THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
features
D
Triple 10-bit D/A Converters
D
Minimum 80 MSPS Operation
D
Direct Drive of Doubly-Terminated 75-Ω
Load Into Standard Video Levels
D
3×10 Bit 4:4:4, 2×10 Bit 4:2:2 or 1×10 Bit
4:2:2 (ITU-BT.656) Multiplexed YPbPr/GBR
Input Modes
D
Bi-Level (EIA) or Tri-Level (SMPTE) Sync
Generation With 7:3 Video/Sync Ratio
D
Integrated Insertion of Sync-On-Green/
Luminance or Sync-On-All Channels
D
Configurable Blanking Level
D
Internal Voltage Reference
applications
D
High-Definition Television (HDTV) Set-Top
Boxes/Receivers
D
High-Resolution Image Processing
D
Desktop Publishing
D
Direct Digital Synthesis/I-Q Modulation
See ALSO: THS8134 (8 bit, pin-compatible)
description
The THS8133 is a general-purpose triple high-speed D/A converter (DAC) optimized for use in video/graphics
applications. The device operates from a 5-V analog supply and a 3-V to 5-V range digital supply . The THS8133
has a sampling rate up to 80 MSPS. The device consists of three 10-bit D/A converters and additional circuitry
for bi-level/tri-level sync and blanking level generation in video applications.
THS8133 is also well suited in applications where multiple well-matched and synchronously operating DACs
are needed; for example, I-Q modulation and direct-digital synthesis in communications equipment.
The current-steering DACs can be directly terminated in resistive loads to produce voltage outputs. The device
provides a flexible configuration of maximum output current drive. Its output drivers are specifically designed
to produce standard video output levels when directly connected to a single-ended doubly-terminated 75 Ω
coaxial cable. Full-scale video/sync are generated in a 7:3 ratio, compliant with SMPTE standards for GBR and
YPbPr signals.
Furthermore, the THS8133 can generate both a traditional bi-level sync or a tri-level sync signal, as per the
SMPTE standards, via a digital control interface. The sync signal is inserted on one of the analog output
channels (sync-on-green/luminance) or on all output channels. Also, a blanking control signal sets the outputs
to defined levels during the nonactive video window.
Finally the input format can be either 3×10 bit 4:4:4, 2×10 bit 4:2:2, or 1×10 bit 4:2:2. This enables a direct
interface to a wide range of video DSP/ASICs including parts generating ITU-BT.656 formatted output data.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
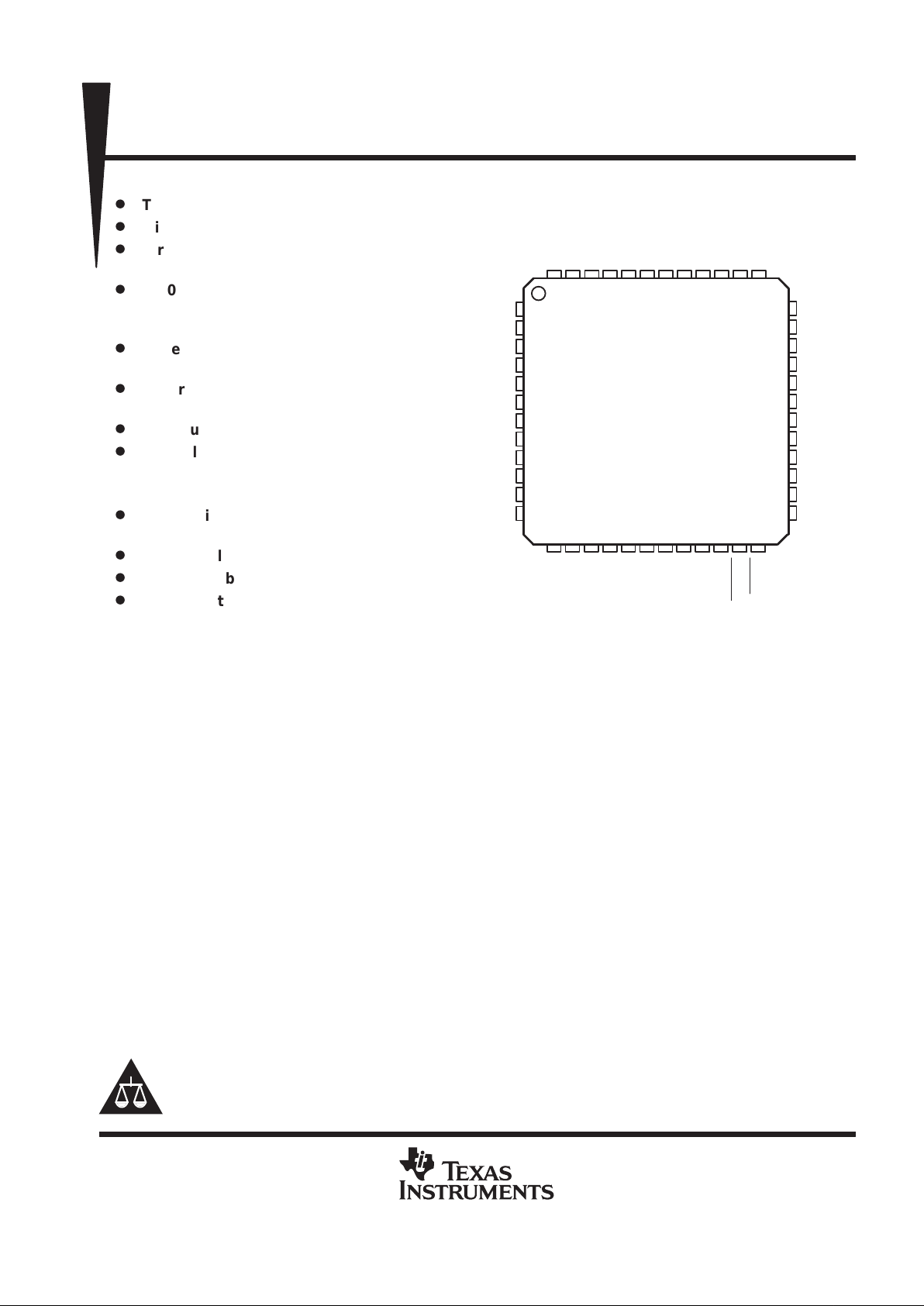
14 15
GY0
GY1
GY2
GY3
GY4
GY5
GY6
GY7
GY8
GY9
CLK
SYNC_T
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
BPb9
BPb8
BPb7
BPb6
BPb5
BPb4
BPb3
BPb2
BPb1
BPb0
DV
SS
DV
DD
17 18 19 20
AGYAVCOMP
FSADJ
47 46 45 44 4348 42
M2M1AV
ABPb
AV
RPr9
BLANK
SYNC
RPr2
RPr4
RPr5
RPr6
RPr7
RPr8
40 39 3841
21
22 23 24
37
13
V
ARPr
AV
RPr1
RPr0
RPr3
TQFP-48 PowerPAD PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
SS
DD
SS
DD
REF
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGE
T
A
TQFP-48 PowerPAD
°
°
THS8133CPHP
0°C to 70°C
THS8133ACPHP
†
†
The imbalance between DACs applies to all possible pairs of
the three DACs. K
IMBAL
is assured over full temperature
range. In parts labeled THS8133CPHP, K
IMBAL(SYNC)
is
assured at 25°C. In parts labeled THS8133ACPHP,
K
IMBAL(SYNC)
is assured over the full temperature range.
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME PIN
I/O
DESCRIPTION
ABPb 45 O
Analog red, green and blue respectively Pr, Y and Pb current outputs, capable of directly driving a doubly
AGY 41 O
terminated 75-Ω coaxial cable.
ARPr 43 O
AV
DD
40,44 I Analog power supply (5 V ±10%). All AVDD terminals must be connected.
