Page 1

Cable Modem/Router
Cable Modem plus
Dual-band Wireless-AC Router
USER MANUAL
Page 2

NOTICE
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright, and this Manual and all the
accompanying hardware, software, and documentation are copyrighted. No part of this document may be
photocopied or reproduced by mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form.
The manufacturer does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications, and
makes no warranty or representation, either expressed or implied, with respect to the quality, performance,
merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose of the software or documentation. The manufacturer reserves
the right to make changes to the hardware, software, and documentation without obligation to notify any person
or organization of the revision or change.
All brand and product names are the trademarks of their respective owners.
© Copyright 2014 Zoom Telephonics, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Safety Issues & Warnings
SAFETY
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it.
However, special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity
when working with electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture
must therefore be allowed at all times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
CAUTION:
• Do not put the cable modem in water.
• Do not use the cable modem outdoors.
• Keep the cable modem in an environment that is between 0°C and 40°C (between 32°F
and 104°F).
• Do not place any object on top of the cable modem since this may cause overheating.
• Do not place the cable modem in a confined space that may cause overheating.
• Do not restrict the flow of air around the cable modem.
• Zoom Telephonics assumes no liability for damage caused by any improper use of the
cable modem.
Page 3

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 GETTING STARTED.....................................................................6
PackageContents............................................................................................................................................6
CHAPTER 2 INSTALLING THE CABLE MODEM/ROUTER............................. 8
CHAPTER 3 CONNECTING DEVICES TO THE CABLE MODEM/ROUTER.. 14
EstablishingyourWirelessNetwork ................................................................................................. 15
ConnectingaWireless‐enabledDevice(includingtheiPhoneorothercellularphones,iPadorother
tablets,theiPodTouch,etc.)totheCableModem/Router............................................................... 17
ConnectingaWindows8.1orWindows8ComputerwithBuilt‐inWirelessCapabilities ............................18
ConnectingaWindows7ComputerwithBuilt‐inWirelessCapabilities........................................... 19
ConnectingaWindowsVistaComputerwithBuilt‐inWirelessCapabilities .................................... 20
ConnectingaWindowsXPComputerwithBuilt‐inWirelessCapabilities.........................................21
ConnectingaMacintoshOSXComputerwithBuilt‐inWirelessCapabilities.................................... 22
ConnectingaComputerwithaWirelessadaptertotheCableModem/Router ............................... 23
UsingWPSasanalternativewaytosetupyourWirelessNetwork .............................................................24
ConnectingAdditionalComputersand/orOtherDevicestotheCableModem/Router’sEthernet/LANports
......................................................................................................................................................................28
CHAPTER 4 CHANGING THE DEFAULT WIRELESS SETTINGS.................29
AboutWirelessSecurity ............................................................................................................................... 29
ChangingyourWirelessNetworkName(SSID)andPre‐SharedKey ............................................................30
SettingUpSecurityUsing WEP .....................................................................................................................32
DisablingSecurity .........................................................................................................................................33
CHAPTER 5 ONLINE GAMING ....................................................................... 34
Gaming .........................................................................................................................................................34
DMZHost............................................................................................................................... .......................35
PortTr igge rs ..................................................................................................................................................37
CHAPTER 6 ADVANCED SETTINGS.............................................................. 40
ChangingDefaultSettings.............................................................................................................................40
AccessingtheZoomConfigurationManager ................................................................................................41
UnderstandingtheConfigurationManagerInterfaceScreens......................................................................42
ConfigurationManagerInterfaceMenus .....................................................................................................43
CHAPTER 7 STATUS PAGE............................................................................ 45
Status............................................................................................................................................................45
CHAPTER 8 WIRELESS SETTINGS...............................................................46
Radio.............................................................................................................................................................46
Page 4

PrimaryNetwork ..........................................................................................................................................49
GuestNetwork..............................................................................................................................................53
Advanced ......................................................................................................................................................58
WPS ..............................................................................................................................................................60
Bridging ........................................................................................................................................................62
AccessControl ..............................................................................................................................................63
WMM(Wi‐FiMultimedia) ............................................................................................................................66
NeighborAPs ................................................................................................................................................68
CHAPTER 9 BASIC MENU OPTIONS.............................................................70
BasicLANSettings ........................................................................................................................................ 70
DHCP.............................................................................................................................................................72
WANSettings................................................................................................................................................73
MyNetwork..................................................................................................................................................75
CHAPTER 10 ADVANCED MENU OPTIONS.................................................. 77
MACFiltering ................................................................................................................................................77
IPFiltering ....................................................................................................................................................79
PortFiltering.................................................................................................................................................81
PortForwarding ............................................................................................................................................83
PortTr igge rs ..................................................................................................................................................85
DMZHost............................................................................................................................... .......................87
DDNS ............................................................................................................................... .............................89
RIPSetup ......................................................................................................................................................91
Options ............................................................................................................................... ..........................93
CHAPTER 11 FIREWALL MENU OPTIONS.................................................... 96
Basic..............................................................................................................................................................96
EventLog ......................................................................................................................................................97
CHAPTER 12 PARENTAL CONTROL MENU OPTIONS .............................. 103
Basic............................................................................................................................................................103
UserSetup ..................................................................................................................................................106
ToDFilter(TimeofDayFilter) ....................................................................................................................109
EventLog ....................................................................................................................................................111
CHAPTER 13 VPN (VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORK) MENU OPTIONS ...... 112
BasicSetting ...............................................................................................................................................112
IPSec ...........................................................................................................................................................114
L2TP/PPTP...................................................................................................................................................120
EventLog ....................................................................................................................................................122
CHAPTER 14 MANAGEMENT MENU OPTIONS.......................................... 123
AdminAccount ...........................................................................................................................................123
RemoteManagement.................................................................................................................................124
SNMPEventLog..........................................................................................................................................125
Diagnostics ............................................................................................................................... ..................127
Page 5

Backup/RestoreSettings.............................................................................................................................129
CHAPTER 15 CABLE MODEM MENU OPTIONS......................................... 131
CableModemDeviceInformation..............................................................................................................131
Connection .................................................................................................................................................133
Restart/RestoreFactory/Frequencyset......................................................................................................135
APPENDIX A: TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS...................................................136
APPENDIX B: IF YOU NEED HELP .............................................................. 140
APPENDIX C: COMPLIANCE........................................................................ 141
7
Page 6

1
Getting Started
This User Manual provides instructions for connecting and configuring your Model 5363
Cable Modem/Router and for setting up wireless and wired connections to Model 5363.
This manual also includes details about security, firewalls, VPNs (Virtual Private
Networks), administrative tasks, and troubleshooting.
Most users should use the Quick Start Flyer to install their cable modem. This
User Manual is best used if you need to go beyond the Quick Start Flyer for some
reason.
Package Contents
Your package contains the following items:
• Cable Modem/Router
• Power cube
• Ethernet RJ-45 cable
• Quick Start flyer
Before installing your cable modem, please read this.
You need to connect the cable modem to a cable modem service that uses any of the
popular DOCSIS standards – 3.0, 2.0, or 1.1. If you need to get cable modem service,
please speak with your cable service provider.
Your cable service provider will need to know your modem's MAC ADDRESS, which is
printed on a label on the bottom of your modem. You provide this when you order
cable modem service, or by calling the cable company before or after installing your
modem, or by entering your CM MAC ADDRESS on an account setup web page that
appears when you first connect your cable modem to your provider’s network. Normally
your cable service provider will tell you when to provide the CM MAC address. You may
also be asked for your cable modem's model name and number, which is ZOOM 5363.
If you need the modem's serial number, you can find it near the MAC address on the
bottom label. Below is a guide to some of the chapters of this manual.
6
Page 7

• If you haven’t already set up your Cable Modem/Router using the Quick Start, go
to
Chapter 2: Installing the Cable Modem/Router.
• If you have already installed your cable modem and want to learn more about
how to connect both wired and wireless computers and other devices to your
Cable Modem/Router go to:
Chapter 3: Connecting Devices to your Cable
Modem/Router.
• Your Cable Modem/Router comes from the factory with a default SSID (Wireless
Network Name), wireless security enabled and a random Pre-Shared Key
(Wireless Password). These default settings for your modem/router are listed on
the bottom label of your cable modem/router. Most users can simply use the
default settings. You may want to change the wireless settings if you are
replacing a wireless router and want to use the same wireless network name and
wireless password as the existing router instead of changing all your wireless
devices to use the Cable Modem/Router’s defaults, or in the unlikely event that
one of the wireless devices only supports WEP security. If you want to make
changes to the default wireless settings, please refer to
Chapter 4: Changing
your Wireless Settings.
• If you are using the Cable Modem/Router for online gaming and need to make
changes to the router’s firewall, please see
Chapter 5: Online Gaming.
• If you are like most users, you will not need to make changes to the Cable
Modem/Router’s advanced settings. If your setup requires you to make changes
to advanced settings, go to
Chapter 6: Advanced Settings.
7
Page 8

2
Installing the Cable Modem/Router
This chapter provides basic instructions for setting up your cable modem/router. This chapter is
almost identical to the printed Quick Start.
If you are replacing an “old” cable modem, do this:
1 Disconnect the coaxial cable from the old cable modem and connect it to your
Zoom modem. If the coaxial cable has a screw-on connector, turn the connector
clockwise when tightening the cable onto the Zoom cable modem.
2 If there’s an Ethernet cable plugged into the old cable modem, unplug the
Ethernet cable from the old cable modem and plug it into any of the Zoom cable
modem’s LAN jacks.
3 Connect the Zoom power cube between the Zoom cable modem and a live
power jack. DO NOT use your old cable modem’s power cube on your Zoom
cable modem.
4 What you do next depends on your cable modem company. Typically you can
call your cable modem company’s support department and tell them your cable
modem is hooked up. They’ll normally ask for the information mentioned above
in
Before installing your cable modem, please read this. Some cable companies
also let you just open the browser on a computer that’s connected to the Zoom
cable modem. A setup page comes up, and you follow the instructions.
5 Go to Now that your cable modem is connected, do this below.
If this is a first-time cable modem installation (that is, you are NOT
replacing an “old” cable modem), do this:
1 Connect a “live” coaxial cable from your cable service provider to your cable
modem. (If you’re not sure a cable is live, you can see whether you get a good
8
Page 9

TV signal when that cable is used with a working TV set-top box.) Here are
some ways you can get the live cable:
Coaxial Cable Cable TV Jack
¾ You have a cable TV cable (“coaxial cable”) with a male connector on the
end that isn’t connected to anything. This cable may be coming out of a
wall or connected to a cable TV jack.
¾ There’s a cable TV jack in your wall. You can connect a cable TV “coaxial
cable” between that jack and your cable modem. You may have a coaxial
cable, possibly one that came with a cable modem starter kit from your
cable service provider. If you don’t have a coaxial cable, you can get one
at most electronics stores. You want one with a screw-in male F
connector at each end, with a length that works for your installation.
¾ If you don’t have an available cable TV cable or wall jack, use a coaxial
“T adapter” or “splitter” available from most electronics retailers.
Make sure you get one designed for cable modems and/or cable TV.
These typically have one female IN jack and two female OUT jacks. You
can disconnect a live cable from your TV set-top box and screw it into the
IN jack of the splitter. Then connect one coaxial cable from an OUT jack
to your TV set-top box and another coaxial cable from the other OUT
jack to your cable modem. You can see that this approach uses one
splitter and 2 additional coaxial cables, each of which has male
connectors on each end. Some electronics retailers carry the Zoom
9
Page 10

Cable Modem Connection Kit which has an excellent splitter and 2
coaxial cables packaged together at a reasonable price. You can also
purchase splitters and coaxial cable separately if you prefer to do that,
perhaps because you need a special length of coaxial cable.
2 Connect the supplied Ethernet cable between any cable modem LAN jack and a
computer’s Ethernet jack. We recommend that you do this even if you later plan
to disconnect this computer. If connecting the Ethernet cable to a computer is
difficult or impossible, you can make a wireless connection as discussed below
in
Connecting your Cable Modem/Router wirelessly to some device.
3 Connect the Zoom power cube between the Zoom cable modem and a live
power jack.
4 What you do next depends on your cable modem company. Typically you can
call your cable modem company’s support department and tell them your cable
modem is hooked up. They’ll normally ask for the information mentioned above
in
Before installing your cable modem please read this. Some cable companies
also let you just open the browser on a computer that’s connected to the Zoom
cable modem. A setup page comes up automatically, and you follow the
instructions.
5 Go to Now that your cable modem is connected, do this below.
10
Page 11

