PRESONUS StudioLive 24R, StudioLive 32, StudioLive 16 Networking Manual
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
www.presonus.com
®
English
Table of Contents
1 Overview — 1
1.1 An Introduction to Audio Networking — 2
1.2 Distributed Audio — 2
1.3 Network Foundations — 3
1.4 Addressing — 3
2 AVB Networking — 4
2.1 System Overview — 4
2.2 What is AVB? — 5
2.3 How Does AVB Work? — 6
2.4 AVB Hardware Components — 6
2.5 Overcoming Latency — 7
2.6 Channels and Streams — 7
2.7 Clocking — 8
2.7.1 Wordclock — 8
2.7.2 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) — 9
2.7.3 Multiple Stream Reservation Protocol
(MSRP) — 9
2.7.4 Clocking a PreSonus AVB Network — 11
3 AVB Networking Basics — 13
3.1 Selecting the Right Switch — 13
3.1.1 PreSonus SW5E AVB Switch
with PoE — 13
3.2 Adding a Wireless Router — 15
3.3 Choosing the Right Cables — 16
3.3.1 Cat5e and Cat6 — 16
3.3.2 Shielded vs. Unshielded — 17
3.3.3 Solid-core vs. Stranded — 18
3.3.4 Plug Termination — 19
3.3.5 T568A or T568B — 19
3.3.6 Twisted Pair Tips — 19
3.4 Understanding Hops — 20
3.5 Network Topologies — 21
3.5.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) — 21
3.5.2 Daisy-Chain — 22
3.5.3 Star — 23
4 Configuring Your AVB
Network — 24
4.1 Using AVB with a StudioLive Series III Mixer and a
Mac — 24
4.1.1 What You Will Need — 24
4.1.2 Making the Connections — 24
4.1.3 Setting Up Your Mac — 25
4.2 NSB-series Stage Box with a StudioLive Series III
Console Mixer — 26
4.2.1 Step 1: Connect Your Stage Box
to Your Mixer — 26
4.2.2. Step 2: Routing Stage Box Inputs
to Mixer — 28
4.2.3 Step 3: Engage Network Sources — 28
4.3 NSB-series Stage Box UC Surface Setup — 29
4.3.1 Step 1: Connect Your Stage Box
to Your Mixer — 29
4.3.2 Step 2: Routing Stage Box Inputs
to Your Mixer — 30
4.3.3 Step 3: Engage Network Sources — 30
4.4 EarMix 16M with StudioLive
Console Mixers — 31
4.5 EarMix 16M Setup from UC Surface — 32
5 Large Network:
Real-world Example — 34
5.1 Example Network Overview — 34
5.2 Network Connections — 37
5.2.1 Connecting Your Mixers — 39
5.2.2 Connect Your NSB-series Stage Boxes
to Your Console Mixers — 41

5.3 Analog Input Connections — 44
5.3.1 Routing AVB Sends
to Your Console Mixers — 46
5.3.2 Routing the NSB-series Inputs
to Your StudioLive 24R — 48
5.3.3 Routing Audio to the
Console Mixers — 49
5.4 Analog Output Connections — 51
5.4.1 Routing the Main Outputs — 51
5.4.2 Routing Monitor Mixes — 52
5.5 EarMix Setup — 53
5.5.1 Routing AVB Streams to Your
EarMix 16M — 53
5.5.2 Routing StudioLive 24R Sources
to AVB Sends — 54
1
1 Overview
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
1 Overview
Most people who have used a digital mixer in the last ten years are familiar with
incorporating networking technology into their audio application. Remote control
over wireless LAN networks, proprietary audio-over-Ethernet protocols, and
extensible audio networking platforms have all become relatively commonplace.
As networking speed and reliability have increased and the underlying technology
has become more affordable, transporting audio over an Ethernet cable can now
offer dramatic savings of both time and money, making it more attractive than ever.
While there are several protocols currently in use for audio networking, AVB
has many unique benefits that have made it the protocol of choice for the
latest generation of PreSonus pro audio equipment. This guide explains the
basics of AVB networking as well as best practices and use cases. While this
guide covers AVB networking in detail for supported PreSonus products,
much of the information here is relevant for other IEEE 1722.1-compliant AVB
devices. PreSonus StudioLive Series III mixers are fully compliant with the IEEE
1722.1 standard, which is the protocol for Discovery, Enumeration, Connection
management, and Control of AVB devices, also known as AVDECC.
Note: Earlier generations of PreSonus AVB products (StudioLive RM-AI and RML-AI mixers,
StudioLive CS18AI, and AI-series consoles equipped with the SL-AVB-MIX option card) are
not 1722.1 AVDECC compliant and can only be used with each other. These products are
not compatible with IEEE 1722.1 devices like the StudioLive Series III mixers or other
third-party AVB products that follow the 1722.1 AVDECC standard.

2
1 Overview
1.1 An Introduction to Audio Networking
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
1.1 An Introduction to Audio Networking
As its name implies, audio networking allows you to transport large amounts of
data over a single cable. The bandwidth for modern networking transport protocols
is enough to carry hundreds of audio channels without the compression once
necessary to do so. This means that audio can be moved quickly over long distances
without signal degradation or the expense of conventional analog cabling.
The flexibility demanded by data network protocols also opens up
possibilities for audio system configuration that were once impossible.
Many nodes of I/O can be placed throughout a facility or venue without the
limitations imposed by analog cabling. Because networked audio is digital,
electromagnetic interference and cable capacitance that can degrade
audio signal quality in the analog domain are no longer problematic.
Because many modern digital audio devices also offer remote control over
LAN networks, this also reduces the amount of cabling. In an audio network,
control data and audio can travel over the same connection, facilitating
flexible routing, preamp control, and more using a single cable.
1.2 Distributed Audio
In a traditional analog system, remote analog I/O must be located within a relatively
short distance between the source and the destination. Let’s take a common
example: the multichannel snake. In a live setting, the stage box to which the
musicians are connecting their gear is located with them on stage. This shortens the
cable runs coming from multiple locations (e.g., the lead singer’s mic, the guitarist’s
amp, etc.). These cables are connected to a stage box which is attached to a shielded
multichannel snake that makes the long run to the mixer at Front-of-House.
In a distributed audio network, each musician could have their own node
on the network, potentially. Multiple networked stage boxes can be spread
around the stage, making the analog cable runs as short as possible to minimize
signal degradation. Take this concept a step further, and multiple sources
can be spread throughout a large facility, each sitting on the network to be
sent to many mixers on the network, not just the one at front-of-house.
This flexibility makes distributed audio networking an appealing concept for both
mobile and installed applications, not only because of the affordability of Ethernet
cabling, but because of the ability to customize each system for the people using it.
On the surface, this level of flexibility lends itself to a deeper complexity than a
standard analog system. However, when one considers the function of an analog
patch bay within a studio setting, audio networking can seem a bit less daunting.
An analog patchbay’s purpose is to facilitate the routing of audio. In
this way, you can insert your favorite boutique compressor into any
channel on your console without rewiring your entire rack. This also lets
you route audio from the wall panel in your live room to any preamp
you wish to use, audition multiple effects chains, and much more.
