Sipex Corporation SPX2950ACN-3.0, SPX2950ACN-3.3, SPX2950ACN-5.0, SPX2950CN-3.0, SPX2950CN-3.3 Datasheet
...
|
SPX2950/SPX2951 |
|
|
150mA Low Dropout Voltage Regulators |
|
FEATURES |
APPLICATIONS |
• 5.0V, 3.3V, and 3.0V Versions at 150mA Output |
• Battery Powered Systems |
• Very Low Quiescent Current |
• Cordless Telephones |
• Low Dropout Voltage |
• Radio Control Systems |
• Extremely Tight Load and Line Regulation |
• Portable/Palm Top/Notebook Computers |
• Very Low Temperature Coefficient |
• Portable Consumer Equipment |
• Needs Only 1 F for Stability |
• Portable Instrumentation |
• Current & Thermal Limiting |
• Avionics |
• Unregulated DC Input can Withstand -20V Reverse Battery |
• Automotive Electronics |
and +60V Positive Transients |
• SMPS Post-Regulator |
• Similar Replacement With Higher IOUT for LP2950/LP2951 Sockets |
• Voltage Reference |
SPX2951 Versions Only
•Error Flag Warns of Output Dropout
•Logic-Controlled Electronic Shutdown
•Output Programmable From 1.24V to 29V
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The SPX2950 and SPX2951 are low power voltage regulators. These devices are an excellent choice for use in battery-powered applications such as cordless telephones, radio control systems, and portable computers. The SPX2950 and SPX2951 feature very low quiescent current and very low dropout voltage (Typ. 50mV at light load and 380mV at 100mA). This include a tight initial tolerance of 0.5% typ., extremely good load and line regulation of 0.05% typ. and very low output temperature coefficient, making the SPX2950/SPX2951 useful as a low-power voltage reference. Other key additional features of this device includes higher output current (150mA), positive transient protection up to 60V (Load dump), and the ability to survive an unregulated input voltage transient of -20V below ground (reverse battery).
The error flag output feature is used as power-on reset for warning of a low output voltage, due to falling voltage input of batteries. Another feature is the logic-compatible shutdown input which enables the regulator to be switched ON and OFF. The SPX2950 is offered in a 3-Pin TO-92 package compatible with other 5V regulators. The SPX2951 is also available in 8-Pin Plastic, SO-8 and TO-99 metal can packages.
The regulator output voltage may be pin-strapped for a 5V, 3.3V and 3.0V or programmed from 1.24V to 29V with an external pair of resistors. Look for SPX2954 for 250mA and SPX2955 for 350mA.
PIN CONNECTIONS
8-Pin Surface Mount |
TO-92 (N) |
|
OUTPUT |
1 |
|
8 |
INPUT |
2 |
3 |
SENSE |
2 |
|
|
1 |
||
ALPHA |
7 |
FEEDBACK |
|
|
||
|
SPX2951 |
|
|
|
||
SHUTDOWN |
3 |
AS2930 |
6 |
5V or 3.3V TAP |
|
|
GROUND |
|
|
|
4 |
5 |
|
|
|
ERROR |
VOUT |
VIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Top View
Bottom View
Rev. 10/30/00

SPX2950/SPX2951
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Power Dissipation.......................................... |
Internally Limited |
Lead Temp. (Soldering, 5 Seconds) ................................ |
260°C |
Storage Temperature Range ......................... |
-65°C to +150°C |
Operating Junction Temperature Range |
|
SPX2951................................................ |
-55°C to +150°C |
SPX2950AC/SPX2950C |
|
SPX2951AC/SPX2951C ....................... |
-40°C to +125°C |
Input Supply Voltage (Survival) |
.........................-20 to +60V |
Feedback Input Voltage ..................................... |
-1.5 to +30V |
Shutdown Input Voltage..................................... |
-0.3 to +30V |
Error Comparator Output ................................... |
-0.3 to +30V |
ESD Rating ............................................................. |
2KV Min |
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS at VS=15V, TA=25°C, unless otherwise specified.
