Page 1

HP Embedded Capture (HP EC)
API Reference Guide
Version 1.3.0
Page 2

© Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard
Development Company, L.P.
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are U.S.
registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
June 2014
Confidential computer software. Valid license
from HP required for possession, use, or
copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and
12.212, Commercial Computer Software,
Computer Software Documentation, and
Technical Data for Commercial Items are
licensed to the U.S. Government under
vendor’s standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to
change without notice. The only warranties for
HP products and services are set forth in the
express warranty statements accompanying
such products and services. Nothing herein
should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained herein.
Page 3

Table of contents
1 API Introduction ............................................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Basic and Advanced modes ............................................................................................................................. 1
1.1.1 Basic API ..................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1.2 Advanced API .............................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 Accessing the API on a device (%API_URL%) .................................................................................................. 1
1.2.1 XML encoding ............................................................................................................................. 2
1.2.2 XSD validation ............................................................................................................................ 2
1.2.3 Response codes ......................................................................................................................... 2
2 API security .................................................................................................................................................. 3
2.1 Administrator and API accounts ...................................................................................................................... 3
2.1.1 Admin account ............................................................................................................................ 3
2.1.1.1 “apiuser” user account ......................................................................................... 3
2.1.2 Using the API without authentication ........................................................................................ 3
2.2 Basic access authentication ............................................................................................................................ 4
3 Compatible API .............................................................................................................................................. 5
3.1 Graph and job services ..................................................................................................................................... 5
3.1.1 Put job ........................................................................................................................................ 5
3.1.2 View job ...................................................................................................................................... 8
3.1.3 Delete job ................................................................................................................................. 10
3.1.4 Get files .................................................................................................................................... 11
3.1.5 Set purge settings .................................................................................................................... 12
3.2 Configuration services ................................................................................................................................... 13
3.2.1 Get device info .......................................................................................................................... 13
3.2.2 Get device status ...................................................................................................................... 14
3.2.3 Get solution info ....................................................................................................................... 15
3.2.4 Get solution status ................................................................................................................... 16
3.2.5 Wake up .................................................................................................................................... 17
3.2.6 Cancel scan ............................................................................................................................... 18
3.2.7 Reset Solution .......................................................................................................................... 19
3.3 Extensibility services ..................................................................................................................................... 20
3.3.1 Set button ................................................................................................................................ 20
3.3.2 Remove button ........................................................................................................................ 21
3.4 Accessibility services ..................................................................................................................................... 22
3.4.1 Set API password ..................................................................................................................... 22
iii
Page 4

3.4.2 Block Embedded Capture UI .................................................................................................... 23
3.4.3 Unblock Embedded Capture UI ................................................................................................ 24
3.5 Logging services ............................................................................................................................................ 25
3.5.1 Enable log ................................................................................................................................. 25
3.5.2 Get log ...................................................................................................................................... 26
3.5.3 Disable log ................................................................................................................................ 26
4 Advanced API .............................................................................................................................................. 27
4.1 Graph and job services .................................................................................................................................. 27
4.1.1 Set graph .................................................................................................................................. 27
4.1.2 Append graph ........................................................................................................................... 32
4.1.3 View graph ............................................................................................................................... 33
4.1.4 Clear graph ............................................................................................................................... 34
4.1.5 Modify node .............................................................................................................................. 35
4.1.6 Delete node .............................................................................................................................. 36
5 Appendix I: API settings reference ................................................................................................................ 38
5.1 Navigation settings ....................................................................................................................................... 38
5.2 Scan settings ................................................................................................................................................. 38
5.3 Metadata and Custom options ...................................................................................................................... 39
5.4 Notifications .................................................................................................................................................. 39
5.5 Destinations ................................................................................................................................................... 40
6 Appendix II: Error codes ............................................................................................................................... 41
iv
Page 5

List of tables
Table 3-1 Put a new job ........................................................................................................................................................ 5
Table 3-2 View job ................................................................................................................................................................ 8
Table 3-3 Delete job ........................................................................................................................................................... 10
Table 3-4 Get files ............................................................................................................................................................... 11
Table 3-5 Set purge settings .............................................................................................................................................. 12
Table 3-6 Get device info .................................................................................................................................................... 13
Table 3-7 Get device status ................................................................................................................................................ 14
Table 3-8 ADF Status possible values ................................................................................................................................ 15
Table 3-9 Get solution info ................................................................................................................................................. 15
Table 3-10 Get solution status ........................................................................................................................................... 16
Table 3-11 Navigation status possible values ................................................................................................................... 17
Table 3-12 Wake up ............................................................................................................................................................ 17
Table 3-13 Device Status possible values ......................................................................................................................... 18
Table 3-14 Cancel scan ....................................................................................................................................................... 18
Table 3-15 Reset Solution .................................................................................................................................................. 19
Table 3-16 Set button ........................................................................................................................................................ 20
Table 3-17 Remove button ................................................................................................................................................ 21
Table 3-18 Set API Password ............................................................................................................................................. 22
Table 3-19 Block device ..................................................................................................................................................... 23
Table 3-20 Unblock device ................................................................................................................................................. 24
Table 3-21 Enable log ......................................................................................................................................................... 25
Table 3-22 Get log .............................................................................................................................................................. 26
Table 3-23 Disable log ........................................................................................................................................................ 26
Table 4-1 Set graph ............................................................................................................................................................ 27
Table 4-2 Append graph ..................................................................................................................................................... 32
Table 4-3 View graph .......................................................................................................................................................... 33
Table 4-4 Clear graph ......................................................................................................................................................... 34
Table 4-5 Modify node ........................................................................................................................................................ 35
Table 4-6 Delete node ........................................................................................................................................................ 36
Table 5-1 Notification email ............................................................................................................................................... 39
Table 6-1 API Error codes ................................................................................................................................................... 41
v
Page 6

