Page 1
VivoTAC / OrthoTAC
Instructions for Use
Page 2
Verarbeitungsanleitung
Seite 12
Mode d’emploi
Page 22
Istruzioni d’uso
Pagina 32
Instrucciones de uso
Pagina 42
Instruções de Uso
Página 52
SR
SR
Page 2

Instructions for Use
Introduction
Please read these Instructions for Use carefully
and familiarize yourself with the application
techniques.
The prefabricated SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC tooth line
is a diagnostic, radiopaque tool that is designed to help
dental technicians fabricate implant-supported
restorations. Because of their special composition, these
teeth are radiopaque.
Advantages
– A defined radiopacity achieved through industrial
fabrication
– Moulds corresponding to those of the popular
SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp and SR Vivodent PE /
SR Orthotyp PE tooth lines
– Easily prepared diagnostic aid
– The shape of radiopaque teeth can be modified with
radiopaque monomers and polymers
– Strong bond with heat-curing as well as cold-curing
polymers
– Prefabricated radiopaque teeth save time in the
fabrication of stents
– The teeth ensure the accurate placement of dental
implants during the planning phase
– Homogeneous dispersion of the radiopaque material
in the teeth
Composition
The resin teeth are composed of the following
ingredients:
Polymethyl methacrylate and barium sulphate
66–67 wt%
Methyl methacrylate and dimethacrylate 33–34 wt%
Additional components: catalysts and stabilizers
0.5 wt%
Modifier Monomer:
Methyl methacrylate and dimethacrylate 99 wt%
Catalysts and stabilizers 1 wt%
Modifier Polymer:
Polymethyl methacrylate and barium sulphate
> 99 wt%
Catalyst < 1 wt%
Indication
For the fabrication of fixed and removable implantsupported dental restorations in situations where the
set-up of teeth is beneficial to the pre-surgical radiological diagnosis (CT, teleradiography as well as OPG),
eg:
– severe dysgnathia
– severe atrophy of the alveolar ridge
– reconstructive surgery of the mouth, jaw or face
Pre-surgical planning of the restoration enables the ideal
placement, location and angulation of the implant to be
established.
Contraindication
The product is contraindicated for all the applications
that are not specifically recommend by Ivoclar Vivadent
as well as for permanent restorations in the mouth of
patients.
In case of fixed metal prosthetics, metal fillings or metal
osteosynthetic materials, the image quality of the CT and
thus the recognizability of the radiopaque tooth may be
impaired.
Side effects
To date, no systemic side effects are known. In rare
cases, allergic reactions have been reported in
conjunction with methyl methacrylate and polymethyl
methacrylate materials. Do not use SR Vivo TAC / SR
Ortho TAC or Modifier Polymer and Monomer if a
patient is known to be allergic to any of the products’
ingredients.
2
Page 3
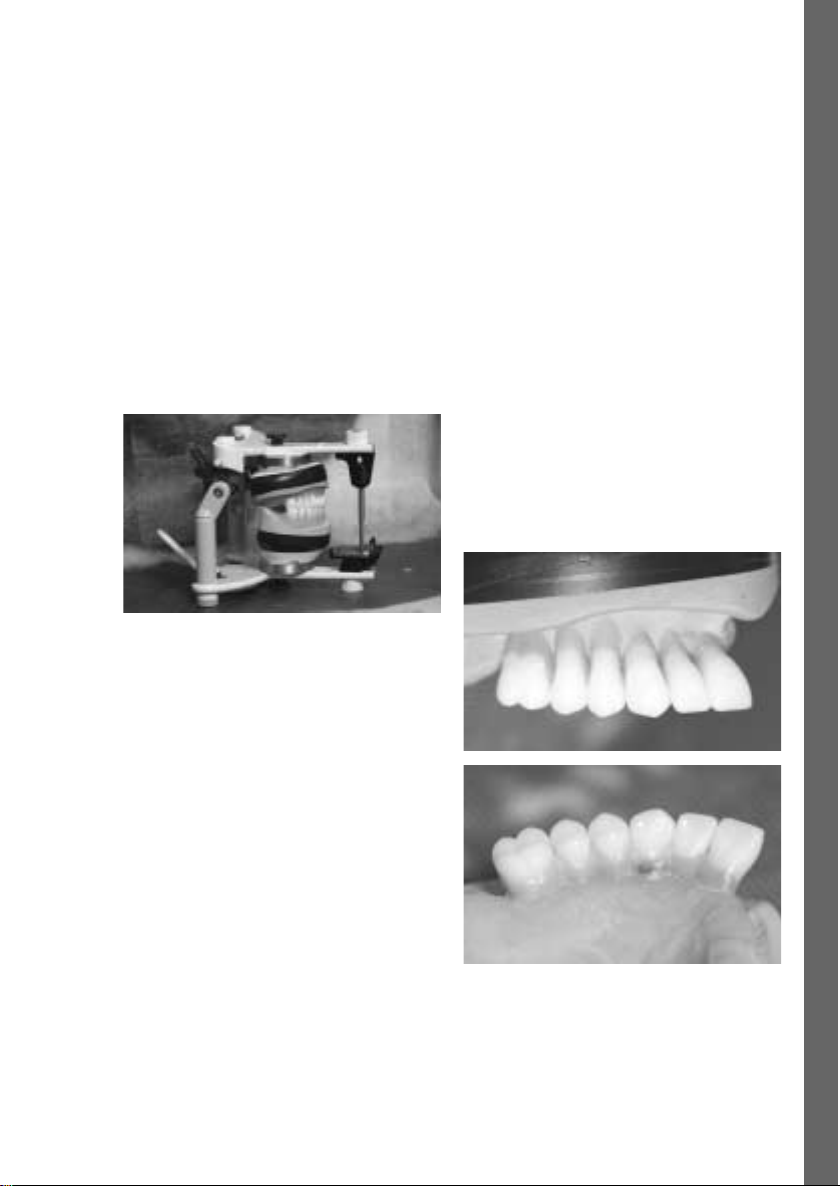
1. Laboratory
Diagnostic stents are fabricated to allow the implantsupported complete denture to be set up according to
the instructions of the dentist, taking aesthetic, phonetic
and functional aspects into account. In the process,
SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC are used like conventional
denture teeth.
The use of set-up aids such as the 2D/3D setting up
template (Ivoclar Vivadent AG) is recommended.
Suggested procedure
Once the radiopaque teeth have been set up in wax,
excess wax in the vestibular region is removed to
lengthen the cervical region with the Monomer/Polymer
Modifier until the base of the tooth rests on the model.
Consequently, the entire length of the tooth is made of
radiopaque material.
English
Processing
The radiopaque teeth SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC are
set up according to conventional principles.The moulds
of the radiopaque teeth are identical to those of the
SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp tooth line. SR Vivo TAC /
SR Ortho TAC exhibit excellent, consistent radiopacity.
Consequently, the two and three-dimensional
relationship between the position of the implant and
that of the subsequent superstructure can be
established.
Fabrication of diagnostic stents
Wax model with lengthened cervical regions
3
Page 4
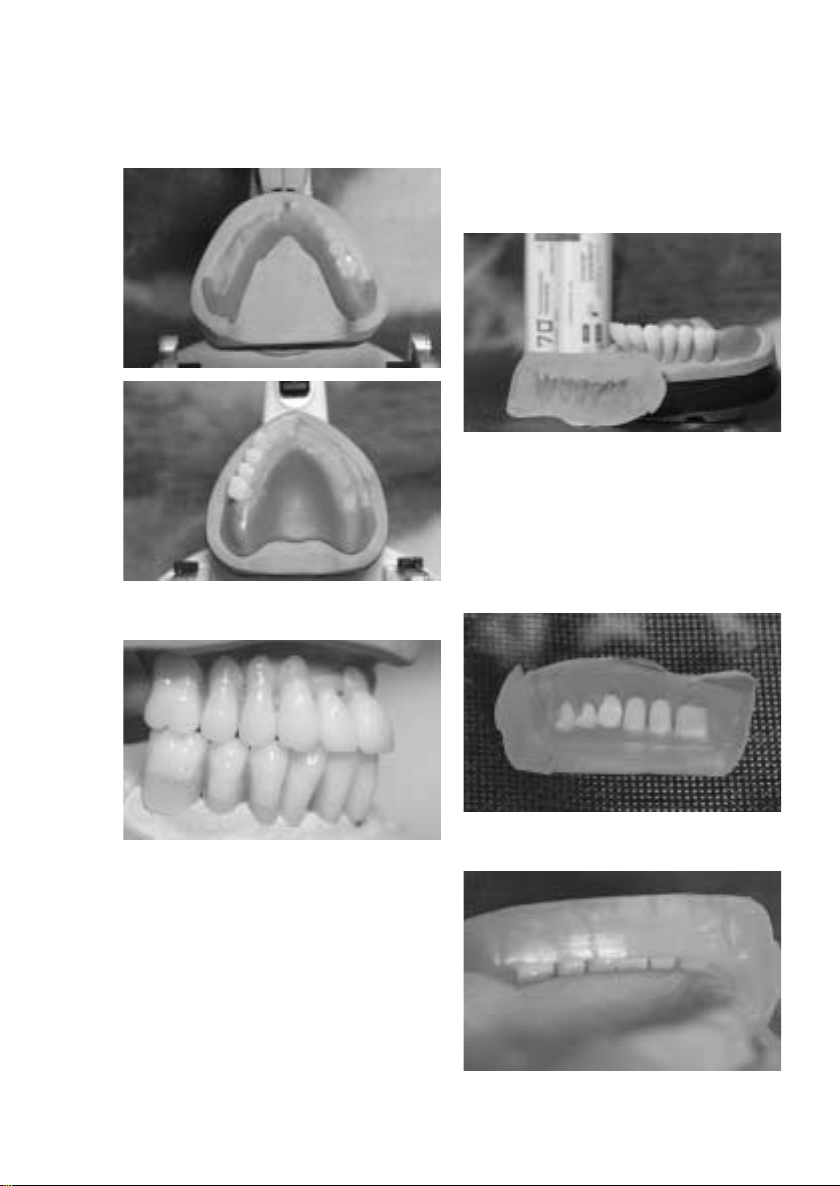
Adjustment of shape
– Following the set-up and wax-up procedures, a key is
fabricated using silicone or plaster.
– Remove wax from the model and teeth without
leaving any residue. If a plaster key is used, the model
and the key have to be isolated with Ivoclar Vivadent
Separating Fluid. In addition, the tooth surfaces
requiring adjustments must be roughened.
Completed wax model
Completed model with lengthened cervical regions
Key of teeth set up in wax
Reposition the teeth in the key
Check the accuracy of fit
4
Page 5
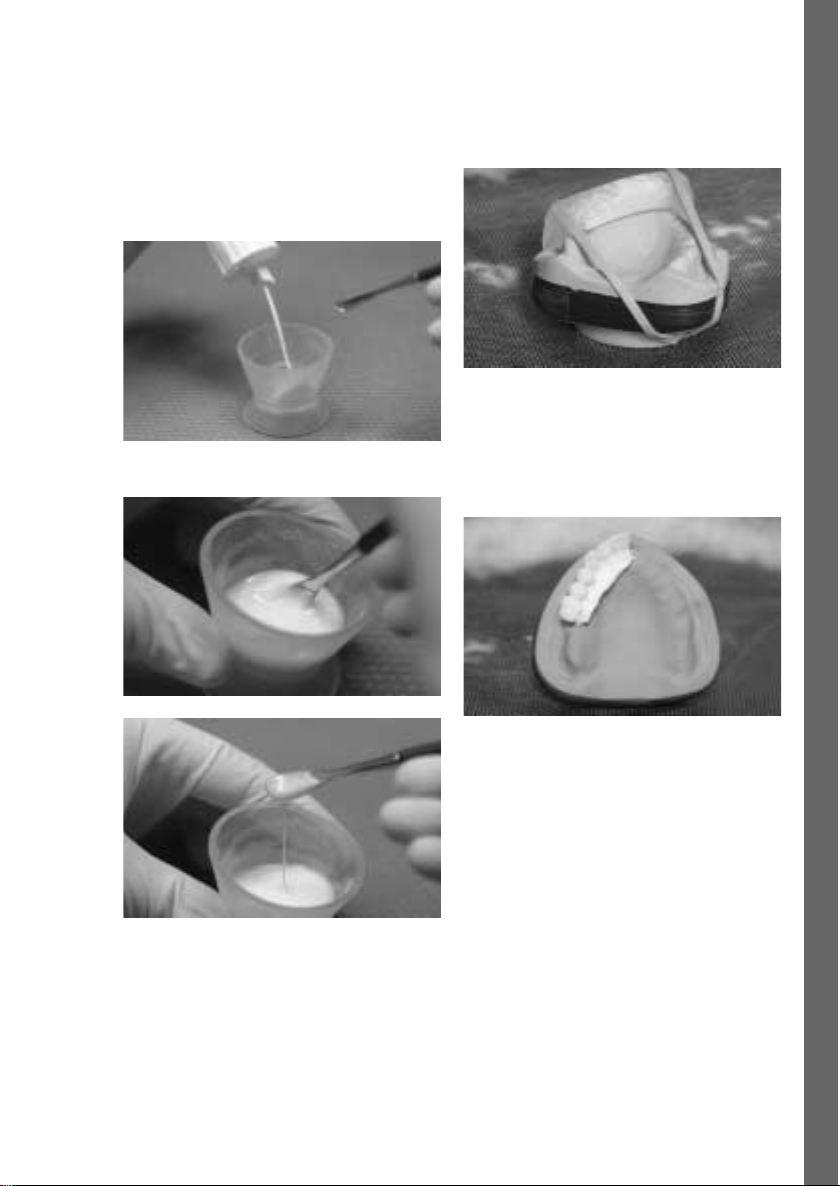
English
– Mix the Polymer and Monomer Modifier in a 1.3 : 1
ratio and leave to rest uncovered for 2–3 minutes.