The only difference between an analog patchbay and the digital patching
available in a distributed audio network is that you must physically trace a
cable connection if you are unsure of a particularly complex routing in an
analog system. In a distributed audio network, the control panel for all your
digital routing allows you to do the same thing from a single screen.

3
1 Overview
1.3 Network Foundations
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
1.3 Network Foundations
No matter what protocol is used, an Ethernet-based
audio network will consist of the following:
• Network Interface Controller (NIC). These are built into a computer,
digital mixer, networked stage box, etc. and, as their name implies, allows
these devices to communicate with other devices on a digital network.
• Ethernet Cables. Both data and audio networks rely on a set
of standards for cabling infrastructure to ensure that network
performance is both reliable and consistent. These standards include
specifications for the cable construction itself, as well as specifications
for the termination of cabling and physical connections to devices.
More information on cabling can be found in Section 4.4.
• Switches. These devices bring all the cables together into a central hub
and enable the correct routing of information throughout the network.
1.4 Addressing
Every Network Interface Controller (NIC) on the network must have an address
so that the switches know where to send the data packets appropriately. Every
NIC must have a Media Access Control (MAC) address programmed by the
manufacturer. Every MAC address is unique, and the allocation of MAC addresses to
networking manufacturers is strictly managed by the IEEE standards organization.
In addition to a device’s MAC address, every NIC has a user-definable
addressing layer to make it easier for network managers to configure their
local network. Called the Internet Protocol or ‘IP’ address, this is normally 4
bytes long (IPv4) consisting of the network number and a host address. The
division between the two is also 4 bytes long and called the subnet mask.
Every bit in the IP address that has the number 1 in the subnet mask
belongs to the same network number. Every bit that has the number 0
belongs to the host address. Where things get tricky is that only NICs with
the same network number can exchange data with one another.
If you’ve ever glanced at the network settings on your personal computer, some of
this may seem familiar to you. The operating system on your computer displays the
IP and subnet values as four decimal number (0-255). These numbers correspond
to the four bytes in the IP address and subnet mask. If we use the example of a
small office network, the subnet mask usually has a default value of 255.255.255.0.
This provides the network administrator with 255 host addresses to use because
only the last byte can be changed when it is assigned to devices on the network
(255.255.255.1, 255.255.255.13, etc.). For networks that require more than 255 host
addresses, the subnet mask can be changed to accommodate more devices.
The IP addresses can be programmed manually for systems that require it, but
in many cases, a central device, such as a router, will automatically assign an IP
address whenever a NIC is connected or reconnected. This automatic IP assignment
is accomplished using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
StudioLive mixers support DHCP, self-assigned IP addressing, as well as
manually assigned adressing. This provides network administrators with the
most flexibility when designing a system that includes StudioLive mixers. For
more information, please review the StudioLive Series III Owners Manual.
4
2 AVB Networking
2.1 System Overview
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
2 AVB Networking
2.1 System Overview
AVB networks behave very much like an analog audio system.
Like an analog audio system, audio networks consist of sources,
destinations, and intermediate processing along the way.
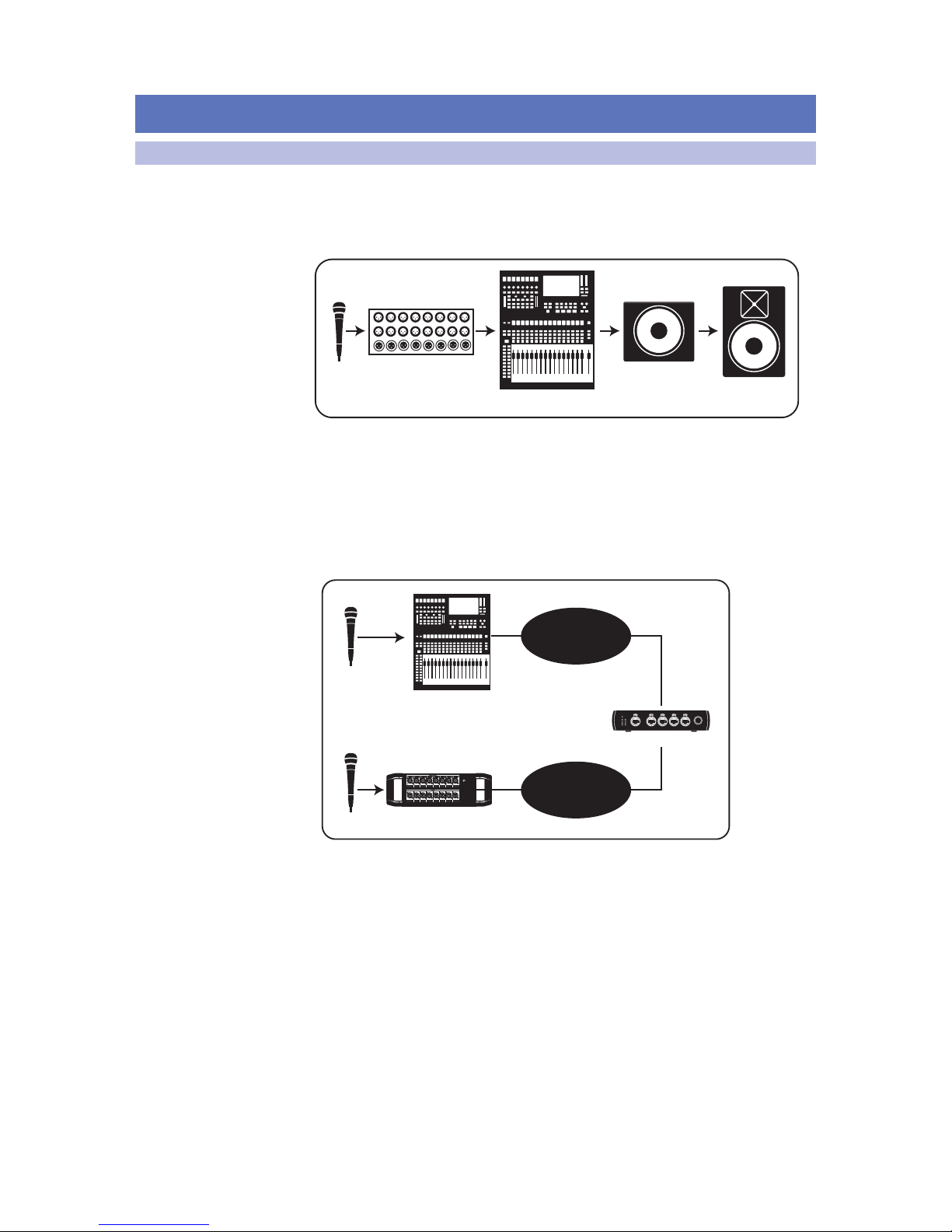
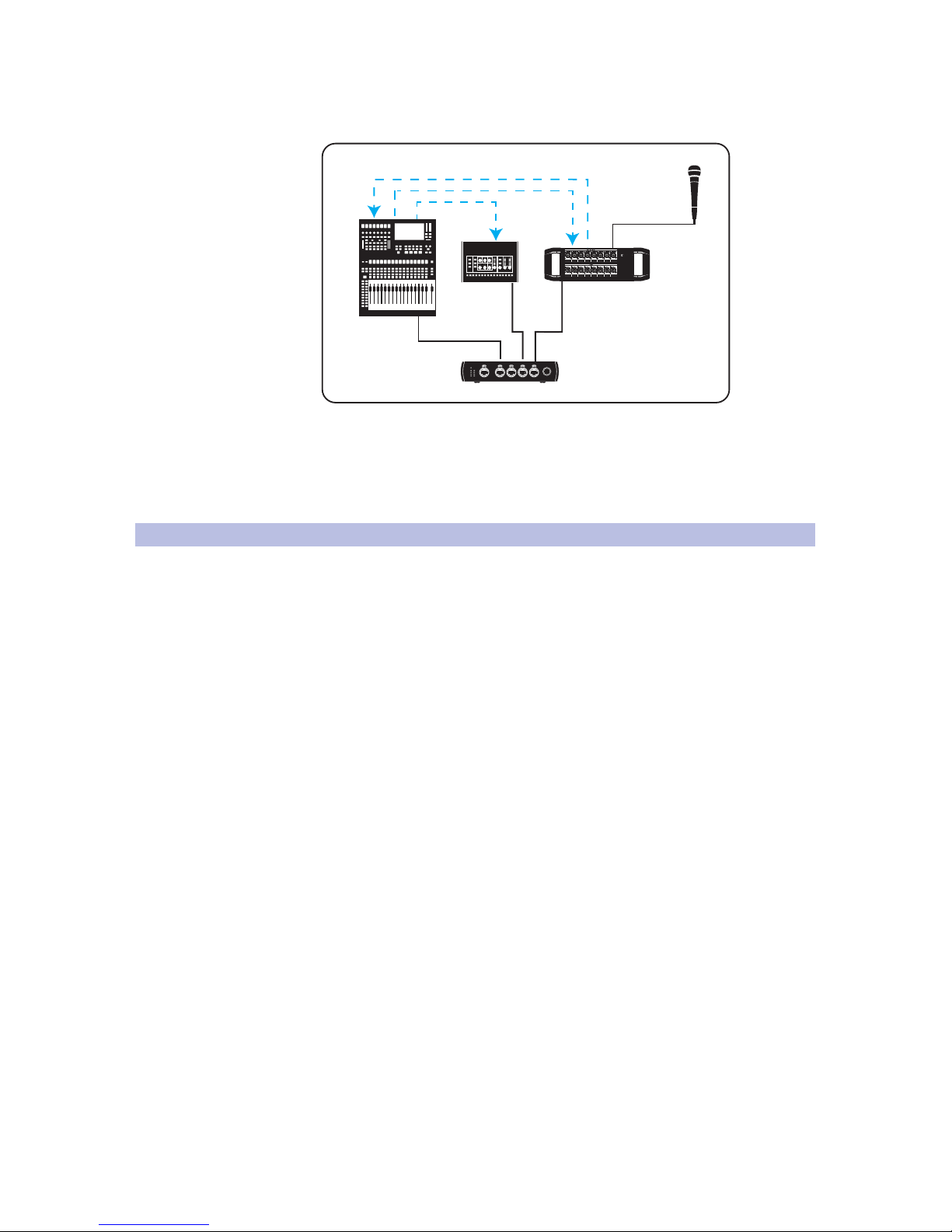
Let’s look at a simple live-sound setup:
mic
stagebox
mixer
active sub
active
loudspeaker
In the above example, an audio signal goes out of the microphone and into the stage
box. It then goes to the mixer, where the microphone signal is amplified, routed to
the appropriate output, and sent to an active subwoofer, where it is finally passed
