Page 1

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1 HP Deskjet 6800 series printer
To find an answer to a question, click the appropriate topic below:
• Notices
• Special features
• Getting started
• Connecting to the printer
• Printing from a digital camera
• Printing photos from a computer
• Printing other documents
• Printing tips
• Printer software
• Maintenance
• Troubleshooting
• Optional accessories
• Specifications
• Supplies
1
Page 2

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
2 Notices
• Notices and acknowledgements
• Terms and conventions
2.1 Notices and acknowledgements
Hewlett-Packard company notices
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without prior written permission is
prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein
should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable
for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Acknowledgements
Apple, the Apple logo, AppleTalk, ColorSync, the ColorSync logo, Finder, Mac,
Macintosh, MacOS, Powerbook, Power Macintosh, and Quickdraw are trademarks
of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
TrueType is a U.S. trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
Adobe and Acrobat are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
© 2004 Copyright Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
2.2 Terms and conventions
The following terms and conventions are used in the user's guide.
Terms
The HP Deskjet printer may be referred to as the HP printer or printer.
Cautions, warnings, and notes
A Caution indicates possible damage to the HP Deskjet printer or to other
equipment. For example:
2
Page 3

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Caution: Do not touch the print cartridge ink nozzles or copper contacts.
Touching these parts will result in clogs, ink failure, and bad electrical
connections.
A Warning indicates possible harm to you or to others. For example:
Warning: Keep both new and used print cartridges out of the reach of
children.
A Note indicates that additional information is provided. For example:
Note: For great results use HP products.
3
Page 4

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3 Special features
Congratulations! You have purchased an HP Deskjet printer that is equipped with
several exciting features:
• Built-in networking capabilities: Connect to either a wired or a wireless network
without using an external print server.
• Ink-backup mode: Ink-backup mode lets you continue printing with one print
cartridge when the other print cartridge has run out of ink.
• Print Cancel button: Cancel print jobs at the touch of a button.
• Print multiple pages on a single sheet of paper: Use the printer software to print
up to 16 pages on a single sheet of paper.
• Borderless printing: Use the entire page surface when printing photos and
cards by using the borderless printing feature.
• Digital photo printing: Use the enhanced digital photo printing capabilities.
• Six-ink upgradeable printing: Enhance photo printing with a photo print
cartridge.
• Direct camera printing: Use the PictBridge port on the front of the printer to print
photographs directly from a digital camera.
• Optional Automatic Two-Sided Printing Accessory: Purchase a Automatic Two-
Sided Printing Accessory to print two-sided documents automatically.
• Optional Auto Two-Sided Print Accessory with Small Paper Tray: Purchase
a Optional Auto Two-Sided Print Accessory with Small Paper Tray to print two-
sided documents automatically and load small media from the back of the
printer.
• Optional 250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory: Purchase an optional 250-
Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory and expand the printer's paper-handling
capability.
4
Page 5
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
4 Getting started
For an overview of the printer features, see the printer features page.
Click the appropriate topic below for a description of a printer feature:
• Buttons and lights
• Print Cartridge Status lights
• Paper trays
• Photo/envelope feeder
• Print cartridges
• Ink-backup mode
• Automatic Paper Type Sensor
• PictBridge port
For a description of the optional accessories, see the optional accessories page.
4.1 Printer features
The HP printer has several features to make printing easier and more efficient.
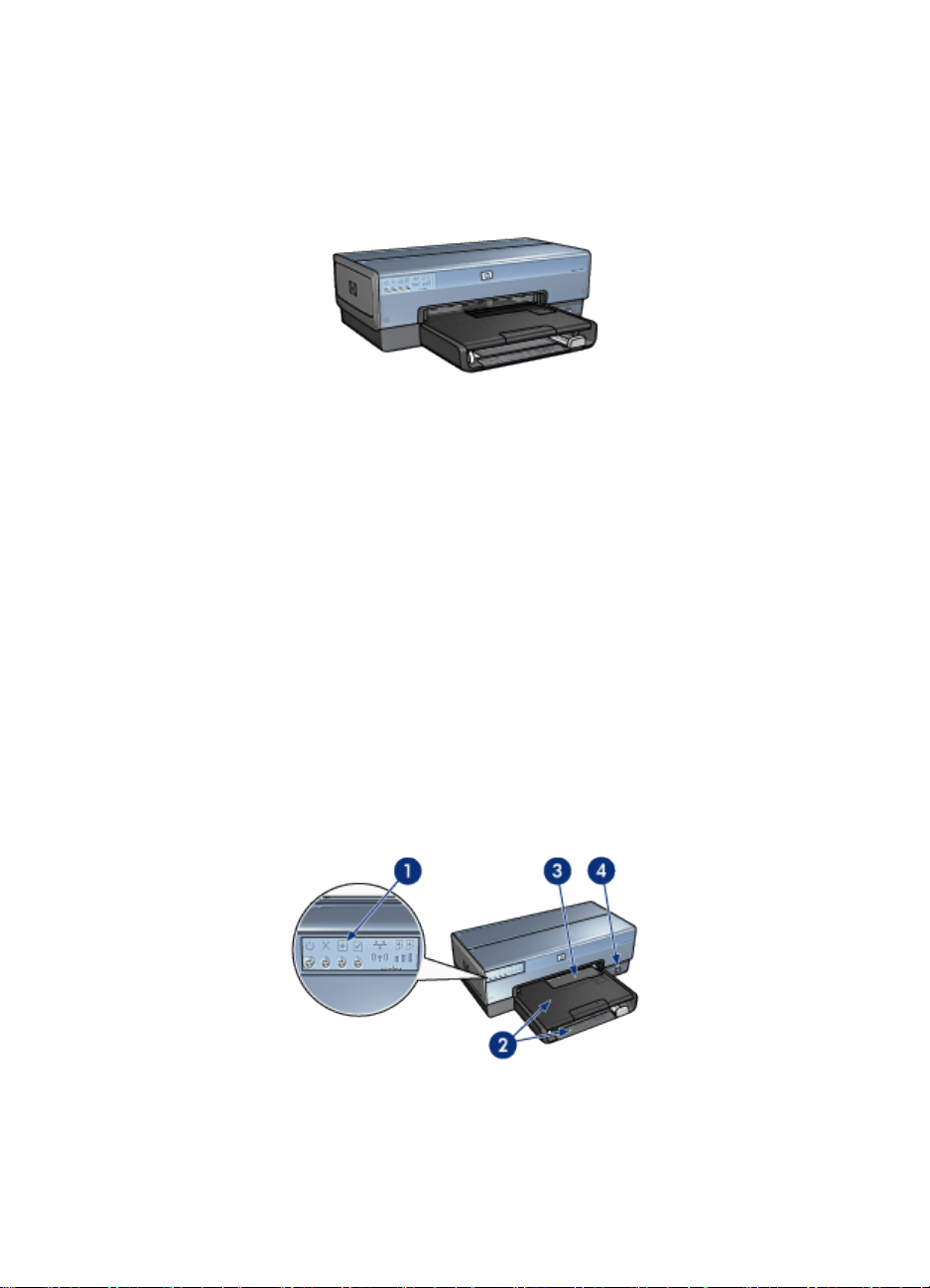
1. Buttons and lights
5
Page 6

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
2. Paper trays
3. Photo/envelope feeder
4. PictBridge port
1. Print cartridges
2. Automatic Paper-Type Sensor (not illustrated)
3. Ink-backup mode (not illustrated)
1. Rear USB port
2. Wired Ethernet port
Optional accessories
6
Page 7
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Automatic Two-Sided
Printing Accessory (optional)
250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray
Accessory (optional)
Auto Two-Sided Print
Accessory with Small Paper
Tray (optional)
4.2 Buttons and lights
Use the printer buttons to turn the printer on and off, cancel a print job, and restart
a job. The printer lights give you visual cues about the status of the printer.
1. Power button and light
2. Print Cancel button
3. Resume button and light
4. Report Page button
5. Wireless Status light and Signal Strength indicator
6. Print Cartridge Status lights
7. Network icon
For a description of the following buttons and lights, click the appropriate option:
• Report Page button
• Network icon
7
Page 8
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
• Wireless Status light and Signal Strength indicator
• Print Cartridge Status lights
Power button and light
The Power button turns the printer on and off. It might take a few seconds for the
printer to turn on after you press the Power button.
The Power light flashes when the printer is processing.
Caution: Always use the Power button to turn the printer on and off. Using
a power strip, surge protector, or a wall-mounted switch to turn the printer
on and off can cause printer failure.
Print Cancel button
Pressing the Print Cancel button cancels the current print job.
Resume button and light
The Resume light flashes when an action is required, such as loading paper or
clearing a paper jam. When the problem is solved, press the Resume button to
continue printing.
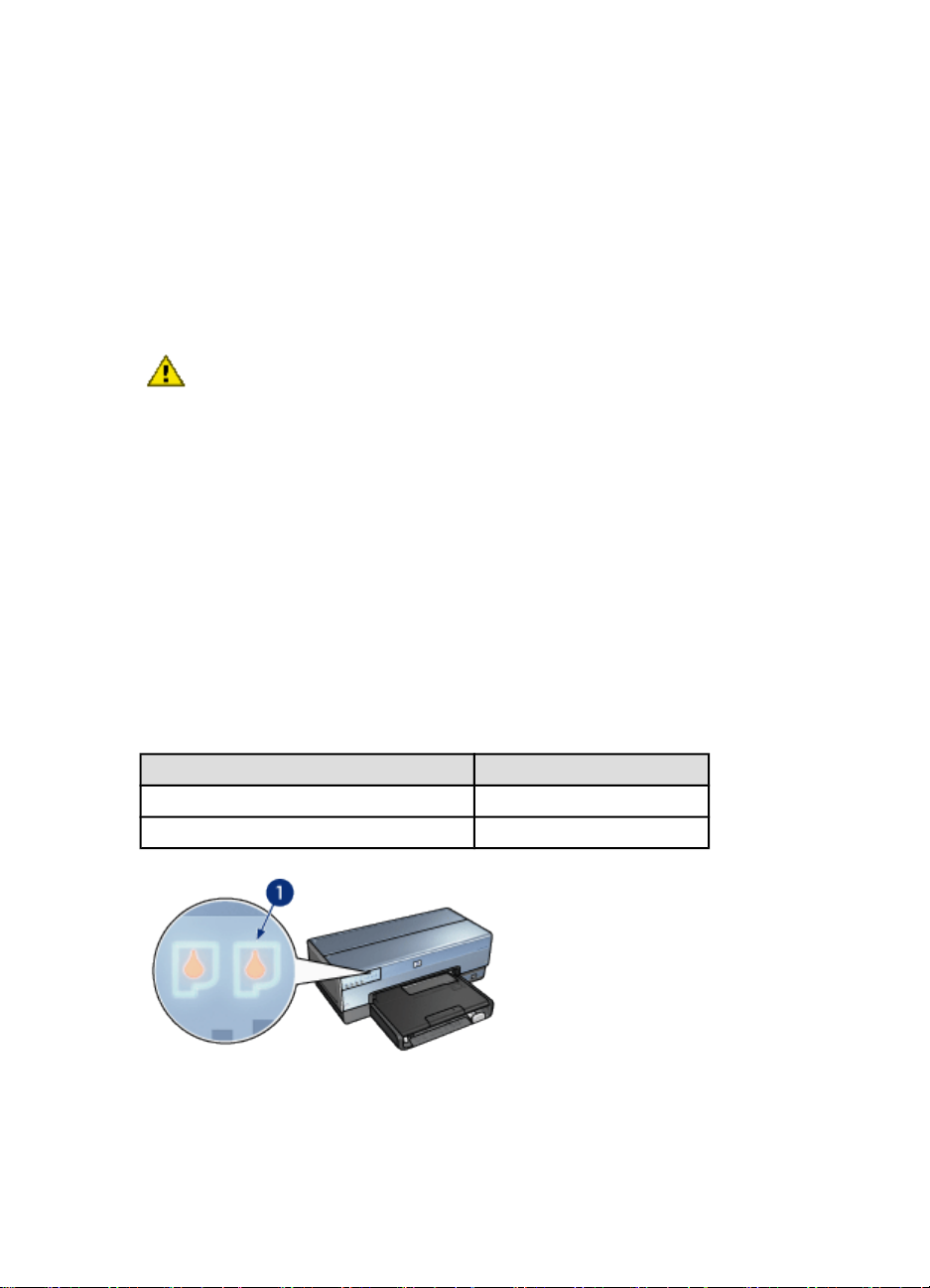
4.3 Print Cartridge Status lights
The Print Cartridge Status lights indicate the status of the print cartridges.
Status of the Print Cartridge Status lights Status of the print cartridges
On and solid Low on ink
Flashing Service required
1. Print Cartridge Status lights
8
Page 9

