Campbell Hausfeld WG2020 User Manual
Operating Instructions & Parts Manual |
Model WG2020 |
|
|
Please read and save these instructions. Read carefully before attempting to assemble, install, operate or maintain the product described. Protect yourself and others by observing all safety information. Failure to comply with instructions could result in personal injury and/or property damage! Retain instructions for future reference.
|
|
Wire Feed |
|
TM |
Arc Welder |
BUILT TO LAST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SU |
NC |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
E |
P |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|||
|
T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
G |
||
AL |
I |
|
|
|
Need |
R |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|||||
U |
|
Assistance? |
M |
|||||||
Q |
|
|
||||||||
Call Us First!
1-800-746-5641
Description
The Campbell Hausfeld WG2020 is a 70 amp, single phase 115 volt input, wire feed arc welding machine equipped with infinite wire speed control to accurately select proper wire feed rate needed for various welding conditions. Internal components are thermostatically protected.
This welding system is designed for use with the Flux Core Arc Welding (FCAW) or the Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) process. As delivered from the factory, this welder can weld with .024” (.6mm) to .035” (.9mm) diameter wire. A starter spool of flux-cored wire is included.
Unpacking
All welding accessories for the welder are inside the wire feed compartment. Lift and remove wire feed cover to find handle, workclamp, etc. When unpacking, inspect carefully for any damage that may have occurred during transit. Make sure any loose fittings and screws, etc. are tightened before putting unit into service.
CIRCUIT REQUIREMENTS
This equipment requires a dedicated
115 volt circuit. Refer to the following chart for correct circuit breaker or fuse rating. Do not run other appliances, lights or tools on this circuit while operating this equipment. Extension cords are not recommended. Blown fuses and tripped circuit breakers can result from failure to comply with this recommendation.
4 
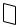
6
5
|
2 |
|
1 |
Figure 1 - |
3 |
Welder Components |
and Controls
For parts, product & service information
Heat |
Circuit Breaker or |
Selector |
Slow Blow Fuse |
Low |
15 amp |
High |
20 amp |
See page 7 for supply cable replacement instructions.
COMPONENTS AND CONTROLS
1.Work Clamp - connect to work piece.
2.Wire Feed Gun
3.Power Cord - plug into 115 volt outlet.
4.On/Off Switch - illuminates if thermostat has automatically shut unit off.
5.Infinite Wire Speed Control - turns clockwise to increase wire speed and counterclockwise to decrease wire speed.
6.Heat Selector - Selects welding power. Four selections are possible; low 1, low 2, high 1 and high 2.
General Safety
Danger means a hazard that will
cause death or serious injury if the warning is ignored.
Warning means a hazard that could
cause death or serious injury if the warning is ignored.
Caution means a hazard that may cause minor or moderate injury if the
warning is ignored. It also may mean a hazard that will only cause damage to property.
NOTE: Note means any additional information pertaining to the product or its proper usage.
IN212800AV 7/99
visit www.campbellhausfeld.com
Wire Feed Arc Welder
General Safety
(Continued)
Always keep a fire extinguisher accessible while performing arc welding operations.
● Before starting or servicing any electric arc welder, read and
understand all MANUAL instructions. Failure
to follow safety
precautions or instructions can cause equipment damage and/or serious personal injury or death.
●All installation, maintenance, repair and operation of this equipment should be performed by qualified persons only in accordance with national, state, and local codes.
Improper use of electric arc welders can cause electric shock, injury, and death! Take all precautions described in
this manual to reduce the possibility of electric shock.
●Verify all components of the arc welder are clean and in good condition prior to operating welder. Be sure insulation on all cables, wire feed gun and power cord is not damaged. Always repair or replace damaged components before operating the welder. Always keep welder panels, shields, etc. in place when operating welder.
●Always wear dry, protective clothing, welding gloves and insulated footwear when operating unit.
●Always operate welder in a clean, dry, well ventilated area. Do not operate welder in humid, wet, rainy or poorly ventilated areas.
●Be sure work piece is properly supported and grounded prior to beginning any electric arc welding operation.
●Spread out coiled welding cable
before use to avoid overheating and damage to insulation.
Never immerse wire or wire feed
gun in water. If welder becomes wet for any reason, be absolutely certain it is completely clean and dry before use!
●Always shut equipment off and unplug power cord prior to moving the unit.
●Always attach the work lead first.
●Verify work piece is securely grounded.
●Always shut off electric arc welding equipment when not in use and cut off any excess wire from wire feed gun.
●Never allow any part of the body to touch flux core wire and ground or grounded work piece at the same time.
●Awkward welding conditions and positions can be electrically hazardous. When crouching, kneeling or at elevations, be sure to insulate all conductive parts, wear appropriate protective clothing and take precautions to prevent injury from falls.
●Never attempt to use this equipment at current settings or duty cycles higher than specified on equipment labels.
●Never use an electric arc welder to thaw frozen pipes.
Flying sparks and hot
metal can cause injury. As welds cool, slag can
be thrown off. Take all precautions described in
this manual to reduce the possibility of injury from flying sparks and hot metal.
●Wear ANSI approved face shield or safety glasses with side shield protection when chipping or grinding metal parts.
●Wear ear plugs when welding overhead to prevent spatter or slag from falling into ears.
Electric arc welding operations produce intense light and heat and ultraviolet (UV) rays. This intense light
and UV rays can cause injury to eyes and skin. Take all precautions described in this manual to reduce the possibility of injury to eyes and skin.
●All persons operating this equipment or in the area while equipment is in use, must wear protective welding gear including: welding helmet or shield with at least shade 10 lens, flame resistant clothing, leather welding gloves and full foot protection.
The welding wire is live whenever the
welder is turned on - whether the trigger is pulled or not.
Never look at arc welding operations
without eye protection as described above. Never use a shade filter lens that is cracked, broken, or rated below number 10. Warn others in the area not to look at the arc.
Electric arc welding operations cause sparks and heat metal to temperatures that can cause severe burns! Use
protective gloves and clothing when performing any metal working operation. Take all precautions described in this manual to reduce the possibility of skin and clothing burns.