through to the full-range loudspeaker. All of this is readily apparent to any audio
engineer just by looking at the diagram—a good thing because the skills required to
configure an analog system are nearly identical those needed by a network engineer.
Let’s compare the audio system above with components in a network:
mic
mic
mixer
Stage Box
AVB Switch
Input, Processing,
& Output
Input & Output
Link PoE
Blue= PoE On
(Hold to toggle)
White= PoE Off
1 2 3 4 5
SW5E
AVB SWITCH WITH PoE
PoE
Link PoE
1
2
3
4
5
In our network example, the microphones connected to the mixer and stagebox
can be freely available on either or both, depending on the routing.
5
2 AVB Networking
2.2 What is AVB?
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
Let’s take a quick look at a microphone signal’s signal flow on a simple AVB network.
In the example below, the microphone’s signal is represented by the blue line:
mic
Mixer
Monitoring
Stage Box
AVB Switch
Link PoE
Blue= PoE On
(Hold to toggle)
White= PoE Off
1 2 3 4 5
SW5E
AVB SWITCH WITH PoE
PoE
Link PoE
1
2
3
4
5
Network
As you can see, tracing a device’s signal path becomes a little more complex
because the routing is handled entirely in the digital domain. But because
experienced audio engineers understand signal flow and are used to
troubleshooting problems in an analog system at the various points of
weakness, configuring an audio network becomes that much easier.
2.2 What is AVB?
AVB (Audio Video Bridging) is an extension to the Ethernet standard designed to
provide guaranteed quality of service, which simply means that audio samples will
reach their destinations on time. AVB allows you to create a single network for audio,
video, and other data like control information, using an AVB-compatible switch.
This enables you to mix normal network data and audio network data on the same
network, making it easier to create both simple and complex networks. Numerous
audio companies have adopted it, and more companies are adding it all the time.
Audio-over-Ethernet has become increasingly attractive in Pro Audio
applications especially for distribution in large-scale systems, such as those
used in sporting venues, concert halls, and education institutions. The problem
is that most solutions are proprietary, making these systems too expensive
and too complex for most smaller applications. AVB is intended to change
that by providing an open source collection of IEEE standards available
for use by the pro audio market and its manufacturing community.
AVB networking offers several features that make it ideal for audio applications:
• Long, light cable runs. A single lightweight CAT5e or CAT6 cable can
be run up to 100 meters (328 feet). This makes it easy to have audio
I/O located in different rooms (or even different venues in the same
building) and run multichannel audio between them in real time.
• Low, predictable latency. AVB provides latency of no longer than 2 ms
sending an audio stream point-to-point over up to seven “hops” (trips through
switches or other devices) on a 100 Mbps network. With higher speed
networks, many AVB devices support lower latencies and additional hops.
Please note that while PreSonus AVB products operate at faster Gigabit network
speeds, they are currently fixed to 2 ms of latency.
• Scalable, with high channel counts. AVB’s bandwidth is sufficient to carry
hundreds of real-time channels using a single Ethernet cable. This offers the
future possibility of expanding your system with additional devices that contain
different kinds of audio I/O, multiple controllers, and other useful functions.

6
2 AVB Networking
2.3 How Does AVB Work?
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
• Guaranteed bandwidth. AVB networks intelligently manage the data traffic
giving priority to AVB data. This means standard network traffic, such as Internet
streaming, won’t prevent your audio from being delivered reliably and on time.
• Integrated clock signal. In a digital audio system with multiple devices, having
a master clock is critical to maintaining audio fidelity. The AVB specification
defines such a clock to be accurately distributed to all devices in the system.
2.3 How Does AVB Work?
On the simplest level, AVB works by reserving a portion of the available
Ethernet bandwidth for its own traffic. Because packets of AVB data are
sent regularly in allocated slots within the reserved bandwidth, there are
no interruptions or interference, making AVB extremely reliable.
