Transition Networks SISTF10XX-140-LRT, SISTF10XX-160-LRT, SISTF10XX-170-LRT User Manual
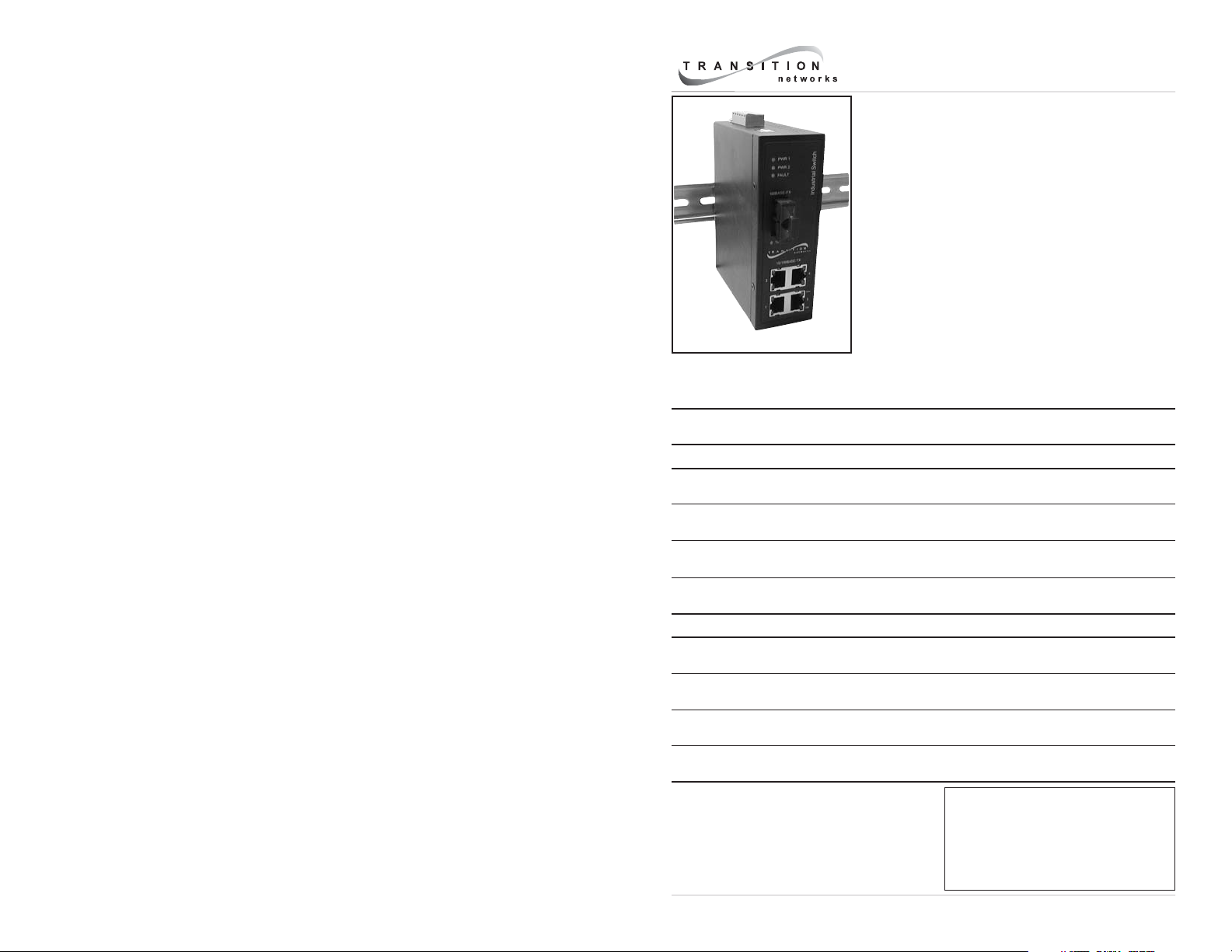
User’s Guide
SISTF10xx-140-LR(T)
SISTF10xx-160-LR(T)
SISTF10xx-170-LR(T)
Stand-Alone Ethernet Switch
• 10Base-T / 100Base-TX to 100Base-FX
• Extended Temperature
• Hazardous Environment
Transition Networks industrial Ethernet switch
connects 10Base-T / 100Base-TX twisted-pair
copper cable to 100Base-FX fiber-optic cable. It is
designed for harsh industrial environments and is
SISTF10xx-140-LR(T)
The SISTF10xx-140-LR(T) model includes four (4) copper RJ-45 ports and one (1)
duplex fiber-optic port.