List of figures
Figure 3-1 Put job, Request payload example ..................................................................................................................... 6
Figure 3-2 View job, success response example ............................................................................................................... 10
Figure 3-3 Delete job, success response example ............................................................................................................. 11
Figure 3-4 Get files, response example (Applicable only for format=links) ..................................................................... 12
Figure 3-5 Set purge settings, request payload example ................................................................................................. 13
Figure 3-6 Set purge settings, success response example ............................................................................................... 13
Figure 3-7 Get device info, success response example ..................................................................................................... 14
Figure 3-8 Get device status, response example ............................................................................................................... 15
Figure 3-9 Get solution info, response example ................................................................................................................ 16
Figure 3-10 Get solution status, Response example ......................................................................................................... 17
Figure 3-11 Wake up, success response example ............................................................................................................. 18
Figure 3-12 Cancel scan, Success response example ........................................................................................................ 19
Figure 3-13 Reset solution, success response example ................................................................................................... 20
Figure 3-14 Extensibility services, Set button — request payload example ................................................................... 21
Figure 3-15 Extensibility services, Set button — success response example ................................................................. 21
Figure 3-16 Remove button, success response example .................................................................................................. 22
Figure 3-17 Set API password, request payload example ................................................................................................. 23
Figure 3-18 Set API password, success response example ............................................................................................... 23
Figure 3-19 Block Embedded Capture UI, success response example .............................................................................. 24
Figure 3-20 Unblock Embedded Capture UI, success response example ......................................................................... 24
Figure 3-21 Enable log, request payload example ............................................................................................................ 25
Figure 3-22 Enable log, success response example .......................................................................................................... 25
Figure 3-23 Disable log, success response example ......................................................................................................... 26
Figure 4-1 Set graph, request payload example ............................................................................................................... 28
Figure 4-2 Success response example ............................................................................................................................... 32
Figure 4-3 Append graph, success response example ...................................................................................................... 33
Figure 4-4 View graph, success response example ........................................................................................................... 34
Figure 4-5 Clear graph, response example ........................................................................................................................ 35
Figure 4-6 Modify node, request payload example ........................................................................................................... 36
Figure 4-7 Modify node, response example ...................................................................................................................... 36
Figure 4-8 Delete node, response example ....................................................................................................................... 37
vi
Page 7
1 API Introduction
The HP Embedded Capture (HP EC) Application Programming Interface (API) enables client applications
integration that interacts with MFP devices to manage workflow and remote document capture. API services
are provided as part of the professional services agreement for HP Embedded Capture 1.1 or higher versions.
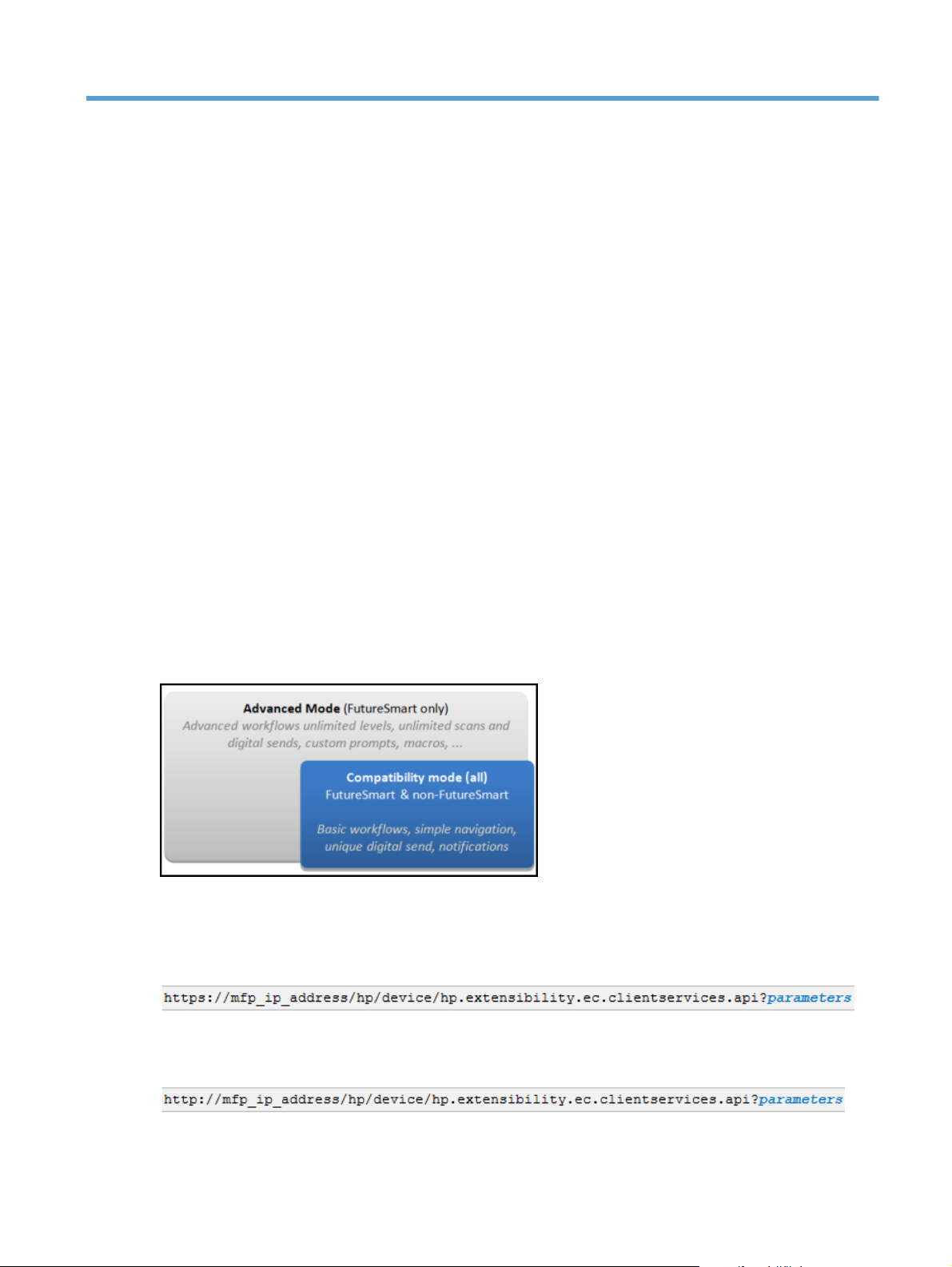
1.1 Basic and Advanced modes
The Embedded Capture solution works with a set of FutureSmart and non-FutureSmart MFP devices.
FutureSmart offers an advanced set of functionalities that can take advantage of all the power of Embedded
Capture. Non-FutureSmart devices cover a subset of those functionalities (basic) with standard document
capture capabilities like Scan, metadata (with restrictions), and certain navigation levels (2) that cover the
majority of the use cases.
The API is divided into two categories: Basic and Advanced
1.1.1 Basic API
The Basic API is compatible with the entire fleet (FutureSmart and non-FutureSmart devices). API integrators
do not need to distinguish between device models. The same API calls and URLs are available on both
models.
1.1.2 Advanced API
The Advanced API extends the complexity and flexibility of workflows managed on a device, offering extra
functionalities in addition to what the Basic API provides.
1.2 Accessing the API on a device (%API_URL%)
The Embedded Capture API is exposed throughout the MFP in specific URLs by using SSL (recommended).
Although it is possible to use the API in http mode without encryption, this is NOT recommended. Deployment
of workflows with associated parameters (including passwords) will be transferred in plain text over the
network, and may be exposed to unauthorized access.
Some API calls will send parameters by GET and others by POST. This is specified on each API definition table.
Section 1.1 Basic and Advanced modes 1
Page 8
NOTE: Changes to the transport protocol — to use or stop using SSL — should be done during device
configuration (Embedded webserver). See the HP Embedded Capture Admin Guide for more information.
NOTE: For all API methods described in this document, URLs have been simplified by replacing the value
with %API_URL%
1.2.1 XML encoding
All API parameters are based on standard XML documents. The conventions used for this XML are the
following:
●
PascalCase for elements
●
camelCase for attributes
Example:
1.2.2 XSD validation
Embedded Capture API is validated by an XSD schema that is available for downloading from the devices.
Each API includes a “schema” section that helps obtain the XSD document in real time.
To identify any issues with content on a client PC, it is highly recommended that XSD schemas be used to
validate the content before sending it to the API.
1.2.3 Response codes
Each API call response message will include a code and a descriptive message. The message description may
change on future releases of HP Embedded Capture (HP EC).
TIP: Any client application using the response information may use the error codes in place of strings to
ensure future compatibility.
2 Chapter 1 API Introduction
Page 9
2 API security
To avoid unauthorized access, all API calls can be password protected by the administrator. Protecting the
API guarantees that the MFP cannot be accessed by any client PC or application that does not know the
credentials to execute the API calls.
NOTE: It is highly recommended that the API be protected by setting the access control password.
2.1 Administrator and API accounts
2.1.1 Admin account
The admin account corresponds with the device administrator account credentials (admin). An MFP device
needs to be protected with an administrator password so that advanced options, network settings, etc...
(embedded webserver) can be accessed.
The administrator completes the following operations during the installation and normal setup of Embedded
Capture:
●
setButton
●
removeButton
●
setApiPassword
●
put (silent mode)
●
resetSolution
It is, however, recommended that a different password be used for standard API calls. This is explained in the
following sections.
2.1.1.1 “apiuser” user account
Setting up this account is optional, but highly recommended. Though once set, it is required for all API
operations except the ones specified above (setButton, removeButton, setApiPassword, put (silent mode),
resetSolution).
2.1.2 Using the API without authentication
If authentication is not used on the API, certain operations still require setup using an administrator
password. This is due to the following standard device usage constraints:
●
setButton, removeButton, resetSolution:
Administrator user/password is required for execution of these calls. When the solution is installed
from the administrator console, a default button is created, and this password is already used in a
transparent way for the administrator (specified on the device list).
●
putSilent:
Administrator user/password is required to execute this call. Once the solution is installed, the
administrator password is remembered by HP Embedded Capture. This is to avoid having to specify a
password on the API "put (silent mode)" calls. If the device administrator password is changed, the
Embedded Capture “cached” password must be refreshed using ONE of the following two options:
Section 2.1 Administrator and API accounts 3
Page 10

