Page 1

CCS Technical Documentation
RH-3 Series Transceivers
System Module
Issue 1 06/2003 Confidential Nokia Corporation
Page 2

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
Page 2 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 3

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
Contents
Page No
Transceiver RH-3/RH-3P/RH-3DNG............................................................................ 5
Introduction ..................................................................................................................5
Operational Modes .......................................................................................................5
Engine Module .............................................................................................................7
Environmental Specifications ................................................................................... 7
Temperature Conditions............................................................................................ 7
Baseband Module ........................................................................................................7
UEM.......................................................................................................................... 8
BB-RF Interface Connections ....................................................................................10
UPP.......................................................................................................................... 12
Flash Memory ......................................................................................................... 13
User Interface Hardware ............................................................................................13
LCD......................................................................................................................... 13
Keyboard................................................................................................................. 14
Lights....................................................................................................................... 14
Vibra........................................................................................................................ 15
Audio Hardware .........................................................................................................15
Earpiece................................................................................................................... 15
Microphone ............................................................................................................. 15
Buzzer...................................................................................................................... 16
Battery ........................................................................................................................16
Phone Battery.......................................................................................................... 16
Battery Connector ................................................................................................... 17
Accessories Interface .................................................................................................17
System Connector ................................................................................................... 17
Charger IF ............................................................................................................... 21
Test Interfaces ............................................................................................................21
Production Test Pattern........................................................................................... 21
General Information About Testing........................................................................ 23
RF Module .................................................................................................................24
Requirements........................................................................................................... 24
Temperature Conditions.......................................................................................... 24
Main Technical Characteristics............................................................................... 24
Antenna ................................................................................................................... 24
Transmitter.............................................................................................................. 25
Synthesizer.............................................................................................................. 26
Receiver................................................................................................................... 28
GPS Engine.................................................................................................................. 29
Introduction ................................................................................................................29
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 3
Page 4

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
Page 4 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 5