AV
SS
42,46 I Analog ground
BLANK 23 I Blanking control input, active low. A rising edge on CLK latches BLANK. When asserted, the ARPr, AGY and
ABPb outputs are driven to the blanking level, irrespective of the value on the data inputs. SYNC takes
precedence over BLANK, so asserting SYNC (low) while BLANK is active (low) will result in sync generation.
BPb0–BPb9 10–1 I Blue or Pb pixel data input bus. Index 0 denotes the least significant bit. Refer to functional description for
different operating modes.
CLK 26 I Clock input. A rising edge on CLK latches RPr0-9, GY0-9, BPb0-9, BLANK, SYNC, and SYNC_T . The M2 input is
latched by a rising edge on CLK also, but only when additional conditions are satisfied, as explained in its
terminal description.
COMP 39 O Compensation terminal. A 0.1 µF capacitor must be connected between COMP and AVDD.
DV
DD
12 I Digital power supply (3-V to 5-V range)
DV
SS
11 I Digital ground
FSADJ 38 I Full-scale adjust control. The full-scale current drive on each of the output channels is determined by the value of
a resistor RFS connected between this terminal and AVSS. The nominal value of RFS is 430 Ω, corresponding to
26.67 mA full-scale current. The relationship between RFS and the full-scale current level for each operation
mode is explained in the functional description.
GY0–GY9 36–27 I Green or Y pixel data input bus. Index 0 denotes the least significant bit. Refer to functional description for
different operating modes.
M1 47 I Operation mode control 1. M1 is directly interpreted by the device (it is not latched by CLK). M1 configures device
according to Table 1.
M2 48 I Operation mode control 2. The second rising edge on CLK after a transition on SYNC latches M2. The
interpretation is dependent on the polarity of the last SYNC transition:
SYNC L to H: latched as M2_INT
SYNC H to L: latched as INS3_INT
T ogether with M1, M2_INT configures the device as shown in T able 1. When INS3_INT is high, the sync output is
inserted on all DAC outputs; a low will insert it only on the AGY output. See also Figure 2 and T able 2. The value of
M2 at powerup is undetermined. Therefore at least 1 L –>H transition on SYNC
is required to set M2.
RPr0–RPr9 13–22 I Red or Pr pixel data input bus. Index 0 denotes the least significant bit. Refer to functional description for different
operating modes.
SYNC 24 I Sync control input, active low. A rising edge on CLK latches SYNC. When asserted, only the AGY output
(INS3_INT=L, see terminal M2) or ARPr, AGY and ABPb outputs (INS3_INT=H, see terminal M2) are driven to
the sync level, irrespective of the values on the data or BLANK inputs. Consequently, SYNC should remain low
for the whole duration of sync, which is in the case of a tri-level sync both the negative and positive portion (see
Figure 7).
THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Terminal Functions (Continued)
TERMINAL
NAME PIN
I/O
DESCRIPTION
SYNC_T 25 I Sync tri-level control, active high. A rising edge on CLK latches SYNC_T . When asserted, a positive sync (higher
than blanking level) is generated when SYNC is low. When disabled, a negative sync (lower than blanking level)
is generated when SYNC is low. When generating a tri-level (negative-to-positive) sync, a L →H transition on
this signal positions the start of the positive transition. See Figure 6 for timing control.
The value on SYNC_T is ignored when SYNC
is not asserted (high).
V
REF
37 I/O Voltage reference for DACs. An internal voltage reference of nominally 1.35 V is provided, which requires an
external 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor between V
REF
and AVSS. However, the internal reference can be overdriven
by an externally supplied reference voltage.
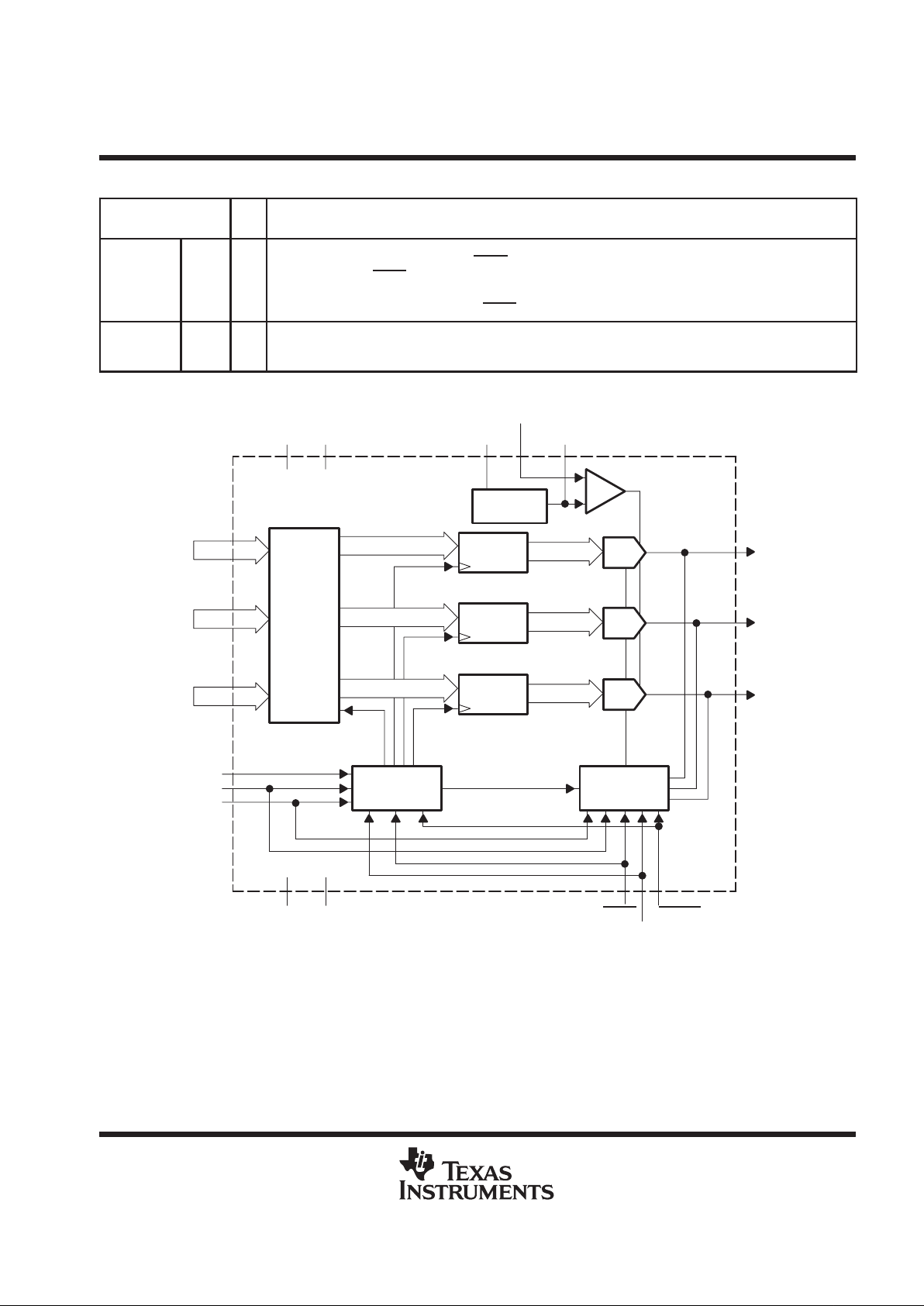
R/Pr
Register
ARPr
RPr[9:0]
DAC
G/Y
Register
B/Pb
Register
DAC
DAC
DV
DD
Configuration
Control
SYNC/BLANK
Control
Bandgap
Reference
GY[9:0]
BPb[9:0]
CLK
M1
M2
AGY
ABPb
DV
SS
COMP V
REF
AVDDAV
SS
SYNC
BLANK
FSADJ
SYNC_T
Input
Formatter
Figure 1. THS8133 Block Diagram
functional description
device configuration
Input data to the device can be supplied from a 3x10b GBR/YPbPr input port. If the device is configured to take
data from all three channels, the data is clocked in at each rising edge of CLK. All three DACs operate at the
full clock speed of CLK.
THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
device configuration (continued)
In the case of 4:2:2 sampled data (for YPbPr) the device can be fed over either a 2x10 bit or 1x10 bit multiplexed
input port. An internal demultiplexer will route input samples to the appropriate DAC: Y at the rate of CLK, Pb
and Pr each at rate of one-half CLK.
According to ITU-BT.656 the sample sequence is Pb-Y-Pr over a 1x10 bit interface (Y-port). The sample
sequence starts at the first rising edge of CLK after BLANK has been taken high (inactive). In this case the
frequency of CLK is two times the Y conversion speed and four times the conversion speed of both Pr and Pb.
With a 2x10 bit input interface, both the Y -port and the Pr-port are sampled on every CLK rising edge. The Pr-port
carries the sample sequence Pb-Pr. The sample sequence starts at the first rising edge of CLK after BLANK
has been taken high (inactive). In this case the frequency of CLK is equal to the conversion speed of Y and 2x
the conversion speed of both Pr and Pb.
The device’s operation mode is set by the M1 and M2 mode selection terminals, according to Table 1. The
operation mode also determines the blanking level, as explained below in the sync/blanking generation
sections.
Table 1. THS8133 Configuration
M1 M2_INT†CONFIGURATION DESCRIPTION
L L GBR
3x10b–4:4:4
GBR mode 4:4:4. Data clocked in on each rising edge of CLK from G, B, and R input channels.
Blanking level corresponds to input code 0 of the DAC on all output channels.
L H YPbPr
3x10b–4:4:4
YPbPr mode 4:4:4. Data clocked in on each rising edge of CLK from Y, Pb and Pr input channels.
Blanking level corresponds to input code 0 of the DAC on the AGY channel and to input code 512 of
the DAC on the ABPb and ARPr channels when sync is inserted on all three channels (INS3_INT=H)
(see Note 1).
H L YPbPr
2x10b–4:2:2
YPbPr mode 4:2:2 2x10 bit. Data clocked in on each rising edge of CLK from Y & Pr input channels. A
sample sequence of Pb–Pr–... should be applied to the Pr port. At the first rising edge of CLK after
BLANK
is taken high, Pb should be present on this port. Blanking level corresponds to input code 0 of
the DAC on the AGY channel and to input code 512 of the DAC on the ABPr and ARPb channels (see
Note 1).
H H YPbPr
1x10b–4:2:2
YPbPr mode 4:2:2 1x10 bit (ITU-BT .656 compliant). Data clocked in on each rising edge of CLK from
Y input channel. Blanking level corresponds to input code 0 of the DAC on the AGY channel and to
input code 512 of the DAC on the ABPb and ARPr channels when sync is inserted on all three
channels (INS3_INT=H) (see Note 1).
†
M2_INT is the logic level on M2 registered on the second rising CLK edge after a L → H transition on SYNC
, as explained in Table 2.
NOTE 1: When sync is inserted on only the Y channel (INS3_INT=L), blanking level corresponds to input code 0 on all channels.
Table 2. INS3_INT/M2_INT Selection on M2
LAST
EVENT ON
SYNC
SYNC_T M1
M2
(see Note 2)
DESCRIPTION
H→L L or H X INS3_INT Sync Insertion Active: SYNC low enables sync generation on 1 (INS3_INT=L) or all 3
(INS3_INT=H) DAC outputs. SYNC_T determines the sync polarity.
L→H X X M2_INT Device mode programming active: The DAC outputs reflect the DAC inputs
(BLANK
=H) or are forced to the blanking level (BLANK=L). M2 is interpreted according
to Table 1.
X =
don’t care
NOTE 2: M1 and M2 start configuring the device as soon as they are interpreted, which is continuously for M1 (static pin) or on the second rising
edge on CLK after a transition on SYNC
for M2. M2 is interpreted as either INS3_INT or M2_INT, as shown in Table 2.
THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
programming example
Configuration of the device will normally be static in a given application. If M2_INT and INS3_INT need to be
both low or high, the M2 pin is simply tied low or high. If M2_INT and INS3_INT need to have different levels,
these can be easily derived from the signal on the SYNC pin, as shown in Table 3 and Figure 2.
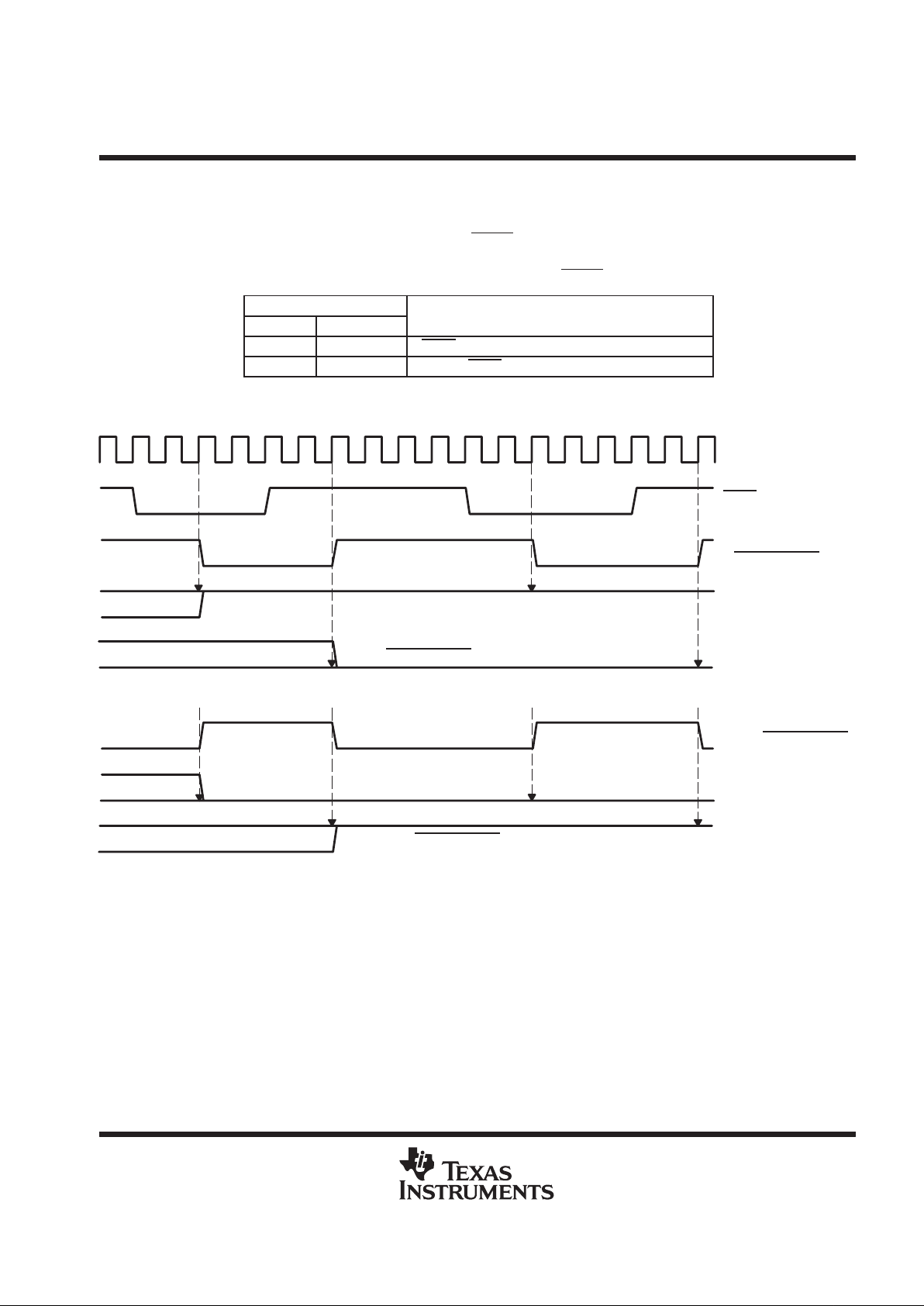
Table 3. Generating M2 From SYNC
In order to have:
M2_INT INS3_INT
Apply to M2
:
L H ...SYNC delayed by 2 CLK periods
H L ...inverted SYNC delayed by 2 CLK periods
The input formats and latencies are shown in Figures 3–5 for each operation mode.
