Nidek RT-2100 User manual
NIDEK
REFRACTOR
Model RT-2100
OPERATOR’S MANUAL

* Specifications are subject to change without notice for improvement.
NIDEK CO., LTD. |
: 34-14, Maehama, Hiroishi-cho, Gamagori, Aichi 443-0038, Japan |
(Manufacturer) |
Telephone: (0533) 67-6611 |
NIDEK CO., LTD |
Facsimile: (0533) 67-6610 |
: 6th Floor, Takahashi Bldg., No.2, 3-chome, Kanda-jinboucho |
|
(Tokyo Office) |
Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-0051, Japan |
|
Telephone: (03) 3288-0571 |
|
Facsimile: (03) 3288-0570 |
NIDEK INCORPORATED |
Telex: 2226647 NIDEK J |
: 47651 Westinghouse Drive Fremont, California 94539, U. S. A. |
|
(United States Agent) |
Telephone: (510) 226-5700 |
NIDEK SOCIETE ANONYME |
Facsimile: (510) 226-5750 |
: Europarc 13, rue Auguste Perret, 94042 CRETEIL, France |
|
(Authorized Representative) |
Telephone: (01) 49 80 97 97 |
|
Facsimile: (01) 49 80 32 08 |
2002.11
34060-P902O Printed in JAPAN
 BEFORE USE, READ THIS MANUAL.
BEFORE USE, READ THIS MANUAL.
This Operator’s Manual contains the operating procedures, safety precautions and specifications for the RT-2100 when it is used in combination with the following chart presenting devices.
In this manual, JIS, IEC 60601 and UL standards are applied.
The refractor head complies with ISO 10341 (Ophthalmic instruments - Refractor heads).
The dioptric powers are indicated with a reference wavelength of 546.07 nm.
For correct use, it is necessary that the contents of this manual, in particular the safety precautions and operating procedures, are thoroughly understood before using the instrument.
Keep the manual handy for reference.
There are no user-serviceable parts inside the instrument except printer paper and fuses. Therefore, if you encounter any problems or have questions about the instrument during use, contact your authorized distributor.
*1 Chart presenting devices used in combination with the RT-2100
•NIDEK SPACE SAVING CHART SSC-300/SSC-330/SSC-350
•NIDEK CHART PROJECTOR CP-670/CP-690
*2 Figures of the control box and charts for CP-690 Type U are used in this manual.
*3 In this manual, visual acuity is represented by fractions (feet). For VA values represented by decimals or fractions (meters), see “Appendix. C Conversion table for VA values” at the back of this manual.
(This applies only to equipment whose power source is 100/120 Vac.)

Table of Contents
§1 INTRODUCTION |
Page |
|
1-1 |
||
1.1 |
Outline of the Instrument ......................................................................................... |
1-1 |
1.2 |
Classifications .......................................................................................................... |
1-1 |
1.3 |
Symbol Information ................................................................................................. |
1-2 |
§2 SAFETY ........................................................................................................................ |
2-1 |
|
2.1 |
Operation .................................................................................................................. |
2-1 |
2.2 |
Storage ...................................................................................................................... |
2-2 |
2.3 |
Installation ................................................................................................................ |
2-3 |
2.4 |
Wiring ....................................................................................................................... |
2-4 |
2.5 |
After Use .................................................................................................................. |
2-4 |
2.6 |
Maintenance ............................................................................................................. |
2-4 |
2.7 |
Disposal .................................................................................................................... |
2-5 |
2.8 |
Labels ....................................................................................................................... |
2-6 |
§3 CONFIGURATIONS ................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
|
3.1 |
Refractor Head ......................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
3.2 |
Control Box .............................................................................................................. |
3-3 |
3.3 |
Relay Box ............................................................................................................... |
3-13 |
§4 OPERATING PROCEDURE...................................................................................... |
4-1 |
|
4.1 |
Operation Flow ......................................................................................................... |
4-1 |
4.2 Power-ON................................................................................................................. |
4-2 |
|
4.3 |
Entering Data............................................................................................................ |
4-2 |
|
4.3.1 Receiving data from the auto refractometers .................................................. |
4-2 |
|
4.3.2 Receiving data from the lensmeter .................................................................. |
4-3 |
|
4.3.3 Manual entry with the dial .............................................................................. |
4-4 |
|
4.3.4 Entering data via an IC card |
|
|
(available only if the RT is equipped with the IC card system) ....................... |
4-5 |
|
4.3.5 Setting prism lenses ........................................................................................ |
4-7 |
|
4.3.5.1 Switching coordinates between rectangular and polar ........................ |
4-7 |
|
4.3.5.2 Setting rectangular coordinates (XY) .................................................. |
4-7 |
|
4.3.5.3 Setting polar coordinates (rθ ) .............................................................. |
4-8 |
|
4.3.5.4 Recording “Blur”, “Break” and “Recovery” ....................................... |
4-8 |
|
4.3.5.5 Removing and replacing prism lenses................................................. |
4-9 |
|
4.3.5.6 Clearing prism data ........................................................................... |
4-10 |
4.4 |
Initial Setups ........................................................................................................... |
4-11 |
4.5 |
Refraction with the Standard Program ................................................................... |
4-12 |
|
4.5.1 Program A ..................................................................................................... |
4-12 |