Now that your cable modem is connected, do this.
When your cable modem first connects to your cable service provider, allow 5 to 30
minutes for the cable modem to connect to the network. The cable modem uses this time
to locate and connect to the appropriate channels for communication. You’ll see the DS
(downstream), US (upstream), and Online modem lights flashing until the Online light
stays steady green to signal success. (Blue US/DS LEDs indicate channel bonding.)
• To check that your cable modem is working, open your browser and go to a
familiar Web site. If it works, congratulations! Installation is complete for a single
PC. For Internet access using a smartphone, tablet, or other wireless device, first
see this chapter’s
Connecting your Cable Modem/Router wirelessly to some
device.
• If you want to connect additional computers or other devices using the
modem/router’s Ethernet/LAN ports, see this chapter’s
Read this only if you are
connecting additional computers and/or other devices to your Cable
Modem/Router’s Ethernet/LAN ports.
• If you are using the Cable Modem/Router for online gaming and need to make
changes to the router’s firewall, please see
Chapter 5: Online Gaming.
• If you are like most users, you will not need to make changes to the Cable
Modem/Router’s advanced settings. If your setup requires you to make
changes to advanced settings, go to
Chapter 6: Advanced Setup.
11
Page 12

Front Panel LEDs
LIGHT COLOR DESCRIPTION
ON: Power is supplied to the Cable
Power
DS
Receive
Downstrea
m sync
US Send
Upstream
sync
Online
Green
Green or
Blue
Green or
Blue
Green
Modem/Router.
OFF: Power is not supplied to the Cable
Modem/Router.
Blinking: Scanning for downstream channel
Green ON: Synchronized on 1 channel only
Blue ON: Synchronized with more than 1
channel (Downstream Bond mode)
Blinking: Ranging is in progress.
Green: Ranging is complete; operate on 1
channel
Blue: Ranging is complete; operate on more
than 1 channel (Upstream Bond mode)
OFF: Upstream channel is inactive
Blinking: Cable interface is acquiring IP
address, time of day, and configuration
ON: Cable Modem/Router is online
OFF: Cable Modem/Router is offline
Wireless
or WPS
WPS
Button
ON: Wireless is enabled or Pairing
completed successfully
Green or
Orange
OFF: Wireless is not enabled
Orange Blinking: WPS is in discovery
mode (pairing)
Pressing the WPS button initiates a WPS
connection with other wireless devices.
12
Page 13

Back Panel
LAN 1-4
(Gigabit Ethernet 1-4)
Four 10/100/1000 auto-sensing Ethernet
ports for computers and other devices that
have an Ethernet port.
RESET
Press and hold this recessed button at
least 8 seconds in the unlikely event that
you want to restore the default factory
settings. This button is recessed to
prevent accidental resets of your cable
modem/router.
COAX
Connect your coaxial cable line to this
port.
POWER
Connect the supplied power cube to this
port
13
Page 14

3
Connecting Devices to the Cable
Modem/Router
This chapter explains how to connect devices (computers, phones, tablets, game
stations, etc.) to the Cable Modem/Router. These devices can be connected either
wirelessly or to one of the Ethernet ports on your Cable Modem/Router.
If you are connecting a computer or other device to an Ethernet LAN port of the Cable
Modem/Router, please go to
the Cable Modem/Router’s Ethernet/LAN ports. If you are connecting one or more Wi-Fi
compatible devices wirelessly to the cable modem/router, please continue below.
Connecting Wi-Fi compatible wireless devices to your Cable
Modem/Router.
Your Cable Modem/Router comes pre-configured wireless settings as discussed below.
Most users should simply use these default settings.
• WPA2-PSK/WPA-PSK security is enabled
• A random Pre-Shared Key (also called a security key or password) is assigned.
The Security Key/Password is printed on the bottom label of your Cable
Modem/Router.
Cable Modem Bottom Label:
Connecting Additional Computers and/or Other Devices to
14
Page 15

• The default SSID (wireless network name) is assigned as Zoomxxxx (where
xxxx are the last 4 hexadecimal characters of the cable modem CM MAC
address). This SSID is printed on the bottom label of your cable modem/router.
The SSID printed on your bottom label is the for the 2.4 GHz network. The SSID
for the 5 GHz network is Zoomxxxx_5G.
Your Cable Modem/Router is capable of sending and receiving wireless data on both the
2.4GHz frequency band and the 5 GHz frequency band at the same time. Almost all
computers, smartphones, tablets, and other client devices support the 2.4 GHz band,
and some also support the 5 GHz band. A major advantage of the 5 GHz band is that it’s
normally much less crowded with other devices trying to use that band. This is especially
important in areas with lots of wireless devices, such as some cities. To select Model
5363’s 5 GHz network for a client device, pick the network ending in 5G. You may want
to try both SSIDs to see which one gives you better speed and range.
If you want to change these default settings please see
Wireless Settings before connecting your wireless computers or devices. You must use
compatible wireless settings for each computer or device that you want to wirelessly
connect to the Cable Modem/Router, as described below.
Chapter 4, Changing the Default
Establishing your Wireless Network
If all the computers or devices on your network support WPS, you can use WPS to easily
set up your network. Windows 8, 8.1 and 7 support WPS. Non Windows devices typically
have a button called WPS on them if they support WPS. (Note: Apple iPads, iPhones,
and Macintosh computers do not support WPS as of March 2013.) Please see
WPS to set up your Wireless network if you want to use WPS for wireless connections to
your cable modem/router.
If some of the wireless devices do not support WPS, or if you do not know whether they
do support WPS, you can configure each computer or device manually. To do that,
select one of the possibilities for that computer or other device below:
¾ If you have a non-computer wireless device like an iPhone or other cellular phone,
iPad or other tablet, iPod Touch, etc., see the instructions on page 17 for
Wireless-enabled Device to the Cable Modem/Router.
¾ Many newer Windows 8.1, 8, 7, Vista, and XP computers have built-in wireless
networking capabilities and do not require the installation of a wireless component.
If this is the case, you should set up that computer’s wireless connection using the
Windows 8.1 or 8, 7, Vista, or XP connect utility. See the sections below on
connecting
Windows 8.1 or 8 (page 18), Windows 7 (page 19), Vista (page 20), or XP
Using
Connecting a
15
Page 16

(page 21) computers with built-in wireless capabilities.
¾ If you are using a Macintosh computer see the instructions on page 22 for
Connecting a Macintosh OS X Computer with Built-in Wireless Capabilities.
¾ Some older Windows computers may have built-in wireless networking capabilities,
but not use the Windows 8, 7, Vista, or XP utility to configure wireless networking. If this is
so, set up your computer’s wireless connection using the instructions on page 23 for
Connecting a Computer with a wireless adapter to the Cable Modem/Router.
¾ Some computers may need a wireless network adapter installed. This can be a USB
adapter, PC Card adapter, or PCI adapter. When you install the adapter, make sure that it
is set to infrastructure or access point mode (NOT ad-hoc or peer-to-peer mode). If
you need help installing your wireless adapter or setting its mode, refer to the
documentation that came with it. After you install the adapter, see the instructions on
page 23 for
Connecting a Computer with a wireless adapter to the Cable Modem/ Router.
16
Page 17

Connecting a Wireless-enabled Device (including the iPhone or other cellular phones, iPad or other tablets, the iPod Touch, etc.) to the Cable Modem/Router
1 Select the wireless-enabled computer or device that you want to add to the network.
The device should have software that will let it perform a site search to scan for
available wireless networks in your area. You may have to click on something like
Settings and then Wi-Fi. When the list of available wireless networks appears, click
on Zoomxxxx_5G to connect to your Cable Modem/Router’s 5 GHz network. If you
do not see Zoomxxxx_5G then most likely your wireless adapter does not support
the 5 GHz network, so click on Zoomxxxx. In both cases, xxxx are the last 4
characters of the cable modem CM MAC address. You can find Zoomxxxx printed
on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router. In the unlikely event that you
changed the SSID from the default, select your new SSID.
2 When prompted for the wireless password, enter your Pre-Shared Key (Security
Key/Password) and click Connect or Join. Your Security Key/Password can be
found on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router.
Tip!
If you need help, refer to the documentation that came with your wireless device.
3 Test your wireless connection. Open your device’s Web browser (for instance,
Internet Explorer, Firefox, or Chrome) and try to connect to a familiar Web address. If
you are unable to connect, make sure you followed the instructions. If you did,
please see
Appendix A: Troubleshooting Tips.
Your device is now connected to your wireless network. If you want to connect additional
computers or devices, follow the instructions for your device by starting at the first page
of this chapter.
To disconnect from the current network:
1 On your wireless device or computer, find the wireless network connection option
(similar to the process of adding your device or computer to the network).
2 Select or click on Disconnect, Forget, Forget this network or similarly-named
button
. In doing this, you may need to select your SSID (wireless network name).
17
Page 18

Connecting a Windows 8.1 or Windows 8 Computer with Built-in Wireless Capabilities
1 On the desktop, click the Wireless Network Icon in your computer’s
notification area.
2 If available, click on Zoomxxxx_5G to connect to your Cable Modem/Router’s 5 GHz
network. If you do not see Zoomxxxx_5G than most likely your computer does not
support the 5 GHz network, so go ahead and click on Zoomxxxx. In both cases,
xxxx are the last 4 characters of the cable modem CM MAC address. You can find
Zoomxxxx printed on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router. In the unlikely
event that you changed the SSID from the default, select your new SSID.
3 Click Connect. If you want to connect to this network automatically in the future,
check the Connect Automatically checkbox.
4 When prompted to enter your Network Security Key, enter your Pre-Shared Key
(Security Key/Password) and click Next. Your Security Key/Password can be found
on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router.
5 When asked “Do you want to turn on sharing between PCs and connect to devices
on this network?” Click Yes to enable sharing and No to disable sharing. Sharing
sets up your firewall to allow other users on your network to share files, folders or
devices such as printers. Most users should select Yes. If you know you don’t want
to share files or devices, select No.
6 Test your wireless connection. Open your computer’s Web browser and try to
connect to a familiar Website. If you are unable to connect, make sure you followed
the instructions. If you did, please see
Your computer is now connected to your wireless network. If you want to connect
additional computers or devices, follow the instructions for your device by starting at the
first page of this chapter.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting Tips.
To disconnect from the current wireless network:
1 Left-click the wireless network icon in the notification area of the Windows taskbar.
2 Left-click your SSID (wireless network name) and select Disconnect.
18
Page 19

Connecting a Windows 7 Computer with Built-in Wireless Capabilities
1 Click the Wireless Network Configuration utility icon in your computer’s
system tray.
2 If available, click on Zoomxxxx_5G to connect to your Cable Modem/Router’s 5 GHz
network. If you do not see Zoomxxxx_5G than most likely your wireless adapter
does not support the 5 GHz network, so go ahead and click on Zoomxxxx. In both
cases, xxxx are the last 4 characters of the cable modem CM MAC address. You can
find Zoomxxxx printed on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router. In the
unlikely event that you changed the SSID from the default, select your new SSID.
3 Click Connect. If you want to connect to this network automatically in the future,
check the Connect Automatically checkbox.
4 When prompted to enter your Network Security Key, enter your Pre-Shared Key
(Security Key/Password) and click OK. Y our Security Key/Password can be found on
the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router.
5 Test your wireless connection. Open your computer’s Web browser and try to
connect to a familiar Website. If you are unable to connect, make sure you followed
the instructions. If you did, please see
Appendix A: Troubleshooting Tips.
Your computer is now connected to your wireless network. If you want to connect
additional computers or devices, follow the instructions for your device by starting at the
first page of this chapter.
To disconnect from the current network:
1 Left-click the wireless network icon in the notification area of the Windows taskbar.
2 Left-click your SSID (wireless network name) and select Disconnect.
19
Page 20

