Page 1

Wireless LAN Access Point 7250
3CRWE725075
(Model WL-455)
User Guide
http://www.3com.com/
http://www.3com.com/support/en_US/productreg/frontpg
Part No. DUA72507-5AAA01
Published April 2005
Page 2

3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive
Marlborough, MA
01752-3064
Copyright © 2005 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be
reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as
translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in
content from time to time without obligation on the part of 3Com Corporation to provide
notification of such revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or condition of any
kind, either implied or expressed, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties, terms or
conditions of merchantability, satisfactory quality, and fitness for a particular purpose. 3Com may
make improvements or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this
documentation at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it is furnished
under a license agreement included with the product as a separate document, in the hard copy
documentation, or on the removable media in a directory file named LICENSE.TXT or
!LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to locate a copy, please contact 3Com and a copy will be
provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the software
described herein are provided to you subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and developed solely at
private expense. Software is delivered as “Commercial Computer Software” as defined in DFARS
252.227-7014 (June 1995) or as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR
provided with only such rights as are provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the
Software. Technical data is provided with limited rights only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015
(November
remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any licensed program or
documentation contained in, or delivered to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the United States and
may or may not be registered in other countries.
3Com, the 3Com logo, and SuperStack are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation.
Wi-Fi is a trademark of the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with
which they are
EXPORT RESTRICTIONS: This product contains Encryption and may require US and/or Local
Government authorization prior to export or import to another country.
1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987), whichever is applicable. You agree not to
associated.
2.101(a) and as such is
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction
Product Features..........................................................................................1
Security..................................................................................................1
Performance and Reliability ....................................................................2
Virtual Access Point (VAP) Support .................................................... 2
WDS Bridging and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Support...................3
Manageability ........................................................................................ 4
802.11g Wireless Network Standard ...........................................................4
Standard Network Configuration and Planning............................................5
Ad Hoc Wireless LAN .............................................................................5
Infrastructure Wireless LAN .................................................................... 5
Infrastructure Wireless LAN for Roaming Wireless PCs ............................6
Advanced Network Configuration and Planning ..........................................7
Public/Private Access Point Service .......................................................... 7
Terminology ................................................................................................8
2 Installing the Access Point
Installation Requirements...........................................................................11
Power Requirements .................................................................................12
Safety Information.....................................................................................12
Deciding Where to Place Equipment and Performing A Site Survey ............13
Before You Begin.......................................................................................14
Connecting the Standard Antennas ...........................................................15
Connecting Power.....................................................................................16
Using the Included AC Adapter ............................................................16
Using an Optional Power-Over Ethernet Injector ...................................17
Using a Power-Over-Ethernet LAN Port ................................................. 18
Checking the LEDs ....................................................................................18
Mounting on a Wall ..................................................................................18
Flat Surface Installation..............................................................................20
Selecting and Connecting a Different Antenna Model ...............................21
Power Settings on the Access Point for External Antennas .........................22
Page 4

Installing Software Utilities.........................................................................23
3 System Configuration
Using the 3Com Wireless Device Manager.................................................25
Launching a Wireless Device Configuration .......................................... 25
Using the Pre-IP Configuration Wizard..................................................27
Configuration Login ..................................................................................27
Setting the Country Code..........................................................................27
Basic Setup................................................................................................28
Advanced Setup ........................................................................................29
Identification .............................................................................................29
TCP/IP Settings ..........................................................................................29
DHCP Client......................................................................................... 29
Web Servers.........................................................................................30
Smart Monitor ..................................................................................... 30
RADIUS .....................................................................................................31
Authentication ..........................................................................................33
Filter Control .............................................................................................36
Filtering by VLAN .................................................................................36
Enabling VLAN Filtering........................................................................ 36
Security Filters ...................................................................................... 37
Client List Timeout ............................................................................... 37
Uplink Port MAC Address Filtering........................................................ 37
Filtering by Ethernet Protocol Type........................................................ 38
SNMP........................................................................................................39
Trap Destination ................................................................................... 39
Trap Configuration ...............................................................................40
SNMP Users .........................................................................................41
Default Groups ............................................................................... 41
Default Security Levels ....................................................................41
Groups.................................................................................................42
SNMP Targets....................................................................................... 43
SNMP Filter .......................................................................................... 43
Administration ..........................................................................................44
WDS/STP Settings......................................................................................45
Configuration Guidelines .....................................................................46
Radio Bridge Roles ............................................................................... 46
Page 5

Bridge Address Entry ............................................................................46
Scanning for WDS Links ....................................................................... 47
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol Settings ........................................47
System Log................................................................................................48
Status........................................................................................................49
Radio Interface ..........................................................................................50
Radio Settings ...........................................................................................50
Virtual Access Point (VAP) Configuration ..............................................50
Enabling Virtual Access Point (VAP) ......................................................50
Changing Radio Settings ......................................................................52
Security .....................................................................................................54
Selecting a Virtual Access Point (VAP) ................................................... 54
Configuring Authentication..................................................................54
Configuring Encryption ........................................................................ 54
WPA Configuration ......................................................................... 55
WEP Configuration ......................................................................... 56
How to setup the access point for RADIUS authentication .........................57
How to setup the access point for WPA with 802.1x Session keys..............58
How to setup the access point for WPA with Pre-Shared (PSK) Key ............59
WPA Configuration for Windows XP .........................................................60
4 Troubleshooting
Regulatory Compliance Information
Index
Page 6

Page 7
1 INTRODUCTION
The 3Com® Wireless LAN Access Point 7250 supports 802.11g and 802.11b
wireless users.
With their flexibility and unfettered access, wireless LANs are changing the way
people work. Now with 3Com’s enterprise-class wireless access points, you can
build a cost-effective, reliable, secure wireless network that provides users with
seamless connectivity to the Internet, company intranet, and the wired corporate
network from anywhere they happen to be—conference room, cafeteria or
office.
Industry-leading security features and comprehensive management and
performance features combine to make these enterprise class wireless access
points an ideal choice for organizations ready to serve their increasingly mobile
workforce.
PRODUCT FEATURES
The single wireless interface 802.11g 2.4 GHz, 54 Mbps access point creates an
enterprise-class wireless LAN supporting up to 250 simultaneous users.
SECURITY
3Com offers one of the most robust suite of standards-based security on the
market today.
To protect sensitive data broadcast over the wireless LAN, 3Com supports the
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). 3Com strengthens this basic security
mechanism with additional security features, including:
MAC address access control lists
IEEE 802.1x per-port user authentication with RADIUS server authentication
support
IEEE 802.1x supplicant support
1
Page 8

SSH v2
HTTP/HTTPS
SNMP v3
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
Legacy WEP 40/64 bit, 128 bit and 152 bit
Wireless Protected Access (WPA)
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) support: EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS,
EAP-TTLS, and PEAP
PERFORMANCE AND RELIABILITY
3Com wireless access point performance features ensure reliable and seamless
connections for users wherever they roam:
Automatic channel selection automatically finds the least loaded channel for
interference-free communication.
Auto network connect and dynamic rate shifting keep users connected
through a wide variety of conditions by changing to the optimum connection
speed as they move through the network.
Virtual Access Point (VAP) support provides flexibility by allowing a single
access point radio to operate as two separate access points.
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) Bridging support allows you to create
large wireless networks in areas where pulling wires is restricted or
cost-prohibitive by linking several wireless access points together with WDS
links.
Virtual Access Point (VAP) Support
Virtual Access Point (VAP) support allows an access point radio to operate as two
separate access points, providing multiple wireless services to clients in a network.
Each VAP can be configured to provide access to different network resources and
can support different levels of security.
For example, in a university network, an AP could be used to offer two services:
The first service provides access to protected data for authenticated university
staff members, while the second service provides open access to the Internet for
unauthenticated users, such as students or visitors.
Two VAPs per radio are available, and each VAP can be configured with its own
security settings.
For information on setting up and configuring VAPs, see “Enabling Virtual Access
Point (VAP)” on page 50.
2
Page 9
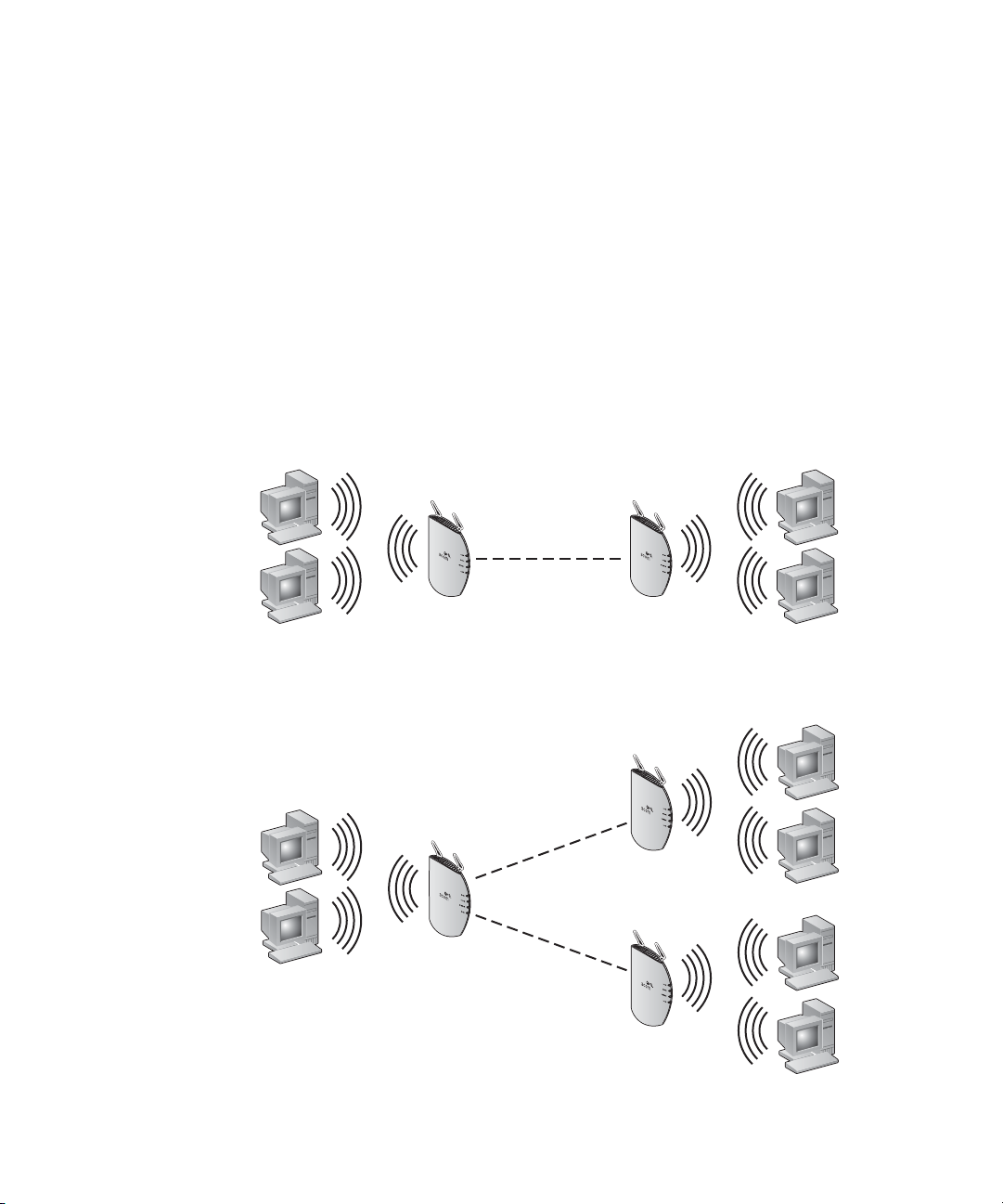
WDS Bridging and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Support
A Distribution System (DS) is a network (typically a wired network) that
interconnects separate access points into a single LAN. With WDS, the
interconnection no longer needs to be physically wired. WDS
medium to interconnect separate access points, thereby eliminating the cost and
inconvenience that may hinder wire installations.
A WDS link can be used in a simple point-to-point link, a complex
point-to-multipoint link, or a multilayer topology.
Point-to-Point WDS Link. The following example shows a point-to-point WDS
link configured between two access points.
Wireless Desktops Wireless Desktops
WDS Link
Point-to-Multipoint WDS Link. The following example shows
point-to-multipoint WDS links configured between multiple access points.
Point-to-Point WDS Link
uses the wireless
Wireless Desktops
Wireless Desktops
WDS Link
Wireless Desktops
WDS Link
3
Page 10

