14.1 Wall-Mounting
This section shows you how to mount your MAX208M2W Series on a wall using the
ZyXEL Wall-Mounting kit (not included).
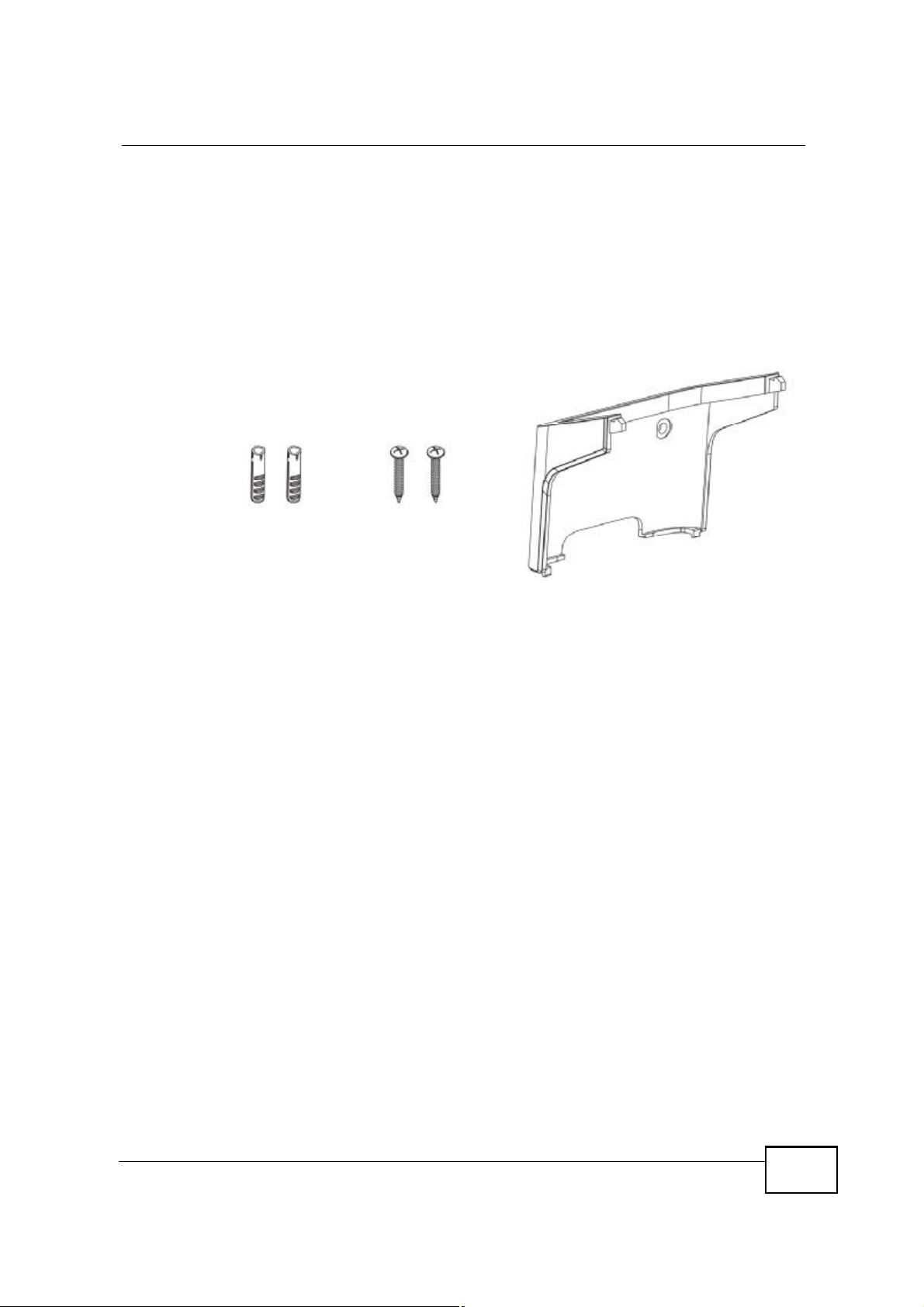
14.1.1 The Wall-Mounting Kit
The wall-mounting kit contains the following parts:
123
Chapter 14Product Specifications
1 Two Mortar Plugs (M4*L30 mm)
2 Two Screws (M4*L30 mm)
3 Wall-Mounting Chassis
If any parts are missing, contact your vendor.
14.1.2 Instructions
To mount the MAX208M2W Series on a wall:
1 Select a position free of obstructions on a sturdy wall.
2 Drill two holes in the wall exactly 70 mm apart. The holes should be 6 mm wide
and at least 30 mm deep.
Be careful to avoid damaging pipes or cables located inside the
wall when drilling holes for the screws.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
201
Chapter 14Product Specifications
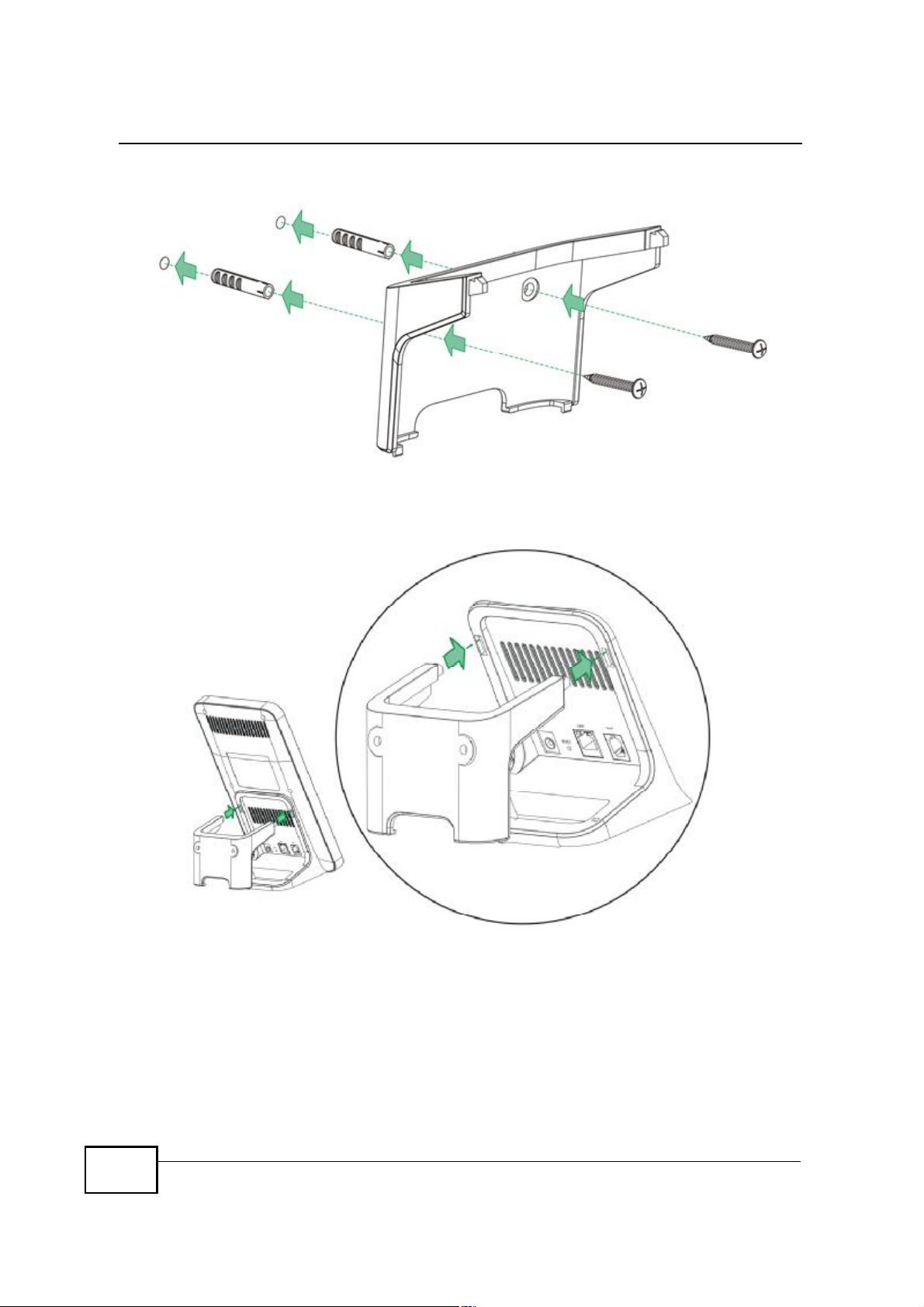
3 Attach the wall mounting chassis with the plugs and screws as shown below:
4 Connect the MAX208M2W Series to the wall mounting chassis by snapping the
chassis two upper chassis hooks into the matching holes on the MAX208M2W
Series:
202
Do not pinch or server the cable connections between the wallmounting chassis the MAX208M2W Series.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
Chapter 14Product Specifications
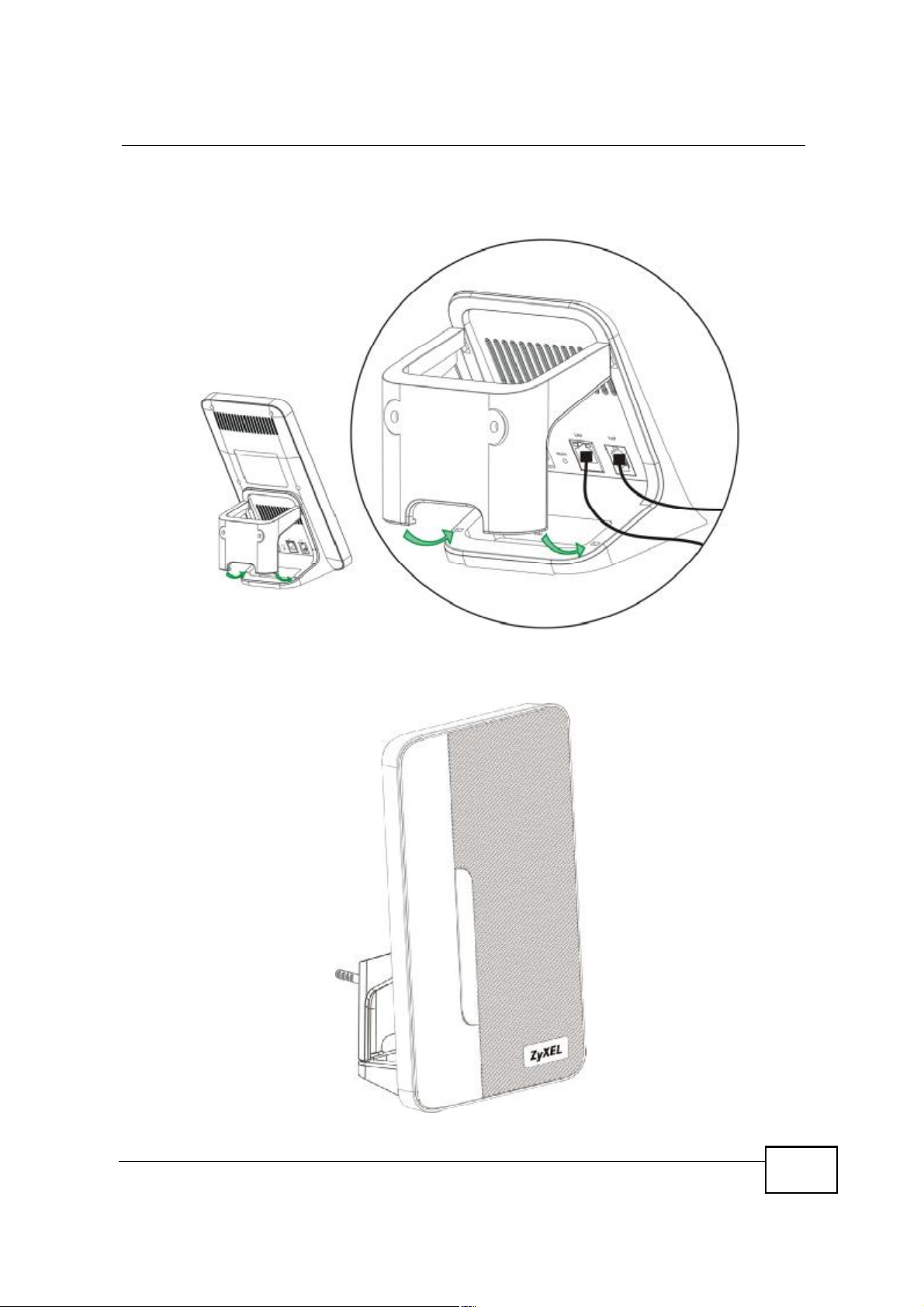
5 Snap the lower chassis hooks into the matching holes on the MAX208M2W Series.
The cable connections should come out either the left or right gaps between the
wall-mounting chassis and the MAX208M2W Series
6 Once you have snapped the wall-mounting chassis in place, the MAX208M2W
Series is securely fastened to the wall.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
203

Chapter 14Product Specifications
204
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

APPENDIX A
WiMAX Security
Wireless security is vital to protect your wireless communications. Without it,
information transmitted over the wireless network would be accessible to any
networking device within range.
User Authentication and Data Encryption
The WiMAX (IEEE 802.16) standard employs user authentication and encryption to
ensure secured communication at all times.
User authentication is the process of confirming a user s identity and level of
authorization. Data encryption is the process of encoding information so that it
cannot be read by anyone who does not know the code.
PKMv2
WiMAX uses PKMv2 (Privacy Key Management version 2) for authentication, and
CCMP (Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Protocol)
for data encryption.
WiMAX supports EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol, RFC 2486) which allows
additional authentication methods to be deployed with no changes to the base
station or the mobile or subscriber stations.
PKMv2 is a procedure that allows authentication of a mobile or subscriber station
and negotiation of a public key to encrypt traffic between the MS/SS and the base
station. PKMv2 uses standard EAP methods such as Transport Layer Security
(EAP-TLS) or Tunneled TLS (EAP-TTLS) for secure communication.
In cryptography, a $key is a piece of information, typically a string of random
numbers and letters, that can be used to $lock (encrypt) or $unlock (decrypt) a
message. Public key encryption uses key pairs, which consist of a public (freely
available) key and a private (secret) key. The public key is used for encryption and
the private key is used for decryption. You can decrypt a message only if you have
the private key. Public key certificates (or $digital IDs ) allow users to verify each
other s identity.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
205

Appendix AWiMAX Security
RADIUS
RADIUS is based on a client-server model that supports authentication,
authorization and accounting. The base station is the client and the server is the
RADIUS server. The RADIUS server handles the following tasks:
! Authentication
Determines the identity of the users.
! Authorization
Determines the network services available to authenticated users once they are
connected to the network.
! Accounting
Keeps track of the client s network activity.
RADIUS is a simple package exchange in which your base station acts as a
message relay between the MS/SS and the network RADIUS server.
Types of RADIUS Messages
The following types of RADIUS messages are exchanged between the base station
and the RADIUS server for user authentication:
! Access-Request
Sent by an base station requesting authentication.
! Access-Reject
Sent by a RADIUS server rejecting access.
! Access-Accept
Sent by a RADIUS server allowing access.
! Access-Challenge
Sent by a RADIUS server requesting more information in order to allow access.
The base station sends a proper response from the user and then sends another
Access-Request message.
The following types of RADIUS messages are exchanged between the base station
and the RADIUS server for user accounting:
! Accounting-Request
Sent by the base station requesting accounting.
! Accounting-Response
Sent by the RADIUS server to indicate that it has started or stopped accounting.
206
In order to ensure network security, the access point and the RADIUS server use a
shared secret key, which is a password they both know. The key is not sent over
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

the network. In addition to the shared key, password information exchanged is
also encrypted to protect the network from unauthorized access.
Diameter
Diameter (RFC 3588) is a type of AAA server that provides several improvements
over RADIUS in efficiency, security, and support for roaming.
Security Association
The set of information about user authentication and data encryption between two
computers is known as a security association (SA). In a WiMAX network, the
process of security association has three stages.
! Authorization request and reply
The MS/SS presents its public certificate to the base station. The base station
verifies the certificate and sends an authentication key (AK) to the MS/SS.
! Key request and reply
The MS/SS requests a transport encryption key (TEK) which the base station
generates and encrypts using the authentication key.
Appendix AWiMAX Security
CCMP
! Encrypted traffic
The MS/SS decrypts the TEK (using the authentication key). Both stations can
now securely encrypt and decrypt the data flow.
All traffic in a WiMAX network is encrypted using CCMP (Counter Mode with Cipher
Block Chaining Message Authentication Protocol). CCMP is based on the 128-bit
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm.
$Counter mode refers to the encryption of each block of plain text with an
arbitrary number, known as the counter. This number changes each time a block
of plain text is encrypted. Counter mode avoids the security weakness of repeated
identical blocks of encrypted text that makes encrypted data vulnerable to
pattern-spotting.
$Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication (also known as CBC-MAC) ensures
message integrity by encrypting each block of plain text in such a way that its
encryption is dependent on the block before it. This series of $chained blocks
creates a message authentication code (MAC or CMAC) that ensures the encrypted
data has not been tampered with.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
207

Appendix AWiMAX Security
Authentication
The MAX208M2W Series supports EAP-TTLS authentication.
EAP-TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Service)
EAP-TTLS is an extension of the EAP-TLS authentication that uses certificates for
only the server-side authentications to establish a secure connection (with EAPTLS digital certifications are needed by both the server and the wireless clients for
mutual authentication). Client authentication is then done by sending username
and password through the secure connection, thus client identity is protected. For
client authentication, EAP-TTLS supports EAP methods and legacy authentication
methods such as PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP and MS-CHAP v2.
208
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

