Page 1

Instructions for Use
Page 2
Table of Contents
4 Product information
Material
Usage
Composition
PRODUCT
Working times/curing depths
Definitions and description
INFORMATION
10 Shade determination – tooth shade, stump shade
Preparation guidelines and minimum thickness
13 Framework-free restorations (inlay/onlay)
Model isolation
Liner application
Inlay/onlay layering
Final polymerization
Finishing/polishing
Preparing for cementation
20 Framework-free restorations (anterior crown)
Model isolation
Liner application
Anterior crown layering
Final polymerization
Finishing/polishing
Preparing for cementation
26 Fixed, metal-supported restorations
Framework design
Framework fabrication
Casting and finishing
Conditioning of the framework
PRACTICAL PROCEDURE
Layering diagram
Optional: Application of SR Nexco Retention Flow
Opaquer application
Cervical, Dentin and Incisal layering
Final polymerization
Finishing/polishing
42 Framework-supported combination dentures
Procedure for combination dentures
Matching the shade of SR Nexco to the shade of SR Phonares
®
II
47 Modification and characterization of denture teeth
Conditioning of the surface
Characterization and customization with Effect and Incisal materials
Final polymerization
Finishing/polishing/outcome
2
Page 3

50 Restorations with gingiva portions
Framework design
Starting situation
Framework design criteria
Contouring
Finishing
Conditioning of the framework
Opaquer application
Cervical, Dentin and Incisal layering
Gingiva layering
Final polymerization
PRACTICAL PROCEDURE
Finishing/polishing
56 General information
Cementation
Polymerization parameters
Subsequent adjustments
GENERAL
Materials combination table A–D shades
Frequently Asked Questions
INFORMATION
3
Page 4

Product Information
MATERIAL
SR Nexco Paste is a purely light-curing lab composite with microopal fillers for framework-based and framework-free dental
restorations.
As the desired shades can be reproduced even with varying layer
thicknesses, a true-to-nature appearance can be achieved for
fixed and removable dental restorations, even with artificial
gingiva. The high content of inorganic opal fillers affords optimum
benefits in terms of abrasion, discolouration, processing and surface
gloss.
Physical properties of SR Nexco Paste
Together with the respective matrix the inorganic micro-opal fillers
impart a homogeneous structure to the material. The balanced ratio
between these two components results in outstanding physical
properties achieved with the most popular polymerization units
available on the market.
SR Nexco Paste
Modulus of elasticity [MPa] 6500 ± 500
Flexural strength [MPa] 90 ± 10
Hardness (Vickers) [MPa] 440 ± 10
Water absorption [µg/mm³] 15 ± 1
Water solubility [µg/mm³] 1 ± 0.5
Esthetic properties of SR Nexco Paste
In transmitted light, the full range of light-optical properties of
SR Nexco Paste becomes evident: The opalescence and translucency
of SR Nexco restorations correspond to the dynamic light effects of
natural teeth.
The light behaviour is very similar to that of natural teeth in all
areas: the tooth neck, the dentin areas and the incisal area.
This image taken with incident light shows the fluorescence and
luminosity of SR Nexco restorations. Natural teeth derive a major
part of their brightness effect from their fluorescence. This
fluorescence plays an important role in the true-to-nature light
behaviour of SR Nexco restorations.
Incisal
Dentin
Margin
Incisal
Dentin
Margin
4
Page 5

USES
Indications
Fixed denture prosthetics
Framework-based
– Veneering of metal-supported restorations
– Veneering of combination dentures (e.g. telescope crown
veneers)
– Veneering of fixed-removable implant superstructures
– Veneering of gingiva portions in fixed-removable implant
superstructures
– Veneering of CAD/ CAM-fabricated metal frameworks
– Masking of model cast frameworks with SR Nexco Opaquer pink
Framework-free
– Inlays/onlays/veneers
– Anterior crowns
Modification/characterization
– Superficial characterization of Ivoclar Vivadent resin teeth with
SR Nexco Stains in conjunction with SR Connect and subsequent
layering with SR Nexco Paste layering materials
– Shape and shade modifications of Ivoclar Vivadent resin teeth
with SR Nexco Paste layering materials in conjunction with
SR Connect
– Modification and characterization of Telio
with SR Nexco Stains, Dentin, Incisal and Effect Shades in con-
junction with SR Connect
®
CAD and Telio Lab
General note
As is generally known, composites have to meet different demands
due to country-specific uses. Composite veneering materials show
specific characteristics and properties and their performance and
durability can therefore not be compared with that of other C&B
materials. The composite restorations may require clinical repair over
time, depending on the situation and the individual case. The
restorations can be repaired by means of microfilled composites, as
described in the section on "Subsequent Adjustments" on page 58.
Contraindications
– Posterior crowns without framework support
– Conventional cementation of fixed, metal-free restorations
– Framework-free long-term temporaries worn for longer than
12 m onths
– Patients with occlusal dysfunctions or parafunctions, such as
bruxism, etc.
– Patients with inadequate oral hygiene and substantial drug intake
(e.g. drugs that reduce salivary flow)
– All the clinical applications that are not described as an indication
by the manufacturer
– Veneering of metal frameworks without the use of SR Link and
SR Nexco Opaquer
– The use of non-recommended polymerization devices or bonding
agents
– Repairing of chipped denture teeth
5
Page 6

COMPOSITION
– SR Nexco Paste layering materials
(Margin, Dentin, Incisal, Effect, Gingiva and Intensive Gingiva
materials)
Dimethacrylates (17–19 wt.%); copolymer and silicon dioxide
(82–83 wt.%). Additional contents are stabilizers,
catalysts and pigments (<1 wt.%).
The total content of inorganic fillers is 64–65 wt.% /
46–47 vol.%. Particle size: 10–100 nm.
– SR Nexco Liner
Dimethacrylates (48 w t.%); barium glass filler, silicon dioxide
(51 wt%). Additional contents are catalysts, stabilizers and
pigments (<1 wt.%).
– SR Nexco Opaquer
Dimethacrylates 65–70 wt.%), inorganic filler (<43 wt.%).
Additional contents are catalysts, stabilizers and pigments
(<2 w t.%) .
– SR Nexco Stains
Dimethacrylates (47–48 wt.%); copolymer and silicon dioxide
(49 –50 wt.%).
Additional contents are catalysts, stabilizers and pigments
(2–3 wt .%) .
– SR Modelling Liquid
Dimethacrylate (approx. 99%). Additionally, initiators and
catalysts are contained.
– SR Nexco Retention Flow
Dimethacrylates (65–70 wt.%), inorganic filler (30–35 wt.%).
Additional contents are catalysts, stabilizers (<2 wt.%).
– SR Link
Dimethacrylate, phosphate ester, solvents and benzol peroxide
– SR Gel
Glycerine, silicon dioxide and aluminium oxide
– SR Retention Adhesive
Copolymer, resin and softening agent (30 wt.%) solved in
acetone (70 wt.%).
Warning
SR Nexco is intended for use in dentistry and dental technology.
Contact of unpolymerized material (pastes) with the skin or eyes
must be prevented. Contact with unpolymerized material may
have a slight irritating effect and may lead to a sensitization
against methacrylates. Customary medical gloves do not provide
protection against the sensitizing effect of methacrylates.
SR Connect contains methyl methacrylate (MMA). MMA is highly
flammable. Therefore, keep away from sources of ignition and do
not smoke. MMA is an irritant and is irritating to eyes, respiratory
organs and skin. Do not inhale vapours.
Do not inhale grinding dust. The safety notes on the individual
primary packages and labels have to be observed.
General note
Failure to observe the stipulated contraindications and processing
restrictions might lead to clinical failure in certain cases.
Side effects
Systemic side effects are not known to date. In individual cases
allergic reactions may occur. In case of a suspected or confirmed
allergy to one of the components, SR Nexco Paste or respective
other system components must not be used.
Storage instructions
– Store SR Link in the refrigerator (2–8 °C / 36–46 °F).
– Store SR Nexco Paste layering materials, SR Model Isolation,
SR Connect at 2–28 °C (36 –82 °F).
– Syringes should be closed immediately after use (exposure to
light causes premature polymerization).
– Protect the materials from direct sunlight.
– Do not use the products after the indicated expiration date.
– Keep material out of children’s reach.
Note on the cleaning of SR Nexco Paste restorations
As the ultrasonic cleaning liquids are highly aggressive, the
composite surface may begin dissolve if the liquid is used
inappropriately. Therefore, alkaline cleaning agents with a pH
higher than 8 must not be used.
– SR Microretentions: 200 –300 µm
– SR Macroretentions: 400–600 µm
Copolymer (99.5 wt.%) and titanium dioxide (0.5 wt.%).
– SR Connect
Methyl methacrylate (60–70%), polymethyl methacrylate (<10%),
dimethacrylate (20–30%) and catalysts (3–5%).
– Universal Polishing Paste
Emulsion of aluminium oxide, ammonium oleate, petroleum
distillate and water.
6
Page 7

WORKING TIMES/CURING DEPTHS
Working times
SR Nexco materials are sensitive to light. The working time depends
on the layer thickness, the shade and the environmental light
conditions. Brighter shades react more quickly than darker ones.
The values indicated below are average values at a light intensity of
3000 Lux, which corresponds to a bright work space lighting. These
maximum values must be taken into consideration when extruding
the respective amount of veneering material.
SR Nexco
SR Nexco Liner
SR Nexco Opaquer
SR Nexco Stains
low viscosity
SR Nexco Margin
SR Nexco Dentin
SR Nexco Incisal
SR Nexco Effect
high viscosity
SR Nexco Gingiva
Curing depths
Due to the light sensitivity, the curing depth (intermediate curing
with the Quick initial curing light) of SR Nexco materials depends on
the shade and above all the layer thickness. Bright and translucent
shades cure better, as light can penetrate through these shades
more easily than through darker and more opaque shades. These
values must be taken into consideration during the layering of the
different materials.
SR Nexco
SR Nexco Opaquer max. 0.05 mm
SR Nexco Stains 0.2 – 0. 8 mm
SR Nexco Paste
Incisal, Dentin, Effect
SR Nexco Paste
Margin, Gingiva, Intensive Gingiva
Curing depths
(20 seco nds with t he Quick)
Time
2–25 min
4–25 min
min. 2.0 mm
min. 1.0 mm
DEFINITIONS AND DESCRIPTION
Compatibility with polymerization units
High-performance polymerization is requisite in the fabrication of
high-quality lab composite restorations. With the excellent lightcuring appliance Lumamat
Vivadent, you can achieve an optimum
polymerization of SR Nexco restorations and
thus benefit from the full potential of this
material's physical properties. In addition,
the sensor-controlled Quick appliance is
available to quickly precure the material. The
Quick can also be used for the intermediate
polymerization of other light-curing veneering
materials.
Apart from Lumamat 100, other polymerization appliances may also be used for
complete or intermediate polymerization. An overview of the tested
appliances and the respective polymerization parameters can be
found on page 57.
Compatibility with Ivoclar Vivadent alloys
A metal framework is the basis for any veneered metal-based restoration. To this end, Ivoclar Vivadent offers a wide range of different
high-quality alloys which are specifically designed to match their
area of indication. This range includes high-gold, reduced gold and
base metal alloys. In conjunction with the SR Link bonding system,
the alloys establish an ideal metal/composite bond.
When using other alloys, please ask your
alloy manufacturer about the
compatibility with SR Link and its
system components.
®
100 from Ivoclar
Alloys Au Pt Pd Ag
High-gold
Academy Gold 77.2 <1.0 – 12.7
®
Harmony
PF 72.0 3.6 – 13.7
Academy Gold XH 70.7 3.6 – 13.7
Reduced gold
Harmony® X-Hard 68.3 2.9 3.6 10.0
®
XL-X
Maxigold
Midigold
®
®
50 50.0 – 3.5 35.0
62.8 – 3.9 16.1
59.5 – 2.7 26.3
Magenta 50.0 – 6.5 21.0
Minigold
Harmony
Universal alloys
®
®
3 3.5 – 25.9 50.8
40.0 – 4.0 47.0
BioUniversal PdF 71.1 9.2 – 11.7
Co Ni Cr Mon
Base metal
d.SIGN® 30 60.2 – 30.1 <1.0
®
Colado
Colado
CC 59.0 – 25.5 5.5
®
NC – 65.6 20.1 1.3
4all – 61.4 25.7 11.0
The range of available alloys may vary from country to country.
7
Page 8