Additionally, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) support prevents loops from being
formed on the network. For more information on these items, see the Wireless
LAN Access Points User Guide.
For WDS and STP configuration instructions, see “WDS/STP Settings” on page 45.
MANAGEABILITY
3Com offers a wide range of standards-based management support, from SNMP
to 3Com Network Supervisor and HP OpenView for seamless integration with
your wired network.
Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager and Wireless LAN Device Discovery tools
let you configure parameters, run diagnostics, backup and restore configurations,
and monitor performance from anywhere on the network using an embedded
web server browser. You can also update wireless device software on multiple
devices using 3Com Network Supervisor to simplify bulk updates.
With Power over Ethernet (PoE) support, the same Category 5 cable that connects
your access point to the data network also provides its power. A single cable
installation dramatically improves your choice of mounting configurations
because you no longer need to consider AC power outlet locations. PoE support
makes it easier than ever to overcome installation problems with difficult-to-wire
or hard-to-reach locations.
802.11G WIRELESS NETWORK STANDARD
802.11g operates in the 2.4 GHz band at up to 54Mbps, and supports the widest
coverage—up to 100 meters (328 feet). However, is subject to a greater risk of
radio interference because it operates in the more popular 2.4 GHz band.
Consider 802.11g when you need wider coverage and vendor compatibility and
you are:
Maintaining support for existing 802.11b users and the existing wireless
investment while providing for expansion into 802.11g.
Implementing a complete wireless LAN solution, including bridges, gateways,
access points and clients; Wi-Fi certification guarantees compatibility
among
Providing access to hot spots in public spaces such as coffee shops or
university cafeterias
vendors
4
Page 11
STANDARD NETWORK CONFIGURATION AND PLANNING
The wireless solution supports a stand-alone wireless network configuration as
well as an integrated configuration with 10/100
The wireless network cards, adapters, and access point can be configured as:
Ad hoc for departmental or SOHO LAN
Infrastructure for wireless LAN
Infrastructure wireless LAN for roaming wireless PCs
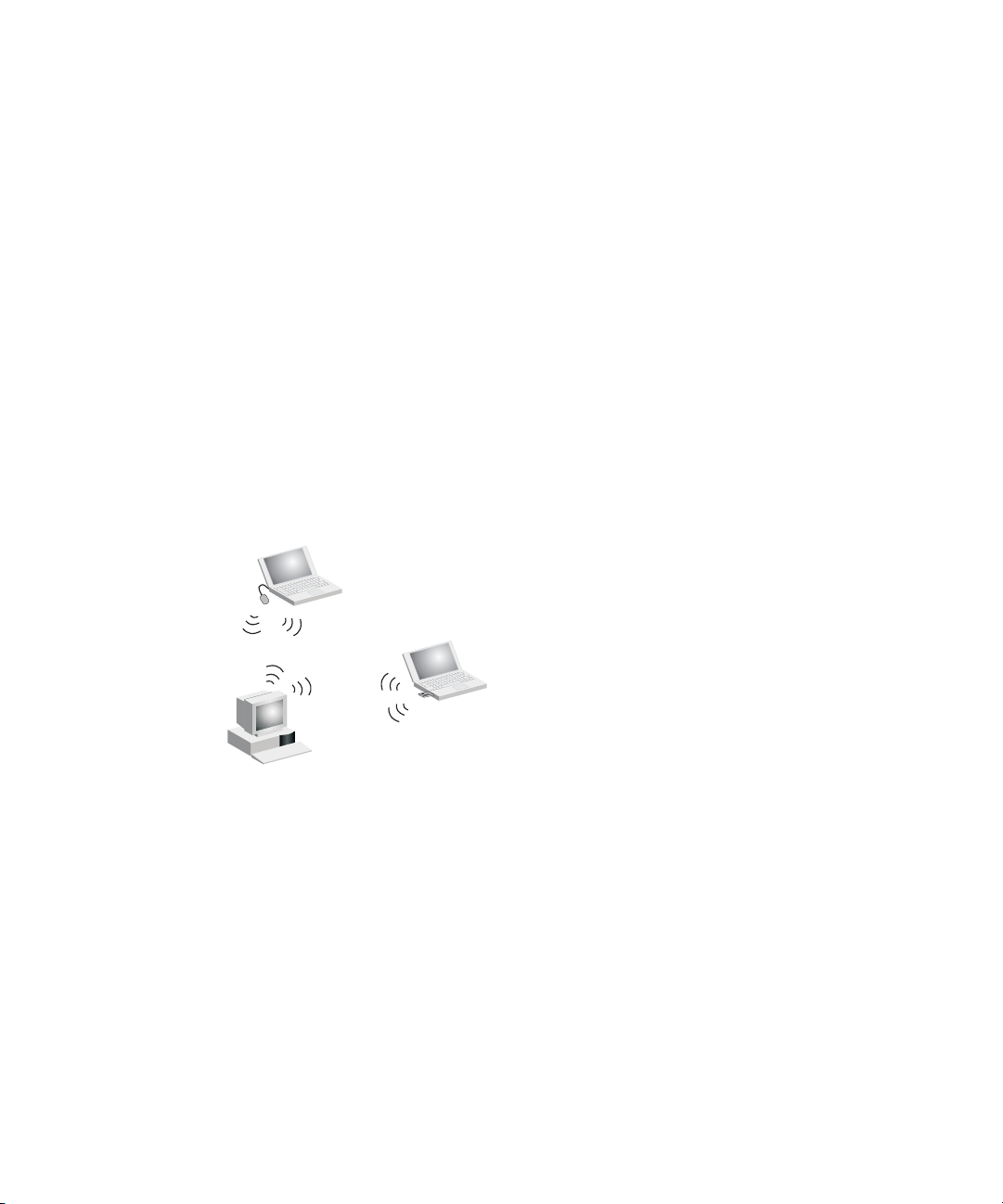
AD HOC WIRELESS LAN
An ad hoc wireless LAN consists of a group of computers, each equipped with a
wireless adapter, connected via radio signals as an independent wireless LAN.
Computers in a specific ad hoc wireless LAN must therefore be configured to the
same radio channel. An ad hoc wireless LAN can be used for a branch office or
SOHO operation.
Ad Hoc Wireless LAN
Notebook with
Wireless USB Adapter
Mbps Ethernet LANs.
Notebook with
Wireless PC Card
PC with Wireless
PCI Adapter
INFRASTRUCTURE WIRELESS LAN
The access point can also provide access to a wired LAN for wireless workstations.
An integrated wired/wireless LAN is called an infrastructure configuration. A Basic
Service Set (BSS) consists of a group of wireless PC users, and an access point that
is directly connected to the wired LAN. Each wireless PC in this BSS can talk to any
computer in its wireless group via a radio link, or access other computers or
network resources in the wired LAN infrastructure via the access point.
The infrastructure configuration not only extends the accessibility of wireless PCs
to the wired LAN, but also increases the effective wireless transmission range for
wireless PCs by passing their signal through one or more access points.
5
Page 12
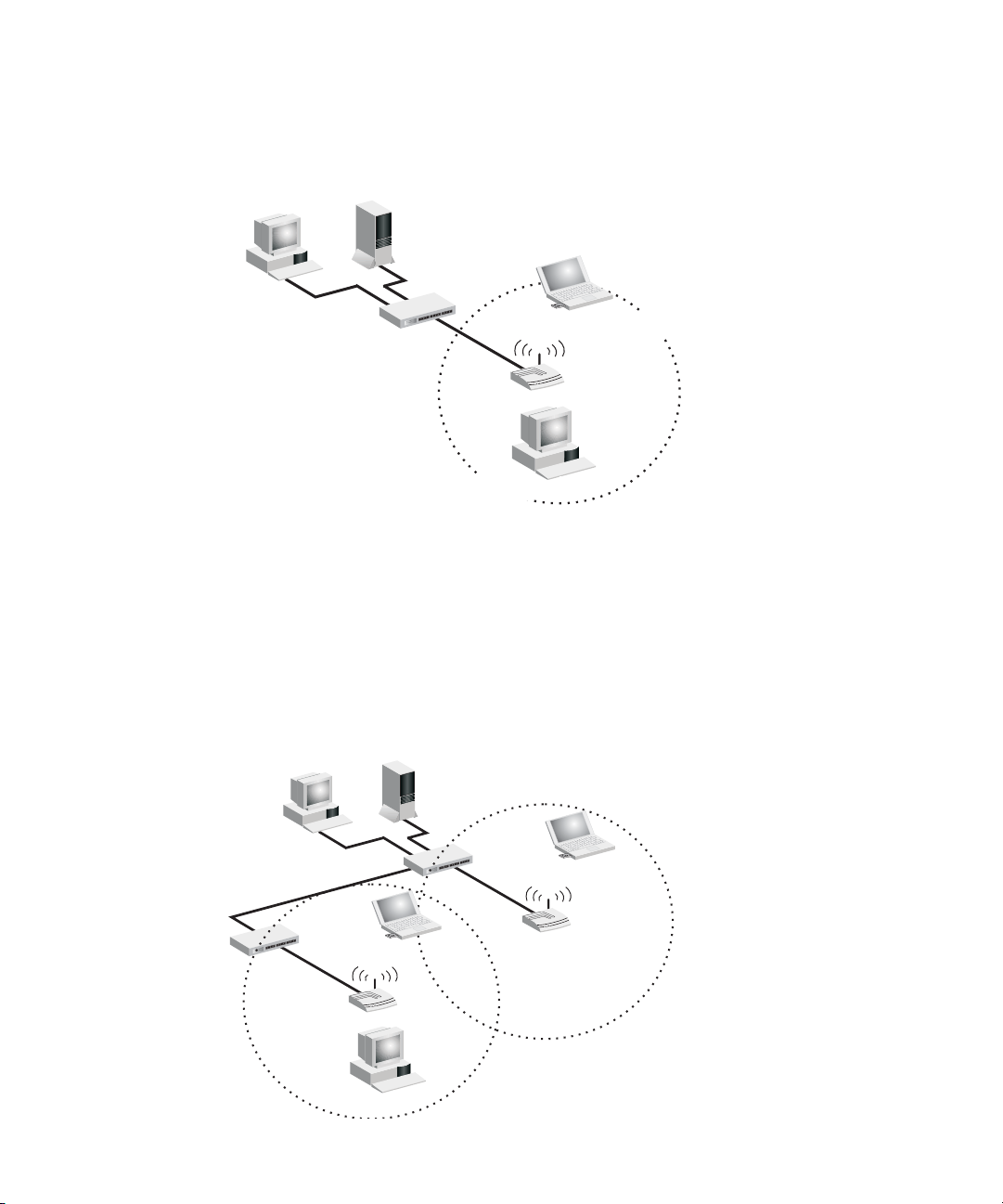
A wireless infrastructure can be used for access to a central database, or for
connection between mobile workers, as shown in the following figure.
Wired LAN Extension
to Wireless Adapters
File
Server
Desktop PC
Switch
Access Point
PC with Wireless
PCI Adapter
Notebook with Wireless
PC Card Adapter
INFRASTRUCTURE WIRELESS LAN FOR ROAMING WIRELESS PCS
The Basic Service Set (BSS) is the communications domain for each access point.
For wireless PCs that do not need to support roaming, set the domain identifier
(SSID) for the wireless card to the SSID of the access point to which you want
connect. A wireless infrastructure can also support roaming for mobile
to
workers. More than one access point can be configured to create an Extended
Service Set (ESS). By placing the access points so that a continuous coverage area
is created, wireless users within this ESS can roam freely.
Desktop PC
Switch
PC with Wireless
PCI Adapter
Access Point
File
Server
Notebook with Wireless
PC Card Adapter
<BSS1>
Switch
Access Point
<ESS>
Seamless Roaming
6
Notebook with Wireless
PC Card Adapter
<BSS2>
Page 13

ADVANCED NETWORK CONFIGURATION AND PLANNING
Virtual Access Point (VAP) and WDS Bridging capabilities allow the access point to
be integrated into many new network configurations. Some common
configurations are explained briefly in this section:
Public/private access point service Remote building wireless access with the AP8250 and 802.11a Bridging Kit Remote building wireless access with the AP8250 and 802.11g Upgrade Kit
PUBLIC/PRIVATE ACCESS POINT SERVICE
The public/private access point service configuration allows the access point to
provide public Internet access while simultaneously providing secure access to the
enterprise network.
In this configuration, an AP7250 access point is configured with two Virtual
Access Points:
The first Virtual Access Point is configured to support one SSID that is
broadcast with no security.
The second Virtual Access Point is configured with a different, private SSID
that is not broadcast.
The private SSID should be assigned to a separate VLAN and use 802.1x
authentication with either TKIP or AES encryption to a RADIUS server.
7
Page 14

TERMINOLOGY
Access Point—An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and
wireless networks.
Ad Hoc—An ad hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with LAN
adapters, connected as an independent wireless LAN.
Backbone—The core infrastructure of a network. The portion of the network
that transports information from one central location to another central location
where it is unloaded onto a local system.
Base Station—In mobile telecommunications, a base station is the central radio
transmitter/receiver that maintains communications with the mobile
radiotelephone sets within its range. In cellular and personal communications
applications, each cell or micro-cell has its own base station; each base station in
turn is interconnected with other cells’ bases.
BSS—Basic Service Set. It is an access point and all the LAN PCs that are
associated with it.
CSMA/CA—Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance.
EAP—Extensible Authentication Protocol, which provides a generalized
framework for several different authentication methods.
ESS—Extended Service Set. More than one BSS is configured to become an ESS.
LAN mobile users can roam between different BSSs in an ESS (ESS-ID, SSID).
Ethernet—A popular local area data communications network, which accepts
transmission from computers and terminals.
Infrastructure—An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an
infrastructure
RADIUS—Remote Access Dial-In User Server is an authentication method used in
conjunction with EAP for 802.1x authentication and session based keys.
Roaming—A wireless LAN mobile user moves around an ESS and maintains a
continuous connection to the infrastructure network.
RTS Threshold—Transmitters contending for the medium may not be aware of
each other (they are “hidden nodes”). The RTS/CTS mechanism can solve this
problem. If the packet size is smaller than the preset RTS Threshold size, the
RTS/CTS mechanism will not be enabled.
configuration.
8
Page 15

VAP—Virtual Access Point. An access point radio capable of operating as two
separate access points.
VLAN—Virtual Local Area Network. A LAN consisting of groups of hosts that are
on physically different segments but that communicate as though they were on
the same segment.
WEP—Wired Equivalent Privacy is based on the use of security keys and the
popular RC4 encryption algorithm. Wireless devices without a valid WEP key will
be excluded from network traffic.
WDS—Wireless Distribution System.
WPA—Wi-Fi Protected Access.
9
Page 16

10
Page 17

2 INSTALLING THE ACCESS POINT
This equipment must be installed in compliance with local and national building
codes, regulatory restrictions, and FCC rules. For the safety of people and
equipment, this product must be installed by a professional technician/installer.
CAUTION: Before installing, see the important warnings and cautions in “Safety
Information” on page 12.
!
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS
The following items are required for installation:
Access Point 7250
Standard detachable antennas
3Com installation CD.
Wall-mount installation hardware (supplied): mounting plate,
mounting
If you do not have IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet LAN equipment, use the
3Com Integrated Power-over-Ethernet power supply that comes with
the
If your LAN equipment complies with the IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet
standard, you can connect directly to the equipment, and the 3Com power
supply is not needed.
Standard category 5 straight (8-wire) Ethernet cable.
The cable must be long enough to reach the power supply or the
power-over-Ethernet LAN port.
If you use the 3Com power supply, you need an additional Ethernet cable to
connect the access point to the LAN.
screws, and plastic anchors for drywall mounting.
access point.
11
Page 18
To access and use the Web configuration management system, you need a
computer that is running Internet Explorer 5.0 or newer and one of the
following operating systems: Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows NT 4.0
Service Pack 6, Windows 2000, or Windows XP. It is recommended that this
computer become the dedicated workstation for managing and configuring
the access point and the wireless network.
POWER REQUIREMENTS
The access point complies with the IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet standard. It
receives power over standard category 5 straight (8-wire) Ethernet cable.
Installation requires the use of either the 3Com power supply provided or
802.3af compliant power supply equipment (output power rated 48 V dc @
IEEE
350 mA maximum). Such equipment must be safety certified according to UL,
CSA, IEC or other applicable national or international safety requirements for the
country of use. All references to the power supply in this document refer to
equipment that meets these
Because the power supply plug is the only means of disconnecting the access
point from power, make sure the power outlet is accessible.
See “Using an Optional Power-Over Ethernet Injector” on page 17 and “Using a
Power-Over-Ethernet LAN Port” on page 18.
requirements.
Note for use of the 3Com power supply (part number 61-0107-000) in Norway:
This product is also designed for use on an IT power system with phase-to-phase
voltage of 230 V.
SAFETY INFORMATION
This equipment must be installed in compliance with local and national building
codes, regulatory restrictions, and FCC rules. For the safety of people and
equipment, only professional network personnel should install the access point,
cables, and antennas.
CAUTION: If you supply your own Ethernet cable for connecting power, be sure
that it is category 5 straight-through (8-wire) cable that has not been altered in
!
any way. Use of nonstandard cable could damage the
CAUTION: To comply with FCC radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, a minimum
body-to-antenna distance of 1 meter (3 feet) must be maintained when the access
!
point is
operational.
access point.
12
Page 19

