Page 1

PAMS Technical Documentation
NSE–8/9 Series Transceivers
Chapter 2
System Module
Amendment 05/00
Page 2

NSE–8/9
System Module
Technical Documentation
Contents
Technical Information 2– 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Modes 2– 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum ratings 2– 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DC Characteristics 2– 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
External Signals and Connections 2– 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Internal Signals and Connections 2– 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Summary 2– 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Baseband 2– 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Description 2– 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Charger Initiated Power Up Procedure 2– 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PAMS
Page No
Power Button Initiated Power Up Procedure 2– 35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Real Time Clock Initiated Power Up Procedure 2– 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Down Schemes 2– 37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clocking Concept 2– 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Resets and Watchdogs 2– 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Supply 2– 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Baseband supplies, CCONT 2– 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Charging 2– 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Baseband ADC’s 2– 50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital Part 2– 53. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAD2PR1 system ASIC 2– 53. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SRAM Memory 2– 58. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EEPROM Memory 2– 59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FLASH Memory 2– 59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Audio 2– 62. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UI 2– 68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Backlight 2– 69. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Buzzer 2– 69. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vibra, NSE–9 only 2– 70. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LCD 2– 70. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Keyboard 2– 71. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 2– 2
Amendment 05/00
Page 3

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
RF 2– 72. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DC Regulators 2– 74. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Frequency Synthesizers 2– 75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver 2– 76. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GSM900 Front–End 2– 77. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GSM1800 Front–End 2– 78. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common Receiver parts for GSM900 and GSM1800 2– 78. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter 2– 80. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common Transmitter Part 2– 81. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GSM900 Transmitter 2– 81. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GSM1800 Transmitter 2– 82. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Power Control for GSM900 and GSM1800 2– 83. . . . . . . . . .
AGC 2– 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AFC function 2– 84. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Module
Interfacing 2– 85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RX: 2– 85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX: 2– 86. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parts Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Module GF7_17 2– 89. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Module GF7_18 2– 102. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Module GF7_20B 2– 115. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Module GD7_18 2– 128. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Module GD7_21 2– 141. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hardware ID Chart 2– 154. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Amendment 05/00
Page 2– 3
Page 4

NSE–8/9
System Module
Technical Documentation
Table of Figures
Figure 1. SIM connector, X100 and Battery terminals, 2– 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2. Display Connector pin location 2– 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3. Bottom Connector, X503, pin locations (top View) 2– 15. . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4. Bottom Connector, X503, pin locations (BottomView) 2– 15. . . . . . .
Figure 5. Internal Speaker Pads 2– 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6. Vibra Motor–connetion pads 2– 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 7. Baseband Block Diagram 2– 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 8. Clocking Scheme 2– 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9. Reset Scheme 2– 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 10. Baseband power Distribution 2– 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 11. DC/DC Converter 2– 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 12. Principle of SMR power Functions 2– 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PAMS
Figure 13. Charging Block Diagram 2– 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 14. Flash Programming Sequence 2– 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 15. Sim Card DetX detection levels 2– 57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 16. Memory Setup 2– 58. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 17. Digital Interface – CCONT and MAD2PR1 2– 60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 18. Digital Interface – COBBA_GJP and MAD2PR1 2– 61. . . . . . . . . .
Figure 19. UI Switch & Transducers 2– 68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 20. RF Frequency Plan 2– 73. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 21. Power Distribution Diagram 2– 74. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 22. Frequency Synthesiser– Block Diagram 2– 75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 23. Receiver Block Diagram 2– 77. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 24. Transmitter Block Diagram 2– 80. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 25. Receiver Interface 2– 85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 26. Transmitter Interface 2– 86. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Schematics/Layouts
(GF7_17) A– 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(GF7_18) A– 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(GF7_20B) A– 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(GD7_18) A– 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(GD7_21) A– 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 2– 4
Amendment 05/00
Page 5

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Technical Information
HD947 is a DCT3.5 based product, i.e. a dual band GSM 900 &
DCS1800, single board concept using the serial version of the MAD2PR1–
and COBBA_GJP chip set. HD947 is based on HD945 (PICA) HW with
significant modifications in the Baseband as listed below:
– HD947 uses a two cell semi fixed NiMH battery–pack only, giving 2.4V nomi-
nal supply voltage. Thus the usual NMP battery interface is modified.
– A special charge control ASIC, PSCC, is used for two cell NiMH charging
instead of CHAPS (basically a Chaps modified for 2cells with reduced features).
– The supply voltage inside the phone is delivered by a DC/DC converter,
which step up the battery voltage to 3.1 – 4.2 V supplying the regulators and
PA’s of the phone.
– The DC/DC converter is supplying 4 different voltages ref. depending upon
the required power level and phone state.
– HD947 has a special non DCT3 compatible Bottom connector, which sup-
ports no DATA, only chargers and external audio.
System Module
– Headset
– The external Audio is dual ended uplink and downlink.
– HD947 supports only internal vibra, and in NSE–9 only.
– No support of FLASH ROM writing outside production or aftersales environ-
ment.
– HD947 has a separate serial EEPROM.
– Battery removal detection is changed compared to previous NMP standard.
– An integrated switch IC, UISwitch, is used for buzzer, vibra and backlight
driving.
– There are no backup supply for the RTC. The watch may have to be reset
after battery removal.
HDC–5 and Handsfree unit PPH–1 are supported.
The only difference in the Baseband between GF7 and GD7 is that ”Col 4”
pin on the MAD2PR1 is logically HIGH in GF7 and logically LOW in GD7,
to indicate to the SW which kind of PCB is in use. The two different
versions are made to accommodate the use of two different sets of PA’s.
The only Baseband difference between NSE–8 and –9 is that the vibra is
mounted in the mechanical assembly in NSE–9.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 5
Page 6

