
MC60 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
Rev. MC60_Hardware_Design_V1.0
Date: 2016-06-28
www.quectel.com

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Our aim is to provide customers with timely and comprehensive service. For any
assistance, please contact our company headquarters:
Quectel Wireless Solutions Co., Ltd.
Office 501, Building 13, No.99, Tianzhou Road, Shanghai, China, 200233
Tel: +86 21 5108 6236
Email: info@quectel.com
Or our local office. For more information, please visit:
http://www.quectel.com/support/salesupport.aspx
For technical support, or to report documentation errors, please visit:
http://www.quectel.com/support/techsupport.aspx
Or email to: Support@quectel.com
GENERAL NOTES
QUECTEL OFFERS THE INFORMATION AS A SERVICE TO ITS CUSTOMERS. THE INFORMATION
PROVIDED IS BASED UPON CUSTOMERS’ REQUIREMENTS. QUECTEL MAKES EVERY EFFORT
TO ENSURE THE QUALITY OF THE INFORMATION IT MAKES AVAILABLE. QUECTEL DOES NOT
MAKE ANY WARRANTY AS TO THE INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN, AND DOES NOT ACCEPT
ANY LIABILITY FOR ANY INJURY, LOSS OR DAMAGE OF ANY KIND INCURRED BY USE OF OR
RELIANCE UPON THE INFORMATION. ALL INFORMATION SUPPLIED HEREIN IS SUBJECT TO
CHANGE WITHOUT PRIOR NOTICE.
COPYRIGHT
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED HERE IS PROPRIETARY TECHNICAL INFORMATION OF QUECTEL
CO., LTD. TRANSMITTING, REPRODUCTION, DISSEMINATION AND EDITING OF THIS DOCUMENT
AS WELL AS UTILIZATION OF THE CONTENT ARE FORBIDDEN WITHOUT PERMISSION.
OFFENDERS WILL BE HELD LIABLE FOR PAYMENT OF DAMAGES. ALL RIGHTS ARE RESERVED
IN THE EVENT OF A PATENT GRANT OR REGISTRATION OF A UTILITY MODEL OR DESIGN.
Copyright © Quectel Wireless Solutions Co., Ltd. 2016. All rights reserved.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 1 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
About the Document
History
Revision Date Author Description
1.0 2016-06-28 Tiger CHENG Initial
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 2 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Contents
About the Document ................................................................................................................................ 2
Contents .................................................................................................................................................... 3
Table Index ............................................................................................................................................... 6
Figure Index .............................................................................................................................................. 8
1 Introduction ..................................................................................................................................... 10
1.1. Safety Information ................................................................................................................. 10
2 Product Concept ............................................................................................................................. 12
2.1. General Description .............................................................................................................. 12
2.2. Directives and Standards ...................................................................................................... 13
2.2.1. 2.2.1. FCC Statement .................................................................................................. 13
2.2.2. FCC Radiation Exposure Statement ............................................................................ 13
2.3. Key Features ......................................................................................................................... 13
2.4. Functional Diagram ............................................................................................................... 17
2.5. Evaluation Board ................................................................................................................... 18
3 Application Functions..................................................................................................................... 19
3.1. Pin of Module ........................................................................................................................ 20
3.1.1. Pin Assignment ............................................................................................................ 20
3.1.2.
Pin Description ............................................................................................................. 21
3.2. Application Modes Introduction ............................................................................................. 25
3.3. Power Supply ........................................................................................................................ 27
3.3.1. Power Features ........................................................................................................... 27
3.3.2. Decrease Supply Voltage Drop .................................................................................... 28
3.3.2.1. Decrease Supply Voltage Drop for GSM Part .................................................. 28
3.3.2.2. Decrease Supply Voltage Drop for GNSS Part ................................................ 29
3.3.3. Reference Design for Power Supply ............................................................................ 29
3.3.3.1. Reference Design for Power Supply of GSM Part ........................................... 29
3.3.3.2. Reference Design for Power Supply of GNSS Part in All-in-one Solution ....... 30
3.3.3.3. Reference Design for Power Supply of GNSS Part in Stand-alone Solution ... 31
3.3.4. Monitor Power Supply .................................................................................................. 32
3.3.5. Backup Domain of GNSS ............................................................................................ 32
3.3.5.1. Use VBAT as the Backup Power Source of GNSS .......................................... 32
3.3.5.2. Use VRTC as Backup Power of GNSS ........................................................... 32
3.4. Operating Modes .................................................................................................................. 34
3.4.1. Operating Modes of GSM Part ..................................................................................... 34
3.4.1.1. Minimum Functionality Mode ........................................................................... 35
3.4.1.2.
SLEEP Mode ................................................................................................... 35
3.4.1.3. Wake up GSM Part from SLEEP Mode ........................................................... 36
3.4.2. Operating Modes of GNSS Part ................................................................................... 36
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 3 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.4.2.1. Full on Mode.................................................................................................... 36
3.4.2.2. Standby Mode ................................................................................................. 37
3.4.2.3. Backup Mode .................................................................................................. 38
3.4.3. Summary of GSM and GNSS Parts’ State in All-in-one Solution .................................. 38
3.4.4. Summary of GSM and GNSS Parts’ State in Stand-alone Solution ............................. 39
3.5. Power on and down Scenarios in All-in-one Solution ............................................................ 39
3.5.1. Power on ..................................................................................................................... 39
3.5.2. Power down ................................................................................................................. 41
3.5.2.1. Power down Module Using the PWRKEY Pin ................................................. 41
3.5.2.2. Power down Module Using AT Command ....................................................... 43
3.5.2.3. Power down GNSS Part Alone Using AT Command ....................................... 43
3.5.2.4. Under-voltage Automatic Shutdown ................................................................ 44
3.5.3. Restart ......................................................................................................................... 44
3.6. Power on and down Scenarios in Stand-alone Solution ........................................................ 44
3.6.1. Power on GSM Part ..................................................................................................... 44
3.6.2. Power down GSM Part ................................................................................................ 46
3.6.2.1. Power down GSM Part Using the PWRKEY Pin ............................................. 46
3.6.2.2. Power down GSM Part using Command ......................................................... 47
3.7. Serial Interfaces .................................................................................................................... 47
3.7.1. UART Port ................................................................................................................... 50
3.7.1.1. Features of UART Port .................................................................................... 50
3.7.1.2. The Connection of UART ................................................................................ 51
3.7.1.3. Firmware Upgrade ........................................................................................... 52
3.7.2. Debug Port................................................................................................................... 53
3.7.3. Auxiliary UART Port and GNSS UART Port ................................................................. 54
3.7.3.1. Connection in All-in-one Solution ..................................................................... 54
3.7.3.2. Connection in Stand-alone Solution ................................................................ 54
3.7.4. UART Application ......................................................................................................... 55
3.8. Audio Interfaces .................................................................................................................... 56
3.8.1. Decrease TDD Noise and Other Noise ........................................................................ 58
3.8.2. Microphone Interfaces Design ..................................................................................... 58
3.8.3. Receiver and Speaker Interface Design ...................................................................... 59
3.8.4. Earphone Interface Design .......................................................................................... 60
3.8.5. Loud Speaker Interface Design.................................................................................... 60
3.8.6. Audio Characteristics ................................................................................................... 61
3.9. SIM Card Interface ............................................................................................................
.... 61
3.10. ADC ...................................................................................................................................... 65
3.11. Behaviors of the RI ............................................................................................................... 65
3.12. Network Status Indication ...................................................................................................... 67
3.13. EASY Autonomous AGPS Technology ................................................................................. 68
3.14. EPO Offline AGPS Technology ............................................................................................. 68
3.15. Multi-tone AIC ....................................................................................................................... 69
4 Antenna Interface ............................................................................................................................ 70
4.1. GSM Antenna Interface ......................................................................................................... 70
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 4 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
4.1.1. Reference Design ........................................................................................................ 70
4.1.2. RF Output Power ......................................................................................................... 71
4.1.3. RF Receiving Sensitivity .............................................................................................. 72
4.1.4. Operating Frequencies ................................................................................................ 72
4.1.5. RF Cable Soldering ..................................................................................................... 72
4.2. GNSS Antenna Interface ....................................................................................................... 73
4.2.1. Antenna Specifications ................................................................................................ 73
4.2.2. Active Antenna ............................................................................................................. 74
4.2.3. Passive Antenna .......................................................................................................... 75
4.3. Bluetooth Antenna Interface .................................................................................................. 75
5 Electrical, Reliability and Radio Characteristics .......................................................................... 78
5.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings .................................................................................................. 78
5.2. Operating Temperature ......................................................................................................... 78
5.3. Power Supply Ratings ........................................................................................................... 79
5.4. Current Consumption ............................................................................................................ 81
5.5. Electrostatic Discharge ......................................................................................................... 83
6 Mechanical Dimensions..........................................................................................................
........ 85
6.1. Mechanical Dimensions of Module ....................................................................................... 85
6.2. Recommended Footprint ....................................................................................................... 87
6.3. Top and Bottom View of the Module ...................................................................................... 88
7 Storage and Manufacturing ............................................................................................................ 89
7.1. Storage.................................................................................................................................. 89
7.2. Soldering ............................................................................................................................... 89
7.3. Packaging ............................................................................................................................. 90
7.3.1. Tape and Reel Packaging ............................................................................................ 91
8 Appendix A References .................................................................................................................. 92
9 Appendix B GPRS Coding Schemes ............................................................................................. 97
10 Appendix C GPRS Multi-slot Classes ............................................................................................ 99
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 5 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Table Index
TABLE 1: KEY FEATURES (GMS/GPRS PART OF MC60) .................................................................... 13
TABLE 2: CODING SCHEMES AND MAXIMUM NET DATA RATES OVER AIR INTERFACE ............... 15
TABLE 3: KEY FEATURES (GNSS PART OF MC60) ............................................................................. 15
TABLE 4: PROTOCOLS SUPPORTED BY THE MODULE ..................................................................... 17
TABLE 5: I/O PARAMETERS DEFINITION ............................................................................................. 21
TABLE 6: PIN DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................................. 21
TABLE 7: MULTIPLEXED FUNCTIONS .................................................................................................. 25
TABLE 8: COMPARISON BETWEEN ALL-IN-ONE AND STAND-ALONE SOLUTION ........................... 27
TABLE 9: OPERATING MODES OVERVIEW OF GSM PART ................................................................ 34
TABLE 10: DEFAULT CONFIGURATION OF FULL ON MODE (GNSS PART) ...................................... 36
TABLE 11: COMBINATION STATES OF GSM AND GNSS PARTS IN ALL-IN-ONE SOLUTION ........... 38
TABLE 12: COMBINATION STATES OF GSM AND GNSS PARTS IN STAND-ALONE SOLUTION ...... 39
TABLE 13: LOGIC LEVELS OF THE UART INTERFACE ....................................................................... 49
TABLE 14: PIN DEFINITION OF THE UART INTERFACES ................................................................... 49
TABLE 15: PIN DEFINITION OF AUDIO INTERFACE ............................................................................ 56
TABLE 16: AOUT2 OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................ 57
TABLE 17: TYPICAL ELECTRET MICROPHONE CHARACTERISTICS ................................................ 61
TABLE 18: TYPICAL SPEAKER CHARACTERISTICS ........................................................................... 61
TABLE 19: PIN DEFINITION OF THE SIM INTERFACE ......................................................................... 62
TABLE 20: PIN DEFINITION OF THE ADC ............................................................................................. 65
TABLE 21: CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ADC ...................................................................................... 65
TABLE 22: BEHAVIORS OF THE RI ....................................................................................................... 65
TABLE 23: WORKING STATE OF THE NETLIGHT ................................................................................ 67
TABLE 24: PIN DEFINITION OF THE RF_ANT ...................................................................................... 70
TABLE 25: ANTENNA CABLE REQUIREMENTS ................................................................................... 71
TABLE 26: ANTENNA REQUIREMENTS ................................................................................................ 71
TABLE 27: RF OUTPUT POWER ........................................................................................................... 71
TABLE 28: RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY .............................................................................................. 72
TABLE 29: OPERATING FREQUENCIES ............................................................................................... 72
TABLE 30: RECOMMENDED ANTENNA SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................. 73
TABLE 31: ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ........................................................................................ 78
TABLE 32: OPERATING TEMPERATURE .............................................................................................. 79
TABLE 33: POWER SUPPLY RATINGS OF GSM PART (GNSS IS POWERED OFF) ........................... 79
TABLE 34: POWER SUPPLY RATINGS OF GNSS PART ...................................................................... 80
TABLE 35: CURRENT CONSUMPTION OF GSM AND GNSS PARTS .................................................. 81
TABLE 36: CURRENT CONSUMPTION OF GSM PART (GNSS IS POWERED OFF) .......................... 81
TABLE 37: CURRENT CONSUMPTION OF THE GNSS PART .............................................................. 83
TABLE 38: ESD ENDURANCE (TEMPERATURE: 25ºC, HUMIDITY: 45%) ........................................... 84
TABLE 39: REEL PACKAGING ............................................................................................................... 91
TABLE 40: RELATED DOCUMENTS ...................................................................................................... 92
TABLE 41: TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS ............................................................................................ 93
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 6 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
TABLE 42: DESCRIPTION OF DIFFERENT CODING SCHEMES ......................................................... 97
TABLE 43: GPRS MULTI-SLOT CLASSES ............................................................................................. 99
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 7 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure Index
FIGURE 1: MODULE FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM ............................................................................................... 18
FIGURE 2: PIN ASSIGNMENT ......................................................................................................................... 20
FIGURE 3: ALL-IN-ONE SOLUTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ......................................................................... 26
FIGURE 4: STAND-ALONE SOLUTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................................................... 26
FIGURE 5: VOLTAGE RIPPLE DURING TRANSMITTING .............................................................................. 28
FIGURE 6: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR THE VBAT INPUT ........................................................................... 28
FIGURE 7: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR THE GNSS_VCC INPUT ................................................................. 29
FIGURE 8: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR POWER SUPPLY OF THE GSM PART .......................................... 30
FIGURE 9: REFERENCE CIRCUIT DESIGN FOR GNSS PART IN ALL-IN-ONE SOLUTION ........................ 31
FIGURE 10: REFERENCE CIRCUIT DESIGN FOR GNSS PART IN STAND-ALONE SOLUTION ................ 31
FIGURE 11: INTERNAL GNSS’S BACKUP DOMAIN POWER CONSTRUCTION .......................................... 32
FIGURE 12: VRTC IS POWERED BY A RECHARGEABLE BATTERY ........................................................... 33
FIGURE 13: VRTC IS POWERED BY A CAPACITOR ...................................................................................... 33
FIGURE 14: TURN ON THE MODULE WITH AN OPEN-COLLECTOR DRIVER ............................................ 39
FIGURE 15: TURN ON THE MODULE WITH A BUTTON ................................................................................ 40
FIGURE 16: TURN-ON TIMING ........................................................................................................................ 41
FIGURE 17: TURN-OFF TIMING BY USING THE PWRKEY PIN .................................................................... 42
FIGURE 18: TURN-OFF TIMING OF GNSS PART BY USING AT COMMAND ............................................... 43
FIGURE 19: TURN-ON TIMING OF GSM PART .............................................................................................. 45
FIGURE 20: TURN-OFF TIMING OF GSM PART BY USING THE PWRKEY PIN .......................................... 47
FIGURE 21: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR FULL-FUNCTION UART ................................................................ 51
FIGURE 22: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR UART PORT (THREE LINE CONNECTION)................................. 52
FIGURE 23: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR UART PORT WITH HARDWARE FLOW CONTROL .................... 52
FIGURE 24: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR FIRMWARE UPGRADE ................................................................. 53
FIGURE 25: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR DEBUG PORT ............................................................................... 53
FIGURE 26: AUXILIARY AND GNSS UART PORT CONNECTION IN ALL-IN-ONE SOLUTION .................... 54
FIGURE 27: AUXILIARY AND GNSS UART PORT CONNECTION IN STAND-ALONE SOLUTION .............. 55
FIGURE 28: LEVEL MATCH DESIGN FOR 3.3V SYSTEM.............................................................................. 55
FIGURE 29: SKETCH MAP FOR RS-232 INTERFACE MATCH ...................................................................... 56
FIGURE 30: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR AIN ................................................................................................. 58
FIGURE 31: HANDSET INTERFACE DESIGN FOR AOUT1 ........................................................................... 59
FIGURE 32: SPEAKER INTERFACE DESIGN WITH AN AMPLIFIER FOR AOUT1 ....................................... 59
FIGURE 33: EARPHONE INTERFACE DESIGN .............................................................................................. 60
FIGURE 34: LOUD SPEAKER INTERFACE DESIGN ...................................................................................... 60
FIGURE 35: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR SIM1 INTERFACE WITH AN 8-PIN SIM CARD HOLDER ............ 63
FIGURE 36: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR SIM1 INTERFACE WITH A 6-PIN SIM CARD HOLDER .............. 63
FIGURE 37: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR SIM2 INTERFACE WITH A 6-PIN SIM CARD HOLDER .............. 64
FIGURE 38: RI BEHAVIOR AS A RECEIVER WHEN VOICE CALLING .......................................................... 66
FIGURE 39: RI BEHAVIOR AS A CALLER ....................................................................................................... 66
FIGURE 40: RI BEHAVIOR WHEN URC OR SMS RECEIVED ....................................................................... 66
FIGURE 41: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR NETLIGHT ..................................................................................... 67
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 8 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
FIGURE 42: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR GSM ANTENNA ............................................................................. 70
FIGURE 43: RF SOLDERING SAMPLE ........................................................................................................... 73
FIGURE 44: REFERENCE DESIGN WITH ACTIVE ANTENNA ....................................................................... 74
FIGURE 45: REFERENCE DESIGN WITH PASSIVE ANTENNA .................................................................... 75
FIGURE 46: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR BLUETOOTH ANTENNA ............................................................... 76
FIGURE 47: MC60 TOP AND SIDE DIMENSIONS (UNIT: MM) ....................................................................... 85
FIGURE 48: MC60 BOTTOM DIMENSIONS (UNIT: MM) ................................................................................. 86
FIGURE 49: RECOMMENDED FOOTPRINT (UNIT: MM) ................................................................................ 87
FIGURE 50: TOP VIEW OF THE MODULE ...................................................................................................... 88
FIGURE 51: BOTTOM VIEW OF THE MODULE .............................................................................................. 88
FIGURE 52: REFLOW SOLDERING THERMAL PROFILE .............................................................................. 90
FIGURE 53: TAPE AND REEL SPECIFICATION .............................................................................................. 91
FIGURE 54: DIMENSIONS OF REEL ............................................................................................................... 91
FIGURE 54: RADIO BLOCK STRUCTURE OF CS-1, CS-2 AND CS-3 ........................................................... 97
FIGURE 56: RADIO BLOCK STRUCTURE OF CS-4 ....................................................................................... 98
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 9 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
1 Introduction
This document defines the MC60 module and describes its hardware interface which is connected with
the customer application as well as its air interface.