CAUTION: To avoid possible injury or damage to equipment, you must use either
the provided power supply or IEEE 802.3af compliant power supply equipment
!
that is safety certified according to UL, CSA, IEC, or other applicable national or
international safety requirements for the country of use. All references to power
supply in this document refer to equipment meeting these requirements.
CAUTION: The 3Com power supply input relies on a 16A rated building fuse or
circuit protector for short circuit protection of the line to neutral conductors.
!
CAUTION: It is the responsibility of the installer to ensure that the
Power-over-Ethernet (POE) power supply is properly connected. Connection to any
!
other device, such as a standard Ethernet card or another POE supply, may result
in permanent damage to equipment, electric shock, or fire. Refer to the
installation instructions for proper installation.
DECIDING WHERE TO PLACE EQUIPMENT AND PERFORMING A SITE SURVEY
The access point is ideally designed for vertical installation on a wall surface, but
can also be flat-surface mounted in an elevated location where it will not
disturbed. Ceiling installation is not recommended.
be
Whether you choose to mount the access point on a wall or place it on a flat
surface, make sure to select a clean, dry location that is elevated enough to
provide good reception and network coverage. Do not mount the access point on
any type of metal surface. Do not install the access point in wet or dusty areas.
The site should not be close to transformers, heavy-duty motors, fluorescent
lights, microwave ovens, refrigerators or any other electrical equipment that can
interfere with radio signals.
If you are connecting the access point to a wired network, the location must
provide an Ethernet connection. You will need to run an Ethernet cable from the
power supply to the access point.
An access point provides coverage at distances of up to 100 Meters (300 Feet).
Signal loss can occur if metal, concrete, brick, walls, floors or other architectural
barriers block transmission. If your location includes these kinds of obstructions,
you may need to add additional access points to improve coverage
13
Page 20
Configuring a wireless LAN can be as easy as placing a 3Com Wireless Access
Point in a central area and making the necessary connections to the AP and the
clients. However, installing multiple Access Points may require more planning.
Using the 3Com Site Survey tool (located on the installation CD) can help you
determine if your wireless LAN connectivity and throughput is adequate and all
users are covered by an Access Point.
If you plan to use an optional antenna instead of the standard detachable
antennas that are supplied, review
Antenna Model” on page 21 before selecting the final location and be sure to
allow for routing the antenna cable as required.
For optimal performance, ensure the access point operates in temperature ranges
between –10° C to 40° C (14° F to 104° F).
Caution: Regulatory restrictions dictate that when this device is operational, the
minimal body-to-antenna distance is 1 Meter (3 Feet).
!
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Record the access point MAC address in a safe place before the access point is
installed in a hard-to-reach location. The MAC address is printed on the back of
the access point housing.
“Selecting and Connecting a Different
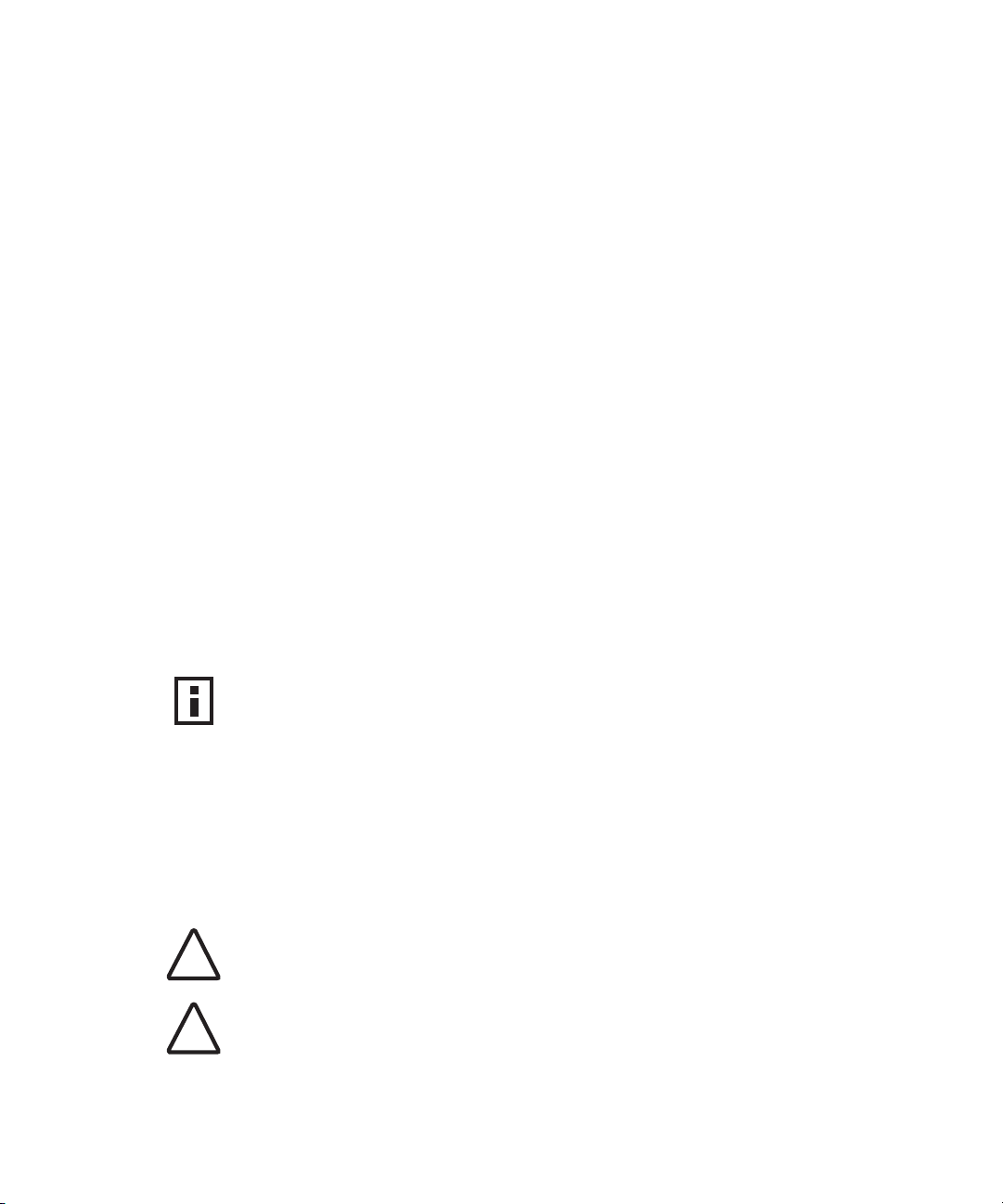
The following illustration shows the front and rear views of the access point,
including the LEDs and connecting ports.
14
Page 21
Caution: Do not connect a telephone cable into the Console port; doing so can
!
cause serious damage to the access point.
CONNECTING THE STANDARD ANTENNAS
The Access Point 7250 is supplied with standard detachable antennas. These
should be attached before the access point is installed. If using an alternate
antenna, see
page 21.
1 Carefully unpack the standard detachable antennas.
CAUTION: Do not handle the antenna tips, especially after they are connected
to the access point, as this could lead to electrostatic discharge (ESD), which
!
could damage the
2 Screw an antenna into each of the sockets in the access point housing.
3 Hand-tighten the antennas at the very base of the SMA connectors without
handling the antenna tips.
4 Position the antennas so they turn out and away from the access point at a
45-degree angle. After network startup, you may need to adjust the
antennas to fine-tune coverage in your area.
“Selecting and Connecting a Different Antenna Model” on
equipment.
Depending on the coverage required for your site, you may want to replace
the standard detachable antennas with one of the external antennas available
for use with the access point. See
Antenna Model” on page 21.
15
“Selecting and Connecting a Different
Page 22
CONNECTING POWER
It is advisable to connect the power and check the Ethernet cables and LEDs
before installing the unit in a hard-to-reach location.
The access point complies with the IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet standard. It
receives power over a standard category 5 straight (8-wire) Ethernet cable.
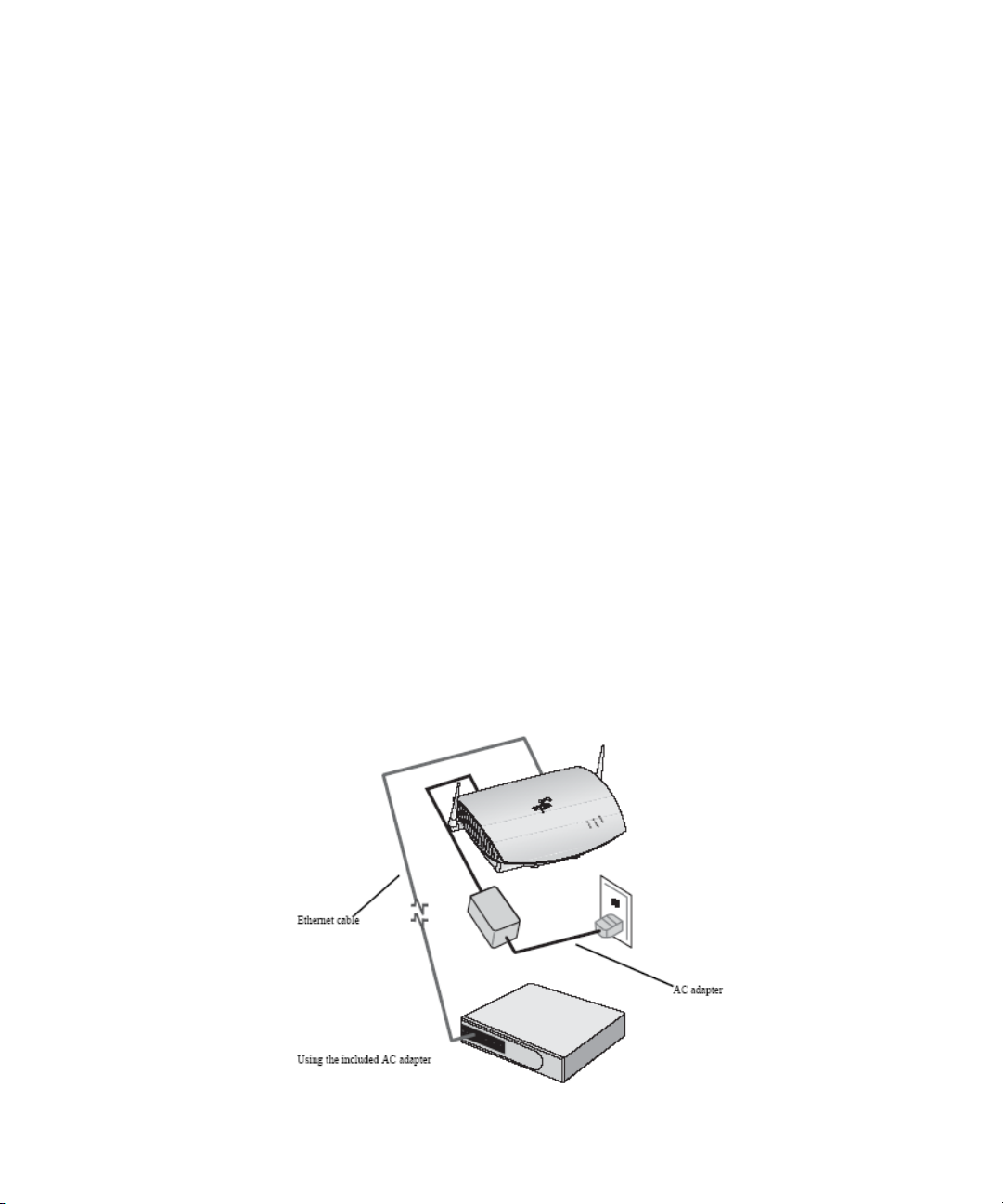
There are three ways to supply power to the access point:
Use the AC adapter included with the Access Point 7250.
Use the 3Com Integrated Power-over-Ethernet power supply. In this case, you
need to supply a second Ethernet cable to connect to the wired LAN.
Connect the access point directly to your own power-over-Ethernet hub or
switch, which must also comply with the IEEE
If you supply your own Ethernet cable for connecting power, be sure that it is
standard category 5 straight-through (8-wire) cable that has not been altered
in any way. Use of nonstandard cable could damage the access point.
USING THE INCLUDED AC ADAPTER
The power supply included with the Access Point 7250 is an AC adapter.
1 Connect the power cord to the AC adapter and plug the cord into a power
outlet.
2 Connect the DC power into the Access Point 7250.
802.3af standard.
16
Page 23
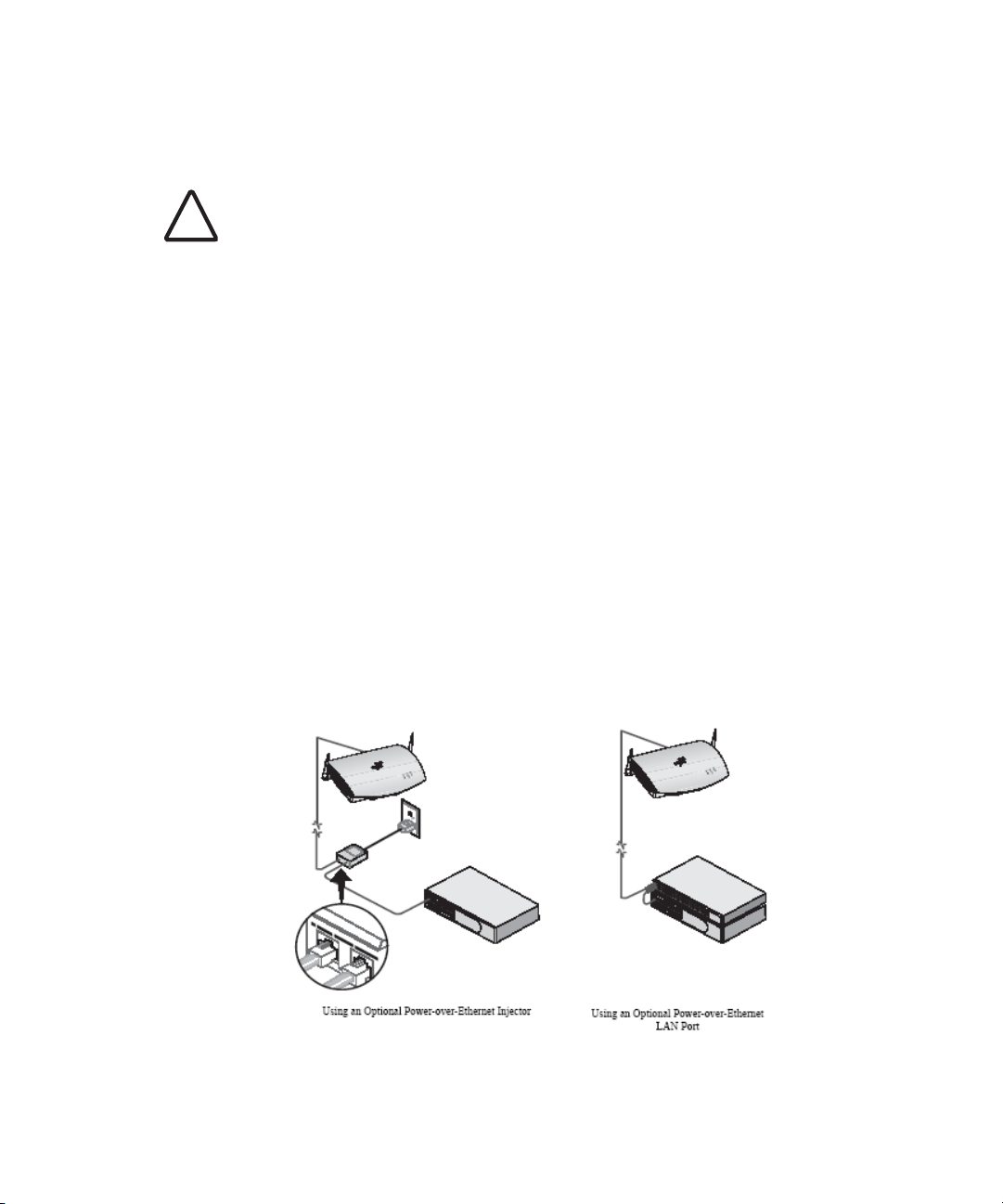
USING AN OPTIONAL POWER-OVER ETHERNET INJECTOR
CAUTION: To avoid damaging network equipment, make sure that the cables
are connected from access point to power supply to LAN as shown above and
!
described
The Power-Over-Ethernet Injector can be located at any point between the access
point and the LAN access port, wherever a convenient power outlet exists. If you
supply your own Ethernet cable for connecting power, be sure that it is standard
category 5 straight-through (8-wire) cable that has not been altered in any way.
Use of nonstandard cable could damage the access point.
Refer to the illustration below, and follow these steps:
1 Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on the access
2 Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the port labeled To Access
3 Connect the power cord to the power supply and plug the cord into a power
4 To link the access point to your Ethernet network, plug one end of another
below.
point.
Point on the power supply.
outlet.
Ethernet cable into the port labeled To Hub/Switch on the power supply, and
plug the other end into a LAN port (on a hub or in a wall).
17
Page 24