– Polymerization is conducted in a pressure device or in
a heat/pressure polymerization unit (eg Ivomat),
15 minutes at 40–50 °C / 104–122 °F and 2–6 bar
pressure.
If necessary, radiographic balls or similar aids may be
integrated into the diagnostic stents where they are
needed.
Mix the Monomer and Polymer Modifier
Secure the key
Pour the liquid material into the key
After polymerization
5
Page 6
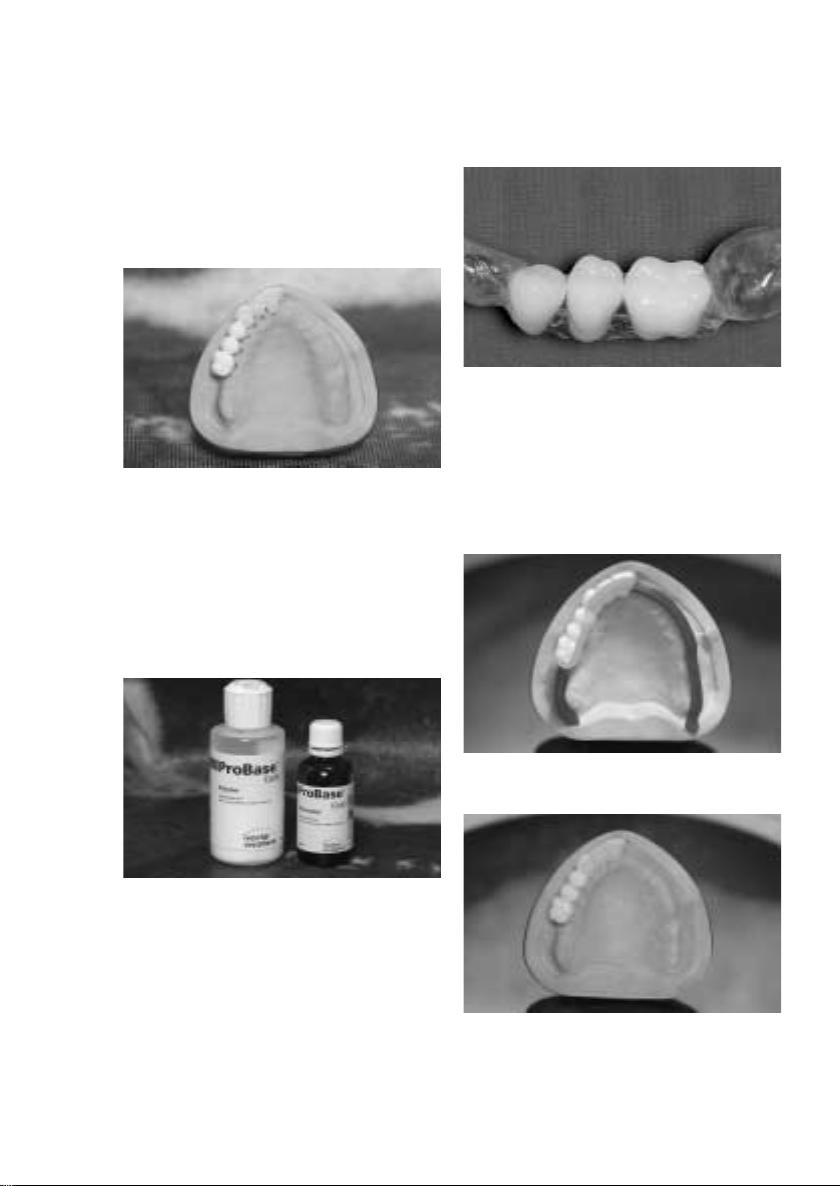
Finishing
Conventional finishing and polishing instruments are
used for finishing (according to the conventional PMMA
working techniques).
If requested by the dentist, a radiopaque alveolar ridge
with mucosa can be created by coating this area with
the Monomer/Polymer Modifier.
Fabrication of base plates
In order to reinforce or stabilize the diagnostic stents, a
base plate is fabricated for the palatal or lingual region.
It is made of clear or pink denture base material (eg
ProBase Cold pink/clear) or a heat-curing polymer (eg
ProBase Hot pink/clear).
When fixed restorations are planned (eg with an
interdental gap), the base plate rests on the mesial or
distal remaining dentition to stabilize and position the
restoration.
After finishing
Space retainer for radiopaque Modifier material
Polymerized stents
Stent design for gaps
ProBase Cold clear (also available in pink)
6
Page 7
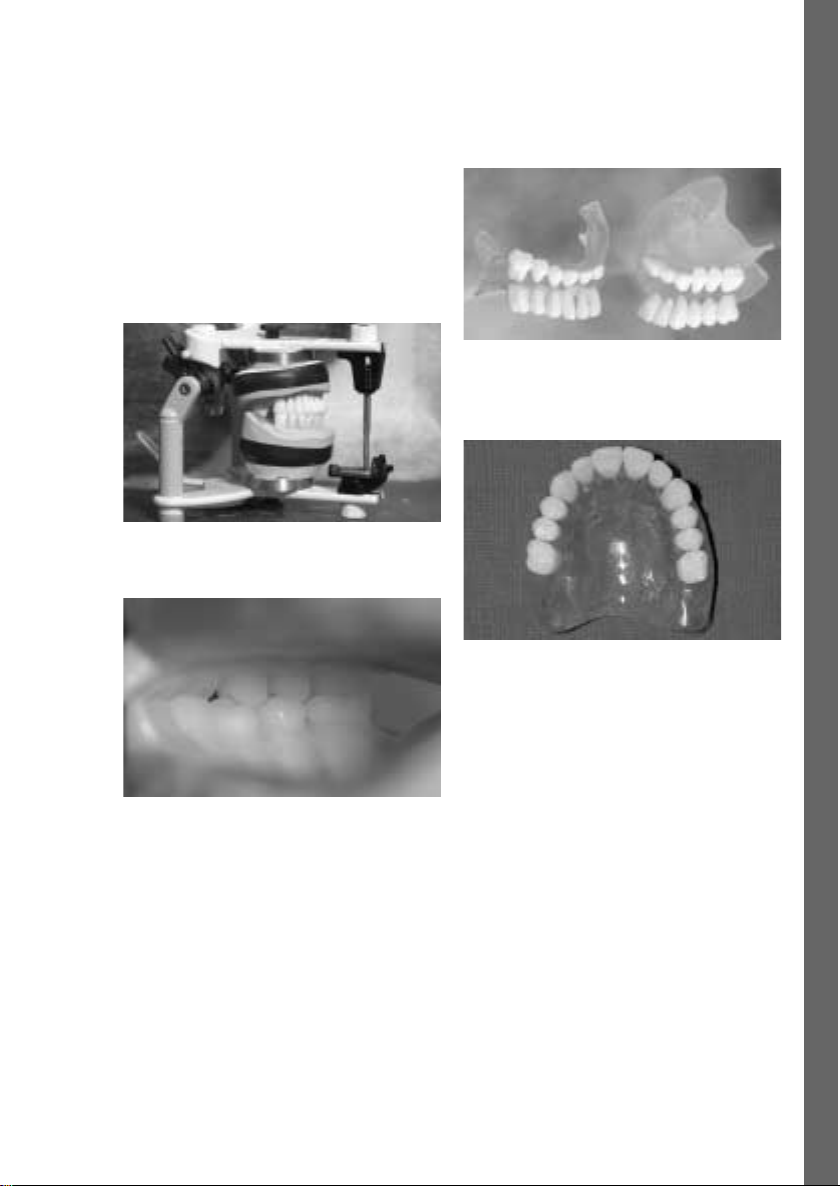
English
Polishing
As the stents are used as a diagnostic tool and/or an aid
during the surgical intervention, thorough prepolishing
with goat’s hair brushes and pumice as well as high
gloss polishing with cotton buffers and polishing paste
(Universal Polishing Paste from Ivoclar Vivadent) is
recommended.
Option
Finished diagnostic stent
Diagnostic stent for complete maxillary denture
Check the occlusion
7
Page 8
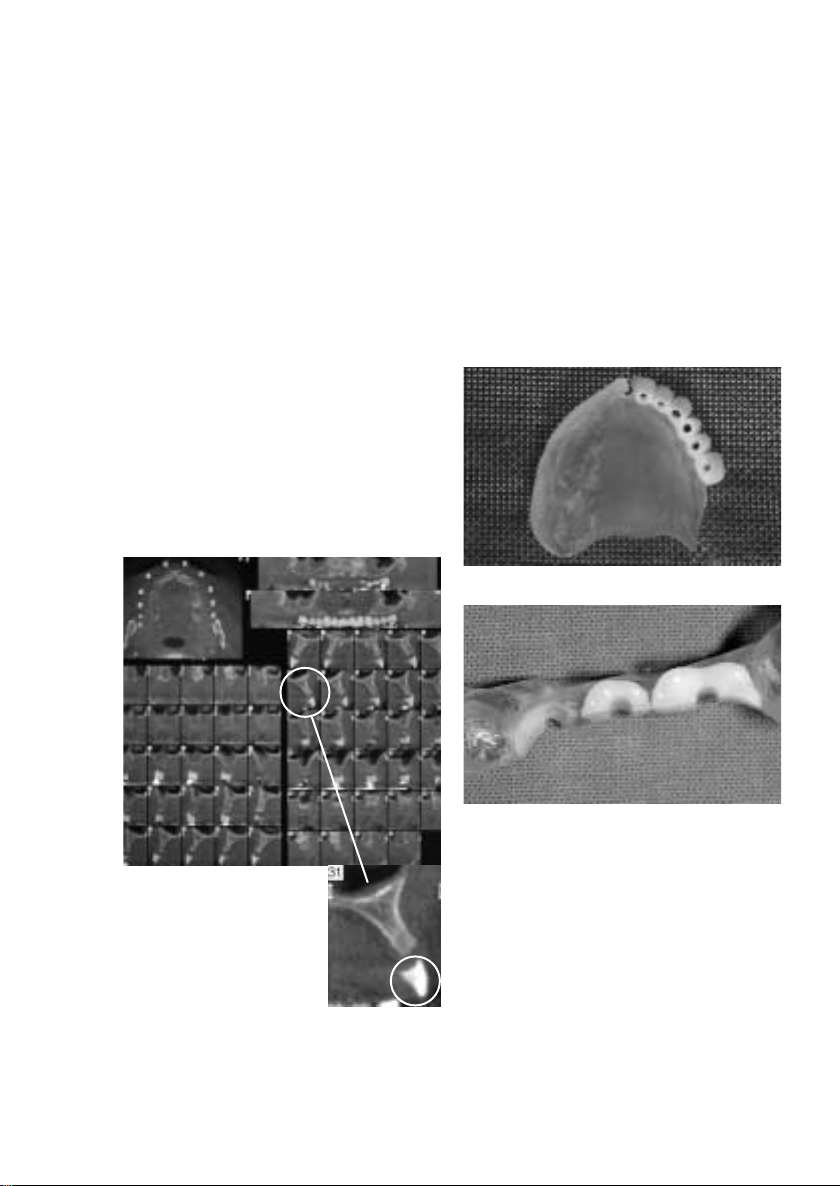
Application
In order to create guide channels prior to the surgical
part of the treatment, the dentist (or dental technician)
drills through the radiopaque teeth. These channels
assist the clinician during the surgical intervention. In
order to establish ideal prerequisites for the subsequent
fabrication of the superstructure, the angles of the
implant axes must be as parallel as possible.
Transformation of the diagnostic stent
into a surgical stent
Practice/Laboratory
When the dentist receives the stent from the laboratory,
he or she can conduct a try-in to examine the aesthetics,
phonetics and function of the planned dental restoration. It is advisable to make any necessary adjustments
before the radiographic examination.
The radiograph serves as an additional treatment
planning instrument. It enables the dental professional
to establish the location and angulation of the implants,
taking the bone substance and functional requirements
of the future restoration into consideration.
(If necessary, radiographic balls or hollow titanium
cylinders may be used with the stent.)
CT image
Creation of guide channels
Reduced teeth as an alternative
The surgical stents are used according to the preferred
method of the user with the customary materials.
8
Page 9
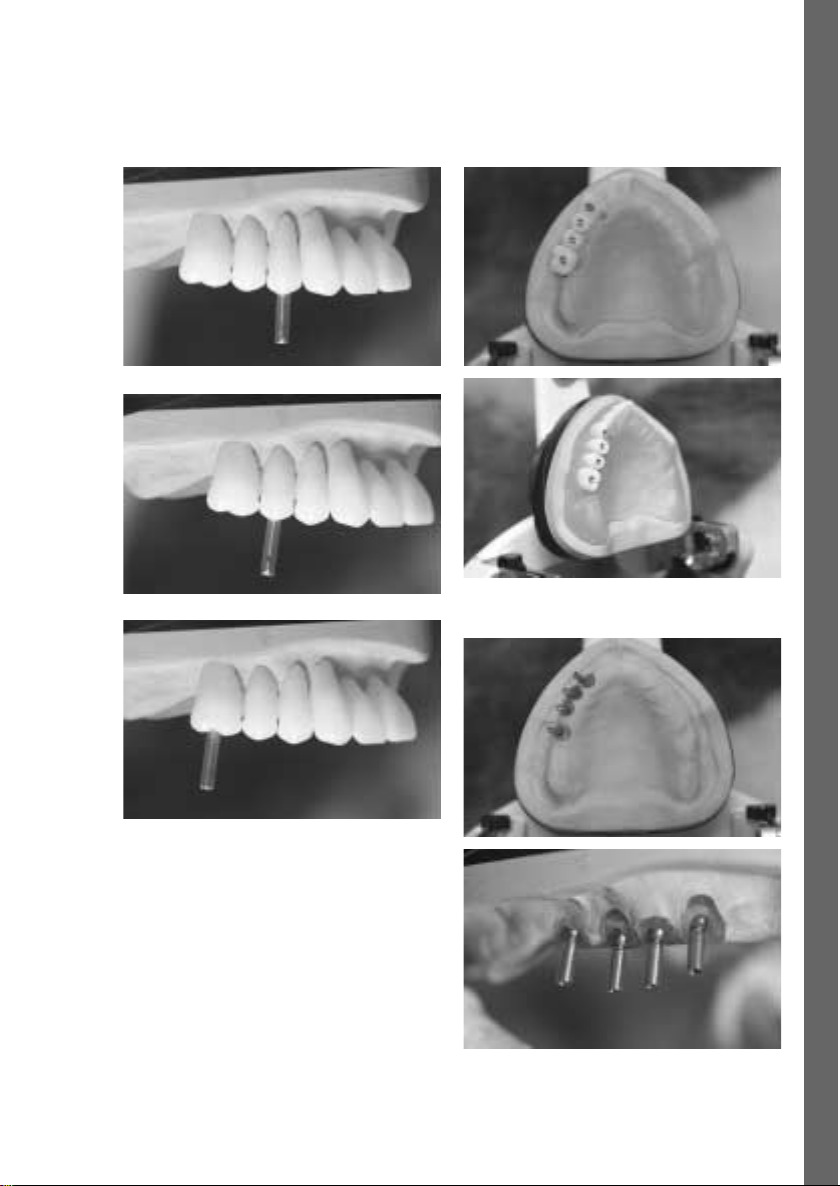
English
Tooth and implant axes
Completed surgical stent
Implant axes on the model
9
Page 10
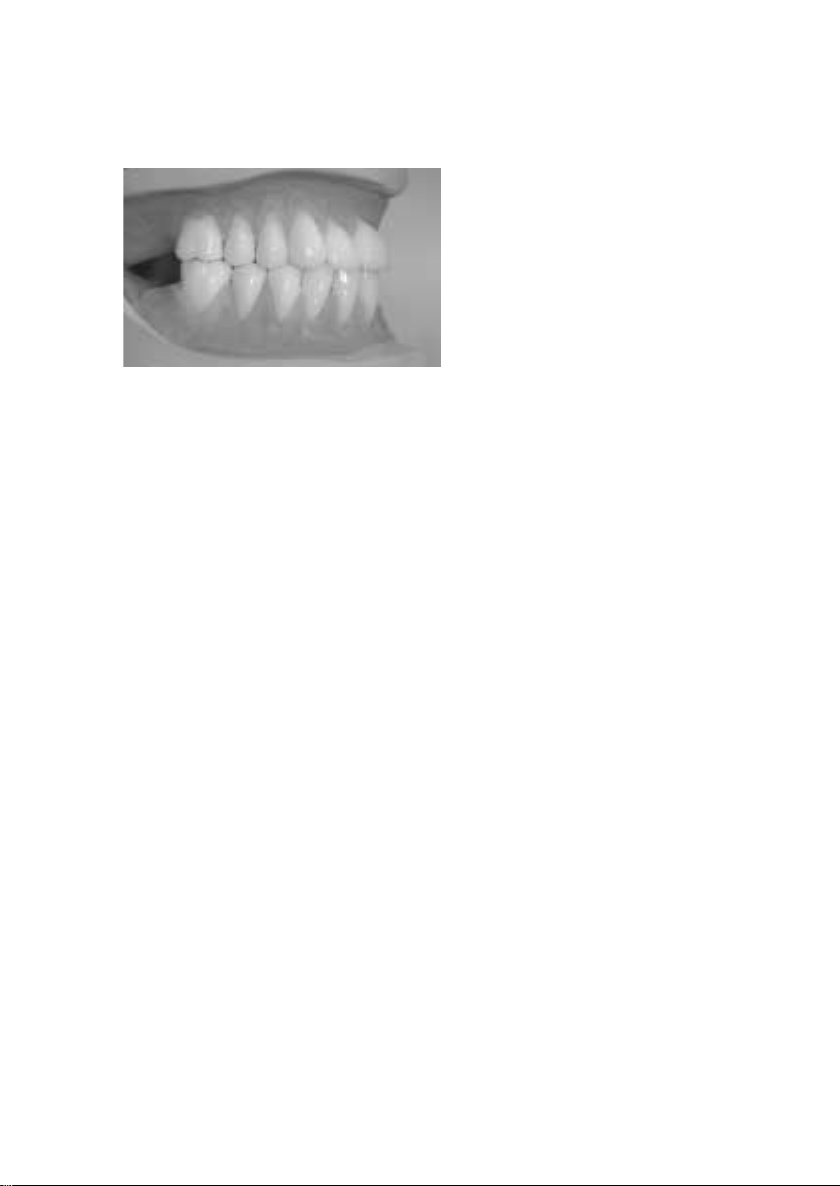
Warnings
– The inhalation of grinding dust must be avoided.
– Mucous membranes must not come into contact with
uncured material.
– Prolonged or repeated skin contact with the mono-
mer and uncured material may cause irritation and
sensitivity to methacrylates.
– The Modifier Monomer contains methyl methacrylate.
– MMA is easily flammable and irritating (flash point
+10 °C / 50 °F).
– Irritating to the eyes, skin and respiratory organs.
– Do not inhale vapours.
– May cause sensitization by skin contact.
– Keep away from ignition sources. Do not smoke.
– Do not empty in drains.
Storage of the Modifier Monomer /
Modifier Polymer
– Store in a cool, dark place.
– Storage temperature: 12–28 °C / 54–82 °F
– See secondary packaging for storage instructions and
expiry date.
– Do not use the product after the indicated date of
expiration.
– Keep out of the reach of children.
Delivery form
Basic Kit
1x SR Vivo TAC upper anterior teeth in moulds A15,
A24B,A25,A27
1x SR Vivo TAC lower anterior teeth in moulds A4,A8,
A9
1x SR Ortho TAC upper posterior teeth in moulds N2,
N6
1x SR Ortho TAC lower posterior teeth in moulds N2,
N6
Modifier Kit (1 Monomer 30 ml, 1 Polymer 30 g)
Instructions for Use
Refills
– SR Vivo TAC A15,A24B, A25, A27, A4, A8,A9
– SR Ortho TAC N2, N6 upper and lower
– Polymer Modifier 30 ml
– Monomer Modifier 30 g
Additional applications
– Insertion of metal guide channels
– Sagittal reduction of the vestibular or oral region of
the guide channel up to the first half of the drill
holes.
Completed acrylic resin denture
Source:
Pictures courtesy of M Nanni, Dr A Fanti, P Miceli, Italy
10
Page 11