The document can help you quickly understand module interface specifications, as well as the electrical
and mechanical details. Associated with application note and user guide, you can use MC60 module to
design and set up mobile applications easily.
1.1. Safety Information
The following safety precautions must be observed during all phases of the operation, such as usage,
service or repair of any cellular terminal or mobile incorporating MC60 module. Manufacturers of the
cellular terminal should send the following safety information to users and operating personnel, and
incorporate these guidelines into all manuals supplied with the product. If not so, Quectel assumes no
liability for the customer’s failure to comply with these precautions.
Full attention must be given to driving at all times in order to reduce the risk of an
accident. Using a mobile while driving (even with a handsfree kit) causes
distraction and can lead to an accident. You must comply with laws and regulations
restricting the use of wireless devices while driving.
Switch off the cellular terminal or mobile before boarding an aircraft. Make sure it is
switched off. The operation of wireless appliances in an aircraft is forbidden, so as
to prevent interference with communication systems. Consult the airline staff about
the use of wireless devices on boarding the aircraft, if your device offers a Airplane
Mode which must be enabled prior to boarding an aircraft.
Switch off your wireless device when in hospitals, clinics or other health care
facilities. These requests are desinged to prevent possible interference with
sentitive medical equipment.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 10 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Cellular terminals or mobiles operating over radio frequency signal and cellular
network cannot be guaranteed to connect in all conditions, for example no mobile
fee or with an invalid SIM card. While you are in this condition and need emergent
help, please remember using emergency call. In order to make or receive a call,
the cellular terminal or mobile must be switched on and in a service area with
adequate cellular signal strength.
Your cellular terminal or mobile contains a transmitter and receiver. When it is ON ,
it receives and transmits radio frequency energy. RF interference can occur if it is
used close to TV set, radio, computer or other electric equipment.
In locations with potencially explosive atmospheres, obey all posted signs to turn
off wireless devices such as your phone or other cellular terminals. Areas with
potencially explosive atmospheres include fuelling areas, below decks on boats,
fuel or chemical transfer or storage facilities, areas where the air contains
chemicals or particles such as grain, dust or metal powders, etc.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 11 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
2 Product Concept
2.1. General Description
MC60 is a multi-purpose module which integrates a high performance GNSS engine and a dual-band
GSM/GPRS engine. It can work as all-in-one solution or stand-alone solution according to customers'
application demands.
The dual-band GSM/GPRS engine can work at frequencies of EGSM900MHz and DCS1800MHz. MC60
features GPRS multi-slot class 12 and supports the GPRS coding schemes CS-1, CS-2, CS-3 and CS-4.
For more details about GPRS multi-slot classes and coding schemes, please refer to the Appendix B &
C.
The GNSS engine is a single receiver integrating GLONASS and GPS systems. It supports multiple
positioning and navigation systems including autonomous GPS, GLONASS, SBAS (including WAAS,
EGNOS, MSAS and GAGAN), and QZSS. It is able to achieve the industry’s highest level of sensitivity,
accuracy and TTFF with the lowest power consumption. The embedded flash memory provides capacity
for storing user-specific configurations and allows for future updates.
MC60 is an SMD type module with 54 LCC pads and 14 LGA pads which can be easily embedded into
applications. With a compact profile of 18.7mm × 16.0mm × 2.1mm, the module can meet almost all the
requirements for M2M applications, including vehicle and personal tracking, wearable devices, security
systems, wireless POS, industrial PDA, smart metering, remote maintenance & control, etc.
Designed with power saving technique, the current consumption of MC60 is as low as 1.2mA in SLEEP
mode when DRX is 5 and the GNSS part is powered off. The GNSS engine also has many advanced
power saving modes including standby and backup modes which can fit the requirement of low-power
consumption in different scenes.
GSM part of MC60 is integrated with Internet service protocols such as TCP/UDP, PPP, HTTP and FTP.
Extended AT commands have been developed for you to use these Internet service protocols easily.
EASY technology as a key feature of GNSS part of MC60 module is one kind of AGPS. Capable of
collecting and processing all internal aiding information like GNSS time, ephemeris, last position, etc., the
GNSS part will have a fast TTFF in either Hot or Warm start.
The module fully complies with the RoHS directive of the European Union.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 12 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
2.2. Directives and Standards
The MC60module is designed to comply with the FCC statements. FCC ID: XMR201609MC60
The Host system using MC60 should have label “contains FCC ID: XMR201609MC60”.
2.2.1. 2.2.1. FCC Statement
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
2.2.2. FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator and
your body as well as kept minimum 20cm from radio antenna depending on the Mobile status of this
module usage. This module should NOT be installed and operating simultaneously with other radio. The
manual of the host system, which uses MC60, must include RF exposure warning statement to advice
user should keep minimum 20cm from the radio antenna of MC60 module depending on the Mobile status.
Note: If a portable device (such as PDA) uses MC60 module, the device needs to do permissive change
and SAR testing.
The following list indicates the performance of antenna gain in certificate testing.
Part
Number
3R007
Frequency Range (MHz)
GSM850:824~894MHz
PCS1900: 1850~1990MHz
Peak Gain
(XZ-V)
1 dBi typ. 1 dBi typ. 2 max 50Ω
Average
Gain(XZ-V)
VSWR Impedance
2.3. Key Features
The following table describes the detailed features of MC60 module.
Table 1: Key Features (GMS/GPRS Part of MC60)
Features Implementation
Power Supply
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 13 / 99
Single supply voltage: 3.3V ~ 4.6V
Typical supply voltage: 4V
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Typical power consumption in SLEEP mode (GNSS is powered off):
Power Saving
1.2mA@DRX=5
0.8mA@DRX=9
Dual-band: EGSM900, DCS1800.
Frequency Bands
The module can search these frequency bands automatically
The frequency bands can be set by AT commands
Compliant to GSM Phase 2/2+
GSM Class Small MS
Transmitting Power
GPRS Connectivity
DATA GPRS
Temperature Range
SMS
SIM Interface
Class 4 (2W) at EGSM900
Class 1 (1W) at DCS1800
GPRS multi-slot class 12 (default)
GPRS multi-slot class 1~12 (configurable)
GPRS mobile station class B
GPRS data downlink transfer: max. 85.6kbps
GPRS data uplink transfer: max. 85.6kbps
Coding scheme: CS-1, CS-2, CS-3 and CS-4
Support the protocols PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
usually used for PPP connections
Internet service protocols TCP/UDP, FTP, PPP, HTTP, NTP, PING
Support Packet Broadcast Control Channel (PBCCH)
Support Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD)
Operation temperature range: -35°C ~ +75°C
Extended temperature range: -40°C ~ +85°C
1)
2)
Text and PDU mode
SMS storage: SIM card
Support SIM card: 1.8V, 3.0V
Support Dual SIM Single Standby
Speech codec modes:
Half Rate (ETS 06.20)
Full Rate (ETS 06.10)
Enhanced Full Rate (ETS 06.50/06.60/06.80)
Audio Features
Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR)
Echo Suppression
Noise Reduction
Embedded one amplifier of class AB with maximum driving power up
to 870mW
UART Port:
Seven lines on UART port interface
UART Interfaces
Used for AT command and GPRS data
Used for NMEA output in all-in-one solution
Multiplexing function
Support autobauding from 4800bps to 115200bps
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 14 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Debug Port:
Two lines on debug port interface DBG_TXD and DBG_RXD
Debug port only used for firmware debugging
Auxiliary Port:
Two lines on auxiliary port interface: TXD_AUX and RXD_AUX
Used for communication with the GNSS Part in all-in-one solution
Phonebook Management Support phonebook types: SM, ME, ON, MC, RC, DC, LD, LA
SIM Application Toolkit Support SAT class 3, GSM 11.14 Release 99
Physical Characteristics
Size: (18.7±0.15) × (16±0.15) × (2.1±0.2)mm
Weight: Approx. 1.3g
Firmware Upgrade Firmware upgrade via UART port
Antenna Interface Connected to antenna pad with 50 Ohm impedance control
NOTES
1. 1) Within operation temperature range, the module is 3GPP compliant.
2. 2) Within extended temperature range, the module remains the ability to establish and maintain a
voice, SMS, data transmission, emergency call, etc. There is no unrecoverable malfunction. There
are also no effects on radio spectrum and no harm to radio network. Only one or more parameters like
P
might reduce in their value and exceed the specified tolerances. When the temperature returns to
out
the normal operating temperature levels, the module will meet 3GPP compliant again.
Table 2: Coding Schemes and Maximum Net Data Rates over Air Interface
Coding Scheme 1 Timeslot 2 Timeslot 4 Timeslot
CS-1 9.05kbps 18.1kbps 36.2kbps
CS-2 13.4kbps 26.8kbps 53.6kbps
CS-3 15.6kbps 31.2kbps 62.4kbps
CS-4 21.4kbps 42.8kbps 85.6kbps
Table 3: Key Features (GNSS Part of MC60)
Features Implementation
GNSS GPS+GLONASS
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 15 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Power Supply Supply voltage: 2.8V~4.3V Typical: 3.3V
Acquisition: 25mA @-130dBm (GPS)
Tracking: 19mA @-130dBm (GPS)
Power Consumption
Acquisition: 29mA @-130dBm (GPS+GLONASS)
Tracking: 22mA @-130dBm (GPS+GLONASS)
Standby: 500uA @VCC=3.3V
Backup: 14uA @V_BCKP=3.3V
Receiver Type
Sensitivity
GPS+GLONASS
Time-to-First-Fix
(EASY Enabled)
1)
Time-to-First-Fix
(EASY Disabled)
Horizontal Position
Accuracy (Autonomous)
GPS L1 1575.42MHz C/A Code
GLONASS L1 1598.0625~1605.375MHz C/A Code
Acquisition: -149dBm
Reacquisition: -161dBm
Tracking: -167dBm
Cold Start: <15s average @-130dBm
Warm Start: <5s average @-130dBm
Hot Start: 1s @-130dBm
Cold Start (Autonomous): <35s average @-130dBm
Warm Start (Autonomous): <30s average @-130dBm
Hot Start (Autonomous): 1s @-130dBm
<2.5 m CEP @-130dBm
Update Rate Up to 10Hz, 1Hz by default
Velocity Accuracy Without aid: 0.1m/s
Acceleration Accuracy Without aid: 0.1m/s²
Maximum Altitude: 18,000m
Dynamic Performance
Maximum Velocity: 515m/s
Acceleration: 4G
GNSS UART port: GNSS_TXD and GNSS_ RXD
Support baud rate from 4800bps to 115200bps; 115200bps by
GNSS UART Port
default
Used for communication with the GSM Part in all-in-one solution
Used for communication with peripherals
in stand-alone solution
NOTE
1)
In this mode, GNSS part’s backup domain should be valid.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 16 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Table 4: Protocols Supported by the Module
Protocol Type
NMEA Input/output, ASCII, 0183, 3.01
PMTK Input, MTK proprietary protocol
NOTE
Please refer to document [2] for details of NMEA standard protocol and MTK proprietary protocol.
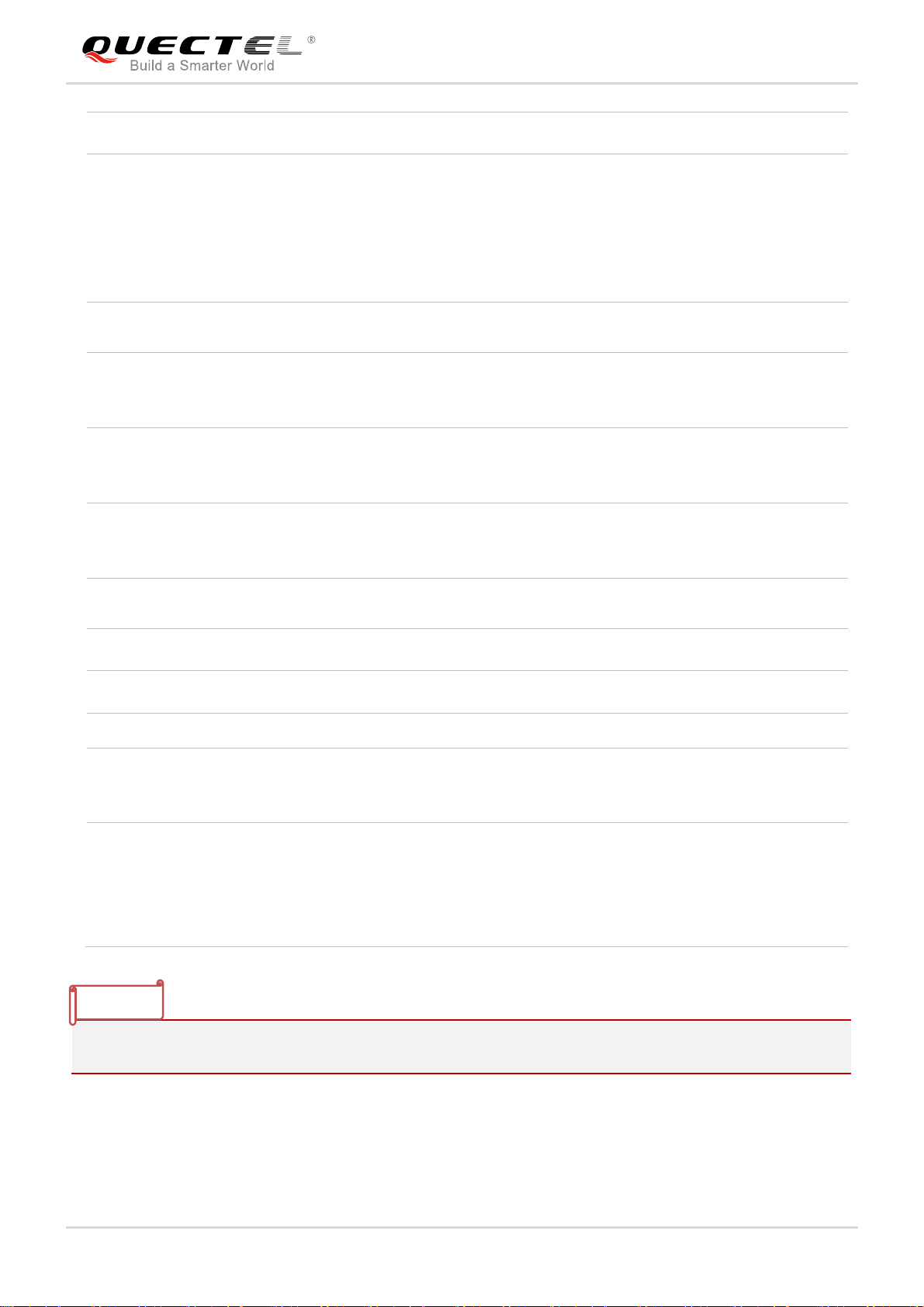
2.4. Functional Diagram
The following figure shows a block diagram of MC60 and illustrates the major functional parts.
