Page 1

3Com Wireless 8760 Dual-radio 11a/b/g PoE Access Point
3CRWE876075 / WL-546
User Guide
www.3Com.com
Part Number 10015153 Rev. AA
Published June, 2006
Page 2

3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive
Marlborough, MA
01752-3064
Copyright © 2006 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any
means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from
3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in content from time to time without
obligation on the part of 3Com Corporation to provide notification of such revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or condition of any kind, either implied or expressed,
including, but not limited to, the implied warranties, terms or conditions of merchantability, satisfactory quality, and fitness for a
particular purpose. 3Com may make improvements or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this
documentation at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it is furnished under a license agreement included with
the product as a separate document, in the hard copy documentation, or on the removable media in a directory file named
LICENSE.TXT or !LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to locate a copy, please contact 3Com and a copy will be provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the software described herein are provided to you
subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and developed solely at private expense. Software is delivered as
“Commercial Computer Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014 (June 1995) or as a “commercial item” as defined in
FAR
2.101(a) and as such is provided with only such rights as are provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the Software.
Technical data is provided with limited rights only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015 (November
1987), whichever is applicable. You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any licensed program or
documentation contained in, or delivered to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the United States and may or may not be registered in
other countries.
3Com, the 3Com logo, and SuperStack are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation.
Wi-Fi is a trademark of the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.
EXPORT RESTRICTIONS: This product contains Encryption and may require US and/or Local Government authorization prior to
export or import to another country.
1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction
Product Features 1-2
Security 1-2
Performance and Reliability 1-3
Virtual Access Point (VAP) Support 1-3
WDS Bridging and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Support 1-3
Manageability 1-4
Wireless Network Standards 1-4
802.11g 1-4
802.11a 1-5
Approved Channels 1-5
2 Installing the Access Point
Installation Requirements 2-1
Power Requirements 2-2
Safety Information 2-2
Deciding Where to Place Equipment and
Performing A Site Survey 2-3
Before You Begin 2-4
Connecting the Standard Antennas 2-5
Connecting Power 2-6
Using the Power Supply 2-8
Using a Power-Over-Ethernet LAN Port 2-8
Checking the LEDs 2-9
Reset Button 2-9
Wall, Ceiling, or Electrical Box Mounting 2-10
Flat Surface Installation 2-12
Selecting and Connecting a Different Antenna Model 2-12
Installing Software Utilities 2-14
3
Page 4

3 Initial Configuration
Networks with a DHCP Server 3-1
Networks without a DHCP Server 3-1
Using the 3Com Installation CD 3-2
Launch the 3COM Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager (Widman)
utility 3-2
Launching the 3com Wireless Interface Device Manager 3-2
First Time Only 3-4
Using the Setup Wizard 3-4
4 System Configuration
Advanced Setup 4-2
System Identification 4-4
TCP / IP Settings 4-5
RADIUS 4-8
Authentication 4-9
Filter Control 4-14
VLAN 4-16
SNMP 4-18
Configuring SNMP and Trap Message Parameters 4-18
Configuring SNMPv3 Users 4-21
Administration 4-22
Changing the Password 4-22
Telnet and SSH Settings 4-23
Upgrading Firmware 4-24
WDS and Spanning Tree Settings 4-27
System Log 4-33
Enabling System Logging 4-33
Configuring SNTP 4-34
Radio Interface 4-35
802.11a Interface 4-36
Configuring Radio Settings 4-36
Configuring Common Radio Settings 4-38
802.11b/g Interface 4-42
Configuring Wi-Fi Multimedia 4-44
Security 4-49
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) 4-52
4
Page 5

Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) 4-56
5 Command Line Interface
Using the Command Line Interface 5-1
Accessing the CLI 5-1
Console Connection 5-1
Telnet Connection 5-2
Entering Commands 5-3
Keywords and Arguments 5-3
Minimum Abbreviation 5-3
Command Completion 5-3
Getting Help on Commands 5-3
Showing Commands 5-4
Partial Keyword Lookup 5-4
Negating the Effect of Commands 5-5
Using Command History 5-5
Understanding Command Modes 5-5
Exec Commands 5-5
Configuration Commands 5-6
Command Line Processing 5-6
Command Groups 5-7
6 Troubleshooting
Index
5
Page 6

6
Page 7

TERMINOLOGY
Access Point—An internetworking device that seamlessly connects
wired and wireless networks.
Ad Hoc—An ad hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with
wireless adapters, connected as an independent wireless LAN.
Backbone—The core infrastructure of a network. The portion of the
network that transports information from one central location to another
central location where it is unloaded onto a local system.
Base Station—In mobile telecommunications, a base station is the
central radio transmitter/receiver that maintains communications with the
mobile radiotelephone sets within its range. In cellular and personal
communications applications, each cell or micro-cell has its own base
station; each base station in turn is interconnected with other cells’ bases.
BSS—Basic Service Set. It is an access point and all the LAN PCs that are
associated with it.
CSMA/CA—Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance.
EAP—Extensible Authentication Protocol, which provides a generalized
framework for several different authentication methods.
ESS—Extended Service Set. More than one BSS is configured to become
an ESS. LAN mobile users can roam between different BSSs in an ESS
(ESS-ID, SSID).
Ethernet—A popular local area data communications network, which
accepts transmission from computers and terminals.
Infrastructure—An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an
infrastructure
RADIUS—Remote Access Dial-In User Server is an authentication method
used in conjunction with EAP for 802.1x authentication and session
based keys.
Roaming—A wireless LAN mobile user moves around an ESS and
maintains a continuous connection to the infrastructure network.
RTS Threshold—Transmitters contending for the medium may not be
aware of each other (they are “hidden nodes”). The RTS/CTS mechanism
can solve this problem. If the packet size is smaller than the preset RTS
Threshold size, the RTS/CTS mechanism will not be enabled.
configuration.
7
Page 8

VAP—Virtual Access Point. An access point radio capable of operating as
four separate access points.
VLAN—Virtual Local Area Network. A LAN consisting of groups of hosts
that are on physically different segments but that communicate as
though they were on the same segment.
WEP—Wired Equivalent Privacy is based on the use of security keys and
the popular RC4 encryption algorithm. Wireless devices without a valid
WEP key will be excluded from network traffic.
WDS—Wireless Distribution System.
WPA—Wi-Fi Protected Access.
8
Page 9

1 INTRODUCTION
The 3Com® Wireless 8760 Dual-radio 11a/b/g PoE Access Point offers a
dual-mode architecture that supports 802.11g, 802.11a, and 802.11b wireless
users on a single device. This means you can mix and match radio bands to meet
different coverage and bandwidth needs within the same area.
With their flexibility and unfettered access, wireless LANs are changing the way
people work. Now with 3Com’s enterprise-class wireless access point, you can
build a cost-effective, reliable, secure wireless network that provides users with
seamless connectivity to the Internet, company intranet, and the wired corporate
network from anywhere they happen to be—conference room, cafeteria or
office.
3Com’s dual-mode design supports 802.11g, 802.11a, and 802.11b wireless
standards on a single access point. This capability increases configuration and
coverage flexibility and protects your network investment for both existing and
emerging wireless standards.
Industry-leading security features and comprehensive management and
performance features combine to make these enterprise class wireless access
points an ideal choice for organizations ready to serve their increasingly mobile
workforce.
1-1
Page 10

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
PRODUCT FEATURES
Access Point 8760—Creates an enterprise-class wireless LAN supporting up to
256 simultaneous users. The access point supports two radios and external
antennas including WDS bridging ability on both radios.
SECURITY
3Com offers one of the most robust suite of standards-based security on the
market today.
To protect sensitive data broadcast over the wireless LAN, 3Com supports WPA
and WPA2 security standards. 3Com strengthens this basic security mechanism
with additional security features, including:
MAC address access control lists
IEEE 802.1x per-port user authentication with RADIUS server support
IEEE 802.1x supplicant support
SSH v2
HTTP/HTTPS
SNMP v3
Legacy WEP 40/64 bit, 128 bit and 152 bit
Wireless Protected Access (WPA) and WPA2
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) support: EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS,
EAP-TTLS, and PEAP
1-2
Page 11

Product Features
PERFORMANCE AND RELIABILITY
3Com wireless access point performance features ensure reliable and seamless
connections for users wherever they roam:
Automatic channel selection automatically finds the least loaded channel for
interference-free communication.
Auto network connect and dynamic rate shifting keep users connected
through a wide variety of conditions by changing to the optimum connection
speed as they move through the network.
Virtual Access Point (VAP) support provides flexibility by allowing a single
access point radio to operate as up to four separate access points.
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) Bridging support allows you to create
large wireless networks in areas where pulling wires is restricted or
cost-prohibitive by linking several wireless access points together with WDS
links.
Virtual Access Point (VAP) Support
Virtual Access Point (VAP) support allows an access point radio to operate as four
separate access points, providing multiple wireless services to clients in a network.
Each VAP can be configured to provide access to different network resources and
can support different levels of security.
For example, in a university network, an access point (AP) could be used to offer
two services: The first service provides access to protected data for authenticated
university staff members, while the second service provides open access to the
Internet for unauthenticated users, such as students or visitors.
Up to four VAPs per radio are available, and each VAP can be configured with its
own security settings.
For information on setting up and configuring VAPs, see “Wired Equivalent
Privacy (WEP)” on page 4-52.
WDS Bridging and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Support
A Distribution System (DS) is a network (typically a wired network) that
interconnects separate access points into a single LAN. With WDS, the
interconnection no longer needs to be physically wired. WDS
medium to interconnect separate access points, thereby eliminating the cost and
inconvenience that may hinder wire installations.
A WDS link can be used in a simple point-to-point link, a complex
point-to-multipoint link, or a multilayer topology.
1-3
uses the wireless
Page 12

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
MANAGEABILITY
3Com offers a wide range of standards-based management support, from SNMP
to 3Com Network Supervisor and HP OpenView for seamless integration with
your wired network.
Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager lets you configure parameters, run
diagnostics, backup and restore configurations, and monitor performance from
anywhere on the network using an embedded web server browser.
With Power over Ethernet (PoE) support, the same Category 5 cable that
connects your access point to the data network also provides its power. A single
cable installation dramatically improves your choice of mounting configurations
because you no longer need to consider AC power outlet locations. PoE support
makes it easier than ever to overcome installation problems with difficult-to-wire
or hard-to-reach locations.
WIRELESS NETWORK STANDARDS
Understanding the characteristics of the 802.11g and 802.11a standards can help
you make the best choice for your wireless implementation plans.
802.11G
802.11g operates in the 2.4 GHz band at up to 54Mbps, and supports the widest
coverage—up to 100 meters (328 feet). However, is subject to a greater risk of
radio interference because it operates in the more popular 2.4 GHz band.
For those organizations demanding even higher speeds, a “turbo mode” feature
can boost throughput rates up to 108 Mbps. Consider 802.11g when you need
wider coverage and vendor compatibility and you are:
Maintaining support for existing 802.11b users and the existing wireless
investment while providing for expansion into 802.11g.
Implementing a complete wireless LAN solution, including bridges, gateways,
access points and clients; Wi-Fi certification guarantees compatibility
among
Providing access to hot spots in public spaces such as coffee shops or
university cafeterias
vendors
1-4
Page 13

Wireless Network Standards
802.11A
802.11a operates at the 5 GHz band and supports data rates at up to 54 Mbps.
For those organizations demanding even higher speeds, a “turbo mode” feature
can boost throughput rates up to 108 Mbps. And because there are fewer
devices in the 5
because it is at an entirely different radio spectrum, it is not compatible with
802.11g.
The higher spectrum provides about 50 meters (164 feet) of coverage—about
half what 802.11g offers.
Consider 802.11a when you need high throughput in a confined space and you are:
Running high-bandwidth applications like voice, video, or multimedia over a
wireless network that can benefit from a fivefold increase in data throughput
Transferring large files like computer aided design files, preprint publishing
documents or graphics files, such as MRI scans for medical applications, that
demand additional bandwidth
Supporting a dense user base confined to a small coverage area. Because
802.11a has a greater number of non-overlapping channels, you can pack
more access points in a tighter space.
GHz band, there’s less potential for RF interference. However,
APPROVED CHANNELS
Use of this product is only authorized for the channels approved by each country.
For proper installation, select your country from the country selection list.
To conform to FCC and other country restrictions your product may be limited in
the channels that are available. If other channels are permitted in your country
please visit the 3Com website for the latest software version.
1-5
Page 14

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1-6
Page 15

2 INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
This equipment must be installed in compliance with local and national building
codes, regulatory restrictions, and FCC rules. For the safety of people and
equipment, this product must be installed by a professional technician/installer.
CAUTION: Before installing, see the important warnings and cautions in “Safety
Information” on page 2-2.
!
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS
The following items are required for installation:
Access Point 8760.
Two standard detachable antennas.
3Com installation CD.
Wall-mount installation hardware (supplied): mounting plate,
mounting
If you do not have IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet LAN equipment, use the
3Com Integrated Power-over-Ethernet power supply that comes with
the
If your LAN equipment complies with the IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet
standard, you can connect directly to the equipment, and the 3Com power
supply is not needed.
Standard category 5 straight (8-wire) Ethernet cable.
The cable must be long enough to reach the power supply or the
power-over-Ethernet LAN port.
If you use the 3Com power supply, you need an additional Ethernet cable to
connect the access point to the LAN.
screws, and plastic anchors for drywall mounting.
access point.
2-1
Page 16

CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
To access and use the Web configuration management system, you need a
computer that is running Internet Explorer 5.0 or newer and one of the
following operating systems: Windows 2000, or Windows XP. It is
recommended that this computer become the dedicated workstation for
managing and configuring the access point and the wireless network.
POWER REQUIREMENTS
The access point complies with the IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet standard. It
receives power over standard category 5 straight (8-wire) Ethernet cable.
Installation requires the use of either the 3Com power supply provided or
IEEE
802.3af compliant power supply equipment (output power rated 48 V dc @
400 mA maximum). Such equipment must be safety certified according to UL,
CSA, IEC or other applicable national or international safety requirements for the
country of use. All references to the power supply in this document refer to
equipment that meets these
Because the power supply plug is the only means of disconnecting the access
point from power, make sure the power outlet is accessible.
See “Using the Power Supply” on page 2-8 and “Using a Power-Over-Ethernet
LAN Port” on page 2-8.
requirements.
SAFETY INFORMATION
This equipment must be installed in compliance with local and national building
codes, regulatory restrictions, and FCC rules. For the safety of people and
equipment, only professional network personnel should install the access point,
cables, and antennas.
CAUTION: If you supply your own Ethernet cable for connecting power, be sure
that it is category 5 straight-through (8-wire) cable that has not been altered in
!
any way. Use of nonstandard cable could damage the
CAUTION: To comply with FCC radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, a minimum
body-to-antenna distance of 20 centimeter (8 inches) must be maintained when
!
the access point is
CAUTION: To avoid possible injury or damage to equipment, you must use either
the provided power supply or IEEE 802.3af compliant power supply equipment
!
that is safety certified according to UL, CSA, IEC, or other applicable national or
international safety requirements for the country of use. All references to power
supply in this document refer to equipment meeting these requirements.
access point.
operational.
2-2
Page 17