CLK
SYNC
M2
[=SYNC_delayed
]
INS3_INT
M2_INT
M2
[=NOT SYNC_delayed
]
INS3_INT
M2_INT
if (M2 = SYNC_delayed) ⇒ M2_INT = L and INS3_INT = H)
if (M2 = NOT SYNC
_delayed) ⇒ M2_INT = H and INS3_INT = L)
Figure 2. Generating INS3_INT and M2_INT from M2
THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
programming example (continued)
T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8
RPr(0) RPr(1) RPr(2) RPr(3) RPr(4) RPr(5) RPr(6) RPr(7) RPr(8)
GY(0) GY(1) GY(2) GY(3) GY(4) GY(5) GY(6) GY(7) GY(8)
BPb(0) BPb(1) BPb(2) BPb(3) BPb(4) BPb(5) BPb(6) BPb(7) BPb(8)
CLK
RPr[9–0]
GY[9–0]
BPb[9–0]
ARPr, AGY,
ABPb output
corresponding
to RPr(0),
GY(0), BPb(0)
data path latency = 7 CLK cycles
RPr(0), GY(0), BPb(0)
registered
Figure 3. Input Format and Latency YPbPr 4:4:4 and GBR 4:4:4 Modes
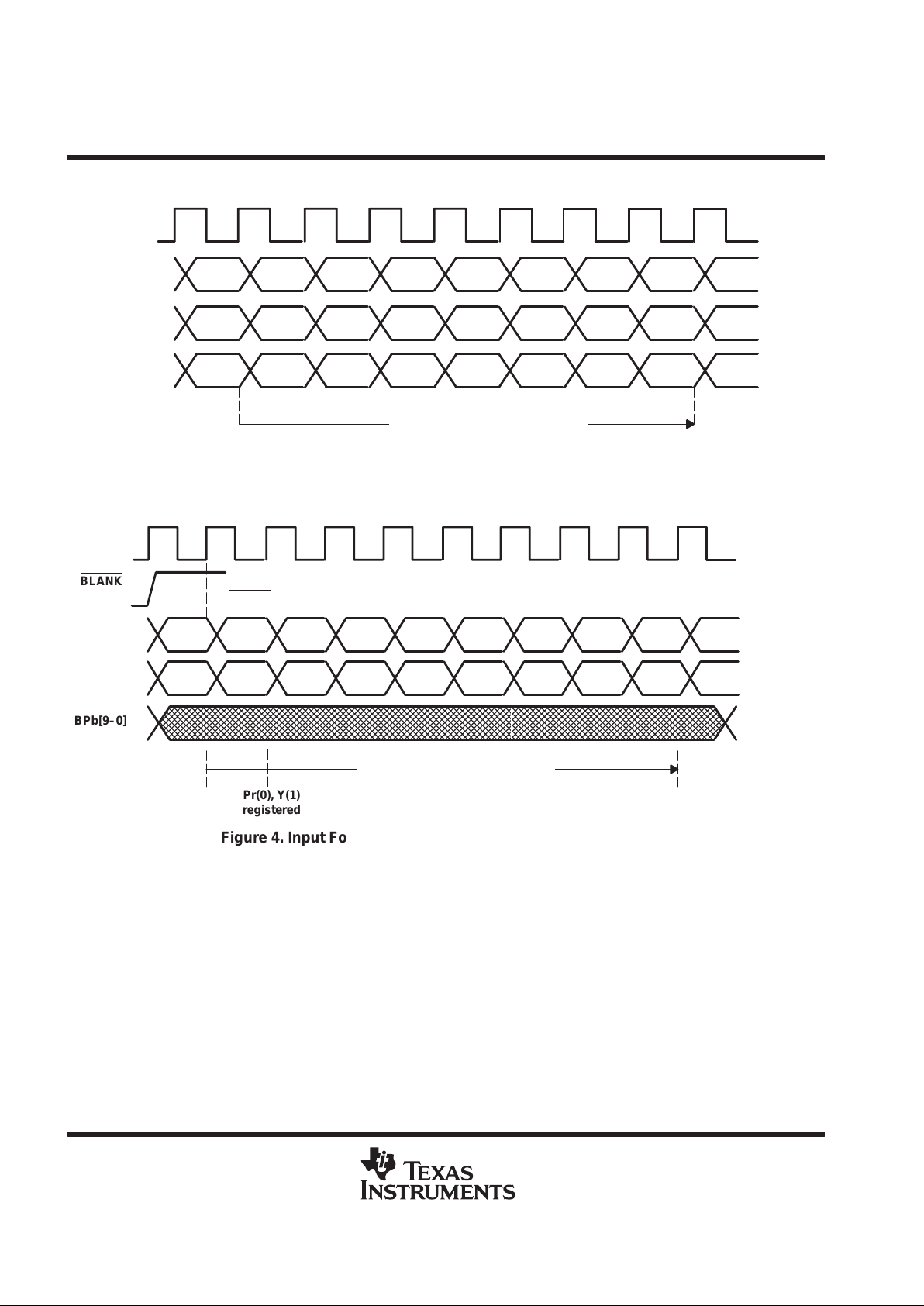
First registered sample on RPr[9–0] after L->H
on BLANK
is interpreted as Pb[9–0]
T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8
Pb(0) Pr(0) Pb(2) Pr(2) Pb(4) Pr(4) Pb(6) Pr(6) Pb(8)
RPr[9–0]
ARPr, AGY,
ABPb output
corresponding to Pr(0),
Y(0), Pb(0)
data path latency = 8 CLK cycles
Pb(0), Y(0)
registered
T9
Pr(8)
Y(0) Y(1) Y(2) Y(3) Y(4) Y(5) Y(6) Y(7) Y(8)
GY[9–0]
Y(9)
BPb[9–0]
BLANK
Pr(0), Y(1)
registered
Figure 4. Input Format and Latency YPbPr 4:2:2 2×10 Bit Mode
THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
programming example (continued)
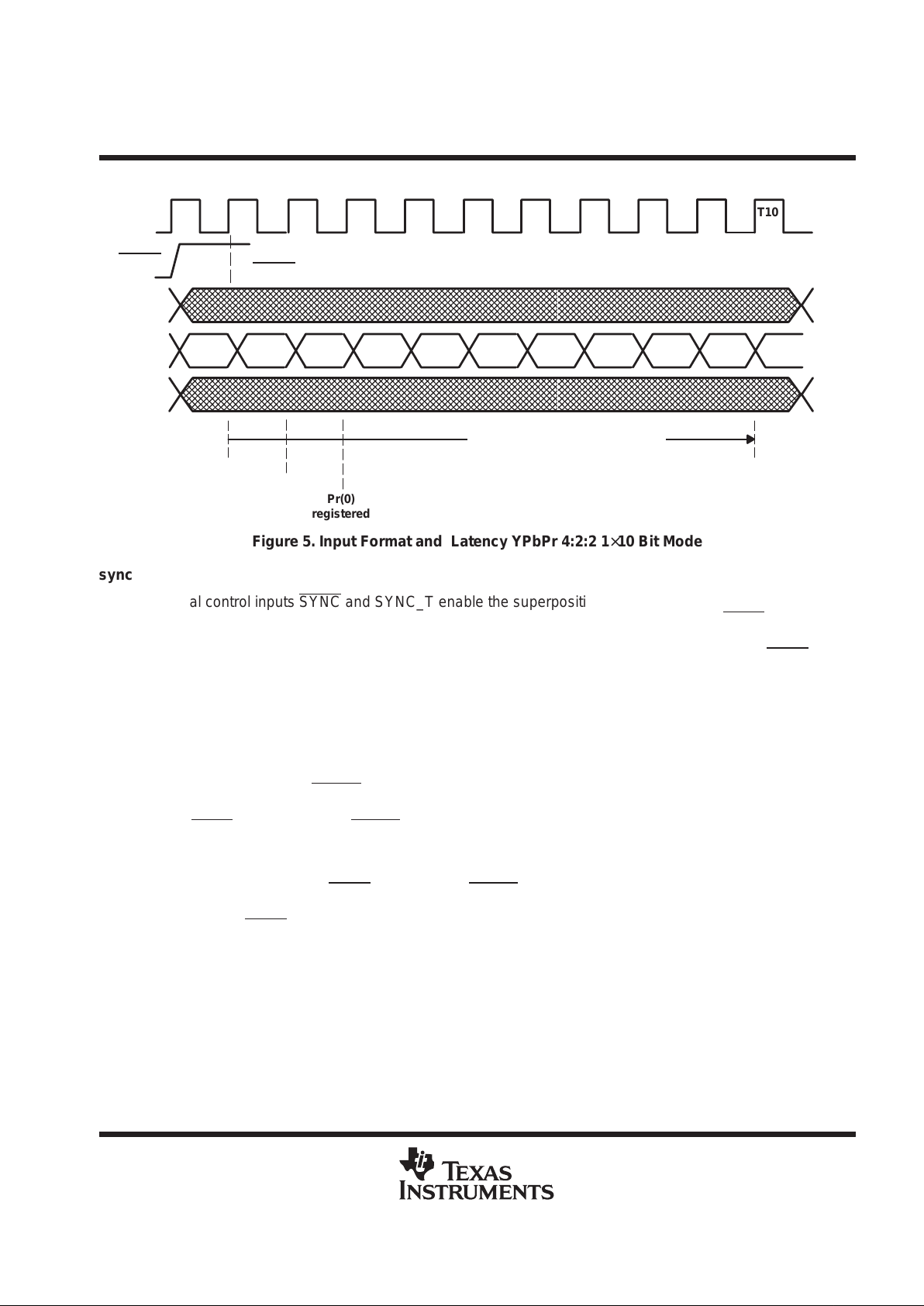
First registered sample on GYr[9–0] after L->H
on BLANK
is interpreted as Pb[9–0]
T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8
Pb(0) Y(0) Pr(0) Y(2) Pb(4) Y(4) Pr(4) Y(6) Pb(8)
RPr[9–0]
ARPr, AGY,
ABPb output
corresponding
to Pr(0),
Y(0), Pb(0)
data path latency = 9 CLK cycles
Pb(0)
registered
T9
Y(8)
GY[9–0]
BPb[9–0]
BLANK
Y(0)
registered
Pr(8)
T10
Pr(0)
registered
Figure 5. Input Format and Latency YPbPr 4:2:2 1×10 Bit Mode
sync generation
Additional control inputs SYNC
and SYNC_T enable the superposition of an additional current onto the AGY
channel or on all three channels, depending on the setting of INS3_INT . By combining the SYNC
and SYNC_T
control inputs, either bi-level negative going pulses or tri-level pulses can be generated. Depending on the timing
controls for these signals, both horizontal and vertical sync signals can be generated. Assertion of SYNC (active
low) will identify the sync period, while assertion of SYNC_T (active high) within this period will identify the
positive excursion of a tri-level sync.
Refer to the application information section for practical examples on the use of these control inputs for sync
generation.
blanking generation
An additional control input BLANK is provided that will fix the output amplitude on all channels to the blanking
level, irrespective of the value on the data input ports. However, sync generation has precedence over blanking;
that is, if SYNC is low , the level of BLANK is
don’t care
. The absolute amplitude of the blanking level with respect
to active video is determined by the GBR or YPbPr operation mode of the device. Refer to the application
information section for practical examples on the use of this control input for blank generation.
