Page 1

AV R 254
AUDIO/VIDEO RECEIVER
OWNER’S M ANUAL
Page 2

SAFETY INFORMATION
Important Safety Instructions
1. Read these instructions.
2. Keep these instructions.
3. Heed all warnings.
4. Follow all instructions.
5. Do not use this apparatus near water.
6. The A/V receiver’s cabinet may be cleaned by gently wiping with a soft cotton
or microfiber cloth. Do not use water or any liquid cleaners.
7. Do not block any of the ventilation openings. Install in accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions.
8. Do not install near any heat sources such as radiators, heat registers, stoves
or other apparatus (including amplifiers) that produce heat.
9. Do not defeat the safety purpose of the polarized or grounding-type plug.
A polarized plug has two blades with one wider than the other. A groundingtype plug has two blades and a third grounding prong. The wide blade or the
third prong is provided for your safety. When the provided plug does not fit into
your outlet, consult an electrician for replacement of the obsolete outlet.
10. Protect the power cord from being walked on or pinched, particularly at plugs,
convenience receptacles and the point where they exit from the apparatus.
11. Only use the attachments/accessories specified by the manufacturer.
12. Use only with a cart, stand, tripod, bracket or table specified by the
manufacturer, or sold with the apparatus. When a cart is used, use
caution when moving the cart/apparatus combination to avoid injury
from tip-over.
13. Unplug this apparatus during lightning storms or when unused for long
periods of time.
14. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. Servicing is required when
the apparatus has been damaged in any way, such as power supply cord
or plug is damaged, liquid has been spilled or objects have fallen into the
apparatus, the apparatus has been exposed to rain or moisture, does not
operate normally, or has been dropped.
Wet Location Marking
Apparatus shall not be exposed to dripping or splashing and no objects filled with
liquids, such as vases, shall be placed on the apparatus.
Service Instructions
CAUTION – These servicing instructions are for use by qualified service personnel
only. To reduce the risk of electric shock, do not perform any servicing other than
that contained in the operating instructions, unless you are qualified to do so.
Outdoor Use Marking
WARNING – To reduce the risk of fire or electric shock, do not expose this
apparatus to rain or moisture.
2
Page 3

SAFETY INFORMATION
Important Safety Information
Verify Line Voltage Before Use
Your AVR 254 has been designed for use with 120-volt AC current. Connection to
a line voltage other than that for which it is intended can create a safety and fire
hazard and may damage the unit.
If you have any questions about the voltage requirements for your specific model, or
about the line voltage in your area, contact your selling dealer before plugging the unit
into a wall outlet.
Do Not Use Extension Cords
To avoid safety hazards, use only the power cord attached to your unit. We do not
recommend that extension cords be used with this product. As with all electrical
devices, do not run power cords under rugs or carpets or place heavy objects on
them. Damaged power cords should be replaced immediately by an authorized service
center with a cord meeting factory specifications.
Handle the AC Power Cord Gently
When disconnecting the power cord from an AC outlet, always pull the plug; never
pull the cord. If you do not intend to use the unit for any considerable length of time,
disconnect the plug from the AC outlet.
Do Not Open the Cabinet
There are no user-serviceable components inside this product. Opening the cabinet
may present a shock hazard, and any modification to the product will void your
guarantee. If water or any metal object such as a paper clip, wire or staple accidentally falls inside the unit, disconnect it from the AC power source immediately, and
consult an authorized service center.
CATV or Antenna Grounding
If an outside antenna or cable system is connected to this product, be certain that it is
grounded so as to provide some protection against voltage surges and static charges.
Section 810 of the National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA No. 70-1984, provides
information with
grounding of the lead-in wire to an antenna
tors, location of antenna discharge unit,
requirements of the grounding electrode.
NOTE TO CATV SYSTEM INSTALLER: This reminder is provided to call the CATV
(cable TV) system installer’s attention to article 820-40 of the NEC, which provides
guidelines for proper grounding and, in particular, specifies that the cable ground
shall be connected to the grounding system of the building, as close to the point
of cable entry as possible.
Installation Location
• To ensure proper operation and to avoid the potential for safety hazards, place the
unit on a firm and level surface. When placing the unit on a shelf, be certain that
the shelf and any mounting hardware can support the weight of the product.
• Make certain that proper space is provided both above and below the unit for
ventilation. If this product will be installed in a cabinet or other enclosed area,
make certain that there is sufficient air movement within the cabinet. Under some
circumstances, a fan may be required.
• Do not place the unit directly on a carpeted surface.
• Avoid installation in extremely hot or cold locations, or in an area that is exposed
to direct sunlight or heating equipment.
• Avoid moist or humid locations.
• Do not obstruct the ventilation slots on the top of the unit, or place objects
directly over them.
• Due to the weight of the AVR 254 and the heat generated by the amplifiers,
there is the remote possibility that the rubber padding on the bottom of the
respect to proper grounding of the mast and supporting structure,
discharge unit, size of grounding conduc-
connection to grounding electrodes and
unit’s feet may leave marks on certain wood or veneer materials. Use caution
when placing the unit on soft woods or other materials that may be damaged
by heat or heavy objects. Some surface finishes may be particularly sensitive to
absorbing such marks, due to a variety of factors beyond our control, including
the nature of the finish, cleaning materials used, and normal heat and vibration
caused by the use of the product, or other factors. We recommend that caution
be exercised in choosing an installation location for the component and in normal
maintenance practices, as your warranty will not cover this type of damage to furniture.
Cleaning
When the unit gets dirty, wipe it with a clean, soft, dry cloth. If necessary, and only after
unplugging the AC power cord, wipe it with a soft cloth dampened with mild soapy
water, then a fresh cloth with clean water. Wipe it dry immediately with a dry cloth.
NEVER use benzene, aerosol cleaners, thinner, alcohol or any other volatile cleaning
agent. Do not use abrasive cleaners, as they may damage the finish of metal parts.
Avoid spraying insecticide near the unit.
Moving the Unit
Before moving the unit, be certain to disconnect any interconnection cords
with other components, and make certain that you disconnect the unit from
the AC outlet.
Important Information for the User
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class-B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. The limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates,
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communication. However, there is no guarantee that harmful interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
NOTE: Changes or modifications may cause this unit to fail to comply with Part
of the FCC Rules and may void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
uses and can radiate radio-frequency energy
different from that to which the
and, if not
15
Unpacking
The carton and shipping materials used to protect your new receiver during shipment were specially designed to cushion it from shock and vibration. We suggest
that you save the carton and packing materials for use in shipping if you move, or
should the unit ever need repair.
To minimize the size of the carton in storage, you may wish to flatten it. This is done
by carefully slitting the tape seams on the bottom and collapsing the carton. Other cardboard inserts may be stored in the same manner. Packing materials that cannot be collapsed should be saved along with the carton in a plastic bag.
If you do not wish to save the packaging materials, please note that the carton and
other sections of the shipping protection are recyclable. Please
ment and discard those materials at a local recycling center.
It is important that you remove the protective plastic film from the front-panel lens.
Leaving the film in place will affect the performance of your remote control.
respect the environ-
3
Page 4

STAPLE INVOICE HERE
4
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
2 SAFETY INFORMATION
6 INTRODUCTION
8 FRONT-PANEL CONTROLS
11 REAR-PANEL CONNECTIONS
14 REMOTE CONTROL FUNCTIONS
17 INTRODUCTION TO HOME THEATER
18 CONNECTIONS
18 Speaker Connections
18 Subwoofer
18 Connecting Source Devices to the AVR
19 Audio Connections
19 Digital Audio
19 Analog Audio
20 Video Connections
20 Digital Video
20 Analog Video
20 Antennas
21 RS-232 Serial Port
SPEAKER PLACEMENT
22
24 INSTALLATION
24 Step One – Connect the Speakers
24 Step Two – Connect the Subwoofer
24 Step Three – Connect the Antennas
24 Step Four – Connect the Source Components
28 Step Five – Connect the Video Display
29 Step Six – Plug in AC Power
29 Step Seven – Insert Batteries in Remote
29 Step Eight – Program Sources Into the Remote
30 Step Nine – Remote IR Inputs and Output (optional)
31 Step Ten – Install a Multizone System (optional)
31 Step Eleven – Turn On the AVR 254
INITIAL SETUP
33
33 Using the On-Screen Menu System
33 Configure the AVR 254 Using EzSet/EQ Technology
35 Set Up Sources
OPERATION
38
38 Turning On the AVR 254
38 Volume Control
38 Mute Function
38 Sleep Timer
38 Audio Effects
38 Video Modes
38 Headphones
39 Source Selection
39 Using the Tuner
40 XM Radio Operation
40 Recording
41 Stereo Jack Input
41 Selecting a Surround Mode
ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
42
42 Audio Processing and Surround Sound
42 Analog Audio Signals
42 Digital Audio Signals
43 Surround Modes
44 Dolby Surround Settings
44 Night Mode
45 Manual Setup
45 Step One – Determine Speaker Crossover
45 Step Two – Measure Speaker Distances
45 Step Three – Manual Setup Menu
46 Number of Speakers
46 Adjust Crossover Frequencies Menu
46 Sub Mode
47 Adjust Speaker Distance Menu
47 Step Four – Setting Channel Output Levels Manually
48 Audio Effects
49 Video Adjustments
49 Video Modes
50 How to Adjust the Custom Picture Settings
51 Multizone Operation
51 Installing a Multizone System
51 Operating the Multizone System
52 System Settings
53 Advanced Remote Control Functions
53 Punch-Through Programming
53 Activities (Macros)
53 Resetting the Remote
53 Processor Reset
54 Memory
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
55
56 APPENDIX
63, 75 Trademark Acknowledgments
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
75
WARNING
To prevent fire or shock hazard, do not expose this
appliance to rain or moisture.