NSE–8/9
System Module
Operating Modes
1. Acting Dead:
2. Active Mode:
PAMS
Technical Documentation
If the phone is off and the switcher is operating with the lowest
output voltage and a charger is connected, the Baseband is
powered on but enters a state called ”acting dead”. To the user
the phone acts as if it was switched off. A battery charging alert
is given and/or a battery charging indication on the display is
shown to acknowledge the user that the battery is being
charged.
In the active mode the phone is in normal operation, scanning
for channels, listening to a base station, transmitting and processing information. The switcher delivers output voltage level
depending upon whether the TX is active and on what power
level or if the TX is not active. All the CCONT regulators are
operating. There are several sub–states in the active mode depending on if the phone is in burst reception, burst transmission, if DSP is working etc..
3. Deep Sleep Mode:
In the sleep mode all the regulators except, Vcobba, Vref, VBB,
(Vcore when MAD2PR1 in C07 is used) and the SIM card
VSIM regulators are off. Sleep mode is activated by the
MAD2PR1 after MCU and DSP clocks have been switched off.
The voltage regulators for the RF section are switched off and
the VCXO power control, VCXOPwr is set low. In this state only
the 32 kHz sleep clock oscillator in CCONT is running. The
flash memory power down input is connected to the VCXO
power control, so that the flash is deep powered down during
sleep mode.
In sleep mode the switcher supplies minimum output voltage.
The sleep mode is exited either by the expiration of a sleep
clock counter in the MAD2PR1 or by some external interrupt,
generated by a charger connection, key press, headset connection etc. The MAD2PR1 starts the wake up sequence and
sets the VCXOPwr control high. After VCXO settling time other
regulators and clocks are enabled for active mode.
If the battery pack is disconnect during the sleep mode, the
CCONT shall power down the SIM in the sleep mode as there
is no time to wake up the MCU.
Page 2– 6
4. Power Off mode:
In this mode all Baseband circuits are powered off. The DC/DC
converter is still running supplying the lowest output voltage.
Thus the CCONT is powered in the same way as in usual
DCT3 products when the phone is powered off and battery remains connected.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 7
PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
System Module
Maximum ratings
Table 1. Maximum ratings
Parameter Rating Condition
Battery voltage, idle mode –0.3 ... 3.6 V Max voltage at which the battery
can be charged by the phone
Charger input voltage –5.0 ... 18V Max voltage which activates the
PSCC input over–voltage protection
Temperature range
DC Characteristics
Table 2. Battery & DC/DC converter Voltages
Line Symbol Signal
Name
Min Typ Max Unit Comments
Battery Supply voltage Vb 1.9 2.4 3.6 V
Converter startup voltage Vb
Converter shutdown voltage Vb 1.2 1.4 1.6 V V109a activation
Output over voltage protection Vdc_out 4.8 6.5 V V109b activation
Power on SW limit, normal mode Vb 2.15 V
Power on SW limit, acting dead
mode
Battery cut off voltage (SW) Vb 1.9 V
Table 3. DC/DC converter output voltages when in TX–mode
Line
Symbol
Vdc_out
Condition **
Vcon1 Vcon2
”L” ”L”
Vb 2.15 V
Min Typ Max Unit @ Power level in
3.1 3.3 3.5 V ***
1.2 1.4 1.6 V V109a release
level
1.4 1.6 1.85 V V105 start up
level
level
level
900MHz 1800MHz
11 –19 5 – 15
current in TX
burst
@Vdc_out
min *
Current between burst
@3.3V
Issue 1 07/99
n/a *) n/a *) 1120 mArms
n/a *) n/a *) 150 mArms
Page 2– 7
Page 8
NSE–8/9
System Module
Table 3. DC/DC converter output voltages when in TX–mode (continued)
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Line
Symbol
Vdc_out
current in TX
burst
@Vdc_out
min *
Current be-
tween TX
burst
Vdc_out
current in TX
burst
@Vdc_out
min *
Current be-
tween TX
burst
Vdc_out
current in TX
burst
@Vdc_out
min *
Vcon1 Vcon2
”H” ”L”
”L” ”H”
”H” ”H”
UnitMaxTypMinCondition **
3.2 3.4 3.6 V ***
n/a *) n/a *) 1360 mArms
n/a *) n/a *) 150 mArms
3.7 3.9 4.1 V ***
n/a *) n/a *) 2650 mArms
n/a *) n/a *) 150 mArms
3.8 4.0 4.2 V ***
n/a *) n/a *) 2900 mArms
@ Power level in
900MHz 1800MHz
9 –10 3 – 4
7 – 8 0 – 2
5 – 6 N/A
Current be-
tween TX
burst
Vdc_out ”H” ”H” 3.8 4.0 4.2 V for buzzer &
*) Note: Maximum load of Vdc_out during TX burst, when Vdc_out is not allowed to
drop below 3.05V, Cout is 20% below nominal and remaining load besides PA is max.
150mA.
**) Note: The SW control makes converter voltage step up before PA power
consumption level is increased, and makes converter voltage stay up until PA power
consumption is lowered.
***) Note: Voltage with no load, voltage will drop during burst, but with the stated current
voltage will not drop below 3.05V.
n/a *) n/a *) 150 mArms
vibra alerting
Page 2– 8
Issue 1 07/99
Page 9
PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 4. DC/DC converter output voltages when non Tx–mode
Line
Symbol
Vdc_out Low Low 3.1 3.3 3.5 V Off mode
Vdc_out Low Low 3.1 3.3 3.5 V Sleep mode
Vdc_out Low Low 3.1 3.3 3.5 V Active mode non TX
Vdc_out Low Low 3.1 3.3 3.5 V Acting dead mode
Vdc_out high high 3.8 4.0 4.2 V for buzzer & vibra op-
Line Symbol Signal
Condition
Vcon1 Vcon2
Table 5. Actual Regulated Baseband supply Voltages *
Minimum Nominal Maximum Unit Comment
Min. Typ Max. Unit Notes
Name
System Module
eration
Vbb Baseband supply voltage Vbb
COBBA analog supply voltage Vcobba
MAD2PR1 core voltage * Vcore
MAD2PR1 core voltage * Vcore
5V SIM supply voltage Vsim
3V SIM supply voltage Vsim
2.7 2.8 2.87 V
15 25 mVac_pp ripple
25 125 mArms
2.67 2.8 2.85 V
10 20 mVac_pp ripple
7 80 mArms no audio input
output
–5 % 1.98 +5 % V @ start up with
MAD2PR1 C07
TBD Vac_pp ripple
TBD mArms
–5 % 1.5 +5 % V for MAD2PR1 in
C07
TBD Vac_pp ripple
TBD mArms
4.8 5.0 5.2 V V
10 20 mVac_pp ripple
2.8 3.0 3.2 V V
Reference Voltage Vref
*) Note: The values will be updated when C07 devices are available. With MAD2PR1
Vcore is not used.
Issue 1 07/99
10 20 mVac_pp ripple
1.4775 1.5 1.5225 V V
5 15 mVac_pp ripple
Page 2– 9
Page 10
NSE–8/9
System Module
External Signals and Connections
This section lists and specifies all the electrical connections from the
Baseband part of the transceiver, i.e. either to the outside world (Bottom– ,
SIM card– and battery connector) , or to items in the mechanical assembly
that has electrical interface (LCD, Vibra, speaker and microphone).
Table 6. external connectors
Parameter connector
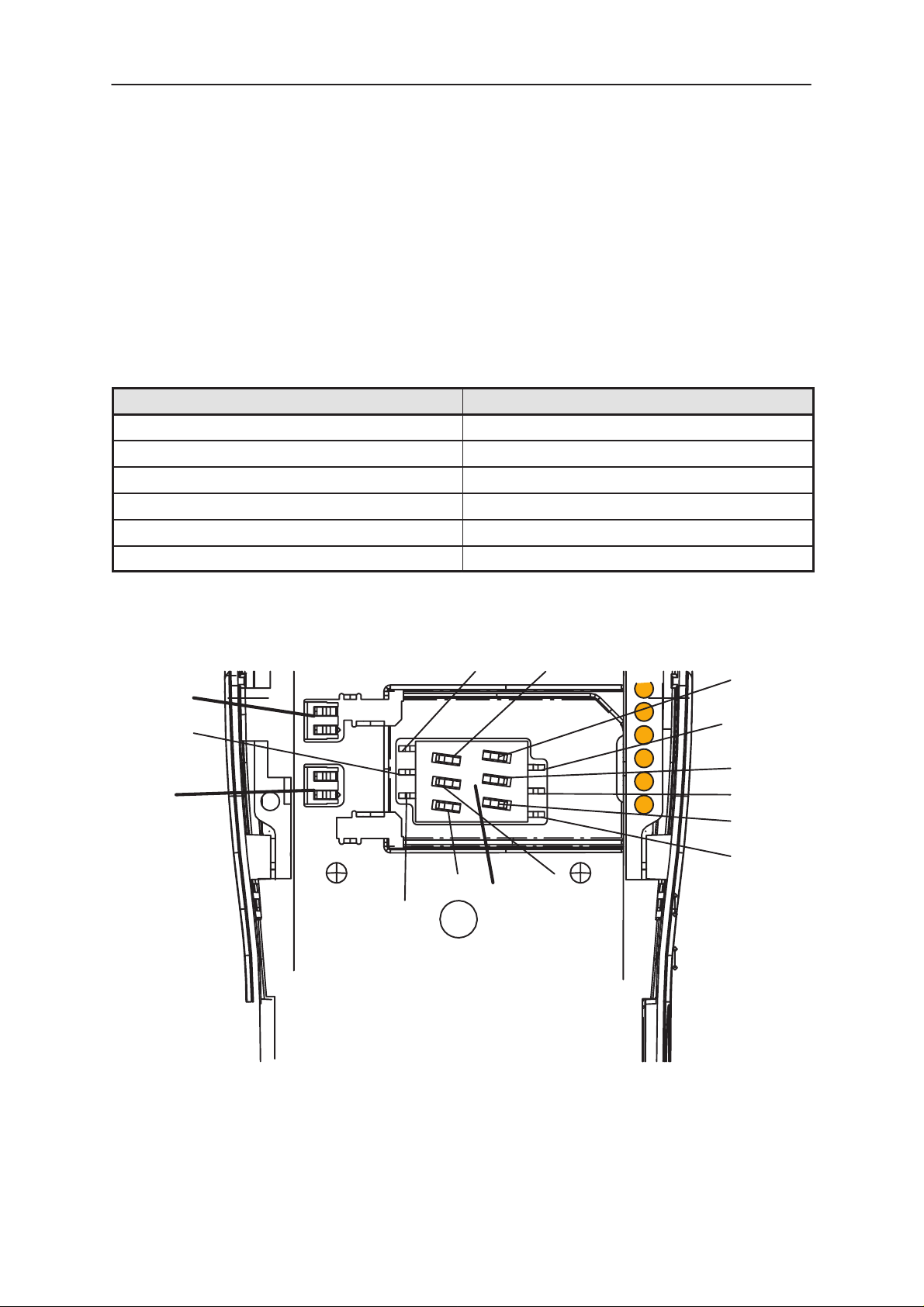
SIM Connector X100
Battery connectors X101 & X102
Display Connector X400
Bottom connector X503
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Speaker Connector B201
Vibra motor connector E103 & E104
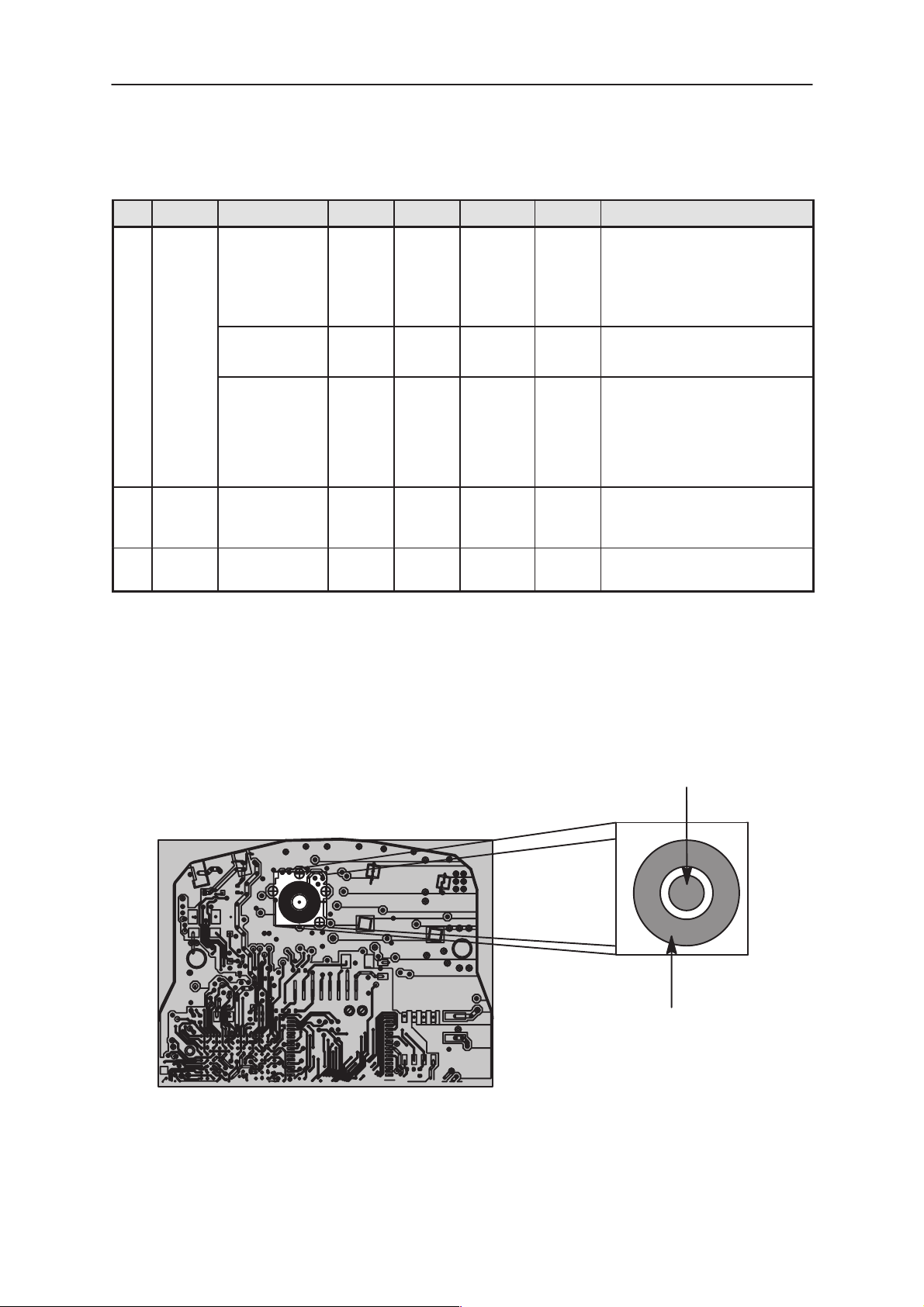
X102
Vb
5
X101
GND
1
X100
6
34
4
3
5
2
6
1
2
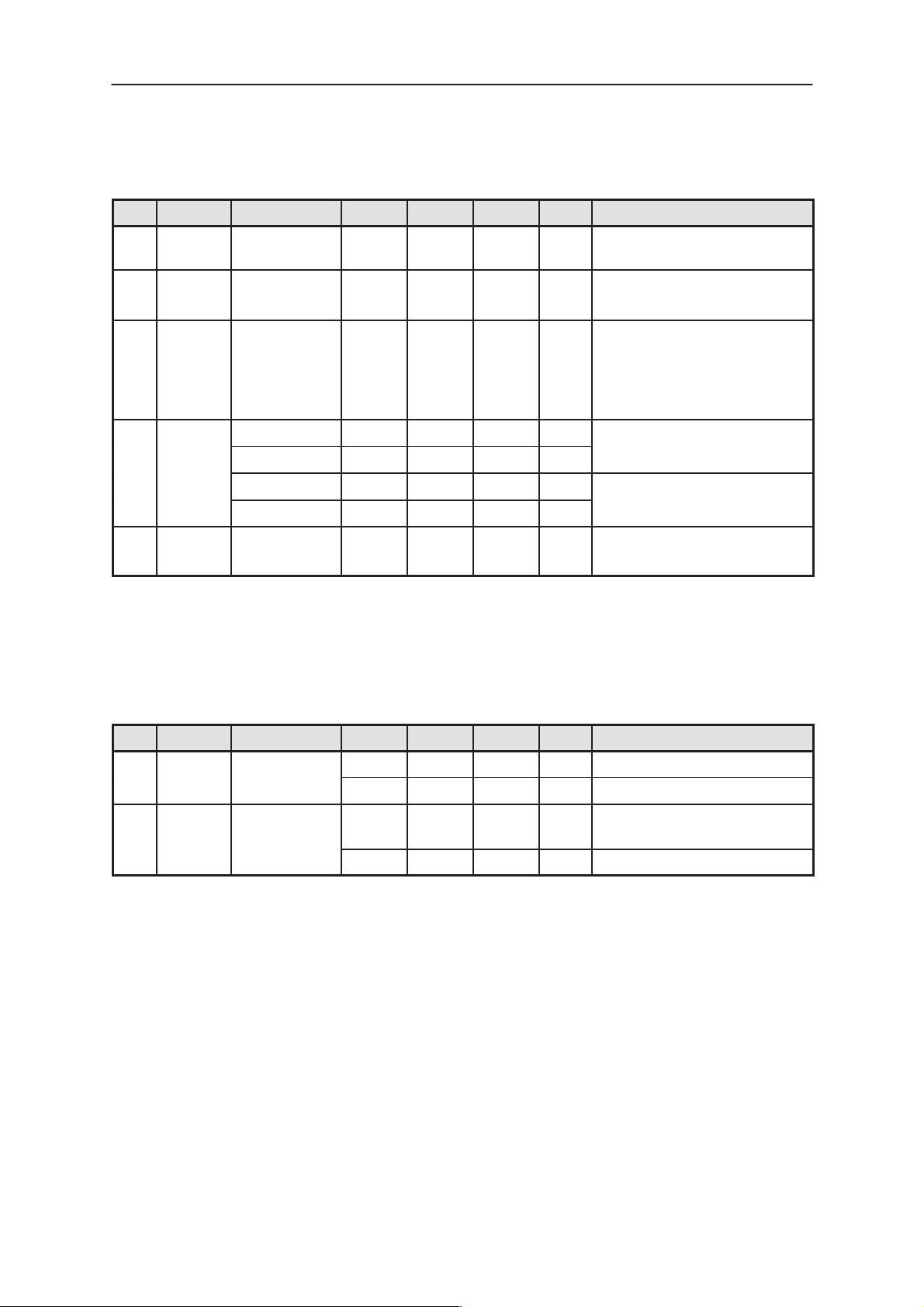
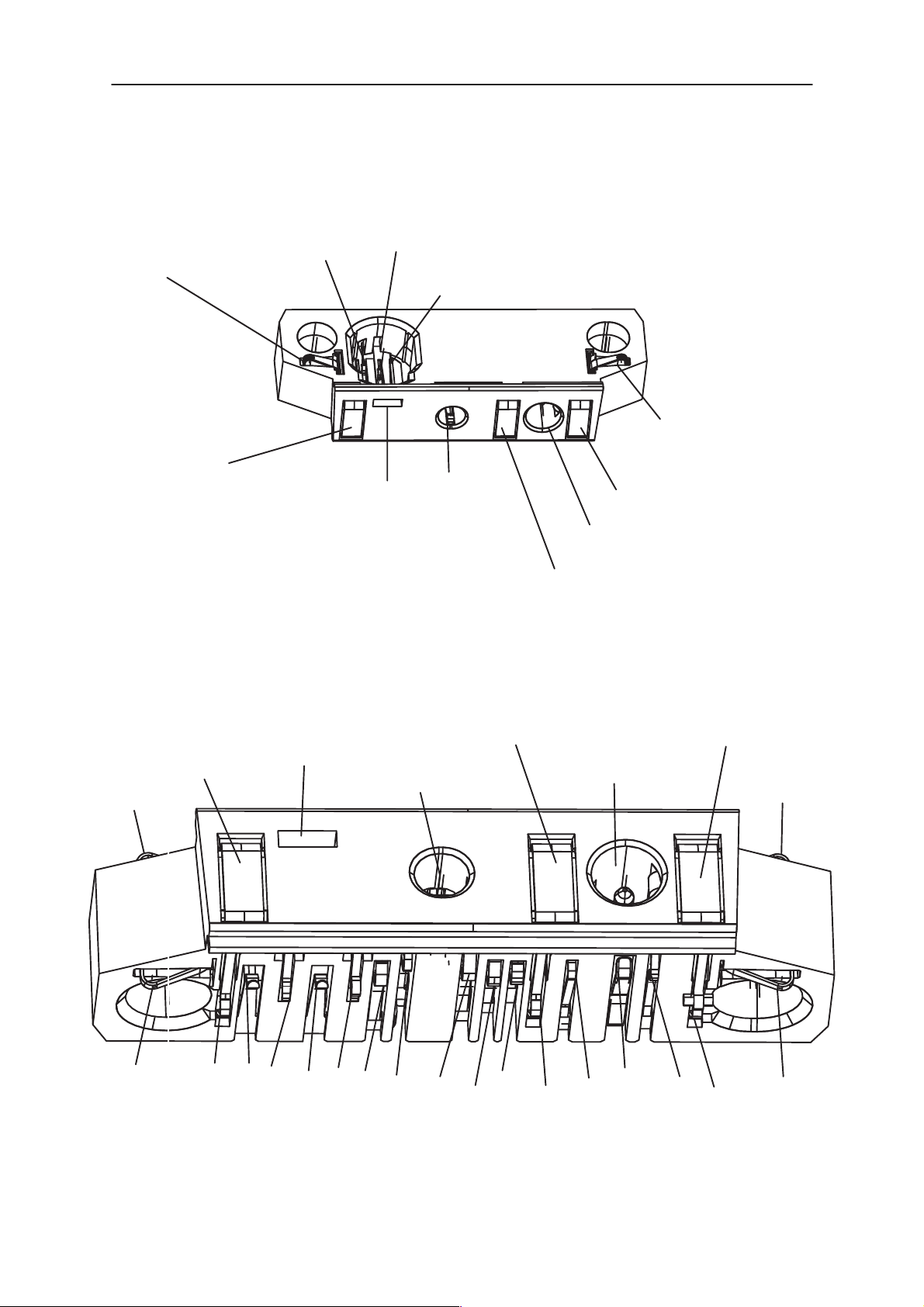
Figure 1. SIM connector, X100 and Battery terminals, X101 & X102, pin locations
Page 2– 10
Issue 1 07/99
Page 11
PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 7. SIM Connector , X100
Pin Name Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
1 GND GND 0 0 V Reference ground for the SIM
2, 6 VSIM 5V SIM Card
3V SIM Card
3 DATA 5V Vin/V out
3V Vin/Vout
4 SIMRST
5 SIMCLK Frequency
5V SIM Card 4.0 ”1” VSIM V
3V SIM Card 2.8 ”1” VSIM V
5V SIM Card 0 ”0” 0.4 V
3V SIM Card 0 ”0” 0.4 V
Trise/Tfall
4.8
2.8
4.0
0
2.8
0
5.0
3.0
”1”
”0”
”1”
”0”
3.25
5.2
3.2
VSIM
0.4
VSIM
0.4
25
V Supply voltage
V SIM data
MHz
ns
System Module
interface signals
Trise/Tfall max 1us
SIM reset
SIM reset not active
SIM clock
VSIM supply voltages are specified to meet type approval requirements
regardless the tolerances in components.
Battery connectors
Table 8. Battery Connectors, X101 & X102
Pin Name Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
1, 2 PGND
X101 ground
3, 4 VB
X102
Power
Battery
Voltage
0 0 V
5 m Total contact resistance
1.8 2.4 3.6 V Supply to the DC/DC converter
5 m Total contact resistance
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 11
Page 12
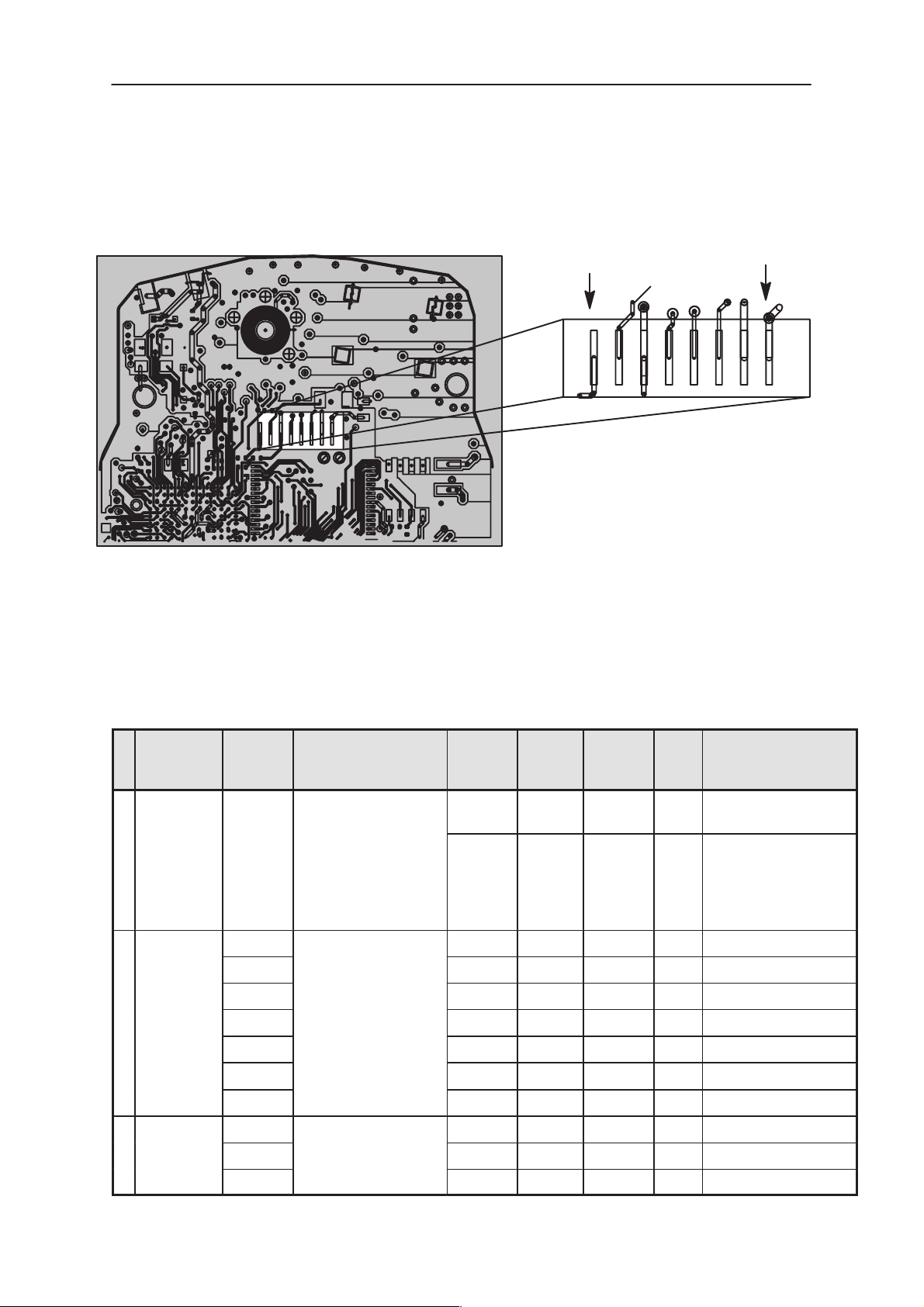
NSE–8/9
System Module
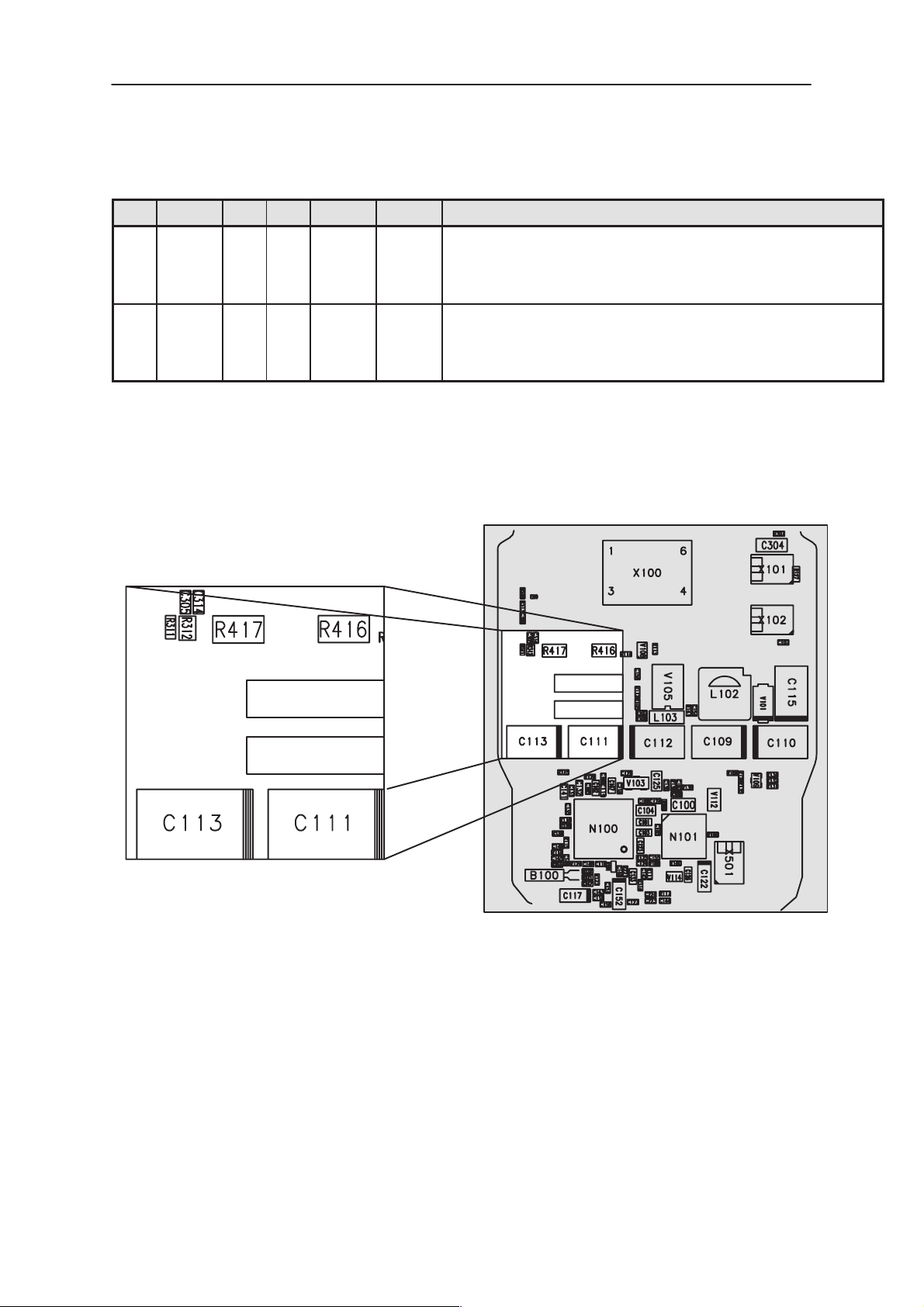
Display connector
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Pad 8 Pad 1
Figure 2. Display Connector pin location
Table 9. Display connector, X400
P
Signal Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit Notes
i
n
1 VBB Supply voltage 2.7 2.8 3.3 V range that LCD sup-
ports
300 uA +25 °C, VL= 2.8 V,
LCDCSX is disabled
with Special Test
Pattern ”12345”
2 GenSIO_0 f
EXT
tscyc 250 ns
tshw 100 ns
tslw 100 ns
ViH 0.7xVbb Vbb V Logic high
Serial clock input 0 1.083 4.00 MHz
ViL 0 0.3xVbb V Logic low
tr / tf 10 ns Rise / fall time
3 GenSIO_1 tsds Serial data input 100 ns
tsdh 100 ns
ViH 0.7xVbb Vbb V Logic high
Page 2– 12
Issue 1 07/99
Page 13
PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 9. Display connector, X400 (continued)
i
n
ViL 0 0.3xVbb V Logic low
tr / tf 10 ns Rise / fall time
4 LCDCD tsas Control/display data
flag input
tsah 100 ns Hold time
ViL 0 0.3xVbb V Logic low, Control
ViH 0.7xVbb Vbb V Logic high, Display
tr / tf 10 ns Rise / fall time
5 LCDEN tcss Chip select input 60 ns
tcsh 100 ns
100 ns Setup time
System Module
NotesUnitMax.Typ.Min.ParameterSymbolSignalP
data
data
ViH 0.7xVbb Vbb V Logic high
ViL 0 0.3xVbb V Logic low, active
tr / tf 10 ns Rise / fall time
6 GND GND Ground 0 V In LCD interface
7 VOUT LCD output voltage
8 LCDRSTX
ViH
ViL 0 0.3xVbb V Logic low, active
trw 100 ns width for valid reset
tinit 1000 ns driver initialization
tr / tf 10 ns Rise / fall time
Reset
0.7xVbb Vbb V Logic high, not ac-
3xVbb 9 V from voltage boost-
er inside LCD driver
6.82 9 V from voltage booster inside LCD driver
Philips display
9 V from voltage boost-
er inside LCD driver
tive
pulse
time after reset
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 13
Page 14
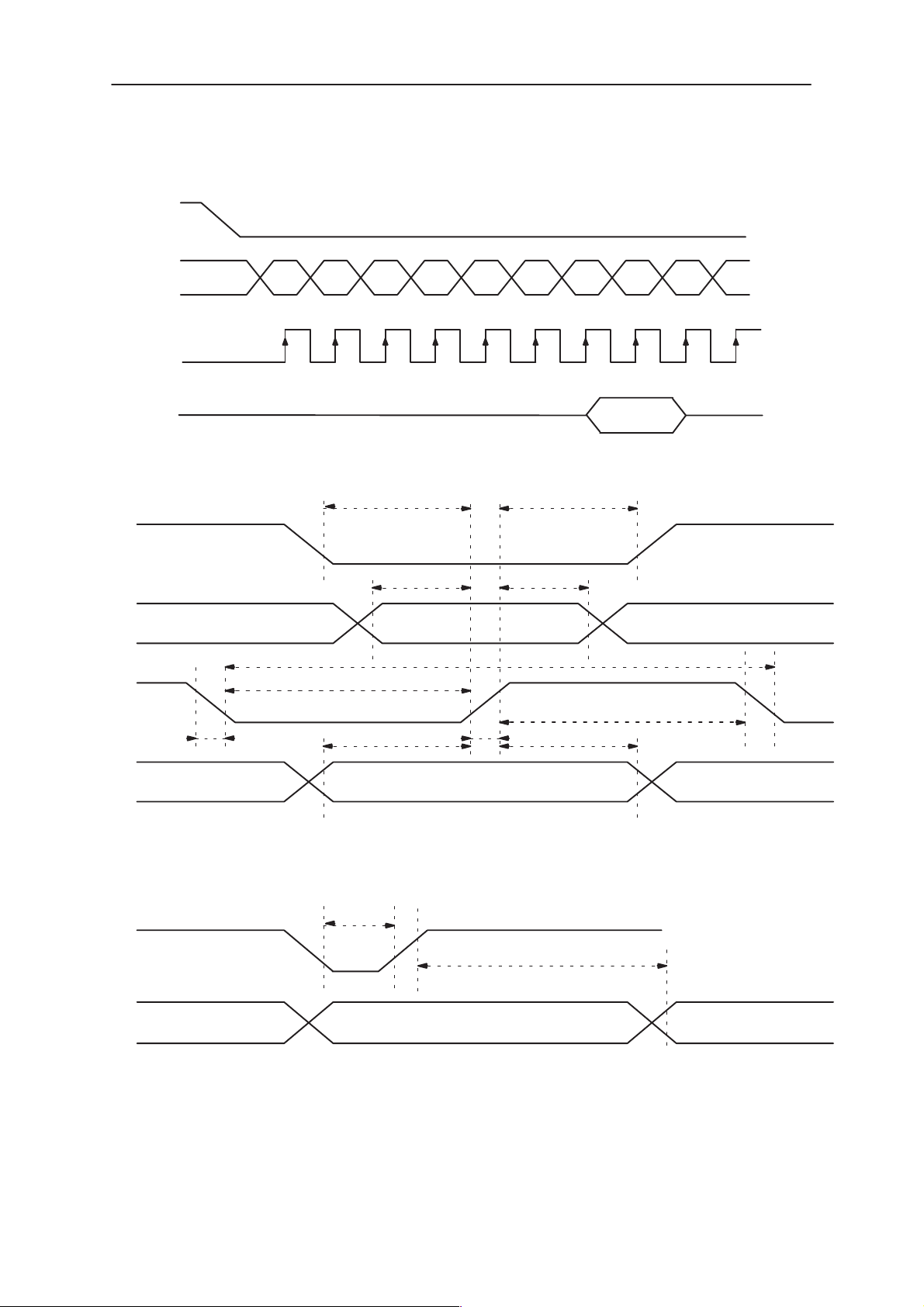
NSE–8/9
System Module
LCDEN
PAMS
Technical Documentation
GenSIO_1
GenSIO_0
LCDCD
LCDEN
LCDCD
GenSIO_0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6
12345678910
Serial interface timing
tslw
tf
tcss tcsh
tsas tsah
tscyc
tr
tsdhtsds
tshw
GenSIO_1
Detailed Serial Interface timing
LCDRSTX
Driver internal
state
Driver Reset timing
trw
Data
In reset
tinit
Ready
Page 2– 14
Issue 1 07/99
Page 15
PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Bottom Connector
D–cover to PCB gronund
1
Charge_GND
Mic sound port
2, IMICP
Microphone well
3, IMICN
4,5,6,7,8
Audio
Jack
System Module
D–cover to PCB gronund
13, V_charge_in Pad
10,11,12 Charger Jack
Charge_GND
D–cover to
PCB GND
9, Charge_Ctrl, pad
Figure 3. Bottom Connector, X503, pin locations (top View)
Mic sound port
1
Audio
Jack
4,5,6,7,8
Charge_ctrl
9
Charger Jack
10,11,12
13, V_charge_in Pad
D–cover to
PCB GND
D–cover to
PCB GND
Issue 1 07/99
2
1
Figure 4. Bottom Connector, X503, pin locations (BottomView)
1515
3
4
6
5
7
98
10
11
12
13
D–cover to
PCB GND
Page 2– 15
Page 16
NSE–8/9
kHz, 0 dBmO network level
System Module
Table 10. Signals of the bottom connector X503
Pin Name Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
Technical Documentation
PAMS
1,10Charge
_GND
2 IMICP IMICP 0.55 4.1 mV
3 IMICN IMICN 0.55 4.1 mV
4 INT
5 XEarP*)positive line
Charger re-
turn
Headint low 0.57 0.65 0.72 V No plug inserted in audio
Headint high Vbbmin Vbb Vbbmax V Plug inserted in audio Jack
for external
audio output
HDC–5 mode
PPH–1 mode
–0.3 0 V W.R.T GND
113 150 188 Ω Output AC impedance (ref.
0.84 Vpp Output level (ref. XEarN)
4.0 4.2 4.4 KΩ Output AC impedance (ref.
1.8 Vpp_ac Output level (ref. XEarN)
Connected to COBBA
MIC2P/N input. The maximum value corresponds to1
with input amplifier gain set
to 32 dB. typical value is
maximum value –16 dB.
jack
XEarN) HDC–5
f<3400 Hz
HDC–5
f<3400 Hz
XEarN) PPH–1
300< f<3400 Hz
PPH–1
f<3400 Hz
Page 2– 16
Issue 1 07/99
Page 17
PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 10. Signals of the bottom connector X503 (continued)
6 XMicN*)Negative line
for external
audio input
to phone
HDC–5 mode
PPH–1 mode
System Module
NotesUnitMaxTypMinParameterNamePin
0.025 Vpp Maximum input signal level
(ref. XMicP) with Cobba gain
18dB,
300< f <3400 Hz
40 dB/dec Input attenuation, f<300 Hz
(ref. XMicP)
775 895 995 mV Hook active DC level ref.
gnd
95 380 mV Hook in–active DC level ref.
gnd
–100 –400 µA Bias current (ref. XMicP)
0.5 Vpp Maximum input signal level
(ref. XMicP) with Cobba gain
12dB,
300< f <3400 Hz
7 XEarN
*)
20 dB/dec Input attenuation, f<300 Hz
(ref. XMicP)
2500 mV Mute (output DC level), wrt.
Charge_gnd without
HFM–8
2130 mV Mute (output DC level), wrt.
Charge_gnd with HFM–8
2230 mV Unmute (output DC level),
wrt. charge_ gnd without
HFM–8
1850 mV Unmute (output DC level),
wrt. charge_ gnd with
HFM–8
Negative line
for external
audio output
HDC–5 mode
PPH–1 mode See XEarP pin definitions
See XEarP pin definitions
output is symmetrical
output is symmetrical
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 17
Page 18
NSE–8/9
contro
control
System Module
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Table 10. Signals of the bottom connector X503 (continued)
NotesUnitMaxTypMinParameterNamePin
8 XMicP*)Positive line
for external
audio input to
phone
HDC–5 mode
PPH–1
0.025 Vpp Maximum input signal level
(ref. XMicN) with Cobba gain
18dB,
300< f <3400 Hz
40 dB/dec Attenuation of input inside
phone,
f<300 Hz (ref. XMicN)
1450 2090 mV Headset identification DC
level ref. gnd @ AUXout =
2.1V and
PDATA_4 =”L”
100 400 µA Bias current (ref. XMicN)
0.5 Vpp Maximum input signal level
(ref. XMicN) with Cobba gain
12dB,
300< f <3400 Hz
20 dB/dec Input attenuation, f<300 Hz
(ref. XMicN)
2060 2180 2300 mV PPH–1 with HFM–8 identifi-
cation DC level, wrt.
Charge_gnd
@ AUXout = ”Z” and PDATA_4 =”L”
9,
Charge
12 _Ctrl nal charge
PWM exter-
l
2490 2600 2720 mV PPH–1 with out HFM–8
identification DC level, wrt.
Charge_gnd
@ AUXout = ”Z” and PDATA_4 =”L”
0 0.5 V Charger control PWM low
2.4 V Charger control PWM high
32 Hz PWM frequency for a 3 wire
charger
1 25 99 % PWM duty cycle
Page 2– 18
Issue 1 07/99
Page 19
PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 10. Signals of the bottom connector X503 (continued)
11.13V_char
ge_IN
15a
Not
15b
used
16,17Charge
_GND
Charger volt-
age input,
ACP–7 type
ACP–8 type 5.7
ACP–9 type 7.1
Not used Internal short circuit in bot-
Charger re-
turn
System Module
NotesUnitMaxTypMinParameterNamePin
7.25
320
500
6.0
720
– 0.3 0 V wrt. Supply ground
7.6
1 1.1
370
6.0
620
8.4
7.1
800
7.95
16.9
420
1.1
6.3
750
9.3
8.0
850
Vrms
Vp
mA
Apeak
VrmsmAUnloaded ACP–8 Charger
Vrms
Vrms
mA
Unloaded ACP–7 Charger
Unloaded Peak voltage
Supply current
Supply current
Supply current
Unloaded & charg_ctrl
PWM= 0%
Unloaded & charg_ctrl
PWM= 25%
Supply current
tom connector. Not used in
NSE–8/9
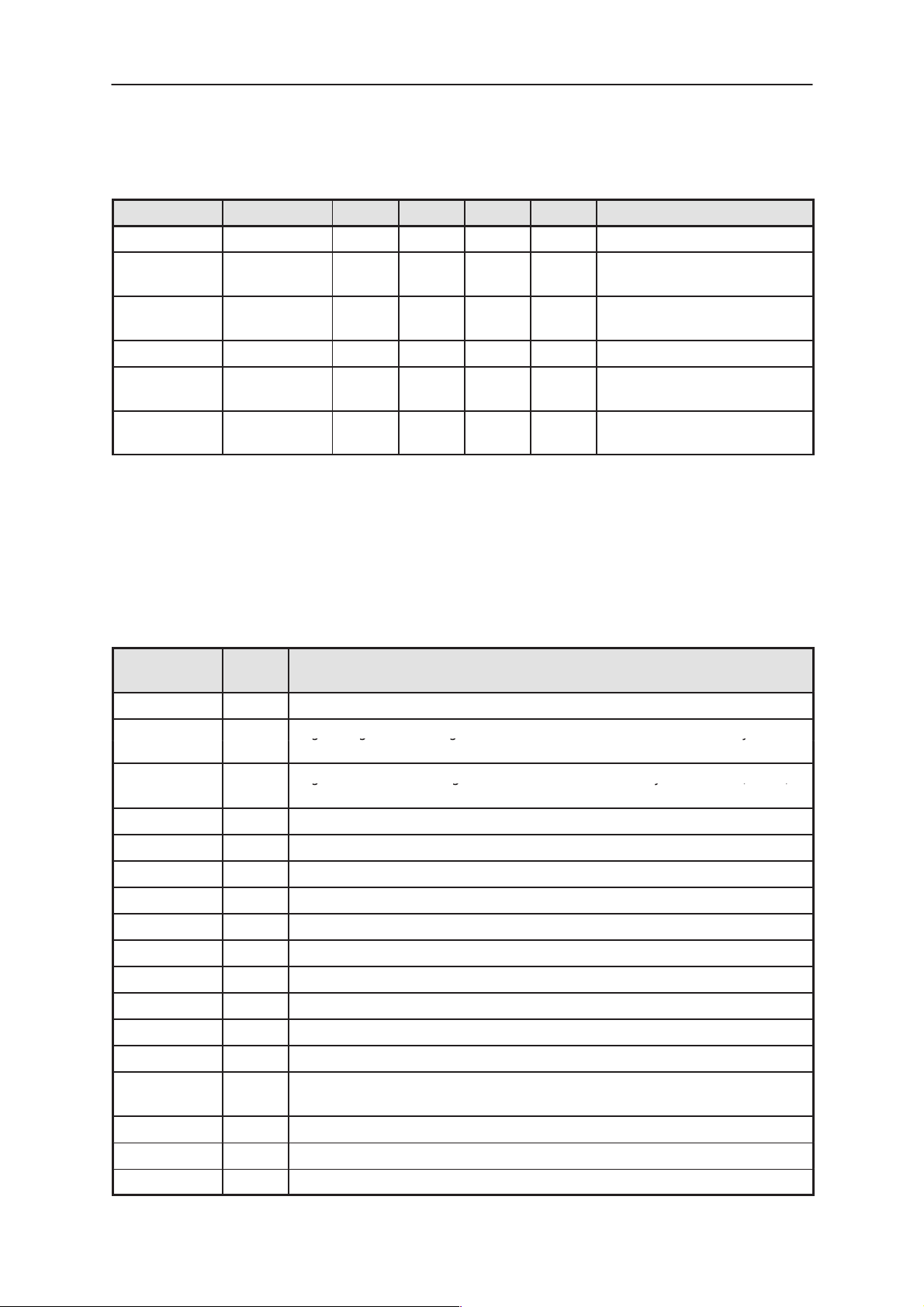
Speaker connection
Pad 1, EarN
Pad 2, EarP
Issue 1 07/99
Figure 5. Internal Speaker Pads
Page 2– 19
Page 20
NSE–8/9
System Module
Table 11. Internal Earpiece connection, B201
Pad Name Min Typ Max Unit Remark
1 EARN 0 14 220 mVac Connected to COBBA_GJP EARN output. Typical level corre-
sponds to –16 dBmO network level with volume control giving
nominal RLR (=+2dB) 8 db below max. Max level is 0dBmO
with max volume (codec gain –11 db)
2 EARP 0 14 220 mVac Connected to COBBA_GJP EARP output. Typical level corre-
sponds to –16 dBmO network level with volume control giving
nominal RLR (=+2dB) 8 db below max. Max level is 0dBmO
with max volume (codec gain –11 db)
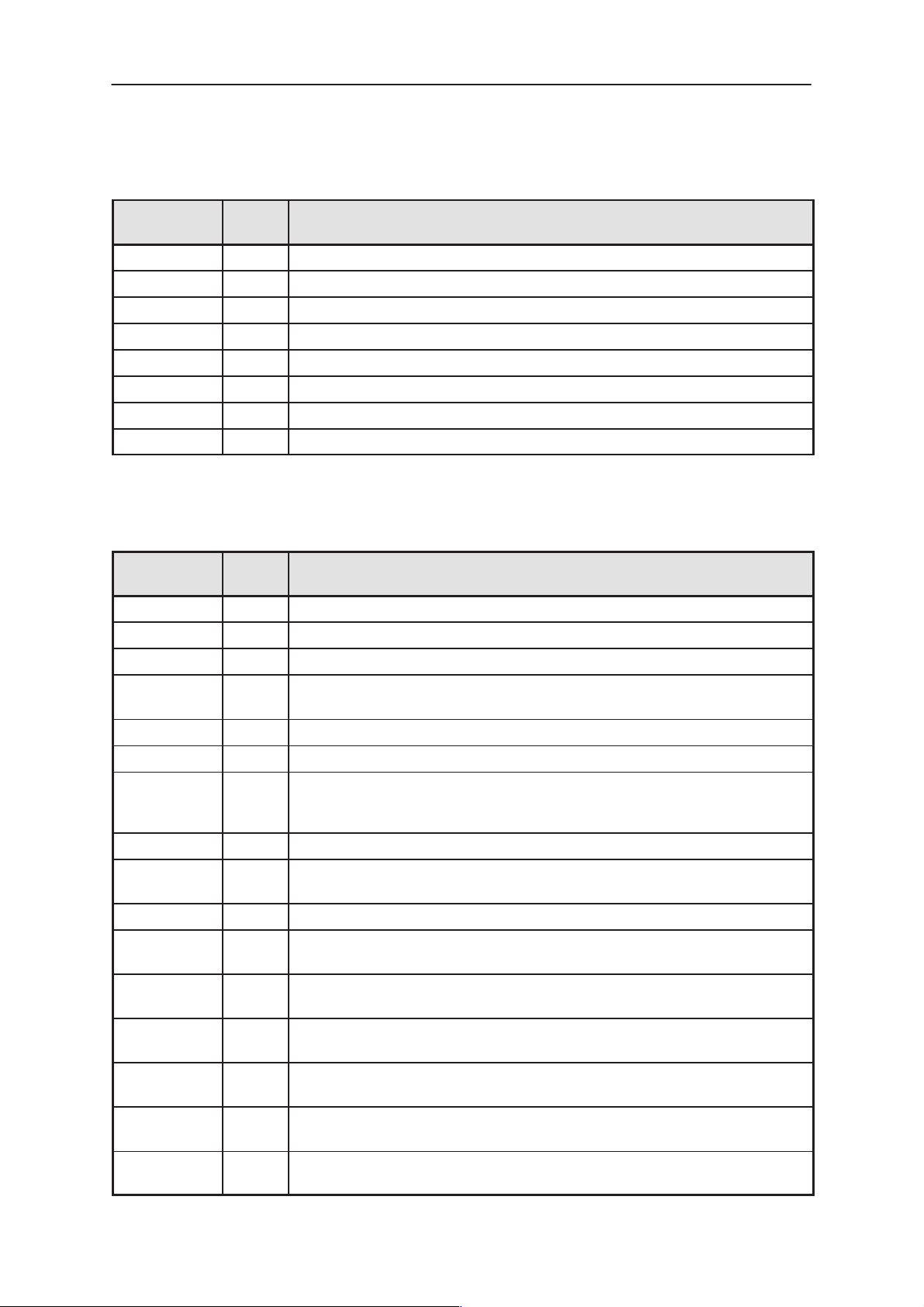
Vibra motor connection
Technical Documentation
PAMS
E104
E103
Figure 6. Vibra Motor–connetion pads
Page 2– 20
Issue 1 07/99
Page 21
PAMS
gg g y
gg y()
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 12. Vibra motor connection, E103 & E104
Pad Name Min Typ Max Unit Comment
E103 to E104 Rated voltage 1.3 V
E103 to E104 Rated current 116 mA
rms
E103 to E104 Operating
voltage
E103 to E104 Start voltage 1.1 V rms
E103 to E104 Start current 135 mA
E103 to E104 internal resis-
tance
1.2 1.9 V rms
rms
10.7 ohm
Internal Signals and Connections
System Module
This section describes all the signal between the Baseband blocks
Additionally the signals between the Baseband and the RF section are
described.
Table 13. Audio Block connections
Name
of signal
charg_ctrl input connected for schematic reasons (use of TVS on audio sheet)
HOOKDET output Logical signal indicating whether hook is active or not in accessory Low
HEADDET output Logical output indicating whether the audio accessory is inserted (HIGH)
XEARP output Positive line of the external audio downlink signal.
XEARN output Negative line of the external audio downlink signal.
XMICP input Positive line of the external audio uplink signal
XMICN input Negative line of the external audio uplink signal
IMICP input Positive line of the internal microphone signal
IMICN input Negative line of the internal microphone signal
EAD output Analog voltage used for accessory identification.
Type Remark
equals button activated.
or not (LOW).
SERRFI(3:0) Bus Serial control for the COBBA_GJP and serial data for the RF interface.
PCM(3:0) Bus Serial digital data for the COBBA_GJP audio
COBBACLK input System clock for the COBBA_GJP
COBBA
RESET
AFC output Analog voltage to RF controlling the system frequency
RXC output Analog voltage for gain control in the RF–receiver (AGC)
TXC output Analog voltage for the TX ramping control
input Reset signal to the COBBA_GJP
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 21
Page 22
NSE–8/9
System Module
Table 13. Audio Block connections (continued)
RemarkTypeName
of signal
TXIN output Negative line of the in phase transmit signal
TXIP output Positive line of the in phase transmit signal
TXQN output Negative line of the quadrature phase transmit signal
TXQP output Positive line of the quadrature phase transmit signal
RXINP input Positive line of the in phase receive signal
RXINN input Negative line of the in phase receive signal
KEY_LIGHT output Logical signal controlling the keyboard backlight driver.
LCD_LIGHT output Logical signal controlling the LCD backlight driver.
Technical Documentation
PAMS
Table 14. CPU connections
Name
of signal
PURX input Power on reset
SLEEPCLK input 32KHz sleep clock signal for MAD2PR1 operation in sleep state
CCONTINT input Interrupt line from CCONT to MAD2PR1, for all events in CCONT
HOOKDET Input Logical signal indicating whether the hook button of the accessory is acti-
HEADDET input Logical signal indicating whether an accessory is inserted or not
CCONTCSX output CCONT Chip select for the serial communication with MAD2PR1
MBUS bi
VIBRA output Logical output from MAD2PR1 to the vibra driver in the UISWITCH
VCXOPWR output Control of power up/down of the 13MHz system clock, sleep mode control
SIMIF(4:0) bus Communication lines between MAD2PR1 and the SIM driver in CCONT
GENSIO(1:0) bus Serial clock and data for the communication between MAD2PR1 and
Type Remark
vated or not
Serial communication line between MAD2PR1 and external service or pro-
direc-
tional
duction equipment.
Clock line for F–bus communication during flashing.
to CCONT
CCONT, and from MAD2PR1 to LCD–driver.
CHARG_OFF output Logical signal controlling charging through PSCC, High disables start–
and PWM–charging.
PSCC_PWM output Logical signal controlling the charger switch inside PSCC, High switch
open, Low switch closed
FBUS_TX output Output for serial communication between MAD2PR1 and external service
or production equipment.
FBUS_RX input Input for serial communication between MAD2PR1 and external service or
production equipment.
SERFI(3:0) bus communication line between MAD2PR1 and COBBA_GJP for cobba con-
trol and receive and transmit data for the RF transmission.
Page 2– 22
Issue 1 07/99
Page 23
PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 14. CPU connections (continued)
RemarkTypeName
of signal
PCM(3:0) bus communication line beteween MAD2PR1 and COBBA_GJP for receive
and transmit data for the audio transmission.
COBBACLK output 13MHz clock for the synchronization COBBA
COBBA
RESET
COL(3:0) output Column addresses for the keyboard scan
ROW(4:0) input Row addresses from the keyboard scan and power–on key.
BUZZER output PWM output from MAD2PR1 to the Buzzer driver in UISWITCH
LCDCD output Control line to the LCD driver
LCDEN output Chip select to the LCD driver
LCDRSTX output Reset of the LCD driver
VCON_1 output Least significant bit in the 2–bit DAC control of the DC/DC–converter out-
output Reset signal from MAD2PR1 to Cobba_GJP
put voltage.
System Module
VCON_2 output Most significant bit in the 2–bit DAC control of the DC/DC–converter out-
put voltage.
LOW_BATT Input Battery removal alert to MAD2PR1
BTEMP Input connection to provide access to BTEMP signal in production and service
SDATA output Serial data for the synthesizer inside SUMMA in the RF
SCLK Output 13/4 MHz clock for the serial communication with the synthesizer inside
SUMMA in RF
SENA1 output Chip select for the serial communication with SUMMA in RF
FRACTRL output Controls signal for the gain in the LNA in the RF
TXP output Logical control signal to indicate the power on of the TX circuitry
RFC Input 13MHz system clock from the RF
BAND_SEL output Logical control of the band selection in the front end GSM 900 or DCS
1800
Table 15. POWER connections
Name
of signal
Type Remark
V_CHARGE_IN input charger voltage input
CHARGE_GND input charger current return
CHARG_CTRL output Charger voltage control signal
PSCC_PWM input Logical signal from MAD controlling the charger switch inside PSCC,
High switch open, Low switch closed
CHARG_OFF input Logical signal from MAD enabling / disabling charging through PSCC,
High disables both start– and PWM–charging.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 23
Page 24
NSE–8/9
System Module
Table 15. POWER connections (continued)
RemarkTypeName
of signal
GENSIO(1:0) bus Serial clock and data for communication between CCONT and
MAD2PR1, and from MAD2PR1 to LCD–driver
SIMIF(4:0) bus 5 signals for MAD2PR1 communication with SIM through CCONT
VCXOPWR input Control from MAD2PR1 to power on/off the 13 MHz oscillator, sleep
mode control
CCONTCSX input Chip select for communication with CCONT
CCONTINT output Common CCONT event interrupt line to MAD2PR1
SLEEPCLK output 32KHz clock for MAD2PR1 sleep mode operation
PURX output Power up reset signal to MAD2PR1
VDC_out_2 output Filtered DC/DC output supply for Synth supply regulator in RF
VRX_1 output Regulator output for Rx part of CRFU in RF
Technical Documentation
PAMS
VRX_2 output Regulator output for Rx part of SUMMA in RF
VSYN_2 output Regulator output for VCO’s and synthezeiser in SUMMA in RF
VXO output Regulator output for 13 MHz oscillator in RF
VTX output Regulator output for TX parts in SUMMA and CRFU in RF
VCP output 5v supply for SUMMA in RF
VREF output 1.5v common voltage reference for Baseband and RF
VDC_OUT output DC/DC output supply voltage for PA’s, backlight, vibra and buzzer
RF_TEMP input Input from temperature sensor in RF
TXP input TX burst synchronization
LOW_BATT output Battery removal alert to MAD2PR1
EAD input external accessory detection, analog voltage to CCONT EAD ADC
PWRON input Phone power on signal to CCONT, watch dog disable
VCON_1 input DC/DC converter voltage control, LSB of two bit DAC
VCON_2 input DC/DC converter voltage control, MSB of two bit DAC
BTEMP output to test pad to provide access to BTEMP for production and service
Table 16. UI connections
Name
of signal
WDDIS input Connection to panel connector in production for watch dog disable
PWRON output Phone power on signal to CCONT
COL(3:0) input Column addresses for the keyboard scan
ROW(4:0) output Row addresses from the keyboard scan and power–on key.
BUZZER input Logical input from MAD2PR1 to the Buzzer driver in UISWITCH
LCDCD input Control line to the LCD driver
Page 2– 24
Type Remark
Issue 1 07/99
Page 25
PAMS
COBBA
COBBA
chi select for SERRFI
CLK
COBBA
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 16. UI connections (continued)
RemarkTypeName
of signal
LCDEN input Chip select to the LCD driver
LCDRSTX input Reset of the LCD driver
VIBRA input PWM output from MAD2PR1 to the vibra driver in the UISWITCH
KEY_LIGHT input Logical signal controlling the keyboard backlight driver in the UISwitch.
LCD_LIGHT input Logical signal controlling the LCD backlight driver in the UISwitch.
GENSIO(1:0) bus Serial clock and data for communication between CCONT and MAD2PR1,
and from MAD2PR1 to LCD–driver
RF control and interface
System Module
The interface signals between the Baseband and the RF section are
shown below.
Table 17. Signals within the Baseband controlling the RF
Signal
name
SERRIF 0 MAD2PR1
SERRIF 1 MAD2PR1
SERRIF 2 MAD2PR1
SERRIF 3 MAD2PR1
COBBA-
RESET
From
To
COBBA
bi–
directional
COBBA
bi–
directional
COBBA
COBBA
MAD2PR1
COBBA
Parameter Mini-
mum
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V
Typi-
cal
Maxi-
mum
Unit Function
Idata for RF
Qdata for RF
CSX,
p
BUS
SD, control data for
cobba
DSPGENOut5
COBBA–
TXP MAD2PR1
Issue 1 07/99
MAD2PR1
CCONT
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V
Page 2– 25
Page 26
NSE–8/9
C
S
S
O
C
C
S
S
CCO
System Module
Table 18. AC and DC Characteristics of signals between Baseband and RF
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Signal
name
VRX_1 CCONT VR2
VRX_2 CCONT VR5
VSYN_2 CCONT VR4
VXO CCONT VR1
VTX CCONT VR7
VCP CCONT V5V
From
To
RFU3
UMMA
VCO’s
VCTCX
RFU3
UMMA
Parameter Mini-
mum
DC–voltage 2.67 2.8 2.85 V
voltage ripple
when on
DC–voltage 2.67 2.8 2.85 V
voltage ripple
when on
DC–voltage 2.67 2.8 2.85 V
voltage ripple 5 mVpp
DC–voltage 2.67 2.8 2.85 V
voltage ripple 5 15 mVpp
DC–voltage 2.67 2.8 2.85 V
Current 150 mA
voltage ripple
when on
DC–voltage 4.8 5.0 5.2
Current 30 –
Typi-
cal
10 15 mVpp
Maxi-
mum
5 15 mVpp
5 15 mVpp
Isim
Unit Function
mA
for Rx part of CRFU
for Rx part of Summa
for VCO’s & Synth. i
umma
for 13 MHz oscillator
for Tx in Summa &
RFU
for Summa
VREF CCONT
SUMMA
Vdc_out DC/DC–con-
verter output
to
RF PA’s
RF_TEM
P
RF
NT
voltage ripple 10 25 mVpp
DC–Voltage 1.478 1.5 1.523 V
Current 100 uA
voltage ripple 5 10 mVpp
DC–Voltage
voltage 0 1.5 V
BB pull up to
Vref
RF pull down to
gnd
ADC resolution 10 bits
–5% 47 +5 % Kohm
47 Kohm
NTC
Reference voltage for
UMMA
Ro = 47Kohm +/–10%
Bo = 4050 +/–3%
Page 2– 26
Issue 1 07/99
Page 27
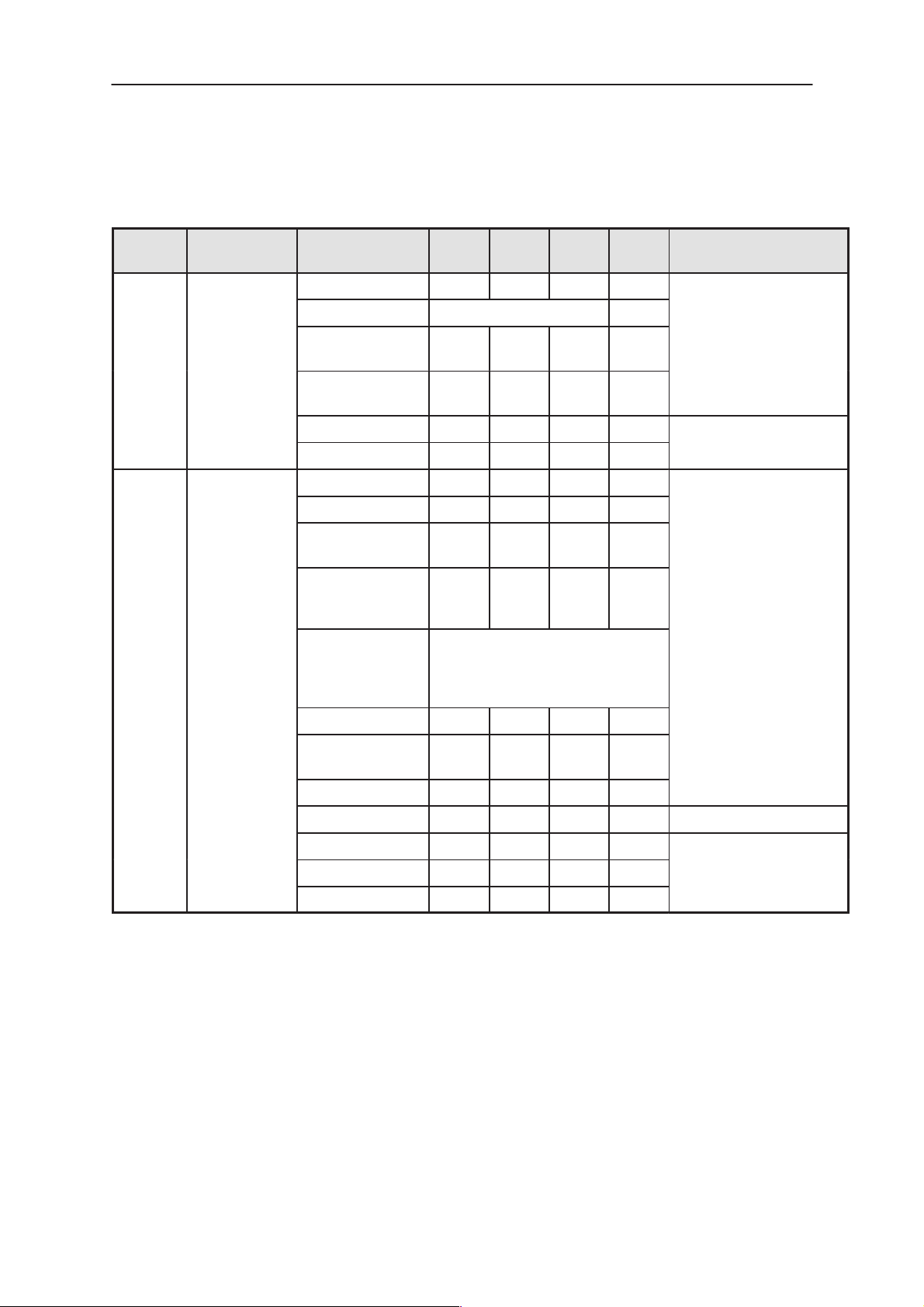
PAMS
O
VCTCXO
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 18. AC and DC Characteristics of signals between Baseband and RF (continued)
Signal
name
AFC COBBA_GJP
RXC COBBA_GJP
To
VCTCXO
SUMMA
ParameterFrom
Voltage 0.046 2.254 V
Resolution 11 bits
Load resistance
(dynamic)
Load resistance
(static)
Noise voltage 500 uVrms
Settling time 0.5 ms
Voltage Min 0.12 0.18 V
Voltage Max 2.27 2.33 V
Vout tempera-
ture dependence
Minimum
10 kohm
1 Mohm
Typi-
cal
mum
10 LSB
System Module
Automatic frequency
control signal for
Receiver gain control
FunctionUnitMaxi-
VCTCX
10...10000Hz
Source imped-
ance
active state
Source imped-
ance
power down
state
Input resistance 1 Mohm
Input capaci-
tance
Settling time 10 us
Noise level 500 uVrms 0...200 kHz
Resolution 10 bits
DNL +/–0.9 LSB
INL +/– 4 LSB
grounded
200 ohm
10 pF
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 27
Page 28
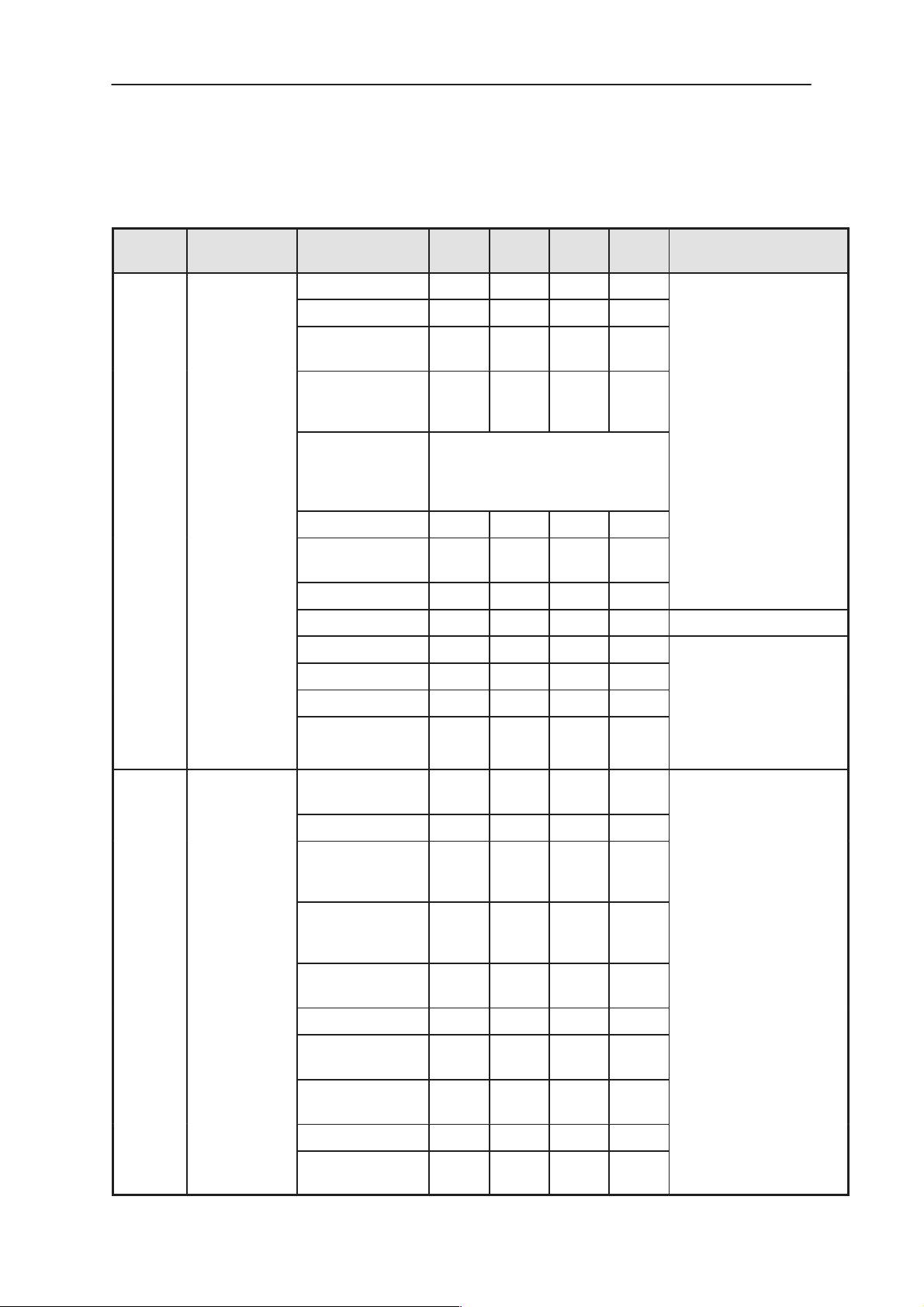
NSE–8/9
RF
System Module
Table 18. AC and DC Characteristics of signals between Baseband and RF (continued)
Technical Documentation
PAMS
Signal
name
TXC COBBA_GJP
To
SUMMA
ParameterFrom
Voltage Min 0.12 0.18 V
Voltage Max 2.27 2.33 V
Vout tempera-
ture dependence
Source imped-
ance
active state
Source imped-
ance
power down
state
Input resistance 10 kohm
Input capaci-
tance
Settling time 10 us
Noise level 500 uVrms 0...200 kHz
Resolution 10 bits
DNL +/–0.9 LSB
Minimum
Typi-
cal
mum
10 LSB
200 ohm
high Z
10 pF
FunctionUnitMaxi-
Transmitter power con-
trol
TXIN /
TXIP
COBBA_GJP
SUMMA
INL +/– 4 LSB
Timing inaccura-
cy
Differential volt-
age swing
DC level 0.784 0.8 0.816 V
Differential offset
voltage (cor-
rected)
Diff. offset volt-
age temp. de-
pendence
Source imped-
ance
Load resistance 40 kohm
Load capaci-
tance
DNL +/–
INL +/–1 LSB
1.022 1.1 1.18 Vpp
1 us
+/–
2.0
+/–
1.0
200 ohm
10 pF
0.9
mV
mV
LSB
Differential in–phase TX
Baseband signal for the
modulator
Page 2– 28
Group delay mis-
smatch
100 ns
Issue 1 07/99
Page 29
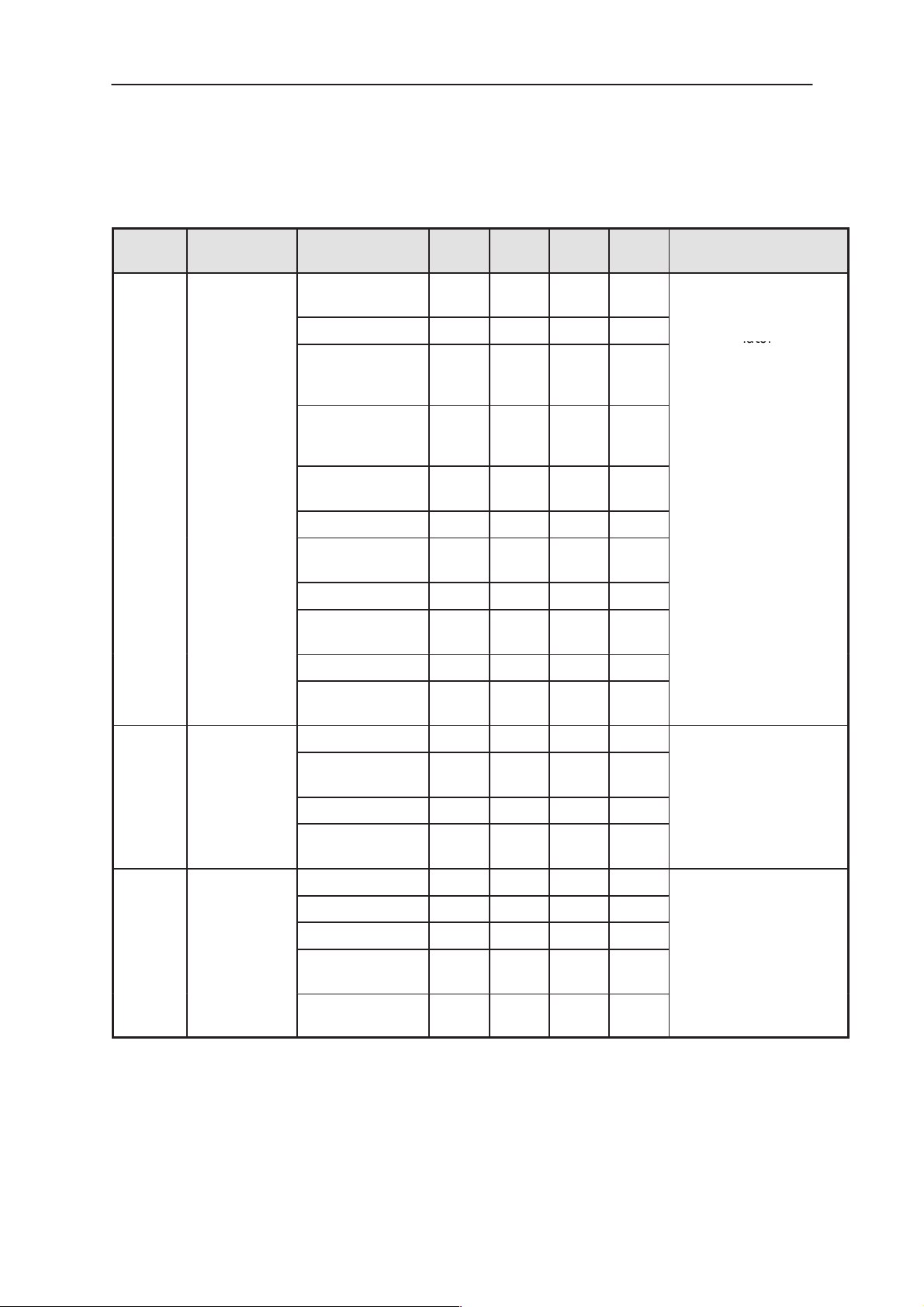
PAMS
lator
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 18. AC and DC Characteristics of signals between Baseband and RF (continued)
Signal
name
TXQN /
TXQP
To
COBBA_GJP
SUMMA
ParameterFrom
Differential volt-
age swing
DC level 0.784 0.8 0.816 V
Differential offset
voltage (cor-
rected)
Diff. offset volt-
age temp. de-
pendence
Source imped-
ance
Load resistance 40 kohm
Minimum
1.022 1.1 1.18 Vpp
Typi-
cal
mum
+/–
2.0
+/–
1.0
200 ohm
System Module
Differential quadrature
phase TX Baseband
signal for the RF modu-
mV
mV
FunctionUnitMaxi-
lator
RXIP/
RXIN
SDATA MAD2PR1
SUMMA
COBBA_GJP
SUMMA
Load capaci-
tance
Resolution 8 bits
DNL +/–
INL +/–1 LSB
Group delay mis-
smatch
Output level 50 1344 mVpp
Source imped-
ance
Load resistance 1 Mohm
Load capaci-
tance
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.5 V
Load impedance 10 kohm
Load capaci-
tance
10 pF
LSB
0.9
100 ns
tbd. ohm
tbd. pF
10 pF
Differential RX 13 MHz
signal to Baseband
PLL data
Issue 1 07/99
Data rate fre-
quency
3.25 MHz
Page 2– 29
Page 30
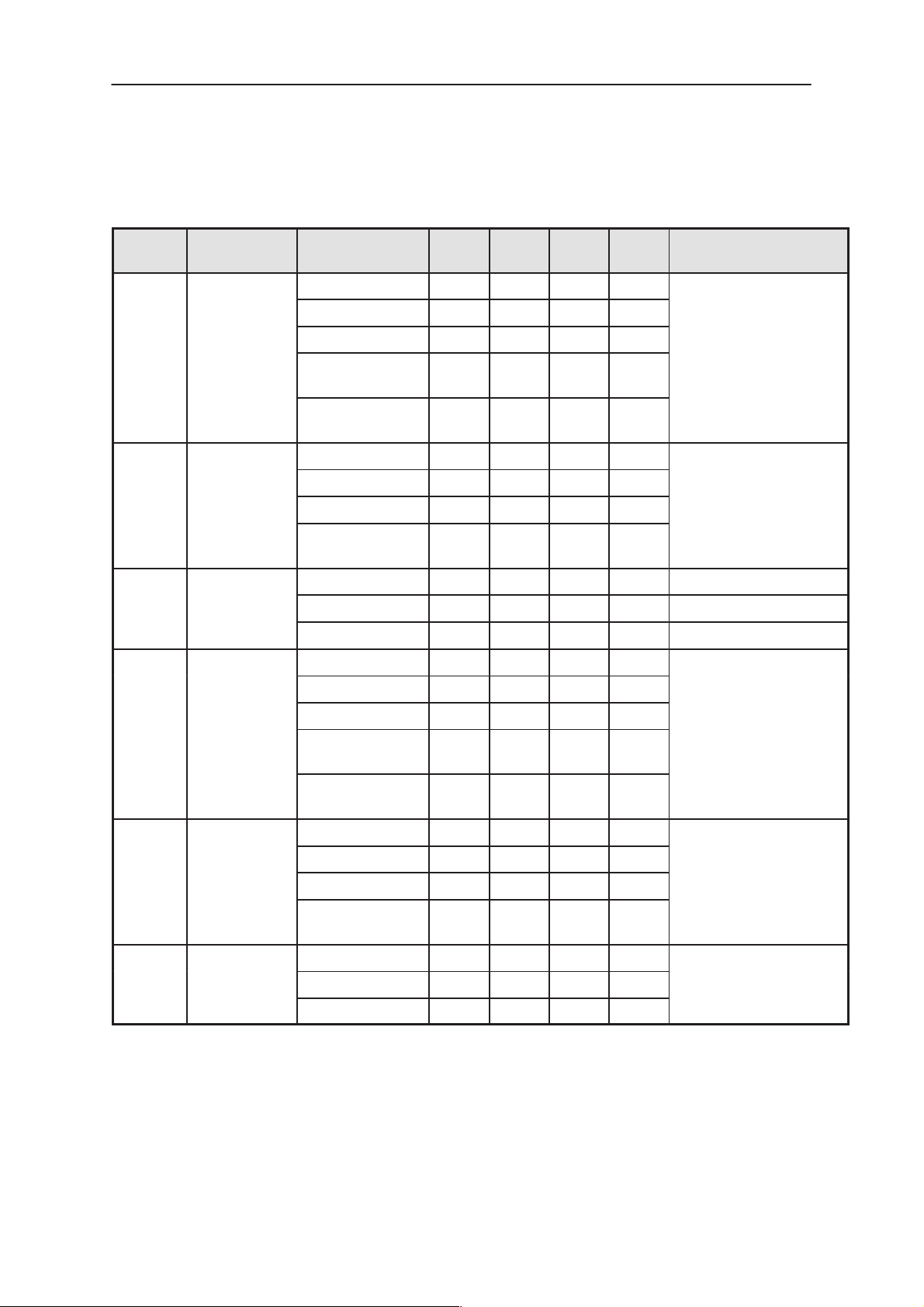
NSE–8/9
SELC
GSM1800
GSM1800
System Module
Table 18. AC and DC Characteristics of signals between Baseband and RF (continued)
Technical Documentation
PAMS
Signal
name
SCLK MAD2PR1
SENA1 MAD2PR1
FRACT
RL
TXP MAD2PR1
To
SUMMA
SUMMA
MAD2PR1
CRFU
SUMMA
ParameterFrom
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.5 V
Load impedance 10 kohm
Load capaci-
tance
Data rate fre-
quency
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.5 V
Current 50 uA
Load capaci-
tance
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V Nominal gain in LNA
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V Reduced gain in LNA
Current 0.1 mA
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.5 V
Minimum
Typi-
cal
3.25 MHz
mum
10 pF
10 pF
FunctionUnitMaxi-
PLL clock
PLL enable
Transmitter power con-
trol enable
RFC VC(TC)XO
MAD2PR1
BAND_
MAD2PR1
RFU 3
NOTE: Logic controls in low state when RF in power off.
Load Resistance 50 kohm
Load Capaci-
tance
Timing inaccura-
cy
Frequency 13 MHz
Signal amplitude 0.5 1.0 2.0 Vpp
Load resistance 10 kohm
Load capaci-
tance
Logic high ”1” 2.0 Vbb V
Logic low ”0” 0 0.4 V
Current 0.1 mA
10 pF
1 us
10 pF
High stability clock sig-
nal for the logic circuits
GSM900 DSPGenOut 4
Page 2– 30
Issue 1 07/99
Page 31