English
This product has been developed solely for use in dentistry. Processing should be
carried out strictly according to the Instructions for Use. Liability cannot be accepted
for damages resulting from failure to observe the Instructions or the stipulated area
of application. The user is responsible for testing the materials for their suitability and
use for any purpose not explicitly stated in the Instructions. Descriptions and data
constitute no warranty of attributes and are not binding.
Date information prepared
03/2004
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
FL-9494 Schaan / Liechtenstein
11
Page 12

Verarbeitungsanleitung
Prämisse
Bitte lesen Sie diese Verabeitungsanleitung aufmerksam durch und machen Sie sich mit der
Anwendung vertraut.
Die präfabrizierten Zähne SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC
stellen ein diagnostisches röntgenopaques Instrument
dar, welches der Zahntechniker zur Unterstützung bei der
nachfolgenden Realisierung von implantatgetragenen
Restaurationen verwenden kann.
Dank der besonderen Zusammensetzung besitzen diese
Zähne eine röntgenopaque Wirkung.
Vorteile:
– Die industrielle Herstellung ermöglicht eine definierte
Röntgenopazität
– Die Formen entsprechen den bekannten Zahnlinien
SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp oder SR Vivodent PE /
SR Orthotyp PE
– Einfaches Erstellen eines diagnostischen Hilfsmittels
– Formveränderungen der röntgenopaquen Zähne
mittels röntgenopaquem Polymer und Monomer mög-
lich
– Hoher Verbund sowohl mit Heisspolymerisat als auch
mit Kaltpolymerisat
– Zeitersparnis bei der Herstellung von Bohrschienen
durch präfabrizierte, röntgenopaque Zähne
– Dient der gezielten Positionsbestimmung dentaler
Implantate während der Planungsphase für dentale,
implantologische Rekonstruktionen
– Homogene Durchmischung der Zähne mit
Röntgenkontrastmittel
Zusammensetzung:
Die Kunststoffzähne bestehen aus folgenden
Inhaltsstoffen:
Polymethylmethacrylat und Bariumsulfat 66–67 Gew.%;
Methylmethacrylat und Dimethacrylat 33–34 Gew.%.
Zusätzlich enthalten sind Katalysator und Stabilisatoren
0.5 Gew.%.
Modifier Monomer:
Methylmethacrylat und Dimethacrylat 99 Gew.%:
Katalysator und Stabilisatoren 1 Gew.%.
Modifier Polymer:
Polymethylmethacrylat und Bariumsulfat > 99 Gew.%:
Katalysator < 1 Gew.%
Indikation:
Zur Anfertigung von festsitzendem und abnehmbarem
implantatgetragenen Zahnersatz, bei dem zur präoperativen, radiologischen Diagnostik (CT, Fernröntgen aber
auch OPG möglich) Zahnaufstellungen von Vorteil sind,
wie z.B. bei:
– ausgeprägter Dysgnathie
– ausgeprägter Alveolarkammatrophie
– mund-, kiefer- und gesichtschirurgischen Korrekturen
und Rekonstruktionen
Durch die präoperative Diagnostik der geplanten
Versorgung kann eine ideale Implantatposition ermittelt
und festgelegt werden.
Kontraindikation:
Für alle Indikationen, die nicht ausdrücklich von Ivoclar
Vivadent empfohlen werden und für die Verwendung als
im Mund des Patienten permanent verbleibenden
Zahnersatz.
Beim Vorliegen von festsitzendem, metallischen
Zahnersatz, metallischen Füllungen oder metallischen
Osteosynthesematerial kann die Bildqualität des CT und
damit die Erkennbarkeit des röntgenopaquen Zahnes
beeinträchtigt werden.
Nebenwirkungen:
Systemische Nebenwirkungen sind bisher keine bekannt.
In Einzelfällen wurden bei Methylmethacrylat- und
Polymethylmethacrylat-Materialien allergische
Reaktionen beschrieben. Bei erwiesener Allergie auf
Bestandteile von SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC und
Modifier Polymer wie Monomer auf die Anwendung verzichten.
12
Page 13
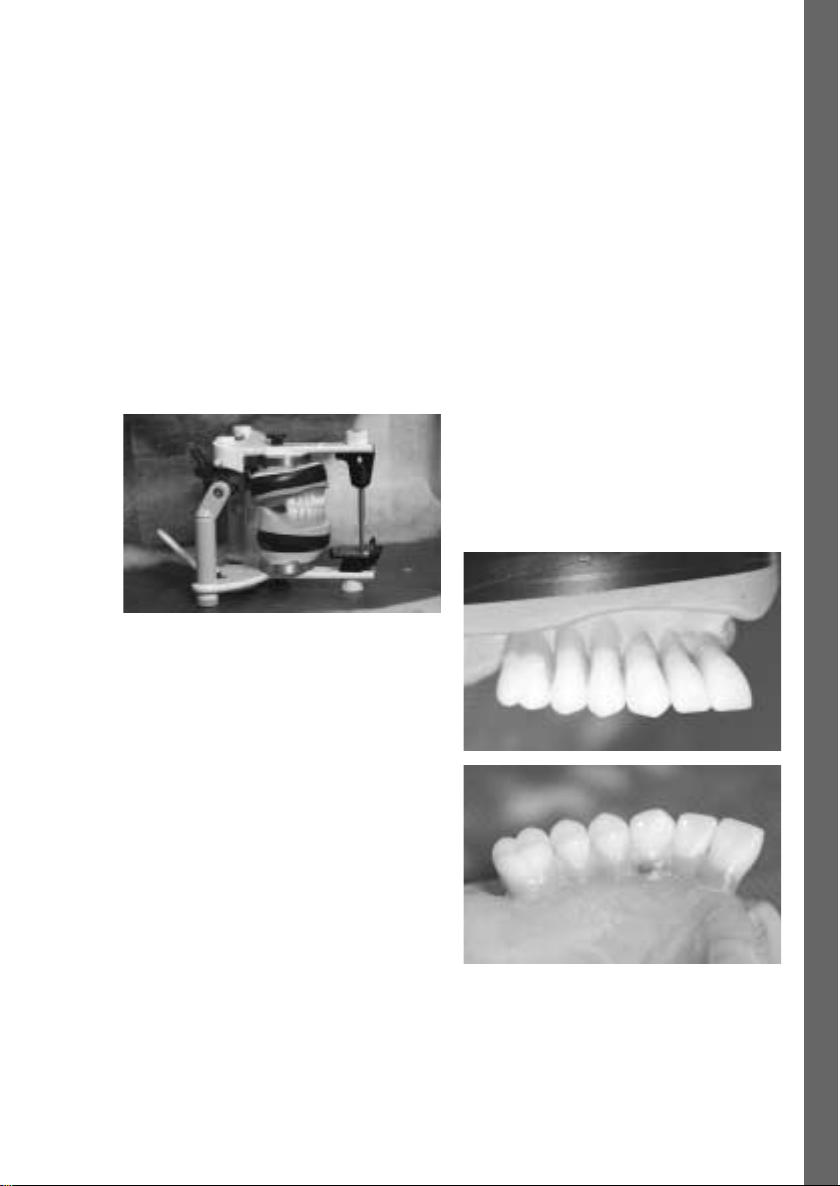
1. Labor
Bei der Herstellung einer diagnostischen Bohrschiene zur späteren Herstellung einer implantatgetragenen Restauration kann anhand der Angaben des
Zahnarztes eine entsprechende Aufstellung unter
Berücksichtigung von Ästhetik, Phonetik und Funktion
erstellt werden. Dabei wird SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC
wie ein konventioneller Prothesenzahn angewendet.
Die Anwendung von Aufstellhilfen wie z.B. 2D/3DAufstellkalotten (Ivoclar Vivadent AG) ist empfehlenswert.
Mögliche Vorgehensweise
Nach der Aufstellung der röntgenopaquen Zähne in
Wachs wird überschüssige, vestibuläre Wachsmodellation
entfernt, um den Zahnhals mit Monomer/Polymer
Modifier so zu verlängern, dass die Zahnbasis auf dem
Modell zu liegen kommt. Somit ist die spätere gesamte
Zahnlänge aus röntgenopaquem Material gefertigt.
Deutsch
Verarbeitung
Die Anwendung der röntgenopaquen Zähne SR Vivo TAC /
SR Ortho TAC erfolgt analog den üblichen Aufstellprinzipien. Die röntgenopaquen Zahnformen sind mit
den entsprechenden Zähnen der SR Vivodent /
SR Orthotyp Zahnlinie formenidentisch. SR Vivo TAC /
SR Ortho TAC besitzen eine ausgezeichnete, konstante
Radiopazität. Somit kann der 2- bzw. 3-dimensionale
Bezug zwischen der Implantatposition und der Position
der späteren Suprakonstruktion hergestellt werden.
Herstellung der diagnostischen Bohrschiene
13
Wachsaufstellung mit verlängerten Zahnhälsen
Page 14
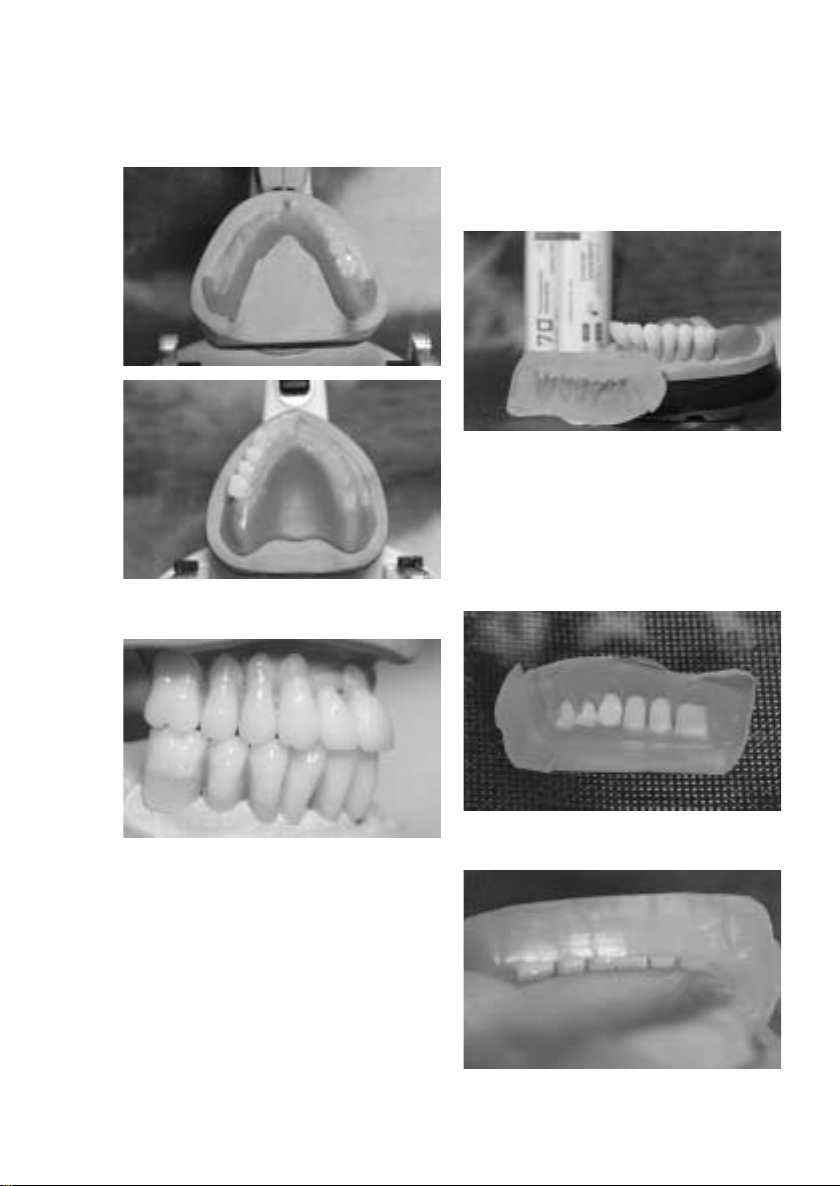
Formänderung
– Nach dem Aufstellen und dem Wax-up, wird ein
Schlüssel in Silikon oder Gips erstellt.
– Wachs rückstandslos von Modell und Zähnen ent-
fernen. Bei Verwendung von Gipsschlüsseln, das
Modell sowie den Schlüssel mit Ivoclar Vivadent
Separating Fluid isolieren und die Zähne an den zu
ergänzenden Flächen anrauhen.
14
Komplette Wachsaufstellung
Komplette Wachsmodellation mit verlängerten Zahnhälsen
Schlüssel der Wachsaufstellung
Repositionierung der Zähne im Schlüssel
Überprüfung der Passgenauigkeit
Page 15

