Page 1

VisorALARM
ARLY Interface
Doc. DM359-I Ver. 2.0
May, 2007
Page 2

INDEX
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION....................................................................................1
1. Introduction to the ARLY Interface ........................................................................................................... 2
2. Introducing the SEPI Interface ................................................................................................................... 3
CHAPTER 2 ARLY INTERFACE CONFIGURATION................................................. 4
1. Initial Configuration..................................................................................................................................... 7
2. Command set................................................................................................................................................. 8
2.1. ALARM-RECEIVER ............................................................................................................................ 8
a) ALARM-RECEIVER PROTOCOL ......................................................................................................8
b) ALARM-RECEIVER RECEIVER-ID .................................................................................................. 9
c) ALARM-RECEIVER LINE-ID............................................................................................................. 9
d) ALARM-RECEIVER LINK-TEST-TIMER ......................................................................................... 9
e) ALARM-RECEIVER PARAMETERS ................................................................................................. 9
f) ALARM-RECEIVER BLOCK............................................................................................................10
2.2. AUTOMATION-SOFTWARE-REQUIRED ......................................................................................11
2.3. BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER......................................................................................................... 11
a) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER TYPE .............................................................................................. 11
b) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER ADDRESS-MAIN.......................................................................... 12
c) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER MAINTENANCE-PASSWORD.................................................... 12
d) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER SYNC-PORT.................................................................................. 12
e) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLL-TIME ................................................................................... 12
f) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLL-FAILURE-TIME................................................................. 13
g) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER RETRIES-NUMBER .....................................................................13
h) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER RETRY-TIME................................................................................ 13
i) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLLING-SYNC-TIME................................................................ 14
2.4. CFG-PATTERN ..................................................................................................................................15
a) CFG-PATTERN n DEFAULT ............................................................................................................ 15
b) CFG-PATTERN n INSTALATOR-PASSWORD...............................................................................16
c) CFG-PATTERN n AUTOMATION-INSTALATION-PASSWORD................................................. 16
d) CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-IP ...................................................................................................... 16
e) CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-UDP-PORT ......................................................................................16
f) CFG-PATTERN n USR PASSWORD................................................................................................ 17
g) CFG-PATTERN n MIP-PASSWORD ................................................................................................17
h) CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-PASSWORD.................................................................................... 18
i) CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER.......................................................................................... 18
j) CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES...................................................................................... 19
k) CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER........................................................................ 19
l) CFG-PATTERN n PHONE-LENGTH ................................................................................................ 20
m) CFG-PATTERN n ALARM-TX-RETRIES........................................................................................ 20
n) CFG-PATTERN n CALLBACK-PHONE ..........................................................................................21
o) CFG-PATTERN n BCK-RECEIVER-IP............................................................................................. 21
p) CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER................................................................................ 21
q) CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES ............................................................................ 22
r) CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES -TIME ................................................................ 22
s) CFG-PATTERN n LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE..................................................................................... 22
- ii -
Page 3

t) CFG-PATTERN n MNT-IP-ADDRESS ............................................................................................. 23
u) CFG-PATTERN n MNT-PASSWORD............................................................................................... 23
2.5. DESCRIPTION.................................................................................................................................... 24
2.6. IO-CONF ............................................................................................................................................. 24
a) IO-CONF INPUTx............................................................................................................................... 24
b) IO-CONF OUTPUT............................................................................................................................. 25
2.7. LIST..................................................................................................................................................... 25
a) LIST ALL ............................................................................................................................................26
b) LIST ALARM-RECEIVER................................................................................................................. 28
c) LIST BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER ............................................................................................... 28
d) LIST CFG-PATTERN......................................................................................................................... 29
e) LIST IO-CONF.................................................................................................................................... 30
f) LIST MONITOR-IP-ADDR................................................................................................................ 30
g) LIST MIP............................................................................................................................................. 31
h) LIST PRIORITY-STANDARD........................................................................................................... 32
i) LIST SERIAL-PARAMETERS ..........................................................................................................32
j) LIST SMS ............................................................................................................................................ 33
k) LIST SUPERVISION .......................................................................................................................... 33
l) LIST USER-DEFINED-EVENTS ....................................................................................................... 33
2.8. LOG ..................................................................................................................................................... 34
a) LOG CLEAR .......................................................................................................................................34
b) LOG INFO........................................................................................................................................... 34
c) LOG SAVE.......................................................................................................................................... 35
2.9. MIP ...................................................................................................................................................... 36
a) MIP accnt Default ................................................................................................................................ 37
b) MIP accnt SERIAL-NUMBER............................................................................................................ 37
c) MIP accnt RECEIVER-IP.................................................................................................................... 38
d) MIP accnt RECEIVER-UDP-PORT.................................................................................................... 38
e) MIP accnt USR-PASSWORD .............................................................................................................38
f) MIP accnt MIP-PASSWORD.............................................................................................................. 39
g) MIP accnt RECEIVER-PASSWORD..................................................................................................39
h) MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER....................................................................................................... 39
i) MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES ................................................................................................... 40
j) MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER...................................................................................... 40
k) MIP accnt PHONE-LENGTH .............................................................................................................41
l) MIP accnt ALARM-TX-RETRIES......................................................................................................41
m) MIP accnt CALLBACK-PHONE........................................................................................................41
n) MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER.............................................................................................. 42
o) MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES.......................................................................................... 42
p) MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER ............................................................................ 43
q) MIP accnt RESET................................................................................................................................ 43
r) MIP accnt LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE .................................................................................................. 43
s) MIP accnt MNT-IP-ADDRESS........................................................................................................... 44
t) MIP accnt MNT-PASSWORD ............................................................................................................ 44
u) MIP accnt LOCAL-IP-PARAMETERS .............................................................................................. 44
v) MIP accnt PSTN-ACTION.................................................................................................................. 44
w) MIP accnt SUBSCRIBER-TELEPHONE ........................................................................................... 44
x) MIP accnt LAST-UPDATE-TIME......................................................................................................45
y) MIP accnt ANTI-SUBSTITUTION.....................................................................................................45
2.10. MONITOR-IP-ADDR ......................................................................................................................... 45
2.11. NO........................................................................................................................................................ 46
2.12. PRINTABLE EVENTS ....................................................................................................................... 46
2.13. PRIORITY-STANDARD.................................................................................................................... 48
2.14. SERIAL-PARAMETERS.................................................................................................................... 49
a) SERIAL-PARAMETERS DATA-BITS .............................................................................................. 49
b) SERIAL-PARAMETERS PARITY.....................................................................................................49
c) SERIAL-PARAMETERS SPEED....................................................................................................... 49
d) SERIAL-PARAMETERS STOP-BITS ............................................................................................... 50
- iii -
Page 4

2.15. SHUTDOWN....................................................................................................................................... 50
2.16. SMS .....................................................................................................................................................50
2.17. SUPERVISION....................................................................................................................................50
2.18. UPDATE.............................................................................................................................................. 51
a) UPDATE MIP accnt Default ............................................................................................................... 52
b) UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-IP................................................................................................... 52
c) UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-UDP-PORT ...................................................................................53
d) UPDATE MIP accnt USR-PASSWORD............................................................................................. 53
e) UPDATE MIP accnt MIP-PASSWORD .............................................................................................53
f) UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-PASSWORD................................................................................. 53
g) UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER ...................................................................................... 54
h) UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES................................................................................... 54
i) UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER ..................................................................... 54
j) UPDATE MIP accnt PHONE-LENGTH............................................................................................. 55
k) UPDATE MIP accnt ALARM-TX-RETRIES..................................................................................... 55
l) UPDATE MIP accnt CALLBACK-PHONE .......................................................................................55
m) UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER ............................................................................56
n) UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES ......................................................................... 56
o) UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER............................................................56
p) UPDATE MIP accnt RESET ............................................................................................................... 57
q) UPDATE MIP accnt LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE.................................................................................. 57
r) UPDATE MIP accnt MNT-IP-ADDRESS .......................................................................................... 57
s) UPDATE MIP accnt MNT-PASSWORD............................................................................................ 57
t) UPDATE MIP accnt LOCAL-IP-PARAMETERS.............................................................................. 58
u) UPDATE MIP accnt PSTN-ACTION ................................................................................................. 58
v) UPDATE MIP accnt SUBSCRIBER-TELEPHONE........................................................................... 58
w) UPDATE MIP accnt LAST-UPDATE-TIME..................................................................................... 59
x) UPDATE MIP accnt ANTI-SUBSTITUTION.................................................................................... 59
2.19. USER-DEFINED-EVENTS ................................................................................................................ 59
a) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-REGISTRATION .......................................................................... 60
b) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-LOSS ............................................................................................. 61
c) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS NETWORK-FAILURE .........................................................................61
d) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS COMMUNICATION-FAILURE........................................................... 61
e) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS CONFIG-ERR........................................................................................ 62
f) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS DOWN-CTIVE-STATE ........................................................................62
g) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PRIMARY-DOWN................................................................................ 62
h) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS BACKUP-DOWN..................................................................................63
i) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AVAILABLE-ROOMFULL ................................................................. 63
j) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-CHANGED............................................................................... 63
k) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-SENSOR-TROUBLE ............................................................... 64
l) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS-TAMPER............................................................................................... 64
m) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PSTN-FAILURE................................................................................... 64
n) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-CHANGED.................................................................................... 65
o) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS ICMP-POLL-FAILURE ........................................................................65
p) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS HDW-FAULT........................................................................................ 65
q) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-HW-FAILURE .............................................................................. 66
r) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS VISORALARM-TIME-INACCURATE ............................................... 66
s) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AC-LOSS............................................................................................... 66
t) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOW-BATTERY................................................................................... 67
u) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-CLEAR......................................................................................... 67
v) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-50LOAD....................................................................................... 67
w) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-90LOAD.......................................................................................68
x) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-OVERFLOW................................................................................ 68
y) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-SAVE............................................................................................68
2.20. EXIT .................................................................................................................................................... 69
CHAPTER 3 SEPI INTERFACE CONFIGURATION ................................................ 70
- iv -
Page 5

1. Initial Configuration................................................................................................................................... 71
2. Command set............................................................................................................................................... 72
2.1. DESCRIPTION.................................................................................................................................... 72
2.2. FLOW-CONTROL.............................................................................................................................. 72
2.3. INTERFACE-BUFFER-SIZE .............................................................................................................72
2.4. LIST..................................................................................................................................................... 73
2.5. NO........................................................................................................................................................ 73
2.6. SERIAL-PARAMETERS.................................................................................................................... 73
a) SERIAL-PARAMETERS DATA-BITS .............................................................................................. 73
b) SERIAL-PARAMETERS PARITY.....................................................................................................74
c) SERIAL-PARAMETERS SPEED....................................................................................................... 74
d) SERIAL-PARAMETERS STOP-BITS ............................................................................................... 74
2.7. SHUTDOWN....................................................................................................................................... 74
2.8. EXIT .................................................................................................................................................... 75
CHAPTER 4 ARLY INTERFACE MONITORING......................................................76
1. Monitoring the Serial Interface................................................................................................................. 77
2. Monitoring the ARLY Interface................................................................................................................ 78
2.1. CLEAR ................................................................................................................................................ 78
a) CLEAR ALARM ................................................................................................................................. 78
b) CLEAR INTERFACE-STATISTICS.................................................................................................. 79
c) CLEAR PROTOCOL .......................................................................................................................... 79
d) CLEAR VISORALARM-STATE .......................................................................................................79
2.2. LIST..................................................................................................................................................... 80
a) LIST ALARM...................................................................................................................................... 80
b) LIST INTERFACE-STATISTICS.......................................................................................................81
c) LIST MIP ............................................................................................................................................. 81
d) LIST REGISTERED-MIP ................................................................................................................... 83
e) LIST MONITOR-IP-ADDR ................................................................................................................ 83
f) LIST PROTOCOL............................................................................................................................... 84
g) LIST SMS............................................................................................................................................ 84
h) LIST UDP-STATISTICS..................................................................................................................... 84
i) LIST VISORALARM-STATE ............................................................................................................ 84
2.3. TEST.................................................................................................................................................... 85
2.4. EXIT .................................................................................................................................................... 86
CHAPTER 5 SEPI MONITORING.............................................................................87
1. Monitoring the Serial Interface................................................................................................................. 88
2. Monitoring the SEPI Interface.................................................................................................................. 89
2.1. CLEAR ................................................................................................................................................ 89
2.2. LIST..................................................................................................................................................... 89
2.3. EXIT .................................................................................................................................................... 89
APPENDIX A UL COMPLIANCE..............................................................................90
1. Intrusion System Installations complying with UL1610.......................................................................... 91
2. Fire System Installations complying with UL864 .................................................................................... 92
- v -
Page 6

Chapter 1
Introduction
Page 7

1. Introduction to the ARLY Interface
The ARLY interface is a serial interface that provides the VisorALARM with complete IP alarm
receiver functionality. The device performs the following tasks:
• Receives alarms from the registered mIP/IPDACTs through an IP network.
• Emulates a conventional alarm receiver sending the alarms through an asynchronous serial
port in order to be processed in automation alarm software.
• Supervises the registered mIP/IPDACTs and generates the corresponding alarm in cases of
loss of communication.
• Supports the installation and maintenance of the registered mIP/IPDACTs.
• From release 10.4.7 onwards, the network backup functionality has been added.
VISOR ALARM - Introduction
I - 2
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 8

2. Introducing the SEPI Interface
The SEPI interface (Serial Event Printing Interface) endows the VisorALARM device with a serial
port function to which a printer serial device can be connected and also admits the ASCII basic
protocol. Traditional alarm receivers commonly have a serial printer to print out events therefore this
functionality has been added to the VisorALARM device.
The SEPI interface is directly linked to the ARLY interface so the events for this interface displayed
on the console are those sent to the printer. Basically, not all the events are printed, only those that are
not repetitive. Additionally the events are organized into different functionalities, being printed by
function and not by event.
VISOR ALARM - Introduction
I - 3
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 9
Chapter 2
ARLY Interface Configuration
Page 10
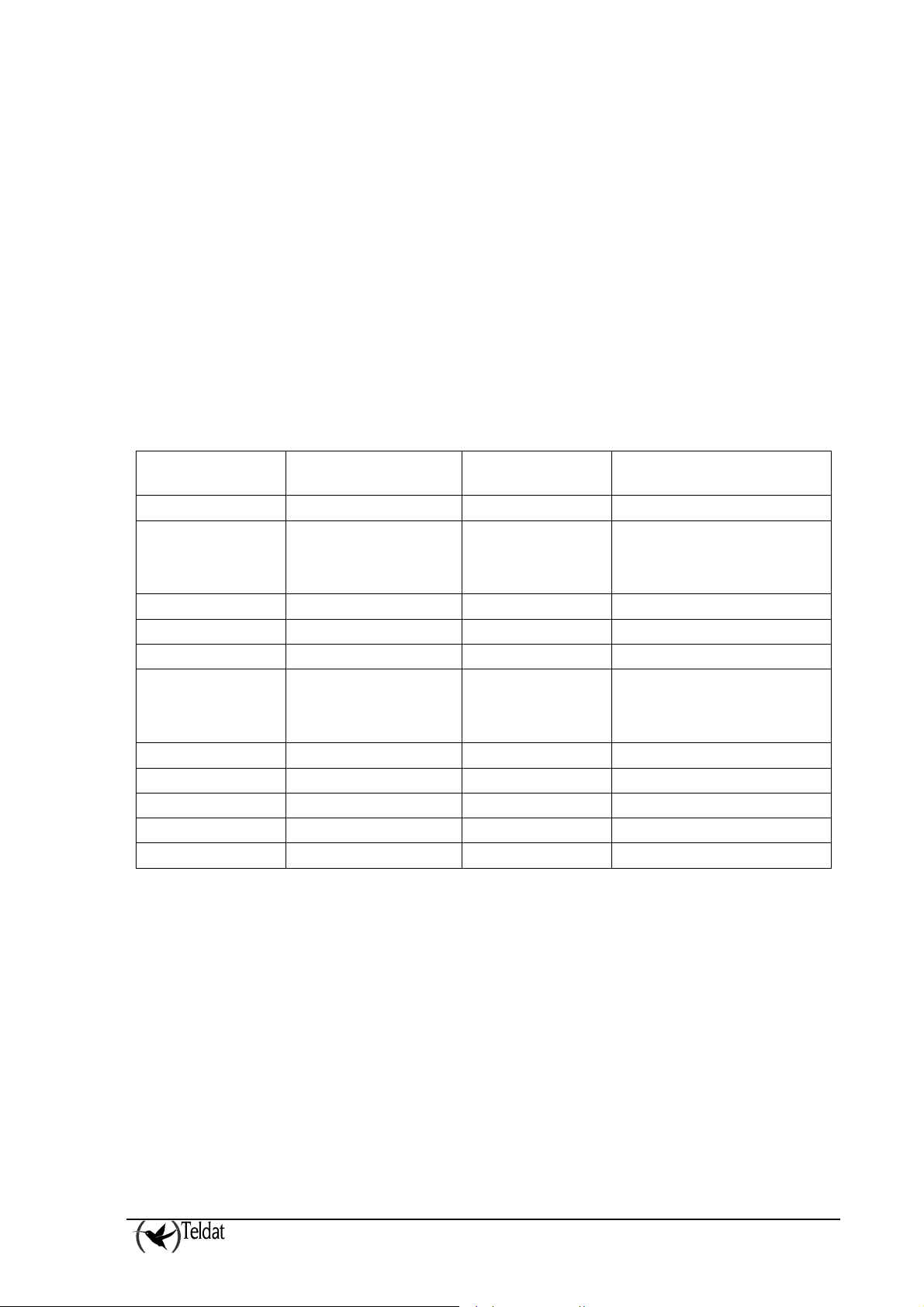
NOTICE TO USERS, INSTALLERS, AUTHORITIES HAVING JURISDICTION,
AND OTHER INVOLVED PARTIES
This product incorporates field-programmable software. In order for the product to comply with the
requirements in the Standard for Control Units and Accessories for Fire Alarm Systems, UL 864,
certain programming features or options must be limited to specific values or not used at all as
indicated below.
Program feature or
option
Permitted in UL 864?
(Y/N)
Possible settings Settings permitted in UL 864
2.1d) N 0-3000 seconds 1-60 seconds
2.1f) N Alarm-signals,
Trouble-signals,
Alarm-signals,
Trouble-signals
None-signals
2.4 i) N 0-90 seconds 1-60 seconds
2.4 j) N 1-9 1
2.4 p) N 0-90 seconds 1-60 seconds
2.6 a) N Disabled,
Ac-loss,
AC loss,
Low battery
Low-battery
2.9 h) N 0-90 seconds 1-60 seconds
2.9 i) N 1-9 1
2.9 j) N 3-9 3
2.9 n) N 0-90 seconds 1-60 seconds
2.9 o) N 1-9 1
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 5
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 11

VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 6
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 12
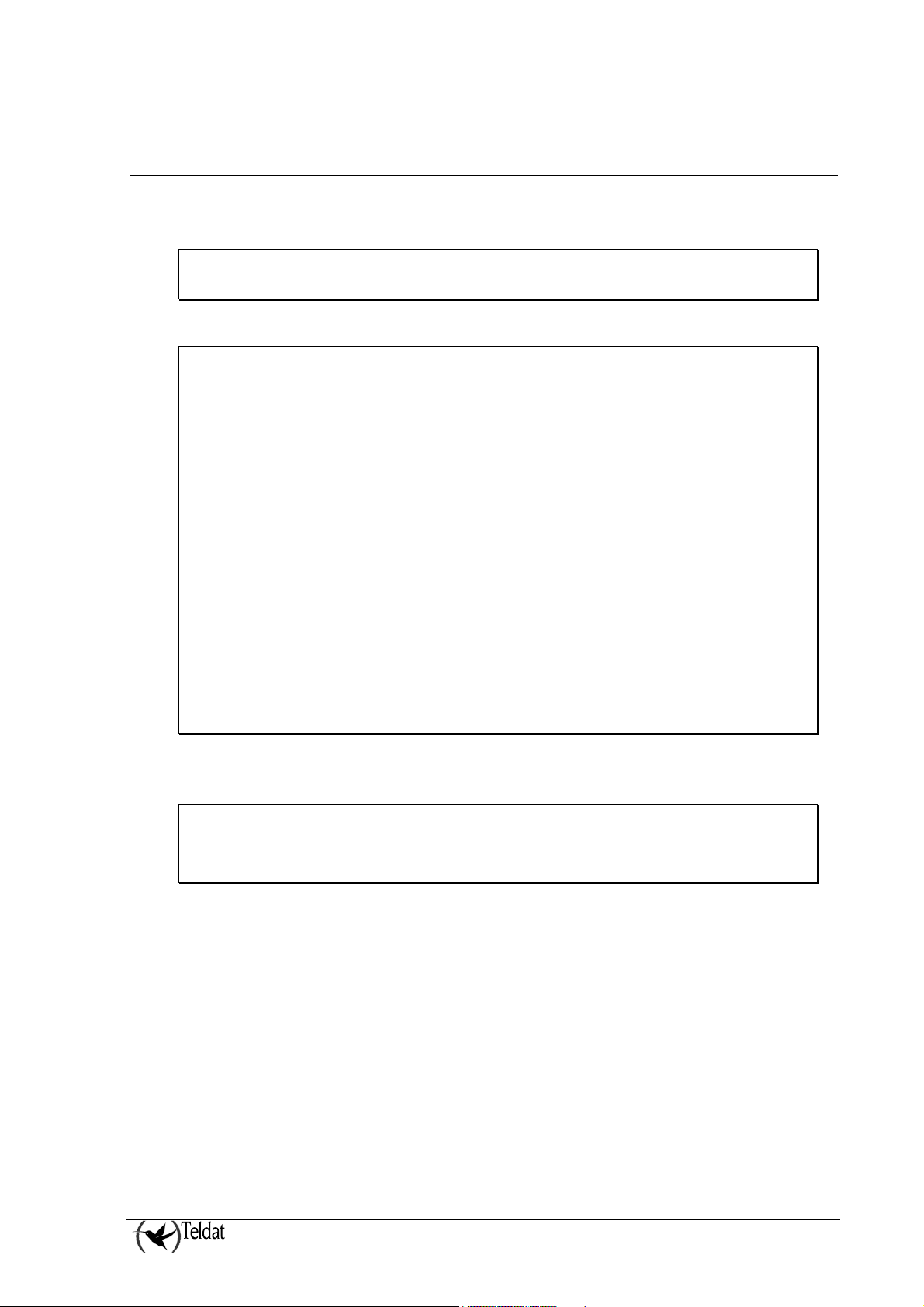
1. Initial Configuration
So that the device can operate as an IP receiver, the first serial interface for this must be an ARLY.
This is achieved through the configuration command:
*P 4
Config>set data-link arly serial0/0
Config>
In order to check that the operation has been correctly executed you can view the entire configuration
for the device or display the state of the configured interfaces:
Config>show config
; Showing System Configuration ...
; VisorALARM IP Alarm Receiver 2 16 Version 10.2.0
log-command-errors
no configuration
set data-link arly serial0/0
set data-link x25 serial0/1
set data-link x25 serial0/2
;
network serial0/0
; -- ARLY Interface Configuration - serial-parameters speed 64000
exit
;
dump-command-errors
end
; --- end --Config>list devices
Interface Con Type of interface CSR CSR2 int
ethernet0/0 LAN1 Fast Ethernet interface FA200E00 27
serial0/0 WAN1 ARLY Async Line FA200A00 FA203C00 5E
serial0/1 WAN2 X25 FA200A20 FA203D00 5D
serial0/2 WAN3 X25 FA200A60 FA203F00 5B
x25-node --- Router->Node 0 0
Config>
As you can see, in both cases the serial0/0 line has been configured as an ARLY interface.
In order to access the ARLY interface configuration, use the NETWORK command and the serial line
associated to the ARLY interface:
Config>
Config>NETWORK SERIAL0/0
-- ARLY Interface Configuration -ARLY-1 Cfg>
From this menu you can configure the type of emulated alarms receiver, the serial line parameters in
order to connect with the automation software, the configuration patterns and the information on all
the supported mIP/IPDACTs. Additionally this permits on-line modification and updating for the
supported mIP/IPDACT base maintenance tasks.
The available commands are as follows:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 7
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 13

2. Command set
ARLY-1 Cfg>?
alarm-receiver Alarm Receiver emulation params
automation-software-required Specify if automation SW is required to
return kissoffs
backup-alarm-receiver Set parameters for network backup
cfg-pattern Config pattern params
description Enter interface description
io-conf Configure the general purpose I/O
list List all config params
log Save/clear SRAM events log
mip MIP configuration params
monitor-ip-addr Internet IP addr to check availavility
no Negates a command or sets its defaults
printable-events Events to be sent to a serial printer device
priority-standard Priority standard used to display signals
serial-parameters Asyncronous serial line params
set
shutdown Change state to administratively down
sms SMS receiving params
supervision MIP supervision params
update Update remote MIP's config
user-defined-events Set codes for user defined events
exit
2.1. ALARM-RECEIVER
Specifies the emulated alarms receiver and permits you to configure the related parameters.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER <parameter, values>
protocol alarm receiver emulation protocol
receiver-id receciver id for Sw Automation
line-id line id for Sw Automation
link-test-timer link test timer
parameters additional parameters
block type of alams to be blocked
a) ALARM-RECEIVER PROTOCOL
Configures the type of alarms receiver going to be emulated. A Sur-Gard receiver, a Radionics 6500
receiver and an Ademco 685 receiver can be emulated. Emulation for the Sur-Gard receiver adjusts to
the MLR2000/MLR2E v1.2 specification. Default is Sur-Gard receiver emulation.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER PROTOCOL protocol
ademco-685
radionics-6500
sur-gard
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER PROTOCOL RADIONICS-6500
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 8
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 14
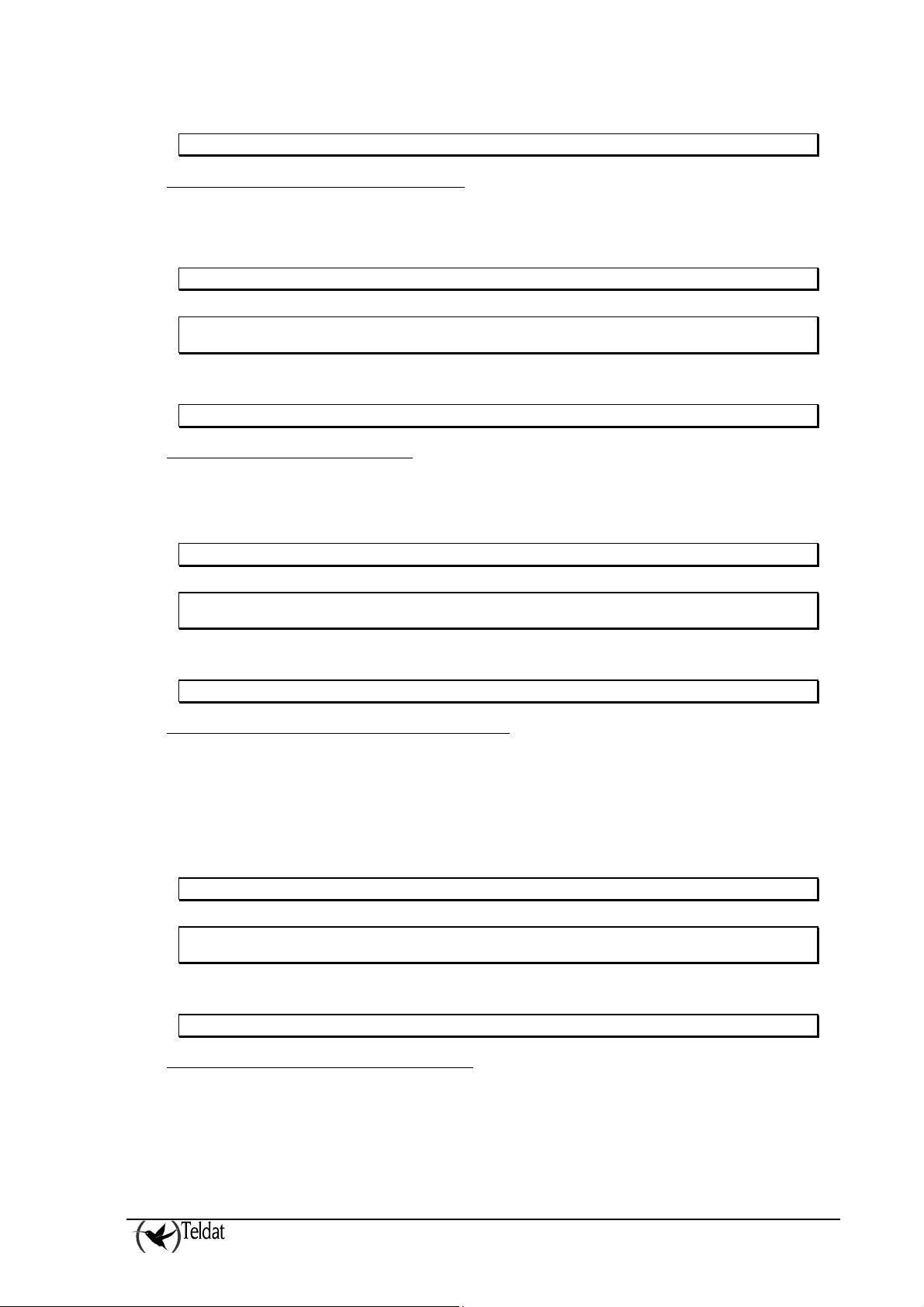
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO ALARM-RECEIVER PROTOCOL protocol
b) ALARM-RECEIVER RECEIVER-ID
Configures the VisorALARM receiver identifier so it can be identified in the Automation Sw.
Admits a maximum of two digits (0 to 9). Default value is 1.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER RECEIVER-ID identifier
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER RECEIVER-ID 8
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO ALARM-RECEIVER RECEIVER-ID identifier
c) ALARM-RECEIVER LINE-ID
Configures the VisorALARM line identifier so it can be identified in the Automation Sw.
Admits a maximum of three digits (0 to 9). Default value is 01.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER LINE-ID identifier
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER LINE-ID 12
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO ALARM-RECEIVER LINE-ID identifier
d) ALARM-RECEIVER LINK-TEST-TIMER
Configures the interval through which the alarms receiver connection is checked – Automation Sw.
Exchanging a particular type of frame carries out this check. If the exchange is satisfactory, the
ARLY interface is considered active (UP) and the WAN1 LED lights up in green.
Admits values between 0 and 3000 seconds. If you configure this parameter with a 0 value, the said
exchange will not take place and the interface will be considered up. Default value is 0.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER LINK-TEST-TIMER value
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER LINK-TEST-TIMER 180
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO ALARM-RECEIVER LINK-TEST-TIMER value
e) ALARM-RECEIVER PARAMETERS
Admits a string of parameters depending on the type of receiver emulated.
In cases where the emulated receiver is Sur-Gard, you can configure:
r Type of emulated receiver: 0 MLR2000/MLR2E, 1 DLR-2. Default is 0.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 9
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 15
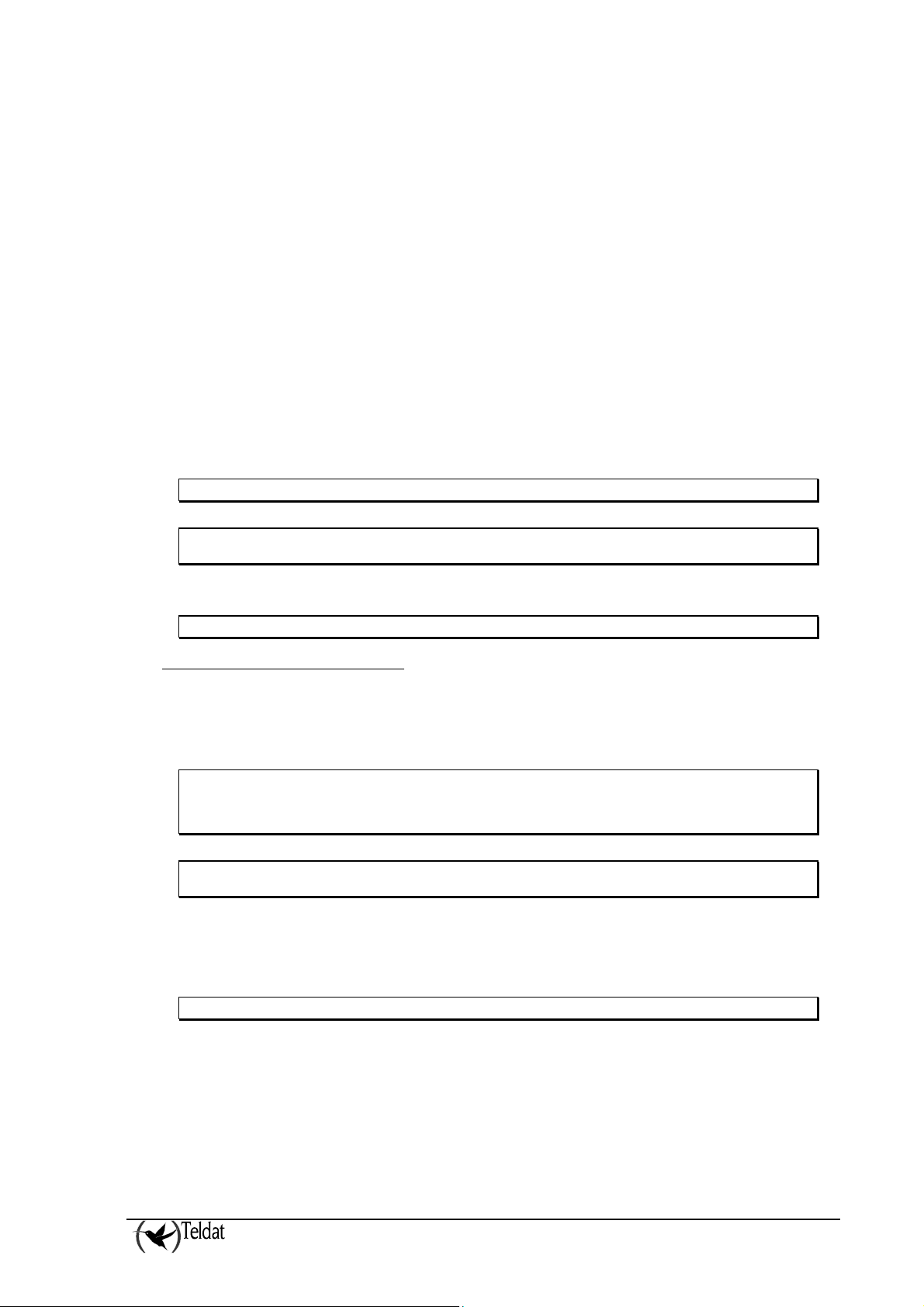
In cases where emulation is Radionics 6500, the following can be configured:
a Decimal value used as message ACK. Default is 6.
n Decimal value used as message NACK. Default is 15.
h Decimal value used as start of message. This is not configured by default.
t Decimal value used as end of message. Default is 14.
In cases where the emulated receiver is an Ademco 685, you can configure:
t Decimal value used as end of message. Default is 13.
p Use of ack, nack protocol for the exchange of messages: 0 not used, 1 used.
The parameters are separated by commas and do not contain spaces. The parameter format is
identifier, even symbol, value. By default the string of parameters is empty and the parameters take
the default values.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER PARAMETERS parameter_list
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER PARAMETERS a=8,n=20,h=7,t=16
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO ALARM-RECEIVER PARAMETERS list_parameters
f) ALARM-RECEIVER BLOCK
This permits you to configure the receiver to filter determined types of signals received. Through this
command, you configure a maintenance receiver to only process trouble signals and a conventional to
process either just alarm signals or all of them.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER BLOCK type_of_signal
alarm-signals
trouble-signals
none-signals
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>ALARM-RECEIVER BLOCK alarm-signals
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Permits a maintenance receiver to process trouble signals only.
To return to the default configuration, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO ALARM-RECEIVER BLOCK type_of_signal
Or
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 10
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 16