◦
Execute any API call with basic authentication using admin user/password.
or
◦
From the administrator console, edit the admin password in all changed devices, and press the
Remove workflow button.
2.2 Basic access authentication
Embedded Capture uses Basic access authentication for any API operation requiring authentication. To transmit credentials through HTTP, this authentication must be used.
For detailed information about basic access authentication, refer to the following:
wiki/Basic_access_authentication
To log in with API user credentials, the user name must be “apiuser” and the password must be the one
specified using the SetApiPassword operation.
http://en.wikipedia.org/
4 Chapter 2 API security
Page 11

3 Compatible API
3.1 Graph and job services
3.1.1 Put job
Table 3-1 Put a new job
?api=jobs&method=put
POST Description Uploads new scan job (simple workflow) to target MFP. Uploading scan job in compatible mode
appends job to existing workflows on device. Uploading scan job with same filtering parameters as an
existing one results in two jobs with same menu options displayed on control panel.
Authentication "admin" or "apiuser" basic authentication required for Silent jobs "put" operation. Optional in others.
Payload IN XML: Job details. Contains:
Navigation settings (optional (*))
Scan settings
Custom options
Metadata options
Notification
Destination
Response
Code
Schema Request
200 OK — success
Response
(*) Silent job: If navigation settings element is not defined, job is considered silent. Silent job
is scan&send workflow that executes immediately after put operation finishes; no user
interaction is possible on device control panel. This is an example of typical use of TWAIN
driver.
OUT If 200, XML response with job identifier.
If 400, XML response with error code.
400 Bad request
Error code -1: Product not licensed
Error code -3: Error parsing XML payload
Error code -10: Device is busy (silent mode)
Error code -11: Media size unsupported
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access — if basic authentication fails
411 Length required — if content length is not or is badly specified
500 Internal Server Error — if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
?api=jobs&schema=put
?api=jobs&rschema=put
Section 3.1 Graph and job services 5
Page 12

