance] or Long [Wi-Fi Interoperable]).
To change this setting, click Wireless
Network under System Configuration.
System Up Time The elapsed time since the Bridge booted up. Day 0, 0:00:00
Date Manufactured The date the Bridge was manufactured. N/A
3Com WWB
None
Varies
100%
N/A
On
Varies
Varies
Long
Click Refresh to update the information.
Page 54

Page 55

4
TROUBLESHOOTING
Diagnosing Problems
If you have difficulty with the Bridge, try the solutions in the following
table.
Table 15 Troubleshooting
Symptom Solution(s)
16 devices have been
connected to the Bridge,
either simultaneously or
sequentially. After
connecting another device,
the new device cannot
associate with the network.
The Bridge supports up to 16 specific clients (for
example, computers and printers) and keeps track of
them using a client list of MAC addresses. After the
client limit is reached, you must clear the client list to
allow a new client to associate. For example, in a hub
configuration with 16 clients connected, if you
disconnect a desktop computer and connect a laptop
in its place, you must clear the client list to establish
network association.
1 Disconnect a client by unplugging its Ethernet cable
from the hub.
2 Use the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device
Manager to select the Bridge and launch its
Configuration Management System.
3 Under System Configuration, click Ethernet Client
List. The Ethernet Client List page appears. Click
Clear Client List.
4 Connect the new client by plugging its Ethernet
cable into the hub.
Page 56

50 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING
Table 15 Troubleshooting (continued)
After you change the IP
address, after you restore a
backup configuration, or
after you reset the Bridge to
factory defaults, the
Configuration Management
System stops responding
and you cannot continue
configuring the Bridge.
The Bridge cannot associate
with an access point.
The Wireless Network Tree
does not appear in the
3Com Wireless
Infrastructure Device
Manager window.
The Bridge has a yellow
exclamation point (!) next to
it in the Wireless
Infrastructure Device
Manager.
Two Bridges cannot
communicate in ad-hoc
mode.
If you change the IP address and click Apply, you
cannot continue to configure the device using the old
IP address. Similarly, after you restore a backup
configuration or reset the Bridge to factory defaults,
the IP address setting may be changed.
To recover from this situation and continue configuring
the Bridge:
1 Close your browser.
2 Return to the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device
Manager and click Refresh.
3 Select the device and click Configure to start a new
configuration session and set its IP address.
■ Adjust the position of the Bridge to improve
reception.
■ Launch the Bridge Configuration Management
System and make sure the security settings on the
Bridge match those on the access point.
Verify that you are using the correct network adapter.
In the device manager window, click Choose NIC.
Select the network adapter for the network you want
to scan, and click OK.
The Bridge is on a different subnet than the computer
attempting to configure it.
To recover from this situation and continue configuring
the Bridge:
1 Close your browser.
2 Return to the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device
Manager and click Refresh.
3 Select the device and click Configure to start a new
configuration session.
4 Make sure the subnet address matches that of the
computer.
■ Adjust the positions of the Bridges to improve reception.
■ To ensure correct operation in ad-hoc mode, the
settings on the two Bridges must match exactly.
Launch the Bridge Configuration Management
System and make sure that the Wireless LAN Service
Area, channel selections, Data Preamble setting, and
security setting are the same on both Bridges.
Page 57

Table 15 Troubleshooting (continued)
Disconnecting the Bridge 51
Disconnecting the Bridge
You are running
Windows NT. After you
connect the Bridge, your
computer cannot obtain a
valid IP address.
Access to the Bridge
through Ethernet is blocked
because of incorrect
settings in the Access
Control List.
The Bridge configuration settings may not be compatible
with the network. If they are not, and your Windows NT
computer is set up to obtain its IP address from a DHCP
server, the Bridge is unable to associate with the network
to obtain the IP address.
To work around this, set a static IP address on your
computer. Then set the Bridge configuration to match
the network. When the Bridge is able to associate,
reset your computer to obtain its IP address from the
DHCP server. If the Bridge should also obtain its IP
settings from the DHCP server, make sure this is
configured properly on the IP Network page and
applied just before ending the session.
Restore the Bridge to factory default settings (see
“Restoring the Bridge to Factory Defaults” on page 43).
The factory default setting for the Access Control List is
disabled. After the factory default settings are restored,
the Bridge can be accessed through Ethernet again.
To disconnect the Bridge:
CAUTION: Disconnecting the Bridge ends the network association. To avoid
possible data loss, exit all networking applications on connected devices before you
disconnect the Bridge.
1 Unplug the Bridge Ethernet cable from the hub or other device.
Uninstalling Software and Documentation
2 Unplug the Bridge power cord.
If you want to uninstall the 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge
software and documentation, you can either use the standard operating
system procedure for removing programs or use the following shortcut:
1 From the Windows Start menu, select Start > Programs > 3Com Wireless
> Uninstall 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager.
2 When prompted to confirm, click OK.
Page 58