§5
§6
4.6 |
Chart Presentation .................................................................................................. |
4-21 |
|
4.6.1 Chart selection............................................................................................... |
4-21 |
|
4.6.2 VA chart masking .......................................................................................... |
4-21 |
4.7 |
Adjustment of Powers (Final Fit) ........................................................................... |
4-24 |
|
4.7.1 Auto adjustment of Far Powers ..................................................................... |
4-24 |
|
4.7.2 Fine adjustment after auto adjustment (Semi-auto adjustment) .................... |
4-26 |
|
4.7.3 Manual adjustment of powers ....................................................................... |
4-27 |
4.8 |
After Use Care ........................................................................................................ |
4-27 |
OTHER FUNCTIONS ................................................................................................. |
5-1 |
|
5.1 |
Programming ............................................................................................................ |
5-1 |
|
5.1.1 Deleting programs ........................................................................................... |
5-1 |
|
5.1.2 Programming ................................................................................................... |
5-2 |
|
5.1.3 Starting a programmed refraction ................................................................... |
5-4 |
5.2 |
Printout ..................................................................................................................... |
5-4 |
|
5.2.1 Changing an ID No. ........................................................................................ |
5-6 |
|
5.2.1.1 Outputting all the data displayed on the screen................................... |
5-6 |
|
5.2.2 Entering comments for printout ...................................................................... |
5-7 |
|
5.2.3 Entering date and time .................................................................................... |
5-8 |
5.3 |
Displaying a Data List .............................................................................................. |
5-9 |
5.4 |
Setting Auxiliary Lenses .......................................................................................... |
5-9 |
5.5 |
Parameter Settings .................................................................................................. |
5-10 |
5.6 |
Recalling Data ........................................................................................................ |
5-17 |
|
5.6.1 Calling up final data ...................................................................................... |
5-17 |
|
5.6.2 Calling up the most recent data ..................................................................... |
5-18 |
5.7 |
Fogging Function with Both Eyes Open ................................................................ |
5-19 |
5.8 |
Linkage OFF Function ........................................................................................... |
5-20 |
5.9 |
Clearing the Saved Data in Memory ...................................................................... |
5-20 |
METHOD OF SINGLE TESTS ................................................................................. |
6-1 |
|
6.1 |
Unaided Visual Acuity Test ...................................................................................... |
6-1 |
6.2 |
Aided Visual Acuity Test ......................................................................................... |
6-2 |
6.3 |
Visual Acuity Test Aided with Addition Power ....................................................... |
6-3 |
6.4 |
Cylinder Tests ........................................................................................................... |
6-4 |
|
6.4.1 Cylinder test with astigmatism clock dial ....................................................... |
6-4 |
|
6.4.2 Cylinder test with XC lens .............................................................................. |
6-5 |
6.5 |
Spherical Refinements.............................................................................................. |
6-5 |
|
6.5.1 Red/Green test ................................................................................................. |
6-5 |
|
6.5.2 Cross Grid test for far vision ........................................................................... |
6-6 |
6.6 |
Binocular Vision Function Test ................................................................................ |
6-7 |
|
6.6.1 Binocular balance test ..................................................................................... |
6-7 |
|
6.6.2 Polarized Red/Green test ................................................................................. |
6-9 |
|
6.6.3 Phoria test ...................................................................................................... |
6-10 |
|
6.6.3.1 For CP-690(670) TYPE U / SSC-330(300) TYPE U ....................... |
6-10 |
|
6.6.3.2 For CP-690(670) TYPE T and F / SSC-330(300) TYPE T .............. |
6-12 |
|
6.6.4 Phoria with fixation test ................................................................................ |
6-14 |
|
6.6.5 Von Graefe test (for horizontal phoria) ......................................................... |
6-16 |
|
6.6.6 Von Graefe test (for vertical phoria) ............................................................. |
6-17 |
§7 §8
|
6.6.7 Vertical coincidence test ................................................................................ |
6-19 |
|
6.6.8 Horizontal coincidence test ........................................................................... |
6-21 |
|
6.6.9 Schober test ................................................................................................... |
6-23 |
|
6.6.10 Stereo test .................................................................................................... |
6-25 |
|
6.6.10.1 For SSC-350 TYPE T/TCG ............................................................ |
6-25 |
|
6.6.10.2 For the others................................................................................... |
6-25 |
|
6.6.11 Worth test .................................................................................................... |
6-26 |
|
6.6.12 Maddox test (for horizontal phoria) ............................................................ |
6-27 |
|
6.6.13 Maddox test (for vertical phoria) ................................................................ |
6-28 |
|
6.6.14 Negative relative convergence test .............................................................. |
6-29 |
|
6.6.15 Positive relative convergence test ............................................................... |
6-30 |
|
6.6.16 Near point of convergence test .................................................................... |
6-31 |
|
6.6.17 Near point of accommodation test .............................................................. |
6-32 |
|
6.6.18 Negative relative accommodation test ........................................................ |
6-33 |
|
6.6.19 Positive relative accommodation test .......................................................... |
6-34 |
COMMON PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS ........................................................... |
7-1 |
|
MAINTENANCE ......................................................................................................... |
8-1 |
|
8.1 |
Cleaning the Forehead Rest...................................................................................... |
8-1 |
8.2 |
Cleaning the Face Shields ........................................................................................ |
8-2 |
8.3 |
Replacing the Printer Paper ...................................................................................... |
8-2 |
8.4 |
Cleaning the Measuring Windows ........................................................................... |
8-4 |
8.5 |
Cleaning the Exterior ............................................................................................... |
8-4 |
8.6 |
Replacement Part No. for Printer Paper ................................................................... |
8-4 |
§9 SPECIFICATIONS ...................................................................................................... |
9-1 |
§10 ACCESSORIES.......................................................................................................... |
10-1 |
10.1 Standard Accessories............................................................................................ |
10-1 |
APPENDIX. A Descriptions of power adjustment ................................................................. |
A-1 |
APPENDIX. B Linkage between charts and auxiliary lenses ................................................ |
B-1 |
APPENDIX. C Conversion table for VA values .................................................................... |
C-1 |
APPENDIX. D Preset Addition Power .................................................................................. |
D-1 |
APPENDIX. E Table for VA values as presented on charts ................................................... |
E-1 |
APPENDIX. F Examples of Programming ............................................................................. |
F-1 |