ARLY-1 Cfg> ALARM-RECEIVER BLOCK none-signals
2.2. AUTOMATION-SOFTWARE-REQUIRED
This lets yo to configure if the acknowledgements to the received signals are done by the Automation
Software or by the VisorALARM receiver.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>automation-software-required
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>automation-software-required
This command specify that an alarm must be acknowledged by the Automation Software in order to
give a kissoff to the Control Unit.
ARLY-1 Cfg>no automation-software-required
This command specify that when the VisorALARM receiver receives an alarm the kissoff will be
returned to the Control Unit.
2.3. BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER
Permits you to configure the network backup functionality. This functionality is operative from
release 10.4.7 onwards. Network backup defines a main VisorALARM which maintains
communications with the installed mIP/IPDACTs. In cases where these communications fail, the
mIP/IPDACTs, from release 2.2 onwards, are able to divert traffic towards a second backup
VisorALARM. Only in cases where the backup VisorALARM fails will the alarms be directly sent
by the alarms panel.
Additionally, for alarm reception through a second IP receiver, the synchronization functionality for
configurations has been added, i.e. the configurations for the two VisorALARMs tend to be similar,
updating every certain time period, which is configurable.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>backup-alarm-receiver ?
type define the alarm receiver as main or secondary
address-main main alarm receiver IP address
maintenance-password password for maintenance alarms.
sync-port configuration synchronization port
poll-time time in seconds between polls
poll-failure-time time in seconds to consider a fail in polling
retries-number number of retries to detect a fail
retry-time time between retries
polling-sync-time Time in seconds between synchronizations
a) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER TYPE
Defines the type of VisorALARM. There are three possible types: main which by default is the
receiver maintaining all the communications with the deployed mIP/IPDACTs; secondary or backup
which is the second communication option for the mIP/IPDACTs in cases where the main one fails
and finally maintenance that is a receiver where all the signals are transmmited.
Usually in a Maintenance receiver the alarm signals are filtered by means of the “block” command and
the trouble signals (with code 3xx) are processed.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg> BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER TYPE option
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 11
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 17

option
MAIN, for the main receiver, SECONDARY for the backup and
MAINTENANCE for the maintenance receiver.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg> BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER TYPE MAIN
ARLY-1 Cfg>
b) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER ADDRESS-MAIN
Configures the main VisorALARM address. This parameter is only logical for the backup
VisorALARM, as it needs to know the IP address of the main in order to execute two functions:
• Poll to 1 main VisorALARM with the aim of detecting if it’s down.
• Establish the connection with the main VisorALARM to synchronize configurations.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER ADDRESS-MAIN value
value
Main VisorALARM IP address.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER ADDRESS-MAIN 80.26.96.183
ARLY-1 Cfg>
c) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER MAINTENANCE-PASSWORD
This parameter only is necessary when the receiver is configured as maintenance. This parameter
configures the keyword that must be used by the receiver to decipher the sent messages from the mIP
devices.
d) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER SYNC-PORT
This parameter is necessary both in the main VisorALARM and in the backup. This value is the port
which listens in the main and where TCP connections are accepted from the backup VisorALARM
through which the configurations synchronization protocol is established. To simplify this port, it can
be the same as that used for mIP/IPDACT supervision tasks. In this way, you only need to make a
single port transparent in the input router.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER SYNC-PORT value
value
Configurations synchronization port. Admits values between 1 and
65535.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER SYNC-PORT 35536
ARLY-1 Cfg>
e) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLL-TIME
This parameter is the time between polls carried out by the backup VisorALARM over the main. The
task of these polls is to detect when the main VisorALARM is down. If the backup device checks
that its output to Internet is correct (its Ethernet physical interface is operative and the polls carried out
over an external server are correct) but the poll fails, you need to assume that rest of the installed
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 12
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 18

mIP/IPDACTs will have the same problem. Consequently all the traffic should be forwarded to the
backup device which activates as if it were the main device. A failure in this poll does not produce the
activation process but subsequently, after a series of retries has been executed until the main
VisorALARM is considered down.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>backup-alarm-receiver poll-time value
value
Time in seconds between polls over the main VisorALARM. This
admits values between 5 and 300 seconds.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>backup-alarm-receiver poll-time 20
ARLY-1 Cfg>
f) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLL-FAILURE-TIME
This is the time the backup VisorALARM waits to receive a response to a polling packet. If during
this period of time the response is not received, the backup device will begin the retry sequence.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLL-FAILURE-TIME value
value
Time waited for the response to the poll. Admits values between 3
and 10 seconds.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLL-FAILURE-TIME 5
ARLY-1 Cfg>
g) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER RETRIES-NUMBER
This is the number of polls making up the retry sequence. If after all the retries have been executed
and there is no response, the main VisorALARM is considered down. The response wait time for the
retry is still poll-failure-time.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER RETRIES-NUMBER value
value
Number of retries. Admits values between 1 and 10.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER RETRIES-NUMBER 3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
h) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER RETRY-TIME
This is the time between retries. Evidently this time must be greater or equal to poll-failuretime.
Syntax:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 13
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 19
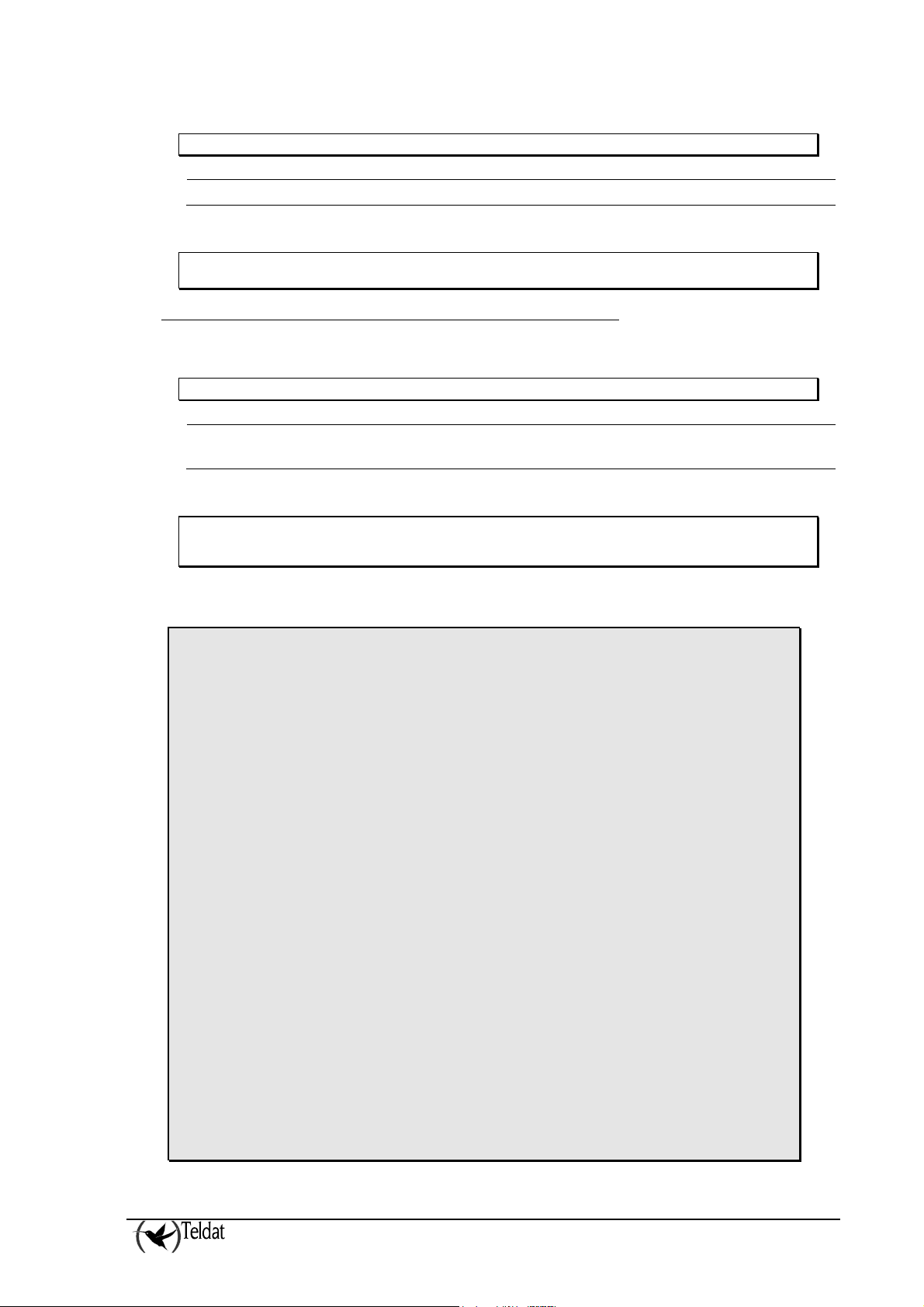
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER RETRY-TIME value
value
Time in seconds between retries. Admits values between 3 and 10.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER RETRY-TIME 5
ARLY-1 Cfg>
i) BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLLING-SYNC-TIME
This value is the time between configuration synchronizations.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLLING-SYNC-TIME value
value
Time in seconds between configuration synchronizations. Admits
values between 1 and 65535.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER POLLING-SYNC-TIME 5
ARLY-1 Cfg>
The right election of the previous values is fundamental for the correct operation of the
backup process. Specifically, these parameters affect the detection of service
interruption for both the main and the backup receivers.
However, a receiver could decide that its complementary receiver (main or backup) has
a failure as the polling between them has been interrupted, however that polling could
have failed because the receiver itself doesn’t have the Ethernet up or because it
doesn’t have Internet access.
So, it is very important that detection of poll failure is slower than detection of failure
in the Ethernet interface or the Internet.
As guide to choose an adequate set of parameters it is strongly recommended that the
values meet the following conditions:
Main VisorALARM receiver:
2 x POLL-TIME > 15
2 x POLL-TIME > 3 x MONITOR-IP-ADDRESS-RATE
1
2
Backup VisorALARM receiver:
POLL-FAILURE-TIME + RETRIES-NUMBER * RETRY-TIME > 15
POLL-FAILURE-TIME + RETRIES-NUMBER * RETRY-TIME > 3 x MONITOR-IP-ADDRESS-RATE
1
2
NOTES:
1
The value 15 is the time in seconds that the equipment takes in detecting a failure in
the Ethernet interface.
2
MONITOR-IP-ADDRESS-RATE is the poll time of an external server in the Internet.
It must be configured according with the MONITOR-IP-ADDR paragraph.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 14
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 20
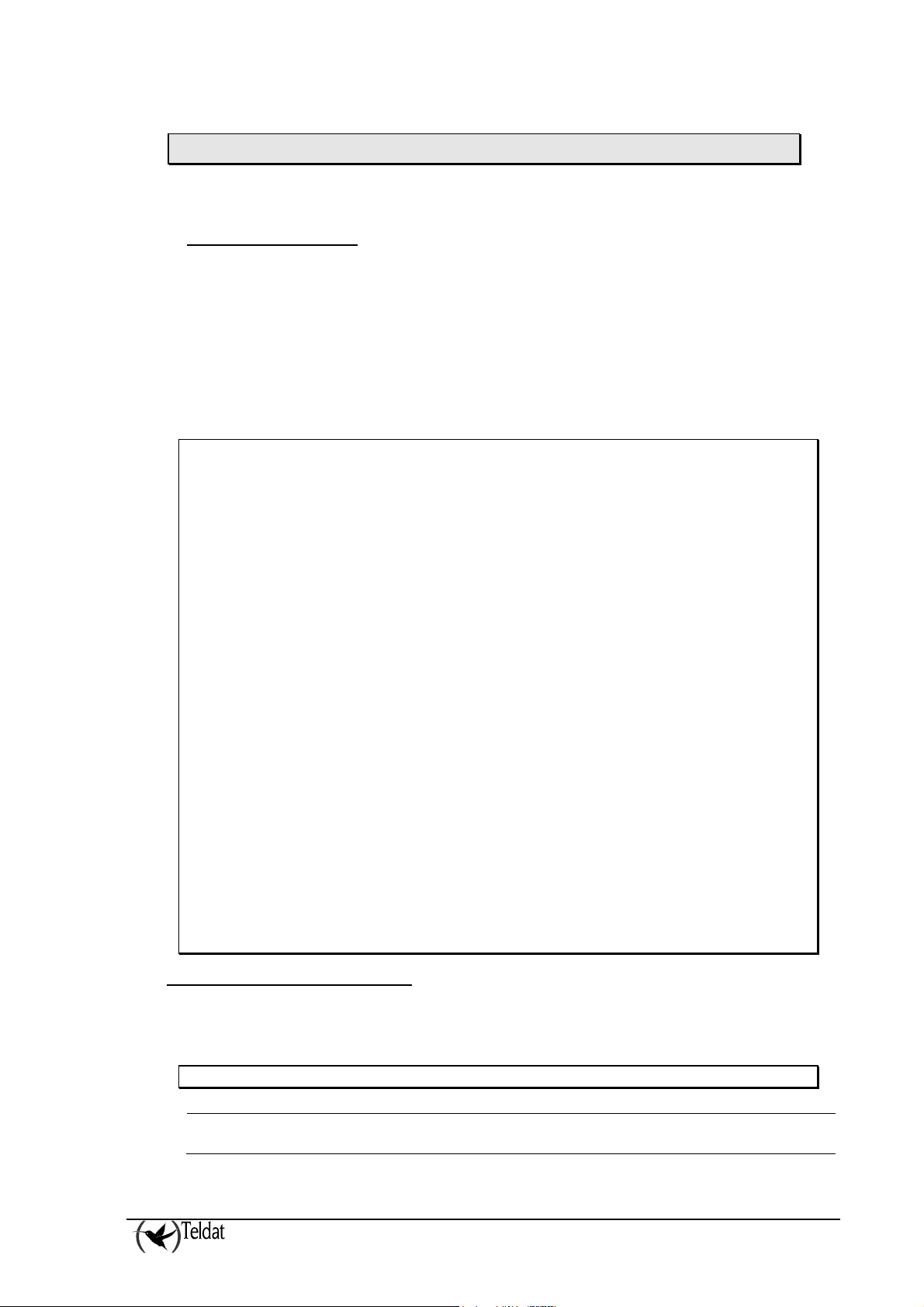
The default values for these parameters meet the previous conditions.
2.4. CFG-PATTERN
Permits you to define a configuration pattern to be used for mIP/IPDACTs installation and register.
From the configuration point of view, a pattern number identifies a pattern.
An important configuration pattern parameter is the installer password as this is the password used to
encrypt the register request. When the VisorALARM receives this petition, it uses the pattern which
permits it to correctly decrypt the mIP/IPDACT request. The rest of the parameters are used by the
mIP/IPDACT in normal operating mode. All the parameters must be configured to ensure correct
mIP/IPDACT registration and configuration.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN <pattern_number>
default sets default values to an existing or a new
entry
instalator-password MIP instalator password to use this cfg
pattern
automatic-instalator-password Automatically generated MIP instalator
password to use this cfg pattern
receiver-ip Public IP address which MIP uses to send
alarms
receiver-udp-port UDP port used to exchange info
usr-password MIP console protected password
mip-password MIP encrypt password used to send alarms
receiver-password Encrypt password this eq. uses on mssg to
that MIP
keep-alive-timer MIP keep-alive timer in seconds
keep-alive-retries MIP keep-alive num of retries
keep-alive-retries-timer MIP time between keep-alive retries in
seconds
phone-length Number DTMF digits Alarm Panel dials to make
calls
alarm-tx-retries Times MIP retransmmit an alarm before abandon
callback-phone Phone number Alarm Panel dials to make a
callback
bck-receiver-ip Public IP address which MIP uses to send
alarms to the backup VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-timer MIP keep-alive timer in seconds for backup
VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-retries MIP keep-alive num of retries for backup
VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-retries-time MIP time between keep-alive retries in
seconds for backup VisorAlarm
local-events-zone Zone number to use in locally generated
events
mnt-ip-address Maintenance IP address
mnt-password Password for maintenance alarms
a) CFG-PATTERN n DEFAULT
Establishes the specified pattern’s default configuration. In order to fully delete a pattern, use the NO
CFG-PATTERN n DEFAULT command.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n DEFAULT
n
Pattern Number. The entries do not require consecutive numbers,
however the numerical order is important as the lowest number is
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 15
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 21

Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 DEFAULT
ARLY-1 Cfg>
checked first. The range is from 1 to 255.
b) CFG-PATTERN n INSTALATOR-PASSWORD
Configures the installer password which permits access to this pattern. Only the encrypted register
petitions with this password can use this pattern.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n INSTALATOR-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 INSTALATOR-PASSWORD 1234FBAA
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return this parameter to the default configuration, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n INSTALATOR-PASSWORD password
c) CFG-PATTERN n AUTOMATION-INSTALATION-PASSWORD
This lets you to generate automatically a keyword for CESAR ciphering (this is valid only for mIP
devices up to 2.2 release) for the mIP installacion process. This is the keyword that must be supplied
to the mIP device for the registration process. This installation keyword specify the parameter set that
the receiver submits to the mIP device in the registration.
d) CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-IP
Configures the alarm receiver IP address in the MIP.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-IP ip_address
ip_address
Alarm receiver IP address.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 RECEIVER-IP 172.24.78.99
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-IP ip_address
e) CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-UDP-PORT
Configures the UDP port for connection with the various mIP/IPDACTs.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-UDP-PORT port_number
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 16
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 22

port_number
Number of the UDP port used. Admits values between 1 and 65535.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 RECEIVER-UDP-PORT 20300
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-UDP-PORT port_number
f) CFG-PATTERN n USR PASSWORD
Configures the mIP/IPDACT configuration / monitoring console password. This is applied to both the
asynchronous console as well as the telephonic console. This password can be dependent on the
account number: assuming the account number is represented through UVWXYZ, you can use these
to generate passwords using the serial number digits. In the example, if the account number is 01234
(X = 2, Y = 3 and Z = 4), then the password is 1223400B4.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n USR-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
This also admits U, V, W, X, Y, Z.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 USR-PASSWORD 12XYZ00BZ
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n USR-PASSWORD password
g) CFG-PATTERN n MIP-PASSWORD
Configures the password with which the mIP/IPDACT encrypts its messages. This password can be
dependent on the mIP/IPDACT account number, in the same way as the above.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n MIP-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
This also admits U, V, W, X, Y, Z
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 MIP-PASSWORD 12XYZ00BZ
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 17
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 23
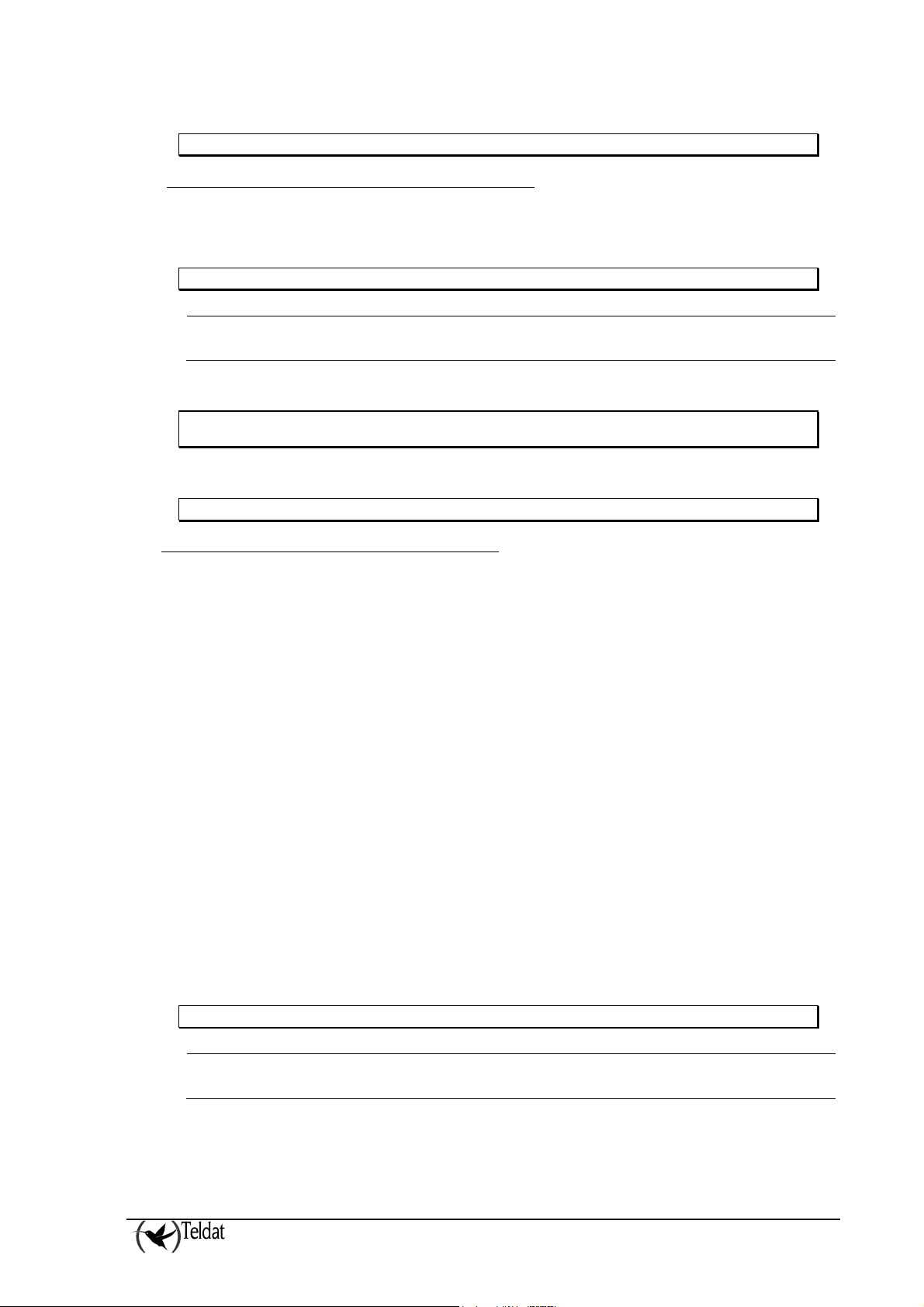
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n MIP-PASSWORD password
=
h) CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-PASSWORD
Configures the password with which the VisorALARM encrypts its messages. This password can be
dependent on the mIP/IPDACT account number, in the same way as both the above.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
This also admits U, V, W, X, Y, Z.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 RECEIVER-PASSWORD 12XYZ00BZ
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n RECEIVER-PASSWORD password
i) CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER
Configures the time interval used by the MIP to check connectivity with the VisorALARM. Each time
this timer times out, a keep-alive frame is sent to notify the VisorALARM that the connection is active
and waits for its response.
Normally the keep-alive interval in the alarms panel is high as this implies a telephone call, however,
in the case of the mIP/IPDACT, this cost is not as such as this is dealing with traffic which in all
likeliness is running over a flat rate connection. In addition a high value is not advisable in cases
where the mIP/IPDACT goes out to Internet through a router executing NAT, a problematic situation.
This is because traffic coming from the ARC towards the NIP reaches this thanks to the router
maintaining the input in the NAT table active during a period of time, the input being refreshed with
supervision traffic. If the supervision interval is greater than the residence time for the input in the
NAT table, communications from the ARC will not be possible. In cases of the TELDAT devices, this
is around 5 minutes. A low value has the problem that the traffic the VisorALARM must process is
high, the same as the bandwidth requirements. If ARC Internet access is ADSL, you need to consider
that the upstream channel is smaller than the downstream one and that supervision traffic returned to
the mIP/IPDACTs is slighter greater than the incoming.
The incoming traffic to the ARC is:
NTC **528
−
mipsALIVEKEEP
The minimum supervision time can be 1 second and a VisorALARM can have 3000 mIP/IPDACTs
registered that give an input traffic of 1,58 Mbps. The return traffic is approximately 6% greater.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames. Admits values between 0
and 90.
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 18
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 24
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
If you use a value of zero for the “keep-alive-timer parameter”, the mIP/IPDACT will
not send supervision trafic to the receiver and the VisorALARM will not be able to
access the device for remote configuration.
j) CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES
Configures the number of times the mIP/IPDACT will send a keep-alive frame without receiving a
response from the VisorALARM. If the mIP/IPDACT, on executing the connectivity test with the
VisorALARM, does not receive a response within the “time-between-send-keep-alive-retries”
seconds, the mIP/IPDACT repeats the process of transmitting the keep-alive frame. Should there be
no response within same time interval, the mIP/IPDACT repeats the process until the number of retries
configured in the register has been completed. The connection with the Teldat VisorALARM is
considered down once the number of configured retries in this register has been executed and
subsequently the control panel can access the telephone network.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
num_times
Number of times that the keep-alive frames are sent when no response
is received. Admits values between 1 and 9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
k) CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER
Configures the time interval used by the mIP/IPDACT to send keep-alive retries to notify the
VisorALARM that the connection is active.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames when a possible
connectivity problem is detected. Admits values between 3 and 9
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER 1
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 19
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 25

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
l) CFG-PATTERN n PHONE-LENGTH
In the mIP/IPDACT this configures the number of digits making up a telephone number. This number
depends on the country’s dialing plan, the existence of switchboards etc. The mIP/IPDACT uses this
to find out how many digits it should expect from the control panel before processing the call.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n PHONE-LENGTH length
length
Number of digits making up a telephone number. Admits values
between 1 and 15.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 PHONE-LENGTH 9
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n PHONE-LENGTH length
m) CFG-PATTERN n ALARM-TX-RETRIES
Configures the number of times that the mIP/IPDACT sends an alarm to the VisorALARM to ensure
that this receives the alarm and sends confirmation to the mIP/IPDACT. Connection with is
considered lost once this number of retries has been completed and permits the control panel to send
the alarm over the telephone line.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n ALARM-TX-RETRIES number
number
Number of times the alarm is sent to the VisorALARM. Admits
values between 5 and 10.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 ALARM-TX-RETRIES 5
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n ALARM-TX-RETRIES number
It is essential that the total time in which the mIP/IPDACT deactivates in cases where
communication between the two IP receivers is less than the highest time for retries
from the alarms panel.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 20
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 26

n) CFG-PATTERN n CALLBACK-PHONE1
Configures the telephone number the control panel uses to execute bi-directional operations in
callback mode.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n CALLBACK-PHONE telephone_number
telephone_number
Telephone number dialed by the control panel to execute bidirectional in call-back mode. Admits values between 1 and 9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 CALLBACK-PHONE 918076123
ARLY-1
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n CALLBACK-PHONE telephone_number
o) CFG-PATTERN n BCK-RECEIVER-IP
Configures the backup address the mIP/IPDACT uses as a second option in cases where
communications fail with the main VisorALARM
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg> CFG-PATTERN n BCK-RECEIVER-IP ip_address
ip_address
Backup VisorALARM IP address.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg> CFG-PATTERN n BCK-RECEIVER-IP 80.26.96.183
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
p) CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-timer however it is applied to the backup
VisorALARM. In the same way it must fulfill that:
T
keep-alive interval
≥ T
interval between retries
x N
send retries
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames. Admits values between 0
and 90.
Example:
1
Not available in US versions
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
Doc.DM359-I
II - 21
Rev.2.0
Page 27

ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
If you use a value of zero for the “bck-keep-alive-timer parameter”, the mIP/IPDACT
will not send supervision trafic to the receiver and the VisorALARM will not be able to
access the device for remote configuration.
q) CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-retries however it is applied to the backup
VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
num_times
Number of times keep-alive frames are sent in situations where
responses are not received. Admits values between 1 and 9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES time
r) CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES -TIME
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-retries-time however it is applied to the
backup VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
Time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames when a possible
connectivity failure has been detected. Admits values between 3 and
9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER 1
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
s) CFG-PATTERN n LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE
This parameter defines the base number for the zone field that will be appear in all the events
generated by a mIP/IPDACT that does not come from the Alarm Panel. This parameter is not sent to
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 22
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 28

the mIP/IPDACT when a register is produced, rather it is stored in the mIP/IPDACT local
configuration and is used for local events generated for this account number.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n local-events-zone identifier-zone
identifier-zone
This is a hexadecimal number of up to three digits.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE 015
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE identifier-zone
t) CFG-PATTERN n MNT-IP-ADDRESS
This parameter defines the VisorALARM, which receives the maintenance signals, address. A
maintenance alarms receiver permits you to configure the system so trouble signals proceeding from
the mIP/IPDACT devices are received and processed in an alternative location where the said receiver
is situated.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n mnt-ip-address ip-address
ip-address
Maintenance VisorALARM IP address.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 MNT-IP-ADDRESS 80.26.96.184
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n MNT-IP-ADDRESS ip-address
u) CFG-PATTERN n MNT-PASSWORD
Configures the password used by the maintenance VisorALARM to encrypt its messages. This
password may be dependent on the mIP/IPDACT account number, in the same way as before.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN n MNT-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
This also admits letter U, V, W, X, Y and Z.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>CFG-PATTERN 10 MNT-PASSWORD 12XYZ00BZ
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 23
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 29

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO CFG-PATTERN n MNT-PASSWORD clave
2.5. DESCRIPTION
Permits the user to add a text which will appear on displaying the device configuration. The aim of
this command is to facilitate the user, reading, compression and modification of the interface
configuration. Admits up to 63 characters including blank spaces. To eliminate the description, use
the NO DESCRIPTION command. Default is no description configured.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>DESCRIPTION text
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>DESCRIPTION Interface emulating ARC is Sur-Gard
ARLY-1 Cfg>
2.6. IO-CONF
Permits the user to configure the general purpose output and each of the two inputs of a VA-UD
expansion board for signaling the selected events from a given list of possibilities.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>io-conf ?
input1 Configure the general purpose input 1
input2 Configure the general purpose input 2
output Configure the general purpose output
a) IO-CONF INPUTx
Configures each of the two inputs (input1, input2) as disabled (no signal will be monitored at the
input) or for indicating ac-loss or low-battery conditions at the UPS power system (Uninterruptible
power supply).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>io-conf <inputX> <condition>
disabled Disable input
ac-loss Signal AC loss
low-battery Signal low system battery
inputX
condition
Selected general purpose input (input1 / input2).
Condition to be signaled by the selected input
• Disabled. No signal monitored.
• AC-loss. AC loss (< 10.2V) at the UPS power system.
• Low-battery. Low battery (Batt 10.2-11.5V) at the UPS
power system.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>io-conf input1 ac-loss
ARLY-1 Cfg>io-conf input2 low-battery
ARLY-1 Cfg>
The default configuration sets input1 to signal AC-loss condition and input2 to indicate Low-battery
condition in the UPS.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 24
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 30

b) IO-CONF OUTPUT
Configures the general purpose output for signaling a specific condition in the VisorAlarmmIP/IPDACT system. Options given to the user are:
• Automation-software-down. Communication between the VisorAlarm and Automation
Software is not active.
• Alarm-pending. There is(are) signal(s), of any type, pending to be acknowledged by the
operator at the VisorAlarm receiver.
• System-trouble-pending. There is(are) system trouble signal(s) pending to be acknowledged by
the operator at the VisorAlarm receiver.
• Alarm-unrestored. There is(are) signal(s), of any type, pending to be restored to normal
conditions in the alarm system.
• System-trouble -unrestored. There is(are) system trouble signal(s) pending to be restored to
normal conditions in the alarm system.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>io-conf output <condition>
automation-software-down
alarm-pending
system-trouble-pending
alarm-unrestored
system-trouble-unrestored
condition
Condition to be signaled by the general purpose output:
• Automation-software-down.
• Alarm-pending.
• System-trouble-pending.
• Alarm-unrestored
• System-trouble-unrestored.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>io-conf output alarm-pending
ARLY-1 Cfg>
The default configuration sets the general purpose output to indicate System-trouble-unrestored at
VisorAlarm receiver.
2.7. LIST
Permits the user to list the configured parameters.
Syntax:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 25
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 31

ARLY-1 Cfg>list ?
all List all config params
alarm-receiver Alarm Receiver emulation params
backup-alarm-receiver Parameters for network backup
cfg-pattern Config pattern params
io-conf General purpose I/O Config parameters
monitor-ip-addr Internet IP addr to check availavility
mip MIP configuration params
priority-standard Priority standard used to display signals
serial-parameters Asyncronous serial line params
sms SMS receiving params
supervision MIP supervision params
user-defined-events Codes for user defined events
printable-events Events to be sent to a serial printer device
a) LIST ALL
Lists all the ARLY interface configuration.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list all
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list all
Serial parameters
----------------Link speed.: 9600 (bit/sec)
Data bits..: 8
Stop bits..: 1
Parity.....: none
Alarm Receiver Parameters:
------------------------Protocol: ademco-685
Receiver ID: 1, Line ID: 0
Link test timer: 120
Receiver specific parameters:
Blocking: NONE
Backup Alarm Receiver Parameters:
-------------------------------CRA type: MAIN.
Synchronization Port: 35001.
MIP Supervision:
--------------Supervision Port: 1234.
Communication Supervision:
------------------------Monitor IP address: None
MIP Configuration Patterns:
-------------------------Config Pattern ID : 1
Instalator Password : 1111
Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.69.152
Backup Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.70.54
Maintenance Receiver IP address : 81.23.56.89
Maintenance Alarm Password : 2AB4
Alarm Receiver UDP Port : 1222
MIP Console Password : 1111
MIP Password : 220771B
Alarm Receiver Password : 220771B
Keep-alives.
Timer : 21
Retries : 3
Retries Timer : 5
Backup Receiver Keep-alives.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 26
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 32

Timer : 15
Retries : 4
Retries Timer : 1
Alarm Transmission Retries : 2
Telephone Number Length : 9
Callback Telephone Number :
Zone ID for local events :
MIPs Configuration:
-----------------Account number : 9997
Serial number : 8209/00270
Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.69.152
Backup Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.70.54
Maintenance Receiver IP address : 81.23.56.89
Maintenance Alarm Password : 2AB4
Alarm Receiver UDP Port : 1222
MIP Console Password : 1111
MIP Password : 220771B
Alarm Receiver Password : 220771B
Keep-alives.
Timer : 21
Retries : 3
Retries Timer : 5
Backup Receiver Keep-alives.
Timer : 15
Retries : 4
Retries Timer : 1
Alarm Transmission Retries : 2
Telephone Number Length : 9
Callback Telephone Number :
Zone ID for local events : 015
SMS Interfaces
--------------
SMS Allowed Accounts:
--------------------
Priority:
-------Priority Standard : UL (US)
I/O Configuration:
----------------Input 1 : AC Loss
Input 2 : Low Battery
Output 1 : System-trouble-unrestored
Output 2 [fixed] : System failure
User defined event codes:
------------------------
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 27
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 33

New MIP instalation (register) : 633
MIP loss of contact : 350
VisorALARM network failure : 356
MIP goes to backup mode : 394
MIP sending events to backup VisorALARM : 395
VisorALARM down-active : 396
Primary VisorALARM down : 399
Secondary VisorALARM down : 358
Alarm store occupation reaches 100% : 393
MIP input active/deactive : 110
MIP input sensor trouble : 380
MIP tamper : 383
MIP PSTN Supervision : 351
MIP change detected : 306
VisorALARM supervised hdw fault : 300
MIP HW Failure : 333
VisorALARM time inaccurate : 397
VisorALARM AC loss : 301
VisorALARM low system battery : 302
VisorALARM log cleared : 621
VisorALARM log 50% loaded : 622
VisorALARM log 90% loaded : 623
VisorALARM log overflowed : 624
VisorALARM log saved to file : 655
ARLY-1 Cfg>
b) LIST ALARM-RECEIVER
Lists the configuration parameters relative to the receiver emulation.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list alarm-receiver
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list alarm-receiver
Alarm Receiver Parameters:
------------------------Protocol: ademco-685
Receiver ID: 1, Line ID: 0
Link test timer: 120
Receiver specific parameters:
Blocking: NONE
c) LIST BACKUP-ALARM-RECEIVER
Displays the information on the receiver backup functionality parameters.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list backup-alarm-receiver
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 28
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 34

ARLY-1 Cfg>list backup-alarm-receiver
Backup Alarm Receiver Parameters:
-------------------------------CRA type: MAIN.
Synchronization Port: 35001.
Backup Alarm Receiver Parameters:
-------------------------------CRA type: BACKUP. Main CRA IP address: 172.24.77.53
Synchronization Port: 35001. Synchronization Timer: 300
Poll Timer: 5. Poll Failure Timer; 3
Number of Retries: 10. Retries timer: 5
d) LIST CFG-PATTERN
Lists the configuration of the configuration patterns.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list cfg-pattern ?
all
<1..255> Config-pattern id
•
LIST CFG-PATTERN ALL
Displays the parameters for all the configured patterns.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list cfg-pattern all
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list cfg-pattern all
MIP Configuration Patterns:
-------------------------Config Pattern ID : 1
Instalator Password : 1111
Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.69.152
Backup Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.70.54
Maintenance Receiver IP address : 81.23.56.89
Maintenance Alarm Password : 2AB4
Alarm Receiver UDP Port : 1222
MIP Console Password : 1111
MIP Password : 220771B
Alarm Receiver Password : 220771B
Keep-alives.
Timer : 21
Retries : 3
Retries Timer : 5
Backup Receiver Keep-alives.
Timer : 15
Retries : 4
Retries Timer : 1
Alarm Transmission Retries : 2
Telephone Number Length : 9
Callback Telephone Number :
Zone ID for local events :
ARLY-1 Cfg>
•
LIST CFG-PATTERN n
Displays the configuration pattern parameters whose identifier is n.
Syntax:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 29
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 35