Connecting a Windows Vista Computer with Built-in Wireless Capabilities
1 From the Start menu select Connect to.
2 If available, click on Zoomxxxx_5G to connect to your Cable Modem/Router’s
5 GHz network. If you do not see Zoomxxxx_5G than most likely your wireless
adapter does not support the 5 GHz network, so go ahead and click on Zoomxxxx.
In both cases, xxxx are the last 4 characters of the cable modem CM MAC address.
You can find Zoomxxxx printed on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router.
In the unlikely event that you changed the SSID from the default, select your new
SSID.
3 Click Connect.
If a message pops up asking you to enter your PIN on the Zoomxxxx page, select “I
want to enter the network key or passphrase instead.” Then click Next.
4 When prompted to enter your Network Security Key, enter your Pre-Shared Key
(Security Key/Password) and hit Connect. Your Security Key/Password can be
found on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router.
5 In the Successfully connected to [desired network] dialog box, you have three
options. You can:
• Select Save the network and Start this connection automatically if you
always want to connect to the same network. Then click Close. The next time
you start your computer, you will automatically connect to the selected network.
• Select Save the network and clear the Start this connection automatically
check box if you don't want to automatically connect to this network every time
you start your computer but you will want to sometimes connect to this wireless
network in the future. Click Close to display the Select a location . . . dialog
box where you choose a location. Windows Vista automatically applies the
correct network security settings. If the User Account Control dialog box
appears, click Continue.
• Click Close to complete the connection procedure. Select this option if you are
connecting to this network only one time.
6 Test your wireless connection. Open your computer’s Web browser and try to
connect to a familiar Website. If you are unable to connect, make sure you followed
the instructions. If you did, please see
Your computer is now connected to your wireless network. If you want to connect
additional computers or devices, follow the instructions for your device by starting at the
first page of this chapter.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting Tips.
20
Page 21

To disconnect from the current network:
1 From the Windows Start menu, select Connect to.
2 In the Disconnect or Connect to another network dialog box, select the current
network and click Disconnect.
3 In the Are You Sure? message box, click Disconnect again.
4 In the next dialog box, you can connect to another network or click Close to complete
the disconnect procedure.
Connecting a Windows XP Computer with Built-in Wireless Capabilities
1 On your Windows desktop, click the Wireless Network Icon in the System Tray.
2 If available, click on Zoomxxxx_5G to connect to your Cable Modem/Router’s 5 GHz
network. If you do not see Zoomxxxx_5G than most likely your wireless adapter
does not support the 5 GHz network, so go ahead and click on Zoomxxxx. In both
cases, xxxx are the last 4 characters of the cable modem CM MAC address. You can
find Zoomxxxx printed on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router. In the
unlikely event that you changed the SSID from the default, select your new SSID.
3 When prompted to enter your Network Security Key, enter your Pre-Shared Key
(Security Key/Password) and click Connect. Your Security Key/Password can be
found on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router.
4 Test your wireless connection. Open your computer’s Web browser and try to
connect to a familiar Website. If you are unable to connect, make sure you followed
the instructions. If you did, please see
Your computer is now connected to your wireless network. If you want to connect
additional computers or devices, follow the instructions for your device by starting at the
first page of this chapter.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting Tips.
To disconnect from the current network:
1 On your Windows desktop, click the Wireless Network Icon in the System Tray.
2 Click View Wireless Networks button.
3 Select your SSID (wireless security name) and click Disconnect.
21
Page 22

Connecting a Macintosh OS X Computer with Built-in Wireless Capabilities
1 Click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar. If the Wi-Fi icon does not appear on your menu
bar, please refer to your built-in Macintosh documentation for how to enable wireless.
Note: On versions prior to OS 10.7 the Wi-Fi icon is called AirPort.
2 If available, click on Zoomxxxx_5G to connect to your Cable Modem/Router’s 5 GHz
network. If you do not see Zoomxxxx_5G than most likely your wireless adapter
does not support the 5 GHz network, so go ahead and click on Zoomxxxx. In both
cases, xxxx are the last 4 characters of the cable modem CM MAC address. You can
find Zoomxxxx printed on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router. In the
unlikely event that you changed the SSID from the default, select your new SSID.
3 When prompted for the password in the next dialog box, enter your Pre-Shared Key
(Security Key/Password) and click Join. Your Security Key/Password can be found
on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router.
4 Test your wireless connection. Open your computer’s Web browser and try to
connect to a familiar Website. If you are unable to connect, make sure you followed
the instructions. If you did, please see
Your computer is now connected to your wireless network. If you want to connect
additional computers or devices, follow the instructions for your device by starting at the
first page of this chapter.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting Tips.
To disconnect from the current network:
1 Click the Wi-Fi icon on the menu bar.
2 Select Turn Wi-Fi Off (OS 10.7 or later) or Turn AirPort Off (OS versions prior to
10.7) to disconnect from the router.
22
Page 23

Connecting a Computer with a Wireless adapter to the Cable Modem/Router
1 Go to the computer that is set up with a wireless adapter that you want to add to the
network. For many wireless adapters, you will use their configuration manager
software and click a Scan button or select a Site Scan, Scan Networks, or other
similarly named tab to do a site search. When the list of available wireless networks
appears, click on Zoomxxxx_5G to connect to your Cable Modem/Router’s 5 GHz
network. If you do not see Zoomxxxx_5G than most likely your wireless adapter
does not support the 5 GHz network, so go ahead and click on Zoomxxxx. In both
cases, xxxx are the last 4 characters of the cable modem CM MAC address. You can
find Zoomxxxx printed on the bottom label of your Cable Modem/Router. In the
unlikely event that you changed the SSID from the default, select your new SSID.
If you need help, refer to the documentation that came with your wireless adapter.
Note for
on a Windows
the adapter (rather than let you use the software provided with the wireless adapter).
You will know this is happening because you will be prompted with a message about
one or more wireless networks being available. You will also be able to click a link to
open the Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog box. If this happens,
click the link, clear the Use Windows to configure my wireless network settings
check box, and then click OK. You can then use the software provided with your
wireless adapter without interruption from Windows.
2 When prompted for the wireless password, enter your Security Key/Password and
hit Connect. Your Security Key/Password can be found on the bottom label of your
Cable Modem/Router.
3 Test your wireless connection. Open your device’s Web browser (for instance,
Internet Explorer, Firefox, or Chrome) and try to connect to a familiar Web address. If
you are unable to connect, make sure you followed the instructions. If you did, please
see
Your device is now connected to your wireless network. If you want to connect additional
computers or devices, follow the instructions for your device by starting at the first page
of this chapter.
Windows 8.1, 8, 7, Vista and XP users: If you installed a wireless adapter
8, 7, Vista or XP computer, Windows may try to automatically configure
Appendix A: Troubleshooting Tips.
To disconnect from the current network:
1 On your computer that has a wireless adapter, find the wireless network connection
option (similar to the process of adding your computer to the network).
2 Click or highlight the Cable Modem/Router’s SSID.
23
Page 24

3 Select or click on Disconnect or similarly-named button.
Using WPS as an alternative way to set up your Wireless Network
If all the Wi-Fi compatible wireless devices on your network support WPS, you can
choose to quickly setup your wireless network by pushing the WPS button on your cable
modem/router and on each wireless device connecting to your cable modem/router.
Windows 8 and Windows 7 users should follow the instructions below: Other computers
or devices such as tablets should go to
other device that supports WPS.
If you are using a Windows 8.1, 8 or 7, computer:
1 On your desktop, open Connect to a Network on that computer by left-clicking the
network icon in the notification area of the Windows taskbar.
2 A list of available networks is displayed.
3 Typically you then click Zoomxxxx_5G to connect to your Cable Modem/Router’s 5
GHz network. If you do not see Zoomxxxx_5G than most likely your wireless
adapter does not support the 5 GHz network, so go ahead and click on Zoomxxxx
where xxxx are the last 4 hexadecimal characters of the cable modem CM MAC
address. Zoomxxxx is the SSID printed on the bottom label of your Cable
Modem/Router. In the unlikely event that you changed the SSID from the default,
select your new SSID.
If you are using a non Windows computer or
4 You will see a screen with a text box for the Security key. If WPS configuration is
supported, you may see a message such as You can also connect by pushing the
button on the router. If you see this message, continue at step 5 below.
24
Page 25

Windows 7
Windows 8.1 or Windows 8
5 Press the Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) button on the router for at least 3 seconds.
(You do not need to type a security key or passphrase in the Security key text box on
your Windows machine). The Cable Modem/Router will automatically set up the
computer to connect to the network and apply the network's security settings.
When asked “Do you want to turn on sharing between PCs and connect to
devices on this network?” Click Yes to enable sharing and No to disable sharing.
Sharing sets up your firewall to allow other users on your network to share files,
25
Page 26

folders or devices such as printers. Most users should select Yes. If you know you
don’t want to share files or devices, select No.
Repeat steps 1-5 above for each Windows computer you want to connect to the Cable
Modem/Router. If you want to connect a non Windows computer or another device such
as a tablet, follow the instructions below.
26
Page 27

If you are using a non Windows computer or other device that supports
WPS
Please refer to the instructions for your device for more information on using WPS. The
directions below should work for most users.
1 Press the WPS LED pushbutton on the front panel of the router for at least 3
seconds. The WPS LED should blink orange.
2 Within 2 minutes (before the WPS LED orange light turns off), press the WPS button
on the device that you’re linking wirelessly to the modem/router. The button may be a
physical pushbutton on the device or a button on a page of the device’s wireless
network configuration menus.
3 Congratulations! You should now have a secure connection between your Cable
Modem/Router and a device. Now is a good time to check that your device’s Internet
connection is working. Open your browser and go to a familiar Web site. If you are
able to connect, continue with the next step below.
If you are not able to connect to the Internet, please see
Troubleshooting Tips.
4 If you have other devices whose WPS security you need to set, repeat steps 1
through 3 for each device. When they are finished, the basic setup for these local
wireless devices should be complete
.
Appendix A:
27
Page 28

Connecting Additional Computers and/or Other Devices to the Cable Modem/Router’s Ethernet/LAN ports
You can plug up to four computers, game consoles, or other Ethernet-capable devices into the
Cabl e Mode m/Rou ter ’s LAN port s. For information about your specific device, please refer
to the documentation that came with that device. Follow the instructions below for each
computer or other device.
1 If you connected the Cable Modem/Router to a computer using a wired connection
when setting up the Cable Modem/Router, unplug the computer now if you don’t
want that computer to stay connected to the Cable Modem/Router.
2 To connect a computer or other Ethernet-capable device, plug one end of an
Ethernet cable into an available Ethernet (LAN 1, 2, 3, or 4) port on the Cable
Modem/Router and plug the other end of the Ethernet cable into the Ethernet port of
the additional device you want to connect to the Cable Modem/Router. (If you are
connecting a hub or a switch, this is typically called an Uplink or Expansion port.) If
you are connecting a computer or game station, go to step 5 of this section.
3 If you are connecting a network device such as a switching hub, use the instructions
that came with that device. Then reboot any computer that is part of your network.
For example, if you connected a switching hub, reboot any computer that will be
connected to that switching hub.
4 If you are connecting a HomePlug adapter pair with one adapter plugged into the
Cable Modem/Router and an AC outlet, and the other adapter plugged into a
computer, game station, or other device and an AC outlet, make those connections
and then go to step 5.
5 Verify that your Internet connection is working. Open a Web browser on each
computer that’s using your network and try to connect to a familiar Web address.
Congratulations! You have connected an additional device to the Internet. You can
connect up to 4 Ethernet-capable devices to the Cable Modem/Router, following the
instructions above for each device by starting at step 2 of this section.
28
Page 29

4
Changing the Default Wireless Settings
Your Cable Modem/Router comes from the factory with a default SSID (Wireless
Network Name), WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK wireless security and a random Wireless
Security Key (Wireless Password). These default settings for your router are listed on the
bottom label of your unit. Most users can go ahead and use the default settings.
You may want to change your wireless settings if the wireless devices on your network
are already configured to use an existing wireless network name and password. Instead
of having to reconfigure all the devices on your network, you can change the Cable
Modem/Router to match the existing settings used by your devices. Read this chapter if
you want to use another wireless security mode, or if you want to change either the SSID
or Wireless Security Key. If you want to use the default wireless settings, you can skip
this chapter.
About Wireless Security
There are two basic wireless security modes, WPA and WEP. There are two versions of
WPA: WPA and WPA2. When configured as part of a typical home or small office
network, WPA and WPA2 require a Pre-Shared Key, or PSK. These modes are typically
called WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK, respectively, though sometimes they’re just called
WPA and WPA2. You can enable either WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK alone, or you can
enable both WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK together. By default, your Cable Modem/Router
has both WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK enabled. You will only need to change the security
mode if you know that you have a device you are connecting to your wireless network
that only supports WEP go to
you want an unsecured network, this is discussed late in this chapter in
Security.
Note: If you have a Radius Server (very unlikely for a home network), select the
WPA/WPA2 options without PSK. All instances of WPA and/or WPA2 that follow refer to
WPA-PSK and/or WPA2-PSK unless noted otherwise.
Setting up Security using WEP. In the unlikely event that
Disabling
29
Page 30