For Canadian model
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian
ICES-003.
For models having a power cord with a polarized plug:
CAUTION: To prevent electric shock, match wide blade
of plug to wide slot, fully insert.
Modèle pour les Canadien
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme
à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Sur les modèles dont la fiche est polarisee:
ATTENTION: Pour éviter les chocs électriques, introduire
la lame la plus large de la fiche dans la borne
correspondante de la prise et pousser jusqu’au fond.
5
Page 6

INTRODUCTION
Please register your AVR 254 on our Web site at www.harmankardon.com.
Note: You’ll need the product’s serial number. At the same time, you can choose to be notified about our new products
and/or special promotions.
WWW.HARMANKARDON.COM
Thank you for choosing a Harman Kardon
®
product!
For more than fifty years, our mission has been to share our passion
for music and entertainment, using leading-edge technology to achieve
premium performance. To this end we invented the receiver, a single
component designed to simplify home entertainment while maintaining
the highest level of quality. Over the years our products have become
easier to use, and have delivered superior value. The AVR 254 multizone
with some of our most advanced video processing capabilities yet, and
a wealth of listening and viewing options.
To obtain the maximum enjoyment from your new receiver, we urge you
to read this manual and refer back to it as you become more familiar
with its features and their operation.
If you have any questions about this product, its installation or its
operation, please contact your retailer or customer installer, or visit our
Web site at www.harmankardon.com.
7.1-channel digital audio/video receiver carries this tradition forward,
Harman Kardon AVR 254 7.1-Channel Audio/Video Receiver
Audio Section
• 50 Watts x 7, seven channels driven at full power at 8 ohms,
20Hz – 20kHz, <0.07% THD (surround modes), 350 watts total
• 65 Watts x 2, two channels driven at full power at 8 ohms,
20Hz – 20kHz, <0.07% THD (surround off mode), 130 watts total
• High-current capability, ultrawide-bandwidth amplifier design with
low negative feedback
• All-discrete amplifier circuitry
• Quadruple-crossover bass management
®
• 24-Bit, twin-core Cirrus Logic
• 192kHz/24-bit D/A conversion
• Sampling upconversion to 96kHz
6
CS 49700 DSP processor
Surround Modes
• Dolby®Digital EX, Dolby Digital Plus, Dolby TrueHD
®
• Dolby Pro Logic
• Dolby Virtual Speaker Version 2 (Reference or Wide, two-channel)
• Dolby Headphone Version 2, up to 96kHz
• DTS-HD, DTS-HD Master Audio
• DTS®(5.1; DTS Stereo; DTS-ES®6.1 Discrete and Matrix)
• DTS 96/24
• DTS Neo:6
up to 96kHz
• Logic 7
®
• 5- or 7-Channel Stereo, up to 96kHz
• Surround Off (DSP or Analog Bypass)
II and IIx (Movie, Music and Game), up to 96kHz
™
™
(DTS Stereo)
®
(Cinema 5- or 6-channel; Music 5- or 6-channel),
(Movie, Music and Game – 5.1 and 7.1), up to 96kHz
Page 7
INTRODUCTION
Audio Inputs
• AM/FM/XM®* tuner
• Analog Audio 1 through 5 (assignable)
• Front-panel Analog Audio (assignable)
• 6-/8-Channel Analog Audio (assignable)
• Stereo mini-jack (assignable)
Audio/Video Inputs
• Three Analog Video (assignable)
• Front-panel Analog Video (assignable)
• Component Video 1 and 2, 100MHz (assignable)
™
• Three HDMI
• Faroudja DCDi Cinema
Transcodes composite and S-video to component video
Transcodes 480i video to component video format, with upscaling
to 1080i
Transcodes 480i video to HDMI output, with upscaling up to 1080p
(V.1.3 with Deep Color and audio/video processing)
®
video processing
Ease of Use
• EzSet/EQ™automated setup (microphone supplied)
• Full-color user interface and setup menu, generated in
high-definition video
• Two-line dot-matrix front-panel display
• Color-coded connections
• Programmable 7-device main remote control
• Source input renaming
• Lip Sync Delay (up to 180msec)
• RS-232 serial port for system upgrades
• Switched accessory power outlet
• Remote infrared (IR) input and output
• Zone 2 IR input
Supplied Accessories
The following accessory items are supplied with the AVR 254. If any
of these items are missing, please contact Harman Kardon customer
service at www.harmankardon.com.
Digital Audio Inputs
• Coaxial: two rear-panel/one front-panel
• Optical: two rear-panel/one front-panel
Outputs
• 7.1-Channel preamp outputs
• Analog Audio 2 and 4
• Analog Video 2
• Video monitor (composite, S-video and component)
• Digital audio (one coaxial)
• HDMI (V.1.3 with Deep Color)
• Multizone audio: speaker- and line-level (shared with surround
back channels)
• Headphone
• System remote control
• EzSet/EQ microphone
• AM loop antenna
• FM wire antenna
• Four AAA batteries
• Two covers for front-panel jacks
*XM antenna module and subscription to XM service required. Hardware and
service sold separately. XM service is not available in Alaska or Hawaii.
7
Page 8
FRONT-PANEL CONTROLS
Main Power Switch: This mechanical switch turns the power supply
on or off. It is usually left pressed in (On position), and cannot be turned
on using the remote control.
Standby/On Switch: This electrical switch turns the receiver on
for playback, or leaves it in Standby mode for quick turn-on using this
switch or the remote control.
Power Indicator: This LED has four possible modes:
• Main Power Off: When the AVR is unplugged or the Main Power
Switch is off, this LED is off.
• Standby: The LED is amber, indicating that the AVR is ready to
be turned on.
• On: The LED is white, when the AVR is on and operating normally.
• Protect: If the PROTECT message ever appears, turn off the AVR
and unplug it. Check all speaker wires for a possible short. If none is
found, bring the unit to an authorized Harman Kardon service center
for inspection and repair before using it again.
Source List: Press this button to select a source device, which
is a component where a playback signal originates, such as DVD,
cable TV, satellite or the tuner.
Volume Knob: Turn this knob to raise or lower the volume.
Message Display: Various messages appear in this two-line display
in response to commands and changes in the incoming signal. In normal
operation, the current source name appears on the upper line, while the
surround mode is displayed on the lower line. When the on-screen display menu system (OSD) is in use, the current menu settings appear.
Headphone Jack/EzSet/EQ Microphone Input: Plug a 1/4"
headphone plug into this jack for private listening.
This jack is also used to connect the supplied microphone for the
EzSet/EQ procedure described in the Initial Setup section. To begin
EzSet/EQ, plug the supplied microphone into this jack, place the microphone at the listening position, and follow the directions given in the
Speaker Setup-Automatic Setup-EzSet/EQ on-screen menu.
Surround Modes: Press this button to select a surround sound
(e.g., multichannel) mode. The Surround Modes menu will appear on
screen, and the menu line will appear in the front-panel display.
⁄/¤
Use the front-panel or remote
menu line: Auto Select, Virtual Surround, Stereo, Movie, Music or Video
Game. Each line represents a type of audio signal, and is set to the
preferred surround mode that you manually select.
Press the OK Button when the menu line is highlighted, and the
available surround mode options for the current signal will appear.
⁄/¤
Use the
OK Button to engage it. Press the Back/Exit Button to exit the Surround
Modes menu.
Buttons to select the desired mode, and press the
Buttons to highlight a different
See the Advanced Functions section for more information on surround
modes.
Analog Audio, Video and Digital Audio Inputs: Connect a
source component that will only be used temporarily, such as a digital
camera or game console, to these jacks. Use only one type of audio
and one type of video connection.
NOTES:
• Each of these connections (analog audio, digital audio and
video) may be independently assigned to any source. See the
Initial Setup section for information on setting up sources,
including assigning audio and video inputs to a source.
• Although these jacks are labeled Optical 3, Coaxial 3 and
Video 4 on the AVR, the AVR’s menus refer to them as the
Optical Front, Coaxial Front, Composite Front, S-Video Front
and Analog Front inputs.
Speaker/Channel Input Indicators: The box icons indicate
which speaker positions you have configured (see the Initial Setup
Section), and the size (frequency range) of each speaker. The letters
will light inside the boxes to indicate which channels are present in
the incoming signal.
Navigation: These buttons are used to navigate the AVR’s menus
and to operate the tuner.
Remote IR Sensor: This sensor receives infrared (IR) commands
from the remote control. It is important to ensure that it is not blocked.
If covering the sensor is unavoidable, such as when the AVR 254 is
placed inside a cabinet, you may use an optional Harman Kardon
HE 1000, or other infrared receiver, connecting it to the Remote IR
Input on the AVR 254’s rear panel. Alternatively, connect the Remote IR
Output of another compatible component to the AVR 254’s Remote
IR Input. Point the remote at the other device’s remote sensor, and the
command will be transmitted to the AVR 254. An external IR “blaster”
may also be used, positioned to point at this area.