APPENDIX B
Setting Up Your Computer!s IP
Address
Note: Your specific ZyXEL device may not support all of the operating systems
described in this appendix. See the product specifications for more information
about which operating systems are supported.
This appendix shows you how to configure the IP settings on your computer in
order for it to be able to communicate with the other devices on your network.
Windows Vista/XP/2000, Mac OS 9/OS X, and all versions of UNIX/LINUX include
the software components you need to use TCP/IP on your computer.
If you manually assign IP information instead of using a dynamic IP, make sure
that your network s computers have IP addresses that place them in the same
subnet.
In this appendix, you can set up an IP address for:
! Windows XP/NT/2000 on page210
! Windows Vista on page213
! Mac OS X: 10.3 and 10.4 on page217
! Mac OS X: 10.5 on page221
! Linux: Ubuntu 8 (GNOME) on page 224
! Linux: openSUSE 10.3 (KDE) on page230
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
209
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
Windows XP/NT/2000
The following example uses the default Windows XP display theme but can also
apply to Windows 2000 and Windows NT.
1 Click Start > Control Panel.
Figure 101 Windows XP: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, click the Network Connections icon.
Figure 102 Windows XP: Control Panel
210
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
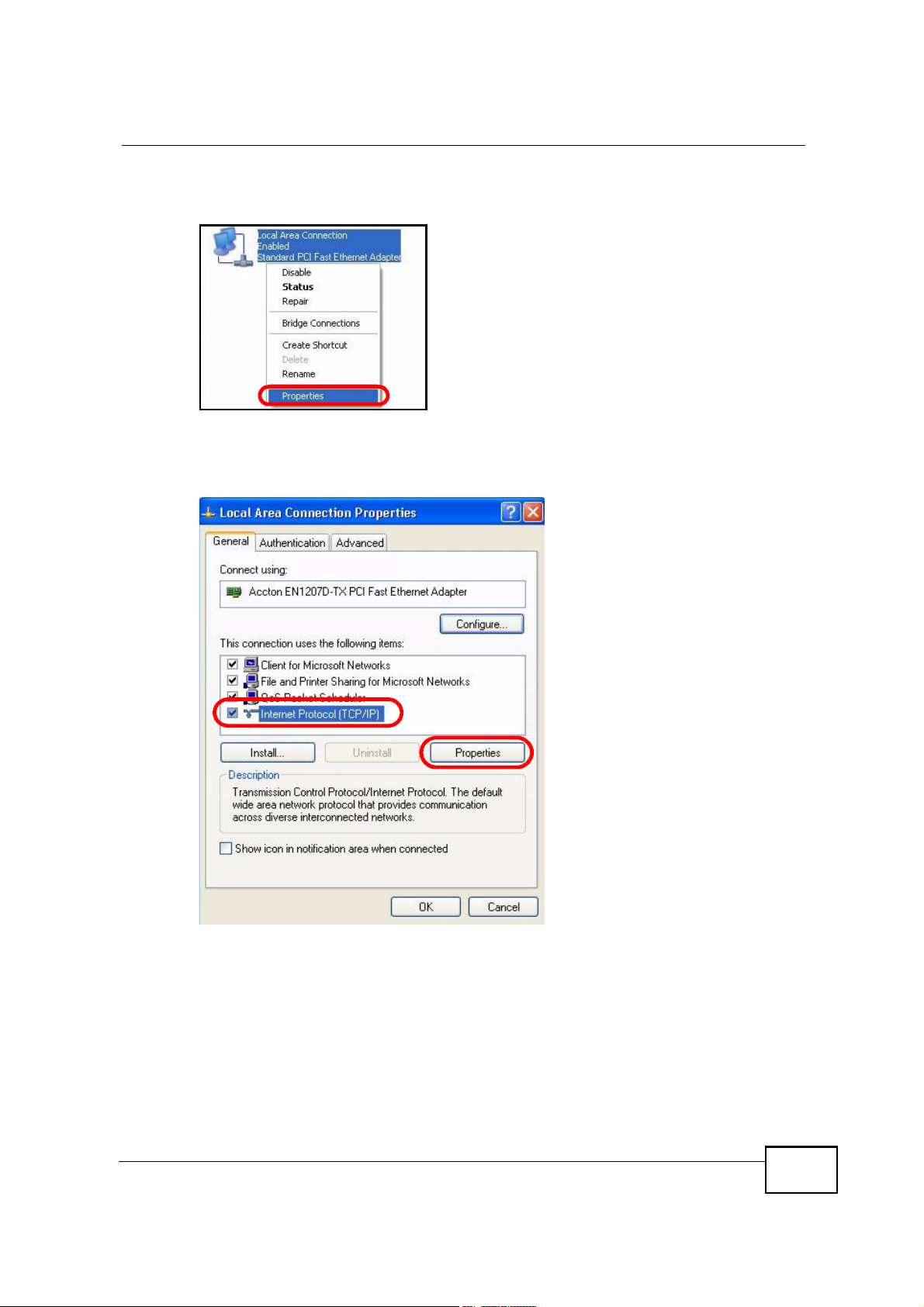
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
3 Right-click Local Area Connection and then select Properties.
Figure 103 Windows XP: Control Panel > Network Connections > Properties
4 On the General tab, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click
Properties.
Figure 104 Windows XP: Local Area Connection Properties
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
211
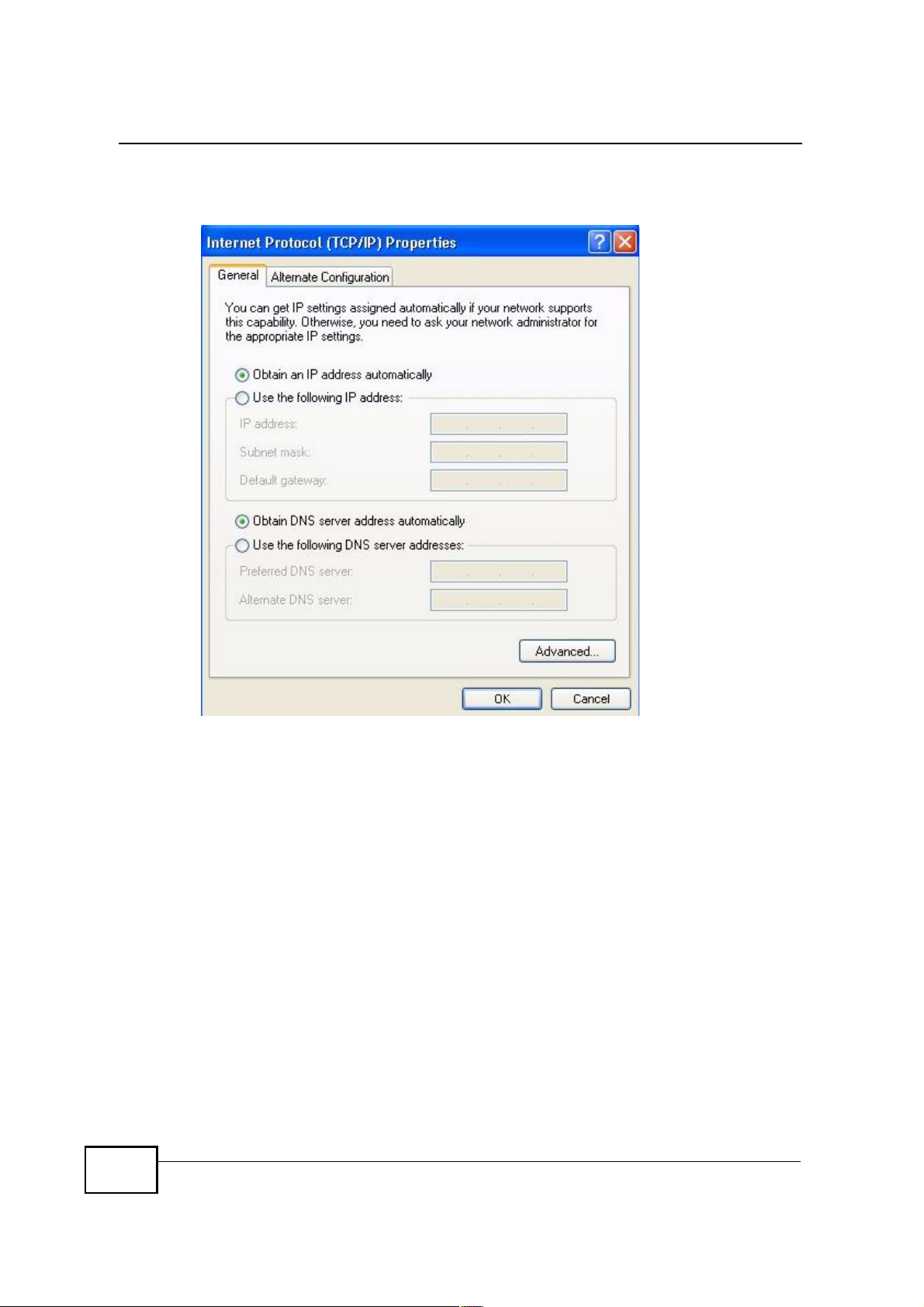
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
5 The Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties window opens.
Figure 105 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
6 Select Obtain an IP address automatically if your network administrator or ISP
assigns your IP address dynamically.
Select Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP address, Subnet mask,
and Default gateway fields if you have a static IP address that was assigned to
you by your network administrator or ISP. You may also have to enter a Preferred
DNS server and an Alternate DNS server, if that information was provided.
7 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.Verifying Settings
1 Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER].
You can also go to Start > Control Panel > Network Connections, right-click a
network connection, click Status and then click the Support tab to view your IP
address and connection information.
212
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
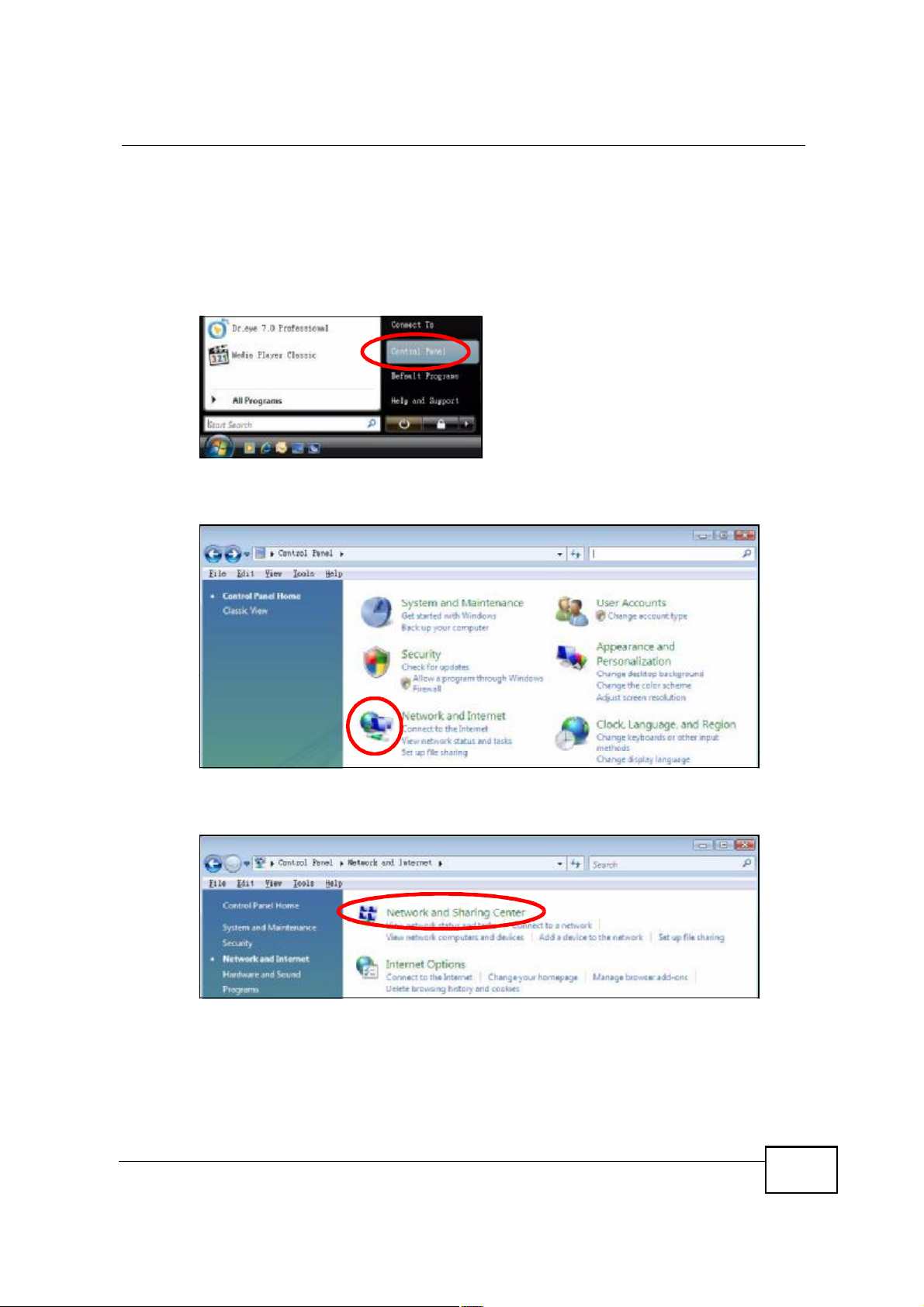
Windows Vista
This section shows screens from Windows Vista Professional.
1 Click Start > Control Panel.
Figure 106 Windows Vista: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, click the Network and Internet icon.
Figure 107 Windows Vista: Control Panel