USING A POWER-OVER-ETHERNET LAN PORT
If your LAN equipment complies with the IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet
standard, you can connect the access point directly to a LAN port. For example,
the illustration above right shows a connection through a 3Com Ethernet Power
Supply to a 3Com SuperStack
CHECKING THE LEDS
When power is connected, the access point LEDs light. The illustration and the
following table describe the LEDs and their functions.
®
Switch.
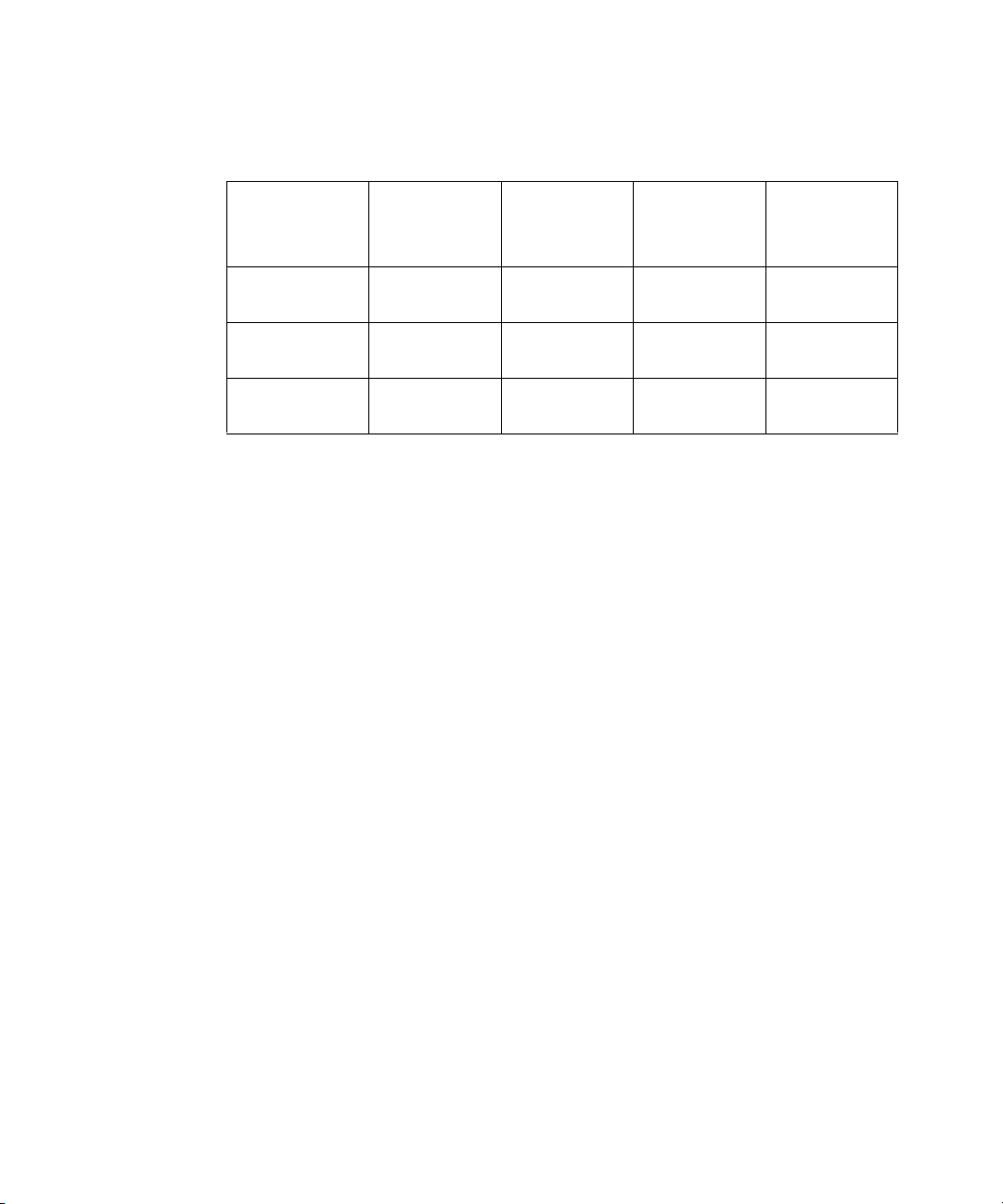
Name Description
Radio
Ethernet
Power
LED blinks red to indicate radio activity. Faster
blinking indicates more activity.
LED lights yellow when a 10 Mbps Ethernet link
is established. LED lights green when a 100
Mbps Ethernet link is established. LED blinks to
indicate activity on the Ethernet. Faster blinking
indicates more activity.
LED lights green when operational code
is running.
MOUNTING ON A WALL
CAUTION: The mounting plate is designed for wall mount installation only. To
avoid equipment damage and possible injury, do not use the mounting plate for
!
a ceiling installation.
The access point comes equipped with all the necessary hardware for mounting
on a wall, including a mounting plate. For a secure installation, the mounting
plate should be placed perpendicular to the floor, with the arrow pointed up, as
indicated on the mounting plate, with the smooth side against the wall.
18
Page 25
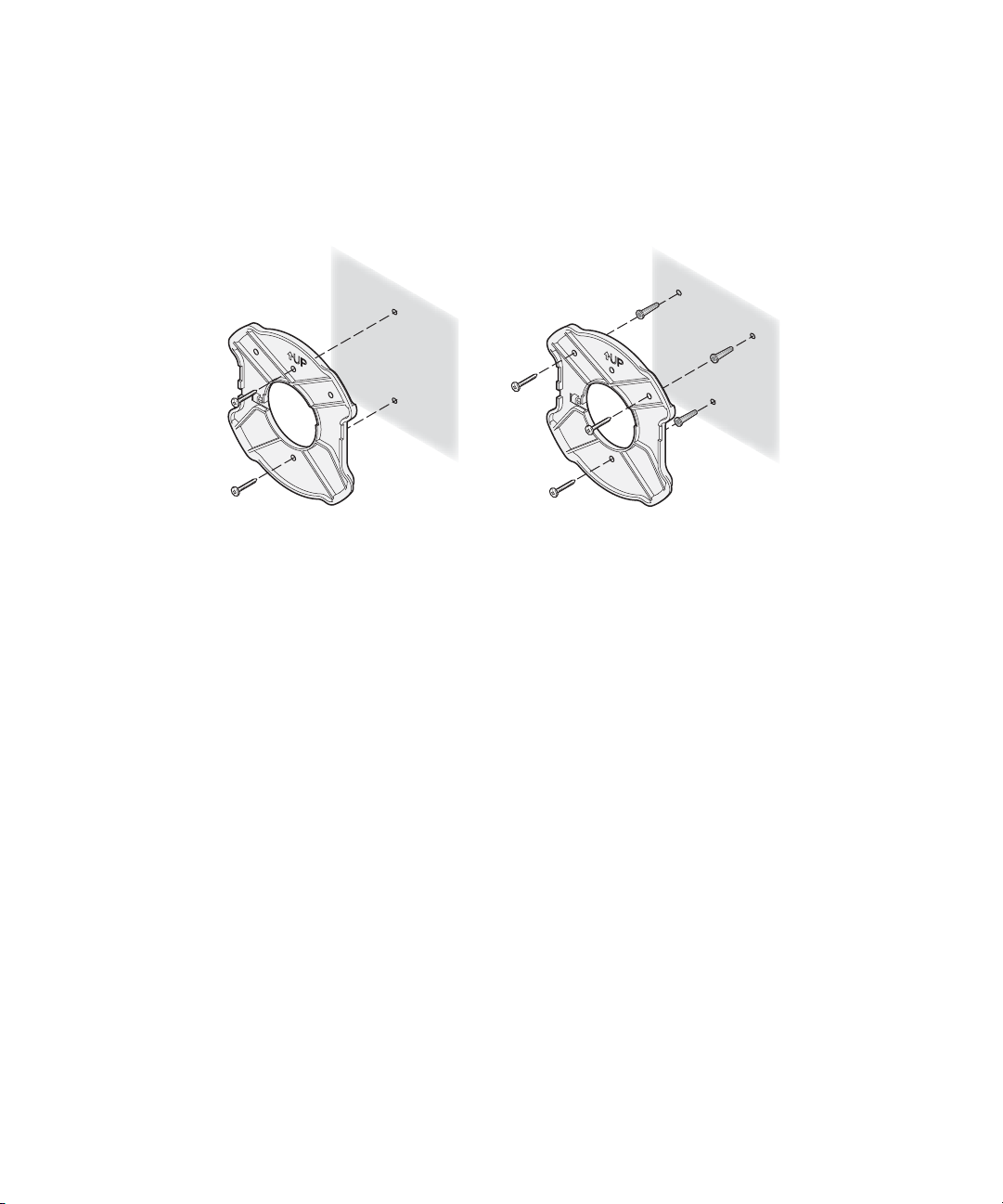
1 Install the mounting plate as shown in the following illustration, on either a
stud (or other hard wall surface), or onto drywall.
If installing into a stud or other
secure vertical surface, use 2 screws.
Allow for a clearance of at least 25 cm (10 Inches) between the ceiling and
If installing into drywall, use
3 plastic anchors and 3 screws.
the top of the mounting plate.
Orient the bracket with the letter “B” at the top of the bracket.
For installation on a wall stud, install the top screw into the stud, as shown
at left in the illustration, and then vertically align the mounting plate before
installing the bottom screw.
For installation on to drywall, mark three screw holes using the mounting
plate as a template for vertical alignment, as shown at right in the
illustration above.
Use a 5-mm (3/16-in.) drill bit if using the plastic anchors provided.
For drywall mounts, you can route the cable through either a side or center
opening for a seamless appearance using one of the methods illustrated
below. Alternatively, you can simply attach the Ethernet cable to the side of
the unit, allowing it to trail along the wall.
If you have routed the Ethernet cable through the center opening, secure
the cable on the hook located on the mounting plate as shown in the
illustration below.
2 Connect the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on the access point.
19
Page 26
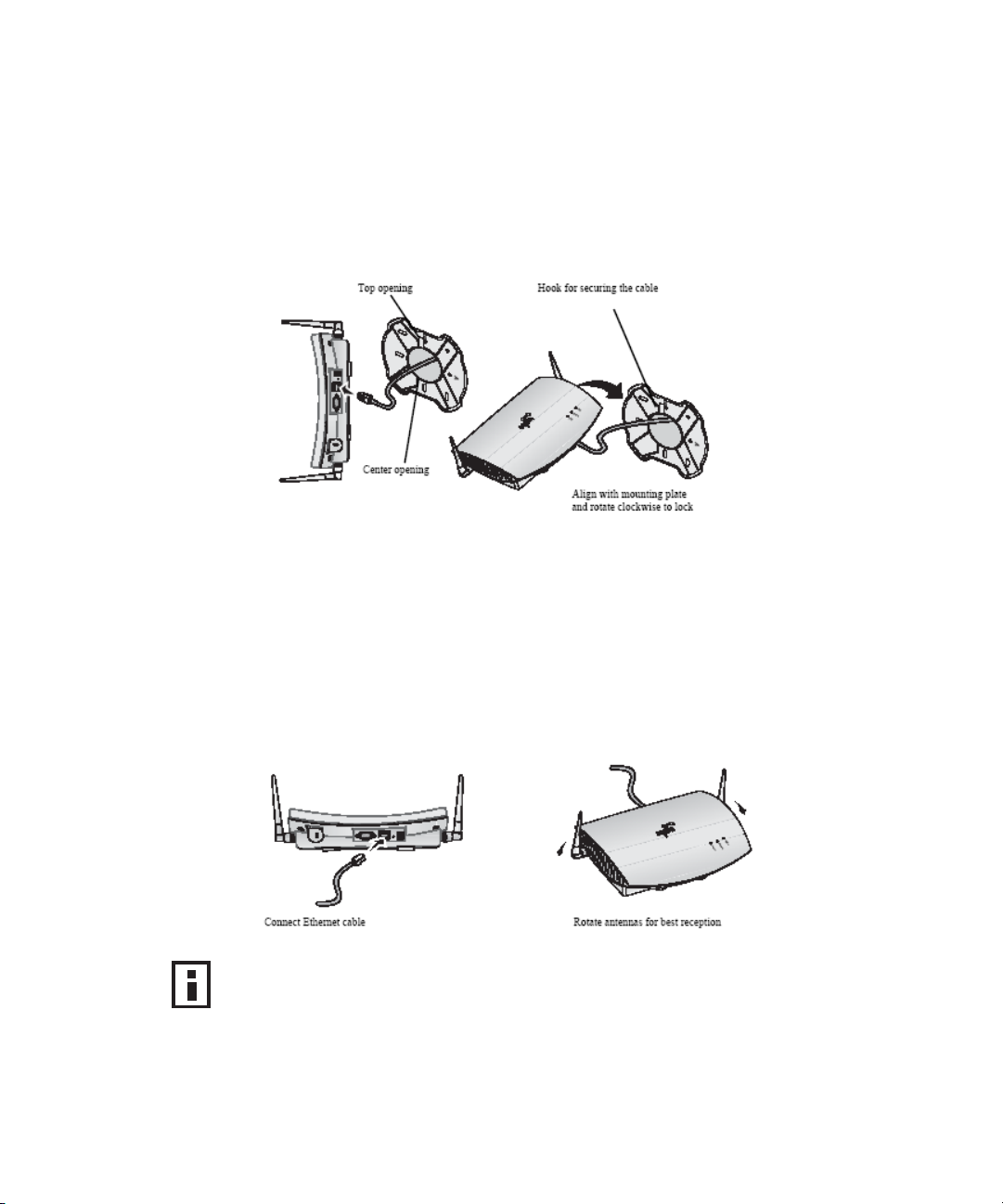
3 Connect the power cable to power port on the rear panel of the access point.
4 Position the access point at an angle to the mounting plate bayonet
connection and turn the unit clockwise until it snaps into place, as shown
below.
FLAT SURFACE INSTALLATION
The access point can also be placed on a flat surface such as a table, desktop or
filing cabinet. Do not install the access point on any type of metal surface. If you
choose a flat surface mount, select a location that is clear of obstructions and
provides good reception.
Note: Regulatory restrictions dictate that when this device is operational, the
minimal body-to-antenna distance is 1 Meter (3 Feet).
20
Page 27
SELECTING AND CONNECTING A DIFFERENT ANTENNA MODEL
Important Note: For FCC regulatory compliance reasons, in the United States,
Canada, and other countries governed by FCC guidelines, external antennas can
only be used in an access point operating temperature range of 15° C - 40° C
F - 104° F)
(59°
If the access point is used with an external antenna, you must also purchase an
antenna cable. For maximum efficiency, use the shortest antenna cable possible.
Antenna cables induce signal loss, which will limit the radiated power output
and range of the access point. Of the options available, we recommend the
3Com 6-foot Antenna Cable (3CSE480).
The standard detachable antennas supplied with the Access Point 7250 are suitable
for a broad variety of environments. If you require a different type of antenna for the
Access Point 7250, several options are available by model number from the 3Com
Web site (www.3Com.com).
For each of the antenna models, you will need either a 6-foot accessory cable
(model 3CWE480) or a 20-foot accessory cable (model 3CWE481) to provide the
transition from the SMA connector on the access point to the N-type connector
on the antenna.
To ensure the physical safety of anyone near the antenna and to prevent damage
to the access point, follow the building codes for antenna installations in your area.
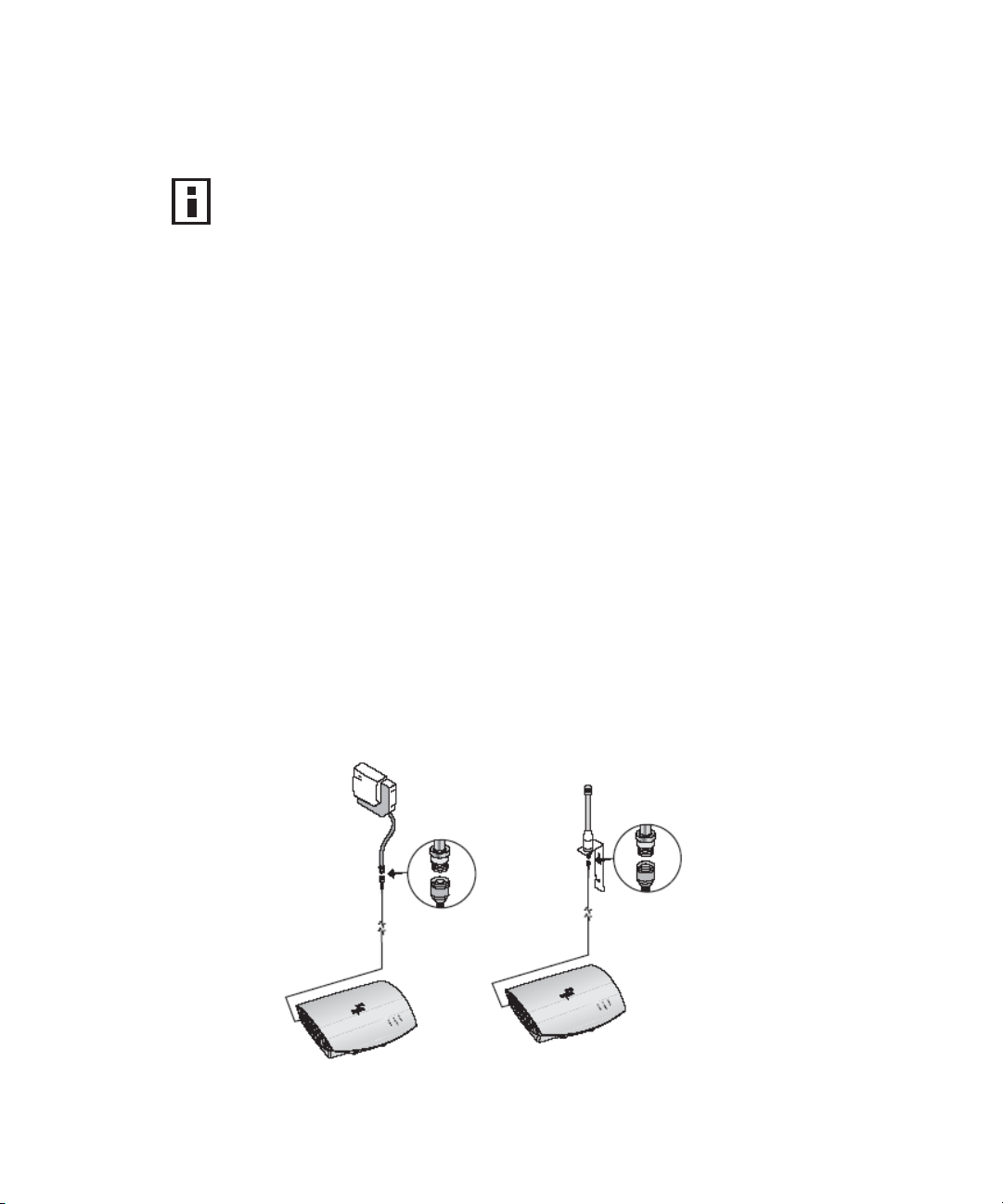
Antennas can be connected to either side of the access point after the standard
detachable antennas have been removed, as shown below.
21
Page 28

1 Position the antenna so that there are minimal obstacles between it and any
client with which it will communicate. While maintaining a direct line of sight
between the antenna and a client is not strictly necessary, such an
arrangement helps to ensure a strong signal. Ensure that access is available
for routing the antenna cable from the antenna to the access point.
2 If they are installed, remove both arms of the standard detachable antenna,
making sure not to handle the tips of the antenna.
3 Connect one end of the optional antenna cable to the antenna and secure
the antenna in place.
4 Connect the free end of the antenna cable to the right-hand side connection
on the access point, as shown in the illustration above.
5 Make certain that the antennas and antenna masts are appropriately
grounded to prevent injury or damage from lightning strikes. Proper
grounding for outdoor installations may require the purchase of a third-party
lightning arrestor.
POWER SETTINGS ON THE ACCESS POINT FOR EXTERNAL ANTENNAS
USA
2.5dBi
(3CWE492)
4dBi
(3CWE490,
3CWE497)
8dBi
(3CWE491,
3CWE498)
6 ft
(3CWE580)
20ft
(3CWE581)
50 ft
(3CWE582)
100% 100% 100%
100% 100% 100%
100% 100% 100%
22
Page 29
European Community
2.5dBi
(3CWE492)
4dBi
(3CWE490,
3CWE497)
8dBi
(3CWE491,
3CWE498)
13dBi
(3CWE495)
6 ft
(3CWE580)
20ft
(3CWE581)
50 ft
(3CWE582)
100% 100% 25% 12.5%
100% 100% 100% 25%
100% 100% 100% 100%
INSTALLING SOFTWARE UTILITIES
The installation CD includes documentation and software utilities to help you set
up and administer the wireless components of your network.
To view product documentation, select View the Documentation from the CD
Startup Menu and then select the item you wish to view.
The software Tools and Utilities include:
3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager. Use this tool to discover
access points and select devices for administrative changes.
3Com 3CDaemon Server Tool. This tool can act in four different capacities:
As a TFTP Server, necessary for firmware upgrades, and backup and restore
functions. Use this option if you do not have a TFTP server set up.
As a SysLog Server, which is necessary to view SysLog messages.
As an optional TFTP Client.
As an optional FTP Server.
3Com Network Supervisor. Click this link to download the 3Com Network
Supervisor (3NS). The 3Com 3NS graphically discovers, maps, and displays
network links and IP devices, including 3Com wireless access points. It is not
required for access point management.
3Com Site Survey Tool. This utility assists in selecting the best location for
your access point before installing the device permanently. Use the Site Survey
Tool to determine if the intended mounting locations will provide adequate
coverage with good signal strength and quality.
Internet Explorer. Click this link to download Internet Explorer.
23
Page 30

To install a tool from the CD:
1 Power up the computer and put the 3Com CD in the CD-ROM drive.
2 The setup menu should appear when the CD autostarts. If no menu appears,
you can run the setup.exe startup program from the Windows Start menu.
For example, if your CD drive is the D drive: Start / Run / d:setup.exe.
3 From the CD startup menu, select Tools and Utilities.
4 Select the item you want to install and follow the instructions on the screen.
24
Page 31
3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
The access point can be configured using a Web browser that has Java support
(Internet Explorer 5.0 or newer). Using the Web management interface, you can
configure the access point and view statistics to monitor network activity.
The 3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager helps you locate 3Com
wireless LAN devices on the network, select a device and view its properties, and
launch the device’s configuration interface in your Web browser. To configure a
device, the device manager must be installed on a computer that has an Ethernet
adapter and is running a supported Windows operating
browser.
USING THE 3COM WIRELESS DEVICE MANAGER
After the 3Com Wireless Device Manager is installed, ensure that the device to be
configured is either wired to the network, associating with the wireless network,
or connected directly to the computer, and connected to power. If more than one
device using the factory default name is connected, make a note of the
address of the device you want to select so that you can identify it in the
MAC
manager.
device
system and Web
LAUNCHING A WIRELESS DEVICE CONFIGURATION
If you do not have a DHCP server on your network, it can take up to one minute
for a device to become discoverable after it has been powered up.
1 To launch the 3Com Device Manager, select Start /Programs /3Com
Wireless/Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager.
If you have more than one network adapter installed on your computer, you
may be prompted to choose a network adapter. Choose the appropriate
adapter and click OK.
The Wireless Network Tree appears in the 3Com Wireless Infrastructure
Device Manager window.
25
Page 32