ARLY-1 Cfg>list cfg-pattern n
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list cfg-pattern 1
Config Pattern ID : 1
Instalator Password : 1111
Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.69.152
Backup Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.70.54
Maintenance Receiver IP address : 81.23.56.89
Maintenance Alarm Password : 2AB4
Alarm Receiver UDP Port : 1222
MIP MIP Console Password : 1111
MIP Password : 220771B
Alarm Receiver Password : 220771B
Keep-alives.
Timer : 21
Retries : 3
Retries Timer : 5
Backup Receiver Keep-alives.
Timer : 15
Retries : 4
Retries Timer : 1
Alarm Transmission Retries : 2
Telephone Number Length : 9
Callback Telephone Number :
Zone ID for local events :
ARLY-1 Cfg>
e) LIST IO-CONF
Lists the configuration parameters relative to the receiver’s inputs and outputs.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list io-conf
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list io-conf
I/O Configuration:
----------------Input 1 : AC Loss
Input 2 : Low Battery
Output 1 : System-trouble-unrestored
Output 2 [fixed] : System failure
f) LIST MONITOR-IP-ADDR
Lists the monitoring parameters for the VisorALARM Internet connection.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list monitor-ip-addr
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 30
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 36

ARLY-1 Cfg> list monitor-ip-addr
Monitor IP address: None
g) LIST MIP
Displays the configuration for the mIP/IPDACTs.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list mip ?
all
<hex 0..ffffff> MIP account ID
•
LIST MIP ALL
Displays the parameters for all the configured mIP/IPDACTs.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list mip all
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list mip all
MIPs Configuration:
-----------------Account number : 9997
Serial number : 8209/00270
Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.69.152
Backup Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.70.54
Maintenance Receiver IP address : 81.23.56.89
Maintenance Alarm Password : 2AB4
Alarm Receiver UDP Port : 1222
MIP Console Password : 1111
MIP Password : 220771B
Alarm Receiver Password : 220771B
Keep-alives.
Timer : 21
Retries : 3
Retries Timer : 5
Backup Receiver Keep-alives.
Timer : 15
Retries : 4
Retries Timer : 1
Alarm Transmission Retries : 2
Telephone Number Length : 9
Callback Telephone Number :
Zone ID for local events : 015
ARLY-1 Cfg>
•
LIST MIP n
Displays the parameters for the mIP/IPDACT with identifier n.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list mip n
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 31
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 37

ARLY-1 Cfg>list mip 9997
Account number : 9997
Serial number : 8209/00270
Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.69.152
Backup Alarm Receiver IP address : 81.23.70.54
Maintenance Receiver IP address : 81.23.56.89
Maintenance Alarm Password : 2AB4
Alarm Receiver UDP Port : 1222
MIP Console Password : 1111
MIP Password : 220771B
Alarm Receiver Password : 220771B
Keep-alives.
Timer : 21
Retries : 3
Retries Timer : 5
Backup Receiver Keep-alives.
Timer : 15
Retries : 4
Retries Timer : 1
Alarm Transmission Retries : 2
Telephone Number Length : 9
Callback Telephone Number :
Zone ID for local events : 015
ARLY-1 Cfg>
h) LIST PRIORITY-STANDARD
Lists the priority standard configured at the VisorALARM receiver.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list priority-standard
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list priority-standard
Priority:
-------Priority Standard : UL (US)
i) LIST SERIAL-PARAMETERS
Lists the serial line configuration parameters for the serial line over which the events are sent
to the automation software.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 32
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 38

Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list serial-parameters
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list serial-parameters
Serial parameters
----------------Link speed.: 9600 (bit/sec)
Data bits..: 8
Stop bits..: 1
Parity.....: none
j) LIST SMS
Displays the SMS message reception configuration. Please see manual Dm 322-I
“VisorALARM SMS” for further information on this command.
k) LIST SUPERVISION
Displays the information on the mIP/IPDACTs supervision parameters.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>list supervision
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg> list supervision
Supervision Port: 1234.
l) LIST USER-DEFINED-EVENTS
Displays the information on the Contact ID codes for events locally generated for technical
alarms.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg> list user-defined-events
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 33
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 39

ARLY-1 Cfg> list user-defined-events
User defined event codes:
-----------------------New MIP instalation (register) : 633
MIP loss of contact : 350
VisorALARM network failure : 356
MIP goes to backup mode : 394
MIP sending events to backup VisorALARM : 395
VisorALARM down-active : 396
Primary VisorALARM down : 399
Secondary VisorALARM down : 358
Alarm store occupation reaches 100% : 393
MIP input active/deactive : 110
MIP input sensor trouble : 380
MIP tamper : 383
MIP PSTN Supervision : 351
MIP change detected : 306
VisorALARM supervised hdw fault : 300
MIP HW Failure : 333
VisorALARM time inaccurate : 397
VisorALARM AC loss : 301
VisorALARM low system battery : 302
VisorALARM log cleared : 621
VisorALARM log 50% loaded : 622
VisorALARM log 90% loaded : 623
VisorALARM log overflowed : 624
VisorALARM log saved to file : 655
2.8. LOG
Permits you to monitor and manage the SRAM events log included in a VisorAlarm receiver equiped
with a VA-UD expansion board.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>log ?
clear Clear current SRAM signals database
info State of SRAM signal database
save Save current SRAM signal database to file [SRAM_date_time.log]
a) LOG CLEAR
Clear the whole SRAM events log. This command is intended to be used after saving the log to a file.
Only use this command if you are fully aware and understand its reach and consequences.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>log clear
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>log clear
ARLY-1 Cfg>
b) LOG INFO
Displays information about SRAM events log:
• Total signals. Total number of signals received and stored at the VisorAlarm receiver.
Percentage of SRAM events log memory already occupied.
• Unacknowledged signals. Number of signals pending to be acknowledged by operator at the
VisorAlarm receiver, specifying how many of them relate to system trouble condition type.
• Unrestored signals. Number of signals pending to be restored to normal status at the
VisorAlarm receiver, specifying how many of them relate to system trouble condition type.
Syntax:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 34
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 40

ARLY-1 Cfg>log info
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>log info
--------------SRAM Log Status
--------------Total signals: 69065 (82%)
Unacknowledged signals: 1 (system trouble 0)
Unrestored signals: 0 (system trouble 0)
ARLY-1 Cfg>
c) LOG SAVE
Saves SRAM events log to a file named “SRAM_<yymmdd>_<hhmmss>.log”. If an integrity error at
the SRAM is detected while saving, the file extension will be set to “.bak”.
This command doesn’t clear the event log but just saves it into a system file.
Generated log files can only be opened in a PC using the Teldat software Load option “VisorAlarm
Serial Line Monitor”. You can use an FTP client for downloading log files from VisorAlarm receiver
to a PC.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>log save
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>log save
Saving signal database to file ...
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
...........................................................
Save complete to file A:SRAM_061027_171514.LOG
ARLY-2 Cfg>exit
Config>file list
Config Media: SmartCard and Flash
A: FW000000.BFW 177408 04/21/05 08:32 Flash
A: FW000002.BFW 210560 04/21/05 08:33 Flash
A: FW000003.BFW 422656 04/21/05 08:33 Flash
A: ROUTER.CFG 8683 02/28/06 19:21 Flash
A: TEST.CFG 304 09/14/06 09:01 Flash
A: VAUL.CFG 2073 10/27/06 17:13 Flash
A: ATLAS2G.BIN 6828160 10/27/06 09:55 Flash
A: SRAM_061027_171514.LOG 863325 10/27/06 17:15 Flash
Flash Available Space : 7506 Kbytes
Config>
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 35
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 41

Example:
Start vaslm.exe, click on the “Load” tab, select file to open and click “Accept”. You can see
percentage of file opened on the right-down corner. If the “Stop” button is not clicked, it’ll be
100%.
2.9. MIP
Contains the configuration for each mIP/IPDACT registered so if necessary these can be remotely
updated. The information consists of the serial number, account number, the passwords needed for
exchange of information, etc. On registering an mIP/IPDACT, this information is automatically
created from the configuration pattern. The information is organized depending on the account
number assigned to the mIP/IPDACT. Default is no mIP/IPDACT has been configured in the device.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP <account number>
default sets default values to an existing or a new
entry
serial-number MIP current serial-number
receiver-ip Public IP address which MIP uses to send
alarms
receiver-udp-port UDP port used to exchange info
usr-password MIP console protected password
mip-password MIP encrypt password used to send alarms
receiver-password Encrypt password this eq. uses on mssg to
that MIP
keep-alive-timer MIP keep-alive timer in seconds
keep-alive-retries MIP keep-alive num of retries
keep-alive-retries-timer MIP time between keep-alive retries in
seconds
phone-length Number DTMF digits Alarm Panel dials to make
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 36
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 42

calls
alarm-tx-retries Times MIP retransmmit an alarm before abandon
callback-phone Phone number Alarm Panel dials to make a
callback
bck-receiver-ip Public IP address which MIP uses to send
alarms to the backup VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-timer MIP keep-alive timer in seconds for backup
VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-retries MIP keep-alive num of retries for backup
VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-retries-time MIP time between keep-alive retries in
seconds for backup VisorAlarm
reset reset remote MIP
local-events-zone Zone number to use in locally generated
events
mnt-ip-address Maintenance IP address
mnt-password Password for maintenance alarms
local-ip-parameters IP parameters for MIP ethernet interface
pstn-action Action to be done in the MIP when PSTN fail.
subscriber-telephone The subscriber┤s telephone in whose premises
are the mIP installed.
last-update-time The date and time of the last MIP
configuration update
anti-substitution Enabling mechanism for detecting the MIP
substitution.
a) MIP accnt Default
Establishes the default configuration for the specified mIP/IPDACT. To completely delete an
mIP/IPDACT configuration, use the NO MIP accnt DEFAULT command.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt DEFAULT
accnt
mIP/IPDACT account number. This is composed of up to 6
hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F). The range is from
000001 to FFFFFF.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 10 DEFAULT
ARLY-1 Cfg>
b) MIP accnt SERIAL-NUMBER
Configures the serial number that the mIP/IPDACT has associated to this account number. The
account number is used to certify that mIP/IPDACT associated to the said account is the correct one,
thus avoiding possible supplanting problems.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt SERIAL-NUMBER serial_number
serial_number
mIP/IPDACT serial number as shown on its label.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 SERIAL-NUMBER 8209/300
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 37
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 43

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt SERIAL-NUMBER serial_number
c) MIP accnt RECEIVER-IP
Configures the alarm receiver’s IP address in the mIP/IPDACT.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt RECEIVER-IP ip_address
ip_address
Alarm receiver IP address.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 RECEIVER-IP 172.24.78.99
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt RECEIVER-IP ip_address
d) MIP accnt RECEIVER-UDP-PORT
Configures the UDP port for connection with the distinct mIP/IPDACTs.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt RECEIVER-UDP-PORT port_number
port_number
Number of the UDP port used. Admits values between 1 and 65535.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 RECEIVER-UDP-PORT 20300
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt RECEIVER-UDP-PORT port_number
e) MIP accnt USR-PASSWORD
Configures the mIP/IPDACT configuration / monitoring console password. This is applied to both the
asynchronous console as well as the telephonic console.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt USR-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 USR-PASSWORD 12FED00B3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 38
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 44

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt USR-PASSWORD password
f) MIP accnt MIP-PASSWORD
Configures the password with which the mIP/IPDACT encrypts its messages.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt MIP-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 MIP-PASSWORD 12FED00B3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt MIP-PASSWORD password
g) MIP accnt RECEIVER-PASSWORD
Configures the password with which the VisorALARM encrypts its messages.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt RECEIVER-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 RECEIVER-PASSWORD 12FED00B3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt RECEIVER-PASSWORD password
h) MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER
Configures the time interval used by the mIP/IPDACT to check connectivity with the VisorALARM.
Each time this timer times out, a keep-alive frame is sent to notify the VisorALARM that the
connection is active and waits for its response.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames. Admits values between 0
and 90.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 39
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 45

To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
If you use a value of zero for the “keep-alive-timer parameter”, the mIP/IPDACT will
not send supervision trafic to the receiver and the VisorALARM will not be able to
access the device for remote configuration.
i) MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES
Configures the number of times the mIP/IPDACT will transmit a keep-alive frame without receiving a
response from the VisorALARM. If the mIP/IPDACT, on executing the connectivity test with the
Teldat VisorALARM, does not receive a response within the “time-between-send-keep-alive-retries”
seconds, the mIP/IPDACT repeats the process of transmitting the keep-alive frame. Should there be
no response within same time interval, the mIP/IPDACT repeats the process until the number of retries
configured in the register has been completed. The connection with the Teldat VisorALARM is
considered down once the number of configured retries in this register has been executed and
subsequently the control panel can access the telephone network.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
num_times
Number of times the keep-alive frames are sent when the no response
is received. Admits values between 1 and 9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
j) MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER
Configures the time interval used by the mIP/IPDACT to send keep-alive retries to notify the
VisorALARM that the connection is active.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames when a possible
connectivity problem is detected. Admits values between 3 and 9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER 1
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 40
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 46

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
k) MIP accnt PHONE-LENGTH
In the mIP/IPDACT this configures the number of digits making up a telephone number. This number
depends on the country’s dialing plan, the existence of switchboards etc. The mIP/IPDACT uses this
to find out how many digits it should expect from the control panel before processing the call.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt PHONE-LENGTH length
length
Number of digits making up a telephone number. Admits values
between 1 and 15.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 PHONE-LENGTH 9
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt PHONE-LENGTH length
l) MIP accnt ALARM-TX-RETRIES
Configures the number of times that the mIP/IPDACT transmits an alarm to the VisorALARM to
ensure that this receives the alarm and sends confirmation to the mIP/IPDACT. Connection with is
considered lost once this number of retries has been completed and permits the control panel to send
the alarm over the telephone line.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt ALARM-TX-RETRIES number
number
Number of times the alarm is sent to the VisorALARM. Admits
values between 5 and 10.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 ALARM-TX-RETRIES 5
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt ALARM-TX-RETRIES number
m) MIP accnt CALLBACK-PHONE2
Configures the telephone number used by the control panel to execute bi-directional operations in callback mode.
2
Not available in US versions
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 41
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 47

Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt CALLBACK-PHONE telephone_number
telephone_number
Telephone number dialed by the control panel to execute bidirectional in call-back mode.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 CALLBACK-PHONE 918076123
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt CALLBACK-PHONE telephone_number
n) MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-timer however it is applied to the backup
VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
Time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames. Admits values between 0
and 90.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
If you use a value of zero for the “bck-keep-alive-timer parameter”, the mIP/IPDACT
will not send supervision trafic to the receiver and the VisorALARM will not be able to
access the device for remote configuration.
o) MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-retries however it is applied to the backup
VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
num_times
Number of times keep-alive frames are sent in situations where
responses are not received. Admits values between 1 and 9.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 42
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 48

Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
p) MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-retries-timer however it is applied to the
backup VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames when a possible
connectivity failure has been detected. Admits values between 3 and
9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER 3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
q) MIP accnt RESET
This command does not handle configuration but restarts the mIP/IPDACT with account accnt.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt RESET
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 101234 RESET
ARLY-1 Cfg>
r) MIP accnt LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE
This parameter defines the base number for the zone field that will be appear in all the events
generated by a mIP/IPDACT that does not come from the Alarm Panel. This parameter is not sent to
the mIP/IPDACT when a register is produced, rather it is stored in the mIP/IPDACT local
configuration and is used for local events generated for this account number.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP accnt local-events-zone identifier-zone
identifier-zone
This is a hexadecimal number of up to three digits.
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 43
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 49

ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP 101234 LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE 015
ARLY-1 Cfg>
s) MIP accnt MNT-IP-ADDRESS
This parameter defines the address of the maintenance receiver that must receive the “Maintenance
Signals”. “Maintenance signals” are those “System Trouble” signals or “Communication Trouble”
signals of a mIP/IPDACT device that must be sent to an alternate site in order to perform an
specialized management of the problems.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt mnt-ip-address ip-address
IP-address
IP Address of the Maintenance VisorALARM.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 77889900 MNT-IP-ADDRESS 80.16.90.104
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt MNT-IP-ADDRESS ip-address
t) MIP accnt MNT-PASSWORD
This parameter is the encryption keyword for the Maintenance VisorALARM messages. This
keyword can depend on the mIP/IPDACT account number as with any other password.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt MNT-PASSWORD password
Password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP 77889900 MNT-PASSWORD 12XYZ00BZ
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt MNT-PASSWORD password
u) MIP accnt LOCAL-IP-PARAMETERS
Not available
v) MIP accnt PSTN-ACTION
Not available.
w) MIP accnt SUBSCRIBER-TELEPHONE
This parameter defines is the Alarm Panel Phone Number.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 44
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 50

Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP accnt subscriber-telephone telephone_number
telephone_number
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP 101234 SUBSCRIBER-TELEPHONE 914567898
ARLY-1 Cfg>
This is the number that UD software dials to make an bi-directional
management operation with a Alarm Panel.
x) MIP accnt LAST-UPDATE-TIME
This parameter is for system use and it holds the date and time of the last configuration update for this
mIP/IPDACT device.
mip 90001234 anti-substitution enable
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP accnt last-update-time "MM/DD/YY hh :mm :ss"
MM/DD/YY hh :mm :ss
Month/Day/Year Hour:Minutes:Seconds
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP 101234 LAST-UPDATE-TIME "04/16/07 11:51:47"
ARLY-1 Cfg>
y) MIP accnt ANTI-SUBSTITUTION
This parameter is for system use and it defines if anti-substitution detection must be performed on this
device. With anti-substitution if a device is replaced with another device with a different serial number
a “System Trouble” signal will be raised and operation of the new device will be disabled.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP accnt anti-substitution flag
flag
enabled: Antisubstitution detection is performed on this device
disabled: Antisubstitution detection is no performed on this device
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP 101234 ANTI-SUBSTITUTION enabled
ARLY-1 Cfg>
2.10. MONITOR-IP-ADDR
If the access network connection drops, it will stop receiving traffic from the registered
mIP/IPDACTs. Once the supervision timer times out, an alarm is generated for each registered
mIP/IPDACT. This situation can flood both the Automation Sw as well as the VisorALARM. To
avoid this, you can monitor the access to a configurable network address. If, after three attempts,
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 45
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 51

access to this address fails, a 356 code alarm is generated (Loss of Poll) to the Automation Sw and the
alarms due to loss of connectivity with the mIP/IPDACTs are not generated.
The parameters required are an IP address and the IP address polling interval. This value is expressed
in seconds and admits values between 5 and 255 seconds. Default is supervision is not configured for
any network address.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MONITOR-IP-ADDR IP_address RATE supervision_interval
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MONITOR-IP-ADDR 172.24.88.34 RATE 15
ARLY-1 Cfg>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MONITOR-IP-ADDR IP_address RATE supervision_interval
2.11. NO
This command is used to negate other commands or to restore the default configuration for a
determined parameter.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>no ?
alarm-receiver Alarm Receiver emulation params
automation-software-required Specify if automation SW is required to
return kissoffs
backup-alarm-receiver Parameters for network backup
cfg-pattern Config pattern params
description Remove interface description
mip MIP configuration params
monitor-ip-addr Internet IP addr to check availability
shutdown Change state to administratively up
sms SMS receiving params
supervision MIP supervision params
update Update a level indicator
user-defined-events Codes for user defined events
In the section for each of the commands that can be preceded by the word “NO”, the effects of this
have been explained. For further information, please see the section on the required command.
2.12. PRINTABLE EVENTS
Normally traditional alarm receivers have a printer connected to a serial port where the events are
dumped, e.g. alarms coming from a panel. With the aim of integrating this functionality in the
VisorALARM IP receiver, the possibility to connect a serial port to the device has been incorporated
so a set of programmable events can be dumped in ASCII format. These events are based on the
device events logging system. The VisorALARM has 37 console events indicating different situations
and errors. However these events can be classified in groups which are characterized by a determined
functionality. This classification produces the following printable events:
Alarm events. These are events indicating alarm reception and storage before being sent to
the automation SW. The console events making up this functionality are as follows:
9 ARLY_16: Receives an alarm from an MIP with a specified account number.
9 ARLY_19: An alarm is received, saved in a temporary buffer, to be subsequently sent
to the automation software.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 46
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 52

9 ARLY_20: Stored alarm is deleted after being sent to the automation software.
9 ARLY_37: Percentage indication for the stored alarms with respect to the size of the
temporary buffer.
MIP events. These events indicate the active MIPs status and the registering of new MIPs.
Events encompassed in this functionality are as follows:
9 ARLY_7: Registers a stored MIP.
9 ARLY_12: A contact frame has been received from an MIP with a specified account
number.
9 ARLY_13: A keep-alive frame has been received from an MIP with a specified
account number.
9 ARLY_24: A register frame from an MIP with a specified account number.
9 ARLY_25: Remote configuration of an MIP with a specified account number.
System events. Indicates the status of the VisorALARM (ACTIVE, BACKUP, etc.) and the
MIP. The events encompassed by this functionality are as follows:
9 ARLY_34: Indicates a change in the status of the main VisorALARM.
9 ARLY_35: Indicates a change in the status of the backup VisorALARM.
9 ARLY_36: Indicates a change in the status of the MIP (failover).
Configuration synchronization protocol events. These events describe the different phases of
the synchronization protocol. Events encompassed in this functionality are as follows:
9 ARLY_29: The main VisorALARM is accessible.
9 ARLY_32: Synchronization protocol events in the main VisorALARM.
9 ARLY_33: Synchronization protocol events in the backup VisorALARM.
Serial line events with the automation SW. These are data transmission/reception events for
the serial line. Events encompassed in this functionality are as follows:
9 ARLY_4: A frame has been received from the serial line connected to the automation
SW.
9 ARLY_5: A frame has been sent to the serial line connected to the automation SW.
Communication events. These are events on the sending and receiving of data in the
VisorALARM. Not all the possible events are displayed, as this would imply overloading the
printer which would consequently operate inefficiently. In any case, you can access the
information on all the packets received and sent by the VisorALARM through the console.
The event encompassed in this functionality is as follows:
9 ARLY_10: A frame has been received from an MIP.
IP address monitoring events. These are events on the monitoring status of a server which
indicates a possible communications error. The event encompassed in this functionality is as
follows:
9 ARLY_3: Monitoring message on the server IP address.
Error events. These events indicate errors detected in the system. Events encompassed in this
functionality are as follows:
9 ARLY_17: Error frame from an MIP with a specified account number.
9 ARLY_18: Lost alarm from an MIP with a specified account number.
9 ARLY_21: Alarm lost. No buffer to process it.
9 ARLY_14: The supervision time for an MIP with a specified account number has
timed out.
9 ARLY_15: Erroneous supervision frame from an MIP with a specified account
number.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 47
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 53

9 ARLY_27: Failure in polling with the main VisorALARM.
9 ARLY_28: Polling retry.
9 ARLY_6: Error detected in the automation SW.
9 ARLY_11: An erroneous frame has been received from an MIP.
9 ARLY_26: Various types of errors.
The operator can select which functionality he/she wises to send to the serial port or whether all the
events are sent to the said port.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>printable-events PARAMETRO enable/disable
alarm set of alarm events
mip set of MIP events
system-status set of system status events
csp set of configuration synchronization protocol events
serial-line set of serial line events
communication set of communication events
ip-monitoring set of IP monitoring event
error set of error event
all set all of events
So that the enabled events can be sent to the serial port, the device must have the SEPI (Serial Event
Printing Interface) interface enabled. If it is not enabled, when enabling one of the groups of printable
events, the following warning message is displayed:
Warning: the Serial Event Printing Interface is not configured
2.13. PRIORITY-STANDARD
Permits you to select the priority to be applied when ordering and displaying received signals:
• Contact-ID: Priorization from highest to lowest, must be used for UL listed systems.
1) Fire Alarm: 11x
2) Hold-up o Panic Alarm: 12x
3) Burglar Alarm: 13x, 14x
4) Industrial supervision with possible danger: 15x 16x
5) Watchman tour:
6) Fire-alarm supervision: 20x
7) Burglar-alarm supervision: 3xx
8) Industrial supervision without possible danger: 35x, 37x y 38x
9) Other
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>priority-standard ?
contact-id Contact-ID higher codes has higher priority
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>priority-standard contact-id
ARLY-1 Cfg>
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 48
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 54

The default configuration for this parameter is Contact-ID.
2.14. SERIAL-PARAMETERS
Permits you to configure the asynchronous serial connection parameters used to connect the
VisorALARM to the Automation Sw. These parameters refer to the line speed, n data bits, stop bits,
etc.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS parameter parameter_value
data-bits
parity
speed
stop-bits
a) SERIAL-PARAMETERS DATA-BITS
Establishes the number of data bits. The available values are 5, 6, 7, and 8. Default is 8.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS DATA-BITS number_data_bits
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS DATA-BITS 7
ARLY-1 Cfg>
b) SERIAL-PARAMETERS PARITY
Establishes the type of parity used. The available values are as follows:
EVEN: EVEN parity.
MARK: MARK parity.
NONE: No parity used.
ODD: ODD parity.
SPACE: SPACE parity
Default is NONE.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS PARITY parity_type
EVEN
MARK
NONE
ODD
SPACE
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS PARITY EVEN
ARLY-1 Cfg>
c) SERIAL-PARAMETERS SPEED
Establishes the transmission / reception speed in the serial line (in bits/s). The available values are
between 300 and 64000 bps. Default is 9600 bps.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS SPEED speed
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 49
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 55

ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS SPEED
Type link speed (300 - 64000) [19200]? 64000
ARLY-1 Cfg>
d) SERIAL-PARAMETERS STOP-BITS
Establishes the number of stop bits. The available values are: 1 and 2. Default is 1.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS STOP-BITS number_stop_bits
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS STOP-BITS 2
ARLY-1 Cfg>
2.15. SHUTDOWN
Permits you to establish the interface administrative state. An interface may or may not be configured;
it can also be active (UP) or inactive (DOWN). Through this command you can configure the
interface activity layer. Under certain conditions, in order to resolve problems, it may be advisable to
leave some interfaces inactive. Default is administrative state UP.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SHUTDOWN
Example:
To establish the physical interface administrative state as DOWN
ARLY-1 Cfg>SHUTDOWN
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To establish the physical interface administrative state as UP:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO SHUTDOWN
ARLY-1 Cfg>
2.16. SMS
Configures the parameters relative to alarm reception through SMS messages.
These commands are only available when you have a GPRS/GSM card for alarm reception through
SMS messages.
For further information, please see manual Dm 322-I “VisorALARM: Alarm Reception through
SMS”.
2.17. SUPERVISION
Permits you to configure the UDP port used to exchange information with the mIP/IPDACTs. This is
the register information, keep-alive, alarms, etc. If there are devices executing NAT, etc, make sure
that this port remains open for information exchange. Additionally, check that this port is not being
used for other tasks. This value must coincide with the UDP port value configured in the supervised
mIP/IPDACTs.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 50
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 56

The port value is between 1 and 65535. Default is 80.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SUPERVISION PORT port_number
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>SUPERVISION PORT 20300
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO SUPERVISION PORT port_number
2.18. UPDATE
Remotely updates the specified mIP/IPDACT. Once this has been executed the said information
updates in the VisorALARM.
Contains the configuration for each mIP/IPDACT registered so if necessary these can be remotely
updated. The information consists of the serial number, account number, the passwords needed for
exchange of information, etc. On registering an mIP/IPDACT, this information is automatically
created from the configuration pattern. The information is organized depending on the account
number assigned to the mIP/IPDACT. Default is no mIP/IPDACT has been configured in the device.
Syntax:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 51
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 57

ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP <account number>
default sets default values to an existing or a new
entry
serial-number MIP current serial-number
receiver-ip Public IP address which MIP uses to send
alarms
receiver-udp-port UDP port used to exchange info
usr-password MIP console protected password
mip-password MIP encrypt password used to send alarms
receiver-password Encrypt password this eq. uses on mssg to
that MIP
keep-alive-timer MIP keep-alive timer in seconds
keep-alive-retries MIP keep-alive num of retries
keep-alive-retries-timer MIP time between keep-alive retries in
seconds
phone-length Number DTMF digits Alarm Panel dials to make
calls
alarm-tx-retries Times MIP retransmmit an alarm before abandon
callback-phone Phone number Alarm Panel dials to make a
callback
bck-receiver-ip Public IP address which MIP uses to send
alarms to the backup VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-timer MIP keep-alive timer in seconds for backup
VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-retries MIP keep-alive num of retries for backup
VisorAlarm
bck-keep-alive-retries-time MIP time between keep-alive retries in
seconds for backup VisorAlarm
reset reset remote MIP
pstn-action Action to be done in the MIP when PSTN fail
subscriber-telephone The subscriber┤s telephone in whose premises
are the mIP installed.
last-update-time The date and time of the last MIP
configuration update
anti-substitution Enabling mechanism for detecting the MIP
substitution.
a) UPDATE MIP accnt Default
Remotely updates the mIP/IPDACT specified through the account number with all the parameters
currently available.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt DEFAULT
accnt
MIP account number. This is composed of up to 6 hexadecimal digits
(0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F). The range is from 000001 to FFFFFF.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 DEFAULT
ARLY-1 Cfg>
b) UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-IP
Configures the alarm receiver IP address in the mIP/IPDACT.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-IP ip_address
ip_address
Alarm receiver IP address.
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 52
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 58

ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 RECEIVER-IP 172.24.78.99
ARLY-1 Cfg>
c) UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-UDP-PORT
Configures the UDP port for connection with the distinct mIP/IPDACTs.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-UDP-PORT port_number
port_number
Number of the UDP port used. Admits values between 1 and 65535.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 RECEIVER-UDP-PORT 20300
ARLY-1 Cfg>
d) UPDATE MIP accnt USR-PASSWORD
Configures the mIP/IPDACT configuration / monitoring console password. This is applied to both the
asynchronous console as well as the telephonic console.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt USR-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 USR-PASSWORD 12FED00B3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
e) UPDATE MIP accnt MIP-PASSWORD
Configures the password with which the mIP/IPDACT encrypts its messages.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt MIP-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 MIP-PASSWORD 12FED00B3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
f) UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-PASSWORD
Configures the password with which the VisorALARM encrypts its messages.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt RECEIVER-PASSWORD password
password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 53
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 59

Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 RECEIVER-PASSWORD 12FED00B3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
g) UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER
Configures the time interval used by the mIP/IPDACT to check connectivity with the VisorALARM.
Each time this timer times out, a keep-alive frame is sent to notify the VisorALARM that the
connection is active and waits for its response.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames. Admits values between 0
and 90.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
h) UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES
Configures the number of times the mIP/IPDACT will transmit a keep-alive frame without receiving a
response from the VisorALARM. If the mIP/IPDACT, on executing the connectivity test with the
Teldat VisorALARM, does not receive a response within the “time-between-send-keep-alive-retries”
seconds, the mIP/IPDACT repeats the process of transmitting the keep-alive frame. Should there be
no response within same time interval, the mIP/IPDACT repeats the process until the number of retries
configured in the register has been completed. The connection with the Teldat VisorALARM is
considered down once the number of configured retries in this register has been executed and
subsequently the control panel can access the telephone network.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
num_times
Number of times the keep-alive frames are sent when the no response
is received. Admits values between 1 and 9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
i) UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER
Configures the time interval used by the mIP/IPDACT to send keep-alive retries to notify the
VisorALARM that the connection is active.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames when a possible
connectivity problem is detected. Admits values between 3 and 9.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 54
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 60

Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER 3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
j) UPDATE MIP accnt PHONE-LENGTH
In the mIP/IPDACT this configures the number of digits making up a telephone number. This number
depends on the country’s dialing plan, the existence of switchboards etc. The MIP uses this to find out
how many digits it should expect from the control panel before processing the call.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt PHONE-LENGTH length
length
Number of digits making up a telephone number. Admits values
between 1 and 15.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 PHONE-LENGTH 9
ARLY-1 Cfg>
k) UPDATE MIP accnt ALARM-TX-RETRIES
Configures the number of times that the mIP/IPDACT transmits an alarm to the VisorALARM to
ensure that this receives the alarm and sends confirmation to the mIP/IPDACT. Connection with is
considered lost once this number of retries has been completed and permits the control panel to send
the alarm over the telephone line.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt ALARM-TX-RETRIES number
number
Number of times the alarm is sent to the VisorALARM. Admits
values between 5 and 10.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 ALARM-TX-RETRIES 5
ARLY-1 Cfg>
l) UPDATE MIP accnt CALLBACK-PHONE
Configures the telephone number used by the control panel to execute bi-directional operations in callback mode.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt CALLBACK-PHONE telephone_number
telephone_number
Telephone number dialed by the control panel to execute bidirectional in call-back mode. Admits values between 1 and 9.
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 55
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 61

ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 CALLBACK-PHONE 918076123
ARLY-1 Cfg>
m) UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-timer however it is applied to the backup
VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames. Admits values between 0
and 90.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-TIMER time
n) UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-retries however it is applied to the backup
VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
num_times
Number of times keep-alive frames are sent in situations where
responses are not received. Admits values between 1 and 9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES 30
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES num_times
o) UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER
This parameter is the same as the keep-alive-retries-timer however it is applied to the
backup VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
time
Time in seconds between keep-alive frames when a possible
connectivity failure has been detected. Admits values between 3 and
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 56
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 62

9.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER 3
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO UPDATE MIP accnt BCK-KEEP-ALIVE-RETRIES-TIMER time
p) UPDATE MIP accnt RESET
Resets the mIP/IPDACT whose account number has been provided.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt RESET
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 101234 RESET
ARLY-1 Cfg>
q) UPDATE MIP accnt LOCAL-EVENTS-ZONE
Only available for mIP/IPDACT command.
r) UPDATE MIP accnt MNT-IP-ADDRESS
This parameter defines the address of the maintenance receiver that must receive the “Maintenance
Signals”. “Maintenance signals” are those “System Trouble” signals or “Communication Trouble”
signals of a mIP device that must be sent to an alternate site in order to perform an specialized
management of the problems.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt mnt-ip-address ip-address
IP-address
IP Address of the Maintenance VisorALARM.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP 77889900 MNT-IP-ADDRESS 80.16.90.104
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt MNT-IP-ADDRESS ip-address
s) UPDATE MIP accnt MNT-PASSWORD
This parameter is the encryption keyword for the Maintenance VisorALARM messages. This
keyword can depend on the mIP/IPDACT account number as with any other password.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>MIP accnt MNT-PASSWORD password
Password
Password of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E and F).
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 57
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 63

Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg> MIP 77889900 MNT-PASSWORD 12XYZ00BZ
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO MIP accnt MNT-PASSWORD password
t) UPDATE MIP accnt LOCAL-IP-PARAMETERS
This command programs the mIP/IPDACT IP parameters. Using this command the IP address, mask
and gateway can be programmed at once.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt LOCAL-IP-PARAMETERS ip-address mask gateway
IP-Address
Mask
Gateway
IP Address of the mIP/IPDACT ethernet interface.
Network mask for the mIP/IPDACT.
Internet Gateway IP Address.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 77889900 LOCAL-IP-PARAMETERS 192.168.1.200 255.255.255.0
192.168.1.1
ARLY-1 Cfg>
u) UPDATE MIP accnt PSTN-ACTION
This parameter sets the action that a mIP/IPDACT must carry out when a supervision failure
in its PSTN input is detected.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP accnt PSTN-ACTION action
Action
NONE-ACTION: Do nothing
SEND-ALARM: A Telco-1 trouble signal is sent
OUTPUT-ACTIVATION: The output is activated
BOTH-ALARM-OUTPUT: Both actions are carried out.
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>UPDATE MIP 77889900 PSTN-ACTION BOTH-ALARM-OUTPUT
ARLY-1 Cfg>
v) UPDATE MIP accnt SUBSCRIBER-TELEPHONE
Only available for mIP/IPDACT command.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 58
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 64

w) MIP accnt LAST-UPDATE-TIME
Only available for MIP command.
x) UPDATE MIP accnt ANTI-SUBSTITUTION
Only available for MIP command.
2.19. USER-DEFINED-EVENTS
Permits you to define the Contact ID codes for the events generated from the VisorALARM when
faced with certain situations.
• Loss of contact with an mIP/IPDACT.
• Registration/Installation of a new mIP/IPDACT.
• Loss of IP connectivity by the VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 59
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 65

mip-registration event code to send when a mip registers
mip-loss event code to send when a mip stop sending
keepalives
network-failure event code to send when the alarm receiver
loss network connectivity
communication-failure event code to send when the backup
alarm-receiver is in standby and it has
received keepalives from a backed-up MIP
config-err event code to send when the backup
alarm-receiver is in standby and it has
received keepalives from a MIP
down-active-state event code to send when the alarm receiver has
changed from active to down state.
primary-down event code to send when the backup alarm
receiver has detected that primary alarm
receiver is down.
backup-down event code to send when the primary alarm
receiver has detected that backup alarm
receiver is down.
available-roomFull event code to send when the alarm receiver has
no room to store alarms.
input-changed event code to send when a input mip has
changed.
input-sensor-trouble event code to send when a input sensor trouble
is detected.
tamper event code to send when a tamper open/close
detected.
PTSN-failure event code to send when a failure in the PTSN
line is detected.
MIP-changed event code to send when a registered MIP has
changed its Serial Number.
icmp-poll-failure event code to send when a ICMP polled device
fails to respond.
Hdw-fault event code to send when a supervised hardware
element faults.
MIP-HW-Failure event code to send when a HW fault is
detected.
visoralarm-time-inaccurate event code to send when the NTP protocol is
unable.
ac-loss event code to send when the AC power supply is
lost.
low-battery event code to send when the load of the system
battery is low.
log-clear event code to send when the log is cleared.
log-50load event code to send when the log is 50% loaded.
log-90load event code to send when the log is 90% loaded.
log-overflow event code to send when the log is overflowed.
log-save event code to send when the log is saved to file.
a) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-REGISTRATION
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the generated alarm when a new mIP/IPDACT
registration is received. Default value for this parameter is 633 (Module Added event).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-REGISTRATION <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-REGISTRATION 532
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 60
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 66