PARAMETER |
CONDITIONS |
|
SPX2951 |
|
SPX2950C/SPX2951C |
SPX2950C/SPX2951C |
UNITS |
||||||
|
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
|
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
|
Max |
|
3.0V Version |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage |
TJ = 25°C |
2.985 |
3.0 |
3.015 |
2.985 |
|
3.0 |
3.015 |
2.970 |
3.0 |
|
3.030 |
V |
|
-25°C < TJ < 85°C |
|
|
|
2.970 |
|
3.0 |
3.030 |
2.955 |
3.0 |
|
3.045 |
|
|
Full Operating Temperature |
2.964 |
|
3.036 |
2.964 |
|
3.0 |
3.036 |
2.940 |
3.0 |
|
3.060 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Output Voltage |
100mA < IL < 150mA |
2.955 |
3.0 |
3.045 |
2.958 |
|
3.0 |
3.042 |
2.928 |
3.0 |
|
3.072 |
V |
|
TJ < TJMAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.3V Version |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage |
TJ = 25°C |
3.284 |
3.3 |
3.317 |
3.284 |
|
3.3 |
3.317 |
3.267 |
3.3 |
|
3.333 |
V |
|
-25°C < TJ < 85°C |
|
|
|
3.267 |
|
3.3 |
3.333 |
3.251 |
3.3 |
|
3.350 |
|
|
Full Operating Temperature |
3.260 |
|
3.340 |
3.260 |
|
3.3 |
3.340 |
3.234 |
3.3 |
|
3.366 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Output Voltage |
100mA < IL < 150mA |
3.251 |
3.3 |
3.350 |
3.254 |
|
3.3 |
3.346 |
3.221 |
3.3 |
|
3.379 |
V |
|
TJ < TJMAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0V Version |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage |
TJ = 25°C |
4.975 |
5.0 |
5.025 |
4.975 |
|
5.0 |
5.025 |
4.95 |
5.0 |
|
5.05 |
V |
|
-25°C < TJ < 85°C |
|
|
|
4.95 |
|
5.0 |
5.050 |
4.925 |
5.0 |
|
5.075 |
|
|
Full Operating Temperature |
4.94 |
|
5.06 |
4.94 |
|
5.0 |
5.06 |
4.90 |
5.0 |
|
5.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Output Voltage |
100 A < IL < 150mA |
4.925 |
5.0 |
5.075 |
4.93 |
|
5.0 |
5.07 |
4.88 |
5.0 |
|
5.12 |
V |
|
TJ < TJMAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All Voltage Options |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage Temperature |
(Note 1) |
|
20 |
120 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
ppm/° |
Coefficient |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
Line Regulation (Note 3) |
6V < VIN < 30V (Note 4) |
|
0.03 |
0.1 |
|
|
0.03 |
0.1 |
|
0.04 |
|
0.2 |
% |
Load Regulation (Note 3) |
100mA < IL < 150mA |
|
0.04 |
0.1 |
|
|
0.04 |
0.1 |
|
0.1 |
|
0.2 |
% |
Dropout Voltage (Note 5) |
IL = 100 A |
|
50 |
80 |
|
|
50 |
80 |
|
50 |
|
80 |
mV |
|
IL = 100mA |
|
380 |
450 |
|
|
380 |
450 |
|
380 |
|
450 |
|
|
IL = 150mA |
|
450 |
500 |
|
|
450 |
500 |
|
450 |
|
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ground Current |
IL = 100 A |
|
150 |
170 |
|
|
150 |
170 |
|
150 |
|
170 |
A |
|
IL = 100mA |
|
3 |
6 |
|
|
3 |
6 |
|
3 |
|
6 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
mA |
|||||||
|
IL = 150mA |
|
5 |
8 |
|
|
5 |
8 |
|
5 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Limit |
VOUT = 0 |
|
130 |
200 |
|
|
130 |
200 |
|
130 |
|
200 |
mA |
Thermal Regulation |
|
|
0.05 |
0.2 |
|
|
0.05 |
0.2 |
|
0.05 |
|
0.2 |
%/W |
Output Noise, |
CL = 1 F |
|
430 |
|
|
|
430 |
|
|
430 |
|
|
Vrms |
10Hz to 100KHz |
CL = 200 F |
|
160 |
|
|
|
160 |
|
|
160 |
|
|
Vrms |
|
CL = 13.3 F |
|
100 |
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
100 |
|
|
Vrms |
|
(bypass = 0.01 F pins 6 to 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(SPX2951) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8-Pin Version Only |
|
|
SPX2951 |