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. The left status light represents the tri-color print cartridge.
2. The right status light represents the print cartridge that is installed in the
compartment on the right side of the print cartridge cradle. That print cartridge can
be the black print cartridge, the photo print cartridge, or the gray photo print
cartridge.
4.4 Paper trays
The printer has two paper trays:
• In tray
• Out tray
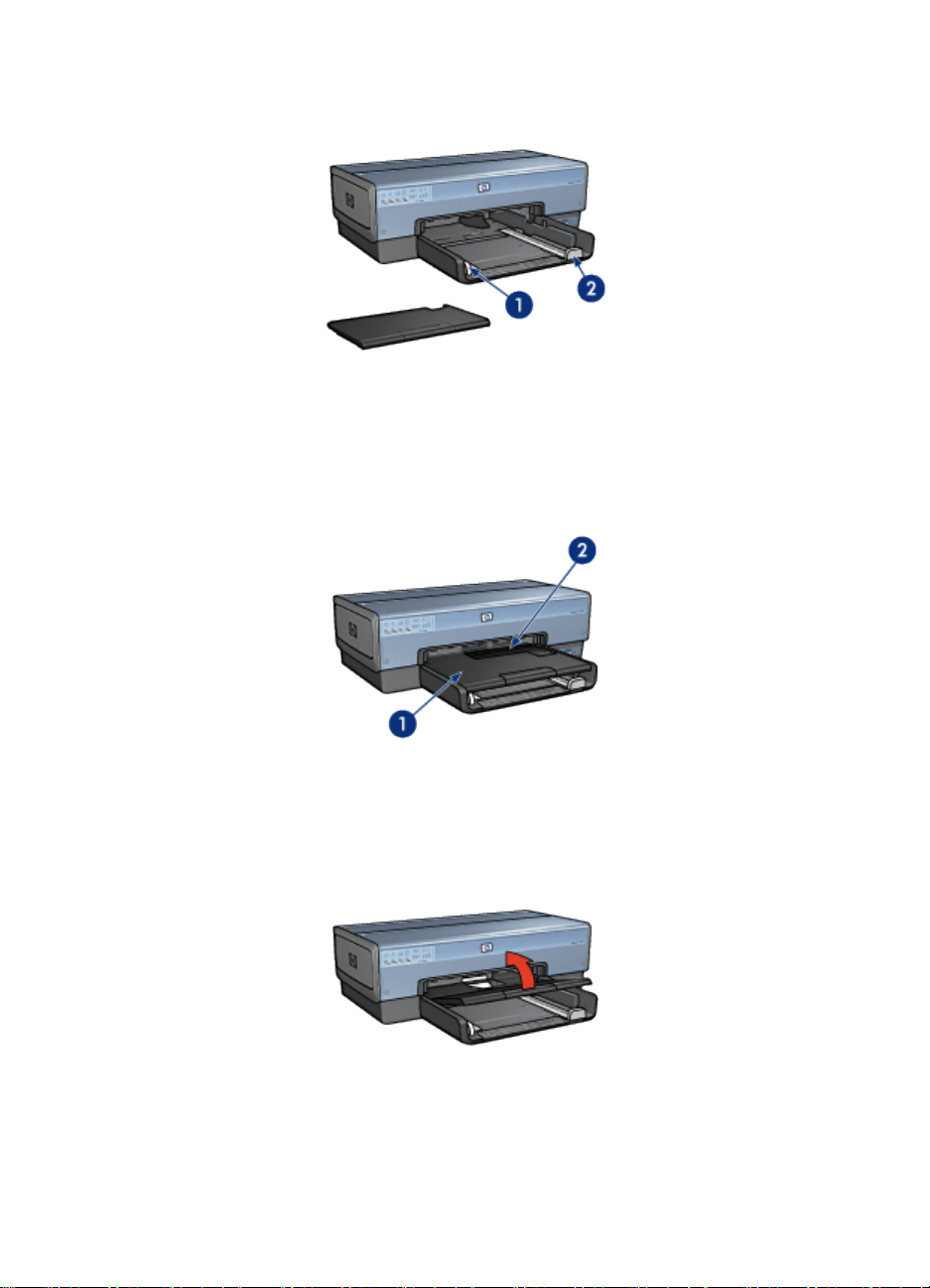
In tray
The In tray holds paper or other media to be printed.
1. In tray
Slide the paper guides firmly against the edges of the media on which you are
printing.
9
Page 10
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. Paper-width guide
2. Paper-length guide
Out tray
Printed pages are deposited in the Out tray.
1. Out tray
2. Photo/envelope feeder
Use the photo/envelope feeder to print single envelopes, small photos, and cards.
Raise the Out tray to load paper.
To prevent paper from falling out of the Out tray, pull out the Out-tray extension, and
then unfold the Out-tray extension stop.
10
Page 11
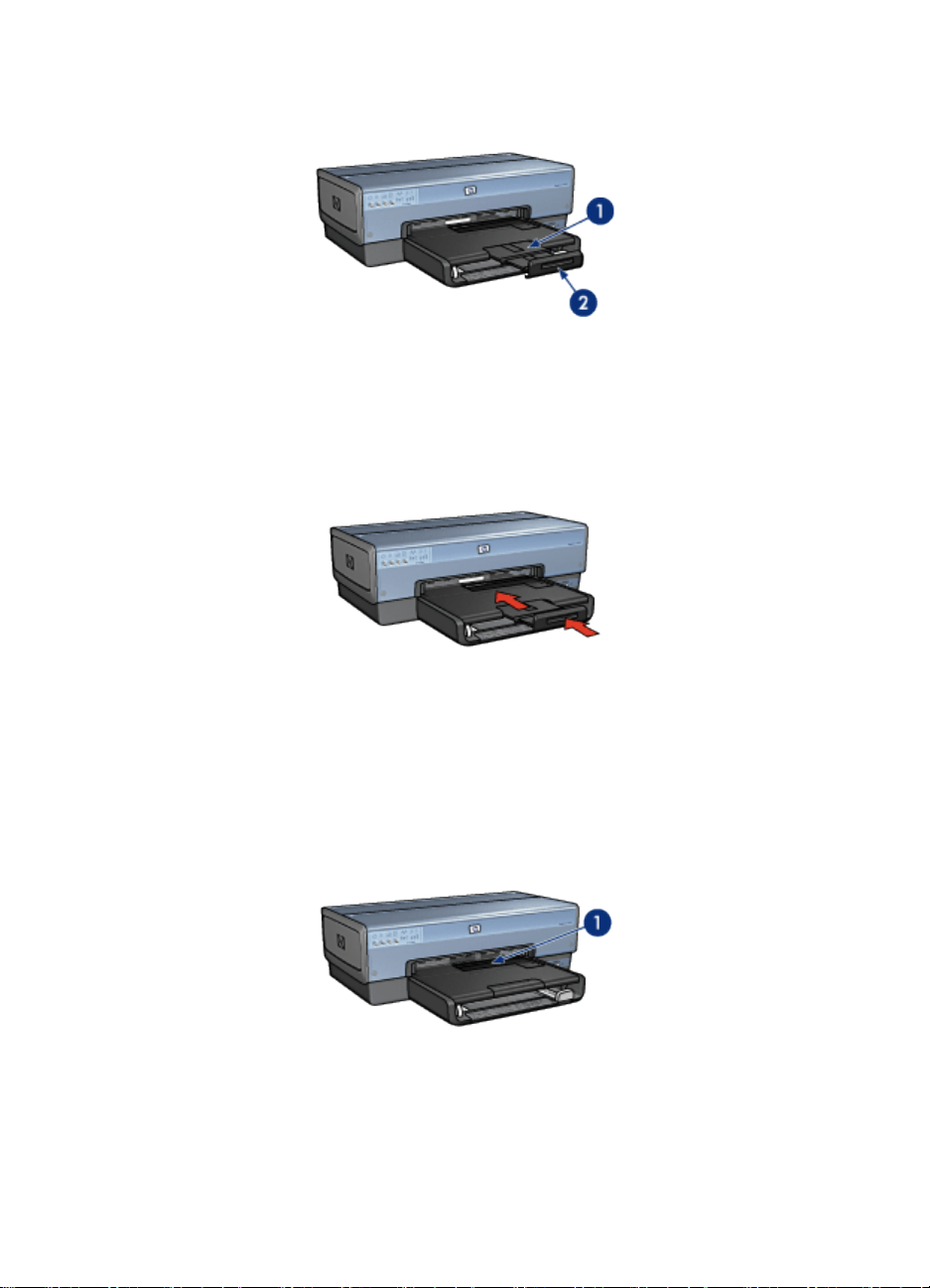
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. Out-tray extension
2. Out-tray extension stop
Do not unfold the Out-tray extension stop when printing on legal paper.
After the print job is complete, fold the Out-tray extension stop, and then push the
Out-tray extension into the Out tray.
4.5 Photo/envelope feeder
Use the photo/envelope feeder to print the following documents:
• Envelopes
• Photos
• Postcards
1. Photo/envelope feeder
11
Page 12

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Envelopes
Follow these steps to use the photo/envelope feeder for single envelopes:
1. Insert the envelope with the side to be printed on facing down and the flap to
the left.
2. Push the envelope into the printer as far as it will go without bending.
3. Print the envelope.
Photos
Follow these steps to use the photo/envelope feeder to print a single photo:
1. Insert the photo paper into the photo/envelope feeder with the side to be printed
on facing down.
2. Gently push the photo paper into the photo/envelope feeder as far as it will go
without bending.
3. Slide the photo/envelope feeder forward as far as it will comfortably go.
Note: If the photo paper touches the back of the paper tray, you have pushed
the feeder in as far as it needs to go.
12
Page 13

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
4. Print the photo.
Postcards
Follow these steps to use the photo/envelope feeder to print a single postcard:
1. Insert the postcard into the photo/envelope feeder with the side to be printed
on facing down.
2. Gently push the postcard into the photo/envelope feeder as far as it will go
without bending.
3. Slide the photo/envelope feeder forward as far as it will go.
4. Print the postcard.
13
Page 14

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
4.6 Print cartridges
Four print cartridges are available for use with the printer.
1. Black
2. Tri-color
3. Photo
4. Gray photo
Note: The availability of print cartridges varies by country/region.
Using print cartridges
Everyday printing
Use the black and tri-color print cartridges for everyday print jobs.
Quality color photos
For more vibrant colors when printing color photographs or other special documents,
remove the black print cartridge and use a photo print cartridge in combination with
the tri-color print cartridge.
Quality black and white photos
For outstanding black and white photographs, remove the black print cartridge and
use a gray photo print cartridge in combination with the tri-color print cartridge.
Replacing print cartridges
When buying print cartridges, look for the print cartridge selection number.
You can find the selection number in these places:
• Selection number label: Look at the label on the print cartridge that you are
replacing.
14
Page 15
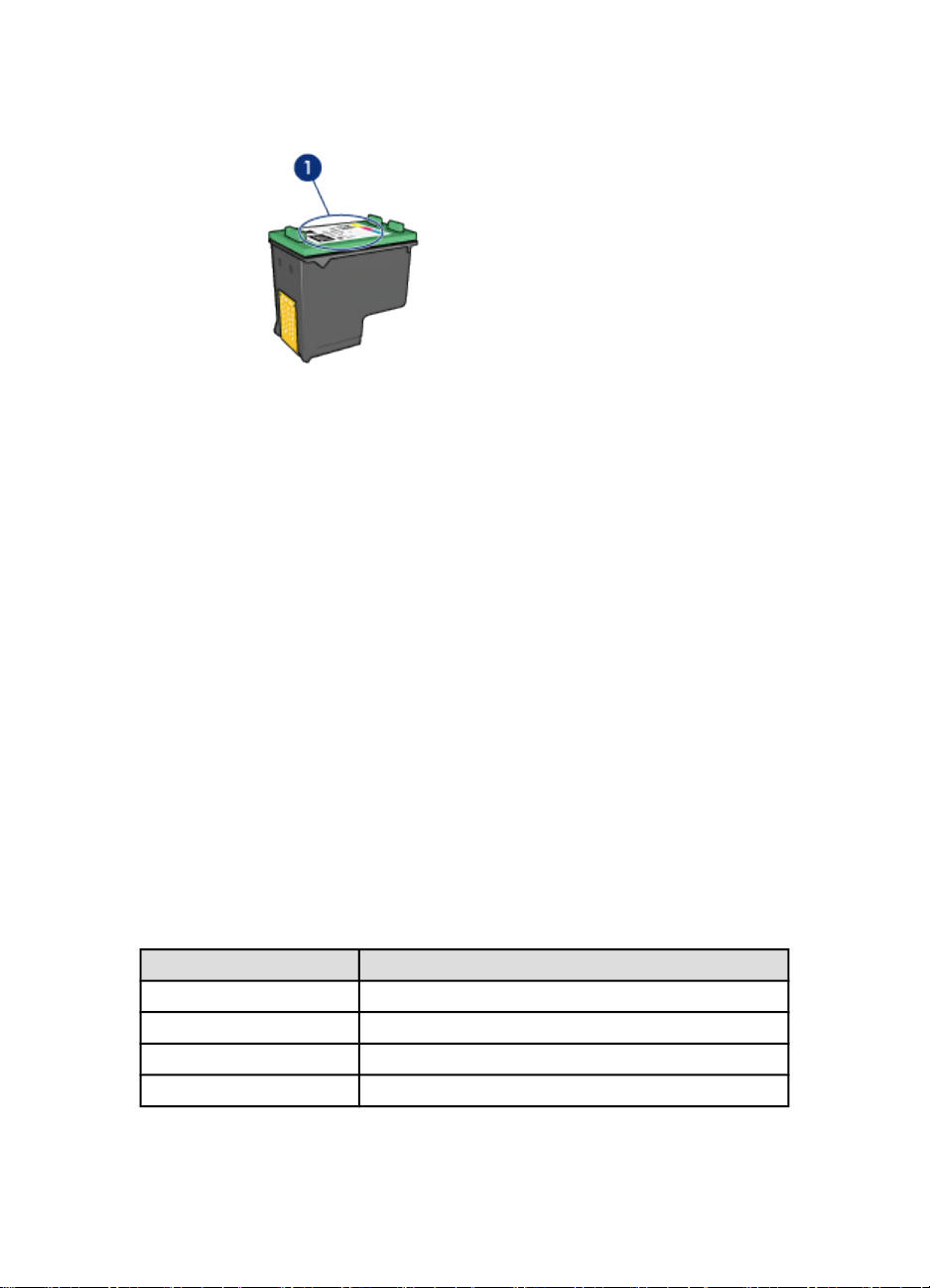
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. Selection number label
• Printer documentation: For a list of print cartridge selection numbers, see the
reference guide that came with the printer.
• HP Inkjet Toolbox: Open the HP Inkjet Toolbox, and then select the Supplies
panel.
If a print cartridge runs out of ink, the printer can operate in the ink-backup mode.
For information about installing a print cartridge, see the print cartridge installation
page.
4.7 Ink-backup mode
In the ink-backup mode, the printer operates by using only one print cartridge. The
ink back-up mode is initiated when a print cartridge is removed from the print
cartridge cradle.
To remove a print cartridge, see the print cartridge installation page.
Ink-backup mode output
Printing in ink-backup mode slows the printer and affects the quality of printed
documents.
Installed print cartridge Result
Black print cartridge. Colors are printed as grayscale.
Tri-color print cartridge. Colors print but black is grayed and is not a true black.
Photo print cartridge. Colors are printed as grayscale.
Gray photo print cartridge. Colors are printed as grayscale.
15
Page 16