You can check to see if all other clients that you plan to put on the network support WPA
or WPA2. You can do this by checking the manual that came with each device or by
checking the configuration software for the installed device. Look under Security or
Encryption or Setup or Advanced Features. Most devices will support one of these
modes.
• To change the Wireless Network Name (SSID) or Wireless Security Key
(Pre-Shared key) used by your Cable Modem/Router go to
Wireless Network Name(SSID) and Pre-Shared Key.
• If any of the devices you want to connect to your wireless network do not support
WPA or WPA2, go to
Setting Up Security Using WEP.
Changing your
• If you need to set up an unsecured network, see Disabling Security.
Changing your Wireless Network Name (SSID) and Pre-Shared Key
Most likely your previous wireless network used 802.11n. If you want to change your
Cable Modem/Router settings to match your existing network settings follow the steps
below. If you have newer devices that support 802.11ac then you should connect to
the Cable Modem/Router’s 5G network. For instructions on connecting to the 5G
network refer to
Chapter 3, Connecting other Devices to the Cable Modem/Router.
To check if your device supports 801.11ac, you can scan for available wireless networks
on your device. If you see a wireless network named Zoomxxxx_5G than your devices
supports 802.11ac and you should follow the instructions for connecting that device to
the Cable Modem/Router found in Chapter 3. If you only see Zoomxxxx then your
device does not support 802.11ac. In both cases, xxxx are the last 4 characters of the
cable modem CM MAC address. You can find Zoomxxxx printed on the bottom label of
your Cable Modem/Router.
1 Open the Zoom Configuration Manager by typing the following in your Web browser's
address bar:
2 In the Login dialog box, type the following User Name and Password in lower case,
then click Login.
http://192.168.0.1
User Name: admin
Password: admin
30
Page 31

3 Click Wireless on the top menu.
4 The Wireless Radio page appears. Under Select 2.4 or 5 GHz option. Select 2.4 GHz
if your existing wireless network used 802.11n. If your existing network used 802.11ac
or you just want to change the SSID for the 802.11ac network select 5 GHz. Click
Apply.
5 Then click Primary Network on the left-side menu and in the text box labeled
Network Name (SSID), type an SSID of your choice. The SSID needs to be at least
one character long, and it’s probably best to pick a name that you’ll recognize as
yours.
6 To change the wireless security, start by setting all the following drop-down menus to
Disable: WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, and WPA2-PSK.
7 Then select Enable for the mode(s) you choose for setting wireless security.
Note: To use WPA2 /WPA, all of the wireless devices on your network must support
either encryption method. In this case, enable:
• WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK (if you want to use a Pre-Shared Key)
or
• WPA and WPA2 (use this only if your network uses a Radius Server.
This is very uncommon for a home network)
If you know that all your devices support the more secure WPA2 you can enable
WPA2 only (or WPA2-PSK if you want to use a Pre-Shared Key) instead of WPA and
WPA2.
8 In the WPA Pre-Shared Key text box (only if you selected an option requiring a
Pre-Shared Key), enter a passphrase of your choice (a minimum of 8 characters).
Write down this passphrase and put it where you can find it – on the bottom of the
Cable Modem/Router case, for instance.
9 Click Apply.
10 Now you may need to set up each of your wireless devices with the SSID and
passphrase.
your setup should be complete, otherwise, see
to the Cable Modem/Router for help on connecting your wireless computers and
devices.
Your security setup configuration is now complete!
If your devices were already setup with this SSID and passphrase then
Chapter 3, Connecting other Devices
31
Page 32

Setting Up Security Using WEP
If any of your network devices DOES NOT support WPA or WPA2, you can use WEP to
configure network security. WEP can be configured two ways: 64-bit and 128-bit. 128-bit
WEP provides more security than 64-bit.
1 Open the Zoom Configuration Manager by typing the following in your Web browser's
address bar:
2 In the Login dialog box, type the following User Name and Password in lower case,
then click Login.
3 Click Wireless on the top menu.
4 The Wireless Radio page appears. Under Select 2.4 or 5 GHz option. Select 2.4 GHz
and click Apply.
5 Then click Primary Network on the left-side menu.
6 To change the wireless security, start by setting the following drop-down menus to
Disable: WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, and WPA2-PSK
http://192.168.0.1
User Name: admin
Password: admin
7 From the WEP Encryption drop-down menu, select WEP-64 bit (or WEP-128 bit for
more security).
8 For Network Key 1, you can either enter your own WEP Key or you can have WEP
Keys generated.
If you are entering a network key of your choice, enter 13 ASCII characters or 26
hexadecimal digits for 128-bit encryption keys. Enter 5 ASCII characters or 10
hexadecimal digits for 64-bit encryption keys.
Otherwise, type something into the text box and click on Generate WEP Keys and
WEP Keys will automatically be generated for you.
Caution! Do not click Apply until you have entered WEP Keys.
9 Click Apply.
10 Now you need to set up each of your wireless devices with the SSID and
passphrase. See
for help on connecting your wireless computers and devices.
Your security setup configuration is now complete!
Chapter 3, Connecting other Devices to the Cable Modem/Router
32
Page 33

Disabling Security
If for some reason you need to set up an unsecured network, you will need to disable the
default security that is currently set up for your Cable Modem/Router. Follow the
instructions below.
1 Open the Zoom Configuration Manager by typing the following in your Web browser's
address bar:
2 In the Login dialog box, type the following User Name and Password in lower case,
then click Login.
3 Click Wireless on the top menu.
4 The Wireless Radio page appears. Under Select 2.4 or 5 GHz option, choose 5 GHz
and click Apply.
5 Then click Primary Network on the left-side menu.
6 Set all the following drop-down menus to Disable: WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, and
WPA2-PSK.
7 Click Apply.
http://192.168.0.1
User Name: admin
Password: admin
8 Click Wireless Radio on the left-side menu. Under Select 2.4 or 5 GHz option,
choose 2.4 GHz and click Apply. Repeat steps 5-7 to disable security on the 2.4
GHz band.
That’s it! You have now disabled security.
33
Page 34

5
Online Gaming
Read this chapter if you are going to use your Cable Modem/Router for online gaming.
Some online games require you to make changes to your firewall. This chapter explains
the different ways you can modify the firewall to allow your online gaming system access.
Gaming
If you are using your router for gaming, you may need to make changes to the router’s
firewall setting for the game to work. This is done by setting up a DMZ or using Port
Triggering so that the Cable Modem/Router’s firewall won’t block the other players
from your system during your gaming. The main difference between the methods is the
amount of access someone has to your system.
A DMZ allows access on all ports of the computer. Because of this, DMZ's are less
secure and should be used with caution with your computer. However DMZ’s work well
with gaming stations since security is not as much of an issue for gaming stations as it is
for computers.
Port triggering works by sensing when data is sent out on a predetermined outgoing port
and then automatically opening up the corresponding incoming port(s). It will
automatically forward the traffic on the incoming port to the computer that accessed the
outgoing port. If your game uses one port to send outgoing data and a different port (or
ports) for incoming data, you may want to use port triggering. You do not need to know
the IP address of your gaming station to set up port triggering. You will need to know
which ports your game requires you to open. This information is usually available with
your gaming software or you should be able to find it by searching for it on the web.
• If you want to set up a DMZ for your gaming system, go to
• If you want to set up Port Triggering for your gaming system, go to
Triggering.
DMZ Host.
Port
34
Page 35

DMZ Host
The DMZ (De-militarized Zone) Host page allows you to configure a network device (e.g.
a PC or gaming system) to be visible directly to the Internet. This may be used if a game
doesn’t work with port triggers or if you are using a gaming system, where security is less
of a concern.
To set up a DMZ for your gaming system, you should first assign your gaming system a
static IP address. Normally the Cable Modem/Router handles assigning IP addresses to
the different devices on your network using DHCP. However DHCP does not guarantee
that your device will always get assigned the same IP address. The DMZ needs to know
the IP address of your gaming system to work, if the IP address changes the DMZ will not
work. Because your IP address could change over time you need to assign a static IP on
your gaming system. To setup a static IP address on your gaming system, please refer to
your gaming system’s documentation. If you no longer have the documentation that
came with your gaming system it usually can be found online.
When assigning a static IP address to your gaming system you should select an address
that is outside the IP addresses assigned by the Cable Modem/Router’s DHCP server.
By default the DHCP Server assigns addresses from 192.168.0.10 to 192.168.0.255.
We recommend using 192.168.0.5 as the static IP address for your gaming system.
To setup a DMZ for your gaming system:
1 Follow the instructions for your gaming system to assign a static IP address. We
recommend using 192.168.0.5.
2 Next access the Cable Modem/Routers configuration menu by launching a Web
browser on a computer that is directly connected to one of the router’s LAN ports.
3 In the browser address bar, type http://192.168.0.1 and press the Enter key.
4 In the Login screen, enter:
default username: admin
default password: admin
Both the username and password are case sensitive. The default username and
password are printed on the bottom label of your unit.
5 Click the Login button to access the Cable Modem/Router. The Status page
appears.
6 Click Router menu tab.
35
Page 36
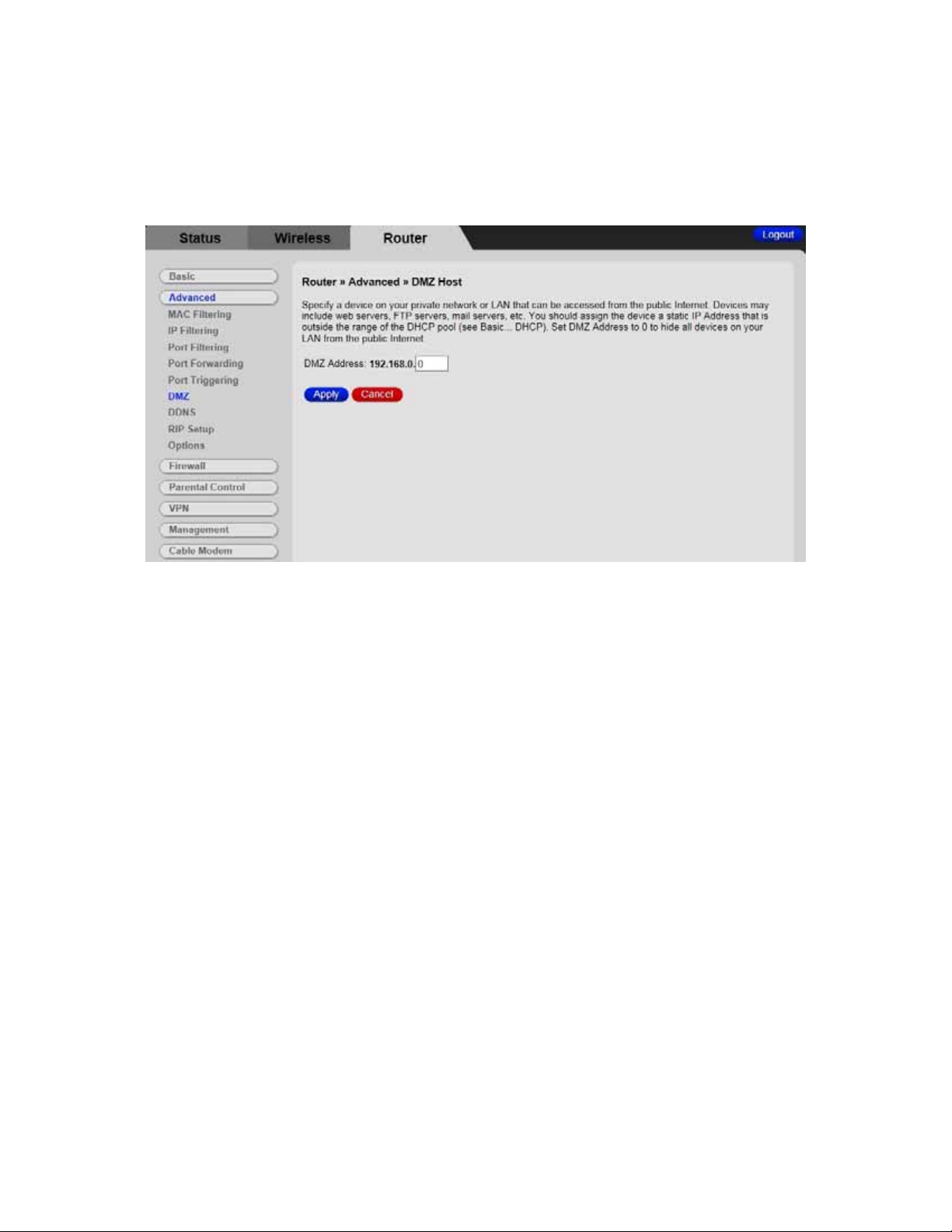
7
Then click the Advanced / DMZ. The DMZ Host page appears:
8 Enter the last byte of the LAN IP address of the static IP address you assigned to
your gaming system. For example if you assigned 192.168.0.5 enter 5.
9 Click Apply.
Your gaming system should now work with all your online games.
36
Page 37

