Page 1

OfficeConnect
®
ADSL Wireless 54 Mbps 11g Firewall
Router
User Guide
WL-552
3CRWDR101A-75
3CRWDR101B-75
http://www.3Com.com/
Part No. 10015091 Rev. AA
Published March 2006
Page 2

3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive,
Marlborough, MA
USA 01752-3064
Copyright © 2004, 2005, 2006, 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be
reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation,
transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in content from time
to time without obligation on the part of 3Com Corporation to provide notification of such revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or condition of any kind, either
implied or expressed, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties, terms or conditions of
merchantability, satisfactory quality, and fitness for a particular purpose. 3Com may make improvements or
changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this documentation at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it is furnished under a license
agreement included with the product as a separate document, in the hard copy documentation, or on the
removable media in a directory file named LICENSE.TXT or !LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to locate a copy,
please contact 3Com and a copy will be provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the software described herein are
provided to you subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and developed solely at private expense.
Software is delivered as “Commercial Computer Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014 (June 1995) or
as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR 2.101(a) and as such is provided with only such rights as are
provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the Software. Technical data is provided with limited rights
only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015 (Nov 1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987), whichever is applicable.
You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any licensed program or
documentation contained in, or delivered to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the United States and may or may not
be registered in other countries.
3Com, and the 3Com logo are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation.
Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows
NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Novell and NetWare are registered trademarks of
Novell, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively
through X/Open Company, Ltd.
Netscape Navigator is a registered trademark of Netscape Communications.
JavaScript is a trademark of Sun Microsystems
Wi-Fi and the Wi-Fi logo are registered trademarks of the WI-Fi Alliance.
IEEE and 802 are trademarks of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are
associated.
ENVIRONMENTAL STATEMENT
It is the policy of 3Com Corporation to be environmentally-friendly in all operations. To uphold our policy, we
are committed to:
Establishing environmental performance standards that comply with national legislation and regulations.
Conserving energy, materials and natural resources in all operations.
Reducing the waste generated by all operations. Ensuring that all waste conforms to recognized environmental
standards. Maximizing the recyclable and reusable content of all products.
Ensuring that all products can be recycled, reused and disposed of safely.
Ensuring that all products are labelled according to recognized environmental standards.
Improving our environmental record on a continual basis.
End of Life Statement
3Com processes allow for the recovery, reclamation and safe disposal of all end-of-life electronic components.
Regulated Materials Statement
3Com products do not contain any hazardous or ozone-depleting material.
Environmental Statement about the Documentation
The documentation for this product is printed on paper that comes from sustainable, managed forests; it is
fully biodegradable and recyclable, and is completely chlorine-free. The varnish is environmentally-friendly, and
the inks are vegetable-based with a low heavy-metal content.
Page 3

CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Naming Convention 7
Conventions 8
Feedback About This User Guide 8
Related Documentation 9
1 INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 54 Mbps 11g Firewall Router 11
Router Advantages 13
Package Contents 13
Minimum System and Component Requirements 14
Physical Features 14
2 INSTALLING THE ROUTER
Introduction 17
Safety Information 17
Positioning the Router 17
Using the Rubber Feet 18
Wall Mounting 18
Powering Up the Router 19
Connecting the Router 19
3 SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically 23
Windows 2000 23
Windows XP 25
Windows 98/ME 25
Macintosh 25
Disabling PPPoE and PPTP Client Software 26
Disabling Web Proxy 26
Page 4

4 RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Accessing the Setup Wizard 27
Setup Wizard - Change Password 30
Setup Wizard - Time and Time Zone 30
Setup Wizard - Connection Type 31
Setup Wizard - LAN Settings 36
Setup Wizard - Wireless Settings 37
Setup Wizard - Configuration Summary 38
5 CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Navigating Through the Router Configuration screens 39
Main Menu 39
Welcome Screen 39
Status 39
LAN Settings 40
LAN Settings 40
DHCP Clients List 41
Wireless Settings 43
Configuration 44
Encryption 45
Connection Control 50
Client List 51
WDS Settings 51
Advance 52
Profile 53
Internet Settings 54
ATM PVC 54
DNS 65
Hostname & Clone MAC address 66
Firewall 67
SPI 67
Special Applications 71
Virtual Servers 72
DMZ 73
Page 5

Schedule Rule 74
PC Privileges 75
URL Filter 77
Server Control 79
Quality of Service 81
QoS Settings 81
Traf fic Map pin g 8 1
Traffic Statistics 82
Advanced 83
Security 83
Static Routes 86
RIP 87
DDNS 88
SNMP 90
Syslog 91
Proxy ARP 92
System Tools 93
Restart Router 93
Configuration 93
Upgrade 94
Time Zone 95
Ping 96
Traceroute 97
DNS Lookup 98
Status and Logs 99
Status 99
ADSL Status 99
ATM PVC Status 100
Routing Table 100
Logs 101
Support/Feedback 102
Support 102
Feedback 102
6 TROUBLESHOOTING
Basic Connection Checks 103
Browsing to the Router Configuration Screens 103
Page 6

Connecting to the Internet 104
Forgotten Password and Reset to Factory Defaults 104
Wireless Networking 105
Recovering from Corrupted Software 107
Frequently Asked Questions 108
A IP ADDRESSING
The Internet Protocol Suite 109
Managing the Router over the Network 109
IP Addresses and Subnet Masks 109
How does a Device Obtain an IP Address and Subnet Mask? 111
DHCP Addressing 111
Static Addressing 111
Auto-IP Addressing 111
B TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 54Mbps 11g Firewall Router 113
Standards 114
C SAFETY INFORMATION
D END USER SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT
E OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT
Register Your Product 123
Purchase Value-Added Services 123
Troubleshoot Online 124
Access Software Downloads 124
Telephone Technical Support and Repair 124
Contact Us 125
Page 7

GLOSSARY
REGULATORY NOTICES
INDEX
Page 8

Page 9
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide describes how to install and configure the 3Com
OfficeConnect
(3CRWDR101A-75/3CRWDR101B-75).
This guide is intended for use by those responsible for installing and
setting up network equipment; consequently, it assumes a basic working
knowledge of LANs (Local Area Networks) and Internet Routers.
If a release note is shipped with the 3Com OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless
54 Mbps 11g Firewall Router and contains information that differs from
the information in this guide, follow the information in the release note.
Most user guides and release notes are available in Adobe Acrobat
Reader Portable Document Format (PDF) on the 3Com World Wide Web
site:
http://www.3Com.com
©
ADSL Wireless 54 Mbps 11g Firewall Router
Naming Convention Throughout this guide, the 3Com OfficeConnect
Mbps 11g Firewall Router is referred to as the “Router”.
Category 3 and Category 5 Twisted Pair Cables are referred to as Twisted
Pair Cables throughout this guide.
©
ADSL Wireless 54
Page 10

8 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions Ta bl e 1 and Tab l e 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Table 1 Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Description
Information note Information that describes important features or
instructions.
Caution Information that alerts you to potential loss of data or
potential damage to an application, system, or device.
Warning Information that alerts you to potential personal
injury.
Table 2 Text Conventions
Convention Description
The words “enter”
and “type”
Keyboard key names If you must press two or more keys simultaneously, the key
Words in italics Italics are used to:
When you see the word “enter” in this guide, you must type
something, and then press Return or Enter. Do not press
Return or Enter when an instruction simply says “type.”
names are linked with a plus sign (+). Example:
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del
■ Emphasize a point.
■ Denote a new term at the place where it is defined in the
text.
■ Identify menu names, menu commands, and software
button names. Examples:
From the Help menu, select Contents.
Click OK.
Page 11
Feedback About This User Guide 9
Feedback About This User Guide
Your suggestions are very important to us. They will help make our
documentation more useful to you. Please e-mail comments about this
document to 3Com at:
pddtechpubs_comments@3com.com
Please include the following information when commenting:
■ Document title
■ Document part number (on the title page)
■ Page number (if appropriate)
Example:
■ 3Com OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 54Mbps 11g Firewall Router User
Guide
■ Part Number 10015091 Rev. AA
■ Page 24
Do not use this e-mail address for technical support questions. For
information about contacting Technical Support, please refer to
Appendix C
.
Related Documentation
In addition to this guide, each Router document set includes one
Installation Guide. This guide contains the instructions you need to install
and configure your Router.
Page 12

10 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Page 13

1
INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
Welcome to the world of networking with 3Com®. In the modern
business environment, communication and sharing information is crucial.
Computer networks have proved to be one of the fastest modes of
communication but, until recently, only large businesses could afford the
networking advantage.
OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 54 Mbps 11g Firewall Router
The OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 54 Mbps 11g Firewall Router is
designed to provide a cost-effective means of sharing a single broadband
Internet connection amongst several wired and wireless computers. The
Router also provides protection in the form of an electronic “firewall”
preventing anyone outside of your network from seeing your files or
damaging your computers. The Router can also prevent your users from
accessing Web sites which you find unsuitable.
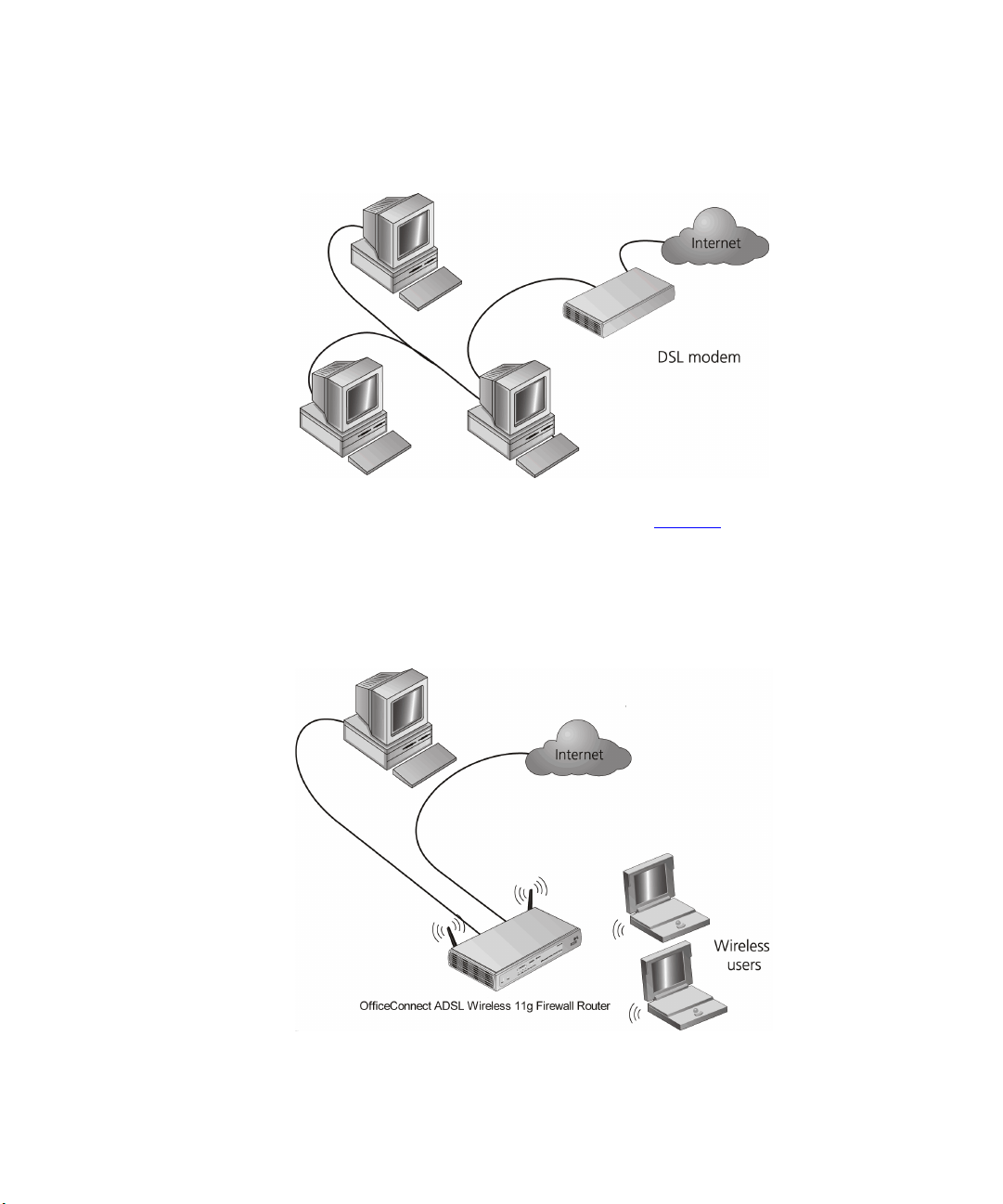
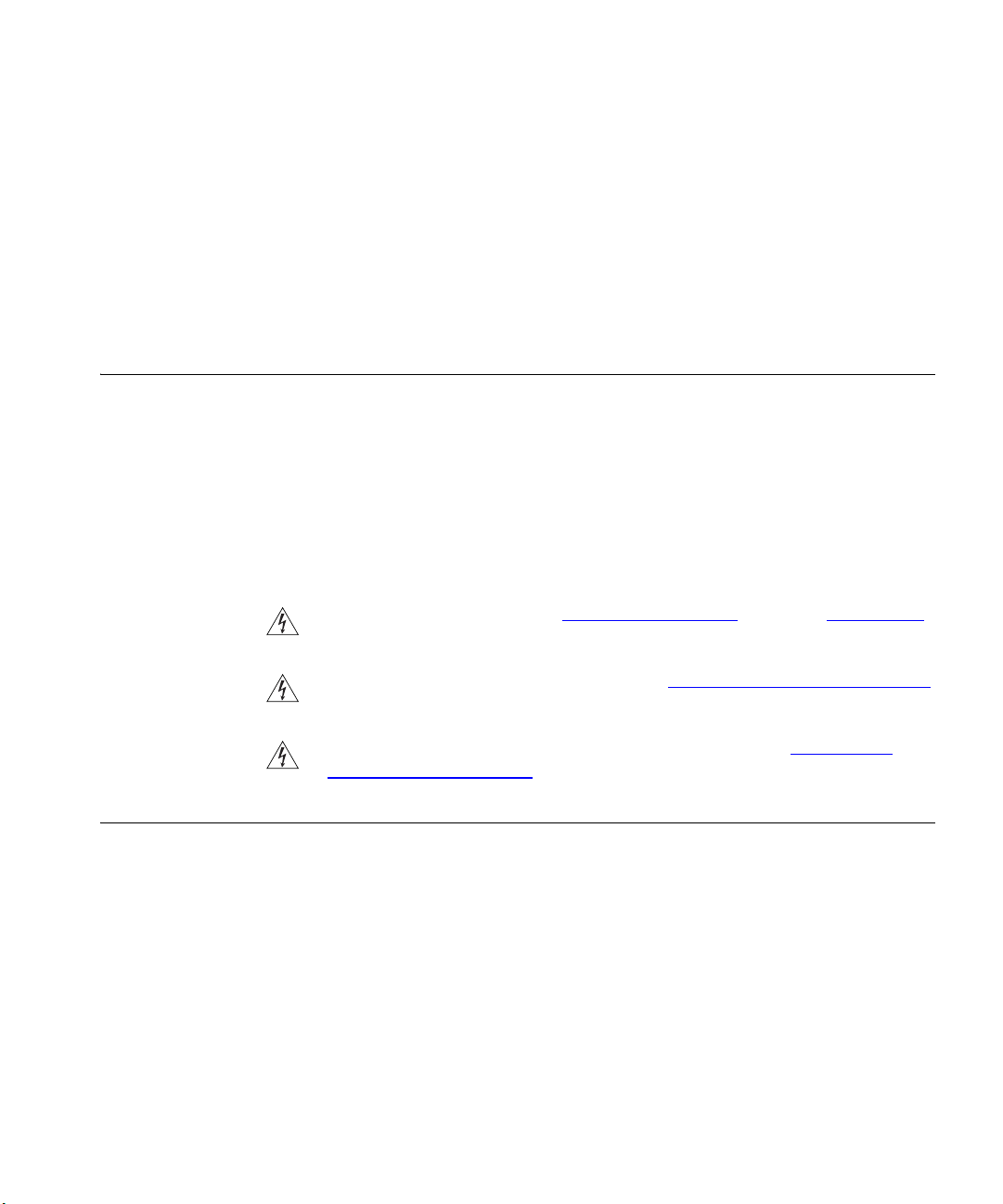
Figure 1
only one computer is connected to the Internet. This computer must
always be powered on for the other computers on the network to access
the Internet.
shows an example network without a Router. In this network,
Page 14
12 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
Figure 1 Example Network Without a Router
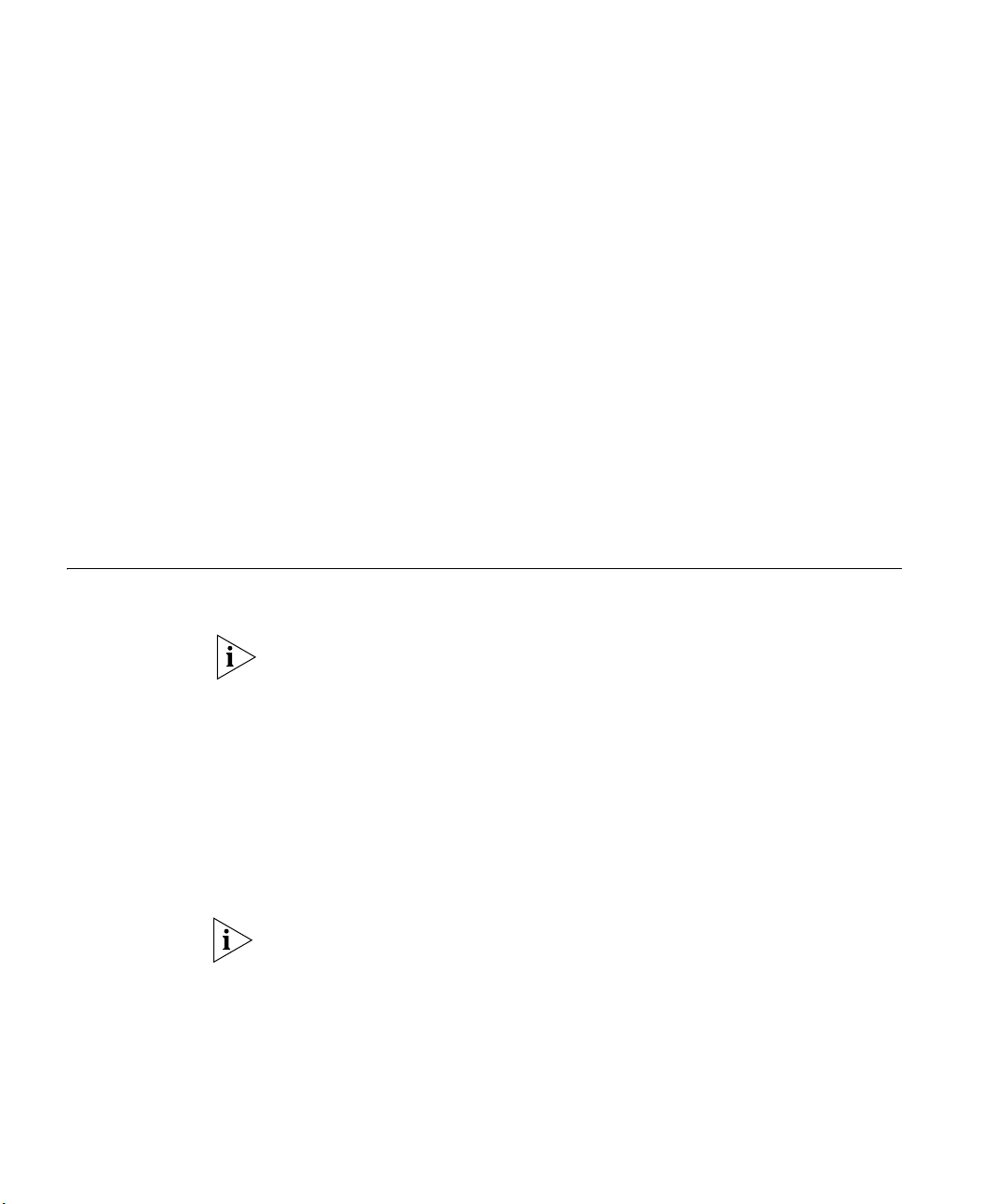
When you use the Router in your network (Figure 2), it becomes your
connection to the Internet. Connections can be made directly to the
Router, or to an OfficeConnect Switch or Hub, expanding the number of
computers you can have in your network.
Figure 2 Example Network Using a Firewall Router
Page 15