Deutsch
– Polymer und Monomer Modifier im Verhältnis 1,3:1
anmischen und 2–3 Minuten abgedeckt ruhen lassen.
– Die Polymerisation erfolgt im Drucktopf oder im
Druck- /Hitze-Polymerisationsgerät (z.B. Ivomat),
15 Min. bei 40–50 °C und 2–6 bar Druck.
Bei Bedarf können in die diagnostische Bohrschiene
Röntgenmesskugeln oder ähnliche Hilfsmittel an geeigneter Stelle integriert werden.
15
Anmischen von Polymer und Monomer Modifier
Schlüssel fixieren
Die noch flüssige Masse in den Schlüssel einfliessen lassen
Nach der Polymerisation
Page 16
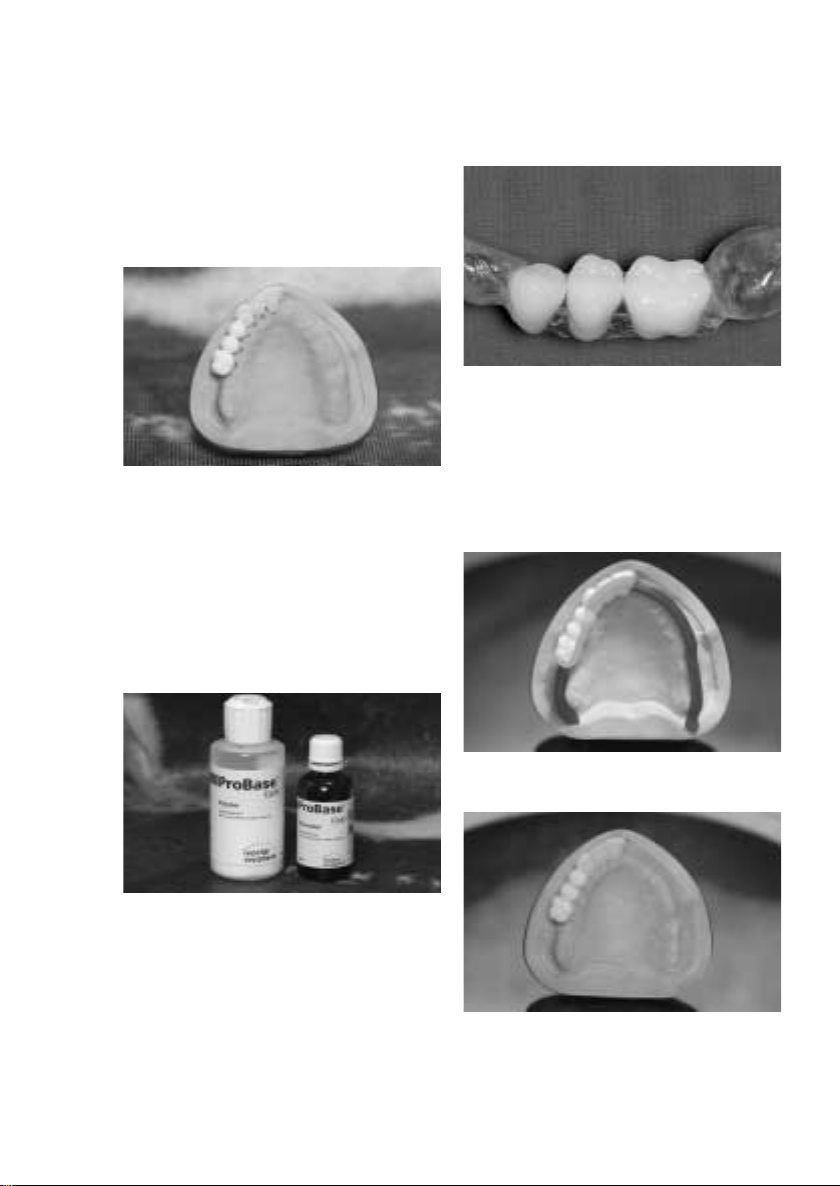
Ausarbeitung
Die Ausarbeitung erfolgt mit üblichen Schleif- und
Polierkörpern (analog der branchenüblichen PMMA
Verarbeitung).
Um dem Wunsch eines Zahnarztkunden gerecht zu werden, den Verlauf des Kieferkammes mit Schleimhaut
röntgenopaque darzustellen, kann dieser Bereich ebenfalls mit dem Monomer/ Polymer Modifier bedeckt
werden.
Fertigung der Basisplatten
Zur Verstärkung bzw. Stabilisierung der diagnostischen
Bohrschiene wird im palatinalen oder lingualen Bereich
eine Basisplatte aus transparentem oder rosa
Prothesenbasis-Kunststoff (z.B. ProBase Cold pink/clear)
oder Heisspolymerisat (z.B. ProBase Hot pink/clear) hergestellt.
Bei der Planung von festsitzenden Versorgungen (mit z.B.
Schaltlücke) wird die Basisplatte zur Stabilisierung und
Positionierung auf der mesialen bzw. distalen Restbezahnung abgestützt.
16
Nach der Ausarbeitung
Platzhalter für röntgenopaques Modifier Material
Polymerisierte Bohrschienen
Bohrschienendesign bei Schaltlücken
ProBase Cold clear (auch in pink erhältlich)
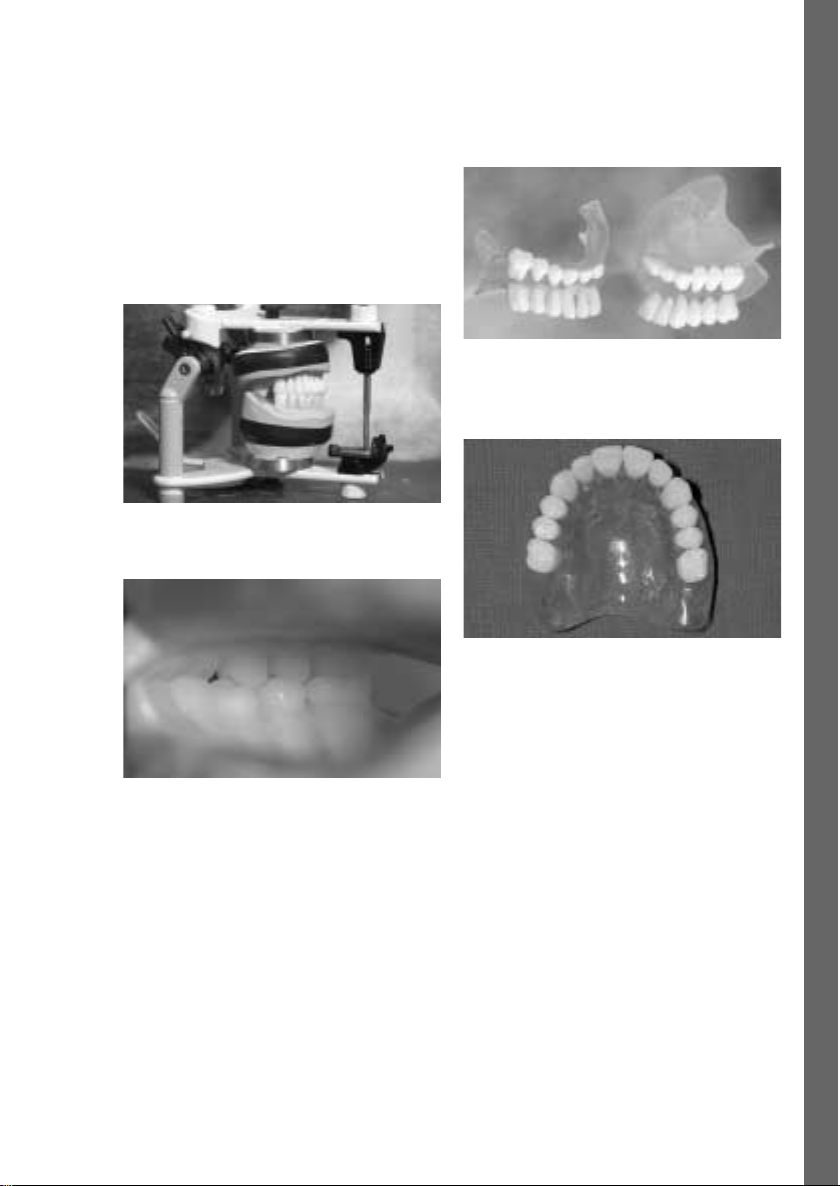
Page 17
Deutsch
17
Politur
Da die Bohrschiene zur Diagnose und/oder als Hilfsmittel
während des chirurgischen Eingriffs dient, wird eine gute
Vorpolitur mit Ziegenhaarbürste, Bimsstein und eine
Hochglanzpolitur mit Baumwollschwabbel und Polierpaste (Ivoclar Vivadent Universal Polierpaste) empfohlen.
Variante
Kontrolle der Okklusion
Fertige diagnostische Bohrschiene
Diagnostische Bohrschiene im Artikulator
Diagnostische Bohrschiene für OK-Totale
Page 18
Anwendungsmöglichkeit
Zur Schaffung von Führungskanälen vor dem chirurgischen Teil wird der Zahnarzt (oder Zahntechniker) die
röntgenopaquen Zähne durchbohren, sodass die
Führungskanäle den Kliniker während dem chirurgischen
Eingriff unterstützen. Dazu ist, um ideale
Voraussetzungen für die spätere Erstellung der
Suprastruktur zu schaffen, eine möglichst parallele
Position der Implantat-Angulation zu definieren.
Umwandlung des diagnostischen
Instruments in eine chirurgische
Bohrschiene
Praxis/Labor
Beim Erhalt der Bohrschiene aus dem Labor kann der
Zahnarzt eine Einprobe durchführen, um die Ästhetik,
Phonetik und Funktion des geplanten Zahnersatzes zu
beurteilen. Bevor die Röntgenaufnahme durchgeführt
wird, empfiehlt es sich, notwendige Korrekturen umzusetzen.
Mit dieser Röntgenaufnahme als unterstützendes
Instrument für die therapeutische Planung kann der
Zahnarzt die Position der Implantate unter Berücksichtigung von Knochensubstanz und funktionellen
Anforderungen der späteren Restauration festlegen
(bei Bedarf kann die Bohrschiene mit metallischen
Röntgenmesskugeln oder Titanhülsen versehen werden.)
18
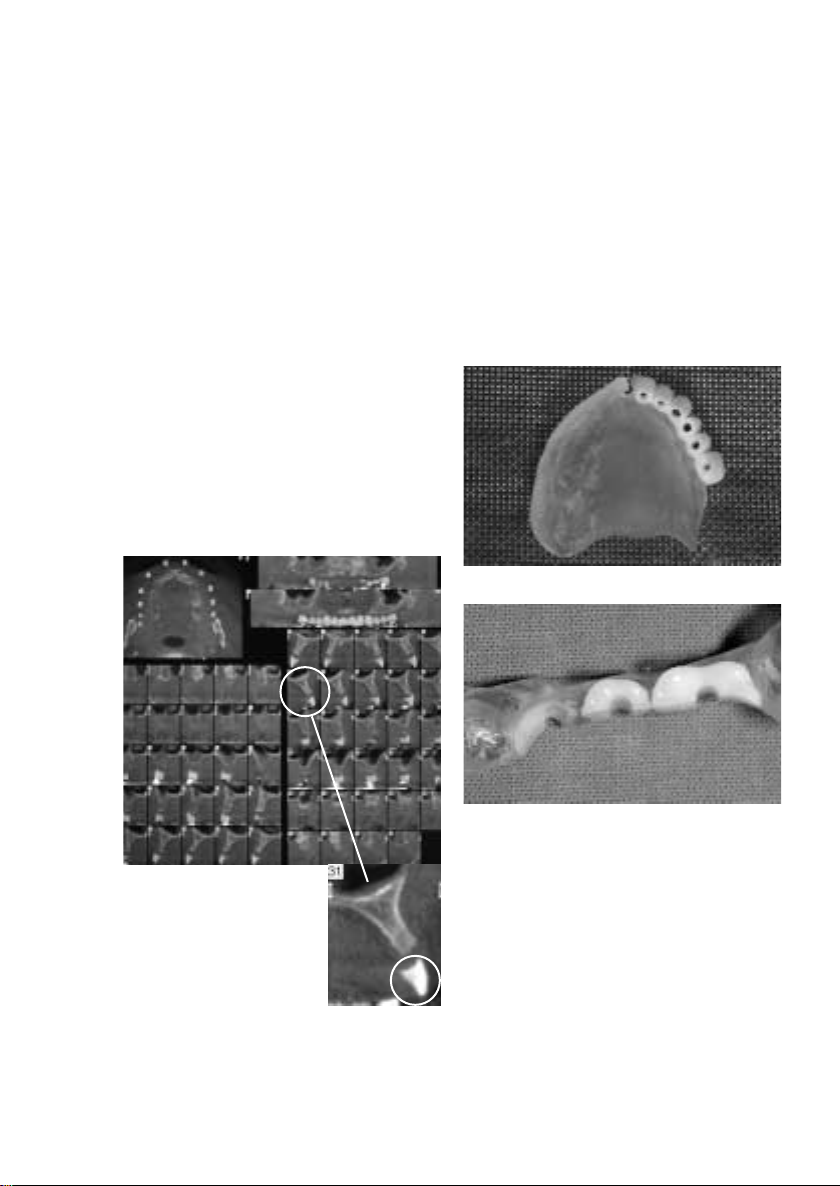
CT Aufnahme
Umsetzung der Führungskanäle
Reduzierte Zähne als Variante
Die Anwendung chirurgischer Bohrschienen erfolgt
grundsätzlich in der vom Anwender gewohnten Weise
unter Verwendung der gewohnten Materialien.
Page 19
Deutsch
19
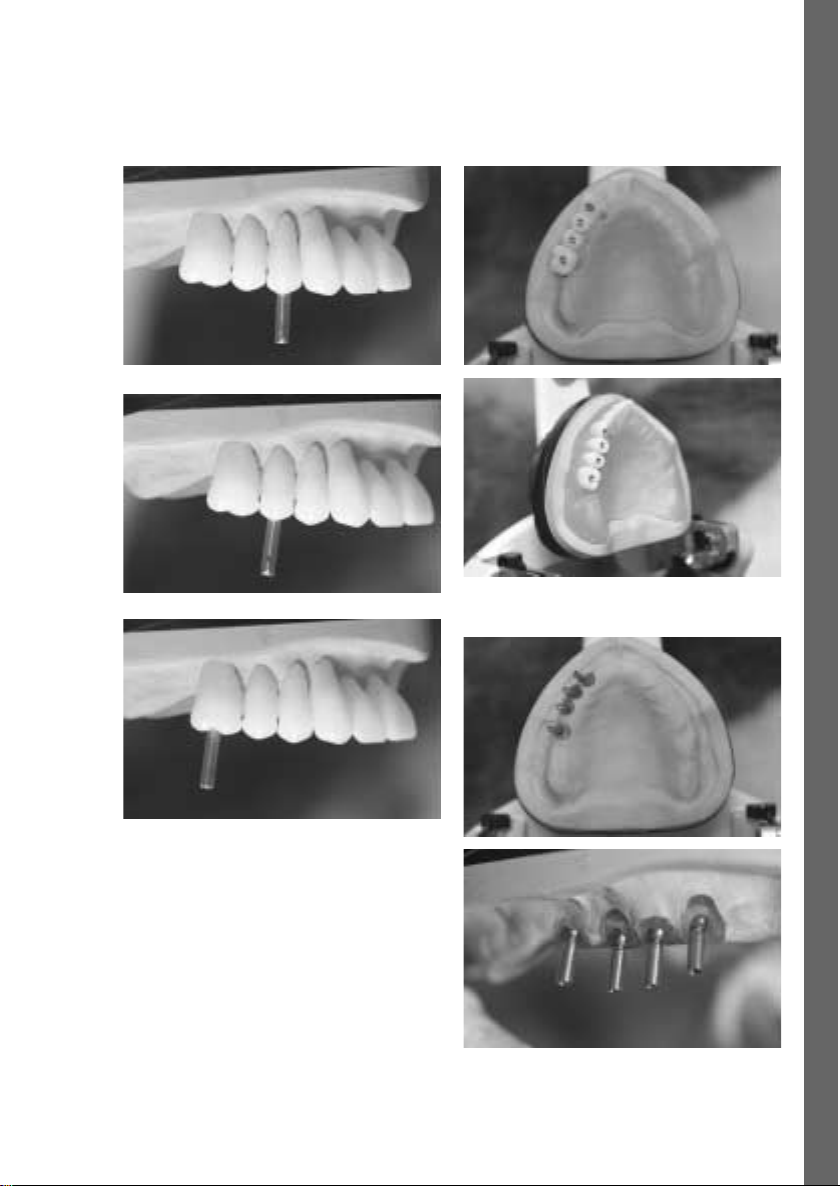
Zahn- und Implantat-Achsen
Fertige chirurgische Bohrschienen
Implantat-Achsen auf dem Modell
Page 20
Gefahrenhinweise
– Generell das Inhalieren von Schleifstaub vermeiden
– Schleimhautkontakt mit unpolymerisiertem Material
unbedingt vermeiden.
– Längerer oder oft wiederholter Hautkontakt mit
Monomer und unausgehärtetem Material kann
reizend wirken und zu einer Sensibilisierung auf
Methylacrylate führen.
– Das Modifier Monomer enthält Methylmethacrylat
– MMA ist leicht entzündlich und reizend (Flammpunkt
+10 °C).
– Reizt die Augen,Atmungsorgane und die Haut
– Dämpfe nicht einatmen.
– Sensibilisierung durch Hautkontakt möglich.
– Von Zündquellen fernhalten. Nicht rauchen.
– Nicht in die Kanalisation gelangen lassen.
Lagerungshinweise Modifier Monomer /
Modifier Polymer
– Kühl, trocken und vor Licht geschützt aufbewahren.
– Lagertemperatur 12–28 °C.
– Lagerhinweise und Verfallsdatum auf der Sekundär-
packung beachten.
– Produkte nach Ablauf des Verfalldatums nicht mehr
verwenden.
– Für Kinder unzugänglich aufbewahren.
Lieferform
Basic Kit
1 x SR Vivo TAC Frontzähne Oberkiefer in den Formen
A15, A24B, A25, A27
1 x SR Vivo TAC Frontzähne Unterkiefer in den Formen
A4, A8,A9
1x SR Ortho TAC Backenzähne Oberkiefer in den
Formen N2, N6
1 x SR Ortho TAC Backenzähne Unterkiefer in den
Formen N2, N6
Modifier Kit (1 Monomer 30 ml, 1 Polymer 30 g)
Verarbeitungsanleitung
Nachfüllpackungen
– SR Vivo TAC A15,A24B, A25, A27, A4, A8,A9
– SR Ortho TAC N2, N6 obere und untere
– Polymer Modifier 30 g
– Monomer Modifier 30 ml
Weitere Anwendungsvarianten
– Einbringung von metallischen Führungshülsen als
Bohrlehre
– Sagittale Reduktion des vestibulären oder oralen
Bereichs der Bohrlehre bis zu den hälftigen Bohrlöchern
20
Umsetzung in Kunststoff
Quelle:
Bildmaterial M. Nanni, Dr. A. Fanti, P. Miceli, Italien
Page 21