The tree lists all WLAN service areas on the network and expands to show the
3Com wireless LAN devices that are associated to each service area. Devices
in a different subnet than your computer are identified with exclamation
points (!). You can refresh this display by clicking Refresh. You should refresh
the display, for example, after you change a device IP address.
2 In the Wireless Network Tree, select the device you want to configure.
If more than one wireless LAN device appears in the tree, click Properties and
check the MAC address to verify that it is the one you want.
3 Click Configure.
If the selected device is on the same subnet as your computer, the
configuration management system main page appears in your Web
browser. (If a password is set on the device, enter it when prompted.)
If the selected device is on a different subnet, the Pre-IP Configuration
Wizard is activated automatically. This wizard lets you configure the IP
settings for the selected wireless device. It proposes IP address and subnet
mask settings derived from your computer’s settings, so the selected device
will then reside on the same subnet as your computer. You can accept the
suggested settings or change them as required. For more information, see
“Using the Pre-IP Configuration Wizard” on page 27.
The next window prompts for an administrative password to allow the new
address to be set. When the units are shipped from the factory, there is no
IP
administration password and you should leave the password field blank. If an
administration password has been set for the device, enter the password and
click Next. The 3Com Web Configuration Management System main screen
appears in your Web browser.
The following table describes the buttons in the 3Com Device Manager.
Button Description
Properties Displays the following for the selected device: Device Name, Device Type, Wireless
LAN Service Area (ESSID), IP Address, Subnet Mask, and MAC Address.
Configure Launches the configuration interface for the selected device. If the
selected device is on a different subnet, you are prompted to assign an
address on the same subnet as your computer.
Refresh
Choose NIC Allows you to choose which card you want to use.
Close Closes the device manager window and ends the session.
Help Launches the device manager help page in your browser.
Scans the network and displays the connected 3Com Wireless LAN
devices.
26
Page 33

USING THE PRE-IP CONFIGURATION WIZARD
You can only configure devices that are on the same subnet as your computer. To
configure a device on a different subnet, you must first assign it an IP address on
the same subnet as your computer. After you launch the configuration, you can
change settings as usual. Just before you finish, you must change the device IP
address back to its original setting. Follow this procedure:
1 In the Wireless Infrastructure Device Pre-IP Configuration window, accept the
suggested settings or change them as required. You can assign a static IP
address or specify that the device obtain its IP address from a DHCP server.
2 The next window prompts for an administrative password. When the units
are shipped from the factory, there is no administration password and you
should leave the password field blank. If an administration password has
been set for the device, enter the password and click Next. The Configuration
Management System main page appears in the Web
CONFIGURATION LOGIN
After you launch the configuration from the device manager, the login page
appears in your browser.
The default username is: admin
The default password is: no password
browser.
For an initial configuration, enter the default username and click LOGIN. Then set
the Country Code as described below.
SETTING THE COUNTRY CODE
The Country Code determines the available channels and transmission power
level based on regulatory restrictions in the country where the access point is
installed. The first time you log in, you must set the Country Code.
To ensure compliance with local regulations, be sure to select the country in
which the access point is installed.
In the Country Code page, select the country from the pull-down list and click
Apply. The configuration interface Home page appears.
27
Page 34

BASIC SETUP
For a basic configuration, use the Setup Wizard as described below.
At any time, you can click Home to return to the Home page of the configuration
interface. If you want to configure more advanced features, click Advanced Setup
in the Home page.
1 In the Home page, click Setup Wizard.
2 In the “1-2-3” Setup Wizard page, select a Virtual Access Point (VAP) you
want to set up, and then click Next to start basic configuration.
3 In the SSID page, enter the same Service Set ID as the other wireless devices in
your network and click Next. (The SSID may be up to 32 alphanumeric
characters and is case sensitive.)
4 In the Channel page, select the channel options for the access point radios
and click
Next. The channel options are:
802.11g—You can select from these options:
Turbo Mode—In some countries you can use Turbo Mode. If Turbo Mode
is not allowed in your country, this option is not available.
802.11g Radio Channel—Set the operating radio channel number.
Auto Channel Select—When this mode is enabled, the access point selects
a radio channel automatically.
5 In the TCP/IP Settings page, you can choose whether the access point obtains
its IP address from a DHCP server or uses a static IP address. Configure the
DHCP Client settings and click
Next.
6 In the Security page, make selections and click Next.
For details on security settings, see “Security” on page 54.
7 Click Finish.
8 Click OK to restart the access point.
28
Page 35

ADVANCED SETUP
The Advanced Setup pages allow you to configure features that are not available in the basic Setup Wizard. On the Home page, click Advanced Setup to open the Advanced Setup menu.
After making selections and entering data on each page, click Apply to save the
changes. The following sections describe the Advanced Setup pages.
IDENTIFICATION
On the Identification page, you can identify the access point by providing a
descriptive name. This name then appears in the device manager window. Enter a
maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters in the System Name field and click
TCP/IP SETTINGS
On the TCP/IP Settings page, you can configure TCP/IP (Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol) settings as described below. When you are finished
configuring items on this page, click Apply.
DHCP CLIENT
When DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Client is enabled, and a
DHCP server is located on the network, the network DHCP server assigns the IP
address, subnet mask and default gateway to the access
Apply.
point.
If there is no DHCP server on the network, the access point automatically uses its
default IP address, 169.254.2.1.
When DHCP Client is disabled, you can specify the IP setup as follows:
IP Address and Subnet Mask—If you configure an IP address and subnet
mask, you must configure the network settings of the computers on your
wireless LAN to use the same subnet mask. The IP addresses specified must be
valid on the same subnet.
Default Gateway—The default gateway address is optional, but may be
required by your Internet Service Provider.
Primary DNS Address and Secondary DNS Address—The Domain Name
Servers (DNS) map numerical IP addresses to the equivalent domain name (for
example, www.3Com.com). Your internet service provider should provide the
IP address of one or more domain name servers. Enter those addresses in
Primary DNS Address and Secondary DNS Address fields.
29
Page 36

WEB SERVERS
This option controls whether the web management interface is enabled. There
are two protocols available for web server connection:
HTTP—Sends data unencrypted over the network.
HTTPS—Uses Secure Socket Layer (SSL) technology to encrypt information
between the access point and the web browser.
By default, both protocols are enabled.
Note: To make a secure connection to the access point using HTTPS, you must
specify
configuration.
HTTP Server—Enable or disable the HTTP protocol, allowing connection to
the access point management interface using unencrypted HTTP.
HTTP Port—If HTTP Server is enabled, enter the HTTP port number. This
parameter determines the port number where the web server accepts HTTP
connections. The default is 80. If you enter a number other than 80, you must
also specify the port number in the browser window address pane (for
example,
1024 and 65535.
HTTPS Server—Enable or disable the HTTPS protocol, allowing connection to
the access point management interface using encrypted HTTPS.
HTTPS Port—If HTTPS Server is enabled, enter the HTTPS port number. This
parameter determines the port number where the web server accepts HTTPS
connections. The default is 443. If you enter a number other than 443, you
must also specify the port number in the browser window address pane (for
example, https://ipaddress:portnumber). This number can be set between
1024 and 65535.
https:// in the browser window address pane when launching the
http://ipaddress:portnumber). This number can be set between
SMART MONITOR
When Smart Monitor is enabled, the access point actively monitors its Ethernet
link to determine if it can provide network service to wireless clients.
If the Ethernet link is down (for example, the cable is unplugged), the access point
shuts down all radios and denies any wireless connections until the Ethernet link
is re-established.
Optionally, the access point may be configured to PING a target on the network
to validate the Ethernet link.
30
Page 37

RADIUS
Disable—The access point does not monitor the wired network, and
therefore, the radio interface does not shut down due to a broken Ethernet
link. This is the default setting.
Enable—The access point monitors the Ethernet link and shuts down radios if
the link is broken.
Host PING Enable—When enabled, the access point periodically PINGs a
target host on the network to determine the status of the Ethernet link. IP
settings must be configured correctly for the PING to work. When disabled,
only the physical Ethernet link is checked.
Target IP Address—Enter the IP address of the reference check target. The
target must be on the Ethernet network and may not be a wireless station.
PING Interval—Enter the time interval (in milliseconds) between PINGs to the
reference target, if enabled.
Number of retries—This is the number of failed PINGs to the reference target
that the access point will accept before if shuts down the radios.
The RADIUS page lets you define servers to be used for authentication and
accounting.
RADIUS (Remote Access Dial-In User Service) is a login authentication protocol
that uses software running on a central AAA (Access, Authentication, and
Accounting) server to control access to RADIUS-compliant devices on the
network. There are no special settings on the access point to distinguish between
the various RADIUS policies or authentication types (for example EAP-MD5,
EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS). These policies are setup and controlled on the AAA server.
Note that for most RADIUS software packages, the access point is actually called
the “RADIUS client” and has a shared secret or secret key corresponding to the
RADIUS setup page (see KEY parameter below).
The access point can send connection parameters to a RADIUS server, as well as
statistics for accounting purposes. The access point is compatible with RFC2866
(the RADIUS Accounting specification).
Configuring a secondary RADIUS server provides a backup in case the primary
server fails. The access point uses the secondary server if a failure is detected in
the primary server. Once the access point switches over to the secondary
authentication server, it periodically attempts to establish communication again
with the primary authentication server. Once communication is established, the
secondary authentication server reverts back to a backup server.
31
Page 38

The access point uses the secondary accounting server if a failure is detected in
the primary accounting server. It continues to use the secondary accounting
server until it fails, in which case it returns to sending data to the primary
accounting server.
In the RADIUS Authentication section, enter the required parameters for a
primary and secondary RADIUS authentication server. When you are finished
configuring items, click Apply.
The RADIUS Authentication parameters are described below.
IP Address—The address of the server.
Port—The network (UDP) port of the server used for messages. The port
defaults to 1812 (1813 for RADIUS Accounting) and must match the port
configured on the RADIUS server.
Key—The encryption key is a shared ASCII string that is used to authenticate
logon access for the client. The maximum length is 255 characters. Do not use
blank spaces in the string. The key must be configured the same on both the
access point and the RADIUS server. The Authentication and Accounting
RADIUS servers can have different secret keys.
Timeout—The number of seconds the access point waits for a reply from the
RADIUS server before it resends the request.
Retransmit attempts—The number of times the access point will try to
authenticate logon access.
RADIUS Servers Assign Client VLAN ID in—Select the VLAN ID format that
matches your RADIUS server VLAN ID format.
In the RADIUS Accounting section, click the Enable radio button, then enter
required parameters for a primary and secondary RADIUS accounting server.
When you are finished configuring items, click Apply.
RADIUS Accounting Update Interval—This is the interval in seconds
between accounting updates sent to the RADIUS accounting server
Accounting Log Options—This option controls which clients generate
.
accounting logs. If set to RADIUS Authenticated Clients Only, only those
clients that successfully complete 802.1x Authentication will generate
accounting logs. The default is for all authenticated clients to generate
accounting logs.
32
Page 39

AUTHENTICATION
The Authentication page allows you to configure the type of upper-layer
authentication the access point uses for wireless clients. This authentication setup
is applicable for both radio interfaces. Access is checked against the MAC
Address authentication database stored on the access point.
NOTE: This level of authentication occurs BEFORE any 802.1x authentication
configured on the Security page. When using Local and RADIUS MAC
Authentication, clients attempting to authenticate to the access point MUST pass
these settings before any subsequent 802.1x authentication is attempted and
verified. If no MAC address filtering is desired, leave this set to the default setting
of Disable.
Configure the options as described below. When you are finished, click Apply.
MAC Authentication— Selecting MAC authentication allows you to define
access permission and
Local MAC— With this option, the MAC address of the associating station
is compared against the local access control list. You must build this list
(called the MAC Authentication Table) as described in
Authentication below. Use this option if you want to restrict wireless clients
authentication to the access point based off their MAC address.
RADIUS MAC— With this option, the MAC address of the associating
station is sent to the configured RADIUS server for validation. You must
specify the authentication sequence and the corresponding parameters for
the remote authentication protocol. See
“802.1x Wireless Setup” below.
Disable— No MAC address related checks are performed on a client
requesting authentication to the access point.
802.1x Wireless Setup—802.1x is designed to enhance the security
management of the wireless network. Select one of the following options:
Disable— The access point will neither initiate nor respond to any 802.1x
authentication requests to or from wireless clients.
Supported — Legacy clients (non 802.1x) and 802.1x clients are both
supported. This is provided for ease of migration. This option works with
WPA key management set to either “WPA authentication over 802.1x” or
“WPA pre-shared key (PSK)” on the radio security page.
precedence. Options are:
Local MAC
“RADIUS” on page 31 and
33
Page 40
Required — Clients authenticate to a RADIUS server via the access point.
Clients are not allowed onto the wired LAN until authentication is
successful. If two Radios are installed and WPA is being used, both radios’
security must be set to “WPA authentication over 802.1x” for the WPA key
management when 802.1x is Required. If one radio’s security is set to
“WPA pre-shared key (PSK)” for WPA key management and the other is
“WPA authentication over 802.1x”, then the 802.1x Wireless Setup must
be set to “Supported” instead.
When 802.1x is enabled, the broadcast and session key rotation intervals can
also be configured. Set these values to force the periodic refresh of broadcast
or session keys for each 802.1x client.
First set up the RADIUS authentication for the client on the RADIUS
authentication server. (See
“RADIUS” on page 31.) Select Supported or
Required on the 802.1x Wireless Setup field above. Enter data as described in
the following table.
Field Default Description
Broadcast Key Refresh
Rate
Session Key Refresh Rate
802.1x Reauthentication
Refresh Rate
0
(minutes)
0
(minutes)
0
(seconds)
Defines how long the RADIUS server will
refresh the primary broadcast key.
Defines how long the RADIUS server will
dynamically re-assign a session key to a
connected client station.
Defines the time interval in which the Access
Point forces a Reauthentication and
subsequently re-issues a new session key.
802.1x Supplicant Setup
802.1x Supplicant provides the access point with the ability to authenticate
itself to an 802.1x-enabled switch port. In an environment where network
access is controlled via 802.1x, the supplicant makes it possible for the access
point to connect to the wired network. The access point assumes the 802.1x
authenticator role (if configured properly) after the supplicant has completed.
The supplicant authentication method supported is EAP-MD5.
Enable—Select Enable to start the supplicant authentication process. The
supplicant retries the authentication process until it has been successfully
authenticated.
Username—Enter a username to be used for EAP-MD5 authentication.
Password—Enter a password to be used for EAP-MD5 authentication.
Confirm Password—Re-enter the password for EAP-MD5 authentication.
34
Page 41

Local MAC Authentication—Client computers can be filtered using the
unique MAC addresses of their network cards.
To build the MAC Authentication Table, enter a MAC address in the space
provided, choose the permission, and click Update.
MAC addresses are listed in the MAC Authentication Table in the order that
they were entered. The Local MAC Authentication parameters are described in
the following table:
Parameter Description
System Default Define the default filtering setting as Deny or Allow.
MAC Address
Permission
Update button
Enter the MAC address of a client for the access control.
You can find the MAC address of a network card as follows:
Windows 95/98/ME—Click Start/Run. Type winipcfg and press
Enter. The MAC address is in the Adapter Address
Windows NT4/2000/XP—At the command prompt, type
ipconfig /all and press Enter. The MAC address is listed as
the Physical Address.
Linux—Run the command “/sbin/ipconfig.” The card’s
MAC address is the value after the word “HWaddr.”
Allows or denies access to the access point of devices
matching the specified MAC address.
Click Update to refresh the MAC Authentication Table. To
avoid the possibility of entering an invalid MAC address on
the Authentication page, always click Update after typing
the address. If you press Enter, address error checking does
occur.
not
section.
35
Page 42

FILTER CONTROL
The Filter Control page allows you to control client communication within the
wireless network. You may enable one or more types of supported filtering;
however, some filter choices may supersede others. Configure the options as
described below. When you are finished, click Apply.
FILTERING BY VLAN
The access point supports filtering of up to 64 VLANs (virtual local area networks).
VLAN IDs must be configured for each client on one of the RADIUS
authentication servers specified on the RADIUS configuration page. If a RADIUS
server is not being used or not setup to update the VLAN ID, then the access
point will tag all ethernet packets with the Native VLAN ID (defaulted to 1).
If a RADIUS authentication server will be used to create/modify the VLAN ID, the
following attributes must be provisioned on the RADIUS Server to be passed back
to the authenticating client:
The AP’s IP address is the RADIUS Client/Radius User
Tunnel_type (64) = VLAN (13)
Tunnel_Medium_type (65) = 802
Tunnel_Private_group_ID (81) = VLAN ID specified in Hexadecimal format.
VLAN Switch ports must be tagged ports that match the VLAN ID on the Access
Point. Associated client VLAN IDs will appear in the Syslog file in ASCII Decimal
format.
When VLAN filtering is enabled, the access point queries the server for the
IDs of associating clients and saves the VLAN IDs. If a client does not have a
VLAN
ID, the access point assigns its own native VLAN ID to that client.
VLAN
ENABLING VLAN FILTERING
To enable VLAN filtering, enter a VLAN ID (a number between 1 and 4095) in the
Management VLAN ID field and select VLAN Enable.
When VLAN filtering is disabled, the access point ignores VLAN-tagged frames.
36
Page 43

SECURITY FILTERS
These options allow you to block communication among wireless clients
(client-to-client blocking) and prevent wireless clients from performing access
point administration.
Ethernet Broadcast Storm Control—This option allows users to limit
broadcast/multicast traffic coming from the Ethernet network. This feature
allows wireless clients to communicate properly under a heavy broadcast
environment.
When enabled, the access point discards broadcast/multicast packets if the
broadcast rate exceeds 180 packets per second or 30KB of data per second.
Additionally, any single source of broadcast/multicast transmissions is limited
to five packets per second or 8KB of data per second.
Ethernet broadcast storm control improves wireless performance on networks
that have high broadcast data rates. However, if the network requires high
broadcast/multicast data rate transmissions (for example, a media streaming
server) this feature should be disabled.
Local Bridge Filter—Enable this filter to prevent direct communication
between wireless clients, creating a more secure wireless
AP Management Filter—Enable this filter to prevent wireless clients from
accessing the access point for management; for example through TELNET or
SNMP.
network.
CLIENT LIST TIMEOUT
This option sets the timeout for inactive clients to be disassociated and removed
from the associated client list. The interval can be set to 1, 5, 10, 30 or 60
minutes (default is 30 minutes).
UPLINK PORT MAC ADDRESS FILTERING
This feature allows associated wireless clients to communicate only with specific
selected MAC addresses on a sub net. By only allowing clients to communicate
with a few specific servers such as DHCP server, a Gateway, or a local web server,
clients are blocked from communicating with other clients on the local sub net,
but are still allowed (via the gateway) to communicate with severs on the
Internet.
Note: In most cases client to client blocking should also be enabled as the
Uplink
Filter only works on packets coming into the AP from its Ethernet (uplink)
port.
37
Page 44