52 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING
Upgrading Bridge Firmware
Firmware is the software that is installed on the Bridge at the factory.
Some problems can be solved by installing a new version of the firmware.
For details on how to download a firmware update from the 3Com
customer support Web site and install it on your Bridge, see “Upgrading
the System” on page 44
Page 59

A
OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR 3COM PRODUCT
3Com offers product registration, case management, and repair services
through eSupport.3com.com. You must have a user name and password to
access these services, which are described in this appendix.
Register Your Product to Gain Service Benefits
Solve Problems
Online
To take advantage of warranty and other service benefits, you must first
register your product at:
http://eSupport.3com.com/
3Com eSupport services are based on accounts that are created or that
you are authorized to access.
The 3Com Knowledgebase helps you to troubleshoot 3Com products.
This query-based interactive tool is located at:
http://knowledgebase.3com.com
It contains thousands of technical solutions written by 3Com support
engineers.
Page 60

54 APPENDIX A: OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR 3COM PRODUCT
Purchase Extended
Warranty and
Professional Services
Access Software
Downloads
To enhance response times or extend your warranty benefits, you can
purchase value-added services such as 24x7 telephone technical support,
software upgrades, onsite assistance, or advanced hardware replacement.
Experienced engineers are available to manage your installation with
minimal disruption to your network. Expert assessment and implementation
services are offered to fill resource gaps and ensure the success of your
networking projects. For more information on 3Com Extended Warranty and
Professional Services, see:
http://www.3com.com/
Contact your authorized 3Com reseller or 3Com for additional product
and support information. See the table of access numbers later in this
appendix.
You are entitled to bug fix / maintenance releases for the version of
software that you initially purchased with your 3Com product. To obtain
access to this software, you need to register your product and then use the
Serial Number as your login. Restricted Software is available at:
http://eSupport.3com.com/
To obtain software releases that follow the software version that you
originally purchased, 3Com recommends that you buy an Express or
Guardian contract, a Software Upgrades contract, or an equivalent support
contract from 3Com or your reseller. Support contracts that include software
upgrades cover feature enhancements, incremental functionality, and bug
fixes, but they do not include software that is released by 3Com as a
separately ordered product. Separately orderable software releases and
licenses are listed in the 3Com Price List and
are available for purchase from
your 3Com reseller.
Contact Us 3Com offers telephone, Internet, and e-mail access to technical support and
repair services. To access these services for your region, use the appropriate
telephone number, URL, or e-mail address from the table in the next section.
Page 61

Contact Us 55
Telephone Technical
Support and Repair
To obtain telephone support as part of your warranty and other service
benefits, you must first register your product at:
http://eSupport.3com.com/
When you contact 3Com for assistance, please have the following
information ready:
■ Product model name, part number, and serial number
■ A list of system hardware and software, including revision level
■ Diagnostic error messages
■ Details about recent configuration changes, if applicable
To send a product directly to 3Com for repair, you must first obtain a
return materials authorization number (RMA). Products sent to 3Com
without authorization numbers clearly marked on the outside of the package
will be returned to the sender unopened, at the sender’s expense. If your
product is registered and under warranty, you can obtain an RMA number
online at
http://eSupport.3com.com/. First-time users must apply for a
user name and password.
Telephone numbers are correct at the time of publication. Find a current
directory of 3Com resources by region at:
http://csoweb4.3com.com/contactus/
Country Telephone Number Country Telephone Number
Asia, Pacific Rim Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Australia
Hong Kong
India
Indonesia
Japan
Malaysia
New Zealand
You can also obtain support in this region at this e-mail address:
apr_technical_support@3com.com
Or request a repair authorization number (RMA) by fax using this number: + 61 2 9937 5048
1 800 678 515
800 933 486
+61 2 9424 5179 or
000800 650 1111
001 803 61009
00531 616 439 or
03 3507 5984
1800 801 777
0800 446 398
Pakistan
Philippines
P.R. of China
Singapore
S. Korea
Taiwan
Thailand
+61 2 9937 5083
1235 61 266 2602 or
1800 1 888 9469
800 810 3033
0 6161 463
80
080 333 3308
00801 611 261
001 800 611 2000
Page 62

