International VT 365 Service Manual

SERVICE MANUAL
INTERNATIONAL® VT 365
DIESEL ENGINE
2004-2006 Model Years
SERVICE MANUAL
EGES-295-2
INTERNATIONAL® VT 365
DIESEL ENGINE
EGES-295-2
2004-2006 Model Years
© 2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
Printed in the United States of America


ENGINE SERVICE MANUAL I
Table of Contents
Foreword................................................... .......................................... ......................1
Service Diagnosis.... ...................................... ................................... ...........................2
Safety Information.............................................................. ..........................................3
ENGINE SYSTEMS.......................................................................................................5
MOUNTING ENGINE ON STAND......................................................................................49
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED VARIABLE GEOMETRY TURB
MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR).....................................................73
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVE TRAIN................................................................................99
FRONT COVER, VIBRATION DAMPER, and GEROTOR OIL PUMP
OIL PAN, UPPER OIL PAN, and OIL PICKUP TUBE. .. .. ... . . .... . ... . . ... . . . . ... . .. ... . . ... . . ... . . ... . . ... . . ....175
POWER CYLINDERS..................................................................................................183
CRANKCASE, CRANKSHAFT and BEARINGS, CAMSHAFT
OIL COOLER and FILTER HOUSING................................................................................229
ENGINE ELECTRICAL.................................................................. ...............................245
HIGH-PRESSURE OIL PUMP.. ..................... ..................................................................281
FUEL SYSTEM...................................... ....................................................................297
REAR COVER, FLYWHEEL, and POWER STEERIN
IN-CHASSIS PROCEDURES..........................................................................................331
G GEAR DRIVE...........................................309
OCHARGER (VGT)................... ...55
...........................................157
and BUSHINGS............................ ...203
Terminology.............................................................................................................355
Appendix A – Specifications...................................................................... ...................363
Appendix B – Torques.................................................................................................373
Appendix C – Special Service Tools
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
.......................................................... ......................389
EGES295-2
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

II ENGINE SERVICE MANUAL
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

ENGINE SERVICE MANUAL 1
Foreword
International Truck and Engine Corporation is
committed to continuous research and development
to improve products and introduce technological
advances. Procedures, specifications, and parts
defined in published technical service literature may
be altered.
NOTE: Photo illustrations identify specific parts or
assemblies that support text and procedures; other
areas in a photo illustration may not be exact.
This manual includes necessary information
and specifications for technicians to maintain
International® diesel engines. See vehicle manuals
and Technical Service Information (TSI) bulletins fo
additional information.
Technical Service Literature
1171814R2
VT 365 Engine Operation and
Maintenance Manual
EGES-295-2 VT 365 Engine Service Manual
EGES-240
VT 365 Engine Diagnostic Manual
EGED-245 VT 365 Hard Start and No Start
Diagnostic Form
EGED-250 VT 365 Performance Diagnostics
Form
EGED-320-1 VT 365 Electronic Control System
Diagnostic Form
CGE-575 Engine Diagnostic Trouble Codes
r
Technical Service Literature is revised periodically
and mailed automatically to “Revision Service”
subscribers. If a technical publication is ordered, the
latest revision will be supplied.
NOTE: The followingorder information isfor technical
service literature only.
International Truck and Engine Corporation
Printing and Distribution Services
C/O Moore Wallace North America
1750 Wallace Avenue
St. Charles, IL 60174
Telephone: 630-313-7507
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

2 ENGINE SERVICE MANUAL
Service Diagnosis
Service diagno sis is an investigative procedure that
must be followed to find and correct an engine
application problem or an engine problem.
If the problem is engine application, see specific
vehicle manuals for further diagnostic information.
If the problem is the engine, see specific Engine
Diagnostic Manual for further diagnostic information.
Prerequisites for Effective Diagnosis
• Availability of gauges and diagnostic test
equipment
• Availability of current information for engine
application and engine systems
• Knowledge of the principles of operation for
engine application and engine systems
• Knowledge to understand and do procedures in
diagnostic and service publications
Technical Service Literature required for Effective
Diagnosis
• Engine Service Manual
• Engine Diagnostic Manual
• Diagnostics Forms
• Electronic Control Systems Diagnostics Forms
• Service Bulletins
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

ENGINE SERVICE MANUAL 3
Safety Information
This manual provides general and specificservice
proceduresessential for reliable engineoperationand
your safety. Since many variations in procedures,
tools, and service parts are involved, advice for all
possible safety conditions and hazards cannot be
stated.
Read safety instructionsbefore doing any service and
test procedures for the engine or vehicle. See related
application manuals for more information.
DisregardforSafety Instructions, Warnings, Cautio
and Notes in this manual can lead to injury, death or
damage to the engine or vehicle.
SAFETY TERMINOLOGY
Three terms are used to stress your safety and saf
operation of the engine: Warning, Caution, and
Warning: A warning describes actions necessar
prevent or eliminate conditions, hazards, an
practices that can cause personal injury
or death.
Caution: A caution describes actions nec
to prevent or eliminate conditions that c
an cause
damage to the engine or vehicle.
Note: A note describes actions necessar
yforcorrect,
efficient engine operation.
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Vehicle
• Make sure the vehicle is in neutral, th
brake is set, and the wheels are block
doing any work or diagnostic proc
ed before
edures on the
engine or vehicle.
Work area
• Keep work area clean, dry, and org
anized.
• Keep tools and parts off the floor.
• Make sure the work area is ventil
• MakesureaFirstAidKitisavail
ated and well lit.
able.
Safety equipment
• Use correct lifting devices.
• Use safety blocks and stands.
Protective measures
ns,
e
Note
yto
d unsafe
essary
eparking
• Wear appropriate hearing protection.
• Wear correct work clothing.
• Do not wear rings, watches, or other jewelry.
• Restrain long hair.
Fire prevention
• Make sure charged fire extinguishers are in the
work area.
NOTE: Check the classification of each fire
extinguisher to ensure that the following fire types
canbeextinguished.
1. Type A — Wood, paper, textiles, and rubbish
2. Type B — Flammable liquids
3. Type C — Electrical equipment
Batteries
Batteries produce highly flammable gas during and
after charging.
• Always disconnect the main negative battery
cable first.
• Always connect the main negative battery cable
last.
• Avoid leaning over batteries.
• Protect your eyes.
• Do not exposebatteries to openflames orsparks.
• Do not smoke in workplace.
Compressed air
• Limit shop air pressure for blow gun to 207 kPa
(30 psi).
• Use approved equipment.
• Do not direct air at body or clothing.
• Wear safety glasses or goggles.
• Wear hearing protection.
• Use shielding to protect others in the work area.
Tools
• Make sure all tools are in good condition.
• Make sure all standard electrical tools are
grounded.
• Wear protective glasses and sa
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
fety shoes.
EGES295-2
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

4 ENGINE SERVICE MANUAL
• Check for frayed power cords before using power
tools.
Fluids under pressure
• Use extreme caution when working on systems
under pressure.
• Follow approved procedures only.
Fuel
• Do not overfill the fueltank. Over fill creates a fire
hazard.
• Do not smoke in the work area.
• Do not refuelthe tank when the engineis running.
Removal of tools, parts, and equipment
• Reinstall all safety guards, shields, and covers
after servicing the engine.
• Make sure all tools, parts, and service equipment
are removed from the engine and vehicle after all
work is done.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

ENGINE SYSTEMS 5
Table of Contents
Engine Identification.....................................................................................................7
Engine Serial Number..........................................................................................7
Emission Labels (2004 and 2005 Model Years)............................................................7
Emission Label (2006) Model Year...........................................................................8
Engine Description..............................................................................................9
Engine Component Locations.. .. .... . . . . . .... . .. ... . . . . . . .... . .. ... . . . . . . .... . . . . . .... . .. ... . . . . . . .... . . . . .11
Engine Systems.........................................................................................................16
Air Management System (AMS).............................................................................17
Charge Air Cooler (CAC)................................... .........................................20
Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT)............................... ...........................21
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System................................................ .......22
Exhaust System......................................................................................24
Fuel Management System.................. ..................................................................25
Fuel Injection..........................................................................................25
Injection Control Pressure (ICP) System.......................................... ...............26
Fuel Injectors....................................................... ............................................28
Fuel Supply System.. . . .... . .. ... . . . . . . ... . . .... . . .... . . . .... . . . . . ... . . . . . . ... . . . . . . ... . . . . .... . . . .... . . ... . . .30
Fuel Flow............................................... .............................................. ...........31
Lubrication System.. . ...... ...................................................................................33
Cooling System................................................................................................37
Electronic Control System.......................................................... ...................................39
Electronic Control System Components ... ...............................................................39
Injection Drive Module (IDM)...................................................... ...........................41
Engine and Vehicle Sensors.. ............................................. ..................................42
Glow Plug Control System.............................................................................................47
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