What makes AVB ideal for audio networking is that it splits network traffic into
real-time traffic and everything else. All real-time traffic is transmitted on an
8 kHz pulse. Anything that’s not real-time traffic is then transmitted around
that pulse. Every 125 µs, all real-time streams send their data. Other packets
are transmitted when there is no more real-time data ready to be transmitted.
To make sure that there is enough bandwidth available for all prioritized realtime traffic, the Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP, IEEE 802.1Qat) is used.
Every AVB compliant switch between each talker and listener will then make
sure sufficient bandwidth is available using SRP, making it a foundational
building block of the AVB standard. Every switch and AVB device on the
network must implement SRP and send real-time traffic at the 8 kHz pulse. If
one of the devices on the network does not employ this standard, then realtime traffic could be potentially delayed, causing jitter in the output.
2.4 AVB Hardware Components
In an AVB network, every device to and from which audio is flowing must
adhere to the AVB standard. These devices consist of the following types:
• AVB Talkers. These devices act as the source for an AVB
stream, sending out audio onto the network.
• AVB Listeners. These devices are the destinations
for the streams sent out by the Talkers.
• AVB Switches. This is the network hub to which every Talker and
Listener must be connected. At its most basic level, an AVB Switch
analyzes and prioritizes traffic on the network. It should be noted
that just like there can be multiple talkers and listeners on the
same AVB network, there can also be multiple AVB Switches.
• AVB Controllers. A controller can be a talker, a listener, or neither. These devices
handle routing, clock, and other settings for AVB devices using AVDECC.
The most important rule to keep in mind when setting up an AVB network is
that the talker (device sending audio) and listener (device receiving audio) must
be connected to an AVB-compatible switch. All the AVB devices on the network
must share a virtual clock that defines when the AVB packet should be played.
As previously mentioned, devices communicate on an AVB network as
“talkers” and “listeners.” An AVB talker transmits one or more audio streams
to the network. AVB listeners receive one or more of these streams from the
network. It should be noted that an AVB device, like the StudioLive Series
III mixers and NSB-series stage boxes, can be both a talker and a listener.
For example, StudioLive 32 can simultaneously “Talk” (send channels out
to the network) and “Listen” (receive channels from the network).
AVB devices stay in sync by selecting the best master PTP clock after the
devices connect with one another. This ensures that every AVB device on the
network will maintain precise timing, which is critical to audio quality.
7
2 AVB Networking
2.5 Overcoming Latency
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
The AVB switch guarantees that real-time audio data packets maintain
their timing without losing information. AVB switches do this by
allowing a maximum of 75% of each port to be used for AVB traffic.
This prevents non-AVB data from being delayed or lost.
When an AVB network is configured, the Talkers and
Listeners identify one another automatically.
2.5 Overcoming Latency
SRP works with the 802.1Qav Queuing and Forwarding Protocol (Qav) to ensure that
once bandwidth is reserved for an AVB stream, it is locked down from end to end.
Qav schedule time-sensitive streaming information to minimize latency. Together,
SRP and Qav make sure that all reserved media streams are delivered on time.
In this way, the AVB network has some intelligence as to how much non-media
traffic as well as how many media packets are on the system at any given
time. This means that on an AVB network, the worst case travel time is known
throughout the entire system. Because of this, only a small amount of buffering
is needed, lowering latency to 2 ms over seven switch hops on a 100 Mbps
Ethernet network. On gigabit networks, even lower latencies can be achieved.
2.6 Channels and Streams
AVB Streams can be thought of as the pipeline that carries a predefined
number of channels between two or more AVB devices. In a PreSonus
StudioLive Series III mixer, for example, there are seven input streams
and seven output streams available, each carrying eight channels.
It should be noted that each stream can carry any combination of eight channels.
The source for the eight channels within each AVB Send stream can be freely
routed from any input channel or bus on a StudioLive Series III mixer via the
Digital Patching menu. For complete information on Digital Patching, please refer
to the StudioLive Series III Owners Manual and UC Surface Reference Manual.
In addition to audio channels, each stream can carry clocking information from
the network’s global clock. Like all digital systems, devices on an AVB network
must receive media clock from a master source to maintain proper sync.
Channel 1
Channel 2
Channel 3
Channel 4
Channel 5
Channel 6
Channel 7
Channel 8
AVB STREAM

8
2 AVB Networking
2.7 Clocking
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
2.7 Clocking
All the audio traffic on an AVB network is synchronized using a global clock so
that audio can be played and recorded while remaining in time from multiple
sources. Obviously, the more audio traffic on a network, the more critical
this becomes. For users familiar with traditional digital audio devices (ADAT,
S/PDIF, etc.) the idea of a global clocking device will not seem unfamiliar.
PreSonus AVB devices have two clocks: one wordclock and one PTP clock.
All AVB devices on the network are synchronized to a common reference time using
the IEEE 802.1AS Precision Time Protocol (PTP). Each stream includes a presentation
time that all the devices in the network use to align their playback by comparing the
presentation time in each stream packet. An advantage to this design is that AVB
networking supports multiple simultaneous sample rates and sample clock sources
which is important for applications where audio and video need to be synchronized,
even though they travel along different paths with different sample rates.
2.7.1 Wordclock
Analog audio is transferred through a cable as a continuous electrical
waveform at almost the speed of light. Because of this, audio signal traveling
from one analog audio device to another arrives nearly instantaneously,
for all practical purposes. Therefore, you don’t have to synchronize analog
audio passing from one analog device to other analog devices.
Transferring digital audio is a very different matter. Computers and other
digital devices operate one step at a time, which happens very quickly but it’s
not instantaneous, and digital signals are not inherently in perfect time. While
uncompressed digital audio plays at a fixed rate (i.e., the sampling frequency), digital
clocks are not perfect; their frequency can drift, and they almost always have at
least some irregular errors, known as jitter. Therefore, two devices, each following its
own clock, are highly unlikely to stay in agreement about precisely when a sample
starts and ends. The result is usually an artifact, like a pop or a glitch in the audio.
To avoid this problem, all digital devices in communication with one another
need to follow a single master clock. That means the master clock must send a
signal that essentially says, “everyone start at this moment and follow me!”
Even if the master clock’s timing is imperfect, all the slave devices will
follow the timing errors exactly and will stay in sync with each other,
eliminating timing-related artifacts. In general, the better the master clock,
the better the resulting audio will sound, so whenever possible, use the
best clock you have, or experiment with your rig to find the best result.
Whenever digital audio devices are synchronized, it is necessary to designate
one device as the “master” wordclock device to which all other digital devices
are synced, or “slaved.” Once you’ve determined which device is to be your
master clock, you will need to sync the remaining digital devices.
The problem of designating a master wordclock is not handled by AVB and
must be set with an AVB controller. Depending on the device, this can be done
manually, by the user, or managed automatically. For example, when setting up
a StudioLive rack mixer as a stage box from a StudioLive console mixer, the rack
mixer is automatically setup to slave from the console mixer’s media clock.
Multiple unrelated wordclocks can co-exist on an AVB network. While there are a
few ways to match wordclocks between a talker and listener, PreSonus AVB devices
currently only support recovering the media clock by listening to the first AVB stream.