56 APPENDIX A: OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR 3COM PRODUCT
Country Telephone Number Country Telephone Number
Europe, Middle East, and Africa Telephone Technical Support and Repair
From anywhere in these regions, call: +44 (0)1442 435529
From the following countries, call the appropriate number:
Austria
Belgium
Denmark
Finland
France
Germany
Hungary
Ireland
Israel
Italy
01 7956 7124
070 700 770
7010 7289
01080 2783
0825 809 622
01805 404 747
06800 12813
01407 3387
1800 945 3794
199 161346
Luxembourg
Netherlands
Norway
Poland
Portugal
South Africa
Spain
Sweden
Switzerland
U.K.
342 0808128
0900 777 7737
815 33 047
00800 441 1357
707 200 123
0800 995 014
9 021 60455
07711 14453
08488 50112
0870 909 3266
You can also obtain support in this region using this URL:
http://emea.3com.com/support/email.html
Latin America Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Antigua
Argentina
Aruba
Bahamas
Barbados
Belize
Bermuda
Bonaire
Brazil
Cayman
Chile
Colombia
Costa Rica
Curacao
Ecuador
Dominican Republic
1 800 988 2112
0 810 444 3COM
1 800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
52 5 201 0010
1 800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
0800 13 3COM
1 800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
Guatemala
Haiti
Honduras
Jamaica
Martinique
Mexico
Nicaragua
Panama
Paraguay
Peru
Puerto Rico
Salvador
Trinidad and Tobago
Uruguay
Venezuela
Virgin Islands
AT&T +800 998 2112
57 1 657 0888
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
571 657 0888
01 800 849CARE
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
54 11 4894 1888
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
57 1 657 0888
You can also obtain support in this region in the following ways:
■ Spanish speakers, enter the URL: http://lat.3com.com/lat/support/form.html
■ Portuguese speakers, enter the URL: http://lat.3com.com/br/support/form.html
■ English speakers in Latin America should send e-mail to: lat_support_anc@3com.com
US and Canada — Telephone Technical Support and Repair
All locations: Network Jacks; Wired or Wireless Network Interface Cards:
All other 3Com products
1 847 262 0070
1 800 876 3266
Page 63

END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
Customer shall take all steps necessary to protect Wind River's and its licensors' proprietary rights in the
Run-Time Module and to ensure that each Run-Time Module distributed by Customer will be accompanied
by a localized copy of an End User License Agreement.
Such End User License Agreement shall prohibit the End User from: (i) copying the Run-Time Module, except
for archive purposes consistent with the End User's archive procedures; (ii) transferring the Run-Time Module
to a third party apart from the Target Application; (iii) modifying, decompiling, disassembling, reverse
engineering or otherwise attempting to derive the Source Code of the Run-Time Module; (iv) exporting the
Run-Time Module or underlying technology in contravention of applicable U.S. and foreign export laws and
regulations; and (v) using the Run-Time Module other than in connection with operation of the Target
Application.
In addition, the End User License Agreement shall: (i) state that the Run-Time Module is licensed, not sold and
that Customer and its licensors retain ownership of all copies of the Run-Time Module; (ii) expressly disclaim
all implied warranties, including without limitation the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a
particular purpose, title and non-infringement; (iii) exclude liability for any special, indirect, punitive,
incidental and consequential damages; and (iv) require that any further distribution of the Run-Time Module
be subject to the same restrictions set forth herein.
The End User License Agreement shall also state that, with respect to the Run-Time Module, Wind River and
its licensors are third party beneficiaries of the End User License Agreement and that the provisions related to
the Run-Time Module are made expressly for the benefit of, and are enforceable by, Wind River and its
licensors.
Page 64