AVR Settings Button: Press this button to access the AVR’s
main menu.
Info Settings Button: Press this button to directly access the
AVR’s Source Info submenu, which contains the settings for the
current source.
Resolution: Each press of this button changes the AVR’s video output
resolution to these settings: 480i, 480p, 720p, 1080i or 1080p.
IMPORTANT NOTE: If the AVR’s video output resolution is set
higher than the capabilities of the actual connection, you will not
see a picture. If the best video connection from the AVR to the
TV is either composite or S-video, press this button until the
resolution is set to 480i.
8
Page 9
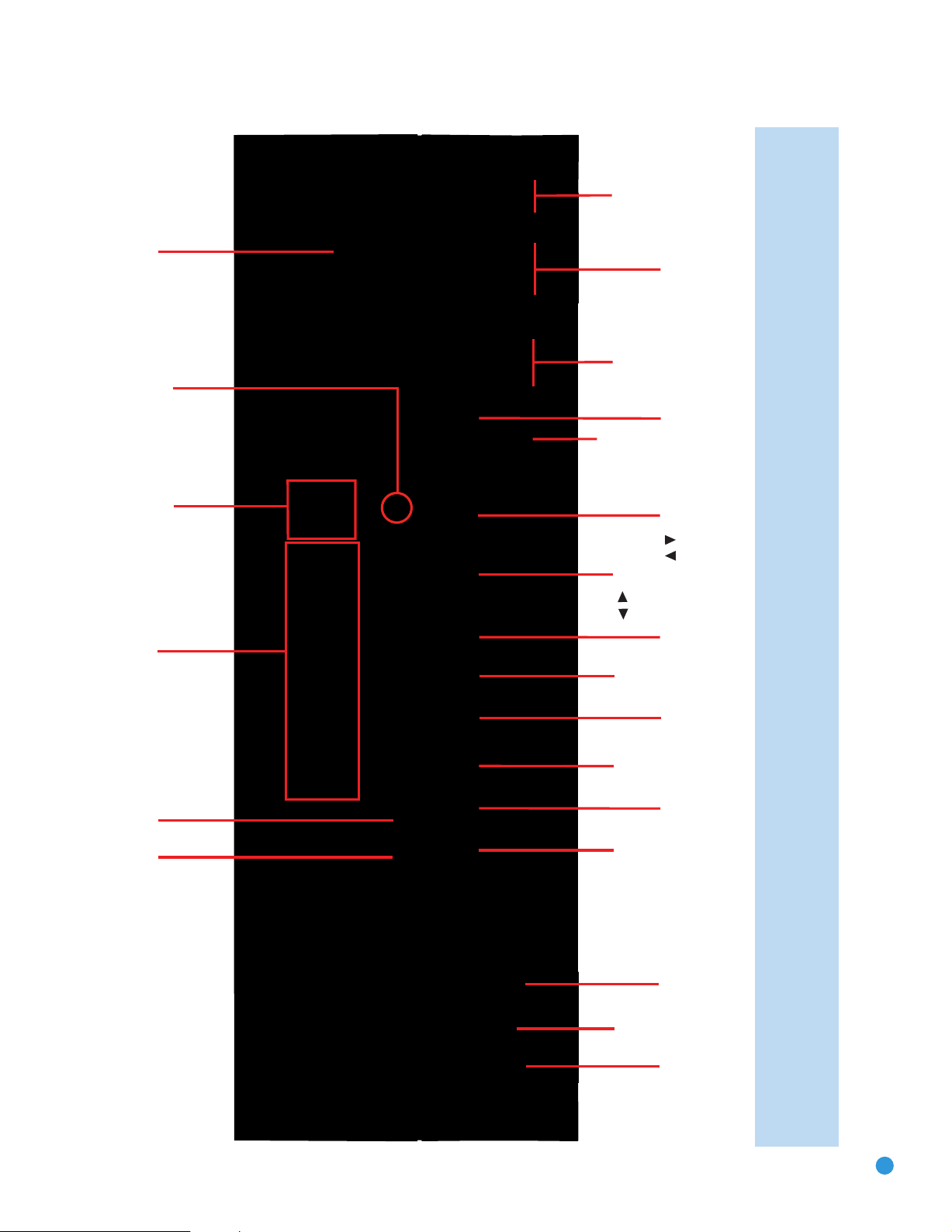
Resolution
Source
List
Navigation
Video
Modes
OK
Back/
Exit
Navigation
Headphone
Jack/EzSet/EQ
Microphone
Input
Digital
Audio Inputs
(Optical 3 and
Coaxial 3)
Video 4
Video Inputs
Video 4 Analog
Audio Inputs
Surround
Modes
Audio
Effects
AVR Info
Power
Indicator
Main Power
Switch
Standby/On
Switch
Volume
Message Display
Speaker/Channel
Input Indicators
Remote
IR Sensor
/
/
NOTE: To make it easier to follow the instructions throughout the manual that refer to this illustration, a copy of this page may be downloaded from the Product Support section at
www.harmankardon.com.
9
Page 10

FRONT-PANEL CONNECTIONS
Audio Effects: Press this button to directly access the Audio Effects
submenu, which allows adjustment of the tone and other controls.
See the Initial Setup section for more information.
Video Modes: Press this button for direct access to the Video Modes
submenu, which contains settings that may be used to improve the
picture if necessary after you have adjusted the picture settings using
the video display or TV.
OK: Press this button to select the currently highlighted item.
Back/Exit: Press this button to return to the previous menu, or
to exit the menu system.
10
Page 11
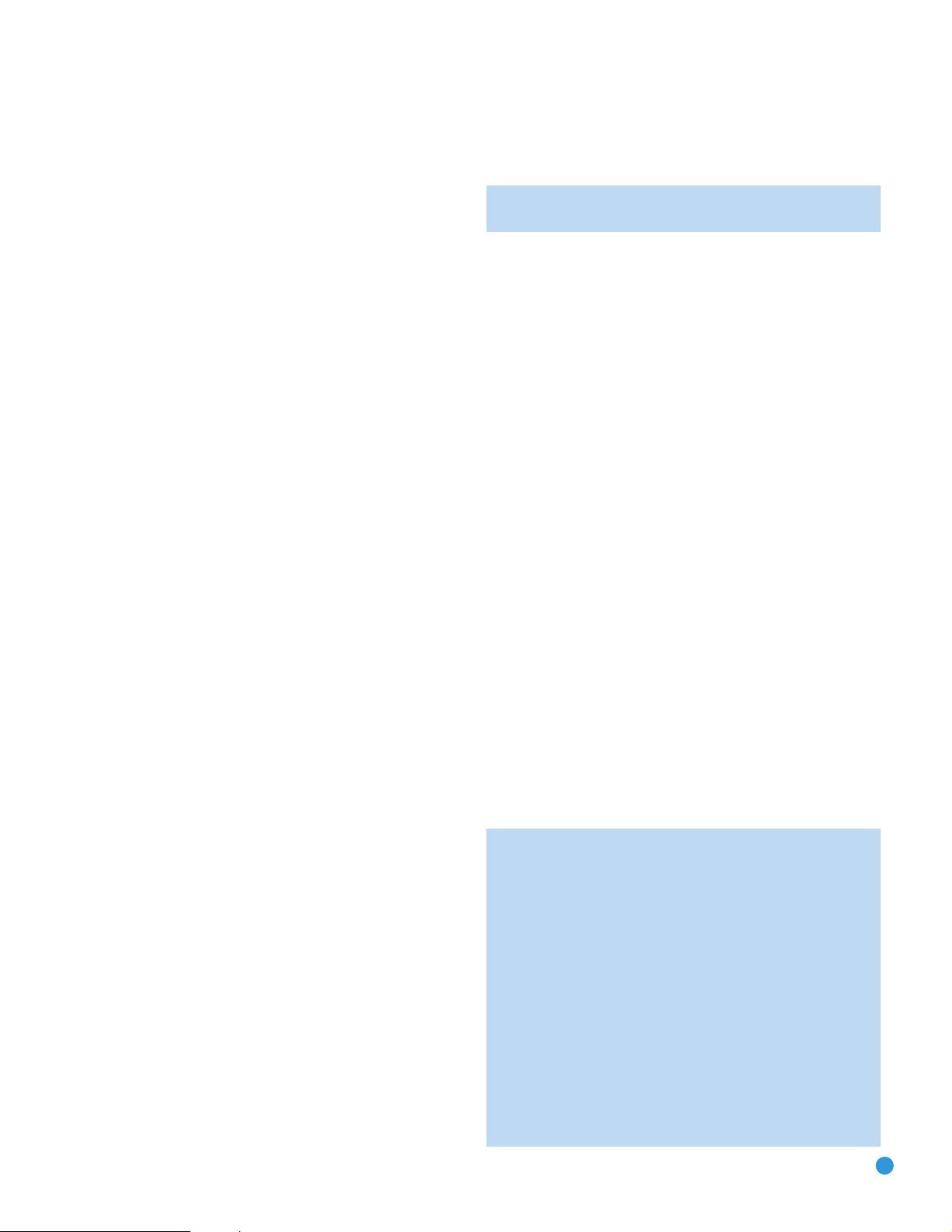
REAR-PANEL CONNECTIONS
AM and FM Antenna Terminals: Connect the included AM
and FM antennas to their respective terminals for radio reception.