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 19. NSE–8/9 Baseband key components
Name
used in this
document
Cobba_GJP N200 Mixed signal RF– and audio Codec
MAD2PR1 D300 System ASIC with MCU and DSP
FLASH D301 FLASH ROM
RAM D302 Static RAM
EEPROM D303 EEPROM
PSCC N101 Charger switch control IC
switcher V105 DC/DC converter IC
CCONT N100 Multi functional power management IC
UISwitch N400 Integrated switch IC for UI transducer driving
Schematic
Ref.
Description
System Module
vibra
motor
LCD
Buzzer
Backlight
TX/RX SIGNALS
COBBA_GJP
UI–
Switch
BASEBAND
COBBA SUPPLY
MAD2PR1
DSP
Eprom
AUDIOLINES
RAM
RF SUPPLIES
MCU
Flash
CCONT
BB SUPPLY
core voltage
Bottom Con
Vdc_out
DC/DC–
converter
13MHz
CLK
32kHz
CLK
SLEEP CLOCK
VB
PSCC
SYSTEM CLOCK
SIM
PA SUPPLY
NiMH
BATTERY
Technical Summary
The Baseband architecture is basically similar to DCT3 GSM phones.
HD947 differs from DCT3 in the single pcb concept and the serial
interface between MAD2PR1 and COBBA_GJP and between MAD2PR1
and CCONT.
In HD947 the MCU, the system specific ASIC and the DSP are
Issue 1 07/99
Figure 7. Baseband Block Diagram
Page 2– 31
Page 32