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
3 Click the Network and Sharing Center icon.
Figure 108 Windows Vista: Network And Internet
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
213
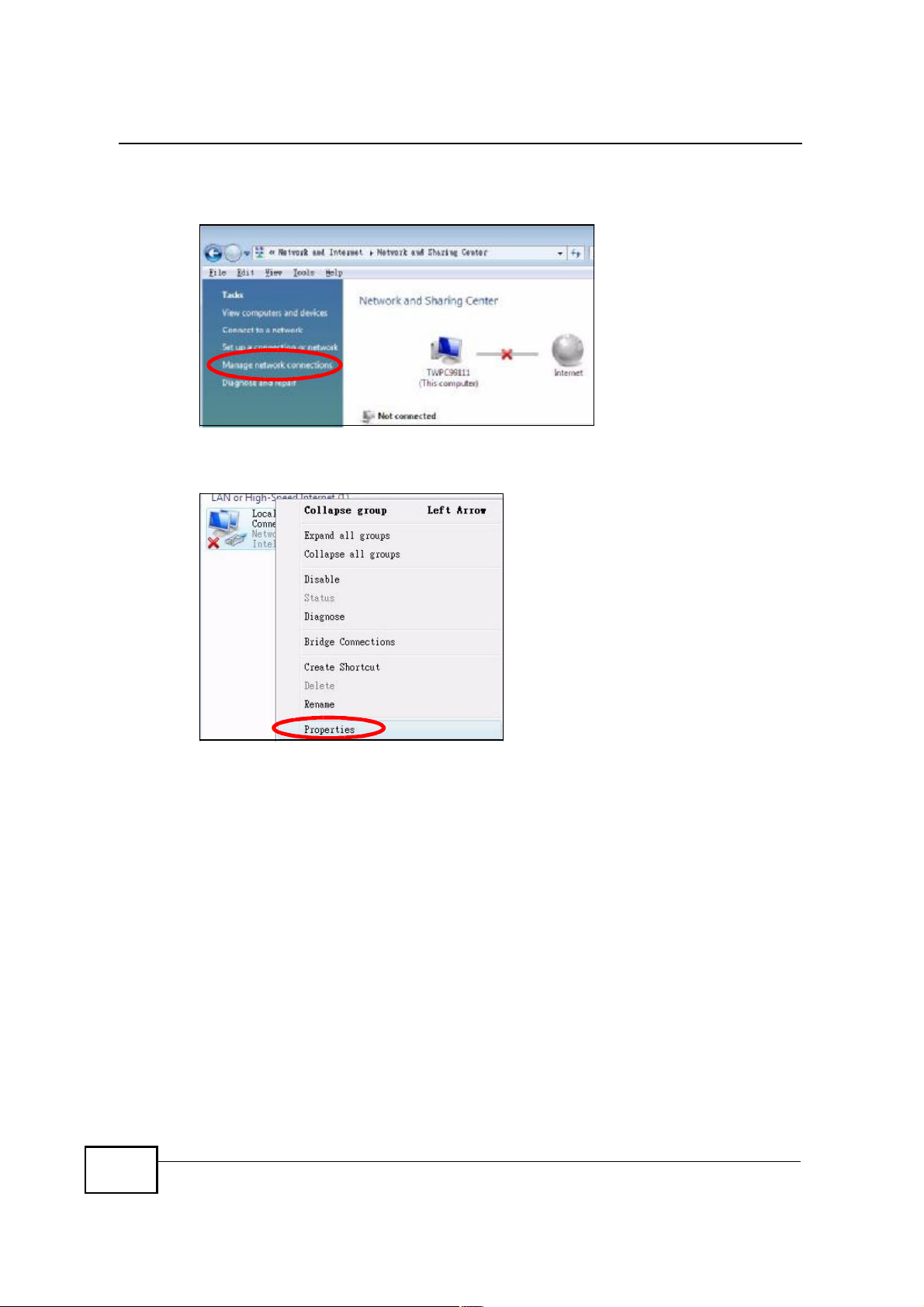
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
4 Click Manage network connections.
Figure 109 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
5 Right-click Local Area Connection and then select Properties.
Figure 110 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
214
Note: During this procedure, click Continue whenever Windows displays a screen
saying that it needs your permission to continue.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
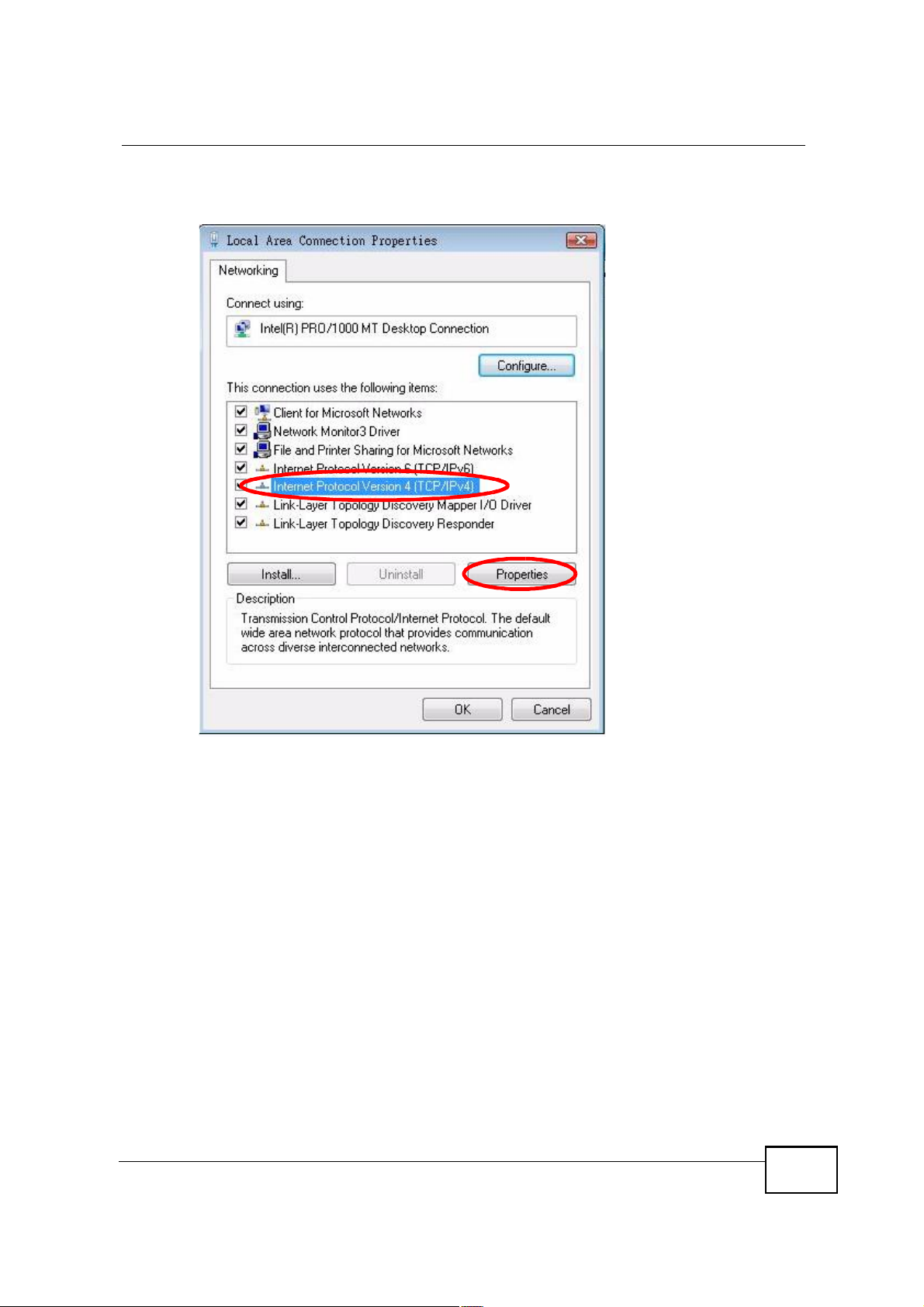
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
6 Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then select Properties.
Figure 111 Windows Vista: Local Area Connection Properties
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
215
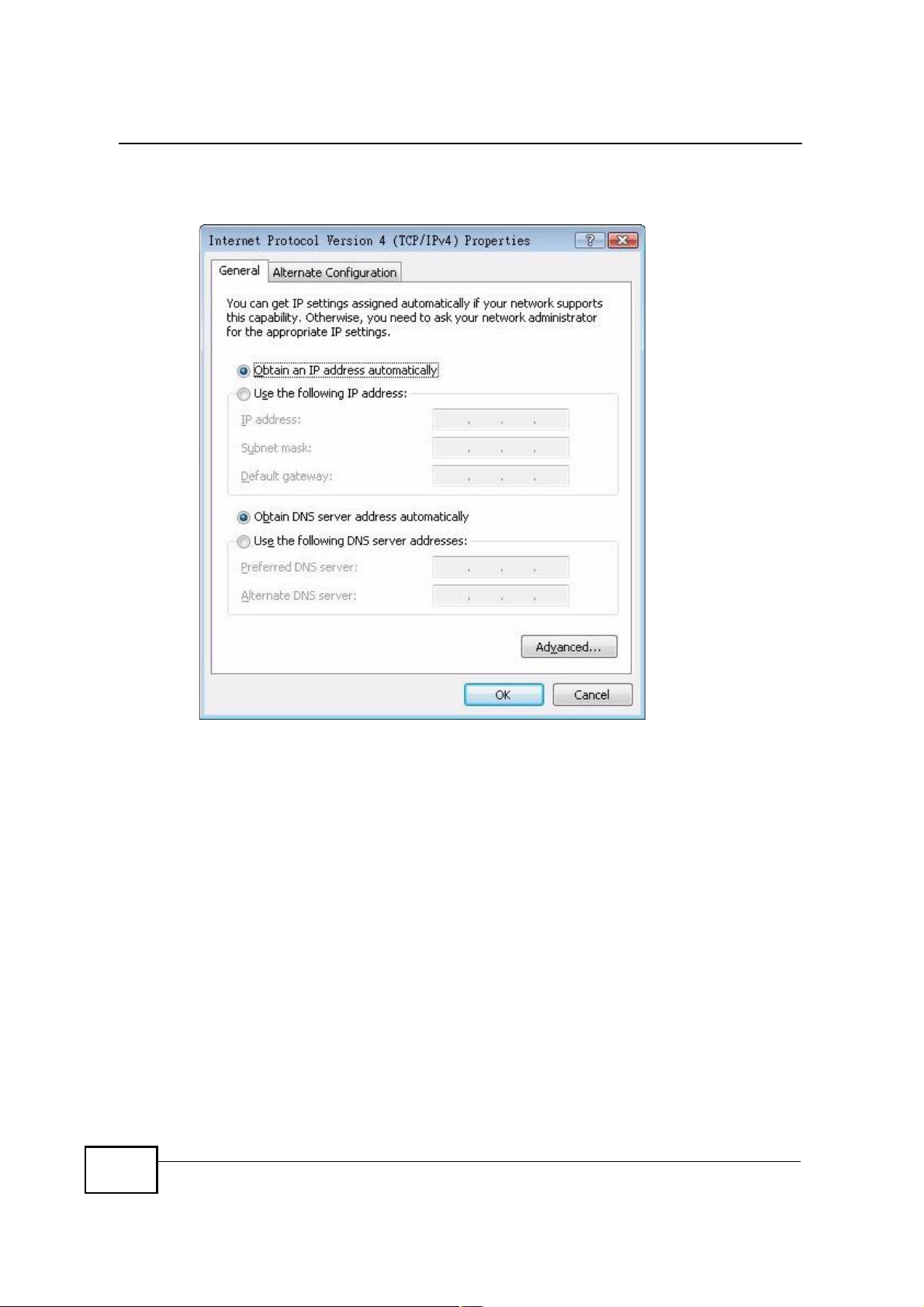
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
7 The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window opens.
Figure 112 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
8 Select Obtain an IP address automatically if your network administrator or ISP
assigns your IP address dynamically.
Select Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP address, Subnet mask,
and Default gateway fields if you have a static IP address that was assigned to
you by your network administrator or ISP. You may also have to enter a Preferred
DNS server and an Alternate DNS server, if that information was
provided.Click Advanced.
9 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.Verifying Settings
1 Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER].
You can also go to Start > Control Panel > Network Connections, right-click a
network connection, click Status and then click the Support tab to view your IP
address and connection information.
216
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
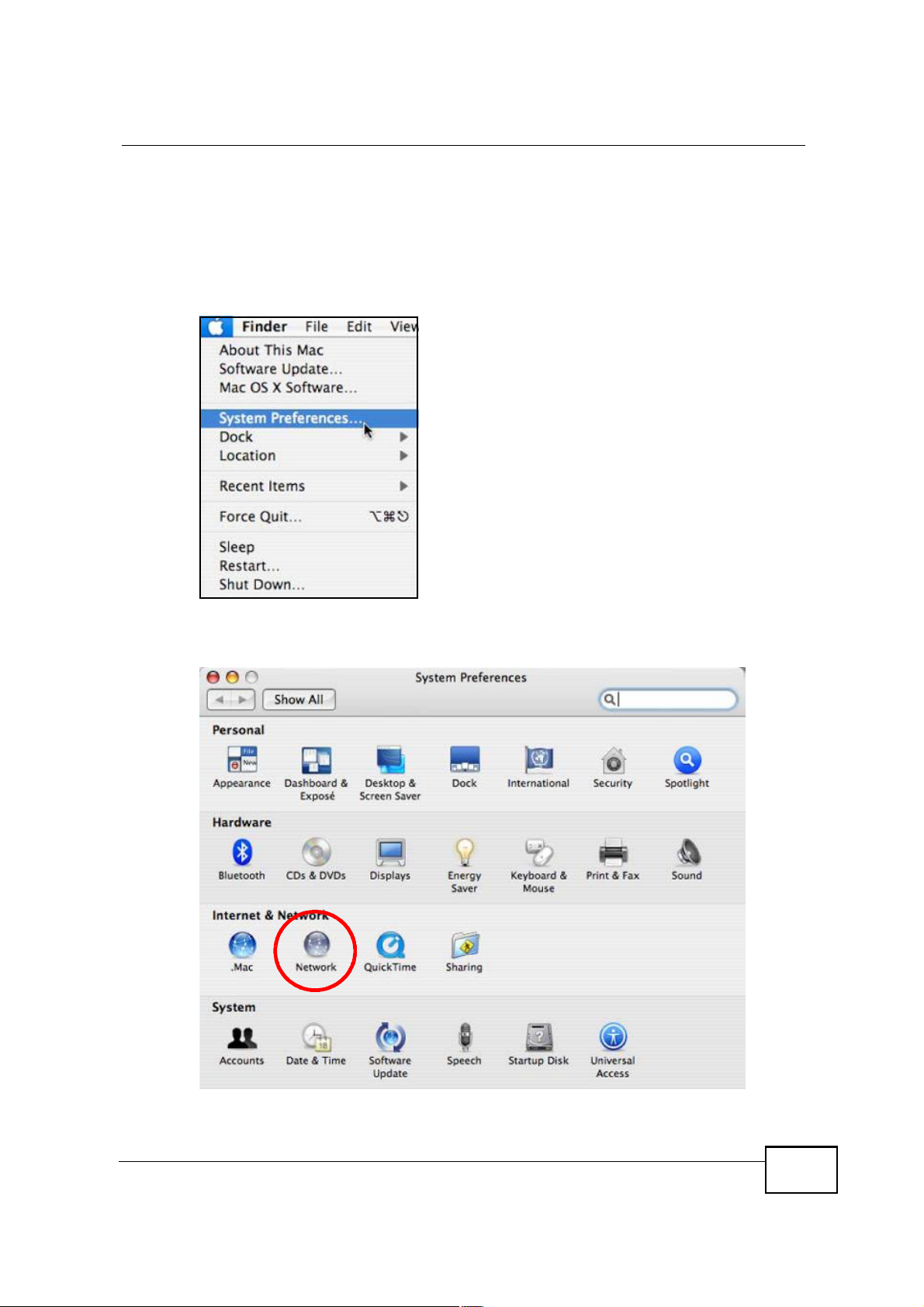
Mac OS X: 10.3 and 10.4
The screens in this section are from Mac OS X 10.4 but can also apply to 10.3.
1 Click Apple > System Preferences.
Figure 113 Mac OS X 10.4: Apple Menu
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
2 In the System Preferences window, click the Network icon.
Figure 114 Mac OS X 10.4: System Preferences
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
217
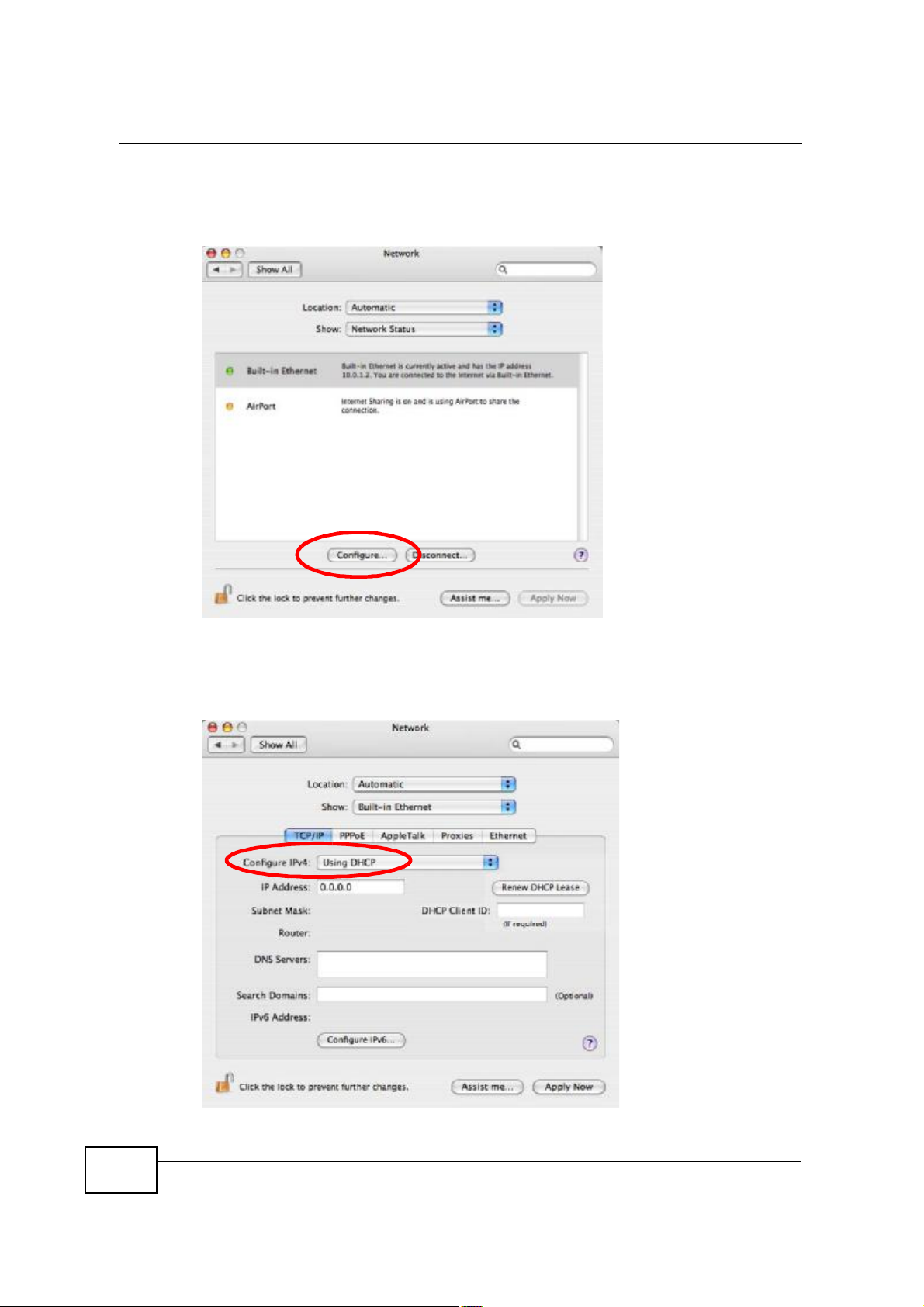
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
3 When the Network preferences pane opens, select Built-in Ethernet from the
network connection type list, and then click Configure.
Figure 115 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences
4 For dynamically assigned settings, select Using DHCP from the Configure IPv4
list in the TCP/IP tab.
Figure 116 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences > TCP/IP Tab.
218
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
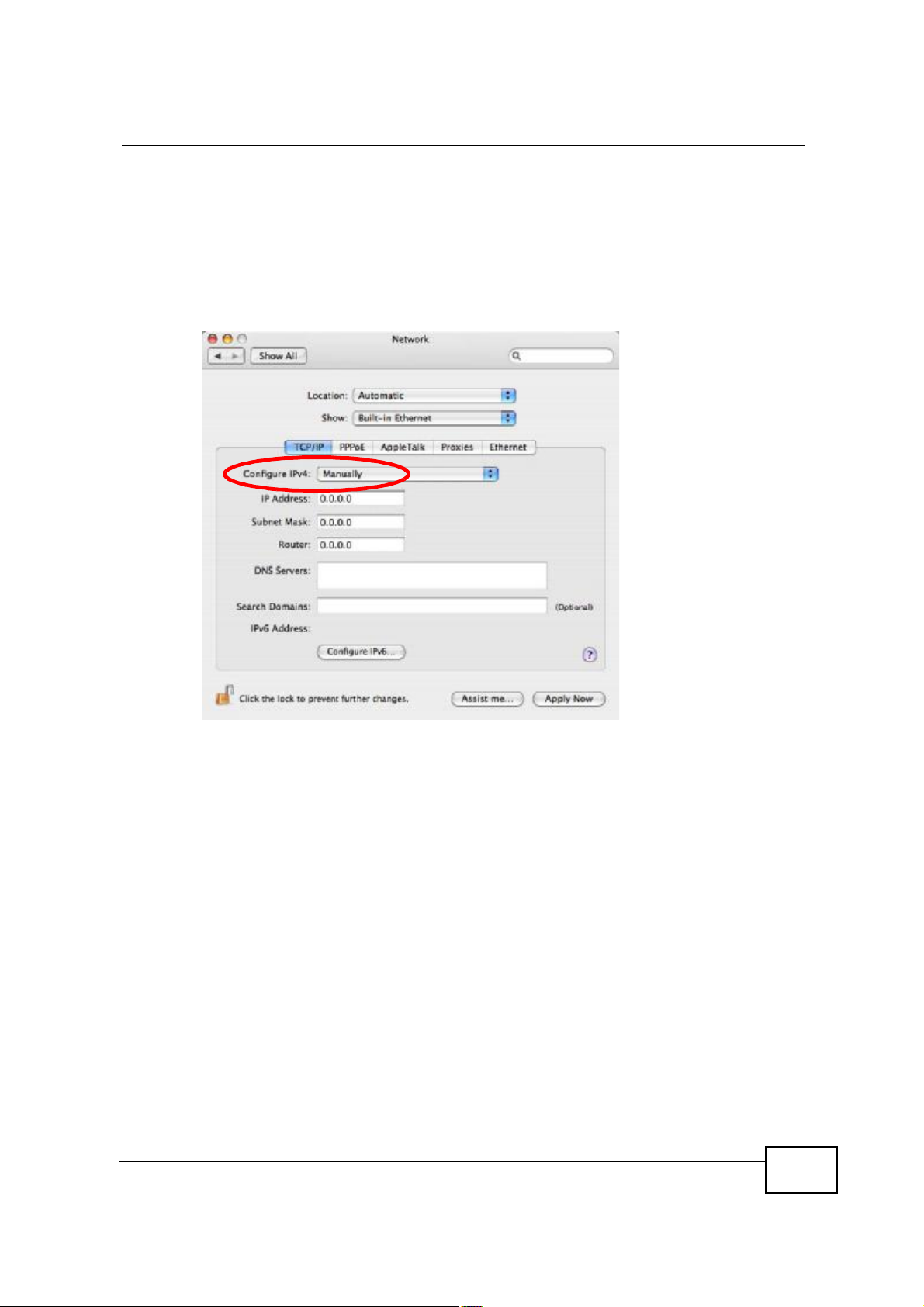
5 For statically assigned settings, do the following:
! From the Configure IPv4 list, select Manually.
! In the IP Address field, type your IP address.
! In the Subnet Mask field, type your subnet mask.