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Note: It is recommended that you do not use the photo print cartridge or the gray
photo print cartridge for ink-backup mode.
Exiting ink-backup mode
Install two print cartridges in the printer to exit the ink-backup mode.
To install a print cartridge, see the print cartridge installation page.
4.8 Automatic Paper-Type Sensor
The Automatic Paper-Type Sensor automatically selects the appropriate print
settings for the media that is being printed on, particularly HP media.
When the Automatic Paper-Type Sensor is engaged, the printer scans the first page
of a document with a red optical sensor light to determine the best paper-type
setting. After the printer determines the paper-type setting, the page is printed.
Do not place the printer in direct sunlight. Direct sunlight can interfere with the
Automatic Paper-Type Sensor.
To use the Automatic Paper-Type Sensor, see the paper-type selection page.
Note: The Automatic Paper-Type Sensor is not available for documents that are
printed from the 250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory or the Auto Two-
Sided Print Accessory with Small Paper Tray.
16
Page 17

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5 Connecting to the printer
• Connecting a digital camera
• USB
• Wireless networking
• Wired networking
5.1 Printing photos from a digital camera
Learn how to print photos directly from a digital camera:
• PictBridge description
• PictBridge printing instructions
• PictBridge troubleshooting
• Using the Auto Two-Sided Print Accessory with Small Paper Tray and
PictBridge
5.2 USB
The printer connects to the computer with a Universal Serial Bus (USB) cable.
For instructions on connecting the printer with a USB cable, see the reference guide
or setup poster that came with the printer.
5.3 Wireless networking
For setup information, click one of the following options:
• Wireless network basics
• Wireless security
• Installing the printer on a wireless network
17
Page 18

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
For a description of the printer's wireless feature, click one of the following options:
• Wireless Status light and Signal Strength indicator
• Report Page button
• Network icon
• Wireless radio
• HP Report page
• Embedded Web server (EWS)
Other information:
• Resetting the printer to the factory defaults
• Troubleshooting
• Glossary
5.3.1 Wireless networking basics
The printer's built-in wireless communications feature allows you to connect the
printer directly to an 802.11g or 802.11b Wi-Fi wireless network without the aid of
an external print server.
To install the printer on a wireless network, follow the wireless installation
instructions.
Wi-Fi
802.11g and 802.11b
Wi-Fi is a wireless communications technology that allows you to connect
computers and other devices (such as printers) to each other and the Internet
without the use of wires. The printer is compatible with two types of Wi-Fi technology:
802.11g and 802.11b.
Both 802.11g and 802.11b operate by radio transmission in the 2.4 gigahertz per
second (GHz) frequency band. 802.11g devices communicate at a maximum speed
of 54 megabits per second (Mb/s). 802.11b devices communicate at a maximum
speed of 11 Mb/s.
In infrastructure mode, the printer operates in either 802.11g or 802.11b mode,
depending on the wireless network. In ad hoc mode, the printer defaults to 802.11b
mode.
802.11a
802.11a is an emerging wireless networking technology that operates in the 5 GHz
frequency band and offers communication speeds similar to those of 802.11g. The
printer cannot communicate with 802.11a devices over a wireless connection.
18
Page 19

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
If you have an 802.11a wireless network, you must use an Ethernet cable to connect
the printer to the network's Wireless Access Point (WAP) in order to achieve a
processing speed comparable to that of the 802.11a network.
To connect the printer to an Ethernet network, follow the Ethernet network
installation instructions.
Adapters and access points
Adapters
While some devices, such as the printer, have built-in Wi-Fi capability, other devices
need an adapter to become Wi-Fi-enabled.
AirPort® cards are available from Apple for Macintosh products. See the card
documentation for installation and configuration instructions.
Access points
A common variety of wireless network is called an infrastructure network. An
infrastructure network requires the use of a Wireless Access Point (WAP).
A WAP acts as a central hub for a wireless network or as a router connecting the
wireless network to another network (such as the Internet or an Ethernet network).
Devices on the network communicate through the WAP.
Macintosh users may use an AirPort® Base Station as a WAP.
Reducing interference in a wireless network
The following tips will help reduce the chances for interference in a wireless network:
19
Page 20

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
• Keep the wireless devices away from large metal objects, such as filing
cabinets, and other electromagnetic devices, such as microwaves and cordless
telephones, as these objects can disrupt radio signals.
• Keep the wireless devices away from large masonry structures and other
building structures as these objects can absorb radio waves and lower signal
strength.
• For an infrastructure network, position the WAP in a central location in line of
sight with the wireless devices on the network.
• Keep all wireless devices on the network within range of one another.
Wireless network examples
To see some examples of wireless networks, see the wireless network examples
page.
Communication modes
There are two types of communication modes for wireless devices:
• Infrastructure mode
• Ad hoc mode
Infrastructure mode
When the printer is set to the infrastructure communication mode, the printer
communicates with other devices on the network, whether the devices are wired or
wireless, through a Wireless Access Point (WAP). WAPs commonly act as
routers or gateways on small networks.
In infrastructure mode, the printer automatically detects whether the wireless
network uses 802.11b or 802.11g.
Ad hoc mode
When the printer is set to the ad hoc, or computer-to-computer, communication
mode, the printer communicates directly with other wireless devices on the network
without the use of a WAP.
20
Page 21

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
The ad hoc communication mode defaults to 802.11b. Follow these steps to use
802.11g in ad hoc mode:
1. Open the printer's embedded Web server (EWS).
2. Click the Networking tab.
3. Under Connection, click Wireless (802.11).
4. Click the Advanced tab.
5. Under Compatibility, clear the In an ad hoc network use 802.11b behavior
check box.
6. Click Apply, and then close the EWS.
Wireless network settings
Devices (such as computers and printers) on a wireless network must share the
following settings:
Network name (SSID)
A network name, or “Service Set Identifier (SSID),” identifies a particular wireless
network. In order to operate on a network, a device must know the network's network
name.
For an in-depth explanation of network names, see the network names page.
Network locations
A network location is a set of network settings unique to a given wireless network.
A wireless device might have network locations for several wireless networks. In
order to use the printer, the computer must be set to the network location for the
printer's wireless network.
For example, a computer that is used both at work and at home, might have one
network location for a wireless network at work and another network location for a
wireless network at home.
The printer does not support multiple network locations.
For an in-depth explanation of network locations, click here.
Wireless security
Devices on a wireless network must share the same security settings.
21
Page 22
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
For a description of the wireless security options available for the printer, see the
wireless security page.
Printing
Computers on the network send print jobs directly to the printer, which prints them
in the order received.
The printer can accept print jobs sent simultaneously from four users.
For example, if five users each send a print job to the printer at the same time, the
printer accepts four of the print jobs and rejects the fifth. The user who sent the fifth
print job should wait a few minutes and then resend the print job.
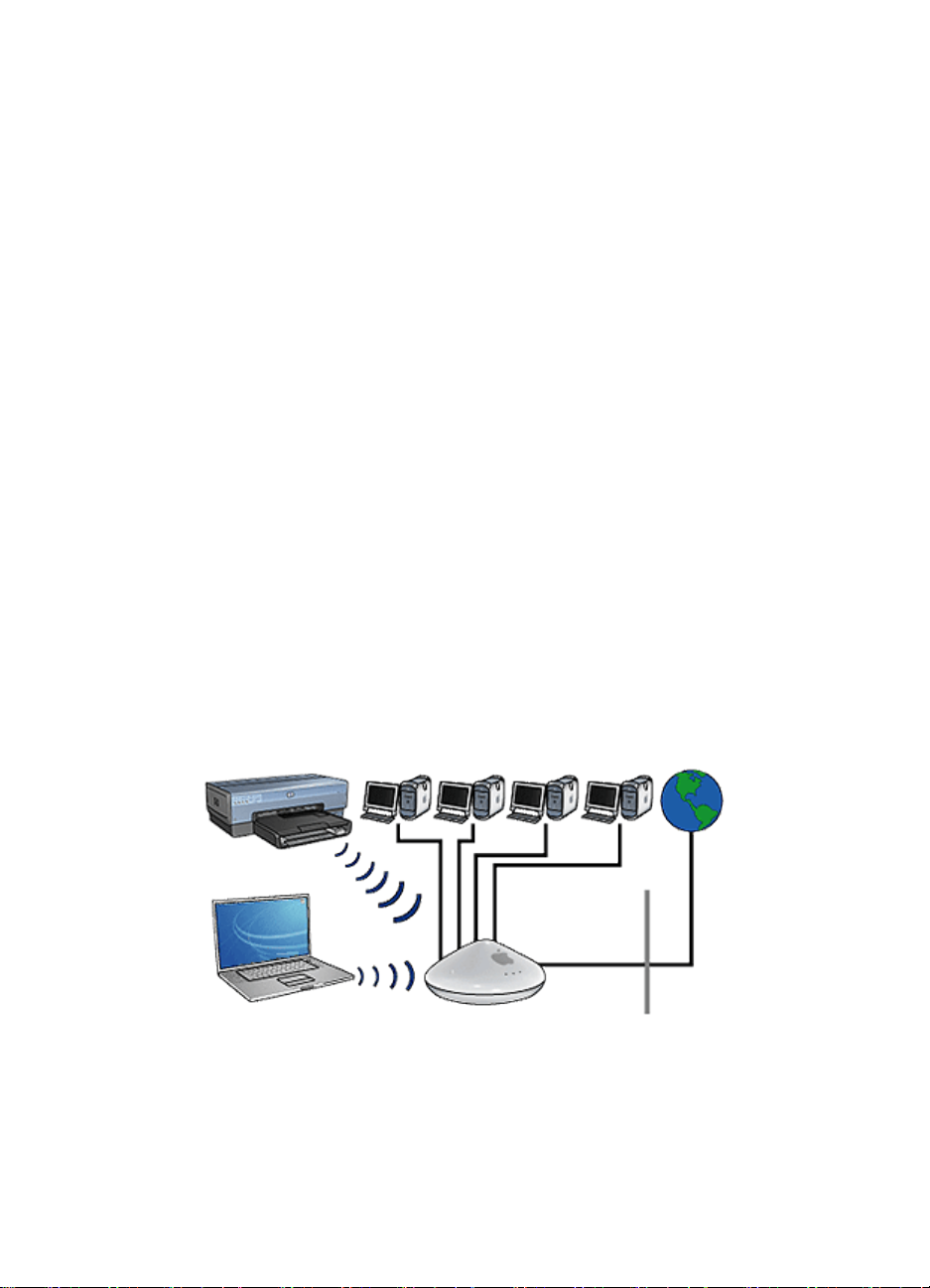
5.3.2 Wireless network examples
There are three common configurations for wireless networks:
• Ad hoc
• Infrastructure
• Mixed wired and wireless
Ad hoc networks
An ad hoc network, also called a computer-to-computer network, is a type of
wireless network in which devices directly communicate with each other rather than
through a Wireless Access Point (WAP).
For example, a simple ad hoc wireless network might consist of a laptop and a printer
communicating directly with one another.
Ad hoc networks are typically small and simple. Performance on these types of
networks can degrade if more than six devices are on the network.
22
Page 23
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
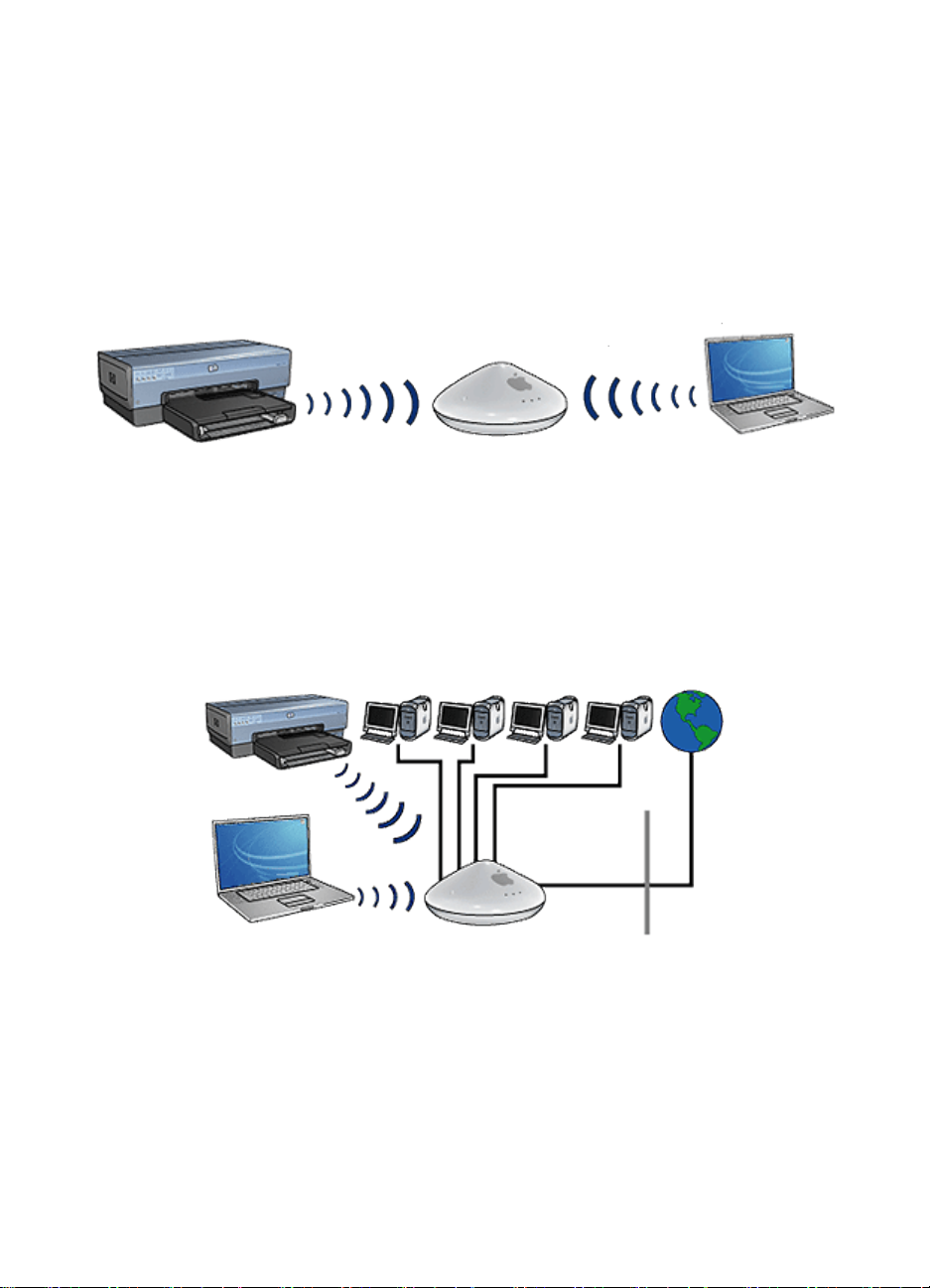
Infrastructure networks
On an infrastructure network, devices, such as computers and printers,
communicate through a Wireless Access Point (WAP). WAPs commonly act as
routers or gateways on small networks.
For example, a simple infrastructure wireless network might consist of a laptop and
a printer communicating through a WAP.
Mixed wired and wireless networks
Wireless devices often exist on a largely wired network.
In this case, a WAP is connected to the main network by an Ethernet cable plugged
into the WAP's WAN port. The WAP acts as the go-between for the wired devices
and the wireless devices. The wired devices communicate with the WAP over the
Ethernet cable, while the wireless devices communicate with the WAP over radio
waves.
For example, a mixed wired and wireless network may consist of the following:
• Several desktop computers
• A WAP connected to an Ethernet network
• A printer connected wirelessly to the WAP
In order to use the printer, a desktop PC sends a print job over the Ethernet cable
to the WAP. The WAP then wirelessly transmits the print job to the printer.
23
Page 24