|
|
|
SPX2951AC |
|
|
SPX2951C |
|
|
|
Reference Voltage |
|
1.22 |
1.235 |
1.25 |
1.22 |
|
1.235 |
1.25 |
1.21 |
1.23 |
|
1.26 |
V |
Reference Voltage |
Over Temperature (Note 6) |
1.19 |
|
1.27 |
1.19 |
|
|
1.27 |
1.18 |
|
|
1.28 |
V |
Rev. 10/30/00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPX2950/SPX2951 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPX2950AC |
SPX2950C |
|
|
|||
PARAMETER |
CONDITIONS |
|
|
SPX2951 |
|
|
SPX2951AC |
SPX2951C |
|
|
|||
|
(Note 2) |
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
|
Typ |
Min |
|
Typ |
UNITS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Max |
|
|
Max |
|
|
|
|
8-Pin Version only (Continued) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feedback Pin Bias Current |
|
|
|
40 |
60 |
|
|
40 |
60 |
|
40 |
60 |
nA |
Reference Voltage Temperature |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
50 |
|
ppm/°C |
Coefficient |
( Note 7 ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feedback Pin Bias Current |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
0.1 |
|
nA/°C |
Temperature Coefficient |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Error Comparator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
Output Leakage Current |
VOH = 30V |
|
|
0.01 |
1 |
|
|
0.01 |
1 |
|
0.01 |
1 |
|
Output Low Voltage |
VIN = 4.5V |
|
|
150 |
250 |
|
|
150 |
250 |
|
150 |
250 |
mV |
|
IOL = 400 A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Upper Threshold Voltage |
(Note 8) |
|
40 |
60 |
|
|
40 |
60 |
|
40 |
60 |
|
mV |
Lower Threshold Voltage |
(Note 8) |
|
|
75 |
95 |
|
|
75 |
95 |
|
75 |
95 |
mV |
Hysteresis |
(Note 8) |
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
15 |
|
mV |
Shutdown Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input logic Voltage |
Low (Regulator ON) |
|
1.3 |
0.6 |
|
|
1.3 |
0.7 |
|
1.3 |
0.7 |
V |
|
|
High (Regulator OFF) |
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
V |
|
Shut down Pin Input Current |
VS = 2.4V |
|
|
30 |
50 |
|
|
30 |
50 |
|
30 |
50 |
A |
|
VS = 30V |
|
|
675 |
800 |
|
|
675 |
800 |
|
675 |
800 |
A |
Regulator Output Current in |
(Note 9) |
|
|
3 |
10 |
|
|
3 |
10 |
|
3 |
10 |
A |
Shutdown |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note 1: Output or reference voltage temperature coefficients defined as the worst case voltage change divided by the total temperature range. |
|
|
|||||||||||
Note 2: Unless otherwise specified all limits guaranteed for TJ = 25°C, VIN = 6V, IL = 100 A and CL = 1 F. Additional conditions for the 8-pin versions are |
|
||||||||||||
feedback tied to 5V Tap and output tied to output sense (VOUT = 5V) and VSHUTDOWN ≤ 0.8V. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 3: Regulation is measured at constant junction temperature, using pulse testing with a low duty cycle. Changes in output voltage due to heating effects are |
|||||||||||||
covered under the specification for thermal regulation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note 4: Line regulation for the SPX2951 is tested at 150°C for IL = 1 mA. For IL = 100 A and TJ = 125°C, line regulation is guaranteed by design to 0.2%. See |
|||||||||||||
typical performance characteristics for line regulation versus temperature and load current. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 5: Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 100 mV below its nominal value measured at 1V differential at |