§1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Outline of the Instrument
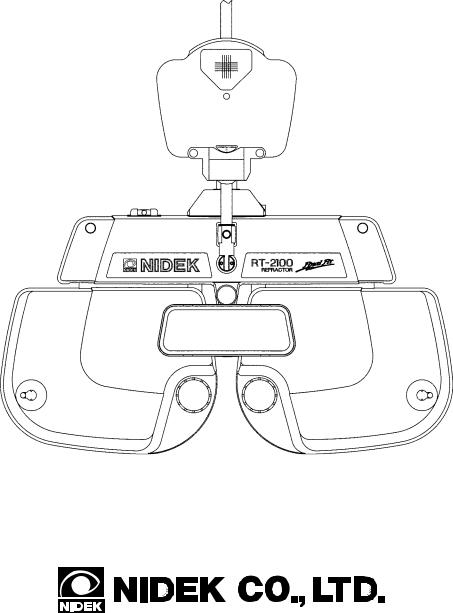
The NIDEK REFRACTOR Model RT-2100 is a computerized refractor used for subjective refraction when connected to the NIDEK AUTO REFRACTOMETER (AR), AUTO REF/ KERATOMETER (ARK) and AUTO LENSMETER (LM)*1. The operator has a fully integrated refraction system that simplifies and speeds up refraction.
The RT-2100 includes a refractor head, a control box, a relay box and a printer.
The relay box serves as a link to the refractor head, control box and printer, and also functions as a communication link to the AR and/or LM.
The control box provides a display for viewing measurements. The control panel allows the operator to perform most operations from an integrated console by linking the refractor and the connected chart presenting device. Both instruments can be operated from the single control box.
Normally, the relay box and the printer are contained in the system table (not included in the RT2100 package.)
1.2 Classifications
[Classification under the provision of 93/42/EEC (MDD)] Class I
The RT-2100 is classified as a Class I instrument.
[Form of protection against electrical shock] Class I
The RT-2100 is classified as a Class I instrument. A Class I instrument is an instrument in which protection against electric shock does not rely solely on basic insulation. A Class I instrument includes additional safety precautions that provide for connection of accessible conductive parts to a protective (earth) grounding conductor in the fixed wiring of the installation.
[Degree of protection against electrical shock] Type B applied part
The RT-2100 is classified as an instrument with a Type B applied part.
A Type B applied part provides an adequate degree of protection against electrical shock, particularly regarding the following:
-allowable leakage currents
-reliability of the protective earth ground connection (if applicable)
*1 Connectable instruments
AR: NIDEK AR-20, ARK-30, AR-600, AR-600A, AR-660A, ARK-700, ARK-700A, ARK760A, AR-800, AR-820, AR-860, ARK-900, AR-1000, AR-1100, AR-1200M, AR-1600, ARK2000, ARK-9000, ARK-10000
LM: NIDEK LM-770, LM-820A, LM-870, LM-990, LM-990A

1 - 2
[Degree of protection against liquid entry] IP20
The RT-2100 is classified as a normal instrument, as such provides only minimal protection against liquid intrusion. The enclosure of the RT-2100 is not completely water proof.
Avoid immersion of any king.
[Degree of protection against flammability]
The RT-2100 is classified as an instrument not suitable to be used in a potentially flammable environment.
Do not operate the instrument near flammable materials.
[Mode of operation]
Continuous operation
[Method(s) of sterilization or disinfection recommended by the manufacturer]
The RT-2100 does not have any parts to be sterilized or disinfected.
1.3 Symbol Information
This symbol on the instrument indicates that caution should be taken. Refer to the Operator’s Manual before operating the instrument.
This symbol indicates that the instrument is classified as an instrument with a Type B applied part.
This symbol on the power switch indicates that the power is ON.
This symbol on the power switch indicates that the power is OFF.
This symbol indicates the proper fuse rating of the device.
This symbol indicates that the instrument must be supplied only with an alternating current.

1 - 3
The symbols printed on the control box and shown on the display correspond to the symbols and those names defined in ISO 10341 (Ophthalmic instruments - Refractor heads) as shown in the following table.
Auxiliary lens |
|
Marking |
|
|
RT-2100 |
|
ISO10341 |
||
|
|
|||
Red maddox rod |
or |
MR |
|
Maddox rods |
|
|
|
|
|
Pinhole plate |
|
PH or |
|
Pinhole |
|
|
|
|
|
Occluder |
|
BL or |
|
Occluder |
|
|
|
|
|
PD check lens |
|
CL or |
|
Cross line |
|
|
|
|
|
Red filter |
|
RF |
|
Red filter |
|
|
|
|
|
Green filter |
|
GF |
|
Green filter |
|
|
|
|
|
Polarizing filter |
or |
PF |
|
Polarization filter |
|
|
|
|
|
Open aperture |
|
OA |
|
Open aperture |
|
|
|
|
|
Lenses for retinoscope |
|
RL |
|
Retinoscopic lens |
|
|
|
|
|

§2 SAFETY
The following safety precautions should always be followed.
In this manual, Signal Words are used to designate a degree or level of safety alerting. The definitions are as follows.
 WARNING: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
WARNING: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury or property damage.
Even cases mentioned in  CAUTION may result in serious injury under certain conditions. Be sure to observe the instructions of
CAUTION may result in serious injury under certain conditions. Be sure to observe the instructions of  CAUTION.
CAUTION.
2.1 Operation
 WARNING
WARNING
•When moving the refractor head in front of or away from the patient, make sure that there are no obstacles in its path.
Inadvertent contact with a person or object could result in personal injury and/or damage to the instrument.
 CAUTION
CAUTION
•Never disassemble or tamper with the inside of the instrument. This may result in an electric shock or an instrument malfunction.
•Be sure to use an electrical current which meets the power specification requirements. If the line voltage is too high or too low, it may affect the performance of the instrument and may start an electrical fire.
•Always remove the power cord from the wall outlet by holding the plug. Never pull on the cord.
This can damage the internal wires and may result in a short circuit, an electric shock or a fire.
•If the internal wires of the power cord are exposed, the power to the instrument will be inconsistent, or the plug will become extremely hot, indicating internal damage to the cord. If this occurs, remove the cord from the outlet immediately. After checking to see that no more smoke is being produced, contact your authorized distributor immediately.
If the instrument is not functioning normally, it may cause an electric shock or a fire.

2 - 2
 CAUTION
CAUTION
• Do not crush or squeeze the power cord with heavy objects.
If the power cord is damaged, it may cause an electric shock or a fire.
•Clean between the prongs of the power plug using a dry cloth every couple of months. If the prongs are exposed to moisture or excessive dirt, the instrument may short circuit or cause a fire.
•If you notice strange odors or smoke being emitted from the instrument, turn OFF the instrument, and disconnect the power cord immediately. After confirming that smoke is no longer being produced, contact your authorized distributor.
If the instrument is used under abnormal conditions, it may cause an electric shock or a fire.
NOTE
• Do not touch the measuring windows.
Dirt or fingerprints on the measuring windows may affect the accuracy of the refraction data.
•Be sure to wipe the forehead rest and face shields with a clean cloth and a diluted neutral detergent solution before each examination.
2.2Storage
NOTE
•Do not store the instrument in a place where it may be exposed to moisture or toxic chemicals.
•Avoid storing the instrument in an area with excessive heat, humidity, or dust.
To preserve the appearance of the instrument, avoid direct exposure to sunlight.