●Make sure all persons in welding area are protected from heat, sparks and ultraviolet rays. Use additional face shields and flame resistant barriers as needed.
●Never touch work pieces until completely cooled.
Heat and sparks produced during electric arc welding and other metal working operations can ignite
flammable and explosive materials! Take all precautions described in this manual to reduce the possibility of flames and explosions.
●Remove all flammable materials within 35 feet (10.7 meters) of welding arc. If removal is not possible, tightly cover flammable materials with fire proof covers.
●Do not operate any electric arc
www.campbellhausfeld.com
2
Model WG2020
General Safety
(Continued)
welder in areas where flammable or explosive vapors may be present.
●Take precautions to ensure flying sparks and heat do not cause flames in hidden areas, cracks, etc.
Fire hazard! Do not weld on containers or pipes that contain or have contained
flammable materials or gaseous or liquid combustibles.
Arc welding closed cylinders or containers such as tanks or drums can cause explosion if not properly vented!
Verify that any cylinder or container to be welded has an adequate ventilation hole, so that expanding gases can be released.
Do not breathe fumes produced by arc welding operation. These fumes
are dangerous. If welding area cannot be
adequately ventilated, be sure to use an air-supplied respirator.
●Keep head and face out of welding fumes.
●Extremely toxic fumes are created when galvanized or cadmium plated metals or metals which contain zinc, mercury or beryllium are heated. Complete the following precautions before performing electric arc welding operations on these metals:
a.Remove coating from base metal.
b.Make sure welding area is well ventilated.
c.Use an air-supplied respirator.
The electromagnetic field generated during arc welding may interfere with the operation of
various electrical and
electronic devices such as cardiac pacemakers. Persons using such devices should consult with their physician prior to performing any electric arc welding operations.
●Route wire gun and work cables together and secure with tape when possible.
●Never wrap arc welder cables around the body.
●Always position wire gun and work leads on the same side of the body.
●Exposure to electromagnetic fields during welding may have other health effects which are not known.
Always be sure welding area is
secure and free of hazards (sparks, flames, glowing metal or slag) prior to leaving. Be sure equipment is turned off and excess wire is cut off. Be sure cables are loosely coiled and out of the way. Be sure all metal and slag has cooled.
Cylinders can explode if damaged. Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can
explode. Since gas cylinders are normally part of the welding process, be sure to treat them carefully.
● Protect compressed gas cylinders |
from excessive heat, mechanical |
shocks and arcs. |
● Install and secure cylinders in an |
upright position by chaining them |
to stationary support or equipment |
cylinder rack to prevent falling or |
tipping. |
● Keep cylinders away from any |
welding or other electrical circuits. |
● Never allow a welding electrode to |
touch any cylinder. |
● Use only correct shielding gas |
cylinders, regulators, hoses and |
fittings designed for the specific |
application; maintain all parts |
properly. |
● Turn face away from valve outlet |
when opening cylinder valve. |
● Keep protective cap in place over |
valve except when cylinder is in use |
or connected for use. |
● Read and follow |
instructions on |
compressed gas |
MANUAL |
cylinders, associated |
equipment, and CGA |
publication P-1 listed in Safety Standards.
Never use flammable gasses
with MIG welders. Only inert or nonflammable gasses such as carbon dioxide, argon, helium or mixtures of one or more of these gasses are suitable for MIG welding.
Never lift cylinders off the ground by
their valves or caps or with chains or slings.
ADDITIONAL SAFETY STANDARDS
ANSI Standard Z49.1 from American Welding Society, 550 N.W. Le June Rd. Miami, FL 33126
Safety and Health Standards
OSHA 29 CFR 1910, from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402
National Electrical Code
NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases
in Cylinders
CGA Pamphlet P-1, from Compressed Gas Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Suite 501, Arlington, VA 22202
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting
CSA Standard W117.2, from Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3
Cutting And Welding Processes
NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269
Safe Practices For Occupational And
Educational Eye And Face Protection
ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018
Refer to Material Safety Data Sheets and manufacturers instructions for metals, wire, coatings and cleaners.
www.campbellhausfeld.com
3
Wire Feed Arc Welder
Installation
LOCATION
Selecting the proper location can significantly increase performance, reliability and life of the arc welder.
●For best results locate welder in a clean and dry environment. Dust and dirt in the welder retain moisture and increase wear of moving parts.
●Place welder in an area with at least twelve inches (305 mm) of ventilation space at both the front and rear of unit. Keep all obstructions out of this ventilation space.
●Store flux core wire in a clean, dry location with low humidity to preserve the flux coating.
●Use a properly grounded receptacle for the welder and ensure welder is the only load on power supply circuit. Refer chart on page 1 for correct circuit capacity.
●Use of an extension cord is not recommended for electric arc welding machines. Voltage drop in the extension cord may significantly degrade performance of the welder.