Figure 6 shows how to control SYNC, SYNC_T , and BLANK signals to generate tri-level sync levels and blanking
at the DAC output. A bi-level (negative) sync is generated similarly by avoiding the positive transition on
SYNC_T during SYNC low.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
blanking generation (continued)
Value
Corresponds
to D(0)
CLK
t
h
t
s
D(0)
t
d(D)
t
d(D)
t
d(D)
t
d(D)
SYNC
SYNC_T
BLANK
RPr[9–0]
GY[9–0]
BPb[9–0]
D(1)
Figure 6. Sync and Blanking Generation
DAC operation
The analog output drivers generate a current of which the drive level can be user-modified by choice of an
appropriate resistor value RFS, connected to the FSADJ terminal. Refer to the paragraph on output amplitude
control for details on how the output drive is affected by the operation mode of the device.
All current sources derive their amplitudes from an internal generator that produces a 1.35 V reference level.
All current source amplitudes (video, blanking, sync) also come from this reference so that the relative
amplitudes of sync/blank/video are always equal to their nominal relationships. For increased stability on the
absolute levels, the user can overdrive the reference by directly driving the V
REF
input terminal.
output amplitude control
The current drive on all three output channels and on the internal sync generator is controlled by a resistor R
FS
that must be connected between FSADJ and A VSS. In all operation modes the relative amplitudes of the current
drivers are maintained irrespective of the R
FS
value, as long as a maximum current drive capability is not
exceeded.
The sync generator is composed of different current sources that are internally routed to a corresponding DAC
output. Depending on the setting of INS3_INT during SYNC low, the sync current drive is added to either only
the green channel output (sync-on-green) if INS3_INT = L or all three channel outputs INS3_INT = H. In either
case the relative current levels, as defined below, are maintained.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
9
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
output amplitude control (continued)
The exact relationship between R
FS
and the current drive level on each channel is dependent on the operation
mode of the device (see Table 4). In GBR mode, the output drive is identical on the three channels, while in
YPbPr mode, a level shift is implemented on Pb and Pr channels. Refer to the application information section
for details on the current drive levels in each mode.
The device has an internal voltage reference derived from a bandgap reference of 1.35 V. The relationship
between the full-scale current drive level and R
FS
is given by:
I
FS
[A] = α x V
REF
[V] ÷ RFS [Ω]
where α is dependent on the operation mode of the device.
Typical operation modes are shown in Table 4 for the nominal R
FS
value. This value will produce the full-scale
current levels mentioned in Table 4 and, when terminated, voltages of standard video levels, as shown in the
applications section. The resistor value is variable provided the maximum current level on each of the DAC
outputs is not exceeded.