Part Number Ports 1 - 4: Copper
Standard Temperature Models: 0°C to 60°C (32°F to 140°F):
SISTF1011-140-LR RJ-45
SISTF1012-140-LR RJ-45
SISTF1013-140-LR RJ-45
SISTF1014-140-LR RJ-45
Extended Temperature Models: -40°C to 75°C (-40°F to 167°F):
SISTF1011-140-LRT RJ-45
SISTF1012-140-LRT RJ-45
SISTF1013-140-LRT RJ-45
SISTF1014-140-LRT RJ-45
* Typical maximum cable distance.
Actual distance is dependent upon the
physical characteristics of the network
installation.
also available in models that operate in either
standard or extended temperature ranges.
Port 5: Duplex Fiber-Optic
10Base-T/100Base-TX
100 m (328 ft)*
100 m (328 ft)*
100 m (328 ft)*
100 m (328 ft)*
100 m (328 ft)*
100 m (328 ft)*
100 m (328 ft)*
100 m (328 ft)*
100Base-FX Duplex
ST, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
ST, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
SC, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
SC, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
ST, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
ST, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
SC, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
SC, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Cable Specifications . . . . . . . . . .12
Technical Specifications . . . . . . .15
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Compliance Information . . . . . . .20

SISTF10xx-140-LR(T) / -160-LR(T) / -170-LR(T)
SISTF10xx-160-LR(T)
The SISTF10xx-160-LR(T) model includes six (6) copper RJ-45 ports and two (2)
duplex fiber-optic ports.
Part Number Ports 1 - 6: Copper
10Base-T/100Base-TX
Standard Temperature Models: 0°C to 60°C (32°F to 140°F):
SISTF1011-160-LR RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1012-160-LR RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1013-160-LR RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1014-160-LR RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
Extended Temperature Models: -40°C to 75°C (-40°F to 167°F):
SISTF1011-160-LRT RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1012-160-LRT RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1013-160-LRT RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1014-160-LRT RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
* Typical maximum cable distance. Actual distance is dependent upon the
physical characteristics of the network installation.
Ports 7 & 8: Duplex Fiber-Optic
100Base-FX Duplex
ST, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
ST, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
SC, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
SC, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
ST, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
ST, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
SC, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
SC, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
SISTF10xx-170-LR(T)
The SISTF10xx-170-LR(T) model includes seven (7) copper RJ-45 ports and one (1)
duplex fiber-optic port.
Part Number Ports 1 - 7: Copper
10Base-T/100Base-TX
Standard Temperature Models: 0°C to 60°C (32°F to 140°F):
SISTF1011-170-LR RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1012-170-LR RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1013-170-LR RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1014-170-LR RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
Extended Temperature Models: -40°C to 75°C (-40°F to 167°F):
SISTF1011-170-LRT RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1012-170-LRT RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1013-170-LRT RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
SISTF1014-170-LRT RJ-45
100 m (328 ft)*
* Typical maximum cable distance. Actual distance is dependent upon the
physical characteristics of the network installation.
Port 8: Duplex Fiber-Optic
100Base-FX Duplex
ST, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
ST, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
SC, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
SC, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
ST, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
ST, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
SC, 1300 nm multimode
2 km (1.2 miles)*
SC, 1310 nm single mode
15 km (9.3 miles)*
2
24-hour Technical Support: 1-800-260-1312 -- International: 00-1-952-941-7600
techsupport@transition.com -- Click the “Transition Now” link for a live Web chat.