9
2 AVB Networking
2.7 Clocking
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
2.7.2 Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
Precision Time Protocol or PTP is used to synchronize clocks throughout a
computer network. PTP is capable of achieving clock accuracy in the submicrosecond range, making it suitable for local area networks that require
tight timing. Similar to wordclock, PTP uses a master-slave architecture
for clock distribution. This protocol defines clock master, link delay and
network queuing (both measurement and compensation), as well as
clock-rate matching and adjustments for Layer 2 network devices.
In this architecture, there are several different clock types:
• Ordinary Clock. This is a device with a single network connection and
either the sync source (master) or the sync destination (slave).
• Boundary Clock. This device has multiple network connections and can
accurately synchronize one network segment to another. A master clock is
selected for each segment in the system using a root timing reference generated
by the grandmaster clock. The grandmaster sends synchronization information
to the all the clocks on its network segment. The boundary clocks on that
segment then send accurate time to other network segments to which they’re
connected. Every AVB Talker is required to be capable of functioning as the
grandmaster; however any network node can be the grandmaster, as long as
it can either source or derive timing from a grandmaster-capable device.
On an AVB network, PTP generates timestamps so that every listener knows
when to playback the audio from the talker. In other words, the PTP clock is
used to align audio samples from multiple sources in time. Each grandmastercapable device broadcasts its clocking using announce messages. The best
master clock is then selected from the available announce messages.
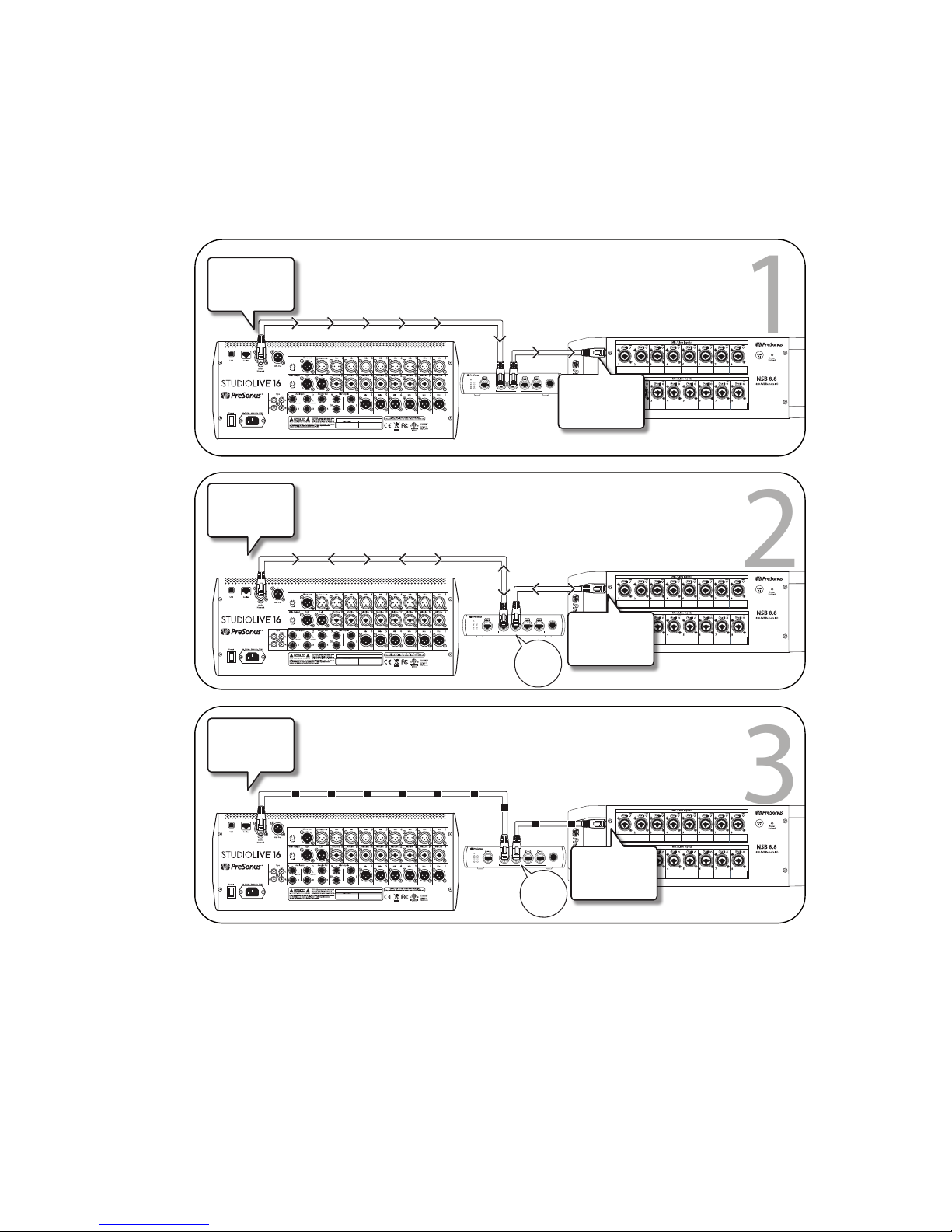
2.7.3 Multiple Stream Reservation Protocol (MSRP)
Multiple Stream Reservation Protocol (MSRP) is the IEEE standard used to reserve
stream bandwidth for audio on an AVB network. This allows endpoints to
automatically route data and reserve bandwidth and eliminates the need for the
user to manually configure Quality of Service (QoS) across network devices. MSRP
looks at the end-to-end bandwidth that is currently available before an audio stream
is sent out. It then reserves a maximum of 75% of the total bandwidth available
on that AVB switch’s port. If the bandwidth is available, it is locked down along the
entire data path, from the Talker, out to every assigned Listener until it is released.
Bandwidth reservations are made based on talker and listener declarations
on the switch ports. Talker declarations come in several forms:
• Advertise Declaration. This declaration announces that a stream doesn’t
have any bandwidth or network constraints on its designated path. This means
that any destined Listener can create a reservation for QoS. Talkers advertise
messages contain all the information necessary to make the reservation.
• Failed Declaration. As its name indicates, this announces that a
stream is not available to a Listener because the necessary bandwidth
is not available or because of other limitations somewhere in the
network path between the Talker and the destined Listener.
As mentioned earlier, Listeners also make declarations within
an AVB network. These consist of the following types:
• Ready. One or more Listeners are requesting a stream and
sufficient bandwidth and resources are available from the Talker
along the network path to every intended Listener.
• Ready Fail. In this instance, one or more Listeners are requesting a
stream, but not all of them have sufficient bandwidth and resources
on the path to the Talker. In other words, at least one Listener has
encountered an obstacle and at least one Listener has not.