XM Antenna Jack: Plug in an XM Connect and Play or Mini Tuner
antenna module here. The XM antenna module is purchased separately,
and should specify that it is for home use with an XM Ready
You will need to subscribe to the XM service, which is available separately, and activate the service for your antenna module. (XM service
is not available in Alaska and Hawaii.)
®
product.
Front, Center and Surround Speaker Outputs: Use two-
conductor speaker wire to connect each set of terminals to the correct
speaker. Remember to observe the correct polarity (positive and negative
connections). Always connect the positive lead to the colored terminal
on the receiver and the red terminal on the speaker. Connect the negative
lead to the black terminal on both the receiver and the speaker. See the
Connections section for more information on connecting your speakers.
Surround Back/Zone 2 Speaker Outputs: These speaker
outputs are used for the surround back channels in a 7.1-channel home
theater, or may be reassigned to a remote room for multizone operation.
When these outputs are reassigned for multizone operation, only a
5.1-channel configuration will be available in the main listening room.
Use the on-screen menu system to configure these channels as desired.
As with the other speaker outputs, remember to observe proper polarity
by connecting the positive and negative output terminals to the corresponding terminals on each speaker.
Subwoofer Output: If you have a powered subwoofer with a
line-level input, connect it to this jack.
Preamp Outputs: Connect these jacks to an external amplifier if
more power is desired.
The Surround Back/Zone 2 Preamp Outputs may be used with an
external amplifier to power the surround back channels, or to power
the remote zone of a multizone system. Use the on-screen menu
system to configure these channels as desired.
Remote Infrared (IR) Input and Output: When the remote IR
receiver on the front panel is blocked, such as when the AVR is placed
inside a cabinet, connect an optional IR receiver to the Remote IR Input
jack for use with the remote control. The Remote IR Output may be
connected to the Remote IR Input of a compatible product to enable
remote control through the AVR. This is particularly useful in multizone
applications to control a source device from the remote room (when
used with the Zone 2 IR Input). When several source devices are used,
connect them in “daisy chain” fashion.
Zone 2 Infrared (IR) Input: Connect a remote IR receiver located
in the remote zone of a multizone system to this jack to control the AVR
(and any source devices connected to the Remote IR Output) from the
remote zone.
Composite and S-Video 1, 2 and 3 Video Inputs: These
jacks may be used to connect your video-capable source components
(e.g., VCR, DVD player, cable TV box) to the receiver. Use only one type
of video connection for each source. These inputs are assignable, which
means they may be paired with any analog or digital audio inputs. This
will be explained in more detail in subsequent sections of this manual.
NOTE: The Video 2 inputs are associated with a set of outputs.
Consider connecting a video recorder here.
Composite and S-Video 2 Outputs: Connect one of these
analog video outputs to the composite or S-video inputs of a recording
device. A signal is available at these outputs whenever an analog video
source is playing. HDMI and component video signals are not available
for recording.
Composite and S-Video Monitor Outputs: If any of your
sources use composite or S-video connections, connect one or both of
these monitor outputs to the corresponding inputs on your television or
video display. If your video display is equipped with HDMI or component
video inputs, these connections are unnecessary. Connect the HDMI
Monitor Output (if available, otherwise use the Component Video Monitor
Output) to your TV, and the AVR 254 will convert the composite or
S-video source signal to the correct format for a single video cable
connection to the TV.
HDMI Inputs and Output: HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia
Interface) is a connection for transmitting digital audio and video signals
between devices. With the AVR 254’s powerful processor, you may
connect up to three HDMI-equipped source devices to the HDMI inputs
using a single-cable connection, while benefiting from superior digital
audio and video performance. If your video display is not HDMI-compatible,
connect the device to one of the analog video inputs, then pair it with
an analog or digital audio input.
If your video display has an HDMI input, make just the HDMI video connection to your display; the AVR 254 will automatically transcode analog
video signals to the HDMI format, upscaling to as high as 1080p.
Analog 1 – 5: Connect the left and right analog audio outputs of
a source device to any of these inputs. These inputs are assignable,
which means they may be paired with any video inputs, as explained
in subsequent sections of this manual.
NOTES:
• The Analog 3 through 5 connectors physically line up below
the Video 1 through 3 (composite and S-video) connectors.
For convenience, consider using Analog 3 with Video 1, Analog 4
with Video 2 and Analog 5 with Video 3, if appropriate for
your system.
• The Analog 1 and 2 connectors don’t physically line up with
any analog video inputs. Consider using them for audio-only
devices, such as a CD player or cassette tape deck.
• The Analog 2 and 4 inputs are each associated with a set of
outputs. Consider using the Analog 2 connectors for an audio
recorder, and the Analog 4 connectors for a video recorder
(along with the Video 2 connectors).
• You may optionally connect a source to both an analog and
digital audio input. This is useful for making recordings, for
multizone applications or simply as a backup.
11
Page 12
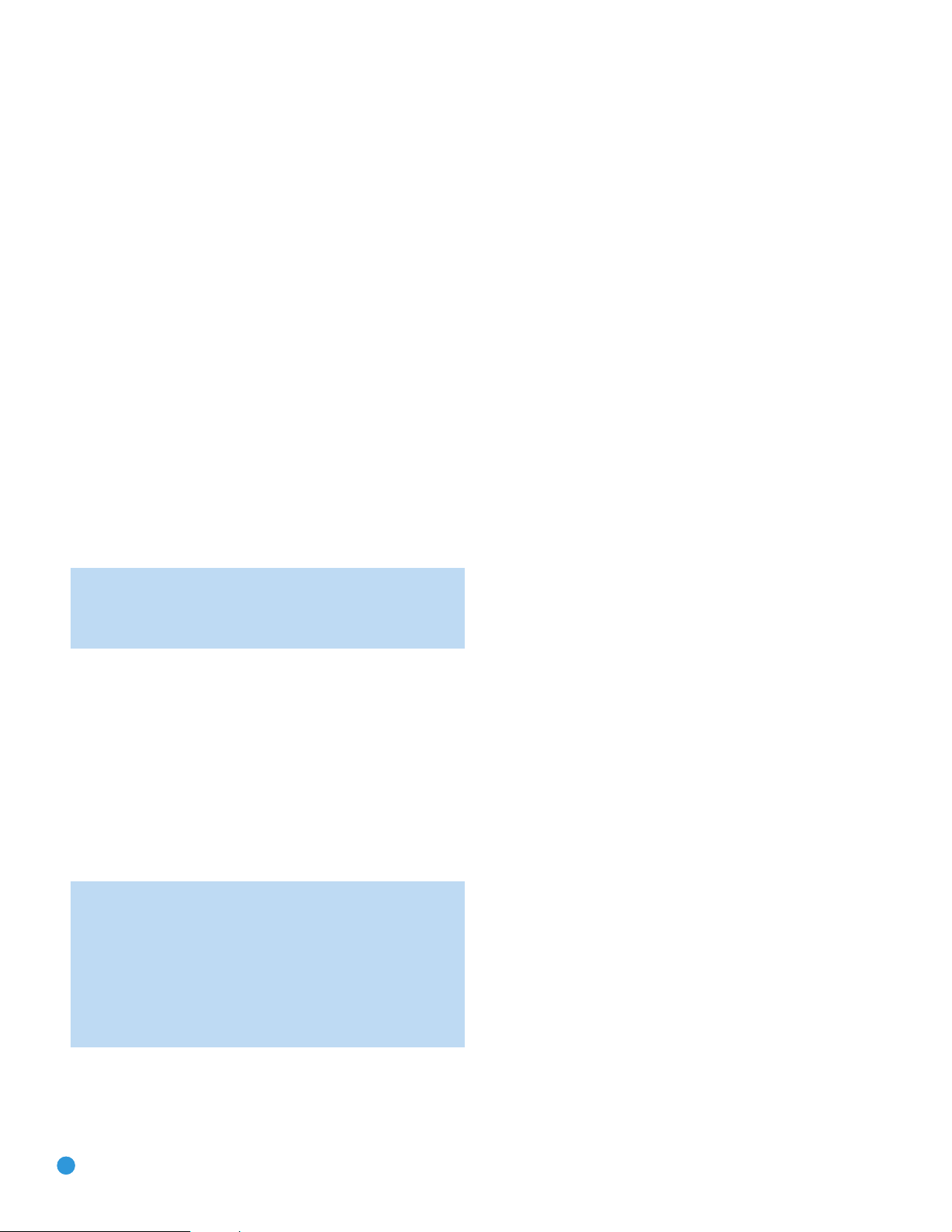
REAR-PANEL CONNECTIONS
Analog 2 and 4 Outputs: Connect either of these analog audio
outputs to the analog audio inputs of a recording device. A signal is
available at these outputs whenever an analog audio source is playing.
However, the AVR 254 does not convert digital audio sources to analog
for recording.
Coaxial 1/2 and Optical 1/2 Digital Audio Inputs: If a
source has a compatible digital audio output, and if you are not using
an HDMI connection for audio for the device, connect it to one of these
jacks to hear digital audio formats, such as Dolby Digital, DTS and linear
PCM. Use only one type of digital audio connection for each source.