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5.3.3 Network locations
A network location is a set of network settings unique to a given wireless network.
Many wireless devices have configuration utilities that allows the device to have
network locations for several wireless networks. In order to use the printer, the
computer must be set to the network location for the printer's wireless network.
Use the Network control panel to create and edit network locations.
Note: Not all wireless devices support multiple network locations.
The printer only supports one network location.
Example
A person uses the same wireless-enabled laptop at work and at home. They have
one wireless network at work, and another wireless network at home.
Each network has a unique set of wireless settings. The person creates the following
network locations on the laptop:
• at_work: Contains the network settings for the office wireless network
• at_home: Contains the network settings for the home wireless network
Where the wireless network is Network location settings
Office
at_work
• Network name: office
• Communication mode: infrastructure
• Security: WPA
24
Page 25
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Where the wireless network is Network location settings
Home
at_home
• Network name: home
• Communication mode: ad hoc
• Security: WEP
When the laptop is being used at work, the person must set the network location to
at_work in order to connect to the office network.
Conversely, the laptop must be set to the at_home network location when the person
is at home and wants to connect the laptop to the home network.
5.3.4 Network name (SSID)
A network name, or “Service Set Identifier (SSID)”, identifies a particular wireless
network. In order to operate on a network, a device must know the network's network
name.
A wireless network only has one network name.
A given location, such as an office, may have several wireless networks, each with
a different network name. Wireless devices use network names to identify
overlapping wireless networks.
Example
The printer is in an office with two wireless infrastructure networks. Each network
has a Wireless Access Point (WAP).
Note: In this example, both wireless networks have the same security settings.
25
Page 26

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. Network name equals “network_1”
2. Network name equals “network_2”
The network name for one wireless network is network_1. The network name for
the other wireless network is network_2.
The printer receives signals from both networks, network_1 and network_2.
The printer is configured for network_1
The printer's network name (SSID) setting has been configured for network_1. The
printer can only communicate to network_1. In other words, the printer can only
accept print jobs from network_1.
The printer communicates with network_1.
The laptop is configured for network_2
The laptop's network name (SSID) settings have been configured for network_2.
The laptop is unable to communicate with the printer and cannot send print jobs to
the printer.
The laptop cannot communicate with the printer.
The laptop is reconfigured for network_1
The laptop's network name (SSID) settings have been reconfigured for network_1.
The laptop is able to communicate with the printer and is ready to send print jobs to
network_1.
26
Page 27

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
The laptop and the printer can communicate.
5.3.5 Wireless security
The printer can be configured for several wireless security options depending on
the type of wireless network of which the printer is part.
Infrastructure networks
• WPA
• WEP
• Open system
Ad hoc networks (computer-to-computer)
• WEP
• Open system
Wireless security basics
For more information about wireless security, see the authentication and encryption
page.
5.3.6 Authentication and encryption
Wireless security is a complex and developing topic. This page gives a brief
overview of the basics involved in making a wireless network secure.
In the simplest terms, wireless security involves two strategies: authentication and
encryption.
A wireless security method, such as WEP or WPA, involves varying levels of
authentication and encryption.
27
Page 28
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Authentication
Definition
Authentication verifies the identity of a user or device before granting access to a
network, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to access network
resources.
In order to be authenticated and allowed to use a network, a device must supply a
known password to other devices on the network. If the device cannot supply the
correct password, then it will not be able to use other devices on the network.
Types of authentication
The printer supports three types of authentication. Each type of authentication has
its benefits and limitations.
Authentication type Description Benefits Limitations
Devices on a
Shared Key
WPA/PSK
network identify
themselves with
the network
name (SSID)
only.
Devices use a
shared master
secret to identify
themselves as
authorized
members of the
network.
Devices use a
single pre-shared
key (PSK) to
identify
themselves as
authorized
members of the
network and to
generate an
encryption key.
Least complicated
strategy.
Convenient to use in
conjunction with
WEP, since a WEP
key can serve as the
shared
authentication key.
The pre-shared key
and the encryption
keys are not
identical.
Allows smaller
networks to use
WPA without the
need for an
authorization
server.
Provides little
protection against
unauthorized users.
All devices must
have the key.
The shared key
does not change
automatically.
All devices must
have the key.
28
Page 29
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Encryption
Definition
Encryption involves using a password to encode data sent over a wireless network
in order to make the data unintelligible to eavesdroppers. Only devices that know
the password can decode the data.
Types of encryption
The printer supports four types of encryption. Each type of encryption has its
benefits and limitations.
Encryption type Description Benefits Limitations
WEP
encryption
Devices on a
network do not
encrypt data.
Devices on a
network share a
password, called a
“WEP key” to
encode and decode
data.
Least complicated
strategy.
Simplest strategy
that provides
encryption.
Provides no
protection against
eavesdroppers.
All devices must
have the key.
The WEP key does
not change
automatically.
WEP encryption
provides less
security than both
AES or TKIP.
29
Page 30
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Encryption type Description Benefits Limitations
Advanced
Encryption Standard
(AES) is a U.S.
government
sponsored
encryption method
AES
TKIP
that uses a complex
algorithm called
“Rijndael.”
AES uses
encryption keys to
encode data. AES
automatically
changes the
encryption keys
after a certain time
interval, thus making
the wireless network
less vulnerable to
eavesdropping.
Temporal Key
Integrity Protocol
(TKIP) uses
encryption keys to
encode data. TKIP
automatically
changes the
encryption keys
after a certain time
interval, thus making
the wireless network
less vulnerable to
eavesdropping.
Since the
encryption key
changes
automatically, the
data is more difficult
for eavesdroppers
to decode.
Since the
encryption key
changes
automatically, the
data is more difficult
for eavesdroppers
to decode.
All devices must
have the key.
All devices must
have the key.
5.3.7 Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) provides security by doing the following:
• Encrypting data sent over radio waves from one wireless device to another
wireless device
• Controlling access to network resources through authentication protocols
Only devices that share the same WPA settings as the printer will be able to
communicate with the printer.
30
Page 31

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
For example, if the printer's network uses WPA, only devices that have the same
WPA settings as the printer will be able to use the printer.
WPA provides better security than WEP.
WPA is a network feature
WPA is an optional wireless network feature. Not all wireless networks use WPA.
Configure the printer for WPA only if the printer's network uses WPA. The printer's
WPA settings must match the network's settings.
If the printer's network does not use WPA, then do not configure the printer to use
WPA.
If you do not know if your network uses WPA, consult the configuration utility for
your computer's NIC card or your network's Wireless Access Point (WAP).
Encryption
WPA uses encryption keys to encode data.
The printer supports two types of WPA encryption: TKIP and AES.
For more information about TKIP and AES, see the authentication and encryption
page.
Configuring the printer to use WPA
Follow these steps to configure the printer to use WPA:
1. Open the printer's embedded Web server (EWS).
2. Click the Networking tab.
3. Under Connections, click Wireless (802.11).
4. On the Wireless Setup tab, click the Start Wizard button, and then follow the
onscreen instructions
5. After configuring the printer, close the EWS.
5.3.8 Wired equivalent privacy (WEP)
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) provides security by encrypting data sent over
radio waves from one wireless device to another wireless device.
WEP can also provide security through authentication. For more information about
authentication and encryption, see the authentication and encryption page.
WEP encodes the data sent across the network making the data unintelligible to
eavesdroppers. Only devices that share the same WEP settings as the printer will
be able to communicate with the printer.
31
Page 32

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
For example, if the printer's network uses WEP, only devices that have the same
WEP settings as the printer will be able to use the printer.
WEP is a network feature
WEP is an optional wireless network feature. Not all wireless networks use WEP.
Configure the printer for WEP only if the printer's network uses WEP. The printer's
WEP settings must match the network's settings. If your network has WEP, you
must use an Ethernet cable to connect the printer to the network in order to install
the printer software.
If the printer's network does not use WEP, then do not configure the printer to use
WEP.
If you do not know if your network uses WEP, consult the configuration utility for
your computer's NIC card or your network's Wireless Access Point (WAP).
WEP keys
Devices on a WEP-enabled network use WEP keys to encode data.
WEP keys can also be used for authentication.
After creating a set of WEP keys, record and store the keys in a secure location.
You may not be able to retrieve the WEP keys if you lose them.
Caution: If you lose the WEP keys, you will not be able to add a new device
to your network without reconfiguring the WEP settings for every device on
the network.
A WEP-enabled network might use multiple WEP keys. Each WEP key is assigned
a key number (such as Key 2). Each device on the network must recognize all the
network's WEP keys and the key number assigned to each WEP key.
Configuring the printer to use WEP
Follow these steps to configure the printer to use WEP:
1. Open the printer's embedded Web server (EWS).
2. Click the Networking tab.
3. Under Connections, click Wireless (802.11).
4. On the Wireless Setup tab, click the Start Wizard button, and then follow the
onscreen instructions
5. After configuring the printer, close the EWS.
32
Page 33