Figure 3-1 Put job, Request payload example
Destination examples
A scan job can be assigned any of the following destinations:
6 Chapter 3 Compatible API
Page 13
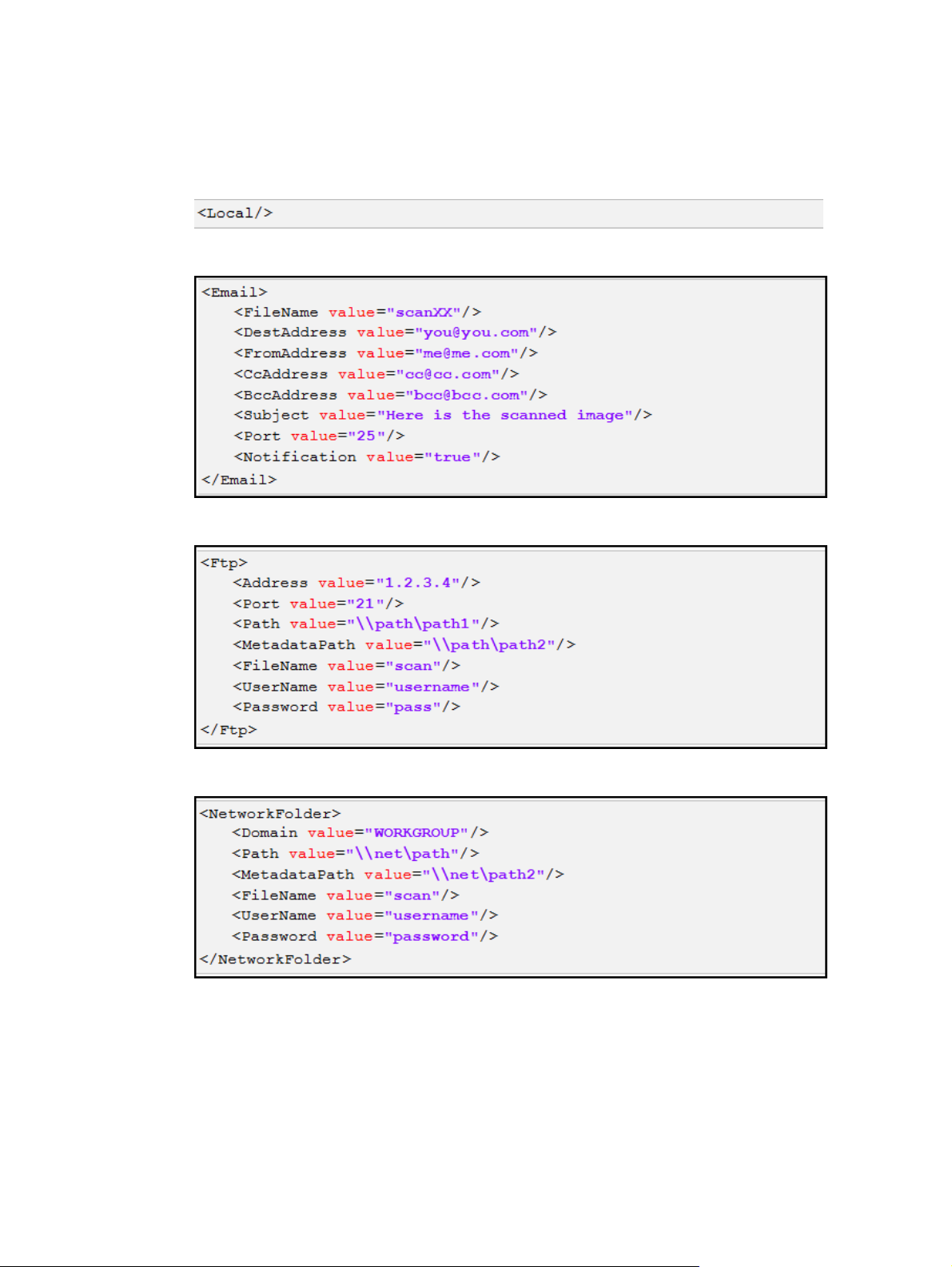
●
Local
The Local destination saves scanned documents to the device hard drive. They are not sent out of the
device, and can only be recovered through an API get operation.
●
Email
●
FTP
●
Network folder
●
Success response example:
Section 3.1 Graph and job services 7
Page 14
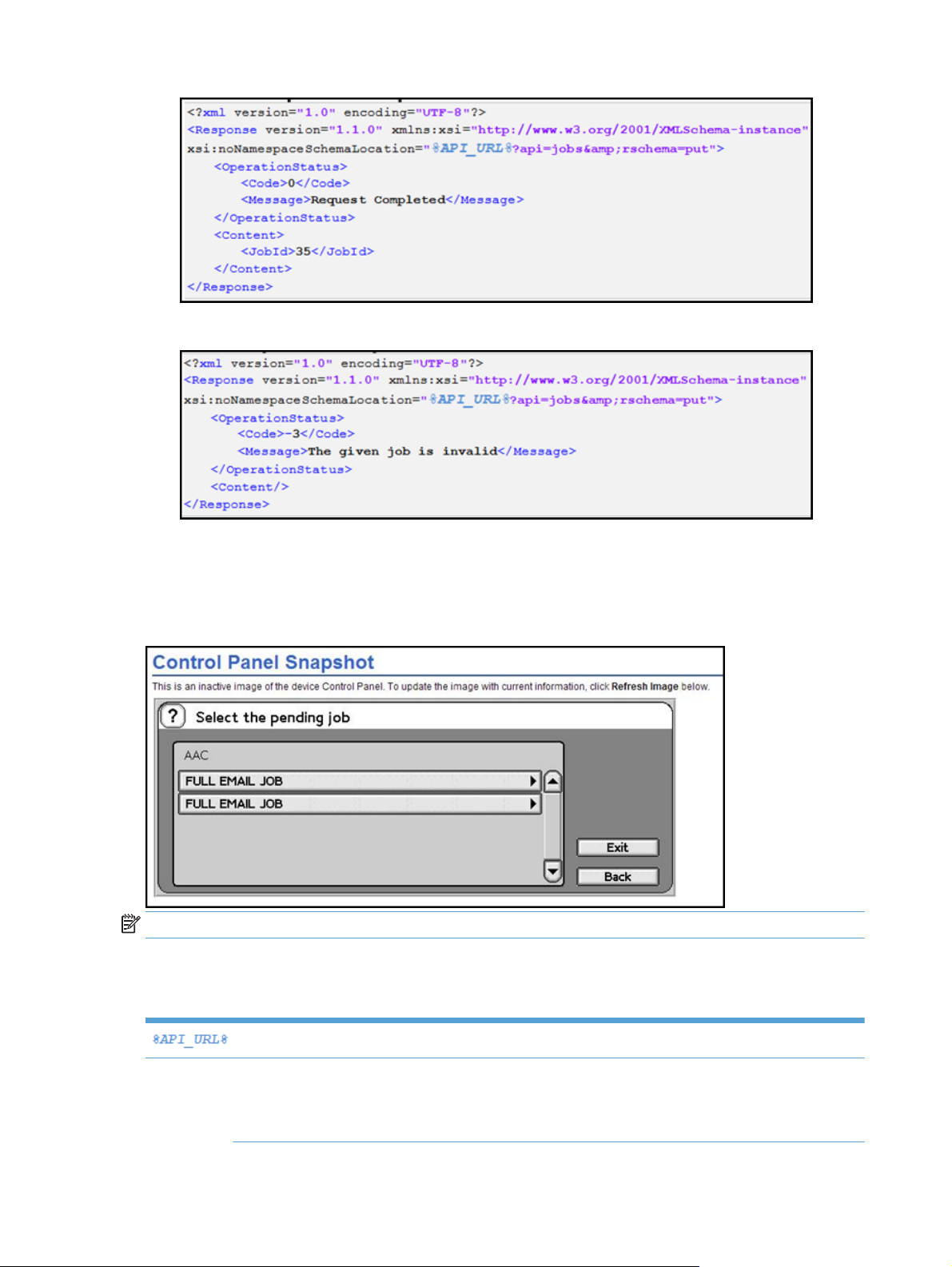
●
Error response example:
As an example, when two jobs with the same navigation filters “label A” and “label B” are uploaded, both will
be visible under “label A.”
Label A: AAC
Label B: FULL EMAIL JOB
NOTE: See APPENDIX I for possible settings and default values.
3.1.2 View job
Table 3-2 View job
?api=jobs&method=view&jobId={jobId}
GET Description Retrieves the job details as they were set up on the put API call.
8 Chapter 3 Compatible API
If the ID is set to 0, returns the details of all the workflow jobs.
If the ID is non-zero, returns the details of the job corresponding to the specified id.
Page 15