Table 4. THS8133 Nominal Full-Scale Currents
AGY ARPr ABPb
OPERATION MODE
DESCRIPTION
M1 M2_INT INS3_INT
I
FS
(mA)
α
I
FS
(mA)
α IFS (mA) α
GBR with sync-on-green L L L 26.67†1461/172 18.67‡1023/172 18.67 1023/172
GBR with sync-on-all L L H 26.67 1461/172 26.67 1461/172 26.67 1461/172
YPbPr with sync-on-Y
(L,H), (H,L) or (HH), ac-
L 26.67 1461/172 18.67 1023/172 18.67 1023/172
YPbPr with sync-on-all
( , ), ( , ) ( ),
cording to Tables 1 and 2
H 26.67 1461/172 18.67 1023/172 18.67 1023/172
†
IFS = 1461/172 × 1.35/430
‡
IFS = 1023/172 × 1.35/430
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage: AVDD to AVSS, DVDD to DVSS –0.5 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AVDD to DVDD, AVSS to DVSS –0.5 V to 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital input voltage range to DVSS –0.5 V to DVDD + 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, TA 0°C to 70°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
–55°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
recommended operating conditions over operating free-air temperature range, T
A
power supply
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
pp
AV
DD
4.75 5 5.25
Suppl
y v
oltage
DV
DD
3 3.3/5 5.25
V

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
recommended operating conditions over operating free-air temperature range, TA (continued)
digital and reference inputs
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
p
DVDD = 3.3 V 2 DV
DD
High-level input voltage, V
IH
DVDD = 5 V 2.4 DV
DD
V
Low–level input voltage, V
IL
DV
SS
0.8 V
Clock frequency, f
clk
0 80 MHz
Pulse duration, clock high, t
w(CLKH)
5 ns
Pulse duration, clock low, t
w(CLKL)
5 ns
Reference input voltage,† V
ref(I)
(see Note 3) 1.35 1.62 V
FSADJ resistor, R
(FS)
(see Note 3) 360 430 Ω
†
Voltage reference input applies to the externally applied voltage (overdrive condition). Internally a 2 kΩ resistor isolates the internal reference
from the externally applied voltage, if any.
NOTE 3: The combination of V
ref
and RFS can be chosen at will as long as the maximum full-scale DAC output current I
(FS)
does not exceed 120%
of its nominal value. Therefore, at fixed R
(FS)
= R
(FSnom)
, V
ref
should not be higher than the maximum value mentioned and at fixed
V
ref
= V
ref(nom)
, R
(FS)
should not be less than the minimum value mentioned.
electrical characteristics over recommended operating conditions with f
CLK
= 80 MSPS and use
of internal reference voltage V
ref
, with R
(FS)
= R
(FSnom)
(unless otherwise noted)
power supply (1 MHz, –1 dBFS digital sine simultaneously applied to all 3 channels)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
p
pp
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V 134 142
IDDOperating supply current
AVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3.3 114 121
mA
p
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V 670 710
PDPower dissipation
AVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3.3 525 565
mW
digital inputs – dc characteristics
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
I
IH
High-level input current 1 µA
I
IL
Low-level input current
AVDD = DVDD = 5 V
p
–1 µA
I
IL(CLK)
Low-level input current, CLK
Digital i
nputs and
CLK at 0 V f
or
I
IL
;
Di
gita
l inputs and CLK at 5 V for I
I
IH(CLK)
High-level input current, CLK
Digital in uts and CLK at 5 V for I
IH
–
1
1µA
C
I
Input capacitance TA = 25_C 7 pF
t
s
Data and control inputs setup time 3 ns
t
H
Data and control inputs hold time 0 ns
RGB and YPbPr 4:4:4 7
t
d(D)
Digital process delay from first registered color
p
p
‡
–
YPbPr 4:2:2 2×10 bit 8
CLK
p
()
com onent of ixel
‡
(see Figures 3–5)
YPbPr 4:2:2 1×10 bit 9
eriods
‡
This parameter is assured by design and not production tested. The digital process delay is defined as the number of CLK cycles required for
the first registered color component of a pixel, starting from the time of registering it on the input bus, to propagate through all processing and
appear at the DAC output drivers. The remaining delay through the IC is the analog delay t
d(A)
of the analog output drivers.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
11
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics over recommended operating conditions with f
CLK
= 80 MSPS and use
of internal reference voltage V
ref
, with R
(FS)
= R
(FSnom)
(unless otherwise noted) (continued)
analog (DAC) outputs
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
DAC resolution 10 10 bits
INL Integral nonlinearity Static, best fit ±0.6 ±1.2 LSB
DNL Dif ferential nonlinearity Static –0.25/0.5 ±1 LSB
Power supply ripple rejection ratio of DAC
f = 100 kHz (see Note 4) 37
PSRR
yj
output (full scale)
f = 1 MHz (see Note 4)
43
dB
XTALK Crosstalk between channels f up to 30 MHz, (see Note 5) –55 dB
V
O(ref)
Voltage reference output 1.30 1.35 1.40 V
r
o(VREF)VREF
output resistance 7K 11K 15K W
G
(DAC)
DAC gain factor
See
T able 4
Imbalance between DACs, (K
IMBAL
) See Note 6 ±5%
Imbalance between positive and negative sync,
(K
IMBAL(SYNC)
)
See Note 6 ±2%
RL = 37.5 Ω, See Note 7 1 1.2
V
O(DAC)
DAC
output compliance voltage (sync+video
)
RL = 75 Ω, See Note 7 2 2.4
V
AGY 24 26.67 28
GBR sync-on-green and YPbPr sync-on-Y/sync-
Int
ernal reference
ABPb and ARPr 17.3 18.67 19.7
yg y y
on-all
AGY 24.9 26.67 27.2
m
A
Ext
ernal reference
ABPb and ARPr 17.5 18.67 19.3
I
(FS)
AGY 24 26.67 28
Int
ernal reference
ABPb and ARPr 24 26.67 28
GBR
sync-on-a
ll
AGY 24.9 26.67 27.2
m
A
Ext
ernal reference
ABPb and ARPr 24.9 26.67 27.2
r
o
DAC output resistance See Note 10 57 92 kΩ
C
O
DAC output capacitance (pin capacitance) 8 pF
t
r(DAC)
DAC output current risetime 10% to 90% of full scale 2 ns
t
f(DAC)
DAC output current falltime 10% to 90% of full scale 2 ns
t
d(A)
Analog output delay
Measured from CLK=V
IH(min)
to 50% of full-scale
transition, See Note 8
9 ns
t
S
Analog output settling time
Measured from 50% of full scale transition on
output to output settling, within 2%, See Note 9
5 9 ns
SNR Signal -to-noise ratio
1 MHz, –1 dBFS digital sine input, measured from
0 MHz to 8.8 MHz
57.5 dB
SFDR Spurious-free dynamic range
1MHz, –1 dBFS digital sine input, measured from
0 MHz to 8.8 MHz
64 dB
BW(1 dB) Bandwidth See Note 11 40 MHz
NOTES: 4. PSRR is measured with a 0.1 µF capacitor between the COMP and AVDD terminal; with a 0.1 µF capacitor connected between the V
REF
terminal and
AVSS. The ripple amplitude is within the range 100 mVp-p to 500 mVp-p with the DAC output set to full scale and a double-terminated 75 Ω (=37.5 Ω)
load. PSRR is defined as 20 × log(ripple voltage at DAC output/ripple voltage at AVDD input). Limits from characterization only.
5. Crosstalk spec applies to each possible pair of the 3 DAC outputs. Limits from characterization only .
6. The imbalance between DACs applies to all possible pairs of the three DACs. K
IMBAL
is assured over full temperature range. In parts labeled
THS8133CPHP, K
IMBAL(SYNC)
is assured at 25°C. In parts labeled THS8133ACPHP, K
IMBAL(SYNC)
is assured over the full temperature range.
7. Nominal values at R
(FS)
= R
(FSnom)
: Maximum values at R
(FS)
= R
(FSnom)
÷ 1.2. Maximum limits from characterization only.
8. This value excludes the digital process delay , t
d(D)
. Limit from characterization only.