For security reasons it is desirable to block client to client communications for
wireless clients associated with an access point (AP). It is also desirable to block
client to client communications between clients associated with different AP’s on
the local sub net. For instance an airport may have several AP’s to service several
"hot spots" within the airport. However the client to client blocking feature of
the AP will only block communications to other clients associated with the same
AP. And will not block client to client of another AP communications. By using
the Uplink Filtering function of the AP communications to all other clients of all
other AP’s on the same sub net can be blocked.
It is important to note that this feature only works if all the AP’s are on the same
sub net. If an AP is located on the far side of the gateway (i.e. on a different sub
net) its clients will NOT be blocked from communicating with clients on the local
sub net of interest.
This feature is accessed on the Filter Page of the user interface. Click Enabled next
to the Uplink Port MAC Address Filtering link and add up to eight MAC addresses
that WILL be allowed to communicate with clients of the AP. Make sure to
include the MAC of the local DHCP server, if it not the same as the gateway as
well as and redirect gateways and other servers that should be allowed to
communicate with the AP’s wireless clients. Make sure to click on the save button
on both the Uplink Filter List page as well as the Filter page to activate the
function.
FILTERING BY ETHERNET PROTOCOL TYPE
Use the Ethernet Type Filter table to filter out Ethernet packet frames that match
the Ethernet protocol type. Select Ethernet Type Filter Enable, then set the status
of each Ethernet frame type in the list.
38
Page 45

SNMP
Use the SNMP page to display and enter a community string for the Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP). To communicate with the access point,
the SNMP agent must first be enabled and the Network Management Station
must submit a valid community string for authentication.
You can set up to four trap destinations, each configurable with the IP address
and community string of the trap manager. Additionally, you can enable trap
notification on a per-user basis. An SNMP filter can be defined on a subtree of the
MIB, and then the filter can be applied to selected SNMP users (also called an
SNMP target). The SNMP target includes the trap notification IP address, port
number, SNMP user name, and the filter to be applied.
Select Enable next to SNMP and enter data into the fields as described below.
When you are finished, click Apply.
Location—Specifies the access point location.
Contact—Sets the system location string that describes the system location.
(Maximum
Community Name (Read Only)—Specifies a community string with
length: 255 characters)
read-only access. Authorized management stations are able to retrieve MIB
objects. (Maximum length: 23 characters)
Community Name (Read/Write)—Specifies a community string with
read-write access. Authorized management stations are able to both retrieve
and modify MIB objects. (Maximum length: 23 characters)
Engine ID—Specifies the name for the local or remote SNMP engine.
Trap Destination
Trap Destination 1—Select Enable to set up a trap manager to receive these
messages.
IP Address—Fill in the IP address box for the trap manager that will receive
these messages.
Community Name—Fill in the community string box for the trap manager
that will receive these messages. (Maximum length: 23
Trap Destination 2—Select Enable to set up a second trap manager to
receive these messages.
IP Address—Fill in the IP address box for the second trap manager that will
receive these messages.
Community Name—Fill in the community string box for the second trap
manager that will receive these messages. (Maximum length: 23
39
characters)
characters)
Page 46

Trap Destination 3—Select Enable to set up a third trap manager to receive
these messages.
IP Address—Fill in the IP address box for the third trap manager that will
receive these messages.
Community Name—Fill in the community string box for the third trap
manager that will receive these messages. (Maximum length: 23
Trap Destination 4—Select Enable to set up a fourth trap manager to receive
characters)
these messages.
IP Address—Fill in the IP address box for the fourth trap manager that will
receive these messages.
Community Name—Fill in the community string box for the third trap
manager that will receive these messages. (Maximum length: 23
characters)
TRAP CONFIGURATION
Select the types of traps you want the access point to generate.
Trap Description (When the Trap is Sent)
sysSystemUp Sent when the access point is fully up and running.
sysSystemDown Sent before the access point is about to reboot.
sysRadiusServerChanged Sent when the RADIUS server has changed from
Primary to Secondary, or Secondary to Primary.
dot11StationAssociation Sent when a station successfully associates with the
access point. The trap also includes the MAC
address of the station that has associated.
dot11StationReAssociation Sent when a station successfully reassociates with
the access point. The trap also includes the MAC
address of the station that has associated.
dot11StationAuthentication Sent when a station successfully authenticates with
the access point. The trap also includes the MAC
address of the station that has associated.
dot11StationRequestFail Sent when a station fails to associate, reassociate, or
authenticate with the access point. The trap also
includes the MAC address of the station and the
reason code for the failure.
dot1xAuthFail Sent when a station fails to authenticate with the
RADIUS server. The trap also includes the MAC
address of the station that failed to authenticate.
dot1InterfaceAGFail Sent when the 802.11g wireless interface fails.
40
Page 47

Trap Description (When the Trap is Sent)
dot1xMacAddrAuthSuccess Sent when a station successfully authenticates the
MAC address with the RADIUS server. The trap also
includes the MAC address of the station that has
authenticated.
dot1xMacAddrAuthFail Sent when a station fails to authenticate the MAC
address with the RADIUS server. The trap also
includes the MAC address of the station that failed
to authenticate.
dot1xAuthNotInitiated Sent when a station did not initiate 802.1x
authentication with the RADIUS server. The trap
also includes the MAC address of the station that
failed to authenticate.
dot1xAuthSuccess Sent when a station successfully authenticates with
the RADIUS server. The trap also includes the MAC
address of the station that has authenticated.
localMacAddrAuthSuccess Sent when a station successfully authenticates the
MAC address with the database stored locally
within the access point. The trap also includes the
MAC address of the station that has authenticated.
localMacAddrAuthFail Sent when a station fails to authenticate the MAC
address with the database s stored locally within the
access point. The trap also includes the MAC
address of the station that failed to authenticate.
sntpServerFail Sent when the access point fails to get time from
the configured SNTP server.
SNMP USERS
Security configuration is accomplished by managing groups and users. There are
three default groups that correspond to three available security levels:
Default Groups
RO (read-only) group
RW Auth (read-write) group
RWPriv (read-write) group
Default Security Levels
NoAuthNoPriv (no authentication no privacy)
AuthNoPriv (authentication, but no privacy)
AuthPriv (both authentication and privacy)
41
Page 48

Users can be created and placed into a group. There are two parameters to
configure: authentication and privacy. The selected authentication and privacy
policy must match the group security level. For example, if an SNMP user is
configured for MD5 authentication and its group does not allow authentication,
an error message appears.
Duplicate user names or group names is not allowed.
User—Specifies the SNMP v3 security name. The security name represents the
user in a format that is Security Model-independent.
Group—Specifies the name of the group to which the SNMP v3 user is
associated. Assigning users to different groups allows the users to have
different access rights.
Auth Type—The SNMP v3 authentication protocol.
Passphrase—The SNMP v3 authentication password.
Priv Type—The SNMP v3 privacy protocol.
Passphrase—The SNMP v3 privacy password.
Action—Click Add to add the SNMP v3 user; click Delete to remove the
SNMP
v3 user.
GROUPS
GroupName—Enter a name for the group.
SecurityLevel—Select a security level:
noAuthNoPriv—The group does not use authentication protocol and
privacy protocol.
authNoPriv—The group is using authentication protocol, but is not using
privacy protocol.
authPriv—The group is using authentication protocol and privacy protocol.
Write View—Assigns write-access to users of this group.
Action—Click Add to add the group; click Delete to remove the group.
Group List—A list of the available groups that the SNMP v3 users can be
assigned to.
42
Page 49

SNMP TARGETS
This table is used to select the management targets for receiving notifications, as
well as the type of notifications that should be sent.
Target ID—The name that identifies the target.
IP Address—The IP address of the target.
UDP port—The UDP port number of the target.
SNMP user—The SNMP user for the target.
Filter ID—Assign a filter ID from the Filter List to the target.
Action—Click Add to add an entry; click Delete to remove an entry.
SNMP FILTER
This table is used to set filter profiles. Filter profiles are used to determine if
particular management targets should receive certain notifications.
Filter ID—The name used to identify the filter.
Filter Type—Indicates whether or not the family of filter subtrees that are
defined by this entry are included in or excluded from a filter.
Subtree—The MIB subtree that defines a family of subtrees which are
included in or excluded from the filter profile.
Action—Click Add to add an entry; click Delete to remove an entry.
43
Page 50
ADMINISTRATION
The Administration page allows you to perform access point management tasks
as described below.
Change Password—A password is required to configure the access point.
Enter the user name and new password in the spaces provided and click
Apply. It is recommended that you change the password from the default
value (no password) to ensure network security.
Telnet and SSH Settings—This option controls whether the console
management interface is enabled. There are two protocols available for
console connection:
Te ln e t—Sends data unencrypted over the network.
SSH—Secures the connection by encrypting the information between the
access point and the user’s computer.
Both options are enabled by default.
Note: SSH connections may appear to be disabled after booting up the access
point from a factory configuration for the first time. This is because the access
point is generating a random key for use with SSH authentication. Wait a few
minutes before trying to make SSH connections.
Telnet Server Enable—Enabling this option allows connection to the access
point management interface using unencrypted Telnet.
SSH Server Enable—Enabling this option allows connection to the access
point management interface using encrypted SSH.
SSH Port Number—This parameter determines the port number where
the access point accepts SSH connections. The default port number is 22.
Enter a value between 1024 and 65535.
Firmware Upgrade—You can upgrade firmware from a remote FTP or TFTP
server. Select FTP or TFTP. Enter the firmware file name, the host IP address
where the file is stored, the user name, and the password. Click Start Upgrade
to start the upgrade
Backup and Restore Configurations—Access point configurations can be
saved as data files and later used to restore the access point configuration. This
option lets you save access point settings in an external file or copy them from
an external file to the access point. You can save an entire configuration for use
as a backup to a single access point, or you can save a basic configuration,
which can then be used in common by several access points in a network,
providing an easy way to reconfigure all access points in a
You must have a TFTP server set up on which to store the backup files.
process.
network.
44
Page 51

To back up a configuration — Type the IP address of the TFTP server and a
name for the backup file in the spaces
provided. Click Basic (to save a partial
configuration) or Complete (to save an entire configuration) and click
Backup
Configuration.
To restore a configuration — Type the IP address of the TFTP server and the
name of the backup file in the spaces provided and click Restore
Configuration.
Restoring a configuration causes the access point to reset. If the file being
restored was saved as a Basic configuration, only general configuration
parameters such as SSID, country code, radio settings, security settings, RADIUS
server settings, and management setup information are restored.
Parameters that are unique to individual access points, such as device names, IP
addresses, and administration passwords, are neither affected nor
overwritten.
Note: Before restoring a configuration, you can view a description of the
restoration point by clicking the Restore User Comment button. Comments made
at the point the backup was created will appear in the “User Comments” field.
This feature allows the user to select the correct restoration point.
To restore comments — Click the Restore Comments button to view
comments saved on previous backups.
Restore Factory Settings—Click Restore to load the factory default
configuration and reboot the access point. All user-configured information is
lost. You must reenter the default user name (admin) to regain management
access to this device.
Reset Access Point—Click Reset to perform a hardware reset of the
point. Current configuration settings are not changed.
access
WDS/STP SETTINGS
The WDS/STP Settings page allows you to configure a Wireless Distribution
System (WDS) link to connect 3Com access points.
WDS provides a flexible way to extend a wireless network. A Distribution System
(DS) is a network (typically a wired network) that interconnects separate access
points into a single LAN. With WDS, the interconnection no longer needs to be a
wired medium. WDS uses the wireless medium to interconnect separate
A WDS link can be a simple, point-to-point link, a complex point-to-multipoint
link, or a multilayer topology. See the WDS Bridging and Antenna Installation
Guide that came with the access point for more details.
45
Page 52

CONFIGURATION GUIDELINES
Before configuring the WDS settings, review the following guidelines:
Only VAP1 in each radio interface can be specified to set up the WDS link.
(There are two Virtual Access Points (VAPs) for each radio interface on the
access point—VAP1 and VAP2. VAP1 is designated as the physical access
point, and therefore, can be the only VAP specified to set up the WDS link.)
The WDS link can be set up between 3Com access points only.
The pair of access points to be configured with a WDS link must have the
same radio channel and SSID.
RADIO BRIDGE ROLES
For each radio interface, there are three WDS roles to select from:
AP—The access point behaves as a regular access point, which forwards data
between the wireless clients and the wired network.
Bridge—The access point behaves as a wireless bridge. The access point must
have a bridge parent to which it forwards data to the Distribution System. The
access point can also have bridge children, for which it acts as the bridge
parent and helps to send data to the DS.
Root-Bridge—The access point behaves as the “parent” of all connected
WDS access points. The Root-Bridge has no bridge parents. Its Ethernet port is
connected to the backbone of the wired LAN.
Note: A Root-Bridge can have a maximum of six child bridges assigned to it. A
bridge can have a maximum of five child bridges assigned to it.
child
BRIDGE ADDRESS ENTRY
When operating in AP mode, bridge address entries are not available.
When operating in Bridge mode, the access point must be connected to a
Root-Bridge and, optionally, to a maximum of five child bridges.
When operating in Root-Bridge mode, the access point can connect to a
maximum of six child bridges, with no bridge parent.
Bridge Parent—Enter the MAC address of the bridge parent. The bridge
parent must have the current access point configured as a child bridge. The
MAC address can be in either
ffffffffffff format.
ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff, or
46
Page 53

Bridge Child—Enter the MAC address of the bridge child. The bridge child
must have the current access point configured as the bridge parent. The MAC
address can be in either
ffffffffffff format. Leave this field blank or enter 00-00-00-00-00-00 if
ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff, or
there are no bridge children to configure.
SCANNING FOR WDS LINKS
For easier configuration of the WDS bridge entry, you can use the RSSI Monitor to
locate nearby WDS bridges and their MAC addresses.
1 Click Scan for WDS Links to start the RSSI Monitor. When the RSSI Monitor
appears, a list of nearby WDS bridges is displayed.
2 Select the bridge entry you want to configure from the list on the left, and a
corresponding station from the list on the right.
3 Click Copy to WDS Configuration to copy the BSSID of the selected station to
the WDS configuration window.
4 Return to the WDS Settings page and click Apply to save the changes.
Note: Only nearby 3Com Access Points models 7250, 8250, 8500, 8700, or 8750
that are running firmware versions 3.0 or later appear in the station list.
Additionally, the nearby access point must be in Bridge or Root-Bridge mode.
CONFIGURING SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL SETTINGS
Spanning Tree Protocol allows the access point to determine the most efficient
path to forward data. It also allows network administrators to set up redundancy
in the network while avoiding problems associated with network loops. This is
primarily useful in a WDS environment.
Configure all parameters within the value ranges displayed.
Bridge—Select Enable to turn on the STP feature.
Dynamic Entry Age-time (1-10000 sec.)—Enter a value, in seconds, to
determine the lifetime of a dynamically learned entry in the address table.
Bridge Priority (1-65535)—Enter a value to determine the priority value of
the bridge, which is used for STP Root Bridge election. Lower values represent
higher priority. When there are two or more bridges with the same priority,
their MAC addresses are used to elect the Root Bridge.
Bridge Max Age (6-40 sec.)—Enter a value to determine how long the access
point retains STP topology information.
47
Page 54

SYSTEM LOG
Bridge Hello Time (1-10 sec.)—Enter a value to determine how often the
access point broadcasts the hello message.
Bridge Forwarding Delay (4-30 sec.)—Enter a value to determine how long
the access point remains in listening and learning states before its ports enter
the forwarding state.
Link Configuration
There are two parameters for the Ethernet link and each WDS link:
Link Path Cost (1-65535)—Enter a value to determine the cost of forwarding
data through this link. Higher cost means the link is less efficient.
Link Port Priority (0-255)—Enter a value to determine the preferred link to
forward data when a network loop is detected. Lower values mean higher priority.
The System Log page allows you to set up a server to store event logs and to
specify how the access point obtains the date and time. When you are finished
configuring items on this page, click Apply.
Each logging message is tagged with a severity level, as defined in RFC3164. The
severity levels are:
Emergency: system is unusable
Alert: action must be taken immediately
Critical: critical conditions
Error: error conditions
Warning: warning conditions
Notice: normal but significant condition
Informational: informational messages
Debug: debug-level messages
To set up a server for event logs: Select System Log Setup Enable, select a
logging severity level from the pulldown list, enable the Logging Host and
Logging Console, and enter the IP address of the server in the space provided.
To designate an SNTP server for obtaining the date and time: Select SNTP
Server Enable and enter the IP addresses for primary and secondary SNTP servers
in the spaces provided.
48
Page 55

