Datasheet UCC3882PW-1, UCC3882DWTR-1, UCC3882DWTR, UCC3882DW-1, UCC3882DW Datasheet (Texas Instruments)
Page 1
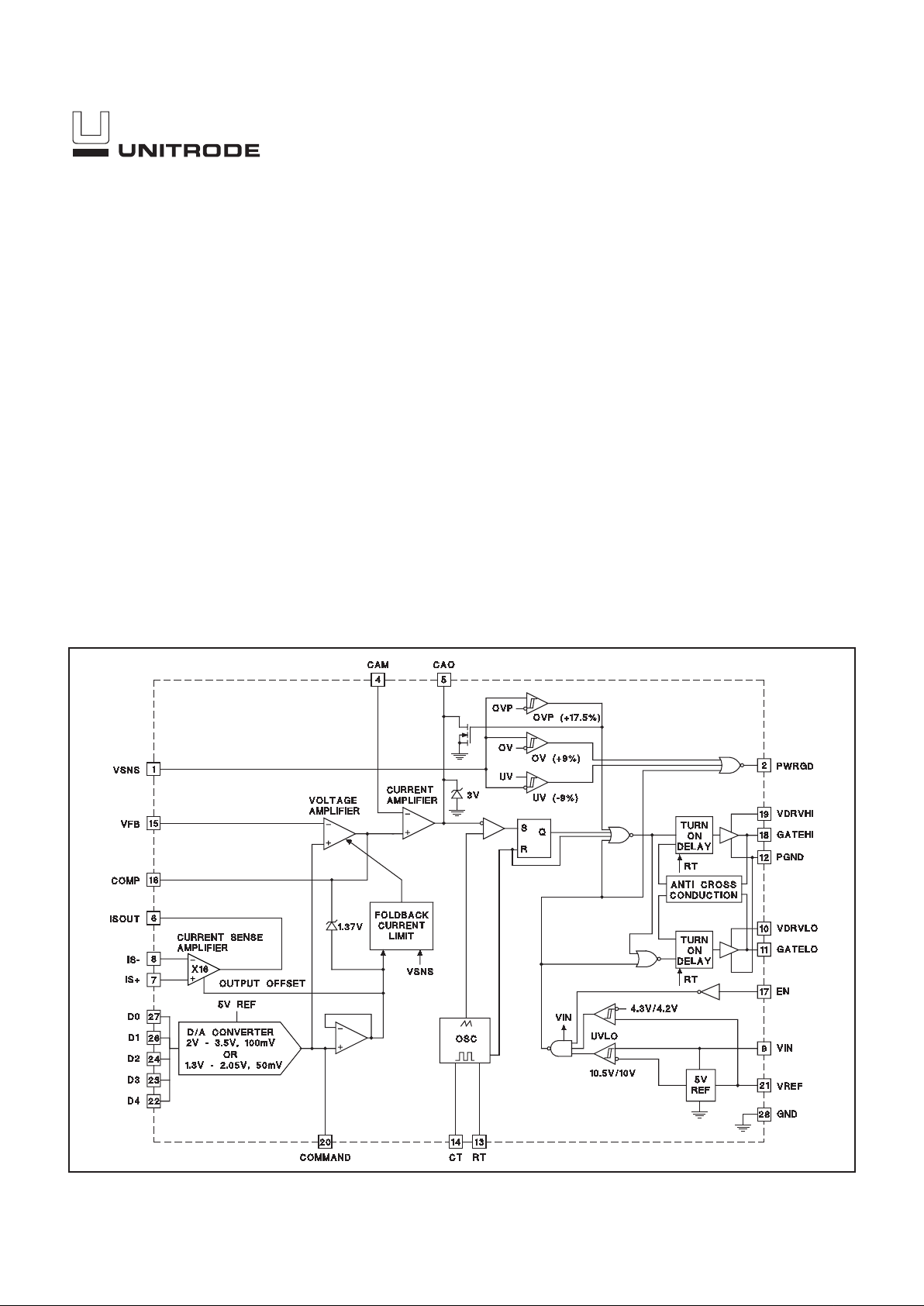
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
03/99
FEATURES
• Combined DAC/Voltage Monitor and PWM
with Synchronous Rectification Functions
• 5-Bit Digital-to-Analog (DAC) Converter
• 1% DAC/Reference Combined Accuracy
• Compatible with 5V and 12V Systems and
12V-only Systems
• Low Offset Current Sense Amplifier
• Programmable Oscillator Frequency Practical
to 700kHz
• Foldback Current Limiting
• Overvoltage and Undervoltage Fault Windows
• 2Ω Totem Pole Outputs with Programmable
Dead Times to Eliminate Cross-Conduction
• Chip Disable Function
Average Current Mode Synchronous Controller With 5-Bit DAC
BLOCK DIAGRAM
UDG-97047-1
DESCRIPTION
The UCC3882 combines high precision reference and voltage
monitoring circuitry with average current mode PWM synchronous rectification controller circuitry to power high-end microprocessors with a minimum of external components. The UCC3882
converts 5V or 12V to an adjustable output ranging from 1.8VDC
to 2.05VDC in 50mV steps and 2.1VDC to 3.5VDC in 100mV
steps with 1% DC system accuracy.
The DAC output voltage is directly compatible with Intel’s 5-bit
VID code (Table 1) which covers 1.3V to 2.05V in 50mV steps
and 2.1V to 3.5V in 100mV steps. The accuracy of the DAC/reference combination is better than 1%. Undervoltage lockout circuitry assures the correct logic states at the outputs during
power up and power down. The overvoltage and undervoltage
comparators monitor the system output voltage and indicate
when it rises above or falls below its designed value by more
than 9%. A second overvoltage comparator digitally forces
GATEHI off and GATELO on when the system output voltage exceeds its designed value by more than 17.5%.