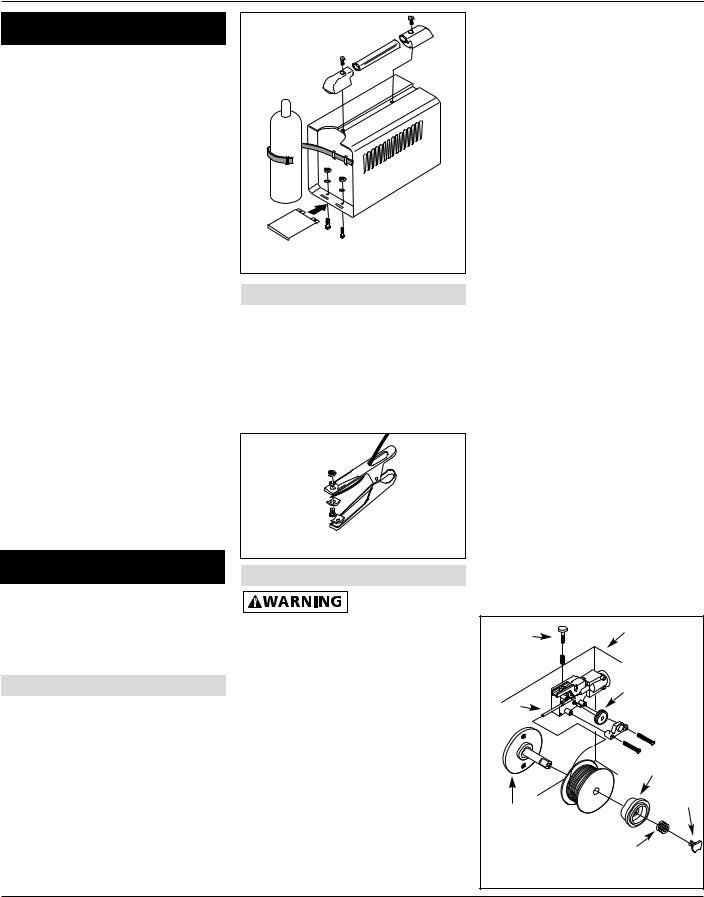
Assembly
All welding accessories for the welder are inside wire feed compartment. Lift and remove wire feed cover to find handle, workclamp, etc.
HANDLE AND BASE ASSEMBLY
1.Slide handle into plastic ends as shown (Fig. 2).
2.Place handle assembly on welder aligning two holes in plastic ends with threaded holes in welder housing.
3.Use washers and fasten screws through handle ends and into cabinet.
4.Attach cylinder base to unit as shown (Fig. 2).
Figure 2 - Handle and Base Assembly |
WORK CLAMP
1.Loosen hex bolt on work clamp.
2.Insert cord (labeled work on the front panel of the welder) through clamp handle and slide bare wire under the clamp block. Tighten hex bolt making sure bare wire is clamped securely (Figure 3).
Figure 3 - Work Clamp Assembly
WIRE INSTALLATION
Welding power may be applied to
output terminals, feed roll, work clamp, gun cable connection and welding wire even when gun switch is not activated. Do not touch these parts when welding machine is on.
NOTE: Before installing welding wire, be sure:
a.The diameter of welding wire matches the groove in drive roller on wire feed mechanism.
b.The wire is compatible with the diameter line in gun hose.
c.The wire matches tip in end of gun.
A mismatch on any item could cause the wire to slip and bind.
1.Verify unit is off and lift welder panel to expose wire feed mechanism.
2.Remove the spool quick lock by pushing in and rotating 1/4 turn counterclockwise. Then remove knob, spring and spool spacer.
3.Loosen wire feed tensioning screw on drive mechanism. This allows initial feeding of wire into gun liner by hand.
4.Install wire spool onto spindle so wire can come off spool on the end closest to the wire feed guide tube.
Do not cut the wire loose yet.
Install spool spacer, spring and quick lock knob by pushing in and turning knob 1/4 rotation clockwise.
5.Hold wire and cut the wire end from spool. Do not allow wire to unravel. Be sure end of wire is straight and free of burrs.
6.Feed wire through wire feed guide tube, over the groove in drive roll and into gun liner. Snugly tighten wire feed tensioning screw. Do not over tighten. Install outer welder panel.
7.Remove nozzle by turning clockwise while pulling off, then unscrew contact tip from end of welding torch (See Figure 5). Plug welder into a proper power supply receptacle.
8.Turn on welder and set wire speed rate to 5. Activate gun switch until wire feeds out past the torch end.
Turn welder off.
Tension |
Panel |
Screw |
|
|
Drive |
Guide |
Roller |
|
|
Tube |
|
|
Spool |
|
Spacer |
|
Spool |
Spindle |
Lock |
|
|
|
Spring |
Figure 4 - Weld Wire Routing |
|
www.campbellhausfeld.com
4
Model WG2020
Assembly (Continued)
9.Carefully slip contact tip over wire and screw tip into torch end. Install nozzle by twisting clockwise while pushing onto torch (See Figure 5). Cut wire off approximately 1/4 inch from nozzle end.
Nozzle
Contact Tip
|
Figure 5 - Torch Nozzle |
Torch neck |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contact Tip Markings |
||
|
Mark |
Wire Size |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 mm |
.024" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.8 mm |
.030” |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.9 mm |
.035” |
|
DUTY CYCLE / THERMOSTATIC PROTECTION
Welder duty cycle is the percentage of actual weld time that can occur in a ten minute interval. For example, at a 10% duty cycle, actual welding can occur for one minute, then the welder must cool for nine minutes.
Internal components of this welder are protected from overheating with an automatic thermal switch. A yellow lamp is illuminated on the front panel (on/off switch) if the duty cycle is exceeded. Welding operations may continue when the yellow lamp is no longer illuminated.
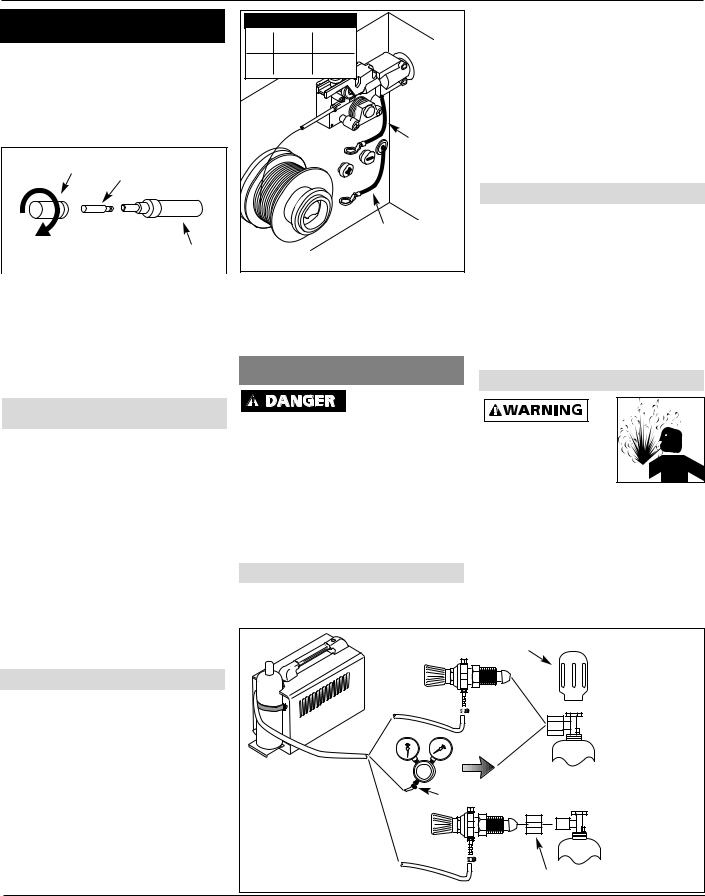
POLARITY
To change between flux wire and MIG wire the polarity must be changed.