Compatibility of SR Phonares® II
Compatibility between denture teeth and
lab composite is an important criterion
particularly in the fields of partial and
removable denture prosthetics. Therefore,
the shade of SR Nexco has been specifically
coordinated with the shades of SR Phonares II.
Compatibility with IPS d.SIGN
®
and IPS InLine
®
The shade concept of SR Nexco and the
IPS InLine system has been modelled
after the shade system used for
IPS d.SIGN. Thus, an Opaquer, a Dentin
and a suitable Incisal material are allocated
to each tooth shade. The shades of the
Effect, Gingiva and Stains materials are
coordinated with the shade systems of
Ivoclar Vivadent ceramic products, so that
a similar esthetic outcome can be achieved with the shadeindependent additional materials. Users are thus offered an efficient
work procedure.
The benefits include an easy and quick processing in the fabrication
of combination dentures and a simplified shade match with existing
ceramic restorations.
SR® Accessories
SR Link, 5 ml
SR Link is a metal /composite bonding agent that
provides a covalent bond between metal frameworks
and SR Nexco. SR Link is an easy-to-use and, above
all, tried-and-tested bonding system that can be used
in conjunction with a wide selection of alloys.
The bonding system is suitable for use on frameworks made of
– alloys that contain less than 90% gold, palladium and platinum
– alloys that contain less than 50% copper and /or silver
– base metal alloys
– titanium and titanium alloys
SR Connect, 5 ml
SR Connect is a light-curing conditioner to bond light-curing
veneering materials to PMMA, heat- or cold-curing polymers and resin denture teeth. These are the areas of
application:
Establishing a bonding layer in the case of
– individual shade and shape modifications of pre-
fabricated teeth and different veneering materials,
such as Telio
– individual shade adjustments of denture base resins.
®
CAD and Telio Lab.
SR Nexco Gingiva concept
The SR Nexco Paste Gingiva shades are coordinated with
the Ivoclar Vivadent Gingiva concept of
the IPS InLine system,
IPS d.SIGN and IPS e.max.
Thus, gingiva with a lifelike
shade effect can be created according to the same diagram with all
veneering systems particularly in implant superstructures.
In addition to the conventional Ivoclar Vivadent Gingiva concept,
SR Nexco Paste offers a new Intensive Gingiva shade (IG5) and a
Basic Gingiva shade (BG34). These materials can be used for
modifications and characterizations of e.g. IvoBase
®
dentures even
more quickly and easily.
SR Nexco Retention Flow
SR Nexco Retention Flow is a low-
viscosity opaquer component,
which can be applied into the
undercuts of the retention beads.
SR Nexco Retention Flow demonstrates a higher curing depth than
the shaded SR Nexco Opaquers and can be quickly and easily
applied due to its flowable consistency. The application of SR Nexco
provides for a reliable bond between the metal framework and the
first opaquer layer.
SR Modelling Liquid, 5 ml
SR Modelling Liquid is used to wet the dental technician's
instruments during modelling and as a modelling aid (wetting of
the brush to disperse the material, etc.). SR Modelling Liquid must
not be used as a bonding agent for the purpose of
modifying the consistency or in the case of subsequent
adjustments. Use SR Modelling Liquid only in very low
quantities.
SR Gel, 30 ml
SR Gel is a glycerine-based masking gel that is impervious to
oxygen. The gel is applied to the restoration before polymerization
to minimize the formation of an inhibition layer on the surface of
the veneering composite. Consequently, the gel ensures
complete curing of the restoration surface. Do not
apply too thick a layer of SR Gel.
8
Page 9
SR Model Seperator, 10 ml
The SR Model Separator is suitable for separating
working dies during the fabrication of metal-free
restorations and adjoining stone surfaces during lab
composite veneering.
SR Retention Adhesive, 20 ml
This adhesive varnish is utilized to affix micro- and
macroretention beads to the restoration surfaces after
contouring.
Universal Holder
Used to handle disposable brushes and
sponges and thereby help facilitate the
working procedures in the dental laboratory.
Disposable Brushes, 50x
The disposable brushes are particularly
suitable for the application of liquid
materials, such as SR Model Separator,
SR Link and SR Nexco Opaquer.
SR Microretention Beads, 15 ml
SR Macroretention Beads, 15 ml
Two different sizes of retention beads are available,
depending on space conditions.
– Microretention: 200–300 microns
– Macroretention: 400–600 microns
SR Mixing Pad, small
SR Mixing Plate, small
Depending on the material to be
processed, the SR Mixing Pad and
SR Mixing Plate may be used. The pad is
mainly used to process liquid SR Nexco
materials so that time-consuming
cleaning of the plate can be avoided. In
contrast, the plate is used to mix the more viscous composite
components. The light protective cover of the plate extends the
working time of the materials.
Universal Polishing Paste, 100 ml
The SR Universal Polishing Paste
enables quick and efficient polishing of composite and metal
restorations.
The paste is particularly suitable for prepolishing and principal
polishing of SR Nexco veneers.
Disposable Sponges, 50x
The disposable sponges have been
modified to fit into the universal holder.
They are used to remove the inhibition
layer after polymerization of the
Opaquer and Liner.
Cannulas, 10x
These application aids can be attached to
Liner, Opaquer and Stains syringes. They
help achieve more accurate dosing and
cleaner application procedures as the
extrusion pressure can be controlled.
Cannula Caps, 20x
The cannula caps prevent the material from
drying out or polymerizing prematurely while
it is in the cannula and provide protection
against contamination.
9
Page 10
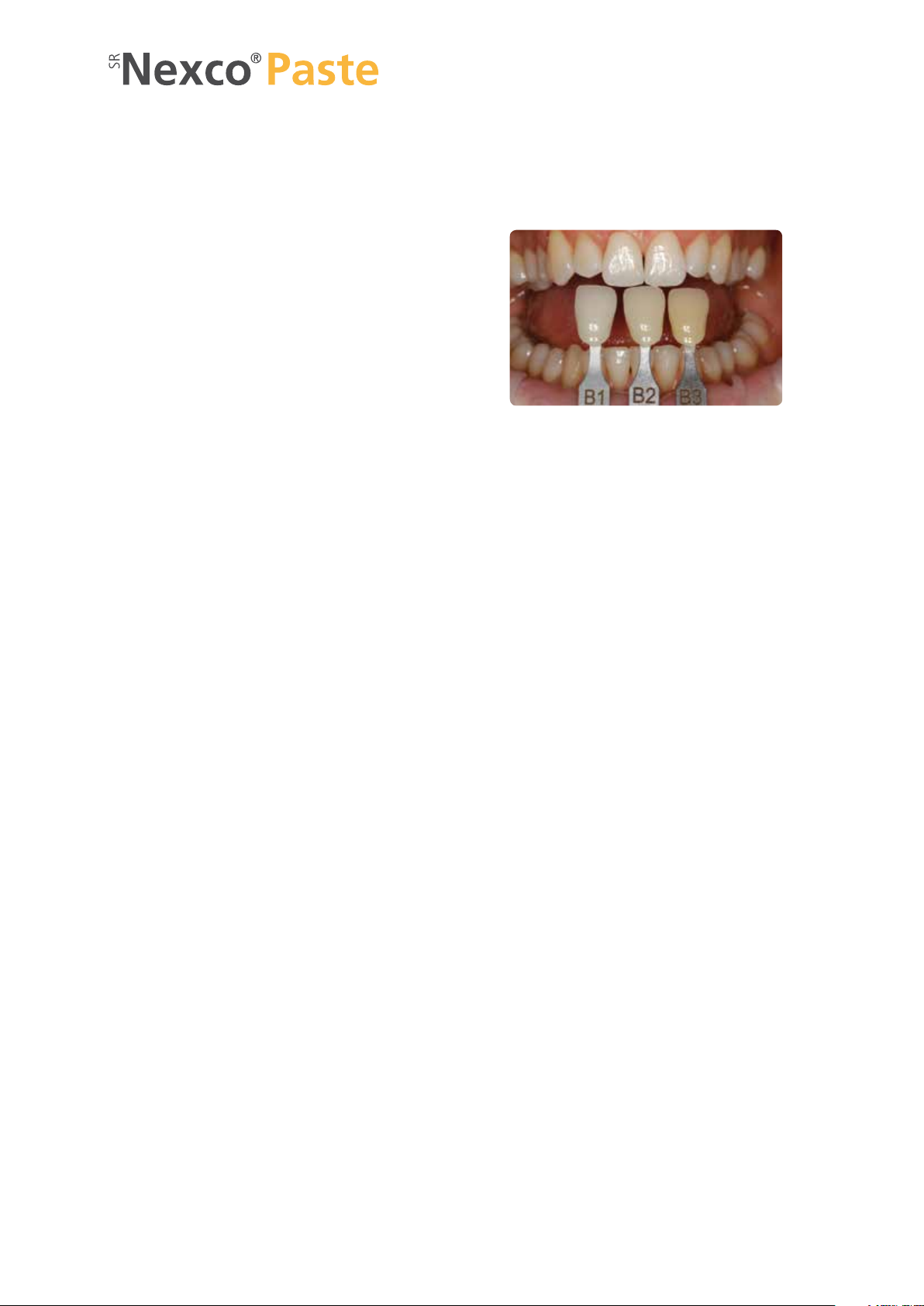
Practical procedure
SHADE DETERMINATION – TOOTH SHADE,
STUMP SHADE
Shade determination of the natural tooth
After tooth cleaning, the tooth shade of the non-prepared tooth
and/or the adjacent teeth is determined with the help of a shade
guide. Individual characteristics have to be considered when
determining the tooth shade. If a crown preparation is planned, for
example, the cervical shade should also be determined. In order to
achieve the best possible true-to-nature results, shade determination
should be carried out at daylight. Furthermore, the patient should
not wear clothes of intensive colours and /or lipstick.
Die shade selection
Based on the IPS Natural Die shade guide, a die for a frameworkfree restoration is fabriacated. This die is used as control die in
conjunction with the restoration to check the shade.
10
Page 11

PREPARATION GUIDELINES AND MINIMUM LAYER THICKNESSES
Successful results can only be achieved with SR Nexco veneering material if the guidelines and minimum
layer thicknesses are strictly observed.
As framework-free SR Nexco restorations are placed using an adhesive cementation method, a toothconserving and defect-oriented preparation technique can be used.
Inlays and onlays
Static and dynamic antagonist contacts must be taken into consideration. The preparation margins
must not be located on centric antagonist contacts. A preparation depth of at least 1.5 mm and an
isthmus width of at least 1.5 mm must be observed in the fissure area. Prepare the proximal box with
slightly diverging walls and observe an angle of >90° between the proximal cavity walls and the
prospective proximal inlay surfaces. For inlays with pronounced convex cavity walls without adequate
support by the proximal shoulder, marginal ridge contacts should be avoided. Round out internal edges
and transitions in order to prevent stress concentration within the composite material. Eliminate the
proximal contacts on all sides. Do not prepare slice-cuts or feather edges.
6°
≥1.5
>90°
≥1.5
60°–80°
For onlays, provide at least 2 mm of space in the cusp areas. On the vestibular side, prepare a bevel
(10°–30°) to improve the esthetic appearance of the transition between the composite and the tooth.
Onlays are indicated if the preparation margin is less than approximately 0.5 mm away from the cusp
tip, or if the enamel is severely undermined.
≥1.5
6°
10–3 0°
≥1.5
≥2.0
Anterior crowns
Evenly reduce the anatomical shape and observe the stipulated
minimum thickness. Prepare a circular shoulder with rounded inner
edges or a pronounced chamfer of at least 0.8 mm. In the anterior
0.8
0.8
region, reduce the labial and/or palatal /lingual surfaces by at least
1.0 mm. Reduce the incisal crown third by at least 1.5 mm. Design
transitions in such a way that no angles or edges are present.
≥1.0
>1.0
Application procedure – Shade Determination | Preparation Guidelines and Minimum Thickness
1.5
11
Page 12