(continued)
Page 2
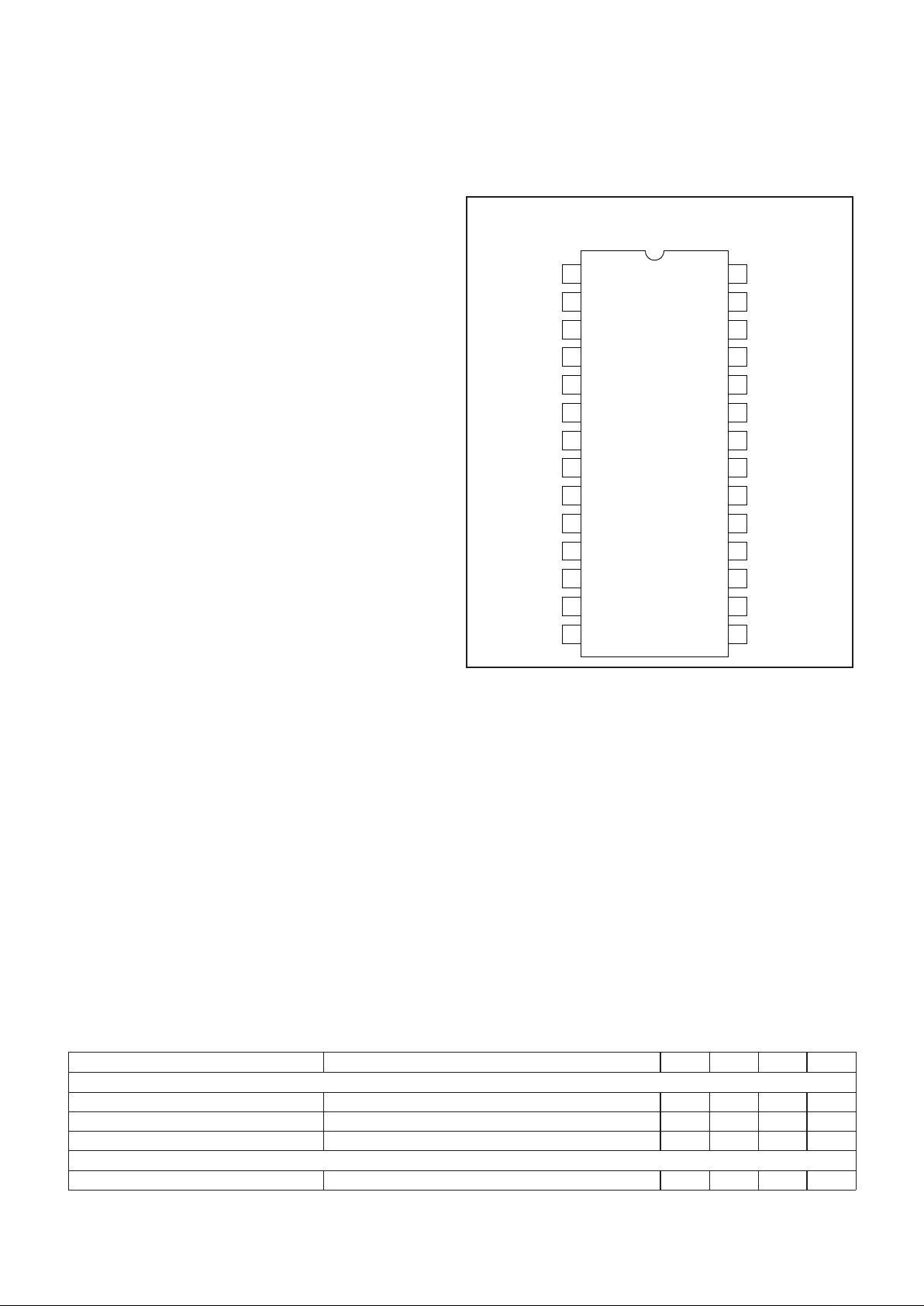
2
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
GATELO
N/C
D1
D0
VDRVHI
D2
D3
D4
GND
N/C
PWRGD
VDRVLO
IS+
VIN
CAM
CAO
ISOUT
VSNS
IS–
PGND EN
VREF
COMMAND
GATEHI
RT
CT VFB
COMP
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
DIL-28, SOIC-28 (Top View)
N, DW or PW Packages
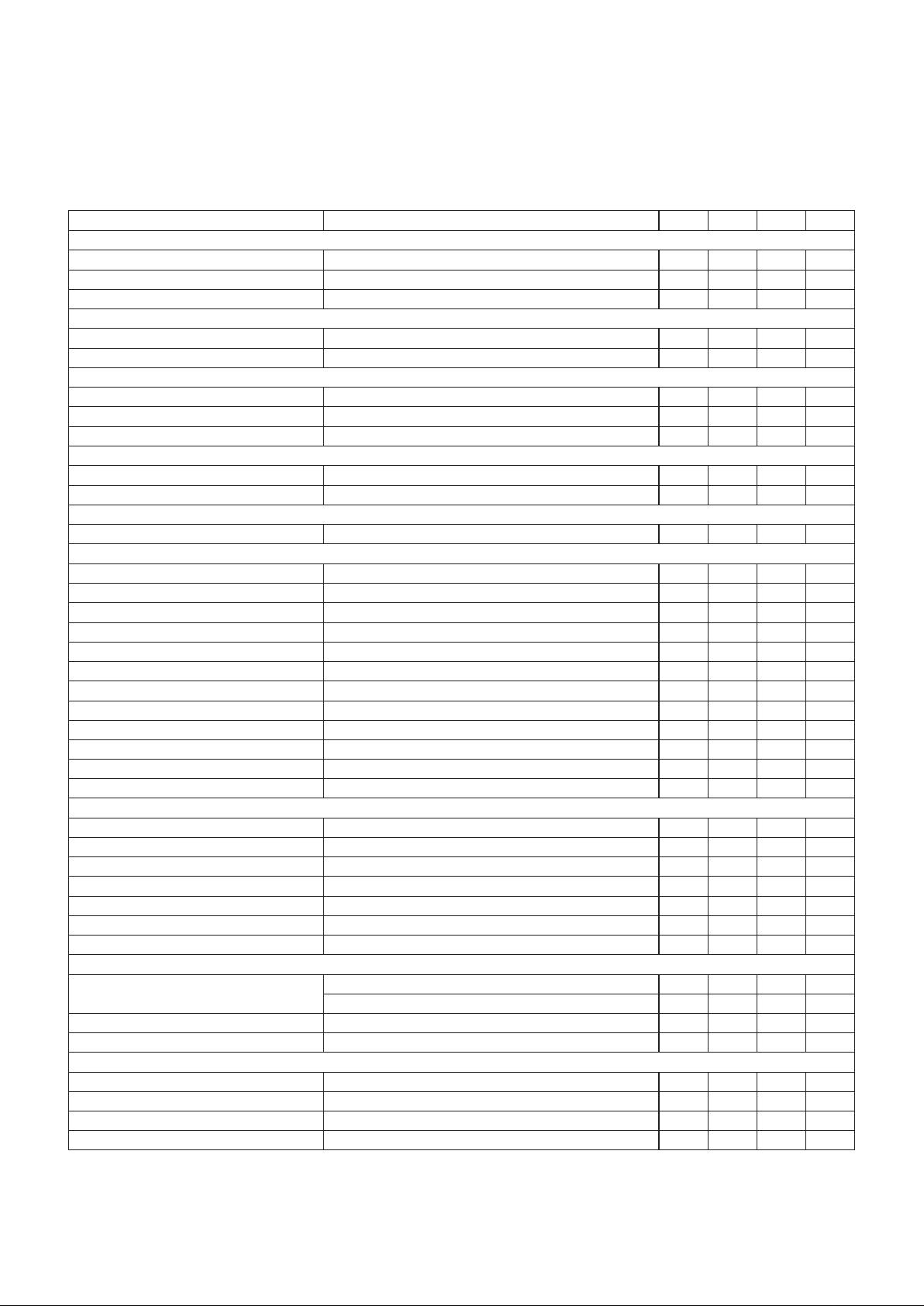
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
Unless otherwise specified, VIN = VDRVHI = VDRVLO = 12V, VSNS = 3.5V, VD0= V
D1
= VD2= VD3= VD4= 0V, RT= 13k, CT= 1.8nF, EN = Open, 0°C < TA< 70°C, TA=TJ.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Undervoltage Lockout
VIN UVLO Turn-on Threshold 10.5 10.8 V
VIN UVLO Turn-off Threshold 9.5 10 V
UVLO Threshold Hysteresis 300 500 700 mV
Supply Current
l
IN EN = 0V 7 12 mA
For all of the parts, grounding the EN pin disables the
GATEHI and GATELO outputs, shutting down the power
supply. For the 2882 and 3882 only, programming a DAC
output voltage below 1.8V, or programming all of the VID
pins high also disables the GATEHI and GATELO outputs. For the “–1" option parts, the GATEHI and GATELO
outputs are switching, and the power supply output voltage regulates at the programmed DAC output voltage for
all VID codes.
The voltage and current amplifiers have 2.5MHz
gain-bandwidth product to satisfy high performance system requirements. The internal current sense amplifier
permits the use of a low value current sense resistor,
minimizing power loss. The oscillator frequency is exter-
nally programmed with R
T and CT. The foldback circuit
reduces the converter short circuit current limit to 50% of
its nominal value when the converter is short-circuited,
minimizing component stress and dissipation during abnormal conditions. The gate drivers are low impedance
totem pole output stages capable of driving large external MOSFETs. Cross conduction is eliminated internally
by programming the dead time between turn-off and turn
on of the external high side and synchronous MOSFETs.
This device is available in a 28-pin wide body surface
mount package. The UCC2882 is specified for operation
from –25°C to +85°C and the UCC3882 is specified for
operation from 0°C to 70°C.
DESCRIPTION (continued)
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
VDRVHI, GATEHI (Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3V to 20V
VDRVLO, GATELO. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3V to 15V
All other pins referenced to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3V to 5.3V
VIN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +15V
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.). . . . . . . . . . . . . +300°C
Currents are positive into, negative out of the specified terminal.
Consult Packaging Section of Databook for thermal limitations
and considerations of packages.
Note 1: 20V at no load. Derate to 18.5V when used with capacitive loads of greater than 1000pF in series with less than 20
Ω
.