Router Advantages The advantages of the Router include:
■ Shared Internet connection for both wired and wireless computers
■ High speed 802.11g wireless networking
■ No need for a dedicated, “always on” computer serving as your
Internet connection
■ Cross-platform operation for compatibility with Windows, Unix and
Macintosh computers
■ Easy-to-use, Web-based setup and configuration
■ Provides centralization of all network address settings (DHCP)
■ Acts as a Virtual server to enable remote access to Web, FTP, and other
services on your network
■ Security — Firewall protection against Internet hacker attacks and
encryption to protect wireless network traffic
Package Contents The Router kit includes the following items:
Router Advantages 13
■ One OfficeConnect ADSL Wireless 54Mbps 11g Firewall Router
■ One power adapter for use with the Router
■ Four rubber feet
■ One Telephone Cable
■ One CD-ROM containing this User Guide
■ Installation Guide
■ One Support and Safety Information Sheet
■ One Warranty Flyer
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact your retailer.
Page 16
14 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
Minimum System and Component Requirements
Your Router requires that the computer(s) and components in your
network be configured with at least the following:
■ A computer with an operating system that supports TCP/IP
networking protocols (for example Windows 98/NT/Me/2000/XP, Unix,
Mac OS 8.5 or higher).
■ An Ethernet 10 Mbps or 10/100 Mbps NIC for each computer to be
connected to the four-port switch on your Router.
■ An 802.11b or 802.11g wireless NIC.
■ An active ADSL subscription and connection.
■ A Web browser that supports JavaScript, such as Netscape 4.7 or
higher, Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher, or Mozilla 1.2.1 or higher.
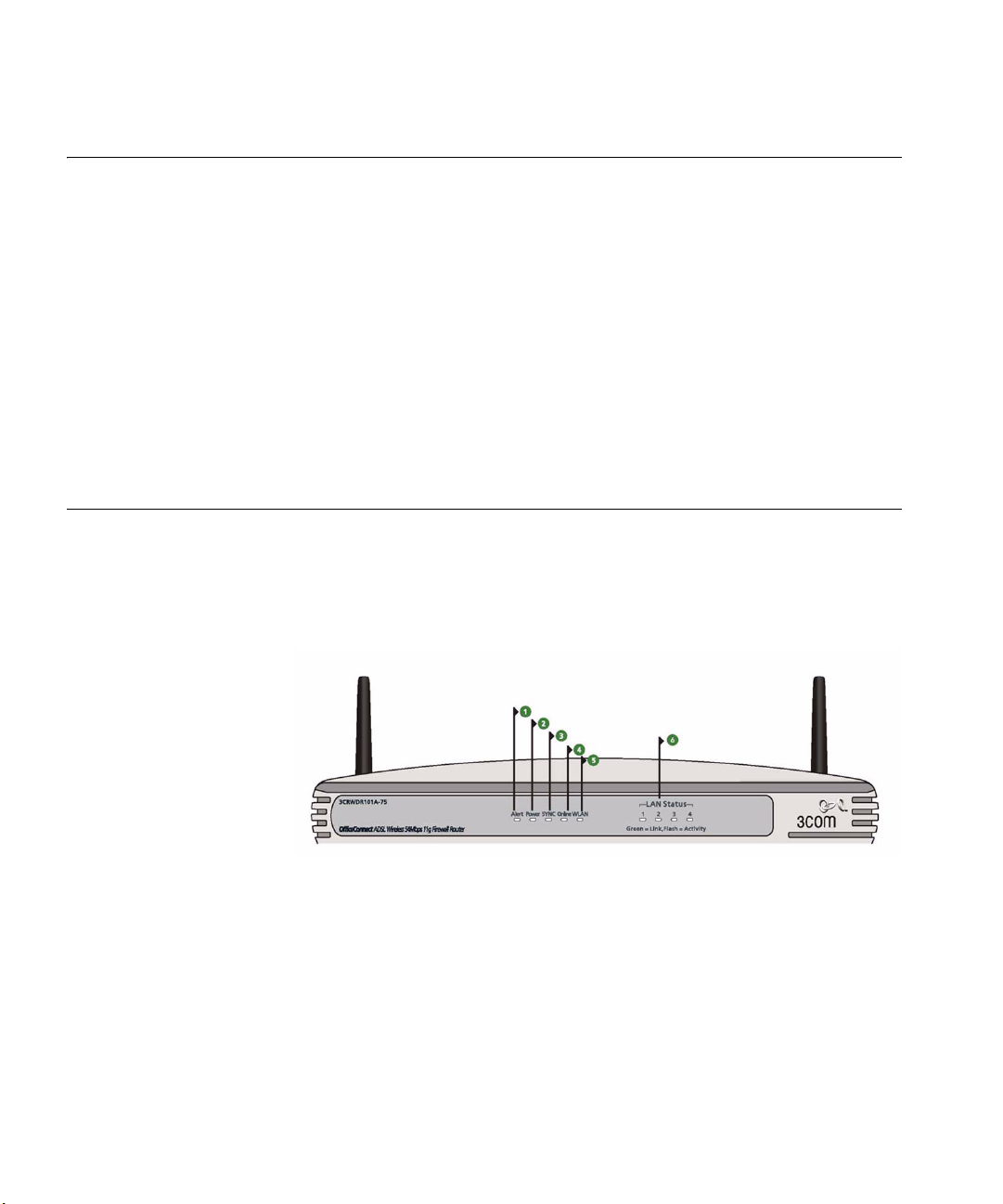
Physical Features The front panel of the Router contains a series of indicator lights (LEDs)
that help describe the state of various networking and connection
operations.
Figure 3 Router - Front Panel
1 Alert LED
Orange
Fast flash during self test. If self test fails the LED will remain on.
Fast flash during software upgrade.
Fast flash for software reset to the factory defaults.
Fast flash for hardware reset to the factory defaults.
The LED is on for 2 seconds when the firewall detects a hacker attack.
Page 17

Physical Features 15
2Power LED
Green
Indicates that the Router is powered on, and the boot up is successful.
3SYNC LED
Green
If the LED is on it indicates that DSL connection is present. This LED
flashes during configuration at power up.
4Online LED
Green
If this LED is on, your username/password has been authenticated
successfully with your ISP.
5 Wireless LAN (WLAN) Status LED
Green
If the LED is on it indicates that wireless networking is enabled. If the LED
is flashing, the link is OK and data is being transmitted or received. If the
LED is off, the Wireless LAN has been disabled in the Router, or there is a
problem. Refer to Chapter 6
“Troubleshooting”.
6 LAN Status LEDs
Green
If the LED is on, the link between the port and the next piece of network
equipment is OK. If the LED is flashing, the link is OK and data is being
transmitted or received. If the LED is off, nothing is connected, or the
connected device is switched off, or there is a problem with the
connection (refer to Chapter 6
“Troubleshooting”). The port will
automatically adjust to the correct speed and duplex.
Page 18