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-REGISTRATION <code>
b) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-LOSS
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the generated alarm when contact with an
mIP/IPDACT is lost, as packets indicating the mIP/IPDACT is active are no longer being received.
Default value for this parameter is 350 (Communication trouble event).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-LOSS <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-LOSS 351
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-LOSS <code>
c) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS NETWORK-FAILURE
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the generated alarm when an IP connectivity
problem is detected in the VisorALARM. Default value for this parameter is 356 (Loss of central
polling event).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS NETWORK-FAILURE <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS NETWORK-FAILURE 357
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command:
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS NETWORK-FAILURE <code>
d) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS COMMUNICATION-FAILURE
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the backup
VisorALARM when an IP connectivity problem between the mIP/IPDACT and the main
VisorALARM is detected. Detection is based on the fact that the backup VisorALARM receives
polls from an mIP/IPDACT which has switched to backup, but has not detected that the main has
failed. Default value for this parameter is 394.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS COMMUNICATION-FAILURE <code>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS COMMUNICATION-FAILURE 394
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 61
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 67

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS COMMUNICATION-FAILURE <code>
e) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS CONFIG-ERR
Permits you to configure an event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the backup VisorALARM
when a configuration problem is detected in an mIP/IPDACT as the backup VisorALARM receives
polls from an mIP/IPDACT that has not switched to backup. Default value for this parameter is 395.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS CONFIG-ERR <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS CONFIG-ERR 395
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS CONFIG-ERR <code>
f) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS DOWN-CTIVE-STATE
Permits you to configure an event code to be sent in the alarm generated both by the main and the
backup VisorALARM when this changes its state from active to down, i.e. when communications
failure has been detected. Default value for this parameter is 396 for the primary VisorALARM and
398 for the secondary.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS DOWN-ACTIVE-STATE <code>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS DOWN-ACTIVE-STATE 396
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS DOWN-ACTIVE-STATE <code>
g) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PRIMARY-DOWN
Permits you to configure an event code to be sent in the alarm generated both by the backup
VisorALARM when this is in backup mode. Default value for this parameter is 399.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PRIMARY-DOWN <code>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PRIMARY-DOWN 399
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 62
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 68

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PRIMARY-DOWN <code>
h) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS BACKUP-DOWN
Permits you to configure an event code to be sent in the alarm generated both by the main
VisorALARM when while not having communication failure, a situation where this is not being
polled by the backup device has been detected. Default value for this parameter is 358.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS BACKUP-DOWN <code>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS BACKUP-DOWN 358
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS BACKUP-DOWN <code>
i) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AVAILABLE-ROOMFULL
Permits you to configure an event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM
when it can not store more signals. Default value for this parameter is 393.
Sintaxis:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AVAILABLE-ROOMFULL <código>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Ejemplo:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AVAILABLE-ROOMFULL 690
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AVAILABLE-ROOMFULL <código>
j) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-CHANGED
Permits you to configure an event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when a
change in the input status alarm is received from the mIP/IPDACT. By default the alarm code is 110
(fire alarm).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-CHANGED <code>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-CHANGED 112
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 63
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 69

ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-CHANGED <code>
In the IP Module hardware, the input has three possible states:
No alarm, where the mIP/IPDACT detects a 1000 ohms resistance at its input.
Short-circuit in the input, which generates and alarm in the mIP/IPDACT whose default code
has a value of 110 (fire alarm).
Open circuit in the input, so the mIP/IPDACT considers there has been sabotage or sensor
failure and sends an alarm. This code is set through the INPUT-SENSOR-TROUBLE event
k) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-SENSOR-TROUBLE
This permits you to configure the event code sent in the alarm generated by the main VisorALARM
when it receives an open circuit in the input alarm from the mIP/IPDACT. The mIP/IPDACT
considers either sabotage has occurred or the sensor has failed. The default code for this alarm is 380
(Sensor trouble).Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-SENSOR-TROUBLE <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-SENSOR-TROUBLE 390
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS INPUT-SENSOR-TROUBLE <code>
l) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS-TAMPER
The IP Module hardware has a tamper input to detect the opening of the alarms panel. Under normal
circumstances, the input must be short-circuited. When this detects an open circuit, the module
considers that the panel has been opened and sends an alarm to the mIP/IPDACT with default code
383 (Sensor Tamper).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS TAMPER <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS TAMPER 384
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS TAMPER <code>
m) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PSTN-FAILURE
The IP Module hardware supervises the telephone line detecting possible failures on this. If a failure
is detected, the IP Module sends an alarm which, by default, the VisorALARM interprets with the
CONTACT-ID 351 code (Fail Telco-1).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PSTN-FAILURE <code>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PSTN-FAILURE 352
ARLY-1 Cfg>
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 64
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 70

To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS PSTN-FAILURE <code>
n) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-CHANGED
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when
a change in the Serial Number of a registered IP Module occurs, i.e. whenever an IP Module is
replaced by other unit. By default the alarm code is 306 (panel programming changed).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-CHANGED <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-CHANGED 306
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-CHANGED <code>
o) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS ICMP-POLL-FAILURE
The VisorALARM supervises the state of activity of each registered IP Module by sending ICMP
packets and listening to the response. Whenever a device fails to respond to the ICMP polling, the
VisorALARM sends an alarm which, by default, is assigned CONTACT-ID 330 code (system
peripheral trouble).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS ICMP-POLL-FAILURE <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS ICMP-POLL-FAILURE 330
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS ICMP-POLL-FAILURE <code>
p) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS HDW-FAULT
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when
a supervised hardware element faults. By default the alarm code is 300 (system trouble) and the zone
number allows the user to identify the specific hardware element which caused the fault:
• Zone 0: Cooling Fan 1.
• Zone 1: Cooling Fan 2.
• Zone 2: Liquid Crystal Display.
• Zone 3: Buzzer.
• Zone 4: Printer.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS HDW-FAULT <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 65
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 71

ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS HDW-FAULT 300
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS HDW-FAULT <code>
q) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-HW-FAILURE
The IP Module accomplishes hardware supervision of its main critical modules (CPU, CMX, etc.). If a
failure is detected, the IP Module sends an alarm which, by default, the VisorALARM interprets with
the CONTACT-ID 333 code (expansion module failure).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-HW-FAILURE <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-HW-FAILURE 333
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS MIP-HW-FAILURE <code>
r) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS VISORALARM-TIME-INACCURATE
The VisorALARM clock must be synchronized with an NTP server in order to guarantee time
accuracy. This command permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by
the VisorALARM when no NTP client configuration is detected or communication with the
configured NTP server fails. The default code for this alarm is 626 (time/date inaccurate).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS VISORALARM-TIME-INACCURATE <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS VISORALARM-TIME-INACCURATE 626
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS VISORALARM-TIME-INACCURATE <code>
s) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AC-LOSS
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when
an AC power loss (voltage under 10.2 V) is detected through the activation of the VisorALARM’s
general purpose input configured for this purpose by the UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply). By
default the alarm code is 301 (AC loss).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AC-LOSS <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 66
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 72

ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AC-LOSS 301
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS AC-LOSS <code>
t) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOW-BATTERY
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when
a low battery condition at the UPS (voltage between 10.2V and 11.5V) is detected through the
activation (by the UPS) of the VisorALARM’s general purpose input configured for this purpose. By
default the alarm code is 302 (low system battery).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOW-BATTERY <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOW-BATTERY 302
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOW-BATTERY <code>
u) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-CLEAR
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM
whenever the SRAM events log is cleared by an user (execution of command “log clear” in the ARLY
interface menu) or by the VisorALARM itself (as a consequence of an integrity error detection at
SRAM events log). By default the alarm code is 621 (event log reset).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-CLEAR <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-CLEAR 621
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-CLEAR <code>
v) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-50LOAD
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when
the SRAM event log is detected to have loaded to 50 % of its current total capacity. By default the
alarm code is 622 (event log 50% full).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-50LOAD <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 67
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 73

ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-50LOAD 622
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-50LOAD <code>
w) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-90LOAD
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when
the SRAM events log is detected to have loaded to 90 % of its current total capacity. By default the
alarm code is 623 (event log 90% full).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-90LOAD <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-90LOAD 623
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-90LOAD <code>
x) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-OVERFLOW
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when
this detects an overflow at the SRAM events log. By default the alarm code is 624 (event log
overflow).
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-OVERFLOW <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-OVERFLOW 624
ARLY-1 Cfg>
To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-OVERFLOW <code>
y) USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-SAVE
Permits you to configure the event code to be sent in the alarm generated by the VisorALARM when
the SRAM events log is saved to a file by a user (execution of command “log save” in the ARLY
interface menu). By default the alarm code is 655.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-SAVE <code>
ARLY-1 Cfg>
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-SAVE 655
ARLY-1 Cfg>
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 68
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 74

To return to the default configuration for this parameter, use the following command.
ARLY-1 Cfg>NO USER-DEFINED-EVENTS LOG-SAVE <code>
2.20. EXIT
Permits you to exit the ARLY interface configuration and return to the Config> prompt.
Syntax:
ARLY-1 Cfg>EXIT
Example:
ARLY-1 Cfg>EXIT
Config>
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Configuration
II - 69
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 75

Chapter 3
SEPI Interface Configuration
Page 76

1. Initial Configuration
So that the printable events defined in the ARLY interface can be sent to a serial printing device with
ASCII format, you need to configure an SEPI interface over one of the serial inputs in the device. The
SEPI interface configuration is carried out as follows:
Syntax:
*p 4
Config>set data-link serial0/X
Config>save yes
The X value corresponds to the VisorALARM serial interface number and must be different to that
used in the ARLY net.
Once the configuration has been saved, you need to restart the device to activate the new interface.
Once you have restarted, you can check that the operation has been correctly executed by displaying
all the device configuration or by displaying the status of the configured interfaces:
Config>show conf
; Showing System Configuration ...
; Visor Alarm Router 2 16 Version 10.5.9.0.2
log-command-errors
no configuration
description "Default configuration: VisorALARM standard"
set data-link arly serial0/0
set data-link sepi serial0/1
set data-link x25 serial0/2
cfg-mode binary
;
network serial0/2
; -- SEPI Interface Configuration -exit
;
exit
;
dump-command-errors
end
; --- end --Config>list device
Interface Connector Type of interface
ethernet0/0 LAN1 Fast Ethernet interface
serial0/0 SERIAL0/WAN1 ARLY Async Line
serial0/1 SERIAL1/WAN2 Serial Event Printer Interface
serial0/2 SERIAL2/WAN3 X25
x25-node --- Router->Node
Config>
How to check, in both cases, that the serial line serial0/1 has been configured as an SEPI interface.
To access the SEPI interface configuration, use the NETWORK command and the serial line
associated to the SEPI interface:
Config>NET serial0/1
-- SEPI Interface Configuration -BACKUP SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>
From this menu you can configure the serial line parameters to connect to the printer serial device.
VISOR ALARM – SEPI Configuration
III - 71
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 77

2. Command set
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>?
description Enter interface description
flow-control Set flow control mode
interface-buffer-size Set serial interface frame size
list List configuration
no Negates a command or sets its defaults
serial-parameters Set serial parameters
shutdown Change state to administratively down
exit
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>
2.1. DESCRIPTION
This is a parameter common to any of the device’s interfaces and is used to assign a string of
characters describing the interface functionality. This parameter is optional.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>description "Serial Relay Port"
To eliminate the description:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>no description
2.2. FLOW-CONTROL
This parameter is used to configure the type of flow control for the serial port. By using flow control,
you can guarantee that there is no loss of data when the receiver is slower at reception than in the
transmitter. The types of flow control supported by the interface are as follows:
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>flow-control ?
hardware Hardware flow control
xon-xoff Software flow control
all Hardware and software flow control
none No flow control
Configuration example:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>flow-control hardware
2.3. INTERFACE-BUFFER-SIZE
Configures the maximum data length that can be sent in a packet.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>interface-buffer-size length
Length
Admits values between 100 and 2048 bytes.
VISOR ALARM – SEPI Configuration
III - 72
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 78

2.4. LIST
Lists the interface parameters with their corresponding values.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>list all
Serial parameters
----------------Link speed.: 9600 (bit/sec)
Data bits..: 8
Stop bits..: 1
Parity.....: NONE
Interface parameters
--------------------
Flow control type.....: None
Interface buffer size.: 2048 (bytes)
2.5. NO
This command is used to negate another command or to reset the default configuration for a
determined parameter.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>no parameter
description Remove interface description
serial-parameters Set default serial parameters
shutdown Change state to administratively up
In the section for each of the commands that can be preceded by the word “NO”, the effects of this
have been explained. For further information, please see the section on the required command.
2.6. SERIAL-PARAMETERS
Permits you to configure the serial port parameters. The configurable parameters are as follows:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>serial-parameters ?
data-bits Set number of bits per character
parity Set character parity
speed Set speed
stop-bits Set number of stop bits per character
a) SERIAL-PARAMETERS DATA-BITS
Establishes the number of data bits. The available values are: 5, 6, 7 and 8. The default value is 8.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1>SERIAL-PARAMETERS DATA-BITS number_data_bits
Example:
SEPI-serial0/1>SERIAL-PARAMETERS DATA-BITS 7
SEPI-serial0/1>
VISOR ALARM – SEPI Configuration
III - 73
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 79

b) SERIAL-PARAMETERS PARITY
Establishes the type of parity used. The available values are as follows:
EVEN: EVEN parity.
MARK: MARK parity.
NONE: No type of parity is used.
ODD: ODD parity.
SPACE: SPACE parity.
Default value is NONE.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS PARITY parity_type
EVEN
MARK
NONE
ODD
SPACE
Example:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS PARITY EVEN
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>
c) SERIAL-PARAMETERS SPEED
Establishes the transmission / reception speed in the serial line (in bits per second –bps-). The
available values are between 300 and 64000 bps. Default is 9600 bps.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS SPEED speed
Example:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS SPEED
Type link speed (300 - 64000) [19200]? 64000
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>
d) SERIAL-PARAMETERS STOP-BITS
Establishes the number of stop bits. Available values are: 1 and 2. Default is 1.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS STOP-BITS number_stop_bits
Example:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>SERIAL-PARAMETERS STOP-BITS 2
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>
The default configuration for the serial parameters is carried out through the following command:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>NO SERIAL-PARAMETERS
2.7. SHUTDOWN
Permits you to establish the SEPI interface administrative state. An interface may or may not be
configured; it can also be active (UP) or inactive (DOWN). Through this command you can configure
VISOR ALARM – SEPI Configuration
III - 74
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 80

the level of activity in the interface. Under certain conditions, in order to resolve problems, it may be
advisable to leave some interfaces inactive. Default is administrative state UP.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>SHUTDOWN
Example:
To establish the interface administrative state to DOWN:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>SHUTDOWN
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>
To establish the interface administrative state to UP:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>NO SHUTDOWN
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>
2.8. EXIT
Permits you to exit the SEPI interface configuration and return to the Config> prompt.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>EXIT
Example:
SEPI-serial0/1 Cfg>EXIT
Config>
VISOR ALARM – SEPI Configuration
III - 75
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 81

Chapter 4
ARLY Interface Monitoring
Page 82

1. Monitoring the Serial Interface
Information on the serial device as such can be seen through the monitoring command DEVICE. As
well as showing the number of times the ARLY interface has dropped and reestablished, it also shows
the signal state, configuration for this and the error statistics. In order to obtain a printed version, enter
the following from the monitoring process:
+device serial0/0
Auto-test Auto-test Maintenance
Interface CSR Vect valids failures failures
serial0/0 FA200A00 5e 0 0 0
Interface DCE
V.24 circuits:105 106 107 108 109 125 141
Nicknames: RTS CTS DSR DTR DCD RI LL
State: OFF ON ON OFF ON --- ---
Speed (bps) = 57600
Throughput (bps) = 0
Last throughput (bps) = 0
Bits per character = 7
Stop bits = 2
Parity selected = EVEN
Parity errors = 0
Data errors = 0
Overrun errors = 0
Last reset = 17 minutes 16 seconds
+
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 77
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 83