Page 3
3
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Unless otherwise specified, VIN = VDRVHI = VDRVLO = 12V, VSNS = 3.5V, V
D0
= V
D1
= VD2= VD3= VD4= 0V, RT= 13k, CT= 1.8nF, EN = Open, 0°C < TA< 70°C, TA=TJ.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DAC/Reference
COMMAND Voltage Accuracy 10.8V < VIN < 13.2V, I
REF = 0mA (Note 1) –1 1 %
D0-D4 Voltage High DX Pin Floating 5 5.2 V
D0-D4 Input Bias Current DX Pin Tied to GND –120 –70 –20 µA
OVP Comparator
Trip Point % Over COMMAND Voltage (Note 2) 10 17 25 %
Hysteresis 20 mV
OV Comparator
Trip Point % Over COMMAND Voltage (Note 2) 5 9 12 %
Hysteresis 20 mV
PWRGD On Resistance 470 Ω
UV Comparator
Trip Point % Over COMMAND Voltage (Note 2) –12 –9 –5 %
Hysteresis 20 mV
Enable Pin
Pull Up Current V
EN = 2.5V –80 –50 –20 µA
Voltage Error Amplifier
Input Offset Voltage V
CM = 3V –10 0 10 mV
Input Bias Current V
CM = 3V –0.5 0.5 µA
Open Loop Gain 2.05V < V
COMP < 3.05V 90 dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 10.8V < VIN < 15V 85 dB
Output Sourcing Current V
VFB = 2V, VCOMMAND = VCOMP = 2.5V –1.6 –0.8 mA
Output Sinking Current V
VFB = 3V, VCOMMAND = VCOMP = 2.5V 1 mA
Current Sense Amplifier
Gain 15 16 17 V/V
Common Mode Rejection Ratio 0V < V
CM < 4.5V 60 dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 10.8V < VIN < 15V 80 dB
Output Sourcing Current V
IS– = 2V, VISOUT = VIS+ = 2.5V –4 –3 mA
Output Sinking Current V
IS– = 3V, VISOUT = VIS+ = 2.5V 3 4 mA
Current Amplifier
Input Offset Voltage V
CM = 3V 1 mV
Input Bias Current V
CM = 3V –0.1 µA
Open Loop Gain 1V < V
CAO < 2.5V 90 dB
Output Voltage High 3V
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 10.8V < VIN < 15V 80 dB
Output Sourcing Current V
CAM = 2V, VCAO = VCOMP = 2.5V –7 mA
Output Sinking Current V
CAM = 3V, VCAO = VCOMP = 2.5V 17 mA
Oscillator
Initial Accuracy T
A = 25°C 324 360 396 kHz
0°C < T
A < 70°C 300 360 420 kHz
Valley to Peak Voltage 1.67 V
Frequency Change With Voltage 10.8V < VIN < 15V 1 %
Output Section (GATEHI and GATELO)
Output Low Voltage I
GATE = –100mA 0.2 V
Output High Voltage I
GATE = 100mA 11.8 V
Rise Time C
GATE = 3.3nF, RSERIES = 10Ω 20 80 ns
Fall Time C
GATE = 3.3nF, RSERIES = 10Ω 15 80 ns
Page 4
4
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
CAM: This pin is the inverting input to the current ampli-
fier. The average load current feedback from the ISOUT
pin is applied through a resistor to this pin. The current
loop compensation network is also connected to this pin
(see CAO below).
CAO: This pin is the current amplifier output. The current
loop compensation network is connected between this
pin and the CAM pin. The voltage on this pin is the input
to the PWM comparator and regulates the output voltage
of the system. The voltage at this output ranges from below 0.5V (forcing 0% duty cycle) to above 2.5V forcing
maximum duty cycle. A 3V clamp circuit prevents the
CAO voltage from rising excessively past the oscillator
peak voltage, for excellent transient response.
COMP: This pin is the voltage error amplifier output voltage. The system voltage compensation network is applied between COMP and VFB. A 1.37V clamp above
COMMAND is used to force the power supply into current limit mode when the output is short circuited. See
the Applications Section for programming current limit.
COMMAND: This pin is the output of the 5-bit digital-to-analog (DAC) converter and is the non-inverting input of the voltage error amplifier. The voltage on this pin
sets the switching regulator output voltage. The COMMAND voltage is set by the DAC input pins D0-D4, according to Table 1. The COMMAND source impedance is
typically 1.2kΩ and must therefore drive only high impedance inputs if accuracy is to be maintained. Bypass
COMMAND with a 0.01µF, low ESR, low ESL capacitor
for best circuit noise immunity.
CT: This pin is used with RT to program the internal
PWM oscillator frequency. Use a high quality capacitor
for best oscillator accuracy. See the Applications Section
for programming the oscillator.
D0-D4: These are the digital input control codes for the
DAC (See Table 1). The DAC is comprised of two ranges
set by D4 and with D0 representing the least significant
bit (LSB) and D3, the most significant bit (MSB). A bit is
set low by being connected to GND; a bit is set high by
floating it, or connecting it to a 5V source. Each control
pin is pulled up to approximately 5V by an internal pull
up.
EN: This input is used to disable the GATEHI and
GATELO outputs, resulting in disabling the power supply.
Pulling EN to GND causes the GATEHI and GATELO
outputs to be held low, while floating the pin or pulling it
up to 5V ensures normal operation. EN is pulled up to 5V
internally.
GATEHI: This output provides a low impedance totem
pole driver to drive the high-side external MOSFET. A series resistor between this pin and the gate of the external
MOSFET is recommended to prevent gate drive ringing
and overshoot. Good layout techniques should be used
to prevent GATEHI from ringing more than 0.3V below
PGND. The VDRVHI pin provides the power for the
GATEHI pin. GATEHI is disabled during UVLO and
overvoltage conditions. For the 2882/3882 only, GATEHI
is also disabled when the COMMAND voltage is programmed between 1.3 and 1.75V, or where the D0-D4
pins are all logic high levels, indicating no processor
present.