10
2 AVB Networking
2.7 Clocking
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
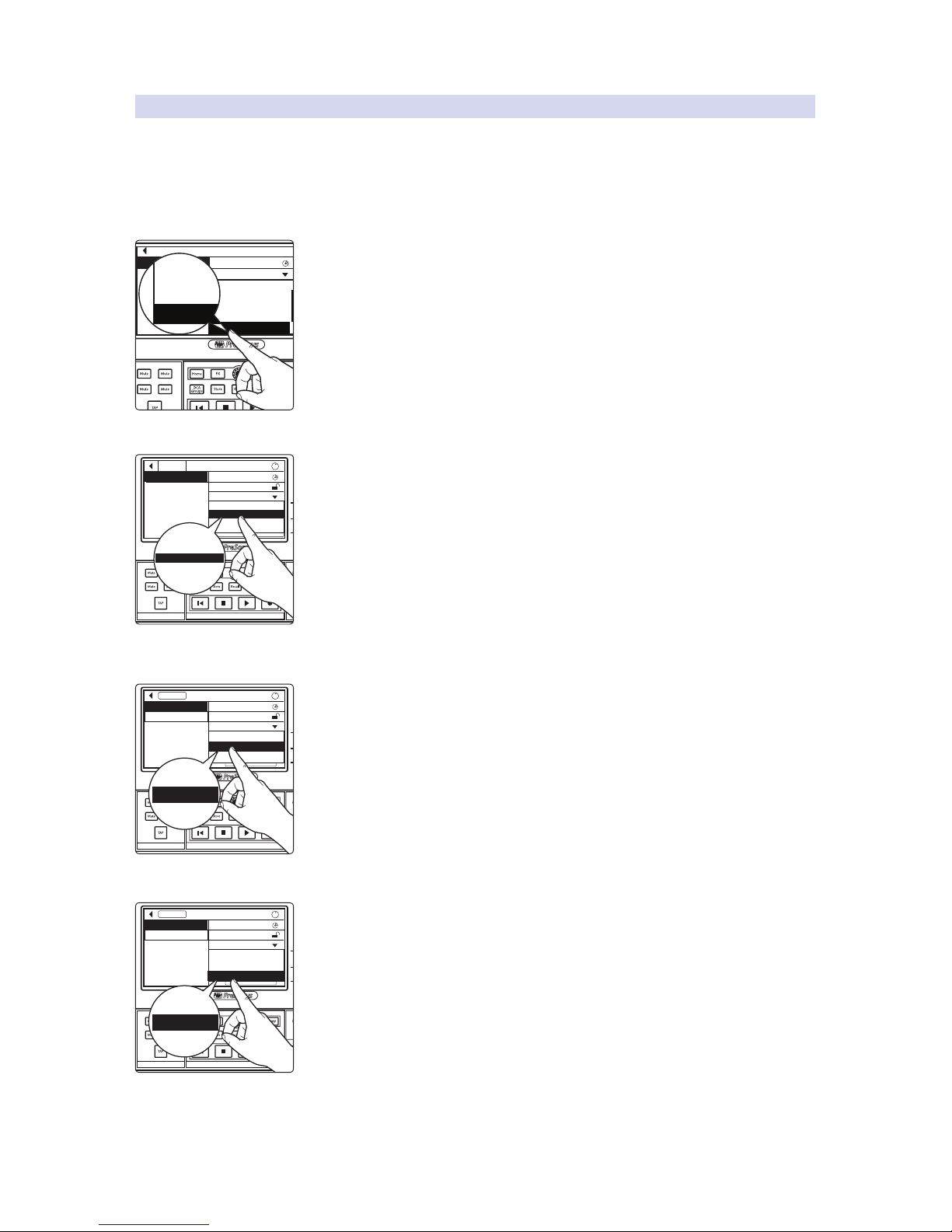
• Fail. When a Fail declaration is sent, one or more Listener has requested
a stream and every Listener that has done so does not have sufficient
bandwidth or resources in the network path to attach to the desired stream.
End-to-end stream reservation is successful as soon as the Listener receives the
Talker’s Advertise Declaration and the Talker receives the Listener’s Ready Declaration.
AVB stream reservation process:
AVB streams are only forwarded once a successful reservation is made. After the
streams stop, switch resources are then released and the process can begin again or
make room for other network traffic. In this way, the AVB standard ensures that audio
data streams always have the highest QoS and all other data is secondary or tertiary.
1
2
3
Link PoE
Blue= PoE On
(Hold to toggle)
White= PoE O
1 2 3 4 5
SW5E
AVB SWITCH WITH PoE
PoE
Link PoE
1
2
3
4
5
AVB Switch
Link PoE
Blue= PoE On
(Hold to toggle)
White= PoE O
1 2 3 4 5
SW5E
AVB SWITCH WITH PoE
PoE
Link PoE
1
2
3
4
5
AVB Switch
Link PoE
Blue= PoE On
(Hold to toggle)
White= PoE O
1 2 3 4 5
SW5E
AVB SWITCH WITH PoE
PoE
Link PoE
1
2
3
4
5
MANUFACTURING DATE
DESIGNED AND ENGINEERED IN BATON ROUGE, LA, USA • MANUFACTURED IN CHINA • PATENTS PENDING • “STUDIOLIVE”
and “PreSonus” ARE REGISTERED TRADEMARSK OF PRESONUS AUDIO ELECTRONICS • SD LOGO IS A TRADEMARK OF SD-3C, LLC
MANUFACTURING DATE
MANUFACTURING DATE
DESIGNED AND ENGINEERED IN BATON ROUGE, LA, USA • MANUFACTURED IN CHINA • PATENTS PENDING • “STUDIOLIVE”
and “PreSonus” ARE REGISTERED TRADEMARSK OF PRESONUS AUDIO ELECTRONICS • SD LOGO IS A TRADEMARK OF SD-3C, LLC
AVB Switch
Talker
Advertises
Talker
Ready
Talker
Sends Stream
Ready!
Ready!
Listener
Receives
Advertisement
Listener
Ready
Listener
Receives
Stream
11
2 AVB Networking
2.7 Clocking
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
2.7.4 Clocking a PreSonus AVB Network
Within the PreSonus AVB ecosystem, a StudioLive Series III mixer must be
used the master word clock for the network. For some devices, clocking is
handled automatically. For others, additional set-up is required. This section
will provide an overview of the steps required for proper system clocking.
EarMix 16M Personal Monitor Mixers
Because the EarMix 16M is a listener only, it defaults to clocking from the incoming
audio streams.As soon as you route an AVB Send to your EarMix 16M, it will sync to
the master mixer.
NSB-Series Stage Boxes
NSB-Series stage boxes are designed to provide both remote inputs and remote
outputs for StudioLive Series III mixers. Like the EarMix 16M, the NSB-series stage
boxes will default to external clock and sync to a StudioLive Series III mixer as soon as
AVB sends are routed to their outputs.
It is important to note that these AVB sends must be routed whether they are needed
or not. Let’s look at the common example of a StudioLive 16 console mixer with
two NSB 8.8 stage boxes. In some situations, the eight outputs on the second NSB
8.8 stage box may not be needed to pass audio. In this case, routing an AVB output
stream from the mixer to the stage box would still be required for proper clocking.
StudioLive Series III Mixers (Monitor Mixer Mode)
StudioLive Series III mixers provide a customized mode when used as Monitor mixer.
This mode allows them to retain independent control over their FlexMix outputs
while sharing input streams as well as the Main Mix with the Front-of-House mixer.
As soon as Monitor Mixer Mode is engaged on a StudioLive Series III rack mixer, its
clock is set to sync to the Front-of-House console as well. No further set-up is
required.