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5.3.9 Open system
A wireless network that does not use any authentication or encryption method is
referred to as an “open system.”
An can still have a minor level of security if the network's wireless access point(s)
does not broadcast the network's network name (SSID). A device trying to join the
network must then know the network name before connecting.
For more information about network names, see the network name (SSID) page.
An is highly vulnerable to eavesdropping and intrusion.
Configuring the printer for an open system
Follow these steps to configure the printer for an open system:
1. Open the printer's embedded Web server (EWS).
2. Click the Networking tab.
3. Under Connections, click Wireless (802.11).
4. On the Wireless Setup tab, click the Start Wizard button, and then follow the
onscreen instructions
5. After configuring the printer, close the EWS.
5.3.10 Installing the printer on a wireless network
For instructions on installing the printer on a wireless network, see the network guide
that came with the printer.
5.3.11 Wireless Status light
The Wireless Status light indicates the status of the printer's internal wireless
communications radio.
State of the Wireless Status light Printer status
Able to receive and transmit data
wirelessly.
On
33
Page 34

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
State of the Wireless Status light Printer status
Is not able to receive and transmit
data wirelessly.
Off
Receiving data.
Flashing
Signal Strength indicator
The Signal Strength indicator shows the strength of the radio signal that the printer
is receiving. When all bars are illuminated, the signal is strong. When no bars are
illuminated, the signal is weak.
5.3.12 Report Page button
Use the Report Page button to do the following:
• Print an HP Report page
• Reset the printer to the factory defaults
34
Page 35

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. Report Page button
5.3.13 Network icon
The Network icon illuminates when the printer is connected to:
• An Ethernet network
• An active wireless network
• An active wireless direct-connection to a computer or other wireless device
Status of the icon
On
Off
Status of the printer network
connection
Connected to either an Ethernet
network or a wireless network.
Not connected to an Ethernet
network or a wireless network.
35
Page 36

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5.3.14 Wireless radio
The printer has an internal wireless radio for wireless communication.
How the wireless radio works
The wireless radio broadcasts on the 2.4 GHz frequency whenever the wireless
radio is powered on and enabled.
The wireless radio automatically turns off when the printer is powered off or
unplugged from a power source.
If the printer is connected to an active Ethernet network with an Ethernet cable, the
wireless radio remains active, but the printer does not attempt to make a wireless
connection.
Note: USB connections have no effect on the radio's functionality.
Wireless Status light
The Wireless Status light indicates the status of the wireless radio. For a description
of the Wireless Status light, see the Wireless Status light page.
Disabling and enabling the wireless radio
Disabling the radio turns the wireless radio off. When disabled, the wireless radio
sends no signals even if the printer is powered on.
Enabling the radio turns the wireless radio on. When enabled, the wireless radio
sends signals if the printer is powered on.
Disabling the wireless radio
Follow these wireless steps to disable the radio:
1. Verify that the printer is powered on and is idle.
2. Press and hold down the Report Page button.
3. While holding down the Report Page button, press the Cancel button once, and
then press the Resume button once.
4. Release the Report Page button.
Enabling the wireless radio
Follow these steps to re-enable the wireless radio:
1. Verify that the printer is powered on and is idle.
2. Press and hold down the Report Page button.
3. While holding down the Report Page button, press the Cancel button once.
4. Release the Report Page button.
36
Page 37

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5.3.15 HP Report page
The HP Report page supplies useful information about the printer's wireless,
wired, and PictBridge connections.
Printing an HP Report page
To print an HP Report page, verify that the printer is powered on and idle, and then
press the Report Page button once.
If the printer has just been connected to a network, wait a few minutes before printing
the HP Report page to allow the printer to obtain valid settings.
Selecting the language
The default language for the HP Report page is English. Follow these steps to print
the page in another language:
1. Press the Report Page button to print the English version of the page.
2. On the lower portion of the page, find the language that you want.
3. To print the page in that language, follow the instructions that correspond to the
language.
For example, to print the page in French, press and hold down the Report
Page button, press the Resume button twice, and then release the Report
Page button.
Understanding the HP Report page
The HP Report page lists the following information that you might frequently need
to know:
General information
General information applies to both Ethernet and wireless networks:
37
Page 38

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Item Meaning
The printer's network status:
Network Status
Active Connection Type
URL
Hardware Address (MAC) The printer's Media Access Control (MAC) address.
Firmware Revision
Host Name The printer's host name on the network.
IP Address The printer's current IP address on the network.
Subnet Mask The printer's subnet mask.
Default Gateway The printer's gateway address.
Configuration Source
DNS Server
mDNS
Admin Password
• Ready: The printer is ready to print.
• Offline: The printer is not connected to a network.
The type of network the printer is connected to:
• Wired: The printer is connected to an Ethernet
network.
• Wireless: The printer is connected to a wireless
network.
• Disabled: The printer is not connected to a
network.
The address to use in order to open the printer's
embedded Web server.
Revision number of the printer's internal software.
This item may be requested by HP Service and
Support.
How the printer obtained its IP address:
• Automatic: AutoIP or DHCP
• Manual: Static IP address
The IP address of the printer's domain name server.
Not Specified means that no IP address has been set.
This setting does not apply to the printer.
The printer's mDNS service name on the network.
This name is used by Apple Rendezvous to identify the
printer on Mac OS X v10.2.3 and higher.
Indicates whether the printer's embedded Web server
is password protected.
• Set: A password is required.
• Not Set: A password is not required.
38
Page 39

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Item Meaning
The network link configuration:
• 802.11
Link Config
802.11 wireless
The 802.11 wireless information applies only to the printer's wireless connection:
Item Meaning
Wireless Status
Communication Mode
Network Name (SSID) The SSID setting to which the printer is set.
Signal Strength (1-5 highest)
• 10T-Full
• 10T-Half
• 100TX-Full
• 100TX-Half
The printer's wireless network status:
• Connected: The printer is connected to the
wireless network.
• Disconnected: The printer is not connected to
the wireless network.
• Disabled: The wireless radio is off and the
printer is connected to an Ethernet network.
The communication mode to which the printer is
configured.
• Infrastructure
• Ad hoc
The strength of the 802.11 radio signal the printer
is receiving:
• 1 through 5: 5 indicates an excellent signal; 1
indicates a poor signal.
• Not applicable: The printer is set to ad hoc
communication mode or the wireless network
is disabled.
39
Page 40

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Item Meaning
One of several pre-set frequencies at which
802.11b-enabled devices communicate in order to
reduce interference.
Channel
Authentication Type
Encryption
Access Point HW address
The number of channels available varies by
country/region.
Not applicable means that the wireless network is
disabled.
The printer's authentication setting:
• Open System: No authentication is being used.
• Shared Key: The printer is using a WEP key for
authentication.
• WPA-PSK: Authentication that uses a PreShared Key (PSK). Used as part of WPA for
small networks.
• None: No authentication is in use.
• 64-bit WEP: Printer is configured with a fivecharacter or 10-digit WEP key.
• 128-bit WEP: Printer is configured with a 13character or 26-digit WEP key.
• AES: An encryption method that can be used
with WPA.
• TKIP: An encryption method that can be used
with WPA.
• None: No encryption is being used.
The MAC address of the Wireless Access Point
(WAP) for the printer's network. This setting applies
only to infrastructure networks. Not applicable
means that the printer is set to ad hoc
communication mode.
Miscellaneous
The Miscellaneous section contains information that applies to Ethernet networks,
wireless connections, and PictBridge connections:
40
Page 41

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Item Meaning
Number of packets sent without error.
Total Packets Transmitted
Total Packets Received
PictBridge Status
PictBridge Last Error
This item may be requested by HP Service and
Support.
Number of packets received without error.
This item may be requested by HP Service and
Support.
• Connected: The printer is connected to a digital
camera.
• Error: Something is wrong with the PictBridge
connection.
The last known error to occur in the printer PictBridge
function since the printer was last turned on.
5.3.16 Embedded Web server (EWS)
The embedded Web server (EWS) provides a simple way to manage your printer
on a network.
Use the printer's EWS to do the following:
• Check the printer's status.
• Adjust the printer's network configuration.
• Check estimated ink levels in the print
cartridges.
• View network statistics.
• Configure the printer's wireless security
settings.
• Visit HP's Web site for support information and
to purchase supplies.
Caution: It is recommended that the printer and the computers that use it be
on the same subnet. Printer installation across subnets can be problematic
depending on the type of router used.
Before using the EWS, verify that the printer and the computer are powered on and
connected to the network.
Follow these steps to open the EWS:
1. Launch your Internet browser.
41
Page 42

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Use Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher, Netscape 4.75 or higher, or Apple
Safariâ„¢.
2. Enter the printer's IP address in the browser's address box.
Note: If your computer uses a proxy server to access the Internet, you might need
to configure your browser to by-pass the proxy server in order to access
the EWS.
If you do not know the printer IP address, print an HP Report page.
Note: For instructions on using the printer's EWS, see the online help. To open
the online help, click Help under the Other Links heading.
Caution: Use caution when changing the print server's wireless network
settings; you may lose your connection. If you lose your connection, you may
need to use the new settings to reconnect. If the printer loses its network
connection, you may need to reset it to factory defaults and reinstall the
software.
5.3.17 Resetting the printer to the factory default settings
Once the printer is configured for a network, its configuration settings are saved in
its memory.
Resetting the printer to its factory default settings will clear all the settings from the
printer's memory for your network. This should only be done as a last resort when
troubleshooting the printer.
Resetting the printer to its factory default settings may require you to reinstall the
printer software. Additionally, you will also have to reconfigure the printer's security
settings.
The printer's default settings are:
Option Default setting
Communication mode Ad hoc
Network Name (SSID) hpsetup
Encryption None
Wireless radio On
EWS administrator password [blank]
Follow these steps to reset the printer to the factory default settings:
1. Verify that the printer is powered on.
42
Page 43

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
2. Press and hold down the Report Page button.
3. While holding down the Report Page button, press the Cancel button three
times.
4. Release the Report Page button.
5.3.18 Networking glossary
numbers
10/100 Base-T: A technical term for Ethernet. 10/100 refers to the speed at which
the Ethernet network functions. 10 indicates 10 megabits per second (Mb/s) for
normal Ethernet, and 100 indicates 100 Mb/s for Fast Ethernet.
802.11a: A type of wireless networking that provides up to 54 Mb/s transmission in
the 5 GHz band.
802.11b: A type of wireless networking that provides up to 11 Mb/s transmission
(with a fallback to 5.5, 2 and 1 Mb/s) in the 2.4 GHz band.
802.11g: A type of wireless networking that provides up to 54 Mb/s transmission in
the 2.4 GHz band.
a
Ad hoc network: A type of wireless network in which devices directly communicate
with each other rather than through a Wireless Access Point (WAP). Ad hoc
networks are typically small and simple (for example, two wireless PCs or a wireless
PC and a wireless printer). Performance on these types of networks can degrade if
more than six devices are on the network. Ad hoc networks are also known as peerto-peer networks, independent basic service stations (IBSS), or direct-connect
wireless networks.
AES: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a U.S. government sponsored
encryption method that uses a complex algorithm called “Rijndael.” AES uses
encryption keys to encode data. AES automatically changes the encryption keys
after a certain time interval, thus making the wireless network less vulnerable to
eavesdropping.
Authentication: Authentication is a wireless network security strategy. On a network
with authentication, devices use a shared key as a password and communicate only
with devices that know the key. Authentication does not encrypt the data sent
between wireless devices. Authentication can be used in conjunction with WEP.
Authentication keys and WEP keys can be identical.
AutoIP: A process by which a device on a network automatically assigns an IP
address to itself.
43
Page 44

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
b
BOOTP: Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) is an Internet protocol that enables a device
to discover its own IP address, the IP address of a BOOTP server on the network,
and a file to be loaded into memory to boot the machine. This enables the device
to boot without requiring a hard or floppy disk drive.
Broadcast packet: A packet sent from one device on a network to all devices on the
network.
c
Channel: One of several pre-set frequencies at which 802.11b-enabled devices
communicate in order to reduce interference. The number of channels available
varies by country/region.
d
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): A protocol used to automatically
assign an IP address to each device on a network.
e
EAP: Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a general protocol for
authentication that also supports multiple authentication methods, such as token
cards, one-time passwords, certificates, and public key authentication. WPA uses
EAP.
Encryption: A network security that encodes the data sent across a wireless network
making the data unintelligible to eavesdroppers. The printer supports WEP, TKIP,
and AES.
Encryption keys: A sequence of characters or digits that a wireless device uses to
encode data. Encryption keys can be static (as they are in WEP) or dynamic (as
they are in WPA).
Ethernet: A popular form of wired computer networking for Local Area Networks.
Ethernet cable: There are two types of Ethernet cables. A straight-through cable is
the most common and is used to connect devices on a network to a hub or router.
A crossover cable is used to connect two devices that have Ethernet ports but that
are not hubs or routers. Use a CAT-5 cable with an RJ-45 plug to connect the printer
to an Ethernet network.
f
Firewall: A combination of hardware and software tools that protects a network from
unwanted entry.
44
Page 45