Coaxial Digital Audio Output: If a source is also an audio
recorder, connect a coaxial digital audio output to the recorder’s input
for improved recording quality. Only PCM digital audio signals are
available for recording.
Stereo Jack: Enjoy audio from an iPod (not included), CD player or
other portable player by connecting its headphone jack to this input
using a 1/8” stereo mini-plug cable (not included). Video and still-image
playback are not available at this input.
6-/8-Channel Inputs: Connect the multichannel analog audio
™
outputs of a DVD-Audio, SACD
(or any other external decoder) to these jacks to enjoy these formats.
NOTE: When the multichannel player has an onboard digital
decoder, it is not necessary to connect it to the 6-/8-Channel
Analog Audio Inputs. Only a digital audio connection (HDMI,
coaxial or optical) is needed.
, Blu-ray Disc™or HD-DVD™player
RS-232 Mode: Leave this switch popped out in the Operate position
unless the AVR 254 is being upgraded.
RS-232 Reset: This switch is only used during a software upgrade.
A standard processor reset is performed by pressing and holding the
front-panel OK Button.
Switched AC Accessory Outlet: You may plug the AC power
cord of one source device into this outlet, and it will turn on whenever
you turn on the receiver. Do not use a source that consumes more than
50 watts of power.
AC Power Cord: After you have made all other connections, plug
the AC power cord into an unswitched outlet.
Component Video 1 and 2 Inputs: If a video source (e.g., DVD
player or HDTV tuner) has analog component video (Y/Pb/Pr) capability,
and if you are not using an HDMI connection for the device, then
connect the component video outputs of the source to one of the two
component video inputs. Do not make any other video connections
to that source.
Component Video Monitor Outputs: If you are using one of
the Component Video Inputs and your television or video display is
component-video-capable, and if you are not connecting the HDMI
Output to your display, connect these jacks to the corresponding inputs
on your video display.
NOTES:
• Due to copy-protection restrictions, there is no output at
the Component Video Monitor Outputs for copy-protected
sources.
• Composite and S-video signals are upscaled to as high as
1080i and available at these outputs. If your video display’s
best connection is component video, it is the only video
connection required from the AVR to the display.
RS-232 Serial Port: This specialized connector may be used with
your personal computer in case we offer a software upgrade for the
receiver at some time in the future.
121212
12
Page 13
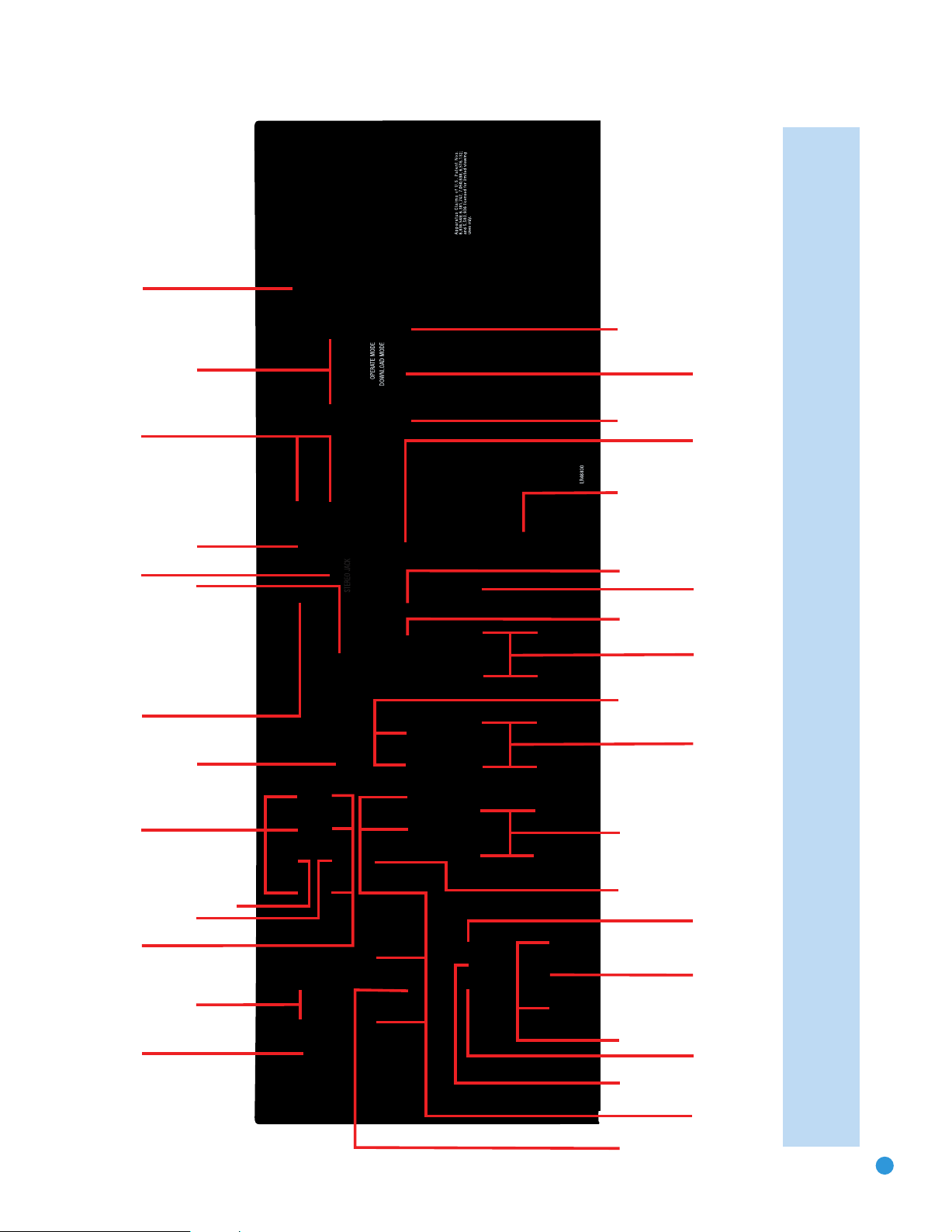
FM Antenna
XM
Antenna
AM Antenna
S-Video 2
Output
Composite 2
Output
Composite
1, 2 and 3
S-Video
1, 2 and 3
Video
Monitor
Outputs
HDMI
1, 2 and 3
AC Power
Cord
Component
1 and 2
Stereo Jack
HDMI
Monitor
Output
Component Video
Monitor Outputs
Subwoofer
Output
Preamp
Outputs
Front Speaker
Outputs
Surround
Speaker
Outputs
6-/8-
Channel
Inputs
Surround
Back/Zone 2
Speaker Outputs
Center Speaker
Outputs
Switched AC
Accessory
Outlet
RS-232
Reset
RS-232
Serial Port
Coaxial
Digital
Audio
Output
Coaxial
1 and 2
Digital
Audio
Optical 1 and 2
Digital Audio
Analog 1-5
Inputs
Zone 2
IR Input
Remote
IR Input
Remote
IR Output
Analog 2
Outputs
Analog 4
Outputs
RS-232
Mode
13
NOTE: To make it easier to follow the instructions throughout the manual that refer to this illustration, a copy of this page may be downloaded from the Product Support section at
www.harmankardon.com. All connectors are inputs except as indicated.
131313
Page 14
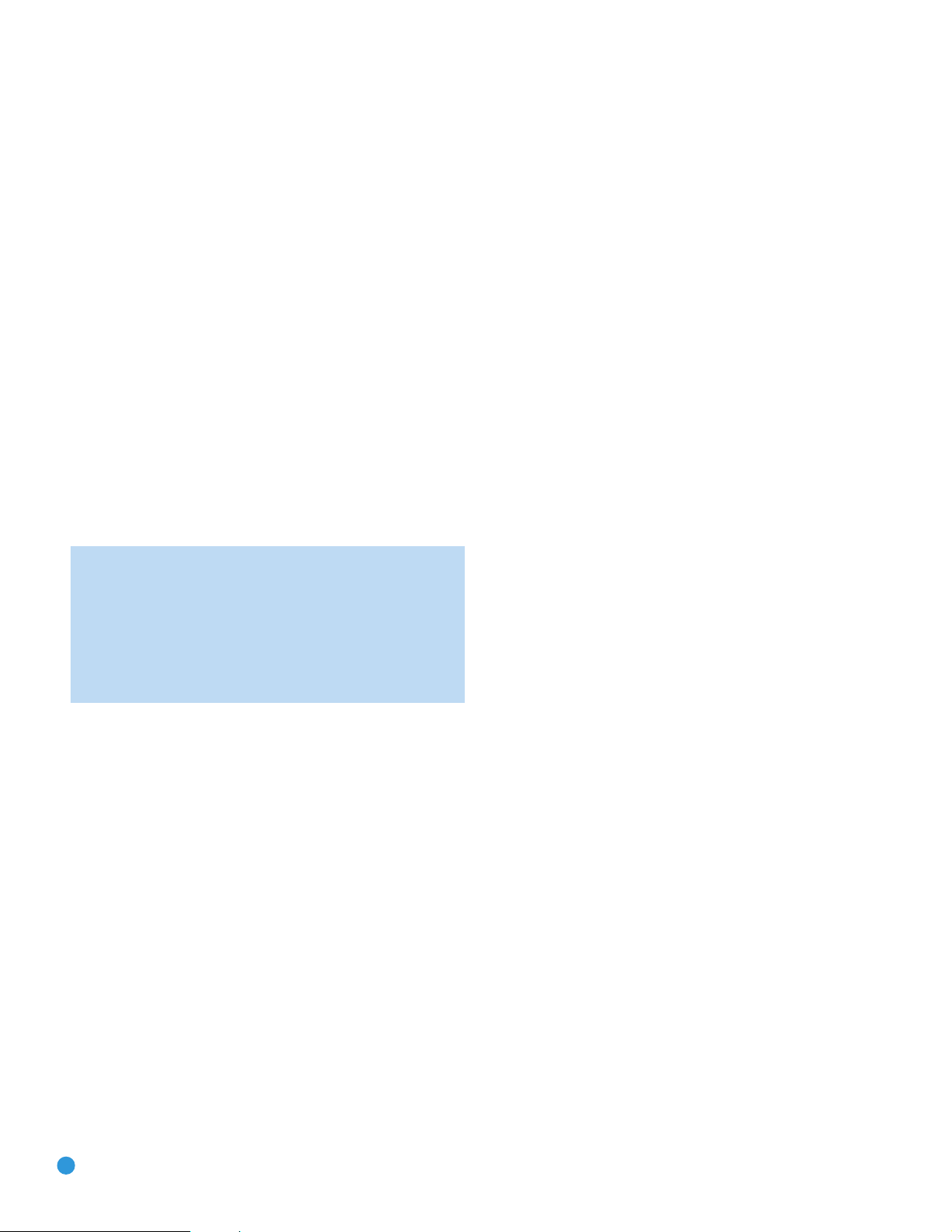
REMOTE CONTROL FUNCTIONS
The AVR 254 remote is capable of controlling 7 devices, including the
AVR itself. During the installation process, you may program the codes
for each of your source components into the remote. Each time you
wish to use the codes for any component, first press its Selector button.