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
Transceiver RH-3/RH-3P/RH-3DNG
Introduction
The current RH-3 family includes Model 2285 (RH-3), Model 2270 (RH-3P), and
Model 2275 (RH-3DNG).
Model 2285 is a CDMA dual-mode engine (1900/800 MHz CDMA), supporting the CDMA
1XRTT Standard Air Interface. In addition, Model 2285 includes a built-in GPS engine
(GE) for E-911 emergency services.
Model 2270 is a PCS single-band CDMA 1900 engine, including a built-in GPS engine
(GE) for E-911 emergency services.
Model 2275 is a dual-band (PCS and Cell) engine. No GPS support is provided.
Note: The RH-3 family does NOT support AMPS.
The RH-3 family uses the following antennas:
• Planar Internal “F” Antenna (PIFA) — Models 2285, 2270, 2275
• external, extendable “whip” — Models 2285, 2270, 2275
• Global Positioning System (GPS) — Models 2285 and 2270 only
RH-3 features include an internal vibra, high-resolution display (96x65 pixels), a 2.5 mm
Universal headset connector with TTY/TDD support, GPS technology (Model 2285 and
2270), T9 predictive text input, and voice dialing, etc.
Operational Modes
There are several different operational modes: Modes have different states controlled by
the cellular SW. Some examples are: Idle State (on ACCH), Camping (on DCCH), Scanning, Conversation, No Service Power Save (NSPS) previously OOR = Out of Range.
In the power-off mode, only the circuits needed for power-up are supplied.
In sleep mode, circuits are powered down and only the 32kHz sleep clock is running. In
slotted mode or idle mode (a combination of sleep mode and receive mode), some circuits will turn on some of the time during the wake-up slot to receive paging messaging
from the base station.
In the active mode, all the circuits are supplied with power, although some parts might
be in idle state part of the time.
The charge mode is effective in parallel with all previous modes. The charge mode itself
consists of two different states, (i.e., the fast charge and the maintenance mode).
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 5
Page 6
RH-3
G
P
S
_
I
N
T
_
U
C
L
K
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
The local mode is used for alignment and testing.
G
P
S
T
X
S
R
X
G
P
Timestamp
3
4
4
JTAG
STIBus
397
FlsCtrl
16
8
UPP8M
11
3
ExtAdDa[15:0]
ExtAd[23:16]
Flash
KeyB[10:0]
LCDCtrl
VIO
Keypad
PwrOnX
KLight/DLight/CalLED
Charger
M
X
C
I
X
E
A
R
FBus
MBus
Card
connector
Tomahawk
2 2
Headset
connector
TX_GATE
TX RF AGC PDM
TX IF AGC PDM
RX IF AGC PDM
VCore
k
l
v
t
n
C
a
n
X
o
s
v
I
u
B
DBus
C
SleepClk
Vibra
Microphone
Buzzer
Earpiece
332
2
Buffered 19.2 MHz
3
RFBus
2
D0-3
VR1A/B to VR7
AFC_DAC
PWR_OUT
19.2MHz
VCTCXO
D
n
R
C
x
M
o
o
U
i
u
E
C
d
P
A
RxIQD
TxIQD
U
F
u
R
A
2
2
UEM
& IQ Signals
Regulated supplies
4
4
VBat
BSI
TxIQ
RxIQ
O
I
V
FBus
MBus
SIMIF
VCore
SleepX
3
32 Khz
2
2
OSC1
OSC2
p
m
e
T
B
Iref1/2
Vref1/2
2.8-4.2v
LCD/
3LS2
2
2
2
4
SIM
4
Falcon Dual Band CDMA + GPS
VR7
VR3
PA_TEMP
VIO
SAW
PCS RF
P_DET
DET_ref
Tx_gate
PATemp
Vdc-dc
SPDT
Shamu
PCS PA
VHF PLL
UHF PLL
VHF VCO
JEDI_B
Det_Buffer
Upconverter, Driver
CELL/PCS: Modulator,
TX VHF LO
2
CELL RF SAW
PCS UHF
Dual Reg
VR8 VR9
VR8 & VR9
FIL_SEL1 & 2
Vbat
CELL UHF
Orca
Cell PA
Iref1,2
Vref1,2
VCO
UHF_CP
VCO
VR3 VR6 VR7
VIO
UHF Cell LO
UHF PCS LO
Cell_vco_sel
PCS_vco_sel
YODA
& VHF PLL
IFVGA, IQ Demod,
BB Filters, VHF VCO
Rx_SW1
Rx_SW2
LO
PCS/CELL_SEL
183.6 IF
VR5
ALFRED
LNA, RFA,
SAW
PCS RF
mixer & IFA
VR4
PCS
RX VHF
SAW
CELL RF
Cellular
Diplexer
Isolator
Cellular
Duplexer
Vbat
Dc-DC
Converter
VR2
D2
D0
D1
Power
Detector
Isolator
PCS
Duplexer
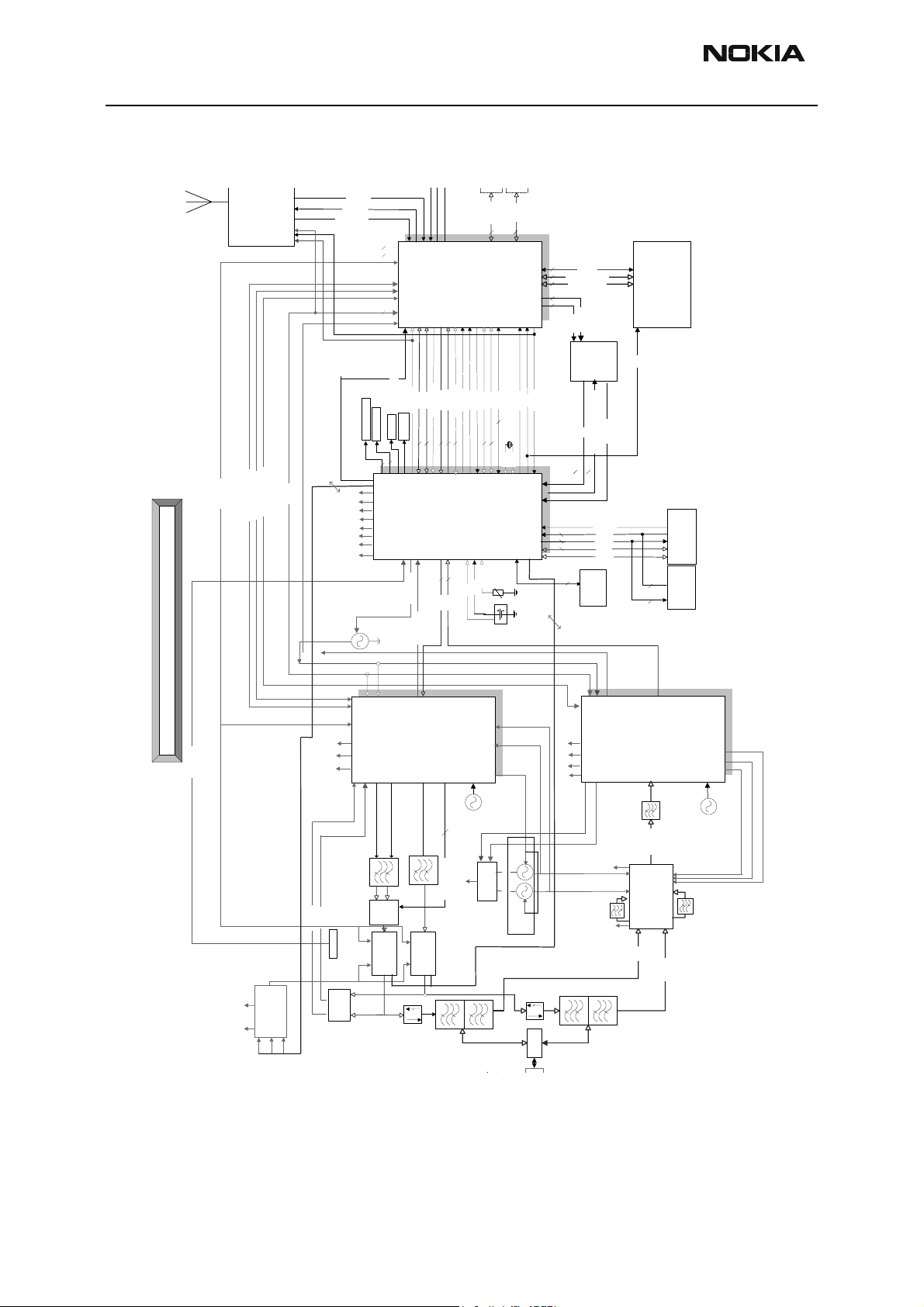
Figure 1: Interconnecting Diagram
Page 6 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 7
RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
Engine Module
Environmental Specifications
Normal and extreme voltages
Voltage range:
• nominal battery voltage: 3.6 V
• maximum battery voltage: 4.5 V
• minimum battery voltage: 3.2 V
Temperature Conditions
Temperature range:
o
• ambient temperature: -30...+ 60
C
• PWB temperature: -30...+85o C
Baseband Module
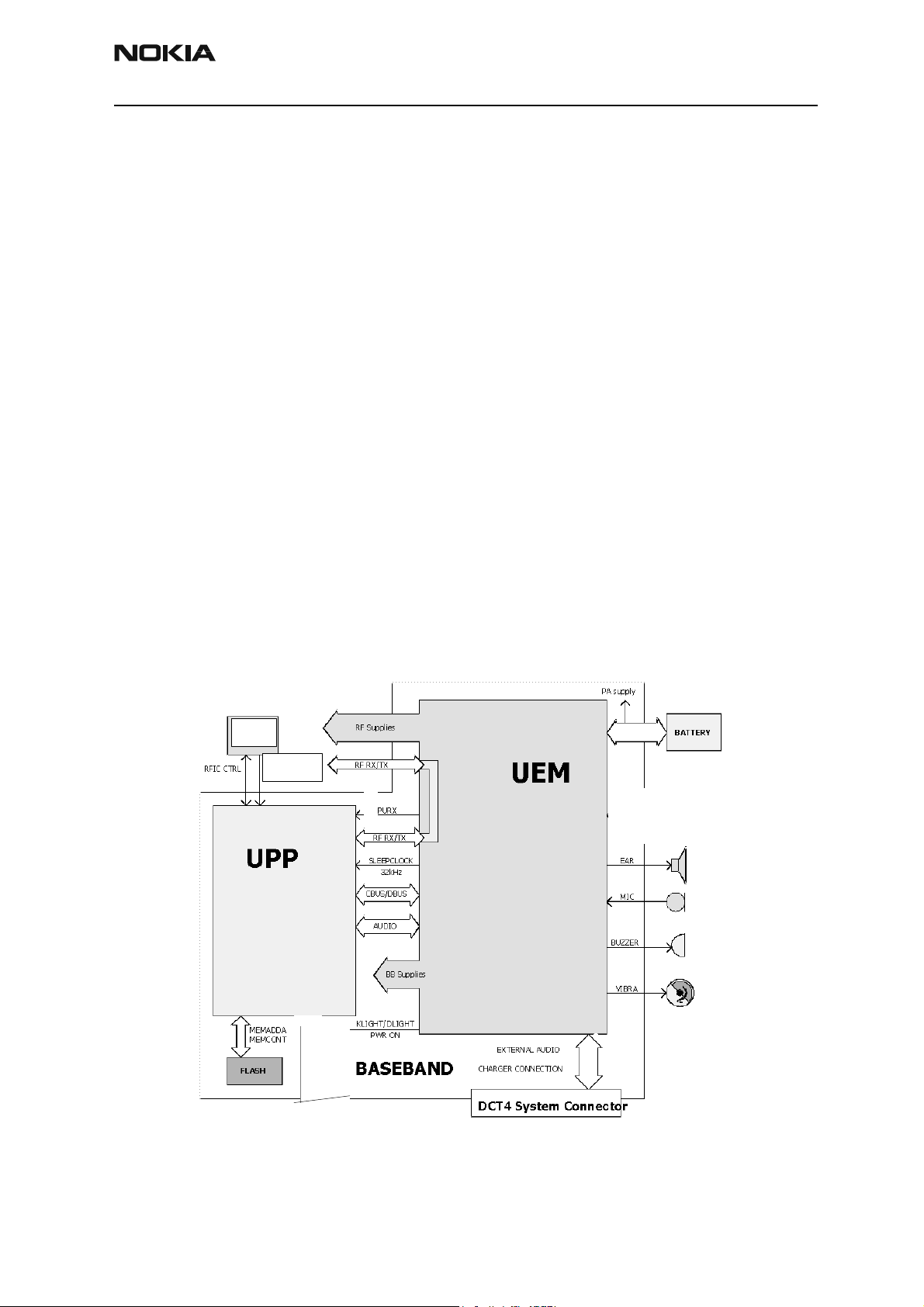
The core part of the RH-3 baseband module consists of three ASICs — UEM and UPP —
and Flash memory. The following sections describe these parts.
Pathfi
nder
19.2
MHz
Figure 2: Baseband module diagram
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 7
Page 8
RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
UEM
UEM Introduction
UEM is the Universal Energy Management IC for DCT4 digital handportable phones. In
addition to energy management, it performs all the baseband mixed-signal functions.
Most of UEM pins have 2kV ESD protection. Those signals that are considered to be
exposed more easily to ESD have 8kV protection inside UEM. Such signals are all audio
signals, headset signals, BSI, Btemp, Fbus, and Mbus signals.
Regulators
UEM has six regulators for baseband power supplies and seven regulators for RF power
supplies. VR1 regulator has two outputs VR1a and VR1b.
Bypass capacitor (1uF) is required for each regulator output to ensure stability.
Reference voltages for regulators require external 1uF capacitors. Vref25RF is reference
voltage for VR2 regulator; Vref25BB is reference voltage for VANA, VFLASH1, VFLASH2,
VR1 regulators; Vref278 is reference voltage for VR3, VR4, VR5, VR6, VR7 regulators;
VrefRF01 is reference voltage for VIO, VCORE, VSIM regulators, and for RF.
BB RF
VANA: 2.78Vtyp 80mA max VR1a: 4.75V 10mA max
VR1b: 4.75V 10mA max
Vflash1: 2.78Vtyp 70mA max
Vflash2: 2.78Vtyp
40mA max
VSim: 1.8/3.0V 25mA max VR3: 2.78V 20mA max
VIO: 1.8Vtyp
150mA max
Vcore: 1.0-1.8V
100mA max
VR2: 2.78V 100mA max
VR4: 2.78V 50mA max
VR5: 2.78V 50mA max
VR6: 2.78V 50mA max
VR7: 2.78V 45mA max
VANA regulator supplies internal and external analog circuitry of BB. It is disabled in
sleep mode.
Vflash1 regulator supplies LCD and digital parts of UEM ASIC. It is enabled during startup
and goes to low Iq-mode in sleep mode.
VIO regulator supplies both external and internal logic circuitries. It is used by LCD, flash,
Jedi, Yoda, GPS RF and GPS Baseband, and UPP. Regulator goes in to low Iq-mode in
sleep mode.
Page 8 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 9