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
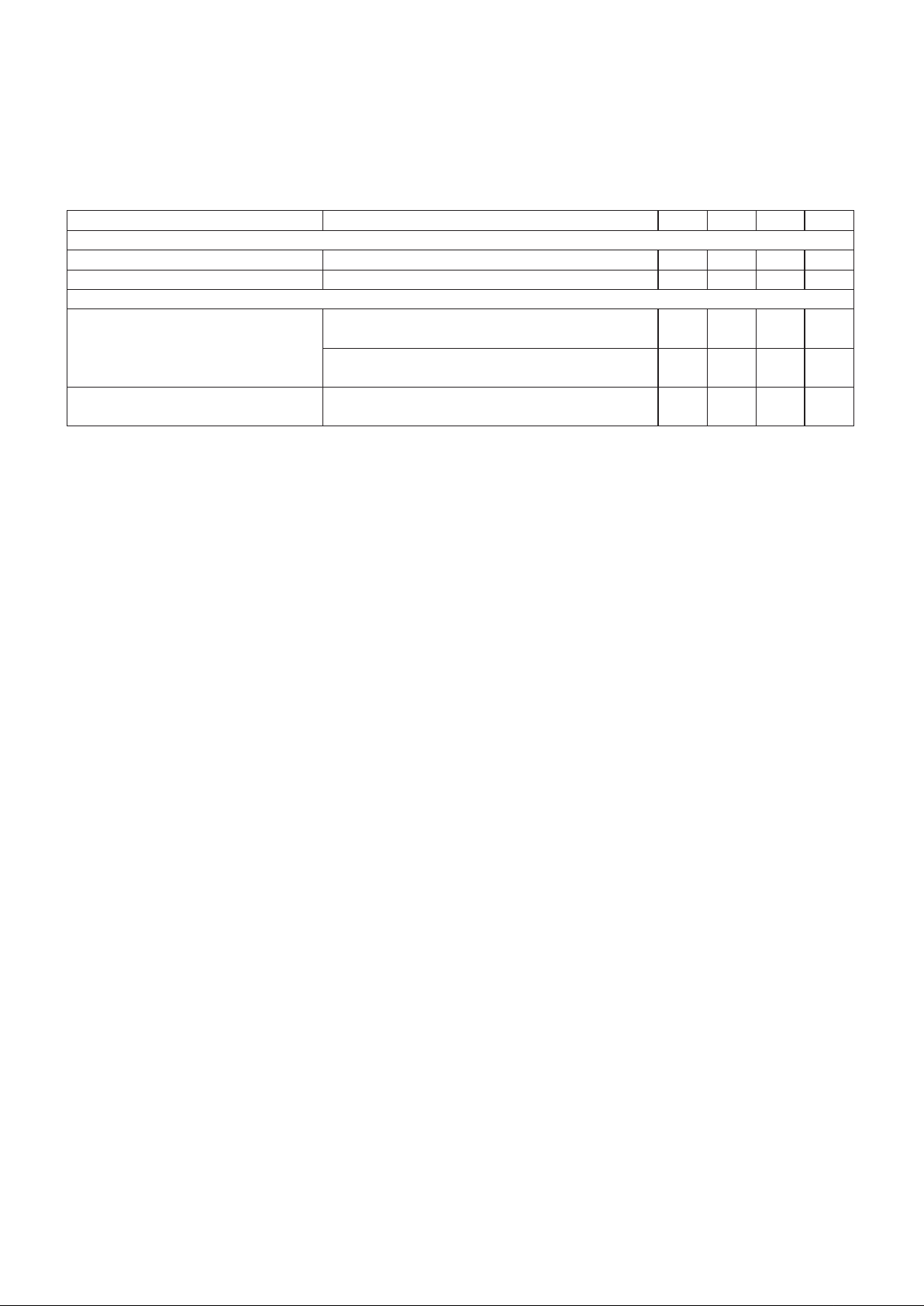
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Unless otherwise specified, VIN = VDRVHI = VDRVLO = 12V, VSNS = 3.5V, V
D0
= V
D1
= VD2= VD3= VD4= 0V, RT= 13k, CT= 1.8nF, EN = Open, 0°C < TA< 70°C, TA=TJ.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Turn On Delay
GATEHI Turn Off to GATELO Turn On 150 ns
GATELO Turn Off to GATEHI Turn On 135 ns
Foldback Current Limit
Clamp Level V
COMMAND = VSNS 1.37 V
V
FB = VCOMMAND – 100mV (Note 3)
V
SNS = 0 0.71 V
V
FB = VCOMMAND – 100mV (Note 3)
System Short Circuit Current Limit V
COMMAND = 2.3V 14.4 17 22 A
V
FB = 0V (Note 4)
Note 1: This test measures the combined errors of the COMMAND voltage and the voltage amplifier offset voltage. Applies to all
DAC codes from 1.8V to 3.5V.
Note 2: This percentage is measured with respect to the ideal COMMAND voltage programmed by the D0 - D4 pins.
Note 3: This voltage is measured with respect to the COMMAND voltage.
Note 4: The calculation of this parameter assumes an offchip sense resistor value of 0.005
Ω
. This test encompasses all sources
of error from the IC.
Page 5

5
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
GATELO: This output provides a low impedance totem
pole driver to drive the low-side synchronous external
MOSFET. A series resistor between this pin and the gate
of the external MOSFET is recommended to prevent gate
drive ringing and overshoot. Good layout techniques
should be used to prevent GATELO from ringing more
than 0.3V below PGND. The VDRVLO pin provides the
power for GATELO. GATELO is disabled during UVLO
conditions. For the 2882/3882 only, GATELO is also disabled when the COMMAND voltage is programmed between 1.3 and 1.75V, or where the D0-D4 pins are all
logic high levels, indicating no processor present.