Table 3-2 View job (continued)
Payload IN -
Response Code 200 OK — success
Schema Request -
OUT If 200, XML response with job details.
If 400, XML response with error code.
400 Bad request:
Error code –2: Invalid job id.
Error code –5: Id does not correspond to a job.
401 Unauthorized access — if basic authentication fails.
500 Internal Server Error — if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Response
?api=jobs&rschema=view
Section 3.1 Graph and job services 9
Page 16

Figure 3-2 View job, success response example
3.1.3 Delete job
Table 3-3 Delete job
?api=jobs&method=delete&jobId={jobId}
10 Chapter 3 Compatible API
Page 17

Table 3-3 Delete job (continued)
GET Description Removes a job by changing its status to “cancelled.” Deleted jobs will still appear in an API
view request, but with a cancelled status until they get purged by the Embedded Capture
garbage collector.
If the jobId is set to 0, all jobs in the graph are removed.
If jobId is non-zero, only the specified job is removed.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0.
If 400, XML response with error code.
Response Code 200 OK – success
400 Bad request:
Error code -2: Invalid job id.
Error code -5: Id does not correspond to a job.
Error code -12: Operation error.
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails.
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Schema Request —
Response
Figure 3-3 Delete job, success response example
3.1.4 Get files
Table 3-4 Get files
GET Description Retrieves the files scanned by the job corresponding to the specified id.
?api=common=default
?api=jobs&method=getFiles&jobId={jobId}&format}={format}
If the format is set to “zip”, returns all files in a zip.
If the format is set to “boundary”, returns all files as a MIME multipart message (http://
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIME).
If the format is set to “links”, returns an xml with direct links to download files.
For silent jobs (no user interaction on the control panel) the getFiles is a blocking operation, i.e.
no result is returned until files are ready or the job is cancelled.
Payload IN —
Section 3.1 Graph and job services 11
Page 18

Table 3-4 Get files (continued)
Response Code 200 OK – success
Schema Request —
OUT If 200, XML response with files or xml with direct download links.
If 400, XML response with error code.
400 Bad request:
Error code -2: Invalid job id
Error code -5: Id does not correspond to a job
Error code -6: Error loading job information
Error code -7: Error creating zip
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Response
Figure 3-4 Get files, response example (Applicable only for format=links)
3.1.5 Set purge settings
Table 3-5 Set purge settings
?api=jobs=getFiles
?api=jobs&method=setPurgeSettings
POST Description Sets the Expiration time and the Garbage Collector period for dynamic scan jobs in the MFP.
12 Chapter 3 Compatible API
These variables control the time that a job will remain in the device.
Expiration time corresponds to the amount of time that dynamic jobs remain in the device.
Collector period corresponds to time interval within subsequent cleanup operations of expired
jobs. Collector period must be smaller than Expiration time. Both values are defined in seconds.
By default, Collector period is set to 30 Minutes and Expiration Time to 12 Hours. Collector
period valid Range is between 1800 sec (30 minutes) and 84000 sec (24 hours). Expiration Time
is not constrained.
Page 19

Table 3-5 Set purge settings (continued)
Payload IN XML Configuration parameters
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
Response Code 200 OK – success
400 Bad request:
Error code -3: Error parsing xml payload
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
If 400, XML response with error code
Schema Request
Response
?api=jobs&schema=setPurgeSettings
?api=common&rschema=default
Figure 3-5 Set purge settings, request payload example
Figure 3-6 Set purge settings, success response example
3.2 Configuration services
3.2.1 Get device info
Table 3-6 Get device info
?api=config&method=getDeviceInfo
GET Description Gets the device information.
Information returned includes:
◦
◦
Device model
Device IP
Section 3.2 Configuration services 13
Page 20

Table 3-6 Get device info (continued)
Payload IN —
Response Code 200 OK — success
Schema Request —
◦
Device Family (“FutureSmart” or “Non-FutureSmart”)
◦
Hostname
◦
Tray width (mm)
◦
Tray height (mm)
OUT If 200, XML response with device info.
401 Unauthorized access — if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error — if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Response
?api=config&rschema=getDeviceInfo
Figure 3-7 Get device info, success response example
3.2.2 Get device status
Table 3-7 Get device status
?api=config&method=getDeviceStatus
GET Description Returns device status information. The information returned includes:
14 Chapter 3 Compatible API
◦
Disk space in bytes.
◦
ADF status
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with device status.
Page 21