6 ENGINE SYSTEMS
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
Engine Identification
Engine Serial Number
Figure 1 Engine serial number
ENGINE SYSTEMS 7
The engine serial number is stamped on the
crankcase pad on the rear left side of
the crankcase
below the cylinder head.
The engine serial number is also on an
identification
sticker on the valve cover.
Engine serial number examples
6.0HM2Y0000500
6.0HA2U0000508
Engine serial number codes
6.0 – Engine displacement
H–Diesel, turbocharged, Charge
Air Cooled, and
electronically controlled
M2 – Truck
A2 – Service
U–USA
Y–USA Huntsville
7digitsuffix–Engine serial number
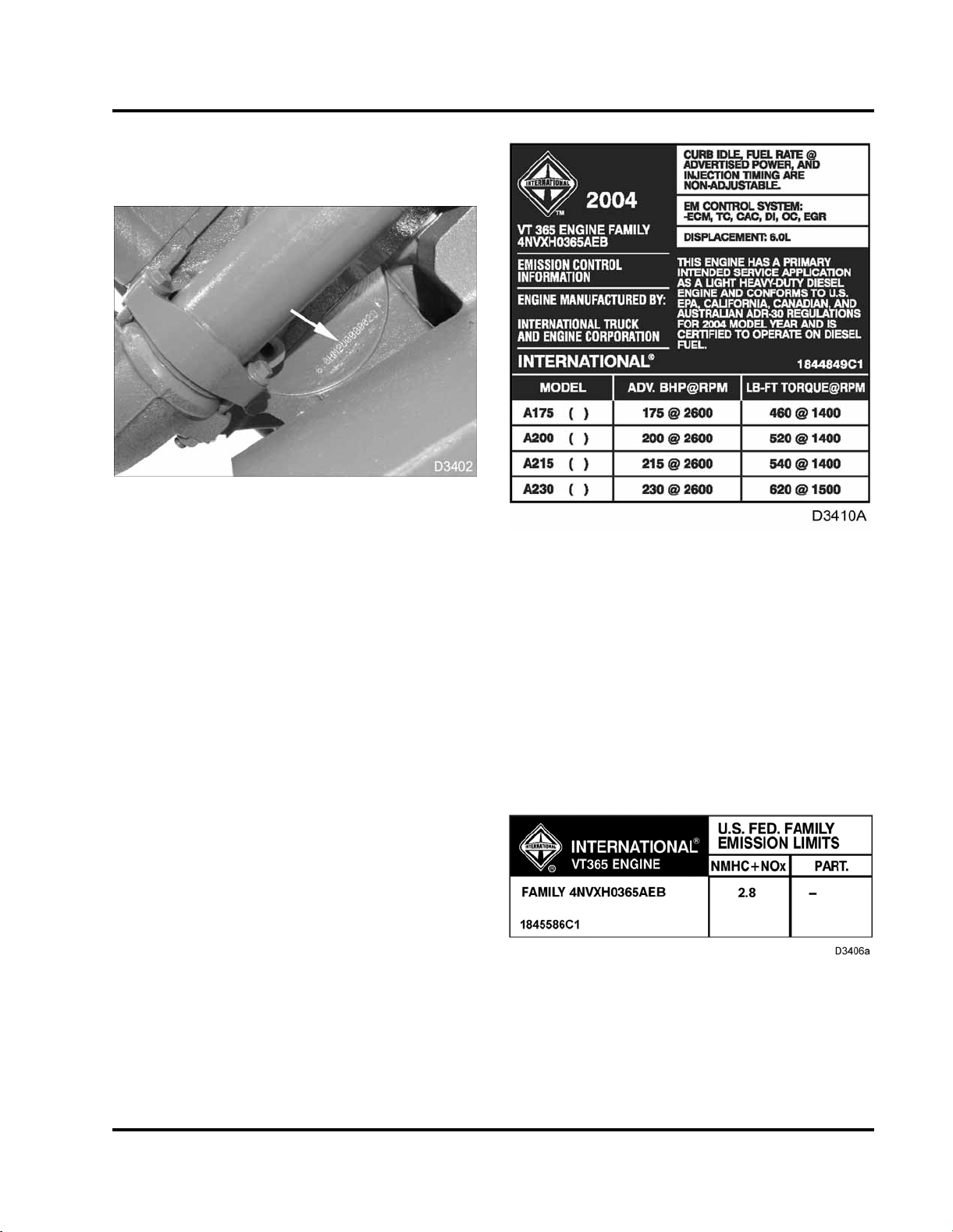
Emission Labels (2004 and 2005 M
Twoemissionlabelsareontherig
sequence
odel Years)
ht valve cover:
Figure 2 50 – State Exhaust Emissions Label
(example)
The 50 – State Exhaust Emissions Label includesthe
following:
• Year the engine was certified to meet EPA
emission standards
• Engine model code
• Service applications
• Advertised brake horsepower ratings
Figure 3 U.S. Federal Family Emission Limits
label (example)
• 50 – State Exhaust Emissions Labe
• U.S. Federal Family Emission L
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
imits Label
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
l
The U.S. Federal Family Emission Limits Label
identifies the engine family and emission limits
established by the manufacturer and certified by the
EPA.
EGES295-2
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
8 ENGINE SYSTEMS
Emission Label (2006) Model Year
One emission label is on the right valve cover.
The 50 – State Exhaust Emissions Label includes the
following:
• Year the engine was certified to meet EPA
emission standards
• Engine model code
• Service applications
• Advertised brake horsepower ratings
Engine accessories
The following engine accessories may have
manufacturer’s labels or identification plates:
• Air compressor (for brake or suspension system )
• Air conditioning compressor
• Alternator
• Cooling fan clutch
• Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT)
• Power steering / fuel pump
•Startermotor
Figure 4 50 – State Exhaust Emissions Label
(example)
Labels or identification plates include information
and specifications helpful to vehicle operators and
technicians.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
ENGINE SYSTEMS 9
Engine Description
Table 1 Engine Features and S pecifications
International® VT 365 engine features and specifications
Engine Diesel, 4 cycle
Configuration 4 OHV/1 Cam-in-Crankcase-V8
Displacement
Bore and stroke
Compression ratio
Aspiration
Rated power @ rpm
Peak torque @ rpm
1
1
365 cu. in (6.0L)
95 mm x 105 mm (3.74 in x 4.134 in)
18.0:1
VGT turbocharged and Charge Air Cooling (CAC)
175 bhp @ 2600 rpm
460 lbf•ft @ 1400 rpm
Engine rotation, facing flywheel Counterclockwise
Combustion system Digital Direct Injection (DDI)
Total engine weight (auto with oil) 459 kg (1094 lb)
Cooling system capacity (engine only) 10.2 liters (10.8 qts)
Lube system capacity (including filter) 18 liters (19 qts)
Lube system capacity (dry) 21.8 liters (23 qts)
Firing order 1–2–7–3–4–5–6–8
1
Base rating shown. See Appendix A for other ratings.
Major features
Air Management System (AMS)
• Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT)
• Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system
• Chassis mounted Charge Air Cooling (CAC)
Digital Direct fuel Injection (DDI)
Two piece crankcase
One piece cylinder head with four valves per cylinder
Dual timing
Rear gear train
Closed crankcase ventilation
Oil cooler
The firing order is 1-2-7-3-4-5-6-8. When viewing the
engine from the rear (flywheel end), the right side
cylinders are numbered 1, 3, 5, and 7. Number one
is the front position. The left side is numbered 2, 4, 6,
and 8 .
A two piece crankcase has been specially designed
to withstand the loads of diesel operation. The lower
crankcase has integral main bearing caps. Coolant
and oil passages are cast and machined in the
crankcase and front cover housing.
The crankshaft has five main bearings with fore and
aft thrust controlled at the upper half of the number 4
main bearing. Two connecting rods are attached to
each crankshaft journal. The piston pin moves freely
inside the piston and rod. Piston pin retaining rings
secure the piston pin within the piston.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