Veneers
If possible, the preparation should be entirely located in the enamel,
either in the form of a simple incisal reduction without incisal overlap or conventional preparation with incisal, chamfer-type incisal
overlap. Make sure that the incisal preparation margin is not located
in the area of the abrasion surfaces. The extent of the incisal reduction depends on the desired translucency of the incisal area to be
built up. The more transparent the incisal edge of the intended
veneer, the more pronounced the incisal reduction should be. The
incisal edge should be reduced by at least 1.0 mm. By preparing orientation grooves using a depth marker, controlled enamel reduction
can be achieved. The minimum preparation thickness is approx.
0.6–1.0 mm, depending on the preparation technique selected.
Elimination of the proximal contacts is not required. Discoloured
teeth may require more preparation. In the cervical area, prepare a
cham fe r.
≥0.6
≥0.7
1.0
12
Page 13
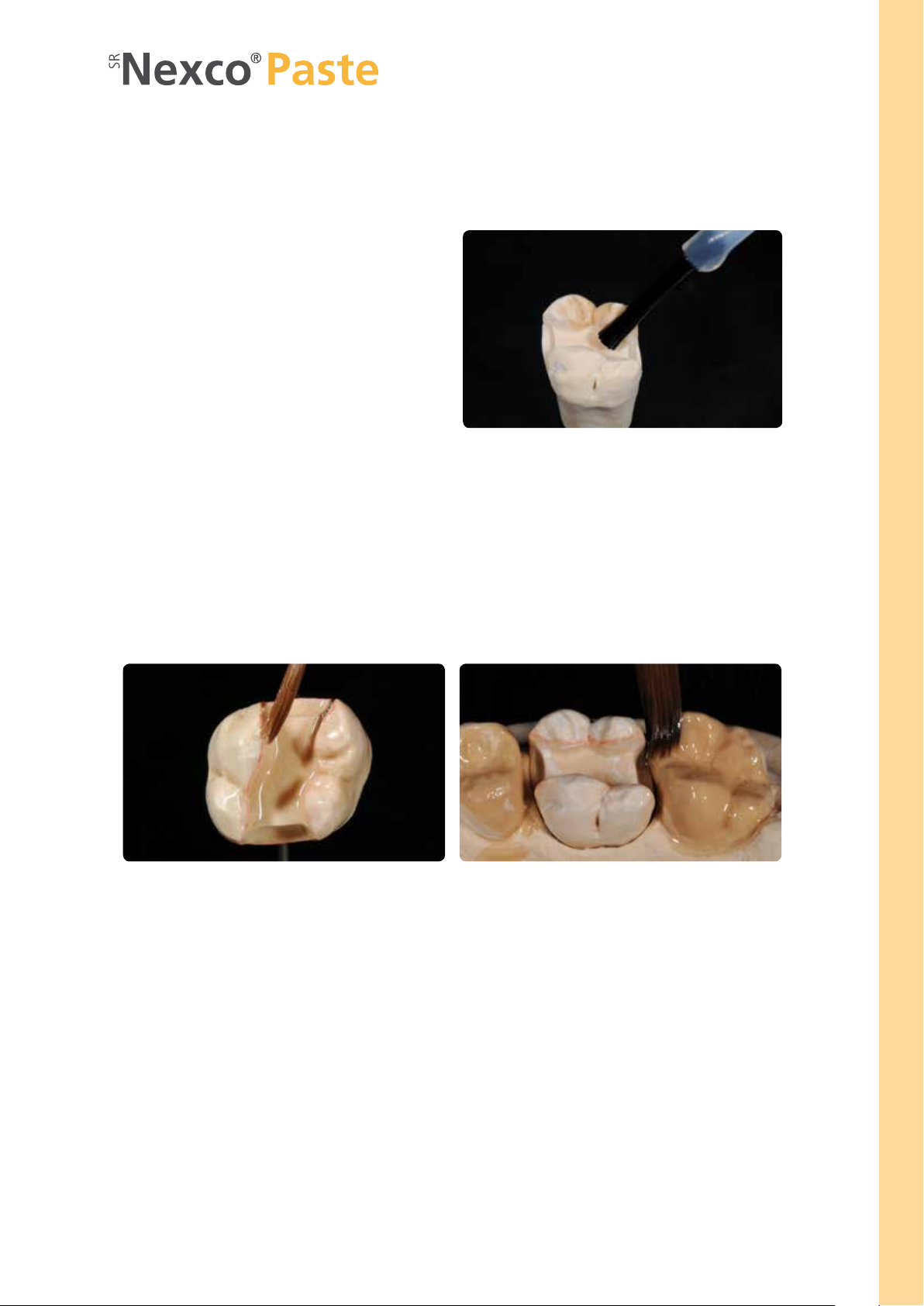
Framework-free restorations (inlay/onlay)
MODEL ISOLATION
Sealer application
Fabricate a master model or a model with detachable
segments according to the impression in the usual manner.
Expose and mark the preparation margin. Block out undercuts with blocking-out wax or blocking-out resin to ensure
that the restoration can be removed after the polymerization process without damaging the die. Basically, the application of a sealer is recommended to harden the surface
and to protect the stone die. However, the sealer layer
must not result in any changes of the dimensions of the
stone die. It is not mandatory to utilize a spacer, as two
coats of SR Model Separator will be applied. If you use a
spacer, check as to whether it is compatible with SR Model
Se parator.
Sealing the dies and adjoining parts of the model
SR Model Separator is applied in two thin coats. Apply the first coat generously and make sure that all areas of the die are
well covered. Watch out for sharp edges (incisal edges) in particular. Then allow to react for 3 minutes. After the reaction
time, apply a second layer in a thin coat, invert the model and allow to dry for 3 minutes.
Additionally, apply SR Model Separator to adjoining model surfaces that may come into contact with SR Nexco including
counterbite, allow to react for a short time, and then disperse excess material with oil-free compressed air.
Fabrication of a die coated with sealer as the working basis.
Practical Procedure – Framework-free Restorations (Inlay/Onlay)
Inlay (and onlay)
Apply first coat of SR Model Separator generously, watch out for sharp edges, and allow to react for 3 minutes. Isolate model areas.
13
Page 14
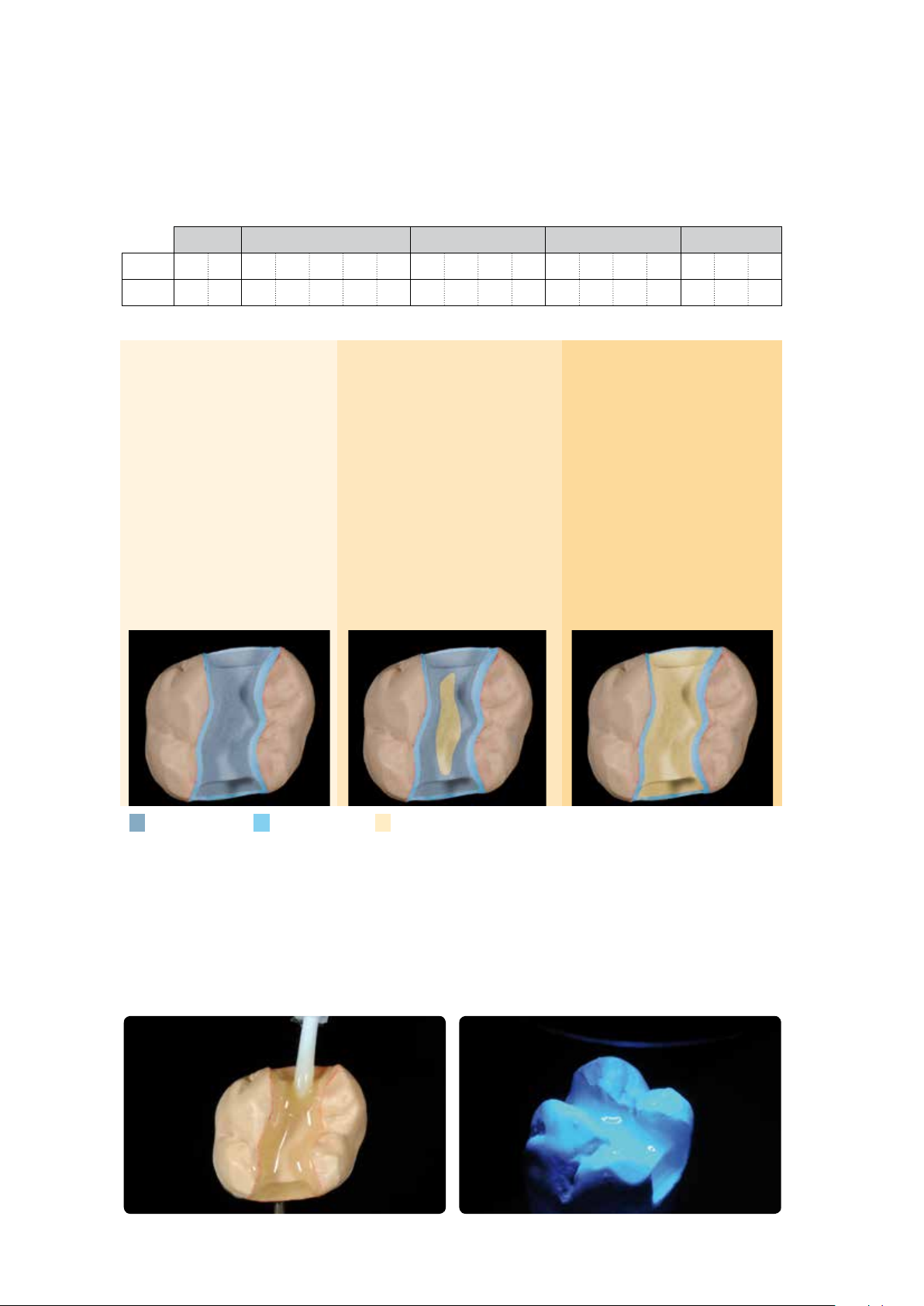
APPLYING THE LINER
SR Nexco Liner combination table
BL A B C D
Tooth BL3 BL4 A1 A2 A3 A3.5 A4 B1 B2 B3 B4 C1 C2 C3 C4 D2 D3 D4
Liner BL BL 1 2 2 3 4 1 2 3 3 1 5 5 4 5 5 5
Procedure for
non-discoloured cavities
– Apply Liner clear to the cavity
walls and the cavity floor (dentin
area) for an optimum chameleon
effect.
– Apply Liner incisal in the
marginal areas (course of natural
enamel) to achieve a harmonious
transition between the shade of
the restoration and natural tooth
structure without grey lines.
Procedure for
slightly discoloured cavities
– Mask dark areas using a Liner in
an appropriate shade (1–5).
– Coat the remaining portions of
the cavity, except the marginal
areas, with Liner clear.
– Apply Liner incisal in the marginal
areas (course of natural enamel)
to achieve a harmonious transition
between the shade of the restoration and natural tooth structure
without grey lines.
Procedure for
severely discoloured cavities
– Mask the entire cavity, except
the marginal areas, using a Liner
in a corresponding shade (1–5).
– Apply Liner incisal in the marginal
areas (course of natural enamel)
to achieve a harmonious transition between the shade of the
restoration and natural tooth
structure without grey lines.
Liner clear
Liner incisal
Liner 1–5
1st Liner application (Clear, 1–5)
Extrude the desired amount of the ready-to-use Liner paste from the syringe and spread it out slightly on the mixing pad
using a disposable brush. First, apply the Liner to the cavity walls and cavity floor in a thick coat and precure each
segment for 20 seconds using a Quick curing light. Make sure to fully cover all areas, as the Liner provides an essential
bonding surface to the luting composite. Do not cover marginal areas at this stage (course of natural enamel).
Generously cover the cavity walls and floor with the 1st liner cover and precure with Quick for 20 seconds for each segment.
14
Page 15
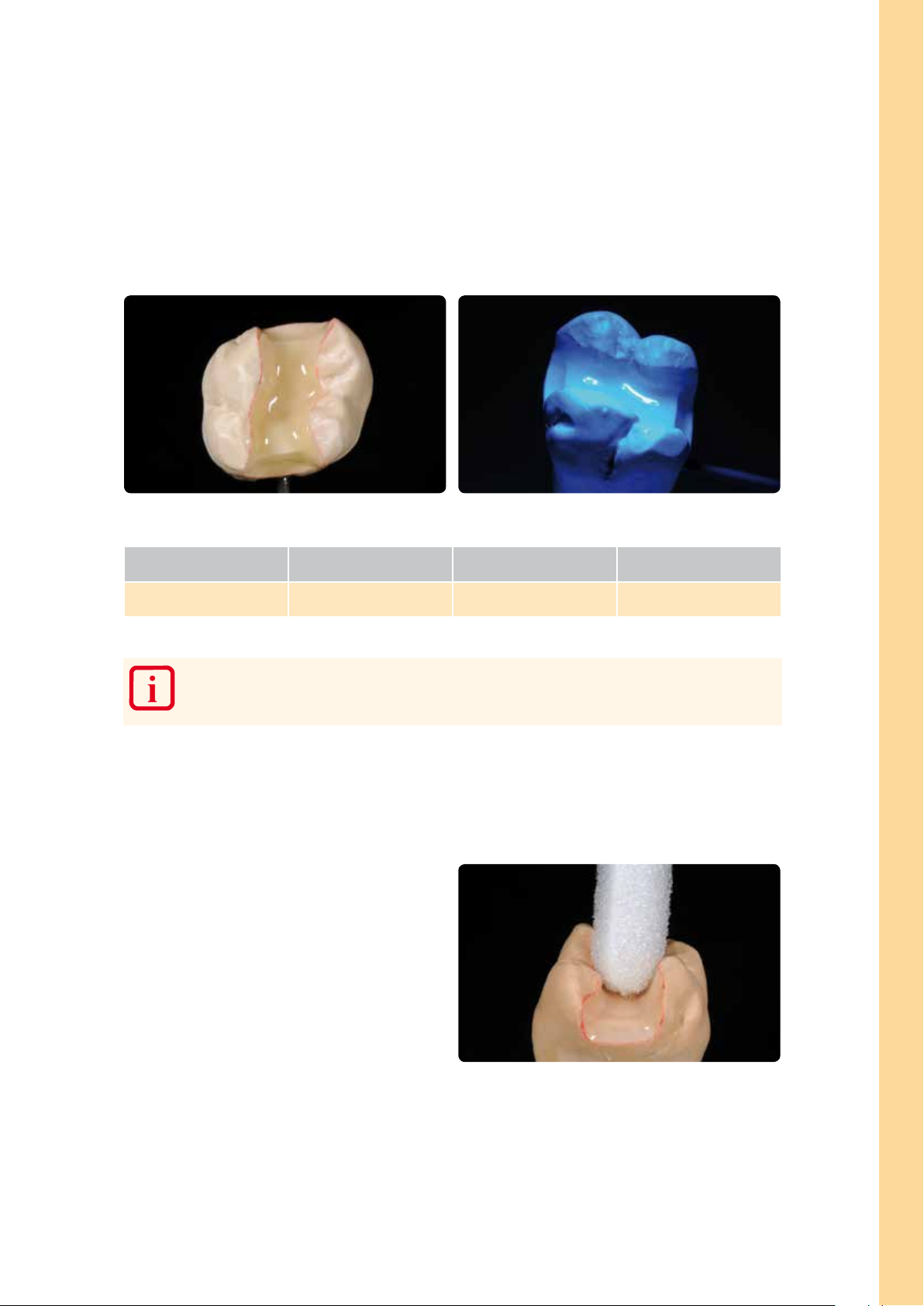
2nd Liner incisal application in the marginal area
After the application of the first Liner layer to the cavity walls and floor, apply Liner incisal in the marginal areas so that all
cavity surfaces are coated with Liner. Apply Liner incisal up to the preparation margin in order to ensure a reliable bond
between the preparation margins and the luting composite. This measure helps to reduce premature discolouration
between the restoration margins and tooth structure.
Apply Liner incisal to the marginal areas or the course of the natural enamel and precure each segment for 20 seconds
Polymerizing the Liner Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Practical Procedure – Framework-free Restorations (Inlay/Onlay)
– The entire inner surface of the restoration has to be covered with SR Nexco Liner. The layer
thickness should be at least 150 µm. Thin out the Liner towards the preparation margin.
– Do not separate polymerized SR Nexco Liner from the die.
Removing the inhibition layer after polymerization of the Liner
Thoroughly remove the resulting inhibition layer using a
disposable sponge (do not use a solvent); make sure that
the Liner surfaces are free of residue. Make sure that the
Liner shows a mat surface.
Thoroughly remove the inhibition layer with clean disposable sponges.
15
Page 16

INLAY/ONLAY LAYERING
Adapt the first layer firmly (press into place) to ensure an effective bond between the Liner and lab composite and precure each segment for 20 seconds using a Quick curing light. The shade effect in the interdental area and cavity may be
increased by means of Occlusal Dentin orange. Slightly emphasize the marginal ridges and cusps with Dentin.
Subsequently, begin the process of building up the cavity with Dentin materials. Make sure to provide adequate space for
the subsequent application of Incisal and Effect materials. The translucency of the restoration may be increased by means
of coloured Transpa materials, such as Transpa orange-grey and Transpa brown-grey. Layer SR Nexco Paste layering
materials step by step and precure each individual layer. After building up and precuring the dental plateau, apply
characterizations with SR Nexco Stains and precure for 20 seconds. Next, complete the restoration using Incisal and
Transpa materials. The cusp tips and triangular ridges may be supplemented with a fine layer of Opal Effect 3 and 4.
Adapt firmly and create smooth, rounded transitions between the layers using SR modelling instruments and synthetic
brushes.
Increase the shade effect in the interdental and cavity area with Occlusal Dentin. Outline the marginal ridges with Dentin and create a plateau with various Dentin materials.
Apply characterizations with SR Nexco Stains, precure with the Quick and cover with Incisal and Transpa materials.
Precure each intermediate segment for 20 seconds using the Quick curing light.
Design a lifelike occlusal morphology and subsequently precure all areas for 20 seconds using
Quick.
– It is essential to observe the stipulated curing depths and maximum layer thickness of the
individual materials during the layering procedure.
– If the maximum layer thickness is exceeded, break up large portions into several increments
and precure each increment for 20 seconds.
– SR Nexco Stains always have to be coated with layering material (e.g. Incisal, Transpa).
16
Page 17