Page 65

REGULATORY INFORMATION
The 3Com 11 a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge (Model WL-560) must be installed and used in strict
accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions as described in the user documentation that comes with the
product. This device complies with the following radio frequency and safety standards.
This product contains encryption. It is unlawful to export out of the U.S. without obtaining a U.S. Export
License.
This product does not contain any user serviceable components. Any unauthorized product changes or
modifications
CAUTION: EXPOSURE TO RADIO FREQUENCY RADIATION.
This device generates and radiates radio-frequency energy. In order to comply with FCC radio-frequency
exposure guidelines for an uncontrolled environment, this equipment must be installed and operated while
maintaining a minimum body to antenna distance of 20 cm (approximately 8 in.).
This device must not be co-located or operated in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
The installer of this radio equipment must ensure that the antenna is located or pointed such that it does not
emit RF field in excess of Health Canada limits for the general population; consult Safety Code 6, obtainable
from Health Canada’s website www.hc-sc.gc.ca/rpb.
USA - RADIO FREQUENCY REQUIREMENTS.
This device is for indoor use only when using channels 36, 40, 44 or 48 in the 5.15 to 5.25 GHz frequency
range.
High power radars are allocated as primary users of the 5.25 to 5.35 GHz and 5.65 to 5.85 GHz bands. These
radar stations can cause interference with and/or damage this device.
USA-FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION (FCC)
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1)
This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy. If not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, it may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined
by tuning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try and correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
■ Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
■ Increase the distance between the equipment and the receiver
■ Connect the equipment to outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected
■ Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
The user may find the following booklet prepared by the Federal Communications Commission helpful:
The Interference Handbook
This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402. Stock No.
004-000-0034504.
3Com is not responsible for any radio or television interference caused by unauthorized modification of the
devices included with this 3Com 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge (Model WL-560), or the substitution or
attachment of connecting cables and equipment other than specified by 3Com.
The correction of interference caused by such unauthorized modification, substitution or attachment will be
the responsibility of the user.
will invalidate 3Com’s warranty and all applicable regulatory certifications and approvals.
Page 66

MANUFACTURER’S DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive
Marlborough, MA 01752-3064, USA
(800) 527-8677
Date: June 30, 2004
Declares that the Product:
Brand Name: 3Com Corporation
Model Number: WL-560
Equipment Type: 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge
Complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Page 67

CANADA – INDUSTRY CANADA (IC)
This device complies with RSS 210 of Industry Canada.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this
device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of this
device.”
L ‘ utilisation de ce dispositif est autorisée seulement aux conditions suivantes: (1) il ne doit pas produire de
brouillage et (2) l’ utilisateur du dispositif doit étre prêt à accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique reçu, même
si ce brouillage est susceptible de compromettre le fonctionnement du dispositif.
The term "IC" before the equipment certification number only signifies that the Industry Canada technical
specifications were met.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that
the equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) is not more than that required for successful
communication. To prevent radio interference to the licensed service, this device is intended to be operated
indoors and away from windows to provide maximum shielding. Equipment (or its transmit antenna) that is
installed outdoors is subject to licensing.
Pour empecher que cet appareil cause du brouillage au service faisant l'objet d'une licence, il doit etre utilize
a l'interieur et devrait etre place loin des fenetres afin de Fournier un ecram de blindage maximal. Si le matriel
(ou son antenne d'emission) est installe a l'exterieur, il doit faire l'objet d'une licence.
High power radars are allocated as primary users of the 5.25 to 5.35 GHz and 5.65 to 5.85 GHz bands. These
radar stations can cause interference with and/or damage this device.
INDUSTRY CANADA (IC) EMISSIONS COMPLIANCE STATEMENT
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
AVIS DE CONFORMITÉ À LA RÉGLEMENTATION D’INDUSTRIE CANADA
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conform à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
SAFETY COMPLIANCE NOTICE
This device has been tested and certified according to the following safety standards and is intended for use
only in Information Technology Equipment which has been tested to these or other equivalent standards:
■ UL Standard 60950 (3rd Edition) or 60950-1
■ CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 60950 or 60950-1
■ IEC 60950 or 60950-1
■ EN 60950 or 60950-1
Page 68