Table 3-7 Get device status (continued)
Response Code 200 OK — success
Schema Request —
401 Unauthorized access — if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error — if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Response
?api=config&rschema=getDeviceStatus
Figure 3-8 Get device status, response example
Table 3-8 ADF Status possible values
Code Meaning Explanation
1 Ready There is paper for scan
0 Empty There is no paper for scan
-1 Initializing Device is still booting
–2 Unsupported Device does not support ADF/Flatbed status monitoring
-3 Not present Device has no ADF/Flatbed
3.2.3 Get solution info
Table 3-9 Get solution info
?api=config&method=getSolutionInfo
GET Description Returns solution information. Information returned includes:
Solution version
License information
Blocked for users (through the accessibility block command)
Log level (all, off)
AdvancedWorkflowSupport (true, false)
Section 3.2 Configuration services 15
Page 22

Table 3-9 Get solution info (continued)
Payload IN —
Response Code 200 OK — success
Schema Request —
OUT If 200, XML response with solution info.
401 Unauthorized access — if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error — if too many request are active. Retry recommended.
Response
Figure 3-9 Get solution info, response example
3.2.4 Get solution status
?api=config&rschema=getSolutionInfo
Table 3-10 Get solution status
?api=config&method=getSolutionStatus
GET Description Returns device status information. Information returned includes:
Payload IN —
Response Code 200 OK — success
Schema Request —
Response
16 Chapter 3 Compatible API
Operating status (Navigating, scanning, processing, unknown)
Error condition indicating whether the status is at the moment interrupted by some error
condition. For example, if there is no paper on ADF.
OUT If 200, XML response with solution status.
401 Unauthorized access — if basic authentication fails.
500 Internal Server Error — if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
?api=config&rschema=getSolutionStatus
Page 23

Figure 3-10 Get solution status, Response example
Table 3-11 Navigation status possible values
Code Meaning
0 Unknown
1 Navigating
2 Scanning
3 Processing
4Idle
3.2.5 Wake up
Table 3-12 Wake up
GET Description Wakes up device if in standby mode.
Schema Request —
?api=config&method=wakeup
If device is in standby mode, starting the operation with Embedded Capture is delayed
by the wake up process. With this API call it is possible to force the wake up
programmatically, so that it is ready when the user arrives.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with current status.
Response Code 200 OK — success
401 Unauthorized access — if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error — if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Response
?api=config&rschema=wakeup
Section 3.2 Configuration services 17
Page 24

Figure 3-11 Wake up, success response example
Table 3-13 Device Status possible values
Code Meaning Explanation
1 OK Device is awake
0 KO Device is not awake
-1 Initializing Device is still booting
3.2.6 Cancel scan
Table 3-14 Cancel scan
?api=config&method=cancelScan
GET Description Cancels/interrupts the scanning process on the device.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, XML response with error code
Response Code 200 OK — success
400 Bad request:
Error code –10: Device is busy
401 Unauthorized access — if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error — if too many request are active. Retry recommended.
Schema Request —
Response
?api=common&rschema=default
18 Chapter 3 Compatible API
Page 25

Figure 3-12 Cancel scan, Success response example
3.2.7 Reset Solution
Table 3-15 Reset Solution
?api=config&method=resetSolution
GET Description This function restores the solution as if it was newly installed on a clean device:
◦
Removes all process data such as scanned files, pending jobs etc.
◦
Restores default solution settings: Deactivates logs, removes icon, resets purge
settings and API passwords.
WARNING! Removing the solution button will cause all access control configuration
to be lost. Upon creating a new button, access will have to be reconfigured.
Authentication Requires basic authentication with device admin credentials.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
Response Code 200 OK — success
400 Bad request:
Error code –10: Device is busy
Error code –12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Schema Request —
Response
If 400, XML response with error code
?api=common&rschema=default
Section 3.2 Configuration services 19
Page 26

Figure 3-13 Reset solution, success response example
3.3 Extensibility services
3.3.1 Set button
Table 3-16 Set button
?api=extensibility&method=setButton
POST Description Creates or modifies the Home screen button on the device. If any fields are not
specified, a default value will be used. If Embedded Capture had no button (silent
mode), it will change to a non-silent mode (interactive) after the button creation.
Icon requirements (*):
Authentication Requires basic authentication using device admin credentials.
Payload IN XML button details
Response Code 200 OK – success
Schema Request
Response
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, response with error code
400 Bad request:
Error code -3: Error parsing xml payload
Error code -10: Device is busy
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified
500 Internal server error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
?aspi=extensibility&rschema=setButton
?api=common&rschema=default
20 Chapter 3 Compatible API
Page 27

Figure 3-14 Extensibility services, Set button — request payload example
Figure 3-15 Extensibility services, Set button — success response example
3.3.2 Remove button
Table 3-17 Remove button
?api=extensibility&method=removeButton
GET Description Removes a Home screen button on the device.
Attention: Removing the solution button will cause all access
control configuration to be lost (authentication agent, embedded
authentication...). Upon creating a new button, the application
access will need to be reconfigured.
Authentication Requires basic authentication with device admin credentials.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, XML response with error code
Response Code 200 OK — success
400 Bad request
Error code -10: Device is busy
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
Section 3.3 Extensibility services 21
Page 28

Table 3-17 Remove button (continued)
Schema Request —
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry
recommended.
Response
Figure 3-16 Remove button, success response example
3.4 Accessibility services
3.4.1 Set API password
Table 3-18 Set API Password
?api=accessibility&method=setApiPassword
?api=common&rschema=default
POST Description Sets a password for API authentication. By default, password is not set, and therefore API is not
protected. For security reasons, it is recommended that API protection be used to avoid
unauthorized access to scanned documents or workflows information.
Once API password is set, all operations will require basic authentication with credentials:
Username: “apiuser”
Password: the password defined.
(Alternatively, device "admin" user/password can be used for API authentication.) To unset API
password, an empty string must be unspecified in payload xml.
Authentication Requires basic authentication with device admin credentials.
Payload IN XML: Containing the password of the administrator of the API
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, XML response with error code
Response Code 200 OK – success
400 Bad request
Error code -3: Error parsing xml payload
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
22 Chapter 3 Compatible API
Page 29