CONDUCT FINAL POLYMERIZATION
After the layering procedure has been completed, all layers must be precured. To make sure that this is the case precure
each segment for 20 seconds using a Quick curing light. Next, apply SR Gel on the entire veneering surface ensuring that
all areas are fully covered and the layer is not too thick.
Apply a covering, but not too thick layer of SR Gel and secure the dies on the object holder in the correct position.
Practical Procedure – Framework-free Restorations (Inlay/Onlay)
Polymerization
Inlay/onlay
Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Conduct final polymerization Lumamat 100 11 m i n P2
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
17
Page 18
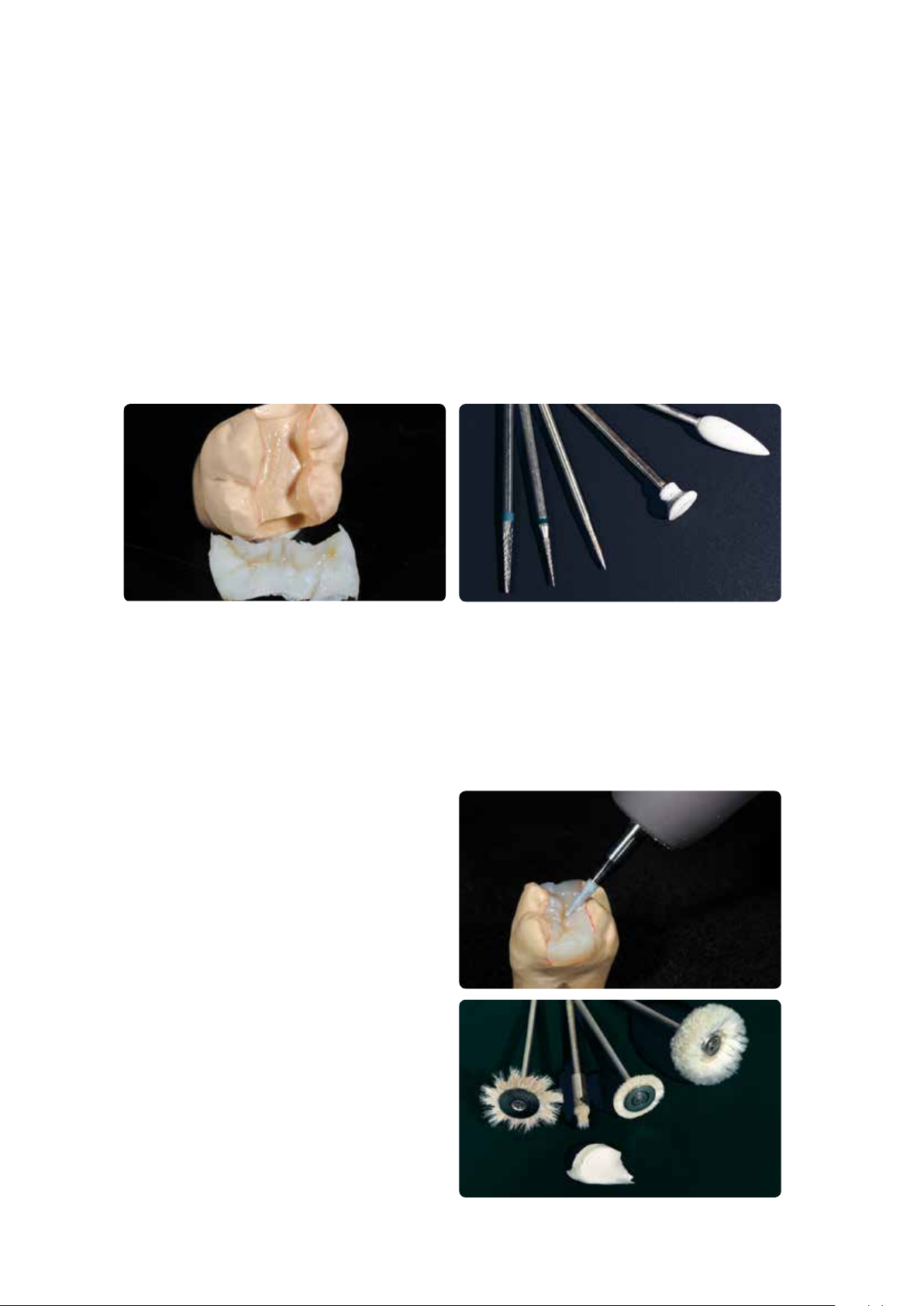
FINISHING / POLISHING
After completion of the polymerization procedure, completely remove SR Gel from the restoration using running water
and/or a steamer. Carefully remove the restoration from the die. If the restoration is removed at a later stage, it is
advisable to warm up the stone die by means of steam/hot water. Finish the restoration with cross-cut tungsten carbide
burs and fine diamonds. It is advisable to use low speed and light pressure. Make sure to rework the entire restoration to
remove the inhibition layer of approximately 30 µm. Carefully taper the margins of the restoration, lightly grind the
margins, and adjust proximal and occlusal contact points. Subsequently, recreate a lifelike tooth shape and surface
structure. The inhibition layer must be removed from the entire SR Nexco surface.
Remove SR Gel and carefully remove the restoration from the die. Remove the inhibition layer and finish the surface with cross-cut burs.
Polishing
Finishing
Carefully smooth out the ridges of the occlusal surface and
proximal surfaces with rubber polishers and silicone
polishing wheels. Pay particular attention to the margins in
order to avoid rendering them too short.
Prepolishing and high-gloss polishing
The restorations are prepolished and polished to a high
gloss using a goat hair brush, cotton or leather buff as
well as Universal Polishing Paste. Use low speed and slight
pressure for prepolishing and high-gloss polishing. Adjust
the pressure at the handpiece, not with the polishing
motor. In order to optimally polish the occlusal surfaces,
we recommend modifying the goat hair brushes to
become star-shaped so that only the desired areas can be
polished due to the smaller size of the brush. Depending
on the type of high gloss desired, leather buffing wheels
can be used to achieve a high shine, while cotton buffs are
used to achieve a lesser degree of lustre.
18
Page 19
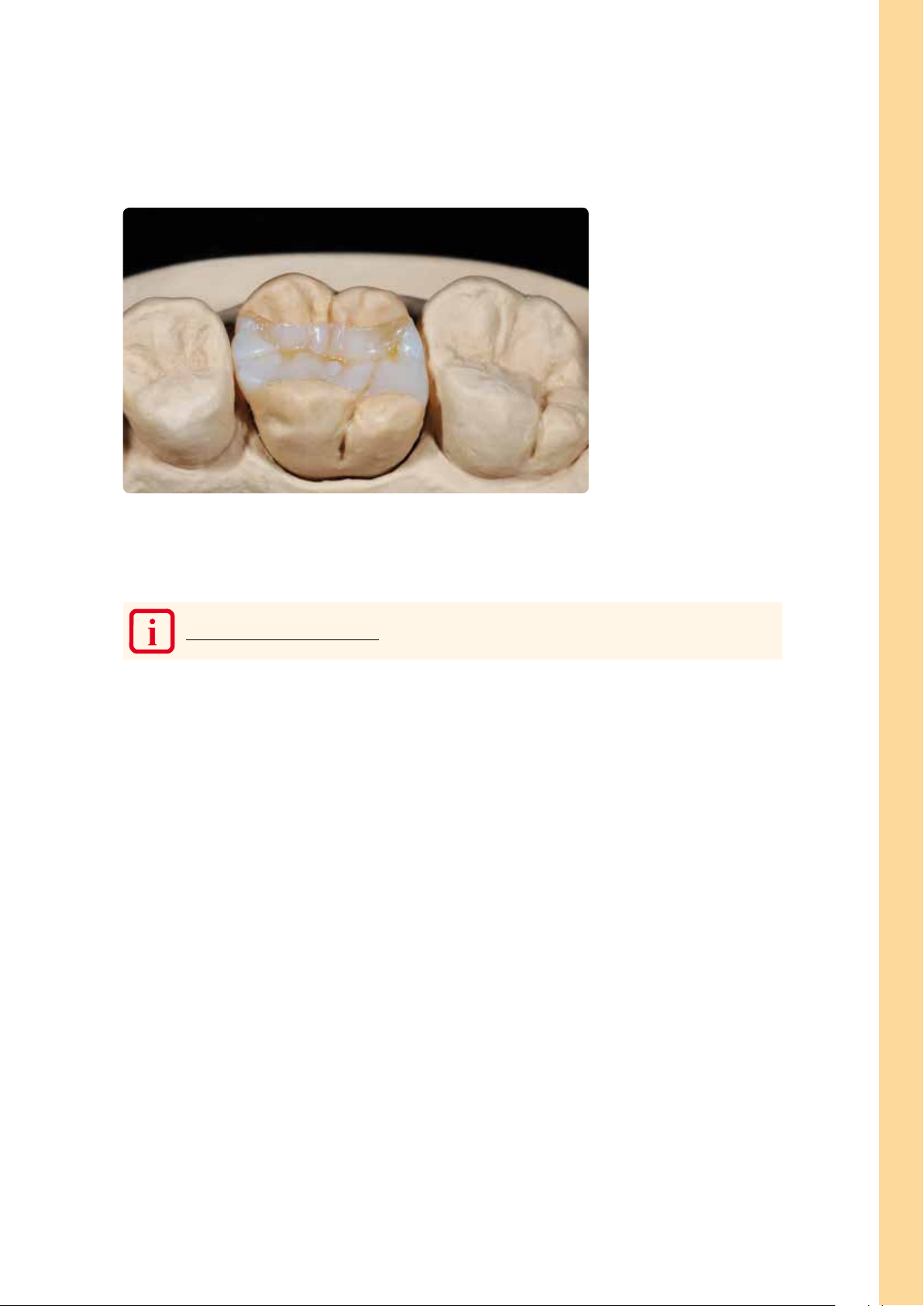
Results
PREPARING FOR CEMENTATION
Practical Procedure – Framework-free Restorations (Inlay/Onlay)
Adhesive cementation is mandatory for framework-free SR Nexco Paste restorations.
In order to achieve an excellent bond with the luting composite, the cavity side of the restoration has to be carefully
blasted with Al
subsequent cleaning, the cavity side is again roughened with a 50–100 µm diamond directly prior to the adhesive
cementation. Finally, the surfaces are silanized (e.g. with Monobond® Plus) to enable a chemical bond.
(80 –100 µm) at 1 bar / 15 psi pressure in the laboratory. Following the try-in in the dental practice and
2O3
19
Page 20
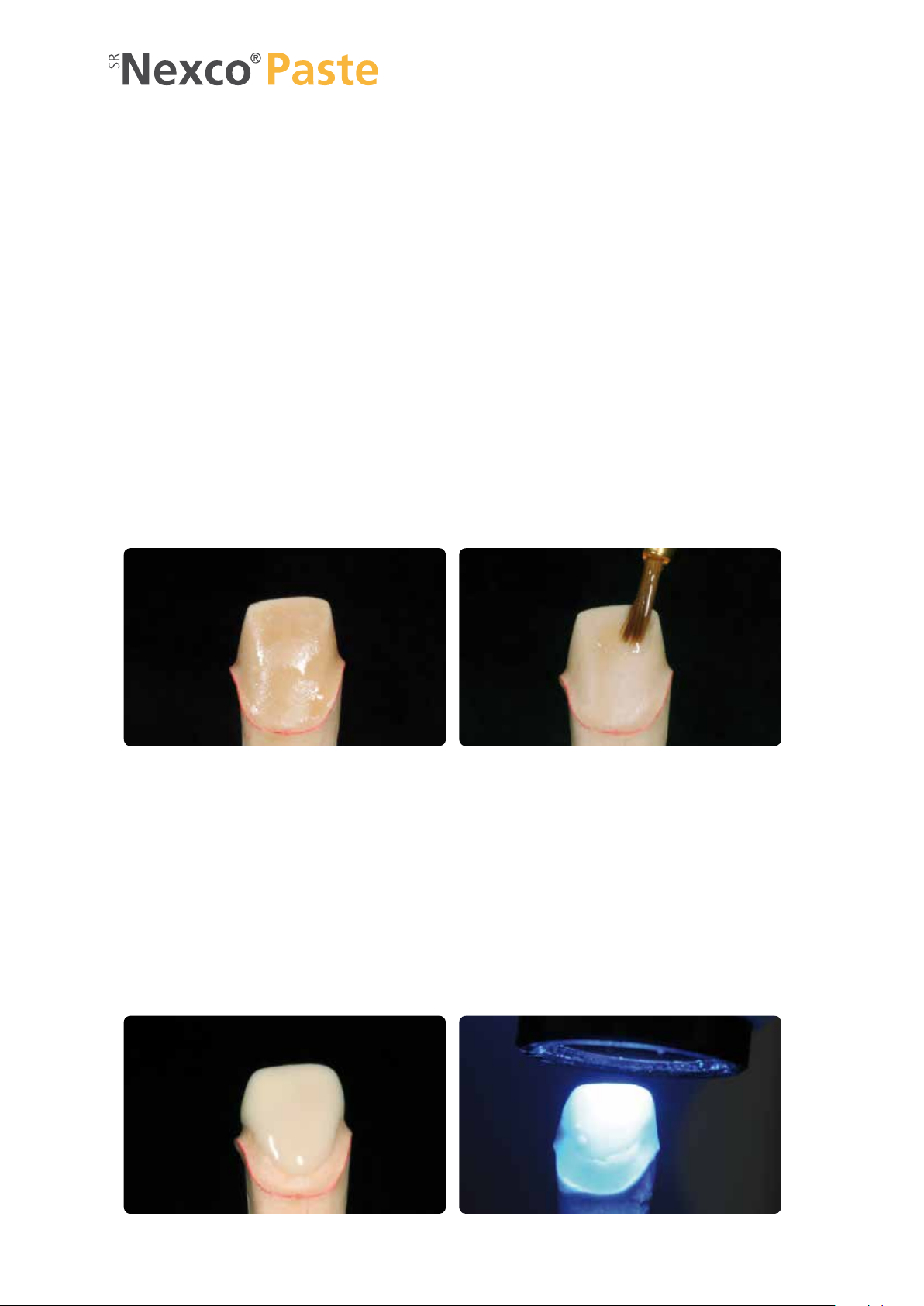
Framework-free restorations (anterior crown)
MODEL ISOLATION
Applying the sealer
Fabricate a master model or a model with detachable segments according to the impression in the usual manner. Expose
and mark the preparation margins. Block out undercuts with blocking-out wax or blocking-out resin to ensure that the
restoration can be removed after the polymerization process without damaging the die. Basically, the application of a
sealer is recommended to harden the surface and to protect the stone die. However, the sealer layer must not result in
any changes of the dimensions of the stone die. It is not mandatory to utilize a spacer, as two coats of SR Model
Separator will be applied. If you use a spacer, check as to whether it is compatible with SR Model Separator.
Sealing the dies and adjoining parts of the model
SR Model Separator is applied in two thin coats. Apply the first coat generously and make sure that all areas of the die
are well covered. Watch out for sharp edges (incisal edges) in particular. Allow the layer to react for 3 minutes. After the
reaction time, apply a second layer in a thin coat, invert the model and allow to dry for 3 minutes. Additionally, apply
SR Model Separator to adjoining model surfaces that may come into contact with SR Nexco including counterbite, allow
to react for a short time, and then disperse excess material with oil-free compressed air.
Fabrication of a die coated with sealer as the working basis
Applying two layers of SR Model Separator
APPLYING THE LINER
Extrude the desired amount of the ready-to-use Liner paste from the syringe and spread it out slightly on the mixing pad
using a disposable brush. First, apply the Liner thinly on the die surfaces. Make sure to fully cover all areas, as the Liner
provides an essential bonding surface to the luting composite. The Liner layer must be at least 150 µm thick and has to be
precured for 20 seconds per segment using the Quick.
Apply the Liner in a minimum layer thickness of 150 µm. Precure each segment for 20 seconds using a Quick curing light.
20
Page 21