16 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE ROUTER
The rear panel (Figure 4) of the Router contains four LAN ports, one ADSL
port, a reset button, a power OK LED, and a power adapter socket.
Figure 4 Router - Rear Panel
7 Wireless Antennae
The antennae should be placed in a ‘V’ position when initially installed.
CAUTION: Do not force the antennae beyond their mechanical stops.
Rotating the antennae further may cause damage.
8ADSL Port
Using the RJ-11 cable provided, you should connect your Router to the
telephone socket via a splitter.
9Power OK LED
Indicates the Router is powered on, the power adapter is working
properly.
10 Power Adapter Socket
Only use the power adapter that is supplied with this Router. Do not use
any other adapter.
11 Reset Button
If you want to reset your Router to factory default settings, and cannot
access the web management interface (for example, due to a lost
password), then you may use this button. Refer to “
Forgotten Password
and Reset to Factory Defaults” on page 104 for further details.
12 Ethernet Ports
Using suitable RJ-45 cables, you can connect your Router to a computer,
or to any other piece of equipment that has an Ethernet connection (for
example, a hub or a switch). These ports have an automatic MDI/MDIX
feature, which means either straight-through or a crossover cable can be
used.
Page 19
INSTALLING THE ROUTER
2
Introduction This chapter will guide you through a basic installation of the Router,
including:
■ Connecting the Router to the Internet.
■ Connecting the Router to your network.
■ Setting up your computers for networking with the Router.
Safety Information Please note the following:
Positioning the Router
WARNING: Please read the “Safety Information”
before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt “Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise”
sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät einschalten.
AVERTISSEMENT: Veuillez lire attentivement la section “Consignes
importantes de sécurité” avant de mettre en route.
You should place the Router in a location that:
■ is conveniently located for connection to the telephone socket.
■ is centrally located to the wireless computers that will connect to the
Router. A suitable location might be on top of a high shelf or similar
furniture to optimize wireless connections to computers in both
horizontal and vertical directions, allowing wider coverage.
■ allows convenient connection to the computers that will be connected
to the four LAN ports on the rear panel, if desired.
■ allows easy viewing of the front panel LED indicator lights, and access
to the rear panel connectors, if necessary.
section in Appendix C
Page 20
18 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ROUTER
When positioning your Router, ensure:
■ It is out of direct sunlight and away from sources of heat.
■ Cabling is away from power lines, fluorescent lighting fixtures, and
sources of electrical noise such as radios, transmitters and broadband
amplifiers.
■ Water or moisture cannot enter the case of the unit.
■ Air flow around the unit and through the vents in the side of the case
is not restricted. 3Com recommends you provide a minimum of
25 mm (1 in.) clearance.
Using the Rubber
Feet
Use the four self-adhesive rubber feet to prevent your Router from
moving around on your desk or when stacking with flat top units. Only
stick the feet to the marked areas at each corner of the underside of your
Router.
Wall Mounting There are two slots on the underside of the Router that can be used for
wall mounting.
When wall mounting the unit, ensure that it is within reach of the power
outlet.
You will need two suitable screws to wall mount the unit. To do this:
1 Ensure that the wall you use is smooth, flat, dry and sturdy and make two
screw holes which are 150 mm (5.9 in.) apart.
2 Fix the screws into wall, leaving their heads 3 mm (0.12 inch) clear of the
wall surface.
3 Remove any connections to the unit and locate it over the screw heads.
When in line, gently push the unit on to the wall and move it downwards
to secure.
When making connections, be careful not to push the unit up and off the
wall.
CAUTION: Only wall mount single units, do not wall mount stacked
units.
Page 21
Powering Up the Router 19
ock
C
ess
Users
r
Powering Up the Router
Connecting the Router
To power up the Router:
1 Plug the power adapter into the power adapter socket located on the
back panel of the Router.
2 Plug the power adapter into a standard electrical wall socket.
3 Press the power button located on the back of the Router.
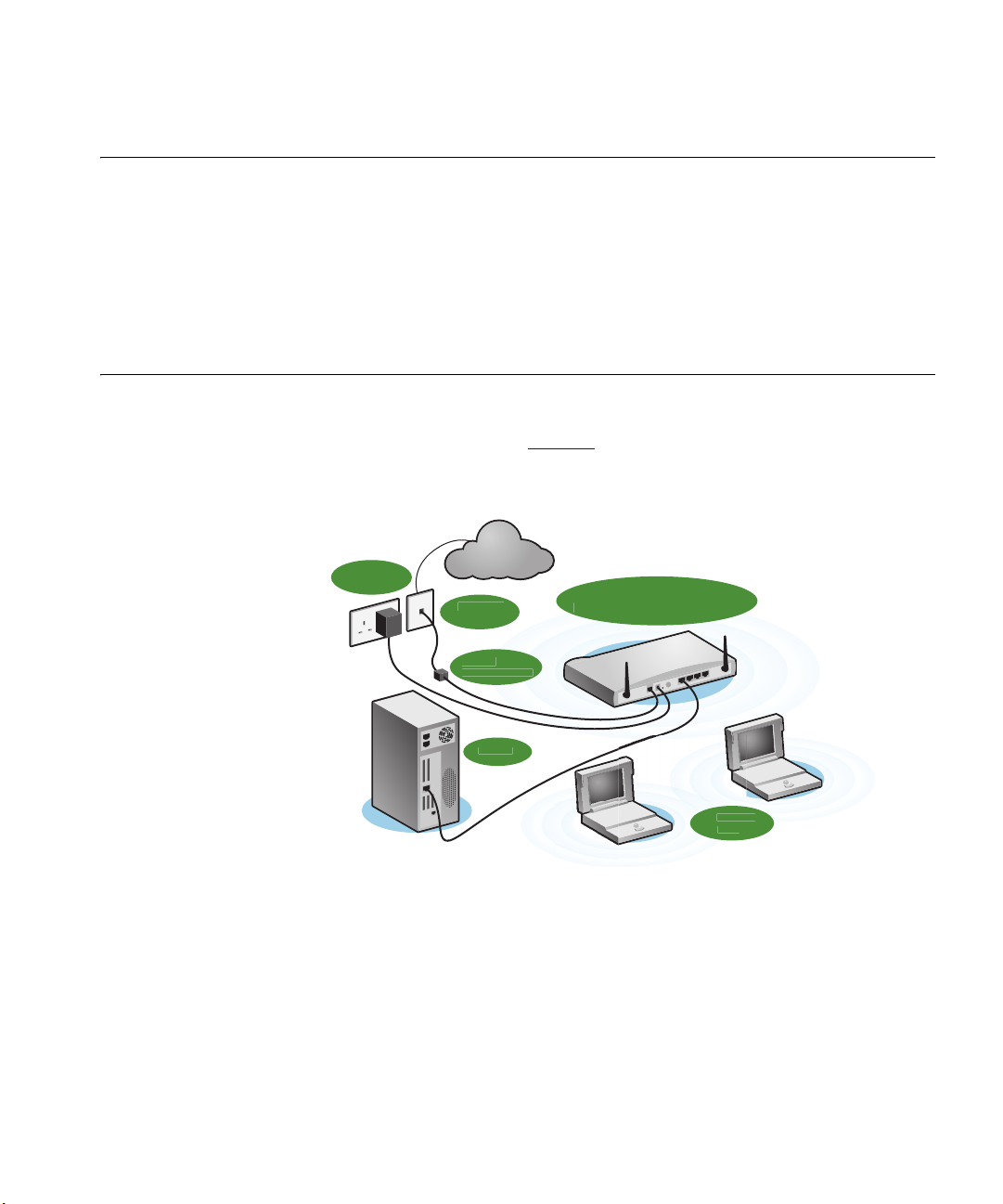
The first step for installing your Router is to physically connect it to the
telephone socket and then connect it to a computer in order to be able to
access the Internet. See Figure 5
Figure 5 Connecting the Router
Power
Supply Unit
Internet
Telephone
Socket
Splitter/
Microfilter Bl
:
3Com OfficeConnect
DSL Wireless 11g Firewall Route
Your P
Wirel
1 Run the provided telephone cable from the wall jack providing ADSL
service to the ADSL port on your Router. When inserting an ADSL RJ-11
plug, be sure the tab on the plug clicks into position to ensure that it is
properly seated. If you are using splitterless ADSL service, add low-pass
filters between the ADSL wall jack and your telephones. (These filters pass
voice signals through but filter data signals out.)
2 Then:
■ If you are using a full-rate (G.dmt) connection, your service provider
will attach the outside ADSL line to a data/voice splitter. In this case
Page 22
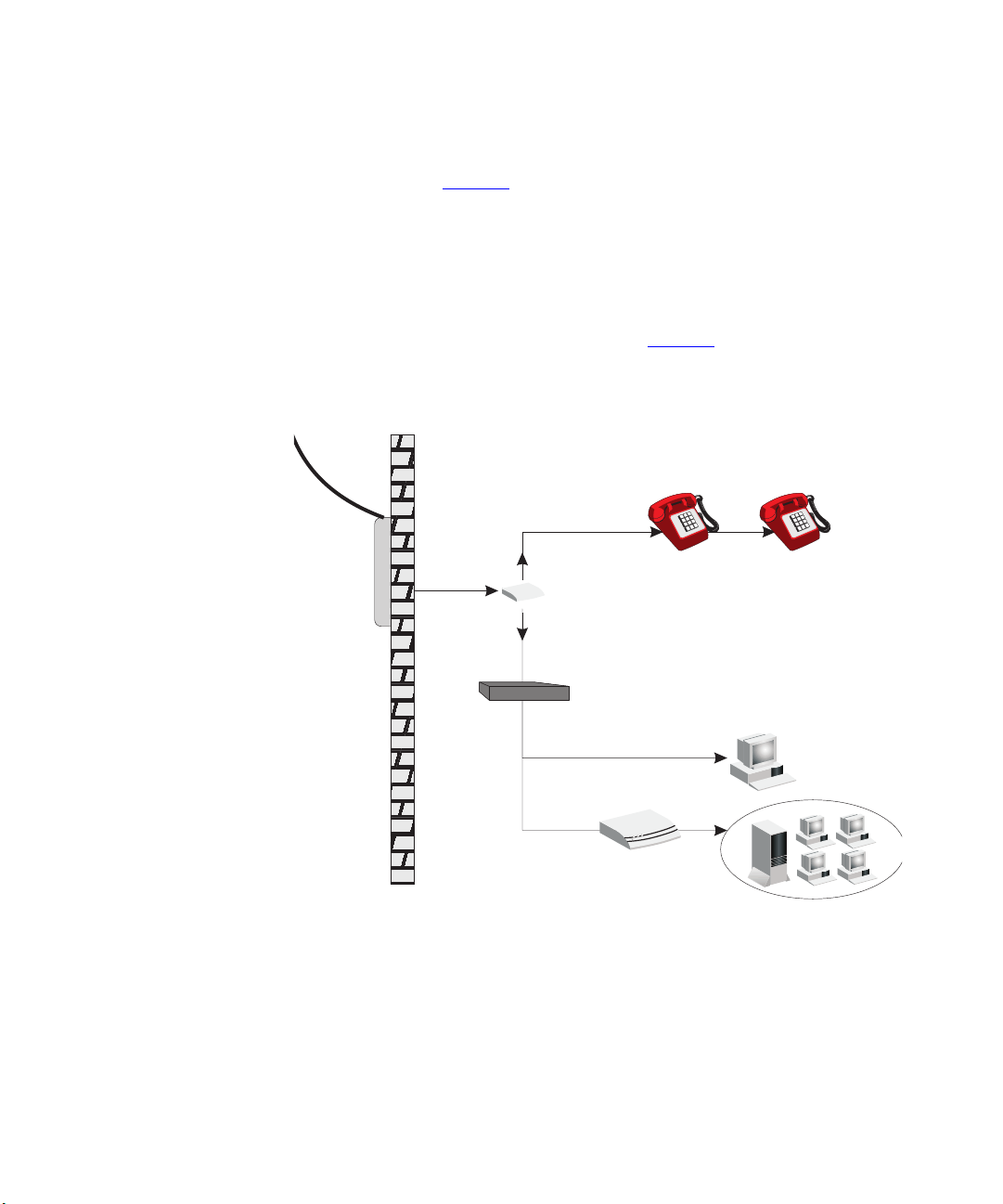
20 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ROUTER
you can connect your phones and computer directly to the splitter as
shown below (Figure 6
or
■ If you are using a splitterless (G.lite) connection, then your service
provider will attach the outside ADSL line directly to your phone
system. In this case you can connect your phones and computer
directly to the incoming ADSL line, but you will have to add low-pass
filters to your phones as shown below (Figure 7
Figure 6 Installing with a splitter
Plain Old
Telephone
System (POTS)
):
)
Residential
Connection
Point (NID)
Voice
Splitter
Data
Router
or
Ethernet
hub or switch
Page 23
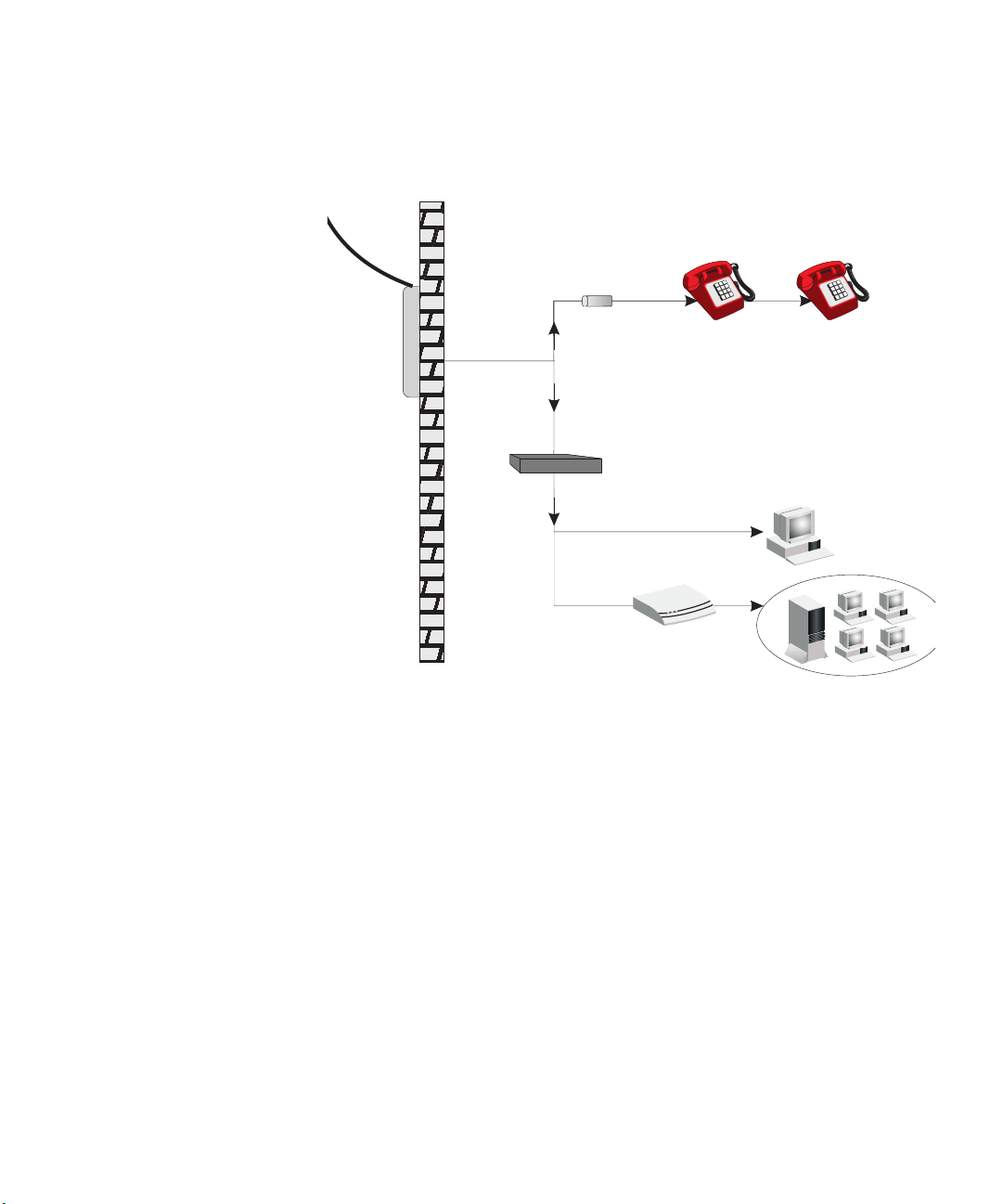
Figure 7 Installing without a splitter
Plain Old
Telephone
System (POTS)
Residential
Connection
Point [Network
Interface
Device (NID)]
Voice
& Data
Voice
& Data
Filter
Connecting the Router 21
Voice
Data
Router
or
Ethernet
hub or switch
You have now completed the hardware installation of your Router. Next
you need to set up your computers so that they can make use of the
Router to communicate with the Internet.
3Com recommends that you perform the initial Router configuration
from a computer that is directly connected to one of the LAN ports.
If you configure the Router from a wireless computer, note that you may
lose contact with the Router if you change the wireless configuration.
To communicate wirelessly with your Router, your wireless NIC should be
set as follows:
■ Encryption — none
■ SSID — 3Com
■ Channel — 11
Page 24