1.Remove the wire feed door.
2.Locate red (+) and black (-) polarity connectors just below wire feed mechanism (See Figure 6).
3.For MIG welding with gas, Connect torch cable from wire feed mechanism to red (+) polarity connector then connect work cable to black (-) connector.
|
Torch |
Work |
Mig |
+ |
— |
Flux |
— |
+ |
|
|
Torch Cable |
|
|
Work Cable |
Figure 6 - Cable connection |
||
4.For flux-core welding, connect torch cable from wire feed mechanism to black (-) polarity connector then connect work cable to red (+) connector.
Shielding Gas Preparation
Improper handling
 and maintenance of compressed gas cylinders and regulators can result in serious injury or death!
and maintenance of compressed gas cylinders and regulators can result in serious injury or death!
Always secure gas cylinders to tank bracket kit, a wall or other fixed support to prevent cylinder from falling over. Read, understand and follow all compressed gas and equipment warnings in the safety instructions.
NOTE: Shielding gas is not required if flux-cored welding wire is used.
GAS TYPES
There are 3 types of gas generally used for gas metal arc welding; 100% argon,
a mixture of 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide (C25) or 100% carbon dioxide. The 75/25 mixture is recommended for general steel welding. For aluminum welding, use 100% argon. Cylinders of either type gas may be obtained at your local welding supply outlet. Secure cylinder in place on your welding machine or other support to prevent the cylinder from falling over.
REGULATOR
The regulator provides a constant shielding gas pressure and flow rate during the welding process. Each regulator is designed to be used with a specific gas or mixture of gases. The argon and argon mixture use the same thread type. The 100% carbon dioxide uses a different thread type. An adapter is available at your local welding gas supplier to change between the two.
HOOKUP PROCEDURE
Cylinder gas is under high pressure. Point cylinder outlet away from yourself and any bystanders before opening.
1.With cylinder securely installed, stand on side of cylinder opposite cylinder outlet then remove cylinder cap and open valve slightly by turning counterclockwise. When gas is emitted from cylinder, close valve by turning clockwise. This will blow out
Cap |
ARGON OR |
|
ARGON MIX |
|
INSTALLATION |
|
OR |
|
Hose |
|
|
Clamp |
OR |
CO2 |
|
|
INSTALLATION
Figure 7 - Hookup |
CO2 Adapter |
www.campbellhausfeld.com
5
Wire Feed Arc Welder
Assembly (Continued)
Shielding Gas Preparation
HOOKUP PROCEDURE (Continued)
dust or dirt that may have accumulated around valve seat.
2.Install regulator onto cylinder valve with face of gauges in the vertical position. Tighten stem nut securely to gas valve.
3.Install one end of gas hose to fitting on the rear of welder and other end of hose to fitting on regulator using hose clamps on each connection. Make sure gas hose is not kinked or twisted.
4.While standing opposite cylinder outlet, slowly open cylinder valve. Inspect for leaks in the connections.
5.Pull trigger on gun to allow gas to flow. Adjust gas regulator to maximum flow. Release trigger.
6.Remember to close gas valve when finished welding.
The welding wire is live whenever the
welder is turned on - whether the trigger is pulled or not.
Operation
1.Be sure to read, understand and comply with all precautions in
MANUAL
the General Safety Information section. Be sure to read entire
"Welding Guidelines" section before using this equipment.
2.Turn welder off.
3.Verify surfaces of metals to be joined are free from dirt, rust, paint, oil, scale or other contaminants. These contaminants make welding difficult and cause poor welds.
All persons operating this
equipment or in the area while equipment is in use must wear protective welding gear including: eye protection with proper shade, flame resistant clothing, leather welding gloves and full foot protection.
If heating, welding or cutting galvanized, zinc
plated, lead, or cadmium plated materials, refer to the General Safety
Information Section for instructions. Extremely toxic fumes are created when these metals are heated.
4.Connect work clamp to work piece or workbench (if metal). Make sure contact is secure. Avoid surfaces with paint, varnish, corrosion or nonmetallic materials.
5.Position Heat Selector on front panel to desired setting.
NOTE: These settings are general guidelines only. Heat setting may vary according to welding conditions and materials.
|
Metal |
Heat |
|
|
Thickness |
Setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 - 24 Gauge |
Low |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thicker Than 14 Gauge |
High |
|
6.Rotate Wire Speed Control to setting number 5 to start then adjust as needed after test weld.
7.Plug power cord into a proper voltage receptacle with proper circuit capacity (See circuit requirements on front page).
8.Switch welder ON/OFF switch to ON position.
9.Verify wire is extended 1/4” from contact tip. If not, squeeze trigger to feed additional wire, release trigger and cut wire to proper length.
10.Position wire feed gun near work piece, lower welding helmet by nodding head or position the hand shield, and squeeze gun trigger. Adjust heat setting and wire speed as needed.
11.When finished welding, turn welder off and store properly.
Maintenance
Disconnect power supply and turn
machine off before inspecting or servicing any components. Keep wire compartment cover closed at all times unless wire needs to be changed.
BEFORE EVERY USE:
1.Check condition of weld cables and immediately repair or replace any cables with damaged insulation.