! In the Router field, type the IP address of your device.
Figure 117 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences > Ethernet
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
219
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
Click Apply Now and close the window.Verifying Settings
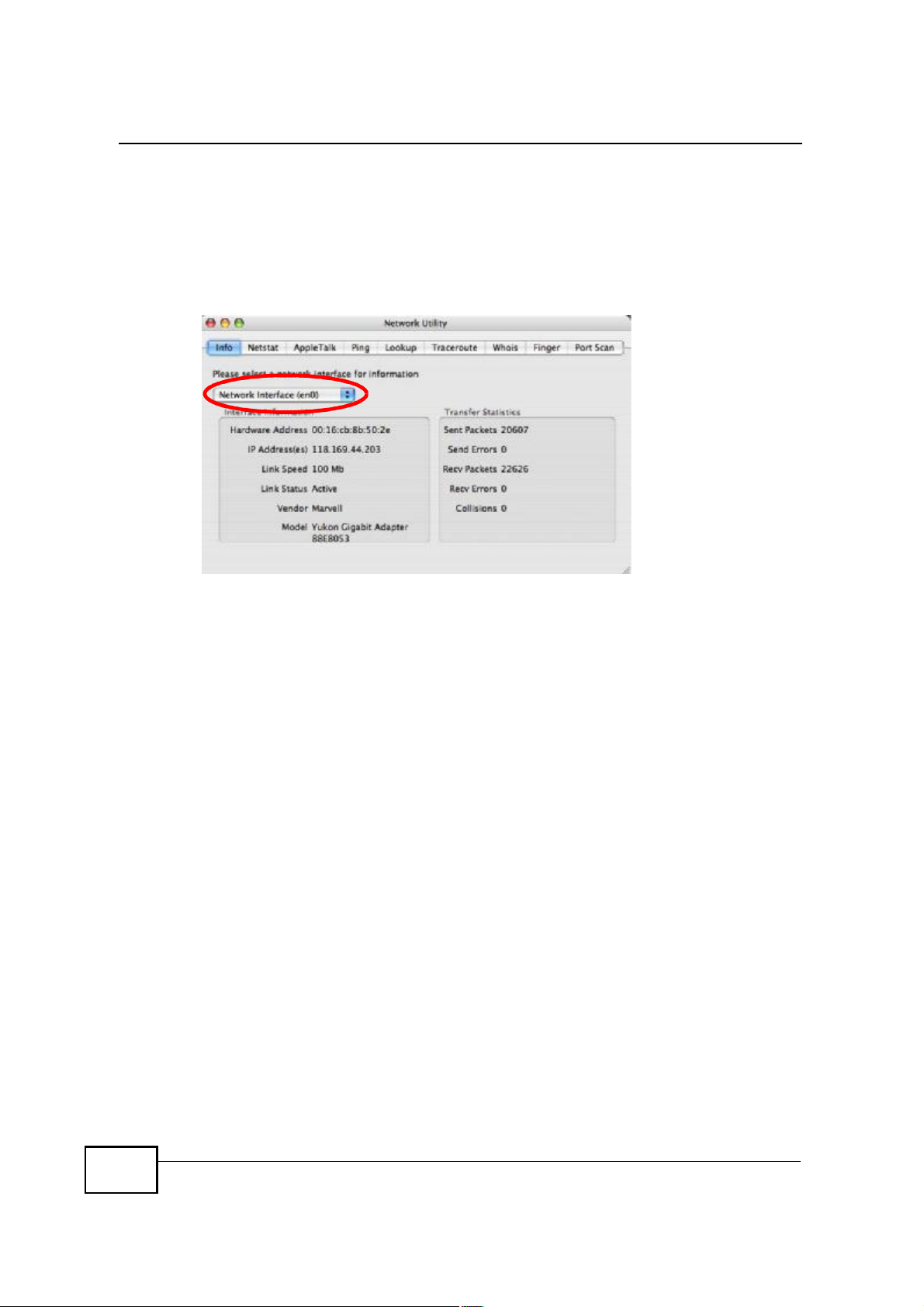
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking Applications > Utilities > Network
Utilities, and then selecting the appropriate Network Interface from the Info
tab.
Figure 118 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Utility
220
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
Mac OS X: 10.5
The screens in this section are from Mac OS X 10.5.
1 Click Apple > System Preferences.
Figure 119 Mac OS X 10.5: Apple Menu
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
2 In System Preferences, click the Network icon.
Figure 120 Mac OS X 10.5: Systems Preferences
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
221
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
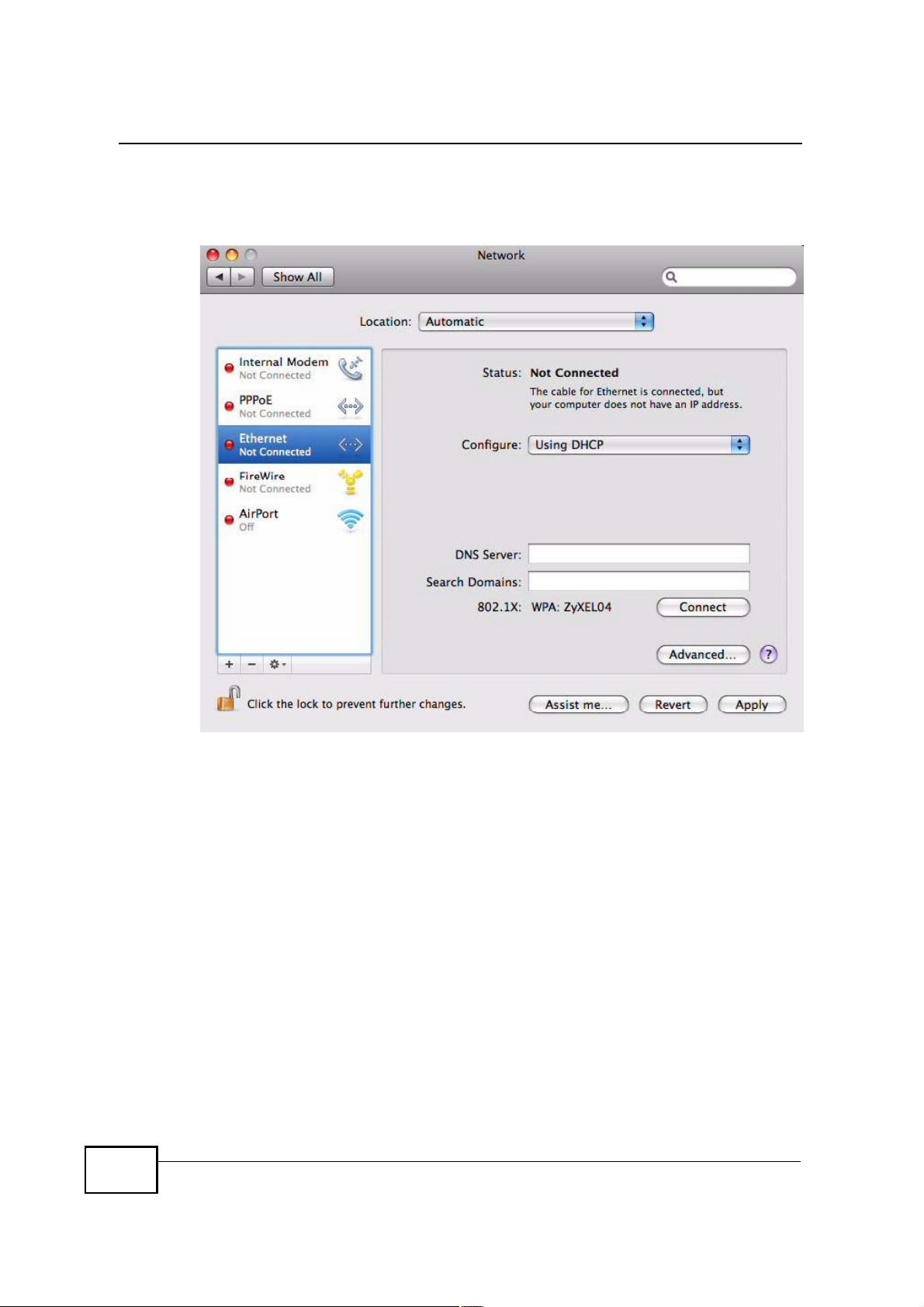
3 When the Network preferences pane opens, select Ethernet from the list of
available connection types.
Figure 121 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Preferences > Ethernet
222
4 From the Configure list, select Using DHCP for dynamically assigned settings.
5 For statically assigned settings, do the following:
! From the Configure list, select Manually.
! In the IP Address field, enter your IP address.
! In the Subnet Mask field, enter your subnet mask.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
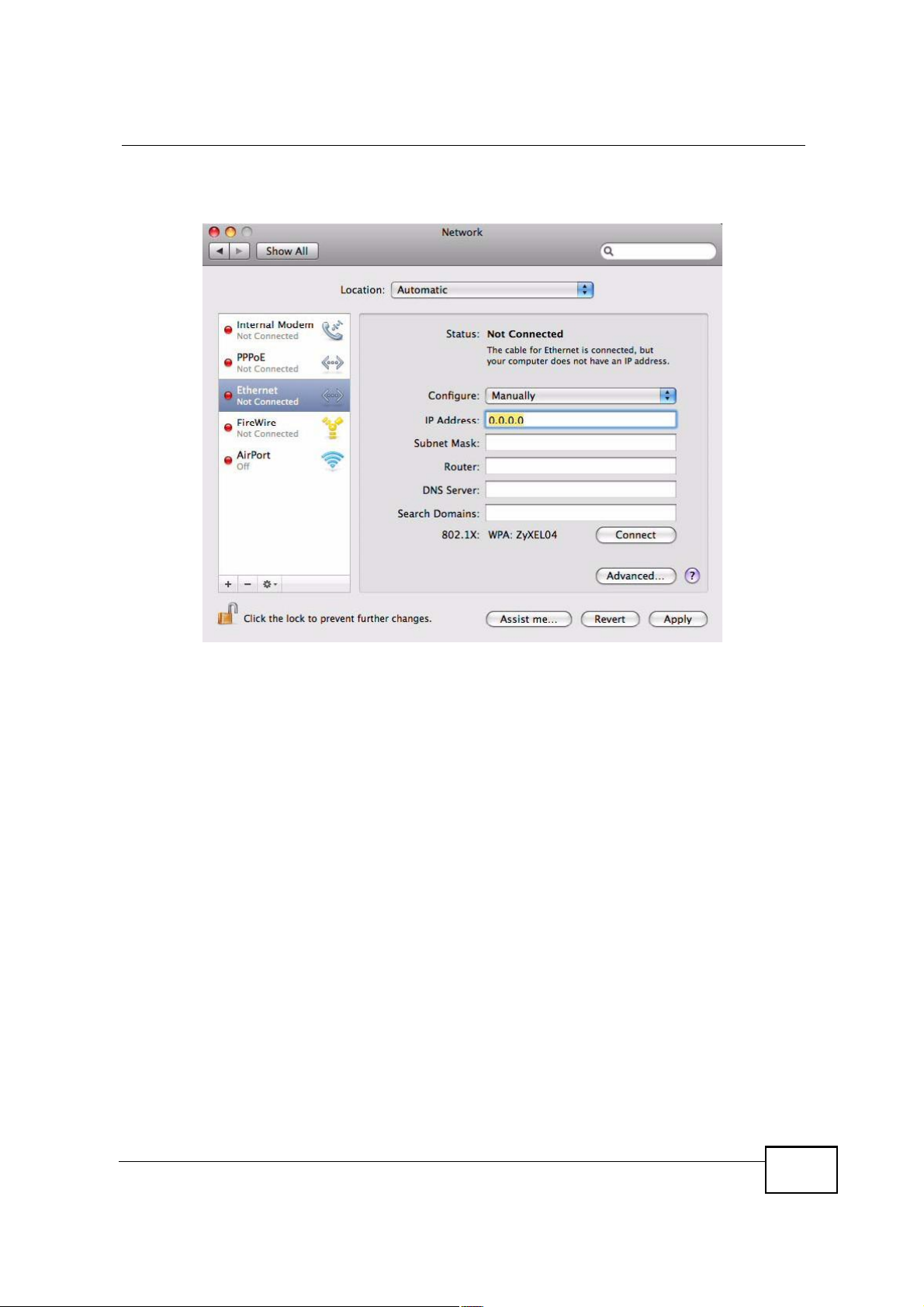
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
! In the Router field, enter the IP address of your MAX208M2W Series.
Figure 122 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Preferences > Ethernet
6 Click Apply and close the window.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
223
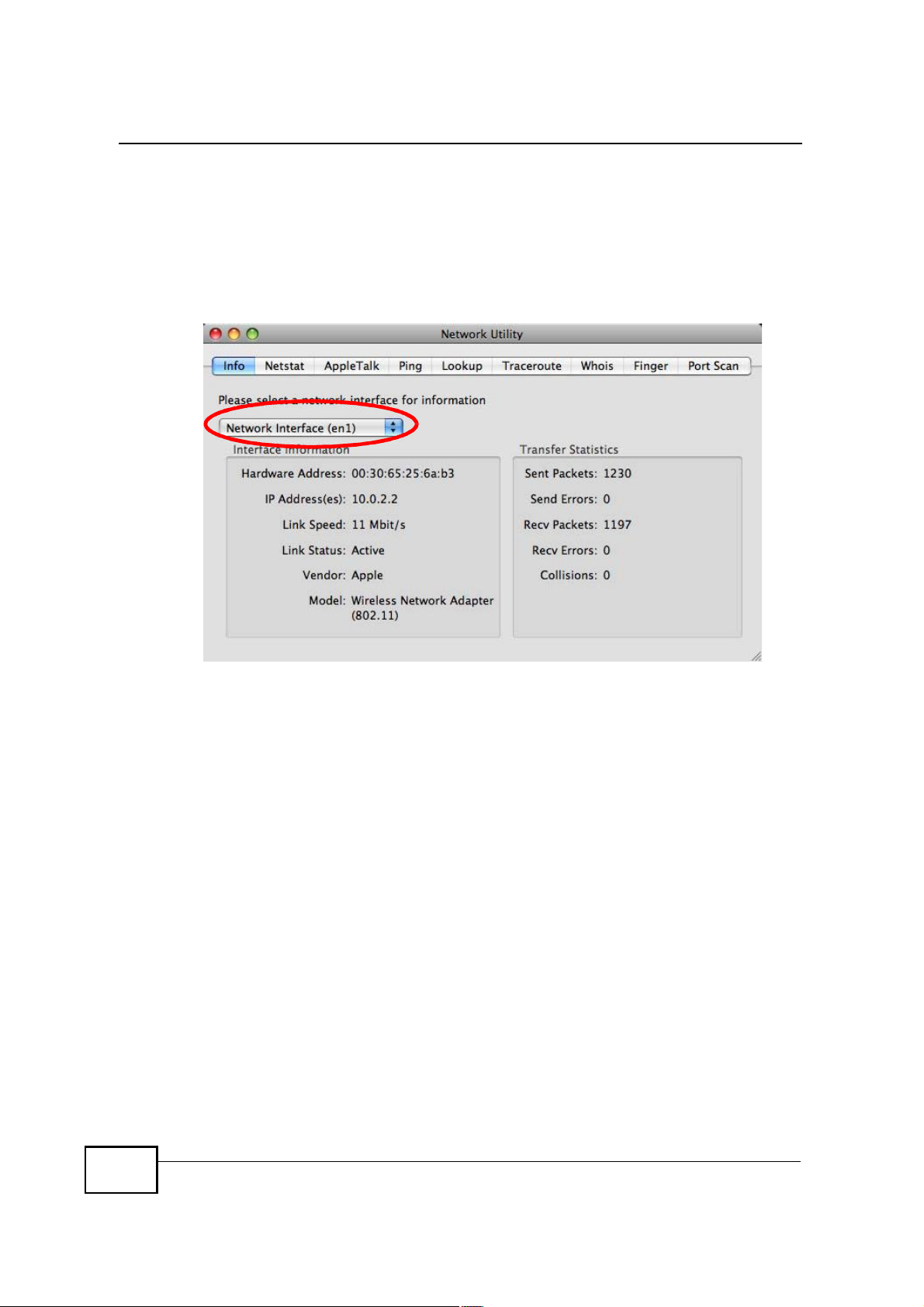
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
Verifying Settings
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking Applications > Utilities > Network
Utilities, and then selecting the appropriate Network interface from the Info
tab.
Figure 123 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Utility
Linux: Ubuntu 8 (GNOME)
This section shows you how to configure your computer s TCP/IP settings in the
GNU Object Model Environment (GNOME) using the Ubuntu 8 Linux distribution.
The procedure, screens and file locations may vary depending on your specific
distribution, release version, and individual configuration. The following screens
use the default Ubuntu 8 installation.
Note: Make sure you are logged in as the root administrator.
Follow the steps below to configure your computer IP address in GNOME:
224
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
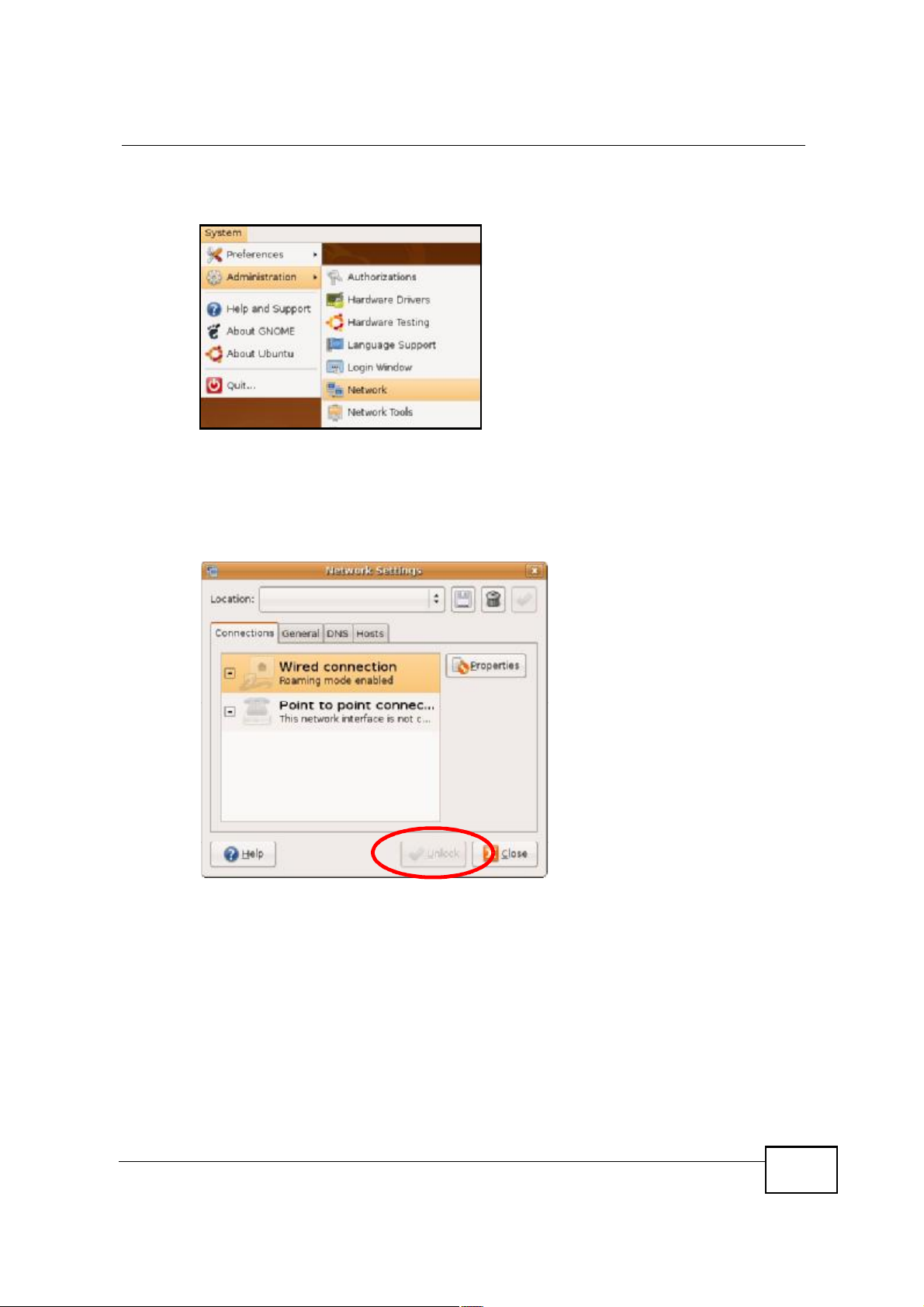
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
1 Click System > Administration > Network.
Figure 124 Ubuntu 8: System > Administration Menu
2 When the Network Settings window opens, click Unlock to open the
Authenticate window. (By default, the Unlock button is greyed out until clicked.)