22 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ROUTER
Page 25

3
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
Windows 2000 If you are using a Windows 2000-based computer, use the following
SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
The Router has the ability to dynamically allocate network addresses to
the computers on your network, using DHCP. However, your computers
need to be configured correctly for this to take place. To change the
configuration of your computers to allow this, follow the instructions in
this chapter.
procedure to change your TCP/IP settings:
1 From the Windows Start Menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2 Double click on Network and Dial-Up Connections.
3 Double click on Local Area Connection.
4 Click on Properties.
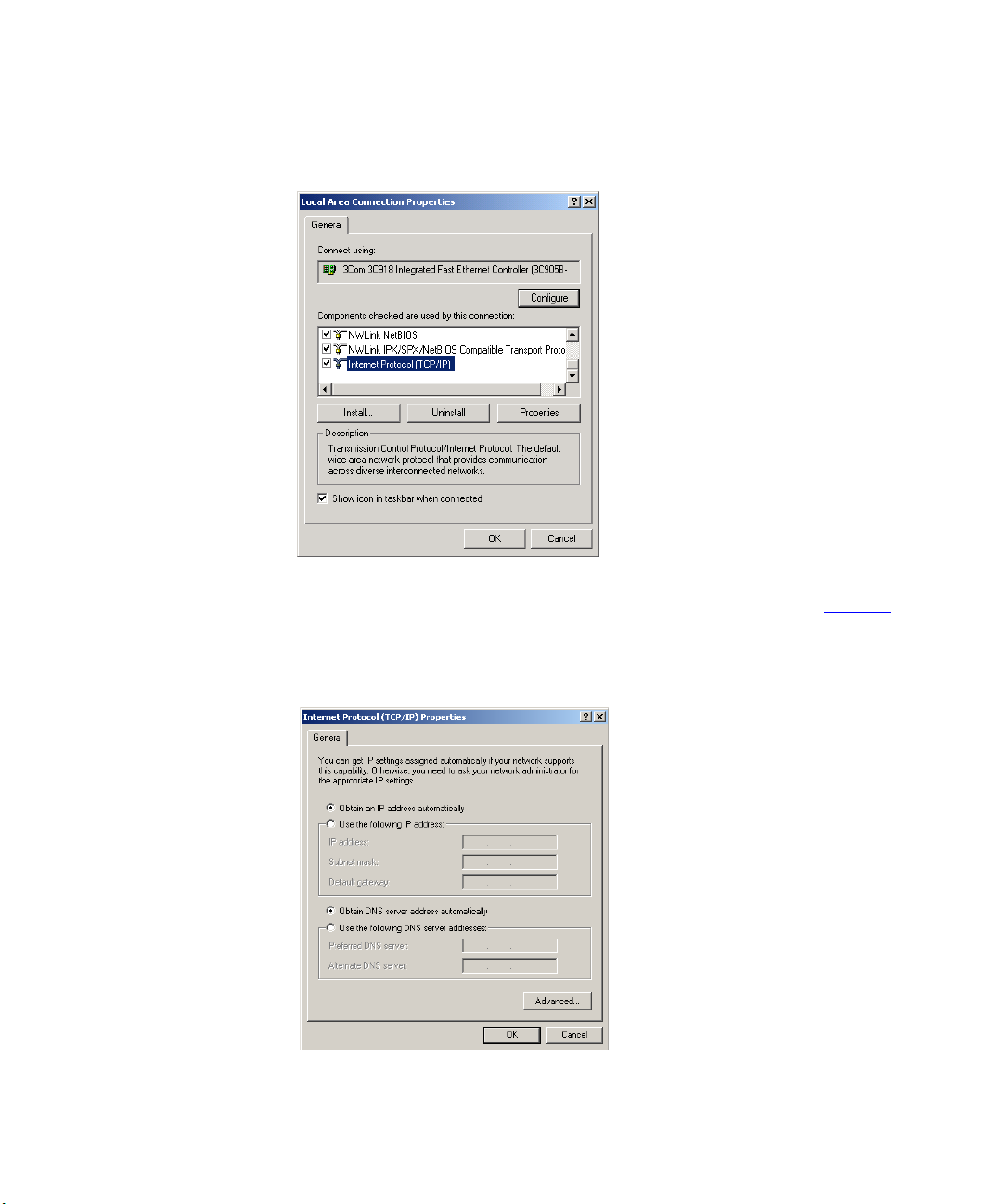
5 A screen similar to Figure 8
TCP/IP and click on Properties.
should be displayed. Select Internet Protocol
Page 26
24 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
Figure 8 Local Area Properties Screen
6 Ensure that the options Obtain an IP address automatically, and Obtain
DNS server address automatically are both selected as shown in Figure 9
Click OK.
.
Figure 9 Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Screen
7 Restart your computer.
Page 27

Windows XP
Windows 98/ME
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically 25
1 From the Windows Start Menu, select Control Panel.
2 Click on Network and Internet Connections.
3 Click on the Network Connections icon.
4 Double click on LAN or High Speed Connection icon. A screen titled Local
Area Connection Status will appear.
5 Select Internet Protocol TCP/IP and click on Properties.
6 Ensure that the options Obtain an IP address automatically, and Obtain
DNS servers automatically are both selected. Click OK.
7 Restart your computer.
1 From the Windows Start Menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2 Double click on Network. Select the TCP/IP item for your network card
and click on Properties.
3 In the TCP/IP dialog, select the IP Address tab, and ensure that Obtain IP
address automatically is selected. Click OK.
Macintosh If you are using a Macintosh computer, use the following procedure to
change your TCP/IP settings:
1 From the desktop, select Apple Menu, Control Panels, and TCP/IP.
2 In the TCP/IP control panel, set Connect Via: to Ethernet.
3 In the TCP/IP control panel, set Configure: to Using DHCP Server.
4 Close the TCP/IP dialog box, and save your changes.
5 Restart your computer.
Page 28
26 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP YOUR COMPUTERS
Disabling PPPoE and PPTP Client Software
If you have PPPoE client software installed on your computer, you will
need to disable it. To do this:
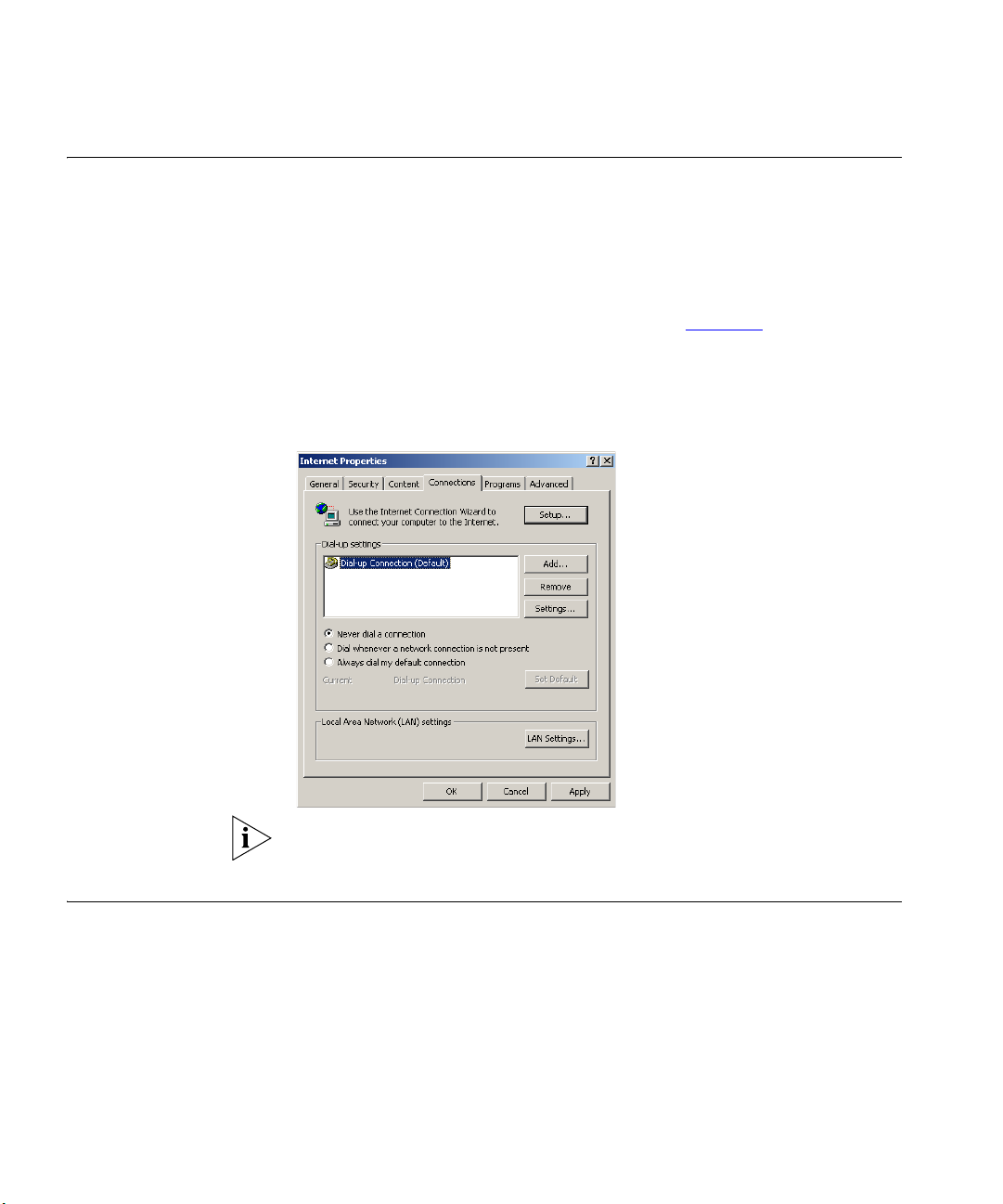
1 From the Windows Start Menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2 Double click on Internet Options.
3 Select the Connections Tab. A screen similar to Figure 10
displayed.
4 Select the Never dial a connection option.
Figure 10 Internet Properties Screen
should be
Disabling Web Proxy
You may want to remove the PPPoE client software from your computer
to free resources, as it is not required for use with the Router.
Ensure that you do not have a web proxy enabled on your computer.
Go to the Control Panel and click on Internet Options. Select the
Connections tab and click LAN Settings at the bottom. Make sure that
the Use Proxy Server option is unchecked.
Page 29
4
RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Accessing the Setup Wizard
The Router setup program is Web-based, which means that it is accessed
through your Web browser (Netscape Navigator 4.7 or higher, Internet
Explorer 5.0 or higher, or Mozilla 1.2.1 or higher).
To use the Setup Wizard:
1 Ensure that you have at least one computer connected to the Router.
Refer to Chapter 2
2 Launch your Web browser on the computer.
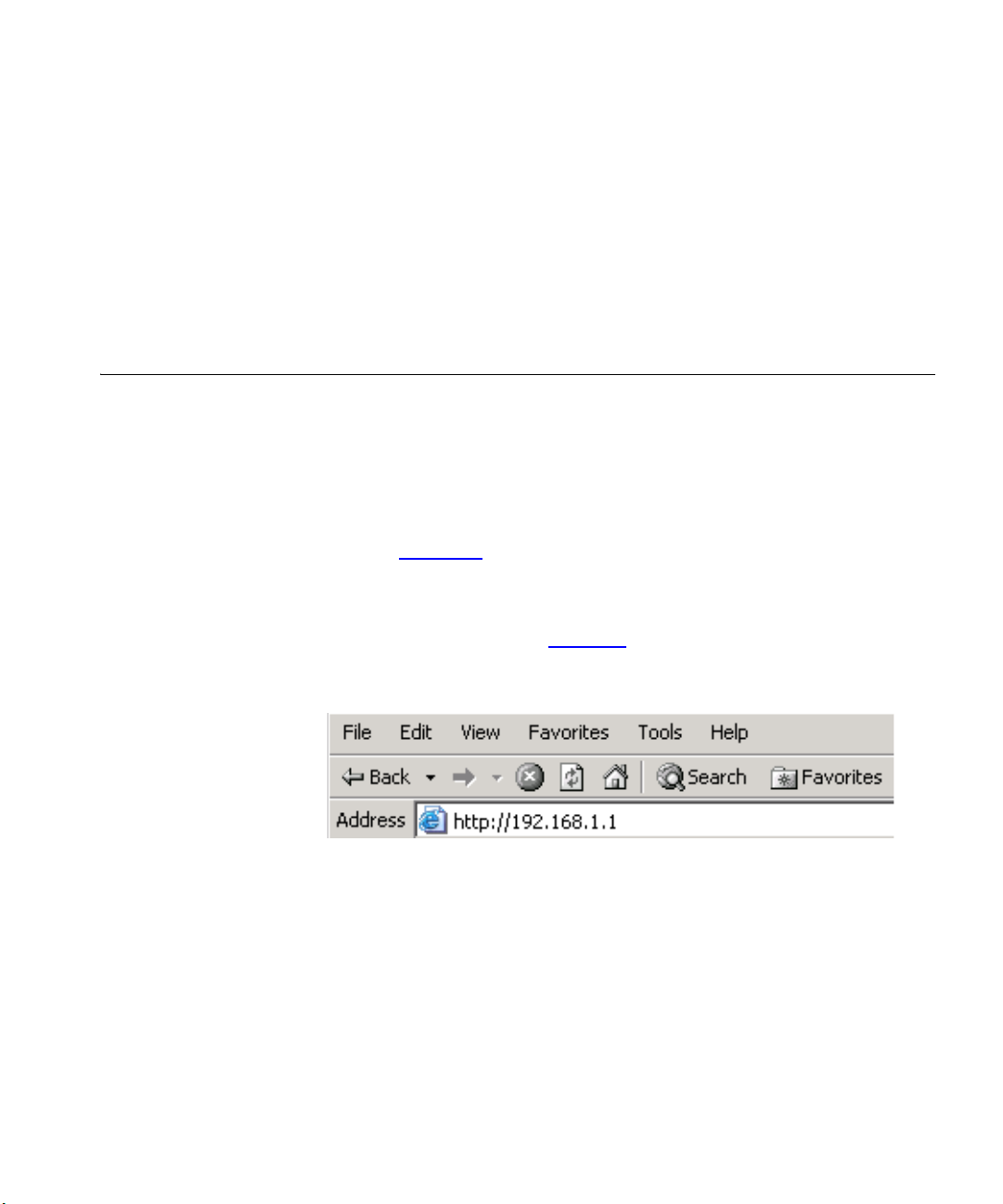
3 Enter the following URL in the location or address field of your browser:
http://192.168.1.1 (Figure 11
Figure 11 Web Browser Location Field (Factory Default)
for details on how to do this.
). The Login screen displays.
Page 30