Table 3-18 Set API Password (continued)
Schema Request
Response
Figure 3-17 Set API password, request payload example
Figure 3-18 Set API password, success response example
3.4.2 Block Embedded Capture UI
?api=accessibility&schema=setApiPassword
?api=common&rschema=default
Table 3-19 Block device
?api=accessibility&method=block
GET Description Disables the Embedded Capture Home screen button on the control panel. This is
highly recommended before performing administration tasks that need to change
workflows structure and may affect the user scanning.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0.
If 400, XML response with error code.
Response Code 200 OK – success
400 Bad request:
Error code –10: Device is busy.
Error code –12: Unexpected error.
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Schema Request —
Response
?api=common&rschema=default
Section 3.4 Accessibility services 23
Page 30

Figure 3-19 Block Embedded Capture UI, success response example
3.4.3 Unblock Embedded Capture UI
Table 3-20 Unblock device
?api=accessibility&method=unblock
GET Description Reactivates solution button on device control panel. After unblocking Embedded Capture
UI, users will be able to execute workflows normally.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
Response Code 200 OK – success
If 400, XML response with error code
400 Bad request:
Error code -10: Device is busy
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Schema Request —
Response
?api=common&rschema=default
Figure 3-20 Unblock Embedded Capture UI, success response example
24 Chapter 3 Compatible API
Page 31

3.5 Logging services
3.5.1 Enable log
Table 3-21 Enable log
?api=logging&method=enable
POST Description Method that enables the Logging Service during a specified number of days. If
Payload IN XML Configuration parameters
Response code 200 OK – success
specifying 0 Days, the Logging Service will be enabled permanently.
NOTE: Take into consideration that enabling the log permanently will shorten the
printer’s hard disk lifetime, and may also affect performance.
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, XML response with error code
400 Bad request:
Error code -3: Error parsing xml payload
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified.
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Schema Request
Response
Figure 3-21 Enable log, request payload example
Figure 3-22 Enable log, success response example
?api=logging&schema=enable
?api=common&rschema=default
Section 3.5 Logging services 25
Page 32

3.5.2 Get log
Table 3-22 Get log
GET Description Method that retrieves the logs of Embedded Capture. The logs are
Schema Request —
?api=logging&method=get
returned in a text file that is downloaded by http protocol.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, response with the file
Response code 200 OK — success
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry
recommended.
3.5.3 Disable log
Table 3-23 Disable log
GET Description Disable the Logging Service.
Schema Request —
Figure 3-23 Disable log, success response example
Response
?api=logging&method=disable
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
Response Code 200 OK – success
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Response
?api=common&rschema=default
?api=common&rschema=default
26 Chapter 3 Compatible API
Page 33

4 Advanced API
The Advanced mode API is only available on FutureSmart devices.
To distinguish between device models when using Advanced API calls in a mixed fleet, it is highly
recommended that you use the getDeviceInfo API call (<Family> element) on Compatible mode to filter and
choose the devices that will accept the advanced calls between the ones that would reject them.
4.1 Graph and job services
4.1.1 Set graph
Table 4-1 Set graph
?api=graph&method=set
POST Description Creates a graph on target MFP. A graph is represented on the MFP as a workflow
Payload IN XML: Graph
that may include all its components.
This operation replaces the previous graph on the MFP.
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
Response Code 200 OK – success
Schema Request
Response
If 400, XML response with error code
400 Bad request
Error code -1: Product not licensed
Error code -3: Error parsing xml payload
Error code -8: Unsupported scan settings
Error code -10: Device is busy (silent mode)
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified.
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
?api=graph&schema=set
?api=common&rschema=default
Section 4.1 Graph and job services 27
Page 34

Figure 4-1 Set graph, request payload example
28 Chapter 4 Advanced API
Page 35

Section 4.1 Graph and job services 29
Page 36

30 Chapter 4 Advanced API
Page 37

Section 4.1 Graph and job services 31
Page 38

Figure 4-2 Success response example
NOTE: See section Appendix I to check the settings possible and default values.
4.1.2 Append graph
Table 4-2 Append graph
?api=graph&method=append&parentID={nodeId}
POST Description Appends a new subgraph on target MFP existing workflow graph.
If parent node Id is not provided, the new graph will be appended to the
root node on the device and will appear as a new menu option when
accessing the first EC screen.
Payload IN XML: Graph
32 Chapter 4 Advanced API
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, XML response with error code
Response Code 200 OK – success
400 Bad request
Error code -1: Product not licensed
Error code -3: Error parsing xml payload
Error code -5: Id not corresponding to a valid job
Error code -8: Unsupported scan settings
Error code -10: Device is busy (silent mode)
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
Page 39

Table 4-2 Append graph (continued)
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry
recommended.
Schema Request
Request payload example:
NOTE: See the Request payload on the API “set” graph method.
Figure 4-3 Append graph, success response example
4.1.3 View graph
Table 4-3 View graph
Response
?api=graph&schema=append
?api=common&rschema=default
?api=graph&method=view&includeScheduled={boolean}
GET Description Gets the graph from device. The graph fetched corresponds to the
graph stored on device at the moment of the api call execution. As
a result, it does not include dynamic jobs already executed,
neither nodes already scheduled whatever its status is.
includeScheduled(optional): Not used in EC1.2.0; its default
value is false
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with the graph data
Response Code 200 OK – success
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry
recommended
Schema Request —
Response
?api=graph&rschema=view
Section 4.1 Graph and job services 33
Page 40

Figure 4-4 View graph, success response example
4.1.4 Clear graph
Table 4-4 Clear graph
?api=graph&method=clear&includeScheduled={boolean}
GET Description Clears the full graph from the device. If includeScheduled is not set, this call has no effect on
Payload IN —
Response Code 200 OK — success
34 Chapter 4 Advanced API
processes already scheduled for execution.
includeScheduled(optional): Not supported in EC 1.2.0; its default value is false.
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, XML response with error code
Page 41

Table 4-4 Clear graph (continued)
Schema Request —
400 Bad request
Error code -2: Invalid request parameters
Error code -10: Device is busy
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Response
Figure 4-5 Clear graph, response example
4.1.5 Modify node
Table 4-5 Modify node
?api=graph&method=modifyNode&includeScheduled={boolean}
POST Description Modifies a graph node on the target MFP.
?api=common&rschema=default
By including scheduled nodes, they can be modified in order to change their parameters before they are
executed.
includeScheduled(optional): Not supported in EC 1.2.0; its default value is false.
Payload IN XML: Node
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, XML response with error code
Response Code 200 OK – success
400 Bad request
Error code -3: Error parsing xml payload
Error code -5: Id not corresponding to a valid node
Error code -8: Unsupported scan settings. (if it is a scan node)
Error code -10: Device is busy
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
Section 4.1 Graph and job services 35
Page 42