StudioLive Series III Rack Mixers (Stagebox Mode)
StudioLive Series III rack mixers also provide a customized mode to function as a
stage box for other StudioLive mixers. This mode allows them to share all their inputs
and outputs with the Front-of-House mixer, effectively disabling all DSP functionality.
As soon as Stagebox Mode is engaged on a StudioLive Series III rack mixer, its clock is
set to sync to the Front-of-House console as well. No further set-up is required.
FX C FX D
FX A FX B
EarMix Setup
Name: EarMix 16M
Apply
Apply All
1-8 Send Source: AVB Send 41-48
9-16 Send Source: AVB Send 49-56
EarMix 16M
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
AVB Send 9-16
FX C FX D
FX A FX B
EFFECTS MASTER MASTER CONTROL
AVB Inputs
Stagebox Setup
Preamp Permissions: All
Name: NSB 16.8
Output Stream: None
Apply
i
NSB 16.8
StudioLive 16: Send 41-48
StudioLive 16: Send 33-40
StudioLive 16: Send 49-56
StudioLive 16: Send 41-48
FX C FX D
FX A FX B
EFFECTS MASTER MASTER CONTROL
AVB Inputs
Stagebox Setup
Preamp Permissions: StudioLive 24
Name: StudioLive 24R
Mode: Monitor Mixer
Apply
i
StudioLive 24R
NSB 8.8
Monitor Mixer
Stand-alone
Stagebox
Monitor Mixer
FX C FX D
FX A FX B
EFFECTS MASTER MASTER CONTROL
AVB Inputs
Stagebox Setup
Preamp Permissions: StudioLive 24
Name: StudioLive 24R
Mode: Monitor Mixer
Apply
i
StudioLive 24R
NSB 8.8
Monitor Mixer
Stand-alone
Stagebox
Stagebox

12
2 AVB Networking
2.7 Clocking
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
StudioLive Series III Mixers (Standalone Mode)
In applications where two or more mixers are on a network, functioning
independently, but configured to send and received streams to and from other AVB
nodes on the network, you must designate one mixer as the clock master.
To do this, simply set all other mixers to receive clock from the Network
Stream and be sure a stream is routed to the first AVB stream of each mixer
from the master mixer. Be sure to leave one mixer on its Internal clock.
On a StudioLive Series III console mixer, configuring external clocking can be done
from the System Menu located on the Home Screen.
On all StudioLive Series III mixers (rack or console), configuring external clocking can
be done from the Device Settings Menu in UC Surface.
FX C FX D
FX A FX B
EFFECTS MASTER MASTER CONTROL
AVB Inputs
Stagebox Setup
Preamp Permissions: StudioLive 24
Name: StudioLive 24R
Mode: Monitor Mixer
Apply
i
StudioLive 24R
NSB 8.8
Monitor Mixer
Stand-alone
Stagebox
Stand-alone
Permissions User Button Assgins
FirmwareFat Ch Load/Paste
Link Aux Mutes Bluetooth Reg.
Sample Rate:
48 kHz
Network Stream
Off
Med HighLow
HighLow
Network Clock:
Show Peak Hold:
LED:
Backlight:
Network Stream
Internal
FX C FX D
FX A FX B
Network Stream

13
3 AVB Networking Basics
3.1 Selecting the Right Switch
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
3 AVB Networking Basics
When configuring an AVB network, it is important to familiarize yourself
with the fundamental components. This section has been designed
to assist you in building your AVB network from the ground up.
3.1 Selecting the Right Switch
By definition, all AVB switches must adhere to every IEEE standard within
the AVB protocol. Ordinary LAN switches (managed or unmanaged)
used in everyday IT applications don’t have this same requirement and
do not support the protocols necessary for AVB networking.
All AVB switches are required to support the following:
• IEEE 802.1Q: Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP) and Traffic Shaping (FQTSS)
• IEEE 802.1AS: Time Synchronization using Generalized Precision
Time Protocol (gPTP) on each AVB enabled Ethernet port
These standards are critical for both reservation
management and tight, synchronized clocking.
3.1.1 PreSonus SW5E AVB Switch with PoE
The PreSonus SW5E AVB Switch with PoE is a 5-port AVB switch that is fully
compatible with all PreSonus AVB devices. In addition to adhering to the required
IEEE standards, the SW5E provides Power over Ethernet (PoE) on four of its five ports.
Power over Ethernet or PoE is an IEEE standard that allows electric power
to be provided over the same Ethernet cable used for data transfer,
similar to how Phantom Power provides enough current over an XLR
cable to power condenser microphones and active direct boxes.
The PreSonus EarMix 16M can be fully powered by PoE using a PreSonus
SW5E switch or any other standard AVB switch that provides it. It should
be noted that while the EarMix 16M can receive PoE, it does not pass that
power through to other devices. So, in order to power multiple EarMix
16M, each mixer must have a direct path back to a PoE AVB Switch.
SW5E AVB Switch
Audio, Data, and Power
EarMix 16M Personal Monitor Mixers
Link PoE
Blue= PoE On
(Hold to toggle)
White= PoE Off
1 2 3 4 5
SW5E
AVB SWITCH WITH PoE
PoE
Link PoE
1
2
3
4
5
14
3 AVB Networking Basics
3.1 Selecting the Right Switch
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
In situations where this is not possible, an external power supply may
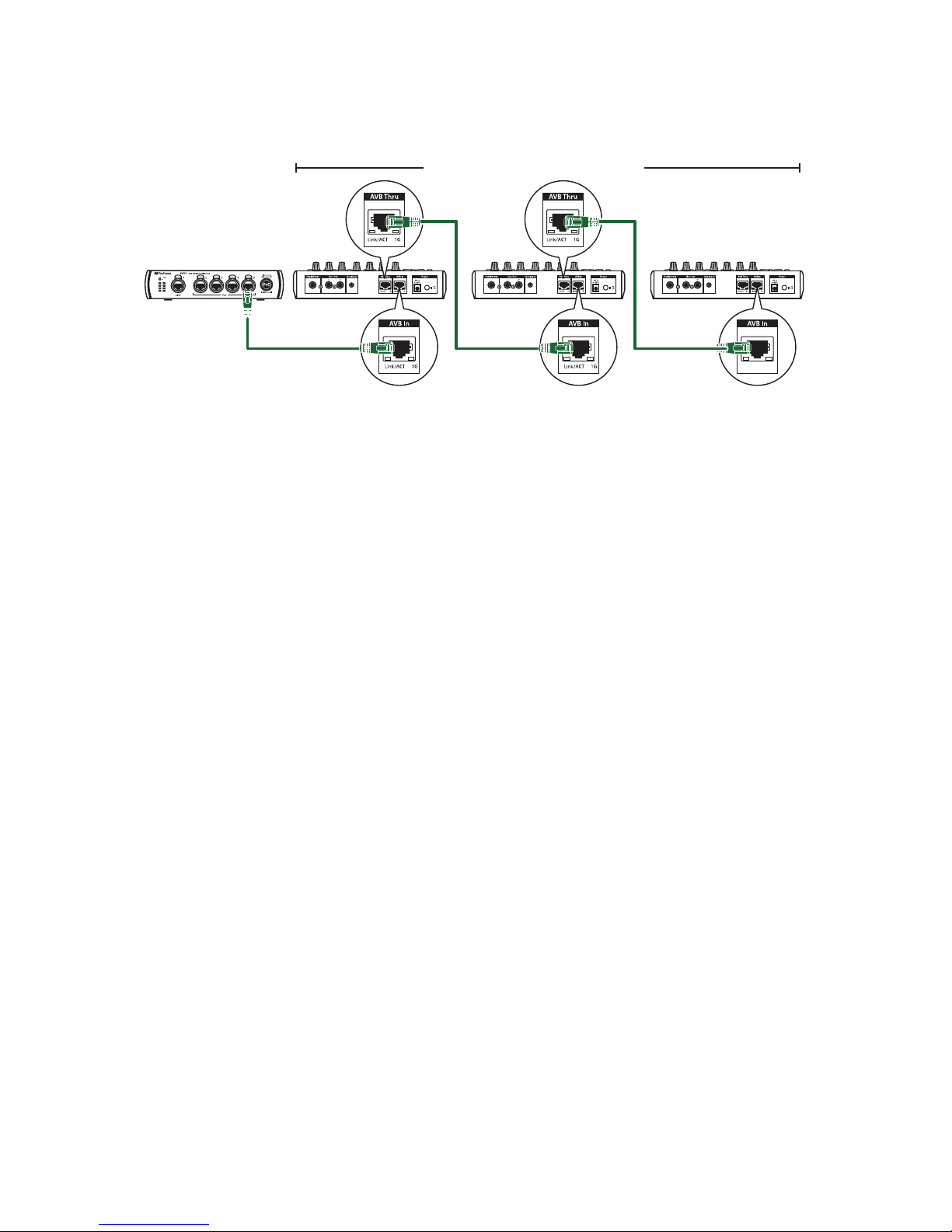
be used to power each EarMix 16M. This also allows you to daisychain multiple units to a single port on your AVB switch.