28 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
4 To log in as an administrator, enter the password (the default password is
admin) in the System Password field and click Log in (Figure 12
Figure 12 Router Login Screen
5 When you have logged in,
■ if you are logging in for the first time, the Country Selection screen
will appear (Figure 13
menu, and click Apply.
Figure 13 Country Selection Screen
).
). Please select the country form the drop-down
The Wizard will then launch automatically (refer to Figure 16). You will be
guided step by step through a basic setup procedure.
■ if the Router has been configured previously, the Welcome screen will
appear (Figure 14
). There are three tabs: Notice Board, Password and
Wizard.
Page 31

Accessing the Setup Wizard 29
Figure 14 Welcome Screen
■ Go to the Notice Board tab to see the current software information. To
view the Web help, click the Help button.
■ Go to the Password tab to change the password (Figure 15).
■ Go to the Wizard tab to do a quick setup of the Router (Figure 16).
The password screen allows you to change the current password and set
the login time limit to the Router’s management interface.
Figure 15 Password Screen
1 To change the current password, enter the password in the Current
Password field.
2 Enter the new password in the New Password field, and enter it again in
the Confirm New Password field.
Page 32

30 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
3 Enter the time period in Login Timeout to set a maximum period of time
for which the login session is maintained during inactivity (Default: 10
minutes).
Setup Wizard -
Change Password
Setup Wizard - Time
and Time Zone
To ensure the security of your Router, it is recommended that you choose
a new password - this should be a mix of letters and numbers, and not
easily guessed by others. To leave the current password unchanged, leave
the fields blank and click Next.
Figure 16 Change Password Screen
The Time and Time Zone screen allows you to set up the time for the
Router.
Figure 17 Time and Time Zone Screen
1 If you want to automatically synchronize the Router with a public time
server, check the Enable box in the Using Time Server NTP field.
2 Select the time zone in the Set Time Zone drop-down menu.
3 Select the desired servers from the Time Server drop-down menu.
Page 33

Accessing the Setup Wizard 31
4 Check the Enable box in the Daylight Savings field, if daylight savings
applies to your area.
5 Click Next.
Setup Wizard -
Connection Type
The Connection Type screen allows you to set up the Router for the type
of Internet connection you have. Before setting up your connection type,
have your account information from your ISP ready.
Figure 18 Connection Type Screen
Select a DSL mode from the following:
■ PPPoE — PPP over Ethernet, providing routing for multiple PCs, see
page 32
■ PPPoA — PPP over ATM, providing routing for multiple PCs, see
page 33
■ Bridge Mode (for a single PC) — RFC1483 Bridged Mode, for single
PCs only, see page 34
■ Routing Mode over ATM — RFC1483 Routed Mode, for multiple PCs,
see page 34
■ Dynamic/Fixed IP in 1483 Bridge Mode (for multiple PCs), see page 35
and click Next.
For further information on selecting a mode see “
page 54
.
Internet Settings” on
Page 34

32 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
PPPoE Mode
To set up the Router for use with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) connection,
use the following procedure:
Figure 19 PPPoE Screen
1 Enter your user name in the Username field.
2 Enter your password in the Password field.
3 Re-type your password in the Retype Password field.
4 Enter your VPI and VCI information in the VPI/VCI fields.
5 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation
drop-down menu. This information should be provided to you by your ISP.
6 Check all of your settings, and then click Next.
The LAN Settings screen will then be displayed (refer to Figure 24
).
Page 35

Accessing the Setup Wizard 33
PPPoA Mode
To set up the Router for use with a PPP over ATM (PPPoA) connection, use
the following procedure:
Figure 20 PPPoA Screen
1 Enter your user name in the Username field.
2 Enter your password in the Password field.
3 Re-type your password in the Retype Password field.
4 Enter your VPI and VCI information in the VPI/VCI fields.
5 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation
drop-down menu. This information should be provided to you by your ISP.
6 Check all of your settings, and then click Next.
The LAN Settings screen will then be displayed (refer to Figure 24
).
Page 36

34 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Bridge Mode (for a single PC)
To set up the Router for use with an RFC1483 bridged connection, use
the following procedure:
Figure 21 Bridged Mode Screen
1 Enter your VPI and VCI information in the VPI/VCI fields.
2 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation
drop-down menu. This information should be provided to you by your ISP.
3 Check all of your settings, and then click Next.
The LAN Settings screen will then be displayed (refer to Figure 24
).
Routing Mode over ATM
To set up the Router for use with an RFC1483 routed connection, use the
following procedure:
Figure 22 Routing Mode Screen
Page 37

Accessing the Setup Wizard 35
1 Enter your Internet IP address in the WAN IP field.
2 Enter the subnet mask in the Subnet Mask field.
3 Enter the default gateway IP address in the Default Gateway field.
4 Enter the DNS address in the DNS field.
5 Enter your VPI and VCI information in the VPI/VCI fields.
6 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation
drop-down menu. This information should be provided to you by your ISP.
7 Check all of your settings, and then click Next.
The LAN Settings screen will then be displayed (refer to Figure 24
).
Dynamic/Fixed IP in 1483 Bridge Mode (For Multiple PCs)
For bridge mode to work, you need to assign an IP address to the Router.
You can either configure the Router to obtain an IP address automatically
from a DHCP server or assign a fixed or static IP address to it.
Figure 23 Dynamic/Fixed IP for Bridge Mode Screen
To obtain an IP address automatically from a DHCP server:
Check the Get WAN IP By DCHP checkbox, and then click Next.
The LAN Settings screen will then be displayed (refer to Figure 24
).
Page 38

36 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
To assign a fixed IP address:
1 Enter your Internet IP address in the WAN IP field.
2 Enter the subnet mask in the Subnet Mask field.
3 Enter the default gateway IP address in the Default Gateway field.
4 Enter the DNS address in the DNS field.
5 Enter your VPI and VCI information in the VPI/VCI text boxes.
6 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation
drop-down menu. This information should be provided to you by your ISP.
7 Check all of your settings, and then click Next.
The LAN Settings screen will then be displayed (refer to Figure 24
).
Setup Wizard - LAN
Settings
The LAN Settings screen allows you to set the default IP address and
DHCP client IP range for the Router.
Figure 24 The LAN Settings Screen
1 To change the Router’s default IP address, enter the new IP address in the
IP Address field, and then enter the subnet mask in the Subnet Mask
field.
2 Select the On/Off button to turn on/turn off the DHCP function in the
DHCP Server field.
3 Enter the client IP address range in the IP Pool Start Address and IP Pool
End Address fields.
4 Click Next. The Wireless Settings screen will be displayed (refer to
Figure 25
).
Page 39

Accessing the Setup Wizard 37
Setup Wizard -
Wireless Settings
The Wireless Settings screen allows you to set up the SSID and radio
channel used for the wireless connection.
Figure 25 Wireless Settings Screen
1 Select the channel you want to use from the Channel drop-down menu.
2 Specify the SSID to be used by your Wireless Network in the SSID field. If
there are other wireless networks in your area, you should give your
wireless network a unique name.
Page 40

38 CHAPTER 4: RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
Setup Wizard -
Configuration
Summary
When you have completed the Setup Wizard, a configuration summary
will appear. Verify the configuration information of the Router and then
click Apply to save your settings. 3Com recommends that you print out
this page for your records.
Figure 26 Configuration Summary Screen
Your Router is now configured and ready for use.
See Chapter 5
for a detailed description of the Router configuration.
Page 41

5
CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Navigating Through the Router Configuration screens
Main Menu The main menu is located on the left side, as shown in Figure 27
Welcome Screen The Welcome screen shows the current software information.
Status
This chapter describes all the screens available through the Router
configuration screens, and is provided as a reference. To get to the
configuration screens, enter the Router’s default IP in the location bar of
your browser. The default IP is http://192.168.1.1.
However, if you changed the Router LAN IP address during initial
configuration, use the new IP address instead. Enter your password to
login to the management interface. (The default password is admin).
you click on an item from the main menu, the corresponding screen will
then appear in the center.
Figure 27 Welcome Screen
. When
Page 42

40 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
LAN Settings Your Router is equipped with a DHCP server that will automatically assign
IP addresses to each computer on your network. The factory default
settings for the DHCP server will work with most applications. If you need
to make changes to the settings, you can do so.
The LAN settings screen allows you to:
■ Change the default IP address of the Router. The default IP is
192.168.1.1
■ Change the Subnet Mask. The default setting is 255.255.255.0
■ Enable/Disable the DHCP Server Function. The default is ON (Enabled).
■ Specify the Starting and Ending IP Pool address. The default is
Starting: 2 / Ending: 254.
■ Specify the IP address Lease Time. The default is Half day.
■ Specify a local Domain Name. The default is NONE.
■ Specify the IP address of 3Com NBX call processor.
The Router will also provide a list of all client computers connected to the
Router.
LAN Settings The LAN Settings screen is used to specify the LAN IP address of your
Router, and to configure the DHCP server.
Figure 28 LAN Settings Screen
Page 43

LAN Settings 41
1 Enter the Router’s IP Address and Subnet Mask in the appropriate fields.
The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
2 If you want to use the Router as a DHCP Server, select On in the DHCP
Server field.
3 Enter the IP address range in the IP Pool Start Address and IP Pool End
Address fields.
4 Specify the DHCP Lease time by selecting the required value from the
Lease Time drop-down menu. The lease time is the length of time the
DHCP server will reserve the IP address for each computer.
5 Specify the Local Domain Name for your network (this step is optional).
6 Enter the IP address of the NBX Call Processor in the 3Com NBX Call
Processor field (this step is optional).
7 Check all of your settings, and then click Apply.
DHCP Clients List The DHCP Clients List provides details on the devices that have received IP
addresses from the Router. The list is only created when the Router is set
up as a DHCP server. A maximum of 253 clients can be connected to the
Router.
Figure 29 DHCP Clients List Screen
For each device that is connected to the LAN, the following information is
displayed:
■ IP address — The Internet Protocol (IP) address issued to the client
machine.
Page 44

42 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
■ Host Name — The client machine’s host name, if configured.
■ MAC Address — The Media Access Control (MAC) address of the
client’s network card.
■ Client Type — Whether the client is connected to the Router by wired
or wireless connection.
■ Check the Fix checkbox to permanently fix the IP address.
■ Click Release to release the displayed IP address.
■ Click New to allocate an IP address to a MAC address (refer to
Figure 30
settings.
Figure 30 Fixed Mapping Clients List Screen
). Enter the required details and click Apply to save your
The DHCP server will give out addresses to both wired and wireless
clients.
Page 45

Wireless Settings 43
Wireless Settings The Wireless Settings screens allow you to configure the settings for the
wireless connections.
You can enable or disable the wireless connection for your LAN. When
disabled, no wireless PCs can gain access to either the Internet or other
PCs on your wired or wireless LAN through this Router.
Figure 31 Wireless Settings Screen
There are seven tabs available:
■ Configuration
■ Encryption
■ Connection Control
■ Client List
■ WDS
■ Advance
■ Profile
Page 46

44 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Configuration The Wireless Configuration Screen allows you to turn on/ turn off the
wireless function, and set up basic wireless settings.
Figure 32 Wireless Configuration Screen
To enable the wireless function:
1 Check Enable Wireless Networking checkbox.
2 Select the wireless channel you want to use from the Channel drop-down
menu.
3 Specify the SSID to be used by your wireless network in the SSID field. If
there are other wireless networks in your area, you should give your
wireless network a unique name.
4 Enable or disable SSID Broadcast.
A feature of many wireless network adapters is that a computer's SSID
can be set to ANY, which means it looks randomly for any existing
wireless network. The available networks are then displayed in a site
survey, and your computer can select a network. By clicking Disable, you
can block this random search, and set the computer's SSID to a specific
network (for example, WLAN). This increases network security. If you
decide to enable SSID Broadcast, ensure that you know the name of your
network first.
5 Select whether your Router will operate in 11b mode only, 11g mode
only, or mixed 11b and 11g from the Wireless Mode drop-down menu.
6 Click Apply.
Page 47

Wireless Settings 45
Encryption This feature prevents any non-authorized party from reading or changing
your data over the wireless network.
Figure 33 Encryption Screen
Select the wireless security mode that you want to use from the
drop-down menu, and click Apply. There are five selections:
■ Disabled (see page 45)
■ 64-bit WEP (see page 46)
■ 128-bit WEP (see page 47)
■ WPA-PSK (no server) (see page 48)
■ WPA (with RADIUS Server) (see page 49)
Disabled
In this mode, wireless transmissions will not be encrypted, and will be
visible to everyone. However, when setting up or debugging wireless
networks, it is often useful to use this security mode.
Page 48

46 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
64-bit WEP
WEP is the basic mechanism to transmit your data securely over the
wireless network. Matching encryption keys must be setup on your
Router and wireless client devices to use WEP.
Figure 34 64-bit WEP Screen
To enable 64-bit WEP:
1 You can enter the 64-bit WEP key manually:
■ enter the WEP key as 5 pairs of hex digits (0-9, A-F).
Or you can generate the 64-bit WEP key automatically:
■ enter a memorable passphrase in the Passphrase box, and then
click Generate to generate the hex keys from the passphrase.
For 64-bit WEP, you can enter up to four keys, in the fields Key 1 to Key 4.
The radio button on the left hand side selects the key that is used in
transmitting data.
Note that all four WEP keys on each device in the wireless network must
be identical.
2 Click Apply.
Page 49