2.Check condition of power cord and immediately repair or replace any cord if damaged.
3.Inspect the condition of the gun tip and nozzle. Remove any weld slag. Replace gun tip or nozzle if damaged.
Do not operate this welding machine
with cracked or missing insulation on welding cables, wire feed gun or power cord.
EVERY 3 MONTHS:
1.Replace any unreadable safety labels on the welder.
2.Use compressed air to blow all dust and lint from ventilation openings.
3.Clean wire groove on drive roll. Remove wire from feed mechanism, remove screws from drive roll housing. Use a small wire brush to clean drive roll. Replace if worn or damaged
Consumable and Wear Parts
The following parts require routine maintenance:
•Wire feed drive roller
•Gun liner - replace if worn
•Nozzle/contact tips
•Wire - This welder will accept either 4” or 8” diameter spools. Flux-cored welding wire is susceptible to moisture and oxidizes over time, so it is important to select a spool size that will be used within approximately 6 months. For mild steel welding, AWS ER70S6 solid wire or AWS E71T-GS Flux-core wire is recommended.
MIG |
FLUX CORE |
SPOT |
WT5011 |
WT5020 |
WELD |
Figure 8 - Nozzles
www.campbellhausfeld.com
6
Maintenance (Con't.)
CHANGING WIRE SIZES
This welder is setup for .035 (.9mm) wire. If a different wire size is used, the wire feed drive roll and contact tip may need changing. There are two grooves in the drive roll. The small groove is for
.023 (.6mm) wire and the other is for
.030-.035 (.8-.9mm) wire. Remove the roller cover and flip the drive roll to choose the correct groove (See parts breakdown). The contact tip should also match the wire diameter used. The tip diameter is marked on the contact tip in inches or millimeters. For aluminum wire, oversize contact tip one size (Ex. - Use .035” tip for .030” diameter wire).
Model WG2020
Supply Cable Replacement
1.Verify that welder is OFF and power cord disconnected.
2.Remove welder cover to expose the ON/OFF switch.
3.Disconnect the black and white power cord wires connected to the ON/OFF switch.
4.Disconnect the green power cord wire connected to welder frame.
5.Loosen the cord strain relief screw(s) and pull cord out of strain relief.
6.Install new cord in reverse order.
Welding Guidelines
General
This line of welding machines can utilize the Flux Cored Arc Welding (Gasless) process or the Gas Metal Arc Welding (MIG) process. The weld must be protected (shielded) from contaminates in the air while it is molten. The gasless process uses a tubular wire with a flux material inside. The flux creates a shielding gas when melted. The MIG process uses inert gas to shield the weld while molten.
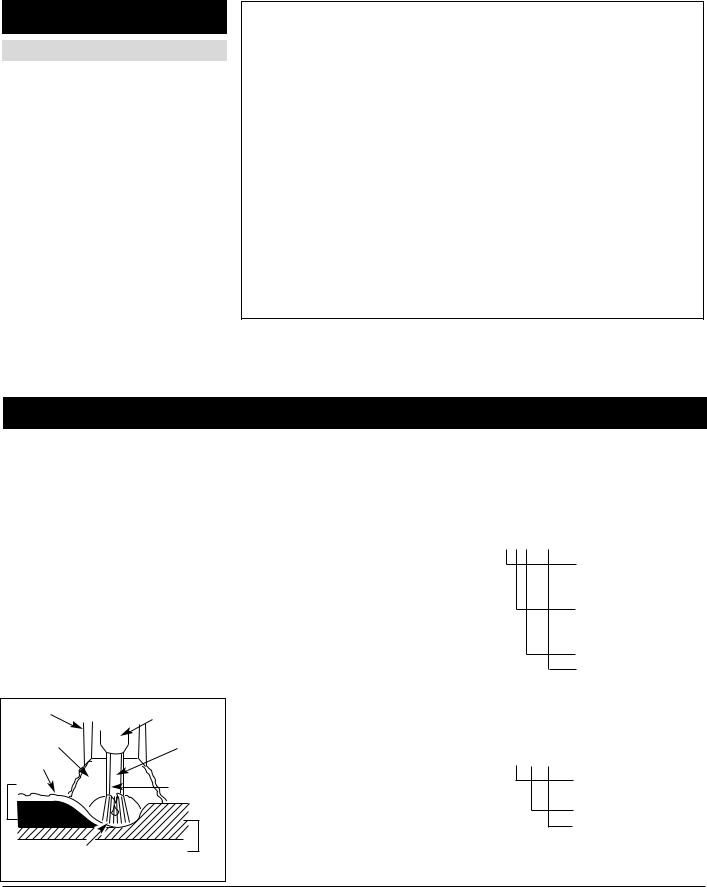
When current is produced by a transformer (welding machine) and flows through the circuit to the weld wire, an arc is formed between the end of the
Nozzle |
Contact |
|
Shielding |
Tip |
|
|
||
Gas |
Flux |
|
Slag |
(Gasless |
|
only) |
||
|
||
Weld |
Wire |
|
Crater |
Work Piece |
|
Figure 9 - Weld Components |
||
weld wire and the work piece. This arc melts the wire and the work piece. The melted metal of the weld wire flows into the molten crater and forms a bond with the work piece as shown (Figure 9).
Arc Welding Basics
Five basic techniques affect weld quality. These are: wire selection, heat setting, weld angle, wire speed, and travel speed. An understanding of these techniques is necessary for effective welds.
HEAT SETTING
The correct heat involves the adjustment of the welding machine to the required setting. Heat or voltage is regulated by a switch on the welder. The heat setting used depends on the size (diameter) and type of wire, position of the weld, and the thickness of the work piece. Consult specifications listed on the welder. It is suggested that the welder practice with scrap metal to adjust settings, and compare welds with Figure 11.
WIRE TYPE AND SIZE
The correct choice of wire type involves a variety of factors, such as welding
position, work piece material type, thickness, and condition of surface to be welded. The American Welding Society, AWS, has set up certain requirements for each type of wire.