3
SISTF10xx-140-LR(T) / -160-LR(T) / -170-LR(T)
g
Installation
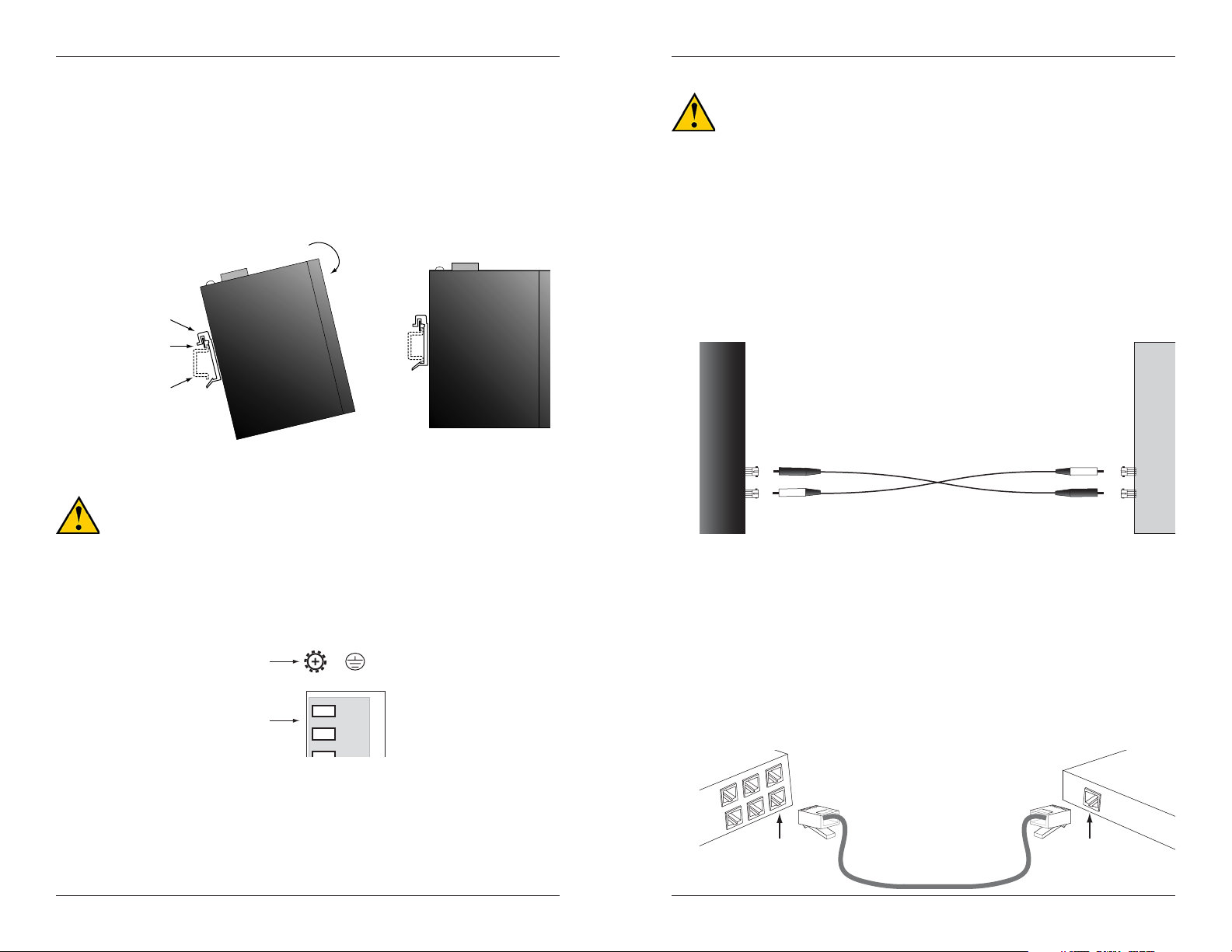
DIN-Rail Mount
The Ethernet switch includes an aluminum DIN-Rail mounting plate attached
to the device’s back panel. To mount the device onto a DIN-Rail:
1. Insert the top of the DIN-Rail into the upper slot of the mounting plate.
The stiff metal spring should be positioned behind the DIN-Rail.
2. Push down and rotate the device to snap it into place on the DIN-Rail as
shown.
Step 1:
mounting
plate
spring
DIN-Rail
NOTE: The Ethernet switch is intended to be grounded to a wellgrounded mounting surface such as a metal plate. Install the grounding
wire prior to connecting any other device.
Step 2:
Installation -- Continued
CAUTION: Disconnect the Ethernet switch from the DC power source
BEFORE installing and/or wiring the device.
Install the Fiber Cable
1. Locate or build 100Base-FX fiber cable with male, two-stranded TX to RX
connectors installed at both ends.
2. Connect the fiber cables to the Ethernet switch as described:
• Connect the male TX cable connector to the female TX port.
• Connect the male RX cable connector to the female RX port.
3. Connect the fiber cables to the other device (another media converter,
hub, etc.) as described:
• Connect the male TX cable connector to the female RX port.
• Connect the male RX cable connector to the female TX port.
Connect the
fiber cable to the
Ethernet switch
as shown.