Wireless Settings 47
128-bit WEP
WEP is the basic mechanism to transmit your data securely over the
wireless network. Matching encryption keys must be set up on your
Router and wireless client devices to use WEP.
Figure 35 128-bit WEP Screen
To enable 128-bit WEP:
1 You can enter the 128-bit WEP key manually:
■ enter your WEP key as 13 pairs of hex digits (0-9, A-F).
Or you can generate the 128-bit WEP key automatically:
■ enter a memorable passphrase in the Passphrase box, and then
click Generate to generate the hex keys from the passphrase.
The WEP keys on each device on the wireless network must be identical.
In 128-bit WEP mode, only one WEP key can be specified.
2 Click Apply.
Page 50

48 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
WPA-PSK (no server)
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) provides dynamic key changes and
constitutes the best security solution. If your network does not have a
RADIUS server. Select the no server option.
Figure 36 WPA-PSK (no server) Screen
1 Select WPA-PSK (no server) from the WPA drop-down menu.
2 Select WPA mode from the drop-down menu, three modes are
supported: WPA, WPA2, and Mixed mode.
3 Select Encryption technique from the drop-down menu, four options are
available: TKIP, AES, Auto for WPA AES for WPA2, and AES for both WPA
and WPA2.
4 Enter the pre-shared key in the Pre-shared Key (PSK) field. The pre-shared
key is a password, in the form of a word, phrase or series of letters and
numbers. The key must be between 8 and 63 characters long and can
include spaces and symbols. Each client that connects to the network
must use the same key.
5 If you want the key that you enter to be shown on the screen as a series
of asterisks (*), then check the Hide PSK checkbox.
6 Click Apply.
Page 51

Wireless Settings 49
WPA (with RADIUS Server)
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) provides dynamic key changes and
constitutes the best security solution. This function requires that a
RADIUS server is running on the network.
Figure 37 WPA (with RADIUS Server) Screen
1 Select WPA with RADIUS server from the Security Mode drop-down
menu.
2 Select WPA mode from the drop-down menu, three modes are
supported: WPA, WPA2, and Mixed mode.
3 Select Encryption technique from the drop-down menu, four options are
available: TKIP, AES, Auto for WPA AES for WPA2, and AES for both WPA
and WPA2.
4 Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server on your network into the
RADIUS Server field.
5 Enter the port number that the RADIUS server is operating on in the
RADIUS Port field.
6 Enter the key for the RADIUS server in the RADIUS Key field.
7 By default, the WPA keys are changed every hour, but if you want to
change this setting, you can do so by specifying the required time in the
Re-key Interval field.
8 Click Apply.
Page 52

50 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Connection Control This feature is used to filter the clients based on their MAC addresses.
Check the Enable MAC Address Filtering checkbox, the Connection
Control screen will appear.
Figure 38 Connection Control Screen
There are two options available in the Access rule for registered MAC
address field:
■ if you click Allow, this means only the MAC addresses registered here
in the list will be allowed to access the Router via wireless link.
■ if you click Deny, this means the registered MAC addresses will not be
able to access the Router via wireless link.
Use the MAC Address Filtering List to quickly copy the MAC addresses of
the current wireless clients into the list table. You can define up to 32
MAC addresses to the list.
You can click Clear to delete the current entry in the list.
Page 53

Wireless Settings 51
Client List You can view the list of all wireless clients that are connected to the
Router.
Figure 39 Client List Screen
Click Refresh to update the list.
WDS Settings The Router supports WDS (Wireless Distribution System). WDS enables
one or more Access Points to rebroadcast received signals to extend
range and reach, though this can affect the overall throughput of data.
Figure 40 Wireless WDS Settings Screen
1 Check the Enable WDS Function checkbox.
2 To refresh the list of available access points, click Rescan Wireless
Networking.
Page 54

52 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
3 Click Add to add the MAC address of the AP to the list, the add WDS
screen will appear (refer to Figure 41).
Figure 41 Add WDS screen
Enter the MAC address(es) of one or more access points in the AP MAC
Address table, and click Apply.
Advance The Advance screen allows you to configure detailed settings for your
wireless connection.
Figure 42 Wireless Advanced Setting screen
There are six parameters that you can configure:
■ Beacon Interval: this represents the amount of time between beacon
transmissions.
Page 55

Wireless Settings 53
■ DTIM Interval: A DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) is a
countdown mechanism used to inform your wireless clients of the
next window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages.
■ Fragmentation Threshold: this is the maximum size for directed data
packets transmitted. The use of fragmentation can increase the
reliability of frame transmissions. Because of sending smaller frames,
collisions are much less likely to occur.
■ RTS Threshold: RTS stands for Request to Send, this parameter
controls what size data packet the low level RF protocol issues to an
RTS packet.
■ CTS Protection Mode: CTS stands for Clear to Send. CTS Protection
Mode boosts the Router’s ability to intercept 802.11b/ 802.11g
transmissions. Conversely, CTS Protection Mode decreases
performance. Leave this feature disabled unless you encounter severe
communication difficulties between the Router and your wireless
clients.
■ WMM Mode: Wireless Multimedia (WMM) mode, which supports
devices that meet the 802.11E QBSS standard.
Profile This feature is used to quickly set up the configuration parameters and
save them into one profile for easy connection.
Figure 43 Profile Screen
Page 56

54 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Internet Settings You can configure the settings for your DSL connection.
ATM PVC This feature is used to configure the parameters for your DSL connection.
The information necessary to complete these screens should be obtained
from your ISP. Check with your ISP first to find out what type of
connection you should choose.
Figure 44 ATM PVC Screen
You should see the first entry already contains information that’s been
configured using the Wizard in the initial setup. If you want to change
that information or set up other connection, click Edit.
There are six options available for the DSL connection mode:
■ PPPoE — PPP over Ethernet, providing routing for multiple PCs (see
page 55
■ PPPoA — PPP over ATM, providing routing for multiple PCs (see
page 57
■ Bridge Mode — RFC1483 Bridged Mode, for single PCs only (see
page 59
■ Routing Mode over ATM — RFC1483 Routed Mode, for multiple PCs
(see page 61
■ Dynamic/Fixed IP in 1483 Bridge Mode (for multiple PCs) (see page 63)
■ Disable — To disable the Internet connection function (see page 64)
)
)
)
)
Click Edit to set the detailed settings.
Page 57

Internet Settings 55
PPPoE
PPP over Ethernet, provides routing for multiple PCs. To configure this
function correctly, you should obtain the information from your ISP.
Figure 45 PPPoE Settings Screen
1 Select PPPoE from the Protocol drop-down menu.
2 Enter the IP address and Subnet Mask information provided by your ISP
into the IP address and Subnet Mask fields.
3 Enter the user name assigned to you by your ISP in the Username field.
And enter the password assigned to you by your ISP in the Password field.
Re-enter your password in the Confirm Password field.
4 Select the connection type from the Connect Type drop-down menu.
■ Always Connected means that Internet connection to your ISP is
always on.
■ Auto - Triggered by Traffic means your Router will automatically
connect to your ISP every time a PC needs to access the Internet.
■ Manual - Start in Disconnected means that after re-booting the
Router, the Internet connection will need to be re-established
manually by the user.
■ Manual - Start in Connected means that after re-booting the
Router, it will automatically establish a connection to your ISP.
Page 58

56 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
■ Manual - Start in Last State means that after re-booting the Router,
the Internet connection will stay in the previous condition before
the reboot.
5 If you want your Router to automatically disconnect from the Internet
after a period of inactivity, specify a time in the Idle Time (Minutes) field.
(Enter a value of 0 to disable this timeout).
6 Enter the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) value supplied by your ISP. If
you do not know this, leave it at the default value.
7 The Router supports the IP Control Protocol (IPCP) Subnet Mask Support
feature, check the IPCP subnet checkbox to enable it.
8 To use the IPCP Subnet Mask Support for the DHCP clients, check the
IPCP Subnet Populate DHCP Server checkbox.
9 Enter the VPI and VCI values provided by your ISP in the VPI and VCI
fields. You can click Auto Search to automatically find out this
information.
10 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation field.
This information should be provided to you by your ISP.
11 Select the type of Quality of Service (CBR, UBR or VBR) in the QoS field.
■ CBR (constant bit rate): the CBR service class is intended for
real-time applications, for example, those requiring tightly
constrained delay and delay variation, such as voice and video
applications. The consistent availability of a fixed quantity of
bandwidth is considered appropriate for CBR service.
■ VBR (variable bit rate): QoS class defined by the ATM Forum for
ATM networks. VBR is subdivided into a real time (RT) class and
non-real time (NRT) class. VBR (RT) is used for connections in which
there is a fixed timing relationship between samples. VBR (NRT) is
used for connections in which there is no fixed timing relationship
between samples, but that still need a guaranteed QoS. Compare
with ABR, CBR, and UBR.
■ UBR (unspecified bit rate): the UBR service class is intended for
delay-tolerant or non-real-time applications, for example, those
which do not require tightly constrained delay and delay variation,
such as traditional computer communications applications. The
UBR service may be considered as "best effort service".
12 Enter the PCR/SCR/MBS values. This information should be provided to
you by your ISP.
Page 59

Internet Settings 57
13 Click Apply.
PPPoA
PPP over ATM, this is a popular choice among European DSL providers. To
configure this function correctly, you should obtain the information from
your ISP.
Figure 46 PPPoA Settings Screen
1 Select PPPoA from the Protocol drop-down menu.
2 IP assigned by ISP:
■ Select Yes, if your ISP assigns your IP address dynamically, and
proceed to next step.
■ If your ISP has assigned you a fixed or static IP address, select No in
the IP assigned by ISP field.
Then enter the IP address and Subnet Mask information provided
by your ISP into the IP address and Subnet Mask fields.
3 Enter the user name assigned to you by your ISP in the Username field.
And enter the password assigned to you by your ISP in the Password field.
Re-enter your password in the Confirm Password field.
Page 60

58 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
4 Select the connection type from the Connect Type drop-down menu.
■ Always Connected means the Internet connection to your ISP is
always on.
■ Auto - Triggered by Traffic means your Router will automatically
connect to your ISP every time a PC needs to access the Internet.
■ Manual - Start in Disconnected means that after re-booting the
Router, the Internet connection will need to be re-established
manually by the user.
■ Manual - Start in Connected means that after re-booting the
Router, it will automatically establish connection to your ISP.
■ Manual - Start in Last State means that after re-booting the Router,
the Internet connection will stay in the previous condition before
the reboot.
5 If you want your Router to automatically disconnect from the Internet
after a period of inactivity, specify a time in the Idle Time (Minutes) field.
(Enter a value of 0 to disable this timeout).
6 Enter the MTU value supplied by your ISP. If you do not know this, leave it
at the default value.
7 The Router supports the IP Control Protocol (IPCP) Subnet Mask Support
feature, check the IPCP subnet checkbox to enable it.
8 To use the IPCP Subnet Mask Support for the DHCP clients, check the
IPCP Subnet Populate DHCP Server checkbox.
9 Enter the VPI and VCI parameters provided to you by your ISP in the VPI
and VCI fields. You can click Auto Search to automatically find out this
information.
10 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation Type
field. This information is provided to you by your ISP.
11 Select the type of Quality of Service (CBR, UBR or VBR) in the QoS field.
■ CBR (constant bit rate): the CBR service class is intended for
real-time applications, for example, those requiring tightly
constrained delay and delay variation, such as voice and video
applications. The consistent availability of a fixed quantity of
bandwidth is considered appropriate for CBR service.
■ VBR (variable bit rate): QoS class defined by the ATM Forum for
ATM networks. VBR is subdivided into a real time (RT) class and
non-real time (NRT) class. VBR (RT) is used for connections in which
there is a fixed timing relationship between samples. VBR (NRT) is
Page 61

Internet Settings 59
used for connections in which there is no fixed timing relationship
between samples, but that still need a guaranteed QoS. Compare
with ABR, CBR, and UBR.
■ UBR (unspecified bit rate): the UBR service class is intended for
delay-tolerant or non-real-time applications, for example, those
which do not require tightly constrained delay and delay variation,
such as traditional computer communications applications. The
UBR service may be considered as "best effort service".
12 Enter the PCR/SCR/MBS values.
13 Click Apply.
Bridge Mode
If your ISP limits access to the Internet to specific computers, this means
that traffic to/from these computers only will be forwarded. In this case,
Bridge Mode is used to connect to the ISP. The ISP will generally give one
Internet account and limit only one computer to access the Internet.
Check with your ISP to determine if this mode is used for your DSL
connection. To configure the settings correctly, you should obtain the
information from your ISP.
Figure 47 Bridge Mode Screen
1 Select Bridge Mode from the Protocol drop-down menu.
2 Enter the VPI and VCI parameters in the VPI and VCI fields. You can click
Auto Search to automatically find out this information.
3 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation Type
field. This information should be provided to you by your ISP.
Page 62

60 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
4 Select the type of Quality of Service that you want from the QoS Class
drop-down menu.
■ CBR (constant bit rate): the CBR service class is intended for
real-time applications, for example, those requiring tightly
constrained delay and delay variation, such as voice and video
applications. The consistent availability of a fixed quantity of
bandwidth is considered appropriate for CBR service.
■ VBR (variable bit rate): QoS class defined by the ATM Forum for
ATM networks. VBR is subdivided into a real time (RT) class and
non-real time (NRT) class. VBR (RT) is used for connections in which
there is a fixed timing relationship between samples. VBR (NRT) is
used for connections in which there is no fixed timing relationship
between samples, but that still need a guaranteed QoS. Compare
with ABR, CBR, and UBR.
■ UBR (unspecified bit rate): the UBR service class is intended for
delay-tolerant or non-real-time applications, for example, those
which do not require tightly constrained delay and delay variation,
such as traditional computer communications applications. The
UBR service may be considered as "best effort service".
5 Enter the PCR/SCR/MBS values.
6 Click Apply.
Page 63

Internet Settings 61
Routing Mode over ATM (RFC 1483 Routed Mode)
This mode is commonly used with either dynamic or static IP addressing.
In this mode the WAN ADSL port will be configured with an IP address
provided by the ISP. To configure the settings correctly, you should obtain
the information on this screen from your ISP.
Figure 48 Routing Mode over ATM Screen
1 Select Routing Mode over ATM from the Protocol drop-down menu.
2 Enter the IP address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway information
provided by your ISP into the IP address, Subnet Mask and Default
Gateway fields.
3 Check the DNS Automatic from ISP checkbox, if your ISP automatically
configure DNS. However, if you need to configure DNS manually, enter
the IP address in the DNS Address field. (If your ISP uses a secondary DNS,
enter the IP address in the Secondary DNS Address field).
4 Enter the host name in the Host Name filed.
5 If your ISP uses DHCP to automatically assign IP addresses, check the
DHCP Client checkbox.
6 Enter the VPI and VCI parameters provided to you by your ISP in the VPI
and VCI fields. You can click Auto Search to automatically find out this
information.
7 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation field.
This information should be provided to you by your ISP.
Page 64