10 ENGINE SYSTEMS
One piece aluminum alloy pistons are fitted with
one keystone cut compression ring, one rectangular
intermediate compression ring, and a two piece oil
control ring. The combustion bowl (in the piston
crown) reduces exhaust emissions.
The camshaft is supported by five insert bushings
pressed into the crankcase. Two cam lobes, cam
followers, push rods and valve bridges control four
valves per cylinder. The camshaft is gear driven
from the rear end of the crankshaft. A thrust flange
is located between the camshaft gear and the
crankcase. Camshaft thrust iscontrolled with the rear
surface of the number 5 cam journal and the cam
gear.
Hydraulic cam followers maintain zero valve lash
and minimize engine noise. This eliminates periodic
adjustment of valvelash. The hydraulic cam followers
have rollers which provide excellent cam lobe and
cam follower durability.
The lubrication system uses a crankshaft driven
gerotor pump mounted o n the front cover. The oil
pressure regulator is built into the front cover and
is accessible from outside the engine. Lube oil is
routed through an oil cooler equipped with a pressure
controlled b ypass valve. Lube oil moves through
passages in the crankcase to lubricate all internal
components and to supply the piston cooling tubes
and high pressure pump reservoir. The VGT and air
compressor use external oil lines.
The VGT is electronically controlled and hydraulically
actuated. The VGT provides boost control at low and
high speeds for improved throttle response.
An exhaust gas recirculation valve allows water
cooled exhaust gases to be fed into the inlet air
stream to reduce exhaust emissions.
A closed crankcase breather system recirculates
crankcase vapors back into the intake air system.
A chassis mounted Charge Air Cooler (CAC), an
air-to-air heat exchanger, increases the density of the
air charge.
Engine operation is controlledby twoengine mounted
control modules:
• Electronic Control Module (ECM)
• Injector Drive Module (IDM)
The ECM receives signals from engine and chassis
mounted sensors. The ECM controls engine
operation with the following actuators:
•IPR
• VGT control valve
•EGR
• Glow plug relay
The IDM controls fuel injector operation using data
from the ECM.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
Engine Component Locations
ENGINE SYSTEMS 11
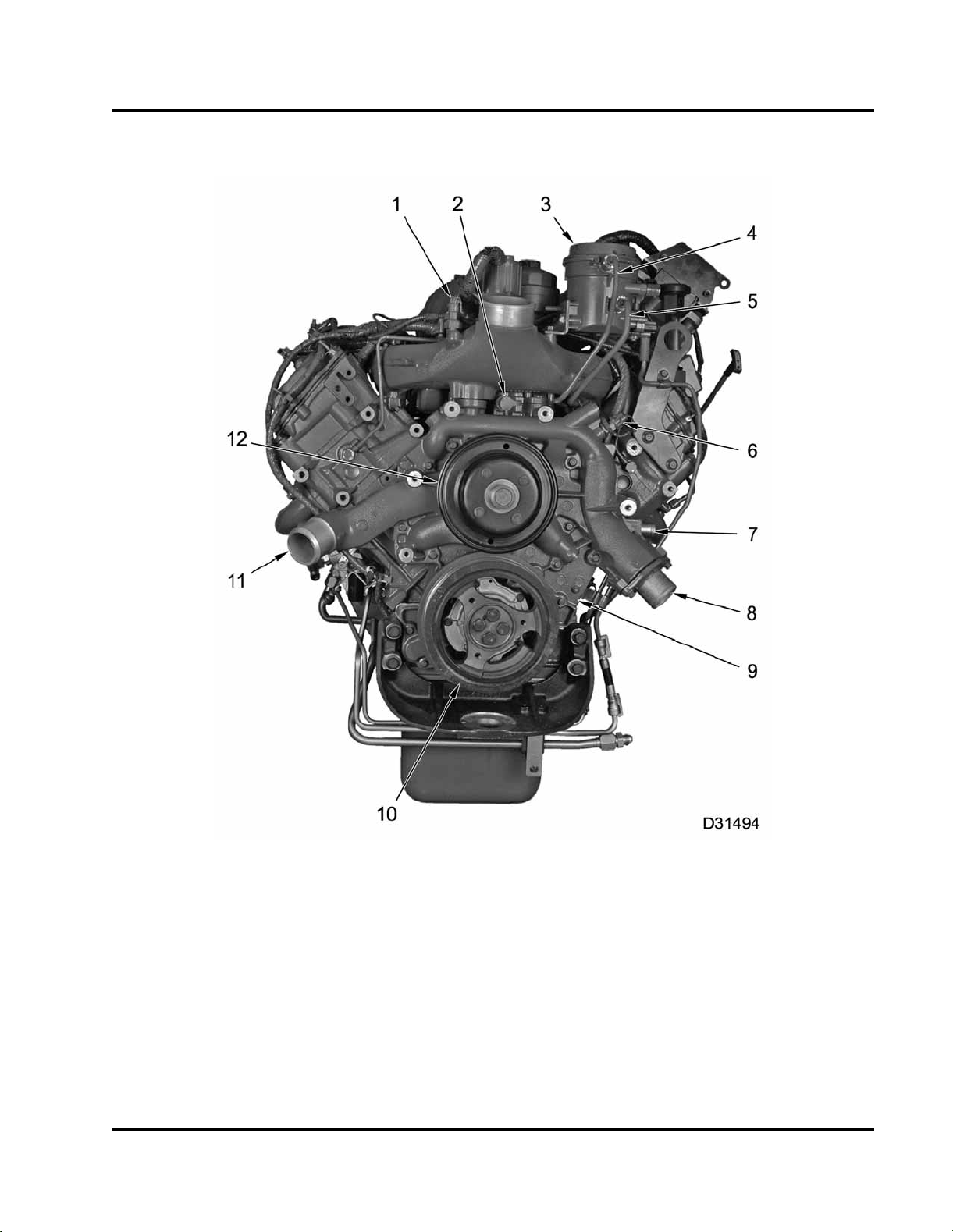
Figure 5 Engine components – Front
1. Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor
2. Lube oil pressure test port
3. Fuel filter assembly
4. Fuel return
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
5. Fuel supply
6. Engine Coolant Temperature
7. Port for coolant deaeration tank
8. Coolant outlet and thermostat
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
(ECT) sensor
EGES295-2
9. Front cover assembly
10. Crankshaft vibration damper
11. Coolant inlet
12. Water pump pulley
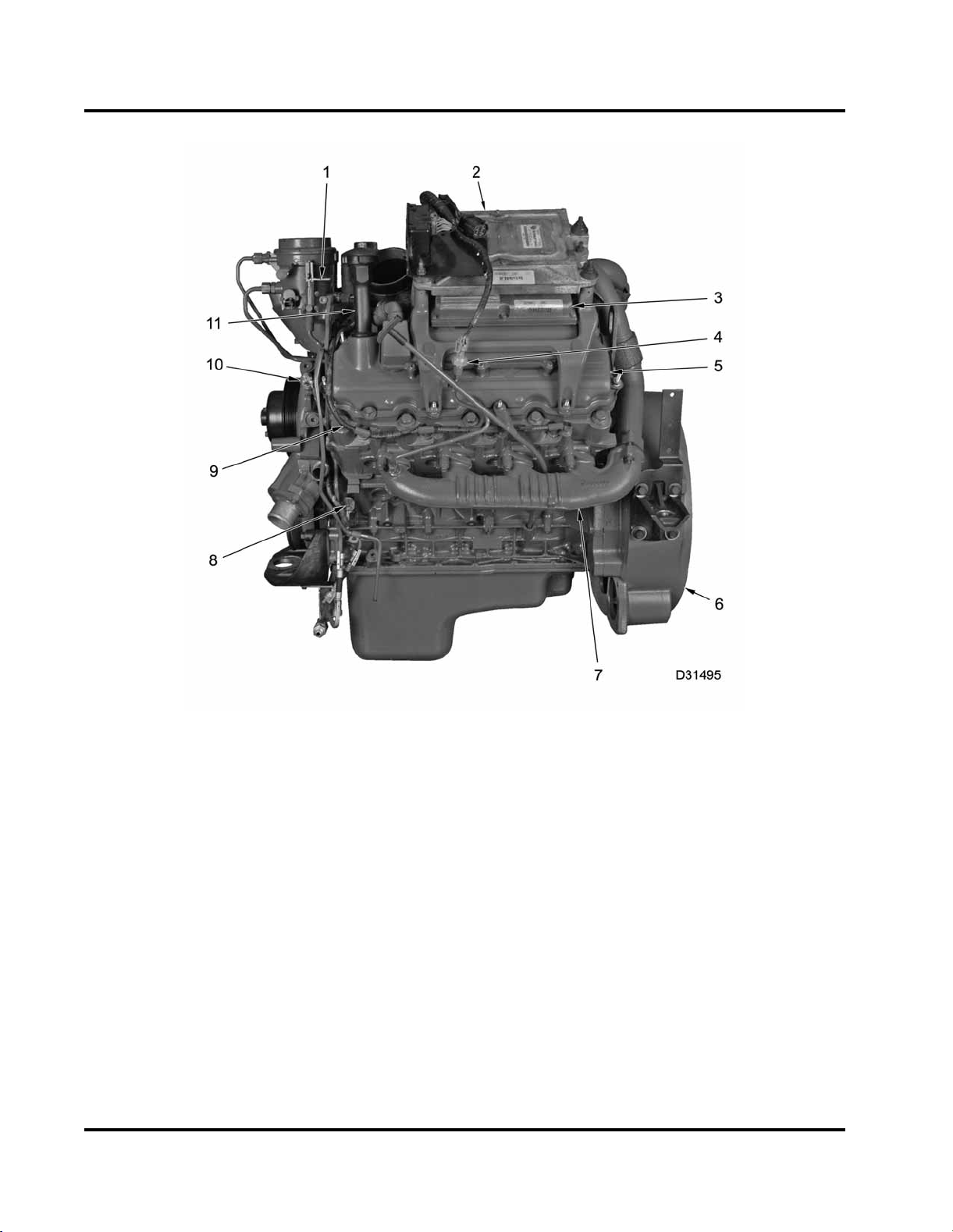
12 ENGINE SYSTEMS
Figure 6 Engine components – Left
1. Fuel filter drain lever
2. Engine Control Module (ECM)
3. Injector Driver Module (IDM)
4. Exhaust Back Pressure (EBP)
sensor
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
5. Valve cover
6. Rear cover
7. Exhaust manifold
8. Camshaft Position(CMP)sensor
9. Glow plug harness
EGES295-2
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
10. Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) sensor
11. Lube oil fill tube