Radio frequency part
Power management
Peripheral interfaces
—Power supply
—Turn-on/off interface
—UART interface
—Audio interface
—SIM interface
—ADC
interface
—RF
interface
interface
interface
interface
—PCM
—BT
—SD
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 17 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 1: Module Functional Diagram
2.5. Evaluation Board
In order to help you develop applications with MC60, Quectel supplies an evaluation board (EVB),
RS-232 to USB cable, power adapter, earphone, antenna and other peripherals to control or test the
module. For details, please refer to document [11].
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 18 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3 Application Functions
MC60 is an SMD type module with 54 LCC pads and 14 LGA pads. The following chapters provide
detailed descriptions about these pins.
Pin of module
Power supply
Operating modes
Power on/down
Power saving
Backup domain of GNSS
Serial interfaces
Audio interfaces
SIM card interface
ADC
Behaviors of the RI
Network status indication
RF transmitting signal indication
EASY autonomous AGPS technology
EPO offline AGPS technology
Multi-tone AIC
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 19 / 99
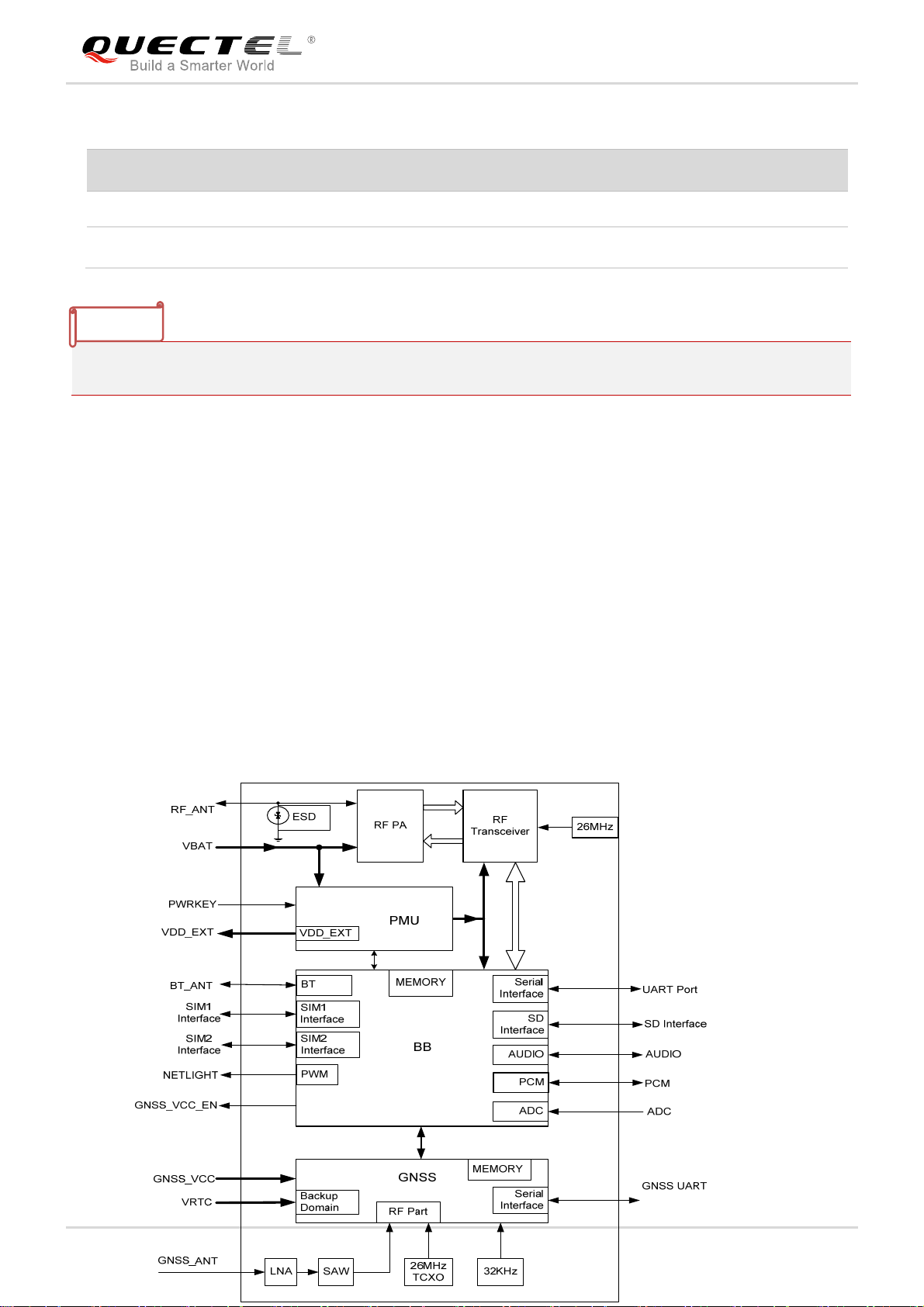
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.1. Pin of Module
3.1.1. Pin Assignment
Figure 2: Pin Assignment
NOTE
Keep all reserved pins open.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 20 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.1.2. Pin Description
Table 5: I/O Parameters Definition
Type Description
IO Bidirectional input/output
DI Digital input
DO Digital output
PI Power input
PO Power output
AI Analog input
AO Analog output
Table 6: Pin Description
Power Supply
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
It must be able to
Power supply of
VBAT 50, 51 PI
GSM/GPRS part:
VBAT=3.3V~4.6V
max=4.6V
V
I
V
min=3.3V
I
V
norm=4.0V
I
provide sufficient
current up to 1.6A
in a transmitting
burst.
GNSS_
VCC
26 PI
Power supply of GNSS
part:
VBAT=2.8V~4.3V
Power supply for GNSS’s
backup domain
VRTC 52 IO
Charging for backup
battery or golden
capacitor when the VBAT
is applied.
V
max=4.3V
I
V
min=2.8V
I
V
norm=3.3V
I
VImax=3.3V
VImin=1.5V
VInorm=2.8V
VOmax=3V
VOmin=2V
VOnorm=2.8V
IOmax=2mA
Iin≈14uA
Assure load
current no less
than 150mA.
Refer to Section
3.3.5
V
VDD_
EXT
43 PO
Supply 2.8V voltage for
external circuit.
max=2.9V
O
V
min=2.7V
O
V
norm=2.8V
O
I
max=20mA
O
1. If unused, keep
this pin open.
2. Recommend
adding a
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 21 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
2.2~4.7uF bypass
capacitor, when
using this pin for
power supply.
14,27,
31,40,
GND
42,44,
Ground
45,48,
49
Turn on/off
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
PWRKEY 5 DI
Power on/off key.
PWRKEY should be
pulled down for a
moment to turn on or
turn off the system.
V
max=
IL
0.1×VBAT
V
min=
IH
0.6×VBAT
V
max=3.1V
IH
Audio Interface
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
MICP
MICN
1,
2
AI
Positive and negative
voice input
If unused, keep
these pins open.
If unused, keep
SPKP
SPKN
3,
4
AO
Channel 1 positive and
negative voice output
these pins open.
Support both
voice and
ringtone output.
Refer to Section 3.8.6
1. If unused, keep
these pins open.
LOUD
SPKP
LOUD
SPKN
54
53
AO
Channel 2 positive and
negative voice output
2. Integrate a
Class- AB
amplifier
internally.
3. Support both
voice and
ringtone output.
Network Status Indicator
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
V
min=
OH
NETLIGHT 47 DO
Network status
indication
0.85×VDD_EXT
V
max=
OL
If unused, keep
this pin open.
0.15×VDD_EXT
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 22 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
UART Port
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
min=0V
V
TXD 33 DO Transmit data
RXD 34 DI Receive data
DTR 37 DI Data terminal ready
RI 35 DO Ring indication
DCD 36 DO Data carrier detection
CTS 38 DO Clear to send
RTS 39 DI Request to send
IL
V
max=
IL
0.25×VDD_EXT
V
min=
IH
0.75×VDD_EXT
V
max=
IH
VDD_EXT+0.2
V
min=
OH
0.85×VDD_EXT
V
max=
OL
0.15×VDD_EXT
If only TXD, RXD
and GND are
used for
communication, it
is recommended
to keep all other
pins open.
Debug Port
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
DBG_
TXD
DBG_
RXD
29 DO Transmit data
30 DI Receive data
The same as UART
port
If unused, keep
these pins open.
Auxiliary UART Port
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
TXD_
AUX
RXD_
AUX
25 DO Transmit data
24 DI Receive data
The same as UART
port
Refer to Section
3.2
GNSS UART Port
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
GNSS_
TXD
GNSS_
RXD
22 DO Transmit data
23 DI Receive data
VOLmax=0.42V
VOHmin=2.4V
VOHnom=2.8V
VILmin=-0.3V
VILmax=0.7V
VIHmin=2.1V
Refer to Section
3.2
VIHmax=3.1V
SIM Interface
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
SIM1_ VDD
SIM2_ VDD
18
13
PO
Power supply for SIM
card
The voltage can be
selected by software
All signals of SIM
interface should
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 23 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
SIM1_ CLK
SIM2_ CLK
SIM1_
DATA
SIM2_
DATA
SIM1_ RST
SIM2_ RST
SIM_
GND
19
10
21
11
DO SIM clock
IO SIM data
automatically. Either
1.8V or 3.0V.
V
max=
OL
0.15×SIM_VDD
V
min=
OH
0.85×SIM_VDD
V
max=
IL
0.25×SIM_VDD
min=
V
IH
0.75×SIM_VDD
max=
V
OL
be protected
against ESD with
a TVS diode
array.
Maximum trace
length is 200mm
from the module
pad to SIM card
holder.
0.15×SIM_VDD
min=
V
OH
0.85×SIM_VDD
V
max=
OL
20
12
DO SIM reset
0.15×SIM_VDD
V
min=
OH
0.85×SIM_VDD
16 SIM ground
V
min =0V
IL
V
max =
SIM1_
PRESENCE
37 I SIM1 card detection
IL
0.25×VDD_EXT
V
min =
IH
0.75×VDD_EXT
VIHmax =
Default DTR
function. Now the
software does not
support it.
VDD_EXT+0.2
ADC
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
General purpose
ADC 6 AI
analog to digital
converter.
Voltage range:
0V to 2.8V
If unused, keep
this pin open.
Digital Audio Interface (PCM)
PCM_CLK 59 DO PCM clock
PCM_OUT 60 DO PCM data output
PCM_SYNC 61 DO
PCM frame
synchronization
PCM_IN 62 DI PCM data input
SD Card Interface
SD_CMD 7 DO SD Command line
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 24 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
SD_CLK 8 DO SD clock
SD_DATA 9 IO SD data line
Antenna Interface
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
RF_
ANT
BT_
ANT
GNSS_
ANT
41 IO GSM antenna pad Impedance of 50Ω
32 IO BT antenna pad
15 I GNSS signal input Impedance of 50Ω
Other Interface
PIN Name PIN No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
Refer to Section
3.3.3.2 in
GNSS_
VCC_EN
28 O GNSS power enabled
V
min=
OH
0.85×VDD_EXT
V
max=
OL
0.15×VDD_EXT
all-in-one
solution.
Keep this pin
open in
stand-alone
solution.
17, 46
55, 56,
RESERVED
57, 58,
63, 64,
Keep these pins
open
65, 66,
67, 68,
Table 7: Multiplexed Functions
PIN Name PIN No. Function After Reset Alternate Function
DTR/SIM1_PRESENCE 37 DTR SIM1_PRESENCE
3.2. Application Modes Introduction
MC60 module integrates both GSM and GNSS engines which can work as a whole (all-in-one solution)
unit or work independently (stand-alone solution) according to customer demands.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 25 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
In all-in-one solution, the MC60 works as a whole unit. The GNSS Part can be regarded as a peripheral of
the GSM Part. This allows for convenient communication between GSM and GNSS Parts, such as AT
command sending for GNSS control, GNSS part firmware upgrading, and EPO data download.
In stand-alone solution, GSM and GNSS Parts work independently, and thus have to be controlled
separately.
All-in-one solution and stand-alone solution schematic diagrams are shown below.
Figure 3: All-in-one Solution Schematic Diagram
Figure 4: Stand-alone Solution Schematic Diagram
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 26 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Table 8: Comparison between All-in-one and Stand-alone Solution
All-in-one. Stand-alone Remarks
Firmware upgrade
Data transmission
GNSS TURN ON/OFF
GNSS wake up GSM
GNSS’s EPO data
download
Firmware upgrade via
UART Port (GSM and
GNSS Parts share the
same firmware package)
Both GSM and GNSS data
are transmitted through
the GSM UART Port
By AT command through
GSM UART Port
GNSS can wake up GSM
by interrupts
EPO data is downloaded
directly through the GSM
part.
Firmware upgrade via
UART Port (GSM and
GNSS Parts share the
Refer to 3.7.1.3
for details
same firmware package)
GSM data is transmitted
through the GSM UART
Port.
GNSS data is transmitted
through the GNSS UART
Port.
Through the external
switch of MCU
Refer to 3.5 and
3.6 for details
N/A
MCU receives the EPO
data which is downloaded
through the GSM part, and
then transmit it to the
Refer to 3.14 for
details
GNSS part.