Procedure for non-vital, discoloured stumps
– Mask the entire die with Liner to block out the dark colour of the underlying tooth stratum and, at the same time, to
attain an adequate degree of brightness.
– Additionally, Stains white may be applied locally to the Liner surface to further increase the degree of brightness.
Polymerizing the Liner
for anterior crowns
Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
– The entire die surface has to be covered with an SR Nexco Liner layer of at least 150 µm. Thin
out the Liner towards the preparation margin.
– Do not separate polymerized SR Nexco Liner from the die.
– If desired, the translucency of the Liners 1–5 may be increased by using Liner clear or Liner
incisal.
Removal of the inhibition layer
Thoroughly remove the resulting inhibition layer using a
disposable sponge (do not use a solvent); make sure that
the Liner surfaces are free of residue. Make sure that the
Liner shows a slightly shiny surface.
Practical Procedure – Framework-free Restorations (Anterior Crown)
Tips and tricks regarding the layering:
Liner incisal may be applied to the marginal area to
facilitate the transmission of light in the cervical area.
This measure provides a harmonious transition between
the gingiva and the restoration.
21
Page 22

ANTERIOR CROWN LAYERING
Adapt the first layer firmly (press into place) to ensure an effective bond between the Liner and lab composite and
precure each segment for 20 seconds using a Quick curing light. The shade effect in the interdental area and palatal fossa
may be increased by means of Stains orange or Occlusal Dentin orange. Build-up the labial surface using various Dentin
materials. Reproduce areas of higher brightness with Opal Effect 3 (cervical). Apply the appropriate Transpa materials to
the dentin core. Build up and precure the incisal extension using Opal Effect materials (OE1 and OE2). Mimic mamelons
using Mamelon materials and Stains and precure. Next, complete the restoration step-by-step using Incisal and Transpa
materials. Build up the palatal ridges using Dentin materials. The triangular ridges may be coated with a fine layer of Opal
Effect 3 and 4. Adapt firmly and create smooth, rounded transitions between the layers using SR modelling instruments
and synthetic brushes. With such or similar individual layering patterns you can achieve an esthetic outcome customized
to the patient using SR Nexco.
Add Dentin material to the marginal areas. Use Stains and Occlusal Dentin matierals to enhance the shade effect in the palatal area.
Precure for 20 seconds with the Quick between the layers. Outline mesial and distal ridges with Opal Effect materials.
Outline the ridges from the palatal aspect with Opal Effect 2 and cover with Incisal material. Apply Mamelon materials and Stains and precure.
22
Page 23

Complete the labial tooth contours with Incisal and Transpa materials. Precure the layered
material for 20 seconds with the Quick.
– It is essential to observe the stipulated curing depths and maximum layer thickness of the
individual materials during the layering procedure.
– If the maximum layer thickness is exceeded, break up large portions into several increments
and precure each increment for 20 seconds.
– An optimum shade reproduction is achieved if the SR Nexco layer is 1 mm thick.
FINAL POLYMERIZATION
After the layering procedure has been completed, all layers must be precured using the Quick curing light. To make sure
that this is the case, you may precure each segment again for 20 seconds. Next, apply SR Gel on the entire veneering
surface ensuring that all areas are fully covered and the layer is not too thick.
Practical Procedure – Framework-free Restorations (Anterior Crown)
Polymerization
anterior crown
Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Final polymerization Lumamat 100 11 m i n P2
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
23
Page 24

FINISHING / POLISHING
After completion of the polymerization procedure, completely remove SR Gel from the restoration using running water
and/or a steamer. Carefully remove the restoration from the die. If the restoration is removed at a later stage, it is
advisable to warm up the stone die by means of steam/hot water. Finish the restoration with cross-cut tungsten carbide
burs and fine diamonds. It is advisable to use low speed and light pressure. Make sure to rework the entire restoration to
remove the inhibition layer of approximately 30 µm from all surfaces. Carefully taper the margins of the restoration,
lightly grind the margins, and adjust proximal contact points. Subsequently, recreate a lifelike tooth shape and surface
structure. The inhibition layer must be removed from the entire SR Nexco surface.
Polishing
Finishing
Carefully smooth out the surfaces with rubber
polishers and silicone polishing wheels. Pay particular
attention to the margins in order to avoid rendering them
too short.
Carefully smooth out surfaces with rubber polishers and silicone polishing wheels.
Prepolishing and high-gloss polishing
The restorations are prepolished and polished to a high gloss using a goat hair brush, cotton or leather buff as well as
Universal Polishing Paste. Use low speed and slight pressure for prepolishing and high-gloss polishing. Adjust the pressure
at the handpiece, not with the polishing motor. Depending on the type of high gloss desired, leather buffing wheels
can be used to achieve a high shine, while cotton buff are used to achieve a lesser degree of lustre.
Prepolish and polish the restorations to a high gloss using a goat hair brush and cotton buff as well as Universal Polishing Paste.
24
Page 25

Results
SR Nexco Paste anterior crown polished to a high gloss
PREPARING FOR CEMENTATION
Practical Procedure – Framework-free Restorations (Anterior Crown)
Adhesive cementation is mandatory for framework-free SR Nexco Paste restorations.
In order to achieve an excellent bond with the luting composite, the cavity side of the restoration has to be carefully
blasted with Al
(80 –100 µm) at 1 bar / 15 psi pressure in the laboratory. Following the try-in in the dental practice
2O3
and subsequent cleaning, the cavity side is again roughened with a 50-100 µm diamond directly prior to the adhesive
cementation. Finally, the surfaces are silanized (e.g. with Monobond® Plus) to enable a chemical bond.
25
Page 26

Fixed, metal-supported restorations
FRAMEWORK DESIGN
The following points must be observed for the design of frameworks veneered with lab composite:
1. Framework design for full-coverage veneers (ideal space conditions)
With full-coverage veneers, the framework has to reflect the shape of the tooth in a reduced form. Design the framework
in such a way that it supports the cusps resulting in a virtually even layer thickness of the lab composite. In this way, the
masticatory forces occurring during functional chewing are exerted on the framework rather than on the veneering
composite. In case of unfavourable preparations, the missing tooth structure has to be compensated by the design of the
framework and not the lab composite. Furthermore, an even layer thickness facilitates the creation of a harmonious
shade effect while full-coverage veneering provides a maximum level of esthetic beauty and function. All areas of the
framework should be smooth and rounded to prevent delamination and cracking. Angles and edges should be rounded
out already in the wax-up and not in the metal in order to avoid undermining the minimum framework thickness. The
thickness of the metal framework must not be less than 0.3 mm for single crowns and 0.5 mm for bridge abutments
after finishing.
Anterior crowns
Premolar crowns
Molar crowns
26
Page 27

2. Framework design for partial veneers (limited space conditions)
A different framework design is required for partial veneers (e.g. telescope and conus crowns). As the space in the
occlusal, palatal and lingual area in particular tends to be limited in many cases, this area of the restoration must be
designed in the metal in such a way that cracks or delamination cannot occur because of too thin layer thicknesses of
the lab composite. In this design, the transition between the metal framework and the lab composite should be clearly
defined and it should incorporate a right angle finish line. The transition areas between the metal framework and the
veneering composite must not be located in the contact point areas, nor on surfaces involved in masticatory functions.
A chamfer or wraparound technique is required in partial veneer preparations to provide adequate support for the
veneer. Observe the palatal area in upper canines (canine guidance) and the occlusal area in posterior teeth. To obtain a
balance between esthetic and functional properties, it is advisable to reduce the mesial corner of the occlusal surface in
upper posterior teeth in particular to attain a harmonious esthetic appearance, especially when the buccal corridor is
exposed. The thickness of the metal framework must not be less than 0.3 mm for single crowns and 0.5 mm for bridge
abutments after finishing. Please refer to the Instructions for Use of the corresponding alloy for further information.
Anterior crowns
Practical Procedure – Fixed, Metal-Supported Restorations
Premolar crowns
Molar crowns
27
Page 28

3. Design of the bridge pontic
Bridge pontics are designed taking esthetic and functional aspects as well as oral hygiene into account. The pontic rest on
the alveolar ridge should consist entirely of metal (polished to a high gloss) or composite material. The transition between
metal and lab composite should always be located in areas where oral hygiene is ensured in an ideal way. If enough
space is available, the rest should consist of composite material. In order to ensure adequate stability between the bridge
pontic and the bridge abutments, a palatal and /or lingual scallop is recommended.
If space is limited, the rest should consist of metal polished to a high gloss. The palatal or lingual restoration surfaces are
designed in metal for reasons of stability. In order to avoid inclusions at the bridge pontic due to massive cast parts, the
bridge pontic should be hollowed out. A wax wire is placed in the hollowed space (ample space available) and formed in
such a way that it is level with the abutment teeth. This creates additional retentive surface and thus allows an even
shade effect to be created in the bridge pontic and abutment.
Sufficient space Limited space
28
Page 29

4. Interface between metal and composite
The interface between the metal framework and the lab composite must be clearly defined, incorporate a right angle
finish line and use a chamfer or wraparound technique whenever possible. The transition areas between the metal framework and the lab composite must not be located in the contact point areas nor on surfaces involved in masticatory
functions. Furthermore, make sure that the interface between metal and lab composite in the cervical area does not
come into contact with the gingiva, particularly if a tapered crown margin is designed (i.e. no metal margin). In this way,
irritation of the gingiva can be prevented. The interface in the interdental area must be designed in such a way that
cleaning of these difficult-to-access areas is possible.
Practical Procedure – Fixed, Metal-Supported Restorations
5. Correct application of retention beads
It is basically advisable to apply retention beads to provide mechanical retention in addition to the chemical bond with
SR Link. If space is limited, it may not always be possible to apply retention beads or they may only be applied in certain
areas. Therefore, retention beads can be applied locally to the bonding surfaces without compromising the space
available or the esthetic appearance of the restoration in particular. The retention adhesive should be applied in as thin a
coating as possible so that the retention beads are not completely immersed in adhesive and enough surface area for
mechanical retention is provided. After casting, the retention beads may be reduced by half of their size (equator) to
preserve a sufficiently large retentive area.
Retention Adhesive (schematic)
29
Page 30

METAL FRAMEWORK FABRICATION
There are two types of frameworks, i.e. frameworks for full-coverage veneers (ideal space) and frameworks for partial
veneers (limited space). Basically, it is advisable to design a full wax-up and then fabricate a silicone key to check the
space conditions during contouring. When fabricating the frameworks, make sure that the minimum wall thickness after
finishing is 0.3 mm for single crowns and 0.5 mm for bridge abutments. These dimensions are the prerequisite for a
stable metal framework and a durable bond between the metal and composite. If the stipulated framework and
connector dimensions are not observed, delamination and cracking may occur.
Full contouring of the anatomical tooth shape
Contouring
The framework reflects the reduced anatomical tooth shape (see page 26 for tooth shape-supporting contouring).
As a result, the lab composite can be applied in an even layer and will consequently be appropriately supported. The
requirements of the different alloys have to be taken into account.
Reducing the model portions and checking using the silicone key.
If the metal framework is too small, the veneering composite is not adequately supported, which
may lead to cracks, delamination and esthetically compromised results. Mechanical retentions
are generally beneficial and advisable, as they support the chemical bond between metal and
composite.
30
Page 31

CASTING AND FINISHING
After having cast the framework (e.g. with Academy Gold XH), carefully divest, sandblast /pickle and fit it on the model.
After separating, the metal framework is finished using tungsten carbide burs. If softer alloys are used, it is recommended
to work with limited pressure. A correct marginal design is paramount to attaining a reliable metal-composite bond. If
possible, create a tapered chamfer or wraparound design in the cervical area.
You are recommended to polish those parts of the restoration which are not veneered with SR Nexco (e.g. palatal or
lingual areas, metal scallops, etc.) before you start the veneering work or before the framework is conditioned. If this is
done after veneering, the quality may be compromised.
Carefully divest, blast and pickle the framework on the model.
Practical Procedure – Fixed, Metal-Supported Restorations
Create the cervical margin as a tapered chamfer using a tungsten carbide bur.
31
Page 32

CONDITIONING OF THE FRAMEWORK
Conditioning with SR Link
After finishing, carefully blast the framework with aluminium oxide Al
(see Instructions for Use of the corresponding alloy). Sandblasting improves the mechanical bond. It roughens and thus
substantially increases the surface of the alloy. After blasting, remove blasting medium residue from the framework by
tapping off and not by cleaning with steam or an air gun. Apply SR Link immediately after having tapped off the
residue. Use a clean disposable brush to apply SR Link and allow to react for 3 minutes. Do not "soak" metal surface in
SR Link.
Carefully blast the framework with Al2O3 (80–100 µm) and 2–3 bar (29–44 psi) pressure and tap off with an instrument.
(80 –100 µm) at 2–3 bar (29–44 psi) pressure
2O3
Immediately after the blasting procedure, tap off blasting medium residue, apply SR Link using
a disposable brush and allow to react for 3 minutes.
– When using SR Link, do NOT clean the framework with steam or with an air gun after blasting.
– Do not touch clean surfaces.
– Do not use SR Link in conjunction with alloys that contain more than 50% silver and /or copper or alloys
with more than 90% gold, palladium and platinum.
32
Page 33