2 - 3
2.3 Installation
 WARNING
WARNING
•The refractor head weights 6.7 kg. Make sure that the refractor’s arm has been designed to bear the weight.
Before attaching the refractor head to the arm, impose weight on the arm, and confirm that the refractor head is stable during normal use.
•Be sure to secure the refractor head to the refractor arm with the set screw.
If the refractor head is dropped or falls, it could cause extensive damage and possible injury.
NOTE
•Store the instrument in the following conditions. Temperature: 10 - 40 °C
Humidity: 30 - 85 %
A dust free environment
Minimal exposure to direct sunlight An area free of vibration
•Be sure to level the refractor head before use.
If it is not level, the accuracy of the refraction data may be affected. Level the refractor head by turning the Leveling adjustment knob until the bubble is centered in the level.
•This instrument has been tested and found to comply with the limits for medical devices to the IEC 60601-1-2: 1993, EN60601-1-2: 1994, Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a typical medical installation. This instrument generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to other devices in the vicinity. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this instrument does cause harmful interference to other devices, which can be determined by turning the instrument off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
-Reorient or relocate the receiving device.
-Increase the separation between the instruments.
-Connect the instrument to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the other device(s) are connected.
-Consult the manufacturer or field service technician for help.

2 - 4
2.4 Wiring
 CAUTION
CAUTION
•Be sure to use a (HOSPITAL GRADE) wall outlet equipped with a grounding terminal in order to avoid an electric shock or fire in the event of a power leak.
•Be sure the plug is securely in place in the wall outlet.
Insecure connections may affect the operation of the instrument or create a fire hazard.
2.5 After Use
 CAUTION
CAUTION
•If the instrument will not be used for an extended period, disconnect the power plug from the wall outlet.
If the instrument is covered with dust and it takes on moisture, it may create a fire hazard. Always use the dust cover supplied with the instrument.
NOTE
• When the instrument is not in use, turn OFF the power switch and put the dust cover on. If the instrument is not covered for an extended period, the accumulation of dust may affect the accuracy of the instrument.
2.6 Maintenance
NOTE
•Never use an organic solvent or abrasive solvent to clean the exterior of the instrument as it may ruin the appearance.
•When the instrument is sent back to NIDEK for repair or maintenance, wipe the surface (especially, the area where the patient’s skin contacts) of the instrument with a clean cloth immersed in ethyl alcohol for disinfection.

2 - 5
2.7 Disposal
NOTE
•Follow local governing ordinances and recycling plans regarding disposal or recycling of device components.
Especially the disposal method of lithium batteries varies according to the government. As the relay and control boxes have lithium batteries on the circuit boards, follow the local governing ordinances and recycling plans when disposing of a circuit board with lithium batteries.
•When disposing of packing materials, sort them by material and follow local governing ordinances and recycling plans.
2 - 6
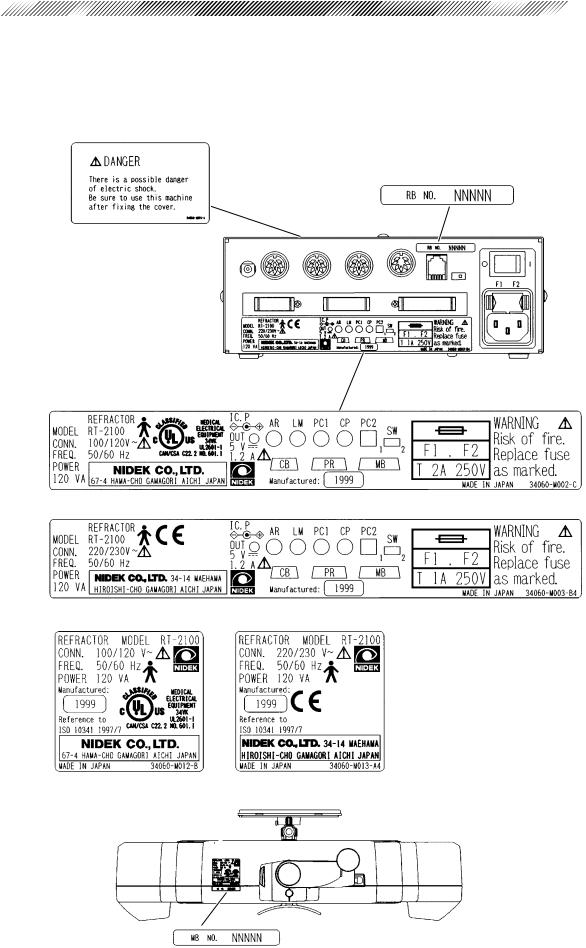
2.8 Labels
• Labels provide safety information about each part.
Relay box
For 100V area
For 200V area
Refractor head
For 100V area |
For 200V area |
|
|

2 - 7
Control box
CB NO. NNNN

2 - 8
§3 CONFIGURATIONS
3.1 Refractor Head
Operator’s side
 Near point rod
Near point rod
 Near point card
Near point card 
 Level adjustment knob
Level adjustment knob
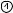 Level
Level
 Forehead rest knob
Forehead rest knob