3.3. Power Supply
3.3.1. Power Features
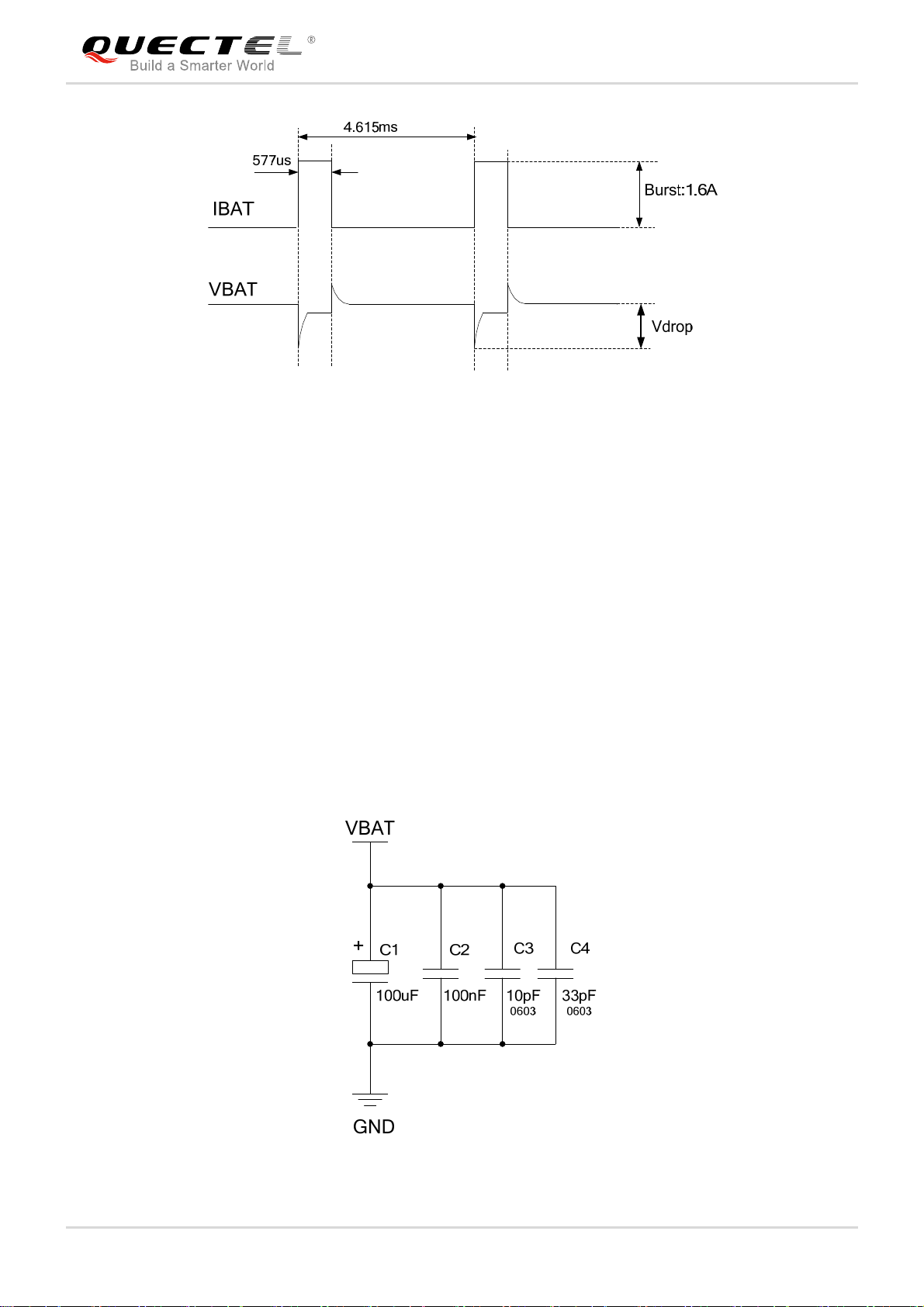
The power supply of the GSM part is one of the key issues in MC60 module design. Due to the 577us
radio burst in GSM part every 4.615ms, the power supply must be able to deliver high current peaks in a
burst period. During these peaks, drops on the supply voltage must not exceed the minimum working
voltage of the module.
For MC60 module, the maximum current consumption could reach 1.6A during a burst transmission. It will
cause a large voltage drop on the VBAT. In order to ensure stable operation of the module, it is
recommended that the maximum voltage drop during the burst transmission does not exceed 400mV.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 27 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 5: Voltage Ripple during Transmitting
3.3.2. Decrease Supply Voltage Drop
3.3.2.1. Decrease Supply Voltage Drop for GSM Part
Power supply range of the GSM part is from 3.3V to 4.6V. Make sure that the input voltage will never drop
below 3.3V even in a burst transmission. If the power voltage drops below 3.3V, the module will be turned
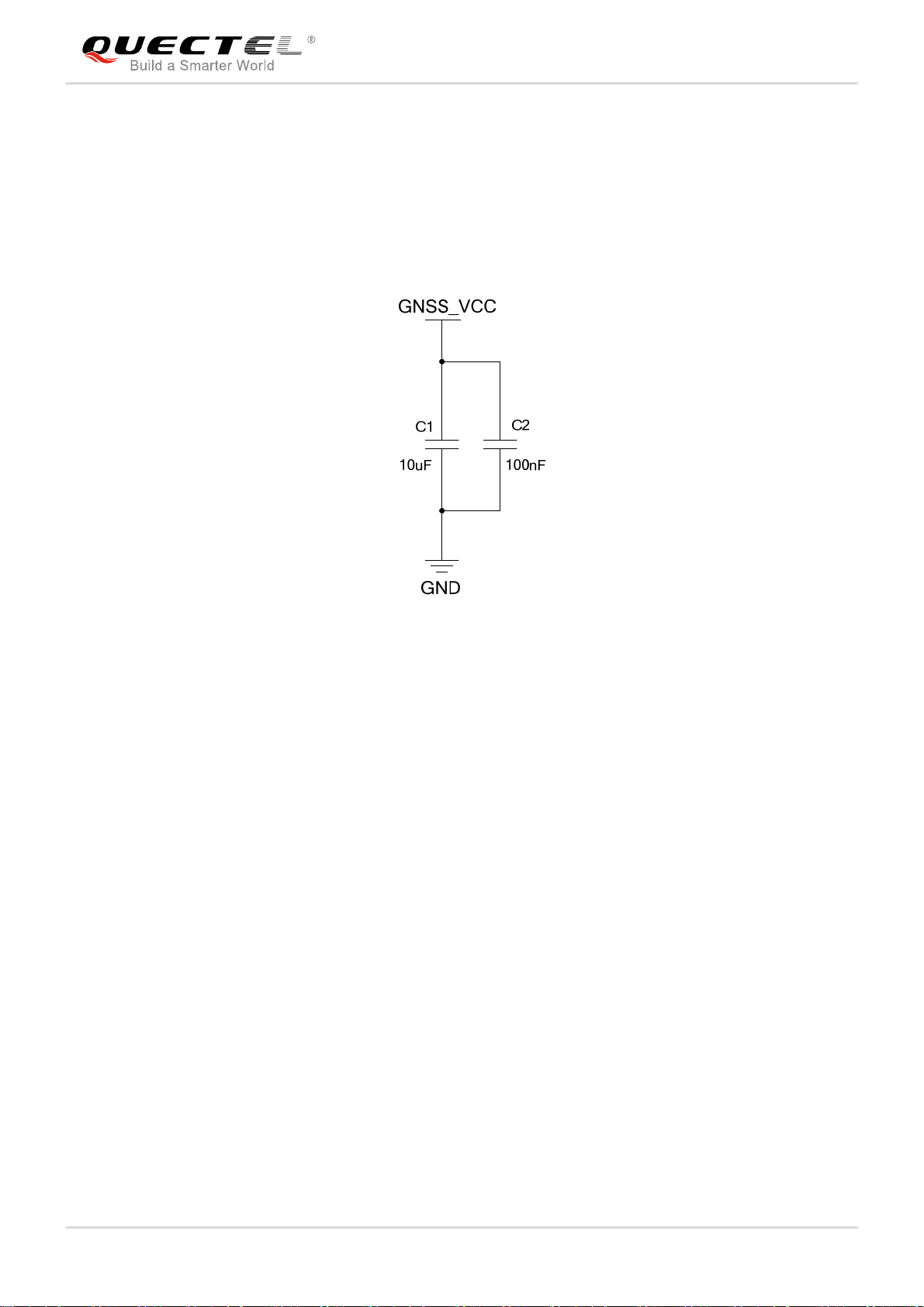
off automatically. For better power performance, it is recommended to place a 100uF tantalum capacitor
with low ESR (ESR=0.7Ω) and ceramic capacitors 100nF, 33pF and 10pF near the VBAT pin. A reference
circuit is illustrated in the following figure.
The VBAT trace should be wide enough to ensure that there is not too much voltage drop during burst
transmission. The width of trace should be no less than 2mm; and in principle, the longer the VBAT trace,
the wider it will be.
Figure 6: Reference Circuit for the VBAT Input
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 28 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.3.2.2. Decrease Supply Voltage Drop for GNSS Part
The same as VBAT, power supply range of GNSS part is from 2.8 to 4.3V. Typical GNSS_VCC peak
current is 40mA during GNSS acquisition after power up. So it is important to supply sufficient current and
make the power clean and stable. The decouple combination of 10uF and 100nF capacitor is
recommended nearby GNSS_VCC pin. A reference circuit is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 7: Reference Circuit for the GNSS_VCC Input
3.3.3. Reference Design for Power Supply
3.3.3.1. Reference Design for Power Supply of GSM Part
In all-in-one solution, the GSM part controls the power supply of the GNSS part. Therefore, the GSM part
share the same power circuit design in both all-in-one and stand-alone solutions.
The power supply of GSM part is capable of providing sufficient current up to 2A at least. If the voltage
drop between the input and output is not too high, it is suggested to use a LDO as the module’s power
supply. If there is a big voltage difference between the input source and the desired output (VBAT), a
switcher power converter is recommended to be used as the power supply.
The following figure shows a reference design for +5V input power source for GSM part. The designed
output for the power supply is 4.0V and the maximum load current is 3A. In addition, in order to get a
stable output voltage, a zener diode is placed close to the pins of VBAT. As to the zener diode, it is
suggested to use a zener diode whose reverse zener voltage is 5.1V and dissipation power is more than 1
Watt.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 29 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 8: Reference Circuit for Power Supply of the GSM Part
NOTE
It is suggested to control the module’s main power supply (VBAT) via LDO enable pin to restart the
module when the module becomes abnormal. Power switch circuit like P-channel MOSFET switch circuit
can also be used to control VBAT.
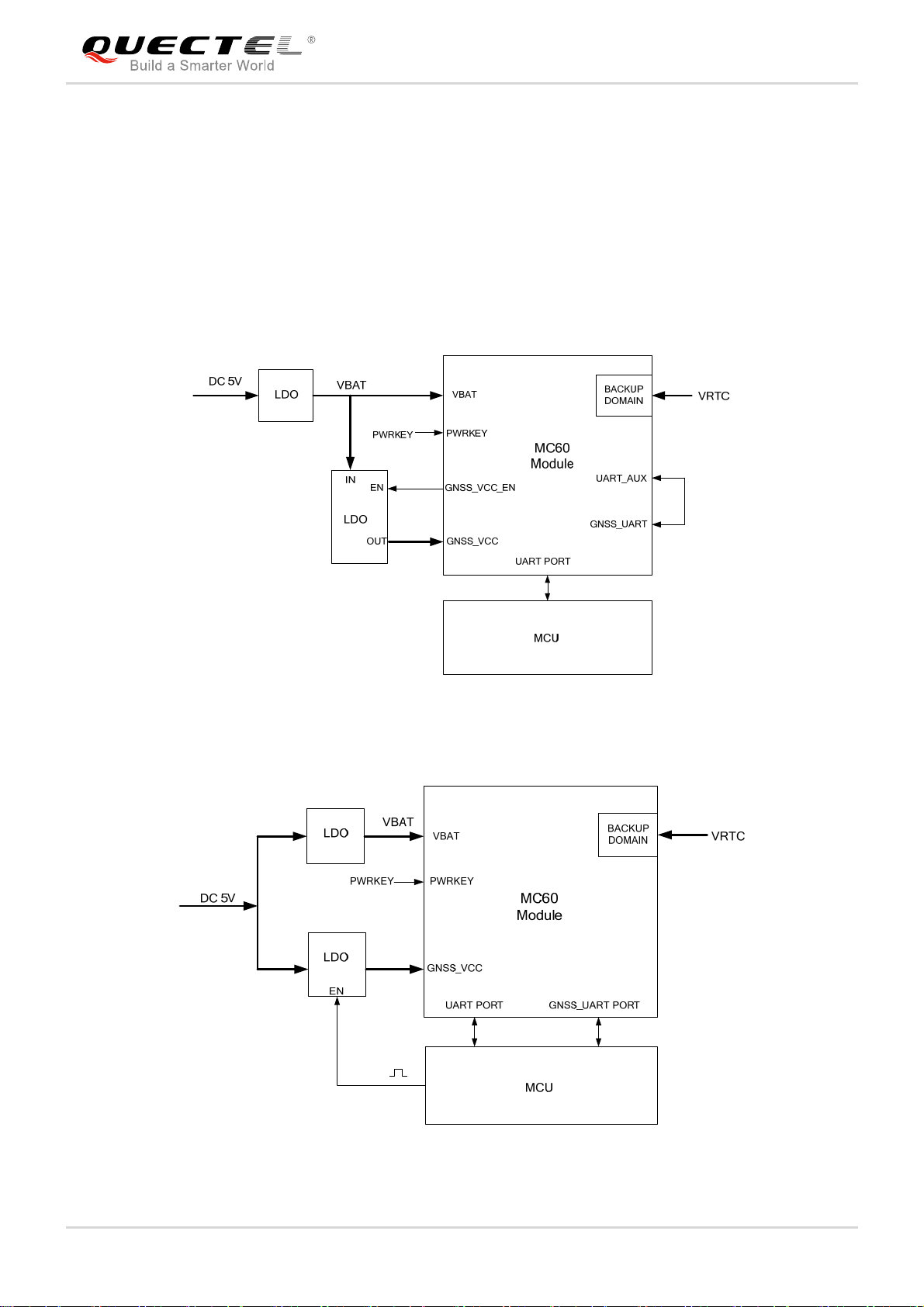
3.3.3.2. Reference Design for Power Supply of GNSS Part in All-in-one Solution
In all-in-one solution, the power supply of GNSS part is controlled by the GSM part through the
GNSS_VCC_EN pin. A reference circuit for the GNSS part power supply is given below. Please pay
attention to the electrical characteristics of GNSS_VCC_EN to match LDO’s EN pin. Please refer to
document [1] for details about the AT commands for GNSS control.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 30 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 9: Reference Circuit Design for GNSS Part in All-in-one Solution
3.3.3.3. Reference Design for Power Supply of GNSS Part in Stand-alone Solution
In stand-alone solution, GNSS is independent to the GSM part, and the power supply of the GNSS part is
controlled by customer’s master control. A reference circuit for the power supply of GNSS part is given
below.
Figure 10: Reference Circuit Design for GNSS Part in Stand-alone Solution
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 31 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.3.4. Monitor Power Supply
The command AT+CBC can be used to monitor the supply voltage of the GSM part. The unit of the
displayed voltage is mV.
For details, please refer to document [1].
3.3.5. Backup Domain of GNSS
The RTC (Real Time Clock) function of GSM part and backup mode of GNSS part are supported. In
GNSS’s backup mode, the backup domain which contains all the necessary GNSS information for quick
start-up and a small amount of user configuration variables is alive. Due to the backed-up memory, EASY
technology is available.
3.3.5.1. Use VBAT as the Backup Power Source of GNSS
In either all-in-one or stand-alone solution, GNSS’s backup mode will be active as long as the main power
supply (VBAT) is remained, even when the module is turned off and GNSS_VCC is powered off; as the
GNSS’s backup domain is powered by VBAT. In this case, the VRTC pin can be kept floating.
When powered by VBAT, the reference internal circuit design in all-in-one and stand-alone solutions is
shown below.
Figure 11: Internal GNSS’s Backup Domain Power Construction
3.3.5.2. Use VRTC as Backup Power of GNSS
In either all-in-one or stand-alone solution, when the main power supply (VBAT) is removed after the
module is turned off, and GNSS_VCC is also powered off, a backup supply such as a coin-cell battery
(rechargeable or non-chargeable) or a super capacitor can be used to power the VRTC pin to keep GNSS
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 32 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
in backup mode.
When powered by VRTC, the reference internal circuit design in all-in-one and stand-alone solutions is
shown below.
Figure 12: VRTC is Powered by a Rechargeable Battery
Figure 13: VRTC is Powered by a Capacitor
A rechargeable or non-chargeable coin-cell battery can also be used here. For more information, please
visit http://www.sii.co.jp/en/.
NOTE
It is recommended to keep SYSTEM_3.3V powered all the time.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 33 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.4. Operating Modes
3.4.1. Operating Modes of GSM Part
The table below briefly summarizes the various operating modes of GSM part mentioned in the following
chapters.
Table 9: Operating Modes Overview of GSM Part
Modes Function
After enabling sleep mode by AT+QSCLK=1, the GSM part will
automatically enter into Sleep Mode if DTR is set to high level
GSM/GPRS
Sleep
and there is no interrupt (such as GPIO interrupt or data on
UART port). In this case, the current consumption of the GSM
part will reduce to the minimal level.
During Sleep Mode, the GSM part can still receive paging
message and SMS from the system normally.
GSM Normal
Operation
POWER DOWN
GSM IDLE
Software is active. The GSM part has registered on GSM
network, and it is ready to send and receive GSM data.
GSM connection is ongoing. In this mode, the power
GSM TALK
consumption is decided by the configuration of Power Control
Level (PCL), dynamic DTX control and the working RF band.
GPRS IDLE
GPRS
STANDBY
The GSM part is not registered on GPRS network. It is not
reachable through GPRS channel.