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
g
Gateway: A dedicated device (router or computer) that connects two different
networks. For example, a computer on an Ethernet network may act as a gateway
between the network and the Internet.
h
Host name: The name by which the printer identifies itself on the network. The
printer's host name appears on the HP Report page. Use the host name to open
the printer's embedded Web server (EWS).
Hub: A simple device that acts as the center of an Ethernet network. Other devices
on the network are connected to the hub.
i
ICS (Internet Connection Sharing): A Windows program that allows a computer to
act as a gateway between the Internet and a network. ICS uses DHCP to assign IP
addresses. See Windows documentation for more information about ICS.
Internet Sharing: A Macintosh OSX program that allows a computer to act as a
gateway between the Internet and a network. See Macintosh documentation for
more information about Internet Sharing.
IP address (Internet Protocol address): A unique number that identifies a device on
a network. The IP address is often automatically assigned by DHCP or AutoIP.
However, a device can be manually assigned a static IP address.
Infrastructure network: A type of wireless network in which devices communicate
with each other through a Wireless Access Point (WAP), such as a wireless network
hub, router, or gateway.
l
LAN (Local Area Network): A high-speed type of computer network that connects
devices that are a relatively short distance from one another. An Ethernet network
is one type of LAN.
m
MAC address (Media Access Control address): The hardware address for a device
on a network. The printer's MAC address appears on the HP Report page.
Mb/s (megabits per second): The measure for the rate at which a network functions.
For example, 1 Mb/s equals 1,000,000 bits per second (or 125,000 bytes per
second).
45
Page 46

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
mDNS: As an alternative to a Domain Name Server, a device issues a Multicast
Domain Name Server (mDNS) notification to provide information regarding its
service. The notification includes the type of service (such as printing), the name of
the service (such as “your printer”), IP and port addresses, and other necessary
information. Each device on the network receives the notification and stores the
information in a personal DNS server.
n
Network name: A network name is an alphanumeric, case-sensitive character string
that provides basic access control to a wireless network. A network name is also
known as a “Service Set Identifier (SSID).”
p
Packet: A message sent from one device on a network to other devices on the
network.
Protocol: A language that devices on a network use to communicate with each other.
A popular network protocol is TCP/IP.
r
RJ-45: The type of plug at the end of an Ethernet cable.
Router: A complex networking device that directs packets from one network to
another network. A router can act as a gateway between a LAN and the Internet.
s
Static IP address: An IP address that is manually assigned to a device on a network.
A static IP address remains fixed until changed manually. Alternative methods for
assigning IP address are DHCP and AutoIP.
Subnet: A small network that acts as part of a large network. It is recommended that
the printer and the computers that use the printer all be on the same subnet.
Subnet mask: A number that identifies the IP addresses that belong to a subnet.
Switch: A network device that manages network traffic in order to minimize collisions
and maximize speed.
t
TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the network
communication protocol used on the Internet. The printer's built-in networking
feature supports LANs that use TCP/IP.
TKIP: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) is an encryption method used in WPA.
46
Page 47

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
u
Unicast packet: A packet sent from one device on a network to another device on
the network.
w
WEP: Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) provides security by encrypting data sent
over radio waves from one wireless device to another wireless device. WEP
encodes the data sent across the network making the data unintelligible to
eavesdroppers. Only devices that share the same WEP settings as the printer will
be able to communicate with the printer. WEP depends on encryption keys that are
static and provides less security than WPA.
WEP key: A WEP key, or encryption key, is a sequence of alphanumeric characters
or hexadecimal digits. After creating a WEP key, you must remember it or store it
in a secure location. You may not be able to retrieve the WEP key if you lose it. A
WEP key is either 64 or 128 bits long. The first 24 bits of the key are provided
automatically. When creating the WEP key, the person creating the key provides
the remaining bits (40 bits in the case of a 64-bit key, or 104 bits in the case of a
128-bit key).
Wireless Access Point (WAP): A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a device through
which devices (for example, computers and printers) on an infrastructure wireless
network communicate with one another. A WAP is also called a base station.
Wireless profile: A wireless profile is a collection of wireless network settings that
applies to a particular wireless network. For example, a wireless LAN card can have
one profile for a home network and another profile for an office network. When
installing a device on a network, be sure to select the appropriate profile.
WPA: Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) provides security by encrypting data sent over
radio waves from one wireless device to another wireless device and by controlling
access to network resources through authentication protocols. Only devices that
share the same WPA settings as the printer will be able to communicate with the
printer. WPA uses encryption keys that change frequently. WPA provides better
security than WEP.
5.4 Wired Ethernet networking
For setup information, click one of the following options:
• Ethernet basics
47
Page 48

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
• Installing the printer on an Ethernet network
For a description of the printer's Ethernet feature, click one of the following options:
• Ethernet lights
• Report Page button
• Network icon
• HP Report page
• Embedded Web server (EWS)
Other information:
• Resetting the printer to the factory defaults
• Troubleshooting
• Glossary
5.4.1 Ethernet basics
The printer's built-in Ethernet feature allows you to connect the printer directly to
a 10/100 Base-T Ethernet network without the aid of an external print server.
To install the printer on an Ethernet network, follow the Ethernet installation
instructions.
Hardware
Hubs, switches, and routers
On an Ethernet network, devices, such as computers and printers, are each
connected to a network hub, switch, or router.
Hubs, switches, and routers may look similar, but there are important differences:
• Hubs are passive. Other devices on the network plug into the hub in order to
communicate with one another. A hub does not manage the network.
• A switch allows devices on a network to communicate directly with one another
in a smooth and efficient manner. A switch monitors and directs network traffic
in order to allow each transmission the most possible bandwidth. By monitoring
network traffic, a switch minimizes collisions and maximizes speed.
• Routers primarily connect different networks (for example, connecting a home
network to the Internet). Routers are active. Routers have network
administration tools, such as firewalls and DHCP. A router can act as a
gateway, while a hub and a switch cannot.
Cables
Use a CAT-5 Ethernet cable to connect the printer to an Ethernet network. Ethernet
cables have an RJ-45 plug.
48
Page 49

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. RJ-45 plug
Network communication
TCP/IP
Devices on a network communicate with one another using a “language” called a
protocol. The printer is designed to operate on networks that use a popular protocol
called TCP/IP.
IP address
Each device on a network identifies itself with a unique IP address. Most networks
use a software tool, such as DHCP or AutoIP, to automatically assign IP addresses.
Internet connections
Networks may or may not be connected to the Internet.
If you place the printer on a network connected to the Internet, it is recommended
that you use a gateway so that the printer's IP address is assigned through DHCP.
A gateway can either be a router or a Macintosh OSX computer running Internet
Sharing. For more information about Internet Sharing, see the documentation that
came with the computer.
Rendezvous
Rendezvous® is a networking feature available with Mac OS X v10.2 and higher.
Rendezvous allows you to create instant IP-based wired or wireless networks of
computers and devices without any configuration.
For more information about Rendezvous, see the documentation that came with
your computer.
Note: Hewlett-Packard supports Rendezvous for Mac OS X v 10.2.3 and higher.
49
Page 50

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Ethernet network examples
To see some examples of Ethernet networks, see the Ethernet network examples
page.
Printing
Computers on the network send print jobs directly to the printer, which prints them
in the order received.
The printer can accept print jobs sent simultaneously from four users.
For example, if five users each send a print job to the printer at the same time, the
printer accepts four of the print jobs and rejects the fifth. The user who sent the fifth
print job should wait a few minutes and then resend the print job.
5.4.2 Ethernet network examples
These are some common Ethernet network configurations:
Shared Internet connection with a router acting as a gateway
In this example, a router manages the network connections and acts as a
gateway between the network and the Internet.
Shared Internet connection with a computer acting as a gateway
In this example, the network devices are connected to a hub. A Macintosh OSX
computer on the network acts as the gateway between the network and the Internet.
The gateway computer uses Internet Sharing to manage the network connections
and provide Internet access to the other devices.
50
Page 51

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
DSL or cable Internet connection without a gateway
This example looks similar to the first example. However, in this example, the
network devices are connected to a hub, rather than a router. The hub is directly
connected to the Internet.
Caution: HP does not recommend this configuration. If possible, use a
gateway to manage your network's Internet access in order to limit exposure
to viruses and guard against unwanted entry.
Ethernet network without an Internet connection
In this example, the network devices are connected to a hub. Devices use AutoIP
to obtain IP addresses.
5.4.3 Installing the printer on an Ethernet network
Installing the printer on an Ethernet network is a two-part process.
First you must connect the printer to the network. Then you must install the printer
software on each computer that will use the printer.
• Connecting the printer to an Ethernet network
• Installing the printer software
5.4.4 Connecting the printer to an Ethernet network
Follow these steps to connect the printer to an Ethernet network:
1. If necessary, set up the printer hardware.
For printer hardware setup instructions, see the setup poster that came with
the printer.
51
Page 52

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
2. Verify that the printer is powered on.
3. Connect the Ethernet cable to an available port on the network hub or router.
Note: Do not plug the Ethernet cable into a port labeled WAN or Uplink.
4. Connect the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on the back of the printer.
Note: The printer's wireless radio is disabled when a Ethernet cable is
connected to the printer.
5. Do one of the following:
State of the Link light Task
On
Go to step 6.
Off
6. Print an HP Report page.
7. Install the printer software on each computer that will use the printer.
Caution: It is recommended that the printer and the computers that use it be
on the same subnet. Printer installation across subnets can be problematic
depending on the type of router used.
Repeat steps 2 through 4. If the lights are still off, then
verify the following items:
• The printer is powered on.
• The network hub or router is powered on.
• All cable connections are secure.
• You are using an Ethernet cable.
52
Page 53

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5.4.5 Installing the printer software
Before installing the printer software on a networked computer, verify the following
items:
• The printer is set up and powered on.
• The network hub, switch, or router is powered on and functioning properly.
• All computers on the network are powered on and connected to the network.
• The printer is installed on the network.
Software installation
For instructions on installing the printer software, see the network guide that came
with the printer.
5.4.6 Ethernet lights
The printer's Ethernet lights indicate the status of the printer's Ethernet connection.
Link light
The Link light is solid when the printer is connected to an Ethernet network and
powered on.
State of the Link light State of the printer
On
Connected to an Ethernet network and powered on.
The printer's wireless radio is disabled when a Ethernet
cable is connected to the printer.
Off
Not connected to an Ethernet network or powered off.
Activity light
The Activity light flashes when the printer is receiving or transmitting data over the
Ethernet connection.
53
Page 54

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
State of the Activity light State of the printer
Flashing
Receiving or transmitting data over the Ethernet
connection.
Off
Not receiving or transmitting data over the Ethernet
connection.
54
Page 55

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
6 Printing photos from a computer
Select the type of photograph that you want to print:
Borderless Photos
Small borderless photo Large borderless photo Panoramic borderless photo
Photos with a white border
Small photo
with a white border
Enhancing your photos
Learn how to enhance your photographs by using the printer's photo printing
features.
PictBridge
Use the printer PictBridge port to print photos directly from a digital camera.
Large photo
with a white border
Panoramic photo
with a white border
6.1 Enhancing your photos
The printer software offers several features to make printing digital photos easier
and improve photo quality:
• Use the HP digital photography options to touch up photos.
• Achieve the highest resolution with Maximum dpi.
• Use HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semi-gloss to save money and ink when
printing photos.
55
Page 56

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Learn how to add professional touches to your digital photographs:
• Use the photo print cartridge for great colors.
• Use these software options for advanced color settings:
• Color options
• CMYK settings
• Advanced color management
• Use the gray photo print cartridge for outstanding black-and-white photos.
• Print black-and-white photos.
• Print to the edges of the photo paper with borderless printing.
To prevent photo paper from curling, follow the photo paper storage guidelines.
6.2 Printing digital photographs
The printer has several features to improve the quality of digital photographs.
Accessing the digital photography options
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
3. Click the Digital Photo tab.
56
Page 57

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Using the digital photography options
1. Options Menu: Select from the following options:
• Red eye removal: Click On to remove or reduce red-eye in the photograph.
• Digital flash: Adjust the exposure in dark areas of photos to bring out detail.
Click Auto to allow the printer driver to automatically balance lightness and
darkness.
• Contrast enhancement: Adjust the contrast to your preference. Click
Auto to allow the printer driver to automatically balance the contrast.
• SmartFocus: Enhance the image quality and clarity. Click On to allow the
printer driver to automatically sharpen details in the image.
• Smoothing: Soften an image. Click Auto to allow the printer driver to
automatically set the level of smoothing for the image.
• Sharpness: Adjust the image sharpness to your preference. Click Auto to
allow the printer driver to automatically set the level of sharpening for the
image.
6.3 Maximum dpi
The Maximum dpi print quality setting offers 4800 x 1200 optimized dpi printing.
57
Page 58