|||||||||||||
very low values of programmed output voltage, the minimum input supply voltage of 2V ( 2.3V over temperature) must be taken into account. |
|
|
|||||||||||
Note 6: VREF ≤VOUT ≤ (VIN - 1V), 2.3 ≤VIN≤30V, 100 A≤IL≤ 150 mA, TJ ≤ TJMAX. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Note 7: Output or reference voltage temperature coefficient is defined as the worst case voltage change divided by the total temperature range. |
|
|
|||||||||||
Note 8: Comparator thresholds are expressed in terms of a voltage differential at the feedback terminal below the nominal reference voltage measured at 6V input. To |
|||||||||||||
express these thresholds in terms of output voltage change, multiply by the error amplifier gain = VOUT/VREF = (R1 + R2)/R2. For example, at a programmed output |
|||||||||||||
voltage of 5V, the Error output is guaranteed to go low when the output drops by 95 mV x 5V/1.235 = 384 mV. Thresholds remain constant as a percent of VOUT as |
|||||||||||||
VOUT is varied, with the dropout warning occurring at typically 5% below nominal, 7.5% guaranteed. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Note 9: VSHUTDOWN ≥ 2V, VIN ≤ 30V, VOUT =0, Feedback pin tied to 5V Tap. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Note 10: All typical values are not guaranteed. The value could vary from lot to lot. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
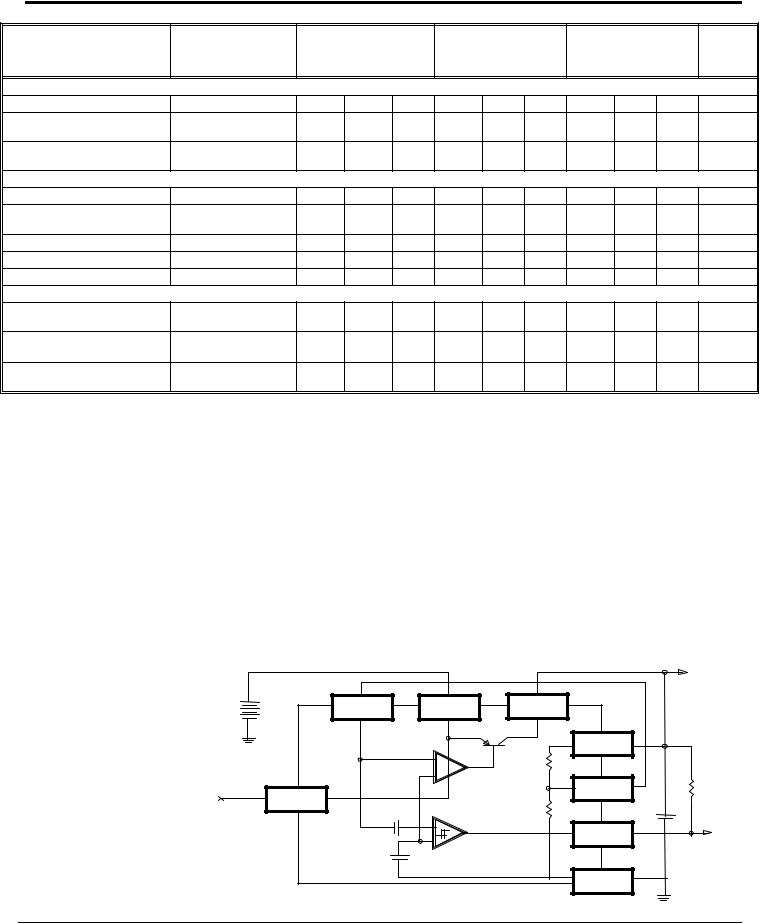
BLOCK DIAGRAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNREGULATED DC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
8 |
|
1 |
|
|
5V @ 150mA |
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAX |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FEEDBACK |
|
INPUT |
|
OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SENSE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
180kΩ .. |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
_ |
ERROR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FROM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMPLIFIER |
|
|
5V TAP |
|
330kΩ |
||
|
CMOS OR |
SHUTDOWN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
TTL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60kΩ .. |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
1µF.. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
______ |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
60 mV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
_ |
ERROR |
|
|
ERROR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
TO CMOS |
|
||
|
|
|
|
1.23V |
|
COMPARATOR |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TTL |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GROUND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPX2950 and SPX2951 Block |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Rev. 10/30/00

SPX2950/SPX2951
APPLICATION HINTS
EXTERNAL CAPACITORS
The stability of the SPX2950/SPX2951 requires a 1.0µF or greater capacitor between output and ground. Oscillation could occur without this capacitor. Most types of tantalum or aluminum electrolytic works fine here. For operations below - 25°C solid tantalum is recommended since many aluminum types have electrolytes that freeze at about -30°C. The ESR of about 5Ω or less and resonant frequency above 500kHz are the most important parameters in the value of the capacitor. The capacitor value can be increased without limit.