You cannot make changes to your configuration unless you first enter your admin
password.
Figure 125 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Connections
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
225
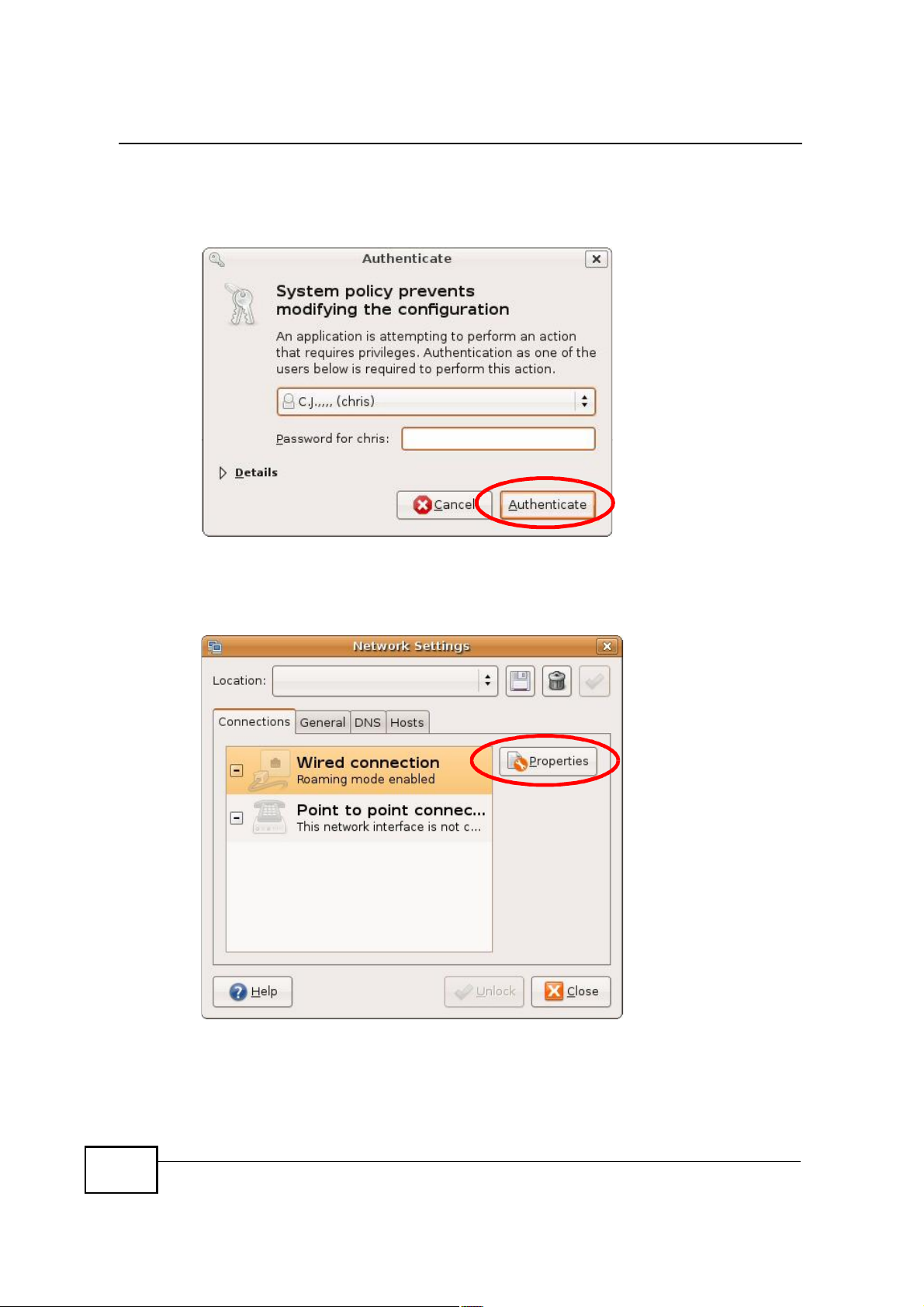
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
3 In the Authenticate window, enter your admin account name and password then
click the Authenticate button.
Figure 126 Ubuntu 8: Administrator Account Authentication
4 In the Network Settings window, select the connection that you want to
configure, then click Properties.
Figure 127 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Connections
226
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
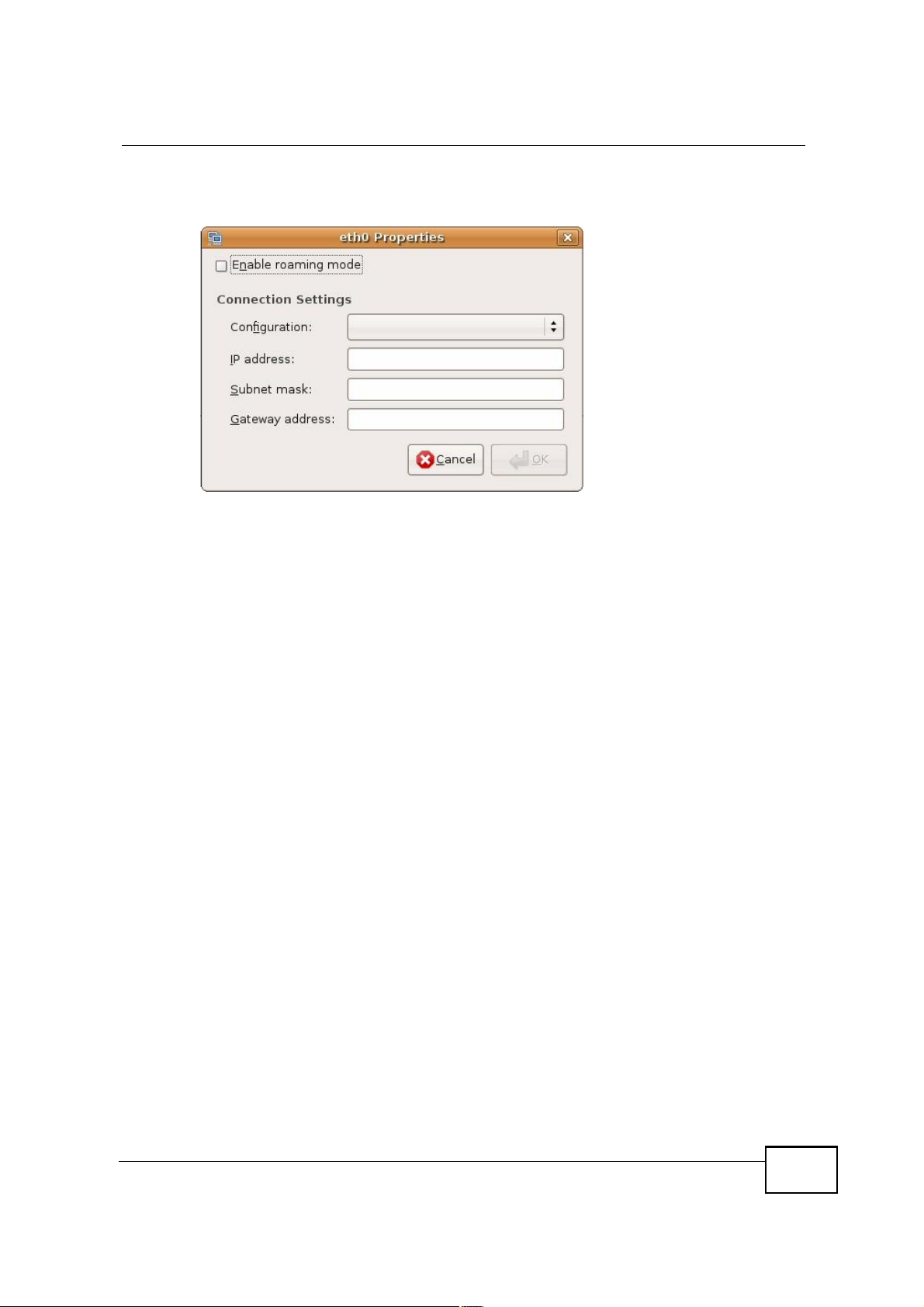
5 The Properties dialog box opens.
Figure 128 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Properties
! In the Configuration list, select Automatic Configuration (DHCP) if you
have a dynamic IP address.
! In the Configuration list, select Static IP address if you have a static IP
address. Fill in the IP address, Subnet mask, and Gateway address fields.
6 Click OK to save the changes and close the Properties dialog box and return to
the Network Settings screen.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
227
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
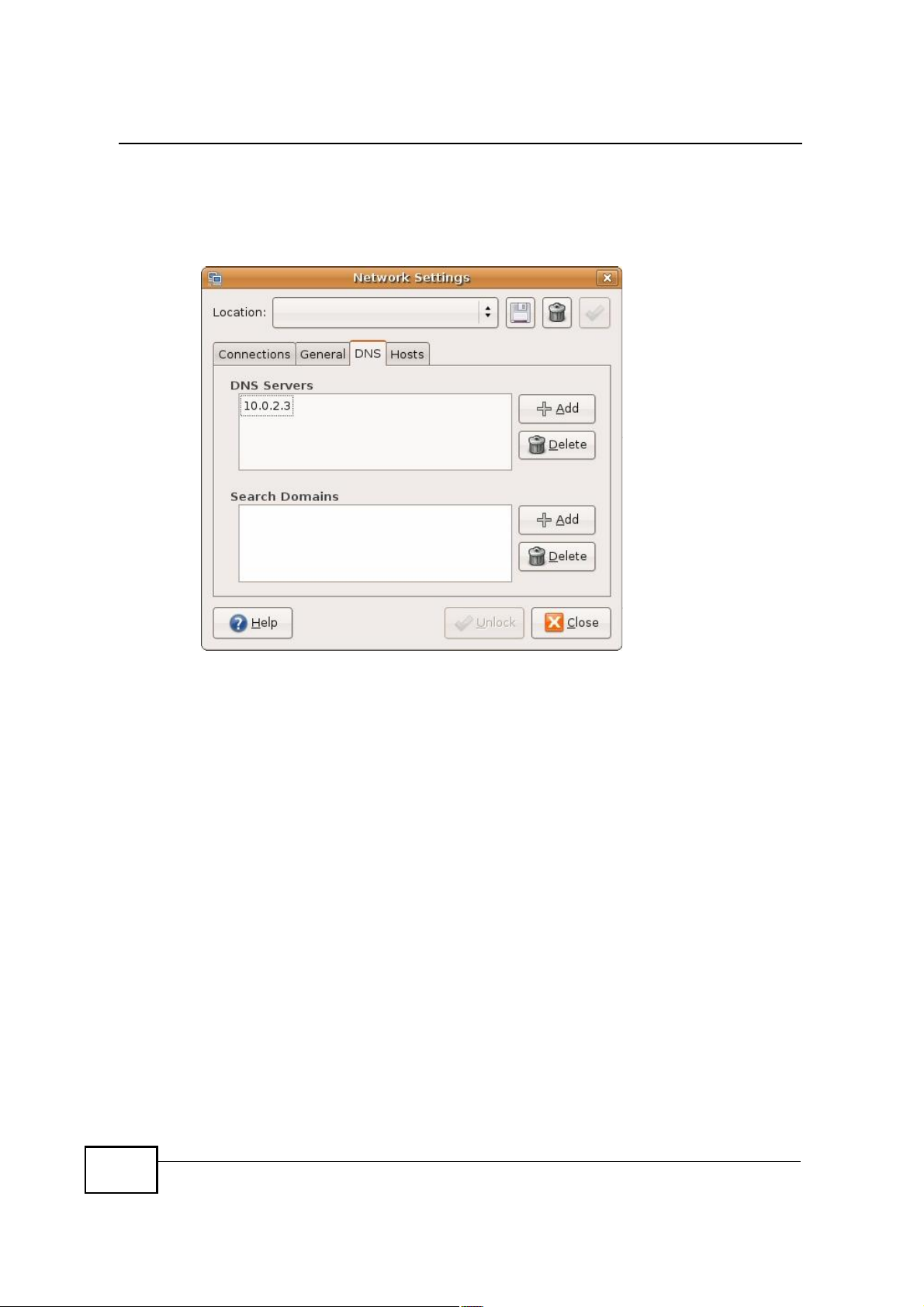
7 If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click the DNS tab in the Network
Settings window and then enter the DNS server information in the fields
provided.
Figure 129 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > DNS
8 Click the Close button to apply the changes.
Verifying Settings
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking System > Administration > Network
Tools, and then selecting the appropriate Network device from the Devices
228
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
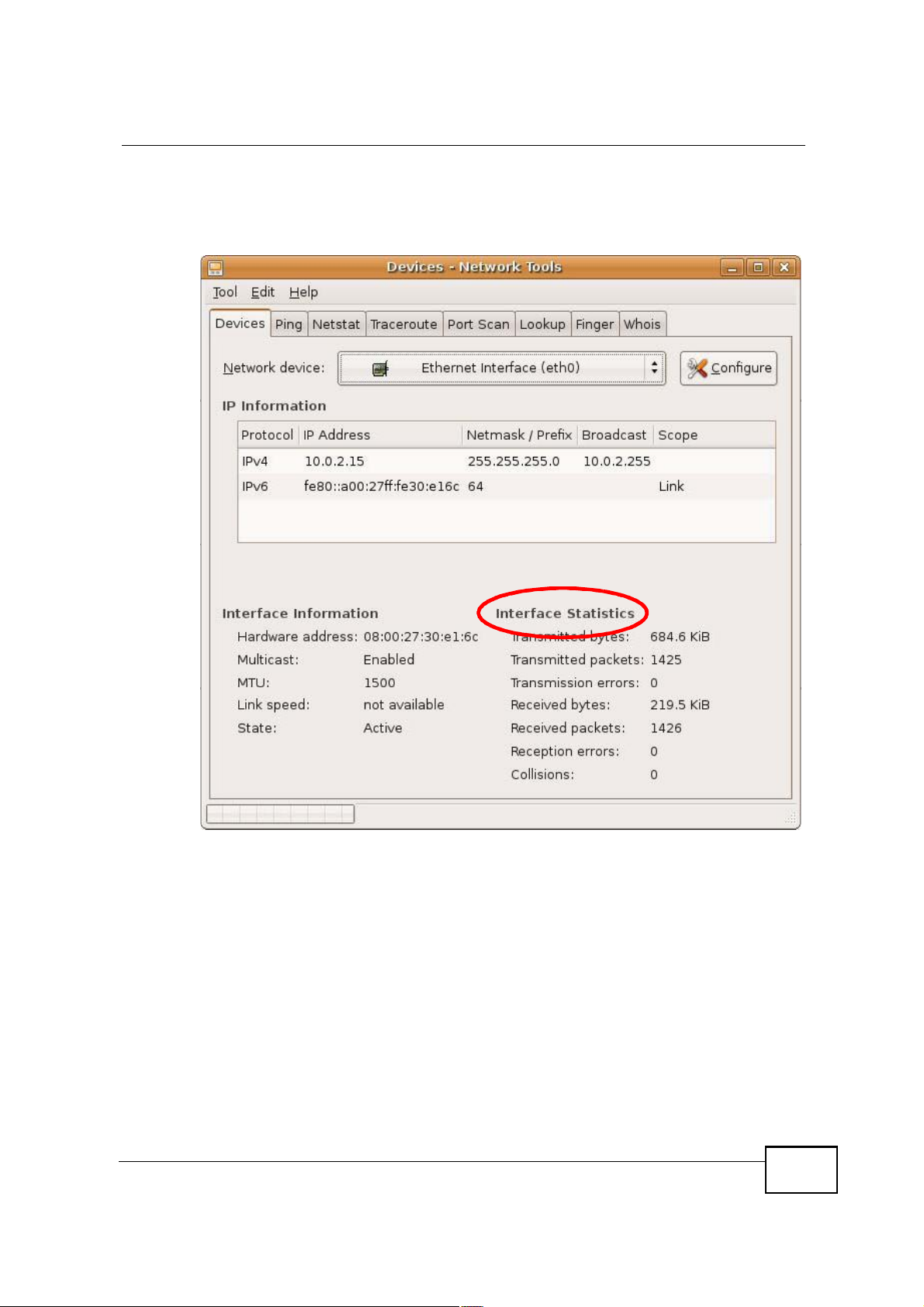
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
tab. The Interface Statistics column shows data if your connection is working
properly.
Figure 130 Ubuntu 8: Network Tools
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
229
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
Linux: openSUSE 10.3 (KDE)
This section shows you how to configure your computer s TCP/IP settings in the K
Desktop Environment (KDE) using the openSUSE 10.3 Linux distribution. The
procedure, screens and file locations may vary depending on your specific
distribution, release version, and individual configuration. The following screens
use the default openSUSE 10.3 installation.
Note: Make sure you are logged in as the root administrator.
Follow the steps below to configure your computer IP address in the KDE:
1 Click K Menu > Computer > Administrator Settings (YaST).
Figure 131 openSUSE 10.3: K Menu > Computer Menu
230
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
2 When the Run as Root - KDE su dialog opens, enter the admin password and
click OK.
Figure 132 openSUSE 10.3: K Menu > Computer Menu
3 When the YaST Control Center window opens, select Network Devices and
then click the Network Card icon.
Figure 133 openSUSE 10.3: YaST Control Center
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
231

Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
4 When the Network Settings window opens, click the Overview tab, select the
appropriate connection Name from the list, and then click the Configure button.
Figure 134 openSUSE 10.3: Network Settings
232
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
5 When the Network Card Setup window opens, click the Address tab
Figure 135 openSUSE 10.3: Network Card Setup
6 Select Dynamic Address (DHCP) if you have a dynamic IP address.
Select Statically assigned IP Address if you have a static IP address. Fill in the
IP address, Subnet mask, and Hostname fields.
7 Click Next to save the changes and close the Network Card Setup window.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
233

Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
8 If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click the Hostname/DNS tab in
Network Settings and then enter the DNS server information in the fields
provided.
Figure 136 openSUSE 10.3: Network Settings
234
9 Click Finish to save your settings and close the window.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Verifying Settings
Click the KNetwork Manager icon on the Task bar to check your TCP/IP
properties. From the Options sub-menu, select Show Connection Information.
Figure 137 openSUSE 10.3: KNetwork Manager
When the Connection Status - KNetwork Manager window opens, click the
Statistics tab to see if your connection is working properly.
Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
Figure 138 openSUSE: Connection Status - KNetwork Manager
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
235

Appendix BSetting Up Your Computer s IP Address
236
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

APPENDIX C
Pop-up Windows, JavaScript
and Java Permissions
In order to use the web configurator you need to allow:
! Web browser pop-up windows from your device.
! JavaScript (enabled by default).
! Java permissions (enabled by default).
Note: Internet Explorer 6 screens are used here. Screens for other Internet Explorer
versions may vary.
Internet Explorer Pop-up Blockers
You may have to disable pop-up blocking to log into your device.
Either disable pop-up blocking (enabled by default in Windows XP SP (Service
Pack) 2) or allow pop-up blocking and create an exception for your device s IP
address.
Disable Pop-up Blockers
1 In Internet Explorer, select Tools, Pop-up Blocker and then select Turn Off
Pop-up Blocker.
Figure 139 Pop-up Blocker
You can also check if pop-up blocking is disabled in the Pop-up Blocker section in
the Privacy tab.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
237
Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
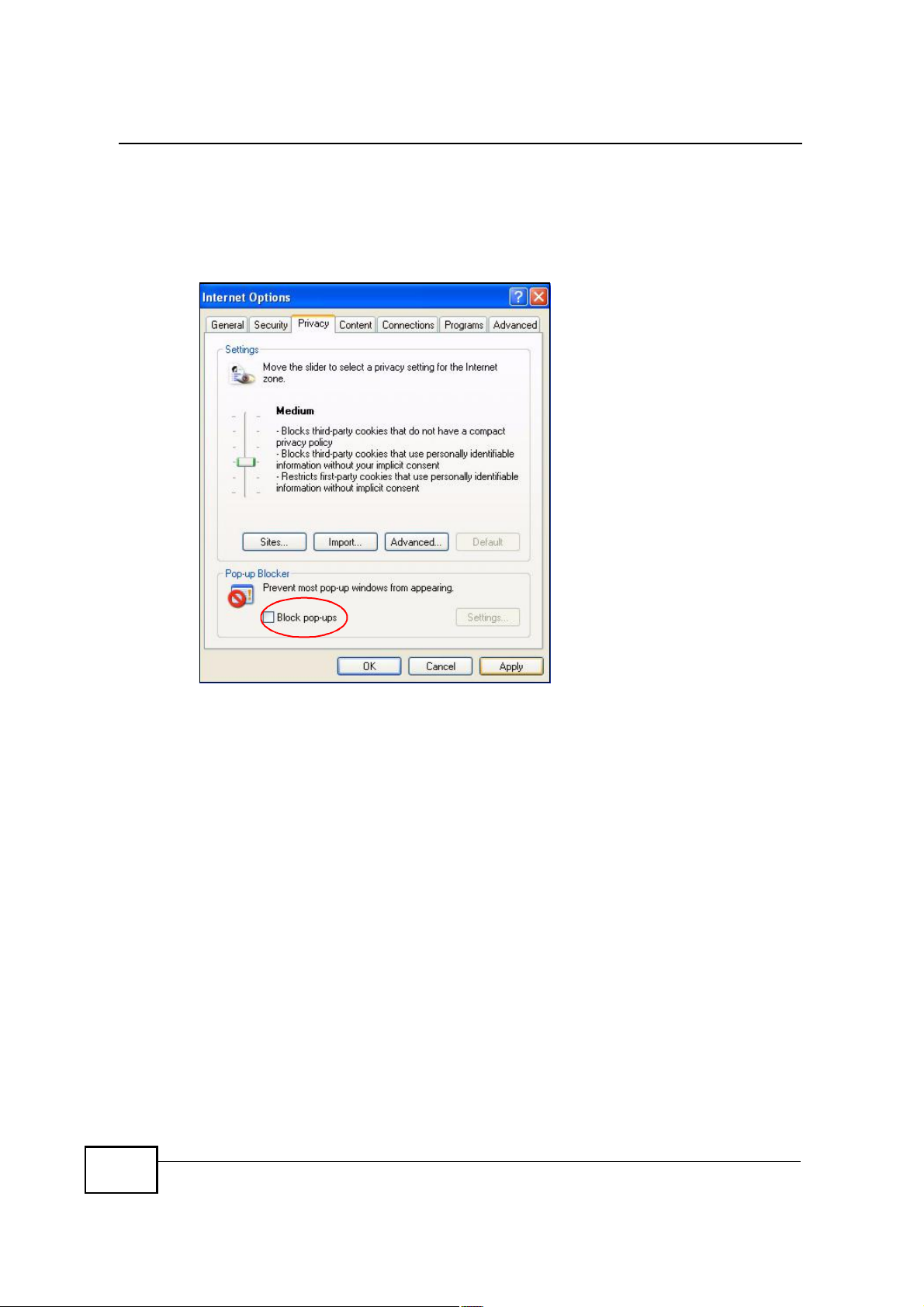
1 In Internet Explorer, select Tools, Internet Options, Privacy.
2 Clear the Block pop-ups check box in the Pop-up Blocker section of the screen.
This disables any web pop-up blockers you may have enabled.
Figure 140 Internet Options: Privacy
3 Click Apply to save this setting.
Enable Pop-up Blockers with Exceptions
Alternatively, if you only want to allow pop-up windows from your device, see the
following steps.
1 In Internet Explorer, select Tools, Internet Options and then the Privacy tab.
238
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
2 Select Settings to open the Pop-up Blocker Settings screen.
Figure 141 Internet Options: Privacy
3 Type the IP address of your device (the web page that you do not want to have
blocked) with the prefix "http://#. For example, http://192.168.167.1.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
239

Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
4 Click Add to move the IP address to the list of Allowed sites.
Figure 142 Pop-up Blocker Settings
5 Click Close to return to the Privacy screen.
6 Click Apply to save this setting.
JavaScript
If pages of the web configurator do not display properly in Internet Explorer, check
that JavaScript is allowed.
240
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
1 In Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options and then the Security tab.
Figure 143 Internet Options: Security
2 Click the Custom Level... button.
3 Scroll down to Scripting.
4 Under Active scripting make sure that Enable is selected (the default).
5 Under Scripting of Java applets make sure that Enable is selected (the
default).
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
241

Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
6 Click OK to close the window.
Figure 144 Security Settings - Java Scripting
Java Permissions
1 From Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options and then the Security
tab.
2 Click the Custom Level... button.
3 Scroll down to Microsoft VM.
4 Under Java permissions make sure that a safety level is selected.
242
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
5 Click OK to close the window.
Figure 145 Security Settings - Java
JAVA (Sun)
1 From Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options and then the Advanced
tab.
2 Make sure that Use Java 2 for <applet> under Java (Sun) is selected.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
243

Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
3 Click OK to close the window.
Figure 146 Java (Sun)
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox 2.0 screens are used here. Screens for other versions may vary.
You can enable Java, Javascript and pop-ups in one screen. Click Tools, then click
Options in the screen that appears.
Figure 147 Mozilla Firefox: TOOLS > Options
244
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
Click Content.to show the screen below. Select the check boxes as shown in the
following screen.
Figure 148 Mozilla Firefox Content Security
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
245

Appendix CPop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
246
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

APPENDIX D
IP Addresses and Subnetting
This appendix introduces IP addresses and subnet masks.
IP addresses identify individual devices on a network. Every networking device
(including computers, servers, routers, printers, etc.) needs an IP address to
communicate across the network. These networking devices are also known as
hosts.
Subnet masks determine the maximum number of possible hosts on a network.
You can also use subnet masks to divide one network into multiple sub-networks.
Introduction to IP Addresses
One part of the IP address is the network number, and the other part is the host
ID. In the same way that houses on a street share a common street name, the
hosts on a network share a common network number. Similarly, as each house
has its own house number, each host on the network has its own unique
identifying number - the host ID. Routers use the network number to send packets
to the correct network, while the host ID determines to which host on the network
the packets are delivered.
Structure
An IP address is made up of four parts, written in dotted decimal notation (for
example, ). Each of these four parts is known as an octet. An octet is an eightdigit binary number (for example 11000000, which is 192 in decimal notation).
Therefore, each octet has a possible range of 00000000 to 11111111 in binary, or
0 to 255 in decimal.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
247

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
The following figure shows an example IP address in which the first three octets
(192.168.1) are the network number, and the fourth octet (16) is the host ID.
Figure 149 Network Number and Host ID
How much of the IP address is the network number and how much is the host ID
varies according to the subnet mask.
Subnet Masks
A subnet mask is used to determine which bits are part of the network number,
and which bits are part of the host ID (using a logical AND operation). The term
"subnet# is short for "sub-network#.
A subnet mask has 32 bits. If a bit in the subnet mask is a "1# then the
corresponding bit in the IP address is part of the network number. If a bit in the
subnet mask is "0# then the corresponding bit in the IP address is part of the host
ID.
The following example shows a subnet mask identifying the network number (in
bold text) and host ID of an IP address (192.168.1.2 in decimal).
Table 88 IP Address Network Number and Host ID Example
IP Address (Binary)11000000101010000000000100000010
Subnet Mask (Binary) 111111111111111111111111 00000000
Network Number 110000001010100000000001
Host ID00000010
1ST
OCTET:
(192)
2ND
OCTET:
(168)
3RD
OCTET:
(1)
4TH
OCTET
(2)
248
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
By convention, subnet masks always consist of a continuous sequence of ones
beginning from the leftmost bit of the mask, followed by a continuous sequence of
zeros, for a total number of 32 bits.
Subnet masks can be referred to by the size of the network number part (the bits
with a "1# value). For example, an "8-bit mask# means that the first 8 bits of the
mask are ones and the remaining 24 bits are zeroes.
Subnet masks are expressed in dotted decimal notation just like IP addresses. The
following examples show the binary and decimal notation for 8-bit, 16-bit, 24-bit
and 29-bit subnet masks.
Table 89 Subnet Masks
BINARY
1ST
OCTET
8-bit mask 11111111 00000000 00000000 00000000 255.0.0.0
16-bit
mask
24-bit
mask
29-bit
mask
11111111 11111111 00000000 00000000 255.255.0.0
11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000 255.255.255.0
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111000 255.255.255.24
2ND
OCTET
3RD
OCTET
4TH
OCTET
DECIMAL
8
Network Size
The size of the network number determines the maximum number of possible
hosts you can have on your network. The larger the number of network number
bits, the smaller the number of remaining host ID bits.
An IP address with host IDs of all zeros is the IP address of the network
(192.168.1.0 with a 24-bit subnet mask, for example). An IP address with host
IDs of all ones is the broadcast address for that network (192.168.1.255 with a
24-bit subnet mask, for example).
As these two IP addresses cannot be used for individual hosts, calculate the
maximum number of possible hosts in a network as follows:
Table 90 Maximum Host Numbers
SUBNET MASK HOST ID SIZE
8 bits255.0.0.024 bits2
16 bits255.255.0.016 bits2
24 bits255.255.255.08 bits2
29 bits255.255.255.2483 bits2
MAXIMUM NUMBER OF
HOSTS
24
% 216777214
16
% 265534
8
% 2254
3
% 26
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
249

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
Notation
Since the mask is always a continuous number of ones beginning from the left,
followed by a continuous number of zeros for the remainder of the 32 bit mask,
you can simply specify the number of ones instead of writing the value of each
octet. This is usually specified by writing a "/# followed by the number of bits in
the mask after the address.
For example, 192.1.1.0 /25 is equivalent to saying 192.1.1.0 with subnet mask
255.255.255.128.
The following table shows some possible subnet masks using both notations.
Table 91 Alternative Subnet Mask Notation
SUBNET
MASK
255.255.255.0 /24 0000 0000 0
255.255.255.128/25 1000 0000 128
255.255.255.192/26 1100 0000 192
ALTERNATIVE
NOTATION
LAST OCTET
(BINARY)
LAST OCTET
(DECIMAL)
255.255.255.224/27 1110 0000 224
255.255.255.240/28 1111 0000 240
255.255.255.248/29 1111 1000 248
255.255.255.252/30 1111 1100 252
Subnetting
You can use subnetting to divide one network into multiple sub-networks. In the
following example a network administrator creates two sub-networks to isolate a
group of servers from the rest of the company network for security reasons.
In this example, the company network address is 192.168.1.0. The first three
octets of the address (192.168.1) are the network number, and the remaining
octet is the host ID, allowing a maximum of 28 % 2 or 254 possible hosts.
250
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
The following figure shows the company network before subnetting.
Figure 150 Subnetting Example: Before Subnetting
You can "borrow# one of the host ID bits to divide the network 192.168.1.0 into
two separate sub-networks. The subnet mask is now 25 bits (255.255.255.128 or
/25).
The "borrowed# host ID bit can have a value of either 0 or 1, allowing two
subnets; 192.168.1.0 /25 and 192.168.1.128 /25.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
251
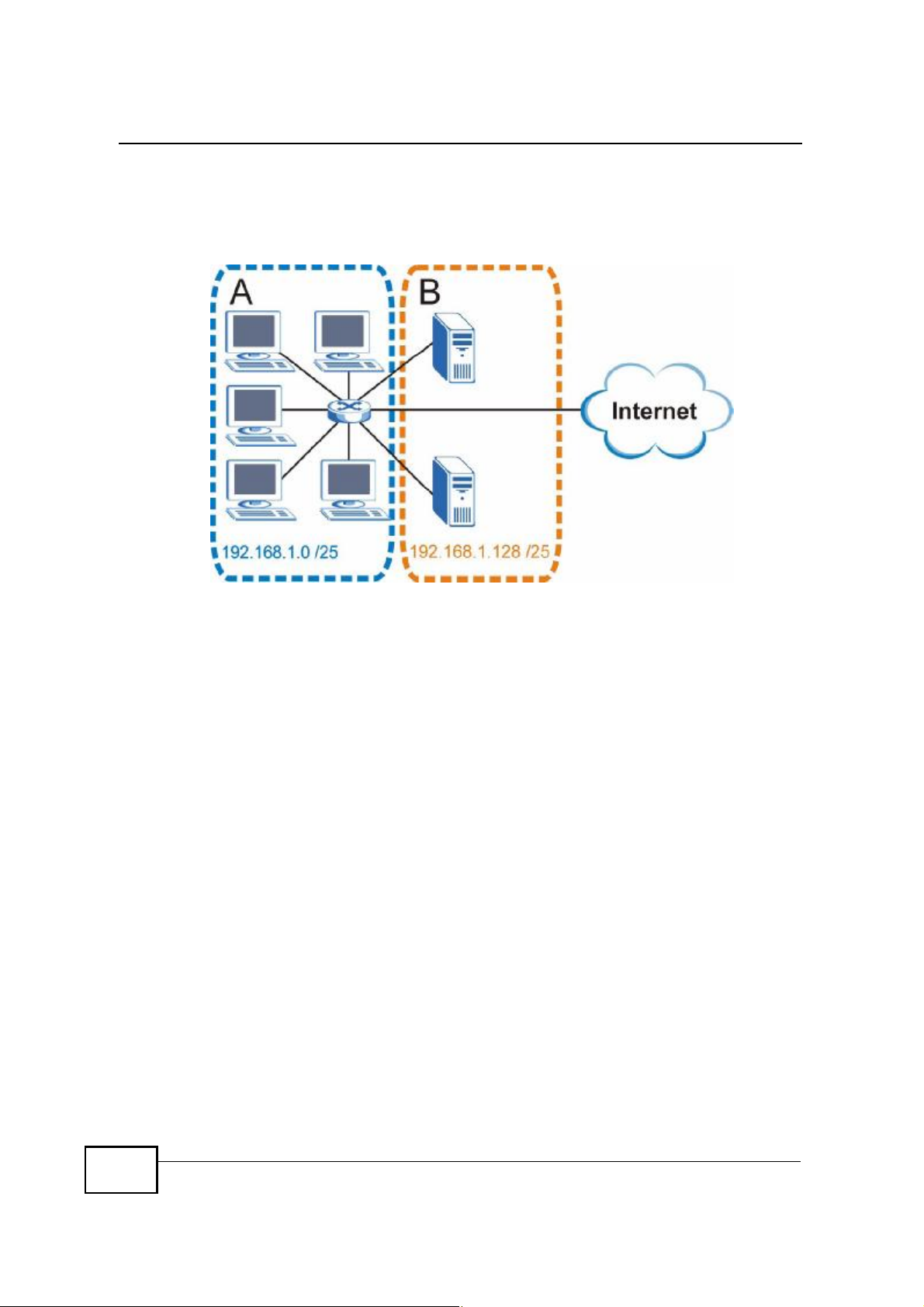
Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
The following figure shows the company network after subnetting. There are now
two sub-networks, A and B.
Figure 151 Subnetting Example: After Subnetting
In a 25-bit subnet the host ID has 7 bits, so each sub-network has a maximum of
27 % 2 or 126 possible hosts (a host ID of all zeroes is the subnet s address itself,
all ones is the subnet s broadcast address).
192.168.1.0 with mask 255.255.255.128 is subnet A itself, and 192.168.1.127
with mask 255.255.255.128 is its broadcast address. Therefore, the lowest IP
address that can be assigned to an actual host for subnet A is 192.168.1.1 and
the highest is 192.168.1.126.
Similarly, the host ID range for subnet B is 192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.254.
Example: Four Subnets
The previous example illustrated using a 25-bit subnet mask to divide a 24-bit
address into two subnets. Similarly, to divide a 24-bit address into four subnets,
you need to "borrow# two host ID bits to give four possible combinations (00, 01,
10 and 11). The subnet mask is 26 bits
(11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000) or 255.255.255.192.
252
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
Each subnet contains 6 host ID bits, giving 26 - 2 or 62 hosts for each subnet (a
host ID of all zeroes is the subnet itself, all ones is the subnet s broadcast
address).
Table 92 Subnet 1
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
IP Address (Decimal) 192.168.1. 0
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000000
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111. 11000000
Subnet Address:
192.168.1.0
Broadcast Address:
192.168.1.63
Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.1
Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.62
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
Table 93 Subnet 2
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
IP Address 192.168.1. 64
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001. 01000000
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111. 11000000
Subnet Address:
192.168.1.64
Broadcast Address:
192.168.1.127
Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.65
Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.126
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
Table 94 Subnet 3
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
IP Address 192.168.1. 128
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001. 10000000
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111. 11000000
Subnet Address:
192.168.1.128
Broadcast Address:
192.168.1.191
Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.129
Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.190
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
Table 95 Subnet 4
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
IP Address 192.168.1. 192
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001. 11000000
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111. 11000000
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
253