 Chart check mirror
Chart check mirror
Vertex distance check windows |
Measuring |
|
windows |
||
|
||
|
Lens banks |
Patient’s side
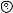 Forehead rest
Forehead rest
 Face shields
Face shields
 Measuring windows
Measuring windows
 Measuring windows
Measuring windows
Patients look at the chart through these windows.
 Vertex distance check windows
Vertex distance check windows
Used to check the patient’s VD (the distance from a corneal vertex point to the lens). The window has calibration markings of 12, 13.75, 16, 18 and 20 mm.
 Forehead rest knob
Forehead rest knob
Used to move the forehead rest forward and backward in order to adjust the vertex distance (VD).
 Level
Level
Used to verify that the refractor head is level. Turn the level adjustment knob until the air bubble is centered in the level.
 Near point card
Near point card
Used for Addition Power measurement.
Number of the chart |
Name of the chart |
|
on the rear side |
||
|
Chart
The refracting distance is printed at the top of the card.
3 - 2
 Near point rod
Near point rod
The distances from the patient’s eye to the near point card is marked in inches and centimeters.
•The black line at the near point card holder is aligned with the tick of the desired distance.
•The red number represents the power (diopter), the reciprocal of each distance in meters.
Adjust the chart to a desired distance from the patient’s eyes and tighten the knob to fix the position.
 Level adjustment knob
Level adjustment knob
Used to adjust the level of the refractor head. It can be inclined 2.5º toward the left or right at the maximum.
 Chart check mirror
Chart check mirror
An operator confirms the selected chart with this mirror.
 Forehead rest
Forehead rest
Patient’s forehead should touch the rest during measurement. Clean it before each measurement.
See “8.1 Cleaning the Forehead Rest”. (p. 8- 1)
 Face shields
Face shields
Patient’s face touches the shields during measurement. Clean them before measurement. See “8.2 Cleaning the Face Shields”. (p. 8-2)
Explanation of the chart
3 - 3
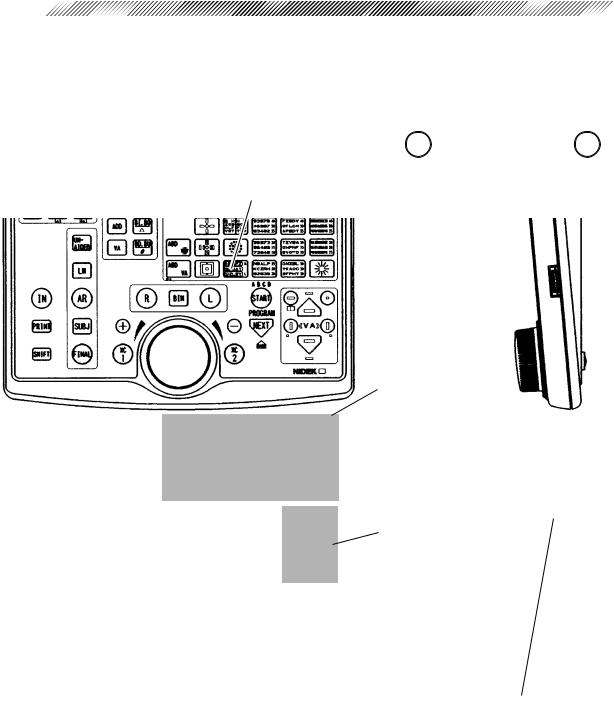
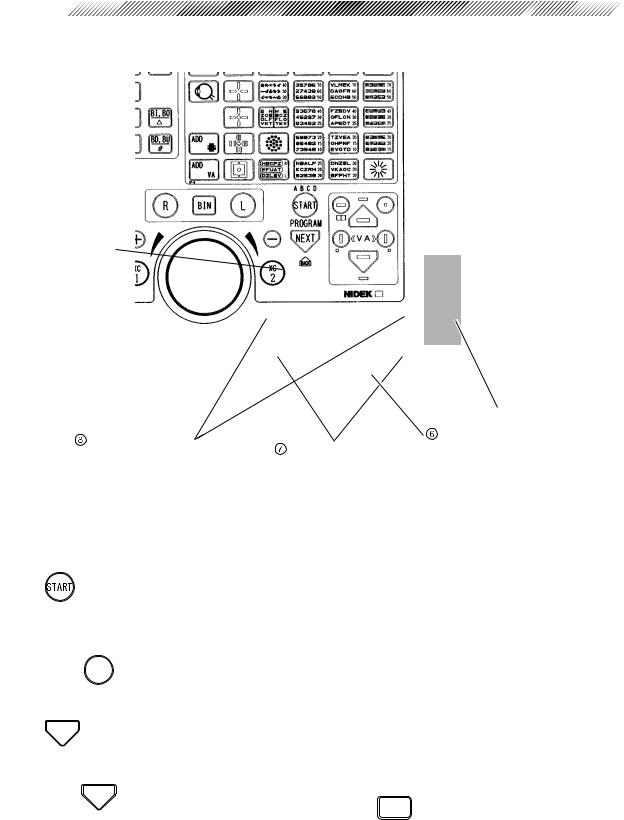
3.2 Control Box
The blue colored keys are used for basic operation.
*Some switches function differently when they are used in conjunction with  .
.
In this manual, when you see instructions such as: “ +
+ 
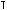 ”, it means “Press the
”, it means “Press the 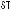
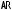
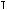 key while pressing the
key while pressing the  key.”
key.”
 Display
Display

 Chart keys
Chart keys

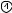 Masking keys
Masking keys
 Contrast adjustment knob
Contrast adjustment knob
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 - 4 |
|
|
Display |
- 2 |
, |
|
||
|
|
Shows SPH, CYL, AXIS data and the chart |
|
Used to isolate a vertical line on the VA chart. |
|||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
|
|
that is being presented. |
• Used to move the isolation to the right or |
||||
|
|
Date |
|
left after the vertical line mask or a single |
|||
|
|
Time |
|
letter mask has been applied. |
|||
|
|
Previous data window |
• |
+ |
/ |
Isolates a single let- |
|
|
|
(Sub-window) |
|
ter at the lower-left or lower-right corner of |
|||
|
|
Current data window |
|
||||
|
|
|
a VA chart. |
|
|||
|
|
(Main window) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Present chart |
- 3 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Used to isolate a single letter at the upper- |
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
right corner of a VA chart. |
|||
|
|
Contrast adjustment knob |
• |
+ |
Isolates a single letter at the |
||
|
|
|
upper-left corner of a VA chart. |
||||
|
|
Used to adjust the contrast of the display. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Chart keys |
|
- 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Used to isolate a middle line of a VA chart. |
||||
|
|||||||
|
|
Used to select charts. |
|||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
• |
+ |
Adds the Red/Green filter |
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Masking keys |
|
to a VA chart that has been selected. |
|||
|
|
|
Again, |
+ |
Releases the Red/ |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Used to isolate any acuity line or letter on the |
Green filter. |
|
chart that has been selected. |
||
|
||
To remove the mask, press any of the chart |
|
|
keys. |
|
|
VA (Visual Acuity) of the selected line or let- |
|
|
ter is shown at “VA” on the Main window of |
|
|
the display. |
|
 - 1 ,
- 1 ,
Used to isolate a horizontal line (letters of the same VA) on the VA chart.
•Used to move an isolation up and down after the mask has been applied.
• +
+  A horizontal line mask will be applied to the top line of the chart.
A horizontal line mask will be applied to the top line of the chart.
+ |
A horizontal line mask |
will be applied to the bottom line of the chart.
3 - 5
Keys of Control Box
 Eye selection keys
Eye selection keys 
 Program keys
Program keys
Value change keys |
Dial |
|
Cross cylinder keys |
||
|
 Program keys
Program keys
For more information on using the programmed refraction sequence, see “4.5 Refraction with the Standard Program” (p. 4-12).
 - 1
- 1
Starts a program.
•Press to start a programmed refraction sequence and activate the initial steps.
• +
+
 Switches among program modes (A, B, C, D, E) in order.
Switches among program modes (A, B, C, D, E) in order.
 - 2 0':6
- 2 0':6
Used to progress through each step of a programmed refraction sequence.
•  + 0':6 Allows the user to go back to a previous step in the refraction program. (This key combination is inoperative while in the Final Fit mode.)
+ 0':6 Allows the user to go back to a previous step in the refraction program. (This key combination is inoperative while in the Final Fit mode.)
 Dial
Dial
Changes any highlighted value.
Turn it clockwise The value changes to the negative.
Turn it counterclockwise The value changes to the positive.
The highlighted value changes by turning the knob while holding  down.
down.
 Cross cylinder keys
Cross cylinder keys
Place a cross cylinder lens to refine axis or Cylindrical Power.
When it is pressed during binocular tests, the left measuring window is covered in order to allow testing of the right-eye only.
To perform the test with both windows open, press  of the covered-side window. The 0.25 or 0.50 diopter lens should be selected in the “XC test” parameter of “Set parameter 1/5” screen prior to testing. A cross cylinder lens will be inserted as follows unless “Auto” is selected instead of “XC test” of “Set parameter 1/5”.
of the covered-side window. The 0.25 or 0.50 diopter lens should be selected in the “XC test” parameter of “Set parameter 1/5” screen prior to testing. A cross cylinder lens will be inserted as follows unless “Auto” is selected instead of “XC test” of “Set parameter 1/5”.