Port Triggers
Port Triggering works by sensing when your game sends data out through a specific
port. The outgoing data signals the router to allow the incoming game traffic to be passed
through the firewall on the correct port. Since the ports are only open when you are
gaming, port triggering is a very secure method for online gaming.
To set up port triggering you need to know what ports your game is using and whether
they use TCP, UDP or both on those ports. Typically this should be included with your
gaming software. If it is not included, try entering the name of your gaming software
followed by “ports used”.
Some games use the same ports for both incoming and outgoing traffic, while other
games use different ports for incoming and outgoing traffic.
®
Below is an example of setting up the popular game, World of Warcraft
triggering. Looking online, we find that World of Warcraft uses the following ports:
1119-1120, 3724, 4000, 6112-6114, and 6881-6999. We can also find out that these
ports are all TCP. In this case the same ports are used for both incoming and outgoing
traffic, so we would use the same ports as both the triggering port and the target port as
shown below.
To setup port triggering for World of Warcraft:
1 Launch a Web browser.
2 In the browser address bar, type http://192.168.0.1 and press the Enter key.
for port
3 In the Login screen, enter:
default username: admin
default password: admin
Both the username and password are case sensitive. The default username and
password are printed on the bottom label of your unit.
4 Click the Login button to access the Cable Modem/Router. The Status page
appears.
5 Click the Router menu tab.
6 Then click Advanced / Port Triggering. On the Port Triggering page, click on
Create Rule. The following page appears.
37
Page 38

7 We will need to setup 5 triggers for World of Warcraft. The first rule would cover ports
1119-1120. Enter 1119 in the Trigger Start Port field and 1120 in the Trigger End
Port field. Since these ports are used to send data both directions enter 1119 in the
Target Start Port and 1120 in the Target End Port.
8 Select TCP in the Protocol drop down menu since these ports use TCP.
9 Enter a name for this rule, for example WOW1. Select ON to enable, then click
Apply. Your new rule will appear in the table.
10 Repeat steps 7-9 for the next rule. In this case only one port is used, 3724. Enter
3724 in the Trigger Start/End Port and Target Start/End Port fields.
11 Repeat steps 7-9 for the remaining ports that need to be opened. When you are
complete the table should look like this:
38
Page 39

If your online game does not work and you are sure that you entered the correct ports
on the port triggering page, check to see if you have a firewall running on your
computer that is preventing you from playing your online game. This firewall may be
either the built-in Windows firewall or may be part of a third party security package
you are using on your computer. You will need to allow access through these
firewalls to be able to play your online game.
39
Page 40

6
Advanced Settings
Advanced Settings is primarily for technically advanced users. For most people, the
options that are set by default when the Cable Modem/Router is installed are sufficient.
However, those who want or need to change the default settings can do so using the
advanced setup pages in the Zoom Configuration Manager.
This chapter includes:
• Suggestions for settings that you might want to change
• Instructions for launching the Zoom Configuration Manager program
• An overview of the available configuration menus and settings and a guide on
what chapter to go to for more information on each settings.
Changing Default Settings
Here are some reasons why you might want to use the Configuration program to change
the router's default settings.
•
Your Cable provider instructs you to enable, disable, or change the default settings
for your router
•
You want to set up a wireless guest network to give users access to the internet but
not your internal network.
•
You want to change the default firewall settings to block particular IP addresses and
intrusive hosts.
•
You want to access your corporate network and need to use the built-in VPN
function.
•
You wish to control the hours that a user on your network can access the Internet.
40
Page 41

Accessing the Zoom Configuration Manager
From your Web browser, you will log in to the interface to define system parameters,
change password settings, view status windows to monitor network conditions, and
control the Cable Modem/Router and its ports.
To access the Zoom Configuration Manager, use the following procedure:
1 Launch a Web browser.
Note: Your computer does not have to be online to configure your Cable
Modem/Router.
2 In the browser address bar, type http://192.168.0.1 and press the Enter key.
For example:
The Login screen appears (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Login Screen
41
Page 42

3
In the Login screen, enter:
default username: admin
default password: admin
Both the username and password are case sensitive. The default username and
password are printed on the bottom label of your unit. After you log in to the Zoom
Configuration Manager interface, you can change the default password on the
Management – Admin Account page.
4 Click the Login button to access the Cable Modem/Router. The Status page
appears, showing information about your Cable Modem/Router.
Understanding the Configuration Manager Interface Screens
The top of the management interface contains three tabs you use to select menus for
configuring the Cable Modem/Router. When you click a menu item, information and any
configuration settings associated with the menu appear in the main area of the interface
(see
Figure 2). If the displayed information exceeds what can be shown in the main area,
scroll bars appear to the right of the main area so you can scroll up and down through the
information.
Figure 2. Main Areas on the Configuration Manager Interface
In the upper right hand corner of the page is the logout option. Click it to log out from the
Configuration Manager interface.
42
Page 43

Configuration Manager Interface Menus
You can skip to specific sections of this User Manual based on your intended use of the
Cable Modem/Router. Each of the menu options in your Configuration Manager is
covered as a separate chapter in the remaining portions of the User Manual.
• For a description of the Status Tab see
• To configure and use the wireless features supported by the Cable
Modem/Router see
Chapter 8: Wireless Settings.
The Router tab has several different menus from which you can select. Each menu
heading is covered in a separate chapter. Please see Table 1 for a description of each
menu heading.
Table 1. Configuration Manager Interface Menus
Menus
Chapter
Menu
Options
Go to this section if
you want to…
Chapter 7: Status Page.
See
Page
9
10
11
12
Basic
Advanced
Firewall
Parental
Control
Make some
modifications for more
advanced uses
Make use of advanced
router features
supported by the Cable
Modem/Router
Configure the firewall
application to protect the
private LAN from attacks
from the WAN interface
Configure access
policies or rules to
specific network devices
based on the time of day
and Internet contents
70
77
96
103
43
Page 44

13
14 Manageme nt
15
VPN
Cable
Modem
Enable the VPN protocol
and configure IPSec
tunnels, L2TP and PPTP
server options
Configure for Admin
Account, Remote
Management,
Backup/Restore Settings
and run Diagnostics.
View Event Log.
View Device Information,
and Connection. To
Restart and Restore to
Factory Defaults
112
123
131
44
Page 45

7
Status Page
The Status Menu lets you
• View the status and connection information of the Cable Modem/Router.
• Click on the Modem box to bring you to the Cable Modem Connection page.
• Click on the Wireless box to bring you to the Wireless page.
• Click on the My Network box to bring you to the My Network page.
Status
The Status page provides a basic overview of your Cable Modem/Router. It displays the
connection status, how many wired and wireless devices are connected and information
about your wireless networks.
45
Page 46

8
Wireless Settings
The Wireless Menu lets you:
• Configure the Cable Modem/Router to serve as a wireless access point (AP)
• Configure essential and advanced settings of a wireless network
• Configure a guest network for temporary visitors
• Configure WMM QoS
Note: Your Cable Modem/Router has been preconfigured to support wireless
connections without any further configuration. Please see
Devices to your Cable Modem/Router for details. Most users will not need to read this
chapter.
Radio
The Radio page allows you to modify wireless settings.
To access the Radio page:
Chapter 3: Connecting Other
1 Click the Wireless menu tab.
2 The Radio submenu page will appear.
Figure 3 shows an example of the menu and Table 2 describes the items you can
select.
46
Page 47

Figure 3 Example Wireless Radio Page
Table 2. Primary Radio Menu Options
Option Description
Select which frequency band you want to set up. Any setup
Select 2.4 GHz or
5 GHz
Wireless
Country
Output Power
802.11 Band
changes you make will apply to this band only. For example, if
you select 5GHz any changes you make on this page will apply
to the 5 GHz band only.
Select Enable to enable the wireless function.
Your device is configured for operation in the U.S. only.
Set the strength of the wireless signal that the Cable
Modem/Router transmits. Most users should use the default
setting. In some scenarios reducing your output power may help
reduce wireless interference. If the Cable Modem/Router is
interfering with neighboring Access Points, reducing the power
level may reduce this interference, causing the neighboring APs
to have fewer retransmissions of their data. This results in less
wireless traffic and less congestion. Lowering your power level
however will reduce the wireless range of your router.
This field displays the current band selected.
47
Page 48

802.11n-mode
Bandwidth
Sideband for
Control Channel
(40 MHz only)
Control Channel
Regulatory Mode
TPC Mitigation
(db)
OBSS
Coexistence
STBC Tx
Restore Wireless
Defaults
Beamforming
Transmission
(BFR)
Beamforming
Reception (BFE)
In Auto mode, your Cable Modem/Router will automatically
adjust to avoid interference with neighboring devices. Most
users should use the default setting of Auto.
Specify radio frequency bandwidth, either 20 MHz single, or
40MHz (dual channel), that the Cable Modem/Router will use
when 802.11n mode is configured as Automatic and the Control
Channel is configured as Automatic. Normally 20 MHz is the
best choice.
You may select Sideband and the secondary extension
channels if your Cable Modem/Router is operating at 40 MHz
bandwidth and the 802.11n-mode is configured as Auto. Most
users will not need to change this setting.
Select the channel for AP operation next to the drop-down list
box. The current channel number is displayed. The list of
detailed control channel and extension channels are shown in
the Table below. Most users will not need to change this setting.
By default is Off. Most users will not need to change this setting.
By default is Off. Most users will not need to change this setting.
By default is set to 1 (Enabled). This allows the wireless
bandwidth to fall back from 40Mhz to 20Mhz when the
modem/router detects interference in the area. You may select 0
(Disabled) to disable this feature. Disabling OBSS Coexistence
can result in poor wireless performance if there is interference in
your area. Most users will not need to change these settings.
By default is set to Auto. Most users will not need to change this
setting.
Click on the Restore Wireless Defaults button to restore the
Wireless settings.
By default is set to Enable. Most users will not need to change
this setting.
By default is set to Enable. Most users will not need to change
this setting.
48
Page 49

Table 3. Country Extension Channel List
Control Channel Sideband for
Control
Channel
US Channel 1-7 Lower Channel
US Channel 5-11 Upper Channel
Example 1: If your control channel is set to 1, the extension channel will be transmitted
on channel 5. The total bandwidth of the signals on channel 1 and 5 equals 40 MHz.
Example 2: If your control channel is set to 11, the extension channel will be transmitted
on channel 7. The total bandwidth of the signals on channel 11 and 7 equals 40 MHz.
Extension
Channel
Number + 4
Number - 4
Primary Network
The Primary Network page allows you to configure the primary wireless network and its
security settings. Strong security is the best way to prevent unauthorized wireless
network access. To access the Primary Network page:
1 Click the Wireless menu tab.
2 Then click the Primary Network submenu.
Figure 4 shows an example of the menu and Table 4 describes the items you can select
49
Page 50