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
VCORE supplies DSP, Core part of UPP, and GPS Baseband ASIC. Voltage is programmable
and the startup default is 1.5V. Regulator goes to low Iq-mode in sleep mode.
VR1 regulator (VR1a, VR1b) uses two LDOs and a charge pump. VR1a is used to bias the
cellular PA and VR1b is for PCS PA.
VR2 is a linear regulator used to supply Jedi RF ASIC.
VR3 is a linear regulator used by Yoda RF ASIC and VCTCXO circuitry.
VR4 is a linear regulator used by Alfred’s LNA RF front end ASIC circuitry.
VR5 is a linear regulator used by the Jedi RFIC.
VR6 is a linear regulator used by Jedi RF ASIC.
VR7 is a linear regulator used by Jedi and Yoda RF ICs.
RF Interface
In addition to the RF regulators mentioned, UEM handles the interface between the
baseband and the RF section. It provides A/D and D/A conversion of the in-phase and
quadrature receive and transmit signal paths, and also A/D and D/A conversions of
received and transmitted audio signals to and from the UI section. The UEM supplies the
analog AFC signal to the RF section according to the UPP DSP digital control. It also
converts PA temperature into real data for the DSP. The UPP controls the RFIC through
the 3-wire RFIC bus. UPP also provides PDM regulator for RF interface (RX/TX AGC control).
Charging Control
The CHACON block of UEM asics controls charging. Needed functions for charging controls are pwm-controlled battery charging switch, charger-monitoring circuitry, and battery voltage monitoring circuitry. In addition, external components are needed for EMC
protection of the charger input to the baseband module. The DCT4 baseband is designed
to electrically support both DCT3 and DCT4 chargers.
Digital Interface
Data transmission between the UEM and the UPP is implemented using two serial connections, DBUS (9.6 MHz) for DSP and CBUS (1.2 MHz in CDMA) for MCU. UEM is a dualvoltage circuit: the digital parts are running from 1.8V and the analog parts are running
from 2.78V. Vbat (3.6V) voltage regulators inputs also are used.
Audio Codec
The baseband supports two external microphone inputs and one external earphone output. The inputs can be taken from an internal microphone, from a headset microphone,
or from an external microphone signal source through a headset connector. The output
for the internal earpiece is a differential type output, and the differential output is capable of driving 4Vpp to the earpiece with a 60 dB minimum signal to total distortion ratio.
Input and output signal source selection and gain control is performed inside the UEM
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 9
Page 10