NSE–8/9
System Module
integrated into one ASIC, called the MAD2PR1 chip, which takes care of
all the signal processing and operation controlling tasks of the phone.
The Baseband architecture supports a power saving function called ”sleep
mode”. This sleep mode shuts off the VCTCXO, which is used as system
clock source for both RF and Baseband. During the sleep mode the
system runs from a 32 kHz crystal.
The phone is waken up by a timer running from this 32 kHz clock supply.
The sleeping time is determined by some network parameters. When the
sleep mode is entered both the MCU and the DSP are in standby mode
and the normal VCTCXO clock has been switched off.
The battery voltage in HD947,called Vb, is 1.8V to 3.6V depending on the
battery charge amount. The battery voltage is up converted to one of 4
voltage levels in the range from 3.1 V to 4.2 V, called Vdc_out, by means
of a DC/DC converter. The nominal level of the four Vdc_out voltages,
depends upon the required power level of the RF. The DC/DC converter is
always operating, provided that the input supply is greater than 1.8V and
with sufficient current capability.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
The main part of the Baseband is running from 2.8V power rails, which is
supplied by a power controlling asic, CCONT.
The supply, Vcobba, for the analog audio parts, and the supply Vbb for the
main digital parts of the Baseband along with Vcore as supply possibility
for the core of MAD2PR1.
In the CCONT asic there are 7 individually controlled regulator outputs for
the RF–section. In addition there is one +5V power supply output (V5V),
also supplied to the RF.
The CCONT also contains a SIM interface, which supports both 3V and
5V SIM–cards. The SIM is supplied from a separate regulator, VSIM, in
CCONT.
A real time clock function is integrated into the CCONT, which utilizes the
same 32kHz clock supply as the sleep clock. The supply for the RTC is
taken directly from Vdc_out. Which means that when the battery is
removed the RTC may have to be set again at power up. However the
RTC will run for at least 24h after the phone has cut off due to low battery
power. Last but not least the CCONT supplies a 1.5V reference voltage,
Vref, for AD–converter usage in the Baseband and as reference voltage to
the RF.
The COBBA_GJP asic provides A/D and D/A conversion of the in–phase
and quadrature receive and transmit signal paths to the RF along with
AFC frequency control, AGC receiver gain control and TXC transmitter
power control. The remaining RF control signals are supplied by the
MAD2PR1, i.e. BAND_SEL for selection between 900 or 1800 MHz band,
FrACtrl for amplification control in the receiver front end, and tree signals
Page 2– 32
Issue 1 07/99
Page 33

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
for the control of the RF synthesizer.
The COBBA_GJP asic also provides A/D and D/A conversions of
received and transmitted audio signals to and from the internal and
external audio transducers.
System Module
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 33
Page 34

NSE–8/9
System Module
Data transmission between the COBBA_GJP and the MAD2PR1 is
implemented using two serial busses, SERRFI for RF digital data and
COBBA_GJP control. PCM for digital audio data.
Digital speech processing is handled by the MAD2PR1 asic.
Last but not least the COBBA_GJP emits the backlight control signals to
the UISWITCH IC, which drives the keyboard– and LCD backlight LEDs.
The Baseband supports 3 microphone inputs together with 2 earphone
outputs.
The mic inputs can be taken from an internal microphone, a headset
microphone or from an external active microphone signal source. The
microphone signals from different sources are connected to separate
inputs at the COBBA_GJP asic.
The output for the internal earphone is a dual ended type output capable
of driving a dynamic type speaker. Input and output signal source
selection and gain control is performed inside the COBBA_GJP asic
according to control messages from the MAD2PR1.
Keypad tones, DTMF, and other audio tones except ringing alert are
generated and encoded by the MAD2PR1 and transmitted to the
COBBA_GJP for decoding.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
MAD2PR1 generates a PWM output for the buzzer and a logical high/low
signal for driving the internal vibra motor. These control signals together
with light control are fed to the UIswitch which drives the backlight, vibra
and buzzer units.
The MAD2PR1 communicates via an IIC bus with the EEProm which
contains all user changeable data and tuning values. Additionally the
memory of HD947 is made up of a FLASH Rom and a SRAM for MCU
memory, both sharing a common address– data bus. The DSP memory is
completely integrated into the MAD2PR1 asic.
Two wire and three wire chargers can be connected to the phone. Three
wire chargers are equipped with a control input, through which the phone
gives PWM charging control signal to the charger.
The battery charging is controlled by two different PWM signals, one from
CCONT to the charger, CHARG_CTRL, and one from MAD2PR1 to
PSCC, PSCC_PWM.
The CHARG_CTRL, is constant 25%, to make the phone the master in
case it’s inserted into a DCH–9 deskstand.
The PSCC_PWM duty cycle is determined by the charging software.
A 84 by 48 dot matrix LCD is connected via a zebra connector. The
MAD2PR1 commands the display driver via a serial write only interface.
Page 2– 34
Issue 1 07/99
Page 35

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Baseband
Functional Description
There are four actions that initiate the power up procedure of the phone;
1. pressing the power on/off button
2. connecting a charger to the phone
3. power up initiated by a pulse on BTEMP (DCT3 IBI pulse)
4. power up initiated by RTC
Because the power up procedure is somewhat different depending on the
initializing action they are described below separately. The power up
procedures are described up to the point when the system control
switches from CCONT to MAD2PR1, i.e. when power up reset (PURX) is
released.
Charger Initiated Power Up Procedure
System Module
0. INITIAL CONDITIONS:
– all components except DC/DC converter and CCONT RTC powered off
– all resets active
– battery connected
1. CHARGER ADDED:
1.1 The PSCC starts charging the battery with initial current. When
the battery voltage reaches the switcher startup voltage level, the switcher
1
will start up and supply the CCONT
, which identifies the charger
presence (VCHAR)
1.2 CCONT waits until Vdc_out exceeds 3.0 V
2
1.3 CCONT powers on its digital logic and sets the PWM output
to100%
1.4 CCONT releases the reset of its digital logic after 50 us setup
time
2. CCONT RELEASES BB, VCXO and COBBA–ANALOG
3
REGULATORS:
2.1 CCONT releases SLEEPX/VXOEna signal
2.2 CCONT waits 62 ms
4
3. AFTER 62 ms DELAY CCONT RELEASES POWER UP RESET
(PURX) AND SETS CCONT_INT SIGNAL ACTIVE:
This may take some seconds depending upon the battery / switcher being able to supply
sufficient current, if the battery is almost empty,
If charger is connected to empty battery this may take some seconds
VCXO regulator is controlled by SLEEPX/VXOEna signal. The regulator for the COBBA
analog parts must follow the VCXO regulator to enable the AFC
62 ms setup time is used for VCXO settling
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 35
Page 36

NSE–8/9
System Module
3.1 MAD takes over the system control
3.2 the SLEEPX signal control switches to MAD
3.3 MAD notices the CCONT_INT active
3.4 MAD reads the CCONT interrupt register, identifies the charger
interrupt and starts to control the charging
In the end of the power up procedure initialized by adding the charger the
phone goes to ”POWER ON ACTING DEAD” state. In this state the only
indication to the user are the battery charging alert and the scrolling
battery mark in the display. In ”POWER ON ACTING DEAD” state no
actions against GSM network are done, the phone remains unknown to
the network.
Power Button Initiated Power Up Procedure
0. INITIAL CONDITIONS:
– all components except DC/DC converter and CCONT RTC are powered
off
– all resets active
– battery connected with sufficient energy for power up
– charger is not connected
5
PAMS
Technical Documentation
1. POWER BUTTON PRESSED:
1.1 CCONT identifies the PWRONX signal activation
1.2 CCONT checks that the Vdc_out exceeds 3.0 V
1.3 CCONT powers on its digital logic
1.4 CCONT releases the reset of its digital logic after 50 us setup
time
2. CCONT RELEASES VBB, VCXO and Vcobba REGULATORS:
2.1 CCONT releases SLEEPX/VXOEna signal
2.2 CCONT waits 62 ms
6
3.a. IF PWRONX ACTIVE AFTER 62 ms DELAY THEN CCONT
RELEASES POWER UP RESET (PURX):
3.1 MAD takes over the system control
3.2 the SLEEPX signal control switches to MAD
3.b. ELSE PWRONX NOT ACTIVE AFTER 62 ms THEN CCONT GOES
TO POWER OFF:
4.a IF THE KEYBOARD POWER INTERRUPT IS ACTIVE LONG
7
ENOUGH
THEN THE PHONE GOES TO POWER ON/POWER BUTTON
STATE
4.a.1 MAD system logic releases MCU reset
4.a.2 MCU serves the power button interrupt
4.a.3 MCU turns on the SIM regulator (SIMCardPwr)
If charger is connected the phone is not in power off state but in POWER ON ACTING
DEAD state and hence this power up procedure is not applicable
The 62 ms setup time is used for VCXO settling
The time is checked by MCU SW
Page 2– 36
Issue 1 07/99
Page 37

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
4.a.4 MCU turns on the keyboard and display lights
4.a.5 MCU performs PIN enquiry i.e. checks if PIN code needs to be
asked and if yes, asks it
4.b ELSE THE KEYBOARD POWER INTERRUPT IS NOT ACTIVE LONG
ENOUGH THEN THE PHONE STARTS POWER DOWN
PROCEDURE
In the end of this power up procedure the phone is in a state where it is
ready for network synchronization and communication with the user.
Real Time Clock Initiated Power Up Procedure
The RTC initiated power up procedure is used when a time alarm set in
the RTC is reached. The phone will be powered up to the POWER
ON/RTC ALARM state.
0. INITIAL CONDITIONS:
– all components except DC/DC converter and CCONT RTC powered off
– all resets active
– battery connected with sufficient energy for power up
– ALARM value set
System Module
1. REAL TIME MATCHES ALARM VALUE:
1.1 RTC logic sends power on command to CCONT analog part
1.2 CCONT checks that Vdc_out exceeds 3.0 V
1.3 CCONT powers on its digital logic
1.4 CCONT releases the reset of its digital logic after 50 us setup
time
2. CCONT RELEASES VBB, VXO and Vcobba REGULATORS:
2.1 CCONT releases SLEEPX/VXOEna signal
2.2 CCONT waits 62 ms
3. AFTER 62 ms DELAY CCONT RELEASES POWER UP RESET
(PURX) AND SETS CCONT_INT SIGNAL ACTIVE:
3.1 MAD2PR1 takes over the system control
3.2 the SLEEPX signal control switches to MAD2PR1
3.3 MAD2PR1 notices the CCONT_INT active
3.4 MADPR1 reads the CCONT interrupt register and identifies the
alarm interrupt
4. THE PHONE GOES TO POWER ON/RTC
4.1 MCU serves the alarm
4.2 MCU turns on the SIM regulator (SIMCardPwr)
4.3 MCU flashes the keyboard and display lights and sounds the
alert
4.4 The SW asks IF the alert should be delayed IF navi–key
pressed THEN go to INITIAL CONDITION ELSE the SW asks
if the phone should be
activated for network connection
4.5 MCU performs PIN enquiry i.e. checks if PIN code needs to be
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 37
Page 38