Deciding Where to Place Equipment and Performing A Site Survey
CAUTION: The 3Com power supply input relies on a 16A rated building fuse or
circuit protector for short circuit protection of the line to neutral conductors.
!
CAUTION: It is the responsibility of the installer to ensure that the
Power-over-Ethernet (POE) power supply is properly connected. Connection to any
!
other device, such as a standard Ethernet card or another POE supply, may result
in permanent damage to equipment, electric shock, or fire. Refer to the
installation instructions for proper installation.
DECIDING WHERE TO PLACE EQUIPMENT AND
PERFORMING A SITE SURVEY
The access point is ideally designed for vertical installation on a wall surface, but
can also be flat-surface mounted in an elevated location where it will not
be
disturbed. Ceiling installation is not recommended.
Whether you choose to mount the access point on a wall or place it on a flat
surface, make sure to select a clean, dry location that is elevated enough to
provide good reception and network coverage. Do not mount the access point on
any type of metal surface. Do not install the access point in wet or dusty areas.
The site should not be close to transformers, heavy-duty motors, fluorescent
lights, microwave ovens, refrigerators or any other electrical equipment that can
interfere with radio signals.
If you are connecting the access point to a wired network, the location must
provide an Ethernet connection. You will need to run an Ethernet cable from the
power supply to the access point.
An access point provides coverage at distances of up to 100 Meters (300 Feet).
Signal loss can occur if metal, concrete, brick, walls, floors or other architectural
barriers block transmission. If your location includes these kinds of obstructions,
you may need to add additional access points to improve coverage
2-3
Page 18

CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
Configuring a wireless LAN can be as easy as placing a 3Com Wireless Access
Point in a central area and making the necessary connections to the AP and the
clients. However, installing multiple Access Points may require more planning.
If you plan to use an optional antenna instead of the standard detachable
antennas that are supplied, review
Antenna Model” on page 2-12 before selecting the final location and be sure to
allow for routing the antenna cable as required.
For optimal performance, ensure the access point operates in temperature ranges
between 0° C to 50° C (14° F to 122° F).
CAUTION: Regulatory restrictions dictate that when this device is operational,
the minimal body-to-antenna distance is 20 cm (8 inches).
!
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Record the access point MAC address in a safe place before the access point is
installed in a hard-to-reach location. The MAC address is printed on the back of
the access point housing.
“Selecting and Connecting a Different
The following illustration shows the front and rear views of the access point,
including the LEDs and connecting ports.
2-4
Page 19

Figure 1 Front and Rear Panel Description
LEDs
Connecting the Standard Antennas
Kensington Lock Slot
POE Port
Console Port
CONNECTING THE STANDARD ANTENNAS
The Access Point 8760 is supplied with standard detachable antennas. These
should be attached before the access point is installed. If using an alternate
antenna, see
page 2-12.
1 Carefully unpack the standard detachable antennas.
CAUTION: Do not handle the antenna tips, especially after they are connected
to the access point, as this could lead to electrostatic discharge (ESD), which
!
could damage the
2 Screw an antenna into each of the sockets in the access point housing.
3 Hand-tighten the antennas at the very base of the RSMA connectors.
4 Position the antennas so they turn out and away from the access point at a
45-degree angle. After network startup, you may need to adjust the antennas
to fine-tune coverage in your area.
“Selecting and Connecting a Different Antenna Model” on
equipment.
2-5
Page 20

CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
Figure 2 Antenna Adjustment
Depending on the coverage required for your site, you may want to replace
the standard detachable antennas with one of the external antennas available
for use with the access point. See
Antenna Model” on page 2-12.
CONNECTING POWER
It is advisable to connect the power and check the Ethernet cables and LEDs
before installing the unit in a hard-to-reach location.
The access point complies with the IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet standard. It
receives power over a standard category 5 straight (8-wire) Ethernet cable.
There are two ways to supply power to the access point:
Use the 3Com Integrated Power-over-Ethernet power supply. In this case, you
need to supply a second Ethernet cable to connect to the wired LAN.
Connect the access point directly to your own power-over-Ethernet hub or
switch, which must also comply with the IEEE
“Selecting and Connecting a Different
802.3af standard.
2-6
Page 21

Connecting Power
If you supply your own Ethernet cable for connecting power, be sure that it is
standard category 5 straight-through (8-wire) cable that has not been altered
in any way. Use of nonstandard cable could damage the access point.
Figure 3 Connecting Power
2-7
Page 22

CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
USING THE POWER SUPPLY
CAUTION: To avoid damaging network equipment, make sure that the cables
are connected from access point to power supply to LAN as shown above and
!
described
The power supply can be located at any point between the access point and the
LAN access port, wherever a convenient power outlet exists. If you supply your
own Ethernet cable for connecting power, be sure that it is standard category 5
straight-through (8-wire) cable that has not been altered in any way. Use of
nonstandard cable could damage the access point.
Refer to the illustration above, and follow these steps:
1 Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on the access
2 Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the port labeled To Access
3 Connect the power cord to the power supply and plug the cord into a power
below.
point.
Point on the power supply.
outlet.
4 To link the access point to your Ethernet network, plug one end of another
Ethernet cable into the port labeled To Hub/Switch on the power supply, and
plug the other end into a LAN port (on a hub or in a wall).
USING A POWER-OVER-ETHERNET LAN PORT
If your LAN equipment complies with the IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet
standard, you can connect the access point directly to a LAN port. For example,
the illustration above right shows a connection through a 3Com Ethernet Power
Supply to a 3Com Switch.
2-8
Page 23

CHECKING THE LEDS
When power is connected, the access point LEDs light. The illustration and the
following table describe the LEDs and their functions.
Ta bl e 1 System LEDs
Checking the LEDs
LED Color Indicates
Power Green The access point is powered up
and operating normally.
Off The access point is not receiving
power or there is a fault with the
power supply.
Link Green The access point has a 10/100
Mbps Fast Ethernet connection.
Flashing Indicates that the access point is
transmitting or receiving data on a
10/100 Mbps Ethernet LAN.
Flashing rate is proportional to
network activity.
Off No link is present.
11a Green The access point has WLAN frame
transmission over the 802.11a 5.3
GHz radio band.
Off No link is present.
11g Green The access point has WLAN frame
transmission over the 802.11g 2.4
GHz radio band.
Off No link is present.
RESET BUTTON
This button is used to reset the access point or restore the factory default
configuration. If you hold down the button for less than 5 seconds, the access
point will perform a hardware reset. If you hold down the button for 10 seconds
or more, any configuration changes you may have made are removed, and the
factory default configuration is restored to the access point.
2-9
Page 24

CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
WALL, CEILING, OR ELECTRICAL BOX MOUNTING
To mount the access point to a wall, ceiling, or electrical box:
1 Remove the access point from the mounting bracket.
2 Screw the mounting bracket to a wall, ceiling, or electrical box (NEMA
enclosure):
If mounting to a solid surface wall or ceiling, use two of the sheet metal
screws and two of the wall anchors (included).
If mounting to drywall, use two sheet metal screws and two wall anchors
(not included).
If mounting to an electrical box (NEMA enclosure), use two threaded
screws (not included).
3 Route the power cable (if using an external power supply) and Ethernet cable
through the large opening on the back of the mounting bracket.
CAUTION: For easy installation and removal of the access point from the
mounting bracket, make sure that there is sufficient flexibility with the cable and
!
that there is adequate service loop (that is, enough cable routed through the
mounting bracket to easily connect the cable to the access point.) If not enough
cable is routed through the back of the mounting bracket, or if the cable is
inflexible, it can be difficult to install or remove the access point from the
mounting bracket.
The figures below show a cable being routed through the large opening on
the back of the mounting bracket and then the mounting bracket being
mounted to a wall.
2-10
Page 25
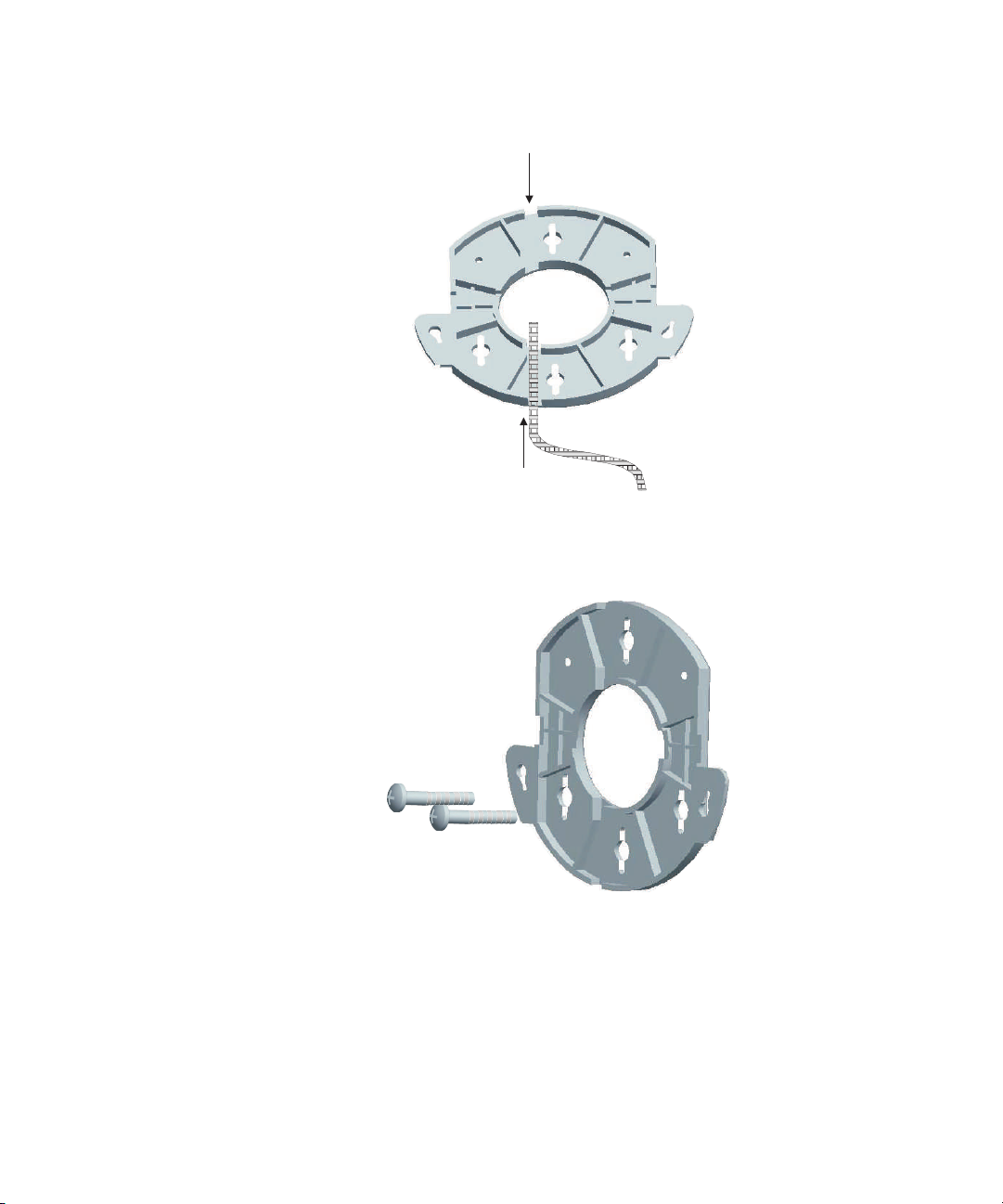
Figure 4 Routing a Cable
Figure 5 Mounting Bracket
Wall, Ceiling, or Electrical Box Mounting
Routing a cable
Installing the mounting bracket
4 Connect the Ethernet cable to the port on the back of the access point.
2-11
Page 26
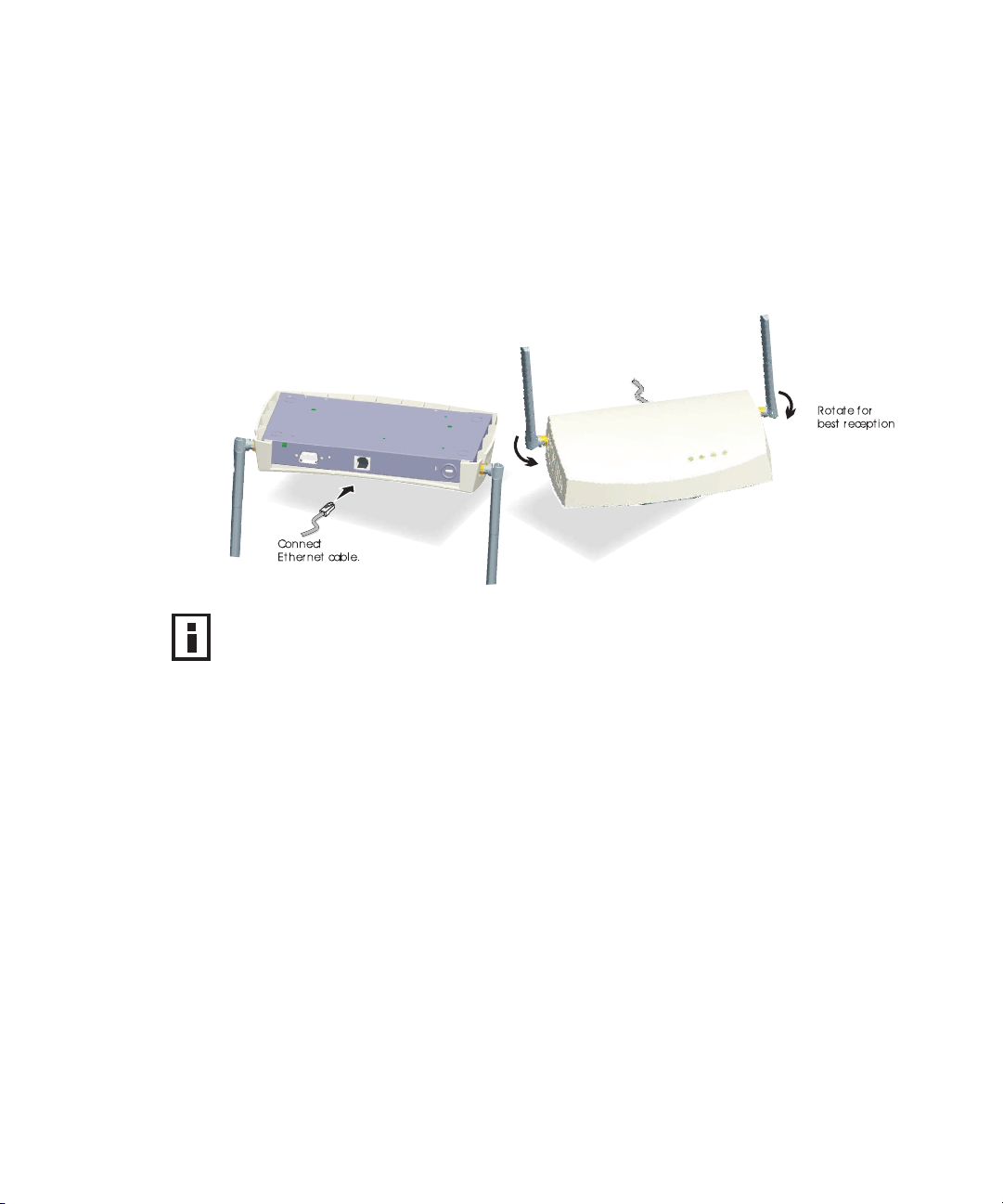
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
FLAT SURFACE INSTALLATION
The access point can also be placed on a flat surface such as a table, desktop or
filing cabinet. Do not install the access point on any type of metal surface. If you
choose a flat surface mount, select a location that is clear of obstructions and
provides good reception.
Figure 6 Flat Surface Installation
NOTE: Regulatory restrictions dictate that when this device is operational, the
minimal body-to-antenna distance is 20 cm (8 inches).
SELECTING AND CONNECTING A DIFFERENT ANTENNA MODEL
The standard detachable antennas supplied with the Access Point are suitable for a
broad variety of environments. If you require a different type of antenna for the
Access Point, several options are available by model number from the 3Com Web site
(www.3Com.com).
For each of the antenna models, you will need an RSMA to SMA adapter cable
(model 3CRWE586), either a 6-foot accessory cable (model 3CWE580) or a
20-foot accessory cable (model 3CWE581) to provide the transition from the
RSMA connector on the access point to the N-type connector on the antenna.
2-12
Page 27