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
ASIC according to control messages from the UPP. Both a buzzer and an external vibra
alert control signals are generated by the UEM with separate PWM outputs.
UI Drivers
The vibra, display LED, and keyboard LEDs are driven by open collector output drivers
inside UEM. These drivers can generate PWM square wave signals to these devices.
AD Converters
There is an 11-channel analog-to-digital converter in UEM. The AD converters are calibrated in the production line.
BB-RF Interface Connections
All the signal descriptions and properties in the following tables are valid only for active
signals.
Table 1: PDM Interface
Signal name From To Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Function
RX_IF_AGC UPP
GenIO 9
TX_IF_AGC UPP
GenIO 7
TX_RF_AGC UPP
GenIO 26
Yoda Voltage Min
Max
---------------Clk Rate
Jedi Voltage Min
Max
---------------Clk Rate
Jedi Voltage Min
Max
---------------Clk Rate
(1)
(1)
(3)
0.0
1.75
--------
0.0
1.75
-------
0.0
1.75
--------
1.8
------
9.6
1.8
-------
9.6
1.8
--------
9.6
0.1
1.86
-------
19.2
0.1
1.86
--------
19.2
0.1
1.86
--------
19.2
V
-------MHz
V
-------MHz
V
-------MHz
Controls gain of VGA r
in receiver
Controls gain of VGA
in IF VGA in Robin
Controls gain of TX
driver in Robin
Table 2: General I/O Interface
Signal
name
TX_Gate UPP
From To Parameter Input characteristics Function
Punctures the PA’s and
the Jedi ASIC
Digital Into RF
Gen IO 8
pullup
Jedi and
PA Gating
Transistorsr
“1” Transmitter On
“0” Transmitter Off
Timing Accuracy
1.38 1.88 V
0 0.4 V
4 chips, and can be up
to a total of 255 chips
D0 UPP
Gen IO 10
D1 UPP
Gen IO 13
D2 UPP
Gen IO 12
PMIC Voltage Min
Max
PMIC Voltage Min
Max
PMIC Voltage Min
Max
0.4V max
1.72V-1.86V
0.4V max
1.72-1.86V
0.4V max
1.72V-1.86V
Enable PMIC
Set PMIC output voltage
Set PMIC output voltage
Page 10 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 11

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
Table 3: VCTCXO Interface
Signal name From To Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Function
19.2M_UPP Yoda UPP Frequency
-----------------------Signal amplitude
19.2M_GPS Yoda GPS BB Frequency
-----------------------Signal amplitude
AFC UEM VCTCXO Voltage Min
Max
------------------------Settling time
Table 4: Regulated Supplies from UEM to RF
Signal
name
VBAT Battery PA & UEM,
VR1A UEM Cell PA Voltage
From To Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Function
Voltage
external driver
amps
----------------
Current
----------------
Current
(4)
-------
0.5
-------
0.5
0.0
2.4
------- -------
3.2
----0
4.6
-----0
3.5
------
4.75
-----4
19.2
-------
1.0
19.2
-------
1.0
-------
1.5
-------
1.5
0.1
2.55
-------
0.2
5.1
-----2A
peak
4.9
-----5
MHz
------Vpp
MHz
-------
-Vpp
V
------ms
V
------
V
-----mA
High stability clock
signal for logic circuits, AC coupled
squarewave.
High stability clock
signal for logic circuits, AC coupled
squarewave.
Automatic frequency control
signal for VCTCXO
Digital Into RF
Battery supply.
Lower limit is to
guarantee regulator PSRR
Charge pump + linear regulator.
VR1B UEM PCS PA Vol tage
----------------
Current
VR2 UEM Jedi Voltage
----------------
Current
VR3 UEM VCTXO, Yoda Voltage
----------------
Current
VR4 UEM Alfred Voltage
----------------
Current
VR5 UEM Jedi Voltage
----------------
Current
VR6 UEM Yoda Voltage
----------------
Current
VR7 UEM Jedi Vo ltage
----------------
Current
VIO UEM Jedi, Yoda Voltage
----------------
Current
4.6
-----0
2.70
------
2.70
------
2.70
------
2.70
------
2.70
------
2.70
------
1.70
------
4.75
-----4
2.78
------
2.78
------
2.78
------
2.78
------
2.78
------
2.78
------
1.8 1.88
4.9
-----5
2.86
-----100
2.8
-----20
50
50
50
45
-----50
V
-----mA
V
-----mA
V
-----mA
V
-----mA
V
-----mA
V
-----mA
V
-----mA
V
-----mA
Charge pump + linear regulator
Linear regulator
Low noise linear
regulator for
VCTCXO
Low lq linear regulator
Low lq linear regulator
Low lq linear regulator
Low noise linear
regulator for synthesizer
Supply for RF-BB
digital interface
and some digital
parts of RF.
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 11
Page 12

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
Table 5: Slow A/D Converters
Signal name From To Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Function
PA_TEMP Thermistor UEM Input voltage
range
PWROUT Jedi UEM Input voltage
range
0 2.78 V PA temperature sen-
sor output voltage
Analog Out of RF
0 2.78 V Buffered output of TX
output detector
Table 6: RF-BB Analog Signals
Signal name From To Parameter M in Typ Max Unit Function
RX_IP_RF
RX_IN_RF
RX_QP_RF
RX_QN_RF
TX_IP_RF
TX_IN_RF
TX_QP_RF
TX_QN_RF
Yoda UEM Differential volt-
age swing (static)
-------------------------DC level
-------------------------Input Bandwidth
UEM Jedi Differential volt-
age swing (static)
--------------------------DC level
---------------------------
-3 dB Bandwidth
0.3
--------
1.3
--------
0.4
--------
1.65
-------650
0.5
-------
1.35
-------
0.8
-------
1.7
-------
1.0
--------
1.4
-------615
1.2
-------
1.75
-------1950
Vpp
------V
------kHz
Vpp
------V
------kHz
Differential in-phase
and quadrature RX
baseband signal
Analog Out of RF
Differential quadra-
ture phase TX baseband signal for RF
modulator
Analog into RF
Table 7: RFIC Control
Signal name From To Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Function
RF_BUS_CLK
RF_BUS_DATA
RF_BUS_EN1X
UPP Jedi Yoda High-level input
voltage, V
Low-level input
voltage, V
High-level output
voltage, V
Low-level output
voltage, V
Clock
IH
IL
OH
OL
1.72
1.72
1.8
1.8
9.6
1.86
0.4
1.86
0.4
V
V
V
V
MHz
Serial Clock =
Digital Into RF
Bidirectional
Serial Date =
Digital I/O
Latch enable
for Batman and
Robin = Digital
Into RF
UPP
UPP Introduction
RH-3 uses UPP8Mv2.6 ASIC. The RAM size is 8Mbit. The UPP ASIC is designed to operate
in a DCT4 engine, and is designed as part of the DCT4 common baseband task force. The
DCT4 processor architecture consists of both DSP and MCU processors.
Page 12 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 13