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
The 4800 x 1200 optimized dpi print mode is the highest quality resolution for this
printer. When 4800 x 1200 optimized dpi is selected in the printer driver, the tri-color
print cartridge prints in the 4800 x 1200 optimized dpi mode (up to 4800 x 1200
optimized dpi color and 1200-input dpi). If a photo print cartridge is also installed,
the print quality is enhanced. A photo print cartridge can be purchased separately
if it is not included with your printer.
Follow these steps to print in the 4800 x 1200 optimized dpi mode:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
3. In the Paper Type drop-down list, click Photo Paper, and then click the
appropriate photo paper type.
4. In the Quality drop-down list, click Maximum dpi.
5. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
6.4 Saving money when printing photos
HP Everyday Photo Paper
To save money and ink when printing photos, use HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semigloss and set the Print quality to Normal.
58
Page 59

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semi-gloss is designed to create quality photos with less
ink.
Note: For higher-quality photos, use HP Premium Plus Photo paper and set the
Print quality to Best or Maximum dpi.
6.5 Photo print cartridge
The photo print cartridge, used in conjunction with the tri-color print cartridge,
provides six-ink, virtually grain-free photos that have exceptional fade resistance.
The photo print cartridge can be purchased separately if it is not included with your
product.
Installing the photo print cartridge
To install the photo print cartridge, remove the black print cartridge from the printer,
and then install the photo print cartridge in the compartment on the right of the print
cartridge cradle.
For more information, see the print cartridge installation page.
Using the photo print cartridge
Follow these steps to print in the six-ink color print mode:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
3. Select the appropriate photo paper type from the Paper Type drop-down list.
4. Select one of the following print-quality modes from the Quality drop-down list.
• Normal
• Best
• Maximum dpi
5. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
59
Page 60

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Storing the photo print cartridge
To maintain the health of the print cartridge, follow the print cartridge storage
guidelines.
6.6 Using color options
Adjusting the color options causes the printed colors to differ from the colors that
appear on your computer monitor.
Follow these steps to set color options:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
3. Verify that ColorSmart/sRGB is selected in the Color drop-down list.
4. Click the Color Options tab.
60
Page 61

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5. Adjust the Saturation, Brightness, and Color Tone to affect how overall colors
are printed.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
6.7 CMYK settings
Follow these steps to specify the CMYK settings:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Click the Paper Type/Quality tab.
3. Click the CMYK tab.
61
Page 62

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
4. Adjust the Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black sliders to specify the level of each
color that is used in printing.
5. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
6.8 Advanced color management
Color management defines the range of colors that can be printed. The printer
software translates the colors of your document from their current color settings to
the color-management option that is selected.
Follow these steps to select a color-management option:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
62
Page 63

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. In the Color drop-down list, click one of the following options:
• AdobeRGB: When printing from a professional application with
AdobeRGB, turn off the color management in the application and allow the
printer software to manage the color space. Use the AdobeRGB setting for
documents or photos that were originally created in the AdobeRGB color
space.
• ColorSync: This option allows the printer driver to manage the color of the
document.
• Managed by application: This option allows the application from which you
are printing to manage the color of the document.
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
6.9 Gray photo print cartridge
The gray photo print cartridge, used in conjunction with the tri-color print cartridge,
prints high-quality black-and-white photographs.
63
Page 64

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
The gray photo print cartridge can be purchased separately if it is not included with
your product.
Installing the gray photo print cartridge
To install the gray photo print cartridge, remove the black print cartridge from the
printer, and then install the gray photo print cartridge in the compartment on the right
of the print cartridge cradle.
For more information, see the print cartridge installation page.
Using the gray photo print cartridge
To use the gray photo print cartridge, follow the steps to print a black-and-white
photo.
Storing the gray photo print cartridge
To maintain the health of the print cartridge, follow the print cartridge storage
guidelines.
6.10 Printing black-and-white photos
You can perform the following tasks with the printer:
• Print a black-and-white photo
• Print a color photo in black-and-white
For great black-and-white photos, install a gray photo print cartridge and a tri-color
printer cartridge in the printer.
Printing a black-and-white photo
To print a photo that is already black-and-white, simply follow the instructions for
the type and size of photo that you want to print.
Printing a color photo in black and white
Follow these steps to print a color photo in black-and-white:
64
Page 65

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
3. In the Color drop-down list, click Grayscale.
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
6.11 Printing borderless photos
Use borderless printing to print to the edges of certain paper types and on a range
of standard paper sizes.
Guidelines
• Do not print borderless documents in ink-backup mode. Always have two print
cartridges installed in the printer.
• Open the file in a software application and assign the image size. Ensure that
the size corresponds to the paper size on which you want to print the image.
Printing
Follow these steps to print a borderless document:
1. Open the file that you want to print.
2. Open the Page Setup dialog box.
65
Page 66

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. Click the appropriate borderless paper size in the Paper Size list.
4. Click OK.
5. Open the Print dialog box.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
If you printed on photo paper that has a tear-off tab, remove the tab to make
the document completely borderless.
6.12 Storing and handling photo paper
Follow these instructions to maintain the quality of your HP brand photo paper.
66
Page 67

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Storage
• Keep unused photo paper in a resealable plastic bag, in the box in which it was
originally packaged. Store the packaged photo paper on a flat surface in a cool
place.
• When you are ready to print, remove only the paper that you plan to use
immediately from the plastic bag. When you have finished printing, return any
unused photo paper to the plastic bag.
• Do not leave unused photo paper in the printer paper tray. The paper might
start to curl, which can reduce the quality of your photographs.
Handling
• Always hold photo paper by its edges. Fingerprints on photo paper can reduce
print quality.
• Verify that the photo paper is not curled. If the photo paper is curled, place the
paper in a plastic bag and gently bend it the opposite direction of the curl until
the paper lies flat. If the problem persists, use photo paper that is not curled.
6.13 Small borderless photos
Guidelines
• For high-quality results, use a photo print cartridge in combination with the tricolor print cartridge.
• For maximum fade resistance, use HP Premium Plus Photo Paper and install
a photo print cartridge in the printer.
• To learn how to use the photo printing features, see the photo enhancing page.
• Use HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semi-gloss to save money and ink when
printing photos.
• Verify that the photo paper that you are using is flat. For information about
preventing photo paper from curling, see the photo paper storage instructions.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 25 sheets.
Preparing to print
To print a single photo, use the photo/envelope feeder.
To print multiple photos, follow these steps:
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Remove the Out tray, and then remove all of the paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
67
Page 68

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
4. Verify that the photo paper is flat.
If the photo paper is not flat, see the photo paper storage instructions.
5. Place the photo paper in the In tray with the side to be printed on facing down.
If you are using a photo paper that has a tear-off tab, verify that the tab is
pointing away from the printer.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
7. Replace the Out tray.
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: The appropriate borderless paper size
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then select the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate photo paper type
• Quality: Best or Maximum dpi
5. If you want to use them, set the HP digital photography options.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
6.14 Large borderless photos
Guidelines
• For high-quality results, use a photo print cartridge in combination with the tricolor print cartridge.
• For maximum fade resistance, use HP Premium Plus Photo Paper and install
a photo print cartridge in the printer.
• To learn how to use the photo printing features, see the photo enhancing page.
68
Page 69

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
• Use HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semi-gloss to save money and ink when
printing photos.
• Verify that the photo paper that you are using is flat. For information about
preventing photo paper from curling, see the photo paper storage instructions.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 25 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray, and then remove all of the paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Verify that the photo paper is flat.
If the photo paper is not flat, see the photo paper storage instructions.
5. Place the photo paper in the In tray with the side to be printed on facing down.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
7. Lower the Out tray.
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: The appropriate borderless paper size
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then select the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate photo paper type
• Quality: Best or Maximum dpi
5. If you want to use them, set the HP digital photography options.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
69
Page 70

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
6.15 Panoramic borderless photos
Guidelines
• For high-quality results, use a photo print cartridge in combination with the tricolor print cartridge.
• For maximum fade resistance, use HP Premium Plus Photo Paper and install
a photo print cartridge in the printer.
• To learn how to use the photo printing features, see the photo enhancing page.
• Use HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semi-gloss to save money and ink when
printing photos.
• Verify that the photo paper that you are using is flat. For information about
preventing photo paper from curling, see the photo paper storage instructions.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 25 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray, and then remove all of the paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Verify that the photo paper is flat.
If the photo paper is not flat, see the photo paper storage instructions.
5. Place the photo paper in the In tray with the side to be printed on facing down.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
Note: Some panoramic paper sizes may extend beyond the edge of the In
tray. When printing on such papers, be sure to slide the paper widthguide firmly against the edge of the paper.
7. Lower the Out tray.
70
Page 71

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: The appropriate borderless paper size
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then select the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate photo paper type
• Quality: Best or Maximum dpi
5. If you want to use them, set the HP digital photography options.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
6.16 Small photos with a white border
Guidelines
• For high-quality results, use a photo print cartridge in combination with the tricolor print cartridge.
• For maximum fade resistance, use HP Premium Plus Photo Paper and install
a photo print cartridge in the printer.
• To learn how to use the photo printing features, see the photo enhancing page.
• Use HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semi-gloss to save money and ink when
printing photos.
• Verify that the photo paper that you are using is flat. For information about
preventing photo paper from curling, see the photo paper storage instructions.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 25 sheets.
Preparing to print
To print a single photo, use the photo/envelope feeder.
To print multiple photos, follow these steps:
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Remove the Out tray, and then remove all of the paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Verify that the photo paper is flat.
71
Page 72

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
If the photo paper is not flat, see the photo paper storage instructions.
5. Place the photo paper in the In tray with the side to be printed on facing down.
If you are using a photo paper that has a tear-off tab, verify that the tab is
pointing away from the printer.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
7. Replace the Out tray.
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: The appropriate paper size
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then select the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate photo paper type
• Quality: Best or Maximum dpi
5. If you want to use them, set the HP digital photography options.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
6.17 Large photos with a white border
Guidelines
• For high-quality results, use a photo print cartridge in combination with the tricolor print cartridge.
• For maximum fade resistance, use HP Premium Plus Photo Paper and install
a photo print cartridge in the printer.
• To learn how to use the photo printing features, see the photo enhancing page.
72
Page 73

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
• Use HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semi-gloss to save money and ink when
printing photos.
• Verify that the photo paper that you are using is flat. For information about
preventing photo paper from curling, see the photo paper storage instructions.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 25 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray, and then remove all of the paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Verify that the photo paper is flat.
If the photo paper is not flat, see the photo paper storage instructions.
5. Place the photo paper in the In tray with the side to be printed on facing down.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
7. Lower the Out tray.
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: The appropriate paper size
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then select the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate photo paper type
• Quality: Best or Maximum dpi
5. If you want to use them, set the HP digital photography options.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
73
Page 74

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
6.18 Panoramic photos with a white border
Guidelines
• For high-quality results, use a photo print cartridge in combination with the tricolor print cartridge.
• For maximum fade resistance, use HP Premium Plus Photo Paper and install
a photo print cartridge in the printer.
• To learn how to use the photo printing features, see the photo enhancing page.
• Use HP Everyday Photo Paper, Semi-gloss to save money and ink when
printing photos.
• Verify that the photo paper that you are using is flat. For information about
preventing photo paper from curling, see the photo paper storage instructions.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 25 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray, and then remove all of the paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Verify that the photo paper is flat.
If the photo paper is not flat, see the photo paper storage instructions.
5. Place the photo paper in the In tray with the side to be printed on facing down.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
Note: Some panoramic paper sizes may extend beyond the edge of the In
tray. When printing on such papers, be sure to slide the paper widthguide firmly against the edge of the paper.
7. Lower the Out tray.
74
Page 75

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: The appropriate paper size
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then select the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate photo paper type
• Quality: Best or Maximum dpi
5. If you want to use them, set the HP digital photography options.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
75
Page 76

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
7 Printing other documents
E-mail Letters Documents Envelopes
Postcards Brochures Greeting cards Transparencies
Labels Index cards Banners Iron-on
transfers
Printing tips
Minimize your cost and effort while maximizing the quality of your printouts by using
these printing tips.
Printer software
Learn about the printer software.
7.1 Email
Guidelines
Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 150 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray.
76
Page 77

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Place plain paper in the In tray, pushing the paper into the printer until it stops.
5. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
6. Lower the Out tray.
Printing
1. If necessary, open the Page Setup dialog box and set the paper size, scaling,
or orientation options.
2. Open the Print dialog box.
3. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
4. In the Paper Type drop-down list, click Automatic or Plain paper.
5. Select the following print settings as appropriate:
• Print quality
• Paper source
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
7.2 Letters
Guidelines
• For help printing on an envelope, see the envelope page.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 150 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, then pull out the paper-length
guide.
4. Place plain paper in the In tray, pushing the paper into the printer until it stops.
77
Page 78

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
1. Letter or A4 paper
Note: If you are using letterhead, verify that the letterhead is facing down
and towards the interior of the printer.
6. Lower the Out tray.
Do not extend the Out-tray extension stop when printing on legal paper.
2. Legal paper
Printing
1. If necessary, open the Page Setup dialog box and set the paper size, scaling,
or orientation options.
2. Open the Print dialog box.
3. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
4. In the Paper Type drop-down list, click Automatic or Plain paper.
5. Select the following print settings as appropriate:
• Print quality
• Paper source
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
7.3 Documents
Guidelines
• Save paper with two-sided printing.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 150 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray.
78
Page 79