The GSM part is registered on GPRS network, but no GPRS
PDP context is active. The SGSN knows the Routing Area
where the module is located at.
The PDP context is active, but no data transfer is ongoing. The
GPRS READY
GSM part is ready to receive or send GPRS data. The SGSN
knows the cell where the module is located at.
There is GPRS data in transfer. In this mode, power
GPRS DATA
consumption is decided by the PCL, working RF band and
GPRS multi-slot configuration.
Normal shutdown by sending the AT+QPOWD=1 command or using the
PWRKEY pin. The power management ASIC disconnects the power supply from
the base band part of the GSM part. Software is not active. The UART interfaces
are not accessible. Operating voltage (connected to VBAT) remains applied.
Minimum
Functionality Mode
(without removing
power supply)
AT+CFUN command can set the GSM part to a minimum functionality mode
without removing the power supply. In this case, the RF part of the GSM part will
not work or the SIM card will not be accessible, or both RF part and SIM card will
be disabled; but the UART port is still accessible. The power consumption in this
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 34 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
case is very low.
Based on system requirements, there are several actions to drive the GSM part to enter into low current
consumption status. For example, AT+CFUN can be used to set the part into minimum functionality mode,
and DTR hardware interface signal can be used to lead the system to Sleep Mode.
3.4.1.1. Minimum Functionality Mode
Minimum functionality mode reduces the functionality of the GSM part to a minimum level. The
consumption of the current can be minimized when the slow clocking mode is activated at the same time.
The mode is set via the AT+CFUN command which provides the choice of the functionality levels
<fun>=0, 1, 4.
0: minimum functionality
1: full functionality (default)
4: disable from both transmitting and receiving RF signals
If the GSM part is set to minimum functionality by AT+CFUN=0, the RF function and SIM card function
would be disabled. In this case, the UART port is still accessible, but all AT commands related with RF
function or SIM card function will be unavailable.
If the GSM part is set by the command AT+CFUN=4, the RF function will be disabled, but the UART port
is still active. In this case, all AT commands related with RF function will be unavailable.
After the GSM part is set by AT+CFUN=0 or AT+CFUN=4, it can return to full functionality mode by
AT+CFUN=1.
For detailed information about AT+CFUN, please refer to document [1].
3.4.1.2. SLEEP Mode
SLEEP mode is disabled by default. It can be enabled by AT+QSCLK=1 and the premise is that the
GNSS is powered off. The default setting is AT+QSCLK=0, and in this mode, the GSM part cannot enter
SLEEP mode.
When the GSM part is set by the command AT+QSCLK=1, you can control the part to enter into or exit
from the SLEEP mode through pin DTR. When DTR is set to high level, and there is no on-air or hardware
interrupt such as GPIO interrupt or data on UART port, the GSM part will enter into SLEEP mode
automatically. In this mode, the GSM part can still receive voice, SMS or GPRS paging from network, but
the UART port does not work.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 35 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.4.1.3. Wake up GSM Part from SLEEP Mode
When the GSM part is in the SLEEP mode, it can be woken up through the following methods:
If the DTR Pin is set low, it would wake up the GSM part from the SLEEP mode. The UART port will
be active within 20ms after DTR is changed to low level.
Receiving a voice or data call from network wakes up the GSM part.
Receiving an SMS from network wakes up the GSM part.
NOTE
DTR pin should be held at low level during communication between the GSM part and the DTE.
3.4.2. Operating Modes of GNSS Part
3.4.2.1. Full on Mode
Full on mode includes tracking mode and acquisition mode. Acquisition mode is defined as that the GNSS
part starts to search satellites, and to determine the visible satellites, coarse carrier frequency & code
phase of satellite signals. When the acquisition is completed, it switches to tracking mode automatically.
Tracking mode is defined as that the GNSS part tracks satellites and demodulates the navigation data
from specific satellites.
When the GNSS_VCC is valid, the GNSS part will enter into full on mode automatically. The following
table describes the default configuration of full on mode.
Table 10: Default Configuration of Full on Mode (GNSS Part)
Item Configuration Comment
Baud Rate 115200bps
Protocol NMEA RMC, VTG, GGA, GSA, GSV and GLL
Update Rate 1Hz
SBAS Enable
AIC Enable
LOCUS Disable
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 36 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Easy Technology Enable
EASY will be disabled automatically when update
rate exceeds 1Hz.
GNSS GPS+GLONASS
In full on mode, the consumption complies with the following regulations:
When the GNSS part is powered on, the average current will rush to 40mA and last for a few seconds;
then the consumption will be decreased to the acquisition current marked in table 3 and we defined this
state as acquisition state, and also it will last for several minutes until it switches to tracking state
automatically. The consumption in tracking state is less than that in acquisition state. The value is also
listed in table 3.
Sending PMTK commands allows for switching among multiple positioning systems:
$PMTK353,0,1*36: search GLONASS satellites only
$PMTK353,1,0*36: search GPS satellites only
$PMTK353,1,1*37: search GLONASS and GPS satellites
NOTE
In all-in-one solution, make sure the GNSS part is powered on before sending these PMTK commands.
3.4.2.2. Standby Mode
Standby mode is a low-power consumption mode. In standby mode, the internal core and I/O power
domain are still active; but RF and TCXO are powered off, and the GNSS part stops satellites search and
navigation. The way to enter into or exit from standby mode is using
PMTK commands.
When the GNSS part exits from standby mode, it will use all internal aiding information like GNSS time,
ephemeris, last position, etc., to ensure the fastest possible TTFF in either Hot or Warm start. The typical
current consumption is about 500uA @GNSS_VCC=3.3V in standby mode.
Sending the following PMTK command can make GNSS part enter into standby mode:
$PMTK161,0*28: make sure the GNSS part is powered on before sending the command in all-in-one
solution.
The following methods will make GNSS part exit from standby mode:
Sending any data via UART will make GNSS part exit from standby mode in all-in-one solution.
Sending any data via GNSS_UART will make GNSS part exit from standby mode in stand-alone
solution.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 37 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.4.2.3. Backup Mode
Backup mode requires lower power consumption than standby mode. In this mode, the GNSS part stops
acquiring and tracking satellites, but the backed-up memory in backup domain which contains all the
necessary GNSS information for quick start-up and a small amount of user configuration variables is alive.
Due to the backed-up memory, EASY technology is available. The current consumption in this mode is
about 14uA.
The following methods will make GNSS part enter into backup mode:
Sending PMTK command “$PMTK225,4*2F” will make GNSS part enter into backup mode.
Cutting off GNSS_VCC and keeping VRTC powered will make GNSS part enter into back mode from
full on mode.
The following method will make GNSS part exit from backup mode:
As long as the GNSS_VCC is powered, the GNSS part will exit from backup mode and enter full on
mode immediately.
NOTES
1. In all-in-one solution, all PMTK commands used for the GNSS part should be sent through GSM
UART when the GSM part is in Normal Mode or Minimum Functionality Mode and when the GNSS
part is powered on. Make sure the GSM UART Port is accessible.
2. In all-in-one solution, if the GSM part is in sleep mode, it is recommended to set the GNSS part to
backup mode to save power. This is because the GSM UART Port does not work in sleep mode, and
due to this, customers cannot obtain the location information through GSM UART Port even if the
GNSS part works in normal mode.
3. In stand-alone solution, all PMTK commands used for the GNSS part can be sent through GNSS
UART in any mode of GSM part.
3.4.3. Summary of GSM and GNSS Parts’ State in All-in-one Solution
Table 11: Combination States of GSM and GNSS Parts in All-in-one Solution
GSM Part Modes GNSS Part Modes
Full on Standby Backup
Normal
Sleep
Minimum Functionality
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 38 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
NOTE
The mark means that the Part supports this mode.
3.4.4. Summary of GSM and GNSS Parts’ State in Stand-alone Solution
Table 12: Combination States of GSM and GNSS Parts in Stand-alone Solution
GSM Part Modes GNSS Part Modes
Full on Standby Backup
Normal
Sleep
Minimum Functionality
3.5. Power on and down Scenarios in All-in-one Solution
In all-in-one solution, GNSS function is turned on or off by the AT command sent from GSM part.
3.5.1. Power on
The module can be turned on by driving the pin PWRKEY to a low level voltage. An open collector driver
circuit is suggested to control the PWRKEY. A simple reference circuit is illustrated as below.
Figure 14: Turn on the Module with an Open-collector Driver
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 39 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
NOTES
1. MC60 module is set to autobauding mode (AT+IPR=0) by default. In autobauding mode, URC RDY is
not reported to the host controller after the module is powered on. When the module is powered on after
a delay of 4 or 5 seconds, it can receive AT commands. Host controller should first send an AT string in
order that the module can detect baud rate of host controller, and it should continue to send the next AT
string until receiving OK string from the module. Then enter AT+IPR=x;&W to set a fixed baud rate for
the module and save the configuration to flash memory of the module. After these configurations, the
URC RDY would be received from the UART Port of the module every time when the module is
powered on. For more details, refer to the section AT+IPR in document [1].
2. When AT command is responded, it indicates the module is turned on successfully; or else the module
fails to be turned on.
The other way to control the PWRKEY is through a button directly. While pressing the key, electrostatic
strike may generate from the finger, and thus, a TVS component is indispensable to be placed nearby the
button for ESD protection. For the best performance, the TVS component must be placed nearby the
button. A reference circuit is shown in the following figure.
Figure 15: Turn on the Module with a Button
Command AT+QGNSSC=1 should be sent to enable the GNSS power supply after the GSM part is
running. When the GNSS_VCC is valid, the GNSS will enter into full on mode automatically. The turn-on
timing is illustrated in the following figure.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 40 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 16: Turn-on Timing
NOTE
Make sure that VBAT is stable before pulling down PWRKEY pin. The time of T1 is recommended to be
100ms.
3.5.2. Power down
The following procedures can be used to turn off the module:
Normal power down procedure: Turn off module using the PWRKEY pin
Normal power down procedure: Turn off module using command AT+QPOWD
Under-voltage automatic shutdown: Take effect when under-voltage is detected.
3.5.2.1. Power down Module Using the PWRKEY Pin
It is a safe way to turn off the module by driving the PWRKEY to a low level voltage for a certain time. The
power down scenario is illustrated in the following figure.
The power down procedure causes the module to log off from the network and allows the firmware to
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 41 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
save important data before completely disconnecting the power supply.
Before the completion of the power down procedure, the module sends out the result code shown below:
NORMAL POWER DOWN
NOTES
1. When unsolicited result codes do not appear when autobauding is active and DTE & DCE are not
correctly synchronized after start-up, the module is recommended to be set to a fixed baud rate.
2. As network logout time is related to the local mobile network, it is recommended to delay about 12
seconds before disconnecting the power supply or restarting the module.
After that moment, no further AT commands can be executed. Then the module enters the power down
mode.
Figure 17: Turn-off Timing by Using the PWRKEY Pin
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 42 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.5.2.2. Power down Module Using AT Command
It is also a safe way to turn off the module via AT command AT+QPOWD=1. This command will let the
module log off from the network and allow the firmware to save important data before completely
disconnecting the power supply.
Before the completion of the power down procedure, the module sends out the result code shown below:
NORMAL POWER DOWN
After that moment, no further AT commands can be executed. And then the module enters into the power
down mode.
Please refer to document [1] for details about the AT command AT+QPOWD.
3.5.2.3. Power down GNSS Part Alone Using AT Command
It is a safe way to turn off the GNSS part alone via AT command AT+QGNSSC=0. The power down
scenario for GNSS part is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 18: Turn-off Timing of GNSS Part by Using AT Command
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 43 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.5.2.4. Under-voltage Automatic Shutdown
The module will constantly monitor the voltage applied on the VBAT. If the voltage is ≤3.5V, the following
URC will be presented:
UNDER_VOLTAGE WARNING
The normal input voltage range is from 3.3V to 4.6V. If the voltage is <3.3V, the module will automatically
shut down.
If the voltage is <3.3V, the following URC will be presented:
UNDER_VOLTAGE POWER DOWN
After that moment, no further AT commands can be executed. The module logs off from network and
enters into power down mode.
NOTE
When unsolicited result codes do not appear when autobauding is active and DTE & DCE are not
correctly synchronized after start-up, the module is recommended to be set to a fixed baud rate.
3.5.3. Restart
Restart is a process of module power down first and then power on. The module can be restarted by
driving the PWRKEY to a low level for a certain time, which is similar to the way of turning on the module
but differs in the time for PWRKEY driving. In order to make the internal LDOs discharge completely after
turning off the module, it is recommended to delay about 500ms before restarting the module.
3.6. Power on and down Scenarios in Stand-alone Solution
In stand-alone solution, GSM and GNSS parts are controlled separately, and thus the power on and down
control of them are independent from each other as well. The GSM part can be turned on/off or restarted
via PWRKEY pin control, which is the same as that in all-in-one solution. The GNSS part is turned on/off
via an external switch of MCU.
3.6.1. Power on GSM Part
The GSM part can be turned on by driving the pin PWRKEY to a low level voltage. An open collector
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 44 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
driver circuit is suggested to control the PWRKEY. A simple reference circuit is illustrated in Figure 14.
NOTES
1. The GSM module is set to autobauding mode (AT+IPR=0) by default. In the autobauding mode, URC
RDY is not reported to the host controller after the module is powered on. When the GSM module is
powered on after a delay of 4 or 5 seconds, it can receive AT command. Host controller should first
send an AT string in order that the GSM module can detect baud rate of host controller, and it should
continue to send the next AT string until receiving OK string from the module. Then enter
AT+IPR=x;&W to set a fixed baud rate for the module and save the configuration to flash memory of
the module. After these configurations, the URC RDY would be received from the UART Port of the
GSM module every time when the module is powered on. For more details, refer to the section AT+IPR
in document [1].
2. When AT command is responded, it indicates the GSM module is turned on successfully; or else the
module fails to be turned on.
The other way to control the PWRKEY is through a button directly. While pressing the key, electrostatic
strike may generate from the finger, and thus, a TVS component is indispensable to be placed nearby the
button for ESD protection. For the best performance, the TVS component must be placed nearby the
button. A reference circuit is shown in Figure15.
The turn-on timing is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 19: Turn-on Timing of GSM Part
NOTE
Make sure that VBAT is stable before pulling down PWRKEY pin. The time of T1 is recommended to be
100ms.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 45 / 99
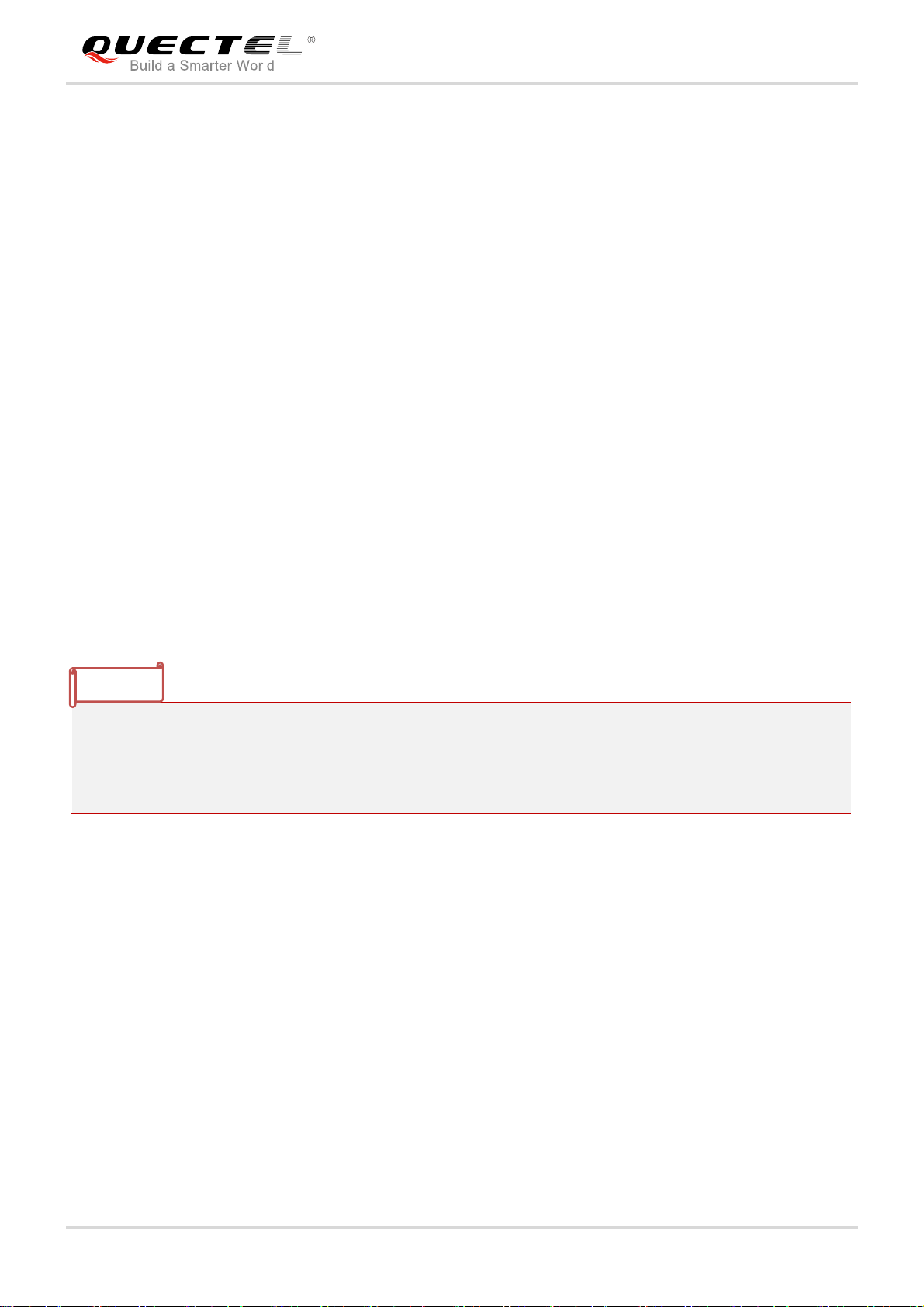
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.6.2. Power down GSM Part
The following procedures can be used to turn off the GSM part:
Normal power down procedure: Turn off GSM part using the PWRKEY pin
Normal power down procedure: Turn off GSM part using command AT+QPOWD
Under-voltage automatic shutdown: Take effect when under-voltage is detected.