GND: Ground reference for the device. All voltages, with
the exception of the GATE voltages, are measured with
respect to GND. Bypass capacitors on VIN, VREF, VSNS
and COMMAND should be connected directly to the
ground plane near GND.
IS-: This pin is the inverting input to the current sense
amplifier and is connected to the low side of the average
current sense resistor.
IS+: This pin is the non-inverting input to the current
sense amplifier and is connected to the high side of the
average current sense resistor.
ISOUT: This pin is the output of the current sense amplifier.The voltage on this pin is equal to the voltage across
the sense resistor multiplied by 16 and biased up by the
COMMAND voltage. This voltage is used for Average
Current mode control and for current limiting.
PGND: This pin provides a dedicated ground for the output gate drivers. The GND and PGND pins should be
connected externally using a short PC board trace or
plane. Decouple VDRVHI and VDRVLO to PGND with
low ESR capacitor of at least 0.1µF.
PWRGD: This pin is an open drain output which is driven
low to reset the microprocessor when VSNS rises above
or falls below its nominal value by 9%. The on resistance
of the open-drain switch will be no higher than 470Ω.
This output should be pulled up to a logic level voltage
and should be programmed to sink 1mA or less.
RT: This pin is used with CT to program the internal
PWM oscillator frequency. It is also used to program the
delay times between the external MOSFET turn on and
turn off periods, which eliminates cross conduction in
those MOSFETs. See the Applications Section for programming the oscillator and for controlling cross conduction.
VDRVHI: This pin supplies power to the high side output
driver, GATEHI. Connect VDRVHI to an 18V or lower
source for power supplies converting 12VDC to lower
voltages, and to a 12V source for systems for power supplies converting 5VDC. This pin should be bypassed directly to PGND using a low ESR capacitor.
VDRVLO: This pin supplies power to the low side output
driver, GATELO. VDRVLO is typically connected to a 12V
source, but may be connected to a 5V source for driving
logic level MOSFETs. This pin should be bypassed directly to PGND using a low ESR capacitor.
VIN: This pin supplies power to the chip. Connect VIN to
a stable voltage source that is at least 10.8V above GND.
The GATEHI, GATELO and PWRGD outputs will be held
low until VCC exceeds the upper undervoltage lockout
threshold. This pin should be bypassed directly to GND.
VFB: This pin is the inverting input to the error amplifier.
This input is connected to COMP through a feedback
network and to the power supply output through a resistor or a divider network.
VREF: This pin provides an accurate 5V reference and is
internally short circuit current limited. VREF powers the
D/A Converter and also provides a threshold voltage for
the UVLO comparator. For best reference stability, bypass VREF directly to GND with a low ESR, low ESL capacitor of at least 0.01µF.
VSNS: This pin is connected to the system output voltage through a low pass R-C filter. When the voltage on
VSNS rises above or falls below the COMMAND voltage
by 9%, the PWRGD output is driven low to reset the microprocessor. When the voltage on VSNS rises above
the COMMAND voltage by 17.5%, the OVP comparator
disables the GATEHI output and enables the GATELO
output, forcing 0% duty cycle on the power supply. This
pin is also used by the foldback current limiting circuitry
to indicate when the output voltage has been short circuited. VSNS should be decoupled very closely to the IC
with a capacitor to GND. The OV and UV comparators’
hysteresis is typically 20mV, requiring good layout and filtering techniques to insure that noise and ground-bounce
do not inadvertently trip the OV and UV comparators. It is
recommended that an R-C filter set to approximately
Fs/10 be used to filter noise from the system output,
where Fs is the oscillator frequency.
PIN DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
Page 6

6
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
This IC is intended to be used in a high performance
power supply to power the Pentium
®
II or a similar processor.Figure 1 shows a typical power supply application
circuit which converts +5V to lower voltages required by
the Pentium
®
II Processor.
Synchronous Switching Delay Time
Figure 2 shows that the fundamental difference between
a Buck and a Synchronous Buck regulator is the use of a
MOSFET rather than a Schottky diode as the low side or
free-wheeling switch.
In order to maintain safe and efficient operation of a Synchronous Buck regulator, both MOSFETs, Q1 and Q2,
should never be turned on at the same time. Having both
MOSFETs on at the same time results in cross conduction, which can result in excessively high power dissipation in one or both MOSFETs. The UCC3882 has a built
in delay between the turn OFF of one MOSFET and the
turn ON of the other MOSFET. This delay is a controlled
delay between the GATEHI and GATELO drive outputs
and is programmable by the selection of the resistor R
T.
Controlling the delay between the gate drive outputs is
only part of the solution. The power supply designer
must also understand intrinsic delays involving MOSFET
turn on, turn off, rise and fall times in order to insure that
there is no cross conduction.
It is recommended that a value between 10kΩ and 15kΩ
be used for R
T, which minimizes the delay and can result
in the highest efficiency operation. A higher value of R
T
will result in a larger delay between the MOSFET Gate
transitions. R
T should be between 10kΩ minimum and
50kΩ maximum.
Programming the Oscillator
The first step in programming the oscillator is choosing
the value of R
T as described above. The second step is
to program the frequency according to the curves shown
in Figure 3, by choosing the appropriate capacitor value.
For convenience, values are shown in Table 1 for nominal
frequencies from 100kHz to 700kHz using standards resistors and capacitor values.