FLUX-CORED WIRE
E - 7 0 T - GS
Weld strength, times 10,000 pounds per square inch Welding positions (0
for flat or horizontal, 1 for any position) Tubular flux core wire Flux type
AWS E71T-GS or E71T-11 is recommended for this welder.
SOLID WIRE
ER - 70 S - 6
Weld strength, times 1,000 PSI
Solid wire
Wire composition ER-70S6 is recommended for this welder.
www.campbellhausfeld.com
7
Wire Feed Arc Welder
Welding Guidelines (Continued)
WELD ANGLE
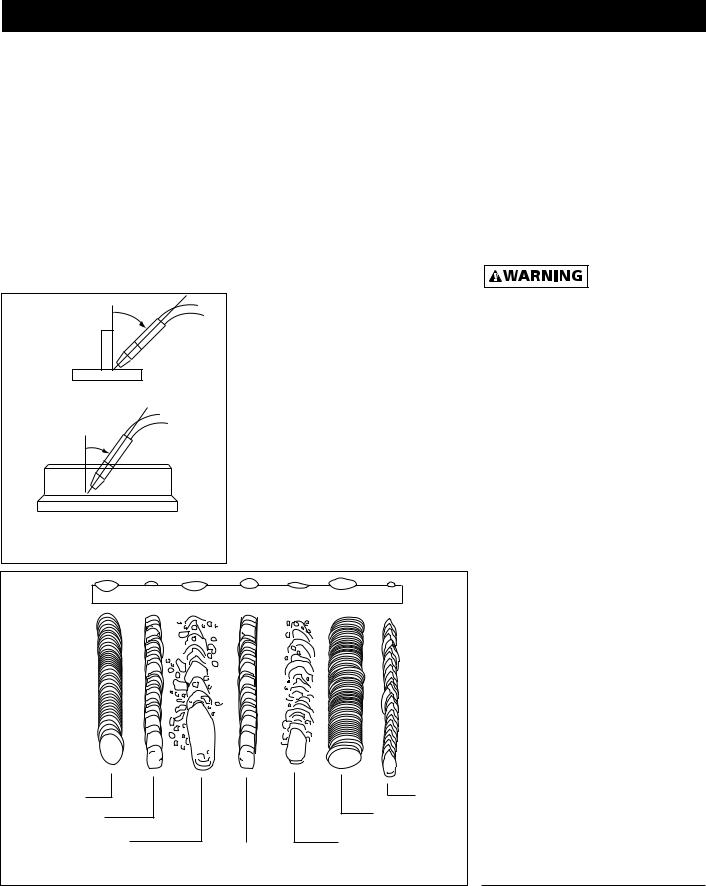
Weld angle is the angle at which the nozzle is held during the welding process. Using the correct angle ensures proper penetration and bead formation. As different welding positions and weld joints become necessary, nozzle angle becomes an increasingly important factor in obtaining a satisfactory weld. Weld angle involves two positions - travel angle and work angle.
Travel angle is the angle in the line of welding and may vary from 5º to 45º from the vertical, depending on welding conditions.
5º - 45º
WORK ANGLE
5º - 45º
TRAVEL ANGLE
Figure 10 - Weld Angle
Work angle is the angle from horizontal, measured at right angles to the line of welding. For most applications, a 45º travel angle and 45º work angle is sufficient. For specific applications, consult an arc welding handbook.
WIRE SPEED
The wire speed is controlled by the knob on the front panel. The speed needs to be “tuned” to the rate at which the wire is being melted in the arc. Tuning is one of the most critical functions in wire feed welding. Tuning should be performed on a scrap piece of metal the same type and thickness as that to be welded. Begin welding with one hand “dragging” the gun nozzle across the scrap piece while adjusting the wire speed with the other hand. Too slow of speed will cause sputtering and the wire will burn up into the contact tip. Too fast a speed will also cause a sputtering sound and the wire will push into the plate before melting. A smooth buzzing sound indicates the wire speed is properly tuned. Repeat the tuning procedure each time there is a change in heat setting, wire diameter or type, or work piece material type or thickness.
Base 
Metal
Normal Heat, |
Travel Speed |
Wire Speed, |
|
Travel Speed |
Too Fast |
Heat Too Low |
Travel Speed |
Heat Too High |
Too Slow |
Wire Speed Too Slow |
|
|
Wire Speed |
Figure 11 - Weld Appearance |
Too Fast |
|
|
www.campbellhausfeld.com |
|
TRAVEL SPEED
The travel speed is the rate at which the torch is moved across the weld area. Factors such as diameter and type of weld wire, amperage, position, and work piece material thickness all effect the speed of travel necessary for completing a good weld (See Fig. 11). When the speed is too fast, the bead is narrow and bead ripples are pointed as shown. When the speed is too slow, the weld metal piles up and the bead is high and wide.
SLAG REMOVAL (FLUX-CORED WIRE ONLY)
Wear ANSI approved safety
glasses (ANSI Standard Z87.1) and protective clothing when removing slag. Hot, flying debris can cause personal injury to anyone in the area.
After completing the weld, wait for the welded sections to cool. A protective coating called slag now covers the weld bead which prevents contaminants in the air from reacting with the molten metal. Once the weld cools to the point that it is no longer glowing red, the slag can be removed. Removal is done with a chipping hammer. Lightly tap the slag with the hammer and break it loose from the weld bead. The final clean-up is done with a wire brush. When making multiple weld passes, remove the slag before each pass.
WELDING POSITIONS
Four basic welding positions can be used; flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead. Welding in the flat position is easier than any of the others because welding speed can be increased, the molten metal has less tendency to run, better penetration can be achieved, and the work is less fatiguing. Welding is performed with the wire at a 45º travel angle and 45º work angle.
Other positions require different techniques such as a weaving pass, circular pass, and jogging. A higher skill level is required to complete these welds.
Overhead welding is the least desirable position as it is the most difficult and dangerous. Heat setting and wire selection will vary depending upon the position.