Deutsch
21
Die Produkte wurden für den Einsatz im Dentalbereich entwickelt und müssen
gemäss Gebrauchsinformation verarbeitet werden. Für Schäden, die sich aus anderer
Verwendung oder nicht sachgemässer Verarbeitung ergeben, übernimmt der
Hersteller keine Haftung. Darüber hinaus ist der Verwender verpflichtet, das Produkt
eigenverantwortlich vor dessen Einsatz auf Eignung und Verwendungsmöglichkeit für
die vorgesehenen Zwecke zu prüfen, zumal wenn diese Zwecke nicht in der
Gebrauchsinformation aufgeführt sind.
Erstellung der Verarbeitungsanleitung:
03/2004
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
FL-9494 Schaan / Liechtenstein
Page 22

Mode d'emploi
Suggestion :
Une lecture attentive de ce mode d'emploi vous
familiarisera avec l'utilisation des dents
SR Vivo TAC/SR Ortho TAC.
Les dents SR Vivo TAC/ SR Ortho TAC sont un outil de
diagnostic radio-opaque, utilisé comme guide par
l'implantologiste lors de pose d'implants.
Grâce à leur composition particulière, ces dents
possèdent un effet radio-opaque.
Avantages :
– un degré de radiopacité adapté et constant
– formes correspondant à la ligne de dents connue SR
Vivodent/SR Orthotyp ou SR Vivodent PE/
SR Orthotyp PE.
– moyen de diagnostic facile à réaliser
– personnalisation possible des formes des dents radio-
opaques à l'aide d'un polymère et d'un
monomère radiopaque joint
– économie de temps lors de la réalisation du guide
implantaire
– aide à déterminer la position future des implants
durant la phase de projets
Composition :
Les dents en résine se composent de :
Polyméthacrylate de méthyle et de sulfate de barium 66–
67 % en poids ; Méthacrylate de méthyle et
diméthacrylate 33–34 % en poids.
Sont contenus en plus des catalyseurs et des
stabilisateurs 0,5 % en poids.
Modifier monomère :
Méthacrylate de méthyle et diméthacrylate 99 % en
poids. Catalyseur et stabilisateur 1 % en poids.
Modifier polymère :
Polyméthacrylate de méthyle et sulfate de barium
> 99 % en poids. Catalyseur < 1 % en poids.
Indication :
Ces dents radio-opaques sont une aide précieuse lors du
diagnostic pré-opératoire :
– anomalie maxillo-faciale prononcée
– atrophie prononcée de la crête alvéolaire
– corrections en chirurgie bucco-dentaire et faciale et
reconstitution
et servent de guide esthétique permettant d'apprécier le
volume de la future prothèse ainsi que l'approche
personnalisée souhaitée par le praticien et le patient.
Grâce à un diagnostic pré-opératoire du traitement
prévu, une position idéale de l'implant pourra être
communiquée et retenue.
Contre-indication :
Pour toutes les indications qui ne sont pas expressément
recommandées par Ivoclar Vivadent et pour l'utilisation
d'une prothèse restant en permanence dans la bouche
du patient.
La présence de restauration fixe métallique ou de
matériau d'ostéosynthèse métallique peut avoir une
influence sur la qualité de l'image de tomographie
éalisée par ordinateur et par là même sur la possibilité
de reconnaissance de la dent radio-opaque.
Effets secondaires :
Aucun effet systémique connu à ce jour. Dans des cas
isolés, des réactions allergiques au méthacrylate de
méthyle et au polyméthacrylate de méthyle ont été
relevées.A ne pas utiliser dans le cas d'une allergie
reconnue à l'un des composants de SR Vivo TAC /
SR Ortho TAC et au Modifier polymère ou monomère.
22
Page 23

1. Laboratoire
En réalisant un guide implantaire de diagnostic préalable
à une restauration sur implants, il est possible, suite aux
données du chirurgien-dentiste, de réaliser le montage
en tenant compte de l'esthétique, de la phonétique et de
la fonction. Pour cela, on utilise SR Vivo TAC/SR Ortho
TAC telle une dent de prothèse conventionnelle.
Procédure possible
Après le montage des dents radio-opaques dans la cire,
le modelage en cire vestibulaire, résiduel est éliminé
pour prolonger le collet avec le modifier monomère/polymère de façon à ce que la base de la dent repose sur le
modèle.Ainsi, la longueur totale de la future dent est
réalisée à partir de matériau radio-opaque.
Français
Mise en œuvre
L'utilisation des dents radio-opaques SR Vivo TAC /
SR Ortho TAC s'effectue de la même manière que lors de
montages traditionnels. Les formes de dents radioopaques sont identiques en forme avec les dents
correspondantes de la ligne de dents SR Vivodent/
SR Orthotyp. SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC ont une
radio-opacité excellente et constante. C'est ainsi qu'est
établi le rapport bi et tri-dimensionnel entre la position
implantaire et la position de la suprareconstitution
ultérieure.
Réalisation de guides implantaires de diagnostic
23
Montage en cire avec des collets prolongés
Page 24