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
Table 95 Subnet 4 (continued)
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
Subnet Address:
192.168.1.192
Broadcast Address:
192.168.1.255
Example: Eight Subnets
Similarly, use a 27-bit mask to create eight subnets (000, 001, 010, 011, 100,
101, 110 and 111).
The following table shows IP address last octet values for each subnet.
Table 96 Eight Subnets
SUBNET
1 0 1 30 31
2 32 33 62 63
3 64 65 94 95
4 96 97 126 127
5 128 129 158 159
6 160 161 190 191
7 192 193 222 223
8 224 225 254 255
SUBNET
ADDRESS
Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.193
Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.254
FIRST ADDRESS
LAST
ADDRESS
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
BROADCAST
ADDRESS
Subnet Planning
The following table is a summary for subnet planning on a network with a 24-bit
network number.
Table 97 24-bit Network Number Subnet Planning
NO. #BORROWED$
HOST BITS
1 255.255.255.128 (/25) 2 126
2 255.255.255.192 (/26) 4 62
3 255.255.255.224 (/27) 8 30
4 255.255.255.240 (/28) 16 14
5 255.255.255.248 (/29) 32 6
6 255.255.255.252 (/30) 64 2
7 255.255.255.254 (/31) 128 1
254
SUBNET MASK NO. SUBNETS
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
NO. HOSTS PER
SUBNET

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
The following table is a summary for subnet planning on a network with a 16-bit
network number.
Table 98 16-bit Network Number Subnet Planning
NO. #BORROWED$
HOST BITS
1 255.255.128.0 (/17) 2 32766
2 255.255.192.0 (/18) 4 16382
3 255.255.224.0 (/19) 8 8190
4 255.255.240.0 (/20) 16 4094
5 255.255.248.0 (/21) 32 2046
6 255.255.252.0 (/22) 64 1022
7 255.255.254.0 (/23) 128 510
8 255.255.255.0 (/24) 256 254
9 255.255.255.128 (/25) 512 126
10 255.255.255.192 (/26) 1024 62
11 255.255.255.224 (/27) 2048 30
12 255.255.255.240 (/28) 4096 14
13 255.255.255.248 (/29) 8192 6
14 255.255.255.252 (/30) 16384 2
15 255.255.255.254 (/31) 32768 1
SUBNET MASK NO. SUBNETS
NO. HOSTS PER
SUBNET
Configuring IP Addresses
Where you obtain your network number depends on your particular situation. If
the ISP or your network administrator assigns you a block of registered IP
addresses, follow their instructions in selecting the IP addresses and the subnet
mask.
If the ISP did not explicitly give you an IP network number, then most likely you
have a single user account and the ISP will assign you a dynamic IP address when
the connection is established. If this is the case, it is recommended that you select
a network number from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.0. The Internet Assigned
Number Authority (IANA) reserved this block of addresses specifically for private
use; please do not use any other number unless you are told otherwise. You must
also enable Network Address Translation (NAT) on the MAX208M2W Series.
Once you have decided on the network number, pick an IP address for your
MAX208M2W Series that is easy to remember (for instance, 192.168.1.1) but
make sure that no other device on your network is using that IP address.
The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your
MAX208M2W Series will compute the subnet mask automatically based on the IP
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
255

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
address that you entered. You don't need to change the subnet mask computed by
the MAX208M2W Series unless you are instructed to do otherwise.
Private IP Addresses
Every machine on the Internet must have a unique address. If your networks are
isolated from the Internet (running only between two branch offices, for example)
you can assign any IP addresses to the hosts without problems. However, the
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three
blocks of IP addresses specifically for private networks:
! 10.0.0.0 ' 10.255.255.255
! 172.16.0.0 ' 172.31.255.255
! 192.168.0.0 ' 192.168.255.255
You can obtain your IP address from the IANA, from an ISP, or it can be assigned
from a private network. If you belong to a small organization and your Internet
access is through an ISP, the ISP can provide you with the Internet addresses for
your local networks. On the other hand, if you are part of a much larger
organization, you should consult your network administrator for the appropriate IP
addresses.
Regardless of your particular situation, do not create an arbitrary IP address;
always follow the guidelines above. For more information on address assignment,
please refer to RFC 1597, Address Allocation for Private Internets and RFC 1466,
Guidelines for Management of IP Address Space.
IP Address Conflicts
Each device on a network must have a unique IP address. Devices with duplicate
IP addresses on the same network will not be able to access the Internet or other
resources. The devices may also be unreachable through the network.
Conflicting Computer IP Addresses Example
More than one device can not use the same IP address. In the following example
computer A has a static (or fixed) IP address that is the same as the IP address
that a DHCP server assigns to computer B which is a DHCP client. Neither can
access the Internet. This problem can be solved by assigning a different static IP
256
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

address to computer A or setting computer A to obtain an IP address
automatically.
Figure 152 Conflicting Computer IP Addresses Example
Conflicting Router IP Addresses Example
Since a router connects different networks, it must have interfaces using different
network numbers. For example, if a router is set between a LAN and the Internet
(WAN), the router s LAN and WAN addresses must be on different subnets. In the
following example, the LAN and WAN are on the same subnet. The LAN computers
cannot access the Internet because the router cannot route between networks.
Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
Figure 153 Conflicting Computer IP Addresses Example
Conflicting Computer and Router IP Addresses Example
More than one device can not use the same IP address. In the following example,
the computer and the router s LAN port both use 192.168.1.1 as the IP address.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
257

Appendix DIP Addresses and Subnetting
The computer cannot access the Internet. This problem can be solved by
assigning a different IP address to the computer or the router s LAN port.
Figure 154 Conflicting Computer and Router IP Addresses Example
258
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

APPENDIX E
Importing Certificates
This appendix shows you how to import public key certificates into your web
browser.
Public key certificates are used by web browsers to ensure that a secure web site
is legitimate. When a certificate authority such as VeriSign, Comodo, or Network
Solutions, to name a few, receives a certificate request from a website operator,
they confirm that the web domain and contact information in the request match
those on public record with a domain name registrar. If they match, then the
certificate is issued to the website operator, who then places it on the site to be
issued to all visiting web browsers to let them know that the site is legitimate.
Many ZyXEL products, such as the NSA-2401, issue their own public key
certificates. These can be used by web browsers on a LAN or WAN to verify that
they are in fact connecting to the legitimate device and not one masquerading as
it. However, because the certificates were not issued by one of the several
organizations officially recognized by the most common web browsers, you will
need to import the ZyXEL-created certificate into your web browser and flag that
certificate as a trusted authority.
Note: You can see if you are browsing on a secure website if the URL in your web
browser s address bar begins with https:// or there is a sealed padlock
icon () somewhere in the main browser window (not all browsers show the
padlock in the same location.)
In this appendix, you can import a public key certificate for:
! Internet Explorer on page 260
! Firefox on page 270
! Opera on page 276
! Konqueror on page 284
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
259

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Internet Explorer
The following example uses Microsoft Internet Explorer 7 on Windows XP
Professional; however, they can also apply to Internet Explorer on Windows Vista.
1 If your device s web configurator is set to use SSL certification, then the first time
you browse to it you are presented with a certification error.
Figure 155 Internet Explorer 7: Certification Error
2 Click Continue to this website (not recommended).
Figure 156 Internet Explorer 7: Certification Error
260
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 In the Address Bar, click Certificate Error > View certificates.
Figure 157 Internet Explorer 7: Certificate Error
4 In the Certificate dialog box, click Install Certificate.
Figure 158 Internet Explorer 7: Certificate
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
261

Appendix EImporting Certificates
5 In the Certificate Import Wizard, click Next.
Figure 159 Internet Explorer 7: Certificate Import Wizard
6 If you want Internet Explorer to Automatically select certificate store based
on the type of certificate, click Next again and then go to step 9.
Figure 160 Internet Explorer 7: Certificate Import Wizard
262
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
7 Otherwise, select Place all certificates in the following store and then click
Browse.
Figure 161 Internet Explorer 7: Certificate Import Wizard
8 In the Select Certificate Store dialog box, choose a location in which to save the
certificate and then click OK.
Figure 162 Internet Explorer 7: Select Certificate Store
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
263

Appendix EImporting Certificates
9 In the Completing the Certificate Import Wizard screen, click Finish.
Figure 163 Internet Explorer 7: Certificate Import Wizard
10 If you are presented with another Security Warning, click Yes.
Figure 164 Internet Explorer 7: Security Warning
264
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
11 Finally, click OK when presented with the successful certificate installation
message.
Figure 165 Internet Explorer 7: Certificate Import Wizard
12 The next time you start Internet Explorer and go to a ZyXEL web configurator
page, a sealed padlock icon appears in the address bar. Click it to view the page s
Website Identification information.
Figure 166 Internet Explorer 7: Website Identification
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
265

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Installing a Stand-Alone Certificate File in Internet Explorer
Rather than browsing to a ZyXEL web configurator and installing a public key
certificate when prompted, you can install a stand-alone certificate file if one has
been issued to you.
1 Double-click the public key certificate file.
Figure 167 Internet Explorer 7: Public Key Certificate File
2 In the security warning dialog box, click Open.
Figure 168 Internet Explorer 7: Open File - Security Warning
266
3 Refer to steps 4-12 in the Internet Explorer procedure beginning on page260 to
complete the installation process.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Removing a Certificate in Internet Explorer
This section shows you how to remove a public key certificate in Internet Explorer
7.
1 Open Internet Explorer and click TOOLS > Internet Options.
Figure 169 Internet Explorer 7: Tools Menu
Appendix EImporting Certificates
2 In the Internet Options dialog box, click Content > Certificates.
Figure 170 Internet Explorer 7: Internet Options
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
267

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 In the Certificates dialog box, click the Trusted Root Certificates Authorities
tab, select the certificate that you want to delete, and then click Remove.
Figure 171 Internet Explorer 7: Certificates
4 In the Certificates confirmation, click Yes.
Figure 172 Internet Explorer 7: Certificates
5 In the Root Certificate Store dialog box, click Yes.
Figure 173 Internet Explorer 7: Root Certificate Store
268
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
6 The next time you go to the web site that issued the public key certificate you just
removed, a certification error appears.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
269

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Firefox
The following example uses Mozilla Firefox 2 on Windows XP Professional;
however, the screens can also apply to Firefox 2 on all platforms.
1 If your device s web configurator is set to use SSL certification, then the first time
you browse to it you are presented with a certification error.
2 Select Accept this certificate permanently and click OK.
Figure 174 Firefox 2: Website Certified by an Unknown Authority
270
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 The certificate is stored and you can now connect securely to the web configurator.
A sealed padlock appears in the address bar, which you can click to open the Page
Info > Security window to view the web page s security information.
Figure 175 Firefox 2: Page Info
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
271

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Installing a Stand-Alone Certificate File in Firefox
Rather than browsing to a ZyXEL web configurator and installing a public key
certificate when prompted, you can install a stand-alone certificate file if one has
been issued to you.
1 Open Firefox and click TOOLS > Options.
Figure 176 Firefox 2: Tools Menu
2 In the Options dialog box, click ADVANCED > Encryption > View Certificates.
Figure 177 Firefox 2: Options
272
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 In the Certificate Manager dialog box, click Web Sites > Import.
Figure 178 Firefox 2: Certificate Manager
4 Use the Select File dialog box to locate the certificate and then click Open.
Figure 179 Firefox 2: Select File
5 The next time you visit the web site, click the padlock in the address bar to open
the Page Info > Security window to see the web page s security information.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
273

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Removing a Certificate in Firefox
This section shows you how to remove a public key certificate in Firefox 2.
1 Open Firefox and click TOOLS > Options.
Figure 180 Firefox 2: Tools Menu
2 In the Options dialog box, click ADVANCED > Encryption > View Certificates.
Figure 181 Firefox 2: Options
274
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 In the Certificate Manager dialog box, select the Web Sites tab, select the
certificate that you want to remove, and then click Delete.
Figure 182 Firefox 2: Certificate Manager
4 In the Delete Web Site Certificates dialog box, click OK.
Figure 183 Firefox 2: Delete Web Site Certificates
5 The next time you go to the web site that issued the public key certificate you just
removed, a certification error appears.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
275

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Opera
The following example uses Opera 9 on Windows XP Professional; however, the
screens can apply to Opera 9 on all platforms.
1 If your device s web configurator is set to use SSL certification, then the first time
you browse to it you are presented with a certification error.
2 Click Install to accept the certificate.
Figure 184 Opera 9: Certificate signer not found
276
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 The next time you visit the web site, click the padlock in the address bar to open
the Security information window to view the web page s security details.
Figure 185 Opera 9: Security information
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
277

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Installing a Stand-Alone Certificate File in Opera
Rather than browsing to a ZyXEL web configurator and installing a public key
certificate when prompted, you can install a stand-alone certificate file if one has
been issued to you.
1 Open Opera and click TOOLS > Preferences.
Figure 186 Opera 9: Tools Menu
278
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
2 In Preferences, click ADVANCED > Security > Manage certificates.
Figure 187 Opera 9: Preferences
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
279

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 In the Certificates Manager, click Authorities > Import.
Figure 188 Opera 9: Certificate manager
4 Use the Import certificate dialog box to locate the certificate and then click
Open.
Figure 189 Opera 9: Import certificate
280
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
5 In the Install authority certificate dialog box, click Install.
Figure 190 Opera 9: Install authority certificate
6 Next, click OK.
Figure 191 Opera 9: Install authority certificate
7 The next time you visit the web site, click the padlock in the address bar to open
the Security information window to view the web page s security details.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
281

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Removing a Certificate in Opera
This section shows you how to remove a public key certificate in Opera 9.
1 Open Opera and click TOOLS > Preferences.
Figure 192 Opera 9: Tools Menu
2 In Preferences, ADVANCED > Security > Manage certificates.
Figure 193 Opera 9: Preferences
282
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 In the Certificates manager, select the Authorities tab, select the certificate
that you want to remove, and then click Delete.
Figure 194 Opera 9: Certificate manager
4 The next time you go to the web site that issued the public key certificate you just
removed, a certification error appears.
Note: There is no confirmation when you delete a certificate authority, so be
absolutely certain that you want to go through with it before clicking the button.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
283

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Konqueror
The following example uses Konqueror 3.5 on openSUSE 10.3, however the
screens apply to Konqueror 3.5 on all Linux KDE distributions.
1 If your device s web configurator is set to use SSL certification, then the first time
you browse to it you are presented with a certification error.
2 Click Continue.
Figure 195 Konqueror 3.5: Server Authentication
3 Click Forever when prompted to accept the certificate.
Figure 196 Konqueror 3.5: Server Authentication
284
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
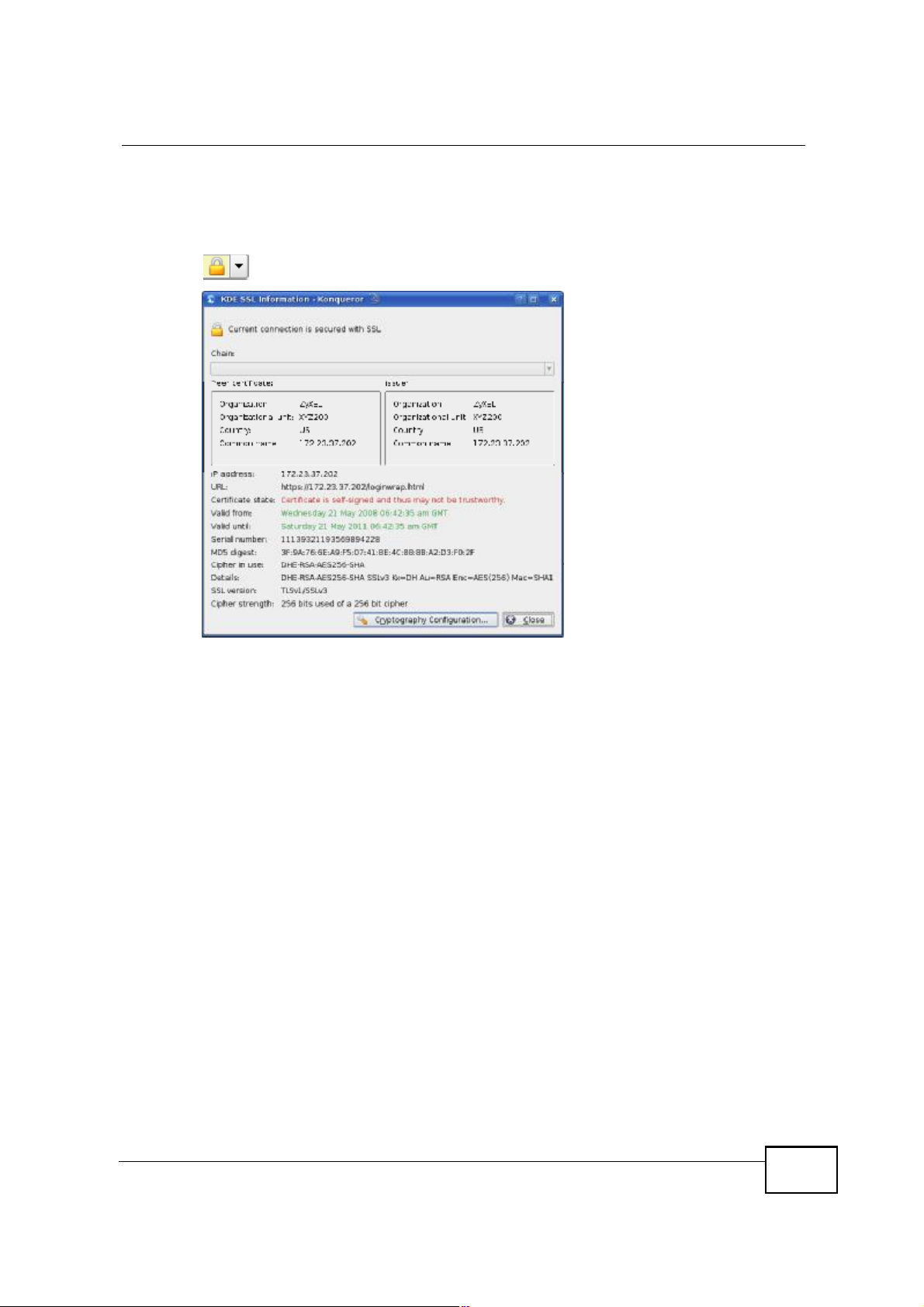
Appendix EImporting Certificates
4 Click the padlock in the address bar to open the KDE SSL Information window
and view the web page s security details.
Figure 197 Konqueror 3.5: KDE SSL Information
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
285