NSE–8/9
System Module
4.6 MCU starts communicating with the world
5. POWER ON/RTC:
– BB regulator active
– VCXO regulator active
– COBBA–analog regulator active
– SIM regulator active
– MAD controls the system
– power on indicated to the user
In the end of this power up procedure the phone is in ”POWER ON/RTC”
state where it will indicate the alarm to the user by beeps and/or display
information. It shall be noted that the RF part of the phone is not turned on
in this state in order to disable the transmissions not controlled by the
user. How the phone changes state from ”POWER ON/RTC” state to
normal operational mode is a matter of MCU SW and UI SW
specifications.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
asked and if yes, asks it
Power Down Schemes
There are four ways to power down the phone:
1. by pressing power on/off button,
2. by letting the CCONT watchdog expire,
3. by letting the battery voltage drop below the operation limit (either by
not charging the battery or by removing it)
4. by removing the charger (in ”POWER ON/ACTING DEAD” state
only).
Power button initiated power down procedure
0. INITIAL CONDITIONS: ANY OPERATIONAL STATE
1. POWER BUTTON PRESSED (FOR POWER OFF):
1.1 MCU SW detects that power button is pressed long enough to
start power down procedure
1.2 MAD2PR1 (MCU SW) updates and disconnects SIM, close
down network and UI connections
2.a IF CHARGER CONNECTED (CCONT_INT ACTIVE ) THEN GO TO
”POWER ON ACTING DEAD” STATE:
– BB regulator active
– VCXO regulator active
– COBBA–analog regulator active
– MAD controls the system and the charging
2.b ELSE SEND POWER OFF COMMAND TO CCONT:
2.b.1 MAD sends power off command (writes short delay to WDOG)
3. POWER DOWN THE SYSTEM
3.1 CCONT waits until the watchdog expires
Page 2– 38
Issue 1 07/99
Page 39

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
3.2 CCONT activates power up reset (PURX) signal which
disables all regulators (system control switches to CCONT at
PURX activation)
3.3 CCONT powers itself off
4. POWER OFF STATE
– all components except CCONT RTC and DC/DC converter are powered
off
– all resets active
There is a delay of 100 us between the expiring of the watchdog and
reaching the power off state. During this time CCONT does not accept
charger detection nor power on interrupts, i.e. if user generates these
interrupts during the 100 us delay they don’t have any effect and the
phone stays off.
Watchdog Initiated Power Down Procedure
System Module
Watchdog initiated power down is typically a result of a phone malfunction,
like SW errors, when the CCONT watchdog is not reset by SW. Because
of this the watchdog initiated power down can be entered in any
operational state. Watchdog can be disabled by HW means by connecting
the CCONT WDDisX pin to ground.
0. INITIAL CONDITIONS: ANY OPERATIONAL STATE
– watchdog enabled
1. CCONT WATCHDOG EXPIRES
2. POWER DOWN THE SYSTEM
2.1 CCONT activates power up reset (PURX) signal which
disables all regulators (system control switches to CCONT at
PURX activation)
2.2 CCONT powers itself off
3. POWER OFF STATE
– all components except CCONT RTC and DC/DC converter are powered
off
– all resets active
There is a delay of 100 us between the expiring of the watchdog and
reaching the power off state. During this time CCONT does not accept
charger detection nor power on interrupts, i.e. if user generates these
interrupts during the 100 us delay they don’t have any effect and the
phone stays off.
Battery Voltage Drop Initiated Power Down Procedure
When battery voltage approaches the cutoff voltage the phone will notify
the user of the situation. If the user does not charge the battery the battery
voltage will eventually drop below the operation cutoff voltage and the
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 39
Page 40

NSE–8/9
System Module
phone powers off. The power down procedure can be entered from any
operational state.
A brutal way for power down is to remove a battery when the phone is
powered on. The phone gets warning of this by LOW_BATT detection
signal which is connected directly to MAD (CARDDETX) . When MAD
realizes that battery is being removed it has 2 – 4 ms time to power down
the SIM interface in order to protect the SIM card. MAD2PR1 forces down
the SIM reset, SIM clock, SIM data and SIM power in this order.
Charger Removal Initiated Power Down Procedure
0. INITIAL CONDITIONS: POWER ON/ACTING DEAD STATE
1. CHARGER REMOVED
1.1 MAD gets CCONT_INT interrupt
1.2 MCU reads the status of the CCONT interrupt register and
notifies charger removal
1.3 MAD sends power off command (writes short delay to WDOG)
PAMS
Technical Documentation
2. CCONT WATCHDOG EXPIRES
3. POWER DOWN THE SYSTEM
3.1 CCONT activates power up reset (PURX) signal which
disables all regulators (system control switches to CCONT at
PURX activation)
3.3 CCONT powers itself off
4. POWER OFF STATE
– all components except CCONT RTC and DC/DC converter powered off
– all resets active
Page 2– 40
Issue 1 07/99
Page 41

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Clocking Concept
This section describes the main clocks in the system.
CCONT
GENSIO_0
1.083MHz
SIM CLK
3.25 MHz
32 kHz SLEEP
CLOCK
VCXO
13 MHz
SINE
WAVE
MAD2PR1
13 MHz
PLL
52 MHz
DSP
AFC
COBBA_GJP
13 MHz
520KHz PCM
8 kHz PCM SYNC
3.25 MHz SYNTE CLK
System Module
Summa
LCD DRIVER
osc
16.3KHz
Figure 8. Clocking Scheme
The system clock in the HD947 phone is 13 MHz. It is generated in the
RF VCTCXO circuit. The clock frequency is controlled by AFC which is in
COBBA_GJP. The 13 MHz sine wave signal goes to MAD2PR1 RFC block
which generates a square wave signal from the sine wave signal.
MAD2PR1 provides the clocks to its internal system components from the
13 MHz system clock. The MCU receives 13 MHz clock. For the DSP the
MAD2PR1 system logic provides an 13 MHz clock which is up converted
by the DSP PLL 52 MHz. MAD2PR1 generates also the clocks to its own
system logic blocks.
The real time clock logic consists of RTC logic in CCONT, and the 32
kHz crystal.
In normal situation the real time clock takes the power from the switcher
output. When the cutoff voltage is reached the switcher continues to
operate at least 24h, providing supply for the RTC.
In case the main battery is removed the RTC is powered by the output
capacitors on the switcher until they are drained and the RTC loses it’s
timing. The time must be set again upon power on.
CCONT generates a 32 kHz sleep clock signal which is used as a time
base during the sleep state. The 32 kHz clock signal goes to MAD2PR1
which has the sleep state counter. Sleep clock output to MAD2PR1 is
active always when the phone is powered on.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 41
Page 42

NSE–8/9
System Module
Cobba_GJP uses the 13 MHz clock,COBBACLK, coming from MAD2PR1
as a system clock. The 520KHz PCM codec master clock,PCMDClk, and
the 8 KHz PCM codec frame synchronization clock,PCMSClk, are the two
PCM codec related clocks going from COBBA_GJP to MAD2PR1 . The
master clock is used to clock the transfer of the PCM samples between
COBBA PCM codec and MAD2PR1 DSP. The frame synchronization clock
frequency is used to indicate the sample rate of the PCM samples.
A 3.25 MHz synthesizer clock, SynthClk, is used to load the synthesizers.
The clock is generated in MAD2PR1 and it goes to SUMMA in RF.
MAD2PR1 provides the SIM clock, 3.25 MHz, to the SIM card via CCONT
SIM interface.
The MAD2PR1 general purpose serial output, GenSIO_0, is a 1.083 MHz
clock which is used in the communication between MAD2PR1 – CCONT
and MAD2PR1 – LCD driver.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
The LCD driver IC is equipped with an internal free running clock oscillator
of typically 16.3 KHz used for internal logical operation and divided into
the display frame frequency of 80 Hz.
Resets and Watchdogs
This section describes the resets and the watchdogs of the system. They
are described together because they are linked together, i.e. expired of a
certain watchdog causes a certain reset to happen.
SIM RESET
CCONT
WATCHDOG
LCD DRIVER RESET
PURXCCONT
LCDRSTX
MAD2PR1
SOFT
WATCHDOG
COBBA_GJP
COBBA
RESET
Flash Rom
SYSTEM
RESET
LCD DRIVER
Page 2– 42
RAM
Figure 9. Reset Scheme
Issue 1 07/99
Page 43

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Power up reset, PURX, is the main reset of the system. It is controlled by
the CCONT digital part and is released in the power up. PURX is related
to the CCONT watchdog which in turn is the main watchdog of the
system. CCONT watchdog is controlled by the MCU SW which has to
update it at regular intervals. If the CCONT watchdog expires then PURX
goes activate and the power of the phone is turned off. The watchdog
maximum value is 64 s and the default value is 32 s.
System reset is a general purpose reset and is used to reset the phone at
any time when the phone is operating, i.e. PURX is not active. System
reset goes asynchronously active if MCU writes the software reset or if the
software watchdog expires. System reset follows also the power up reset,
i.e. system reset is active when PURX is active.
One of the DSP controlled general purpose output lines, DSPGenOut_5 is
used for COBBARESET. The reason for having a separate reset for
COBBA is to allow the DSP SW to reset COBBA without resetting other
parts of the system. Because COBBA reset is a lower level reset than
power up reset, system reset and DSP reset, it is activated also when
these resets are activated. COBBA reset is released by DSP software.
System Module
The MCU controlled general purpose I/O line, MCUGenIO_2, is used as
the LCD driver reset. MCU SW can activate and release the reset. LCD
driver is not connected to the system reset because having a separate
reset for it allows resetting the system without the user knowing it.
MAD2PR1 generates reset to SIM card, SIMIF_2. The reset goes to the
SIM card via the CCONT SIM interface block.
Power Supply
The DC/DC converter is the only unit which draws current from the 2 cell
NiMH battery pack. The battery voltage, Vb, is up converted through the
DC/DC converter to an output voltage level, Vdc_out, which is dependent
on the phone state (operating mode) and in call mode depending upon
which band and on what power level the phone is transmitting at.
The DC/DC converter feeds power directly to four parts of the system: the
CCONT, the power amplifier, the UI (buzzer, Vibra, display– and
keyboard– lights) and for a separate regulator in the RF.
The Baseband contains components that control power distribution to the
whole phone, except for the PA control in RF.
The battery consists of two NiMH cells and a polyswitch, all assembled
into the battery pack. An external charger can be used for recharging the
battery and supplying power to the phone. The charger can be either a
two wire type of charger, or a 3–wire charger, so called performance
charger.
The power management circuit PSCC provides protection against over
voltages, charger failures and pirate chargers etc. that would otherwise
cause damage to the phone.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 43
Page 44

NSE–8/9
System Module
PAMS
Technical Documentation
LCD
Vibra
VBB
Buzzer
LED’s
UISwitch
VBB
EEProm
VBB
RAM
COBBA
Vdc_out
VBB
Flash Rom
Vpp
Ctrl
VBB
VBB
VCOBBA
BASEBAND
RF SUPPLIES
CCONT
PWRONX
VBB
Ctrl
VBB
PURX
Vcon_1/2
MAD2PR1
PSCC_pwm
Charge_off
VSIM
PWM
Vdc_out
Vcore
BOTTOM CONNECTOR
RF reg.
Converter
PSCC
VIN
PA SUPPLY
SIM
DC/DC
VB
BATTERY
DC/DC Converter
The DC/DC–converter principal implementation in NSE–8/9 is shown
Figure 11. V105 is the switcher ic, TEA1210 which contains the control
logic together with the switching transistors.
R102, R105 and R112 forms the main voltage divider for the feedback
voltage to the FB pin. The switcher will adjust the output voltage in order
to achieve 1.24V at the FB pin. The two transistors V108a & b forms
together with R113 and R114 a simple 2 bit DAC, which depending upon
the control signals Vcon_1 (LSB) and Vcon_2 (MSB) from the MAD2PR1,
changes the voltage divider. V105 responds by changing Vdc_out in order
to keep the voltage on the FB pin constant.
The voltage control has been implemented to reduce Baseband loss in
idle mode and PA loss at low Tx power levels while achieving better
conversion efficiency due to lower conversion ratio. Additionally at high
power levels it is necessary to increase the output voltage to
accommodate the PA current consumption which exceeds the current
capability of the converter IC.
Figure 10. Baseband power Distribution
Page 2– 44
Issue 1 07/99
Page 45

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
The main portion of the power for the PAs during Tx burst are supplied by
the output capacitors, C109 – C113, the switcher current being limited to
1.6 A in burst, and 1.0 A in between bursts. The capacitors are recharged
in between the Tx bursts, with less current to obtain a better converter
efficiency. The output voltage is selected as low as possible, but still
sufficiently high, in order to prevent Vdc_out from dropping below the
CCONT regulation level of 3.1V, due to the current drawn during Tx burst.
Vb Vdc_out
L102
C115
Vdc_out
Battery
Vdc_out R135
R144
470u
R132R131
V109a
V109b
V1016u8H
R128
R141
R134
R109
R108
C154
MAD2PR1
LOW_BATT
LX Vout
RLimH
RLimL
SHDN
V105
ILimSel
U/D GND
FB
System Module
L103
R102R105R112
C109 C111
C110
R114
R113
470u
470u
V108b
3x
470u
C112
C113
MAD2PR1
TXP
MAD2PR1
VCON_2
R 143
V108a
Figure 11. DC/DC Converter
MAD2PR1
VCON_1
The 5 x 470uF output capacitors has been chosen to have low ESR to
achieve a compromise between output ripple, drop during Tx burst,
conversion ratio and efficiency.
The TXP from MAD2PR1 selects between two current limits, determined
by R108 and R109. TXP is active during the TX burst thus commanding a
higher current through the converter without saturating the coil L102. In
between the Tx bursts, when in call, the switcher current is lowered for
efficiency reasons, but still insuring full re–charge of the output capacitors
at the succeeding Tx burst.
The switching frequency is app. 600 KHz and in order to avoid emission in
neighboring channels, due to the PA being supplied from Vdc_out a ferrite
bead, L103 is inserted to attenuate the switching frequency.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 45
Page 46

NSE–8/9
System Module
The schottky diode, V101 is only conducting during the small time when
power FET conduction inside V105 is shifted.
The resistors R131 and R132 forms together with the transistor V109a
and R134 a circuit which will shut down the switcher when the battery
voltage reaches 1.4V in order not to drain the battery below a limit of
insufficient current capability. Additionally this circuit generates via V109b
an interrupt to the MAD2PR1 SIMCardDetX, when the battery is removed,
in order to insure the proper shutdown sequence of the SIM card.
Baseband supplies, CCONT
The heart of the Baseband power distribution is the CCONT. It includes all
the voltage regulators and feeds the power to the whole system. The
Baseband digital parts are powered from the VBB regulator which
provides 2.8V supply. The Baseband regulator is active always when the
phone is powered on. The VBB Baseband regulator feeds MAD2PR1,
memories, COBBA_GJP digital parts and the LCD driver.
Additionally the NSE–8/9 is prepared for a separate supply, Vcore for the
core logic in the future version of MAD2PR1 C07 process. The core
supply can be enabled by inserting R315 and removing R314. The SW
identifies the MAD2PR1 type (to be C07) and commands the CCONT core
regulator accordingly.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
The COBBA_GJP analog parts are powered from a dedicated 2.8V
supply, Vcobba, which can be turned off in sleep mode.
The CCONT contains a real time clock function, which internally is
powered from the switcher output. When the phone is powered off the
switcher continues to operate at it’s lowest output voltage level, thus still
supplying the RTC. When the battery SW cutoff voltage is reached the
switcher continues to operate at least 24h, providing supply for the RTC.
In case the main battery is removed the RTC is powered by the output
capacitors on the switcher until they are drained and the RTC loses it’s
timing. The time must be set again upon power on.
Table 20. Regulator activity in different operating modes
Operating mode Vref RF REG VCOB-
VBB VSIM SIMIF
BA
Power off Off Off Off Off Off Pull
down
Power on On On/Off On On On On/Off
Reset On Off
VXO On
On On Off Pull
down
Sleep On Off On On On On/Off
Page 2– 46
Issue 1 07/99
Page 47

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Vsim
System Module
There is a switched mode supply for SIM–interface. The SIM voltage is
selected via serial IO. The 5V SMR can be switched on independently of
the SIM voltage selection, but can’t be switched off when VSIM voltage
value is set to 5V.
Table 21. Electrical characteristics of VSIM and V5V
Characteristics Condition Min Typ Max Unit
Output voltage VSIM Over temperature
Over current
Output voltage V5V Over temp & cur-
rent
Output voltage V5V_2 Over temperature 5.0 6.0 V
Output current VSIM Continuous DC 30 *) mA
2.8
4.8
3.0
5.0
3.2
5.2
V
4.8 5.0 5.2 V
Output current V5V Continuous DC 30 *) mA
current consumption
VSIM
NOTE: VSIM and V5V can give together a total of 30mA.
on
sleep
200
100
330
150
uA
uA
In the next figure the principle of the SMR / VSIM–functions is shown.
CCONT
C134
V104
V5V_3
Vdc_out
V5V_4
C136
V5V_2
VSIM
5V reg
Issue 1 07/99
V5V
VSIM
Figure 12. Principle of SMR power Functions
5V
5/3V
C132C137
Page 2– 47
Page 48

NSE–8/9
System Module
Charging
At the phone end there is no difference between a plug–in charger or a
desktop charger. The DC–jack pins and bottom connector charging pads
are connected together inside the phone.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
MAD2PR1
PSCC_PWM
Vb
MAD2PR1
R140
R137
RSSI_adc
CCONT
N100
CCONTINT
TRANSCEIVER
BSI_adc
PWM_OUT
Vchar_adc
GND
Vbb
Ctim
PSCC
V105
PWM
VBat
VCH
Vchout
C122
GND
R117
C158
Figure 13. Charging Block Diagram
C126
R100
V114bV114a
R101
MAD2PR1
Charge_off
1.5A
30V
R142
V–charge_in
Charge_Ctrl
Charge_GND
CHARGER
NOT IN ACP–7 or –8
The PSCC is the charging control ASIC, basically a CHAPS known from
DCT3 but modified for operation on lower supply level and reduced for 2
cell NiMH battery only. The ASIC has the following main functions:
– controlled low drop power switch
– input transient voltage protection
– thermal self protection
– output over voltage protection (voltage limit for phone hardware)
– start–up regulator with limited charge current, Istart
– provision for soft switching (external capacitor needed), C126
– control of different charger types (different PWM frequencies 1Hz and 32Hz)
Page 2– 48
Issue 1 07/99
Page 49

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
The power switch is controlled according to PWM input via V114a.
PSCC_PWM is supplied from the MAD and is different from the external
charge control PWM signal, which is supplied by the CCONT.
When PSCC_PWM is low, the switch is turned ON and the output current,
Iout, equals the charger current , except for the internal PSCC supply
consumption.
When PSCC_PWM is high, the switch is OFF and the output current is
zero or Istart , depending upon Vb. In MAD2PR1 power on / reset mode
PSCC_PWM is default high.
When Vb is below Vstart limit and it is needed to stop any charging
current (even Istart), e.g. when detecting external audio accessory, the
MAD can disable any charge current by commanding CTIM pin low via
V114b by setting CHARG_OFF signal high. The MAD pin controlling
V114b is low during power on / reset. The CHARGE_OFF signal always
takes precedence over PSCC_PWM, i.e. Istart is zero.
System Module
Table 22. PSCC characteristics
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Vb limit @ IStart cutoff Vstart 2.33 2.43 2.52 V
Start–up regulator output current
@Vb = 0V ... Vstart
Charging current limitation Icharge 1.5 1.8 2.1 A
Vb Output voltage cutoff limit Vlim 3.32 3.46 3.6 V
Charger input voltage protection
limit
Vb threshold voltage to enter PWM
mode
PWM input logic control levels
Startup charging
Istart 150 180 210 mA
Vch 18 V
Vpwm 1.9 2.0 2.1 V
Vil 0 0.7 V
Vih 1.8 2.85 V
When a charger is connected, the PSCC is supplying a startup current,
Istart to the battery.
Istart provides initial charging to the phone with an empty battery. The
PSCC charges the battery until Vb reaches the switcher start up voltage,
where the DC/DC converter powers up at it’s lowest output voltage level.
When Vdc_out reaches 3.0 V the CCONT powers up, recognizes charger
input, releases PURX reset signal and program execution starts.
If the current consumption is too high, Vb will drop below the switcher
shutdown limit, and it shuts down. The PSCC will continue charging with
Istart. Vb increases again and the power on sequence will repeat as
described until Vb and the energy content of the battery is sufficiently high
to support a full Baseband / MCU power on by the phone.
The MCU SW controls when the charging mode is changed from
startup–charging to PWM–charging (fast charging).
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 49
Page 50

NSE–8/9
System Module
If the battery voltage reaches Vstart limit, before the SW has taken
control over the charging, the startup current is switched off by the PSCC.
Software controlled charging
PWM charging (fast charging) is controlled by the MCU software. The sw
performs a charger detection and tries to recognize the charger by a mix
of charger voltage, and charger current measurement ) via the ADC’s in
CCONT.
When the charger has been recognized as valid, the SW tries to force the
PSCC into fast charging, by pulling PSCC_PWM low, no matter how low
the battery voltage is. As soon as Vb reaches the threshold when the
internal state of the PSCC is changed to PWM mode (
responds to the PWM control and closes the internal power switch. In this
state the charging current is determined by the actual charger.
When using a 3 wire charger (ACP–9 type) the external charge control
signal, CHARG_CTRL, is supplied with a constant 32Hz with a duty cycle
of 25% high, 75% low PWM signal originated from the PWM output in
CCONT. The three wire charger is thus supplying a voltage of about 7 V.
The PSCC_PWM is controlled as for the other chargers. Two wire
chargers supplies maximum voltage according to their current capability.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Vb>Vpwm) the PSCC
The SW is capable of controlling the charge current by PSCC_PWM
signal from MAD. When PSCC_PWM is low the PSCC power switch is
closed thus max current is flowing. When PSCC_PWM is high the switch
is open, thus no current is flowing (except Istart, if Vb is below the
threshold, and the state of the CHARGE_OFF signal).
Battery over voltage protection
Vb over voltage protection is used to protect the phone against damage.
This function is also used to define the charging cutoff voltage for the
battery.
Output over voltage protection is needed also in the case if the battery is
removed when a charger is connected (or a charger is connected to the
phone before the battery ).
The power switch is immediately opened if Vb rises above the threshold
voltage VLIM. When the switch in output over voltage state has once
turned OFF, it stays OFF until the charger has been disconnected and
re–inserted.
Page 2– 50
Issue 1 07/99
Page 51

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
System Module
Baseband ADC’s
The NSE–8/9 Baseband ADC’s are configured completely different
compared to conventional DCT3 products.
Table 23. NSE–8/9 CCONT ADC Usage
Property Signal name HD947 ADC DCT3 ADC Comment
Charger Voltage V_charge_in Vchar Vchar ADC to be aligned
Battery Voltage Vb RSSI Vbat ADC to be aligned
switcher output voltage Vdc_out Vbat Not used ADC to be checked in
alignment
PSCC ouput voltage Vchout BSI Ichar Not to be checked in
alignment
Charger current N/A (BSI–RSSI)
––––––––––
Rsens
Battery Temperature BTEMP BTEMP BTEMP ADC to be checked in
Ichar charger current is as a
voltage difference over a
sense resistor
alignment
RF–temperature RF_temp VCXOTEMP VCXOTEMP ADC to be checked in
alignment
External Accessory identification
Charger V oltage
Parameter min typ max Unit Comment
Resolution 10 bits 1024 ADC output values
Conversion error 29.6 32.2 35.8 mV corresponding to +/– 2
V_charge_in range 0 16.9 V Charger voltage range
V_charge_in voltage @
ADC saturation
V_charge_in ADC reso-
lution
Vchar_adc input range 0.1 Vref V Vref =1.5V +/– 2%
Uncalibrated ADC reading @8.4V
EAD EAD EAD ADC to be checked in
alignment
Table 24. Charger voltage ADC properties
LSB
14.8 16.5 18.4 V adc reading 1023
14.5 16.1 17.9 mV/bit
min limit due to CCONT
465 521 585 For calibration in produc-
tion and service
The capacitor C146 is applied to attenuate the noise originated from the
different ground reference points and general TDMA and other noise.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 51
Page 52

NSE–8/9
System Module
Battery Voltage
Technical Documentation
The ADC is to be calibrated in production / service, with a one point
calibration at 2.7V.
Table 25. Battery voltage, ADC properties
Parameter min typ max Unit Comment
Resolution 10 bits 1024 ADC output values
Conversion error 8.6 9.4 10.2 mV corresponding to +/– 2 LSB
Vb range 0 3.6 V range given by PSCC
PAMS
Vb voltage @ ADC saturation
Vb ADC resolution 4.3 4.7 5.1 mV/bit
Vrssi_adc input range 0.1 Vref V Vref =1.5V +/– 2%
Un–calibrated ADC reading @2.7V
4.4 4.8 5.2 V ADC reading 1023
min limit due to CCONT
525 575 625
The capacitor C154, is applied to attenuate the noise originated from the
different ground reference points and general TDMA and other noise.
Battery Temperature
The battery temperature is measured with a NTC (R0=47k ± 10 % with
B = 4050 ±3 %), R127, placed on the transceiver PCB close to the battery
ground terminal,X101, which acts as a thermal conductor. The BTEMP
line has a 100k pull–up,R125, to VREF.
The MCU can calculate the battery temperature by reading the BTEMP
line DC–voltage level with the CCONT BTEMP A/D–converter.
Table 26. Temperature conversion constants
Value Reference Nominal
value
Vref [volt] N100 1.5 1.5 %
R0 [Kohm] R127 47 10%
Tref [Kelvin] 298 0
B [Kelvin] 4050 3 %
Rpu [Kohm] R125 47 5.0 %
Table 27. ADC reading and NTC resistance vs. temperature
T [C] ADC
read
–40 976 2074 5 568 124.8 50 144 16.4
–35 957 1440 10 502 96.5 55 122 13.6
–30 931 1015 15 439 75.3 60 104 11.3
R [k] T [C] ADC
read
R [k] T [C] ADC
Page 2– 52
Tolerances
read
Issue 1 07/99
R [k]
Page 53