Modification de forme
– Après le montage et le Wax-up, confection d'une clef
en silicone ou en plâtre.
– Retirer les résidus de cire du modèle et des dents. Si
l'on utilise des clefs en plâtre, isoler le modèle et la
clef avec le Separating Fluid Ivoclar Vivadent puis
dépolir les dents aux endroits à compléter.
24
Montage en cire complet
Modelage en cire avec des collets prolongés
Clef du montage en cire
Repositionnement des dents dans la clef
Contrôle de la précision d'adaptation
Page 25

Français
– Mélanger le Modifier polymère et monomère dans un
rapport de 1,3 : 1 et laisser reposer couvert pendant
2–3 minutes.
– La polymérisation se fait dans un appareil à poly-
mérisation par pression/chaleur (par ex. Ivomat),
pendant 15 minutes à 40–50°C et sous 2–6 bar de
pression.
En cas de besoin, il est possible d'insérer dans le guide,
aux endroits adaptés, des billes de contrôle radiographiques ou accessoires similaires.
25
Mélanger le Modifier polymère et monomère
Fixer la clef
Laisser couler la masse encore liquide dans la clef
Après la polymérisation
Page 26

Finition
La finition s'effectue avec des instruments à meuler et
polir habituels (selon la mise en œuvre des PMMA).
Pour répondre au souhait du patient et indiquer la ligne
de la crête alvéolaire avec la muqueuse, cette zone peut
être également recouverte de Modifier monomère/
polymère.
Finition des plaques-base
Pour renforcer ou stabiliser le guide de diagnostic, une
plaque-base sera confectionnée en résine transparente
ou rose (par ex. ProBase Cold pink/clear) ou en résine
thermopolymérisable (par ex. ProBase Hot pink/clear) au
niveau palatin ou lingual.
Si l'on prévoit des restaurations fixes, la base sera
stabilisée et positionnée par les appuis mésiaux et
distaux de la denture résiduelle.
26
Après la finition
Place ntermédiaire pour du matériau radio-opaque Modifier
Guide polymérisé
Design de guide
ProBase Cold clear (disponible également en pink)
Page 27

Français
27
Polissage
Les guides servant de diagnostic et/ou d'accessoires
pendant l'intervention chirurgicale doivent être
parfaitement prépolis avec une brosse en poils de
chèvre et de la ponce puis polis au brillant avec un
disque de coton et une pâte à polir (Ivoclar Vivadent
Universal).
Variante
Contrôle de l'occlusion
Guides de diagnostic terminés
Guide de diagnostic complet pour le maxillaire supérieur
Page 28

Possibilités d'utilisation
Pour réaliser les canaux de guidage avant la partie
chirurgicale, le chirurgien-dentiste (ou le prothésiste)
perforera les dents radio-opaques de façon à ce que les
canaux facilitent l'intervention du clinicien.
Changement de l'instrument de
diagnostic en un guide chirurgical
Cabinet dentaire / Laboratoire
A réception du guide, le chirurgien-dentiste peut
effectuer un essai pour apprécier l'esthétique, la
phonétique et la fonction de la future prothèse.Avant de
réaliser la radiographie, il est conseillé d'y apporter les
corrections nécessaires.
Avec cette radiographie à l'appui pour le projet
thérapeutique, le chirurgien-dentiste peut définir la
position de l'implant en tenant compte de la substance
osseuse et des exigences fonctionnelles de la future
restauration (en cas de besoin, le guide perforateur peut
être muni de billes métalliques de contrôle ou de gaine
en titane).
28
Images Scanner
Changement des canaux de guidage
Dents réduites comme variante
Page 29

Français
29
Axes pour dent et implant
Guide chirurgical terminé
Axes pour implant sur le modèle
Page 30

Consignes de sécurité
– éviter l'inhalation de poussière de meulage
– éviter absolument le contact des muqueuses avec le
matériau non polymérisé
– un contact cutané plus long ou souvent répété avec
du monomère et du matériau non polymérisé peut
avoir des effets irritants et conduire à une sensibilité
au méthylacrylate
– le Modifier monomère contient du méthacrylate de
méthyle (MMA)
– le MMA s'enflamme facilement et est irritant (point
d'inflammation +10°C)
– il irrite les yeux, les organes respiratoires et la peau
– ne pas inhaler les vapeurs
– une sensibilité est possible par contact cutané
– éloigner de toute source inflammable, ne pas fumer
– ne pas jeter dans les canalisations
Recommandations de stockage du
Modifier monomère/Modifier polymère
– conserver dans un endroit frais, sec et à l'abri de la
lumière
– température de stockage 12–28°C
– respecter les recommandations de stockage et la date
de péremption indiquées sur l'emballage secondaire
– ne plus utiliser le produit au-delà de la date de
péremption
– conserver à l'abri des enfants
Présentation
1 x SR Vivo TAC, dents antérieures, maxillaire supérieur
dans les formes A15,A24B, A25, A27
1 x SR Vivo TAC, dents antérieures, maxillaire inférieur
dans les formes A4,A8,A9
1 x SR Ortho TAC, dents postérieures, maxillaire
supérieur dans les formes N2, N6
1 x SR Ortho TAC, dents postérieures, maxillaire
inférieur dans les formes N2, N6
Modifier Kit (1 monomère de 30 ml, 1 polymère de 30 g)
Mode d'emploi
Réassortiment
– SR Vivo TAC A15,A24B, A25, A27, A4, A8,A9
– SR Ortho TAC N2, N6 supérieur et inférieur
– Modifier polymère 30 ml
– Modifier monomère 30 g
Autres variantes d'utilisation
– insertion de coquilles de guidage métalliques en tant
que gabarit de perçage
– réduction sagittale de la zone vestibulaire ou orale du
gabarit de perçage jusqu'aux trous de perçage
30
Transfert en résine
Photos :
M. Nanni, Dr. A. Fanti, P. Miceli, Italy
Page 31

Français
31
Ce matériau a été développé en vue d’une utilisation dans le domaine dentaire et
doit être mis en œuvre selon son mode d’emploi. Les dommages résultant du nonrespect de ces prescriptions ou d’une utilisation à d’autres fins que celles indiquées
n’engagent pas la responsabilité du fabricant. L’utilisateur est tenu de vérifier sous sa
propre responsabilité l’appropriation du matériau à l’utilisation prévue et ce d’autant
plus si celle-ci n’est pas citée dans le mode d’emploi.
Edition du mode d'emploi :
03/2004
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
FL-9494 Schaan / Liechtenstein
Page 32

Istruzioni d’uso
Premessa
La preghiamo di leggere attentamente le
presenti istruzioni d’uso e di prenderne
conoscenza.
I denti prefabbricati SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC sono
strumenti diagnostici radiopachi che l’odontotecnico
potrà utilizzare nella realizzazione di protesi fisse o
rimovibili supportate da impianti. Grazie alla loro
particolare composizione i denti hanno un effetto
radiopaco.
Vantaggi
– La produzione industriale permette una radiopacità
costante
– Corrispondenza di forma con i denti SR Vivodent PE /
SR Orthotyp PE e SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp
– Semplice realizzazione di uno strumento diagnostico
– Modificabili nella forma, grazie all’apposito
monomero e polimero
– Elevato legame sia con resine termopolimerizzanti che
autopolimerizzanti
– Risparmio di tempo nella realizzazione di dime
diagnostiche/chirurgiche grazie ai denti prefabbricati
– Durante la fase di pianificazione serve alla deter-
minazione della posizione degli impianti dentali e
come guida alla riabilitazione protesica
Composizione
I denti in resina sono composti come segue:
polimetilmetacrilato e solfato di bario 66–67% in peso;
metilmetacrilato e dimetacrilato 33–34% in peso.
Inoltre sono contenuti catalizzatore e stabilizzatore
0,5% in peso.
Modifier monomero
metilmetacrilato e dimetacrilato 99% in peso;
catalizzatore e stabilizzatore 1% in peso.
Modifier polimero
polimetilmetacrilato e solfato di bario >99% in peso;
catalizzatore < 1% in peso.
Indicazioni
Per la realizzazione di restauri protesici fissi e mobili
supportati da impianti, nei quali per la diagnosi radiologica preoperativa (TAC, teleradiografia, ma è possibile
anche l'ortopantomografia) è vantaggioso il montaggio
di denti, come p.e. in caso di:
– disgnazia pronunciata
– pronunciata atrofia della cresta alveolare
– correzioni e ricostruzioni in chirurgia maxillo-facciale
Grazie alla diagnosi preoperativa del trattamento
pianificato, è possibile rilevare e determinare la posizione
ideale dell'impianto.
Controindicazioni
Il prodotto è controindicato per tutte le indicazioni non
espressamente consigliate da Ivoclar Vivadent e per
l'impiego permanente in cavo orale come restauro
protesico definitivo.
La presenza di restauri protesici fissi, otturazioni metalliche
o materiali metallici per osteosintesi, può influire sulla
qualità dell’immagine della TC e pertanto sulla visibilità
del dente radiopaco.
Effetti collaterali
Non sono finora noti effetti collaterali di tipo sistemico.
In singoli casi sono state descritte reazioni allergiche
locali a materiali a base di metilmetacrilati e polimetilmetacrilati. In caso di allergia dimostrata a componenti
di SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC e Modifier polimero e
monomero evitarne l’uso.
32
Page 33

1. Laboratorio
Per la realizzazione di una dima diagnostica, per la
successiva realizzazione di un restauro supportato da
impianti si dovrà considerare in base alla prescrizione
dell’odontoiatra, di realizzare un montaggio ideale per
ciò che riguarda estetica, fonetica, e funzione. Il dente
SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC in questa fase viene
utilizzato come un dente tradizionale. È consigliabile
avvalersi di supporti di montaggio come, la calotta
bidimensionale o tridimensionale (Ivoclar Vivadent).
Possibile procedimento
Una volta terminato il montaggio si trasformerà la
modellazione (Wax-up) della parte vestibolare in una
modellazione a vivo, che permetta di far appoggiare il
dente direttamente sul tessuto, per allungare il colletto
con Modifier monomero/polimero in modo tale che la
base del dente sia a contatto con il modello. In tal modo
l'intera lunghezza del dente sarà realizzata in materiale
radiopaco.
Italiano
Lavorazione
L’utilizzo dei denti SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC avviene
secondo i consueti principi di montaggio. Le forme dentali radiopache sono identiche ai corrispondenti denti
della linea denti SR Vivodent PE / SR Orthotyp PE.
SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC possiedono un'eccellente
radiopacità costante. In tal modo è possibile ottenere la
relazione bi-, rispettivamente tridimensionale fra
posizione dell'impianto e posizione della successiva
sovrastruttura.
Montaggio in cera delle dime diagnostiche/
chirurgiche in articolatore
33
Montaggio in cera con colletti dentali allungati
Page 34

Modifica della forma
– Realizzato il montaggio ed il wax-up realizzare una
mascherina in silicone duro o gesso.
– Eliminare completamente la cera dal modello e dai
denti. In caso di utilizzo di mascherina in gesso,
isolare sia il modello che la mascherina con
Separating Fluid Ivoclar Vivadent e irruvidire i denti
nei punti da completare.
34
Montaggio in cera completo
Montaggio in cera completo con colletti dentali allungati
Mascherina del montaggio in cera
Riposizionamento dei denti nella mascherina
Controllo della precisione
Page 35

italiano
– Miscelare polimero e monomero Modifier in rapporto
1,3:1 e lasciarlo riposare coperto per 2–3 minuti.
– La polimerizzazione avviene in pentola a pressione o
apparecchio idropneumatico (p.e. Ivomat) 15 min. a
40–50°C e 2–6 bar di pressione.
In caso di necessità si possono integrare nella dima
diagnostica, nei punti idonei, sfere o altri ausili di
misurazione radiografica.
35
Miscelazione di polimero e monomero Modifier
Fissaggio della mascherina
La massa ancora fluida viene colata nella mascherina
Dopo la polimerizzazione
Page 36

Rifinitura
La rifinitura avviene secondo la consuete procedure per i
materiali PMMA, tramite frese.
Per soddisfare le esigenze di clienti odontoiatri che
desiderano raffigurare in modo radiopaco il decorso del
giunto periferico, è possibile colmare anche questa zona
con Modifier monomero/polimero.
Realizzazione della placca base
Per il rafforzamento, rispettiv. per la stabilizzazione della
dima diagnostica, si realizza lingualmente o palatalmente una placca in resina autopolimerizzante (p.e. ProBase
Cold clear) o polimerizzante a caldo (p.e. ProBase Hot
clear).
Nel caso si debba realizzare una dima diagnostica in una
breccia tra denti naturali il supporto sarà realizzato nei
confronti dei denti residui come di consueto.
36
Dopo la rifinitura
Mantenitore di spazio per il materiale radiopaco Modifier
Dime polimerizzate
Design della dima in caso di breccia
ProBase Cold clear (disponibile anche in pink)
Page 37

Italiano
37
Lucidatura
Poichè la dima viene impiegata per la diagnosi e/o come
ausilio durante l'intervento chirurgico, si consiglia
un’accurata prelucidatura con spazzolini di pelo di capra
e pomice, una lucidatura a specchio con feltrino e pasta
per lucidatura (pasta per lucidatura universale Ivoclar
Vivadent).
Variante
Controllo dell'occlusione
Esempi di dime diagnostiche/chirurgiche ultimate
Dima diagnostica per protesi totale superiore con modelazione
intera (senza allungamento dei denti)
Dima diagnostica in articolatore
Page 38

Possibilità di impiego
Prima di procedere con la chirurgia l’odontoiatra eseguirà o farà eseguire dall’odontotecnico la perforazione
degli elementi protesici in modo consueto preparando
così la dima a divenire un ausilio durante la fase di
posizionamento degli impianti. A tale scopo, per creare i
presupposti ideali alla successiva realizzazione della
sovrastruttura, deve essere definita una posizione
possibilmente parallela dell'angolazione dell'impianto.
Trasformazione della dima diagnostica
in dima chirurgica
2. Studio/laboratorio
Ricevuta dal laboratorio la dima sarà cura
dell’odontoiatra valutare anche con un’eventuale prova
intermedia l’estetica, la fonetica e la funzione della
riabilitazione in via di realizzazione. Prima di effettuare
l'esame radiografico, si consiglia di eseguire eventuali
necessarie correzioni.
Con l'esame radiografico quale strumento di supporto
alla pianificazione terapeutica, l'odontoiatra può
determinare la posizione degli impianti tenendo in
considerazione la sostanza ossea ed i requisiti funzionali
del successivo restauro. (Se necessario la dima
diagnostica può essere provvista di sfere o cannule
guida in titanio di misurazione radiografica).
38
Tomografia assiale computerizzata
Realizzazione dei canali di guida
Denti ridotti come possibile variante
L'utilizzo di dime chirurgiche avviene di principio nel modo consueto e con l'utilizzo dei soliti materiali.
Page 39