9. Maximum limit from characterization only
10. Limit from characterization only
11. This bandwidth relates to the output amplitude variation in excess of the droop from the sinx/x sampled system. Since the output is a sample-and-hold
signal, a sin(π × Fin ÷ F
clk
) ÷ (π × Fin ÷ F
clk
) roll-off is observed, which accounts e.g. at Fin = 40 MHz and F
clk
= 80 MSPS for –3.92 dB signal drop (
sync
droop
). The total DAC output variation (
device droop
) consists of this and an additional amount (
excess droop
) caused by the output impedance of the
device, as shown in Table 5.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
performance plots of AGY output channel at 80 MSPS and use of internal reference
–0.6
–1.2
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Static DNL (LSB)
0
0.6
DAC Code
STATIC DNL (LSB)
vs
DAC CODE
1.2
700 800 900 1023
–1.0
–0.8
–0.4
–0.2
0.2
0.4
0.8
1.0
Figure 7. Static DNL
–0.6
–1.2
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Static INL (LSB)
0
0.6
DAC Code
STATIC INL (LSB)
vs
DAC CODE
1.2
700 800 900 1023
–1.0
–0.8
–0.4
–0.2
0.2
0.4
0.8
1.0
Figure 8. Static INL

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
13
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
performance plots of AGY output channel at 80 MSPS and use of internal reference (continued)
0.6 1.2 1.7 2.3 2.9 3.4 4.0
Amplitude (dBFS)
–120
–60
Frequency (MHz)
SPECTRUM OF DAC OUTPUTS
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
vs
FREQUENCY (MHz)
0
4.5 5.1 5.7 6.2
–100
–80
–40
–20
6.8 7.3 7.9 8.5 9.0 9.6 10.1
Figure 9. Spectral Plot for 1.02 MHz Digital Sine Input at 80 MSPS
–25.0–22.2–19.4–16.6–13.8–11.0–8.2
Blank to Full-Scale Video Output (mV)
0.5
0.8
Time (ns)
DAC OUTPUT WAVEFORM
BLANK TO FULL-SCALE VIDEO OUTPUT (mV)
vs
TIME (ns)
1.1
–5.4 –2.6 0.2 3.0
0.6
0.7
0.9
1
5.8 8.6 11.4 14.2 17.0 19.8 22.6
0.4
0.3
0.2
Figure 10. DAC Output Waveform (rise/fall and settling times)
Table 5. DAC Output Amplitude Variation Over Varying Fin at F
clk
= 80 MSPS
Fin (kHz) F
clk
(MSPS) SYNC DROOP (dB) EXCESS DROOP (dB)
500 80 0 0
5000 80 –0.056 –0.02
10000 80 –0.22 –0.08
20000 80 –0.91 –0.29
30000 80 –2.11 –0.39
40000 80 –3.92 –0.40

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
14
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
configuring THS8133 for generating SMPTE compliant signals
Table 6 lists the standards that relate to the definition of analog interfaces for component video signals.
Table 6. Relevant Video Standards
STANDARD TITLE SCOPE
SMPTE 253M 3-channel RGB Analog Video Interface
Component analog video for studio applications using 525 lines, 59.94
fields, 2:1 interlace and 4:3 or 16:9 aspect ratio.
SMPTE 274M
1920x1080 Scanning and Analog and Parallel
Digital Interfaces for Multiple-Picture Rates
Definition of image format of 1920x1080 pixels inside a total raster of
1125 lines, with an aspect ratio of 16:9. Interlaced format used for 1080I
display definition of the ATSC HDTV standard.
SMPTE 296M
1280x720 Scanning, Analog and Digital
Representation and Analog Interface
Definition of image format of 1280x720 pixels inside a total raster of 750
lines, with an aspect ratio of 16:9. Progressive format used for 720P
display definition of the ATSC HDTV standard.
THS8133 can be used to generate output signals compliant to each of these standards. The configuration for
each is detailed below. In each of the cases the current output of each DAC can be converted into
standard-compliant voltage levels by connecting a double terminated 75Ω load, as shown in the top part of
Figure 11.
Ω
DACs
37.5
75Ω
(source)
75Ω
75Ω
(monitor)
Ω
DACs
50
150Ω
(source)
75Ω
75Ω
(monitor)
Figure 11. Typical Video Loads
The use of THS8133 for each of these standards is discussed next.
SMPTE 253M
This standard defines a component analog video interface using GBR color signals carried on parallel channels
for the interconnection of television equipment. The scanning structure is typically 525 lines, 59.94 fields, 2:1
interlace and 4:3 or 16:9 aspect ratio. The analog signals of this standard are suitable for the generation of, or
they can be generated from, digital video signals compliant to SMPTE 125M and SMPTE 267M by A/D or D/A
conversion respectively. Furthermore SMPTE 253M signals can be the input to NTSC composite encoders
compliant with SMPTE 170M. Table 7 lists the scope of the standards mentioned.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
15
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
SMPTE 253M (continued)
Table 7. Video Standards Compatible with SMPTE 253M
STANDARD TITLE
SMPTE 125M Component V ideo Signal 4:2:2 – Bit–Parallel Digital Interface
SMPTE 267M Bit–Parallel Digital Interface – Component V ideo Signal 4:2:2 16x9 Aspect Ratio
SMPTE 170M Composite Analog V ideo Signal – NTSC for Studio Applications
The SMPTE 253M standard defines a GBR component set with positive going signals and a maximum peak
level of 700 mV from blanking level. The green signal has a negative-going sync pulse of amplitude 300 mV
from blanking level. The dc offset, as defined by the blanking level of the signal, is 0.0 V ±1.0 V . Figure 12 shows
the waveform of the green channel, onto which the horizontal sync is inserted.
H Blanking rise time
90%
50%
10%
Sync rise time
Horizontal
reference
point
Blanking Start
to H reference
50%
90%
10%
Sync
H reference to Blanking End
50%
50%
Figure 12. SMPTE 253M Line Waveform (green channel)
For this mode, the INS3_INT control should be kept low to enable sync-on-green only and the device is put in
GBR 4:4:4 mode. This corresponds to the GBR with sync-on-green operation mode of Table 1.
Table 8 lists the THS8133 output currents that will produce compliant signals to this standard after proper
termination, together with the required input signals.
Table 8. THS8133 Signals for SMPTE 253M Compliant Operation
AGY ARPr,ABPb
LEVEL
(mA) (V) (mA) (V)
SYNC
SYNC_T
BLANK
DAC INPUT
White 26.67 1.000 18.67 0.7000 1 X 1 3FF
h
Video video+8.00 video+0.3 video video 1 X 1 data
Black 8.00 0.3000 0 0 1 X 1 000
h
Blank 8.00 0.3000 0 0 1 X 0 xxx
h
Sync 0 0 0 0 0 0 x xxx
h

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
16
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
SMPTE 253M (continued)
BLANK can be tied high in this mode if the data input is kept to 000h during the blanking time, since black and
blanking level are at identical levels. Furthermore the SYNC_T terminal remains low, since only a bi-level sync
is generated.
SMPTE 274M
This standard defines a raster scanning format of 1920×1080 pixels inside a total raster of 1125 lines and an
aspect ratio of 16:9, GBR and YPbPr color encoding formats and both analog and digital interfaces for GBR
and YPbPr formats.
With respect to the analog interface, SMPTE 274M defines the position of the start of each line at the positive
zero-crossing of a tri-level sync pulse. The sync pulse has a negative-going transition on a fixed number of clock
cycles preceding this instant and another negative transition on a fixed number of clock cycles following this
instant, as shown in Figure 13. The positive peak of sync is 300 mV; the negative peak of sync –300 mV.
The interface can carry both GBR or YPbPr signals. The tri-level horizontal sync is inserted on all analog outputs
and has identical absolute amplitude levels in all cases. For Y , black corresponds to a level of 0 V and peak white
is 700 mV. Pb and Pr on the other hand have amplitudes between –350 mV and 350 mV.
The relative amplitudes of the current sources are identical to the case of SMPTE 253M. However, in this case
a tri-level sync needs to be generated instead of a bi-level negative sync, and it needs to be present on all three
component outputs. THS8133 supports the tri-level sync via an additional internal current source, activated by
asserting SYNC_T. The sync insertion on all outputs is under the control of the INS3_INT pin. When asserted
(high), the sync is inserted on all three output channels.