3.6.2.1. Power down GSM Part Using the PWRKEY Pin
It is a safe way to turn off the GSM part by driving the PWRKEY to a low level voltage for a certain time.
The power down scenario is illustrated as the following figure.
The power down procedure causes the GSM module to log off from the network and allows the firmware
to save important data before completely disconnecting the power supply.
Before the completion of the power down procedure, the GSM module sends out the result code shown
below:
NORMAL POWER DOWN
NOTES
1. When unsolicited result codes do not appear when autobauding is active and DTE & DCE are not
correctly synchronized after start-up, the GSM module is recommended to be set to a fixed baud rate.
2. As logout network time is related to the local mobile network, it is recommended to delay about 12
seconds before disconnecting the power supply or restarting the module.
After that moment, no further AT commands can be executed. Then the GSM module enters the power
down mode.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 46 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 20: Turn-off Timing of GSM Part by Using the PWRKEY Pin
3.6.2.2. Power down GSM Part using Command
It is also a safe way to turn off the GSM module via AT command AT+QPOWD=1. This command will let
the GSM module log off from the network and allow the firmware to save important data before completely
disconnecting the power supply.
Before the completion of the power down procedure, the GSM module sends out the result code shown
below:
NORMAL POWER DOWN
After that moment, no further AT commands can be executed. And then the GSM module enters into the
power down mode.
Please refer to document [1] for details about the AT command AT+QPOWD.
3.7. Serial Interfaces
The module provides four serial ports: UART Port, Debug Port, Auxiliary UART Port and GNSS UART
Port. The module is designed as DCE (Data Communication Equipment), following the traditional
DCE-DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) connection. Autobauding function supports baud rate from
4800bps to 115200bps.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 47 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
The UART Port:
TXD: Send data to RXD of DTE.
RXD: Receive data from TXD of DTE.
RTS: Request to send.
CTS: Clear to send.
DTR: DTE is ready and inform DCE (this pin can wake the module up).
RI: Ring indicator (when there is a call, SMS or URC output, the module will inform DTE with the RI
pin).
DCD: Data carrier detection (the validity of this pin demonstrates successful set-up of the
communication link).
The Debug Port:
DBG_TXD: Send data to the COM port of peripheral.
DBG_RXD: Receive data from the COM port of peripheral.
The Auxiliary UART Port:
In all-in-one solution:
TXD_AUX: Send data to the GNSS part.
RXD_AUX: Receive data from the GNSS part.
In stand-alone solution:
TXD_AUX: Keep open
RXD_AUX: Keep open
The GNSS UART Port
In all-in-one solution:
GNSS_TXD: Send data to the GSM part.
GNSS_RXD: Receive data from the GSM part.
In stand-alone solution:
GNSS_TXD: Send GNSS data to the COM port of peripheral.
GNSS_RXD: Receive GNSS data from the COM port of peripheral.
The logic levels are described in the following table.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 48 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Table 13: Logic Levels of the UART Interface
Parameter Min. Max. Unit
VIL 0 0.25×VDD_EXT V
VIH 0.75×VDD_EXT VDD_EXT +0.2 V
VOL 0 0.15×VDD_EXT V
VOH 0.85×VDD_EXT VDD_EXT V
Table 14: Pin Definition of the UART Interfaces
Interface Pin Name Pin No. Description
UART Port
Debug Port
Auxiliary UART Port1)
TXD 33 Transmit data
RXD 34 Receive data
DTR 37 Data terminal ready
RI 35 Ring indication
DCD 36 Data carrier detection
CTS 38 Clear to send
RTS 39 Request to send
DBG_RXD 30 Receive data
DBG_TXD 29 Transmit data
1)
RXD_AUX
24 Receive data
TXD_AUX1) 25 Transmit data
GNSS_RXD 23 Receive data
GNSS UART Port
GNSS_TXD 22 Transmit data
NOTE
1)
It is recommended to keep these pins open in stand-alone solution.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 49 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.7.1. UART Port
3.7.1.1. Features of UART Port
Seven lines on UART interface
Contain data lines TXD and RXD, hardware flow control lines RTS and CTS, as well as other control
lines DTR, DCD and RI.
Used for AT command, GPRS data, etc. Multiplexing function is supported on the UART Port. NMEA
output and PMTK command can be supported in all-in-one solution.
Support the following communication baud rates:
300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400, 57600, 115200bps.
The default setting is autobauding mode. Support the following baud rates for autobauding function:
4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200bps.
Hardware flow control is disabled by default. When hardware flow control is required, RTS and CTS
should be connected to the host. AT command AT+IFC=2,2 is used to enable hardware flow control.
AT command AT+IFC=0,0 is used to disable the hardware flow control. For more details, please refer
to document [1].
After setting a fixed baud rate or autobauding, please send “AT” string at that rate. The UART port is
ready when it responds “OK”.
Autobauding allows the module to detect the baud rate by receiving the string “AT” or “at” from the host or
PC automatically, which gives module flexibility without considering which baud rate is used by the host
controller. Autobauding is enabled by default. To take advantage of the autobauding mode, special
attention should be paid according to the following requirements:
Synchronization between DTE and DCE:
When DCE (the module) is powered on with autobauding enabled, it is recommended to wait 2 to 3
seconds before sending the first AT character. After receiving the “OK” response, DTE and DCE are
correctly synchronized.
If the host controller needs URC in the mode of autobauding, it must be synchronized firstly. Otherwise
the URC will be discarded.
Restrictions on autobauding operation:
The UART port has to be operated at 8 data bits, no parity and 1 stop bit (factory setting).
The “At” and “aT” commands cannot be used.
Only the strings “AT” or “at” can be detected (neither “At” nor “aT”).
The Unsolicited Result Codes like RDY, +CFUN: 1 and +CPIN: READY
the module is turned on with autobauding enabled and not be synchronized.
Any other Unsolicited Result Codes will be sent at the previous baud rate before the module detects
will not be indicated when
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 50 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
the new baud rate by receiving the first “AT” or “at” string. The DTE may receive unknown characters
after switching to a new baud rate.
It is not recommended to switch to autobauding from a fixed baud rate.
If autobauding is active it is not recommended to switch to multiplex mode.
NOTE
To assure reliable communication and avoid any problems caused by undetermined baud rate between
DCE and DTE, it is strongly recommended to configure a fixed baud rate and save it instead of using
autobauding after start-up. For more details, please refer to the Section AT+IPR in document [1] .
3.7.1.2. The Connection of UART
The connection between module and host using UART Port is very flexible. Three connection styles are
illustrated as below.
A reference design for Full-Function UART connection is shown as below when it is applied in
modulation-demodulation.
Figure 21: Reference Design for Full-Function UART
Three-line connection is shown as below.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 51 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 22: Reference Design for UART Port (Three Line Connection)
A reference design for UART Port with hardware flow control is shown as below. The connection will
enhance the reliability of the mass data communication.
Figure 23: Reference Design for UART Port with Hardware Flow Control
3.7.1.3. Firmware Upgrade
TXD and RXD can be used for firmware upgrade in both all-in-one solution and stand-alone solution. The
PWRKEY pin must be pulled down before firmware upgrade. A reference circuit is shown as below:
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 52 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 24: Reference Design for Firmware Upgrade
NOTE
1. In stand-alone solution, make sure the Auxiliary UART Port is connected to the GNSS UART Port
before firmware upgrade. So it is recommended to retain this firmware upgrade circuit in design.
2. The firmware of module might need to be upgraded due to a certain reasons. It is thus recommended
to reserve these pins in the host board for firmware upgrade.
3.7.2. Debug Port
Two lines: DBG_TXD and DBG_RXD.
The port outputs log information automatically.
Debug Port is only used for firmware debugging and its baud rate must be configured as 460800bps.
Figure 25: Reference Design for Debug Port
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 53 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.7.3. Auxiliary UART Port and GNSS UART Port
3.7.3.1. Connection in All-in-one Solution
In all-in-one solution, the Auxiliary UART Port and GNSS UART Port should be connected together, thus
allowing for communication between GSM and GNSS parts. A reference design is shown below.
Figure 26: Auxiliary and GNSS UART Port Connection in All-in-one Solution
NOTE
As the GNSS part of MC60 module outputs more data than a single GNSS system, the default output
NMEA types running in 4800bps baud rate and 1Hz update rate will lose some data. The solution to avoid
losing data in 4800bps baud rate and 1Hz update rate is to decrease the output NMEA types. 115200bps
baud rate is enough to transmit GNSS NMEA in default settings and it is thus recommended.
3.7.3.2. Connection in Stand-alone Solution
In stand-alone solution, the GNSS UART Port is connected to the COM port of peripheral, and the
Auxiliary UART Port is recommended to keep open.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 54 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 27: Auxiliary and GNSS UART Port Connection in Stand-alone Solution
3.7.4. UART Application
A reference design of 3.3V level match is shown as below. If the host is a 3V system, please change the
5.6K resistors to 10K ones.
Figure 28: Level Match Design for 3.3V System
NOTE
It is highly recommended to add the resistor divider circuit on the UART signal lines when the host’s level
is 3V or 3.3V. For a higher voltage level system, a level shifter IC could be used between the host and the
module. For more details about UART circuit design, please refer to document [13].
The following figure shows a sketch map between the module and the standard RS-232 interface. As the
electrical level of module is 2.8V, a RS-232 level shifter must be used. Note that you should assure the
I/O voltage of level shifter which connects to module is 2.8V.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 55 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 29: Sketch Map for RS-232 Interface Match
Please visit vendors’ websites to select a suitable IC, such as: http://www.maximintegrated.com and
http://www.exar.com/.
3.8. Audio Interfaces
The module provides one analog input channel and two analog output channels.
Table 15: Pin Definition of Audio Interface
Interface Pin Name Pin No. Description
MICP 1 Microphone positive input
MICN 2 Microphone negative input
AIN/AOUT1
SPKP 3 Channel 1 Audio positive output
SPKN 4 Channel 1 Audio negative output
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 56 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
MICP 1 Microphone positive input
MICN 2 Microphone negative input
AIN/AOUT2
LOUDSPKP 54 Channel 2 Audio positive output
LOUDSPKN 53 Channel 2 Audio negative output
AIN can be used for input of microphone and line. An electret microphone is usually used. AIN are
differential input channels.
AOUT1 is used for output of receiver. The channel is typically used for building a receiver into a handset.
AOUT1 channel is a differential channel.
AOUT2 is used for loudspeaker output as it is embedded with an amplifier of class AB whose maximum
drive power is 870mW. AOUT2 is a differential channel.
AOUT2 also can be used for output of earphone, and can be used as a single-ended channel.
LOUDSPKP and AGND can establish a pseudo differential mode.
All these audio channels support voice and ringtone output, and so on, and can be switched by
AT+QAUDCH command. For more details, please refer to document [1].
Use AT command AT+QAUDCH to select audio channel:
0--AIN/AOUT1, the default value is 0.
1--AIN/AOUT2, this channel is always used for earphone.
2--AIN/AOUT2, this channel is always used for loudspeaker.
For each channel, you can use AT+QMIC to adjust the input gain level of microphone. You can also use
AT+CLVL to adjust the output gain level of receiver and speaker. AT+QSIDET is used to set the
side-tone gain level. For more details, please refer to document [1].
Table 16: AOUT2 Output Characteristics
Item Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
8ohm load
VBAT=4.2v
870 mW
THD+N=1%
RMS Power
8ohm load
VBAT=3.3v
THD+N=1%
530 mW
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 57 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.8.1. Decrease TDD Noise and Other Noise
The 33pF capacitor is applied for filtering out 900MHz RF interference when the module is transmitting at
EGSM900MHz. Without placing this capacitor, TDD noise could be heard. Moreover, the 10pF capacitor
here is used for filtering out 1800MHz RF interference. However, the resonant frequency point of a
capacitor largely depends on the material and production technique. Therefore, customers would have to
discuss with their capacitor vendors to choose the most suitable capacitor for filtering out EGSM900MHz,
DCS1800MHz.
The severity degree of the RF interference in the voice channel during GSM transmitting period largely
depends on the application design. In some cases, EGSM900 TDD noise is more severe; while in other
cases, DCS1800 TDD noise is more obvious. Therefore, you can have a choice based on test results.
Sometimes, even no RF filtering capacitor is required.
The capacitor which is used for filtering out RF noise should be close to the audio interface. Audio
alignment should be as short as possible.
In order to decrease radio or other signal interference, the position of RF antenna should be kept away
from audio interface and audio alignment. Power alignment and audio alignment should not be parallel,
and power alignment should be far away from audio alignment.
The differential audio traces must be routed according to the differential signal layout rule.
3.8.2. Microphone Interfaces Design
AIN channels come with internal bias supply for external electret microphone. A reference circuit is shown
in the following figure.
Figure 30: Reference Design for AIN
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 58 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.8.3. Receiver and Speaker Interface Design
Figure 31: Handset Interface Design for AOUT1
Figure 32: Speaker Interface Design with an Amplifier for AOUT1
A suitable differential audio amplifier can be chosen from the Texas Instrument’s website
(http://www.ti.com/). There are also other excellent audio amplifier vendors in the market.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 59 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.8.4. Earphone Interface Design
Figure 33: Earphone Interface Design
3.8.5. Loud Speaker Interface Design
Figure 34: Loud Speaker Interface Design
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 60 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.8.6. Audio Characteristics
Table 17: Typical Electret Microphone Characteristics
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Working Voltage 1.2 1.5 2.0 V
Working Current 200 500 uA
External Microphone Load Resistance 2.2 K Ohm
Table 18: Typical Speaker Characteristics
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Load resistance 32 Ohm
Single-ended
AOUT1
Output
Reference level 0 2.4 Vpp
Load resistance 32 Ohm
Differential
Reference level 0 4.8 Vpp
Load resistance 8 Ohm
Differential
AOUT2
Output
Reference level 0 2×VBAT Vpp
Load resistance 8 Ohm
Single-ended
Reference level 0 VBAT Vpp
3.9. SIM Card Interface
The SIM interface supports the functionality of the GSM Phase 1 specification and also the functionality of
the new GSM Phase 2+ specification for FAST 64 kbps SIM card (intended for use with a SIM application
tool-kit.