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Digital Command Command GATEHI/GATELO Digital Command Command GATEHI/GATELO
D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Voltage Status
D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Voltage Status
01111 1.300 Note 1 11111 2.000 Note 1
01110 1.350 Note 1 11110 2.100 Enabled
01101 1.400 Note 1 11101 2.200 Enabled
01100 1.450 Note 1 11100 2.300 Enabled
01011 1.500 Note 1 11011 2.400 Enabled
01010 1.550 Note 1 11010 2.500 Enabled
01001 1.600 Note 1 11001 2.600 Enabled
01000 1.650 Note 1 11000 2.700 Enabled
00111 1.700 Note 1 10111 2.800 Enabled
00110 1.750 Note 1 10110 2.900 Enabled
00101 1.800 Enabled 10101 3.000 Enabled
00100 1.850 Enabled 10100 3.100 Enabled
00011 1.900 Enabled 10011 3.200 Enabled
00010 1.950 Enabled 10010 3.300 Enabled
00001 2.000 Enabled 10001 3.400 Enabled
00000 2.050 Enabled 10000 3.500 Enabled
Table 1. Programming the Command Voltage for the UCC3882
The 5-bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) is programmed according to Table 1.The COMMAND voltage
is always active as long as the UCC3882 VIN pin is
above the undervoltage lockout voltage. For the
2882/3882 only, the output gate drives GATEHI and
GATELO are disabled at certain DAC codes, as shown
in Table 1. Disabling the gate drives disables the power
supply. For the 2882 -1 and 3882 -1, the GATEHI and
GATELO drives are enabled for all DAC codes. For a
given code, the power supply output regulates at the corresponding COMMAND voltage.
DAC INFORMATION
Page 7

7
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
Figure 1. Application circuit - Pentium®II power supply.
UDG-97048-1
FREQUENCY RT CT
(kHz) (kΩ) (pF)
100 14.7 5600
200 11.0 3900
300 10.5 2700
400 11.3 1800
500 12.7 1200
600 10.7 1200
700 11.0 1000
Table 2. Programming Standard Frequencies
An excessively long delay time between gate drive signals, or a delay time that is too small, will result in a inefficient power supply design. The third step in
programming the oscillator is to observe the actual circuit
waveforms to insure that the delay is optimal. The designer should vary R
T and CT accordingly to adjust the
delay time and to program the proper oscillator frequency.
Using an External Schottky Diode in Parallel With the
Low Side MOSFET
The purpose of using a synchronous buck regulator is to
substitute a low voltage drop MOSFET in place of a
Schottky diode as the low side switch. An external
Schottky diode may still be required however, in order to
reduce the losses due to the reverse recovery of the
low-side MOSFET body diode. Figure 4 illustrates the effects on power losses due to the non-ideal nature of a
typical MOSFET body diode. I
RM is the peak recovery
current of the body diode of Q2 and I
LOUT is the current
of the output inductor. Using a parallel Schottky diode
can reduce these losses and increase circuit efficiency.
The size of the diode should be increased as a function
of load current, input voltage, and operating frequency.
The diode should be as close to the lower MOSFET, Q2,
as possible, to reduce stray inductance.
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
Page 8

8
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
Choosing RSENSE to Set the Current Limit
R
SENSE is chosen to limit the maximum (short circuit)
current of the power supply. The short circuit current
equation for the UCC3882 is:
ISC =
1.37V
RSENSE •16
and therefore, the value of the sense resistor, for a chosen short circuit current is:
RSENSE =
1.37V
ISC •16
The short circuit current limit does vary slightly as a function of the switching regulator’s output inductor value and
operating frequency because a high value of ripple current will reduce the average short circuit current limit.
Figure 5 shows the variation in Isc given common values
for the UCC3882. The UCC3882 is nominally configured
so that a 0.005mΩ resistor will set the current limit to approximately 17A.
The UCC3882 incorporates short circuit current foldback,
as shown in Figure 6. When the output of the power supply is short circuited, the output voltage falls. When the
output voltage reaches 1/2 of its nominal voltage (COMMAND/2) then the output current is reduced. This feature
reduces the amount of current in the MOSFETs and capacitors, and insures high reliability.
Choosing VDRVLO, VDRVHI and VIN
The UCC3882 requires a nominal 12V input supplied at
VIN. VDRVLO and VDRVHI can be set to any voltage
less than 18.5V, and may be set individually. A power
supply deriving its power from +5V should use +12V at
the VDRVHI pin, but may use either +5V or +12V depending on the drive requirements of the synchronous
low-side MOSFET. A power supply deriving its power
from +12V should use +18V at VDRVHI in order to provide adequate voltage (6V) gate drive to the high-side
MOSFET.VIN must be less than +15V.
Input Capacitors
The input capacitors are chosen primarily based on their
switching frequency RMS current handling capability and
their voltage rating. The input capacitors must handle virtually all of the RMS current at the switching frequency,
even if the circuit does not have an input inductor. The
switching current in the input capacitors appears as
shown in Figure 7.
Aluminum or tantalum capacitors can be used. The
amount of RMS current in an Electrolytic capacitor has a
strong impact on the reliability and lifetime of the capacitor. Other factors which affect the life of an input capacitor are internal heat rise, external airflow, the amount of
time that the circuit operates at maximum current and
the operating voltage. The curves in Figure 8 show the
RMS current handled by the total input capacitance in
typical VRM circuits powered from 5V or from 12V.
APPLICATION INFORMATION
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
10 15 20 25
RT [kW]
FREQUENCY [kHz]
1.0nF
1.2nF
1.8nF
2.2n
2.7nF
3.9nF
5.6nF
Figure 3. Programming UCC3882 oscillator
frequency.