This changes the button functions to the appropriate codes.
Each Source Selector has been preprogrammed to control certain types
of components, with only the codes specific to each brand and model
changing, depending on which product code is programmed. The AUX
Source Selector may be used for any of five device types: a CD player,
an HDTV set-top box, a PVD recorder used with cable or satellite television, a TiVO
on the product code programmed into the AUX Source Selector as
described in the Initial Setup section. CD players use codes beginning
with a 0, 1 or 2; VCRs use codes beginning with a 3 or 4; HDTV
set-top boxes use codes beginning with a 6; PVDs use codes beginning
with a 7 and TiVO set-top boxes use codes beginning with an 8.
The remote automatically switches to the correct device mode, and
it will operate the device as described in the function list in Table A13
in the appendix.
Similarly, the CBL/SAT Source Selector automatically selects cable or
satellite television operation depending on the first digit of the product
code: 0, 1 or 2 for cable and 3 or 4 for satellite boxes.
Most of the buttons on the remote have dedicated functions, although the
precise codes transmitted will vary depending on which source device
has been selected for operation. Due to the wide variety of functions
unique to various source devices, we have included only a few of the mostoften used functions on the remote, including alphanumeric keys, transport
controls, television-channel control, menu access and power on and off.
Please refer to the descriptions below for more specific information.
Some buttons are only used to operate the AVR, and their functions are
available at any time, even if the remote has been switched to another
device’s mode: AVR Power On and Off, Audio Effects, Video Modes,
Surround Modes, Volume and Mute. Press the AVR Settings button near
the bottom of the remote to return it to AVR mode.
Any given button may have different functions, depending on which
component is being controlled. Some buttons are labeled with these
functions. For example, the Page Up/Down Buttons are labeled for use
as Channel Up/Down Buttons when controlling a television or cable box.
See Table A13 in the appendix for listings of the different functions for
each type of component.
®
set-top box or a VCR. The device mode will depend
IMPORTANT NOTE: All of the AVR 254’s audio and video
inputs are independently assignable. As explained in the Initial
Setup section, it is necessary to set up each source, which
includes selecting the inputs to which the device is physically
connected. Any device may be connected to any compatible
input and given any name (e.g. DVD or Game). The Source
Selectors’ device types may be changed. For example, the TV
Source Selector may be reprogrammed to operate a DVD player.
IR Transmitter Lens: As buttons are pressed on the remote,
infrared codes are emitted through this lens. Make sure it is pointing
toward the component being operated.
AVR Power On Button: Press this button to turn on the AVR. The
Master Power Switch on the AVR 254’s front panel must first have been
switched on.
Device Power Off Button: When the remote has been switched to
a device’s mode by pressing its Source Selector, press this button to
turn off the device.
Device Power On Button: When the remote has been switched
to a device’s mode by pressing its Source Selector, press this button to
turn on the device.
Mute Button: Press this button to mute the AVR 254’s speaker and
headphone outputs temporarily. To end the muting, press this button
or adjust the volume. Muting is also canceled when the receiver is
turned off.
AVR Power Off Button: Press this button to turn off the AVR 254.
Source Selectors: Press one of these buttons to select a source
device, which is a component where a playback signal originates, e.g.,
DVD, CD, cable TV, satellite or HDTV tuner. This will also turn on the
receiver and switch the remote’s mode to operate the source device.
The first press of the Radio Selector switches the AVR to the last-used
tuner band (AM, FM or XM). Each successive press changes the band.
Audio Effects: This button is only used to operate the AVR. Press it
to directly access the Audio Effects submenu, which allows adjustment
of the tone and other controls. Each successive press scrolls to the next
line in the menu. See the Initial Setup section for more information.
Video Modes: This button is only used to operate the AVR. Press it
for direct access to the Video Modes submenu, which contains settings
that may be used to improve the picture if necessary after you have
adjusted the picture settings using the video display or TV. Each successive press scrolls to the next line in the menu. See the Advanced
Functions section for more information.
Surround Modes: This button is only used to operate the AVR. Press
it to directly access the Surround Modes submenu. Each successive
⁄/¤
press scrolls to the next line in the menu, or use the
to scroll to the next line: Auto Select, Virtual Surround, Stereo, Movie,
Music or Video Game. Each menu line represents a type of audio signal,
and is set to the preferred surround mode that you manually select.
Press the OK Button when the menu line is highlighted, and the available
surround mode options for the current signal will appear. Use the
Buttons to select the desired mode, and press the OK Button to engage
it. Press the Back/Exit Button to exit the Surround Modes menu and
display the next higher menu in the hierarchy.
See the Advanced Functions section for more information on surround
modes.
Buttons
⁄/¤
Sleep Settings Button: Press this button to activate the sleep timer,
which turns off the receiver after a programmed period of time of up to
90 minutes. Each successive press increases the timer by 10 minutes,
ending with the “Sleep Off” message.
14
14
Page 15
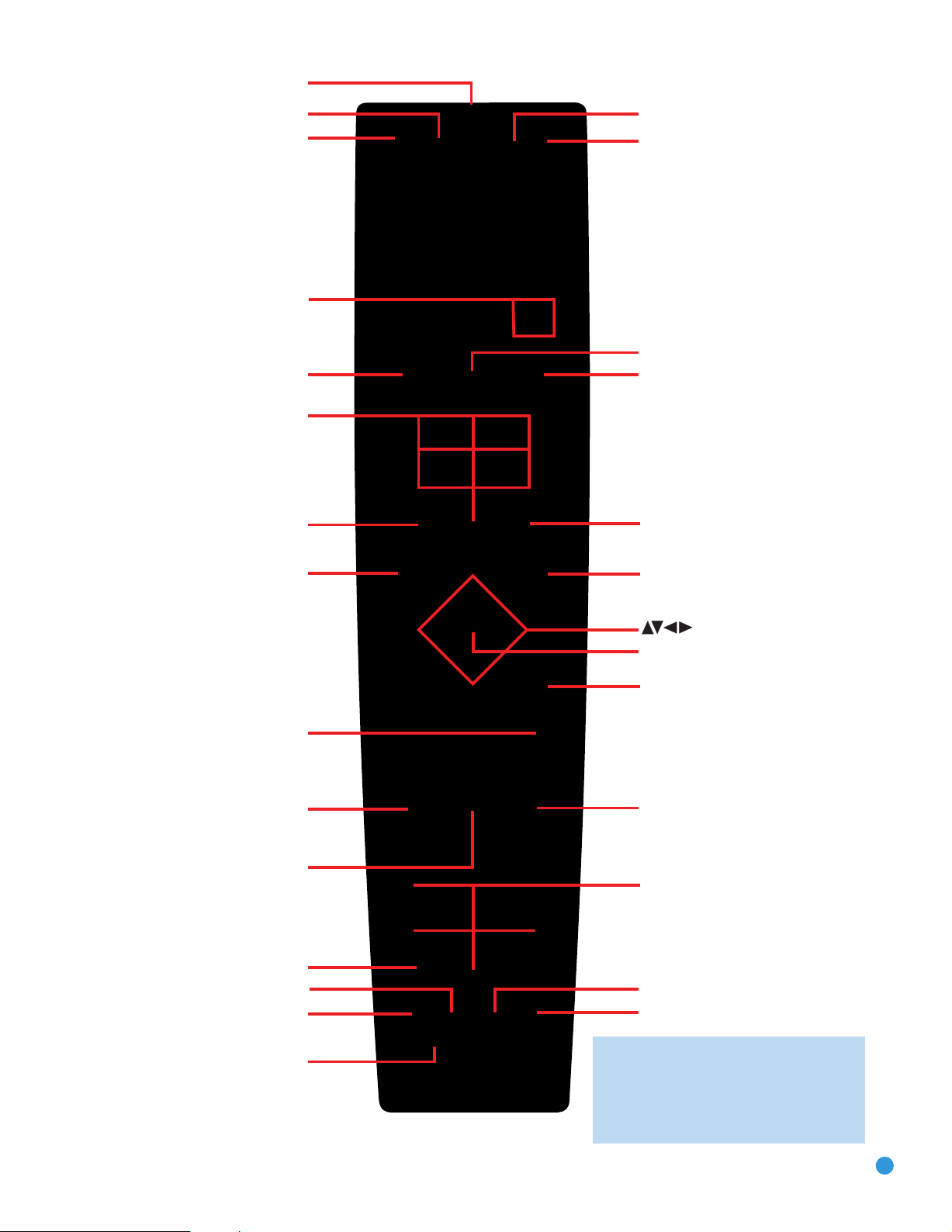
AVR Power Off
AVR Power On
Source Selectors
Audio Effects
Alphanumeric Keys
Teletext
Volume
Mute
Device Power On
Device Power Off
Surround Modes
Video Modes
OK
Navigation
Activity
Menu
Disc Menu
Channel
Sleep Settings
Transport Controls
Source Settings
IR Transmitter Lens
Last
Back/Exit
Record
Info Settings
AVR Settings
Zone Selector
15
NOTE: To make it easier to follow the
instructions throughout the manual that refer
to this illustration, a copy of this page may
be downloaded from the Product Support
section at www.harmankardon.com.