8
Welding Guidelines (Continued)
All work should be performed in the flat position if possible. For specific applications, consult an arc welding technical manual.
WELD PASSES
Sometimes more then one pass is necessary to fill the joint. The root pass is first, followed by filler passes and the cover pass. If the pieces are thick, it may be necessary to bevel the edges that are joined at a 60º angle. Remember to remove the slag before each pass for gasless process.
Cover
Filler
Root
Figure 12 - Weld Passes |
Figure 13 - Multiple Weld Passes |
T1
|
S4 |
Heat |
- |
|
6 |
Selector |
|
Thermal |
Switch |
Max. |
|
|
|
||
Breaker |
|
S2 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
X |
|
|
|
Min. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
On/Off |
S1 |
4 |
1 |
2 |
Switch |
S5 1
Plug
L2(N) |
L1 |
Ground |
White |
Black |
Green |
|
|
Figure 15 - Wiring Schematic
Model WG2020
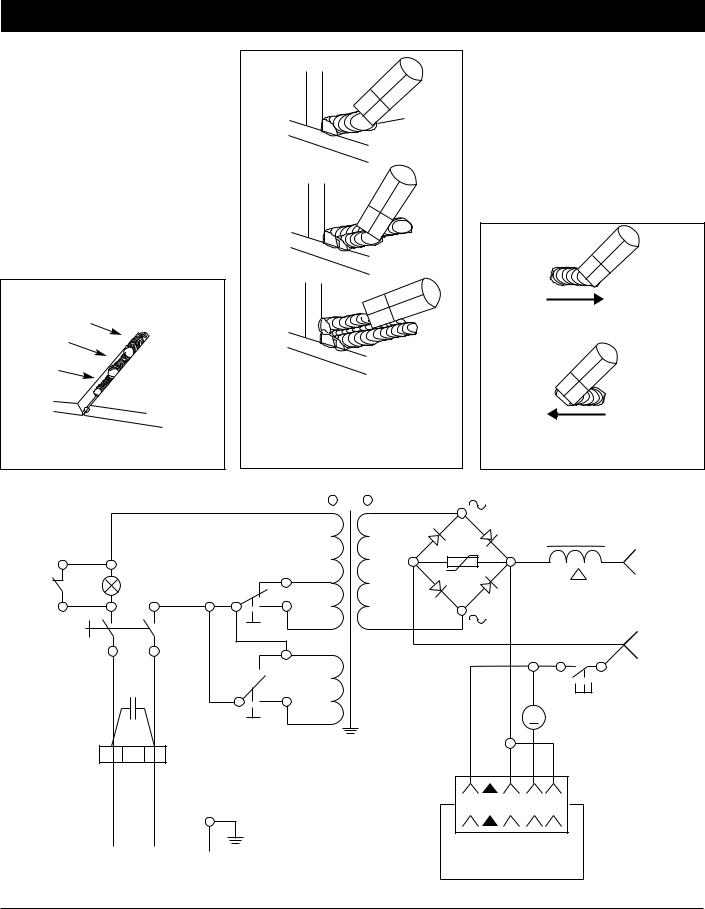
PUSH VS PULL TECHNIQUE
The type and thickness of the work piece dictates which way to point the gun nozzle. For thin materials (18 gauge and up) and all aluminum, the nozzle should point out in front of the weld puddle and push the puddle across the workpiece. For thicker steel, the nozzle should point into the puddle to increase weld penetration. This is called backhand or pull technique (See Figure 14).
PULL
PUSH
Figure 14
AC to DC Converter
T2
+
(+)
S4 Thermal Breaker
(-)
S3 Gun Trigger
-
HWire Feed Motor
+
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
Wire Speed
Control
www.campbellhausfeld.com
9

Wire Feed Arc Welder
For Information About This Product Call 1-800-746-5641
Troubleshooting Chart - Welder
Symptom |
Possible Cause(s) |
Corrective Action |
No output |
1. Duty cycle exceeded |
1. Allow welder to cool until ON/OFF Switch lamp goes out |
|
2. Poor work clamp |
2. Be sure all connections are secure, and attaching surface is |
|
connection |
clean |
|
3. Defective ON/OFF |
3. Replace switch |
|
switch |
|
|
4. Blown breaker or fuse |
4. Reduce circuit load, reset breaker or replace fuse |
|
|
|
Wire tangles at drive roller |
1. Wrong size gun tip |
1. Use proper size gun tip |
|
2. Gun liner clogged or |
2. Clean or replace gun liner |
|
damaged |
|
|
3. Gun tip clogged or |
3. Clean or replace gun tip |
|
damaged |
|
|
4. Feed roller worn |
4. Replace |
|
5. Not enough tension |
5. Tighten tensioning screw |
|
|
|
Gun nozzle arcs to work surface |
Slag inside gun nozzle |
Clean slag from gun nozzle |
|
|
|
Work clamp and/or cable gets |
Poor contact |
Be sure all connections are secure, and attaching surface is |
hot |
|
clean |
|
|
|
Wire does not feed |
1. Wire jammed |
1. Reload wire |
|
2. Out of wire |
2. Replace wire spool |
|
3. Not enough tension |
3. Tighten tensioning screws if wire is slipping |
|
4. Wire liner worn |
4. Replace liner |
|
5. Fuse blown |
5. Replace fuse on wire feed control board inside welder |
|
|
(1.6 amp) |
Troubleshooting Chart - Welds
|
|
Symptom |
Possible Cause(s) |
Corrective Action |
|
|
|
|
Bead is intermittently too thin |
1. Inconsistent travel speed |
1. Decrease and maintain constant travel speed |
|
|
|
|
|
2. Output heat setting too low |
2. Increase output heat setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bead is intermittently too thick |
1. Slow and/or inconsistent |
1. Increase and maintain travel speed |
|
|
|
|
|
travel speed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Output heat setting too high |
2. Reduce output heat setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ragged depressions at edge of |