Table 4-5 Modify node (continued)
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry recommended.
Schema Request
Response
?api=graph&schema=modifyNode
?api=common&rschema=default
Figure 4-6 Modify node, request payload example
Figure 4-7 Modify node, response example
4.1.6 Delete node
Table 4-6 Delete node
?api=graph&method=deleteNode&nodeId={nodeId}&includeScheduled={boolean}
GET Description Removes a node from graph. Removing a node will also remove any
36 Chapter 4 Advanced API
sub-graph depending directly exclusively on this node.
NOTE: If not provided includeScheduled is considered false. HP EC
1.2.0 only supports includeScheduled=false.
Payload IN —
OUT If 200, XML response with code 0
If 400, XML response with error code
Response Code 200 OK – success
400 Bad request
Page 43

Table 4-6 Delete node (continued)
Schema Request —
Error code -5: Id not corresponding to a valid node
Error code -10: Device is busy (silent mode)
Error code -12: Unexpected error
401 Unauthorized access – if basic authentication fails
411 Length required – if content length is not or is badly specified
500 Internal Server Error – if too many requests are active. Retry
recommended
Response
Figure 4-8 Delete node, response example
?api=common&rschema=default
Section 4.1 Graph and job services 37
Page 44

5 Appendix I: API settings reference
The following completes the information provided in the API XSD documents that are more related to the
structure and content type. Depending on the device model, some parameters may vary, and are subject to
device specific capabilities outlined in the specifications.
5.1 Navigation settings
NAME TYPE DEFAULT REQUIRED (PUT)
LabelA string “Default Name” TRUE
LabelB string
JobDescription string Null FALSE
Permanent boolean — TRUE
HideDeleteButton boolean false FALSE
HideFileName boolean false FALSE
OneButton boolean false FALSE
ShowSummaryScreen boolean true FALSE
5.2 Scan settings
NAME TYPE DEFAULT REQUIRED (PUT)
Type string — TRUE
Color string — TRUE
Resolution string — TRUE
Duplex boolean — TRUE
Source string
FALSE
TRUE
MediaSize string
PageContent string Null FALSE
QualityMode string Null FALSE
Sharpness integer –1 FALSE
Darkness integer –1 FALSE
BackgroundRemoval integer –1 FALSE
Orientation string Null FALSE
Multipage boolean false FALSE
NumOfPages integer –1 FALSE
38 Chapter 5 Appendix I: API settings reference
TRUE
Page 45

NAME POSSIBLE VALUES
Type “jpg”, “pdf”, “tiff”, “mtiff”, “xps”
Color “color”, “bw”, “grayscale”
Resolution “75”, “150”, “200”, “300”, “400”, “600”
Duplex boolean
Source “auto”, “adf”, “flatbed”
MediaSize “auto”, “letter”, “legal”, “exec”, “a3”, “a4”, “a5”, “b5”, “b5_env”,
“j_double_postcard”, “dl_env”
PageContent “text”, “graphic”, “mixed”
QualityMode “small”, “medium”, “large”
Sharpness “1”, “2”, “3”, “4”, “5”
Darkness “0”, “1”, “2”, “3”, “4”, “5”, “6”, “7”, “8”
BackgroundRemoval “1”, “2”, “3”, “4”, “5”, “6”, “7”, “8”, “9”
Orientation “portrait”, “landscape”
Multipage boolean
NumOfPages integer
5.3 Metadata and Custom options
Metadata and Custom options are both optional. When specifying Custom options, there are a set of possible
options. Any other option will raise an exception:
KEY POSSIBLE VALUES
removeBlankPages “on”, “off”
duplexEditable “true”, “false”
userName String
bitRate integer
5.4 Notifications
Notification tag is mandatory with a valid type and condition.
Table 5-1 Notification email
NAME TYPE DEFAULT VALUE REQUIRED (PUT)
Port Integer 25 FALSE
DestAddress String
TRUE
FromAddress String
Subject String “Scanning Notification.” FALSE
TRUE
Section 5.3 Metadata and Custom options 39
Page 46

5.5 Destinations
●
Destination tag: obligatory
●
Type attribute: mandatory
●
Metadata attribute: optional (default value = false)
Destination email:
NAME TYPE DEFAULT VALUE REQUIRED (PUT)
Port Integer 25 FALSE
DestAddress String
FromAddress String
CcAddress String
BccAddress String
Subject String “Scanning Notification” FALSE
FileName String “Document” FALSE
Notification Boolean false FALSE
TRUE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
Destination FTP:
NAME TYPE DEFAULT VALUE REQUIRED (PUT)
Address String
Port Integer 25 FALSE
Path String
UserName String
Password String
FileName String “Document” FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
MetadataPath String
Destination Network Folder:
NAME TYPE DEFAULT VALUE REQUIRED (PUT)
Domain String 25 TRUE
Path String
UserName String
Password String
FileName String “Document” FALSE
MetadataPath String
40 Chapter 5 Appendix I: API settings reference
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Page 47

6 Appendix II: Error codes
The following table provides a summary of all possible API error codes returned when something does not
work as expected, or in some cases, to inform of a situation needing attention from the user/operator side,
possibly requiring a retry of the failed operation. The generic error message indicates the category of the
error, but the description is different for each API call, providing more detailed information of each case.
Table 6-1 API Error codes
Error code Old error codes (*NSE) Generic description
-1 -11 Product not licensed.
-2 -8 Invalid request parameters.
-3 -10 Error parsing request xml payload.
-4 — The given admin password is invalid. Please update it (nonFutureSmart only)
-5 -5 Id not corresponding to a valid job.
-6 -8 Job settings could not be loaded.
-7 -8 Unexpected error creating zip file.
-8 Unsupported scan settings.
-9 n/a
-10 -7 Device is busy. Please repeat operation within a few seconds.
-11 -9 Unsupported media size value.
-12 -4 Unexpected error.
(*) Old error codes indicate values that product NSE notified on similar situations. They are provided as a
reference for backwards compatibility for programmers adapting client applications for integration with HP
Embedded Capture API.
41
 Loading...
Loading...