15
Page 16

REMOTE CONTROL FUNCTIONS
Volume Control: Press this button to raise or lower the volume.
Navigation (
used to make selections within the menu system. These buttons are
also used to operate the tuner.
⁄/¤
›
/‹/
) and OK Buttons: These buttons are
Alphanumeric Keys: Use these buttons to enter numbers for
radio station frequencies or to select station presets. Use the alphabetic
keys with other products as required. When prompted for a text entry,
the first press of the key displays the first letter printed above the key.
Each additional press displays the other letters. When the desired letter
appears, wait a moment for it to be entered before moving to the next
character.
Last Channel: When controlling a cable, satellite or HDTV set-top
box or a TV, press this button to return to the previous television channel.
Activity: This button may be programmed to transmit a series of
commands with a single press, which is useful for powering on all
devices and selecting the correct settings on each device, or for selecting
multi-digit channels with a single press. See the Advanced Functions
section for more information on Activities.
Back/Exit: Press this button to return to the previous menu or to exit
the menu system. This button may have the same effect with some
source devices.
Zone Selector: Use this switch to select whether AVR commands
will affect the main listening area (Zone 1) or the remote zone of a
multizone system (Zone 2). For normal operation, leave the switch in
the Zone 1 position.
Track Skip: These buttons have no effect on the receiver, but are
used with source components to change tracks or chapters.
Transport Controls: These buttons have no effect on the receiver,
but are used to control many source components.
Menu Button: This button is used to display the main menu on some
source devices. To display the AVR 254’s main menu, press the AVR
Settings Button.
Disc Menu: While a DVD is playing, press the DVD Source Selector,
then this button, to display the disc’s menu.
Teletext Buttons: Use these buttons with a Teletext-capable televi-
sion if your broadcast, cable or satellite provider offers Teletext service.
They are normally not used in North America. These buttons are also
used to operate some source devices. See Table A13 in the appendix
for details.
Channel/Page Control: When the tuner has been selected, this
control selects a preset radio station. Press these buttons while operating a cable, satellite or HDTV set-top box or a television to change
channels. The Page control may be available with some DVD players
when playing a DVD Audio disc containing pages of images associated
with a track.
Record Button: Use this button to make recordings when an audio
or video recorder is in use.
AVR Settings Button: Press this button to display the AVR’s Main
Menu. It is also used to switch the remote’s device mode from a source
device to the AVR.
Info Settings Button: Press this button to display the AVR’s Info
Menu, which contains the settings for the current source.
Source Settings Button: Press a Source Selector and then this
button to display a source device’s settings menu.
16
16
Page 17

INTRODUCTION TO HOME THEATER
The AVR 254 may be the first multichannel surround sound receiver
you have owned. Although it has more connections and features than
2-channel receivers, many of the principles are similar and the new
concepts are easy to understand. This introductory section will help you
to familiarize yourself with the basic concepts, which will make setup
and operation smoother.
If you are already familiar with home theater, you may skip this section
and proceed to the Connections section on page 18.
Typical Home Theater System
A home theater typically includes an audio/video receiver, which con
the system; a DVD player; a source component for television broad
which may be a cable box, a satellite dish receiver, an HDTV tuner or
simply an antenna connected to the TV; a video display (television);
and loudspeakers.
All of these components are connected using various types of cables
for audio and video signals.
Multichannel Audio
The main benefit of a home theater system is that several loudspeakers
are used in various locations around the room to produce “surround
sound.” Surround sound immerses you in the musical or film presentation
for increased realism.
The AVR 254 may have up to seven speakers connected directly to it
(plus a subwoofer). Each main speaker is powered by its own amplifier
channel inside the receiver. When more than two speakers are used, it
is called a multichannel system.
•
Front Left and Right – The main speakers are used the same
way as in a 2-channel system. However, you may notice that in
many surround modes, these speakers are used more for ambient
sound while the main action, especially dialogue, is moved to the
center speaker.
•
Center – The center speaker is usually placed above or below the
video screen, and is used mostly for dialogue in movies and television
programs. This placement allows the dialogue to originate near the
actors’ faces, for a more natural sound.
•
Surround Left and Right – The surround speakers are used to
improve directionality of ambient sounds. In addition, by using more
loudspeakers in the system, more dynamic soundtracks may be
played without risk of overloading any one speaker.
•
Surround Back Left and Right – Additional surround speakers may be
placed behind the listening position, improving the precision with which
ambient sounds may be placed and allowing for more realistic-sounding
pans. By using more speakers in the system, the same sound levels may
be attained with less burden placed on any individual speaker.
The surround back speakers may also be used with specialized
surround modes that are designed for use with 7.1-channel systems,
such as Dolby Digital EX, Dolby Digital Plus, Dolby TrueHD, DTS-ES
(Discrete and Matrix), DTS-HD High Resolution Audio, DTS-HD Master
Audio and Logic 7 (7.1 modes). However, the surround back speakers
17
trols
casts,
are optional. In fact, the AVR 254 enables you to set up a 5.1-channel
system in your main listening area, and reassign the surround back
channels for use with a multizone system, in which you use the
surround back channels to power a pair of loudspeakers located in
another room.
Many people expect the surround speakers to play as loudly as the
front speakers. Although all of the speakers in the system will be
calibrated to sound equally loud at the listening position, most artists
use the surround speakers for ambient effects only, and they program
their materials to steer very little sound to these speakers.
•
Subwoofer – A subwoofer is a special-purpose speaker designed
to play only the lowest frequencies (the bass). It may be used to
augment smaller, limited-range satellite speakers used for the other
channels. In addition, many digital-format programs, such as movies
recorded in Dolby Digital and other digital formats, may contain a
special low-frequency effects (LFE) channel which is directed only
to the subwoofer. The LFE channel packs the punch of a rumbling
train or airplane, or the power of an explosion, adding realism and
excitement to your home theater. Many people use two subwoofers,
placed on the left and right sides of the room, for additional power
and even distribution of the sound.
Surround Modes
There are different theories as to the best way to present surround
sound and to distribute soundtrack information among the various
speakers. A variety of algorithms have been developed in an effort to
accurately reproduce the way we hear sounds in the real world. The
result is a rich variety of surround mode options. Some modes are
selected automatically, depending on the signal being received from
the source. In many cases, you may select a surround mode manually.
Several companies have taken surround sound in slightly differing
directions. It is helpful to group the numerous surround modes:
•
Dolby Laboratories, Inc. Modes – Dolby TrueHD, Dolby Digital Plus,
Dolby Digital, Dolby Digital EX, Dolby Pro Logic II and IIx, Dolby Virtual
Speaker, Dolby Headphone
•
DTS Modes – DTS-HD, DTS-HD Master Audio, DTS, DTS-ES
(Discrete and Matrix), DTS Neo:6, DTS 96/24
•
Harman International (the Harman Kardon parent company) –
Logic 7
•
Stereo Modes – Generic modes that expand upon conventional
2-channel stereo, including 5- and 7-Channel Stereo
Table A12 in the appendix contains detailed explanations of the
differences between the various mode groups, and the mode options
available within each group. Digital modes, such as Dolby Digital and
DTS, are only available with specially encoded programs, such as HDTV,
DVDs and digital cable or satellite television. Other modes may be used
with various digital and analog signals to create a different surround
presentation, or to use a different number of speakers. Surround mode
selection depends upon the number of speakers in your system, the
materials you are watching or listening to, and your personal tastes.
Feel free to experiment.