At lower values of output current, less output capacitance is required for stability. For the currents below 10mA the value of the capacitor can be reduced to 0.5µF and 0.15µF for 1mA. More output capacitance is needed for the 8-pin version at voltages below 5V since it runs the error amplifier at lower gain. At worst case 5µF or greater must be used for the condition of 150mA load at 1.23V output.
The SPX2950, unlike other low dropout regulators will remain stable in regulation with no load in addition to the internal voltage divider. This feature is especially important in applications like CMOS RAM keep-alive. When setting the output voltage of the SPX2951 version with external resistors, a minimum load of 1uA is recommended.
If there is more than 10 inches of wire between the input and the AC filter capacitor or if a battery is used as the input then a 1µA tantalum or aluminum electrolytic capacitor should be placed from the input to the ground.
Instability can occur if there is stray capacitance to the SPX2951 feedback terminal (pin 7). This could cause more problems when using a higher value of external resistors to set the output voltage. This problem can be fixed by adding a 100pF capacitor between output and feedback and increasing the output capacitor to at least 3.3µF.
ERROR DETECTION COMPARATOR OUTPUT
The Comparator produces a logic low output whenever the SPX2951 output falls out of regulation by more than around 5%. This is around 60mV offset divided by the 1.235 reference voltage. This trip level remains 5% below normal regardless of the programmed output voltage of the regulator. Figure 1 shows the timing diagram depicting the ERROR signal and the regulator output voltage as the SPX2951 input is ramped up and down. The ERROR signal becomes low at around 1.3V input, and goes high around 5V input (input voltage at which VOUT = 4.75 ). Since the SPX2951’s dropout voltage is load dependent, the input voltage trip point (around 5V) will vary with the load current. The output voltage trip point (approx. 4.75V) does not vary with load.
.
The error comparator has an open-collector output which requires an external pull-up resistor. Depending on the system requirements the resistor may be returned to 5V output or other supply voltage in determining the value of this resistor, note that the output is rated to sink 400µA, this value adds to battery drain in a low battery condition. Suggested values range from 100K to 1MΩ. If the output is unused this resistor is not required.
PROGRAMMING THE OUTPUT VOLTAGE OF SPX2951
The SPX2951 may be pin-strapped for 5V using its internal voltage divider by tying Pin 1 (output) to Pin 2 (sense) and Pin 7 (feedback) to Pin 6 (5V Tap). Also it may be programmed for any output voltage between its 1.235V reference and its 30V maximum rating . As seen in Figure 2, an external pair of resistors is required.
Refer to the below equation for the programming of the output voltage.
VOUT = VREF × ( 1 + R1/R2 )+ IFBR1
The VREF is 1.235 and IFB is the feedback bias current, nominally
-20 nA. The minimum recommended load current of 1µA forces an upper limit of 1.2 MΩ on value of R2. If no load presented the IFB produces an error of typically 2% in VOUT which may be eliminated at room temperature by trimming R1. To improve the accuracy choose the value of R2 = 100k this reduces the error by 0.17% and increases the resistor program current by 12µA. Since the SPX2951 typically draws 60µA at no load with Pin 2 open-circuited this is a small price to pay.
REDUCING OUTPUT NOISE
It may be an advantage to reduce the AC noise present at the output. One way is to reduce the regulator bandwidth by increasing the size of the output capacitor. This is the only way that noise can be reduced on the SPX2950 but is relatively inefficient, as increasing the capacitor from 1µF to 220 µF only decreases the noise from 430µV to
160µVRMS. for a 100kHz bandwidth at 5V output.
Noise could also be reduced fourfold by a bypass capacitor across R1, since it reduces the high frequency gain from 4 to unity. Pick
CBYPASS 1 / 2πR1 × 200 Hz
or choose 0.01µF. When doing this, the output capacitor must be increased to 3.3µF to maintain stability. These changes reduce the output noise from 430µV to 100µVRMS. for a 100kHz bandwidth at 5V output. With the bypass capacitor added, noise no longer scales with output voltage so that improvements are more dramatic at higher output voltages.
Rev. 10/30/00
 Loading...
Loading...