62 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
8 Select the type of Quality of Service that you want from the QoS Class
drop-down menu.
■ CBR (constant bit rate): the CBR service class is intended for
real-time applications, for example, those requiring tightly
constrained delay and delay variation, such as voice and video
applications. The consistent availability of a fixed quantity of
bandwidth is considered appropriate for CBR service.
■ VBR (variable bit rate): QoS class defined by the ATM Forum for
ATM networks. VBR is subdivided into a real time (RT) class and
non-real time (NRT) class. VBR (RT) is used for connections in which
there is a fixed timing relationship between samples. VBR (NRT) is
used for connections in which there is no fixed timing relationship
between samples, but that still need a guaranteed QoS. Compare
with ABR, CBR, and UBR.
■ UBR (unspecified bit rate): the UBR service class is intended for
delay-tolerant or non-real-time applications, for example, those
which do not require tightly constrained delay and delay variation,
such as traditional computer communications applications. The
UBR service may be considered as "best effort service".
9 Enter the PCR/SCR/MBS values.
10 Click Apply.
Page 65

Internet Settings 63
Dynamic/Fixed IP in 1483 Bridge Mode (For Multiple PCs)
In this example, the ISP uses fixed/dynamic IP to provide the Internet
connection. To configure this function correctly, you should obtain the
information on this screen from your ISP.
Figure 49 Dynamic/Fixed IP for Bridge Mode Screen
1 Select Dynamic/Fixed IP in 1483 Bridge Mode from the Protocol
drop-down menu.
2 Enter the IP address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway information
provided by your ISP into the IP address, Subnet Mask and Default
Gateway fields.
3 Check the DNS Automatic from ISP checkbox, if your ISP automatically
configures DNS. However, if you need to configure DNS manually, enter
the IP address in the DNS Address field. (If your ISP uses a secondary DNS,
enter the IP address in the Secondary DNS Address field).
4 Enter the host name in the Host Name field.
5 If your ISP uses DHCP to automatically assign IP addresses, check the
DHCP Client checkbox.
6 Enter the VPI and VCI parameters provided by your ISP in the VPI and VCI
fields. You can click Auto Search to automatically find out this
information.
7 Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC MUX) in the Encapsulation field.
This information will have been provided to you by your ISP.
Page 66

64 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
8 Select the type of Quality of Service that you want from the QoS Class
drop-down menu.
■ CBR (constant bit rate): the CBR service class is intended for
real-time applications, for example, those requiring tightly
constrained delay and delay variation, such as voice and video
applications. The consistent availability of a fixed quantity of
bandwidth is considered appropriate for CBR service.
■ VBR (variable bit rate): QoS class defined by the ATM Forum for
ATM networks. VBR is subdivided into a real time (RT) class and
non-real time (NRT) class. VBR (RT) is used for connections in which
there is a fixed timing relationship between samples. VBR (NRT) is
used for connections in which there is no fixed timing relationship
between samples, but that still need a guaranteed QoS. Compare
with ABR, CBR, and UBR.
■ UBR (unspecified bit rate): the UBR service class is intended for
delay-tolerant or non-real-time applications, for example, those
which do not require tightly constrained delay and delay variation,
such as traditional computer communications applications. The
UBR service may be considered as "best effort service".
9 Enter the PCR/SCR/MBS values.
10 Click Apply.
Disable
Selecting this option means that you do not want your Router to connect
to the Internet.
Figure 50 Disable Internet Connection Screen
Page 67

Internet Settings 65
DNS Domain Name Service (or Server) is an Internet service that translates
domain names into IP addresses. Because domain names are alphabetic,
they're easier to remember. The Internet however, is really based on IP
addresses. Every time you use a domain name, a DNS service must
translate the name into the corresponding IP address. For example, the
domain name www.example.com might translate to 198.105.232.4.
Check with your ISP for information on this screen.
Figure 51 DNS Screen
If the DNS information is automatically provided by your ISP every time
you connect to it, check the Automatic from ISP checkbox.
If your ISP provided you with specific DNS addresses to use, enter them
into the appropriate fields on this screen and click Apply.
Many ISPs do not require you to enter this information into the Router. If
you are using a Static IP connection type, you may need to enter a
specific DNS address and secondary DNS address for your connection to
work properly. If your connection type is Dynamic, PPPoA or PPPoE, it is
likely that you do not have to enter a DNS address.
Page 68

66 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Hostname & Clone
MAC address
To configure the Hostname and Clone MAC Address information for your
Router, select Internet Settings, then go to the Clone MAC address tab.
The Hostname and MAC Address screen displays.
Figure 52 Hostname and MAC Address Screen
1 Some ISPs require a host name. If your ISP has this requirement, enter the
host name in the Host Name field.
2 Three different ways to configure the WAN MAC Address:
■ If your ISP requires an assigned MAC address, enter the values in the
WAN MAC address field.
or
■ If the computer you are now using is the one that was previously
connected directly to the cable modem, click Clone.
or
■ To reset the MAC Address to the default, click Reset MAC.
3 Click Apply to save the settings.
Page 69

Firewall 67
Firewall From these screens, you can configure settings for the firewall.
Your Router is equipped with a firewall that will protect your network
from a wide array of common hacker attacks including Ping of Death
(PoD) and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. You can turn the firewall
function off if needed. Turning off the firewall protection will not leave
your network completely vulnerable to hacker attacks, but 3Com
recommends that you leave the firewall enabled whenever possible.
SPI Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) - The Intrusion Detection Feature of the
Router limits access for incoming traffic at the WAN port.
This feature is called a "stateful" packet inspection, because it examines
the contents of the packet to determine the state of the communications;
i.e., it ensures that the stated destination computer has previously
requested the current communication. This is a way of ensuring that all
communications are initiated by the recipient computer and are taking
place only with sources that are known and trusted from previous
interactions. In addition to being more rigorous in their inspection of
packets, stateful inspection firewalls also close off ports until connection
to the specific port is requested.
Figure 53 Firewall Screen
To enable the firewall function:
1 Select the level of protection (High, Medium, or Low) that you desire from
the Firewall level drop-down menu.
2 Click Apply.
Page 70

68 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
For low and medium levels of firewall protection, refer to Figure 54.
For high level of firewall protection, refer to Figure 55
.
Figure 54 Low and Medium Level Firewall Protection Screen
When abnormal network activity occurs, an alerting email will be sent out
to you. Enter the following information to receive the email:
■ Your E-mail Address
■ SMTP Server Address
■ User name
■ Password
Page 71

Figure 55 High Level Firewall Protection Screen
Firewall 69
If you select high level of protection, you will need to configure additional
parameters for the firewall.
■ Fragmentation half-open wait - Configures the number of seconds
that a packet state structure remains active. When the timeout value
expires, the Router drops the un-assembled packet, freeing that
structure for use by another packet.
■ TCP SYN wait - Defines how long the software will wait for a TCP
session to synchronize before dropping the session.
■ TCP FIN wait - Specifies how long a TCP session will be maintained
after the firewall detects a FIN packet.
■ TCP connection idle timeout - The length of time for which a TCP
session will be managed if there is no activity.
■ UDP session idle timeout - The length of time for which a UDP session
will be managed if there is no activity.
■ H.323 data channel idle timeout - The length of time for which an
H.323 session will be managed if there is no activity.
Page 72

70 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
■ Total incomplete TCP/UDP sessions HIGH - Defines the rate of new
unestablished sessions that will cause the software to start deleting
half-open sessions.
■ Total incomplete TCP/UDP sessions LOW - Defines the rate of new
unestablished sessions that will cause the software to stop deleting
half-open sessions.
■ Incomplete TCP/UDP sessions (per min) HIGH - Maximum number of
allowed incomplete TCP/UDP sessions per minute.
■ Incomplete TCP/UDP sessions (per min) LOW - Minimum number of
allowed incomplete TCP/UDP sessions per minute.
■ Maximum incomplete TCP/UDP sessions number from same host -
Maximum number of incomplete TCP/UDP sessions from the same
host.
■ Incomplete TCP/UDP sessions detect sensitive time period - Length of
time before an incomplete TCP/UDP session is detected as incomplete.
■ Maximum half-open fragmentation packet number from same host -
Maximum number of half-open fragmentation packets from the same
host.
■ Half-open fragmentation detect sensitive time period - Length of time
before a half-open fragmentation session is detected as half-open.
■ Flooding cracker block time - Length of time from detecting a flood
attack to blocking the attack.
Page 73

Firewall 71
Special Applications Special Applications let you choose specific ports to be open for specific
applications to work properly with the Network Address Translation (NAT)
feature of the Router.
Figure 56 Special Applications Screen
A list of popular applications has been included to choose from. Select
your application from the Popular Applications drop-down menu. Then
select the row that you want to copy the settings to from the Copy To
drop-down menu, and click Copy To. The settings will be transferred to
the row that you specified. Click Apply to save the setting for that
application.
If your application is not listed, you will need to check with the
application vendor to determine which ports need to be configured. You
can manually enter the port information into the Router.
To manually enter the port information:
1 Specify the trigger port (the one used by the application when it is
initialized) in the Trigger Port column, and specify whether the trigger is
TCP or UDP.
2 Specify the Public Ports used by the application, that will need to be
opened up in the firewall for the application to work properly. Also
specify whether these ports are TCP or UDP.
3 Check the Enabled checkbox, then click Apply.
Page 74

72 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Virtual Servers The Virtual servers feature allows you to route external (Internet) calls for
services such as a web server (port 80), FTP server (Port 21), or other
applications through your Router to your internal network. Since your
internal computers are protected by a firewall, machines from the
Internet cannot get to them because they cannot be 'seen'.
If you need to configure the Virtual Server function for a specific
application, you will need to contact the application vendor to find out
which port settings you need.
The maximum number of virtual servers that can be configured is 20.
Figure 57 Virtual Servers Screen
A list of popular servers has been included to choose from. Select the
server from the Popular servers drop-down menu. Then click Add, your
selection will be added to the table.
If the server that you want to use is not listed in the drop-down menu,
you can manually add the virtual server to the table.
To manually configure your virtual servers:
1 Enter the IP address, and the description in the spaces provided for the
internal machine.
2 Select the protocol type (TCP, UDP, or both TCP and UDP) from the
drop-down menu.
3 Specify the public port that will be seen by clients on the Internet, and the
LAN port which the traffic will be routed to.
Page 75

Firewall 73
4 You can enable or disable each Virtual Server entry by checking or
unchecking the appropriate Enabled checkbox.
5 Click Apply to save the changes for each Virtual Server entry.
DMZ If you have a client PC that cannot run an Internet application properly
from behind the firewall, you can open the client up to unrestricted
two-way Internet access. This may be necessary if the NAT feature is
causing problems with an application such as a game or video
conferencing application.
Figure 58 DMZ Screen
Use this feature on a temporary basis. The computer in the DMZ is not
protected from hacker attacks.
To put a computer in the DMZ:
1 Check the Enable 1-to-1 NAT checkbox.
2 Enter the last digits of the LAN IP address in the Client PC IP Address field.
Enter the IP address (if known) that will be accessing the DMZ PC into the
Public IP Address field, so that only the computer on the Internet at this
address can access the DMZ PC without firewall protection. If the IP
address is not known, or if more than one PC on the Internet will need to
access the DMZ PC, then set the Public IP Address to 0.0.0.0.
3 Click Apply.
Page 76

74 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Schedule Rule The Router can be configured to restrict access to the Internet, email or
other network services at specific days and times. Define the time in this
screen, and define the rules in the PC Privileges screen (see page 75
Figure 59 Schedule Rule Screen
1 Click Add Rule to add a schedule rule (a screen similar to Figure 60 will
appear).
).
Figure 60 Add Schedule Rule Screen
2 Enter a name and comment for the schedule rule in the Name and
Comment fields.
3 Specify the schedule rules for the required days and times - note that all
times should be in 24 hour format.
4 Click Apply.
Page 77

Firewall 75
PC Privileges The Router can be configured to restrict access to the Internet, email or
other network services at specific days and times. Restriction can be set
for a single computer, a range of computers, or multiple computers.
You can define the traffic type permitted or not-permitted to the Internet.
Figure 61 PC Privileges Screen
To edit or delete specific existing filtering rules, click on Edit or Delete for
the appropriate filtering rule.
To configure a new filtering rule:
1 Check the Enable Filtering Function checkbox.
2 Click Add PC (a screen similar to Figure 62
Figure 62 PC Privileges Add PC Screen
will appear).
Page 78

76 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
3 Enter a description in the Client PC Description field, and the IP address or
IP address range into the Client PC IP Address fields.
4 To bypass the URL Filter and Content Filter, check the corresponding
Bypass checkbox.
If you check the two options: Bypass URL Filter, and Bypass Content Filter,
then the Web sites and keywords defined in this screen will not be filtered
out.
5 Select the services to be blocked. A list of popular services is given on this
screen, to block a particular service, check the appropriate Blocking
checkbox.
If the service to be restricted is not listed here, you can enter a custom
range of ports at the bottom of the screen, under User Defined Blocked
Ports.
6 If you want the restriction to apply only at certain times, select the
schedule rule to apply from the Schedule Rule drop-down menu.
Note that schedule rules are defined on the Schedule Rules screen
(see page 74
).
7 Click Apply to add the settings.
Page 79

Firewall 77
URL Filter To configure the URL filter feature, use the table on the URL Filter screen
to specify the Web sites (www.somesite.com) and/or keywords you want
to filter on your network.
For example, entering a keyword of xxx would block access to any URL
that contains the string xxx.
Figure 63 URL Filter Screen
1 Check the Enable URL Filtering Function checkbox.
2 Enter the URL address or keywords in the URL/Keyword field.
3 Select Denied or Allowed from the Mode drop-down menu.
To complete this configuration, you will need to create or modify the
filtering rule in the PC Privileges screen (see page 75
From the PC Privileges Add PC screen (Figure 62
).
), if you check the two
options: Bypass URL Filter, and Bypass Content Filter, then the Web sites
and keywords defined in this screen will not be filtered out.
Page 80