Figure 7 Connecting Antennae
Selecting and Connecting a Different Antenna Model
Side Side
1 Position the antenna so that there are minimal obstacles between it and any
client with which it will communicate. While maintaining a direct line of sight
between the antenna and a client is not strictly necessary, such an
arrangement helps to ensure a strong signal. Ensure that access is available
for routing the antenna cable from the antenna to the access point.
2 If they are installed, remove both standard detachable antennas.
3 Connect one end of the optional antenna cable to the antenna and secure
the antenna in place.
4 Connect the free end of the antenna cable to the connection on the access
point, as shown in the illustration above.
5 Make certain that the antennas and antenna masts are appropriately
grounded to prevent injury or damage from lightning strikes. Proper
grounding for outdoor installations may require the purchase of a third-party
lightning arrestor.
2-13
Page 28

CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
INSTALLING SOFTWARE UTILITIES
The installation CD includes documentation and software utilities to help you set
up and administer the wireless components of your network.
To view product documentation, select View the Documentation from the CD
Startup Menu and then select the item you want to view.
The software Tools and Utilities include:
3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager. Use this tool to discover
access points and select devices for administrative changes.
3Com 3CDaemon Server Tool. This tool can act in four different capacities:
As a TFTP Server, necessary for firmware upgrades, and backup and restore
functions. Use this option if you do not have a TFTP server set up.
As a SysLog Server, which is necessary to view SysLog messages.
As an optional TFTP Client.
As an optional FTP Server.
To install a tool from the CD:
1 Power up the computer and put the 3Com CD in the CD-ROM drive.
2 The setup menu should appear when the CD autostarts. If no menu appears,
you can run the setup.exe startup program from the Windows Start menu.
For example, if your CD drive is the D drive: Start / Run / d:setup.exe.
3 From the CD startup menu, select Tools and Utilities.
4 Select the item you want to install and follow the instructions on the screen.
2-14
Page 29
3 INITIAL CONFIGURATION
The Access Point 8760 offers a variety of management options, including a
web-based interface.
The initial configuration steps can be made through the web browser interface.
The access point requests an IP address via DHCP by default. If no response is
received from the DHCP server, then the access point uses the default address
169.254.2.1.
If the default AP configuration does not meet your network requirements, or if
you want to customize the settings for your own network, you can use these
tools to change the configuration:
1 Launch the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager (Widman) utility
2 Directly connect to the device through it’s Ethernet port or console port
NETWORKS WITH A DHCP SERVER
If your network has a DHCP server, an IP address is automatically assigned to the
AP. It takes between one and two minutes for the Access Point to determine if
there is a DHCP server on the network. Use the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure
Device Manager (Widman) included on the 3Com Installation CD to locate the
Access Point on the network and view its IP address. After you determine the AP’s
IP address, you can enter that IP address into a web browser on a computer on
the same subnet to view the Access Point’s system status or change its
configuration.
NETWORKS WITHOUT A DHCP SERVER
If your network does not have a DHCP server, the Access Point uses a factory
assigned IP address (169.254.2.1). You can use that IP address to configure the
Access Point, or you can assign a new IP address to the Access Point. To verify that
the Access Point is using the default IP address assigned at the factory:
3-1
Page 30

CHAPTER 3: INITIAL CONFIGURATION
1 Connect a computer directly to the Access Point using the supplied standard
Category 5 UTP Ethernet cable.
2 Enter the Access Point’s default IP address (169.254.2.1) into the computer’s
web browser. If the Configuration Management System starts, the Access
Point is using the factory assigned IP address. You can configure the Access
Point with the following login information:
Login name: admin
Password: password
If the Configuration Management System does not start, the Access Point is
on a different subnet than the computer. Install and start the 3Com Wireless
Infrastructure Device Manager to discover the Access Point’s IP address.
USING THE 3COM INSTALLATION CD
The 3Com Installation CD contains the following tools and utilities: 3Com
Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager-an administration tool that helps you
select 3Com wireless LAN devices and launch their configurations in your Web
browser.
LAUNCH THE 3COM WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE DEVICE
M
ANAGER (WIDMAN) UTILITY
1 Turn on the computer.
2 Insert the 3Com Installation CD into the CD-ROM drive.
The CD will Autorun. If it does not Autorun, you can start the setup menu
from the Windows Start menu. For example: Start > Run > d: setup.exe.
3 In the menu, click Tools and Utilities.
4 In the next screen, click the software you want to install.
5 Follow the on screen instructions to complete the installation.
Reboot the computer if prompted to do so.
LAUNCHING THE 3COM WIRELESS INTERFACE DEVICE MANAGER
To be able to configure the Access Point you need to run the Wireless Interface
Device Manager. Go to Start > Programs > 3Com Wireless > Wireless
Interface Device Manager.
If the device is working correctly the following screen should be seen.
3-2
Page 31

Figure 8 Wireless Interface Device Manager
Click on the Properties button to see the following screen
Figure 9 Wireless Interface Device Manager - Properties
3-3
Page 32

CHAPTER 3: INITIAL CONFIGURATION
Directly connect to the device through its Ethernet port or console port.
Follow the instructions below to login into the AP Configuration screen:
1 Load a web browser and enter <http://169.254.2.1>.
2 The Logon screen appears.
To log on to the Web interface:
1 Username, type admin (case sensitive).
2 Password, type password
3 Click Log On.
FIRST TIME ONLY
When you log in for the first time, you may be asked to select your country.
Choose your country from the drop-down list and then click Apply.
Click on the Setup Wizard for initial configuration.
For a new access point installation, the default WLAN Service Area (ESSID) is
3Com1 to 3Com4 for the 11a interface, and 3Com5 to 3Com8 for the 11b/g
interface, with no security set. Unless it detects a DHCP server on the network,
the access point uses Auto IP to assign an IP address of the form 169.254.2.1.
Use the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager to locate 3Com Wireless
LAN devices and launch their configurations. When installing the device manager,
make sure the computer is connected to the same network as the device to be
configured. After installing and launching the device manager, select the device
to be configured from network tree and click Configure to launch the
configuration Web interface.
USING THE SETUP WIZARD
There are only a few basic steps you need to complete to connect the access
point to your corporate network and provide network access to wireless clients.
The Setup Wizard takes you through configuration procedures for the wireless
Service Set Identifier, the radio channel selection, IP configuration and basic
authentication for wireless clients.
The access point can be managed by any computer using a web browser (such as
Internet Explorer 5.0 or above). Enter the default IP address: http://169.254.2.1.
3-4
Page 33

Using the Setup Wizard
NOTE: If you changed the default IP address via the command line interface above,
use that address instead of the one shown here.
Logging In – Enter the username “admin,” and password “password,” then
click LOGIN. For information on configuring a user name and password, see
page
4-22.
Figure 10 Login Page
3-5
Page 34

CHAPTER 3: INITIAL CONFIGURATION
The home page displays the Main Menu.
Figure 11 Home Page
Launching the Setup Wizard – To perform initial configuration, click Setup
Wizard on the home page, select the VAP you wish to configure, then click on the
[Next] button to start the process.
Figure 12 Setup Wizard - Start
3-6
Page 35

Using the Setup Wizard
1 Service Set ID – Enter the service set identifier in the SSID box which all
wireless clients must use to associate with the access point. The SSID is case
sensitive and can consist of up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
Figure 13 Setup Wizard - Step 1
2 Radio Channel – You must enable radio communications for 802.11a and
802.11b/g, and set the operating radio channel.
NOTE: Available channel settings are limited by local regulations, which determine
the channels that are available. This User Guide shows channels and settings that
apply to North America (United States and Canada), with 13 channels available for
the 802.11a interface and 11 channels for the 802.11g interface. Other regions my
have different channels and settings available.
3-7
Page 36

CHAPTER 3: INITIAL CONFIGURATION
Figure 14 Setup Wizard - Step 2
802.11a
Turbo Mode – If you select Enable, the access point will operate
in turbo mode with a data rate of up to 108 Mbps. Normal
mode support 13 channels, Turbo mode supports only 5
channels. (Default: Disabled)
802.11a Radio Channel – Set the operating radio channel
number. (Default: 60ch, 5.300
is not enabled.)
Auto Channel Select – Select Enable for automatic radio
channel detection. (Default: Enabled)
802.11b/g
GHz when Auto Channel Select
Turbo Mode - If you select Enable, the access point will operate in
turbo mode with a data rate of up to 108 Mbps. Normal mode support
11 channels, Turbo mode supports only 1 channel. (Default: Disabled)
802.11g Radio Channel - Set the operating radio channel number.
(Range 1-11; Default: 1 when Auto Channel Select is not enabled.
Auto Channel Select – Select Enable for automatic radio channel
detection. (Default: Enabled)
3-8
Page 37

Using the Setup Wizard
3 IP Configuration – Either enable or disable Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) for automatic IP configuration. If you disable DHCP, then
manually enter the IP address and subnet mask. If a management station
exists on another network segment, then you must enter the IP address for a
gateway that can route traffic between these segments. Then enter the IP
address for the primary and secondary Domain Name Servers (DNS) servers to
be used for host-name to IP address resolution.
Figure 15 Setup Wizard - Step 3
DHCP Client – With DHCP Client enabled, the IP address, subnet mask and
default gateway can be dynamically assigned to the access point by the
network DHCP server. (Default: Disabled)
NOTE: If there is no DHCP server on your network, then the access point will
automatically start up with its default IP address, 169.254.2.1.
4Security – Set the Authentication Type to “Open” to allow open access
without authentication, or “Shared” to require authentication based on a
shared key. Enable encryption to encrypt data transmissions. To configure
other security features use the Advanced Setup menu as described in
Chapter 4.
3-9
Page 38

CHAPTER 3: INITIAL CONFIGURATION
Figure 16 Setup Wizard - Step 4
Authentication Type – Use “Open System” to allow open access to all wireless
clients without performing authentication, or “Shared Key” to perform
authentication based on a shared key that has been distributed to all stations.
(Default: Open System)
WEP – Wired Equivalent Privacy is used to encrypt transmissions passing
between wireless clients and the access point. (Default: Disabled)
Shared Key Setup – If you select “Shared Key” authentication, enable WEP,
then configure the shared key by selecting 64-bit or 128-bit key type and
entering a hexadecimal or ASCII string of the appropriate length. The key can
be entered as alphanumeric characters or hexadecimal (0~9, A~F, e.g., D7 0A
9C 7F E5). (Default: 128 bit, hexadecimal key type)
64-Bit Manual Entry: The key can contain 10 hexadecimal digits, or 5
alphanumeric characters.
128-Bit Manual Entry: The key can contain 26 hexadecimal digits or 13
alphanumeric characters.
NOTE: All wireless devices must be configured with the same Key ID values to
communicate with the access point.
3-10
Page 39

5 Click Finish.
6 Click the OK button to complete the wizard.
Figure 17 Setup Wizard - Completed
Using the Setup Wizard
3-11
Page 40

CHAPTER 3: INITIAL CONFIGURATION
3-12
Page 41

4 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Before continuing with advanced configuration, first complete the initial
configuration steps described in Chapter 4 to set up an IP address for the access
point.
The access point can be managed by any computer using a web browser (such as
Internet Explorer 5.0 or above). Enter the configured IP address of the access
point, or use the default address: http://169.254.2.1.
To log into the access point, enter the default user name “admin” and the
password “password,” then press “LOGIN.”
For a new access point installation, the default WLAN Service Area (ESSID) is
3Com and no security is set. Unless it detects a DHCP server on the network, the
access point uses Auto IP to assign an IP address of the form 169.254.2.1.
Use the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager to locate 3Com Wireless
LAN devices and launch their configurations. When installing the device manager,
make sure the computer is connected to the same network as the device to be
configured. After installing and launching the device manager, select the device
to be configured from network tree and click Configure to launch the
configuration Web interface.
When the home page displays, click on Advanced Setup. The following page will
display.
4-1
Page 42

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Figure 18 Advanced Setup
The information in this chapter is organized to reflect the structure of the web
screens for easy reference. However, it is recommended that you configure a user
name and password as the first step under Administration to control
management access to this device (
ADVANCED SETUP
The Advanced Setup pages include the following options.
Ta bl e 2 Advanced Setup
Menu Description Page
System Configures basic administrative and client access 4-4
Identification Specifies the host name 4-4
TCP / IP Settings Configures the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and domain
RADIUS Configures the RADIUS server for wireless client authentication 4-8
Authentication Configures 802.1X client authentication, with an option for MAC
Filter Control Filters communications between wireless clients, access to the
page 4-22).
4-5
name servers
4-9
address authentication
4-14
management interface from wireless clients, and traffic matching
specific Ethernet protocol types
4-2
Page 43

Advanced Setup
Menu Description Page
SNMP Configures SNMP settings 4-18
Administration Configures user name and password for management
WDS/STP Settings Configures WDS bridging and Spanning Tree Protocol features 4-27
Syslog Set-up Controls logging of error messages; sets the system clock via SNTP
Status Displays information about the access point and wireless clients 4-59
AP Status Displays configuration settings for the basic system and the
Station Status Shows the wireless clients currently associated with the access
Event Logs Shows log messages stored in memory 4-61
802.11a Interface Configures the IEEE 802.11a interface 4-35
Radio Settings Configures common radio signal parameters and other settings
Security Enables each virtual access point (VAP) interface, sets the Service
802.11b/g Interface Configures the IEEE 802.11g interface 4-35
Radio Settings Configures common radio signal parameters and other settings
Security Enables each VAP interface, sets the SSID, and configures wireless
upgrades software from local file, FTP or TFTP server;
configuration settings to factory defaults; and resets the access
point
server or manual configuration
wireless interface
point
for each VAP interface
Set Identifier (SSID), and configures wireless security
for each VAP interface
security
access;
resets
4-22
4-33
4-59
4-60
4-36
4-49
4-42
4-49
4-3
Page 44

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
The system name for the access point can be left at its default setting. However,
modifying this parameter can help you to more easily distinguish different devices
in your network.
Figure 19 System Identification
System Name – An alias for the access point, enabling the device to be uniquely
identified on the network. (Default: Enterprise Wireless AP; Range: 1-32
characters)
4-4
Page 45