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
Blocks
UPP is internally partitioned into two main parts: the Brain and the Body.
The Brain consists of the Processor and Memory System (i.e., Processor cores, Mega-cells,
internal memories, peripherals, and external memory interface). The following blocks are
included: the DSP Subsystem (DSPSS), the MCU Subsystem (MCUSS), the emulation control EMUCtl, the program/data RAM PDRAM, and the Brain Peripherals–subsystem
(BrainPer).
The Body consists of the NMP custom cellular logic functions. These contain all interfaces and functions needed for interfacing with other DCT4 baseband and RF parts. It
includes the following sub-blocks: MFI, SCU, CTSI, RxModem, AccIF, UIF, Coder, GPRSCip,
BodyIF, SIMIF, PUP, and CDMA (Corona).
Flash Memory
Introduction
Flash memory is a high-performance, 64-Mbit, single power supply 1.8 Volt-only FLASH
memory device. This device is designed to be programmed in-system with the standard
system 1.8-volt Vcc supply. A 12.0 volt Vpp is not required for program or erase operations, although an acceleration pin is available if faster write performance is required.
The device is a boot-sectored device, consisting of eight 8Kb and 63 sectors of 64Kb
each.
The Flash device has two read modes: asynchronous read and burst mode read. Device
powers-up in an asynchronous read mode. In the asynchronous mode, the device has two
control functions which must be satisfied in order to obtain data at the outputs. In the
linear mode, the device will deliver a continuous sequential word stream starting at the
specified word and continuing until the end of the memory or until the user loads in a
new starting address or stops the burst advance. The burst mode read operation is a synchronous operation tied to the rising edge of the clock. The microprocessor supplies only
the initial address; all subsequent addresses are automatically generated by the device at
the rising edge of subsequent clock cycles. The burst read cycle consists of an address
phase and a corresponding data phase. The device also is capable of Burst Suspend and
Burst Resume operations.
In order to reduce the power consumption on the bus, a Power Save function is introduced. This reduces the amount of switching on the external bus.
User Interface Hardware
LCD
Introduction
The LCD used in RH-3 is a 96 lines x 64 rows black-and-white LCD. The interface includes
a reset signal from UPP, a serical control with 3-wire also from UPP (CS, Data CLK)., and
two power supplies (1.8V for digital and 2.8V for analog) circuitries. The LCD also has the
booster output that needs to be connected to a booster capacitor.
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 13
Page 14

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
Interface
LCD is controlled by UI SW and control signals.
Booster capacitor (C302 1µF) is connected between booster pin (Vout) and ground. The
capacitor stores boosting voltage.
Keyboard
Introduction
RH-3 keyboard design is Nokia Jack style, with up and down navigation keys, two soft
keys, and 12 number keys. The PWR key is located on top.
Power Key
All signals for keyboard are coming from UPP asic except pwr key signal which is connected directly to UEM. Pressing of pwr key is detected so that switch of pwr key connects PWONX is of UEM to GND and creates an interrupt.
Keys
Other keys are detected so that when a key is pressed down, the metal dome connects
one S-line and one R-line of UPP to GND and creates an interrupt for SW. Matrix of how
lines are connected and which lines are used for different keys is described in the following table. S-line S0 and R-line R5 are not used.
NC = Not Connected
Lights
Introduction
RH-3 has seven white LEDs for lighting purposes: four (V300-V303) are for keyboard
(type LWL88S) and three (V304-V306) are for display (type LWY87C). LED type is
white-light emitting diode.
Returns /
Scans
R0 Send End NC NC
R1 Soft left Up Down Soft right
R2 1 4 7 *
R3 2 5 8 0
R4 3 6 9 #
S1 S2 S3 S4
Interfaces
Display and keyboard lighting is controlled by a DC/DC driver (charge-pump type). The
driver is enabled by Klight. The current for the display is controlled from the driver, with
the current setting coming from R300. The keyboard lighting LEDs each have a separate
current source and the currents are controlled by R304-R307.
Page 14 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 15

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
Technical Information
LEDs have white plastic body around the diode itself, which directs the emitted light to
UI side.
Vibra
Introduction
Vibra is located on the D-cover and is connected by spring connectors on the PWB. It is
located in the left bottom side of the engine.
Interfaces
Vibra is controlled by pwm signal VIBRA from UEM. This signal allows control of both
frequency and pulse width of signal. Pulse width is used to control current when battery
voltage changes. Frequency control searches for optimum frequency to ensure silent and
efficient vibrating.
Audio Hardware
Earpiece
Introduction
The 13 mm speaker capsule that is used in DCT3 products also is used in RH-3. The
speaker is dynamical—very sensitive, and capable of producing relatively high sound
pressure at low frequencies. The speaker capsule and surrounding mechanics comprise
the earpiece.
Parameter Requirement Unit
Rated DC Voltage 1.25 V
Rated speed 9700 ±2500 rpm
Rated current 125 mA
Starting current 160 max mA
Armature resistant 8.8 ohm
Rated DC voltage available 1.1 to 2.0 V
Starting DC voltage min. 1.0 V
Microphone
Introduction
The microphone is an electric microphone with omnidirectional polar pattern. It consists
of an electrically polarized membrane and a metal electrode, which form a capacitor. Air
pressure changes (i.e., sound) move the membrane, which causes voltage changes across
the capacitor. Since the capacitance is typically 2 pF, a FET buffer is needed inside the
microphone capsule for the signal generated by the capacitor. The microphone needs
bias voltage as a result of the FET.
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 15
Page 16

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
Buzzer
Introduction
The buzzer driver is very similar to that of the vibra buzzer. The driver is a PWM-type,
capable of producing 0-VBAT level squarewave signals with a duty cycle in between
0-100%. The frequency can be set anywhere in between 0-9600Hz.
Battery
Phone Battery
Interface
The battery block contains BSI resistors and battery identification. The BSI fixed resistor
value indicates the chemistry and default capacity of a battery. This resistor is connected
to the BSI pins of battery connector. Phone has pull-up resistors for this line so that it
can be read by A/D inputs in the phone (see the following figure). Resistor array (R206) is
ESD protection. There also are spark caps in the BSI lines to prevent ESD.
Figure 3: Interconnection diagram inside the battery pack
Batteries have a specific red line to indicate if the battery has been subjected to excess
humidity. The batteries are delivered in a "protection" mode, which gives longer storage
time. The voltage seen in the outer terminals is zero (or floating), and the battery is activated by connecting the charger. Battery has internal protection for overvoltage and
overcurrent.
Figure 4: Battery pack pin order
Page 16 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 17