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Installing a Stand-Alone Certificate File in Konqueror
Rather than browsing to a ZyXEL web configurator and installing a public key
certificate when prompted, you can install a stand-alone certificate file if one has
been issued to you.
1 Double-click the public key certificate file.
Figure 198 Konqueror 3.5: Public Key Certificate File
2 In the Certificate Import Result - Kleopatra dialog box, click OK.
Figure 199 Konqueror 3.5: Certificate Import Result
286
The public key certificate appears in the KDE certificate manager, Kleopatra.
Figure 200 Konqueror 3.5: Kleopatra
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
3 The next time you visit the web site, click the padlock in the address bar to open
the KDE SSL Information window to view the web page s security details.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
287

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Removing a Certificate in Konqueror
This section shows you how to remove a public key certificate in Konqueror 3.5.
1 Open Konqueror and click Settings > Configure Konqueror.
Figure 201 Konqueror 3.5: Settings Menu
2 In the Configure dialog box, select Crypto.
3 On the Peer SSL Certificates tab, select the certificate you want to delete and
then click Remove.
Figure 202 Konqueror 3.5: Configure
4 The next time you go to the web site that issued the public key certificate you just
removed, a certification error appears.
288
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix EImporting Certificates
Note: There is no confirmation when you remove a certificate authority, so be
absolutely certain you want to go through with it before clicking the button.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
289

Appendix EImporting Certificates
290
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

APPENDIX F
Common Services
The following table lists some commonly-used services and their associated
protocols and port numbers. For a comprehensive list of port numbers, ICMP type/
code numbers and services, visit the IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority)
web site.
! Name: This is a short, descriptive name for the service. You can use this one or
create a different one, if you like.
! Protocol: This is the type of IP protocol used by the service. If this is TCP/
UDP, then the service uses the same port number with TCP and UDP. If this is
USER-DEFINED, the Port(s) is the IP protocol number, not the port number.
! Port(s): This value depends on the Protocol. Please refer to RFC 1700 for
further information about port numbers.
! If the Protocol is TCP, UDP, or TCP/UDP, this is the IP port number.
! If the Protocol is USER, this is the IP protocol number.
! Description: This is a brief explanation of the applications that use this service
or the situations in which this service is used.
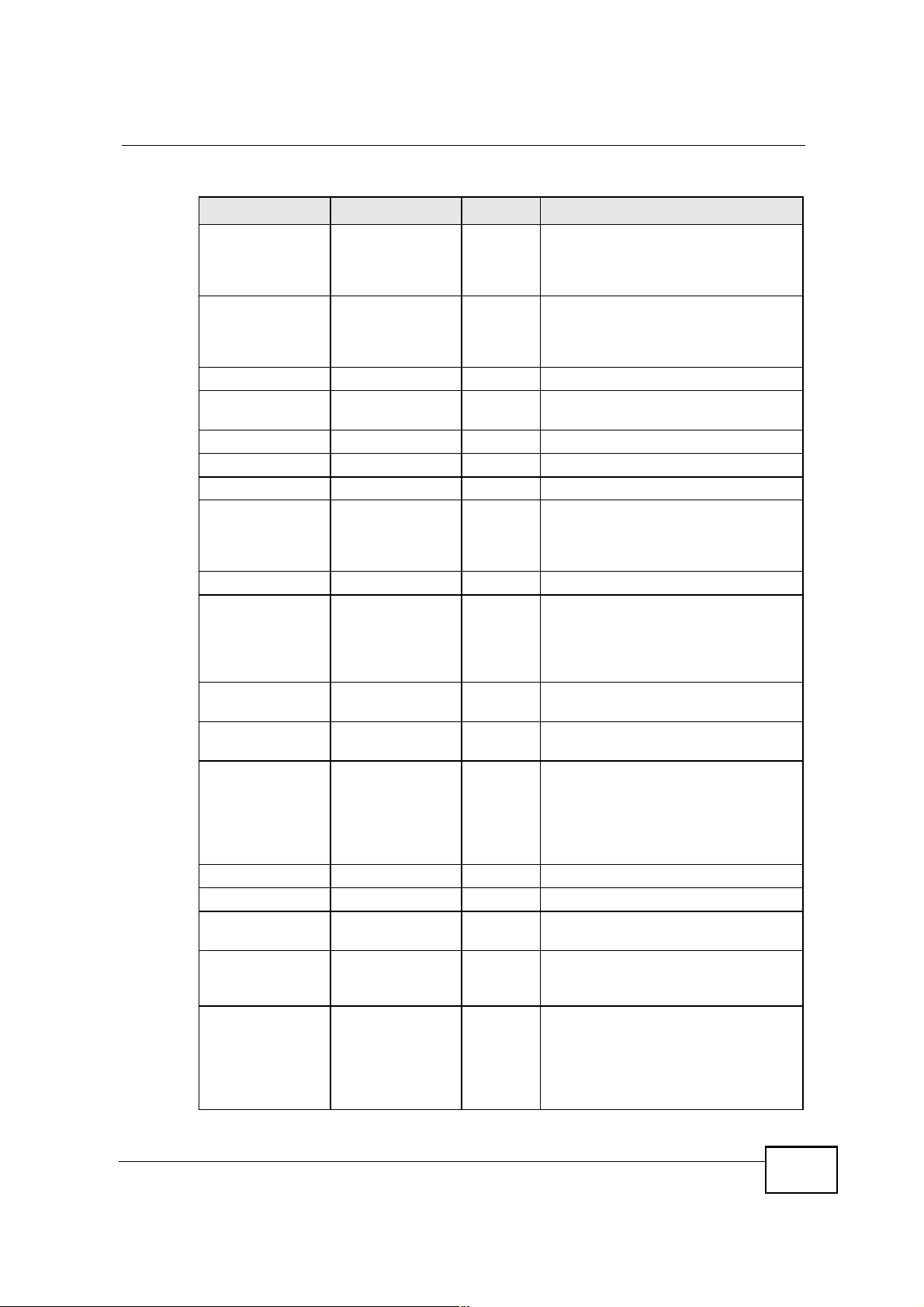
Table 99 Commonly Used Services
NAME PROTOCOL PORT(S) DESCRIPTION
AH
(IPSEC_TUNNEL)
AIM/New-ICQ TCP 5190 AOL s Internet Messenger service. It
AUTH TCP 113 Authentication protocol used by some
BGP TCP 179 Border Gateway Protocol.
BOOTP_CLIENT UDP 68 DHCP Client.
BOOTP_SERVER UDP 67 DHCP Server.
CU-SEEME TCP
DNS TCP/UDP 53 Domain Name Server, a service that
User-Defined 51 The IPSEC AH (Authentication
Header) tunneling protocol uses this
service.
is also used as a listening port by
ICQ.
servers.
UDP
7648
24032
A popular videoconferencing solution
from White Pines Software.
matches web names (for example
www.zyxel.com) to IP numbers.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
291

Appendix FCommon Services
Table 99 Commonly Used Services (continued)
NAME PROTOCOL PORT(S) DESCRIPTION
ESP
(IPSEC_TUNNEL)
FINGER TCP 79 Finger is a UNIX or Internet related
FTP TCP
H.323 TCP 1720 NetMeeting uses this protocol.
HTTP TCP 80 Hyper Text Transfer Protocol - a
HTTPS TCP 443 HTTPS is a secured http session often
ICMP User-Defined 1 Internet Control Message Protocol is
ICQ UDP 4000 This is a popular Internet chat
IGMP
(MULTICAST)
IKE UDP 500 The Internet Key Exchange algorithm
IRC TCP/UDP 6667 This is another popular Internet chat
MSN Messenger TCP 1863 Microsoft Networks messenger
NEW-ICQ TCP 5190 An Internet chat program.
NEWS TCP 144 A protocol for news groups.
NFS UDP 2049 Network File System - NFS is a client/
NNTP TCP 119 Network News Transport Protocol is
PING User-Defined 1 Packet INternet Groper is a protocol
POP3 TCP 110 Post Office Protocol version 3 lets a
User-Defined 50 The IPSEC ESP (Encapsulation
Security Protocol) tunneling protocol
uses this service.
command that can be used to find out
if a user is logged on.
20
TCP
User-Defined 2 Internet Group Management Protocol
21
File Transfer Program, a program to
enable fast transfer of files, including
large files that may not be possible by
e-mail.
client/server protocol for the world
wide web.
used in e-commerce.
often used for diagnostic or routing
purposes.
program.
is used when sending packets to a
specific group of hosts.
is used for key distribution and
management.
program.
service uses this protocol.
server distributed file service that
provides transparent file sharing for
network environments.
the delivery mechanism for the
USENET newsgroup service.
that sends out ICMP echo requests to
test whether or not a remote host is
reachable.
client computer get e-mail from a
POP3 server through a temporary
connection (TCP/IP or other).
292
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
Appendix FCommon Services
Table 99 Commonly Used Services (continued)
NAME PROTOCOL PORT(S) DESCRIPTION
PPTP TCP 1723 Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
enables secure transfer of data over
public networks. This is the control
channel.
PPTP_TUNNEL
(GRE)
RCMD TCP 512 Remote Command Service.
REAL_AUDIO TCP 7070 A streaming audio service that
REXEC TCP 514 Remote Execution Daemon.
RLOGIN TCP 513 Remote Login.
RTELNET TCP 107 Remote Telnet.
RTSP TCP/UDP 554 The Real Time Streaming (media
SFTP TCP 115 Simple File Transfer Protocol.
SMTP TCP 25 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is the
SNMP TCP/UDP 161 Simple Network Management
SNMP-TRAPS TCP/UDP 162 Traps for use with the SNMP
SQL-NET TCP 1521 Structured Query Language is an
SSH TCP/UDP 22 Secure Shell Remote Login Program.
STRM WORKS UDP 1558 Stream Works Protocol.
SYSLOG UDP 514 Syslog allows you to send system logs
TACACS UDP 49 Login Host Protocol used for (Terminal
TELNET TCP 23 Telnet is the login and terminal
User-Defined 47 PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling
Protocol) enables secure transfer of
data over public networks. This is the
data channel.
enables real time sound over the web.
control) Protocol (RTSP) is a remote
control for multimedia on the
Internet.
message-exchange standard for the
Internet. SMTP enables you to move
messages from one e-mail server to
another.
Program.
(RFC:1215).
interface to access data on many
different types of database systems,
including mainframes, midrange
systems, UNIX systems and network
servers.
to a UNIX server.
Access Controller Access Control
System).
emulation protocol common on the
Internet and in UNIX environments. It
operates over TCP/IP networks. Its
primary function is to allow users to
log into remote host systems.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
293

Appendix FCommon Services
Table 99 Commonly Used Services (continued)
NAME PROTOCOL PORT(S) DESCRIPTION
TFTP UDP 69 Trivial File Transfer Protocol is an
VDOLIVE TCP 7000 Another videoconferencing solution.
Internet file transfer protocol similar
to FTP, but uses the UDP (User
Datagram Protocol) rather than TCP
(Transmission Control Protocol).
294
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

APPENDIX G
Legal Information
Copyright
Copyright © 2011 by ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole,
transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, translated into any language, or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic,
optical, chemical, photocopying, manual, or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Published by ZyXEL Communications Corporation. All rights reserved.
Disclaimers
ZyXEL does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
products, or software described herein. Neither does it convey any license under
its patent rights nor the patent rights of others. ZyXEL further reserves the right
to make changes in any products described herein without notice. This publication
is subject to change without notice.
Your use of the MAX208M2W Series is subject to the terms and conditions of any
related service providers.
Do not use the MAX208M2W Series for illegal purposes. Illegal downloading or
sharing of files can result in severe civil and criminal penalties. You are subject to
the restrictions of copyright laws and any other applicable laws, and will bear the
consequences of any infringements thereof. ZyXEL bears NO responsibility or
liability for your use of the download service feature.
Trademarks
Trademarks mentioned in this publication are used for identification purposes only
and may be properties of their respective owners.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
295

Appendix GLegal Information
This
e
quipment
h
as been tested
a
nd found
to c
omply
w
ith the limits
f
or a C
lass B d
igital
d
evice,
p
ursuant
to P
art
nterference
i
n
ot
ommunications.
oes
quipment
ompliance
his
ncluding
his
Certifications
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference Statement
The device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful i
a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if n
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio c
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment d
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the e
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for c
could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) T
device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, i
interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. T
equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
following two conditions:
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the condition that this device does not cause harmful
interference.
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This device generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy,
and if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this device does cause harmful interference to radio/television reception, which
can be determined by turning the device off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1 Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2 Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
3 Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
4 Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
296
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, a separation
distance of at least 20 cm must be maintained between the antenna of this
device and all persons.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Appendix GLegal Information
Notices
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du
Canada.
Viewing Certifications
1 Go to http://www.zyxel.com.
2 Select your product on the ZyXEL home page to go to that product's page.
3 Select the certification you wish to view from this page.
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
ZyXEL warrants to the original end user (purchaser) that this product is free from
any defects in materials or workmanship for a period of up to two years from the
date of purchase. During the warranty period, and upon proof of purchase, should
the product have indications of failure due to faulty workmanship and/or
materials, ZyXEL will, at its discretion, repair or replace the defective products or
components without charge for either parts or labor, and to whatever extent it
shall deem necessary to restore the product or components to proper operating
condition. Any replacement will consist of a new or re-manufactured functionally
equivalent product of equal or higher value, and will be solely at the discretion of
ZyXEL. This warranty shall not apply if the product has been modified, misused,
tampered with, damaged by an act of God, or subjected to abnormal working
conditions.
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
297

Appendix GLegal Information
Note
Repair or replacement, as provided under this warranty, is the exclusive remedy of
the purchaser. This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, express or implied,
including any implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular use or
purpose. ZyXEL shall in no event be held liable for indirect or consequential
damages of any kind to the purchaser.
To obtain the services of this warranty, contact your vendor. You may also refer to
the warranty policy for the region in which you bought the device at http://
www.zyxel.com/web/support_warranty_info.php.
Registration
Register your product online to receive e-mail notices of firmware upgrades and
information at www.zyxel.com.
298
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide

Index
Index
A
AAA 70
AbS 134
accounting server
see AAA
ACK message 155
activity 70
Advanced Encryption Standard
see AES
AES 207
ALG 92
alternative subnet mask notation 250
analysis-by-synthesis 134
Application Layer Gateway
see ALG
authentication 70, 205
inner 208
key
server 70
types 208
authorization 205
request and reply 207
server 70
auto-discovery
UPnP 118
B
CBC-MAC 207
CCMP 205, 207
cell 69
certificates 205
CA 71
formats 72
verification 207
certification
notices 297
viewing 297
Certification Authority, see CA
chaining 207
chaining message authentication
see CCMP
circuit-switched telephone networks 133
Class of Service (CoS) 134
client-server
protocol 155
SIP 155
CMAC
see MAC
codec 133
comfort noise 157
copyright 295
CoS 134
counter mode
see CCMP
coverage area 69
cryptography 205
base station
see BS
BS 69$70
links 70
BYE request 155
C
CA 71, 72
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
D
data 205$207
decryption 205
encryption 205
flow 207
DHCP 89
server 89
diameter 70
299

Index
Differentiated Services
see DiffServ
DiffServ 134
DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) 134
marking rule 138
digital ID 72, 205
DS field 137
DSCP
see DiffServ
DTMF 143
dual-tone multi-frequency
see DTMF
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
see DHCP
E
EAP 70
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) 72
EAP-TLS 72
EAP-TTLS 72
echo cancellation 157
encryption 205$207
traffic 207
Ethernet
encapsulation 91
Extensible Authorization Protocol
see EAP
H
hybrid waveform codec 134
I
IANA 256
identity 70, 205
idle timeout 162
IEEE 802.16 69, 205
IEEE 802.16e 69
IGD 1.0 93
inner authentication 208
Internet
access 70
gateway device 93
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
see IANA 256
Internet Telephony Service Provider
see ITSP
interoperability 69
IP-PBX 133
ITSP 133
ITU-T 157
K
F
FCC interference statement 296
firewall 127
FTP 161
restrictions 161
G
G.168 157
G.711 134
G.729 134
300
key 205
request and reply 207
M
MAC 207
MAN 69
Management Information Base (MIB) 164
Message Authentication Code
see MAC
message integrity 207
Metropolitan Area Network
see MAN
microwave 69, 70
MAX208M2W Series User s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...