1. Travel speed too fast |
1. Decrease travel speed |
|
|
|
|
weld |
2. Wire speed too fast |
2. Decrease wire speed |
|
|
|
|
|
3. Output heat setting too high |
3. Reduce output heat setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weld bead does not penetrate |
1. Inconsistent travel speed |
1. Decrease and maintain constant travel speed |
|
|
|
|
base metal |
2. Output heat setting too low |
2. Increase output heat setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wire sputters and sticks |
1. Damp wire |
1. Use dry wire and store in dry location |
|
|
|
|
|
2. Wire speed too fast |
2. Reduce wire speed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.campbellhausfeld.com |
|
|
|
|
|
10
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Model WG2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
32 |
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
24 |
29 |
27 |
22 |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
Inside |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
37 |
|
|
12 |
9, 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
31 |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
2 |
|
For Information About |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
This Product |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Call 1-800-746-5641 |
|
|
|
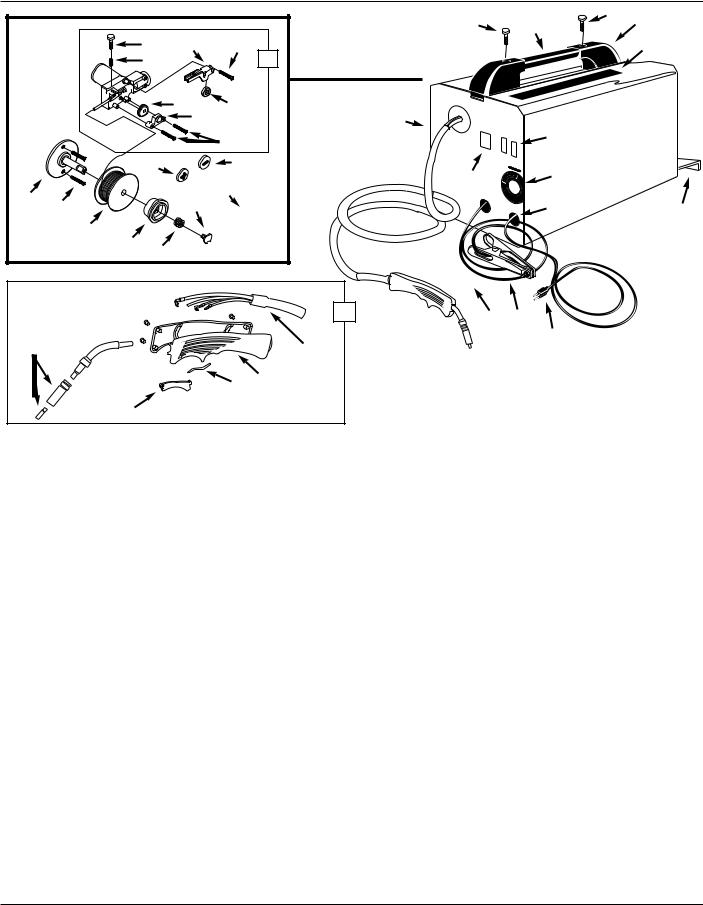
Figure 16 - Replacement Parts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ref. |
|
|
|
|
No. |
Description |
Part Number |
Qty |
1 |
Torch assembly and hose |
|
|
|
|
|
(includes Nos. 2-6 and 34) |
WC600300AV |
1 |
2 |
Torch body, front and back |
WC600201AV |
1 |
|
3 |
Hanger clip (not shown) |
WC600003AV |
1 |
|
4 |
Nozzle/contact tip kit |
WT501000AJ |
1 |
|
5 |
Trigger knob |
WC600202AV |
1 |
|
6 |
Torch contact spring |
WC600203AV |
1 |
|
7 |
Work clamp (Cord not included) |
WC100000AV |
1 |
|
8 |
Welding cable 6 AWG (6 ft) |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
Wire speed knob |
WC400201AV |
1 |
|
10 |
Wire speed switch |
WC400200AV |
1 |
|
11 |
Heat switch |
WC400300AV |
2 |
|
12 |
On/off switch |
WC400000AV |
1 |
|
13 |
Safety decal |
DK404000AV |
1 |
|
14 |
Handle |
WC300100AV |
1 |
|
15 |
Power cord 14-3 AWG (6 ft) |
|
|
|
|
|
Type SJT |
WC000100AJ |
1 |
16 |
Spool spindle |
WC500300AV |
1 |
|
17 |
#10-32 x .5” Pan head sheet |
|
|
|
|
|
metal screw |
|
2 |
18 |
Wire flux core .035” |
|
|
|
|
|
(.9mm) diameter |
WE200500AJ |
1 |
Ref. |
|
|
|
|
No. |
Description |
Part Number |
Qty |
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
Spool adapter |
WC500200AV |
1 |
|
20 |
Spool spring |
WC500101AV |
1 |
|
21 |
Spool locking hub |
WC500100AV |
1 |
|
22 |
Drive deck assembly |
|
|
|
|
(Includes Nos.23-28) |
WC500000AV |
1 |
|
23 |
Tension spring |
WC500003AV |
1 |
|
24 |
Tension screw |
WC500002AV |
1 |
|
25 |
Roller, .6-.9mm (.024-.035 in.) |
WC500001AV |
1 |
|
26 |
Roller cover |
WC500004AV |
1 |
|
27 |
#8-36 x 1.5” Pan head screw |
|
3 |
|
28 |
Swing arm |
WC500005AV |
1 |
|
29 |
Swing arm roller |
WC500007AV |
1 |
|
30 |
Side panel |
WC700000AV |
1 |
|
31 |
Strain relief |
WC102000AV |
2 |
|
32 |
M8 x 16mm Machine screw |
|
2 |
|
33 |
Handle caps |
WC300101AV |
2 |
|
34 |
Liner |
WC600008AV |
1 |
|
35 |
Cylinder base |
WC703900AV |
1 |
|
36 |
Polarity cap (Red) |
WC704000AV |
1 |
|
37 |
Polarity cap (Black) |
WC704100AV |
1 |
|
Standard hardware item, available at local hardware or welder supply store
www.campbellhausfeld.com
11
 Loading...
Loading...