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 27. ADC reading and NTC resistance vs. temperature
T [C]
read
–25 899 725.7 20 381 59.3 65 88 9.4
–20 860 525.7 25 327 47.0 70 75 7.9
–15 812 385.7 30 279 37.6 75 64 6.7
–10 758 286.2 35 238 30.2 80 55 5.7
–5 698 214.8 40 201 24.5 85 47 4.8
0 634 162.9 45 171 20.0 90 41 4.1
Table 28. Battery voltage, ADC properties
Parameter min typ max Unit Comment
Resolution 10 bits 1024 ADC output values
Conversion error –3.5 0 3.5
T [C]R [k]ADC
read
C
T [C]R [k]ADC
incl. comp tolerances and +/– 2
LSB,
System Module
read
between – 20 and +70 C
R [k]ADC
BTEMP voltage range 0 Vref V range given by NTC
voltage @ ADC saturation Vref V ADC reading 1023
BTEMP_adc input range 0.1 Vref V Vref =1.5V +/– 2%
min limit due to CCONT
Un–calibrated ADC reading @25 C
294 327 361
The capacitor C143, is applied to attenuate the noise originated from the
different ground reference points and general TDMA and other noise.
PSCC out voltage
Table 29. PSCC output voltage, ADC properties
Parameter min typ max Unit Comment
Resolution 10 bits 1024 ADC output values
Conversion error 8.6 9.4 10.2 mV corresponding to +/– 2 LSB
PSCC Vchout range 0 3.6 V range given by PSCC
PSCC Vchout voltage @
ADC saturation
4.4 4.8 5.2 V ADC reading 1023
PSCC Vchout ADC resolution 4.3 4.7 5.1 mV/bit
Vbsi_adc input range 0.1 Vref V Vref =1.5V +/– 2%
min limit due to CCONT
Un–calibrated ADC reading
@2.7V no charging current
525 575 625
The capacitor C162, is applied to attenuate the noise originated from the
different ground reference points and general TDMA and other noise.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 53
Page 54

NSE–8/9
System Module
Vdc_out voltage
Table 30. Switcher output voltage, ADC properties
Parameter min typ max Unit Comment
Resolution 10 bits 1024 ADC output values
Conversion error 13 mV corresponding to +/– 2 LSB
Vdc_out range 0 6.5 V range given by Vdc_out over
Technical Documentation
voltage protection
PAMS
Vdc_out voltage @ADC
saturation
Vdc_out resolution 6.4 6.5 6.6 mV/bit
Vbat_adc range 0.1 Vbat-
Un–calibrated ADC reading
6.52 6.65 6.78 V ADC reading 1023
V Vbat_max =6.65V +/– 2.0%
max
618 631 644 @ Vdc_out = 4.1V
Digital Part
The Baseband functions are controlled by the MAD2PR1 asic, which
consists of MCU, system logic and DSP, all integrated into one common
asic.
MAD2PR1 system ASIC
MAD2PR1 contains following building blocks:
– ARM RISC processor with both 16–bit instruction set (THUMB mode) and
32–bit instruction set (ARM mode)
min limit due to CCONT
– TMS320C542 DSP core with peripheral:
– BUSC (BusController for controlling accesses from ARM to API, System
– System Logic
Page 2– 54
– API (Arm Port Interface memory) for MCU–DSP communication,
DSP code down load, MCU interrupt handling vectors (in DSP
RAM) and DSP booting
– Serial port (connection to PCM)
– Timer
– DSP memory
Logic and MCU external memories, both 8– and 16–bit memories)
– CTSI (Clock, Timing, Sleep and Interrupt control)
– MCUIF (Interface to ARM via B
USC). Contains MCU BootROM
– DSPIF (Interface to DSP)
– MFI (Interface to COBBA_GJP AD/DA Converters)
– CODER (Block encoding/decoding and A51&A52 ciphering)
Issue 1 07/99
Page 55

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
– AccIF(Accessory Interface)
– SCU (Synthesizer Control Unit for controlling 2 separate synthe-
– UIF (Keyboard interface, serial control interface for COBBA_GJP
– UIF+ (roller/ slide handling)
– SIMI (SimCard interface with enhanced features)
– PUP (Parallel IO, USART)
– FLEXPOOL (DAS00308 FlexPool Specification)
– SERRFI (DAS00348 COBBA_GJP Specifications)
MAD Power Up Procedures
Because MAD2PR1 includes three functional units it is beneficial to
describe also the MAD2PR1 internal power up behavior. It can be divided
into two parts:
1. normal power up.
System Module
sizer)
PCM Codec, LCD Driver and CCONT)
2. FLASH down loading power up
MAD2PR1 Normal Power Up
0. INITIAL CONDITIONS: POWER UP RESET (PURX) IS ACTIVE
– MAD2PR1 is in RESET mode
– FLASH prommer not connected
1. POWER UP RESET (PURX) RELEASED:
1.1 MAD2PR1 releases the MCU reset (MCUResetX) and the external
system reset (ExtSysReset)
2. MCU BOOTS UP FROM SYSTEM LOGIC BOOT ROM:
2.1 MCU starts to read the boot code from system logic boot ROM
2.2 MCU checks if the FLASH prommer is connected (by studying the
status of serial synchronous clock input at MBUS line)
2.3 If prommer not connected (MBUS not LOW) then continue this
procedure,else go to MAD FLASH down loading power up procedure
2.4 MCU reads the system configuration data from FLASH memory
2.5 If system configuration data OK then continue this procedure,else
jump to 4 (system configuration data not ok).
2.6 MCU disables boot ROM and switches to read code from FLASH
memory
3. MAD2PR1 NORMAL POWER UP DONE AND MCU CONTINUES
INITIALIZATION FROM FLASH MEMORY:
4. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION DATA NOT OK:
4.1 MCU aborts all program execution and drives the FBUS–TX line low
(to indicate unsuccessful booting)
4.2 CCONT watchdog expires and the phone is turned off
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 55
Page 56

NSE–8/9
System Module
MAD FLASH down loading power up
The FLASH down loading power up procedure is similar to that of DCT2.
The only difference is that instead of external RAM the internal API RAM
may be used to store the FLASH down loading program (if the down
loading program fits into the API RAM it is stored there, if not then it is
stored to external RAM). The procedure is described below.
0. INITIAL CONDITIONS: POWER UP RESET (PURX) IS ACTIVE
– MAD2PR1 is in RESET mode
1. POWER UP RESET (PURX) RELEASED:
1.1 MAD2PR1 releases the MCU reset (MCUResetX) and the external
system reset (ExtSysReset)
2. MCU BOOTS UP FROM SYSTEM LOGIC BOOT ROM:
2.1 MCU starts to read the boot code from system logic boot ROM
2.2 MCU checks if the FLASH prommer is connected (by studying the
status of serial synchronous clock input at MBUS line)
2.3 If prommer connected (MBUS low) then continue this procedure,else
go to normal MAD2PR1 power up procedure
2.4 MAD2PR1 acknowledges the presence of the prommer by setting the
FBUS–TX line low
2.5 FLASH prommer sends the first two bytes of data to MCU which
indicate the length of the secondary boot code
2.6 MCU acknowledges the reception of the secondary boot code length
by setting the FBUS–TX line high
2.7 FLASH prommer loads the secondary boot code to API RAM using the
serial syn chronous interface (PUP USART, FBUS–RX as data line and
MBUS line as clock)
2.8 MCU acknowledges the reception of the secondary boot code by
setting the FBUS–TX line low
PAMS
Technical Documentation
3. MCU CONTINUES BOOTING FROM API BOOT CODE
3.1 MCU disables the system logic boot ROM
3.2 MCU starts to test the external RAM and sets the FBUS TX line high
3.3 If external RAM test is passed then MCU sets the FBUS TX line low, if
failed the booting is interrupted
3.4 MCU reads the system configuration data from FLASH memory (two
bytes)
3.5 MCU sends (parts of) the system configuration data to FLASH
prommer
3.6 MCU sets the FBUS TX line high to indicate that it is ready to receive
the FLASH programming SW (to either API RAM or external RAM)
3.7 FLASH prommer loads the FLASH programming SW to the RAM
4. MCU SWITCHES TO RUN THE CODE FROM THE FLASH
PROGRAMMING SW
4.1 MCU initializes itself according to the FLASH programming SW
Page 2– 56
Issue 1 07/99
Page 57

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
4.2 MCU sets the FBUS TX line low to indicate that it has successfully
received the FLASH programming SW, has initialized itself correctly and it
is ready to accept a command from FLASH prommer
After this power up procedure MCU receives commands from the FLASH
programmer and acts accordingly using the FLASH loading SW either in
the API RAM or the external RAM.
System Module
CCONT
(PurX)
MAD
(FCLK (MBUS))
MAD
(FRX (FRxData))
MAD
(FTX (FTxData))
SRAM (Chip Sel)
FLASH (Chip Sel)
CCONT
(PurX)
MAD
(FCLK (MBUS))
MAD
(FRX (FRxData))
MAD
(FTX (FTxData))
Issue 1 07/99
SRAM (Chip Sel)
FLASH (Chip Sel)
Figure 14. Flash Programming Sequence
Page 2– 57
Page 58

NSE–8/9
System Module
Battery removal
SIMCardDetX input on MAD is a threshold detector with a nominal input
switching level 0.85xVbb for a rising edge and 0.55xVbb for a falling edge.
The battery removal detection is used as a trigger to power down the SIM
card before the power is lost. V109a pulls SIMCardDetX high, telling the
MAD to power down RF, SIM and Baseband, which takes about 2ms. Vbb
is maintained for about 4ms by the energy stored in the switcher output
capacitors, thus providing a sufficient delay between battery removal
detection and supply power off.
0.850.05 Vbb
0.550.05 Vbb
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Vbb
Memories
SIMCARDDETX
S
GND
Figure 15. Sim Card DetX detection levels
IGOUT
If the battery pack is disconnect during the sleep mode, the CCONT pulls
the SIM interface lines low as there is no time to wake up the MCU.
The program code resides in an external FLASH program memory.
The DSP operates entirely from the internal MAD2PR1 memory, the DSP
code is down loaded from the external Flash via the (API ram) interface in
MAD2PR1. The MCU operates from the external Flash memory as well as
from the external RAM memory. A serial EEPROM is used for storing the
system and tuning parameters, user settings and selections etc.
Page 2– 58
Issue 1 07/99
Page 59

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
MCUWrX
ROM1SelX
MCUGenIO1
MAD2PR1
MCUGenIODa(7:0)
ExtMCUDa(7:0)
MCUGenIO0
MCUGenIO3
MCUGenIO4
MCURdX
RAMSelX
ESysResetX
System Module
MCUAD(20:0)
MCUAD(16:0)
CS
CS RPVpp
Data
Clock
RAM Flash Rom
128k x 8
SDA
SCL
WC
EEProm
WE WE
MCUDa(7:0)
MCUDa(15:8)
16K x 8
MCUAD(20:1)
OEOE
1M x 16
WP
CS
R307
Figure 16. Memory Setup
Inside MAD2PR1 the memory interfacing is controlled by the
BusController block, BusC, in the system logic. Based on signals from the
MCU core the BusC generates chip selects for the address lines, number
of wait states for memory access,and read write strobes. The
BusController controls MCU access to the internal MAD2PR1 system logic
memories
The HD947 MCU memory requirements are shown below
Table 31. HD947 Memory Requirements
Device Organiza-
tion
FLASH 1024kx16 110 1 uBGA48
SRAM 128kx8 120 1 Shrink TSOP32
EEPROM 16kx8
serial
Access
Time
ns
Wait
States
Used
Remarks
IIC SO8
ESysResetX
SRAM Memory
The MCU work memory is a static ram of size 128kx8 in a Shrink TSOP32
package. The work memory is supplied from the common Baseband VBB
voltage and the memory contents are lost when the Baseband voltage is
switched off. All retainable data should be stored into the EEPROM (or
FLASH) when the phone is powered down.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 59
Page 60

NSE–8/9
System Module
MAD2PR1 interfaces to the RAM via a parallel memory bus which
consists of 17 address lines, MCUAd(16:0) and 8 data lines, MCUDA(7:0)
both shared with the Flash memory bus. Read and write strobes and two
chip selects, one of which is the system reset.
EEPROM Memory
An EEPROM is used for a nonvolatile data memory to store the tuning
parameters and phone setup information. The short code memory for
storing user defined information is also implemented in the EEPROM. The
EEPROM size used is 16Kbytes. The memory is accessed through a
serial IIC bus and the default package is SO8.
FLASH Memory
The MCU program code resides in the program memory. The program
memory size is 16 Mbits (1024kx16bit) in the uBGA48 –package.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
The flash memory has a power down pin that is kept low,by ESysResetX,
during the power up phase of the flash to ensure that the device is
powered up in the correct state, read only. The power down pin is utilized
in the system sleep mode by connecting the ExtSysResetX to the flash
power down pin to minimize the flash power consumption during the
sleep.
MAD2PR1 interfaces to the Flash via a parallel memory bus which
consists of 20 address lines, MCUAd(20:1) and 16 data lines,
MCUDA(7:0) for LSB and MCUDA(15:8) for MSB. Read and write strobes
and two chip selects, one of which is the system reset, ExtSysResetX.
The flash is HW protected against accidental writes by, R307, pull down
on Vpp.
Flash Programming
The phone have to be connected to the flash loading adapter FLA–5 so
that supply voltage for the phone and data transmission lines can be
supplied from/to FLA–5. When FLA–5 switches supply voltage to the
phone, the program execution starts from the BOOT ROM and the MCU
investigates in the early start–up sequence if the flash prommer is
connected.
Page 2– 60
Issue 1 07/99
Page 61

PAMS
ast
fast rogramming
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 32. Flash programming, Vpp, properties
Parameter signal min typ max Unit Comment
Normal phone operation
Aftersales programming
TDS–7 & MJS–13
Production programming
”f
programming”
System Module
Vpp 0 1.0 V HW protected against
programming
Ipp
leak
Vpp 1.65 3.6 V Valid range to tell
Ipp 0.05 0.1 mA Programming current
Ibb 18 55 mA Programming current
Vpp 11.4 12.6 V
Ipp 8 22 mA
Ibb 8 15 mA Programming current
0.2 mA Max allowed leakage
current from Vpp pin
on flash for safe write
protection. Phone has
4k7 pull down resistor.
FLASH to use Vbb as
programming supply
drawn from Vpp
drawn from Vbb
Programming current
drawn from Vpp
drawn from Vbb
A 2.8V programming voltage is supplied from the Vbb, provided that Vpp
is in range. Otherwise the fast programming voltage must be supplied to
the pad, J105, in the service interface.
CCONT
GenSDIO
GenSClk
GenCCONTCSX
CCONTInt CCONTINT CCINTINT
Clk32K SLEEPCLK SLClk
PURX
VCXOPwr
SIMCardPwr
SIMCardIOC
SIMCardRstX
GenSIO_1
GenSIO_0 Data_clk
CCONTCSX DataSELX
TxPa TXP TXPWR
PURX PURX
VCXOPWR SLEEPX
SIMIF_0
SIMIF_1
SIMIF_2 SIMRST_A
SIMIF_3 SIMclkSIMCardClk
Data_in/out
SIM_PWR
SIM_I/O_C
CCONTMAD2PR1
VSIM
SIMRST_O
SIMCLK_O
SIM
Figure 17. Digital Interface – CCONT and MAD2PR1
Issue 1 07/99
SIMIF_4 Data_ASIMCardData
DATA_O
Page 2– 61
Page 62

NSE–8/9
System Module
As opposed to DCT3 only two signals are used for direct regulator control:
– VCXOPwr to control VCTCXO supply On/Off
– SIMCardPwr to turn SIM card supply on/off
All other regulators are controlled via the serial control bus. Which is
implemented with the 3 lines CCONTCSX for chip select, GenSIO_1 for
data and GenSIO_0 for 1.083MHz clock. The bus is a general purpose
bi–directional bus shared with the LCD–driver.
The CCONT ADC is controlled and measurements read out via the serial
bus. The ADC conversion is synchronized to the TXP signal which
indicates the Tx–burst.
When an event has occurred in the ccont , it creates an interrupt on
CCONTINT line to the MAD2PR1, which serves it and reads the event
register via the serial bus.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
The SIM interface is made up of 3 lines, reset, clock and data which are
fed to the SIM card via the CCONT. Additionally The SIMCardIOC signal
controls the direction of the data line, LOW data to SIM card, High data
from SIM card.
COBBA_GJP
DSPGenOut5
CobbaCLK
CobbaCSX
CobbaSD SerRFI_SD SD
Qdata SerRFI_Qdata Qdata
Idata SerRFI_Idata Idata
PCMTxData
PCMRxData
PCMDClk
PCMSClk 8KHz
Cobba reset
13MHz
SerRFI_CSX
PCM_0
PCM_3
PCM_1
PCM_2
ResetX
RFIClk
CSX
520KHz
Cobba_GJPMAD2PR1
PData(0)
PData(1)
PData(2)
PData(3)
PData(4)
n/c
UISwitchLCD_light
TP J349
KEY_Light
V202
Figure 18. Digital Interface – COBBA_GJP and MAD2PR1
Page 2– 62
Issue 1 07/99
Page 63

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
The Cobba_GJP is a mixed signal IC including the Baseband RF analog
interface and the Baseband audio PCM interface. The Cobba converts the
down link audio PCM stream from the DSP to analog signals feeding the
audio output transducers. The Coba converts the analog audio input from
the microphone devices to an uplink PCM bit stream to be feed to the
DSP for further processing. The MAD a separate pin for resetting the
Cobba.
There are two separate busses between the Cobba and the MAD2PR1:
– The SerRFI bus which is used to control the COBBA device and for trans-
ferring the data to and from the RF. The bus is implemented with 5 lines
– The PCM interface that transfers the PCM coded voice data to and from the
audio CODEC part of the Cobba. The bus contains receive– and transmit–
data, frame synchronization (8KHz) which indicates the rate of the PCM
samples, and the clock (520 KHz). The cobba is generating both clocks from
the 13MHz signal delivered from the MAD.
PData (0 – 4) are logical output ports on the Cobba, controlled by the
DSP. The MCU can control the pins by a MDI message sent to the DSP
(all inside the MAD). The pins are used to:
– interfaces to the UI Switch, with two enable signals for the keyboard and dis-
play back light drivers
System Module
Audio
– drive the Mute transistor V202 for the external audio PPH–1 Unit
– connection to a test pad J349, SW request for in field debugging possibility
The Cobba audio interface includes:
– 3 differential microphone inputs (MIC1,MIC2, MIC3). MIC1 and MIC 3 are
connected together and to the bottom connector for handsfree (MIC1) and
headset (MIC3) use. MIC2 is for the internal microphone.
– two differential audio outputs EAR for internal earpiece, and HF/HFCM for
external audio output
– MBias which are used for bias supply for the internal microphone
– Auxout (0V; 1.5V ; 2.1 V or high impedance) are used for bias supply for the
headset microphone, or control voltage for accessory identification
The audio paths and the voltage of Auxout and MBias are selected with
control bits in the audio control register inside Cobba
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 63
Page 64

NSE–8/9
System Module
Internal Audio
Microphone, uplink audio:
The internal uplink audio circuitry consists of basically 5 blocks:
PAMS
Technical Documentation
1. The microphone device:
Which converts air pressure variations to current variations. The internal microphone is placed in a well in the bottom connector part,
it’s connected to the bottom connector by means of mounting
springs for automatic assembly.
2. The microphone bias circuitry:
MBIAS from Cobba generates a 2.1V dc suppply, which is filtered by
R214 and C220 for better TDMA suppression. R215 and R216 converts the current variations created by the microphone to a voltage
variation.
3. Filtering:
The microphone signal are filtered by the second order high pass
filter (made by R219, R220, C226,C229,R230,C258,C259 and the
input impedance of the Cobba MIC2 port) to suppress low frequency
noise, especially from car environment (since the internal mic is
used for Handsfree unit PPH–1)
4. Conversion:
The Cobba GJP ASIC converts the analog audio signal to a PCM
bitstream which is supplied to the DSP for further speech processing
5. EMC protection:
The microphone unit are equipped with two internal capacitors for
removal of RF noise generated by the phones own PA via the antenna and demodulated by the FET inside the mic device. Additional
27pF capacitors are inserted to remove GSM signals coupled to the
mic wires in the PCB from the bottom connector to the Cobba input.
EDS protection are made up by V200.
Page 2– 64
Issue 1 07/99
Page 65

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Table 33. Internal uplink audio Baseband specifications
Parameter min typ max Unit Comment
Mic Bias current 100 500 uA Max supply by the cobba
Microphone sensitivity –2 42 +2 dB 0dB = 1V/Pa @ 1kHz
Internal cobba gain 18 dB set by MCU SW in cobba regis-
ter
total internal cobba gain –0.5 38 +0.5 dB 300 < f <3400 Hz
Signal level at cobba
MiC2P/N input
BB HP filter f
Internal Cobba HP filter En-
–6dB
135 Hz
abled
25 mV 300 < f <3400 Hz, to not satu-
rate the Cobba input stage with
Cobba gain (MCU value) 18 dB
below 200mV
System Module
Earphone, down link audio:
The internal down link audio circuitry consists of basically 3 blocks:
1. The cobba ASIC:
Which converts the PCM bitstream from the speech processor in
the DSP to analog signals which are feed to the earpiece.
2. The earpiece unit:
Which converts the voltage variations to air pressure variations
(sound). The low impedance (32 ohm), dynamic type internal earphone is connected to the PCB by means of mounting springs for
automatic assembly.
3. EMC suppression:
L202 and L203 prevents the RF radiated by the antenna from getting demodulated in by the earpiece in the low impedance output of
the Cobba. Additionally are added 27pF capacitors to remove GSM
signals coupled to the earpiece wires in the PCB from the cobba
output to the earpiece unit.
Table 34. Internal downlink audio Baseband specifications
Parameter min typ max Unit Comment
Earphone sensitivity –3 103 +3 dB @1mW at 1KHz
Internal cobba gain –10 dB set by MCU SW in cobba regis-
ter
total internal cobba gain –0.5 –10 +0.5 dB 300 < f <3000 Hz
Key press and user function response beeps are generated with the
earpiece.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 65
Page 66

NSE–8/9
System Module
External Audio
The external audio of NSE–8/9 is designed only for support of the Janette
Accessory program units:
– PPH–1 Carkit with and without external microphone HFM–8
– HDC–5 button headset
The PPH–1 uses Cobba input MIC1 since to output from PPH–1 is higher
there is less gain in the NSE–8/9 Baseband. HDC–5 uses MIC3, since
the headset microphone generates a weaker signal there is need for
higher amplification in the NSE–8/9 Baseband.
Uplink signal path
The uplink audio circuitry consists of basically 7 blocks:
PAMS
Technical Documentation
1. Input from the external device
1..a The HDC–5 microphone device:
Which is connected by cable directly to the bottom connector
X503. It converts air pressure variations to current variations.
1..b The PPH–1 output is a well conditioned analog voltage connected by cable directly to the bottom connector X503, if
HFM–8 is used. If HFM–8 is not used the uplink audio is handled by internal microphone of NSE–8/9
2. DC circuitry:
2..a The HDC–5 microphone bias circuitry:
AUXOUT from Cobba generates a 2.1V dc suppply, which is
filtered by R205 and C206 for better TDMA suppression.
R206, R231 and R232 converts the current variations created
by the microphone to a voltage variation.
2..b In PPH–1 conversation the DC circuitry plays no important
role. AUXOUT from Cobba generates 0V. The DC levels are
determined by the PPH–1 unit.
3. Filtering:
3..a With PPH–1 with HFM–8 the uplink signal is filtered by the first
order high pass filter (made by R217, R218, C207,C210, the
input impedance of the Cobba MIC1 port) to suppress low frequency noise, especially from car environment.
3..b With HDC–5 the uplink signal is filtered through the same
stages as 3..a with an additional HP filter (made by C208,
C213 and the input impedance of the Cobba MIC3 port) to
suppress low frequency noise, especially from car environment even further. The usage of the input impedances from
the not used Cobba stages is possible since they are biased
no matter which input is used.
Page 2– 66
Issue 1 07/99
Page 67

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
4. Conversion:
The Cobba GJP ASIC converts the analog audio signal to a PCM
bitstream which is supplied to the DSP for further speech processing. The selection between which inputs to use is handled by the
MCU through control registers inside Cobba
5. EMC protection:
The Low pass filter mad by R231, C257 and R232, C256 improves
the immunity towards high frequency signals picked up by the audio
accessory cable. C209 makes the GSM burst signal level picked up
by the cable to common mode signals on the input, which are very
well suppressed by the differential amplifier in the cobba, if it’s not
attenuated by the LP filter made by R218, C215 and R217, C216 to
suppress the remaining HF signals.
ESD protection is made by V207 and R231, R232.
6. HDC–5 HOOK detect:
The transistor V202 (pins 2,3,4) makes together with R212, R225
and R226 a simple level converter, to condition the Hook signal
(generated in the HDC–5 by shorting the mic terminal) to the valid
input range of the MAD2PR1 HookDet input. In the sw is implemented a delay in order not to generate un intended Hook signals due to
hook switch bouncing or blowing in the HDC–5 microphone. Hook
signal is not implemented in PPH–1.
System Module
7. PPH–1 mute:
Down link signal path
The external down link audio circuitry consists of basically 3 blocks:
1. The cobba ASIC:
2. The DC separation:
3. EMC suppression:
Since the pull–down in AUXOUT is app. 5Kohm when AUXOUT is
set to 0 volt V202 (pins 1,5,6) is used to pull down the dc–level
when activated by PData(4) from Cobba. This is used to signal to
the PPH–1 unit to mute it’s up– and downlink– signals.
Which converts the PCM bitstream from the speech processor in
the DSP to analog signals.
C201 and C203 separates the DC bias levels needed by the Cobba
output stage from the external audio dc–levels. R227 and R228 is
used to separate the capacitive load of the EMC filter capacitors
from the output stage of the Cobba in order not to cause instability.
L200 and L201 prevents the RF radiated by the antenna or pickled
up by the accessory cable from getting demodulated by the HDC–5
earpiece in the low impedance output of the Cobba. Together with
C235 and C236 the filter improves the immunity of the accessory
cable towards CE related test signals. Additionally are added 27pF
capacitors to remove GSM signals coupled to the wires in the PCB
from the cobba output to the bottom connector. ESD protection is
made by V207
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 67
Page 68