ENGINE SYSTEMS 13
Figure 7 Engine components – R ear
1. Injection Pressure Regulator
(IPR valve)
2. Turbocharger exhaust outlet
3. Exhaust tube assembly, right
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
4. Flywhee l or flexplate assembly
5. Rear cover assembly
6. Reinforcement ring
EGES295-2
7. Shielded exhausttubeassembly,
left
8. Lifting eye (3)
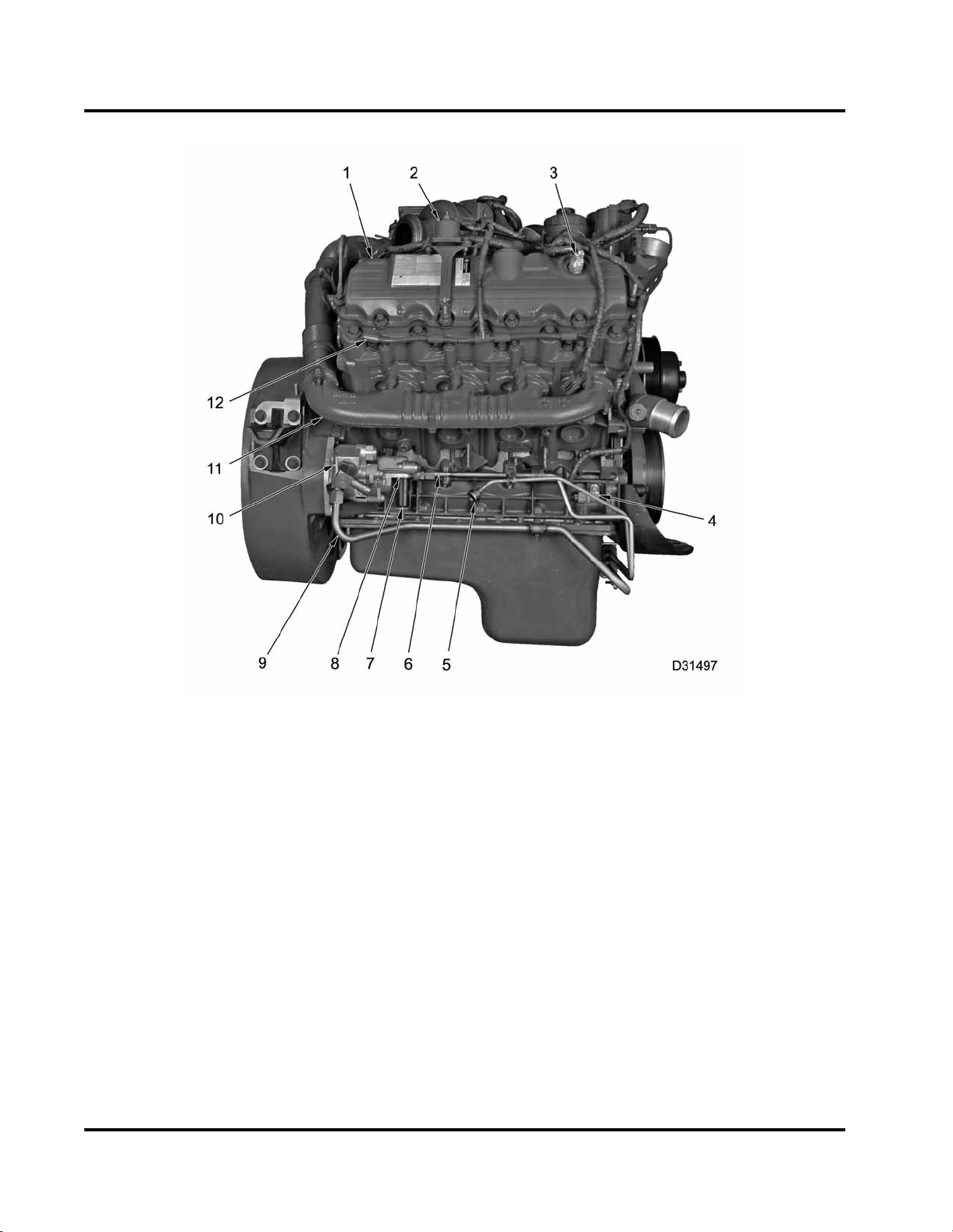
14 ENGINE SYSTEMS
Figure 8 Engine components – Right
1. Valve cover
2. Glow plug relay
3. Injection Control Pressure (ICP)
sensor
4. Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
5. Fuel return line
6. Fuel supply line
7. Fuel filter strainer
8. Fuel supply pump (transfer)
9. Power steering line
10. Power steering pump
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
11. Exhaust Manifold
12. Glow plug harness
EGES295-2
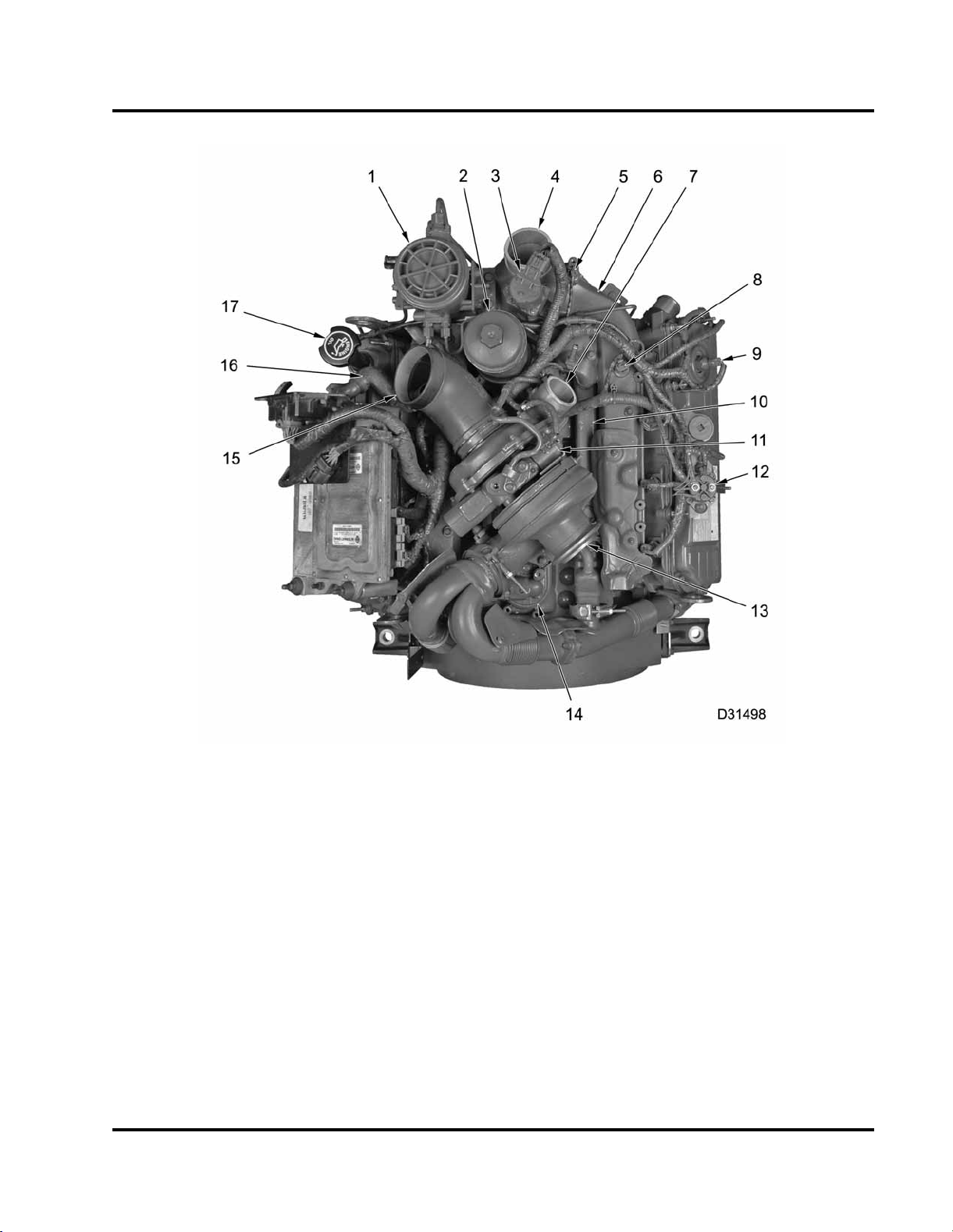
ENGINE SYSTEMS 15
Figure 9 Engine compon
1. Fuel filter assembly
2. Oil filter housing
3. Exhaust Gas Recircul
(EGR) valve
4. Intake manifold air i
5. Manifold Absolute Pre
(MAP) sensor
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
ation
nlet
ssure
ents–Top
6. Intake manifold
7. Compressor outlet
8. Manifold Air Tempera
sensor
9. ICP sensor
10. EGR cooler
11. VGT control valve
EGES295-2
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
ture (MAT)
12. Glow plug relay
13. VGT
14. High-pressure oil pu
15. Air inlet duct
16. Breather hose assembl
pitot tube
17. Lube oil fill
mp cover
ywith
16 ENGINE SYSTEMS
Engine Systems
The primary engine systems are AirManagementand
Fuel Management, which share some subsystems or
have a subsystem that contributes to their operation.
• The Electronic Control System controls the Air
Management System and Fuel Management
System.
• The Coolant System provides heat transfer for
EGR gases and lubrication oil.
• The ICP system uses lube oil for hydraulic fluid to
actuate the fuel injectors.
• The Fuel Supply System pressurizes fuel for
transfer to the fuel injectors.
• The Lube Oil S ystem provides lubrication and
heat transfer to engine components.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
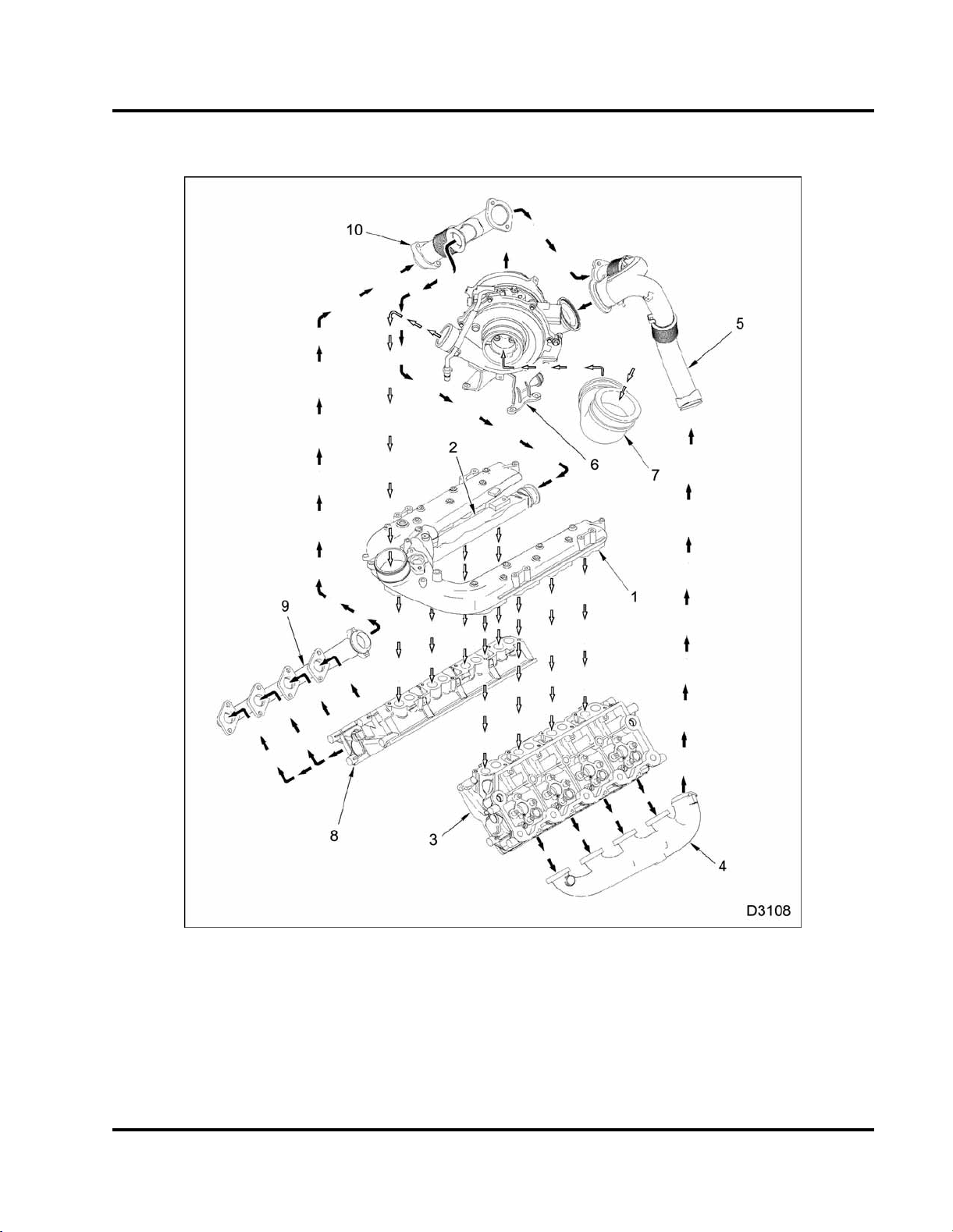
Air Management System (AMS)
ENGINE SYSTEMS 17
Figure 11 Air Management System (AMS)
1. Intake manifold
2. EGR cooler
3. Left cylinder head
4. Left exhaust manifold
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
5. Shielded tube exhaust assembly
6. VGT with mounting bracket
7. Air inlet duct
8. Righ t cylinder head
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
9. Right exhaust manifold
10. Exhaust tube assembly, right
EGES295-2