TCP / IP SETTINGS
Configuring the access point with an IP address expands your ability to manage
the access point. A number of access point features depend on IP addressing to
operate.
NOTE: You can use the web browser interface to access IP addressing only if the
access point already has an IP address that is reachable through your network.
By default, the access point will be automatically configured with IP settings from
a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. Use 3Com Wireless
Infrastructure Device Manager to discover or set the initial IP address of the unit.
WIDMAN will allow you to launch a web browser on the Access Point's web
management interface by selecting the Access Point and the configure button.
NOTE: If there is no DHCP server on your network, or DHCP fails, the access point
will automatically start up with a default IP address of 169.254.2.1.
Figure 20 TCP/IP Settings
TCP / IP Settings
4-5
Page 46

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
DHCP Client (Enable) – Select this option to obtain the IP settings for the access
point from a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. The IP address,
subnet mask, default gateway, and Domain Name Server (DNS) address are
dynamically assigned to the access point by the network DHCP server.
(Default:
DHCP Client (Disable) – Select this option to manually configure a static address
for the access point.
IP Address: The IP address of the access point. Valid IP addresses consist of four
decimal numbers, 0 to 255, separated by periods.
Subnet Mask: The mask that identifies the host address bits used for routing to
specific subnets.
Default Gateway: The default gateway is the IP address of the router for the
access point, which is used if the requested destination address is not on the
local subnet.
If you have management stations, DNS, RADIUS, or other network servers
located on another subnet, type the IP address of the default gateway router in
the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the address as all zeros (0.0.0.0).
Primary and Secondary DNS Address: The IP address of Domain Name Servers
on the network. A DNS maps numerical IP addresses to domain names and can
be used to identify network hosts by familiar names instead of the IP addresses.
Enabled)
If you have one or more DNS servers located on the local network, type the IP
addresses in the text fields provided. Otherwise, leave the addresses as all zeros
(0.0.0.0).
Web Servers – Allows monitoring of the access point from a browser and secure
connection.
HTTP Server: Allows the access point to be monitored or configured from a
browser.
HTTP Port: Specifies the port to be used by the web browser interface.
HTTPS Server: Enables the secure HTTP server on the access point.
HTTPS Port: Specifies the UDP port number used for a secure HTTP connection
to the access pointís Web interface.
4-6
Page 47

TCP / IP Settings
Figure 21 Smart Monitor
By enabling Smart Monitor (known as Link Integrity in the CLI) and setting a
target IP address, the AP will periodically (set by the ping interval) check to see if
the target address responds to pings. If it fails to respond to a ping after the
configured number of retries, it will disable both radios so that no clients can
connect to the AP.
This is used to disable the AP when it cannot not reach a critical network element
such as the RADIUS server, VPN Terminator, Mail Server etc.
Disable / Enable: Disables or enables a link check to a host device on the wired
network.
Target IP address: Specifies the IP address of a host device in the wired network.
Enable: Enables traffic between the host’s IP address and the AP.
Ping Interval: Specifies the time between each Ping sent to the link host.
(Range:300~30000 miliseconds; Default: 30 miliseconds)
Number of Retries allowed: Specifies the number of consecutive failed Ping
counts before the link is determined as lost. (Range:1~30; Default:6)
4-7
Page 48

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) is an authentication protocol
that uses software running on a central server to control access to RADIUS-aware
devices on the network. An authentication server contains a database of user
credentials for each user that requires access to the network.
A primary RADIUS server must be specified for the access point to implement IEEE
802.1X network access control and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) wireless
security. A secondary RADIUS server may also be specified as a backup should the
primary server fail or become inaccessible.
In addition, the configured RADIUS server can also act as a RADIUS Accounting
server and receive user-session accounting information from the access point.
RADIUS Accounting can be used to provide valuable information on user activity
in the network.
NOTE: This guide assumes that you have already configured RADIUS server(s) to
support the access point. Configuration of RADIUS server software is beyond the
scope of this guide, refer to the documentation provided with the RADIUS server
software.
Figure 22 RADIUS Authentication
Primary RADIUS Server Setup – Configure the following settings to use RADIUS
authentication on the access point.
IP Address: Specifies the IP address or host name of the RADIUS server.
4-8
Page 49

Authentication
Port: The UDP port number used by the RADIUS server for authentication
messages. (Range: 1024-65535; Default:
Key: A shared text string used to encrypt messages between the access point
1812)
and the RADIUS server. Be sure that the same text string is specified on the
RADIUS server. Do not use blank spaces in the string. (Maximum length: 255
characters)
Timeout: Number of seconds the access point waits for a reply from the
RADIUS server before resending a request. (Range:
Retransmit attempts: The number of times the access point tries to resend a
1-60 seconds; Default: 5)
request to the RADIUS server before authentication fails. (Range: 1-30;
Default: 3)
NOTE: For the Timeout and Retransmit attempts fields, accept the default values
unless you experience problems connecting to the RADIUS server over the
network.
Secondary RADIUS Server Setup – Configure a secondary RADIUS server to
provide a backup in case the primary server fails. The access point uses the
secondary server if the primary server fails or becomes inaccessible. Once the
access point switches over to the secondary server, it periodically attempts to
establish communication again with primary server. If communication with the
primary server is re-established, the secondary server reverts to a backup role.
VLAN ID Format – A VLAN ID (a number between 1 and 4094) can be assigned to
each client after successful authentication using IEEE 802.1X and a central
RADIUS server. The user VLAN IDs must be configured on the RADIUS server for
each user authorized to access the network. VLAN IDs can be entered as
hexadecimal numbers or as ASCII strings.
AUTHENTICATION
Wireless clients can be authenticated for network access by checking their MAC
address against the local database configured on the access point, or by using a
database configured on a central RADIUS server. Alternatively, authentication can
be implemented using the IEEE 802.1X network access control protocol.
A client’s MAC address provides relatively weak user authentication, since MAC
addresses can be easily captured and used by another station to break into the
network. Using 802.1X provides more robust user authentication using user
names and passwords or digital certificates. You can configure the access point to
4-9
Page 50

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
use both MAC address and 802.1X authentication, with client station MAC
authentication occurring prior to IEEE 802.1X authentication. However, it is better
to choose one or the other, as appropriate.
IEEE 802.1X is a standard framework for network access control that uses a
central RADIUS server for user authentication. This control feature prevents
unauthorized access to the network by requiring an 802.1X client application to
submit user credentials for authentication. The 802.1X standard uses the
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to pass user credentials (either digital
certificates, user names and passwords, or other) from the client to the RADIUS
server. Client authentication is then verified on the RADIUS server before the
access point grants client access to the network.
The 802.1X EAP packets are also used to pass dynamic unicast session keys and
static broadcast keys to wireless clients. Session keys are unique to each client and
are used to encrypt and correlate traffic passing between a specific client and the
access point. You can also enable broadcast key rotation, so the access point
provides a dynamic broadcast key and changes it at a specified interval.
The access point can also operate in a 802.1X supplicant mode. This enables the
access point itself to be authenticated with a RADIUS server using a configured
MD5 user name and password. This prevents rogue access points from gaining
access to the network.
Take note of the following points before configuring MAC address or 802.1X
authentication:
Use MAC address authentication for a small network with a limited number of
users. MAC addresses can be manually configured on the access point itself
without the need to set up a RADIUS server, but managing a large number of
MAC addresses across many access points is very cumbersome. A RADIUS
server can be used to centrally manage a larger database of user MAC
addresses.
Use IEEE 802.1X authentication for networks with a larger number of users and
where security is the most important issue. When using 802.1X authentication,
a RADIUS server is required in the wired network to centrally manage the
credentials of the wireless clients. It also provides a mechanism for enhanced
network security using dynamic encryption key rotation or W-Fi Protected
Access (WPA).
NOTE: If you configure RADIUS MAC authentication together with 802.1X,
RADIUS MAC address authentication is performed prior to 802.1X authentication.
If RADIUS MAC authentication succeeds, then 802.1X authentication is
performed. If RADIUS MAC authentication fails, 802.1X authentication is not
performe
d.
4-10
Page 51

Figure 23 Authentication
Authentication
MAC Authentication – You can configure a list of the MAC addresses for wireless
clients that are authorized to access the network. This provides a basic level of
authentication for wireless clients attempting to gain access to the network. A
database of authorized MAC addresses can be stored locally on the access point
or remotely on a central RADIUS server.
(Default: Disabled)
Disabled: No checks are performed on an associating station’s MAC address.
4-11
Page 52

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Local MAC: The MAC address of the associating station is compared against
the local database stored on the access point. Use the Local MAC
Authentication section of this web page to set up the local database, and
configure all access points in the wireless network service area with the same
MAC address database.
RADIUS MAC: The MAC address of the associating station is sent to a
configured RADIUS server for authentication. When using a RADIUS
authentication server for MAC address authentication, the server must first be
configured on the RADIUS page (see
MAC addresses and filtering policy must be defined in the RADIUS server. The
MAC address of the associating station is used for both the username and
password. For example, an associating station with a MAC address of
12-34-56-78-9A-BC would use a username and password of “12345678abc.”
The username and password sent to the server will use the format defined by
“radius-server radius-mac-format” (See
has a default setting of “no-delimiter.”
NOTE: MAC addresses on the RADIUS server can be entered in four different
formats (see
“RADIUS” on page 4-8). The database of
“RADIUS Client” on page 5-64), which
“radius-server radius-mac-format” on page 5-68).
You can enable 802.1X as optionally supported or as required to enhance the
security of the wireless network. (Default: Disable)
Disable: The access point does not support 802.1X authentication for any
wireless client. After successful wireless association with the access point, each
client is allowed to access the network.
Supported: The access point supports 802.1X authentication only for clients
initiating the 802.1X authentication process (i.e., the access point does not
initiate 802.1X authentication). For clients initiating 802.1X, only those
successfully authenticated are allowed to access the network. For those clients
not initiating 802.1X, access to the network is allowed after successful wireless
association with the access point. The 802.1X supported mode allows access
for clients not using WPA or WPA2 security.
Required: The access point enforces 802.1X authentication for all associated
wireless clients. If 802.1X authentication is not initiated by a client, the access
point will initiate authentication. Only those clients successfully authenticated
with 802.1X are allowed to access the network.
NOTE: If 802.1X is enabled on the access point, then RADIUS setup must be
completed (
See “RADIUS” on page 8.)
4-12
Page 53

Authentication
When 802.1X is enabled, the broadcast and session key rotation intervals can also
be configured.
Broadcast Key Refresh Rate: Sets the interval at which the broadcast keys are
refreshed for stations using 802.1X dynamic keying. (Range: 0-1440 minutes;
Default: 0 means disabled)
Session Key Refresh Rate: The interval at which the access point refreshes
unicast session keys for associated clients. (Range: 0-1440 minutes; Default: 0
means disabled)
802.1X Reauthentication Refresh Rate: The time period after which a
connected client must be re-authenticated. During the re-authentication
process of verifying the client’s credentials on the RADIUS server, the client
remains connected the network. Only if re-authentication fails is network
access blocked. (Range: 0-65535 seconds; Default: 0 means disabled)
802.1X Supplicant – The access point can also operate in a 802.1X supplicant
mode. This enables the access point itself to be authenticated with a RADIUS
server using a configured MD5 user name and password. This prevents rogue
access points from gaining access to the network.
Local MAC Authentication – Configures the local MAC authentication database.
The MAC database provides a mechanism to take certain actions based on a
wireless client’s MAC address. The MAC list can be configured to allow or deny
network access to specific clients.
System Default: Specifies a default action for all unknown MAC addresses (that
is, those not listed in the local MAC database).
• Deny: Blocks access for all MAC addresses except those listed in the local
database as “Allow.”
• Allow: Permits access for all MAC addresses except those listed in the local
database as “Deny.”
MAC Authentication Settings: Enters specified MAC addresses and permissions
into the local MAC database.
• MAC Address: Physical address of a client. Enter six pairs of hexadecimal
digits separated by hyphens; for example, 00-90-D1-12-AB-89.
• Permission: Select Allow to permit access or Deny to block access. If Delete
is selected, the specified MAC address entry is removed from the database.
• Update: Enters the specified MAC address and permission setting into the
local database.
MAC Authentication Table: Displays current entries in the local MAC database.
4-13
Page 54

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
FILTER CONTROL
The access point can employ network traffic frame filtering to control access to
network resources and increase security. You can prevent communications
between wireless clients and prevent access point management from wireless
clients. Also, you can block specific Ethernet traffic from being forwarded by the
access point.
Figure 24 Filter Control
Inter Client STAs Communication Filter – Sets the global mode for
wireless-to-wireless communications between clients associated to Virtual AP
(VAP) interfaces on the access point. (Default: Prevent Inter and Intra VAP client
Communication)
Disable: All clients can communicate with each other through the access
point.
Prevent Intra VAP client communication: When enabled, clients associated
with a specific VAP interface cannot establish wireless communications with
each other. Clients can communicate with clients associated to other VAP
interfaces.
Prevent Inter and Intra VAP client communication: When enabled, clients
cannot establish wireless communications with any other client, either those
associated to the same VAP interface or any other VAP interface.
4-14
Page 55

Filter Control
AP Management Filter – Controls management access to the access point from
wireless clients. Management interfaces include the web, Telnet, or SNMP.
(Default:
Disabled: Allows management access from wireless clients.
Enabled: Blocks management access from wireless clients.
Disabled)
Uplink Port MAC Address Filtering Status – Prevents traffic with specified source
MAC addresses from being forwarded to wireless clients through the access
point. You can add a maximum of eight MAC addresses to the filter table.
(Default: Disabled)
MAC Address: Specifies a MAC address to filter, in the form xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx.
Permission: Adds or deletes a MAC address from the filtering table.
Ethernet Type Filter – Controls checks on the Ethernet type of all incoming and
outgoing Ethernet packets against the protocol filtering table. (Default:
Disabled: Access point does not filter Ethernet protocol types.
Enabled: Access point filters Ethernet protocol types based on the configuration
Disabled)
of protocol types in the filter table. If the status of a protocol is set to “ON,”
the protocol is filtered from the access point.
NOTE: Ethernet protocol types not listed in the filtering table are always forwarded
by the access point.
4-15
Page 56

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
VLAN
The access point can employ VLAN tagging support to control access to network
resources and increase security. VLANs separate traffic passing between the
access point, associated clients, and the wired network. There can be a VLAN
assigned to each associated client, a default VLAN for each VAP (Virtual Access
Point) interface, and a management VLAN for the access point.
Note the following points about the access point’s VLAN support:
The management VLAN is for managing the access point through remote
management tools, such as the web interface, SSH, SNMP, or Telnet. The
access point only accepts management traffic that is tagged with the specified
management VLAN ID.
All wireless clients associated to the access point are assigned to a VLAN. If IEEE
802.1X is being used to authenticate wireless clients, specific VLAN IDs can be
configured on the RADIUS server to be assigned to each client. If a client is not
assigned to a specific VLAN or if 802.1X is not used, the client is assigned to
the default VLAN for the VAP interface with which it is associated. The access
point only allows traffic tagged with assigned VLAN IDs or default VLAN IDs to
access clients associated on each VAP interface.
When VLAN support is enabled on the access point, traffic passed to the wired
network is tagged with the appropriate VLAN ID, either an assigned client
VLAN ID, default VLAN ID, or the management VLAN ID. Traffic received from
the wired network must also be tagged with one of these known VLAN IDs.
Received traffic that has an unknown VLAN ID or no VLAN tag is dropped.
When VLAN support is disabled, the access point does not tag traffic passed to
the wired network and ignores the VLAN tags on any received frames.
NOTE: Before enabling VLAN tagging on the access point, be sure to configure the
attached network switch port to support tagged VLAN frames from the access
point’s management VLAN ID, default VLAN IDs, and other client VLAN IDs.
Otherwise, connectivity to the access point will be lost when you enable the VLAN
feature.
Using IEEE 802.1X and a central RADIUS server, up to 64 VLAN IDs can be
mapped to specific wireless clients, allowing users to remain within the same
VLAN as they move around a campus site. This feature can also be used to control
access to network resources from clients, thereby improving security.
4-16
Page 57