 - 1 :%
- 1 :%
•During axis refinement, the cross cylinder lens is inserted so that the minus axis is located at 45º from the minus axis position of the cylinder lens.
•During Cylindrical Power refinement, the cross cylinder lens is inserted so that the minus axis is located at 90º from the minus axis position of the cylinder lens.
•When using the Prism refinement mode (BI/ BO), this switch can be pressed to clear out the values and start at zero in the right eye.
 - 2 :%
- 2 :%
•During axis refinement, the cross cylinder lens is inserted so that the minus axis is located at 135º from the minus axis position of the cylinder lens.
•During Cylindrical Power refinement, the cross cylinder lens is inserted so that the minus axis is located 0º from the minus axis position of the cylinder lens.
•When using the Prism refinement mode (BI/ BO), this key can be pressed to clear out the values and start at zero in the left eye.
•Press this key while pressing  and the time display changes to the stopwatch display. This enables you to measure how long the test took and this function is sometime used for special tests to be carried out in a few seconds.
and the time display changes to the stopwatch display. This enables you to measure how long the test took and this function is sometime used for special tests to be carried out in a few seconds.
 Value change keys
Value change keys
Provides the same function as the dial.
 - 1
- 1
A value increases by increments of 1 each time it is pressed.
 - 2
- 2 
3 - 6
 Eye selection keys
Eye selection keys
Used to select right eye (R), left eye (L), or both eyes (BIN) for subjective measurements.
•The measuring window of the non-selected eye will automatically be covered. However, the occluder will not be inserted during binocular testing using prism lenses or polarizing filters.
• |
+ 4 or . Specifies the domi- |
|
nant eye. |
|
will be shown next to R or L on the |
|
measurement screen to indicate the domi- |
|
nant eye. |
 - 1 4
- 1 4
Leaves open or opens the right measuring window and leaves closed or closes the left measuring window. If a binocular testing chart is selected and binocular testing is desired, the left measuring window will not be covered and the right eye value is highlighted. In this situation, only right eye data can be adjusted.
 - 2 .
- 2 .
Leaves open or opens the left measuring window and leaves closed or closes the right measuring window. If a binocular testing chart is selected and binocular testing is desired, the right measuring window will not be covered and the left eye value is highlighted. In this situation, only left eye data can be adjusted.
 - 3
- 3
Keeps or makes both measuring windows open. When changing values in this situation, data of both eyes can be changed to the same values with each adjustment.
A value decreases by increments of 1 each time it is pressed.

3 - 7
Keys of Control Box
 Key
Key
 Key
Key
 Input key
Input key 
 Print key
Print key 
 Shift key
Shift key 
 Data keys
Data keys
 Data keys
Data keys
Used to specify the field for receiving data or storing measurements.
Measurements in the specified field are shown on the main window.
The specified field will be indicated at the up- per-left corner of the main window.
If one of the data keys is pressed without receiving data from an AR or LM, then the current measurements which have been on the main window, will be copied to the corresponding field to the selected data.
If one of these keys is pressed while holding
 down, measurements on the screen will be copied to the corresponding field regardless of whether any data has been received and stored.
down, measurements on the screen will be copied to the corresponding field regardless of whether any data has been received and stored.
To enter data to the RT-2100, see “4.3 Entering Data” (p. 4-2)
- 1 70
#+&'&
Used to open the field for measuring unaided visual acuity. The corrective lens power in the refractor head will be set to 0 D.
 - 2
- 2
Used to open the field for receiving lensometry data.
 - 3
- 3
Used to open the field for receiving auto-re- fractometry or retinoscopic measurements.
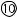 - 4
- 4 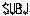
Used to open the field for subjective refinement. When data is received from the AR or LM, this field will automatically open. The elapsed time starts to be measured from the point where any data is entered to the SUBJ field when the “Auto test time” parameter is set at “Yes”.