Figure 4. Example Wireless Primary Network page
50
Page 51

Table 4. Primary Network Menu Option
Option Description
Primary Network
Network Name (SSID)
Closed Network
Mode Required
AP Isolate
WPA
WPA-PSK
WPA2
Select Enable to enable the primary wireless network.
Set the Network Name (also known as SSID) of the
wireless network. This is a 1-32 Alphanumeric character
string.
Select Enable to suppress broadcast of the SSID.
Default set to None. Choice to select None, HT and VHT.
Most users will leave this None.
Prevents wireless clients on your network from
communicating with other wireless clients.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) offers stronger encryption
than WEP. Enable WPA alone if you have a RADIUS
server (unlikely for most home users) – otherwise use
WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK.
Offers stronger encryption than WEP. When enabled, you
must also enter a Pre-Shared Key that will by used by all
wireless clients to access the wireless network.
Offers state-of-the-art security. Enable WPA2 alone only if
you have a RADIUS server(unlikely for most home users)
otherwise use WPA2-PSK.
WPA2-PSK
WPA/WPA2 Encryption
WPA Pre-Shared Key
RADIUS Server
Offers state-of-the-art security. When enabled, you must
also enter a Pre-Shared Key below that will by used by all
wireless clients to access the wireless network.
Select Enable to use WPA/WPA2 encryption. Most users
should use the default setting of TKIP+AES.
Enter a 8-63 Alphanumeric character string if you have
enabled WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK.
If you’re using a RADIUS server, enter it’s IP address
here. The RADIUS server may be on either public network
(WAN) or private network (LAN).
51
Page 52

RADIUS Port
(Relevant only when the
RADIUS server is enabled)
RADIUS Key
(Relevant only when the
RADIUS server is enabled)
Enter the UDP port number of the RADIUS server. The
default port is 1812.
Enter the RADIUS Key.
Group Key Rotation
Interval
(Relevant only when the
RADIUS server is enabled)
WPA/WPA2 Re-auth
Interval
WEP Encryption
Shared Key
Authentication
802.1x Authentication
(only available when WEP
is enabled)
Network Key 1-4
When enabled, the Cable Modem/Router generates the
best possible random group key and updates all
key-management capable clients periodically. Set to zero
to disable periodic rekeying.
Interval (in seconds) at which the Cable Modem/Router (if
using WPA-PSK key management) or RADIUS server (if
using WPA key management) sends a new group key out
to all clients. The re-keying process is the WPA equivalent
of automatically changing the WEP key for an AP and all
stations in a WLAN on a periodic basis.
WEP Encryption can be set to WEP 128-bit, 64-bit, or
Disable. Both the wireless clients and the Cable
Modem/Router must use the same WEP key.
Select Enable to enable. Shared Key authentication is only
available when WEP is enabled.
Select Enable to enable 802.1x authentication. Enable
802.1x Authentication only if you have a RADIUS server.
Most users will leave this disabled.
You can pre-define up to 4 keys for 64-bit or 128-bit WEP.
64-bit keys require 10 hexadecimal digits and 128-bit key
require 26 hexadecimal digits.
Current Network Key
PassPhase
Generate WEP Keys
Select one of the four pre-defined keys as the current
network key.
Enter a word or group of printable characters and click
Generate WEP keys to generate WEP encryption key.
These characters are case sensitive.
Click to generate 4 WEP keys automatically.
52
Page 53

Guest Network
The Guest Network page allows you to configure a guest network. A guest network is a
small section of an organization's computer network designed for use by temporary
visitors. This guest network often provides full Internet connectivity, but it also strictly
limits access to any internal (intranet) Web sites or files.
Traditionally, you needed to use different Wireless Access Points to configure different
wireless networks. Your Cable Modem/Router supports Multiple SSIDs, which allows
you to use the same access point to provide several wireless networks simultaneously.
You can then assign various privileges to different SSIDs and associated networks.
y Up to eight wireless networks are allowed on one Cable Modem/Router
simultaneously, one for Admin access and seven for Guest Networks.
y If you are using WEP, you must use different WEP keys for different wireless
networks.
y You should use different Passwords for different wireless networks if you are using
WPA/WPA2.
To access the Guest Network page:
1 Click Wireless in the menu tab.
2 Then click the Guest Network submenu.
Figure 5 shows an example of the menu and Table 5.GuestNetworkMenuOption
describes the items you can select.
53
Page 54

Figure 5. Example of Guest Network Page
54
Page 55

Table 5. Guest Network Menu Option
Option Description
Guest Network Selection
Guest Network
Guest Network Name
(SSID)
Closed Network
Mode Required
AP Isolate
WPA
WPA-PSK
WPA2
Select which Guest Network to setup.
Select Enable to enable guest network.
Enter a name for the guest network.
Select Enable to suppress broadcast of the SSID.
Default set to None. Choice to select None, HT and VHT.
Most users will leave this None.
Prevents wireless clients on your network from
communicating with other wireless clients.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) offers stronger encryption
than WEP. Enable WPA alone if you have a RADIUS
server (unlikely for most home users) – otherwise
WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK
Offers stronger encryption than WEP. When enabled, you
must also enter a Pre-Shared Key that will by used by all
wireless clients to access the wireless network.
Offers state-of-the-art security. Enable WPA2 alone only if
you have a RADIUS server (unlikely for most home users);
otherwise use WPA2-PSK.
WPA2-PSK
WPA/WPA2 Encryption
WPA Pre-Shared Key
RADIUS Server
Offers state-of-the-art security. When enabled, you must
also enter a Pre-Shared Key that will by used by all
wireless clients to access the wireless network.
Select Enable to use WPA/WPA2 encryption. Most users
should leave the default settings of TKIP+AES.
Enter a 8-63 Alphanumeric character string if you have
enabled WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK.
If you’re using a RADIUS server, enter it’s IP address
here. The RADIUS server may be on either public network
(WAN) or private network (LAN).
55
Page 56

RADIUS Port
(Relevant only when the
RADIUS server is enabled)
RADIUS Key
(Relevant only when the
RADIUS server is enabled)
Enter the UDP port number of the RADIUS server. The
default port is 1812.
Enter the RADIUS Key.
Group Key Rotation
Interval
(Relevant only when the
RADIUS server is enabled)
WPA/WPA2 Re-auth
Interval
WEP Encryption
Shared Key
Authentication
802.1x Authentication
(only available when WEP
is enabled)
Network Key 1-4
When enabled, the Cable Modem/Router generates the
best possible random group key and updates all
key-management capable clients periodically. Set to zero
to disable periodic rekeying.
Interval (in seconds) at which the Cable Modem/Router (if
using WPA-PSK key management) or RADIUS server (if
using WPA key management) sends a new group key out
to all clients. The re-keying process is the WPA equivalent
of automatically changing the WEP key for an AP and all
stations in a WLAN on a periodic basis.
WEP Encryption can be set to WEP 128-bit, 64-bit, or
Disable. Both the wireless clients and the Cable
Modem/Router must use the same WEP key.
Select Enable to enable. Shared Key authentication is only
available when WEP is enabled.
Select Enable to enable 802.1x authentication. Enable
802.1x Authentication only if you have a RADIUS server.
Most users will leave this as disabled.
You can pre-define up to 4 keys for 64-bit or 128-bit WEP.
64-bit keys require 10 hexadecimal digits and 128-bit key
require 26 hexadecimal digits.
Current Network Key
PassPhase
Generate WEP Keys
Guest LAN Settings
Select one of the four pre-defined keys as the current
network key.
Enter a word or group of printable characters and click
Generate WEP keys to generate WEP encryption key.
These characters are case sensitive.
Click to generate 4 WEP keys automatically.
Select LAN for existing LAN - same as Primary Network -
56
Page 57

IP Address
or GUEST to create a Virtual LAN.
Enter the IP address to be the default Cable
Modem/Router address for clients connected this guest
network.
Subnet Mask
Lease Pool Start
Lease Pool End
Lease Time
UPnP Enable
Firewall Enable
DHCPv6 Server
Restore Guest Network
Defaults
Enter the subnet mask for this guest network.
Enter the starting IP address of this DHCP address pool.
Enter the ending IP address of this DHCP address pool.
Enter the lease time for DHCP clients. DHCP clients will
resend DHCP request before expiration. Maximum value
is 86400 seconds.
Select Enabled to enable UPnP on your guest network
Enables or Disables the Firewall on your guest network.
Selecting Enabled allows the DHCP server to assign IPv6
addresses.
Click the Restore Guest Network Defaults button to
restore the Guest Network factory settings.
57
Page 58

Advanced
The Advanced p age allows you to configure advanced wireless settings. Most users will
have no need to change these settings.
To access the Advanced page:
1 Click the Wireless menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced submenu.
Figure 6 shows an example of the menu and Table 6 describes the items you can
select.
Figure 6. Example of Advanced Page
58
Page 59

Table 6. Advanced Menu Option
Option Description
54gTM Mode
XPressTM Technology
802.11n Protection
Short Guard Interval
Basic Rate Set
Multicast Rate
Auto by default.
When Xpress is turned on, aggregate throughput can
improve significantly.
The 802.11g standards provide a protection method so
802.11g and 802.11b devices can co-exist in the same
network without “speaking” at the same time. Do not disable
802.11n protection if there is a possibility that 802.11b or
802.11g devices will use your wireless network. In
mode, the wireless devices use RTS/CTS to improve
802.11n performance in mixed 802.11g/802.11b networks.
Turn protection off to maximize 802.11n throughput under
most conditions.
Provides compatibility with certain devices that do not meet
802.11 specifications.
Select the wireless transmission rate to a particular speed
or leave it as default (Auto) to allow the AP adjusts speed
automatically.
Specify the rate at which multicast packets are transmitted
and received on your wireless network. Multicast packets
are used to send a single message to a set of recipients in a
defined group. Teleconferencing, videoconferencing and
group email are some examples of multicast applications.
Specifying a high multicast rate may improve performance
of multicast features. The rates are in Mbps. You can select
Aut
omatic, 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48 and 54.
Auto
NPHY Rate
Legacy Rate
Set the Physical Layer (NPHY) rate. These rates are only
applicable when the
Automatic.
Auto by default.
59
802.11n mode is configured as
Page 60

Beacon Interval
DTIM Interval
Fragmentation Threshold
RTS Threshold
A beacon is a packet broadcast by the router to synchronize
the wireless network. The default interval is 100 ms.
Interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM). A
DTIM field is a countdown field informing clients of the next
window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages.
When the router has buffered broadcast or multicast for
associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM
Interval value. Its clients hear the beacons and awaken to
receive the broadcast and multicast message. The default
value is 1.
This value specifies the maximum size for a packet before
data is fragmented into multiple packets. If you experience
a high packet error rate, you may slightly increase the
fragmentation threshold. Setting the fragmentation
threshold too low may result in poor network performance.
Only minor reduction of the default value is recommended.
In most cases, it should remain at its default value of 2346.
Using this setting can regulate your wireless network if you
experience any inconsistent data flow. Make only minor
adjustments to the default value of 2347.
WPS
The WPS page allows you to configure settings for WPS. Most users will have no need
to change these settings.
To access the WPS page:
1 Click the Wireless menu tab.
2 Then click the WPS submenu.
Figure 7 ExampleWPSpageshows an example of the menu and Table 7 describes the
items you can select.
60
Page 61

Figure 7 Example WPS page
Table 7 WPS Menu Options
Option
Description
WPS
AP Self-PIN number:
Configure by External
Registrar
Push-Button
Configuration (PBC)
Personal Identification
Number (PIN)
Disable or enable WPS. WPS does not work with WEP.
Click the Generate AP PIN button to generate new PIN
number.
Default is enabled.
Select this option and press the Add Client button is
equivalent to pushing the WPS button on your Cable
Modem/Router. After clicking the Add Client button, within
2 minutes, activate WPS on your client device(s).
Select this option and press the Add Client button to allow
Client PIN number field appear. For devices that require a
PIN, enter the PIN in the Client PIN’s number field, and
then click Add Client button.
61
Page 62

Bridging
The Bridging page allows you to configure WDS (Wireless Distribution System) feature.
Only those bridges listed in the Remote Bridges table will be granted access. APs must
operate in the same channel to be bridged together.
To access the Bridging page:
1 Click the Wireless menu tab.
2 Then click the Bridging submenu.
Figure 8. Example of Bridging Page shows an example of the menu and Table 8 describes
the items you can select.
Figure 8. Example of Bridging Page
62
Page 63