Filter Control
A VLAN ID (1-4094) can be assigned to a client after successful IEEE 802.1X
authentication. The client VLAN IDs must be configured on the RADIUS server for
each user authorized to access the network. If a client does not have a configured
VLAN ID on the RADIUS server, the access point assigns the client to the
configured default VLAN ID for the VAP interface.
NOTE: When using IEEE 802.1X to dynamically assign VLAN IDs, the access point
must have 802.1X authentication enabled and a RADIUS server configured.
Wireless clients must also support 802.1X client software.
When setting up VLAN IDs for each user on the RADIUS server, be sure to use the
RADIUS attributes and values as indicated in the following table.
Number RADIUS Attribute Value
64 Tunnel-Type VLAN (13)
65 Tunnel-Medium-Type 802
81 Tunnel-Private-Group-ID VLANID
(1 to 4094 as hexadecimal or string)
VLAN IDs on the RADIUS server can be entered as hexadecimal digits or a string
(see
“radius-server vlan-format” on page 5-69).
NOTE: The specific configuration of RADIUS server software is beyond the scope
of this guide. Refer to the documentation provided with the RADIUS server
software.
Figure 25 Filter Control - VLAN ID
VLAN – Enables or disables VLAN tagging support on the access point.
Management VLAN ID – The VLAN ID that traffic must have to be able to manage
the access point. (Range 1-4094; Default: 1)
4-17
Page 58

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a communication protocol
designed specifically for managing devices on a network. Equipment commonly
managed with SNMP includes switches, routers and host computers. SNMP is
typically used to configure these devices for proper operation in a network
environment, as well as to monitor them to evaluate performance or detect
potential problems.
Managed devices supporting SNMP contain software, which runs locally on the
device and is referred to as an agent. A defined set of variables, known as
managed objects, is maintained by the SNMP agent and used to manage the
device. These objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB) that
provides a standard presentation of the information controlled by the agent.
SNMP defines both the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol used to
access this information over the network.
The access point includes an onboard agent that supports SNMP versions 1, 2c,
and 3 clients. This agent continuously monitors the status of the access point, as
well as the traffic passing to and from wireless clients. A network management
station can access this information using SNMP management software that is
compliant with MIB II. To implement SNMP management, the access point must
first have an IP address and subnet mask, configured either manually or
dynamically. Access to the onboard agent using SNMP v1 and v2c is controlled by
community strings. To communicate with the access point, the management
station must first submit a valid community string for authentication.
Access to the access point using SNMP v3 provides additional security features
that cover message integrity, authentication, and encryption; as well as
controlling notifications that are sent to specified user targets.
CONFIGURING SNMP AND TRAP MESSAGE PARAMETERS
The access point SNMP agent must be enabled to function (for versions 1, 2c, and
3 clients). Management access using SNMP v1 and v2c also requires community
strings to be configured for authentication. Trap notifications can be enabled and
sent to up to four management stations.
4-18
Page 59

Figure 26 SNMP
SNMP
SNMP – Enables or disables SNMP management access and also enables the
access point to send SNMP traps (notifications). (Default: Disable)
Location – A text string that describes the system location. (Maximum length: 255
characters)
Contact – A text string that describes the system contact. (Maximum length: 255
characters)
Community Name (Read Only) – Defines the SNMP community access string that
has read-only access. Authorized management stations are only able to retrieve
MIB objects. (Maximum length: 23 characters, case sensitive; Default: public)
Community Name (Read/Write) – Defines the SNMP community access string that
has read/write access. Authorized management stations are able to both retrieve
and modify MIB objects. (Maximum length: 23 characters, case sensitive;
Default:
private)
Trap Destination (1 to 4) – Enables recipients (up to four) of SNMP notifications.
Trap Destination IP Address – Specifies the recipient of SNMP notifications.
Enter the IP address or the host name. (Host Name: 1 to 63 characters, case
sensitive)
4-19
Page 60

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Trap Destination Community Name – The community string sent with the
notification operation. (Maximum length: 23 characters, case sensitive;
Default:
Engine ID – Sets the engine identifier for the SNMPv3 agent that resides on the
access point. This engine protects against message replay, delay, and redirection.
The engine ID is also used in combination with user passwords to generate the
security keys for authenticating and encrypting SNMPv3 packets. A default
engine ID is automatically generated that is unique to the access point. (Range:
10 to 64 hexadecimal characters)
NOTE: If the local engine ID is deleted or changed, all SNMP users will be cleared.
All existing users will need to be re-configured. If you want to change the default
engine ID, change it first before configuring other SNMP v3 parameters.
Figure 27 Trap Confiiguration
public)
Trap Configuration – Allows selection of specific SNMP notifications to send. The
following items are available:
sysSystemUp - The access point is up and running.
sysSystemDown - The access point is about to shutdown and reboot.
sysRadiusServerChanged - The access point has changed from the primary
RADIUS server to the secondary, or from the secondary to the primary.
dot11StationAssociation - A client station has successfully associated with the
access point.
dot11StationReAssociation - A client station has successfully re-associated with
the access point.
dot11StationAuthentication - A client station has been successfully
authenticated.
dot11StationRequestFail - A client station has failed association, re-association,
or authentication.
dot11InterfaceGFail - The 802.11b interface has failed.
4-20
Page 61

SNMP
dot11InterfaceAFail - The 802.11a or 802.11g interface has failed.
dot1xMacAddrAuthSuccess - A client station has successfully authenticated its
MAC address with the RADIUS server.
dot1xMacAddrAuthFail - A client station has failed MAC address
authentication with the RADIUS server.
dot1xAuthNotInitiated - A client station did not initiate 802.1X authentication.
dot1xAuthSuccess - A 802.1X client station has been successfully
authenticated by the RADIUS server.
dot1xAuthFail - A 802.1X client station has failed RADIUS authentication.
localMacAddrAuthSuccess - A client station has successfully authenticated its
MAC address with the local database on the access point.
localMacAddrAuthFail - A client station has failed authentication with the local
MAC address database on the access point.
sntpServerFail - The access point has failed to set the time from the configured
SNTP server.
CONFIGURING SNMPV3 USERS
The access point allows up to 10 SNMP v3 users to be configured. Each user must
be defined by a unique name, assigned to one of three pre-defined security
groups, and configured with specific authentication and encryption settings.
Figure 28 Configuring SNMPv3 Users
User – The SNMPv3 user name. (32 characters maximum)
Group – The SNMPv3 group name. (Options: RO, RWAuth, or RWPriv; Default:
RO)
RO – Read-only access.
RWAuth – Read/write access with user authentication.
RWPriv – Read/write access with both user authentication and data encryption.
Auth Type – The authentication type used for the SNMP user; either MD5 or
none. When MD5 is selected, enter a password in the corresponding Passphrase
field.
Priv Type – The data encryption type used for the SNMP user; either DES or none.
When DES is selected, enter a key in the corresponding Passphrase field.
4-21
Page 62

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Passphrase – The password or key associated with the authentication and privacy
settings. A minimum of eight plain text characters is required.
Action – Click the Add button to add a new user to the list. Click the edit button
to change details of an existing user. Click the Del button to remove a user from
the list.
NOTE: Users must be assigned to groups that have the same security levels. For
example, a user who has “Auth Type” and “Priv Type” configured to MD5 and DES
respectively (that it, uses both authentication and data encryption) must be
assigned to the RWPriv group. If this same user were instead assigned to the
read-only (RO) group, the user would not be able to access the database.
ADMINISTRATION
CHANGING THE PASSWORD
Management access to the web and CLI interface on the access point is
controlled through a single user name and password. You can also gain additional
access security by using control filters (see
“Filter Control” on page 4-14).
To protect access to the management interface, you need to configure an
Administrator’s user name and password as soon as possible. If the user name
and password are not configured, then anyone having access to the access point
may be able to compromise access point and network security. Once a new
Administrator has been configured, you can delete the default “admin” user
name from the system.
NOTE: Pressing the Reset button on the back of the access point for more than
10
seconds resets the user name and password to the factory defaults. For this
reason, we recommend that you protect the access point from physical access by
unauthorized persons.
4-22
Page 63

Administration
Figure 29 Administration
Username – The name of the user. The default name is “admin.” (Length: 3-16
characters, case sensitive)
New Password – The password for management access. (Length: 3-16 characters,
case sensitive)
Confirm New Password – Enter the password again for verification.
TELNET AND SSH SETTINGS
Telnet is a remote management tool that can be used to configure the access
point from anywhere in the network. However, Telnet is not secure from hostile
attacks. The Secure Shell (SSH) can act as a secure replacement for Telnet. The
SSH protocol uses generated public keys to encrypt all data transfers passing
between the access point and SSH-enabled management station clients and
ensures that data traveling over the network arrives unaltered. Clients can then
securely use the local user name and password for access authentication.
Note that SSH client software needs to be installed on the management station to
access the access point for management via the SSH protocol.
NOTE: The access point supports only SSH version 2.0.
NOTE: After boot up, the SSH server needs about two minutes to generate host
encryption keys. The SSH server is disabled while the keys are being generated.
Figure 30 Telnet and SSH Settings
4-23
Page 64

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Telnet Server: Enables or disables the Telnet server. (Default: Disabled)
SSH Server: Enables or disables the SSH server. (Default: Enabled)
SSH Port Number: Sets the UDP port for the SSH server. (Range: 1-65535;
Default: 22)
UPGRADING FIRMWARE
You can upgrade new access point software from a local file on the management
workstation, or from an TFTP server. New software may be provided periodically
from your distributor.
After upgrading new software, you must reboot the access point to implement
the new code. Until a reboot occurs, the access point will continue to run the
software it was using before the upgrade started. Also note that new software
that is incompatible with the current configuration automatically restores the
access point to the factory default settings when first activated after a reboot.
4-24
Page 65

Figure 31 Firmware Upgrade
Administration
Before upgrading new software, verify that the access point is connected to the
network and has been configured with a compatible IP address and subnet mask.
If you need to download from an FTP or TFTP server, take the following additional
steps:
Obtain the IP address of the FTP or TFTP server where the access point software
is stored.
4-25
Page 66

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
If upgrading from an FTP server, be sure that you have an account configured
on the server with a user name and password.
If VLANs are configured on the access point, determine the VLAN ID with which
the FTP or TFTP server is associated, and then configure the management
station, or the network port to which it is attached, with the same VLAN ID. If
you are managing the access point from a wireless client, the VLAN ID for the
wireless client must be configured on a RADIUS server.
Current version – Version number of runtime code.
Firmware Upgrade Local – Downloads an operation code image file from the web
management station to the access point using HTTP. Use the Browse button to
locate the image file locally on the management station and click Start Upgrade
to proceed.
New firmware file: Specifies the name of the code file on the server. The device
will only accept firmware files named “3Com-img.bin”.
Firmware Upgrade Remote – Downloads an operation code image file from a
specified remote FTP or TFTP server. After filling in the following fields, click Start
Upgrade to proceed.
New firmware file: Specifies the name of the code file on the server. The
firmware file must be named “3com-img.bin”.
IP Address: IP address or host name of the TFTP server.
Configuration File Backup/Restore – Uploads the current access point
configuration file to a specified remote TFTP server. A configuration file can also
be downloaded to the access point to restore a specific configuration.
Config file: Specifies the name of the configuration file. A path on the server
can be specified using “/” in the name, providing the path already exists; for
example, “myfolder/syscfg.” Other than to indicate a path, the file name must
not contain any slashes (\ or /), the leading letter cannot be a period (.), and the
maximum length for file names on the TFTP server is 255 characters. (Valid
characters: A-Z, a-z, 0-9, “.”, “-”, “_”)
IP Address: IP address or host name of the TFTP server.
Restore Factory Settings – Click the Restore button to reset the configuration
settings for the access point to the factory defaults and reboot the system. Note
that all user configured information will be lost. You will have to re-enter the
default user name (admin) to re-gain management access to this device.
Reboot Access Point – Click the Reset button to reboot the system.
4-26
Page 67

NOTE: If you have upgraded system software, then you must reboot the access
point to implement the new operation code. New software that is incompatible
with the current configuration automatically restores the access point to default
values when first activated after a reboot.
WDS AND SPANNING TREE SETTINGS
Each access point radio interface can be configured to operate in a bridge or
repeater mode, which allows it to forward traffic directly to other access point
units. To set up bridge links between access point units, you must configure the
wireless Distribution System (WDS) forwarding table by specifying the wireless
MAC address of all units to which you want to forward traffic. Up to six WDS
bridge or repeater links can be specified for each unit in the wireless bridge
network.
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) can be used to detect and disable network
loops, and to provide backup links between bridges. This allows a wireless bridge
to interact with other bridging devices (that is, an STP-compliant switch, bridge or
router) in your network to ensure that only one route exists between any two
stations on the network, and provide backup links which automatically take over
when a primary link goes down.
WDS and Spanning Tree Settings
4-27
Page 68

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Figure 32 WDS and Spanning Tree Settings
4-28
Page 69

WDS and Spanning Tree Settings
WDS Bridge – Up to six WDS bridge or repeater links (MAC addresses) per radio
interface can be specified for each unit in the wireless bridge network. One unit
only must be configured as the “root bridge” in the wireless network. The root
bridge is the unit connected to the main core of the wired LAN. Other bridges
need to specify one “Parent” link to the root bridge or to a bridge connected to
the root bridge. The other five WDS links are available as “Child” links to other
bridges.
Bridge Role – Each radio interface can be set to operate in one of the following
four modes: (Default: AP)
• AP (Access Point): Operates as an access point for wireless clients, providing
connectivity to a wired LAN.
• Bridge: Operates as a bridge to other access points. The “Parent” link to the
root bridge must be configured. Up to five other “Child” links are available
to other bridges.
• Repeater: Operates as a wireless repeater, extending the range for remote
wireless clients and connecting them to the root bridge. The “Parent” link
to the root bridge must be configured. In this mode, traffic is not forwarded
to the Ethernet port from the radio interface.
• Root Bridge: Operates as the root bridge in the wireless bridge network. Up
to six ”Child” links are available to other bridges in the network.
Bridge Parent – The physical layer address of the root bridge unit or the bridge
unit connected to the root bridge. (12
hexadecimal digits in the form
“xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx”)
Bridge Child – The physical layer address of other bridge units for which this
unit serves as the bridge parent or the root bridge. Note that the first entry
under the list of child nodes is reserved for the root bridge, and can only be
configured if the role is set to “Root Bridge.” (12
hexadecimal digits in the form
“xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx”)
4-29
Page 70

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Figure 33 Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol – STP uses a distributed algorithm to select a bridging
device (STP-compliant switch, bridge or router) that serves as the root of the
spanning tree network. It selects a root port on each bridging device (except for
the root device) which incurs the lowest path cost when forwarding a packet
4-30
Page 71