Italiano
39
Assi del dente e dell'impianto
Dime chirurgiche ultimate
Assi dell'impianto sul modello
Page 40

Avvertenze
– In generale, evitare l'inalazione di polvere di rifinitura
– Evitare assolutamente il contatto di materiale non
polimerizzato con le mucose.
– Il contatto prolungato e ripetuto con monomero e
con materiale non indurito può avere un effetto
irritante e può condurre ad una sensibilizzazione a
metacrilati.
– Il monomero contiene metilmetacrilato.
– Il MMA è facilmente infiammabile ed irritante (punto
d’infiammabilità 10 °C).
– Irrita gli occhi, gli organi respiratori e la pelle.
– Non inalare i vapori.
– Possibile sensibilizzazione da contatto cutaneo.
– Tenere lontano da fonti infiammabili. Non fumare.
– Non lasciare defluire nella canalizzazione.
Nota per la conservazione Modifier monomero /
Modifier polimero
– Conservare il materiale in luogo fresco, scuro e ben
arieggiato.Temperatura di conservazione 12–28 °C.
– Attenersi alle note per la conservazione riportate sul
confezionamento secondario ed alla data di
scadenza.
– Non utilizzare più il prodotto dopo la data di
scadenza.
– Conservare fuori della portata dei bambini.
Presentazione
Basic Kit
1 x SR Vivo TAC denti anteriori superiori
A15, A24B, A25, A27
1 x SR Vivo TAC denti anteriori inferiori
A4, A8,A9
1x SR Ortho TAC denti posteriori superiori
N2, N6
1 x SR Ortho TAC denti posteriori inferiori
N2, N6
Modifier Kit (1x monomero 30 ml, 1x polimero 30 gr.)
Istruzioni d'uso
Ricambi
– SR Vivo TAC A15,A24B, A25, A27, A4, A8,A9
– SR Ortho TAC N2, N6 superiore ed inferiore
– Modifier polimero 30 ml
– Modifier monomero 30 g
Ulteriori varianti di utilizzo
– Applicazione di cannule guida in titanio come guida
per la perforazione
– Riduzione sagittale della zona vestibolare della dima
fino alla metà dei fori.
40
Dima diagnostica ultimata
Fonte:
Materiale iconografico M. Nanni, Dr. A. Fanti, P. Miceli,
Italia
Page 41

Italiano
41
Il prodotto è stato realizzato per l’impiego nel campo dentale e deve essere utilizzato
secondo le istruzioni d’uso. Il produttore non si assume nessuna responsabilità per
danni derivanti da diverso o inadeguato utilizzo. L’utente è tenuto a controllare personalmente l’idoneità del prodotto per gli impieghi da lui previsti soprattutto, se
questi impieghi non sono riportati nelle istruzioni d’uso.
Stesura delle istruzioni d’uso :
03/2004
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
FL-9494 Schaan / Liechtenstein
Page 42

Instrucciones de uso
Premisa
Le rogamos lea atentamente estas instrucciones
de uso para familiarizarse con ellas.
Los dientes prefabricados SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC
son un instrumento de diagnóstico radiopaco, que el
odontólogo y el protésico pueden utilizar como ayuda en
la realización de restauraciones implantosoportadas.
Gracias a su especial composición estos dientes poseen
un efecto radiopaco.
Ventajas
– Determina de forma adecuada la posición de los
implantes dentales durante la fase de planificación
para la reconstrucción implantológica dental,
– La fabricación industrial permite una radiopacidad
homogénea
– Las formas se corresponden con las de la conocida
línea de dientes SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp o
SR Vivodent PE / SR Orthotyp PE.
– Sencilla preparación de un elemento auxiliar de
diagnóstico
– Modificación de la forma de los dientes radiopacos
mediante polímero y monómero modificador
radiopaco
– Elevada unión tanto con material termo como auto-
polimerizable
– Ahorro de tiempo en la preparación de férulas
quirúrgicas mediante dientes radiopacos
prefabricados
– Mezcla homogénea de los dientes con material de
contraste radiopaco
Composición
Los dientes de resina están compuestos por los
siguientes materiales:
Polimetilmetacrilato y sulfato de bario 66–67% en peso;
metilmetacrilato y dimetacrilato 33–34% peso.Además
contiene catalizador y estabilizadores 0,5% peso.
Monómero modificador
Metilmetacrilato y dimetacrilato 99% peso, catalizador y
estabilizadores 1% peso
Polímero modificador
Polimetilmetacrilato y sulfato de bario > 99% peso,
catalizador < 1% peso.
Indicación
Suponen una ventaja en el montaje de los dientes en el
diagnóstico radiopaco preoperatorio (CT, rayos X y
también OPG) para la preparación de prótesis fija y
removible implantosoportada:
– Marcada dysgnathia
– Marcada atrofia de la cresta alveolar
– Correcciones quirúrgicas bucales, mandibulares y
faciales, así como en reconstrucciones
Mediante el diagnóstico preoperatorio del tratamiento se
puede fijar y definir la posición ideal del implante.
Contraindicaciones
Para todas aquellas indicaciones que no estén
expresamente recomendadas por Ivoclar Vivadent, así
como para su uso como prótesis definitiva en la boca del
paciente.
En caso de prótesis fijas metálicas, obturaciones
metálicas o materiales Osteosintéticos metálicos, la
calidad de la imagen del TAC y por lo tanto la de los
dientes radiopacos puede verse afectada negativamente.
Efectos secundarios
Hasta ahora no se han descrito efectos secundarios
sistémicos. En casos aislados se han descrito reacciones
alérgicas a los materiales de metilmetacrilato y polimetilmetacrilato. Evitar su uso en caso de alergia
conocida a alguno de los componentes de SR Vivo TAC /
SR Ortho TAC o polímero y monómero modificador.
42
Page 43

1. Laboratorio
En la preparación de una férula quirúrgica de
diagnóstico para la posterior realización de una
restauración implantosoportada se puede efectuar un
montaje en base a los datos facilitados por el odontólogo considerando estética, fonética y función. Para ello
se utiliza SR Vivo TAC / ST Ortho TAC como un diente
convencional. Se recomienda el uso de accesorios de
montaje como la matriz de montaje 2D / 3D (Ivoclar
Vivadent AG).
Posible procedimiento
Después del montaje de los dientes radiopacos en cera
se retira la cera vestibular sobrante, con el fin de prolongar los cuellos de los dientes con polímero / monómero
modificador, de forma que la base del diente asiente
sobre el modelo.Así, posteriormente toda la longitud
del cuello del diente estará preparada con material
radiopaco.
Español
Manipulación
El uso de los dientes radiopacos SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho
TAC es similar a los principios de montaje convencionales. Las formas de los dientes radiopacos son idénticas a
las de los dientes SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp.
SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC poseen una excelente y
constante radiopacidad. De esta forma se puede
establecer una relación tridimensional entre la posición
del implante y la posición de la posterior
supraconstrucción.
Elaboración de la férula quirúrgica
43
Modelado en cera con cuellos prolongados
Page 44

Modificación de la forma
– Después del montaje y del encerado, se realiza una
llave de silicona o yeso.
– Eliminar la cera del modelo y de los dientes sin dejar
residuos. En caso de utilizar llave de yeso, aislar el
modelo y la llave con Separating Fluid de Ivoclar
Vivadent y repasar los dientes en las zonas a
completar.
44
Montaje completo en cera
Montaje completo en cera con cuellos prolongados
Llave del modelado en cera
Reposicionamiento de los dientes en la llave
Control del ajuste
Page 45

Español
– Mezclar el polímero y monómero modificador en pro-
porción 1,3 : 1 y dejar reposar durante 2–3 minutos.
– La polimerización se realiza en aparato de presión o
en aparato de polimerización con presión / calor (p.ej.
Ivomat) 15 minutos a 40–50ºC y 2–6 bar de
presión.
En caso necesario se pueden incorporar bolas radiopacas
o cualquier otra medida auxiliar en un lugar apropiado
de la férula quirúrgica de diagnóstico.
45
Mezcla de polímero y monómero modificador
Fijar la llave
Verter la masa todavía fluida en la llave
Una vez polimerizado
Page 46

Repasado
El repasado se realiza con instrumentos convencionales
(de forma similar al repasado de PMMA).
Para satisfacer los deseos del odontólogo de realizar la
trayectoria de la cresta con mucosa radiopaca, esta zona
se puede cubrir asimismo con monómero / polímero
modificador.
Realización de planchas base
Para reforzar o estabilizar la férula quirúrgica de diagnóstico se confecciona en la zona palatina o lingual una
placa base de resina transparente o rosa (p.ej. ProBase
Cold pink/clear) o resina termopolimerizable (p.ej.
ProBase Hot pink / clear).
Si se planifica una prótesis fija, la placa base se apoya
para su estabilización en la cara mesial o distal de los
dientes remanentes.
46
Después del repasado
Mantenedor de espacio para material modificador radiopaco
Férula quirúrgica polimerizada
Diseño de la férula quirúrgica
ProBase Cold clear (también disponible en color rosa)
Page 47

Español
47
Pulido
Puesto que la férula quirúrgica sirve para el diagnóstico
y / o como instrumento auxiliar durante la intervención
quirúrgica, se recomienda un buen prepulido con cepillo
de pelo de cabra, piedra pómez y un pulido a alto brillo
con borrego de lana y pasta de pulir (pasta de pulir
Ivoclar Vivadent).
Alternativa
Control de la oclusión
Férula de diagnóstico terminada
Férula de diagnóstico en el articulador
Férula quirúrgica de diagnóstico para prótesis superior
Page 48

Posibilidades de uso
Para crear canales guía antes de la fase quirúrgica, el
odontólogo (o protésico) perfora las dientes radiopacos,
de forma que los canales guía le sirvan de ayuda al
clínico durante la intervención quirúrgica. Para obtener
condiciones ideales en la posterior realización de la
supraestructura, es necesario definir una posición lo más
paralela posible de la angulación del implante.
Conversión del instrumento de
diagnóstico en una férula quirúrgica
Clínica / Laboratorio
A la recepción de la férula quirúrgica del laboratorio, el
odontólogo puede realizar una prueba para comprobar
la estética, la fonética y la función de la prótesis planificada. Antes de realizar la radiografía es aconsejable
realizar las correcciones necesarias. Con esta radiografía,
como instrumento auxiliar para la planificación terapéutica, el odontólogo puede determinar la posición de los
implantes teniendo en cuenta la sustancia ósea y los
requisitos funcionales de la posterior restauración (en
caso necesario puede dotarse a la férula quirúrgica con
bolas metálicas radiopacas o cofias de titanio).
48
TAC
Canales guía
Alternativa con dientes reducidos
El uso de férula quirúrgica se realiza básicamente en la
forma acostumbrada por el usuario, utilizando materiales
habituales
Page 49

Español
49
Diente y eje del implante
Férula quirúrgica terminada
Eje de los dientes sobre el modelo
Page 50

Advertencias
– Evitar la inhalación de polvo de repasado
– Evitar el contacto de la mucosa con material sin
polimerizar
– Un prolongado o frecuente contacto con monómero y
material sin polimerizar puede provocar irritación o
sensibilización al metilmetacrilato
– El monómero modificador contiene metilmetacrilato
– MMA es ligeramente inflamable e irritante (punto de
combustión + 10ºC)
– Irrita los ojos, las vías respiratorias y la piel
– No inhalar los vapores
– Posible sensibilización al contacto con la piel
– Mantener alejado de fuentes de calor. No fumar
– No verter por la canalización
Notas sobre el almacenamiento de
monómero modificador / polímero
modificador
– Almacenar en lugar fresco, seco y protegido de la luz
– Temperatura de almacenamiento 12–28ºC
– Tener en cuenta las notas sobre almacenamiento y
fecha de caducidad del envase secundario
– No utilizar el producto una vez caducado
– Mantener fuera del alcance de los niños
Suministro
Basic Kit
1 x 6 SR Vivo TAC anterior superior en las formas
A15, A24B, A25, A27
1 x 6 SR Vivo TAC anterior inferior en las formas
A4, A8,A9
1 x 8 SR Ortho TAC molar superior en las formas
N2, N6
1 x 8 SR Ortho TAC molar inferior en las formas
N2, N6
Modificador (1 monómero 30 ml, 1 polímero 30 g)
Instrucciones de uso
Reposiciones
– SR Vivo TAC A15,A24B, A25, A27, A4, A8,A9
– SR Ortho TAC N2, N6 superior e inferior
– Polímero modificador 30 g
– Monómero modificador 30 ml
Otras posibilidades de aplicación
– Colocación de cofias guía metálicas como guía
quirúrgica para el tallado
– Reducción sagital de la zona vestibular u oral de la
guía quirúrgica hasta la mitad de los orificios
50
Realización en resina
Material fotográfico:
M Nanni, Dr A Fanti, P Miceli, Italy
Page 51

Español
51
Los materiales han sido fabricados para uso dental y deben manipularse según
instrucciones de uso. El fabricante no se hace responsable de los daños ocasionado
por otros usos o una manipulación inadecuada. Además,el usuario está obligado a
comprobar, bajo su propia responsabilidad,antes de su uso si el material es apto
para los fines previstos, sobre todo si estos no figuran en las instrucciones de uso.
Instrucciones de uso elaboradas:
03/2004
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
FL-9494 Schaan / Liechtenstein
Page 52