NSE–8/9
System Module
Audio accessory detection
When a jack is plugged into the bottom connector X503 it activates the
bottom connector switch, thus opens the connection between R200 and
R202 which will make HEADDET pin on MAD go high indicating an
interrupt to the SW. When no accessory is present the switch inside the
bottom connector X503 is closed and HEADDET is pulled low by R202.
When SW has acknowledged the interrupt it starts a sequence of
commanding the AUXOUT voltage of the Cobba to different levels while
reading the voltage at EAD (by way of the EAD ADC in CCONT. When the
PPH–1 unit is connected the sw even stops the charger current from
flowing in order not to make it offset the level measured during the
identification, due to charge gnd. being the only common dc reference.
For a full description of the audio accessory detection including detection
levels.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Page 2– 68
Issue 1 07/99
Page 69

PAMS
VIBRA_CNT
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
UI
The UISWITCH IC is an integrated switch IC for UI purposes. It includes
control switches for buzzer–, vibra– , LED– (display & keyboard) control
and two current sinks for LED’s.
UISWITCH, N400
MAD2PR1
BuzzPWM
VibraPWM
Cobba_GJP
PData(1)
PData(3) R417
Vbb ENABLE
Buzzer
Vibra
LCD_light
Key_light
BUZZ_CNT
VIBRA_CNT
LCDLED_CNT
KBDLED_CNT
LCDLED_ADJ
VBAT
BUZZER
VIBRA
Vdc_out
BUZZER
System Module
Vdc_out Vdc_out
M
VIBRA
4 LEDs
R416
6 LEDs
R415
12K
KBDLED_ADJ
R418
10K
Parameter Pin Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
CONTROL
input voltage KBDLED_CNT
Internal pull–down resistor
LCD LED ADJUSTMENT
max. 60mA sink current
KBD LED ADJUSTMENT
max. 60mA sink current
GND
Table 35. Input and output characteristics of the UISwitch IC
LCD_LED
KBD_LED
TEST
Figure 19. UI Switch & Transducers
LCDLED_CNT
BUZZ_CNT
VIBRA CNT
LCDLED_ADJ Radj. –5% 12 +5% k
LCD light current ILCD 50 mA
KBDLED_ADJ Radj. –5% 10 +5% k
Keyboard light
current
VIL 0 0.5 V
VIH 2.0 Vbb VbbmaxV
Rpd 60 100 180 k
Ikbd 60 mA
BUZZER average current
@ 50% duty cycle
@ VBAT = 3.6V
Rbuzzer (typ.) = 16
Series inductance = 0.5mH
Issue 1 07/99
BUZZER Ibuzz 110 mA
Page 2– 69
Page 70

NSE–8/9
System Module
Table 35. Input and output characteristics of the UISwitch IC (continued)
Buzzer FET switch Rdson BUZZER 1
Technical Documentation
PAMS
UnitMaxTypMinSymbolPinParameter
VIBRA nominal current
@ VBAT = 3.6V
Rvibra (typ.) = 10
VIBRA FET switch Rdson VIBRA 1
VIBRA Ivibra 120 mA
For a complete specification of the UISwitch IC.
Backlight
4 LEDs are used for LCD back lighting. They are controlled by the signal
LCD_light coming from the Cobba_GJP. When LCD_light is HIGH, lights
are ON and when LCD_light is LOW, lights are OFF. Default state for
LCDLED_CNT pin is LOW (internal pull–down resistor).
The UISWITCH has an adjustable constant current sink for the pin
LCD_LED. The current can be adjusted by means of an external resistor
connected to adjustment pin LCDLED_ADJ. The typical LCD backlight
current is 50 mA with R415 of 12k. LCD backlight current can be
reduced linearly by increasing the value of adjustment resistor in
LCDLED_ADJ line.
6 LEDs are used for keyboard back light. They are controlled by the
signal Key_light from Cobba_GJP. When Key_light is HIGH, lights are ON
and when Key_light is LOW, lights are OFF. Default state for UIswitch
KBDLED_CNT pin is LOW (internal pull–down resistor).
Buzzer
The UISWITCH has an adjustable constant current sink for the pin
KBD_LED. The current can be adjusted by means of an external resistor
connected to adjustment pin KBDLED_ADJ. The typical keyboard
backlight current is 60 mA with R418 of 10 k. Keyboard backlight
current can be reduced linearly by increasing the value of adjustment
resistor in KBDLED_ADJ line.
A buzzer is used for giving alerting tones and/or melodies as a signal of
an incoming call. The buzzer is controlled with a PWM output signal,
BUZZER from the MAD2PR1. A dynamic type of buzzer is used since the
supply voltage available can not produce the required sound pressure for
a piezo type buzzer. The alert volume can be adjusted either by changing
the pulse width causing the level to change or by changing the frequency
to utilize the resonance frequency range of the buzzer.
Each time the buzzer is activated the sw commands the DC/DC converter
output to max level to have the highest voltage swing available for the
buzzer.
Page 2– 70
Issue 1 07/99
Page 71

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
When the signal , BUZZER, is high, current runs through the buzzer, and
when it’s low no current flow. The BUZZ_CNT pin is has an internal
pull–down resistor.
UISWITCH has a low on–resistance FET switch for the buzzer (pin
BUZZER) and an internal protection diode.
Vibra, NSE–9 only
A vibra alerting device is used for giving silent signal to the user of an
incoming call. The device is controlled with by a PWM signal, VIBRA,
which is supplied by MAD2PR1. The vibra alert can be adjusted either by
changing the pulse width or by changing the pulse frequency. The vibra
device is inside the phone.
Each time the vibra is activated the sw commands the DC/DC converter
output to max level to have the highest voltage swing available for the
vibra.
System Module
LCD
When the signal , VIBRA, is high, current runs through the vibra, and
when it’s low no current flow. The VIBRA_CNT pin is has an internal
pull–down resistor.
The UISWITCH has a low on–resistance FET switch for the vibra (pin
VIBRA) and a internal protection diode.
The LCD module for NSE–8/9 consists of a 84 by 48 dot matrix display
with a driver chip on the display glass. The driver has an internal free
running clock oscillator used for the logic inside the driver as well as for
the display frame frequency. The oscillator frequency is 16.3 KHz and the
frame frequency is 80 Hz.
The display driver has an internal voltage tripler circuitry for generation of
a negative supply rail required for operation of the liquid crystal material.
Capacitor C401 is used by this voltage booster.
R420 and R421 are used for improved ESD protection, thus preventing
the display from resetting, when ESD is applied to the display frame etc.
The display is connected to the system board via a Zebra connector X400.
Besides the supply voltage, Vbb, GND and external capacitor connection,
C401, the interface consists of a 5 wire write only serial interface:
– LCDRSTX reset signal from MAD2PR1 (MCUGenIO2) which is protected
– LCDEN chip enable from MAD2PR1 (LCDCSX)
– LCDCD Command/Data signal from MAD2PR1
Issue 1 07/99
against un intended resets by R421 and R420, caused by ESD on the display frame.
Page 2– 71
Page 72

NSE–8/9
matrix col
System Module
– GenSIO_0: Serial data clock, 1.083 MHz from MAD2PR1 (GenSClk)
– GenSIO_1: Serial Data from MAD2PR1 (GenSDIO),
Data is read on the rising edge of the clock. On every eight clock pulse,
the data is transferred from the shift register and processed as 8–bit
parallel data. LCDCD is read on the rising edge of every eight clock
signal.
Keyboard
Keypad switch matrix
The keypad consists of a matrix of 16 switches, (0 – 9, #, *, Clear,
Previous (B), NEXT (Y) and SOFT–A (Navi–key) ). These are the
references on the schematics. Bold indicates the keyboard functionality,
which is determined by software.
The keypad keys are connected in a 4 by 4 matrix. The 4 columns
(outputs) are normally held logic low by the MAD2PR1. The 4 rows
(inputs) are connected to the MAD2PR1 – when any of these inputs goes
low (there are pull–ups inside the MAD2PR1) the MAD2PR1 interrupts the
MCU, which then commences scanning. This involves taking all the
columns high then taking each individual column low in turn. When a low
is received on a row input, it can be deduced, which key is pressed from
the row input number and the column output, which is currently low.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Table 36. Keyboard matrix signal levels
Name Property Min Typ Max Unit Notes
COL (3:0)
ROW (4:1)
VoL 0 Logic Low 0.5 V
VoH 2.1 Logic High Vbb V
ViL 0 Logic Low 0.6 V
ViH 2.0 Logic High Vbb V
Keyboard
umns
Keyboard
matrix rows
The keypad consists of gold flashed PCB tracks above which are placed
metal keydomes.
The ROW inputs on the MAD are protected against ESD by V301 since
rows are the outer ring of the pcb pads.
The power key, S416, is connected through R413 to the CCONT via the
line ’PWRON’ and to ’ROW0’ trough the diode V410 and R423. When
activated both lines are pulled low.
When the key is pressed, row0 will go low, but the value of row0 will not
be changed when the column outputs are set high at the start of the
scanning process. This fact uniquely identifies the key. A diode is
necessary to protect the MAD2PR1 against the pull up of ”PWRON” to
Vdc_out inside CCONT.
R423 is used for ESD suppression of discharges on the power on key,
before reaching the MAD input.
-
Page 2– 72
Issue 1 07/99
Page 73

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
RF
The RF module converts the signal received by the antenna to a
baseband signal and vice versa.
It consists of a conventional superheterodyne receiver and a transmitter
for each band and also two frequency synthesizers for the required
mixing.
The architecture contains two integrated circuits, a CRFU3_D1 and a
SUMMA. They are both BiCMOS ASICs, which is a suitable technology for
integration of RF functions.
The CFRU3 includes:
– A LNA for each band with a step AGC
– Down converters for the receiver
– Image rejection upconversion mixers for the transmitter
System Module
– A prescaler for the 2 UHF VCO
– The SUMMA includes:
– An AGC amplifier for the receiver
– A receiver mixer for the 13 MHz down conversion
– PLLs for the UHF and VHF synthesizers
– IQ–modulators for the transmitter
– A power control circuit for the transmitter
The power amplifiers (PAs) are MMIC technology (Monolithic Microwave
Integrated Circuit). They include three amplifier stages with input,
interstage and output matching.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 73
Page 74

NSE–8/9
System Module
RX
PAMS
Technical Documentation
13 MHz
VCTCXO
TXI TXQ
71 MHz
13 MHz
58 MHz
VHF
PLL
VCO
Divider System
464 MHz
UHF
PLL
VCO
116 MHz
1942–2067 MHz
IQ–Mod
232 MHz
IQ–Mod
SUMMA
232 MHz 116 MHz
187 MHz
1805–1800 MHz
Page 2– 74
116 MHz
1942–2017 MHz
f
f / 2
1992–2067 MHz
1006–1031 MHz
935–960 MHz
Figure 20. RF Frequency Plan
1710–1785 MHz
CRFU3
890–915 MHz
Issue 1 07/99
Page 75

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
DC Regulators
The transceiver has a multi function power management IC, which
contains among other functions 7 pcs of 2.8 V regulators. All regulators
can be controlled individually with 2.8 V logic directly or through a control
register. However, in the chosen configuration of the CCONT, direct
control is only used with VR1. The control register is used to switch off the
regulators when they are not in use.
The CCONT also provides a 1.5 V reference voltage for the SUMMA. This
reference voltage is used for the DACs and ADCs in the COBBA too.
The use of the regulators can be seen in the Power Distribution Diagram.
BATTERY
SWITCHER
System Module
VDC out
VCXOPWR
VR
1
VCTCXO
VSYN_2
CtrlReg1
D0
0
>=1
0
0
VRX_1 VRX_2VXO
CRFU3
LO_BUF
RX/TX/SYN
VR
2
CRFU3
RX
D1
VR
4
SUMMA
PLL’s
PA
RFReg
D3 D4 D6
VR
5
SUMMA
RX
VR
7
VDC out
VR
N702
UHF–VCO
VHF–VCO
CRFU3
SUMMA
VTX
TX
Serial
Interface
CCONT–ASIC
VR
REF
SUMMA
VREF
VCP
DATA_CLK
DATASELX
DATA_IN/OUT
V5V
SUMMA
CHARGE
PUMPS
Issue 1 07/99
Figure 21. Power Distribution Diagram
Page 2– 75
Page 76

NSE–8/9
System Module
Frequency Synthesizers
Both the UHF- and the VHF-VCO are locked with PLLs to a stable
frequency source, which is a VCTCXO-module (Voltage Controlled
Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator). The VCTCXO is running at
13 MHz and is locked to the frequency of the base station by means of an
AFC (Automatic Frequency Control).
PAMS
Technical Documentation
LO to GSM1800
LO to GSM900
Figure 22. Frequency Synthesiser– Block Diagram
The UHF PLL is common for both systems and is located in the SUMMA
except for an external UHF–VCO. The part in the SUMMA includes a
64/65 (P/P+1) prescaler, a N- and A-divider, a reference divider, a phase
detector and a charge pump for the external loop filter. The UHF–VCO is
running at 2 GHz. The UHF local oscillator signal is generated by first
dividing the UHF-VCO signal by two in the CRFU3 prescaler. After that the
signal is fed to the SUMMA prescaler. The latter prescaler is a dual
modulus divider. The output of the prescaler is fed to N- and A-divider,
which produce the input to the phase detector. The phase detector
compares this signal to the reference signal, which is derived by dividing
the output from the VCTCXO.
The output of the phase detector is connected to the charge pump, which
charges or discharges the integrator capacitor in the loop filter in
accordance with the phase difference between the measured frequency
and the reference frequency. The loop filter serves to filter the voltage
across the integrator capacitor and generates a DC voltage that controls
the frequency of UHF-VCO. The loop filter defines the step response of
the PLL (settling time) and effects the stability of the loop.
Page 2– 76
Issue 1 07/99
Page 77

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
To preserve the stability of the loop a resistor is included for phase
compensation. Other filter components are for sideband rejection.
The dividers are controlled via the serial bus. SDATA is for data, SCLK is
the serial clock for the bus and SENA1 is a latch enable, which enables
storing of new data into the dividers. The UHF-synthesizer is the channel
synthesizer, so each step equals the channel spacing (200 kHz). When
GSM900 operation is active, a 200 kHz reference frequency is used for
the phase detector. For GSM1800 operation, a 100 kHz reference
frequency has to be used.
This is because the GSM1800 UHF parts use a 2GHz LO–signal, but the
UHF synthesizer is locked to a 1GHz LO–signal, which is derived by
dividing the 2GHz LO–signal by two.
Except for the VHF–VCO the VHF PLL is located in the SUMMA. It is
common for both systems like the UHF PLL. The part in the SUMMA
includes a 16/17 (P/P+1) dual modulus prescaler, an N- and A-dividers, a
reference divider, a phase detector and a charge pump for the loop filter.
The VHF–VCO is running at 464MHz. The operation of the VHF PLL is
identical to that of the UHF PLL, except for the use of the prescaler in the
CRFU3. The used reference frequency is 333kHz.
System Module
Receiver
The receiver is a conventional dual conversion for GSM900 and triple
conversion for GSM1800. Both receivers use upper side LO injection in
the first RF mixer, after that lower side LO injection is used. Because of
this there is no need for changing I/Q phasing in baseband when receiving
band is changed between GSM1800 and GSM900.The two receiver
chains are combined in 71 MHz IF so that they use the same RX chain
from that point down to 13MHz AD converter. Because there is only used
one external antenna connector, common for both bands, a dualband
diplexer that has one common antenna input/output is used. The selection
between GSM900 and GSM1800 operation modes in the CRFU3 is done
with the band selection signal (BAND_SEL) from the MAD in baseband.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 77
Page 78

NSE–8/9
System Module
PAMS
Technical Documentation
GSM900 Front–End
The GSM900 receiver is a dual conversion linear receiver. The front–end,
which is located in the CRFU3 RF-, is activated with the band-selection
signal (BAND_SEL) set to high-state. The received RF-signal from the
antenna is fed via the diplex filter and the duplex filter to the LNA (Low
Noise Amplifier) in the CRFU3. The active parts (RF-transistor and biasing
and AGC-step circuitry) are integrated into this chip. Input and output
matching networks are external. The Gain selection is done with the
FRACTRL signal. The gain step in the LNA is activated when the RF-level
at the antenna is about -47 dBm. After the LNA, the amplified signal (with
low noise level) is fed to the bandpass filter, which is a SAW-filter (Surface
Acoustic Wave). The duplex filter and the RX interstage bandpass filters
together define how good the blocking characteristics are.
The bandpass filtered signal is then mixed down to 71 MHz, which is the
first GSM900 intermediate frequency. The first mixer is located in the
CRFU3 and upper side injection is used for the down mixing. The
integrated mixer is a double balanced Gilbert cell. It is driven balanced. All
active parts and biasing are integrated. Matching components are
external. Because it is an active mixer it also amplifies the IF-signal.
Buffering of the local signal is integrated too. The first local signal is
generated by the UHF-synthesizer.
Figure 23. Receiver Block Diagram
Page 2– 78
Issue 1 07/99
Page 79

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
GSM1800 Front–End
The GSM1800 receiver is a triple conversion linear receiver. The received
RF-signal from the antenna is fed via the diplex filter, the RX–TX switch
and the first RX SAW filter to the LNA in CRFU3. The RX–TX switch is
controlled by the band selection signal (BAND_SEL = low) and the supply
voltage for the transmitter part (VTX = low). VTX ensures that the switch
can not turn to transmit position when the transceiver is in receive mode.
The front–end in the CRFU3 is activated with band-selection signal
(BAND_SEL) set to low-state. The active parts (RF-transistor and biasing
and AGC-step circuitry) are integrated in this chip. The input and output
matching networks are external. The gain selection is done with the
FRACTRL signal. The gain step in the LNA is activated when the RF-level
at the antenna is about -47 dBm. After the LNA, the amplified signal (with
low noise level) is fed to the second RX–SAW bandpass filter. The two
RX–SAW bandpass filters together define how good the blocking
characteristics are.
The bandpass filtered signal is then mixed down to 187 MHz IF, which is
the first GSM1800 intermediate frequency. The first mixer is located in the
CRFU3 and upper side injection is used for the down mixing. The
integrated mixer is a double balanced Gilbert cell. It is driven balanced. All
active parts and biasing are integrated. Matching components are
external. Because it is an active mixer it also amplifies the IF-signal.
Buffering of the local signal is integrated too. The first local signal is
generated by the VHF-synthesizer.
System Module
There is a balanced discrete LC-bandpass filter in the output of the first
mixer which e.g. attenuates the critical spurious frequencies 161 MHz and
277 MHz and also the 151,5 MHz half-IF. It also matches the impedance
of 187MHz output to the input of the following stage. After this filter, the
187MHz IF-signal is mixed down to 71MHz IF, which is the second
GSM1800 IF. The VHF-mixer is also a double balanced Gilbert cell and is
located into the CRFU3. Lower side injection of the LO signal is used for
this down conversion.
The 116MHz LO signal comes from the SUMMA-, where it is derived by
dividing the 464MHz VHFLO signal by four. There is an external lowpass
filter for the 116MHz LO signal that attenuates the harmonics (especially
232MHz) so that the critical mixing spurious will be attenuated.
Common Receiver parts for GSM900 and GSM1800
After the down conversions in the CRFU3– the RX-signal path is common
for both systems. The 71MHz IF-signal is bandpass filtered with a
selective SAW-filter. From the output of to IF-circuit input of the SUMMA,
signal path is balanced. IF-filter provides selectivity for channels greater
than +/-200 kHz. Also it attenuates image frequency of the following mixer
and intermodulating signals. Selectivity is required in this place, because
of needed linearity and without filtering adjacent channel interferes would
be on too high signal level for the stages following.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 79
Page 80

NSE–8/9
System Module
Next stage in the receiver chain is an AGC-amplifier. It is integrated into
the SUMMA. The AGC gain control is analog. The control voltage for the
AGC is generated with a DA-converter in the COBBA in baseband. The
AGC-stage provides an accurate gain control range (min. 57 dB) for the
receiver. After the AGC-stage, the 71MHz IF-signal is mixed down to
13MHz. The needed 58MHz LO signal is generated in the SUMMA by
dividing the VHF-synthesizer output (464 MHz) by eight.
The following IF-filter is a ceramic bandpass filter. It attenuates the signals
in the adjacent channels, except for those separated +/- 200 kHz relative
to the carrier. Very little attenuation is achieved for those signals in the
filter, but they are filtered digitally by the baseband. Because of this the
RX DACs has to be so good, that there is enough dynamic range for the
faded 200 kHz interferers. The whole RX has to be able to handle signal
levels in a linear way too. After the 13 MHz filter there is a buffer for the
IF-signal, which also converts and amplifies the single–ended signal from
filter to a balanced signal for the buffer and AD-converters in the COBBA.
The Buffer in the SUMMA has a voltage gain of 36 dB and the buffer gain
setting in the COBBA is 0 dB. It is possible to set the gainstep (95 dB) in
the COBBA via the control bus, if needed.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Page 2– 80
Issue 1 07/99
Page 81

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
Transmitter
The transmitter consists of an IQ-modulator that is common for the
GSM900 and the GSM1800 chain, two image rejection upconversion
mixers, two power amplifiers and a power control loop.
System Module
Figure 24. Transmitter Block Diagram
Common Transmitter Part
The I- and Q-signals are generated by the COBBA in baseband. After the
post filtering (RC-network) they are fed into the IQ-modulator in the
SUMMA.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 81
Page 82

NSE–8/9
System Module
GSM900 Transmitter
The IQ–modulator generates a modulated TX IF-signal centered at 116
MHz, which is the VHF-synthesizer output divided by four. The
TX-amplifier in the SUMMA has two selectable gain levels. The output,
which is balanced, is set to maximum via a control register in the SUMMA.
After the SUMMA there is a bandpass LC-filter for reduction of noise and
harmonics before the signal is upconverted to the final TX-frequency. Both
the input and output of the bandpass LC–filter are balanced. The
upconversion mixer, which is located in the CRFU3, is a so–called image
rejection mixer. It is able to attenuate unwanted frequency components in
the upconverter output. The mixer type is a double balanced Gilbert cell.
The phase shifters required for image rejection are also integrated. The
local oscillator signal needed for the upconversion, is generated by the
UHF-synthesizer, but buffers for the mixer are integrated in the CRFU3.
The output of the upconverter is single–ended and requires an external
matching.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
The next stage is the TX interstage filter, which attenuates unwanted
frequency components from the upconverter further. These unwanted
component mainly originates from LO-leakage and insufficient
suppression of the image frequency in the upconversion. The interstage
filter attenuates wideband noise too. The filter is a bandpass SAW-filter.
Between the interstage filter and the GSM900 PA an attenuator is placed.
The attenuator ensures both stability of the GSM900 PA because of
konstant 50 on the PA input and the right input level.
After the attenuator, the TX-signal is fed to the input of the GSM900 PA,
which is a MMIC consisting of three amplifier stages and an interstage
matching. It has a 50 input and output impedance. The gain control is
integrated in the PA and is controlled with a power control loop circuit. The
PA has more than 35 dB power gain and the maximum output power is
approx. 35 dBm at an input level of 0 dBm. The gain control range is over
35 dB to ensure the desired power levels and power ramping up and
down. The harmonics generated by the nonlinear PA (class AB) are
filtered out with the duplexer.
After the duplexer the signal is fed to the diplexer. There is a directional
coupler connected between the PA output and the duplex filter input to
provide feedback for the power loop.
Page 2– 82
Issue 1 07/99
Page 83

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
GSM1800 Transmitter
The IQ–modulator generates a modulated TX IF-signal centered at 232
MHz, which is the VHF-synthesizer output divided by two. The
TX-amplifier in the SUMMA has two selectable gain levels. The output
(single-ended) is set to maximum via a control register in the SUMMA.
After the SUMMA there is a SAW filter for reduction of noise and
harmonics before the signal is fed for upconversion into the final
TX-frequency in the CRFU3. The input of the SAW filter is single ended
but the output is balanced. The upconversion mixer for GSM1800 is an
image rejection mixer as well as the one for GSM900. The local oscillator
signal needed in the upconversion is generated by the UHF-synthesizer.
Buffers for the mixer are integrated into the CRFU3. The output of the
upconverter is single ended and requires external matching to 50
impedance.
Then the GSM1800 TX signal passes through the first attenuator in the
GSM1800 TX chain. This attenuator ensures the right input level to the
buffer, also called pre–amplifier, which will be mentioned later.
System Module
The next stage is the first TX interstage filter, which attenuates unwanted
frequency components from the upconverter. These unwanted component
mainly originates from LO-leakage and insufficient suppression of the
image frequency in the upconversion. The interstage filter attenuates
wideband noise too. The filter is a bandpass SAW-filter.
To ensure enough power gain in the GSM1800 TX chain the TX signal
then passes through the buffer (pre amplifier). The buffer is driven into
saturation to compensate for variations in CRFU3 output level and ripple
in the first TX interstage filter and to ensure constant input level at the
GSM1800 PA.
The next stage is the second TX interstage filter, which attenuates
unwanted frequency components from the buffer. The interstage filter also
attenuates wideband noise. Both interstage filters is the same type of
bandpass SAW-filter.
Between the second interstage filter and the GSM1800 PA the second
attenuator is placed. The attenuator ensures both stability of the PA
because of konstant 50 on the PA input and the right input level.
After the second attenuator in the GSM1800 TX chain, the TX–signal is
fed into the input of the GSM1800 PA. The GSM1800 PA contains three
amplifier stages, interstage, input and output matchings. The PA has more
than 33 dB power gain and the maximum output power is approx. 33 dBm
at an input level of 0 dBm. The gain control range is over 35 dB to get the
desired power levels and power ramping up and down.
The GSM1800 transmitter has no duplexer, but a TX/RX switch instead.
This is due to space limitations.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 83
Page 84