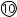 - 5
- 5 
Used to open the field for obtaining a final prescription and visual acuity.
The refined values are copied from the “SUBJ” field and are adjusted to determine final data.
 +
+ 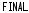
This will automatically activate the Final Fit mode where Far Powers are automatically adjusted. (See “4.7.1 Auto adjustment of Far Powers”.) (p. 4-24)
While holding down this key, indication increments change or modes change when the dial is turned or when a key is pressed.
 24+06
24+06
Used to print out measurements or to export data to an external computer. See “5.2 Printout” (p. 5-4)
 +0
+0
Used to receive data from the LM or AR. Press the key and make sure that the data No. on the display is the same as the one on the printout from the LM or AR. Specify either ( ,
,  ) with the data keys.
) with the data keys.
Used to close the measuring windows. Used for monocular testing or cover testing.  +
+  Insert a pinhole plate with a diameter of 1 mm.
Insert a pinhole plate with a diameter of 1 mm.
•The Focal depth of the eye becomes deeper.
•Can be used when visual acuity obtained with the corrective lenses is below expectations. If the pinhole improves the patient’s VA, the eye may have an irregular astigmatism.
3 - 8
Used to open the measuring window. Auxiliary lenses will be removed.
 + Right
+ Right 
6 ∆ base UP prism lens will be placed in the right measuring window. It appears to the patient that one chart is dissociated into the upper and lower parts. Used to detect horizontal phoria.
 + Left
+ Left 
10 ∆ base IN prism lens will be placed in the left measuring window. It appears to the patient that one chart is dissociated into the left and right parts. Used to detect vertical phoria.
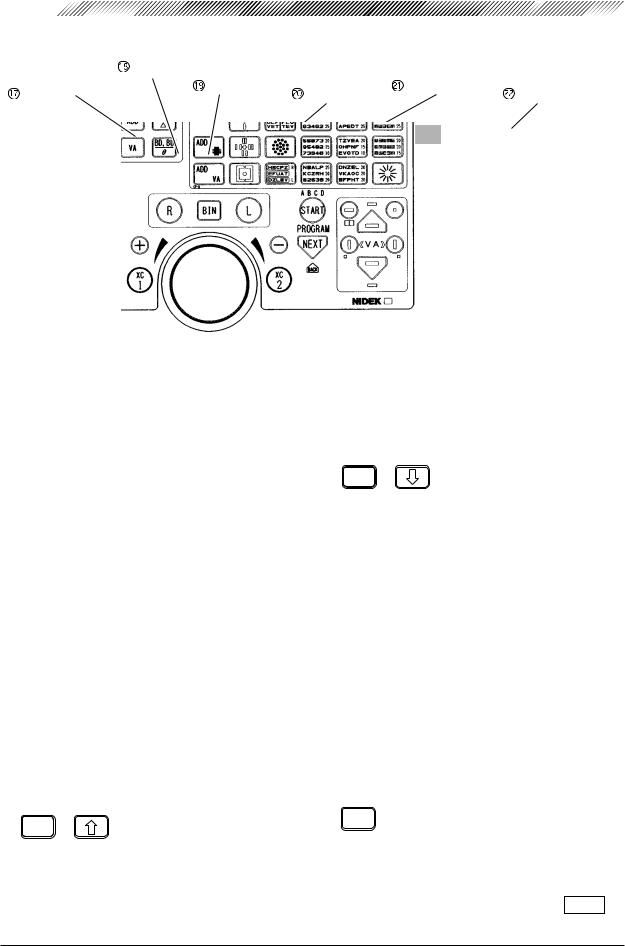
3 - 9
Keys of Control Box
|
C+/– key |
|
|
|
Help key |
F/N key |
Mode keys |
Function keys |
Clear key |
|
|
 Setting keys
Setting keys 
 Setting keys
Setting keys
Used to open the field for changing parameter settings or programming refraction. See “§5 OTHER FUNCTIONS”. (p. 5-1)
 - 1
- 1 
Used to open the “Set up menu” screen.
 - 2
- 2  ,
, 
Used to select a menu option.
These keys are also used to adjust the chart position when the SSC-300/SSC-330/SSC- 350 is connected to the RT-2100.
When programming, they are used to select the comments. See “5.1.2 Programming” (p. 5-2).
 +
+  *2
*2
Makes the intensity of the glare lamp higher by one increment while the glare lamp is illuminated. The brightness, however, does not change when the lamp intensity is the highest even though these switches are pressed.
 +
+  *2
*2
Makes the intensity of the glare lamp lower by one increment while the glare lamp is illuminated. The brightness, however, does not change when the lamp intensity is the lowest even though these switches are pressed.
 - 3
- 3 
Used to determine the selected menu options. If the RT-2100 interfaces with the SSC-300/ SSC-330/SSC-350, this key is used to adjust the chart position. See “4.4 Initial Setups” (p. 4-11).
 +
+  *2
*2
Turns the glare lamp ON/OFF.
 *'.2
*'.2
Used to call up on-screen explanations and instructions for the selected chart.
To cancel, press the key again or press the function key which corresponds to END .
*2 This function is available only when the optional glare lamp is attached to the connected SSC330.

3 - 10
Switches Cylindrical Power to either + or –.
Switches to either the Distance (Far) mode or Near mode. The selected mode is indicated in the upper-right corner of the main window as “FAR” or “NEAR”.
•The system will automatically operate in the Far mode when the power is turned ON and after data is cleared.
•The Near mode is used after distance vision has been refined and Addition Power has been calculated in order to perform near vision function testing such as relative accommodation and horizontal or vertical phoria testing. When the Near mode is selected, both lens banks will converge to the preset working distance of 40 cm (variable) automatically.
•The ADD key will not work in the Near mode. The Near SPH value will be calculated by adding ADD value to the distance SPH value (distance SPH + ADD). It is also possible to transfer the distance SPH value alone into the Near mode by selecting the “SPH + ADD” option in the “SPH Far → Near” parameter.
 Mode keys
Mode keys
Selects the measurement field in which measurements are to be refined (or changed). Once the field is selected, a data field will be highlighted, indicating that changes can be made.
The measurement can be changed with the dial or  ,
,  .
.
 - 1
- 1
Places the system into the SPH mode which allows Spherical Power to be adjusted.
 - 2
- 2
Places the system into the CYL mode which allows Cylindrical Power to be adjusted.
 - 3
- 3
Places the system into the AXIS mode which allows the cylindrical axis to be adjusted.
 - 4
- 4
Places the system into the ADD mode which allows the Addition Power to be adjusted.*3 Both lens banks will automatically converge to the preset working distance of 40 cm (variable). See the explanation of “Working dist. (WD)” parameter. (p. 5-13).
•When the “Preset ADD” parameter is set to “Yes”, the patient’s general age can be selected*4 and the expected spherical lens will be inserted and Addition Power will be displayed.
•Each time the key is pressed, a spherical lens with an Addition Power will be added or removed alternately and the lens banks will
remain converged.
The reversed ADD indicator  on the main window will change to
on the main window will change to  and date indication will also change to “ADD-OFF” showing that the lens is re-
and date indication will also change to “ADD-OFF” showing that the lens is re-
moved.
By pressing  again, the Addition Power indicator will be highlighted and the addition power of the lens will be added.
again, the Addition Power indicator will be highlighted and the addition power of the lens will be added.
*3 When the system is placed into the ADD mode during standard program (Program A) operation, ±0.5 D cross cylinder lens (minus axis: 90°) will automatically be placed into the measuring windows. The ±0.5 D cross cylinder lens will not be inserted when  is pressed during non-programmed measurement.
is pressed during non-programmed measurement.
To insert the ±0.5 D cross cylinder lens, press  .
.
*4 The expected spherical lens with Addition Power will automatically be added according to the selected age. See “Appendix. D Preset Addition Power”.