2. Monitoring the ARLY Interface
To access the ARLY interface monitoring, use the NETWORK command and the serial line
associated to the ARLY interface from the monitoring process:
+network serial0/0
ARLY Monitoring
ARLY-1+
The available commands are as follows:
ARLY-1+?
CLEAR
LIST
TEST
EXIT
ARLY-1+
The commands relative to the supervised mIP/IPDACTs permit you to display the state of all
monitored mIP/IPDACTs or a specified one as well as the statistics for these. This provides a simpler
supervision method and a quicker way to detect problems. The commands are LIST MIP
STATISTICS and LIST MIP INFORMATION, etc.
The commands relative to the received alarms display the statistics for the said received alarms, alarms
lost as they could not be sent to the Automation SW and there was insufficient space to store these,
alarms sent to the Automation Sw, etc. This also shows the stored alarms for cases where these could
not be sent to the Automation Sw. These commands are LIST ALARM STATISTICS, LIST ALARM
INFORMATION, CLEAR ALARM INFORMATION, CLEAR ALARM STATISTICS, etc.
2.1. CLEAR
Permits you to delete statistics for processed alarms, received frames, those received both by the serial
interface as well as by the UDP, etc. This also permits you to delete stored alarms.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+CLEAR ?
ALARM
INTERFACE-STATISTICS
PROTOCOL
VISORALARM-STATE
a) CLEAR ALARM
Deletes information relative to alarms received from the various mIP/IPDACTs. The statistics or the
alarms stored in the device can also be deleted. These alarms are temporarily stored in the device if
they cannot be sent to the Automation Sw.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+CLEAR ALARM ?
INFORMATION
STATISTICS
•
CLEAR ALARM INFORMATION
Deletes alarms temporarily stored in the VisorALARM. These alarms are stored until they can be
sent to the Automation Sw through the serial interface or the corresponding interface. In order to
avoid accidental deletion, confirmation is requested before proceeding with the operation. This
information can be seen through the monitoring command LIST ALARM INFORMATION.
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 78
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 84

Syntax:
ARLY-1+CLEAR ALARM INFORMATION
Example:
ARLY-1+CLEAR ALARM INFORMATION
Are you sure ?(Yes/No) [No]? y
ARLY-1+
•
CLEAR ALARM STATISTICS
Deletes statistics supported by the VisorALARM relative to sent and received alarms. These statistics
can be viewed through the monitoring command LIST ALARM STATISTICS.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+CLEAR ALARM STATISTICS
Example:
ARLY-1+CLEAR ALARM STATISTICS
ARLY-1+
b) CLEAR INTERFACE-STATISTICS
Deletes statistics relative to the transmitting and receiving of data through the serial interface. These
statistics can be viewed through the monitoring command LIST INTERFACE-STATISTICS.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+CLEAR INTERFACE-STATISTICS
Example:
ARLY-1+CLEAR INTERFACE-STATISTICS
ARLY-1+
c) CLEAR PROTOCOL
Deletes statistics relative to the transmitting and receiving of data through the configured UDP port for
the ARLY interface. This also deletes statistics relative to the protocol used to communicate the MIPs
and the VisorALARM. These statistics can be viewed through the LIST UDP-STATISTICS and
LIST PROTOCOL commands.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+CLEAR PROTOCOL
Example:
ARLY-1+CLEAR PROTOCOL
ARLY-1+
d) CLEAR VISORALARM-STATE
Deletes the last date when configuration synchronization was produced and in the case of a backup
VisorALARM, this also deletes the period of time the device has been in BACKUP state.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1+CLEAR VISORALARM-STATE
Example:
SEPI-serial0/1+CLEAR VISORALARM-STATE
SEPI-serial0/1+
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 79
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 85

2.2. LIST
Permits you to consult statistics for processed alarms, frames sent, received both through the serial
interface as well as through the UDP, etc. This also permits you to check the state of one or all of the
supervised mIP/IPDACTs.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST ?
ALARM
INTERFACE-STATISTICS
MONITOR-IP-ADDR
MIP
PROTOCOL
SMS
UDP-STATISTICS
VISORALARM-STATE
a) LIST ALARM
Displays information relative to the alarms received from the various mIP/IPDACTs. The statistics or
the alarms stored in the device can be shown. These alarms are temporarily stored in the device if they
cannot be sent to the Automation Sw.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST ALARM ?
INFORMATION
STATISTICS
•
LIST ALARM INFORMATION
Displays the alarms temporarily stored in the VisorALARM. These alarms are stored until they can
be sent to the Automation Sw through the serial interface or the corresponding interface. This
information can be deleted through the CLEAR ALARM INFORMATION command.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST ALARM INFORMATION
Example:
ARLY-1+LIST ALARM INFORMATION
09/02/03 10:06:20- 101234 1234181131010158
ARLY-1+
•
LIST ALARM STATISTICS
Displays statistics supported by the VisorALARM relative to the sent and received alarms. The
number of alarms stored in the VisorALARM is displayed and the number of alarms that can still be
stored. These alarms are temporarily stored in the VisorALARM until they can be sent to the
Automation Sw through the serial interface or the corresponding interface. If alarms are received and
cannot be stored, they are lost. These are counted as Alarms Lost. These statistics can be deleted
through the monitoring command CLEAR ALARM STATISTICS.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST ALARM STATISTICS
Example:
ARLY-1+LIST ALARM STATISTICS
Alarms received: 0 Current alarms: 0
Alarms sent: 0 Available blocks: 500
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 80
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 86

Alarms lost: 0
ARLY-1+
b) LIST INTERFACE-STATISTICS
Displays statistics relative to the transmitting and receiving of data through the serial interface. These
statistics can be deleted through the monitoring command CLEAR INTERFACE-STATISTICS.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST INTERFACE-STATISTICS
Example:
ARLY-1+LIST INTERFACE-STATISTICS
Interface statistics:
--------------------Device status: ABSENT
Tx frames: 0 Rx frames: 0
Tx bytes: 0 Rx bytes: 0
ARLY-1+
c) LIST MIP
Displays information and statistics on the mIP/IPDACTs registered in the VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST MIP ?
INFORMATION
STATISTICS
STATUS
ALL
•
LIST MIP INFORMATION
Displays all known information on one or all the supervised mIP/IPDACTs. The command requests
an mIP/IPDACT account number to execute the operation. The account number is composed of one
to 8 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9 and letters A to F). If the account number is FFFFFFFF, information
on all the supervised mIP/IPDACTs is displayed.
The information shows the mIP/IPDACT account number, the state of this due to supervision, its
serial number and software version, configuration data and data relative to the UDP connection.
From the VisorALARM point of view, the mIP/IPDACT can adopt various states:
alive A keep-alive frame has been received from the mIP/IPDACT indicating that the
connection is operative. The connection is active.
clr Temporary state the mIP/IPDACT enters to check that keep-alive traffic is being
received. The connection is considered active. If the supervision timer times out
and the mIP/IPDACT state has not passed to alive, the connection is considered
lost and passes to a lost state.
lss-sgn The configured supervision time has timed out and a keep-alive frame has not been
received from the mIP/IPDACT. The connection is considered lost.
rgstr State taken by an mIP/IPDACT after the VisorALARM has started up. The
connection is not considered active. It is considered active once the mIP/IPDACT
has sent keep-alive traffic. If the supervision period times out without receiving
any frame from the mIP/IPDACT, the connection is considered lost.
cnt A contact frame has been received from the mIP/IPDACT. Until a keep-alive
frame has been received, the connection cannot be considered active. If the
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 81
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 87

supervision period times out without receiving a keep-alive frame from the
mIP/IPDACT, the connection is considered lost.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST MIP INFORMATION
Example:
ARLY-1+LIST MIP INFORMATION
MIP Account[ffffffff]?
Account: 101234 State: alive
IP addr: 172.24.51.23 S/N: 8209/300
Remote UDP port: 20300 Sw Rls: v1.3 Oct 07 2003
Local UDP port: 20300
Keep-Alv tmr: 20 MIP pwd : 11223344
Keep-Alv retry: 0 Rcvr pwd: 0022244412340
Keep-Alv_retry tmr: 0 Phone len:4
Alarm retry: 0 Subs Phone:
ARLY-1+
•
LIST MIP STATISTICS
Displays statistics on the mIP/IPDACTs supervised by the VisorALARM.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST MIP STATISTICS
Example:
ARLY-1+LIST MIP STATISTICS
MIP supervised: 1
ARLY-1+
•
LIST MIP STATUS
Displays the status of the selected mIP/IPDACT. The different states for a mIP/IPDACT have just
been described in the command MIP INFO.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST MIP STATUS
Example:
ARLY-1+LIST MIP STATUS
MIP Account[ffffffff]? 5656
Account Serial Num MIP-Address VA-Port MIP SW Release Status
-------- ---------- --------------- ------- ------------------- -----5656 0563/33333 172.24.76.94 1222 v5.0 US Apr 13 2007 rgstr
•
LIST MIP ALL
Displays the status of the set of mIP/IPDACTs that the VisorALARM receiver is supervising. The
different states for a mIP/IPDACT have just been described in the command MIP INFO.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST MIP ALL
Example:
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 82
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 88

ARLY-1+LIST MIP ALL
Account Serial Num MIP-Address VA-Port MIP SW Release Status
-------- ---------- --------------- ------- ------------------- ------
88888 8209/02134 172.24.77.26 1222 v3.0 Oct 31 2005 alive
2323 0563/00250 172.24.76.96 1222 v5.0 US Mar 16 2007 alive
5678 0563/01000 172.24.76.91 1222 v5.0 EU Apr 13 2007 alive
1357 0563/10001 172.24.6.230 1222 v5.0 EU Apr 13 2007 alive
7777 0540/10002 172.24.77.98 1222 v5.0 US Apr 13 2007 alive
1010 0441/22222 --------------- 0 ------------------- lss-sgn
80001234 8209/02905 172.24.6.221 1222 v5.0 EU Apr 13 2007 alive
70001234 0441/00200 172.24.77.22 1222 v3.1 EU Jul 06 2006 alive
90001234 0540/10007 172.24.77.20 1222 v4.2 US Feb 12 2007 alive
5656 0563/33333 172.24.76.94 1222 v5.0 US Apr 13 2007 alive
d) LIST REGISTERED-MIP
Displays the maximum number of mIP/IPDACTs that can be registered and the number of
mIP/IPDACTs currently registered.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST REGISTERED-MIP
Example:
ARLY-1+ LIST REGISTERED-MIP
Supported Registered MIPs: 3000
Current Registered MIPs: 100
ARLY-1+
e) LIST MONITOR-IP-ADDR
Displays the configured IP address monitoring status. Monitoring is executed through ICMP echo
packets (ping) to the said IP address. This also displays the total number of access failures to this
address and the dates of the last time access was lost and when it was recovered. If this functionality
has not been configured, all data is shown as zero.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST MONITOR-IP-ADDR
Example:
ARLY-1+ LIST MONITOR-IP-ADDR
IP Address: 172.24.51.23 Rate 5
State : OK
Last Loss: 10/08/03 17:29:05
Last Recovery: 10/08/03 17:29:06
N. Losses: 0
ARLY-1+
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 83
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 89

f) LIST PROTOCOL
Displays statistics relative to the protocol used by the mIP/IPDACTs and the VisorALARM to
exchange information. Within these statistics both the sent frames as well as the received frames and
within the latter those received correctly, those received with error etc., are counted and displayed.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+ LIST PROTOCOL
Example:
ARLY-1+LIST PROTOCOL
MIP Protocol statistics:
----------------------Rx RSrvc frm: 834 Rx RAlarm frm: 0
Rx RSrvc error frm: 0 Rx RAlarm error frm: 0
Rx RSrvc accnt error frm: 0 Rx RAlarm accnt error frm: 0
Rx Contact frm: 3 Rx Kplv frm: 831
Rx Contact error frm: 0 Rx Kplv error frm: 0
Tx RCnfg frm: 0 Rx RReg frm: 0
Rx RCnfg Rsp frm: 0 Rx RReg drop frm: 0
Rx RCnfg OK rsp frm: 0 Rx RReg OK frm: 0
Rx RCnfg NO OK rsp frm: 0 Rx RReg error frm: 0
Rx RCnfg error Rsp frm: 0
Rx RCnfg s/n error Rsp frm: 0
ARLY-1+
g) LIST SMS
Monitors the parameters relative to alarm reception through SMS messages.
These commands are only applied if you have a GPRS/GSM card for alarm reception through SMS
messages.
For further information, please see manual DM 322-I “VisorALARM: Alarm Reception through
SMS”.
h) LIST UDP-STATISTICS
Displays statistics relative to the transmitting and receiving of data through the UDP port configured
for the ARLY interface. These statistics can be deleted through the CLEAR PROTOCOL command.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+LIST UDP-STATISTICS
Example:
ARLY-1+LIST UDP-STATISTICS
UDP statistics:
--------------Tx frames: 795 Rx frames: 795
Tx bytes: 22260 Rx bytes: 25584
ARLY-1+
i) LIST VISORALARM-STATE
Displays the statistics relative to the device state, the date when the last configuration synchronization
took place and in cases of devices configured as backup, the accumulated time the device has been in
BACKUP mode.
Case of a main VisorALARM
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 84
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 90

Syntax:
ARLY-1+list visoralarm-state
State of VisorALARM:
-------------------Type: MAIN
Main State: ACTIVE
Backup State: RUNNING
Synchronization:
---------------Last sync: 18-07-05 12:20:33
MAIN ARLY-1+
The Main State parameter refers to the device state in cases where the main device is ACTIVE
(the device has not detected any communication failure) or DOWN (the device has detected
communication failure). The Backup State parameter refers to the backup device. The
RUNNING state corresponds to the fact that the main VisorALARM has received a poll from
the backup device. The OUT OF ORDER state corresponds to the fact that having received
polls from a backup device, these are no longer being received.
Case of a backup VisorALARM
Syntax:
ARLY-1+list visoralarm-state
State of VisorALARM:
-------------------Type: BACKUP
Main State: OUT OF ORDER
Backup State: BACKUP
Synchronization:
---------------Last sync: 18-07-05 12:20:33
Failover:
--------Time lasts in backup state: 2 days, 5 hours, 7 minutes, 26 seconds
BACKUP ARLY-1+
The Main State parameter refers to the state of the VisorALARM configured as main. The state is
RUNNING when this responds to polls sent from the backup device. OUT OF ORDER is the state
due to the main device not responding to the polls. The Backup State can be BACKUP when the
device does not detect the main VisorALARM and takes over the main function, WARM-WAIT when
the main device is operative and DOWN when the backup device detects communication failure.
2.3. TEST
This permits you to test the communication between the VisorALARM and the Automation SW,
locally generating an alarm. If the ARLY interface is UP, the said alarm is sent to the Automation SW
through the serial interface. Contrariwise, the alarm will remain stored in the device until the said
interface has recovered.
The alarm has to be given in Contact-ID format and does not contain the validation digit which the
said protocol specifies in order to make management as simple as possible. The alarm is made up of
15 hexadecimal digits (0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F).
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 85
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 91

Syntax:
ARLY-1+TEST
Example:
ARLY-1+TEST
Alarm[]? 123418113101015
ARLY-1+
which generates alarm 131 (Perimeter) pertaining to client group 01 and zone 015 with account
number 1234.
2.4. EXIT
Permits you to exit the ARLY interface monitoring and return to the + prompt.
Syntax:
ARLY-1+EXIT
Example:
ARLY-1+EXIT
+
VISOR ALARM – ARLY Monitoring
IV - 86
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 92

Chapter 5
SEPI Monitoring
Page 93

1. Monitoring the Serial Interface
Information on the serial interface as such can be checked through the DEVICE monitoring command.
This, in addition to showing the number of times the SEPI interface has dropped and returned to up,
also displays the state of the signals, configuration for this and the error statistics. To obtain this, enter
the following in the monitoring process:
+device serial0/1
Auto-test Auto-test Maintenance
Interface CSR Vect valids failures failures
serial0/1 FA200A00 5e 0 0 0
Interface DCE
V.24 circuits:105 106 107 108 109 125 141
Nicknames: RTS CTS DSR DTR DCD RI LL
State: OFF ON ON OFF ON --- ---
Speed (bps) = 57600
Throughput (bps) = 0
Last throughput (bps) = 0
Bits per character = 7
Stop bits = 2
Parity selected = EVEN
Parity errors = 0
Data errors = 0
Overrun errors = 0
Last reset = 17 minutes 16 seconds
+
VISOR ALARM – SEPI Monitoring
V - 88
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 94

2. Monitoring the SEPI Interface
To access the SEPI interface monitoring, user the NETWORK command and the serial line associated
to the SEPI interface from the monitoring process:
+network serial0/0
SEPI-serial0/1 Monitoring
SEPI-serial0/1+
The available commands are as follows:
SEPI-serial0/1+?
CLEAR
LIST
EXIT
ARLY-1+
2.1. CLEAR
This command deletes the interface statistics.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1+clear all
2.2. LIST
This command displays the interface statistics.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1+list all
Interface statistics:
---------------------
Device status................................: PRESENT
Frames sent to serial device.................: 1
Bytes sent to serial device..................: 94
Frames received from serial device...........: 0
Bytes received from serial device............: 0
2.3. EXIT
Permits you to exit the SEPI interface monitoring and return to the + prompt.
Syntax:
SEPI-serial0/1+EXIT
Example:
SEPI-serial0/1+EXIT
+
VISOR ALARM – SEPI Monitoring
V - 89
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 95

Appendix A
UL compliance
Page 96

1. Intrusion System Installations complying with
UL1610
Configure the configuration profiles for all the mIP devices so they comply with the requirements
established by the UL. This states that detection of any circumstances, which prevents transmission of
a signal, must occur in a maximum time of 200 seconds. We strongly recommend you set the ‘keepalive-timer’, keep-alive-retries’ and ‘keep-alive-retries-timer’, so they comply with the following
formula:
keep-alive-timer + (keep-alive-retries * keep-alive-retries-timer) < 200
Configure the configuration profiles for all the mIP devices so the “MIP Console Password” parameter
contains the access password for the mIP devices.
Add a password to the VisorALARM receiver. This password is used both for connections via the
console as well as via telnet. Make sure the administration staff at the Central Station both know it
and keep it in a safe place for future use.
Configure the ‘link-test-timer’ parameter for both the main receiver and the backup to a value between
60 and 200 seconds.
VISOR ALARM – Appendix
A - 91
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
Page 97

2. Fire System Installations complying with UL864
Configure the configuration profiles for all the mIP devices so they comply with the requirements
established by the UL. This states that automatic switching to the backup receiver must occur in a
maximum time of 30 seconds. We strongly recommend you set the ‘keep-alive-timer’, keep-aliveretries’ and ‘keep-alive-retries-timer’, so they comply with the following formula:
keep-alive-timer + (keep-alive-retries * keep-alive-retries-timer) < 25
Configure the configuration profiles for all the mIP devices so the “MIP Console Password” parameter
contains the access password for the mIP devices.
Add a password to the VisorALARM receiver. This password is used both for connections via the
console as well as via telnet. Make sure the administration staff at the Central Station both know it
and keep it in a safe place for future use.
Configure the ‘link-test-timer’ parameter for both the main receiver and the backup to a value between
60 and 200 seconds.
VISOR ALARM – Appendix
A - 92
Doc.DM359-I
Rev.2.0
 Loading...
Loading...