STATUS
To use the access point as an SNTP server: Select SNTP Server Disable, specify
time values in the spaces provided, select the time zone from the pull-down list. If
you select Enable Daylight Saving, the time adjusts automatically for standard and
daylight savings time. When the SNTP Server setting is disabled, date and time
settings revert to the defaults after an access point is reset, affecting the accuracy
of log reports. To avoid this situation, enable the SNTP server setting and allow
the access point to obtain the date and time from an
SNTP server. (The event log
page displays the default time after a reset until the access point receives the
correct information from the SNTP server.)
The Status pages display additional information about the access point status and
station status. View the information as described below. To return to the
Advanced Setup page, click Advanced Setup in the left pane.
AP Status—Click AP Status to view the access point system configuration,
wireless configuration, and Virtual Access Point configuration.
Stations Status—Click Stations Status to view the configurations of
connected stations. The Station Status page displays basic connection
information for all associated stations. Select “refresh” on you browser to see
update station status.
Event Logs—Click Event Logs to display the activity log of the access point.
The event log resets to zero if the access point is reset. The log saves 128
events, then overwrites the first event and continues.
RSSI Monitor—Click RSSI Monitor to search for and display parameters for
each nearby access point within the radio’s operating range. The access point
reports back any nearby wireless LAN signal that it finds.
For each nearby station, eight parameters are displayed:
SSID—The Service Set ID being broadcast by the station.
Encryption—Identifies if this station uses encryption to transmit data.
RSSI Indicator—A graphical representation of the signal strength, with
five levels of lengths and three shades of colors:
- Red indicates a low signal (below 20%)
- Yellow indicates a medium signal (20% to 60%)
- Blue represents a high signal (60% to 100%)
RSSI Value—The numerical percentage value of the signal strength.
Higher percentage means a stronger signal.
Operation Mode—Displays the type of radio mode the station is
operating in (11a, 11g, turbo a, turbo g).
49
Page 56

Channel—Displays the radio channel that the station is using.
BSSID—The Basic Service Set Identifier of the station. This is the MAC
address of the broadcasting radio.
STA Role—Describes the role of a nearby 3Com access point (model 7250,
8250, 8500, 8700, or 8750) if the access point is running firmware version
3.0 or later. Possible roles are:
-AP: This station is a physical interface (VAP1) of a 3Com access point and
is not acting as a WDS bridge.
-VAP: This station is a virtual interface (VAP2) of a 3Com access point and
is not acting as a WDS bridge.
-Bridge: This station is acting as a WDS bridge.
-Root Bridge: This station is acting as a WDS Root-Bridge.
RADIO INTERFACE
The access point radio interface detects the number of radios installed and their
type (802.11g Radio or 802.11b
for the radio interface are described in the following sections.
RADIO SETTINGS
The Radio Settings page allows you to setup standard settings for each radio. It
also allows you to enable Virtual Access Point (VAP) service, and configure the
VAP settings.
Radio). The Radio Settings and Security options
VIRTUAL ACCESS POINT (VAP) CONFIGURATION
This feature allows a single access point to behave as two virtual access points.
Each of these two virtual access points can form a wireless network with its own
service parameters.
ENABLING VIRTUAL ACCESS POINT (VAP)
Two Virtual Access Points per radio are available. Each VAP has its own security
settings. Additionally, the first VAP (VAP1) on each radio may be configured as
an:
Access Point
Root Bridge
Child Bridge
50
Page 57

To enable VAP service:
1 Open the Radio Settings page for the Radio Interface you want to configure.
2 Click Enabled next to VAP1 to enable a single VAP.
3 Click Enabled next to VAP2 to enable a second VAP.
Note: Enabling this option turns on the Virtual Access Point. VAP 1 must be
enable to enable VAP2. A disabled VAP does not accept any wireless connection.
4 Configure the following information for each VAP:
SSID—Enter the Service Set ID (up to 32 alphanumeric characters). Clients
must set their SSIDs to match the access point. The SSID is case sensitive.
The two VAPs must not have the same SSID.
VLAN ID—Enter the VLAN ID number for this VLAN. This parameter
determines what VLAN a client is placed in when the client attaches to this
SSID. This field must not be left blank. Integer values between 1 and 4095
are accepted. If VLAN is not enabled, it is recommended to use 1. VLAN
must be enabled on the access point from the Filter Control page before
this setting takes effect; otherwise, this value is ignored.
Note: If clients have VLAN IDs assigned by a RADIUS server, the
RADIUS-assigned VLAN ID takes precedence over the VLAN ID configured
here.
Closed System— Enabling this option prevents publicly broadcasting the
SSID.
Maximum Associations—Setting this option limits the number of
wireless stations that can associate to the SSID. Integer values between 1
and 64 are accepted.
Authentication Timeout Interval—This parameter determines the time
interval (in minutes) before an authenticated station is removed if it never
succeeds in association. Enter a time interval between 5 and 60.
Association Timeout Interval—This parameter determines the time
interval (in minutes) before an associated station is removed if it has been
inactive. Enter a time interval between 5 and 60.
5 Configure the radio settings for the VAP(s), following the instructions in the
next section,
“Changing Radio Settings”.
51
Page 58

CHANGING RADIO SETTINGS
To change radio settings on a VAP, select a VAP from the list to display its current
configuration.
When you are finished configuring items on this page, click Apply.
Country Code—Displays the country where this access point is installed and
running.
Description—Enter a description for this access point.
Turbo Mode (802.11g and 802.11a only)—Turbo Mode is an enhanced
wireless LAN operating mode that can provide a higher data rate.
In normal mode the channel bandwidth is 20 MHz. In Turbo Mode the
channel bandwidth is increased to 40 MHz. However, only a limited number
of channels are available when Turbo Mode is enabled.
Auto Channel Select (802.11g only)—Select Auto Channel Select Enable to
allow the access point to select a radio channel automatically.
Radio Channel—From the pull-down list, select the radio channel over which
the access point communicates to computers in its BSS. Available channel
settings are limited by local regulations that determine which channels are
allowed. The client channel for wireless users is automatically set to that used
by the access point to which they are linked.
When multiple access points are deployed in the same area, be sure to choose
channels separated by at least five channels to avoid channel interference. You
can deploy up to three access points in the same area; for example, Ch1, Ch6,
and Ch11.
Output Antenna—Select the antenna to use on the access point. The
point has two antenna connectors for each radio. For the 802.11g
access
radio, the A
the LEDs.
Transmission Power (802.11g only)—Set the signal strength transmitted
from the access point. The longer the transmission distance, the higher the
transmission power required. (Default: 100%)
Maximum Transmit Data Rate—Select the appropriate data rate from the
drop-down list for the data transfer speed running on your network. (802.11b
default: 11 Mbps.) In order to reach all clients, this rate should be set lower
(for example, 1 or 2 Mbps on an 802.11b radio). To isolate clients that are
unable to connect at higher rates, set this value higher.
antenna is near the Ethernet connector and the B antenna is near
52
Page 59

Maximum Multicast Data Rate—Select the appropriate maximum
broadcast/multicast data rate for your network. Setting a low multicast data
rate helps to ensure that data can reach all client stations. Setting a high data
rate can improve performance for high-bandwidth multicast applications (for
example, multimedia streaming service).
Beacon Interval (20-1000)—Sets the beacon signal interval at which beacon
frames are transmitted from the access point. The beacon signals allow
wireless devices to maintain contact with each other. They may also carry
power-management information. The Beacon Interval unit is TU, which
corresponds to 1024 microseconds. (Default: 100 TU)
Data Beacon Rate (DTIM) (1-255)—Determines how often the beacon
signal contains a delivery traffic indication message(DTIM). This tells client
devices that are in power-saving mode that a packet is waiting for them.
Fragment Length (256-2346) (802.11g only)—The Fragment Length can be
set between 256 and 2,346. If the packet size is smaller than the preset
fragment size, the packet will not be segmented.
Fragmentation of the PDUs (Package Data Unit) can increase the reliability of
transmissions because it increases the probability of a successful transmission
due to smaller frame size. If there is significant interference present, or
collisions due to high network utilization, try setting the fragment size to send
smaller fragments. This will speed up the retransmission of smaller frames.
However, it is more efficient to set the fragment size larger if very little or no
interference is present because it requires overhead to send multiple frames.
(Default: 2346)
RTS Threshold (0-2347)—Set the RTS (Request to Send) frame length. You
may configure the access point to initiate an RTS frame sequence always, never,
or only on frames longer than a specified length. If the packet size is smaller
than the preset RTS threshold size, the RTS/CTS mechanism will not be
enabled.
The access point sends RTS frames to a particular receiving station to
negotiate the sending of a data frame. After receiving an RTS frame, the
station sends a CTS (Clear to Send) frame to acknowledge the right of the
sending station to send data frames.
The access points contending for the medium may not be aware of each other.
The RTS/CTS mechanism can solve this hidden node problem. (Default: 2346)
Preamble Length (802.11g and 802.11b only)—IEEE 802.11 frames begin
with an alternating pattern of 1s and 0s called the preamble, which tells
receiving stations that a frame is arriving. This provides time for the receiving
station to synchronize to the incoming data stream. Enabling the Short
preamble can boost your throughput; however, this can cause interoperability
issues. (Default:
Long)
53
Page 60

SECURITY
The Security page allows you to set up lower-layer client authentication and data
encryption parameters as described below.
Note: Because of limitations in the Virtual Access Point feature, VAPs on the same
physical interface share the same WEP keys; therefore, the WEP configuration
section applies to both VAPs.
When you are finished configuring items on this page, click Apply.
SELECTING A VIRTUAL ACCESS POINT (VAP)
Open the Virtual AP drop-down box and select the VAP you want to configure.
Each VAP has its own set of security parameters except for the WEP key table,
which is shared between two VAPs.
CONFIGURING AUTHENTICATION
The following types of authentication can be configured:
Open System (the default)—Allows access to everyone.
Shared Key—If Shared Key is enabled, Encryption must also be enabled as
described in
“Configuring Encryption” on page 54.
CONFIGURING ENCRYPTION
The following types of data encryption are available:
WPA—Wi-Fi Protected Access.
WEP—Wired Equivalent Privacy
The access point and the wireless devices must have the same encryption settings
communicate. You can choose to allow only clients using WPA encryption, or
to
you can allow both WPA and WEP clients.
The following sections describe how to configure each type of encryption. When
you are finished configuring the encryption, click
54
Apply.
Page 61

WPA Configuration
To configure WPA encryption:
1 Choose open system, and then click the Required check box on the
authentication page if you want to limit access to clients using WPA
encryption. If you also want to allow WEP clients, do not check this box.
2 Select the Cipher Mode, which determines the method by which keys are
computed. WEP is the weakest Multicast Cipher Mode and is only provided
for support of legacy clients which do not fully support WPA. Clients
associated with WPA-TKIP will have unicast packets directed at them with
corresponding encryption keys. However, with WEP selected as the Cipher
Mode, ALL multicast traffic is sent out with WEP encryption. It is
recommended to only select WEP as the Cipher Mode if legacy client support
is critical.
AES - Advanced Encryption Standard (Highest Security)
TKIP—(Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) provides per-packet key mixing, a
message integrity check and a re-keying mechanism
WEP—Provides standard WEP ciphering (Least Secure)
3 Select the type of WPA Key Management:
WPA authentication over 802.1x (More secure, but requires a RADIUS
authentication server setup. See WPA note below)
WPA Pre-shared Key (PSK) (see WPA note below)
4 Select the Key Type:
Hexadecimal (0~9, A~F; for example, D7 0A 9C 7F E5)
ASCII (0~9, A~F; for example 01234)
5 Enter the pre-shared key in the space provided if necessary.
WPA Note:
The WPA key management must match the settings on the Authentication Page.
When using 802.1x, the access point uses session keys provided during the
802.1x EAP key exchange as the “seed key” for WPA. This is more secure than
PSK, since each client starts with a unique session key for all subsequent keys
generated. Otherwise, the PSK is used for the “seed key”.
The 802.1x Wireless Setup on the Authentication Page should be set as follows:
If only one Radio is installed, and “WPA pre-shared key (PSK)” is selected on
the security page, then the 802.1x Wireless Setup can be either “Disabled” or
“Supported” on the Authentication Page.
55
Page 62

If only one Radio is installed and “WPA authentication over 802.1x” is
selected on the security page, then 802.1x Wireless Setup must be either
“Supported” or “Required” on the Authentication Page.
If two Radios are installed and WPA is being used with “WPA authentication
over 802.1x” selected for both radios’ WPA key management, then set the
802.1x Wireless Setup to “Required” on the Authentication Page.
If one radio’s security is set to “WPA pre-shared key (PSK)” for WPA key
management and the other is set to “WPA authentication over 802.1x”, then
the 802.1x Wireless Setup must be set to “Supported” on the Authentication
Page instead.
WEP Configuration
WEP encryption is based on the use of security keys and the popular RC4
encryption algorithm.
At least one transmit key must be defined in the WEP Configuration. Wireless
devices without a valid WEP key will be excluded from network traffic.
The key selected as the transmit key index is used by the access point for all
transmissions. Other keys defined can be used by the access point for decrypting
station communications. When enabling 802.1x security with dynamic session
keys, key index 4 is reserved for the 802.1x client session key. Therefore, when
802.1x clients are in the network, the access point should not be configured to
use key index 4 as the transmit key index.
To configure WEP encryption:
1 Under Encryption, select Enable.
2 Under WEP Configuration, select the Key Size.
The access point supports shared key encryption with key lengths of 64-bits,
128-bits, or 152-bits.
3 Select the Key Type.
Hexadecimal (0~9, A~F; for example, D7 0A 9C 7F E5)
ASCII (0~9, A~F; for example 01234)
3Com Passphrase(a string, described below)
4 Enter the keys in their fields.
64-bit—Each key contains 10 hexadecimal digits or 5 alphanumeric
characters.
128-bit—Each key contains 26 hexadecimal digits or 13 alphanumeric
characters.
56
Page 63

152-bit—Each key contains 32 hexadecimal digits or 16 alphanumeric
characters.
3Com Passphrase—This encryption string is for use only with other 3Com
Wireless LAN devices. It is a case-sensitive string between 6 and 30 characters
long. To enter the string, click 3Com Passphrase. Then type any combination
of letters and numbers in the Key 1 field and click Apply.
5 Uncheck box under WPA Configuration
6 Choose the WEP option under Multicast Cipher Mode.
HOW TO SETUP THE ACCESS POINT FOR RADIUS
AUTHENTICATION
1 Using the Wireless Infrastructure Device Manger access the configuration
screen for the AP7250.
2 Enter your User Name and Password and click LOGIN (Default: admin with no
password).
3 Select Advanced Setup.
4 Click on RADIUS from the left frame page Menu.
5 Enter all the settings of your Primary RADIUS Authentication Server (make
sure the IP Address and Key match those on the RADIUS Authentication
software).
6 Click on Apply.
7 Choose Authentication from the left frame page Menu.
8 Make sure the following settings are set on the Authentication page:
aMAC Authentication is Disabled. (if Local or RADIUS MAC Authentication
is chosen MAC address filtering or authentication, respectively, will be
done before the 802.1x authentication. Therefore, these setups must be
validated individually and verified functional before 802.1x can be done).
b 802.1x Wireless Setup: is set to Supported (if non-RADIUS clients need
access too) or Required (if only RADIUS clients are to be allowed).
c Click on Apply.
9 Click Security on the 802.11b/g radio from the left frame page Menu.
10 Make sure the following settings are set from the Security page:
a Authentication is set to Open System.
b Encryption is Enabled.
c WPA Configuration Required “Allow only WPA Clients” is left unchecked.
57
Page 64

d Cipher Mode is set to WEP.
e WEP Configuration has at least one valid WEP key.
f Click on Apply.
11 The Access Point is now configured for RADIUS Authentication.
HOW TO SETUP THE ACCESS POINT FOR WPA WITH 802.1X SESSION KEYS
1 Using the Wireless Infrastructure Device Manger access the configuration
screen for the AP7250.
2 Enter your User Name and Password and click LOGIN (Default: admin with no
password).
3 Select Advanced Setup.
4 Click on RADIUS from the left frame page Menu.
5 Enter all the settings of your Primary RADIUS Authentication Server (make
sure the IP Address and Key match those on the RADIUS Authentication
software).
6 Click on Apply.
7 Choose Authentication from the left frame page Menu.
8 Make sure the following settings are set on the Authentication page:
aMAC Authentication is Disabled. (if Local or RADIUS MAC Authentication
is chosen MAC address filtering or authentication, respectively, will be
done before the 802.1x authentication. Therefore, these setups must be
validated individually and verified functional before 802.1x can be done).
b 802.1x Wireless Setup: is set to Supported (if non-RADIUS clients need
access too) or Required (if only RADIUS clients are to be allowed).
c Click on Apply.
9 Click Security on the 802.11b/g radio from the left frame page Menu.
10 Make sure the following settings are set from the Security page:
a Authentication is set to Open System.
b Encryption is Enabled.
c WPA Configuration is Checked to “Allow only WPA Clients”.
d Cipher Mode is set to AES/TKIP/WEP (WEP Cipher Mode is intended ONLY
for support of legacy clients. If only WPA clients are on the network,
choose AES or TKIP for increased security).
e WEP Configuration has at least one valid WEP key.
58
Page 65

f WPA Key Management set to WPA Authentication over 802.1x.
g Click on Apply.
11 The Access Point is now configured for WPA Authentication over 802.1x.
HOW TO SETUP THE ACCESS POINT FOR WPA WITH PRE-SHARED (PSK) KEY
1 Using the Wireless Infrastructure Device Manger access the configuration
screen for the AP7250.
2 Enter your User Name and Password and click LOGIN (Default: admin with no
password)
3 Select Advanced Setup.
4 Choose Authentication from the left frame page Menu
5 Make sure the following settings are set on the Authentication page:
aMAC Authentication is Disabled. (if Local or RADIUS MAC Authentication
is chosen MAC address filtering or authentication, respectively, will be
done before the 802.1x authentication. Therefore, these setups must be
validated individually and verified functional before 802.1x can be done).
b 802.1x Wireless Setup: is set to Disabled or Optional (if RADIUS clients
need access too).
c Click on Apply.
6 Click Security on the 802.11b/g radio from the left frame page Menu.
7 Make sure the following settings are set from the Security page:
a Authentication is set to Open System.
b Encryption is Enabled.
c WPA Configuration is Checked to “Allow only WPA Clients”.
d Cipher Mode is set to AES/TKIP/WEP (WEP Cipher Mode is intended ONLY
for support of legacy clients. If only WPA clients are on the network,
choose AES or TKIP for increased security).
e WEP Configuration has at least one valid WEP key (select the appropriate
key length, key type, and key index).
f WPA Key Management select WPA Pre-shared Key (PSK) and Key Type.
g Enter the WPA PSK
h Click on Apply.
8 The access point is now configured for WPA Pre-shared Key.
59
Page 66
WPA CONFIGURATION FOR WINDOWS XP
The following table shows how to configure the access point to support the
various authentication and encryption options available for Windows XP Wireless
Zero Configuration.
The following notes apply to configuring the access point for WPA under
Windows XP:
A WPA-capable wireless network interface card is required.
The Windows XP Support Patch for Wireless Protected Access, which you can
download from the Microsoft Web site, is
To allow WEP clients, clear the WPA Configuration Required check box and
enter an appropriate WEP key.
For all WPA configurations, 802.1x must be enabled on the
Authentication
page.
Windows XP Wireless Zero
Configuration
Authentication Encryption Authentication Encryption Other
Disabled Open System Disable
Open
Shared
WPA
WEP Open System Enable
Disabled Not available
WEP Shared Key Enable
AES Not available on 8200
TKIP
WEP Open System Enable
Open System
(for 8750)
required.
Access Points 8250/8750
Enable
Enter static keys
under WEP
Configuration
Enter static keys
under WEP
Configuration
WPA Configuration:
Required
Multicast Cipher
Mode: AES
WPA Key
Management: WPA
802.1x
WPA Configuration:
Required
Multicast Cipher
Mode: WEP
WPA Key
Management: WPA
802.1x
60
Page 67
Windows XP Wireless Zero
Configuration
Access Points 8250/8750
Authentication Encryption Authentication Encryption Other
AES Not available on 8200
WPA Configuration:
Required
Multicast Cipher
Mode: AES
WPA Key
Management:
WPA 802.1x
WPA Configuration:
Required
Multicast Cipher
Mode: TKIP
WPA Key
Management:
WPA-PSK
Select Key Type and
enter Pre-Shared Key
WPA Configuration:
Required
Multicast Cipher
Mode: WEP
WPA Key
Management:
WPA-PSK
Select Key Type and
enter Pre-Shared Key
WPA-PSK
Open System
(for 8750)
TKIP Open System Enable
WEP Open System Enable
Enable
61
Page 68