WDS and Spanning Tree Settings
from that device to the root device. Then it selects a designated bridging device
from each LAN which incurs the lowest path cost when forwarding a packet from
that LAN to the root device. All ports connected to designated bridging devices
are assigned as designated ports. After determining the lowest cost spanning
tree, it enables all root ports and designated ports, and disables all other ports.
Network packets are therefore only forwarded between root ports and
designated ports, eliminating any possible network loops.
Once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for Hello
BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units) transmitted from the root bridge. If a bridge
does not get a Hello BPDU after a predefined interval (Maximum Age), the bridge
assumes that the link to the root bridge is down. This bridge will then initiate
negotiations with other bridges to reconfigure the network to reestablish a valid
network topology.
Bridge – Enables/disables STP on the wireless bridge or repeater.
(Default:
Bridge Priority – Used in selecting the root device, root port, and designated
Disabled)
port. The device with the highest priority becomes the STP root device.
However, if all devices have the same priority, the device with the lowest MAC
address will then become the root device. (Note that lower numeric values
indicate higher priority.)
• Range: 0-65535
• Default: 32768
Bridge Max Age – The maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without
receiving a configuration message before attempting to reconfigure. All device
ports (except for designated ports) should receive configuration messages at
regular intervals. Any port that ages out STP information (provided in the last
configuration message) becomes the designated port for the attached LAN. If
it is a root port, a new root port is selected from among the device ports
attached to the network. (Range: 6-40 seconds)
• Default: 20
• Minimum: The higher of 6 or [2 x (Hello Time + 1)].
• Maximum: The lower of 40 or [2 x (Forward Delay - 1)]
Bridge Hello Time – Interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a
configuration message. (Range: 1-10 seconds)
• Default: 2
• Minimum: 1
• Maximum: The lower of 10 or [(Max. Message Age / 2) -1]
4-31
Page 72

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Bridge Forwarding Delay – The maximum time (in seconds) this device waits
before changing states (i.e., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is
required because every device must receive information about topology
changes before it starts to forward frames. In addition, each port needs time to
listen for conflicting information that would make it return to a discarding
state; otherwise, temporary data loops might result. (Range: 4-30 seconds)
• Default: 15
• Minimum: The higher of 4 or [(Max. Message Age / 2) + 1]
• Maximum: 30
Link Path Cost – This parameter is used by the STP to determine the best path
between devices. Therefore, lower values should be assigned to ports attached
to faster media, and higher values assigned to ports with slower media. (Path
cost takes precedence over port priority.)
• Range: 1-65535
• Default: Ethernet interface: 19; Wireless interface: 40
Link Port Priority – Defines the priority used for this port in the Spanning Tree
Protocol. If the path cost for all ports on a switch are the same, the port with
the highest priority (i.e., lowest value) will be configured as an active link in the
spanning tree. This makes a port with higher priority less likely to be blocked if
the Spanning Tree Protocol is detecting network loops. Where more than one
port is assigned the highest priority, the port with lowest numeric identifier will
be enabled.
• Default: 128
• Range: 0-240, in steps of 16
4-32
Page 73

SYSTEM LOG
The access point can be configured to send event and error messages to a System
Log Server. The system clock can also be synchronized with a time server, so that
all the messages sent to the Syslog server are stamped with the correct time and
date.
Figure 34 System Log
System Log
ENABLING SYSTEM LOGGING
The access point supports a logging process that can control error messages
saved to memory or sent to a Syslog server. The logged messages serve as a
valuable tool for isolating access point and network problems.
System Log Setup – Enables the logging of error messages. (Default: Disable)
Logging Level – Sets the minimum severity level for event logging.
(Default:Informational)
Logging Host – Enables the sending of log messages to a Syslog server host. Up
to four Syslog servers are supported on the access point. (Default: Disable)
Server Name / IP – Specifies a Syslog server name or IP address. (Default: 0.0.0.0)
SNTP Server – Enables the sending of log messages to a Syslog server host.
(Default: Disable)
Primary Server – The IP address the primary Syslog server. (Default: 0.0.0.0)
Secondary Server – The IP address the secondary Syslog server. (Default: 0.0.0.0)
4-33
Page 74

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Enter Time Zone – Sets the desired time zone + or - GMT.
Enable Daylight Saving – Adjusts the clock for summertime and wintertime.
The system allows you to limit the messages that are logged by specifying a
minimum severity level. The following table lists the error message levels from the
most severe (Emergency) to least severe (Debug). The message levels that are
logged include the specified minimum level up to the Emergency level.
Ta bl e 3 Logging Levels
Error Level Description
Emergency System unusable
Alerts Immediate action needed
Critical Critical conditions (e.g., memory allocation, or free memory error - resource
Error Error conditions (e.g., invalid input, default used)
Warning Warning conditions (e.g., return false, unexpected return)
Notice Normal but significant condition, such as cold start
Informational Informational messages only
Debug Debugging messages
NOTE: The access point error log can be viewed using the Event Logs window in
the Status section (
messages logged in chronological order, from the newest to the oldest. Log
messages saved in the access point’s memory are erased when the device is
rebooted.
exhausted)
page 4-61). The Event Logs window displays the last 128
CONFIGURING SNTP
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) allows the access point to set its internal
clock based on periodic updates from a time server (SNTP or NTP). Maintaining an
accurate time on the access point enables the system log to record meaningful
dates and times for event entries. If the clock is not set, the access point will only
record the time from the factory default set at the last bootup.
The access point acts as an SNTP client, periodically sending time synchronization
requests to specific time servers. You can configure up to two time server IP
addresses. The access point will attempt to poll each server in the configured
sequence.
SNTP Server – Configures the access point to operate as an SNTP client. When
enabled, at least one time server IP address must be specified.
Primary Server: The IP address of an SNTP or NTP time server that the access
point attempts to poll for a time update.
4-34
Page 75

Secondary Server: The IP address of a secondary SNTP or NTP time server. The
access point first attempts to update the time from the primary server; if this
fails it attempts an update from the secondary server.
NOTE: The access point also allows you to disable SNTP and set the system clock
manually.
Set Time Zone – SNTP uses Coordinated Universal Time (or UTC, formerly
Greenwich Mean Time, or GMT) based on the time at the Earth’s prime meridian,
zero degrees longitude. To display a time corresponding to your local time, you
must indicate the number of hours your time zone is located before (east) or after
(west) UTC.
Enable Daylight Saving – The access point provides a way to automatically adjust
the system clock for Daylight Savings Time changes. To use this feature you must
define the month and date to begin and to end the change from standard time.
During this period the system clock is set back by one hour.
RADIO INTERFACE
The IEEE 802.11a and 802.11g interfaces include configuration options for radio
signal characteristics and wireless security features. The configuration options are
nearly identical, and are therefore both covered in this section of the manual.
Radio Interface
The access point can operate in three modes, IEEE 802.11a only, 802.11b/g only,
or a mixed 802.11a/b/g mode. Also note that 802.11g is backward compatible
with 802.11b. These interfaces are configured independently under the following
web pages:
802.11a Interface
802.11b/g Interface
Each radio supports up to four virtual access point (VAP) interfaces numbered 1to
4. Each VAP functions as a separate access point, and can be configured with its
own Service Set Identification (SSID) and security settings. However, most radio
signal parameters apply to all four VAP interfaces.
The VAPs function similar to a VLAN, with each VAP mapped to its own VLAN ID.
Traffic to specific VAPs can be segregated based on user groups or application
traffic.
4-35
Page 76

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
NOTE: The 8760 Access Point ships from the factory enabled only for channels
allowed in the US/Canada. If you live in an area where additional channels are
allowed, go to the 3Com web site (http://www.3com.com) and download the
latest software that will allow additional channels in your country.
802.11A INTERFACE
The IEEE 802.11a interface operates within the 5 GHz band, at up to 54 Mbps in
normal mode or up to 108 Mbps in Turbo mode.
First configure the radio settings that apply to the individual VAPs (Virtual Access
Point) and the common radio settings that apply to the overall system. After you
have configured the radio settings, go to the Security page under the 802.11a
Interface (
interfaces, and then set an SSID to identify the wireless network service provided
by each VAP. Remember that only clients with the same SSID can associate with a
VAP.
NOTE: You must first select a country before the wireless interfaces are enabled.
See “Security” on page 49.), enable the radio service for any of the VAP
Configuring Radio Settings
To configure VAP radio settings, select the Radio Settings page.
Figure 35 Radio Settings A
Radio Status – Displays if the radio is enabled or disabled for this VAP.
NOTE: You must first enable VAP interface 1 before you can enable other VAP
interfaces.
4-36
Page 77

Radio Interface
SSID – The name of the basic service set provided by a VAP interface. Clients that
want to connect to the network through the access point must set their SSID to
the same as that of an access point VAP interface. (Default: 3Com1 to 3Com4 for
802.11a, 3Com5 to 3Com8 for 802.11b/g; Range: 1-32 characters)
Default VLAN ID – The VLAN ID assigned to wireless clients associated to the VAP
interface that are not assigned to a specific VLAN by RADIUS server configuration.
(Default: 1)
Closed System – When enabled, the VAP interface does not include its SSID in
beacon messages. Nor does it respond to probe requests from clients that do not
include a fixed SSID. (Default: Disable)
Maximum Associations – This command configures the maximum number of
clients that can be associated with the access point at the same time.
Authentication Timeout Interval – The time within which the client should finish
authentication before authentication times out. (Range: 5-60 minutes; Default:
60 minutes)
Association Timeout Interval – The idle time interval (when no frames are sent)
after which a client is disassociated from the VAP interface. (Range: 5-60 minutes;
Default: 30 minutes)
4-37
Page 78

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
CONFIGURING COMMON RADIO SETTINGS
To configure common radio settings, select the Radio Settings page, and scroll
down to below the VAP radio settings.
Figure 36 Radio Settings A
Country Code – The current country code setting. This setting restricts operation
of the access point to radio channels and transmit power levels permitted for
wireless networks in the specified country.
Description – Adds a comment or description to the wireless interface. (Range:
1-80 characters)
Turbo Mode – The normal 802.11a wireless operation mode provides connections
up to 54 Mbps. Turbo Mode is an enhanced mode (not regulated in IEEE 802.11a)
that provides a higher data rate of up to 108 Mbps. Enabling Turbo Mode allows
the access point to provide connections up to 108 Mbps. (Default: Disabled)
4-38
Page 79

Radio Interface
NOTE: In normal mode, the access point provides a channel bandwidth of 20
MHz, and supports the maximum number of channels permitted by local
regulations (e.g., 13 channels for the United States). In Turbo Mode, the channel
bandwidth is increased to 40 MHz to support the increased data rate. However,
this reduces the number of channels supported (e.g., 5 channels for the United
States).
NOTE: .Check your country’s regulations to see if Turbo Mode is allowed.
Super Mode – The Atheros proprietary Super A performance enhancements are
supported by the access point. These enhancements include bursting,
compression, and fast frames. Maximum throughput ranges between 40 to 60
Mbps for connections to Atheros-compatible clients. (Default: Disabled)
Auto Channel Select – Enables the access point to automatically select an
unoccupied radio channel. (Default:
NOTE: Check your country’s regulations to see if Auto Channel can be disabled.
Enabled)
Radio Channel – The radio channel that the access point uses to
communicate with wireless clients. When multiple access points
are deployed in the same area, set the channel on neighboring
access points at least four channels apart to avoid interference
with each other. For example, in the United States you can
deploy up to four access points in the same area (e.g., channels
36, 56, 149, 165). Also note that the channel for wireless
clients is automatically set to the same as that used by the
access point to which it is linked. (Default: Channel 60 for
normal mode, and channel 42 for Turbo mode)
Antenna ID – Selects the antenna to be used by the access
point; either the included diversity antennas or an optional
external antenna. The optional external antennas that are
certified for use with the access point are listed in the
drop-down menu. Selecting the correct antenna ID ensures that
the access point's radio transmissions are within regulatory
power limits for the country of operation. (Default: 3Com
Integrated Antenna)
4-39
Normal Mode
Turbo Mode
Page 80

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
NOTE: The Antenna ID must be selected in conjunction with the Output Antenna
to configure proper use of any of the antenna options.
Output Antenna – Selects the use of both fixed antennas operating in diversity
mode or a single antenna. (Default: Diversity)
Both: The radio uses both antennas in a diversity system. Select this method
when the Antenna ID is set to “3Com Integrated Antenna” to use the access
point's integrated antennas.
Right: The radio only uses the antenna on the right side (the side closest to the
access point LEDs). Select this method when using an optional external antenna
that is connected to the right antenna connector.
Left: The radio only uses the antenna on the left side (the side farthest from the
access point LEDs). Select this method when using an optional external antenna
that is connected to the left antenna connector.
Tra ns mi t P ow e r – Adjusts the power of the radio signals transmitted from the
access point. The higher the transmission power, the farther the transmission
range. Power selection is not just a trade off between coverage area and
maximum supported clients. You also have to ensure that high-power signals do
not interfere with the operation of other radio devices in the service area.
(Options: 100%, 50%, 25%, 12%, minimum; Default: 100%)
NOTE: When operating the access point using 5 GHz channels in a European
Community country, the end user and installer are obligated to operate the device
in accordance with European regulatory requirements for Transmit Power Control
(TPC).
Maximum Transmit Data Rate – The maximum data rate at which the access point
transmits unicast packets on the wireless interface. The maximum transmission
distance is affected by the data rate. The lower the data rate, the longer the
transmission distance. (Options: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54 for 802.11a; 1,
2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54 for 802.11b/g; Default: 54 Mbps)
Maximum Multicast Data Rate – The maximum data rate at which the access
point transmits multicast and broadcast packets on the wireless interface.
(Options: 24, 12, 6 Mbps; Default: 6 Mbps for 802.11a; 1, 2, 5.5, 11, Default
5.5 Mbps for 802.11b/g)
Beacon Interval – The rate at which beacon signals are transmitted from the
access point. The beacon signals allow wireless clients to maintain contact with
the access point. They may also carry power-management information.
(Range: 20-1000 TUs; Default: 100 TUs)
4-40
Page 81

Radio Interface
Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) – The rate at which stations in sleep
mode must wake up to receive broadcast/multicast transmissions.
The DTIM interval indicates how often the MAC layer forwards
broadcast/multicast traffic, which is necessary to wake up stations that are using
Power Save mode. The default value of 1 indicates that the access point will save
all broadcast/multicast frames for the Basic Service Set (BSS) and forward them
after every beacon. Using smaller DTIM intervals delivers broadcast/multicast
frames in a more timely manner, causing stations in Power Save mode to wake up
more often and drain power faster. Using higher DTIM values reduces the power
used by stations in Power Save mode, but delays the transmission of
broadcast/multicast frames.
(Range: 1-255 beacons; Default: 1 beacon)
Fragment Length (256~2346)– Configures the minimum packet size that can be
fragmented when passing through the access point. Fragmentation of the PDUs
(Package Data Unit) can increase the reliability of transmissions because it
increases the probability of a successful transmission due to smaller frame size. If
there is significant interference present, or collisions due to high network
utilization, try setting the fragment size to send smaller fragments. This will speed
up the retransmission of smaller frames. However, it is more efficient to set the
fragment size larger if very little or no interference is present because it requires
overhead to send multiple frames. (Range:
256-2346 bytes; Default: 2346 bytes)
RTS Threshold – Sets the packet size threshold at which a Request to Send (RTS)
signal must be sent to a receiving station prior to the sending station starting
communications. The access point sends RTS frames to a receiving station to
negotiate the sending of a data frame. After receiving an RTS frame, the station
sends a CTS (clear to send) frame to notify the sending station that it can start
sending data.
If the RTS threshold is set to 0, the access point always sends RTS signals. If set to
2347, the access point never sends RTS signals. If set to any other value, and the
packet size equals or exceeds the RTS threshold, the RTS/CTS (Request to Send /
Clear to Send) mechanism will be enabled.
The access points contending for the medium may not be aware of each other.
The RTS/CTS mechanism can solve this “Hidden Node Problem.” (Range: 0-2347
bytes: Default: 2347 bytes)
4-41
Page 82