Table 8. Bridging Menu Option
Option Description
Wireless
Bridging
Remote Bridges
Select to enable or disable wireless bridging.
Table of remote bridge MAC addresses authorized to establish a
wireless bridge. Up to 4 remote bridges may be connected.
Typically, you will also have to enter your AP’s MAC address on the
remote bridge. The Cable Modem/Router’s wireless MAC address
can be found on the Wireless Interfaces page.
Access Control
This page allows you to control which wireless clients can access your wireless network.
It also provides information about wireless clients connected to your access point.
To access the Access Control page:
1 Click the Wireless menu tab.
2 Then click the Access Control submenu.
Figure 9. Example of Access Control P age shows an example of the menu and Table 9
describes the items you can select.
63
Page 64

Figure 9. Example of Access Control Page
64
Page 65

Table 9. Access Control Menu Option
Option Description
Wireless
Interface
MAC Restrict
Mode
MAC
Addresses
Connected
Clients
Select the wireless interface to configure the access control list.
Select whether wireless clients with the specified MAC address are
allowed or denied wireless access. To allow all clients, select
Disabled.
Shows the list of wireless client MAC addresses to allow or deny
based on the Restrict Mode setting. Valid MAC address formats are
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
Shows the list of connected wireless clients. When a client
connects (associates) to the network, it is added to the list; when a
client leaves (disassociates) from the network, it is removed from
the list. For each client, the age (in seconds), estimated average
receive signal strength (in dBm), IP address, and host name are
presented. The age is the amount of time elapsed since data was
transmitted to or received from the client.
65
Page 66

WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia)
The WMM page allows you to configure WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) feature. WMM is a
subset of the 802.11e wireless LAN (WLAN) specification that enhances quality of
service (QoS) on a network by prioritizing data packets according to their categories.
WMM enhances QoS at the wireless driver level. It provides a mechanism to prioritize
wireless data traffic to and from the associated (WMM capable) stations.
If you enable the WMM feature, you may need to decide whether or not to broadcast
Cable Modem/Router’s network name. Broadcasting allows you to easily recognize
your wireless network in the list of available networks. Once you have configured your
wireless clients, it is recommended that you disable the broadcasting feature.
To access the WMM page:
1 Click the Wireless menu tab.
2 Then click the WMM submenu.
Figure 10 shows an example of the menu and Table 10 describes the items you can
select.
Figure 10. Example of WMM Page
66
Page 67

Table 10. WMM Menu Option
Option Description
WMM Support
No-Acknowledgement
Power Save Support
Select On to include the WME Information Element in the
beacon frame.
Select On to not transmit acknowledgments for data.
Select On to allow the AP (Cable Modem/Router) queuing
packets for stations/clients in power-save mode. Queued
packets are transmitted when the station/client notifies AP that
it has left power-save mode.
67
Page 68

Neighbor APs
This page allows you to view Nearby Wireless Access Points.
To access the Neighbor APs page:
1 Click the Wireless menu tab.
2 Then click the Neighbor APs submenu.
Figure 11 shows an example of the menu and Table 11 describes the items you can
select.
Figure 11 Neighbor APs page
68
Page 69

Table 11. Neighbor APs Options
Option Description
Network Name
Security Mode
Mode
PHY Mode
RSSI
Channel
BSSID
Shows the list of Wireless Access Points.
Shows the Wireless Security mode associated to the AP.
Shows the status of the AP.
Shows the Physical layer mode as 802.11ac, 802.11n, 802.11g, or
802.11b.
Shows the Wireless signal strength.
Shows the channel being broadcast.
Shows the APs MAC being broadcast.
69
Page 70

9
Basic Menu Options
The Basic Menu lets you:
• Configure LAN Settings
• Configure the DHCP server for the LAN and UPnP
• Configure WAN Settings
• View the list of wireless or wired connected devices
Basic LAN Settings
The LAN Settings page allows you to configure the LAN Settings and UPnP.
To access the LAN Settings page,
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Basic submenu.
Figure 12 shows an example of the menu and Table 12 describes the items you can
select.
70
Page 71

Figure 12. Example of Setup Page
Table 12. LAN Settings Menu Option
Option Description
LAN IP
Address
UPnP
Set the base LAN IP for your private network. By default this is
192.168.0.1 There is normally no need to change this.
Select Enable to enable the UPnP agent in the Cable
Modem/Router. If you are running an application that requires UPnP,
check this box.
71
Page 72

DHCP
The DHCP page allows you to configure your Cable Modem/Router’s DHCP server.
To access the DHCP page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the DHCP submenu.
Figure 13 shows an example of the menu and Table 13 describes the items you can
select.
Figure 13. Example of DHCP Page
In the unusual event that you have a separate DHCP server on your LAN, you can
disable the Cable Modem/Router’s DHCP server by selecting the No radio button. If you
do this, make sure the IP address assigned to the Cable Modem/Router is on the same
subnet as that of the external DHCP server, or you won’t be able to access the Cable
Modem/Router from the LAN. The base LAN IP address of the Cable Modem/Router can
be set from the Basic Setup page.
Note that the Cable Modem/Router will only operate on a class C subnet, with subnet
mask 255.255.255.0
You may also want to disable the DHCP server if you have assigned static IP addresses
to all devices on your network.
72
Page 73

Table 13. DHCP Menu Options
Option Description
DHCP Server
Starting Local
Address
Number of
CPEs
Lease Time
Reserved IP
Addresses
Select Yes to use the internal DHCP server of the Cable
Modem/Router, or select No to disable it.
Configure the starting IP address for IP leases available to devices
on the LAN.
Configure the number of PCs supported on the LAN.
Configure the time a lease will last before it must be renewed.
Default is 86400 seconds, or 1 day.
Configure the MAC Address and IP Address to allow fixed IP
address.
WAN Settings
The WAN Settings page allows you to configure your Cable Modem/Router’s in Bridging
(NAT off) or Routing (NAT on) operation mode.
To access the WAN Settings page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the WAN Settings submenu.
Figure 14 shows an example of the menu and Figure 14 Wan Settings page
Table 14 describes the items you can select.
73
Page 74

Figure 14 Wan Settings page
Table 14. WAN Settings Menu Options
Option Description
Operation
Mode
Release WAN
Lease
Renew WAN
Lease
Click the Bridge button if you do not wish to use the 5363 as a
router. Most users should not change this setting.
Click to release the WAN IP address.
Click to renew the WAN IP address.
74
Page 75

My Network
The My Network page allows you to view all users wired or wireless connected to the
device.
To access the My Network page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the My Network submenu.
Figure 15 shows an example of the menu and Table 6 describes the items you can
select.
Figure 15. My Network Page
75
Page 76

Table 15. My Network Menu Options
Option Description
Mac Address
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Lease Time
Speed (kbps)
Connected to
View status of the connected client’s MAC address.
View status of connected client’s IP address.
View status of the connected client’s Subnet Mask.
View status of the connected client’s Lease Time.
View status of the connected client’s Speed.
View whether the connected client is Ethernet or Wireless.
76
Page 77

10
Advanced Menu Options
The Advanced Menu lets you:
• Enable advanced features of the Cable Modem/Router
• Configure the LAN IP address, MAC address, and port number filtering
• Configure WAN to LAN port forwarding and triggers
• Configure DMZ hosting
• Configure DDNS
• Configure RIP parameters
• Configure Options
MAC Filtering
The MAC Filtering page allows you to configure MAC address filters in order to block
Internet traffic to specific network devices on your LAN.
To access the MAC Filtering page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/MAC Filtering submenu.
Figure 16 shows an example of the menu and Table 16 describes the items you can
select.
77
Page 78

Figure 16. Example of MAC Filtering Page
Table 16. MAC Filtering Menu Option
Option Description
PCs and other devices can be added to the MAC filter table by
entering their MAC addresses into the Add MAC Address box, and
clicking the Add MAC Address button. Internet traffic to and from
each listed Address will be blocked.
MAC Address
The Mac Addresses of the computers attached to your network can
be found in the My Network table. To access the DHCP Clients
table click on Router on the menu tab then Basic/My Network
submenu.
78
Page 79

IP Filtering
The IP Filtering page allows you to configure IP address filters in order to block specific
network devices on your LAN from accessing the Internet. By entering starting and
ending IP address ranges, you can configure which local PCs are denied access to the
WAN.
We recommend assigning a static IP address to your computer when using IP Filtering.
By default, the Cable Modem/Router uses DHCP to assign IP addresses. DHCP does
not guarantee that your computer will be assigned the same IP address. When assigning
a static IP address to your computer you should select an address that is outside the IP
addresses assigned by the Cable Modem/Router’s DHCP server. By default the DHCP
Server assigns addresses from 192.168.0.10 to 192.168.0.255. We recommend using
192.168.0.6 as the static IP address for your computer.
To access the IP Filtering page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/IP Filtering submenu.
Figure 17 shows an example of the menu and Table 17 describes the items you can
select.
79
Page 80

Figure 17. Example of IP Filtering Page
80
Page 81

To activate the IP address filter:
1 Enter the last byte (the numbers after the last period) of the IP address in Start
Address and End Address.
2 Check the Enable box to the right of the entry to store settings.
3 Click the Apply button to activate the filter rules.
Table 17. IP Filtering Menu Option
Option Description
Start/End
Address
Enable
Enter the last byte of the IP address. The upper bytes of the IP
address are set automatically from the Cable Modem/Router IP
address.
To activate the IP address filter, you must also check the Enable box
and click Apply. You can disable this filter while retaining the
addresses you entered for later use.
Port Filtering
The Port Filtering page allows you to configure port filters in order to block Internet traffic
to specific ports on all devices on your LAN.
Similarly, you can prevent PCs from sending outgoing TCP/UDP traffic to the Internet
from specific IP port numbers. This can be configured using the Port Filtering page.
To access the Port Filtering page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/Port Filtering submenu.
Figure 18 shows an example of the menu and
81
Page 82

Table 18 describes the items you can select.
Figure 18. Example of Port Filtering Page
For example, if you would like to block all PCs on the private LAN from accessing HTTP
sites (or “web surfing”):
1 Set the Start Port to 80, the End Port to 80.
2 Set the protocol to TCP.
3 Check the Enable box to the right of the entry to store settings.
4 Click Apply button to activate the filter rules.
82
Page 83

Table 18. Port Filtering Menu Option
Option Description
Start/End Port
Protocol
Enters the start and end port of the port filter range
Filter either both TCP and UDP traffic or just UDP or just TCP.
Port Forwarding
The Port Forwarding page allows you to run a publicly accessible server from your LAN
by specifying the mapping of TCP/UDP ports to a local PC. It allows incoming requests to
specific port numbers to reach a web server, FTP server, mail server, etc.
To access the Port Forwarding page,
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/Forwarding submenu.
3 To add a new rule, click on the Create IPv4 Rule button.
Figure 19 shows an example of the menu and
83
Page 84

Table 19 describes the items you can select.
Figure 19. Example of the Port Forwarding Page
To activate the port forwarding:
1 Enter the port range of the Internet traffic that you want to forward, and the IP
address of the server to which you want to forward that traffic. If you enter no
External device on the public internet; doing so will grant access to those devices
only.
2 Select the protocol(s) to be forwarded.
3 Enter the Description name.
4 Select ON for the Enable box to enable Port Forwarding rule.
5 Click the Apply button to activate the forwarding rules.
84
Page 85

Table 19. Forwarding Menu Option
Option Description
Local IP
Address
Start/End Port
External IP
External
Start/End Port
Protocol
Description
Enable
Note: You may need to assign static IP addresses to devices on your LAN to insure that
the port forwarding you have set up will always apply to them.
Enter the IP address to which forwarded traffic should be sent.
Enter the range of port numbers (start and end port) to forward. If
only a single port is desired, enter the same port number in the Start
and End locations.
You may optionally enter Addresses of External devices on the
public internet; doing so will grant access to those devices only. If
you enter no External device Addresses, any device on the public
Internet may access your devices.
Enter the range of port numbers (start and end port). If only a single
port is desired, enter the same port number in the Start and End
locations.
Select the protocol(s) to be forwarded.
Enter the Description name here.
Select ON or OFF to enable Port Forwarding rule.
Port Triggers
The Port Triggers page allows you to configure dynamic triggers to specific devices on
the LAN. This allows for special applications that require specific port numbers with
bi-directional traffic to function properly. Applications such as video conferencing, voice,
gaming, and some messaging program features may require these special settings.
Port Triggers are similar to Port Forwarding except that they are not static ports held
open all the time. With the port triggering function, the Cable Modem/Router detects
outgoing data on a specific IP port number and opens corresponding target ports for
incoming data. If no outgoing traffic is detected on the Trigger Range ports for 10
minutes, the Target Range ports will close.
85
Page 86