18 ENGINE SYSTEMS
The Air Management system includes the
following:
•Airfilter assembly
• Closed crankcase breather
• Chassis mounted Charged Air Cooler (CAC)
• Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT)
• Intake manifold
• Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system
• Exhaust system
• Catalytic converter– dependent on application
• Catalyzed Diesel Particulate Filter (CDPF) –
dependent on application
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
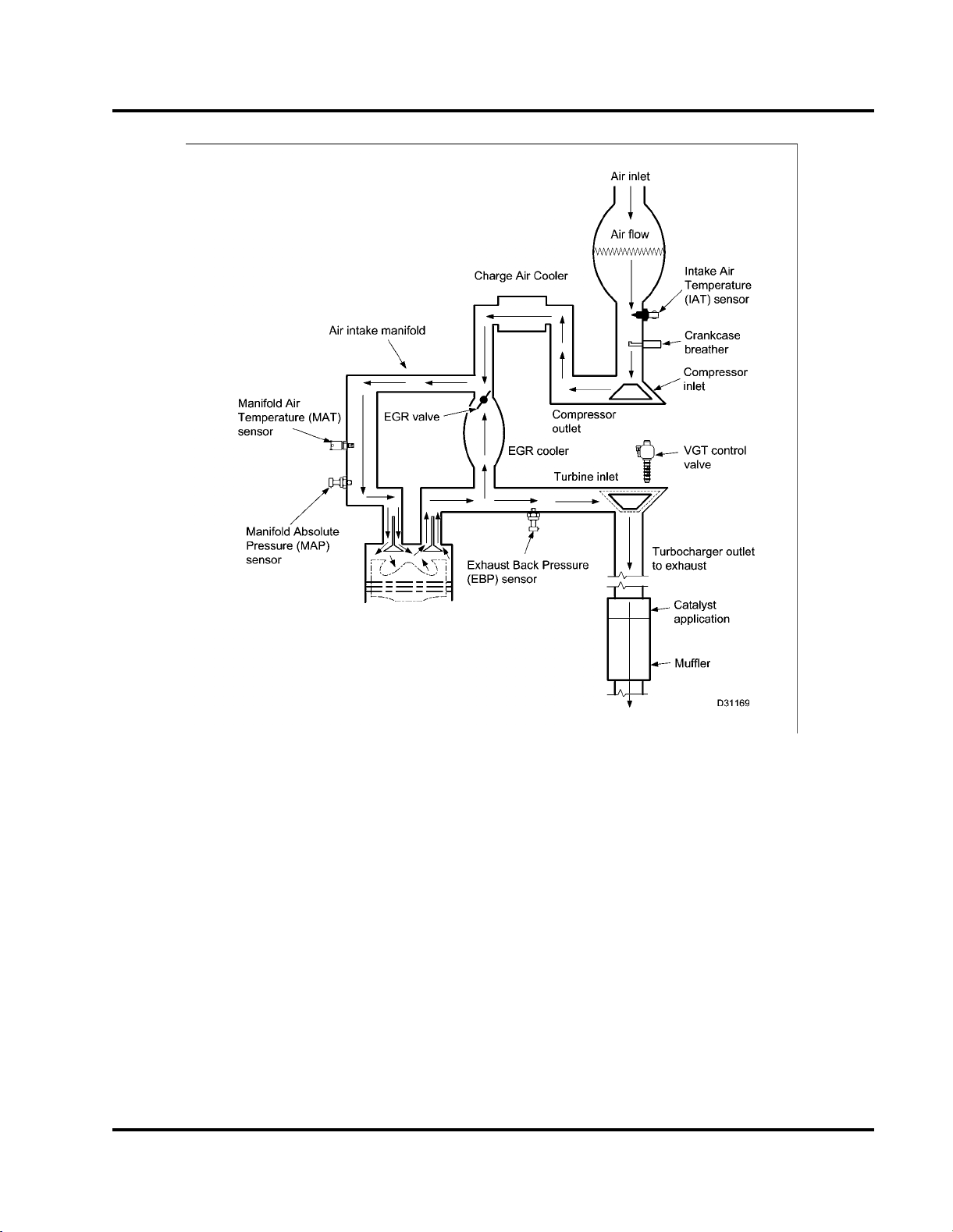
ENGINE SYSTEMS 19
Figure 12 Air flow diagram
Air flow
Airentersand flows throughtheairfilterassembly and
mixes with air from crankcase ventilation. The VGT
compressestheairmixturebeforeitenterstheCharge
Air Cooler (CAC). Cooled compressed air flows from
the CAC into the air intake manifold that directs air to
the intake ports for each cylinder head.
After combustion, hot exhaust gas is forced through
the exhaust manifolds to the EGR cooler and VGT.
• Somehotexhaust gas is cooled intheEGRcooler
and flows through the EGR control valve back
through the air intake manifold to mix with filtered
air. This reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions
and noise.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
• Therestof the hot exhaust gas expandsandflows
to the VGT, spins the turbine wheel, and flows
from the VGT outlet to the engine exhaust pipe.
• The VGT compressor wheel, on the same shaft
as the turbine wheel, compresses the mixture of
filtered air and air from crankcase ventilation.
The VGT responds directly to engine loads. During
heavy load, an increased flow of exhaust gases turns
the turbine wheel faster. This increased speed turns
the compressor impeller faster and supplies more air
or greater boost to the intake manifold. Conversely,
when engine load is light, the flow of exhaust gases
decreases and less air is pumped into the intake
manifold.