RX
TX
Connect the fiber cable
to the other device
(media converter,
switch, etc.) as shown
RX
TX
Ground the Ethernet Switch
Grounding the Ethernet switch helps limit the effects of noise due to
electromagnetic interference (EMI). The grounding screw is located on the top
panel next to the terminal block.
rounding screw
terminal block
To ground the device:
1. Connect one end of the grounding wire (not included) to the grounding
screw by looping one end of the grounding wire under the star washer.
2. Tighten the grounding screw with a phillips-head screwdriver.
3. Connect the other end of the grounding wire to earth ground.
4
24-hour Technical Support: 1-800-260-1312 -- International: 00-1-952-941-7600
Install the Copper Cable
The AutoCross feature allows either straight-through (MDI) or crossover (MDIX) copper cable to be used when connecting devices via the RJ-45 port.
1. Locate or build 10Base-T or 100Base-TX copper cables with male, RJ-45
connectors installed at both ends.
2. Connect the RJ-45 connector at one end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on
the Ethernet switch.
3. Connect the RJ-45 connector at the other end of the cable to the RJ-45
port on the other device (PLC, workstation, etc.).
RJ-45 ports on the
Ethernet switch
techsupport@transition.com -- Click the “Transition Now” link for a live Web chat.
RJ-45 port
on the other device
(PLC, work station, etc.)
5
SISTF10xx-140-LR(T) / -160-LR(T) / -170-LR(T)
d
Installation -- Continued
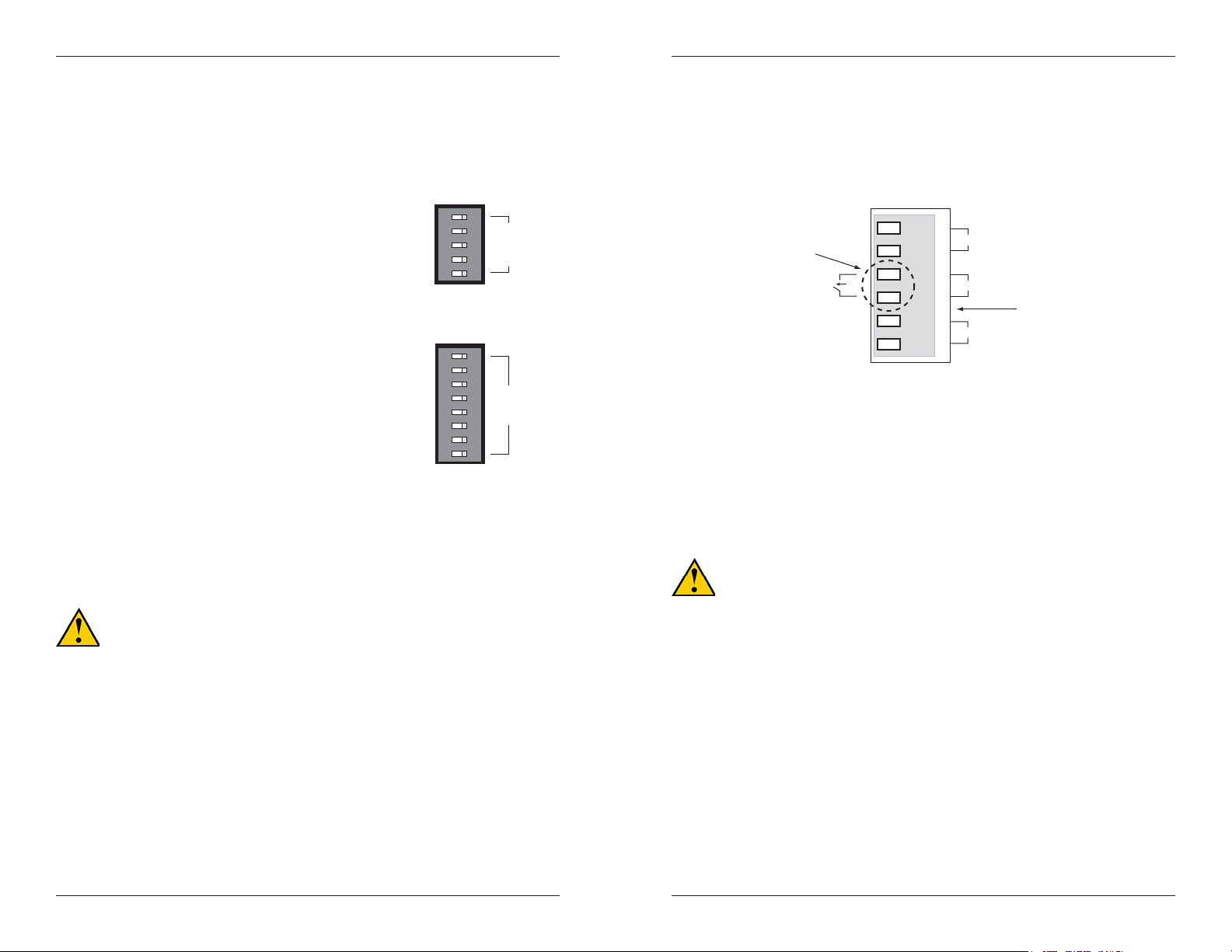
Set the Port Alarm Switches
The port alarm feature is used to determine faults at the copper or fiber ports.