78 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Content Filter
You can use the list on the Content Filter screen to specify the type of
content that you want to filter out.
The Router comes with a 14-day free trial of the 3Com Content Filter
Service (3CSBCFS). To activate the 14-day free trial of the service, you
must first register your Router at www.3com.com. To continue using the
service after the trial period, you must purchase the 12-month
subscription license.
Figure 64 Content Filter Screen
To configure the Content Filter feature:
1 Check the Enable Content Filtering Function checkbox.
2 Select the server that you want to use from the Content Filter Server
drop-down menu. If the server you want to use is not listed, enter the
server address manually.
3 Define the time in the Server Timeout field (the default value is 3000ms).
If the Content Filter Server does not respond within this time period, the
Router will use the default content filter rule. The default rule is either
Allow or Deny None of the above (Uncategorized URL). You can configure
this rule at the bottom of the Content Filter screen.
Page 81

Firewall 79
4 If you are not sure about your subscription status, click CHECK in
Subscription Filtering Status to find out if you have a current, valid
subscription.
5 Subjects are listed under Core Categories and Productivity Categories.
You can define what content should be viewed/blocked using the
Allow/Deny option. The Deny option is used to filter out the content that
contains the specific subject matter. Content with a specific subject
matter will not be filtered out if the Allow option is checked.
6 Click Apply for the changes to take effect.
Server Control The Router can be configured to restrict access to the Internet, email or
other network services at specific days and times. Restriction can be set
for the servers.
You can define the traffic type permitted or not-permitted to the Internet.
Figure 65 Server Control Screen
In the Service Filtering Mode, select one option:
■ Denied except listed below.
■ All Allowed.
Click Add to add a new entry to the table (see Figure 66
).
Page 82

80 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Figure 66 Server Control Add Server Screen
1 Enter a description in the Server Description field, and the IP address or IP
address range into the Server IP Address fields.
2 Select the services that will be allowed. A list of popular services is given
on this screen, to unblock a particular service, check the appropriate
Allowed checkbox.
If the service to be allowed is not listed here, you can enter a custom
range of ports at the bottom of the screen, under User Defined Service
Ports.
3 Select the time that the rule will be enforced from the Scheduling Rule
drop-down menu.
4 Click Apply to save the settings.
Page 83

Quality of Service 81
Quality of Service The QoS (Quality of Service) function allows you to differentiate your
network traffic and provide it with high-priority forwarding service.
QoS Settings The bandwidth gap between LAN and WAN may significantly degrade
performance of critical network applications, such as VoIP, gaming, and
VPN. This QoS function allows you to classify traffic of applications and
provides them with differentiated services (Diffserv).
Figure 67 QoS Settings Screen
Define the minimum percentage of bandwidth for each type of traffic.
Traf fic M app i ng You can define up to 16 rules to classify traffic into Diffserv forwarding
groups and outgoing VCs in this screen.
Figure 68 Traffic Mapping screen
Page 84

82 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Click Add to add a new traffic class rule (see Figure 69).
Figure 69 Add New Traffic Class Rule Screen
Traffic Statistics This screen shows the WAN outbound traffic statistics of all the Diffserv
forwarding groups in the last 12 hours. This screen automatically updates
every 5 minutes.
Figure 70 Traffic Statistics Screen
Page 85

Advanced From the Advanced screen, you can configure:
■ Security
■ Static Routes
■ RIP
■ DDNS
■ SNMP
■ Syslog
■ Proxy Arp
Security Use the Security screen to set the advanced security settings for the
Router.
Figure 71 Security Screen
Advanced 83
■ NAT — Before you enable NAT (Network Address Translation), make
sure you have changed the administrator password. NAT is the
method by which the Router shares the single IP address assigned by
your ISP with the computers on your network.
This function should only be disabled by advanced users, and if your
ISP assigns you multiple IP addresses or you need NAT disabled for an
advanced system configuration. If you have a single IP address and
Page 86

84 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
you turn NAT off, the computers on your network will not be able to
access the Internet. Other problems may also occur.
■ IPSEC NAT-T Pass-through — NAT-T (NAT Traversal) is an Internet
Draft proposed to IETF in order to help the problems associated
with passing IPsec traffic through NAT Routers. For NAT-T to work,
both ends of the connection need to support this function. Ensure
that you select NAT-T only if it is needed as it will reduce LAN-WAN
throughput. This Router supports NAT-T draft 2 implementation.
■ Universal Plug and Play — This is a technology that offers seamless
operation of voice messaging, video messaging, games, and other
applications that are Universal Plug and Play compliant. Some
applications require the Router's firewall to be configured in a specific
way to operate properly. This usually requires opening TCP and UDP
ports and in some instances setting trigger ports. An application that
is Universal Plug and Play compliant has the ability to communicate
with the Router, basically "telling" the Router which way it needs the
firewall configured. The Router ships with the Universal Plug and Play
feature disabled. If you are using any applications that are Universal
Plug and Play compliant, and want to take advantage of the Universal
Plug and Play features, you can enable this feature. Simply check the
Enable Universal Plug and Play checkbox. Click Apply to save the
change.
■ WAN Ping Blocking — Computer hackers use what is known as
"Pinging" to find potential victims on the Internet. By pinging a
specific IP address and receiving a response from the IP address, a
hacker can determine that something of interest might be there.
The Router can be set up so it will not respond to an Internet Control
Message Protocol (ICMP) Ping from the outside. This heightens the
level of security of your Router. To turn off the ping response, check
Block ICMP Ping and click Apply; the Router will not respond to an
ICMP ping from the Internet.
■ MSS Clamping — You might not be able to browse some Web sites or
to send email messages that contain attachments from an Internet
Connection Sharing client computer if your outbound connection is
through a Windows XP-based Internet Connection Sharing host
computer that uses Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE).
This issue may occur if the Windows XP-based Internet Connection
Sharing host computer uses a smaller Maximum Transmission Unit
(MTU) size on the WAN interface (the PPPoE connection to the
Internet) than it uses on the private interface (the Ethernet connection
to the Internet Connection Sharing client). If a packet is larger than
Page 87

Advanced 85
the MTU size on the WAN interface, the client sends an Internet
Control Message Protocol (ICMP) error to the external server to
request that the server negotiate the TCP Maximum Segment Size
(MSS). However, this message may be blocked by some firewalls.
When this occurs, the packet is dropped. To allow the message to go
through the firewall, enable MSS Clamping. MSS clamping will make
Internet Connection Sharing set the MSS value low enough to match
the external interface.
■ Remote Administration — This feature allows you to make changes to
your Router’s settings from anywhere on the Internet. Four options are
available:
■ If you do not want to use this feature, select Disable Remote
Administration.
■ Select Enable administration from a single Internet Host, and enter
the IP address, to allow only one computer to use the remote
administration. This is more secure, as only the specified IP address
will be able to manage the Router.
■ Select Enable administration from a whole Subnet Internet Host,
and enter the IP address and subnet mask, to allow PCs from that
specific subnet group to use the remote administration.
■ Select Enable administration from any Internet Host, this allows
any computer to access the Router remotely.
Before you enable this function, ensure that you have set the
Administration Password.
Page 88

86 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Static Routes You can configure static routes in this screen.
To add a static route entry to the table, click Add.
To change an existing entry, click Edit. To delete an entry, click Delete.
Figure 72 Static Routes Screen
This screen shows a list of current static route entries. For each entry, the
following information is displayed:
■ Index — the index of the entry.
■ Network Address — the network address of the route.
■ Subnet Mask — the subnet mask of the route.
A network address of 0.0.0.0 and a subnet mask of 0.0.0.0 indicates the
default route.
■ Gateway — the router used to route data to the network specified by
the network address.
After you have finished making changes to the table, click Apply.
Page 89

Advanced 87
RIP RIP (Routing Information Protocol) - RIP allows the network administrator
to set up routing information on one RIP-enabled device and send that
information to all RIP-enabled devices on the network.
Figure 73 RIP Parameter Screen
You can set up RIP independently on both LAN and WAN interfaces.
1 Check the Enable RIP checkbox.
2 Check the Enable Auto summary checkbox. Auto summarization sends
simplified routing data to other RIP-enabled devices rather than full
routing data.
3 Select the Operation Mode:
■ Disabled — RIP is not enabled for the WAN or LAN interface.
■ Enabled — RIP is enabled for the WAN or LAN interface. The router
will transmit RIP update information to other RIP-enabled devices.
■ Silent — RIP is enabled, however the Router only receives RIP update
messages, it will not transmit any messages itself.
4 In the Version field, select 1 or 2.
3Com recommends that you only use RIPv1 if there is an existing
RIP-enabled device on your network that does not support RIPv2. In all
other cases, you should use RIPv2.
Page 90

88 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
5 Use the Poison Reverse drop-down menu to enable or disable Poison
Reverse on the Router. Enabling Poison Reverse on your Router allows it
to indicate to other RIP-enabled devices that they have both routes that
point to each other, preventing data loops.
6 Use the Authentication Required field to choose the mode of
authentication:
■ None — Switches off authentication on the specified interface.
■ Password — An unencrypted text password that needs to be set on all
RIP-enabled devices connected to this Router. RIP information is not
shared between devices whose passwords do not match.
7 In the Authentication Code field, enter the password that is required if
the Password option has been selected.
8 Click Apply.
DDNS The Router provides a list of dynamic DNS providers for you to choose
from. Dynamic Domain Name Server (DDNS) enables you to map a static
domain name to a dynamic IP address.
The Router supports five DDNS providers:
■ DynDNS.org
■ TZO.com
■ Dt DNS.com
■ No-IP.com
■ Zoneedit.com
Page 91

Advanced 89
Before you set up DDNS, you must obtain an account, password or key
and static domain name from your DDNS provider.
DDNS is disabled by default.
Figure 74 Dynamic Domain Name Server (DDNS) Screen
1 Check Enable DDNS.
2 Select the provider, and then enter the necessary information provided by
your DDNS provider.
3 Click Apply.
Page 92

90 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
SNMP SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) allows remote
management of your Router by a PC that has an SNMP management
agent installed.
Figure 75 SNMP Screen
To Configure SNMP Community:
1 In the Community column, enter the name of the SNMP communication
channel. Your SNMP management agent needs to be configured with this
name so that it can communicate with your Router.
2 In the Access column, select Read to allow the management agent to
collect data (for example, bandwidth usage) from your Router. Select
Write to allow the management agent to change the configuration of
your Router.
3 Check the appropriate Valid checkbox to enable the communication
channel.
Page 93

Advanced 91
You can configure your Router to send status messages to the SNMP
management agent if a problem occurs on the network. To configure
SNMP traps:
1 In the IP Address field, enter the IP address of the PC to which you want
your Router to send status messages.
2 In the Community field, enter the name of the SNMP communication
channel to which you want your Router to send status messages.
3 Set the Version field to match the version of trap messaging that your
SNMP management agent supports. The Router supports V1 and V2c
trap messaging.
Syslog Using third party syslog software, this Syslog Server tool will automatically
download the Router log to the specified server IP address.
Figure 76 Syslog Server Screen
1 Check the Enable Syslog Server checkbox.
2 Enter the Server LAN IP Address in the space provided.
3 Click Apply.
Page 94

92 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Proxy ARP Proxy ARP is the technique in which one host, usually a Router, answers
ARP requests intended for another machine. By "faking" its identity, the
Router accepts responsibility for routing packets to the "real" or intended
destination. This heightens the security for your network.
Figure 77 Proxy ARP Screen
Enter the corresponding IP address in the IP Address From and IP Address
To fields.
Page 95

System Tools 93
System Tools These screens allow you to manage different parameters of the Router
and perform certain administrative functions.
Restart Router Sometimes it may be necessary to restart (or reboot) the Router.
Restarting the Router from this screen will not delete any of your
configuration settings.
Click the Restart the Router button to restart the Router.
Figure 78 Restart Router Screen
Configuration Use this configuration screen to backup, restore or reset the
configuration details of the Router.
Figure 79 Configuration Screen
Page 96

94 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
■ Backup Configuration — You can save your current configuration by
clicking the Backup button. Saving your configuration will allow you
to restore it later if your settings are lost or changed. It is
recommended that you backup your current configuration before
performing a firmware update.
■ Restore Configuration Data — The Restore Settings option will allow
you to restore a previously saved configuration. Please select the
configuration file using the Browse button and click Restore.
■ Reset to Factory Default — Using this option will reset all of the
settings in the Router to the factory default settings. It is
recommended that you backup your settings before you restore all of
the defaults. To restore the factory default settings, click Reset.
Upgrade From time to time 3Com may release new versions of the Router’s
firmware. Firmware updates contain improvements and fixes to problems
that may have existed.
Figure 80 Upgrade Screen
Please download the firmware file to your PC first, and then click Browse
and select the firmware file. Click Upgrade to upload the firmware to the
Router.
Page 97

System Tools 95
Time Zone You can set the time settings for the Router on this screen.
Figure 81 Time Zone Screen
The Router keeps time by connecting to a Network Time Protocol (NTP)
server. This allows the Router to synchronize the system clock to the
Internet. The synchronized clock in the Router is used to record the
security log and control client filtering. Select the time zone that you
reside in. If you reside in an area that observes Daylight Saving, then
check the checkbox for Enable Daylight Saving. The system clock may not
update immediately. Allow at least 15 minutes for the Router to contact
the time servers on the Internet and get a response. You cannot set the
clock yourself.
You can specify which NTP servers the Router will use to update the
system clock, although doing this should only be necessary if you are
experiencing difficulty.
Page 98

96 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
Ping The ping tool is used to test if the network is working properly.
Figure 82 Ping Screen
1 Enter the IP address or domain name in the IP Address or Domain Name
field, and click Ping.
2 Select from the Number of times to Ping drop-down menu.
3 The Router keeps a log of the ping test, click Clear Log to delete the
records.
Page 99

System Tools 97
Traceroute Traceroute is the program that shows you the route over the network
between two systems, listing all the intermediate routers a connection
must pass through to get to its destination. It can help you determine
why your connections to a given server might be poor, and can often help
you figure out where exactly the problem is. It also shows you how
systems are connected to each other, letting you see how your ISP
connects to the Internet as well as how the target system is connected.
Figure 83 Traceroute Screen
1 Enter the IP address or domain name in the IP Address or Domain Name
field, and click Trace ro ut e.
2 The Router keeps a log of the traceroute test, click Clear Log to delete the
records.
Page 100

98 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE ROUTER
DNS Lookup DNS Lookup is the process of resolving an IP address
(i.e. 192.168.11.137) to a host name (i.e. xxxcompany.net).
Figure 84 DNS Lookup Screen
1 Enter the IP address or domain name in the IP Address or Domain Name
field, and click Dns lookup.
2 The Router keeps a log of the DNS lookup test, click Clear Log to delete
the records.
 Loading...
Loading...