SW5E AVB Switch
Audio, Data, and Power Audio and Data Audio and Data
EarMix 16M Personal Monitor Mixers
15
3 AVB Networking Basics
3.2 Adding a Wireless Router
StudioLive™ Series III
AVB Networking Guide
3.2 Adding a Wireless Router
Many modern digital audio devices support some level of control over a Local Area
Network. Unlike its AVB counterpart, a standard LAN network does not prioritize the
traffic on it. While this is fine for control information and other simple data, it is less
than ideal for transmitting low-latency audio. PreSonus StudioLive Series III mixers
support both AVB and LAN networking, each with its own dedicated Ethernet port.
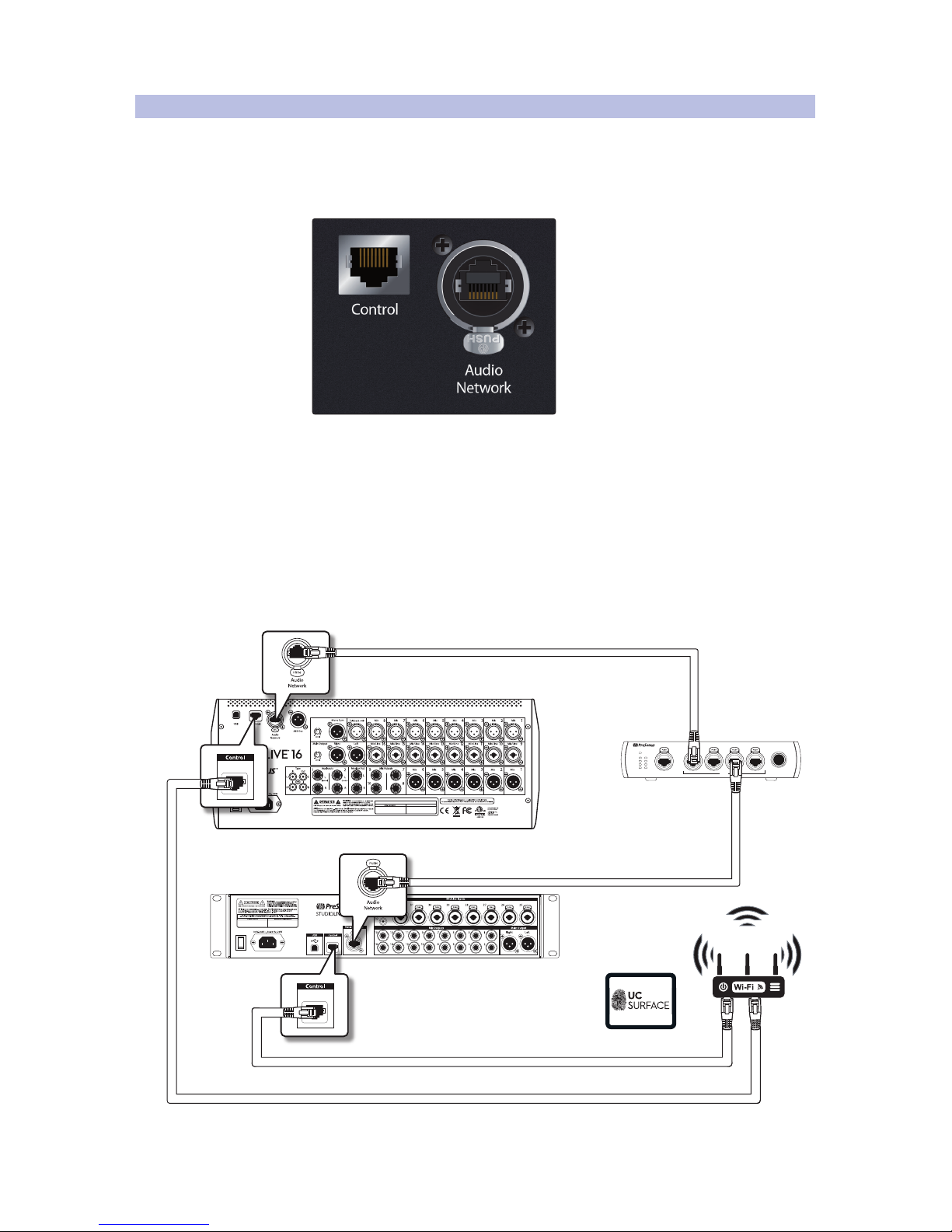
For StudioLive Series III mixers, the Audio Network connection should
attach to the AVB network, while the control port should be connected to
a wireless router, or an access point, so that the mixer can be controlled
remotely from UC Surface or QMix-UC. The control port should also be
used to network your mixer to your computer while using DAW mode.
It should be noted that while a wireless router can be connected to an
AVB switch, you would still need to connect both the Audio Network and
the Control port to a network configured in this manner. Because of this,
PreSonus recommends that you create two networks for your StudioLive
mixer: one dedicated to control data and a second dedicated to AVB data.
MANUFACTURING DATE
Link PoE
Blue= PoE On
(Hold to toggle)
White= PoE Off
1 2 3 4 5
SW5E
AVB SWITCH WITH PoE
PoE
Link PoE
1
2
3
4
5
StudioLive 16
StudioLive 32R
SW5E AVB Switch
iPad running UC Surface
 Loading...
Loading...