Instruções de Uso
Introdução
Por favor, leia estas Instruções de Uso, com muita
atenção, para tomar conhecimento das corretas
técnicas de aplicação.
A linha de dentes pré-fabricados SR Vivo TAC /
SR Ortho TAC é um instrumento radiopaco de
diagnóstico, que auxilia os técnicos dentais na
elaboração de restaurações suportadas por implantes.
Devido à sua especial composição, estes dentes são
radiopacos.
Vantagens:
– Radiopacidade definida e conseguida através de
fabricação industrial.
– Formas correspondentes às formas das populares
linhas de dentes SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp e
SR Vivodent PE / SR Orthotyp PE.
– Ajuda para diagnóstico de fácil elaboração.
– A forma do dente radiopaco pode ser modificada com
monômeros e polímeros radiopacos.
– Forte união com polímeros termo e
autopolimerizáveis.
– O emprego dos dentes radiopacos pré-fabricados
economiza tempo na elaboração de guias e
dispositivos cirúrgicos (stents).
– Os dentes asseguram o correto posicionamento dos
implantes dentais, durante a fase de planejamento.
– Dentes com homogênea dispersão do material
radiopaco.
Composição:
Os dentes de resina estão constituídos pelos seguintes
componentes:
Polimetilmetacrilato e sulfato de bário: 66–67 % em
peso. Metilmetacrilato e dimetacrilato: 33–34 % em
peso. Ingredientes adicionais: catalisadores e
estabilizadores: 0,5 % em peso.
Modifier Monomer:
Metilmetacrilato e dimetacrilato: 99 % em peso.
Catalisadores e estabilizadores: 1 % em peso.
Modifier Polymer:
Polimetilmetacrilato e sulfato de bário: > 99 % em
peso. Catalisador: <1 % em peso.
Indicação:
Para a elaboração de restaurações dentais implantosuportadas, em situações onde a montagem de dentes é
benéfica para o diagnóstico radiológico pré-cirúrgico (CT,
tele-radiografia, como a OPG):
– severa disfunção maxilo-mandibular.
– severa atrofia da crista alveolar.
– cirurgia reconstrutiva da boca, maxila, mandíbula ou
face
O planejamento pré-cirúrgico da restauração permite
que possam ser estabelecidas a colocação, a localização
e a angulação corretas e ideais para o implante.
Contra-indicação:
O produto é contra-indicado para todas as aplicações
que não estão especificamente recomendadas pela
Ivoclar Vivadent, como, p.ex., para restaurações
permanentes nas cavidades bucais de pacientes.
Nos casos de próteses fixas metálicas, de restaurações
metálicas e de materiais metálicos osteossintéticos, a
qualidade de imagem da CT e o reconhecimento do
dente radiopaco podem ser prejudicados.
Efeitos colaterais:
Até a presente data, nenhum efeito sistêmico colateral é
conhecido. Em casos raros, foram relatadas reações
alérgicas com os materiais metilmetacrilato e polimetilmetacrilato. Não usar SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC,
Modifier Polymer ou Modifier Monomer, quando existir
comprovada alergia a qualquer um dos seus
ingredientes.
52
Page 53

1. Laboratório
Os guias de diagnóstico são fabricados para possibilitar
que a prótese total implanto-suportada possa ser montada conforme as instruções do dentista, levando em
consideração os aspectos estéticos, fonéticos e
funcionais. Neste processo, os dentes SR Vivo TAC/
SR Ortho TAC são usados da mesma maneira que os
convencionais dentes protéticos. O emprego de auxiliares de montagem, como a matriz de montagem 2D/3D
(Ivoclar Vivadent AG), é recomendado.
Procedimento sugerido
Depois da montagem dos dentes radiopacos em cera, o
excesso de cera da região vestibular é removido para
permitir o alongamento da região cervical até a base do
dente, que está apoiada no modelo. Isto deve ser feito
com o uso de Modifier Monomer e Modifier Polymer.
Conseqüentemente, o material radiopaco torna-se presente em todo o comprimento do dente.
Português
Processamento
Os dentes radiopacos SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC são
montados de acordo com os princípios convencionais.As
formas dos dentes radiopacos são idênticas às formas
das linhas de dentes SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp e
SR Vivodent PE / SR Orthotyp PE. Os dentes de resina
SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC exibem excelente e
consistente radiopacidade. Como conseqüência, as
relações bi e tridimensionais, entre a posição do
implante dental e da subseqüente supra-estrutura,
podem ser estabelecidas.
Fabricação de guias de diagnóstico
53
Modelagem em cera, com regiões cervicais alongadas.
Page 54

Ajuste de forma
– Após os procedimentos de enceramento e montagem,
uma chave de silicone ou de gesso deve ser
elaborada.
– Remover a cera do modelo e dos dentes, sem deixar
resíduos. Quando usar gesso, o modelo e a chave
devem ser isolados com Ivoclar Vivadent Separating
Fluid. Além disto, as superfícies dos dentes, que
requerem ajustes, devem ser asperizadas.
54
Modelagem em cera terminada.
Modelagem terminada, com regiões cervicais alongadas.
Chave dos dentes montados em cera.
Recolocação dos dentes na chave.
Checagem da justeza de adaptação.
Page 55

Português
– Misturar Modifier Monomer e Modifier Polymer, na
proporção de 1 : 1,3, e deixar repousar, descoberto,
durante 2 a 3 minutos.
– A polimerização deve ser conduzida em um dispositi-
vo de pressão ou numa unidade de polimerização por
calor/pressão (p.ex., Ivomat), durante 15 minutos, na
temperatura de 40–50 °C / 104–122 °F, com 2–6 bar
de pressão.
Se preciso, referências para radiografias ou ajudas
similares podem ser integradas às guias de diagnóstico,
nos locais onde forem necessárias.
55
Misturar Modifier Monomer e Modifier Polymer.
Proteger a chave.
Vazar o material líquido na chave.
Após a polimerização.
Page 56

Acabamento
Instrumentos convencionais de acabamento e polimento
devem ser usados para acabamento (de acordo com as
técnicas habituais de trabalho para PMMA).
Se requisitado pelo dentista, uma crista alveolar
radiopaca, com mucosa, pode ser criada. Isto é feito pelo
recobrimento desta área com Modifier Monomer e
Modifier Polymer.
Fabricação de placas bases
Com a finalidade de reforçar ou estabilizar a guia de
diagnóstico, uma placa base pode ser fabricada para a
região lingual (ou região palatal). Isto deve ser feito com
material de base de prótese transparente (clear) ou rosa
(pink) (p.ex., ProBase Cold pink/clear) ou com um
polímero termopolimerizável (p.ex., ProBase Hot
pink/clear).
Quando restaurações fixas são planejadas (p.ex., com
espaço interdental), a placa base deve estar apoiada na
dentição remanescente mesial ou distal, para permitir a
localização e estabilização das restaurações.
56
Após o acabamento.
Espaço retentor para material radiopaco Modifier.
Guias (stents) polimerizados.
Guia (stent), designado para espaços interdentais.
ProBase Cold transparente (também disponível em rosa).
Page 57

Português
57
Polimento
Como os guias são utilizados como um instrumento de
diagnóstico e/ou como um auxiliar durante a intervenção
cirúrgica, o pré-polimento, com escovas de pêlos de
cabra e pedra-pomes, e o polimento de alto brilho,com
discos de feltro e pasta de polimento (Universal Polishing
Past da Ivoclar Vivadent), são recomendados.
Opção
Checagem da oclusão.
Guia (stent) de diagnóstico terminado.
Guia (stent) de diagnóstico para prótese total.
Page 58

Aplicação
Para criar os canais-guias, antes da parte cirúrgica do
tratamento, o dentista (ou técnico dental) confecciona
perfurações nos dentes radiopacos. Estes canais ajudam
o dentista durante a intervenção cirúrgica. Com o
objetivo de estabelecer os pré-requisitos ideais para a
subseqüente fabricação da supra-estrutura, os ângulos
dos eixos dos implantes devem ser tão paralelos quanto
possível.
Transformação do guia de diagnóstico
em guia cirúrgico
Clínica / Laboratório
Quando recebe o guia do laboratório, o dentista pode
conduzir uma prova para examinar a estética, a fonética
e a função da planejada restauração dental. É conveniente que sejam feitos os necessários ajustes, antes do
exame radiográfico.A radiografia serve como um
instrumento adicional para o tratamento planejado. Ela
permite que o dentista possa estabelecer a localização e
angulação dos implantes,levando em consideração a
estrutura óssea e os requisitos funcionais da futura
restauração (Se necessário, referências para radiografias
ou cilindros de titânio podem ser usados com o guia).
58
Imagem CT.
Criação dos canais-guias.
Dentes reduzidos, como uma alternativa.
Os guias cirúrgicos são empregados de acordo com o
método preferido pelo usuário, com a utilização dos
materiais habituais.
Page 59

Português
59
Eixos dos dentes e implantes.
Guia (stent) cirúrgico terminado.
Eixos dos implantes sobre o modelo.
Page 60

Aplicações adicionais
– Inserção de canais-guias de metal.
– Redução sagital da região vestibular ou lingual do
canal-guia, até a primeira metade das perfurações.
60
Prótese de resina acrílica terminada.
As figuras são cortesia de
M Nanni, Dr. UM Fanti, P Miceli, Itália
Advertências
– A inalação do pó de desgaste deve ser evitada.
– A mucosa nunca deve entrar em contato com o
material não polimerizado.
– Prolongado ou repetido contato com o monômero
e com material não polimerizado pode promover irri-
tação e sensibilização aos metacrilatos.
– O Modifier Monomer contém metilmetacrilato.
– MMA é altamente irritante e inflamável (ponto de
inflamação: 10ºC/50°F).
– Irritante para os olhos, pele e órgãos respiratórios.
– Não inalar os gases.
– Pode causar sensibilização pelo contato na pele.
– Manter distante de fontes de combustão. Não fumar.
– Não descartar o monômero em sistemas de drena-
gem.
Armazenagem do Modifier Monomer /
Modifier Polymer
– Armazenar em local frio e escuro.
– Temperatura de armazenagem: 12–28 °C / 54–82 °F.
– Ver embalagem secundária para instruções de
armazenagem e prazo de validade.
– Não usar o produto com data de validade vencida.
– Manter fora do alcance das crianças.
Forma de apresentação
Basic Kit
1x SR Vivo TAC dentes anteriores superiores nas
formas A15, A24B,A25,A27.
1x SR Vivo TAC dentes anteriores inferiores nas formas
A4, A8,A9.
1x SR Ortho TAC dentes posteriores superiores nas
formas N2, N6.
1x SR Ortho TAC dentes posteriores inferiores nas
formas N2, N6.
Modifier Kit (1 Monomer 30 ml, 1 Polymer 30 g.).
Instruções de Uso.
Reposições
– SR Vivo TAC A15, A24B, A25, A27, A4, A8,A9.
– SR Ortho TAC N2, N6 superior e inferior.
– Modifier Monomer 30 ml.
– Modifier Polymer 30 g
Page 61

Português
61
Este produto foi fabricado somente para uso dental e deve ser manipulado de acordo
com as Instruções de Uso. O fabricante não é responsável pelos danos causados por
outros usos ou por manipulação incorreta. Além disto,o usuário está obrigado a
comprovar,antes do emprego e sob sua responsabilidade, se este material é compatível com a utilização desejada, principalmente quando esta utilização não está
indicada nas Instruções de Uso. Descrições e dados não constituem nenhum tipo de
garantia e, por isto,não possuem qualquer vinculação.
Data de elaboração destas Instruções de Uso:
03/2004
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
FL-9494 Schaan / Liechtenstein
Page 62

62
Page 63

63
Page 64

Gedruckt in Liechtenstein
© Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein
564292/0304/2/WE1/H
Ivoclar Vivadent – worldwide
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
Bendererstrasse 2
FL-9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Tel. +423 235 35 35
Fax +423 235 33 60
www.ivoclarvivadent.com
Ivoclar Vivadent Pty. Ltd.
1 – 5 Overseas Drive
P.O. Box 367
Noble Park,Vic. 3174
Australia
Tel. +61 3 979 595 99
Fax +61 3 979 596 45
Ivoclar Vivadent Ltda.
Rua Maestro João Gomes de
Araújo 50; Salas 92/94
Sao Paulo, CEP 02332-020
Brasil
Tel. +55 11 69 59 89 77
Fax +55 11 69 71 17 50
Ivoclar Vivadent Inc.
2785 Skymark Avenue, Unit 1
Mississauga
Ontario L4W 4Y3
Canada
Tel. +1-905 238 57 00
Fax +1-905 238 57 11
Ivoclar Vivadent Marketing Ltd.
Calle 134 No. 13-83, Of. 520
Bogotá
Colombia
Tel. +57 1 627 33 99
Fax +57 1 633 16 63
Ivoclar Vivadent SAS
B.P. 118
F-74410 Saint-Jorioz
France
Tel. +33 450 88 64 00
Fax +33 450 68 91 52
Ivoclar Vivadent GmbH
Dr.Adolf-Schneider-Str. 2
D-73479 Ellwangen, Jagst
Germany
Tel. +49 (0) 79 61 / 8 89-0
Fax +49 (0) 79 61 / 63 26
Ivoclar Vivadent UK Limited
Meridian South
Leicester
LE19 1WY
Great Britain
Tel. +44 116 265 40 55
Fax +44 116 265 40 57
Ivoclar Vivadent s.r.l.
Via dell’Industria 16
I-39025 Naturno (BZ)
Italy
Tel. +39 0473 67 01 11
Fax +39 0473 66 77 80
Ivoclar Vivadent S.A. de C.V.
Av. Mazatlán No. 61, Piso 2
Col. Condesa
06170 México, D.F.
Mexico
Tel. +52 (55) 55 53 00 38
Fax +52 (55) 55 53 14 26
Ivoclar Vivadent Ltd
12 Omega St, Albany
PO Box 5243 Wellesley St
Auckland, New Zealand
Tel. +64 9 914 9999
Fax +64 9 914 9990
Ivoclar Vivadent Polska Sp. z.o.o.
ul. Jana Pawla II 78
PL-01-501 Warszawa
Poland
Tel. +48 22 635 54 96
Fax +48 22 635 54 69
Ivoclar Vivadent S.A.
c/Emilio Muñoz, 15
Esquina c/Albarracín
E-28037 Madrid
Spain
Tel. + 34 91 375 78 20
Fax + 34 91 375 78 38
Ivoclar Vivadent AB
Dalvägen 16
S-169 56 Solna
Sweden
Tel. +46 8 514 93 930
Fax +46 8 514 93 940
Ivoclar Vivadent, Inc.
175 Pineview Drive
Amherst, N.Y. 14228
USA
Tel. +1 800 533 6825
Fax +1 716 691 2285
 Loading...
Loading...