0
H
Analog
Waveform
(Y’R’G’B’)
Duration in
Reference
Clock Period
44T 44T
1920T
Figure 13. SMPTE 274M Line Waveform
†
†
This figure is for illustration purposes only. Consult the latest SMPTE 274M standard when designing a compliant system.
Figure 14 shows the relative amplitudes of video and horizontal/vertical sync. The level of vertical sync (broad
pulse) is identical to the negative excursion of horizontal sync and therefore can be generated by the same
current source on THS8133 by appropriately asserting the sync control inputs.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
17
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
SMPTE 274M (continued)
+300
0
–300
+350
+300
0
–300
–350
+700
+300
0
–300
Blanking
Broad Pulse
O
H
Vertical
Sync
P’B, P’
r
Y’,R’,G’,B’
O
H
Figure 14. SMPTE 274M Analog Interface Horizontal Timing Details
†
†
This figure is for illustration purposes only. Consult the latest SMPTE 274M standard when designing a compliant system.
For GBR operation, Table 9 lists the THS8133 full-scale output currents that produce compliant signals to the
standard after proper termination. These amplitudes are valid also in YPbPr mode for the Y channel. For GBR
operation, the device needs to be configured with INS3_INT high, corresponding to the GBR with sync-on-all
operation mode of Table 1.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
18
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
SMPTE 274M (continued)
Table 9. THS8133 Signals for SMPTE 274M Compliant Operation on GBR and Y Channels
GBRY
LEVEL
(mA) (V)
SYNC
SYNC_T
BLANK
DAC INPUT
White 26.67 1.000 1 X 1 3FF
h
Video video+8.00 video+0.3 1 X 1 data
Sync Pos 16.00 0.600 0 1 X xxx
h
Black 8.00 0.3000 1 X 1 000
h
Blank 8.00 0.3000 1 X 0 xxx
h
Sync Neg 0 0 0 0 X xxx
h
In the YPbPr mode of this standard, the sync is centered around the center span of the video amplitude levels,
as shown in Figure 14. So the current for Pb and Pr is down-shifted with respect to Y to accommodate the
minimum data level at 0 mA. Thus, an input code of 00h corresponds now to an output drive of 0 mA while the
negative sync level is at 1.33 mA, corresponding to 50 mV. The Pb and Pr data input format is offset binary.
Table 10 lists the THS8133 full-scale output currents for Pb and Pr channels in the YPbPr operation mode of
the device. The operation mode corresponds to YPbPr with sync-on-all of Table 1.
Table 10. THS8133 Signals for SMPTE 274M Compliant Operation on Pb and Pr Channels
Pb, Pr
LEVEL
(mA) (V)
SYNC
SYNC_T
BLANK
DAC INPUT
Max 18.67 0.7000 1 X 1 3FF
h
Video video video 1 X 1 data
Sync Pos 17.33 0.650 0 1 X xxx
h
Blank 9.33 0.350 1 X 0 xxx
h
Sync Neg 1.33 0.050 0 0 x xxx
h
Min 0 0 1 X 1 000
h
SMPTE 296M
This standard defines a raster scanning format of 1280x720 and an aspect ratio of 16:9, the analog and digital
representation, and the definition of an analog interface. Both GBR and YPbPr component color encoding can
be used.
With respect to the sync and video level definition, this standard is analogous to SMPTE 274M with the use of
a tri-level sync pulse. Therefore, for the generation of output signals compliant to this standard, refer to the
configuration of THS8133 for SMPTE 274M.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
19
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
comparison to EIA RS-343/RS-170 levels
Traditionally, video amplitude levels are specified according to the EIA RS-343 or RS-170 standards. RS-343
uses a bi-level negative going sync. Also, there is a difference between the reference blanking and black video
level. Figure 15 shows the relative amplitudes and the current drives that would be needed to generate
compliant relative amplitudes with a double-terminated 75-Ω load, as is specified for RS-343. RS-170 compliant
levels can be reached using the same current sources but a different 150-Ω source termination resistor , which
brings the load to 150 || 75 Ω = 50 Ω. In this case a blank-to-white level of approximately 1 V is reached
(0.714 V × 50 ÷ 37.5) as required by RS-170.
7.5 IRE
40 IRE
92.5 IRE
BLACK Level
BLANK Level
SYNC Level
With Sync Insertion Without Sync Insertion
VmA VmA
1.00026.67 0.71419.05
0.3409.05 0.3401.44
0.2867.62 00
00
Figure 15. RS-343 Video Definition
The video signal contains 140 IRE, equal to 1 Vpp. This is split into 40 IRE for the composite sync, 7.5 IRE for
blanking-to-black and 92.5 IRE for the active video portion.
designing with PowerPAD
The THS8133 is housed in a high-performance, thermally enhanced, 48-pin PowerP AD package (TI package
designator: 48PHP). Use of the PowerP AD package does not require any special considerations except to note
that the PowerP AD which is an exposed die pad on the bottom of the device, is a metallic thermal and electrical
conductor. Therefore, if not implementing the PowerPAD PCB features, solder masks (or other assembly
techniques) may be required to prevent any inadvertent shorting by the exposed PowerPAD of connection
etches or vias under the package. The recommended option, however, is not to run any etches or signal vias
under the device, but to have only a grounded thermal land as explained below. Although the actual size of the
exposed die pad may vary, the minimum size required for the keepout area for the 48-pin PHP PowerPAD
package is 7 mm × 7 mm.
It is recommended that there be a thermal land, which is an area of solder-tinned-copper, underneath the
PowerP AD package. The thermal land will vary in size, depending on the PowerPAD package being used, the
PCB construction, and the amount of heat that needs to be removed. In addition, the thermal land may or may
not contain numerous thermal vias, depending on PCB construction.
More information on this package and other requirements for using thermal lands and thermal vias are detailed
in the TI application note
PowerP AD Thermally Enhanced Package Application Report
, TI literature number
SLMA002, available via the TI Web pages beginning at URL: http://www.ti.com.

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
20
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
designing with PowerPAD (continued)
For the THS8133 this thermal land should be grounded to the low impedance ground plane of the device. This
improves not only thermal performance but also the electrical grounding of the device. It is also recommended
that the device ground terminal landing pads be connected directly to the grounded thermal land. The land size
should be as large as possible without shorting device signal terminals. The thermal land may be soldered to
the exposed PowerPAD using standard reflow soldering techniques.
While the thermal land may be electrically floated and configured to remove heat to an external heat sink, it is
recommended that the thermal land be connected to the low impedance ground plane for the device.
Table 11 lists a comparison for thermal resistances between the PowerPAD package (48PHP) used for this
device and a regular 48-pin TQFP package (48PFB).
Table 11. Junction-Ambient and Junction-Case Thermal Resistances
48PHP PowerPAD vs 48PFB
REGULAR TQFP
AIRFLOW IN lfm
0 150 250 500
θJA (°C/W) 48PHP 29.1 23.1 21.6 19.9
θ
JC
(°C/W) 48PHP 1.14
θ
J
A
(°C/W) 48PFB 97.5 78.3 71.6 63.5
θ
J
C
(°C/W) 48PFB 19.6

THS8133, THS8133A
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204B – APRIL 1999 – REVISED OCT OBER 1999
21
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
PHP (S-PQFP-G48) PowerPAD PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK
Thermal Pad
(see Note D)
Gage Plane
0,13 NOM
0,25
0,45
0,75
Seating Plane
4146927/A 01/98
0,17
0,27
24
25
13
12
SQ
36
37
7,20
6,80
48
1
5,50 TYP
SQ
8,80
9,20
1,05
0,95
1,20 MAX
0,50
M
0,08
0,08
0°–7°
0,05
0,15
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusions.
D. The package thermal performance may be enhanced by bonding the thermal pad to an external thermal plane. This pad is electrically
and thermally connected to the backside of the die and possibly selected leads.
E. Falls within JEDEC MO-153
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICA TIONS IS UNDERSTOOD T O
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...