EUROPE – EU DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Marking by the above symbol indicates compliance with the Essential Requirements and other relevant
provisions of the R&TTE Directive of the European Union (1999/5/EC). This equipment meets the following
conformance standards:
EN300 328, EN301 893, EN301 489-17, EN60950
NOTE: To ensure product operation is in compliance with local regulations, select the country in which the
product is installed. Refer to “Configuring the Bridge” in the user guide.
EUROPE - DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY IN LANGUAGES OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITY
English Hereby, 3Com Corporation, declares that this 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge
Finnish 3Com Corporation vakuuttaa täten että 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge
Dutch Hierbij verklaart 3Com Corporation dat het toestel 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup
French Par la présente 3Com Corporation déclare que l'appareil 11a/b/g Wireless
Swedish Härmed intygar 3Com Corporation Company att denna 11a/b/g Wireless
Danish Undertegnede 3Com Corporation Company erklærer herved, at følgende udstyr
German Hiermit erklärt 3Com Corporation, dass sich dieser/diese/dieses 11a/b/g Wireless
Greek М Е ФЗН РБСП ХУБ 3Com Corporation ДЗЛЩНЕЙ П ФЙ 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup
Italian Con la presente 3Com Corporation dichiara che questo 11a/b/g Wireless
is in compliance with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of
Directive 1999/5/EC.
tyyppinen laite on direktiivin 1999/5/EY oleellisten vaatimusten ja sitä koskevien
direktiivin muiden ehtojen mukainen.
Bridge in overeenstemming is met de essentiële eisen en de andere relevante
bepalingen van richtlijn 1999/5/EG
Bij deze verklaart 3Com Corporation dat deze 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge
voldoet aan de essentiële eisen en aan de overige relevante bepalingen van
Richtlijn 1999/5/EC.
Workgroup Bridge est conforme aux exigences essentielles et aux autres
dispositions pertinentes de la directive 1999/5/CE
Par la présente, 3Com Corporation déclare que ce 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup
Bridge est conforme aux exigences essentielles et aux autres dispositions de la
directive 1999/5/CE qui lui sont applicables
Workgroup Bridge står I överensstämmelse med de väsentliga egenskapskrav och
övriga relevanta bestämmelser som framgår av direktiv 1999/5/EG.
11a/b/g Wirelss Workgroup Bridge overholder de væsentlige krav og øvrige relevante
krav i direktiv 1999/5/EF.
Workgroup Bridge in Übereinstimmung mit den grundlegenden Anforderungen
und den anderen relevanten Vorschriften der Richtlinie 1999/5/EG befindet".
(BMWi)
Hiermit erklärt 3Com Corporation die Übereinstimmung des Gerätes 11a/b/g
Wireless Workgroup Bridge mit den grundlegenden Anforderungen und den
anderen relevanten Festlegungen der Richtlinie 1999/5/EG. (Wien)
Birdge УХМ М П СЦЩНЕФБЙ РСП У ФЙУ П ХУЙЩДЕЙУ БРБЙФЗУЕЙУ КБЙ ФЙУ ЛП
ЙРЕУ УЧЕФЙКЕУ ДЙБФБОЕЙУ ФЗУ П ДЗГЙБУ 1999/5/ЕК
Workgroup Bridge è conforme ai requisiti essenziali ed alle altre disposizioni
pertinenti stabilite dalla direttiva 1999/5/CE.
Page 69