The SIM interface is powered by an internal regulator in the module. Both 1.8V and 3.0V SIM cards are
supported, and Dual SIM Single Standby function is supported.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 61 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Table 19: Pin Definition of the SIM Interface
Pin Name Pin No. Description
NOTE
Alternate
Function1)
Supply power for SIM card. Automatic detection of
SIM1_VDD 18
SIM1 card voltage. 3.0V±5% and 1.8V±5%.
Maximum supply current is around 10mA.
SIM1_CLK 19 SIM1 card clock.
SIM1_DATA 21 SIM1 card data I/O.
SIM1_RST 20 SIM1 card reset.
SIM1_PRESENCE 37 SIM1 card detection. DTR
SIM_GND 16 SIM card ground.
Supply power for SIM card. Automatic detection of
SIM2_VDD 13
SIM2 card voltage. 3.0V±5% and 1.8V±5%.
Maximum supply current is around 10mA.
SIM2_CLK 10 SIM2 card clock.
SIM2_DATA 11 SIM2 card data I/O.
SIM2_RST 12 SIM2 card reset.
1)
If several interfaces share the same I/O pin, to avoid conflict between these alternate functions, only one
peripheral should be enabled at a time.
The following figure is a reference design for SIM1 interface with an 8-pin SIM card holder.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 62 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 35: Reference Circuit for SIM1 Interface with an 8-pin SIM Card Holder
If SIM1 card detection function is not used, keep SIM1_PRESENCE pin open. A reference circuit for a
6-pin SIM card socket is shown in the following figure.
Figure 36: Reference Circuit for SIM1 Interface with a 6-pin SIM Card Holder
The following figure is a reference design for SIM2 interface with a 6-pin SIM card holder.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 63 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 37: Reference Circuit for SIM2 Interface with a 6-pin SIM Card Holder
For more information of SIM card holder, you can visit http://www.amphenol.com/ and
http://www.molex.com/.
In order to enhance the reliability and availability of the SIM card in application, please conform to the
following criteria in the SIM circuit design:
Keep layout of SIM card as close to the module as possible. Assure the trace length is less than
200mm.
Keep SIM card signal away from RF and VBAT alignment.
Assure the ground between module and SIM cassette short and wide. Keep the width of ground no
less than 0.5mm to maintain the same electric potential. The decouple capacitor of SIM_VDD is less
than 1uF and must be near to SIM cassette.
To avoid cross talk between SIM_DATA and SIM_CLK, keep them away from each other and shield
them with surrounded ground.
In order to offer good ESD protection, it is recommended to add a TVS diode array. For more
information of TVS diode, please visit http://www.onsemi.com/. The most important rule is to place
the ESD protection device close to the SIM card socket and make sure the nets being protected will
go through the ESD device first and then lead to module. The 22Ω resistors should be connected in
series between the module and the SIM card so as to suppress the EMI spurious transmission and
enhance the ESD protection. Please note that the SIM peripheral circuit should be close to the SIM
card socket.
Place the RF bypass capacitors (33pF) close to the SIM card on all signals lines to improve EMI
suppression performance.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 64 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.10. ADC
The module provides an ADC channel to measure the value of voltage. Please give priority to the use of
ADC0 channel. Command AT+QADC can read the voltage value applied on ADC0 pin. For details of this
AT command, please refer to document [1]. In order to improve the accuracy of ADC, the layout of ADC
should be surrounded by ground.
Table 20: Pin Definition of the ADC
Pin Name Pin No. Description
ADC 6 Analog to digital converter.
Table 21: Characteristics of the ADC
Item Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Voltage Range 0 2.8 V
ADC Resolution 10 bits
ADC Accuracy 2.7 mV
3.11. Behaviors of the RI
Table 22: Behaviors of the RI
State RI Response
Standby HIGH
Change to LOW, and then:
1. Change to HIGH when call is established.
2. Change to HIGH when use ATH to hang up the call
Voice Call
3. Change to HIGH first when calling part hangs up and then change to LOW for
120ms indicating “NO CARRIER” as an URC. After that, RI changes to HIGH
again.
4. Change to HIGH when SMS is received.
SMS
When a new SMS comes, the RI changes to LOW and holds low level for about
120ms, and then changes to HIGH.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 65 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
URC
Certain URCs can trigger 120ms low level on RI. For more details, please refer to
document [1]
If the module is used as a caller, the RI would maintain high except when the URC or SMS is received.
When it is used as a receiver, the timing of RI is shown below.
Figure 38: RI Behavior as a Receiver When Voice Calling
Figure 39: RI Behavior as a Caller
Figure 40: RI Behavior When URC or SMS Received
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 66 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.12. Network Status Indication
The NETLIGHT signal can be used to drive a network status indicator LED. The working state of this pin
is listed in the following table.
Table 23: Working State of the NETLIGHT
State Module Function
Off The module is not running.
64ms On/800ms Off The module is not synchronized with network.
64ms On/2000ms Off The module is synchronized with network.
64ms On/600ms Off GPRS data transmission after dialing the PPP connection.
A reference circuit is shown as below.
Figure 41: Reference Design for NETLIGHT
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 67 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.13. EASY Autonomous AGPS Technology
Supplying aiding information like ephemeris, almanac, rough last position, time and satellite status, can
help improve the acquisition sensitivity and the TTFF for a module. This is called as EASY technology and
MC60’s GNSS part supports it.
EASY technology works as embedded software which can accelerate TTFF by predicting satellite
navigation messages from received ephemeris. The GNSS part will calculate and predict orbit information
automatically up to 3 days after first receiving the broadcast ephemeris, and save the predicted
information into the internal memory. GNSS part of MC60 will use the information for positioning if no
enough information from satellites, so the function is helpful for positioning and TTFF improvement.
The EASY function can reduce TTFF to 5s in warm start. In this case, GNSS’s backup domain should be
valid. In order to gain enough broadcast ephemeris information from GNSS satellites, the GNSS part
should receive the information for at least 5 minutes in good signal conditions after it fixes the position.
EASY function is enabled by default. Command “$PMTK869,1,0*34” can be used to disable EASY
function. For more details, please refer to document [2].
NOTE
In all-in-one solution, make sure the GNSS part is powered on before sending the PMTK command.
3.14. EPO Offline AGPS Technology
MC60 module features a function called EPO (Extended Prediction Orbit) which is a world leading
technology. When MC60 module is powered on, EPO function can be enabled via AT command
AT+QGNSSEPO=1. When the GSM part detected that the EPO data has expired, the EPO data will be
automatically downloaded to the GSM part’s FS from MTK server via GSM/GPRS network; and the GNSS
part will get the EPO data via build-in GNSS command from GSM's FS when it detected that the local
EPO data has expired. When there is no local EPO data or when the data has expired, MC60 module will
download the data (4KB) for 6 hours’ orbit predictions in order to achieve cold start in the shortest time,
and then continue to download the EPO data (48KB) for 3 days. The technology allows the module to
realize fast positioning. Command AT+QGNSSEPO=0 can turn off the EPO function.
NOTE
Make sure the EPO function is enabled if you need to download the EPO data.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 68 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
3.15. Multi-tone AIC
MC60 module has a function called multi-tone AIC (Active Interference Cancellation) to decease
harmonic of RF noise from Wi-Fi, GSM, 3G and 4G.
Up to 12 multi-tone AIC embedded in the module can provide effective narrow-band interference and
jamming elimination. The GNSS signal could be demodulated from the jammed signal, which can ensure
better navigation quality. AIC function is enabled by default. Enabling AIC function will increase current
consumption by about 1mA @VCC=3.3V. The following commands can be used to set AIC function.
Enable AIC function: $PMTK 286,1*23
Disable AIC function: $PMTK 286,0*22
NOTE
In all-in-one solution, make sure the GNSS part is powered on before sending these PMTK commands.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 69 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
4 Antenna Interface
MC60 has two antenna interfaces: GSM antenna and GNSS antenna. The Pin 41 is the GSM antenna
pad. The Pin 15 is the GNSS antenna pad. The RF interface of the two antenna pads has an impedance
of 50Ω.
4.1. GSM Antenna Interface
There is a GSM antenna pad named RF_ANT for MC60.
Table 24: Pin Definition of the RF_ANT
Pin Name Pin No. Description
GND 40 Ground
RF_ANT 41 GSM antenna pad
GND 42 Ground
4.1.1. Reference Design
The external antenna must be matched properly to achieve the best performance; so the matching circuit
is necessary. A reference design for GSM antenna is shown below.
Figure 42: Reference Design for GSM Antenna
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 70 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
MC60 provides an RF antenna pad for antenna connection. The RF trace in host PCB connected to the
module’s RF antenna pad should be coplanar waveguide line or microstrip line, whose characteristic
impedance should be close to 50Ω. MC60 comes with grounding pads which are next to the antenna pad
in order to give a better grounding. Besides, a π type matching circuit is suggested to be used to adjust
the RF performance.
To minimize the loss on RF trace and RF cable, please pay attention to the design. The following table
shows the requirement on GSM antenna.
Table 25: Antenna Cable Requirements
Type Requirements
EGSM900 Cable insertion loss <1dB
DCS1800 Cable insertion loss <1.5dB
Table 26: Antenna Requirements
Type Requirements
Frequency Range Depend on the frequency band(s) provided by the network operator
VSWR ≤ 2
Gain (dBi) 1
Max. Input Power (W) 50
Input Impedance (Ω) 50
Polarization Type Vertical
4.1.2. RF Output Power
Table 27: RF Output Power
Frequency Max. Min.
EGSM900 33dBm±2dB 5dBm±5dB
DCS1800 30dBm±2dB 0dBm±5dB
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 71 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
NOTE
In GPRS 4 slots TX mode, the maximum output power is reduced by 2.5dB. This design conforms to the
GSM specification as described in section 13.16 of 3GPP TS 51.010-1.
4.1.3. RF Receiving Sensitivity
Table 28: RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Receive Sensitivity
EGSM900 < -109dBm
DCS1800 < -109dBm
4.1.4. Operating Frequencies
Table 29: Operating Frequencies
Frequency Receive Transmit ARFCH
EGSM900 925~960MHz 880~915MHz 0~124, 975~1023
DCS1800 1805~1880MHz 1710~1785MHz 512~885
4.1.5. RF Cable Soldering
Soldering the RF cable to RF pad of module correctly will reduce the loss on the path of RF, please refer
to the following example of RF soldering.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 72 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 43: RF Soldering Sample
4.2. GNSS Antenna Interface
The GNSS part of MC60 module supports both GPS and GLONASS systems. The RF signal is obtained
from the GNSS_ANT pin. The impedance of RF trace should be controlled as 50 Ohm, and the trace
length should be kept as short as possible.
4.2.1. Antenna Specifications
The module can be connected to a dedicated GPS/GLONASS passive or active antenna to receive
GPS/GLONASS satellite signals. The recommended antenna specifications are given in the following
table.
Table 30: Recommended Antenna Specifications
Antenna Type Specification
GPS frequency: 1575.42±2MHz
GLONASS frequency: 1602±4MHz
Passive Antenna
VSWR: <2 (Typ.)
Polarization: RHCP or Linear
Gain: >0dBi
GPS frequency: 1575.42±2MHz
Active Antenna
GLONASS frequency:1602±4MHz
VSWR: <2 (Typ.)
Polarization: RHCP or Linear
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 73 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Noise figure: <1.5dB
Gain (antenna): >-2dBi
Gain (embedded LNA): 20dB (Typ.)
Total gain: >18dBi (Typ.)
4.2.2. Active Antenna
The following figure is a typical reference design with active antenna. In this mode, the antenna is
powered by GNSS_VCC.
Figure 44: Reference Design with Active Antenna
C1, R1 and C2 are reserved matching circuit for antenna impedance modification. By default, C1 and C2
are not mounted; R1 is 0 ohm.
The external active antenna is powered by GNSS_VCC. The voltage ranges from 2.8V to 4.3V, and the
typical value is 3.3V. If the voltage does not meet the requirements for powering the active antenna, an
external LDO should be used.
The inductor L1 is used to prevent the RF signal from leaking into the GNSS_VCC pin and route the bias
supply to the active antenna, and the recommended value of L1 is no less than 47nH. R2 can protect the
whole circuit in case the active antenna is shorted to ground.
NOTE
In all-in-one solution, please note that the power supply of GNSS_VCC is controlled by the GSM part
through AT command.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 74 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
4.2.3. Passive Antenna
Figure 45: Reference Design with Passive Antenna
The above figure is a typical reference design with passive antenna.
C1, R1 and C2 are reserved matching circuit for antenna impedance modification. C1 and C2 are not
mounted by default; R1 is 0 ohm. Impedance of RF trace should be controlled as 50 ohm and the trace
length should be kept as short as possible.
4.3. Bluetooth Antenna Interface
MC60 provides a Bluetooth antenna interface. Bluetooth is a wireless technology that allows devices to
communicate, or transmit data/voice, wirelessly over a short distance. It is described as a short-range
communication technology intended to replace the cables connecting portable and/or fixed devices while
maintaining high level of security. Bluetooth is standardized as IEEE802.15 and operates in the 2.4 GHz
range using RF technology. Its data rate is up to 3Mbps.
MC60 is fully compliant with Bluetooth specification 3.0, and supports profiles including SPP and HFP-AG.
The external antenna must be matched properly to achieve the best performance, so the matching circuit
is necessary. The connection is recommended as in the following figure:
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 75 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
0R
BT_ANT
Module
Figure 46: Reference Design for Bluetooth Antenna
NM NM
There are some suggestions for component placement and RF trace layout for Bluetooth RF traces:
Antenna matching circuit should be closed to the antenna;
The impedance of RF trace should be controlled as 50Ω;
The RF traces should be kept far away from the high frequency signals and strong disturbing source.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 76 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
The proposed antenna type is Chip antenna,and the detailed description is as follows:
Table 31: Recommended Antenna Specifications
ITEM SPECIFICATION
Type Chip Antenna
Frequency Band 2.40GHz~2.50GHz
Peak Gain 3 dBi Typ
Impedance 50Ω Typ
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 77 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
5 Electrical, Reliability and Radio
Characteristics
5.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings for power supply and voltage on digital and analog pins of the module are
listed in the following table:
Table 32: Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Min. Max. Unit
VBAT -0.3 +4.73 V
GNSS_VCC -0.3 +4.5 V
Peak Current of Power Supply (VBAT) 0 2 A
RMS Current of Power Supply (VBAT, during one
TDMA-frame)
Voltage at Digital Pins -0.3 3.08 V
Voltage at Analog Pins -0.3 3.08 V
Voltage at Digital/analog Pins in Power Down Mode -0.25 0.25 V
0 0.7 A
5.2. Operating Temperature
The operating temperature is listed in the following table:
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 78 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Table 33: Operating Temperature
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Operation temperature range 1) -35 +25 +75
Extended temperature range 2) -40 +85
℃
℃
NOTES
1. 1) Within operation temperature range, the module is 3GPP compliant.
2. 2) Within extended temperature range, the module remains the ability to establish and maintain a
voice, SMS, data transmission, emergency call, etc. There is no unrecoverable malfunction. There
are also no effects on radio spectrum and no harm to radio network. Only one or more parameters like
P
might reduce in their value and exceed the specified tolerances. When the temperature returns to
out
the normal operating temperature levels, the module will meet 3GPP compliant again.
5.3. Power Supply Ratings
Table 34: Power Supply Ratings of GSM Part (GNSS is Powered off)
Parameter Description Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Voltage must stay within the
Supply voltage
min/max values, including
3.3 4.0 4.6 V
voltage drop, ripple, and spikes.
VBAT
Voltage drop
during
transmitting
Maximum power control level
on GSM850 and EGSM900.
400 mV
burst
I
VBAT
Power down mode
SLEEP mode @DRX=5
Minimum functionality mode
AT+CFUN=0
IDLE mode
Average supply
current
SLEEP mode
AT+CFUN=4
IDLE mode
SLEEP mode
TALK mode
GSM850/EGSM900
DCS1800/PCS1900
1)
2)
150
1.2
13
0.98
13
1.0
174/175
153/151
uA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 79 / 99
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
NOTES
Peak supply
current (during
transmission
slot)
DATA mode, GPRS (3Rx, 2Tx)
GSM850/EGSM900
DCS1800/PCS1900
1)
2)
DATA mode, GPRS (2 Rx, 3Tx)
GSM850/EGSM900
DCS1800/PCS1900
1)
2)
DATA mode, GPRS (4 Rx, 1Tx)
GSM850/EGSM900
DCS1800/PCS1900
1)
2)
DATA mode, GPRS (1Rx, 4Tx)
GSM850/EGSM900
DCS1800/PCS1900
1)
2)
Maximum power control level
on GSM850 and EGSM900.