20 ENGINE SYSTEMS
The VGT modifies more efficient exhaust flow
characteristics.
Charge Air Cooler (CAC)
Figure 13 Charge Air Cooler
1. Air outlet
2. Charge Air Cooler
3. Air inlet
4. Radiator
The CAC cooler is mounted on top of the radiator.
Air from the VGT is pushed through a network of
heat exchanger tubes before entering the air intake
manifold. Outside air flowing over the tubes and
fins cools the charged air. Charged air is cooler and
denser than the uncooled air; cooler and denser
air improves the fuel-to-air ratio during combustion,
resulting in improved emission control and power
output.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
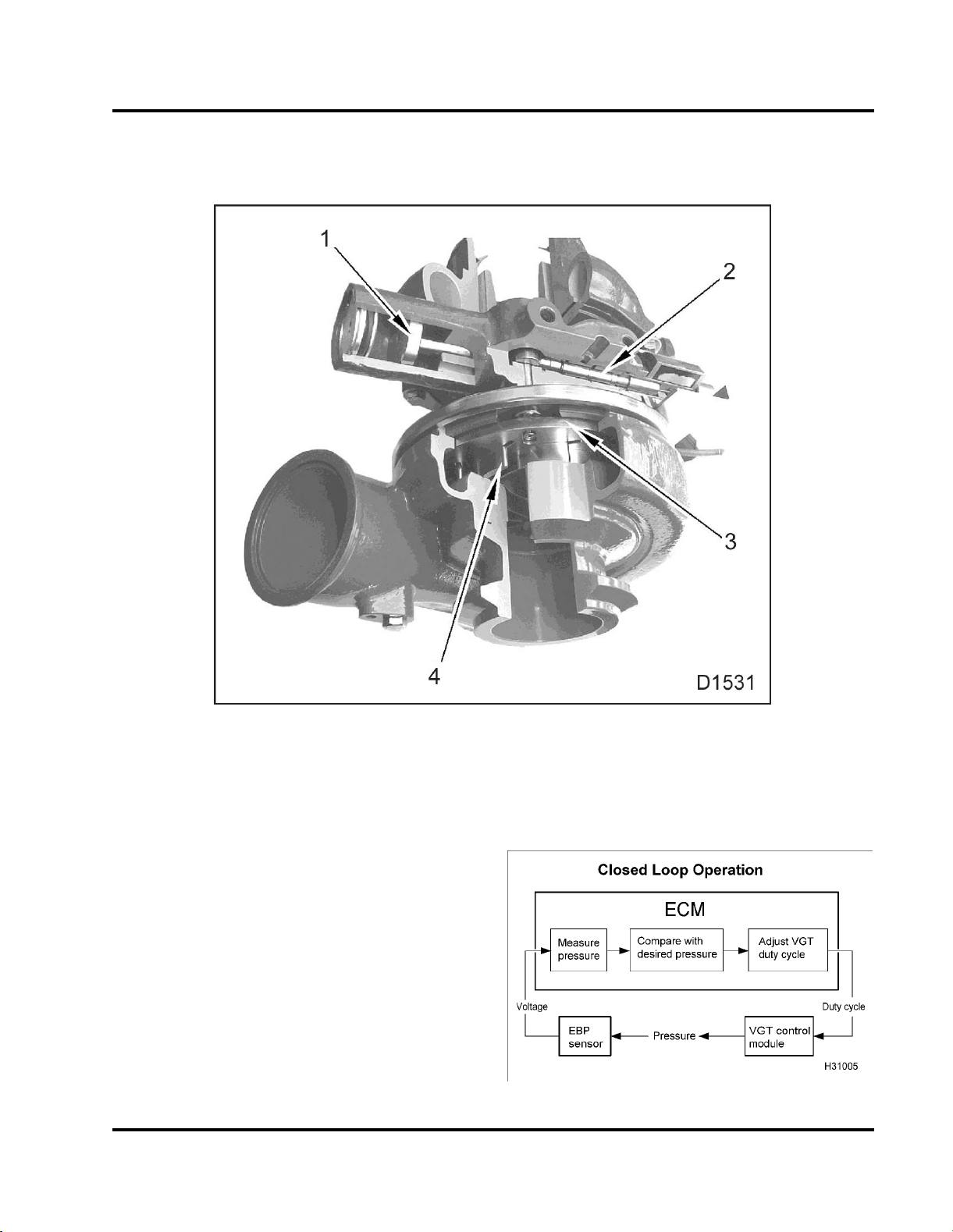
Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT)
ENGINE SYSTEMS 21
Figure 14 VGT
1. Actuator
2. VGT control valve
3. Unison ring
4. Vanes
The key feature of the VGT is actuated vanes
in the turbine housing. The vanes modify flow
characteristics of exhaust gases through the turbine
housing. The benefit is the ability to con trol boost
pressure needed to accommodate various engine
speeds and load conditions. An additional benefitis
lower exhaust emissions.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
VGT closed loop system
Figure 15 VGT closed loop system