Figure 2. Buck vs. synchronous buck regulator.
UDG-97049
Page 9

9
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
4
4.5
5
5.5
6
6.5
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT (A)
RSENSE (mW)
200kHz, 1.5mH
400kHz, 3mH
200kHz, 3mH
300kHz, 1.5mH
400kHz, 1.5mH
{
Figure 5. Short circuit current limit vs. RSENSE for
various frequency and inductor values.
0
20
40
60
80
100
0 20406080100
% SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT
% NOMINAL VOUT
Figure 6. Short circuit foldback reduces stress on
circuit components by reducing short circuit current.
Figure 7. Input capacitors current waveform.
UDG-96216
Figure 4. Effects of reverse recovery in a
synchronous rectifier.
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
UDG-97051
0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
9.0
10.0
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
LOAD CURRENT (A)
RMS CURRENT FOR INPUT CAPS [ARMS] .
VIN5V, VOUT1.8V
VIN5V, VOUT2.8V
VIN12V,VOUT2.8V
VIN12V,VOUT1.8V
Choose the type and number of input capacitors based on
these curves by choosing the input voltage and nominal
output voltage. Example: For a 5V input, 1.8V output power
supply with a load of 15 Amperes, the input capacitors
should be chosen for 7.5 Amperes RMS current.
Figure 8. Load current vs RMS current for input
capacitors - Pentium
®
II Family.
Page 10

10
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
Demonstration Kit Design and Performance
A demonstration circuit was built based on the UCC3882
and utilizing an Intel VRM 8.1 form factor connector. The
schematic is shown in Figure 9 and the Bill of Materials
in Table 3. The circuit is configured for the following operating parameters:
• Switching Frequency = 225kHz
• Rated Output Current = 15A
• Short Circuit Current = 17A Nominal
• Output Voltage: 1.8V to 2.8V Configured by VID Code
• Airflow: 100 LFM
• Temperature: 0 to 60°C
• Regulation: Per Intel VRM 8.1 DC-DC Converter
Design Guidelines
Figures 12 - 14 show the performance of the circuit.
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
REF DESCRIPTION PACKAGE
U1 Unitrode UCC3882 DAC/PWM SOIC-28 WIDE
C01 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
C02 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
C03 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
C04 Sprague/Vishay 595D475X0016A2B, 4.7uF 16V Tantalum SPRAGUE Size A
C05 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
C06 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
C07 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
C08 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
C09 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
C10 0.10µF Ceramic 1206 SMD
C11 0.10µF Ceramic 1206 SMD
C12 0.01µF Ceramic 0603 SMD
C13 0.01µF Ceramic 0603 SMD
C14 0.01µF Ceramic 0603 SMD
C15 0.10µF Ceramic 1206 SMD
C17 68pF NPO Ceramic 0603 SMD
C18 1000pF Ceramic 0603 SMD
C19 220pF NPO Ceramic 0603 SMD
C20 Sanyo 6MV1500GX, 1500µF, 6.3V, Aluminum Electrolytic 10x20mm Radial Can
CT 3900pF Ceramic 0603 SMD
J1 AMP 532956-7 40 Pin Connector 40 Pin
L1 Toroid T51-52C, 5 Turns #16AWG, 1.6µH Toroid
Q1 International Rectifier IRL3103, 30V, 56A TO-220AB, layed down
Q2 International Rectifier IRL3103D1, 30V, 56A TO-220AB, layed down
R01 5mΩ, PCB Resistor Copper Trace
R02 10kΩ, 5%, 1/16 Watt 0603 SMD
R03 5.62kΩ, 1%, 1/16 Watt 0603 SMD
R05 365kΩ, 1%, 1/16 Watt 0603 SMD
R06 100kΩ, 5%, 1/16 Watt 0603 SMD
R07 5.6kΩ, 5%, 1/16 Watt 0603 SMD
R08 10kΩ, 5%, 1/16 Watt 0603 SMD
R09 3.3Ω, 5%, 1/16 Watt 0603 SMD
R10 3.3Ω, 5%, 1/16 Watt 0603 SMD
Table 3. Bill of materials.
Page 11

11
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
Figure 9. Reference design - UCC3882 5-bit synchronous rectifier PWM controller for the Intel Pentium®II
processor.
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
UDG-97140
Page 12

12
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
Figure 10. Demo board.
Figure 11a. COMP silkscreen. Figure 11b. COMP side.
Figure 11c. GND layer. Figure 11d. PWR layer. Figure 11e. Solder side.
Figure 11f. Drill drawing.
Page 13

13
UCC2882/-1
UCC3882/-1
UNITRODE CORPORATION
7 CONTINENTAL BLVD.• MERRIMACK, NH 03054
TEL. (603) 424-2410 • FAX (603) 424-3460
APPLICATION INFORMATION (cont.)
Figure 12. Transient response to 15.2A step load
channel 2 scale is 50mV/A.
50%
55%
60%
65%
70%
75%
80%
85%
90%
95%
0.0 5.0 10.0 15.0
DC LOAD CURRENT (A)
EFFICIENY (%)
0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
9.0
POWERDISSIPATION (W)
POWER
DISSIPATION
EFFICIENCY
Figure 13. UCC3882 demo kit efficiency.
-5.00%
-3.00%
-1.00%
1.00%
3.00%
5.00%
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
LOAD CURRENT (A)
VOLTAGE REGULATION
Figure 14. Load regulation.
Pentium®II is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
Page 14

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. T esting and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICA TIONS IS UNDERSTOOD T O
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...