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
Battery Connector
RH-3 uses a spring-type battery connector. This makes the phone easier to assemble in
production and ensures a more reliable connection between the battery and PWB.
Signal
#
name
1 VBAT (+) (batt.) VBAT I/O Vbat
2 BSI BSI (batt.) UEM Out Ana.
3 GND GND GND Gnd
Connected
from - to
Batt. I/O
Signal properties
A/D--levels--freq./timing
Accessories Interface
System Connector
Introduction
RH-3 models use the Tomahawk accessories via the Tomahawk connection.
Interface
Tomahawk bottom connector consists of charging plug socket and Tomahawk system
connector (see figures that follow). Minimum configuration of Tomahawk interface
includes charging, mono audio, power out, ACI and Fbus. USB and stereo audio out are
optional.
Description /
Notes
Tomahawk system connector includes:
•Charging
Pads for 2-wire charging in cradles
• Audio (stereo audio optional)
4-wire fully differential stereo audio
FM radio antenna connection
2-wire differential mic input
• Power out
2.78V 70 mA output to accessories (bb4.0, bb4.5)
2.5V 90 mA output to accessories (bb5.0)
• Detection/controlling
ACI
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 17
Page 18

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
Point-to-point bi-directional data line
• USB (optional)
Power in 5V in from USB host
USB v2.0 device mode (full speed 12M)
•Fbus
Standard Fbus
AT command mode (Nokia Serial Bus)
Phonet message mode
Fast Fbus, fast data bus to add on modules
Figure 5: Tomahawk system connector
Page 18 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 19

RH-3
XMIC P
2.70
HSEAR P HSEAR N
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
6.50
9.50
5.70
6.55
5.40
0.30
Metal
shielding
1.00
ACI
Charge GND
Shielding GND
Vout
21.20
PWB
3.50
USB Vbus
USB D+ / Fbus RX
USB D- / Fbus TX
XMIC N
DATA GND
HSEAR R P
HSEAR R N
Shielding GND
Figure 6: Mechanical dimensions and signals of Tomahawk bottom connectors
An accessory is detected by the ACI line. All accessories will generate interrupt while
inserted or removed from the phone’s Tomahawk system connector. Insertion of an
accessory will generate HEADINT interrupt by pulling ACI line down. Vout is enabled by
UPP. The MBUS line is connected to HEADINT line. If HEADINT interrupt from low to high
transition occurs within 20msec, a more advanced accessory is connected, else a basic
headset is connected. The accessory flowchart outlines the routines used for all accessory detection.
The following diagram illustrates accessory detection/external audio flowchart:
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 19
Page 20

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
Accessory
detection
Headint from hi to low tran
Power Vout line
Enable Vbus if USB not in use
Connect MBUS to Headint line
= 4.7k pullup to headint line
Low to high tran in
Headint line in 20ms
NO
Headint YES
ACI or Fbus
accessory connected
Start ACI detection
USB
detection
High to low tran in Vp
and Vm - lines
Connect 1.3k resistor to D+ line
Host with detect phone as
full speed device
USB host
detected
Disconnect MBUS
from headint
Disable FBUS
Unpower VOUT line
Basic
headset
detected
NO
3.th trial?
YES
Nokia Serial Bus
accessory detected
(AT mode)
Send ACI reset pulse
Phone gets learning
sequence from ACI
ASIC
Enable FBUS HW and
set FBUS to
requested command
mode, default is AT
command mode
Wait accessory ID
from Fbus Rx line
Fbus access or y
detected (phone
mode)
YESNO
YES
Read acc features
from ACI ASIC
FBUS needed?
NO
ACI access or y
detected
Figure 7: Accessories detection flowchart
Page 20 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 21

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
TTY/TTD and Universal Headset Jack
TTYTTD devices use standard 2.5mm 3-pin plug (tip = transmit, ring = receive, sleeve =
ground) while universal headset also uses same type of plug (tip = microphone, ring =
earpiece, sleeve = ground). Since only three pins are available for both transmit and
receive at the same time, both paths have to use single-end design (share the ground).
The detection scheme for this interface uses a built-in normally closed switch in the universal headset jack. When there is no device being plugged in, the switch is closed, which
forces the level on the detection line (GENIO(28)) to 1.8V. When a device is plugged in,
the voltage is set to 0V. The detection line can then identify whether a device is plugged
in or not.
Charger IF
Introduction
The charger connection is implemented through the bottom connector. DCT-4 bottom
connector supports charging with both plug chargers and desktop stand chargers. There
are three signals for charging. Charger gnd pin is used for both desktop and for plug
chargers as well as charger voltage, PWM control line, which is needed for 3-wire chargers, is connected directly to gnd in module PWB so the RH-3 engine doesn’t provide any
PWM control to chargers. Charging controlling is done inside UEM by switching UEM
internal charger switch on/off.
Interface
The fuse F100 protects from high currents (e.g., when broken or pirate chargers are used).
L100 protects engine from RF noises that may occur in charging cable. D100 protects
UEM ASIC from reverse polarity charging and from high charging voltage. C106 also is
used for ESD and EMC protection.
Test Interfaces
Production Test Pattern
Interface for RH-3 production testing is 5-pin pad layout in BB area (see following figure). Production tester connects to these pads by using spring connectors. Interface
includes MBUS, USRX, FBUSTX, VPP, and GND signals. Pad size is 1.7mm. The same pads
also are used for AMS test equipment such as module jig and service cable.
2.
FBUS_TX
6.
VPP
3.
FBUS_R X
8.
GND
7.
MBUS
Figure 8: 5-pin Pad Layout in BB area
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 21
Page 22

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
FBUSRX
PURX
DBUSCLK
VR5
VR3
MBUSRX
VR7
VR4
CBUSCLK
GENIO17
GENIO16
GENIO18
MBUSTX
FBUSTX
GENIO14
RFCONVCLK
GENIO15
UEMRSTX
BSI
VIO
VR2
VR6
Vcore
VR1B
VR1A VFlash1
Figure 9: RH-3 Test Points - Top
VANA
Page 22 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 23