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, then pull out the paper-length
guide.
4. Place plain paper in the In tray, pushing the paper into the printer until it stops.
5. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
1. Letter or A4 paper
6. Lower the Out tray.
Do not extend the Out-tray extension stop when printing on legal paper.
2. Legal paper
Printing
1. If necessary, open the Page Setup dialog box and set the paper size, scaling,
or orientation options.
2. Open the Print dialog box.
3. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
4. In the Paper Type drop-down list, click Automatic or Plain paper.
5. Select the following print settings as appropriate:
• Print quality
• Paper source
• Two-sided printing
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
7.4 Envelopes
Guidelines
• Avoid using envelopes that have the following qualities:
• Have clasps or windows
• Have thick, irregular, or curled edges
• Are shiny or embossed
79
Page 80

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
• Are wrinkled, torn, or otherwise damaged
• Align the envelope edges before inserting them in the In tray.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 20 envelopes.
Preparing to print
If you are printing on a single envelope, use the photo/envelope feeder.
If you are printing on multiple envelopes, follow these steps:
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Remove the Out tray, and then remove all paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Place the envelopes, with the sides to be printed on facing down and the flaps
to the left, into the In tray and to the right. Push the envelopes into the printer
until they stop.
5. Slide the paper guides firmly against the envelopes.
6. Replace the Out tray.
Printing
1. If necessary, open the Page Setup dialog box and set the paper size, scaling,
or orientation options.
2. Open the Print dialog box.
3. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
4. In the Paper Type drop-down list, click Automatic or Plain paper.
5. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
80
Page 81

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
7.5 Postcards
If the optional Auto Two-Sided Print Accessory with Small Paper
Tray is attached to the printer, follow the steps for printing
postcards with the Auto Two-Sided Print Accessory with Small
Paper Tray.
Guidelines
• Use only cards and small media that meet the printer paper-size specifications.
For specifications, see the reference guide that came with the printer.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 60 cards.
Preparing to print
To print a single card, use the photo/envelope feeder.
To print multiple cards, follow these steps:
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Remove the Out tray, then remove all paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, then pull out the paper-length
guide.
4. Place the cards, with the sides to be printed on facing down and one of the
short sides pointing towards the printer, into In tray and to the right. Push the
cards into the printer until they stop.
5. Slide the paper guides firmly against the cards.
6. Replace the Out tray.
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: The appropriate paper size
81
Page 82

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Note: To print a borderless card, click the borderless photo size that
matches the card size.
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then select the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate paper type
• Quality: Normal, Best, or Maximum dpi
5. If you want to use them, set the HP digital photography options.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
Note: If an out-of-paper message appears, verify that the cards are
positioned properly in the paper tray.
7.6 Brochures
Guidelines
• Learn to print borderless brochures.
• For great results, use HP Brochure & Flyer Paper.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 25 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, then pull out the paper-length
guide.
4. Place brochure paper in the In tray, pushing the paper into the printer until it
stops.
5. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
82
Page 83

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
6. Lower the Out tray.
Printing
1. If necessary, open the Page Setup dialog box and set the paper size, scaling,
or orientation options.
2. Open the Print dialog box.
3. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then specify the following settings:
• Source: Upper Tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate brochure paper type
• Quality: Normal, Best, or Maximum dpi.
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
7.7 Greeting cards
Guidelines
• Unfold prefolded cards, and then place them in the In tray.
• For great results, use HP Greeting Card Paper.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 30 cards.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray, then remove all paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, then pull out the paper-length
guide.
4. Fan the edges of the greeting cards to separate them, then align the edges.
5. Place the greeting cards in the In tray, with the side to be printed on facing
down. Push the cards into the printer until they stop.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
83
Page 84

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
7. Lower the Out tray.
Printing
1. If necessary, open the Page Setup dialog box and set the paper size, scaling,
or orientation options.
2. Open the Print dialog box.
3. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then specify the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate greeting card paper type
• Quality: Normal, Best, or Maximum dpi.
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
7.8 Transparencies
Guidelines
• For great results, use HP Premium Inkjet Transparency Film.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 30 transparencies.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray, and then remove all paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, then pull out the paper-length
guide.
4. Place the transparencies in the In tray, with the side to printed on facing down
and the adhesive strip facing up and toward the printer.
84
Page 85

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
5. Carefully push the transparencies into the printer until they stop so that none
of the adhesive strips catch on one another.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
7. Lower the Out tray.
Printing
1. If necessary, open the Page Setup dialog box and set the paper size, scaling,
or orientation options.
2. Open the Print dialog box.
3. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then specify the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate transparency film type
• Quality: Normal or Best.
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
7.9 Labels
Guidelines
• Use only labels that are designed specifically for inkjet printers.
• Use only full sheets of labels.
• Verify that the labels are not sticky, wrinkled, or pulling away from the protective
backing.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 30 sheets of labels (use only lettersize or A4-size sheets).
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray, and then remove all paper from the In tray.
85
Page 86

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Fan the edges of the label sheets to separate them, and then align the edges.
5. Place the label sheets in the In tray with the label side facing down. Push the
sheets into the printer until they stop.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the edge of the sheets.
7. Lower the Out tray.
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: A4 or US Letter
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then specify the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or Plain paper
5. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
7.10 Index cards and other small media
Guidelines
• Use only cards and small media that meet the printer paper-size specifications.
For specifications, see the reference guide that came with the printer.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 60 cards.
Preparing to print
To print a single card, use the photo/envelope feeder.
To print multiple cards, follow these steps:
86
Page 87

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Remove the Out tray, then remove all paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, then pull out the paper-length
guide.
4. Place the cards, with the sides to be printed on facing down and one of the
short sides pointing towards the printer, into In tray and to the right. Push the
cards into the printer until they stop.
5. Slide the paper guides firmly against the cards.
6. Replace the Out tray.
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box, and then select the following settings:
• Paper Size: The appropriate paper size
Note: To print a borderless card, click the borderless photo size that
matches the card size.
• Orientation: The appropriate orientation
2. Click OK.
3. Open the Print dialog box.
4. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then select the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or the appropriate paper type
• Quality: Normal, Best, or Maximum dpi
5. If you want to use them, set the HP digital photography options.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
Note: If an out-of-paper message appears, verify that the cards are
positioned properly in the paper tray.
87
Page 88

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
7.11 Banners
Guidelines
• Use HP Banner Paper for great results.
• Remove any perforated strips from the banner paper before loading it in the In
tray.
• Do not exceed the In-tray capacity: up to 20 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Remove the Out tray, and then remove all paper from the In tray.
3. Slide the paper width-guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Place the banner paper in the In tray so that the unattached edge is on top of
the paper stack and pointing toward the printer.
1. Unattached edge
5. Slide the paper-width guide firmly against the paper.
Note: Leave the Out tray off of the printer when printing a banner.
Printing
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box.
2. In the Paper Size drop-down list, click A4 Banner or US Letter Banner.
88
Page 89

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. Click OK.
4. Open the Print dialog box.
5. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then specify the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or Plain paper
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
7.12 Iron-on transfers
Guidelines
• Use HP Iron-on Transfers for great results.
• When printing a mirror image, the text and the pictures are horizontally reversed
from what appears on the computer screen.
• Do not exceed the In tray capacity: Up to 20 sheets.
Preparing to print
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Raise the Out tray.
3. Slide the paper-width guide all the way to the left, and then pull out the paperlength guide.
4. Place iron-on transfer paper with the side to be printed on facing down in the
In tray.
5. Push the paper into the printer until it stops.
6. Slide the paper guides firmly against the paper.
89
Page 90

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
7. Lower the Out tray.
Printing
1. If necessary, open the Page Setup dialog box and set the paper size, scaling,
or orientation options.
2. Open the Print dialog box.
3. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel, and then specify the following settings:
• Source: Upper tray
• Paper Type: Automatic or Plain paper
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
90
Page 91

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
8 Printing tips
Save time
• Use the 250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory to reload the printer less often.
• Print in reverse page order.
• Print collated copies.
Save money
• Print a two-sided document.
• Print multiple pages on a single sheet of paper.
Enhance the quality of printouts
• Select the right paper type.
• Select the right print quality.
• Resize the document as needed.
• Print a borderless brochure.
8.1 Using the 250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory
If the 250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory is not installed on the printer, follow
the installation steps.
Note: The 250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory is not available in all countries/
regions.
Follow these steps to use the 250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
91
Page 92

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. In the Source drop-down list, click Lower tray.
8.2 Setting the page order
Setting the page order determines the order in which your document will be printed.
Frequently, it is convenient to have the first page of a document printed last so that
the complete document is lying face-up in the Out tray.
Follow these steps to set the page order:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Handling panel.
92
Page 93

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. Do one of the following actions:
• Select the Reverse Page Order check box to print the first page of the
document last. This is the appropriate setting for most print jobs.
• Clear the Reverse Page Order check box to print the last page of the
document last.
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
Note: The reverse page order feature is only available in Mac OS X 10.3 and
later.
8.3 Printing collated copies
If you are printing several copies of a document at one time, use collation so that
you do not have to re-arrange the copies after printing.
Note: Some software programs do not allow you to use the printer software to
specify the number of copies to print. If the program that you are using
allows you to specify the number of copies to print, then specify the number
of copies to print in the application.
Follow these steps to print collated copies:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Copies and Pages panel.
3. In the Copies box, type the number of copies that you want to print.
4. Select the Collated check box.
5. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
93
Page 94

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
8.4 Automatic two-sided printing
To print a two-sided document automatically, one of the following accessories must
be attached to the printer:
Automatic Two-Sided Printing Accessory
Auto Two-Sided Print Accessory with Small Paper Tray
The two-sided printing accessories only support certain paper types. For a list of
supported paper types, see the documentation that came with the accessory.
Printing
Follow these instructions to print a two-sided document:
1. Open the Print dialog box, and then select the Two-Sided Printing panel.
2. Select the appropriate binding:
94
Page 95

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
Book binding
Tablet binding
3. Change any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
After the first side of the page is printed, the printer pauses while the ink dries.
After the ink is dry, the paper is pulled back into the duplexer and the reverse
side of the page is printed.
Note: Do not remove the paper from the printer until both sides of the page
have been printed.
8.5 Printing multiple pages on a single sheet of paper
The printer software allows you to print multiple pages of a document on a single
sheet of paper. The printer software automatically resizes the document text and
images to fit on the printed page.
Follow these steps to print multiple pages on a single sheet of paper:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Layout panel.
3. In the Pages per Sheet menu, select the number of pages that you want to
appear on each sheet of paper.
95
Page 96

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
4. For Layout Direction, select the option for how you want the multiple pages
arranged on a single sheet of paper.
5. If you want a border to appear around each page image that is printed on the
sheet of paper, select the border that you want from the Border menu.
6. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
Note: The two-sided printing controls on the Layout panel are not operational
for the printer. To print a two-sided document, see the two-sided
printing page.
8.6 Selecting a paper type
The printer software offers these options for selecting a paper type:
• Use the automatic paper-type sensor
• Select a specific paper type
Using the automatic paper-type sensor
The Automatic Paper-Type Sensor automatically selects the print settings
appropriate for the media be printed on, particularly when used with HP paper and
media.
Note: The Automatic Paper-Type Sensor cannot be used for documents printed
from the 250-Sheet Plain Paper Tray Accessory.
Follow these steps to use the automatic paper-type sensor:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
96
Page 97

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. In the Paper Type drop-down list, click Automatic.
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
Selecting a specific paper type
When printing a higher-quality printout, it is recommended that you select a specific
paper type.
Follow these steps to select a specific paper type:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
97
Page 98

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. In the Paper Type drop-down list, click the appropriate paper type.
4. Select any other print settings that you want, and then click Print.
8.7 Selecting a print quality
Follow these steps to select a print quality from the printer software:
1. Open the Print dialog box.
2. Select the Paper Type/Quality panel.
98
Page 99

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
3. Select one of the following from the Quality drop-down list:
• FastDraft: prints at the fastest printing speed.
• Fast normal: prints more quickly than the Normal mode and at a higher
print quality than FastDraft.
• Normal: provides the best balance between print quality and speed. This
is the appropriate setting for most documents.
• Best: provides high-quality printing.
• Maximum dpi: provides the highest quality printing but requires longer to
print than Best and requires a large amount of disk space.
8.8 Resizing a document
Use this feature to shrink or enlarge printed text and graphics without changing the
paper size.
Follow these steps to shrink or enlarge text and graphics:
1. Open the Page Setup dialog box.
99
Page 100

HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide
2. In the Scale box, type the percentage by which you want to shrink or enlarge
the document.
• Type a number from 25 to 99 to reduce a document image.
• Type a number from 101 to 400 to enlarge a document image.
3. Click OK, and then print the document.
8.9 Printing a borderless brochure
You can print a borderless brochure on glossy brochure paper.
For instructions about printing a borderless photo, see the borderless photo page.
Guidelines
• Do not print borderless documents in ink-backup mode. Always have two print
cartridges installed in the printer.
• Open the file in a software application and assign the image size. Ensure that
the size corresponds to the paper size on which you want to print the image.
Printing
Follow these steps to print a borderless document:
1. Open the file you want to print.
2. Open the Page Setup dialog box.
100
 Loading...
Loading...