22 ENGINE SYSTEMS
The V GT is a closed loop system that uses the
Exhaust Back Pressure (EBP) sensor t o provide
feedback to the ECM. The ECM uses the EBP sensor
to continuously monitorEBP and adjust the dutycycle
to the VGT to match engine requirements.
VGT control
links all the vanes. When the unison ring moves,
all vanes move to the same position. Unison ring
movement occurs when either side of the actuator
piston is pressurized by engine oil.
Exhaust gas flow can be regulated depending on
required exhaust back pressure for enginespeed and
load.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
The EGR system includes the following:
• EGR drive module
•EGRvalve
• EGR cooler
• Air intake manifold
• Exhaust tube assembly, right
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system
reduces Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) emissions.
NO
forms during a reaction between nitrogen and
X
oxygen at high temperature during combustion.
Combustion starts when fu el is injected into the
cylinder before or slightly after the piston reaches
top-dead-center.
Figure 16 VGT control
The solenoid receives a pulse width modulated signal
from the ECM that indicates the on / off time that the
control valve is energized. The control valve directs
lube oil flow to both sides of the piston in the actuator
housing. Directing oil to different sides of the piston
increases or decreases exhaust back pressure.
Actuated vanes are mounted around the inside
circumference of the turbine housing. A unison ring
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
EGR flow
Some exhaust from the right exhaust tube assembly
flows into the EGR cooler. Exhaust from the EGR
cooler flows in to a passage in the air intake manifold
that intersects with the EGR valve.
When EGR is commanded, the EGR control valve
opens allowing cooled exhaust gases to enter the
intake manifold to be mixed with filtered intake air
then recycled through the combustion process.
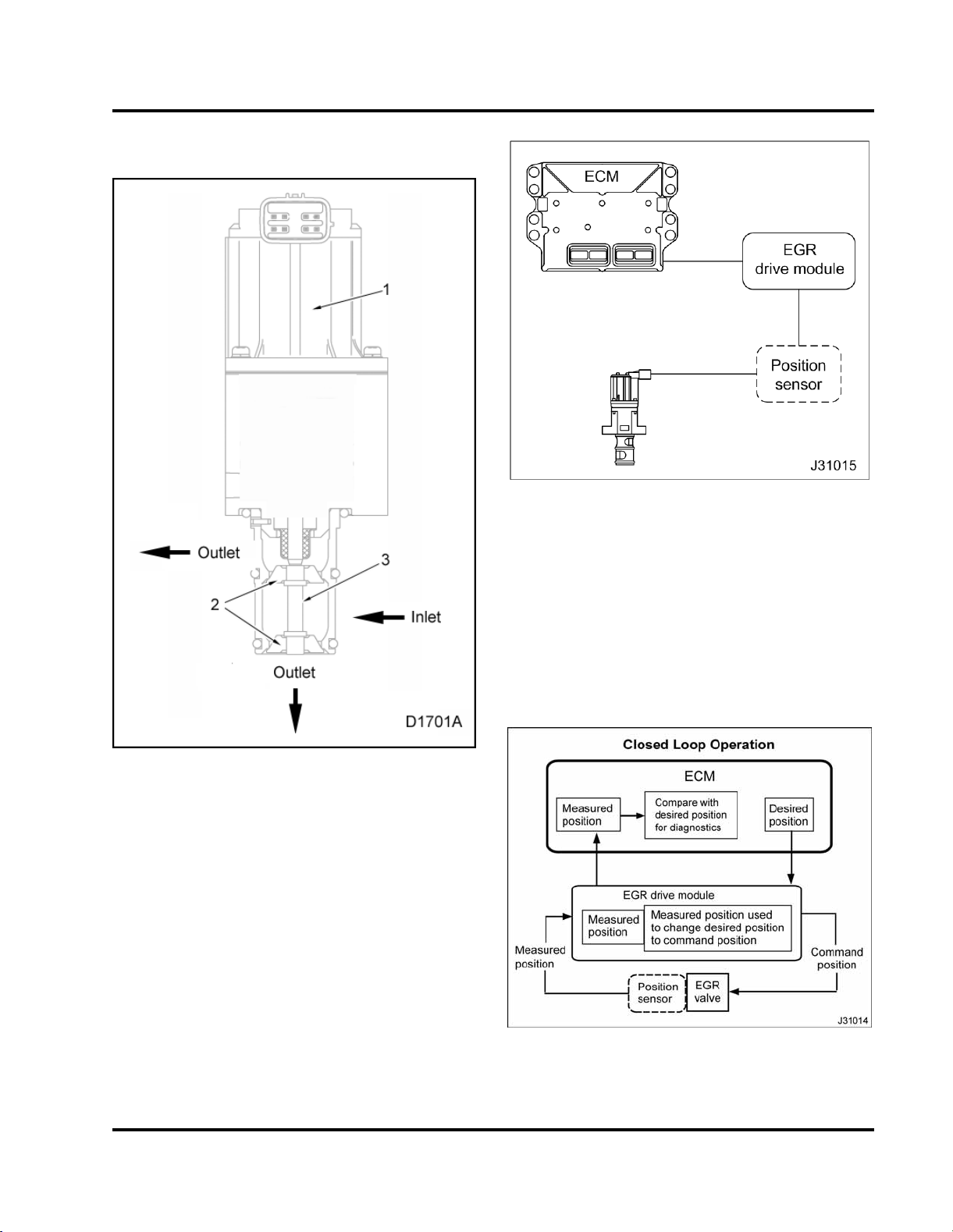
EGR valve
ENGINE SYSTEMS 23
Figure 18 EGR control
Figure 17 EGR valve
1. Ac tuator coil
2. Valve heads (2)
3. Common shaft
A DC motor, in EGR valve, moves and controls the
position of a two head valve assembly.
The EGR valve, installed in the top fron
intake manifold, has th ree major co
head valve assembly, a DC motor, an
Circuit (IC). The IC has three Hal
sensors that monitor valve movem
The EGR drive module, mounted on t
module mounting bracket abov
assembly, controls the DC mo
mponents: a two
d an Integrated
l effect position
ent.
he EGR drive
e the ECM/IDM
tor.
toftheair
Figure 19 EGR closed loop operation
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation

24 ENGINE SYSTEMS
The EGR system is closed loop control, using EGR
position signals.
The EGR drive module receives the desired EGR
valve position from the ECM across the CAN 2
datalink to activate the EGR valve for exhaust gas
recirculation. The EGR drive module provides
feedback to the ECM on the valve position, interprets
the ECM command, and sends the command using
three pulse width modulated signals to the DC motor.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system includes the following:
• Exhaust valves
• Exhaust manifolds
• Turbocharger
• Exhaust piping
•Muffler and catalytic converter – dependent on
application
• Catalyzed Diesel Particulate Filter (CDPF) – if
equipped.
The exhaust s ystem rem o ves exhaust gases from
the engine. Exhaust gases exit from exhaust ports,
through exhaust valves, and flow into the exhaust
manifolds. Expanding exhaust gases are directed
through the exhaust tubes. The right exhaust tube
directs some exhaust gases into the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) cooler. Exhaust gases flowing
into the VGT drive the turbine wheel. Exhaust gases
exit the VGT and flow into the exhaust piping, through
the muffler and catalytic converter or CDPF, and out
the discharge pipe to the atmosphere.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
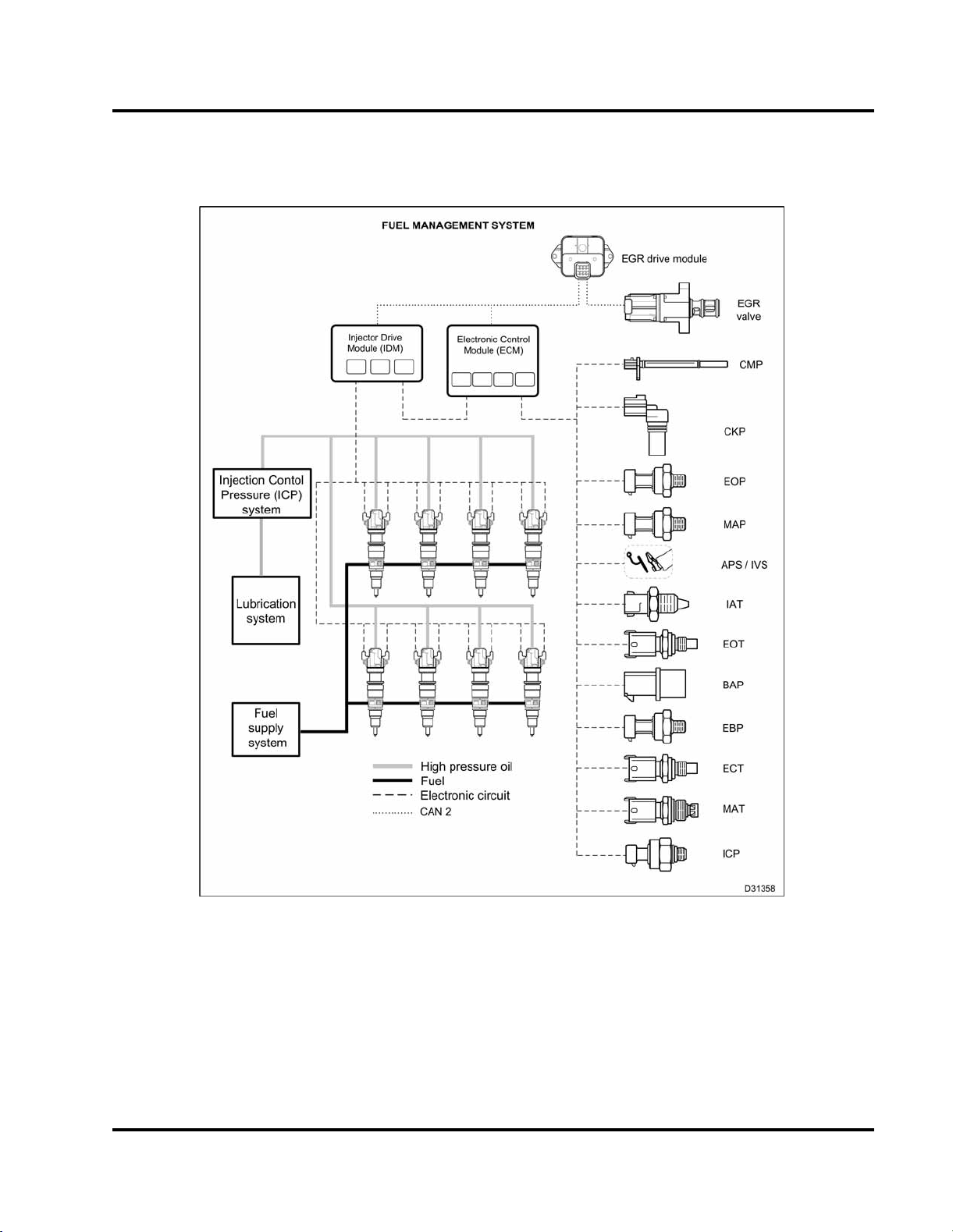
Fuel Managem ent System
Fuel Injection
ENGINE SYSTEMS 25
Figure 20 Fuel management system
The fuel management system includes the following:
• Injection Control Pressure (ICP) system
• Fuel injectors
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
• Electronic control system
• Lubrication system
• Fuel supply system
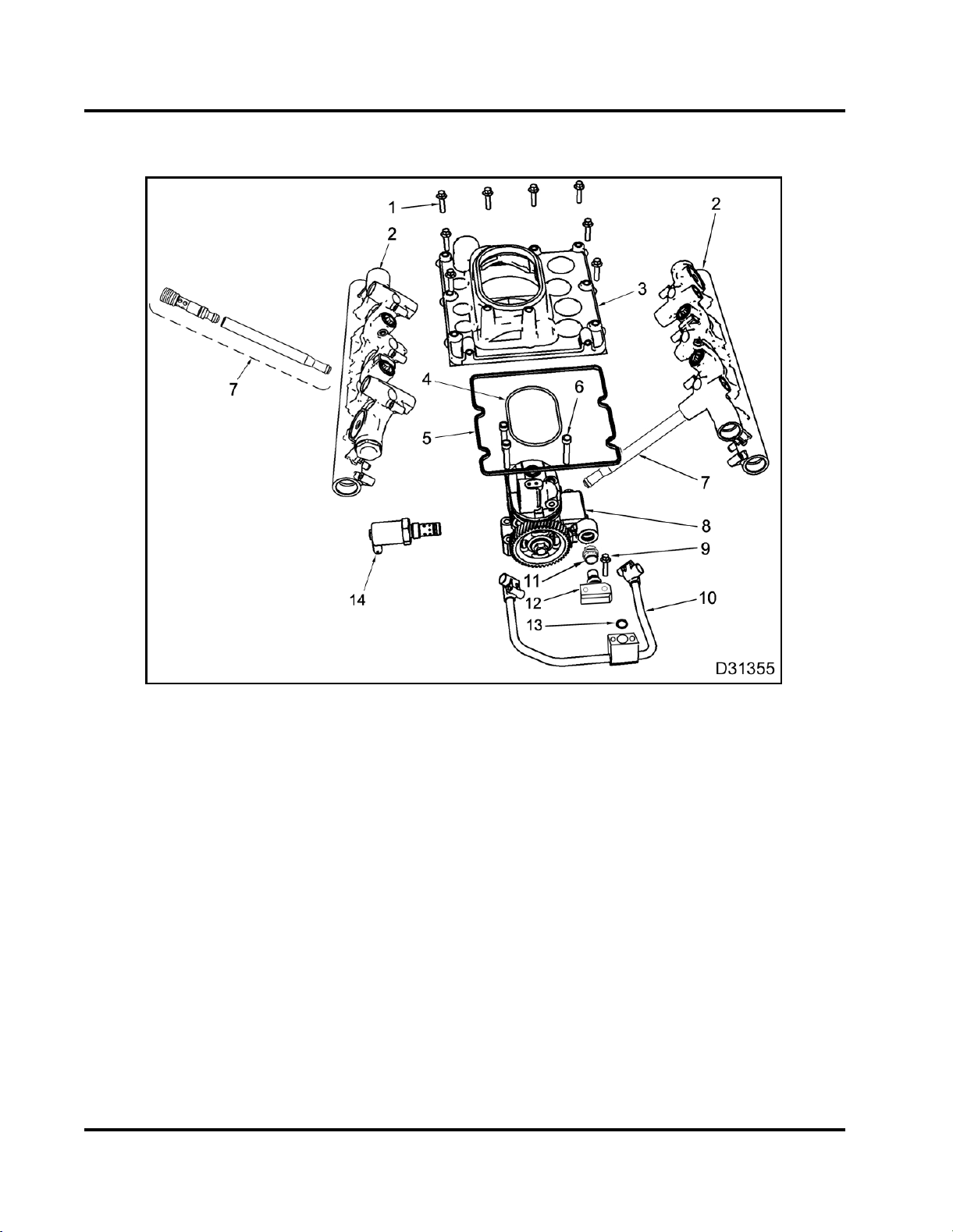
26 ENGINE SYSTEMS
Injection Control Pressure (ICP) System
Figure 21 High-pressure o
1. High-pressure oil pump c
fasteners (8)
2. Oil rail assembly (2)
3. High-pressure oil pump co
4. Pump-to-cover seal ring
5. High-pressure oil pump c
seal
il system
over
ver
over
6. High-pressure oil pump
fasteners (3)
7. Case-to-head tube assem
8. High-pressure oil pump
assembly
9. Branch tube adapter bol
10. Branch tube assembly
High-pressure Oil Flow
A gear driven, high-pressure oil pump draws
oil through a screen in the oil reservoir for the
high-pressure oil pump. The oil reservoir, in the top
of the crankcase below the oil cooler, is kept full by
the engine lubrication system.
TheIPR valve maintains the ICP pressurebydumping
excess oil back to the crankcase.
EGES295-2
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
©2006 International Truck and Engine Corporation
fitting
bly (2)
t(2)
11. Snap to Connection (STC)
12. Branch tube adapter
13. O-ring
14. IPR valve
High-pressure oil from the pump flows through a
branch tube assembly to each case-to-head tube
assembly to each high-pressure oil rail.
High-pressure oil in the oil rails enter the fuel injectors
through sealed ports in the top of the fuel injectors.
When the OPEN coilfor each injectoris energized, the
injector uses high-pressure oil to inject and atomize
fuel into the combustion chamber. The CLOSE coils
are energized to end injection. Exhaust oil exits
through two ports in the top of the injector and drains
back to the crankcase.
 Loading...
Loading...