Spanish Por medio de la presente 3Com Corporation declara que el 11a/b/g Wireless
Portuguese 3Com Corporation declara que este 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge está
Workgroup Bridge cumple con los requisitos esenciales y cualesquiera otras
disposiciones aplicables o exigibles de la Directiva 1999/5/CE
conforme com os requisitos essenciais e outras disposições da Directiva 1999/5/CE.
EUROPE – RESTRICTIONS FOR USE OF 2.4GHZ FREQUENCIES IN EUROPEAN COMMUNITY COUNTRIES
België/
Belgique:
Deutschland: License required for outdoor installations. Check with reseller for procedure to follow
France: Restricted frequency band: only channels 1 to 7 (2400 MHz and 2454 MHz respectively)
Italia: License required for indoor use. Use with outdoor installations not allowed.
Nederland: License required for outdoor installations. Check with reseller for procedure to follow.
For private usage outside buildings across public grounds over less than 300m no special
registration with IBPT/BIPT is required. Registration to IBPT/BIPT is required
for private usage outside buildings across public grounds over more than 300m. For
registration and license please contact IBPT/BIPT.
Voor privé-gebruik buiten gebouw over publieke groud over afstand kleiner dan 300m
geen registratie bij BIPT/IBPT nodig; voor gebruik over afstand groter dan 300m is wel
registratie bij BIPT/IBPT nodig. Voor registratie of licentie kunt u contact opnemen met
BIPT.
Dans le cas d’une utilisation privée, à l’extérieur d’un bâtiment, au-dessus d’un espace
public, aucun enregistrement n’est nécessaire pour une distance de moins de 300m. Pour
une distance supérieure à 300m un enregistrement auprès de I’IBPT est requise. Pour les
enregistrements et licences, veuillez contacter I’IBPT.
Anmeldung im Outdoor-Bereich notwendig, aber nicht genehmigungspflichtig.Bitte mit
Händler die Vorgehensweise abstimmen.
may be used outdoors in France. Please contact A.R.T. (http://www.arttelecom.fr) for
applicable procedures to follow.
Bande de fréquence restreinte: seuls les canaux 1- 7 (2400 et 2454 MHz respectivement)
doivent être utilisés endroits extérieur en France. Vous pouvez contacter I’Autorité de
Régulation des Télécommuniations (http://www.art-telecom.fr) pour la procédure à
suivre.
E’necessaria la concessione ministeriale anche per l’uso interno.
Verificare con i rivenditori la procedura da seguire.
Licentie verplicht voor gebruik met buitenantennes. Neem contact op met verkoper voor
juiste procedure.
Page 70

EUROPE – RESTRICTIONS FOR USE OF 5GHZ FREQUENCIES IN EUROPEAN COMMUNITY COUNTRIES
European Community
Countries
5150-5250 MHz
Channels: 36, 40,
44, 48
Indoor Only
5250-5350 MHz
Channels: 52, 56,
60, 64
Indoor Only
5470-5725MHz
Channels: 100, 104,
108, 112, 116, 120,
124, 128, 132, 136, 140
Indoor/Outdoor
Austria
✔
X X
Belgium, France,
Switzerland,
Liechtenstein
Denmark, Finland,
Germany, Greece,
Iceland, Ireland, Italy,
Luxembourg,
Netherlands, Norway,
Portugal, Spain, Sweden,
UK
✔ allowed X not allowed
■ To remain in conformance with European spectrum usage laws for Wireless LAN operation, the above
2.4GHz and 5GHz channel limitations apply. The user should check the current channel of operation. If
operation is occurring outside of the allowable frequencies as listed above, the user must cease operating
the 11a/b/g Wireless Workgroup Bridge at that location and consult the local technical support staff
responsible for the wireless network.
■ The 5GHz Turbo mode feature is not allowed for operation in any European Community country.
■ This device must not be operated in ad-hoc mode using channels in the 5GHz bands in the European
Community. Ad-hoc mode provides a direct communication between two client devices without a
Wireless LAN Access Point.
■ This device must be used with Access Points that have employed and activated a radar detection feature
required for European Community operation in the 5GHz bands. This device will operate under the control
of the Access Point in order to avoid operating on a channel occupied by any radar system in the area. The
presence of nearby radar operation may result in temporary interruption in communications of this device.
The Access Point’s radar detection feature will automatically restart operation on a channel free of radar.
You may consult with the local technical support staff responsible for the wireless network to ensure the
Access Point device(s) are properly configured for European Community operation.
✔ ✔ X
✔ ✔ ✔
 Loading...
Loading...