LAYERING DIAGRAM
In order to achieve an appropriate shade match, a minimum layer thickness of 1 mm is required.
Full-coverage veneer
Framework
Practical Procedure – Fixed, Metal-Supported Restorations
Opaquer application
Dentin build-up
Completion of the layering using Incisal materials
33
Page 34

OPTIONAL APPLICATION OF SR NEXCO RETENTION FLOW
Application of SR Nexco Retention Flow
Apply SR Nexco Retention Flow in the undercuts of the retention beads using a brush and light-cure with the Quick for
20 seconds. After light-curing, apply the first Opaquer layer.
Opaquer
Retention beads
Retention Flow
SR Link
Metal
As an option, SR Nexco Retention Flow can be applied in the undercuts of the retention beads.
Polymerization
Retention Flow
Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
Important: SR Nexco Retention Flow must be applied in a very thin film along the transition between the metal framework and the veneer. If this is not properly executed, a visible thin Retention Flow line may be visible after the reduction
by grinding of said transition.
OPAQUER LAYER
1st Opaquer application
Extrude the desired amount of the ready-to-use opaquer paste from the syringe and spread it out slightly on the mixing
pad using a brush. Apply the first opaquer layer (wash) thinly using a brush. Make sure to thoroughly smooth out any
roughness and the retention beads (micro- and macroretention beads) on the metal surface, since the wash layer
represents the most important bond between the metal and the composite. Subsequently, precure the wash for 20 seconds per segment using the Quick.
Apply the first opaquer layer (wash) thinly using the brush. Level or fill retentions
or roughness and subsequently precure using the Quick curing light.
If SR Nexco Retention Flow is used, thinly apply the first Opaquer layer (wash) on the surface
with a brush and precure with the Quick.
34
Page 35

2nd Opaquer application
Apply the second opaquer layer in such a way that the metal framework, and particularly the retention beads, are entirely
covered with opaquer, i.e. as much as required and as little as possible. After that, precure the opaquer for 20 seconds
per segment using the Quick and then polymerize it in the Lumamat 100.
Entirely cover the retention beads with the second Opaquer layer and precure each segment for 20 seconds.
Procedure for the bridge pontic with Pontic Fill
Apply the second opaquer layer in such a way that the framework is completely covered and precure each segment for
20 seconds. Next, build up the hollowed out space on the bridge pontic to the level of the abutment teeth using Pontic
Fill and precure for 40 seconds using the Quick curing light. Subsequently, apply an Opaquer layer directly to the
inhibition layer of Pontic Fill, precure for 20 seconds and then directly polymerize it in the polymerization appliance.
Practical Procedure – Fixed, Metal-Supported Restorations
Polymerizing the Opaquer
Opaquer
polymerization
Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Final polymerization Lumamat 100 11 m i n P2
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
– To obtain a smooth transition between the metal and composite, thin out the opaquer at the metal margin.
– If a smooth surface is preferred, lightly tap the top of the surface with a spatula.
– Using a probe, check opaquer for complete polymerization in critical areas and cure again as necessary.
35
Page 36

CERVICAL, DENTIN, AND INCISAL LAYERING
Sealing the model
Isolate all areas of the model which come into
contact with SR Nexco prior to the dentin and incisal
layering. This step helps to prevent the lab composite from
sticking to the model. Use SR Model Separator to seal
adjoining parts of the model (e.g. stone die and pontic
rests). Apply SR Model Separator in a thin layer, allow to
react for a short time, and remove excess with oil-free
compressed air.
Removal of the inhibition layer
Thoroughly remove the resulting Opaquer inhibition layer
using a disposable sponge (do not use a solvent); make
sure that the Opaquer surfaces are free of residue. Make
sure that the Opaquer shows a slightly shiny surface.
Tip
Characterizing the Opaquer
After the inhibition layer has been removed, you may
individualize /modify the shade of sections of the Opaquer
surface with SR Nexco Stains. It is advisable to apply a
thin layer of Stains in the marginal and inter dental area,
particularly if space is limited, to enhance the in-depth
shade effect. Subsequently, precure SR Nexco Stains for
20 seconds using the Quick.
36
Page 37

Tips regarding the different layers
Before layering, avoid mixing and overlapping the pastes to prevent air from being
trapped. Do not dilute the pastes with SR Modelling Liquid or low-viscosity
components. As a general rule, use only small amounts of SR Modelling Liquid.
It is advisable to apply highly opaque pastes, e.g. Mamelon light, to the pontic rest to
ensure adequate shade stability. After that, layer these areas using Margin and Dentin
materials.
It is recommended to build up the veneer segment by segment (tooth by tooth), to
separate them from each other and then to precure. Finally, the individual veneers are
joined.
Practical Procedure – Fixed, Metal-Supported Restorations
Opal Effect pastes provide a true-to-nature opalescent effect in the incisal third. Opal
Effect 1 is applied to the cut-back dentin as extension of the dentin core and then
precured.
Use the shaded Transpa materials to complete and enhance the vitality in the incisal
area. Transpa blue is suitable for the mesial and distal aspects.
Use Mamelon materials to create a lifelike shade effect in the incisal third. They are
applied on the completed incisal area. Create smooth transitions. Avoid edges, since
they may look like stubs after polymerization and the mamelons may appear too
pronounced.
37
Page 38

Dentin/incisal layering
The layering procedure of the individual SR Nexco Paste materials is carried out either in accordance with the layering
diagram (shade guide layering) or individually. Adapt the first layer firmly (press into place) to ensure an effective bond
between the composite and the opaquer surface and precure each segment for 20 seconds using a Quick curing light.
Margin material may be applied in a half-moon shape to cervical areas, pontics and crown margins that are thinning
towards the metal. Pontic Fill is particularly suitable for the pontic area. Adapt firmly and create smooth, rounded
transitions between the layers (Margin–Dentin–Mamelon–Incisal) using SR modelling instruments or synthetic brushes.
After that, build up the dentin layers step by step and precure each segment for 20 seconds with the Quick curing light.
The shade effect in the interdental area may be enhanced by means of chromatic materials, such as Occlusal Dentin
orange. Design the dentin core in such a way that the mamelon shape remains outlined. Make sure to provide adequate
space for the subsequent application of the Incisal and Transpa materials. The mamelons can be individually designed
with either Mamelon material or SR Nexco Stains. After that, the restoration is completed layer by layer using Incisal and
Transpa materials.
The coordinated consistency of the materials ensures that modelled contours are maintained and enables easy layering.
The Incisal materials are coordinated with the Dentin materials so that delicate transitions can be designed. Subsequently,
precure each segment for 20 seconds using the Quick.
Stabilize pontic areas with Pontic Fill. Occlusal Dentin to increase the occlusal shade effect.
Intermediate curing with the Quick. Completing the dentin core.
Stains applied into the fissures and covered with Incisal material.
38
Page 39

An optimum shade reproduction is achieved if the SR Nexco layer is 1 mm thick.
FINAL POLYMERIZATION
After the layering procedure has been completed, all layers must be precured. To make sure that this is the case, you may
precure each segment again for 20 seconds. Next, apply SR Gel on the entire veneering surface ensuring that all areas
are fully covered and the layer is not too thick.
Practical Procedure – Fixed, Metal-Supported Restorations
Polymerization
bridge
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Final polymerization Lumamat 100 11 m i n P2
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
Appliance Time Program
FINISHING / POLISHING
Finishing
After completion of the polymerization procedure, completely remove SR Gel from the restoration using running water
and/or a steamer. Finish the restoration with cross-cut tungsten carbide burs, fine diamonds and flexible discs. It is
advisable to use low speed and light pressure. Make sure to rework the entire restoration to remove the inhibition layer
of approximately 30 µm from all surfaces. Fit the restoration on the model and adjust proximal and occlusal contact
points. Subsequently, recreate a lifelike tooth shape and surface structure. The inhibition layer must be removed from the
entire SR Nexco surface.
Remove SR Gel. Using cross-cut burs and discs, remove the inhibition layer and create a lifelike shape.
39
Page 40

Finishing
Smooth out the surface (convex areas) of the natural structures, as well as the marginal ridges with rubber polishers and
silicone polishing wheels so that they exhibit an extra lustre after high-gloss polishing. Silicone polishing wheels are also
ideally suitable for finishing metal-composite interfaces.
Polish the restoration using customary polishers, such as rubber polishers and silicone wheels.
Prepolishing and high-gloss polishing
The restorations are prepolished and polished to a high gloss using a goat hair brush, cotton or leather buff as well as
Universal Polishing Paste. Use low speed and limited pressure for prepolishing and high-gloss polishing. Adjust the
pressure with the handpiece, not the polishing motor. In order to optimally polish the interdental areas and occlusal
surfaces, we recommend modifying the goat hair brushes to become star-shaped so that only the desired areas can be
polished due to the smaller size of the brush. Depending on the type of high gloss desired, leather buffing wheels can be
used to achieve a high shine, while cotton buffs are used to achieve a lesser degree of lustre.
Polish the surface with Universal Polishing Paste and e.g. goat hair brush.
– Microroughness on the finished veneering surface is conducive to plaque accumulation. Therefore, polish
carefully.
– Pay particular attention to crown margins, interdental areas, occlusal surfaces and the basal rest of pontics.
40
Page 41

Result
Practical Procedure – Fixed, Metal-Supported Restorations
41
Page 42

Framework-based combination dentures
PROCEDURE FOR COMBINATION DENTURES
Veneering with SR Nexco BEFORE setting up and completing the denture saddles
1. Fabricate the primary and secondary components (e.g. telescope crowns)
2. Fabricate the model casting (transversal connector, sublingual saddle bar)
3. Connect the secondary components with the model casting by adhesive joining, soldering or laser technique.
4. Veneer the secondary components with SR Nexco Paste.
5. Polymerize, finish and polish the SR Nexco veneer.
6. Mask the retentions of the model casting with SR Nexco Gingiva Opaquer.
7. Set up and complete the denture with cold-curing denture base material (e.g. ProBase Cold).
MASKING OF MODEL CAST RETENTIONS WITH GINGIVA OPAQUER
Conditioning with SR Link
After finishing the model cast, carefully blast the retentions with aluminium oxide Al
pressure (see Instructions for Use of the corresponding alloy). Sandblasting improves the mechanical bond. This measure
roughens and thus substantially increases the surface of the metal. After blasting, remove blasting medium residue by
tapping off and not by cleaning with steam or an air gun. Apply SR Link immediately after having tapped off the residue.
Apply SR Link with a clean disposable brush and allow it to react for 3 minutes. Do not "soak" metal surface in SR Link.
(80 –100 µm) at 3 bar (44 psi)
2O3
Carefully blast the retentions with Al2O3 (80–100 µm) at 3 bar (44 psi) pressure; then remove any residue by careful tapping with an instrument.
Apply SR Link immediately after the blasting procedure using a disposable brush and allow to
react for 3 minutes.
– When using SR Link, do NOT clean the framework with steam or with an air gun after blasting.
– Do not touch the surface once it has been cleaned!
42
Page 43

Applying Gingiva Opaquer
st
1
Gingiva Opaquer layer (wash)
Extrude the desired amount of the ready-to-use Opaquer paste from the syringe and spread it out slightly on the mixing
pad using a disposable brush. Apply the first Opaquer layer (wash layer) thinly using a disposable brush. Make sure to
thoroughly smooth out any roughness on the metal surface, since the wash layer represents the most important bond
between metal and composite. Subsequently, precure the wash for 20 seconds per segment using the Quick.
Apply the first Opaquer layer (wash) thinly with a disposable brush and level / fill any roughness ...
Practical procedure – Framework-Supported Combination Dentures
... and precure for 20 seconds with the Quick.
Polymerization
Gigiva Opaquer (Wash)
Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
43
Page 44

2nd Gingiva opaquer layer
Apply the second Opaquer layer in such a way that the
retentions are entirely covered with Opaquer, i.e. as much
as required and as little as possible. After that, precure the
Opaquer for 20 seconds per segment using the the Quick,
immediately mount the restoration on the object holder
(without model), and polymerize it in the Lumamat 100
using Program 2.
When positioning the model casting on the object holder, make sure that enough light can reach them (no
shadow casting). After polymerization, check the curing depth with a probe. If necessary, repeat the
polymerization cycle in a Lumamat 100.
Apply a fully covering 2nd Opaquer layer and precure each segment for 20 seconds.
Polymerization
Gigiva Opaquer (Wash)
Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Final polymerization Lumamat 100 11 min P2
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
Preparing for completion
After polymerization check the degree of curing with a
probe. Then, remove the inhibited layer using the
monomer of the corresponding denture base material and
a disposable sponge. This is necessary to prevent streak
formation in the composite while completing the restoration.
Make sure that the Opaquer shows a slightly shiny surface.
The monomers of cold-curing denture base materials, such
®
as ProBase
Cold, are best suited to remove the inhibition
layer.
It is recommended to secure the denture teeth to the
model cast by means of a cold-curing denture base resin
material. Heat polymerization may negatively influence the
bond between the metal framework and the SR Nexco
veneering material.
44
Page 45

MATCHING THE SHADE OF SR NEXCO TO THE SHADE OF SR PHONARES® II
In combination denture prosthetics, matching the shade of composite veneers and denture teeth is very important. As the
shades of SR Nexco and SR Phonares® II are coordinated, matching shades can be achieved in an efficient manner.
SR Phonares II teeth represent a new generation of true-to-nature esthetics in the field of denture prosthetics. The texture
of the vestibular surfaces reproduces the natural wavelike pattern of the enamel surface. The perikymata (horizontal
growth lines) ensure the true-to-nature vitality of the tooth shapes.
In order to achieve matching shades, we recommend that the individual SR Nexco Pastes should be applied in accordance
with the layering diagram of the A–D shade guide.
Framework
Practical procedure – Framework-Supported Combination Dentures
Opaquer application
Dentin build-up
Completion of the layering using Incisal materials
45
Page 46

Tip
As the tooth mould concept of
SR Phonares II has been designed to
match the age and characteristics of the
patient, the incisal layer thickness may vary.
BOLDSOFT
YOUTHFUL
UNIVERSAL MATU RE
46
Page 47