363/356
234/257
496/487
305/348
216/222
171/169
3)
470/471
377/439
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
1.6 2 A
1)
1.
Power control level PCL 5.
2)
2.
Power control level PCL 0.
3)
3.
Under the GSM850 and EGSM900 spectrum, the power of 1Rx and 4Tx is reduced.
Table 35: Power Supply Ratings of GNSS Part
Parameter Description Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Voltage must stay
GNSS_
VCC
Supply voltage
within the min/max
values, including
voltage drop, ripple,
2.8 3.3 4.3 V
and spikes.
1)
I
Peak supply current VCC=3.3V 150 mA
VCCP
VRTC
Backup domain voltage
supply
1.5 2.8 3.3 V
NOTE
1)
This figure can be used to determine the maximum current capability of power supply.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 80 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
5.4. Current Consumption
Table 36: Current Consumption of GSM and GNSS Parts
Parameter Conditions
VBAT
VBAT
Only VBAT is remained; GSM and
GNSS are both powered off
In stand-alone solution, GSM is powered
off while GNSS is in full on mode
Current
Consumption.
223 uA
200 uA
Only the VRTC is remained; GSM is
VRTC
powered off and GNSS is in the backup
14 uA
mode
Table 37: Current Consumption of GSM Part (GNSS is Powered off)
Condition Current Consumption
Voice Call
@power level #5 <300mA, Typical 174mA
GSM850
@power level #12, Typical 83mA
@power level #19, Typical 62mA
Unit
@power level #5 <300mA, Typical 175mA
EGSM900
@power level #12, Typical 83mA
@power level #19, Typical 63mA
@power level #0 <250mA, Typical 153mA
DCS1800
@power level #7, Typical 73mA
@power level #15, Typical 60mA
@power level #0 <250mA, Typical 151mA
PCS1900
@power level #7, Typical 76mA
@power level #15, Typical 61mA
GPRS Data
DATA Mode, GPRS (3 Rx, 2Tx) CLASS 12
@power level #5 <550mA, Typical 363mA
GSM850
@power level #12, Typical 131mA
@power level #19, Typical 91mA
@power level #5 <550mA, Typical 356mA
EGSM900
@power level #12, Typical 132mA
@power level #19, Typical 92mA
DCS1800 @power level #0 <450mA, Typical 234mA
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 81 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
@power level #7, Typical 112mA
@power level #15, Typical 88mA
@power level #0 <450mA, Typical 257mA
PCS1900
@power level #7, Typical 119mA
@power level #15, Typical 89mA
DATA Mode, GPRS (2 Rx, 3Tx) CLASS 12
@power level #5 <640mA, Typical 496mA
GSM850
@power level #12, Typical 159mA
@power level #19, Typical 99mA
@power level #5 <600mA, Typical 487mA
EGSM900
@power level #12, Typical 160mA
@power level #19, Typical 101mA
@power level #0 <490mA, Typical 305mA
DCS1800
@power level #7, Typical 131mA
@power level #15, Typical 93mA
@power level #0 <480mA, Typical 348mA
PCS1900
@power level #7, Typical 138mA
@power level #15, Typical 94mA
DATA Mode, GPRS (4 Rx,1Tx) CLASS 12
@power level #5 <350mA, Typical 216mA
GSM850
@power level #12, Typical 103mA
@power level #19, Typical 83mA
@power level #5 <350mA, Typical 222mA
EGSM900
@power level #12, Typical 104mA
@power level #19, Typical 84mA
@power level #0 <300mA, Typical 171mA
DCS1800
@power level #7, Typical 96mA
@power level #15, Typical 82mA
@power level #0 <300mA, Typical 169mA
PCS1900
@power level #7, Typical 98mA
@power level #15, Typical 83mA
DATA Mode, GPRS (1 Rx, 4Tx) CLASS 12
@power level #5 <600mA, Typical 470mA
GSM850
@power level #12, Typical 182mA
@power level #19, Typical 106mA
@power level #5 <600mA, Typical 471mA
EGSM900
@power level #12, Typical 187mA
@power level #19, Typical 109mA
@power level #0 <500mA, Typical 377mA
DCS1800
@power level #7, Typical 149mA
@power level #15, Typical 97mA
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 82 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
@power level #0 <500mA, Typical 439mA
PCS1900
@power level #7, Typical 159mA
@power level #15, Typical 99mA
NOTE
GPRS Class 12 is the default setting. The GSM module can be configured from GPRS Class 1 to Class
12. Setting to lower GPRS class would make it easier to design the power supply for the GSM module.
Table 38: Current Consumption of the GNSS Part
Parameter Conditions Typ. Unit
I
@Acquisition @VCC=3.3V (GPS) 25 mA
VCC
I
@Tracking @VCC=3.3V (GPS) 19 mA
VCC
I
@Acquisition @VCC=3.3V (GPS+GLONASS) 29 mA
VCC
I
@Tracking @VCC=3.3V (GPS+GLONASS) 22 mA
VCC
I
@Standby @VCC=3.3V 0.5 mA
VCC
I
@backup @V_BCKP=3.3V 14 uA
BCKP
NOTES
1. The VCC_RF current is not reckoned in above consumption.
2. The tracking current is tested in following condition:
For Cold Start, 10 minutes after First Fix.
For Hot Start, 15 seconds after First Fix.
5.5. Electrostatic Discharge
Although the module is generally protected against Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), ESD protection
precautions should still be emphasized. Proper ESD handling and packaging procedures must be applied
throughout the processing, handling and operation of any applications using the module.
The measured ESD values of the module are shown in the following table.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 83 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Table 39: ESD Endurance (Temperature: 25ºC, Humidity: 45%)
Tested Point Contact Discharge Air Discharge
VBAT, GND ±5KV ±10KV
RF_ANT ±5KV ±10KV
GNSS_ANT ±5KV ±10KV
TXD, RXD ±2KV ±4KV
Others ±0.5KV ±1KV
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 84 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
6 Mechanical Dimensions
This chapter describes the mechanical dimensions of the module.
6.1. Mechanical Dimensions of Module
Figure 47: MC60 Top and Side Dimensions (Unit: mm)
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 85 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Figure 48: MC60 Bottom Dimensions (Unit: mm)
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 86 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
6.2. Recommended Footprint
Figure 49: Recommended Footprint (Unit: mm)
NOTES
1. For convenient maintenance, the module should be kept about 3mm away from the other
components in the host PCB.
2. The circular test points with a radius of 1.75mm in the above recommended footprint should be
treated as keepout areas. (“keepout” means do not pour copper on the mother board).
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 87 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
6.3. Top and Bottom View of the Module
Figure 50: Top View of the Module
Figure 51: Bottom View of the Module
NOTE
These are design effect drawings of MC60 module. For more accurate pictures, please refer to the
module that you get from Quectel.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 88 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
7 Storage and Manufacturing
7.1. Storage
MC60 module is stored in a vacuum-sealed bag. The storage restrictions are shown as below.
1. Shelf life in the vacuum-sealed bag: 12 months at <40ºC and <90%RH.
2. After the vacuum-sealed bag is opened, devices that need to be mounted directly must be:
Mounted within 72 hours at the factory environment of ≤30ºC and <60% RH.
Stored at <10% RH.
3. Devices require baking before mounting, if any circumstance below occurs.
When the ambient temperature is 23ºC±5ºC and the humidity indication card shows the humidity
is >10% before opening the vacuum-sealed bag.
Device mounting cannot be finished within 72 hours when the ambient temperature is <30ºC and the
humidity is <60%.
Stored at >10% RH.
4. If baking is required, devices should be baked for 48 hours at 125ºC±5ºC.
NOTE
As the plastic package cannot be subjected to high temperature, it should be removed from devices
before high temperature (125ºC) baking. If shorter baking time is desired, please refer to
IPC/JEDECJ-STD-033 for baking procedure.
7.2. Soldering
Push the squeegee to apply the solder paste on the surface of stencil, thus making the paste fill the
stencil openings and then penetrate to the PCB. The force on the squeegee should be adjusted properly
so as to produce a clean stencil surface on a single pass. To ensure the module soldering quality, the
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 89 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
thickness of stencil at the hole of the module pads should be 0.2 mm for MC60. For more details, please
refer to document [12]
It is suggested that the peak reflow temperature is from 235ºC to 245ºC (for SnAg3.0Cu0.5 alloy). The
absolute maximum reflow temperature is 260ºC. To avoid damage to the module caused by repeated
heating, it is suggested that the module should be mounted after reflow soldering for the other side of
PCB has been completed. Recommended reflow soldering thermal profile is shown below:
250
217
200
150
100
℃
50
Preheat Heating Cooling
Liquids
Temperature
160℃
Between 1~3℃/S
200℃
40s~60s
70s~120s
0
50
100
150 200 250 300
s
Time(s)
Figure 52: Reflow Soldering Thermal Profile
7.3. Packaging
The modules are stored in a vacuum-sealed bag which is ESD protected. It should not be opened until the
devices are ready to be soldered onto the application.
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 90 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
7.3.1. Tape and Reel Packaging
Figure 53: Tape and Reel Specification
Figure 54: Dimensions of Reel
Table 40: Reel Packaging
Model Name
MOQ for
MP
MC60 250pcs
Minimum
Package:250pcs
Size:
370mm×350mm×56mm
N.W: 0.32kg
G.W: 1.08kg
Minimum
Packagex4=1000pcs
Size:
380mm×250mm×365mm
N.W: 1.28kg
G.W: 4.8kg
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 91 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
8 Appendix A References
Table 41: Related Documents
SN Document Name Remark
[1] Quectel_MC60_AT_Commands_Manual MC60 AT commands manual
[2] ITU-T Draft new recommendation V.25ter
[3] GSM 07.07
[4] GSM 07.10
[5] GSM 07.05
[6] GSM 11.14
[7] GSM 11.11
Serial asynchronous automatic dialing
and control
Digital cellular telecommunications
(Phase 2+); AT command set for GSM
Mobile Equipment (ME)
Support GSM 07.10 multiplexing
protocol
Digital cellular telecommunications
(Phase 2+); Use of Data Terminal
Equipment – Data Circuit terminating
Equipment (DTE – DCE) interface for
Short Message Service (SMS) and
Cell Broadcast Service (CBS)
Digital cellular telecommunications
(Phase 2+); Specification of the SIM
Application Toolkit for the Subscriber
Identity module – Mobile Equipment
(SIM – ME) interface
Digital cellular telecommunications
(Phase 2+); Specification of the
Subscriber Identity module – Mobile
Equipment (SIM – ME) interface
Digital cellular telecommunications
[8] GSM 03.38
[9] GSM 11.10
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 92 / 99
(Phase 2+); Alphabets and
language-specific information
Digital cellular telecommunications
(Phase 2); Mobile Station (MS)
conformance specification; Part 1:
Conformance specification

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
[10] GSM_UART_Application_Note UART port application note
[11] GSM_EVB_User_Guide GSM EVB user guide
[12] Module_Secondary_SMT_User_Guide Module secondary SMT user guide
[13] Quectel_GSM_Module_Digital_IO_Application_Note
Table 42: Terms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
ADC Analog-to-Digital Converter
AMR Adaptive Multi-Rate
ARP Antenna Reference Point
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
BER Bit Error Rate
BOM Bill of Material
BT Bluetooth
GSM Module Digital IO Application
Note
BTS Base Transceiver Station
CHAP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CS Coding Scheme
CSD Circuit Switched Data
CTS Clear to Send
DAC Digital-to-Analog Converter
DRX Discontinuous Reception
DSP Digital Signal Processor
DCE Data Communications Equipment (typically module)
DTE Data Terminal Equipment (typically computer, external controller)
DTR Data Terminal Ready
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 93 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
DTX Discontinuous Transmission
EFR Enhanced Full Rate
EGSM Enhanced GSM
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
ETS European Telecommunication Standard
FCC Federal Communications Commission (U.S.)
FDMA Frequency Division Multiple Access
FR Full Rate
FS File System
GMSK Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GSM Global System for Mobile Communications
G.W Gross Weight
HR Half Rate
I/O Input/Output
IC Integrated Circuit
IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity
IOmax Maximum Output Load Current
kbps Kilo Bits Per Second
LED Light Emitting Diode
Li-Ion Lithium-Ion
MO Mobile Originated
MOQ Minimum Order Quantity
MP Manufacture Product
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 94 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
MS Mobile Station (GSM engine)
MT Mobile Terminated
N.W Net Weight
PAP Password Authentication Protocol
PBCCH Packet Switched Broadcast Control Channel
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PDU Protocol Data Unit
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol
RF Radio Frequency
RMS Root Mean Square (value)
RTC Real Time Clock
RX Receive Direction
SIM Subscriber Identification Module
SMS Short Message Service
TDMA Time Division Multiple Access
TE Terminal Equipment
TX Transmitting Direction
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver & Transmitter
URC Unsolicited Result Code
USSD Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
VOmax Maximum Output Voltage Value
VOnorm Normal Output Voltage Value
VOmin Minimum Output Voltage Value
VIHmax Maximum Input High Level Voltage Value
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 95 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
min Minimum Input High Level Voltage Value
V
IH
VILmax Maximum Input Low Level Voltage Value
VILmin Minimum Input Low Level Voltage Value
VImax Absolute Maximum Input Voltage Value
VInorm Absolute Normal Input Voltage Value
VImin Absolute Minimum Input Voltage Value
VOHmax Maximum Output High Level Voltage Value
VOHmin Minimum Output High Level Voltage Value
VOLmax Maximum Output Low Level Voltage Value
VOLmin Minimum Output Low Level Voltage Value
Phonebook Abbreviations
LD SIM Last Dialing phonebook (list of numbers most recently dialed)
MC Mobile Equipment list of unanswered MT Calls (missed calls)
ON SIM (or ME) Own Numbers (MSISDNs) list
RC Mobile Equipment list of Received Calls
SM SIM phonebook
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 96 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
9 Appendix B GPRS Coding Schemes
Four coding schemes are used in GPRS protocol. The differences between them are shown in the
following table.
Table 43: Description of Different Coding Schemes
Scheme
CS-1 1/2 3 3 181 40 4 456 0 9.05
CS-2 2/3 3 6 268 16 4 588 132 13.4
CS-3 3/4 3 6 312 16 4 676 220 15.6
CS-4 1 3 12 428 16 - 456 - 21.4
Radio block structure of CS-1, CS-2 and CS-3 is shown as the figure below.
Code
Rate
USF
Pre-coded
USF
USF
Radio Block
excl.USF and
BCS
Radio Block
Rate 1/2 convolutional coding
Puncturing
456 bits
BCS Tail
Coded
Bits
BCS
Punctured
Bits
Data
Rate
Kb/s
Figure 55: Radio Block Structure of CS-1, CS-2 and CS-3
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 97 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
Radio block structure of CS-4 is shown as the following figure.
USF
Block
Code
Radio Block
BCS
No coding
456 bits
Figure 56: Radio Block Structure of CS-4
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 98 / 99

GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Hardware Design
10 Appendix C GPRS Multi-slot Classes
Twenty-nine classes of GPRS multi-slot modes are defined for MS in GPRS specification. Multi-slot
classes are product dependent, and determine the maximum achievable data rates in both the uplink and
downlink directions. Written as 3+1 or 2+2, the first number indicates the amount of downlink timeslots,
while the second number indicates the amount of uplink timeslots. The active slots determine the total
number of slots the GPRS device can use simultaneously for both uplink and downlink communications.
The description of different multi-slot classes is shown in the following table.
Table 44: GPRS Multi-slot Classes
Multislot Class Downlink Slots Uplink Slots Active Slots
1 1 1 2
2 2 1 3
3 2 2 3
4 3 1 4
5 2 2 4
6 3 2 4
7 3 3 4
8 4 1 5
9 3 2 5
10 4 2 5
11 4 3 5
12 4 4 5
MC60_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 99 / 99
 Loading...
Loading...