To access the Port Triggers page:
1 Click Router in the menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/Port Triggers submenu.
3 To add a new rule, click on the Create Rule button.
Figure 20 shows an example of the menu and Table 20 describes the items you can
select.
Figure 20. Example of port Triggers Page
To activate a port trigger
1 Enter the trigger and target ports range for the Internet traffic to forward to.
2 Select the forwarding protocol(s).
3 Enter a name for your port triggering rule.
4 Select ON for the Enable box to enable Port Triggering.
5 Click the Apply button to activate the forwarding rules.
86
Page 87

Table 20. Port Triggers Menu Option
Option Description
Trigger Range
(Start / End
Port)
Target Range
(Start / End
Port)
Protocol
Description
Enable
Enter the trigger range (starting and ending ports) of the application
for which you want to enable port triggering. The application will
send data from these ports.
Enter the target range (starting and ending ports) to open for the
same application. The application will receive data on these ports.
Select the protocol for this rule.
Enter the Description name here.
Select ON or OFF to enable Port Triggering rule.
DMZ Host
The DMZ (De-militarized Zone) Host page allows you to configure a network device (e.g.
a PC) to be exposed or visible directly to the Internet. This may be used if an application
doesn’t work with port triggers. If you have an application that won’t run properly behind
the NAT firewall, you can configure it for unrestricted two-way Internet access by defining
it as a virtual DMZ host. Adding a client to the DMZ may expose your local network to
various security risks because the client is not protected, so use this option as a last
resort.
To access the DMZ Host page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/DMZ Host submenu.
Figure 21 shows an example of the menu.
87
Page 88

Figure 21. Example of DMZ Host Page
To configure DMZ settings:
1 Enter the last byte of the LAN IP address of the PC or other device on your network
that you want to configure as a DMZ host.
2 Click Apply.
Note: If a specific PC is set as a DMZ Host, remember to set this back to “0” when
finished with the needed application, since this PC will be effectively exposed to the
public Internet.
Note: You may need to assign your DMZ host a static IP address on your LAN to
insure that it will always be at that address.
88
Page 89

DDNS
The DDNS page allows you to make use of a DDNS server. Dynamic DNS (DDNS)
allows a dynamic IP address to be aliased to a static, pre-defined host name so that the
host can be easily contacted by other hosts on the internet even if its IP address
changes. This means you can host a server on your LAN that can be accessed from
anywhere on the Internet.
Caution: Some service providers may consider connection of such a server to be a
breach of your service agreement.
The Cable Modem/Router supports a dynamic DNS client compatible with the Dynamic
DNS service (
use it.
To access the DDNS page:
1 Click Router in the menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/DDNS submenu.
Figure 22 shows an example of the menu and Table 21 describes the items you can
select.
http://www.dyndns.com/). You must sign up with this service if you want to
Figure 22. Example of DDNS Page
89
Page 90

To activate the DDNS client:
1 Go to the DynDNS website and create an account for the Dynamic DNS service.
2 You will create a username and password, and be asked to choose a host name
for your server, and the dynamic DNS domain to which your host will be assigned.
3 You will also be asked for your host’s current IP address. This is the WAN IP
address that has been assigned to your Cable Modem/Router during provisioning.
(See WAN IP Address on the Router tab, Basic/My Network page)
4 Enter your account information on the Advanced / DDNS web page, enable the
service by selecting www.DynDNS.org from the DDNS Service drop-down list, and
click Apply.
5 The DDNS client will notify the DDNS service whenever the WAN IP address
changes so that your chosen host name will be resolved properly by inquiring hosts.
The current status of the service is shown at the bottom of the DDNS web page.
Table 21. DDNS Menu Option
Option Description
DDNS Service
User Name
Password
Host Name
IP Address
Status
Select the type of service that you are registered for from your
DDNS service provider.
Enter your DDNS account username subscribed to the service
provider.
Enter the password of the account.
Enter the host name of your service host.
Shows the current WAN side public IP address.
Shows the status of DDNS service.
90
Page 91

RIP Setup
The RIP Setup page allows you to configure RIP (Router Information Protocol)
parameters. RIP automatically identifies and uses the best known and quickest route to
any given destination address to help reduce network congestion and delays.
RIP is a protocol that requires negotiation from both sides of the network (e.g. both the
Cable Modem/Router and your service provider’s CMTS (Cable Modem Termination
System)). Your service provider will normally set this up based on their knowledge of
their CMTS settings.
To access the RIP Setup page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/RIP Setup submenu.
Figure 23 shows an example of the menu and Table 22 describes the items you can
select.
Figure 23. Example of RIP Setup Page
Note: RIP messages will only be sent when the Cable Modem/Router is configured for Static IP
Addressing.
91
Page 92

It is unlikely that your cable Internet service supports this mode. If they do, and you want
to enable RIP, you will need to ask for the CMTS’s key name and number. You may need
additional information.
To enable the Cable Modem/Router to perform RIP, do the following (this example uses
BRCMV2 as the RIP Authentication Key and 1 as the Key ID):
• To turn on RIP MD5 Authentication, and check the Enable box.
• To specify a RIP MD5 Authentication Key String, type BRCMV2 for this example.
key name = a string value to match CMTS key name value
• To specify a RIP MD5 Auth Key ID, type 1.
key number = a number to match the CMTS key number value
• To change the RIP announcement interval, enter a number in seconds.
reporting interval by default = 30 seconds
• To specify a RIP unicast destination IP address, enter the IP address and subnet
mask.
Table 22. RIP Setup Menu Option
Option Description
RIP Enable
RIP Authentication
RIP Authentication Key
RIP Authentication Key ID
RIP Reporting Interval
RIP Destination IP Address
RIP Destination IP Subnet Mask
Check this box to enable RIP.
Check this box to enable RIP authentication for
routing protocols.
Enter the set of keys for your interface.
Enter the ID to identify the key used to create the
authentication data.
Enter the interval at which to update routing table.
Enter the destination IP address for RIP.
Enter the subnet mask for the destination IP
address.
92
Page 93

Options
The Options page allows you to configure the Cable Modem/Router to operate in
different modes that adjust how the device routes IP traffic.
To access the Options page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Advanced/Options submenu.
Figure 24 shows an example of the menu and Table 23 describes the items you can
select.
93
Page 94

Figure 24. Example of Options Page
To enable a feature:
1 Click the appropriate check box (a check mark will appear).
94
Page 95

2
When you are done with your selections, click on the Apply button.
Table 23. Options Menu Option
Option Description
Prevents the Cable Modem/Router or the PCs from responding to
WAN Blocking
pings to the Cable Modem/Router’s WAN IP address or to the
devices behind it. This makes it more difficult for hackers to attack
your PCs and other devices on your network.
IPSec/PPTP
PassThrough
Multicast
Enable
Primary
Network
Bridged
NAT ALG
Status
PassThrough
Mac Addresses
Enable to support VPN devices or software on your network.
Allows multicast specific traffic (denoted by a multicast specific
address) to be passed to and from the PCs on the private network
behind the Cable Modem/Router.
Allows all LAN hosts to bypass NAT and the Cable Modem/Router's
LAN DHCP Server. Adding MAC addresses into the table is not
required. If MAC addresses are added to the table then only those
MAC addresses in the list will bypass NAT and the LAN DHCP. All
other LAN hosts NOT in the list will use the NAT and LAN DHCP
Server as normal.
The NAT ALG section shows which ALGs (Application Layer
Gateway) are allowed to pass through the NAT Firewall. Most
users will not need to change these settings.
Enter the MAC Address that you want to passthrough and click the
Add Mac Address button.
95
Page 96

11
Firewall Menu Options
The Firewall Menu lets you:
• Configure the level of protection your firewall provides
• View the firewall logs
Basic
The Basic page allows you to configure the level of protection your firewall offers and
also what type of attacks it should detect..
To access the Basic page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Firewall/Basic submenu.
Figure 25 shows an example of the menu and Table 24 describes the items you can
select.
Figure 25. Example of Basic Page
96
Page 97

Table 24. Basic Menu Option
Option Description
IPv4 Firewall
Protection
Block Fragmented IP
packets
Port Scan Detection
IP Flood Detection
ICMP Blocking
By increasing the level from low to medium or high
you can restrict traffic to only certain predefined
ports.
Prevents all fragmented IP packets from passing
through the firewall.
Detects and blocks port scan activity originating on
both the LAN and WAN.
Detects and blocks packet floods originating on
both the LAN and WAN.
Prevents the Cable Modem/Router or the PCs from
responding to pings to the Cable Modem/Router’s
WAN IP address or to the devices behind it. This
makes it more difficult for hackers to attack your
PCs and other devices on your network.
Event Log
The Event Log page allows you to send firewall event log reporting to a standard SysLog
server or via email. Individual attack or configuration items can be selected that will be
sent to the SysLog server or emailed so that only the items of interest can be monitored.
Permitted connections, blocked connections, known Internet attack types, and Cable
Modem/Router configuration events can also be logged. The SysLog server must be on
the same subnet as the Private LAN behind the Cable Modem/Router (typically
192.168.0.x).
To access the Event Log page:
1 Click the Router menu tab.
2 Then click the Firewall/Event Log submenu.
Figure 23 shows an example of the menu and Table 25 describes the items you can
select.
97
Page 98

To enable the automatic email alerts:
1 Configure the email address you want to send alerts to. You also need to configure
the email account you will send from (this may be the same account). This includes
the SMTP (outgoing)/ mail server address, together with username and password.
You may need to contact your service provider to find the information.
2 Check the Enable box and click the Apply button.
Figure 26. Example of Event Log Page
98
Page 99

Table 25. Local Log Menu Option
Option Description
Permitted
Connections
Blocked
Connections
Known Internet
Attacks
Product
Configuration
Events
SysLog server
at 192.168.0.x
Contact Email
Address
SMTP Server
Name
SMTP
Username
Enabling this feature causes the Cable Modem/Router to report all
permitted connection attempts.
Enabling this feature causes the Cable Modem/Router to report all
blocked connection attempts.
Enabling this feature causes the Cable Modem/Router to report any
known Internet attacks.
Enabling this feature causes the Cable Modem/Router to report all
configuration changes.
Enter the address of your local SysLog server, if you have one.
Enter the email address where you want to receive the alert email.
Enter the SMTP (Outgoing) mail server address of the email
account you will send from.
Enter the username of the email account you will send from.
SMTP
Password
E-mail Alerts
Below is a complete list of the capable SysLog server attack/notification types and their
format. The generic format of sysLog messages for traffic or administration-related
events is:
MMM DD HH:MM:SS YYYY SYSLOG[0]: [Host HostIP] Protocol SourceIP,SourcePort
--> DestIP,DestPort EventText
Enter the password of the email account you will send from.
Check to enable sending alert email, when an attack is detected.
99
Page 100

Table 26. SysLog Server Event Format
Parameter Description
MMM
DD
HH:MM:SS
YYYY
HostIP
Protocol
SourceIP
SourcePort
DestIP
The three-letter abbreviation for the month (e.g., JUN, JUL AUG,
etc.)
The two-digit day of the month (e.g., 01, 02, 03, etc.)
The time displayed as two-digit values for the hour, minute, and
second, respectively.
The four-digit year.
The IP address of Cable Modem/Router sending the SysLog event.
This is the LAN IP Address on the Basic - Setup page.
Can be one of the following: “TCP”, “UDP”, “ICMP”, “IGMP” or
“OTHER”. In the case of “OTHER” the protocol type is displayed in
parentheses (). For ICMP packets, the ICMP type is displayed in
parentheses.
The IP address of the originator of the session/packet.
The source port at the originator.
The IP address of the recipient of the session/packet.
DestPort
EventText
The format of SysLog messages for informational events is simplified:
MMM DD HH:MM:SS YYYY SYSLOG[0]: [Host HostIP] EventText
The destination port at the recipient.
A textual description of the event.
100
 Loading...
Loading...