Modification and characterization of denture teeth
Denture teeth can be modified and characterized with SR Connect and SR Nexco. SR Connect is a light-curing conditioner
to bond light-curing veneering materials to PMMA, heat- or cold-curing polymers and resin denture teeth.
CONDITIONING OF THE SURFACE
Sandblast the surface to be characterized with Al2O3 (80 –100 µm) at 2 bar (29 psi) pressure. Remove residue with oil-free
air. Do not clean with steam! Then apply SR Connect in a thin layer and let it react for 2–3 minutes and subsequently
polymerize in a Lumamat 100 using Program 2. Do not destroy the inhibition layer. After this, you can apply the
SR Nexco veneering material.
Practical Procedure – Modification and Characterization of Denture Teeth
Create the cut-back. Sandblast the surface with Al2O3 (80–100 µm) at 2 bar (29 psi) pressure.
Remove residue with oil-free air. Do not clean with steam!
Apply SR Connect in a thin layer and allow to dry for approximately 2–3 minutes. Then polymerize in a Lumamat 100.
47
Page 48

Do not destroy the inhibition layer.
CHARACTERIZATION AND CUSTOMIZATION USING E.G. EFFECT, DENTIN AND
INCISAL MATERIALS
Characterize with Effect Shades and adjust the shape and shade. Cover with Incisal material.
FINAL POLYMERIZATION
Apply a fully covering but not inappropriately thick coat of SR Gel and conduct the final polymerization.
Polymerization
Dentin/Incisal
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Final polymerization Lumamat 100 11 min P2
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
Appliance Time Program
48
Page 49

FINISHING/POLISHING/OUTCOME
Practical Procedure – Modification and Characterization of Denture Teeth
The applied SR Nexco material is more wear resistant than PMMA denture teeth, for instance. This fact must
be taken into account during finishing and polishing. If this is not observed, a "step" may develop in the
transition areas between SR Nexco and PMMA resin during polishing, for example.
49
Page 50

Restorations with gingiva portions
The SR Nexco Paste Gingiva shades are coordinated with the Ivoclar Vivadent Gingiva concept of IPS InLine®, IPS d.SIGN®
and IPS e.max® Ceram. Thus, gingiva with a lifelike shade effect can be created according to the same diagram with all
veneering systems particularly in implant superstructures.
In addition, SR Nexco offers the shades Basic Gingiva 34 and Intensive Gingiva 5. Particularly in implant denture
prosthetics and in conjunction with metal-ceramic restorations, the application of SR Nexco Paste allows an effective
treatment concept to be implemented.
Due to the intraoral application of SR Nexco Paste, the gingiva portions can be supplemented and modified in a lifelike
fashion.
FRAMEWORK DESIGN
The framework design should be meticulously planned and fabricated by means of a wax-up and silicone keys fabricated
from it. This ensures that the SR Nexco veneering material features an even layer thickness. Make sure that the soft-tissue
contacts consist entirely of SR Nexco, so that SR Nexco Paste Gingiva can be used to supplement the restoration in case
of subsequent tissue recession.
Framework design by means of a wax-up and reduced shape.
Completely milled framework.
CONDITIONING OF THE FRAMEWORK
Conditioning with SR Link
After finishing, carefully blast the framework with aluminium oxide Al
(see Instructions for Use of the corresponding alloy). Sandblasting improves the mechanical bond. It roughens and thus
substantially increases the surface of the object. After blasting, remove blasting medium residue from the framework by
tapping off and not by cleaning with steam or an air gun. Apply SR Link immediately after having tapped off the residue.
Use a clean disposable brush to apply SR Link and allow to react for 3 minutes. Do not apply too much SR Link to metal
surfaces.
(80 –100 µm) at 2–3 bar (29–44 psi) pressure
2O3
50
Page 51

Framework blasted with Al2O3 (80–100 µm) and 2–3 bar (29–44 psi) pressure wetted with SR Link.
– When using SR Link, do NOT clean the framework with steam or with an air gun after blasting.
– Do not touch clean surfaces.
– Do not use SR Link in conjunction with alloys that contain more than 50% silver and /or copper or alloys
with more than 90% gold, palladium and platinum.
OPAQUER APPLICATION AND LAYERING OF THE DENTAL PORTIONS
First, the dental framework portions are covered with two layers of the tooth-coloured Opaquer in paste form and intermediately cured. Final polymerization is conducted in a Lumamat 100. After removing the inhibition layer with a disposable sponge, the dental portions are completed with SR Nexco Paste.
Practical Procedure – Restorations with Gingiva Portions
First Opaquer layer as wash, second Opaquer application in a covering layer
Layering of the dental portions with Dentin, Effect and Incisal materials
Basically, the dental veneers may be created first, before the gingival portions are designed. Optionally, the
dental veneers and the gingival portions may also be created simultaneously.
51
Page 52

OPAQUER APPLICATION TO VENEER THE GINGIVAL PORTIONS
Gingiva opaquer layer
Extrude the desired amount of the ready-to-use Opaquer paste from the syringe and spread it out slightly on the mixing
pad using a brush. Apply the first Opaquer layer (wash) thinly using the brush. If retention beads are used, make sure to
thoroughly smooth out or fill up any roughness on the metal surface, since the wash layer represents the most important
bond between the metal and the composite. Subsequently, precure the wash for 20 seconds per tooth using the Quick.
Apply the second Opaquer layer. The metal framework should now be entirely covered with Opaquer. Make sure to apply
as much material as necessary and as little material as possible. Subsequently, polymerize in a Lumamat 100.
Apply the first Gingiva Opaquer layer (wash) thinly with a brush and precure with a Quick curing light.
Entirely cover the gingival area with the second Opaquer layer and polymerize in a Lumamat 100.
Opaquer
polyermization
Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Final polymerization Lumamat 100 11 min P2
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
– If a metal margin has been designed, thin out the Opaquer towards the metal margin to ensure a clean
transition between metal and composite.
– If a smooth surface is preferred, lightly tap the top of the surface with a spatula.
– Using a probe, check opaquer for complete polymerization in critical areas and cure again as necessary.
52
Page 53

GINGIVA LAYERING
After the application and the polymerization of the SR Nexco Gingiva Opaquer, you can directly begin with the
application of SR Nexco Gingiva materials. Due to the different gingiva thickness, blood circulation and pigmentation,
the gingiva shows a very varied shade effect. This effect has to be recreated with SR Nexco material. A lifelike esthetic
appearance is created by applying individual layers with different Gingiva shades.
First, apply Basic Gingiva 34 as the basic material to the entire area from the papilla contours to the model. To achieve an
appropriate depth effect, Gingiva materials with a more intensive shade may be layered. In the process, papilla and the
spaces between the alveolas can be layered in a lifelike fashion. To achieve a natural-looking outcome, use brighter, more
translucent materials towards the surface. Precure each individually applied layer for 20 seconds per segment using the
Quick curing light.
Apply Basic Gingiva BG34 in combination with IG2 and IG4 as the basic material. Characterizations with Intensive Gingiva
Practical Procedure – Restorations with Gingiva Portions
Completion with translucent Gingiva materials
53
Page 54

FINAL POLYMERIZATION
To minimize the inhibition layer, apply a covering but not too thick layer of SR Gel prior to polyermization in a
Lumamat 100. Then conduct the final polymerization in a Lumamat 100. The final processing of SR Nexco Gingiva is
limited to minor shape corrections and polishing of the surface.
Apply a covering but not inappropriately thick coat of SR Gel and conduct the final polymerization.
Final polymerization Appliance Time Program
Precuring time per segment Quick 20 s –
Final polymerization Lumamat 100 11 min P2
For the parameters of other polymerization devices, please go to page 57.
FINISHING / POLISHING
Finishing
After completion of the polymerization procedure, completely remove SR Gel from the restoration using running water.
Use regular tungsten carbide burs and polishers to design and finish the surface and the surface texture. The inhibition
layer must be removed from the entire SR Nexco surface.
Finish with cross-cut tungsten carbide burs and stippling instruments.
Subsequently, polish with Universal Polishing Paste.
54
Page 55

Polishing
To finish the surface, polish the surface in the usual manner with rubber polishers and silicone polishing wheels. The
restorations are prepolished and polished to a high gloss using a goat hair brush, cotton or leather buff as well as
Universal Polishing Paste. Use low speed and limited pressure for prepolishing and high-gloss polishing. Adjust the
pressure with the handpiece, not the polishing motor.
– Microroughness on the finished veneering surface is conducive to plaque accumulation. Therefore, polish
carefully.
– Make sure to polish crown margins, interdental areas, occlusal areas, gingiva portions and direct basal
gingiva rests carefully to a high gloss.
Result
Practical Procedure – Restorations with Gingiva Portions
55
Page 56

General Information
CEMENTATION
Possibilities for esthetic cementation are decisive for the harmonious shade effect of a lab composite restoration.
Depending of the indication, SR Nexco restorations can be seated using either adhesive, self-adhesive or conventional
cementation.
Material SR Nexco
(framework-free)
Indication
Cementation
method
Blasting
Inlays, onlays, veneers
anterior crowns
adhesive adhesive self-adhesive/conventional
Cleaning with Al
O3 at a
2
maximum pressure of 1 bar
(15 psi).
Conditioning/
silanating
Cementation system
60 s with
®
Monobond
Multilink
Plus
®
Automix,
Variolink® Veneer,
Variolink® II
The range of available products may vary from country to country
* No conditioning is required for conventional cementation.
Please read the corresponding Instructions for Use.
Finding your way out of the cements maze
The Cementation Navigation System, a new multimedia application from Ivoclar Vivadent, offers dentists
practical orientation and guidance in the selection of the best luting material for each case.
CNS
www.cementation-navigation.com
SR Nexco
(metal-supported)
Crowns, bridges
Cleaning with Al
O3 according to the instructions
2
of the alloy manufacturer
60 s with
Monobond® Plus
–
Multilink® Automix SpeedCEM®, Vivaglass® CEM
Zinc oxide temporary cements are used for the provisional cementation of framework-based long-term temporaries that
are worn for up to 12 months.
56
Page 57

POLYMERIZATION PARAMETERS
Appliance Manufacturer Opaquer Dentin Liner, Incisal,
Quick
Lumamat 100
Spectramat
Labolight
LV-III
Solidilite V Shofu
Visio Beta
Vario
HiLite
Ivoclar
Vivadent AG
Ivoclar
Vivadent AG
GC
3M
Heraeus
Kulzer
20 s Quick
P2/11 min
20 s
5 min 5 min 2 min 5 min 2 min 2 min 5 min
5 min 2 min 2 min 5 min 2 min 3 min 5 min
3 min 1 min 1 min 3 min 1 min 3 min 5 min
7 min
no vacuum
4x 20 s
Visio Alfa
180 s 90 s 90 s 90 s 90 s 90 s 180 s
Quick
Effect,
Margin
20 s Quick 20 s Quick 20 s Quick
4x 20 s
Visio Alfa
Gingiva Stains SR Connect Final
P2/11 min P2/11 min
4x 20 s
Visio Alfa
4x 20 s
Visio Alfa
4x 20 s
Visio Alfa
polymerization
4x 20 s
no vacuum
– Regular maintance and functional checks of the polymerization appliances are required.
– Appliances for tack-curing: Quick (Ivoclar Vivadent AG), HiLite pre (Heraeus Kulzer), Visio Alfa (3M ESPE),
Sublite V (Shofu), Steplight SL-I (GC).
General Information – Cementation | Polymerization Parameters
57
Page 58

SUBSEQUENT ADJUSTMENTS
Subsequent adjustments, e.g. during cut-back or after final polymerization in the lab
Adjustments with SR Nexco components
1. Roughen the areas to be adjusted with a coarse diamond or carefully blast with aluminium oxide Al
disposable blasting medium) at 2 bar (29 psi) pressure. Sandblasting improves the mechanical bond. This measure
roughens and thus substantially increases the surface.
2. After blasting, remove blasting medium residue with oil-free compressed air.
3. Do not apply Connector, Bonder or Modelling Liquids to the sandblasted surfaces.
4. Immediately after blasting, apply the SR Nexco materials and precure each segment for 20 seconds with the Quick.
5. Cover the entire veneer evenly with a thin layer of SR Gel.
6. Place the restoration on the object holder.
7. Conduct final polymerization (see Polymerization table).
8. After completion of the final polymerization, remove SR Gel under running water.
9. Finish and polish the restoration as described above.
Intraoral adjustments
Subsequent adjustments which may become necessary can be applied with SR Nexco material or a micro-filled direct
restorative (e.g. Heliomolar®). If composite materials are used for adjustments, polishing might cause a step to develop
due to the different hardnesses of the materials.
Repair/adjustments of SR Nexco veneers
Adjustments with SR Nexco material or Heliomolar
1. Clean the entire veneer for shade determination.
2. Adequate isolation is required, preferably with a rubber dam.
3. Roughen the areas to be adjusted with a coarse diamond (80–100 µm) with water irrigation and bevel the margins.
Clean the restoration with water and carefully blow dry.
4. Apply Heliobond, disperse to a thin layer and light-cure for 10 seconds (e.g. Bluephase
5. Subsequently, apply the selected SR Nexco or Heliomolar materials and cure with a curing light.
6. After curing, finish the excess material with suitable finishers.
7. Use water irrigation for polishing with Astropol® or OptraPol® NG. Make sure to observe the individual polishing steps
in order to obtain a smooth surface with a high gloss.
®
).
(8 0 –100 µm,
2O3
Repairing/adjusting metal areas entirely surrounded by composite
1. Clean the entire veneer to determine the shade.
2. Adequate isolation is required, preferably with a rubber dam.
3. Roughen the areas to be adjusted with a coarse diamond (80–100 µm) with water irrigation and bevel the composite
margins. Clean the restoration with water and carefully blow dry. Alternatively, the metal surface may be roughened
with an intraoral sandblasting device or by means of silicoating (observe manufacturer's instructions).
4. Use a brush to apply Monobond
®
Plus to the areas to be adjusted and allow to react for 60 seconds. Subsequently,
dry with oil-free air.
5. Apply Heliobond, disperse to a thin layer and light-cure for 10 seconds (e.g. Bluephase).
6. Subsequently, apply the selected SR Nexco or Heliomolar materials and cure with a curing light.
7. After curing, finish the excess material with suitable finishers.
8. Use water irrigation for polishing with Astropol or OptraPol NG. Make sure to observe the individual polishing steps in
order to obtain a smooth surface with a high gloss.
Repairing exposed metal surfaces which are not entirely surrounded by composite
1. Clean the entire veneer to determine the shade.
2. Use a rubber dam.
3. Bevel the margins of the areas to be repaired with a diamond grinding instrument with water irrigation. Roughen the
metal surface with an intraoral sandblasting device or by means of silicoating (observe manufacturer's instructions).
Clean the restoration with water and carefully blow dry.
4. Use a brush to apply Monobond Plus to the areas to be repaired and allow to react for 60 seconds. Subsequently, dry
with oil-free air.
5. Apply Heliobond, disperse to a thin layer and light-cure for 10 seconds (e.g. Bluephase).
58
Page 59