62
Page 69
4 TROUBLESHOOTING
If you have difficulty with the 3Com Wireless LAN access point, first check the
following items in the configuration:
Radio Settings page: Ensure that the SSID is the same on clients and the
access
point.
Security page: Ensure that Encryption is the same on clients and the
point.
access
Authentication page: Ensure that the Local MAC Authentication System
Default is set to Allow. Ensure that 802.1x Authentication Settings are correct.
TCP/IP Settings page: If the DHCP Client is set to Disabled, then ensure that
the access point IP
If necessary, reset the access point to the factory defaults.
Try the solutions in the following table. If you need further assistance, contact
3Com Technical Support through the following Web page:
http://www.3com.com/products/en_US/supportedindex.jsp
Address is within the same subnet as the wired LAN.
Symptom Solutions
Make sure the Ethernet cable is plugged into the port
Access point does not
up.
power
Access point powers up, but
has no connection to the
wired network.
labeled To Access Point on the power brick.
Check for a faulty access point power supply.
Check for a failed AC power supply
Make sure that the Ethernet cable is plugged into the
port labeled To
Verify the network wiring and topology for proper
configuration. Check that the cables used are the
type.
proper
63
Hub/Switch on the power brick.
Page 70

Symptom Solutions
Verify the access point configuration.
Review access point firmware revisions and update
firmware if necessary.
No operation.
Access point powers up, but
does not associate with
wireless clients.
Mobile users do not have
roaming access to the access
point.
Slow or erratic performance.
Running on a computer
connected to the wired LAN,
the 3Com Device Manager
cannot find an access point.
After you specify an IP
address for an access point,
the 3Com Device Manager
continues to point to the old
IP address when you select
the access point in the
Wireless Network Tree.
Make sure that there are no duplicate IP addresses on
the network. Unplug the access point and ping the
assigned address to make sure that no other device
responds to that address.
Confirm that the service area on the access point
matches that on the clients.
Verify that the clients are operating correctly.
Make sure that security settings on the access point
match those on the
Make sure that the access point antennas are positioned
properly.
Check the range and move clients closer if necessary.
Make sure that all access points and wireless devices in
the ESS in which mobile users can roam are configured
to the same WEP setting, SSID, and authentication
settings.
Try changing the wireless channel on the access point.
Check the access point antennas, connectors, and
cabling for loose
Check the wired network topology and configuration
malfunctions.
for
The 3Com Device Manager cannot discover devices
across routers. Make sure that the computer is
connected on the same segment as the access point.
In the 3Com Device Manager window click the Refresh
button to refresh the Wireless Network Tree. Then click
the access point in the Wireless Network Tree and click
Properties. The IP address you specified is now listed. If
you want to continue configuring the access point,
Configure.
click
clients.
connections.
64
Page 71

Symptom Solutions
To maintain wireless association, the service area and the
security settings on the client and the access point must
exactly. Therefore, if you are associated with the
match
access point that you are configuring and you change
the access point service area or security, make sure to
change the client service area to match.
While you are configuring
the access point, the
Configuration Management
System stops responding.
The access point cannot be
configured using the Web
browser.
If you change the IP address and save the change, you
cannot continue to configure the access point using the
old IP address. Therefore, if you want to continue
configuring this access point after you save this change,
you must do the following:
1 Close your browser.
2 Return to the 3Com Device Manager Wireless
Network Tree and click Refresh.
3 Select the access point and click Configure to start a
new configuration session.
Reset the access point (push the reset button located
near the access point LEDs).
65
Page 72

66
Page 73

REGULATORY COMPLIANCE INFORMATION
3Com Wireless LAN Access Point 7250 (Model WL-455, incorporating WL-463 radio module)
General
The 3Com Wireless LAN Access Point 7250 (3CRWE725075) must be installed and used in strict accordance with the
manufacturer's instructions as described in the user documentation that comes with the product.
This product contains encryption. It is unlawful to export out of the U.S. without obtaining a U.S. Export License.
This product does not contain any user serviceable components. Any unauthorized product changes or modifications will
invalidate 3Com's warranty and all applicable regulatory certifications and approvals.
Only antennas specified for your region by 3Com can be used with this product. The use of external amplifiers or
non-3Com antennas may invalidate regulatory certifications and approvals.
This product must be installed by a professional technician/installer.
Caution: Exposure to Radio Frequency Radiation
This device generates and radiates radio-frequency energy. In order to comply with FCC radio-frequency exposure
guidelines for an uncontrolled environment, this equipment must be installed and operated while maintaining a minimum
body to antenna distance of 20 cm (approximately 8 in.).
The installer of this radio equipment must ensure that the antenna is located or pointed such that it does not emit RF field
in excess of Health Canada limits for the general population; consult Safety Code 6, obtainable from Health Canada's
website www.hc-sc.gc.ca/rpb.
This product must maintain a minimum body to antenna distance of 20 cm. Under these conditions this product will meet
the Basic Restriction limits of 1999/519/EC [Council Recommendation of 12 July 1999 on the limitation of exposure of the
general public to electromagnetic fields (0 Hz to 300 GHz)].
US - Radio Frequency Requirements
This device must not be co-located or operated in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) EMC Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The user may find the following booklet prepared by the Federal Communications Commission helpful:
The Interference Handbook
This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402. Stock No. 004-000-0034504.
3Com is not responsible for any radio or television interference caused by unauthorized modification of the devices
included with this 3Com Wireless LAN Access Point 7250 (3CRWE725075), or the substitution or attachment of
connecting cables and equipment other than specified by 3Com.
The correction of interference caused by such unauthorized modification, substitution or attachment will be the
responsibility of the user.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by 3Com could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
Page 74

US Manufacturer's FCC Declaration of Conformity
3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive
Marlborough, MA 01752-3064, USA
(508) 323-5000
Date: 1 February 2005
Declares that the Product:
Brand Name: 3Com Corporation
Model Number: WL-455
Equipment Type: Wireless LAN Access Point
Complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
3Com Wireless LAN Access Point 7250
Model WL-455
Industry Canada - RF Compliance
This device complies with RSS 210 of Industry Canada.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device must
accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of this device.
L ' utilisation de ce dispositif est autorisée seulement aux conditions suivantes: (1) il ne doit pas produire de brouillage et (2)
l' utilisateur du dispositif doit étre prêt à accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique reçu, même si ce brouillage est susceptible
de compromettre le fonctionnement du dispositif.
The term "IC" before the equipment certification number only signifies that the Industry Canada technical specifications
were met.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that the
equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) is not more than that required for successful communication. To prevent
radio interference to the licensed service, this device is intended to be operated indoors and away from windows to
provide maximum shielding. Equipment (or its transmit antenna) that is installed outdoors is subject to licensing.
Pour empecher que cet appareil cause du brouillage au service faisant l'objet d'une licence, il doit etre utilize a l'interieur et
devrait etre place loin des fenetres afin de Fournier un ecram de blindage maximal. Si le matriel (ou son antenne
d'emission) est installe a l'exterieur, il doit faire l'objet d'une licence.
Industry Canada - Emissions Compliance Statement
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Avis de Conformité à la Réglementation d'Industrie Canada
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conform à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Safety Compliance Notice
This device has been tested and certified according to the following safety standards and is intended for use only in
Information Technology Equipment which has been tested to these or other equivalent standards:
UL Standard 60950 (3rd Edition)
CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 60950-00
IEC 60950
EN 60950
Page 75
EU Compliance
This equipment may be operated in
AT BE CY CZ DK EE FI FR
DE GR HU IE IT LV LT LU
MT NL PL PT SK SI ES SE
GB IS LI NO CH BG RO TR
Intended use: IEEE 802.11b/g radio LAN device
NOTE: To ensure product operation is in compliance with local regulations, select the country in which the product is
installed. Refer to "Setting the Country Code" in the chapter System Configuration.
English Hereby, 3Com Corporation, declares that this RLAN
Finnish 3Com Corporation vakuuttaa täten että RLAN
Dutch Hierbij verklaart 3Com Corporation dat het toestel
French Par la présente 3Com Corporation déclare que
Swedish Härmed intygar 3Com Corporation att denna RLAN
Danish Undertegnede 3Com Corporation erklærer herved,
device is in compliance with the essential
requirements and other relevant provisions of
Directive 1999/5/EC.
device tyyppinen laite on direktiivin 1999/5/EY
oleellisten vaatimusten ja sitä koskevien direktiivin
muiden ehtojen mukainen.
RLAN device in overeenstemming is met de
essentiële eisen en de andere relevante bepalingen
van richtlijn 1999/5/EG
Bij deze verklaart 3Com Corporation dat deze RLAN
device voldoet aan de essentiële eisen en aan de
overige relevante bepalingen van Richtlijn
1999/5/EC.
l'appareil RLAN device est conforme aux exigences
essentielles et aux autres dispositions pertinentes de
la directive 1999/5/CE
Par la présente, 3Com Corporation déclare que ce
RLAN device est conforme aux exigences essentielles
et aux autres dispositions de la directive 1999/5/CE
qui lui sont applicables.
device står I överensstämmelse med de väsentliga
egenskapskrav och övriga relevanta bestämmelser
som framgår av direktiv 1999/5/EG.
at følgende udstyr RLAN device overholder de
væsentlige krav og øvrige relevante krav i direktiv
1999/5/EF.
Page 76

German Hiermit erklärt 3Com Corporation, dass sich
Greek
dieser/diese/dieses Managed Accces Point in
Übereinstimmung mit den grundlegenden
Anforderungen und den anderen relevanten
Vorschriften der Richtlinie 1999/5/EG befindet".
(BMWi)
Hiermit erklärt 3Com Corporation die
Übereinstimmung des Gerätes RLAN device mit den
grundlegenden Anforderungen und den anderen
relevanten Festlegungen der Richtlinie 1999/5/EG.
(Wien).
Italian Con la presente 3Com Corporation dichiara che
Spanish Por medio de la presente 3Com Corporation declara
Portuguese 3Com Corporation declara que este RLAN device
Malti
Estonian Käesolevaga kinnitab 3Com Corporation seadme
Hungarian Alulírott, 3Com Corporation nyilatkozom, hogy a
Slovak
Czech
Slovene
questo RLAN device è conforme ai requisiti
essenziali ed alle altre disposizioni pertinenti stabilite
dalla direttiva 1999/5/CE.
que el RLAN device cumple con los requisitos
esenciales y cualesquiera otras disposiciones
aplicables o exigibles de la Directiva 1999/5/CE.
está conforme com os requisitos essenciais e outras
disposições da Directiva 1999/5/CE.
RLAN device vastavust direktiivi 1999/5/EÜ
põhinõuetele ja nimetatud direktiivist tulenevatele
teistele asjakohastele sätetele.
RLAN device megfelel a vonatkozó alapvetõ
követelményeknek és az 1999/5/EC irányelv egyéb
elõírásainak.
Lithuanian
Latvian
Page 77

A copy of the signed Declaration of Conformity can be downloaded from the Product Support web page for the 3Com
Wireless LAN Access Point 7250 (3CRWE725075) at http://www.3com.com.
Also available at http://support.3com.com/doc/AP7250_WL-463.pdf
EU - Restrictions for Use in the 2.4GHz band
This device may be operated indoors or outdoors in all countries of the European Community using the 2.4GHz band:
Channels 1 - 13, except where noted below.
In Italy the end-user must apply for a license from the national spectrum authority to operate this device outdoors.
In Belgium outdoor operation is only permitted using the 2.46 - 2.4835 GHz band: Channel 13.
In France outdoor operation is only permitted using the 2.4 - 2.454 GHz band: Channels 1 - 7.
Brazil RF Compliance
Este equipamento opera em car·ter secund·rio, isto È, nao tem direito a proteÁao contra interferencia prejudicial, mesmo
de estaÁoes do mesmo tipo, e nao causar interferencia a sistema operando em car·ter prim·rio.
Page 78

Page 79
INDEX
Numbers
3Com 3CDaemon Server Tool 23
3Com Network Supervisor 23
3Com Passphrase encryption 57
3Com Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager 23, 25
802.11a, turbo mode 52
802.1x reauthentication refresh rate 34
802.1x setup 33
A
access point
installation 11
IP address, troubleshooting 64
resetting 45
accounting 32
ad hoc 5
adapter, choosing 26
administration 44
administration tool 25
advanced setup 29
antenna 15, 21
comparison data 21
options 21
standard detachable (Access Point 8200) 15
AP management filter 37
AP status 49
authentication 33, 54
local MAC 35
MAC 33
open system 54
RADIUS MAC 34
shared key 54
automatic channel selection 52
B
backup configuration 44
basic configuration 28
beacon interval 53
broadcast key refresh rate 34
C
cable 11
change password 44
channel 52
choosing a NIC 26
community name 39
configuration 25
advanced 29
basic 28
login 27
Configuration Management System 26, 27
configuration, backup and restore 44
Configure button 26
configuring encryption 54
connecting
power 12, 16
contact 39
country code 27
D
data
encryption 54
transfer speed 52
date and time settings 48, 49
default
gateway 29
device
configuring 26, 27
device manager 25
launching 25
DHCP client 29
E
encryption
3Com Passphrase 57
configuring 54
shared key 56
WEP 54, 56
WPA 54, 55
Ethernet Broadcast Storm Control 37
Page 80

Ethernet cable 11
Ethernet type filter 38
event logs 49
F
filter control 36
firmware upgrade 44
flat surface installation 20
fragment length 53
G
gateway, default 29
glossary of wireless networking terms 7
I
identification 29
IEEE 802.3af power-over-Ethernet 16
infrastructure configuration 5
installation 11
access point 11
antenna 15
cable 11
flat surface 20
location 13
power 12
requirements 11
software utilities 23, 24
wall mount 18
IP address 29
refreshing after changing 26
troubleshooting 64
M
MAC address
locating 35
recording 14
use in locating devices 25, 26
MAC authentication 33
management VLAN ID 36
maximum station data rate 52
mounting
on a wall 18
plate 19
N
network configuration and planning 5
NIC, choosing 26
O
open system 54
P
passphrase 57
password 44
planning a network 5
power 12
connecting 16
requirements 12
supply, 3Com integrated 16, 17
power-over-Ethernet 16
preamble 53
Pre-IP Configuration Wizard 26, 27
Properties button 26
L
launching the device manager 25
LEDs 18
local bridge filter 37
local MAC authentication 35
locating
devices 25, 26
MAC address 35
location
configuration parameter 39
for installation 13
log 48
login 27
R
radio channel 52
radio interface 50
RADIUS
accounting 32
RADIUS Authentication Setup Steps 57
RADIUS MAC authentication 34
reauthentication refresh rate 34
recording MAC address 14
Refresh button 26
resetting the access point 45
restore configuration 44
RF preamble 53
roaming 6
Page 81
RTS threshold 53
S
safety information 12
secure web server connection 30
session key refresh rate 34
setting the time and date 48, 49
settings
TCP/IP 29
Setup Wizard 28
setup, 802.1x 33
shared key 54
shared key encryption 56
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) 39
software utilities, installing 23, 24
SSID 49, 51
stations status 49
statistics, accounting 32
status 49
subnet mask 29
system configuration 25
system log 48
T
TCP/IP settings 29
terminology 7
time and date settings 48, 49
transmission power 52
trap destination 39
troubleshooting 63
turbo mode 52
U
upgrading firmware 44
V
VLAN 36
VLAN ID 36
W
wall mount installation 18
web server, secure connection 30
WEP 54, 56
Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration 60
wireless network tree 25
WPA 54, 55
 Loading...
Loading...