NSE–8/9
System Module
After the TX/RX switch the signal is fed to the diplexer. The TX/RX switch
is set to transmit position with BAND_SEL = low and VTX = high. There is
a directional coupler connected between the PA output and the input of
the TX/RX switch to provide feedback for the power loop.
Transmitter Power Control for GSM900 and GSM1800
The power control circuit consists of the gain control stage of the PA, a
power detector at the PA output and an error amplifier in the SUMMA.
There is a directional coupler connected after the PA output in both
chains, but the power sensing line and detector are common for both
bands. The GSM900 feedback signal is attenuated to the same level as
the GSM1800 feedback signal. The combining of the two feedback signals
is achieved with a diplexer. A sample is taken from the forward going
power. This signal is rectified with a schottky-diode and after RC-filtering a
DC-voltage is available. The DC–voltage reflects the output power. This
power detector is linear on absolute scale, with the exception that it
saturates on very low and high power levels, i.e. it forms an S-shaped
curve.
PAMS
Technical Documentation
The detected voltage is compared in the error-amplifier in the SUMMA to
the TX power control voltage (TXC), which is generated by the
DA-converter in the COBBA. The output of the error amplifier is fed to the
gain control input of the PA. Because the gain control characteristics in the
PA are linear in absolute scale, the control loop defines a voltage loop,
when closed. The closed loop tracks the TXC-voltage. The shape of the
TXC–voltage as function of time has a raised cosine form (cos
4 - function).
This shape reduces the switching transients, when the power is pulsed up
and down.
Because the dynamic range of the detector is not wide enough to control
the power (actually RF output voltage) over the whole range, there is a
control signal named TXP (TX power enable) to work under detected
levels. The burst is enabled and set to rise with TXP until the output level
is high enough for the feedback loop to work. The loop controls the output
power via the control pin on the PA to the desired output level.
Because the feedback loop could be unstable, it is compensated with a
dominating pole. This pole decreases the gain on higher frequencies to
get the phase margins high enough.
Page 2– 84
Issue 1 07/99
Page 85

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
AGC
The purpose of the AGC-amplifier is to maintain a constant output level
from the receiver. To accomplish this, pre-monitoring is used. This
pre-monitoring is done in three phases and determines the settling time
for the RX AGC. The receiver is switched on approximately 150 s before
the burst begins and DSP measures the received signal level. The DSP
then adjusts the AGC-DAC in accordance with the measured signal level
and/or switches on/off the LNA with the front–end amplifier control line
(FRACTRL). The AGC amplifier has a 57 dB continuos controllable gain
(–17 dB to 40 dB) while the gain control of the LNA has two steps. That is
the gain in the LNA is either –16 dB or 15 dB.
The requirement for the received signal level under static conditions is that
the MS shall measure and report to the BS over the range -110 dBm to
-48 dBm. For RF levels above -48 dBm, the MS must report the same
signal level to the BS. Because of those requirements, the LNA is turned
”ON” (FRACTRL = ”0”) for received levels below -48 dBm. This leaves the
AGC in the SUMMA to adjust the gain to desired output value (56mVpp).
This is accomplished in DSP by measuring the received IQ level after the
selectivity filtering (IF-filters, Σ∆±converter and FIR-filter in DSP). For RF
levels below -94 dBm, the output level of the receiver drops dB by dB with
a level of 9 mVp-p @-110 dBm for GSM900 and 7.1 mVp-p @ -110 dBm
for GSM1800.
System Module
This strategy is chosen as a compromise between avoiding saturation
when strong interfering signals are present and not sacrificing the signal to
noise ratio. The 56 mVpp target level is set, because the RX-DAC in the
COBBA in baseband will saturate at 1.4 Vpp. This results in a headroom
of 28 dB which is sufficient for the +/- 200 kHz faded adjacent channel
(approximately 19 dB) and an extra 9 dB for pre-monitoring.
AFC function
In order to maintain the clock of the transceiver, i.e. the 13 MHz VCTCXO,
locked to the frequency of the base station an AFC (Automatic Frequency
Control) is used. The AFC reduces variations in the frequency of the
VCTCXO due to temperature drift. The AFC voltage is generated by
baseband with an 11 bit DAC in the COBBA. There is a RC-filter in the
AFC control line to reduce the noise from the converter.
The AFC voltage is obtained by means of Pure Sine Wave (PSW) slots,
which are a part of the signaling from the base station. The PSW slots are
repeated every 10 frames, meaning that there is a slot in every 46 ms.
Since changes in the VCTCXO -output frequency due to temperature
variations are relatively slow compared to the 46 ms, the transceiver has a
stable clock frequency.
Issue 1 07/99
Page 2– 85
Page 86

NSE–8/9
System Module
When the transceiver is in sleep mode and ”wakes” up to receive mode,
there is only about 5 ms for the AFC-voltage to settle. When the first burst
arrives the system clock has to be settled to +/- 0.1 ppm frequency
accuracy. The VCTCXO-module requires about 4 ms to settle into the final
frequency. The amplitude rises to maximum in about 3 ms, but because
the frequency–settling time is higher, the oscillator must be powered up
early enough to avoid frequency errors.
Interfacing
The interfacing between RF and BB is comprised of the signals stated in
the following diagrams and tables.
RX:
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Page 2– 86
Figure 25. Receiver Interface
Issue 1 07/99
Page 87

PAMS
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
7. RXI
RX, Analogue IQ signal
8. AFC
ÁÁÁÁ
9. VTX
ÁÁÁÁ
10. FraCrl
ÁÁÁÁ
11. BandSel
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁ
12. RXC
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁ
Automatic Frequency
БББББББ
Control
Voltage TX/RX
БББББББ
Front end Amplifier
БББББББ
Control
Band Select
БББББББ
БББББББ
RX control
БББББББ
БББББББ
TX:
System Module
Analogue 13MHz RX signal from SUMMA to
12bit ADC in COBBA.
Fine adjusts to 13MHz clock from Base Station.
БББББББББББББББ
11 bit DC–voltage (0 to 2.346 Volt)
Controls the switch between PCN TX and PCN
БББББББББББББББ
RX. Analogue signal (0 or 3 Volt)
Turns the LNA on and off (30dB difference).
БББББББББББББББ
Selects between GSM and PCN band inside the
БББББББББББББББ
CRFU3. Turns the correct LNA’s and Mixers on
БББББББББББББББ
and off inside the CRFU3.
Analogue control voltage between 0.12 and 2.33
volt (10bit) for the Automatic Gain Control Am-
БББББББББББББББ
plifier.
БББББББББББББББ
Issue 1 07/99
Figure 26. Transmitter Interface
Page 2– 87
Page 88

NSE–8/9
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
System Module
PAMS
Technical Documentation
1. SDATA
ÁÁÁÁ
2. SCLK
3. SENA
ÁÁÁÁ
4. TXI
ÁÁÁÁ
5. TXQ
ÁÁÁÁ
6a. TXC
6b. TXP
Synth Data
ÁÁÁÁ
Synth Clock
Synth Enable
ÁÁÁÁ
TX I–part of
ÁÁÁÁ
IQ signal
TX Q–part of
ÁÁÁÁ
IQ signal
TX control
TX control
Digital information about the conditions for the phone
such as GSM/PCN, TX/RX, selected channel (controls
ББББББББББББББББББ
divider ratio) ect.
Serial clock at 3.25MHz
Enables the serial data to be send to registers (PLL en-
ББББББББББББББББББ
able, latch enable).
I–signal to be transmitted. 8bit analogue signal at 0.8V
ББББББББББББББББББ
with a differential voltage swing of 1.1 Volt.
Q–signal to be transmitted. 8bit analogue signal at 0.8V
ББББББББББББББББББ
with a differential voltage swing of 1.1 Volt.
Controls the output burst shape. Analogue signal.
Controls the output burst.
A specification of the interface signals together with the supply voltages is
given in the above table.
Page 2– 88
Issue 1 07/99
Page 89

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
System Module
Parts Lists
System Module (0201234) GF7_17
(EDMS V 3.11)
Item Code Description Value Type
R100 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R101 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R102 1430801 Chip resistor 2.1 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R103 1825005 Chip varistor vwm14v vc30v 0805
R104 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R105 1430861 Chip resistor 110 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R106 1430812 Chip resistor 220 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R108 1430740 Chip resistor 330 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R109 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R111 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R112 1430215 Chip resistor 68 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R113 1430215 Chip resistor 68 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R114 1430848 Chip resistor 12 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R115 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R116 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R117 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R118 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R121 1430826 Chip resistor 680 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R122 1430830 Chip resistor 1.0 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R123 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R124 1430830 Chip resistor 1.0 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R125 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R126 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R127 1820037 NTC resistor 47 k 10 % 0603
R128 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R131 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R132 1430808 Chip resistor 150 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R134 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R135 1430816 Chip resistor 330 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R137 1419003 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R138 1430812 Chip resistor 220 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R139 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R140 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R141 1430812 Chip resistor 220 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R142 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R143 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
Amendment 05/00
Page 2 – 89
Page 90

NSE–8/9
PAMS
System Module
R144 1430820 Chip resistor 470 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R200 1430816 Chip resistor 330 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R202 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R205 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R206 1620031 Res network 0w06 2x1k0 j 0404
R207 1620025 Res network 0w06 2x100k j 0404
R208 1620019 Res network 0w06 2x10k j 0404
R212 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R214 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R215 1620031 Res network 0w06 2x1k0 j 0404
R216 1620103 Res network 0w06 2x22r j 0404
R217 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R218 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R219 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R220 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R223 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R225 1430215 Chip resistor 68 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R226 1430816 Chip resistor 330 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R227 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R228 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R230 1430784 Chip resistor 15 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R231 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R232 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R300 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R301 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R302 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R303 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R307 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R309 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R310 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R311 1430812 Chip resistor 220 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R312 1620017 Res network 0w06 2x100r j 0404
R313 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R315 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R317 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R318 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R319 1430826 Chip resistor 680 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R413 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R415 1430780 Chip resistor 12 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R418 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R420 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R421 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
Technical Documentation
Page 2 – 90
Amendment 05/00
Page 91

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
R422 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R423 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R424 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R500 1430772 Chip resistor 5.6 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R501 1430772 Chip resistor 5.6 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R502 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R503 1430738 Chip resistor 270 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R504 1430708 Chip resistor 18 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R505 1430738 Chip resistor 270 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R506 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R507 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R508 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R509 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R510 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R511 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R512 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R513 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R514 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R515 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R516 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R518 1820037 NTC resistor 47 k 10 % 0603
R519 1430691 Chip resistor 2.2 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R520 1430691 Chip resistor 2.2 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R521 1430691 Chip resistor 2.2 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R522 1430691 Chip resistor 2.2 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R601 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R602 1430728 Chip resistor 120 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R603 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R604 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R605 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R606 1430832 Chip resistor 2.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R607 1430738 Chip resistor 270 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R608 1430722 Chip resistor 68 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R609 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R610 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R611 1430746 Chip resistor 560 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R612 1430746 Chip resistor 560 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R614 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R619 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R700 1430746 Chip resistor 560 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R701 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R702 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
System Module
Amendment 05/00
Page 2 – 91
Page 92

NSE–8/9
PAMS
System Module
R703 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R704 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R705 1430790 Chip resistor 27 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R706 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R707 1430784 Chip resistor 15 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R708 1620019 Res network 0w06 2x10k j 0404
R709 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R710 1620019 Res network 0w06 2x10k j 0404
R711 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R712 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R713 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R714 1620019 Res network 0w06 2x10k j 0404
R715 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R716 1430740 Chip resistor 330 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R717 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R718 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R719 1430724 Chip resistor 82 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R721 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R722 1620031 Res network 0w06 2x1k0 j 0404
R724 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R725 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R726 1430784 Chip resistor 15 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R727 1430758 Chip resistor 1.5 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R728 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R729 1430790 Chip resistor 27 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R730 1430772 Chip resistor 5.6 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R731 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R732 1620103 Res network 0w06 2x22r j 0404
R733 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R734 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R735 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R736 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R737 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R741 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R742 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R743 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R745 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R765 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R766 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
C100 2312413 Ceramic cap. 220 n 20 % 50 V 1206
C101 2320779 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C102 2320779 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 16 V 0603
Technical Documentation
Page 2 – 92
Amendment 05/00
Page 93

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
C103 2320481 Ceramic cap. 5R 1 u 10 % 0603
C104 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C105 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C107 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C108 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C109 2611689 Tantalum cap. 470 u 20 % 10 V 7.3x4.3x4.1
C110 2611689 Tantalum cap. 470 u 20 % 10 V 7.3x4.3x4.1
C111 2611689 Tantalum cap. 470 u 20 % 10 V 7.3x4.3x4.1
C112 2611689 Tantalum cap. 470 u 20 % 10 V 7.3x4.3x4.1
C113 2611689 Tantalum cap. 470 u 20 % 10 V 7.3x4.3x4.1
C114 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C115 2611725 Tantalum cap. 220 u 20 % 16 V 7.3x4.3x4.1
C116 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C117 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C118 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C119 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C122 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C123 2320779 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C124 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C125 2312211 Ceramic cap. 3.3 u 10 % 0805
C126 2320131 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C127 2320538 Ceramic cap. 12 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C128 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C129 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C130 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C131 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C132 2320779 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C133 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C134 2312403 Ceramic cap. 2.2 u 10 % 10 V 1206
C135 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C136 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C137 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C138 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C139 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C140 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C141 2320131 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C142 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C143 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C144 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C145 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C146 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C147 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
System Module
Amendment 05/00
Page 2 – 93
Page 94

NSE–8/9
PAMS
System Module
C148 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C149 2320915 Ceramic cap. 25 V 0402
C150 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C151 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C152 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C153 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C154 2320783 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C155 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C156 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C158 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C162 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C163 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C165 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C166 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C167 2320779 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C168 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C169 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C201 2610205 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 4 V 2.0x1.3x1.2
C202 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C203 2610205 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 4 V 2.0x1.3x1.2
C204 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C205 2320783 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C206 2610205 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 4 V 2.0x1.3x1.2
C207 2320783 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C208 2320783 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C209 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C210 2320783 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C213 2320783 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C215 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C216 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C218 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C219 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C220 2610205 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 4 V 2.0x1.3x1.2
C221 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C222 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C223 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C224 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C225 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C226 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C227 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C229 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C232 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
Technical Documentation
Page 2 – 94
Amendment 05/00
Page 95

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
C233 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C234 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C235 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C236 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C242 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C243 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C244 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C247 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C248 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C249 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C250 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C251 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C256 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C257 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C258 2320783 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C259 2320783 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C301 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C304 2309570 Ceramic cap. Y5 V 1206
C305 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C306 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C307 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C313 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C314 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C316 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C317 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C400 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C401 2312410 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 16 V 1206
C402 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C500 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C501 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C503 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C504 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C506 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C507 2320538 Ceramic cap. 12 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C508 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C510 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C511 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C512 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C513 2320538 Ceramic cap. 12 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C514 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C515 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C516 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
System Module
Amendment 05/00
Page 2 – 95
Page 96

NSE–8/9
PAMS
System Module
C519 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C521 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C522 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C523 2320538 Ceramic cap. 12 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C524 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C525 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C526 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C600 2320518 Ceramic cap. 1.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C601 2320540 Ceramic cap. 15 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C602 2320530 Ceramic cap. 5.6 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C603 2320540 Ceramic cap. 15 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C604 2320550 Ceramic cap. 39 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C605 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C606 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C607 2320538 Ceramic cap. 12 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C608 2320520 Ceramic cap. 2.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C609 2320522 Ceramic cap. 2.7 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C611 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C612 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C613 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C615 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C616 2320550 Ceramic cap. 39 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C617 2320556 Ceramic cap. 68 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C618 2320556 Ceramic cap. 68 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C619 2320524 Ceramic cap. 3.3 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C621 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C622 2320564 Ceramic cap. 150 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C623 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C624 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C625 2320805 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 10 V 0402
C626 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C627 2320518 Ceramic cap. 1.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C629 2320518 Ceramic cap. 1.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C631 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C632 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C633 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C634 2320526 Ceramic cap. 3.9 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C635 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C636 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C637 2320532 Ceramic cap. 6.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C638 2320518 Ceramic cap. 1.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C639 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
Technical Documentation
Page 2 – 96
Amendment 05/00
Page 97

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
C640 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C641 2320550 Ceramic cap. 39 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C642 2320532 Ceramic cap. 6.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C643 2320518 Ceramic cap. 1.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C645 2320564 Ceramic cap. 150 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C646 2320580 Ceramic cap. 680 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C647 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C648 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C649 2320532 Ceramic cap. 6.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C700 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C701 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C702 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C703 2320530 Ceramic cap. 5.6 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C704 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C705 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C706 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C707 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C708 2320556 Ceramic cap. 68 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C709 2320556 Ceramic cap. 68 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C710 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C712 2320530 Ceramic cap. 5.6 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C713 2320568 Ceramic cap. 220 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C714 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C715 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C716 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C717 2320526 Ceramic cap. 3.9 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C718 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C719 2320568 Ceramic cap. 220 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C720 2320562 Ceramic cap. 120 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C721 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C722 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C723 2320550 Ceramic cap. 39 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C724 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C725 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C726 2320538 Ceramic cap. 12 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C727 2320538 Ceramic cap. 12 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C728 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C729 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C730 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C731 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C732 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C733 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
System Module
Amendment 05/00
Page 2 – 97
Page 98

NSE–8/9
PAMS
System Module
C734 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C735 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C736 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C737 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C738 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C739 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C740 2310209 Ceramic cap. 2.2 n 5 % 50 V 1206
C741 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C742 2312211 Ceramic cap. 3.3 u 10 % 0805
C743 2320524 Ceramic cap. 3.3 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C744 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C745 2320524 Ceramic cap. 3.3 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C746 2320570 Ceramic cap. 270 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C747 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C748 2320091 Ceramic cap. 2.2 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C749 2320516 Ceramic cap. 1.5 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C750 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C751 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C752 2320564 Ceramic cap. 150 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C753 2320564 Ceramic cap. 150 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C754 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C755 2320564 Ceramic cap. 150 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C756 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C757 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C760 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C761 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C762 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
L100 3203705 Ferrite bead 0.015r 42r/100m 0805
L101 3203705 Ferrite bead 0.015r 42r/100m 0805
L102 3640477 Choke 6.– u3A 7.2x7.2
L103 3203717 Ferrite bead 60r/100mhz 6a smd
L105 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603
L106 3203709 Ferrite bead 0.5r 120r/100m 0402
L200 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603
L201 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603
L202 3203723 Ferrite bead 0r35 68r/100mhz 0603
L203 3203723 Ferrite bead 0r35 68r/100mhz 0603
L500 4551005 Dir.coupler 897.5+–17.5mhz 2x1.4
L502 3645185 Chip coil 10.Q n5 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L503 4551007 Dir.coupler 1747.5+–37.5mhz 2x1.4
L505 3203705 Ferrite bead 0.015r 42r/100m 0805
L506 3203705 Ferrite bead 0.015r 42r/100m 0805
Technical Documentation
Page 2 – 98
Amendment 05/00
Page 99

PAMS
NSE–8/9
Technical Documentation
L600 3643037 Chip coil 180 n 5 % Q=35/100 MHz 0805
L601 3643037 Chip coil 180 n 5 % Q=35/100 MHz 0805
L602 3645005 Chip coil 15 n 10 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L603 3645009 Chip coil 33 n 5 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L604 3645035 Chip coil 47.Q n 5 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L605 3645017 Chip coil 5. Q n 10 % Q=10/100 MHz 0603
L606 3645193 Chip coil 18.Q n 5 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L607 3645181 Chip coil 3. Q n 10 % Q=10/100 MHz 0603
L608 3645121 Chip coil 6. Q n 5 % Q=32/800M 0603
L609 3645151 Chip coil 100 n 5 % Q=3/800M 0603
L610 3645151 Chip coil 100 n 5 % Q=3/800M 0603
L611 3645017 Chip coil 5. Q n 10 % Q=10/100 MHz 0603
L612 3645179 Chip coil 2.–0 n Q=8/100M 0603
L613 3645181 Chip coil 3. Q n 10 % Q=10/100 MHz 0603
L614 3645229 Chip coil 120 n 5 % Q=32/150 MHz 0603
L615 3203709 Ferrite bead 0.5r 120r/100m 0402
L616 3646055 Chip coil 8. Q n 5 % Q=28/800 MHz 0402
L617 3645131 Chip coil 8. Q n 5 % Q=8/100M 0603
L618 3645035 Chip coil 47.Q n 5 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L620 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603
L700 3645163 Chip coil 22.Q n 10 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L701 3645031 Chip coil 330 n 10 % Q=20/25 MHz 0805
L702 3641601 Chip coil 150 n 2 % Q=35/100 MHz 0805
L703 3641622 Chip coil 220 n 5 % Q=30/100 MHz 0805
L704 3641622 Chip coil 220 n 5 % Q=30/100 MHz 0805
L705 3645161 Chip coil 150 n 5 % Q=14/100 MHz 0603
L707 3645029 Chip coil 1. Q u 10 % Q=45/10 MHz 0805
L708 3641541 Chip coil 47.Q n 2 % Q=40/200 MHz 0805
L709 3645195 Chip coil 82.Q n 5 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L710 3203709 Ferrite bead 0.5r 120r/100m 0402
B100 4510237 Crystal 32.768 k +–20PPM 12.5PF
B400 514R029 Buzzer 95db 2670hz 4.0v
G700 4350149 Vco 1942–2067mhz 2.8v 10ma
G701 4510217 VCTCXO 13.000 M +–5PPM 2.8V
G702 4350155 Vco 464mhz 2.8v 7ma
F100 5119019 SM, fuse f 1.5a 32v
Z500 4512113 Dupl 890–915/935–960mhz
Z501 4550073 Cer filt 1842.5+–37.5mhz
Z502 4511087 Saw filter 1747.5+–37.5 M
Z503 4550071 Dipl 890–960/1710–1880mhz
Z504 4512097 Ant.sw+filt 1747.5/1842.5
Z505 4550071 Dipl 890–960/1710–1880mhz
System Module
Amendment 05/00
Page 2 – 99
Page 100

NSE–8/9
PAMS
System Module
Z600 4511097 Saw filter 947.5+–12.5 M
Z601 4511015 Saw filter 902.5+–12.5 M/3.8DB
Z602 4511103 Saw filter 1842.5+–37.5 M/3DB
Z603 4511087 Saw filter 1747.5+–37.5 M
Z700 4511109 Saw filter 71+–0.09 M
Z701 4510009 Cer.filt 13+–0.09mhz
Z702 4511085 Saw filter 232+–0.5 M/3DB
T600 3640413 Transf balun 1.8ghz+/–100mhz
V101 4110065 Schottky diode SS1220V1 A SMA
V103 4210215 TransistorMMBT589 pnp 30V 1 A SOT23
V104 4110067 Schottky diode MBR0520L 20V 0.5 A SOD123
V105 4340669 Tea1210 dc/dc conv 1.5a
V108 4219929 Transistor x 22+4X10K npn UMV SOT363
V109 4219904 Transistor x 22 UMX1 npn 40V SOT363
V112 4113651 Trans. supr.QUAD 6V SOT23–5
V200 4113651 Trans. supr.QUAD 6V SOT23–5
V202 4219904 Transistor x 22 UMX1 npn 40 V SOT363
V207 4113651 Trans. supr.QUAD 6V SOT23–5
V301 4113671 Tvs quad 6v1 esda6v1w5
V400 4864461 Led Green 0603
V401 4864461 Led Green 0603
V402 4864461 Led Green 0603
V403 4864461 Led Green 0603
V404 4864461 Led Green 0603
V405 4864461 Led Green 0603
V406 4864461 Led Green 0603
V409 4864461 Led Green 0603
V410 4110601 Diode FAST SOD323
V412 4864461 Led Green 0603
V413 4864461 Led Green 0603
V500 4110079 Sch. diode x 2HSMS282C 15V SOT323
V702 4210100 TransistorBC848W npn 30V SOT323
D300 4370489 Mad2pr1 v5 f721558 33C10 UBGA144
D301 4340585 IC, flash mem.UBGA48
D302 4340397 IC, SRAM STSOP3
D303 4340357 IC, EEPROM SO8
D700 4340451 IC, 1xinv 1input 1v sot3 TC7SL04FU
N100 4370393 Ccont2h dct3 bb asic
N101 4370581 Pscc u463v11g36t
N114 4219941 Transistor x 2
N200 4370575 Cobba_gjp v3.1
N400 4370433 Uiswitch asic
Technical Documentation
Page 2 – 100
Amendment 05/00
 Loading...
Loading...