6. Subsequently, apply the selected SR Nexco or Heliomolar materials and cure with a curing light.
7. After curing, finish the excess material with suitable finishers.
8. Use water irrigation for polishing with Astropol or OptraPol NG. Make sure to observe the individual polishing steps in
order to obtain a smooth surface with a high gloss.
Modifying the shade/adjusting artificial SR Nexco Gingiva parts
Adjustments with SR Nexco material
1. Clean the artificial gingiva portions for shade determination.
2. Roughen the areas to be adjusted with a coarse diamond (80–100 µm), clean with water and carefully blow dry.
3. Apply Heliobond, disperse to a thin layer and light-cure for 10 seconds (e.g. Bluephase).
4. Subsequently, apply the selected SR Nexco or Heliomolar materials and cure with a curing light.
5. After curing, finish the excess material with suitable finishers.
6. Use water irrigation for polishing with Astropol or OptraPol NG. Make sure to observe the individual polishing steps in
order to obtain a smooth surface with a high gloss.
– Read the respective Instructions for Use of Heliomolar®, Monobond® Plus and Heliobond.
– Use only suitable pastes (e.g. Proxyt® fine) which do not roughen the surface to clean SR Nexco veneers
during oral hygiene procedures.
– Observe the maximum layer thicknesses for SR Nexco (max. 2 mm; see page 7 – Curing depths).
– If curing lights with an output of 650 mW /cm2 are used, the polymerization time is 20 seconds for SR Nexco
Paste Incisal and 40 seconds for SR Nexco Paste Dentin.
– Given the low curing depth, the Opaquer should be applied in very thin layers (e.g. by means of a brush) .
The applicaton of a second layer may be necessary after light curing.
General Information – Subsequent Adjustments
59
Page 60

MATERIALS COMBINATION TABLE
Shade group BL A B C D
Tooth shade
SR Nexco
Liner
SR Nexco
Retention Flow
SR Nexco
Opaquer
SR Nexco Paste
Margin
BL3
BL4 A1 A2 A3 A3.5 A4 B1 B2 B3 B4 C1 C2 C3 C4 D2 D3 D4
BL
1 2 2 3 4 1 2 3 3 1 5 5 4 5 5 5
clear incisal
Retention Flow
BL1/BL2 BL3/BL4 A1 A2 A3 A3.5 A4 B1 B2 B3 B4 C1 C2 C3 C4 D2 D3 D4
1 2 2 3 4 1 2 3 3 1 5 5 4 5 5 5
SR Nexco Paste
Pontic Fill
SR Nexco Paste
Dentin
SR Nexco Paste
Schneide
SR Nexco Paste
Effect
SR Nexco Stains
SR Nexco Paste
Gingiva
Pontic Fill
BL3 BL4 A1 A2 A3 A3.5 A4 B1 B2 B3 B4 C1 C2 C3 C4 D2 D3 D4
BL 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 2 3 4
Occlusal
Dentin
Gingiva
Opaquer
orange brown
Basic
Gingiva
pink
Mamelon
light yellow-orange
clear white orange marron mahogany blue
Opal Effect
OE 1 OE 2 OE 3 OE 4
Gingiva
BG34
G1 G2 G3 G4 G5
60
Page 61

General Information – Materials Combination Table
Intensive
Gingiva
Transparent
blue brown-grey orange-grey clear
IG1 IG2 IG3 IG4 IG5
61
Page 62

FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Is it possible to repair SR Adoro® with SR Nexco Paste?
Basically yes. However, the shades of the materials are not
coordinated with each other.
Are the SR Nexco Paste materials radiopaque?
No, the SR Nexco Paste materials feature only a low radiopacity.
Is it possible to use SR Modelling Liquid as bonding agent?
No. SR Modelling Liquid must only be used for the wetting of
instruments. The material has an unfavourable effect on the bond
and might cause the restoration to fail if used excessively.
Is it possible to use SR Modelling Liquid as glaze?
No. It is intended for use during modelling and must not be used as
glaze.
Is it possible to use SR Modelling Liquid to dilute the
consistency?
No. The strength of the material would then no longer be
warranted and the material would be internally inhomogeneous.
As a result, the restoration would fail.
What needs to be given particular attention during the sandblasting procedure (conditioning)?
Use Al
on the alloy used.
Is it possible to mix SR Nexco Pastes (high and low viscosity)
with each other?
High- and low-viscosity pastes must not be mixed with each other
as this would cause bubble formation and due to the different
strength values. SR Nexco must not be mixed or processed with
other veneering materials.
Up to what thickness is it possible to layer SR Nexco Paste?
Do not apply layers thicker than 2 mm in the incisal and occlusal
areas.
Is it possible to apply SR Nexco Stains to the surface?
SR Nexco Stains must always be covered with layering materials
such as Incisal or Transpa materials, the reason being that they are
not wear-resistant and they would promote the accumulation of
plaque.
with a grain size of 80 –100 μm. The jet pressure depends
2O3
How must SR Link be stored?
Store SR Link in the refrigerator (2–8 °C / 36– 46 °F).
On which framework materials can SR Link be used?
– On alloys with a gold, palladium and platinum content of up
to 90%
– On alloys that contain up to 50% copper and /or silver
– On base metal alloys
– On titanium and titanium alloys
Is it possible to use SR Link on high-gold and copper-free bio
alloys and electroplated frameworks?
Due to the high precious metal content (Au, Pt, Pd, Ag) of bio alloys
and the fine gold content (99.9%) of electroplated frameworks,
SR Link cannot be used. Generally, the bond achieved on alloys
containing copper is superior to the one on copper-free alloys.
Is it necessary to use Connector and Bonding Liquids for
subsequent adjustments of SR Nexco veneers?
Roughening and sandblasting is sufficient to apply subsequent
supplements to completed SR Nexco restorations.
Which appliances may be used to polymerize SR Nexco?
SR Nexco Paste can be polymerized in a Lumamat 100 or Targis
Power Upgrade and in all conventional polymerization appliances
which have been tested by Ivoclar Vivadent and which are listed in
the polymerization table.
What happens if the indicated curing depths are not
observed?
If the indicated curing depths are not observed, the material cannot
thoroughly cure, which may result in chipping.
62
Page 63

At what distance from the Quick curing light should the
segments be precured?
The shorter the distance between the light and the object, the
better the level of cure of the material.
Must SR Gel always be used?
For the polymerization of SR Nexco Paste, SR Gel must always be
used. If this is not done, the inhibited layer will be too thick, which
may lead to clinical failure.
Is it possible to use SR Connect also for SR Adoro and Telio?
Yes. SR Connect can be used for all cold- or heat-curing PMMA
resins to which a light-curing composite is applied.
Do I always have to apply SR Nexco Retention Flow?
No, the application of SR Nexco Retention Flow is an option. The
curing depths of the shaded SR Nexco Opaquers are sufficient to
achieve a secure bond between the metal framework and the
veneer. With the more flowable SR Nexco Retention Flow, it is easier
to reach undercuts in the area of the retention beads and thus
achieve additional security for the bond.
General Information – Frequently Asked Questions
63
Page 64

Ivoclar Vivadent – worldwide
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
Bendererstrasse 2
FL-9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Tel. +423 235 35 35
Fax +423 235 33 60
www.ivoclarvivadent.com
Ivoclar Vivadent Pty. Ltd.
1 – 5 Overseas Drive
P.O. Box 367
Noble Park, Vic. 3174
Australia
Tel. +61 3 979 595 99
Fax +61 3 979 596 45
www.ivoclarvivadent.com.au
Ivoclar Vivadent Ltda.
Alameda Caiapós, 723
Centro Empresarial Tamboré
CEP 06460-110 Barueri – SP
Brazil
Tel. +55 11 2424 7400
Fax +55 11 3466 0840
www.ivoclarvivadent.com.br
Ivoclar Vivadent Inc.
1-6600 Dixie Road
Mississauga, Ontario
L5T 2Y2
Canada
Tel. +1 905 670 8499
Fax +1 905 670 3102
www.ivoclarvivadent.us
Ivoclar Vivadent Shanghai)
Trading Co., Ltd.
2/F Building 1, 881 Wuding Road,
Jing An District
200040 Shanghai
China
Tel. +86 21 6032 1657
Fax +86 21 6176 0968
www.ivoclarvivadent.com
Ivoclar Vivadent Marketing Ltd.
Calle 134 No. 7-B-83, Of. 520
Bogotá
Colombia
Tel. +57 1 627 33 99
Fax +57 1 633 16 63
www.ivoclarvivadent.co
Ivoclar Vivadent SAS
B.P. 118
F-74410 Saint-Jorioz
France
Tel. +33 450 88 64 00
Fax +33 450 68 91 52
www.ivoclarvivadent.fr
Ivoclar Vivadent GmbH
Dr. Adolf-Schneider-Str. 2
D-73479 Ellwangen, Jagst
Germany
Tel. +49 (0) 79 61 / 8 89-0
Fax +49 (0) 79 61 / 63 26
www.ivoclarvivadent.de
Ivoclar Vivadent Marketing (India)
Pvt. Ltd.
503/504 Raheja Plaza
15 B Shah Industrial Estate
Veera Desai Road, Andheri (West)
Mumbai, 400 053
India
Tel. +91 (22) 2673 0302
Fax +91 (22) 2673 0301
www.ivoclarvivadent.in
Ivoclar Vivadent s.r.l.
Via Isonzo 67/69
40033 Casalecchio di Reno (BO)
Italy
Tel. +39 051 611 35 55
Fax +39 051 611 35 65
www.ivoclarvivadent.it
Ivoclar Vivadent K.K.
1-28-24-4F Hongo
Bunkyo-ku
Tokyo 113-0033
Japan
Tel. +81 3 6903 3535
Fax +81 3 5844 3657
www.ivoclarvivadent.jp
Ivoclar Vivadent Ltd.
12F W-Tower, 1303-37
Seocho-dong, Seocho-gu,
Seoul 137-855
Republic of Korea
Tel. +82 (2) 536 0714
Fax +82 (2) 596 0155
www.ivoclarvivadent.co.kr
Ivoclar Vivadent S.A. de C.V.
Av. Insurgentes Sur No. 863,
Piso 14, Col. Napoles
03810 México, D.F.
México
Tel. +52 (55) 50 62 10 00
Fax +52 (55) 50 62 10 29
www.ivoclarvivadent.com.mx
Ivoclar Vivadent Ltd.
12 Omega St, Rosedale
PO Box 303011 North Harbour
Auckland 0751
New Zealand
Tel. +64 9 914 99 99
Fax +64 9 914 99 90
www.ivoclarvivadent.co.nz
Ivoclar Vivadent Polska Sp. z o.o.
Al. Jana Pawla II 78
00-175 Warszawa
Poland
Tel. +48 22 635 54 96
Fax +48 22 635 54 69
www.ivoclarvivadent.pl
Ivoclar Vivadent Marketing Ltd.
Prospekt Andropova 18 korp. 6/
office 10-06
115432 Moscow
Russia
Tel. +7 499 418-03-00
Fax +7 499 418-03-10
www.ivoclarvivadent.ru
Ivoclar Vivadent Marketing Ltd.
Qlaya Main St.
Siricon Building No.14, 2
nd
Floor
Office No. 204
P.O. Box 300146
Riyadh 11372
Saudi Arabia
Tel. +966 1 293 83 45
Fax +966 1 293 83 44
www.ivoclarvivadent.com
Ivoclar Vivadent Pte. Ltd.
171 Chin Swee Road
#02-01 San Centre
Singapore 169877
Tel. +65 6535 6775
Fax +65 6535 4991
www.ivoclarvivadent.com
Ivoclar Vivadent S.L.U.
c/ Emilio Muñoz Nº 15
Entrada c/ Albarracin
E-28037 Madrid
Spain
Tel. + 34 91 375 78 20
Fax + 34 91 375 78 38
www.ivoclarvivadent.es
Ivoclar Vivadent AB
Dalvägen 14
S-169 56 Solna
Sweden
Tel. +46 (0) 8 514 93 930
Fax +46 (0) 8 514 93 940
www.ivoclarvivadent.se
Ivoclar Vivadent Liaison Office
: Tesvikiye Mahallesi
Sakayik Sokak
Nisantas’ Plaza No:38/2
Kat:5 Daire:24
34021 Sisli – Istanbul
Turkey
Tel. +90 212 343 08 02
Fax +90 212 343 08 42
www.ivoclarvivadent.com
Ivoclar Vivadent Limited
Ground Floor Compass Building
Feldspar Close
Warrens Business Park
Enderby
Leicester LE19 4SE
United Kingdom
Tel. +44 116 284 78 80
Fax +44 116 284 78 81
www.ivoclarvivadent.co.uk
Ivoclar Vivadent, Inc.
175 Pineview Drive
Amherst, N.Y. 14228
USA
Tel. +1 800 533 6825
Fax +1 716 691 2285
www.ivoclarvivadent.us
Rx only
Date info rmation prepar ed: 2012-08 /RE V.1
These mate rials have bee n develope d solely for us e in dentistr y. Processing s hould be carr ied out stri ctly
according to th e Instruc tions for Use. Li ability ca nnot be accepte d for damages re sulting from fail ure to
observ e the Instruc tions or the s tipulated ar ea of applicat ion. The user i s responsibl e for testing th e
product s for their suit ability and u se for any purpo se not explic itly stated i n the Instruc tions. De scriptions
and data cons titute no warr anty of attr ibutes and are no t binding. The se regulatio ns also apply i f the
materials are u sed in conjunc tion with pro ducts of ot her manufact urers.
© Ivoclar V ivadent AG, Sch aan / Liechtens tein
643544/2012-09-25/e
 Loading...
Loading...