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
802.11B/G INTERFACE
The IEEE 802.11g standard operates within the 2.4 GHz band at up to 54 Mbps.
Also note that because the IEEE 802.11g standard is an extension of the IEEE
802.11b standard, it allows clients with 802.11b wireless network cards to
associate to an 802.11g access point.
First configure the radio settings that apply to the individual VAPs (Virtual Access
Point) and the common radio settings that apply to all of the 802.11g interfaces.
After you have configured the radio settings, enable the radio service for any of
the VAP interfaces, and then set an SSID to identify the wireless network service
provided by each VAP. Remember that only clients with the same SSID can
associate with a VAP.
NOTE: You must first select a country of operation before interfaces can be
enabled.
Most of the 802.11g commands are identical to those used by the 802.11a
interface. For information on the these commands, refer to the following
sections:
“Configuring Radio Settings” on page 4-36
“Configuring Common Radio Settings” on page 4-38
“Configuring Wi-Fi Multimedia” on page 4-44
Only the radio settings specific to the 802.11g interface are included in this
section. To configure the 802.11g radio settings, select the Radio Settings page.
4-42
Page 83

Figure 37 Radio Settings B/G
Radio Interface
Client Access Mode – Selects the operating mode for the 802.11g wireless
interface. (Default: 802.11b+g)
802.11b+g: Both 802.11b and 802.11g clients can communicate with the
access point (up to 54 Mbps).
802.11b only: Both 802.11b and 802.11g clients can communicate with the
access point, but 802.11g clients can only transfer data at 802.11b standard
rates (up to 11 Mbps).
802.11g only: Only 802.11g clients can communicate with the access point (up
to 54 Mbps).
Turbo Mode – The normal 802.11g wireless operation mode provides connections
up to 54 Mbps. Turbo Mode is an enhanced proprietary mode (Atheros 802.11g
Turbo) that provides a higher data rate of up to 108 Mbps. Enabling Turbo mode
allows the access point to provide connections up to 108 Mbps to
Atheros-compatible clients.
NOTE: In normal mode, the access point supports the maximum number of
channels permitted by local regulations (e.g., 11 channels for the United States). In
Turbo mode, channel bonding is used to provide the increased data rate. However,
this reduces the number of channels available to one (Channel 6).
4-43
Page 84

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Super Mode – The Atheros proprietary Super G performance enhancements
are
supported by the access point. These enhancements include bursting,
compression, fast frames and dynamic turbo. Maximum throughput ranges
between 40 to 60 Mbps for connections to Atheros-compatible clients.
(Default:
Radio Channel – The radio channel that the access point uses to communicate
with wireless clients. When multiple access points are deployed in the same area,
set the channel on neighboring access points at least five channels apart to avoid
interference with each other. For example, in the United States you can deploy up
to three access points in the same area (e.g., channels 1, 6, 11). Also note that
the channel for wireless clients is automatically set to the same as that used by
the access point to which it is linked. (Range: 1-11; Default: 1)
Auto Channel Select – Enables the access point to automatically select an
unoccupied radio channel. (Default: Enabled)
Maximum Transmit Data Rate – The maximum data rate at which the
access point transmits unicast packets on the wireless interface. The
maximum transmission distance is affected by the data rate. The lower the
data rate, the longer the transmission distance. (Default: 54 Mbps)
Preamble Length – Sets the length of the signal preamble that is used at
the start of a data transmission. (Default: Long)
Short: Sets the preamble to short (96 microseconds). Using a short
preamble can increase data throughput.
Long: Sets the preamble to long (192 microseconds). Using a long
preamble ensures the access point can support all 802.11b and 802.11g
clients.
Auto: Sets the preamble according to the capability of clients that are currently
asscociated. Uses a short preamble (96 microseconds) if all associated clients
can support it, otherwise a long preamble is used. The access point can increase
data throughput when using a short preamble, but will only use a short
preamble if it determines that all associated clients support it.
Disabled)
CONFIGURING WI-FI MULTIMEDIA
Wireless networks offer an equal opportunity for all devices to transmit data from
any type of application. Although this is acceptable for most applications,
multimedia applications (with audio and video) are particularly sensitive to the
delay and throughput variations that result from this equal opportunity wireless
access method. For multimedia applications to run well over a wireless network, a
Quality of Service (QoS) mechanism is required to prioritize traffic types and
provide an enhanced opportunityî wireless access method.
4-44
Page 85

Radio Interface
The access point implements QoS using the Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) standard.
Using WMM, the access point is able to prioritize traffic and optimize
performance when multiple applications compete for wireless network
bandwidth at the same time. WMM employs techniques that are a subset of the
developing IEEE 802.11e QoS standard and it enables the access point to inter
operate with both WMMenabled clients and other devices that may lack any
WMM functionality.
Access Categories – WMM defines four access categories (ACs): voice, video, best
effort, and background. These categories correspond to traffic priority levels and
are mapped to IEEE 802.1D priority tags. The direct mapping of the four ACs to
802.1D priorities is specifically intended to facilitate inter operability with other
wired network QoS policies. While the four ACs are specified for specific types of
traffic, WMM allows the priority levels to be configured to match any
network-wide QoS policy. WMM also specifies a protocol that access points can
use to communicate the configured traffic priority levels to QoS-enabled wireless
clients.
Ta bl e 4 WMM Access Categories
WMM Access Categories
Access
Category
AC_VO (AC3) Voice
AC_VI (AC2) Video
AC_BE (AC0) Best Effort
AC_BK (AC1) Background
WMM
Designation
Description
Highest priority, minimum delay.
Time-sensitive data such as VoIP (Voice
over IP) calls.
High priority, minimum delay.
Time-sensitive data such as streaming
video.
Normal priority, medium delay and
throughput. Data only affected by long
delays. Data from applications or
devices that lack QoS capabilities.
Lowest priority. Data with no delay or
throughput requirements, such as bulk
data transfers.
802.1D
Tags
7, 6
5, 4
0, 3
2, 1
WMM Operation – WMM uses traffic priority based on the four ACs; Voice,
Video, Best Effort, and Background. The higher the AC priority, the higher the
probability that data is transmitted.
When the access point forwards traffic, WMM adds data packets to four
independent transmit queues, one for each AC, depending on the 802.1D
priority tag of the packet. Data packets without a priority tag are always added to
the Best Effort AC queue. From the four queues, an internal “virtual” collision
4-45
Page 86

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
resolution mechanism first selects data with the highest priority to be granted a
transmit opportunity. Then the same collision resolution mechanism is used
externally to determine which device has access to the wireless medium.
For each AC queue, the collision resolution mechanism is dependent on two
timing parameters:
AIFSN (Arbitration Inter-Frame Space Number), a number used to calculate the
minimum time between data frames
CW (Contention Window), a number used to calculate a random backoff time
After a collision detection, a backoff wait time is calculated. The total wait time is
the sum of a minimum wait time (Arbitration Inter-Frame Space, or AIFS)
determined from the AIFSN, and a random backoff time calculated from a value
selected from zero to the CW. The CW value varies within a configurable range. It
starts at CWMin and doubles after every collision up to a maximum value,
CWMax. After a successful transmission, the CW value is reset to its CWMin
value.
Figure 38 WMM Backoff Times
Time
CWMin CWMax
High Priority
Low Priority
AIFS Random Backoff
Minimum Wait Time Random Wait Time
CWMin CWMax
AIFS
Minimum Wait Time Random Wait Time
Random Backoff
For high-priority traffic, the AIFSN and CW values are smaller. The smaller values
equate to less backoff and wait time, and therefore more transmit opportunities.
To configure WMM, select the Radio Settings page, and scroll down to the WMM
configuration settings.
4-46
Page 87

Radio Interface
Figure 39 WMM Configuration
WMM – Sets the WMM operational mode on the access point. When enabled,
the parameters for each AC queue will be employed on the access point and QoS
capabilities are advertised to WMM-enabled clients. (Default: Support)
Disable: WMM is disabled.
Support: WMM will be used for any associated device that supports this
feature.
Devices that do not support this feature may still associate with the access
point.
Required: WMM must be supported on any device trying to associated with the
access point. Devices that do not support this feature will not be allowed to
associate with the access point.
WMM Acknowledge Policy – By default, all wireless data transmissions require
the sender to wait for an acknowledgement from the receiver. WMM allows the
acknowledgement wait time to be turned off for each Access Category (AC).
Although this increases data throughput, it can also result in a high number of
errors when traffic levels are heavy. (Default: Acknowledge)
WMM BSS Parameters – These parameters apply to the wireless clients.
WMM AP Parameters – These parameters apply to the access point.
logCWMin (Minimum Contention Window) – The initial upper limit of the
random backoff wait time before wireless medium access can be attempted. The
4-47
Page 88

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
initial wait time is a random value between zero and the CWMin value. Specify
the CWMin value in the range 0-15 microseconds. Note that the CWMin value
must be equal or less than the CWMax value.
logCWMax (Maximum Contention Window) – The maximum upper limit of the
random backoff wait time before wireless medium access can be attempted. The
contention window is doubled after each detected collision up to the CWMax
value. Specify the CWMax value in the range 0-15 microseconds. Note that the
CWMax value must be greater or equal to the CWMin value.
AIFS (Arbitration Inter-Frame Space) – The minimum amount of wait time before
the next data transmission attempt. Specify the AIFS value in the range 0-15
microseconds.
TXOP Limit (Transmit Opportunity Limit) – The maximum time an AC transmit
queue has access to the wireless medium. When an AC queue is granted a
transmit opportunity, it can transmit data for a time up to the TxOpLimit. This
data bursting greatly improves the efficiency for high data-rate traffic. Specify a
value in the range 0-65535 microseconds.
Admission Control – The admission control mode for the access category. When
enabled, clients are blocked from using the access category. (Default: Disabled)
Key Type – See Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP).
4-48
Page 89

SECURITY
Security
The access point is configured by default as an “open system,” which broadcasts
a beacon signal including the configured SSID. Wireless clients with an SSID
setting of “any” can read the SSID from the beacon and automatically set their
SSID to allow immediate connection to the nearest access point.
To improve wireless network security, you have to implement two main functions:
Authentication: It must be verified that clients attempting to connect to the
network are authorized users.
Traffic Encryption: Data passing between the access point and clients must be
protected from interception and eavesdropping.
For a more secure network, the access point can implement one or a combination
of the following security mechanisms:
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) page 4-49
IEEE 802.1x page 4-56
Wireless MAC address filtering page 4-11
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA or WPA2) page 4-56
Both WEP and WPA security settings are configurable separately for each virtual
access point (VAP) interface. MAC address filtering, and RADIUS server settings
are global and apply to all VAP interfaces.
The security mechanisms that may be employed depend on the level of security
required, the network and management resources available, and the software
support provided on wireless clients.
A summary of wireless security considerations is listed in the following table.
Ta bl e 5 Wireless Security Considerations
Security
Mechanism
WEP Built-in support on all 802.11a
WEP over 802.1X Requires 802.1X client support
MAC Address
Filtering
Client Support Implementation Considerations
and 802.11g devices
in system or by add-in software
(support provided in Windows
2000 SP3 or later and Windows
XP)
Uses the MAC address of client
network card
• Provides only weak security
• Requires manual key management
• Provides dynamic key rotation for improved WEP
security
• Requires configured RADIUS server
• 802.1X EAP type may require management of
digital certificates for clients and server
• Provides only weak user authentication
• Management of authorized MAC addresses
• Can be combined with other methods for
improved security
• Optionally configured RADIUS server
4-49
Page 90

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Security
Mechanism
WPA over 802.1X
Mode
WPA PSK Mode Requires WPA-enabled system
WPA2 with
802.1X
WPA2 PSK Mode Requires WPA-enabled system
Client Support Implementation Considerations
Requires WPA-enabled system
and network card driver
(native support provided in
Windows XP)
and network card driver
(native support provided in
Windows XP)
Requires WPA-enabled system
and network card driver (native
support provided in Windows
XP)
and network card driver (native
support provided in Windows
XP)
• Provides robust security in WPA-only mode
(i.e., WPA clients only)
• Offers support for legacy WEP clients, but with
increased security risk (i.e., WEP authentication
keys disabled)
• Requires configured RADIUS server
• 802.1X EAP type may require management of
digital certificates for clients and server
• Provides good security in small networks
• Requires manual management of pre-shared key
• Provides the strongest security in WPA2-only
mode
• Provides robust security in mixed mode for WPA
and WPA2 clients
• Offers fast roaming for time-sensitive client
applications
• Requires configured RADIUS server
• 802.1X EAP type may require management of
digital certificates for clients and server
• Clients may require hardware upgrade to be
WPA2 compliant
• Provides robust security in small networks
• Requires manual management of pre-shared key
• Clients may require hardware upgrade to be
WPA2 compliant
NOTE: You must enable data encryption through the web in order to enable all
types of encryption (WEP, TKIP, or AES) in the access point.
The access point can simultaneously support clients using various different
security mechanisms. The configuration for these security combinations are
outlined in the following table. Note that MAC address authentication can be
configured independently to work with all security mechanisms and is indicated
separately in the table. Required RADIUS server support is also listed.
Ta bl e 6 Security Considerations
Client Security
Combination
No encryption and no
authentication
Static WEP only (with
or without shared
key authentication)
Configuration Summary
Authentication: Open System
Encryption: Disable
802.1x: Disable
Enter 1 to 4 WEP keys
Select a WEP transmit key for the interface
Authentication: Shared Key or Open System
Encryption: Enable
802.1x: Disable
4-50
a
MAC
Authentication
Local, RADIUS, or
Disabled
Local, RADIUS, or
Disabled
b
RADIUS
Server
c
Yes
c
Yes
Page 91