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
RFCLK
GPSCLK
FBUSTX FBUSRX
General Information About Testing
Phone Operating Modes
The phone has three different modes for test/repair. Modes can be selected with suitable
resistors connected to BSI- lines as follows:
Mode BSI- resistor Remarks
Normal 68k
Local 33k
Test 6.8k Recommended with baseband
Figure 10: RH-3 Test Points
testing. Same as Local mode, but
making a phone call is possible.
RTCCLK
Vpp
MBUS
GND
The MCU software enters automatically to Local or Test mode at start-up if corresponding resistors are connected.
Note: Baseband doesn’t wake up automatically when the battery voltage is connected (Normal
mode).
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 23
Page 24

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
RF Module
Requirements
RH-3 supports CDMA 1900 and CDMA 800 as described in:
• IS2000-2-A Physical Layer Standard for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems; and
• IS-98D (Draft 4) Recommended Minimum Performance Standard for Spread Spectrum
Mobile Stations.
Temperature Conditions
Surface temperature (SPR5 - Product Safety)
o
Maximum temperature rise is 50
faces at room temperature.
Other temperature requirements (SPR4 - Operating Conditions)
C for nonmetallic surfaces and 30o C for metal sur-
Meeting requirements: -30...+60o C
Storage requirements: -30...+85o C
Main Technical Characteristics
Environmental Specifications
Normal and extreme voltages:
Voltage range:
• nominal battery voltage: 3.6V
• maximum battery voltage: 4.5V
• minimum battery voltage: 3.2V
Temperature conditions:
• ambient temperature: -30...+60o C
• PWB temperature: -30...+85o C
• storage temperature range: -40 to +85o C
Antenna
A dual-band, whip antenna/internal antenna combination is used. The GPS antenna is an
IFA type, embossed on top of the main antenna module.
Page 24 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 25

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
Transmitter
Cell
Cell
RX
RX
Duplexer
Duplexer
Isolator
I
I
From
From
Baseband
Baseband
Q
Q
VHF LO
VHF LO
÷2/÷4
÷2/÷4
Isolator
Cell TX
Isolator
Isolator
Cell TX
PCS TX
PCS TX
Diplexer
Diplexer
Duplexer
Duplexer
0º
UHF LO
0º
0º
90º
90º
UHF LO
0º
0º0º
90º
90º
0º
S
0º
0º0º
90º
90º
90º
90º
S
P
P
D
D
T
T
To Baseband
To Baseband
Power
Power
Power
Detector
Detector
Detector
S
S
P
P
D
D
T
T
Antenna
Antenna
PCS
PCS
RX
RX
Figure 11: RF transmitter block diagram
The transmit chain up to the RF driver stage is integrated into one transmit-integrated
circuit called Jedi, with external power amplifiers (PA). The channel spacing is 50 kHz for
PCS and 30 kHz for Cell.
All data transmitted on the channel is convolutionally encoded and block-interleaved.
Modulation is 64-ary orthogonal (RC1 and RC2) and direct sequence spread by a quadrature pair of PN sequences at a fixed chip rate. The data is filtered, O-QPSK modulated
and up-converted to the appropriate transmission frequency. RC3 and RC4 use HPSK
modulation at data rates up to 153.6 kBPS (RC3) and 115.2 kBPS (RC4).
The baseband I/Q signals are converted to IF frequency in the I/Q modulator by Quadrature mixing. The modulated IF signals go through a variable gain amplifier (IF AGC) and
then are routed either to the PCS TX path or the Cell TX path. The path consists of an
upconverter and a variable gain RF amplifier. The IF signal is converted up to RF with a
differential output upconverter and then fed to the RF amplifier. The RF amplifier has
variable gain capability (RF AGC) with up to 40 dB of dynamic gain control.
The outputs of the RF amplifiers are differential. The differential outputs from Jedi are
combined into single-ended output by an external balun. There are two outputs from this
module that feed a split-band filter. The split-band filter output is connected to a SPDT
RF switch that results in a single output.
This split-band filter provides the needed Rx band rejection performance. The wide PCS
Tx band (60 MHz) and small separation (20 MHz) between TX and Rx band prevents a
single SAW filter from achieving the required Rx rejection. As a result, the PCS band SAW
filter is divided into two bands, each 35 MHz wide.
The output of the SPDT RF switch then is connected to the PA. Out of the PA is an isolator, then antenna.
The PA modules contain all the necessary matching networks and reference current circuitry for variable gain control and biasing ON/OFF. A variable reference current is used
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 25
Page 26

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
to vary the PA gain and PA bias current. The variable gain technique reduces PA current
consumption and improves the signal-to-noise ratio at low output power levels. The precision bias current (and gain) control is achieved by varying the PA reference current
with a PDM control voltage.
The transmitter chain utilizes smart power techniques and only the required circuits are
powered at the appropriate times. In order to save energy in puncture mode, when there
is no speech activity during a call, the driver and power amplifiers and the Jedi IC are
switched ON and OFF rapidly. These units also are in the OFF state when the transmitter
is in standby. The ON/OFF switch commands are issued by a Digital ASIC (UPP). The UPP’s
PDM controls a current mirror in Robin that provides the PA reference current. Switching
each reference current ON/OFF switches each PA ON/OFF. The VHF synthesizer and power
detector circuits are left on during the puncture mode.
Synthesizer
Refer to the following figure for a block diagram that illustrates all three synthesizers
and how they interconnect in the system.
367.2MHz
367.2MHz
VHF
VHF
counter
counter
Yoda
Yoda
UHF LO Synthesizer
The UHF LO synthesizer generates the first RX LO frequency for the receiver (down-conversion) and the second TX LO frequency for the transmitter (up-conversion). The synthesizer is a dual-modulus prescaler type and utilizes a phase-frequency detector with a
charge pump that sinks or sources currents, depending upon the phase difference
between the phase detector input signals.
CELL:457.2MHz
CELL:457.2MHz
PCS:527.2MHz
PCS:527.2MHz
19.2MHz
19.2MHz
VCTCXO
VCTCXO
19.2MHz to
19.2MHz to
UPP
UPP
VHF
VHF
counter
counter
JEDI
JEDI
UHF
UHF
counter
counter
Dual Band UHF VCO
Dual Band UHF VCO
Figure 12: Synthesizer system block diagram
For PCS, channel spacing and the comparison frequency is 50 kHz. For the cellular AMPS/
CDMA band, channel spacing is 30 kHz. An internal buffer is provided for high isolation
between Jedi and the VCO to reduce VCO pulling due to changing load.
Page 26 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 27