The dip switches are located on the top panel of the device. Use a small flat
blade screwdriver or a similar device to set the switches.
SISTF10xx-140-LR(T)
• Switches 1 - 4 correspond to copper
ports 1 - 4, respectively.
• Switch 5 corresponds to fiber port 5.
SISTF10xx-160-LR(T)
• Switches 1 - 6 correspond to copper
ports 1 - 6, respectively.
• Switches 7 and 8 correspond to fiber
ports 7 and 8, respectively.
SISTF10xx-170-LR(T)
• Switches 1 - 7 correspond to copper
ports 1 - 7, respectively.
• Switch 8 corresponds to fiber port 8.
on = Enables the corresponding port alarm. If the link for that port fails (or if
a power supply input fails), the internal relay forms an open circuit and
the FAULT LED lights up.
off = Disables the corresponding port alarm. The internal relay forms a
closed circuit and the FAULT LED remains off.
NOTE: To activate the updated switch setting, cycle the power to the
Ethernet switch by turning off the power, then turning it back on.
Internal Relay
The internal relay that activates the alarm feature is connected to the two
middle contacts on the 6-contact terminal block. A user-supplied fault alarm
device can be connected to these fault contacts. An example would be to
connect the fault circuit to a warning light located in the control room. The
light can be set up to turn on when a fault is detected. (See page 7.)
SISTF10xx-140-LR(T)
1
P1
2
P2
3
P3
4
P4
5
P5
OFF ON
SISTF10xx-160-LR(T)
SISTF10xx-170-LR(T)
1
P1
2
P2
3
P3
4
P4
5
P5
6
P6
7
P7
8
P8
OFF ON
ON
DIP
ON
DIP
PORT
ALARM
PORT
ALARM
Installation -- Continued
Install the Port Alarm Device
A user-supplied port alarm device can be connected to the Ethernet switch to
alert the user whenever a power fault or a port fault occurs. At least one port
alarm switch (see page 6) must be “ON” to enable the port alarm feature.
6-contact terminal block
V2+
fault contacts
V2-
V1+
V1-
V1, V2 INPUTS
12-48 VDC
The contacts for the fault alarm are on the 6-contact terminal block, located
on the top panel of the Ethernet switch. To install a port alarm device:
1. Insert the two wires from the user-supplied port alarm device into the two
terminals marked “FAULT” on the 6-contact terminal block.
2. Secure the wire by tightening the corresponding screw on the side of the
terminal block.
NOTE: Calculate the maximum possible current in each power wire and
signal wire. Observe all electrical codes for maximum current allowed.
If the current goes above the maximum ratings, the wiring would
overheat, causing serious damage to the network equipment.
Please note the following when wiring the network:
• Signal lines must not be directly connected to outdoor wiring.
• Use separate paths to route the power wiring and the signal wiring. If
power wiring and signal wiring paths must cross, make sure the wires are
perpendicular at the intersection point.
• Do not run signal wiring and power wiring in the same wire conduit. To
avoid interference, wires with different signal characteristics should also
be routed separately.
• Use the type of signal transmitted through a wire to determine which
wires should be kept separate. The rule of thumb is that wiring with
similar electrical characteristics can be bundled together.
• Keep input wiring and output wiring separate.
• Where necessary, label the wiring to all devices in the network.
PWR2
FAU LT
PWR1
The screws to secure
the wires are locate
on the side of the
terminal block.
6
24-hour Technical Support: 1-800-260-1312 -- International: 00-1-952-941-7600
techsupport@transition.com -- Click the “Transition Now” link for a live Web chat.
7
 Loading...
Loading...