Security
Client Security
Combination
Dynamic WEP
(802.1x) only
802.1x WPA only Authentication: WPA
Authentication: Open System
Encryption: Enable
802.1x: Required
Set 802.1x key refresh and reauthentication rates
Encryption: Enable
Configuration Summary
WPA Configuration: Required
Cipher Suite: TKIP
802.1x: Required
Set 802.1x key refresh and reauthentication rates
WPA Pre-Shared Key
only
Authentication: WPA-PSK
Encryption: Enable
WPA Configuration: Required
Cipher Configuration: TKIP
802.1x: Disable
WPA Pre-shared Key Type: Hexadecimal or
Alphanumeric
Enter a WPA Pre-shared key
Static and dynamic
(802.1x) WEP keys
Enter 1 to 4 WEP keys
Select a WEP transmit key
Authentication: Open System
Encryption: Enable
802.1x: Supported
Set 802.1x key refresh and reauthentication rates
Dynamic WEP and
802.1x WPA
Authentication: WPA
Encryption: Enable
WPA Configuration: Supported
Cipher Suite: WEP
802.1x: Required
Set 802.1x key refresh and reauthentication rates
Static and dynamic
(802.1x) WEP keys
and 802.1x WPA
Enter 1 to 4 WEP keys
Select a WEP transmit key
Authentication: WPA
Encryption: Enable
WPA Configuration: Supported
Cipher Suite: WEP
802.1x: Supported
Set 802.1x key refresh and reauthentication rates
802.1x WPA2 only Authentication: WPA2
Encryption: Enable
WPA Configuration: Required
Cipher Suite: AES-CCMP
802.1x: Required
Set 802.1x key refresh and reauthentication rates
WPA2 Pre-Shared
Key only
Authentication: WPA2-PSK
Encryption: Enable
WPA Configuration: Required
Cipher Suite: AES-CCMP
802.1x: Disable
WPA Pre-shared Key Type: Hexadecimal or
Alphanumeric
Enter a WPA Pre-shared key
a
MAC
Authentication
Local, RADIUS, or
Disabled
b
RADIUS
Server
c
Yes
Local only Yes
Local only No
Local, RADIUS, or
Yes
Disabled
Local or Disabled Yes
Local or Disabled Yes
Local or Disabled Yes
Local or Disabled No
4-51
Page 92

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Client Security
Combination
802.1x WPA-WPA2
Mixed Mode
WPA-WPA2 Mixed
Mode Pre-Shared Key
a The configuration summary does not include the set up for MAC authentication (see page 4-9) or
RADIUS server (see page 4-8).
b The configuration of RADIUS MAC authentication together with 802.1x WPA or WPA Pre-shared
Key is not supported.
Authentication: WPA-WPA2-mixed
Encryption: Enable
WPA Configuration: Required
Cipher Suite: TKIP
802.1x: Required
Set 802.1x key refresh and reauthentication rates
Authentication: WPA-WPA2-PSK-mixed
Encryption: Enable
WPA Configuration: Required
Cipher Suite: TKIP
802.1x: Disable
WPA Pre-shared Key Type: Hexadecimal or
Alphanumeric
Enter a WPA Pre-shared key
Configuration Summary
a
MAC
Authentication
Local or Disabled Yes
Local or Disabled No
b
RADIUS
Server
NOTE: If you choose to configure RADIUS MAC authentication together with
802.1X, the RADIUS MAC address authentication occurs prior to 802.1X
authentication. Only when RADIUS MAC authentication succeeds is 802.1X
authentication performed. When RADIUS MAC authentication fails, 802.1X
authentication is not performed.
WIRED EQUIVALENT PRIVACY (WEP)
WEP provides a basic level of security, preventing unauthorized access to the
network, and encrypting data transmitted between wireless clients and the access
point. WEP uses static shared keys (fixed-length hexadecimal or alphanumeric
strings) that are manually distributed to all clients that want to use the network.
WEP is the security protocol initially specified in the IEEE 802.11 standard for
wireless communications. Unfortunately, WEP has been found to be seriously
flawed and cannot be recommended for a high level of network security. For
more robust wireless security, the access point provides Wi-Fi Protected Access
(WPA) for improved data encryption and user authentication.
Setting up shared keys enables the basic IEEE 802.11 Wired Equivalent Privacy
(WEP) on the access point to prevent unauthorized access to the network.
If you choose to use WEP shared keys instead of an open system, be sure to
define at least one static WEP key for user authentication and data encryption.
Also, be sure that the WEP shared keys are the same for each client in the wireless
network.
4-52
Page 93

Security
Note that all clients share the same keys, which are used for user authentication
and data encryption. Up to four keys can be specified. These four keys are used
for all VAP interfaces on the same radio.
To set up WEP shared keys, click Radio Settings under 802.11a or 802.11b/g, then
select Authentication ‘Shared’. To use all other than WEP shared keys, select
Authentication ‘Open.’
The following example presumes that you have selected to opt for other methods
of encryption than WEP.
Figure 40 Authentication and Encryption
Authentication – Sets the access point to communicate as an open system that
accepts network access attempts from any client, or with clients using
pre-configured static shared keys. (Default: Open System)
Open System: If you don’t set up any other security mechanism on the access
point, the network has no protection and is open to all users. This is the default
setting.
Shared Key: Sets the access point to use WEP shared keys. If this option is
selected, you must configure at least one key on the access point and all clients.
NOTE: To use 802.1X on wireless clients requires a network card driver and
802.1X client software that supports the EAP authentication type that you want to
use. Windows 2000 SP3 or later and Windows XP provide 802.1X client support.
Windows XP also provides native WPA support. Other systems require additional
client software to support 802.1X and WPA.
4-53
Page 94

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Encryption – Enable or disable the access point to use data encryption (WEP, TKIP,
or AES). If this option is selected when using static WEP keys, you must configure
least one key on the access point and all clients. (Default: Disabled)
at
NOTE: You must enable data encryption through the web or CLI in order to enable
all types of encryption (WEP, TKIP, or AES) in the access point.
Cipher Modes – Selects an encryption method for the global key used for
multicast and broadcast traffic, which is supported by all wireless clients.
AES: AES-CCMP is used as the multicast encryption cipher. AES-CCMP is the
standard encryption cipher required for WPA2.
TKIP: TKIP is used as the multicast encryption cipher.
WEP/TKIP: WEP is used as the multicast encryption cipher. You should select
WEP only when both WPA and WEP clients are supported.
Figure 41 WPA Key Management
WPA Key Management – Specifies the type of WPA encryption to use:
WPA authentication over 802.1x – Requires the use of 802.1x authentication.
WPA Pre-shared Key (PSK) – Requires that 802.1x authentication be disabled.
Key Type – Select the preferred method of entering WEP encryption keys on the
access point and enter up to four keys:
Hexadecimal: Enter keys as 10 hexadecimal digits (0-9 and A-F) for 64 bit keys,
26 hexadecimal digits for 128 bit keys, or 32 hexadecimal digits for 152 bit keys
(802.11a radio only). This is the default setting.
4-54
Page 95

Security
Alphanumeric: Enter keys as 5 alphanumeric characters for 64 bit keys, 13
alphanumeric characters for 128 bit keys, or 16 alphanumeric characters for
152 bit keys (802.11a radio only).
Key – Selects the key number to use for encryption for each VAP interface. If
the clients have all four keys configured to the same values, you can change the
encryption key to any of the four settings without having to update the client
keys. (Default: Key 1)
Figure 42 WEP Keys
Client Types – Specifies the type of client to encrypt:
WEP and WPA clients – Both WEP and TKIP encryption are supported.
WPA clients only – All clients must support TKIP.
WEP clients only – All clients must support WEP.
WEP Configuration – Under open authentication it is still possible to configure
WEP keys.
Key Size – 64 Bit, 128 Bit, or 152 Bit key length. Note that the same size of
encryption key must be supported on all wireless clients. (Default: None)
Key Type – Select the preferred method of entering WEP encryption keys on the
access point and enter up to four keys:
4-55
Page 96

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
• Hexadecimal: Enter keys as 10 hexadecimal digits (0-9 and A-F) for 64 bit
keys, 26 hexadecimal digits for 128 bit keys, or 32 hexadecimal digits for 152
bit keys (802.11a radio only). This is the default setting.
• Alphanumeric: Enter keys as 5 alphanumeric characters for 64 bit keys, 13
alphanumeric characters for 128 bit keys, or 16 alphanumeric characters for
152 bit keys (802.11a radio only).
Key – Selects the key number to use for encryption for each VAP interface. If the
clients have all four keys configured to the same values, you can change the
encryption key to any of the four settings without having to update the client
keys. (Default: Key 1)
NOTE: Key index and type must match that configured on the clients.
NOTE: In a mixed-mode environment with clients using static WEP keys and WPA,
select WEP transmit key index 2, 3, or 4. The access point uses transmit key index
1 for the generation of dynamic keys.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
WPA employs a combination of several technologies to provide an enhanced
security solution for 802.11 wireless networks.
The access point supports the following WPA components and features:
IEEE 802.1X and the Extensible Authentication Protocol
(EAP): WPA employs
802.1X as its basic framework for user authentication and dynamic key
management. The 802.1X client and RADIUS server should use an appropriate
EAP type—such as EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security), EAP-TTLS (Tunneled TLS), or
PEAP (Protected EAP)—for strongest authentication. Working together, these
protocols provide “mutual authentication” between a client, the access point,
and a RADIUS server that prevents users from accidentally joining a rogue
network. Only when a RADIUS server has authenticated a user’s credentials will
encryption keys be sent to the access point and client.
NOTE: To implement WPA on wireless clients requires a WPA-enabled network
card driver and 802.1X client software that supports the EAP authentication type
that you want to use. Windows XP provides native WPA support, other systems
require additional software.
4-56
Page 97

Security
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP): WPA specifies TKIP as the data
encryption method to replace WEP. TKIP avoids the problems of WEP static keys
by dynamically changing data encryption keys. Basically, TKIP starts with a master
(temporal) key for each user session and then mathematically generates other
keys to encrypt each data packet. TKIP provides further data encryption
enhancements by including a message integrity check for each packet and a
re-keying mechanism, which periodically changes the master key.
WPA Pre-Shared Key Mode (WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK): For enterprise deployment,
WPA requires a RADIUS authentication server to be configured on the wired
network. However, for small office networks that may not have the resources to
configure and maintain a RADIUS server, WPA provides a simple operating mode
that uses just a pre-shared password for network access. The Pre-Shared Key
mode uses a common password for user authentication that is manually entered
on the access point and all wireless clients. The PSK mode uses the same TKIP
packet encryption and key management as WPA in the enterprise, providing a
robust and manageable alternative for small networks.
Mixed WPA and WEP Client Support: WPA enables the access point to indicate
its supported encryption and authentication mechanisms to clients using its
beacon signal. WPA-compatible clients can likewise respond to indicate their WPA
support. This enables the access point to determine which clients are using WPA
security and which are using legacy WEP. The access point uses TKIP unicast data
encryption keys for WPA clients and WEP unicast keys for WEP clients. The global
encryption key for multicast and broadcast traffic must be the same for all clients,
therefore it restricts encryption to a WEP key.
When access is opened to both WPA and WEP clients, no authentication is
provided for the WEP clients through shared keys. To support authentication for
WEP clients in this mixed mode configuration, you can use either MAC
authentication or 802.1X authentication.
WPA2: WPA was introduced as an interim solution for the vulnerability of WEP
pending the ratification of the IEEE 802.11i wireless security standard. In effect,
the WPA security features are a subset of the 802.11i standard. WPA2 includes
the now ratified 802.11i standard, but also offers backward compatibility with
WPA. Therefore, WPA2 includes the same 802.1X and PSK modes of operation
and support for TKIP encryption. The main differences and enhancements in
WPA2 can be summarized as follows:
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): WPA2 uses AES Counter-Mode
encryption with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code
(CBC-MAC) for message integrity. The AES Counter-Mode/CBCMAC Protocol
(AES-CCMP) provides extremely robust data confidentiality using a 128-bit
key. The AES-CCMP encryption cipher is specified as a standard requirement
4-57
Page 98

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
for WPA2. However, the computational intensive operations of AES-CCMP
requires hardware support on client devices. Therefore to implement WPA2 in
the network, wireless clients must be upgraded to WPA2-compliant hardware.
WPA2 Mixed-Mode: WPA2 defines a transitional mode of operation for
networks moving from WPA security to WPA2. WPA2 Mixed Mode allows
both WPA and WPA2 clients to associate to a common SSID interface. In
mixed mode, the unicast encryption cipher (TKIP or AES-CCMP) is negotiated
for each client. The access point advertises its supported encryption ciphers in
beacon frames and probe responses. WPA and WPA2 clients select the cipher
they support and return the choice in the association request to the access
point. For mixed-mode operation, the cipher used for broadcast frames is
always TKIP. WEP encryption is not allowed.
Key Caching: WPA2 provides fast roaming for authenticated clients by
retaining keys and other security information in a cache, so that if a client
roams away from an access point and then returns, re-authentication is not
required. When a WPA2 client is first authenticated, it receives a Pairwise
Master Key (PMK) that is used to generate other keys for unicast data
encryption. This key and other client information form a Security Association
that the access point names and holds in a cache.
Preauthentication: Each time a client roams to another access point it has to
be fully re-authenticated. This authentication process is time consuming and
can disrupt applications running over the network. WPA2 includes a
mechanism, known as pre-authentication, that allows clients to roam to a new
access point and be quickly associated. The first time a client is authenticated
to a wireless network it has to be fully authenticated. When the client is about
to roam to another access point in the network, the access point sends
pre-authentication messages to the new access point that include the client’s
security association information. Then when the client sends an association
request to the new access point, the client is known to be already
authenticated, so it proceeds directly to key exchange and association.
The configuration settings for WPA are summarized below:
Ta bl e 7 WPA Configuration Settings
WPA and WPA2 pre-shared key only WPA and WPA2 over 802.1X
Encryption: Enabled
Authentication Setup: WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, or
WPA-WPA2-mixed
Cipher Suite: WEP/TKIP/AES-CCMP
WPA Pre-shared Key Type: Hex/ASCII
1: You must enable data encryption in order to enable all types of encryption in the access point.
2: Select TKIP when any WPA clients do not support AES. Select AES only if all clients support AES.
4-58
Encryption: Enabled
Authentication Setup: WPA, WPA2,
WPA-WPA2-mixed
Cipher Suite: WEP/TKIP/AES-CCMP
(requires RADIUS server to be specified)
Page 99

Security
Status Information
The Status page includes information on the following items:
Access Point Status
The AP Status window displays basic system configuration settings, as well as the
settings for the wireless interface.
Figure 43 AP Status
AP System Configuration – The AP System Configuration table displays the basic
system configuration settings:
System Up Time: Length of time the management agent has been up.
MAC Address: The physical layer address for the Ethernet port.
System Name: Name assigned to this system.
System Country Code: The country for which the device has been set for use.
System Contact: Administrator responsible for the system.
IP Address: IP address of the management interface for this device.
IP Default Gateway: IP address of the gateway router between this device and
management stations that exist on other network segments.
4-59
Page 100

CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
HTTP Server: Shows if management access via HTTP is enabled.
HTTP Server Port: Shows the TCP port used by the HTTP interface.
Version: Shows the software version number.
802.1X: Shows if IEEE 802.1X access control for wireless clients is enabled.
AP Wireless Configuration – The AP Wireless Configuration tables display the
radio and VAP interface settings listed below. Note that Interface Wireless A refers
to the 802.11a radio and Interface Wireless G refers the 802.11b/g radio.
VAP: Displays the VAP number.
Radio Status: Displays if the radio is enabled or disabled for this VAP.
SSID: The service set identifier for the VAP interface.
Radio Channel: The radio channel through which the access point
communicates with wireless clients.
Radio Encryption: The key size used for data encryption.
Radio Auth. Type: Shows the type of authentication used.
Output Antenna: Displays which antenna/e are in use by the VAP.
MAC: The physical layer address of the radio interface.
Station Status
The Station Status window shows the wireless clients currently associated with
the access point.
Figure 44 Station Status
The Station Configuration page displays basic connection information for all
associated stations as described below. Note that this page is automatically
refreshed every five seconds.
Station Address: The MAC address of the wireless client.
Authenticated: Shows if the station has been authenticated. The two basic
methods of authentication supported for 802.11 wireless networks are “open
4-60
 Loading...
Loading...