RH-3
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
1st TX VHF LO Synthesizer (Jedi)
The TX VHF Synthesizer is integrated within the Jedi RFIC and generates the LO signals
for the IQ-modulator in Jedi. The synthesizer has an internal VCO with an external resonator. The VCO operates at two times the CELL and PCS IF frequencies. A band-switch
signal, VCO_Band, is used to shift the center frequency of the external resonator.
The synthesizer is a dual-modulus prescaler type, and utilizes a phase detector with a
charge pump that sinks or sources currents, depending on the phase difference between
the detector input signals. The width of the pulses depends on the phase difference
between the signals at input of the phase detector. The main divider, auxiliary divider,
and reference divider are programmable through the serial interface to Jedi.
The TX VHF Synthesizer generates 357.2 MHz for Cell Band and 457.2 MHz for PCS band.
The TX VHF Synthesizer comparison frequency for Cell Band is 30 kHz and PCS band is
50 kHz.
2nd RX VHF LO Synthesizer (Yoda)
The RX VHF Synthesizer is integrated within the Yoda RFIC and generates the LO signals
for the IQ demodulator in Yoda. The synthesizer has an internal VCO with an external
resonator. The VCO operates at two times the common 183.6 MHz RX IF frequency. A
band-switch signal, Band_Sel, is used to select the band of operation for the UHF VCO.
The synthesizer is a dual-modulus prescaler type, and utilizes a phase detector with a
charge pump that signals or sources currents, depending upon the phase difference
between the detector input signals. The width of the pulses depends on the phase difference between the signals at input of the phase detector. The main divider, auxiliary
divider, and reference divider are programmable through the serial interface to Yoda.
The RX VHF Synthesizer generates 367.2 MHz for both Cell Band and the PCS Band.
VCTCXO - System Reference Oscillator
The VCTCXO provides the frequency reference for all the synthesizers. It is a voltage-controlled, temperature-compensated, 19.2MHz crystal oscillator that can be pulled over a
small range of its output frequency. This allows for an AFC function to be implemented
for any frequency accuracy requirements. This is done by DSP processing of received I/Q
signals.
Closed loop AFC operation allows very close frequency tracking of the base station to be
done in CDMA mode. This will enable the unit to track out aging effects and give the
required center frequency accuracy in cellular and PCS bands.
The most practical way of clock distribution is driving all three chips (UHF PLL, Yoda, and
Jedi) directly from the VCTCXO. An internal buffer is used to drive the UPP in order to isolate the UPP’s digital noise from the VCTCXO, which prevents contamination of the 19.2
MHz reference onto the PLL chips of the system. Since the VCTCXO output is a sinewave,
such clock distribution will not cause any clock signal integrity problems, even for relatively long traces (what might occur in case of a digital square waveform with fast tran-
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 27
Page 28

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
sition times). The VCTCXO output is AC, coupled to Yoda, Jedi, UHF PLL, and the digital
ASICs (see the following figure) to eliminate DC incompatibility between those pins.
Receiver
Figure 13: VCTCXO clock distribution
Figure 14: RH-3 Receiver block diagram
The receiver is a dual conversion I/Q receiver with a first IF of 183.6 MHz. The front-end
RFIC (Alfred) contains a low noise amplifier (LNA), a radio frequency amplifier (RFA), a
down-converter, an intermediate frequency amplifier (IFA), and a local oscillator amplifier (LOA). Between the LNA and the RFA is a bandpass filter which will reject out-ofband spurious and act as image rejection. The IF filter is between the Alfred IC and the
BatmanD IC. The purpose of this filter is to guarantee rejection in adjacent and alternate
channels.
Page 28 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
Page 29

RH-3
4
CLO CK
LO/8 Test Point
k
1
CCS Technical Documentation System Module
The RX IF ASIC Yoda is used to convert the IF down to baseband I and Q. The ASIC contains a VGA section, IQ demodulator, and baseband filters (BBFIL) for CDMA. Switchable
gain baseband amplifier (BBAMP), and RX VHF PLL. The I/Q BB signals are output to UEM
chip for analog-to-digital conversion and further signal processing.
GPS Engine
Introduction
575. 42 MHz
4.092MHz
LNA
BPF
16.368 MHz
TC XO
Figure 15: GPS Engine Block Diagram
The GPS engine (GE) major components consist of two ASICs, the RF Front End with a
Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), a voltage regulator, and a Temperature-Controlled Crystal
Reject
Mixe r
÷ 2
Loo p
Fi l t e r
fcom p=16.368MHz
Oscillator
VCO
Tank
L O=1 571 . 32 8 MHz
÷ 2
÷ 8
Phase
Det
AGC
4 Bit
ADC
196 .416 MHz
Pr ogr am mi ng
In ter fa c e
Po i n ts
DATA
ENA BLE
ADCout
IFout
GPS Cloc
LO/8 Test
SPI
Oscillator (TCXO). The front end provides filtering of out-of-band signals and amplification of the frequency band of interest. The RF ASIC provides further amplification, AGC,
down-conversion to low IF, IF filtering and analog-to-digital conversion of the IF. The
baseband ASIC is responsible for all baseband processing of the GPS signal, including PN
wipeoff, decoding, and GPS measurement calculations. The TCXO provides a 16.368 MHz
signal for down-conversion and sampling and is used by the baseband ASIC for all the
GPS processing. The RF regulator provides voltage regulation from the battery to provide
2.8 volts for the RF components.
The GE is controlled by the Cellular Engine (CE) via the GE/CE Interface. When the CE
powers up, the GE performs a self-test and informs the CE of self-test results. If the selftest results pass, the CE will download the operational code to the GE via the GE/CE
interface. If the self-test of the GE fails, the CE will declare a hardware failure and increment the “Test Mode 0 Failure” PPC. The CE will receive a GPS status message from the
GE after download as to the success of the download. If the download fails, the CE will
Issue 1 06/2003 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 29
Page 30

RH-3
System Module CCS Technical Documentation
reset the GE, increment the “Code Download Failure” PPC, and try to download the code
again. After the third unsuccessful attempt of download, the CE will declare a hardware
failure and hold the GE in reset. If download is successful, it will configure the GE and
then put the GE to sleep. Sleep is the normal state of the GE and the only time it is
woken up is from any of the following:
• To perform periodic self-test
• When an IS-801.1 location session starts
• When a command is sent to it through the test interface in the Location
Server SW in the CE, (e.g., a command from Phoenix)
During sleep of the GE, the RF regulator is off and the RF ASIC is powered down. The
baseband ASIC remains powered on, but has no internal clocks running except the sleep
clock from the CE.
Additional information on GPS can be found in the Troubleshooting - GPS chapter of this
manual.
Page 30 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 06/2003
 Loading...
Loading...