3 - 11 



























After entering Addition Power, the working distance indications appear and the desired working distance can be selected with the corresponding function key.
The procedure for removing and setting Addition Power is the same as that for prism lenses. See “4.3.5.5 Removing and replacing prism lenses”. (p. 4-9)
It is possible to switch fields among LM, AR, SUBJ and FINAL on condition that the lens banks are converged in the ADD mode.
• +
+ 
Used to place the system in the mode which allows the values for NPC, NPA, NRA and PRA*5 to be entered.
For the procedures of each test, see “§6 METHOD OF SINGLE TESTS”. (p. 6-1)
 - 5
- 5
Allows the user to manually enter visual acuity with the dial.
When AR or LM data has been entered and “UNAIDED” or “LM” field key is pressed, an expected VA chart will be presented.*6
 - 6
- 6
Allows the user to select a patient ID No., which will be printed out and can be used as a communication ID for patient records in a PC.
See “5.2.1 Changing an ID No.”. (p. 5-6)
 - 7
- 7
Displays PD measurement and allows the user to adjust the PD measurement in the refractor head.
Monocular PD (1/2 PD)*7 Adjustments
can be made after pressing either |
4 or . |
while in the PD mode. |
|
To exit from the mode Press |
again. |
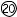 - 8
- 8 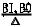

Allows the user to adjust base IN/OUT prism values for horizontal measurements. Either rectangular coordinates or absolute values for polar coordinates may be entered and adjusted. See “4.3.5 Setting prism lenses” for procedure for adjusting Prism Power. (p. 4- 7)
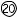 - 9
- 9 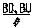
Allows the user to adjust base UP/DOWN prism values for vertical measurements. Either rectangular coordinates or angle for polar coordinates may be entered.
 Function keys
Function keys
Used to select functions displayed on the bottom of the main window.
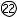 %.'#4
%.'#4
Clears all the data displayed in each field, on the measurement screen. To delete data in each field, press this key simultaneously with
70 |
, |
, |
, |
or |
. |
#+&'& |
*5 NPC: Near Point of Convergence |
NPA: Near Point of Accommodation |
NRA: Negative Relative Accommodation |
PRA: Positive Relative Accommodation |
*6 The expected VA chart will be presented only on condition that the parameter “Preset VA” is set to “1 letter” or “H. line”. For the type of the presented VA chart, see “Appendix. E Table for VA values as presented on charts”.
*7 Even when the monocular PD for only one eye is changed, both the left and right lens banks move concurrently.
3 - 12
Keys of Control Box
* Only when using the SSC-350 TYPE T/TCG in combination with the RT-2100
Glare key |
Low illumination key |
Contrast key |
The following keys are used only when the RT-2100 is used in combination with the SSC-350 TYPE T/TCG.
Turns ON or OFF the glare lamp. (Only the
SSC-350 TYPE TCG)
Used to test at night.
Pressing the key switches between low light and standard light illuminations.
Selects the contrast of charts.
Pressing the key changes the contrast in the order of 25% → 12% → 6% → 100% (standard light illumination). (Only the SSC-350 TYPE TCG)
3 - 13 


























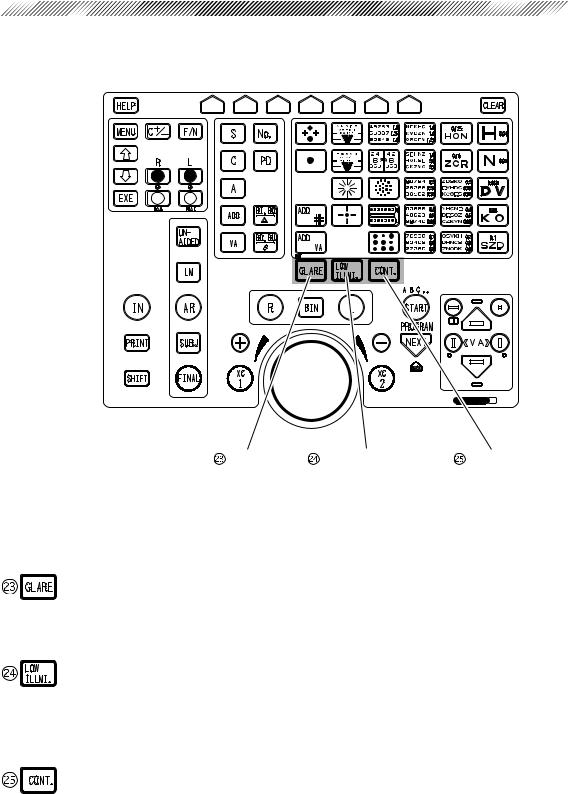
3.3 Relay Box
Normally, the relay box is contained in the system table.
Connector for AR*8 |
Connector for external |
Connector for |
|
|
||
computer*8 |
|
network (optional)*8 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
Power connector |
Connector for LM*8 |
Connector for |
|
Terminator |
Power switch |
|
for IC card |
chart presenting |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
Reader/Writer*8 |
|
|
device*8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CB NO. NNNN |
|
|
Connector for control box |
Connector for |
Connector for |
Fuse holder |
|
printer |
refractor head |
Power connector |
Connector for AR*8 |
|
Terminator |
|
Port to connect the relay box to an Auto-Re- fractometer or IC card Reader/Writer.
 Connector for LM*8
Connector for LM*8
Port to connect the relay box to a lensmeter.
 Connector for external computer*8
Connector for external computer*8
Port to connect the relay box to an external computer.
 Connector for chart presenting device*8
Connector for chart presenting device*8
Port to connect the relay box to a chart presenting device.
 Connector for network*8
Connector for network*8
Port to connect the relay box to an external computer for networking.
Used only when more than one refractor is used on a network. Normally, set at “1”.
 Connector for refractor head
Connector for refractor head
Port to connect the relay box to the refractor head.
 Connector for printer
Connector for printer
Port to connect the relay box to the printer.
 Connector for control box
Connector for control box
Port to connect the relay box to the control box.
 Power connector for IC card Reader/Writer*8
Power connector for IC card Reader/Writer*8
Port to connect IC card Reader/Writer to a power source.
*8 Accessory equipment connected to the analog and digital interfaces must be certified according to respective IEC standards (i. e. IEC 950 for data processing equipment and IEC 60601-1 for medical equipment). Furthermore all configurations shall comply with the system standard IEC 60601-1-1. Anyone who connects additional equipment to the signal input part or signal output part configures a medical system, and is therefore responsible that the system complies with the requirements of IEC 60601-1-1. If in doubt, consult NIDEK or your local representative.
 Loading...
Loading...