17
Page 18
SubwooferPreout
12 3
CONNECTIONS
There are different types of audio and video connections used to
connect the receiver to the speakers and video display, and to connect
the source devices to the receiver. To make it easier to keep them all
®
straight, the Consumer Electronics Association (CEA
) has established
a color-coding standard. See Table 1.
Table 1 – Connection Color Guide
Audio Connections
Left Right
Front (FL/FR)
Center (C)
Surround (SL/SR)
Surround Back (SBL/SBR)
Subwoofer (SUB)
Digital Audio Connections
Coaxial
Optical
Video Connections
Component Y Pb Pr
Composite
S-Video
HDMI™ Connections (digital audio/video)
HDMI
Input
Types of Connections
This section will briefly review different types of cables and connections.
Speaker Connections
Speaker cables carry an amplified signal from the receiver’s speaker
terminals to each loudspeaker. Speaker cables contain two wire conductors, or leads, inside plastic insulation. The two conductors are usually
differentiated in some way, by using different colors, or stripes, or by
adding a ridge to the insulation. Sometimes the wires are different,
colors e.g. copper-colored and silver.
The differentiation is important because each speaker must be connected
to the receiver’s speaker-output terminals using two wires, one positive
(+) and one negative (–), referred to as speaker polarity. It’s important
to maintain the proper polarity for all speakers in the system, or performance can suffer, especially for the low frequencies.
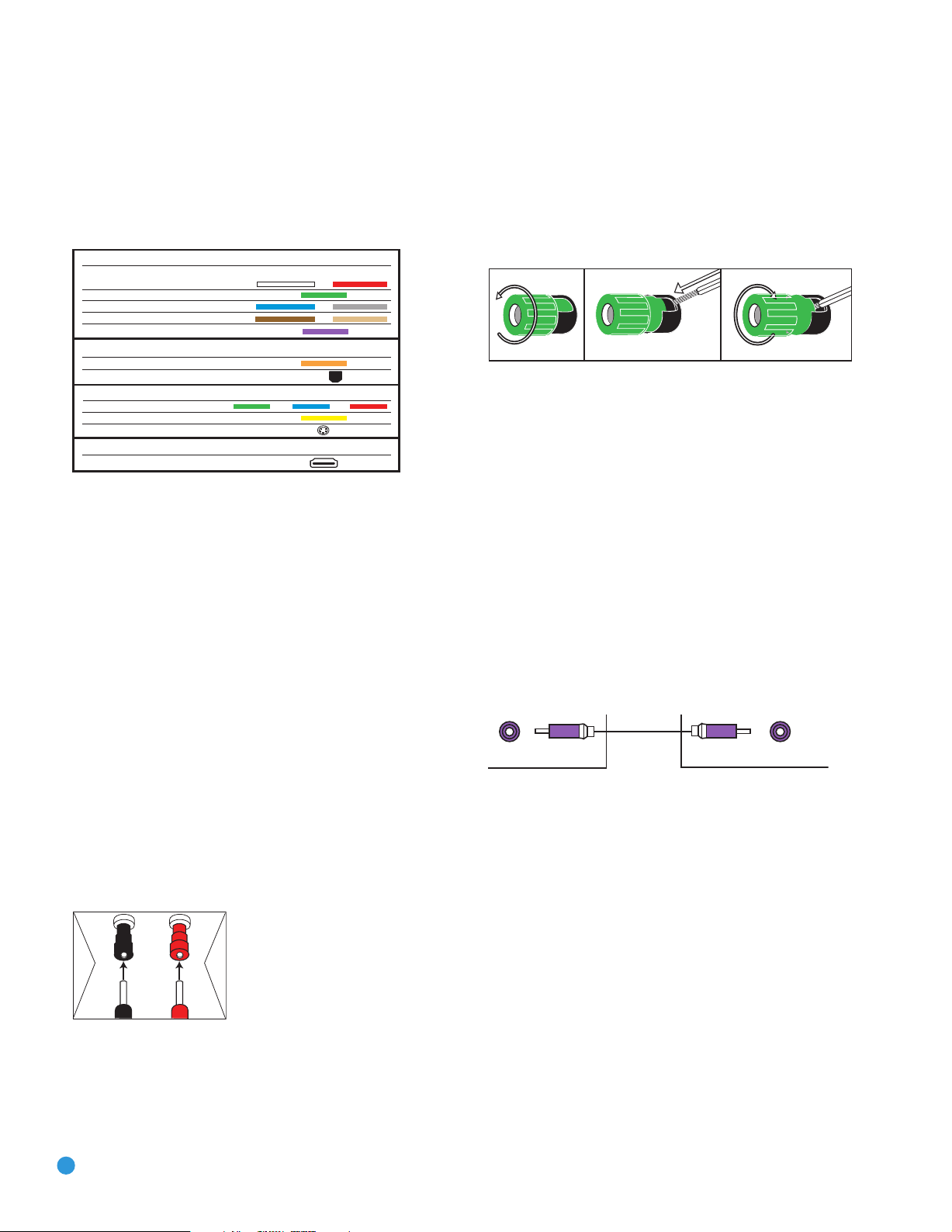
Bare wire cables are installed as follows (see Figure 2):
1. Unscrew the terminal cap until the pass-through hole in the collar is
revealed.
2. Insert the bare end of the wire into the hole.
3. Hand-tighten the cap until the wire is held snugly.
Figure 2 – Binding-Post Speaker Terminals With Bare Wires
Subwoofer
The subwoofer is a specialized type of loudspeaker used to play only
the low frequencies (bass), which require much more power than the
other speaker channels. In order to obtain the best results, most speaker
manufacturers offer powered subwoofers, in which the speaker contains
its own amplifier on board. Usually, a line-level (nonamplified) connection
is made from the receiver’s Subwoofer Output to a corresponding jack
on the subwoofer, as shown in Figure 3, but sometimes the subwoofer
is connected to the receiver using the front left and right speaker outputs,
as with passive in-wall subwoofers, and then the front left and right
speakers are connected to terminals on the subwoofer.
Although the subwoofer output looks similar to the analog audio jacks
used for the various components, it is filtered and only allows the low
frequencies to pass. Don’t connect this output to any other devices.
Although doing so won’t cause any harm, performance will suffer.
Figure 3 – Subwoofer
Always connect the positive terminal on the loudspeaker, which is usually
colored red, to the positive terminal on the receiver, which is colored as
shown in the Connection Color Guide (Table 1). Similarly, always connect
the black negative terminal on the speaker to the black negative terminal
on the receiver.
The AVR 254 uses binding-post speaker
terminals that can accept banana plugs
+
or bare-wire cables. Banana plugs are
simply plugged into the hole in the middle
of the terminal cap. See Figure 1.
Figure 1 – Binding-Post Speaker Terminals With Banana Plugs
18
Connecting Source Devices to the AVR
The AVR 254 is designed to process audio and video input signals,
playing back the audio and displaying the video on a television or
monitor connected to the AVR. These signals originate in what are
known as “source devices,” including your DVD player, CD player, DVR
(digital video recorder) or other recorder, tape deck, game console,
cable or satellite television box or MP3 player. Although the tuner is
built into the AVR, it also counts as a source, even though no external
connections are needed, other than the FM and AM antennas and the
XM antenna module.
Separate connections are required for the audio and video portions of
the signal, except for digital HDMI connections. The types of connections
used depend upon what’s available on the source device, and for video
signals, the capabilities of your video display.
18
Page 19
CONNECTIONS
Coaxial
Coaxial digital
audio cable
Audio Connections
There are two formats for audio connections: digital and analog. Digital
audio signals are required for listening to sources encoded with digital
surround modes, such as Dolby Digital and DTS, or for non-compressed
PCM digital audio. There are three types of digital audio connections:
HDMI, coaxial and optical. Any type of digital audio connection may be
used for each source device, but never more than one for the same
source. However, it’s okay to make both analog and digital audio connections to the same source.
NOTE: Since HDMI signals may carry both audio and video, if
your video display device has an HDMI input, make a single HDMI
connection from your source device (such as a DVD player) to
the AVR. No separate digital audio connection is usually required.
Make sure to turn the volume on your television all the way down.
Digital Audio
The AVR 254 is equipped with three HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia
Interface) inputs, and one output. HDMI technology enables digital audio
and video information to be carried using a single cable, thus delivering
the highest quality picture and sound.
There are different HDMI versions, depending on the capability of
the source device and the type of signal it is capable of transmitting.
In addition, receivers and processors such as the AVR 254 may handle
the incoming signal in several different ways, depending on their capability
as well. The AVR 254 uses HDMI version 1.3a, and is capable of
processing both the audio and video components of the HDMI data,
minimizing the number of cable connections in your system. Thanks to
the higher bandwidth and speed of HDMI version 1.3a, the AVR 254
implements Deep Color, which increases by an order of magnitude the
shades of color that can be displayed; and the latest lossless multichannel
audio formats, including Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio.
NOTE: Some DVD-Audio, SACD, HD-DVD and Blu-ray Disc
players, output mulitchannel audio only through the source’s
multichannel analog outputs. For those devices, make a separate analog audio connection in addition to the HDMI connection, which is still used for video and to listen to Dolby Digital,
DTS or PCM materials that may be stored on the disc.
In addition, the AVR 254 will convert analog video signals to the HDMI
format, upscaling to high-definition 1080p resolution. You may view the
AVR 254’s own on-screen display menus using the HDMI output.
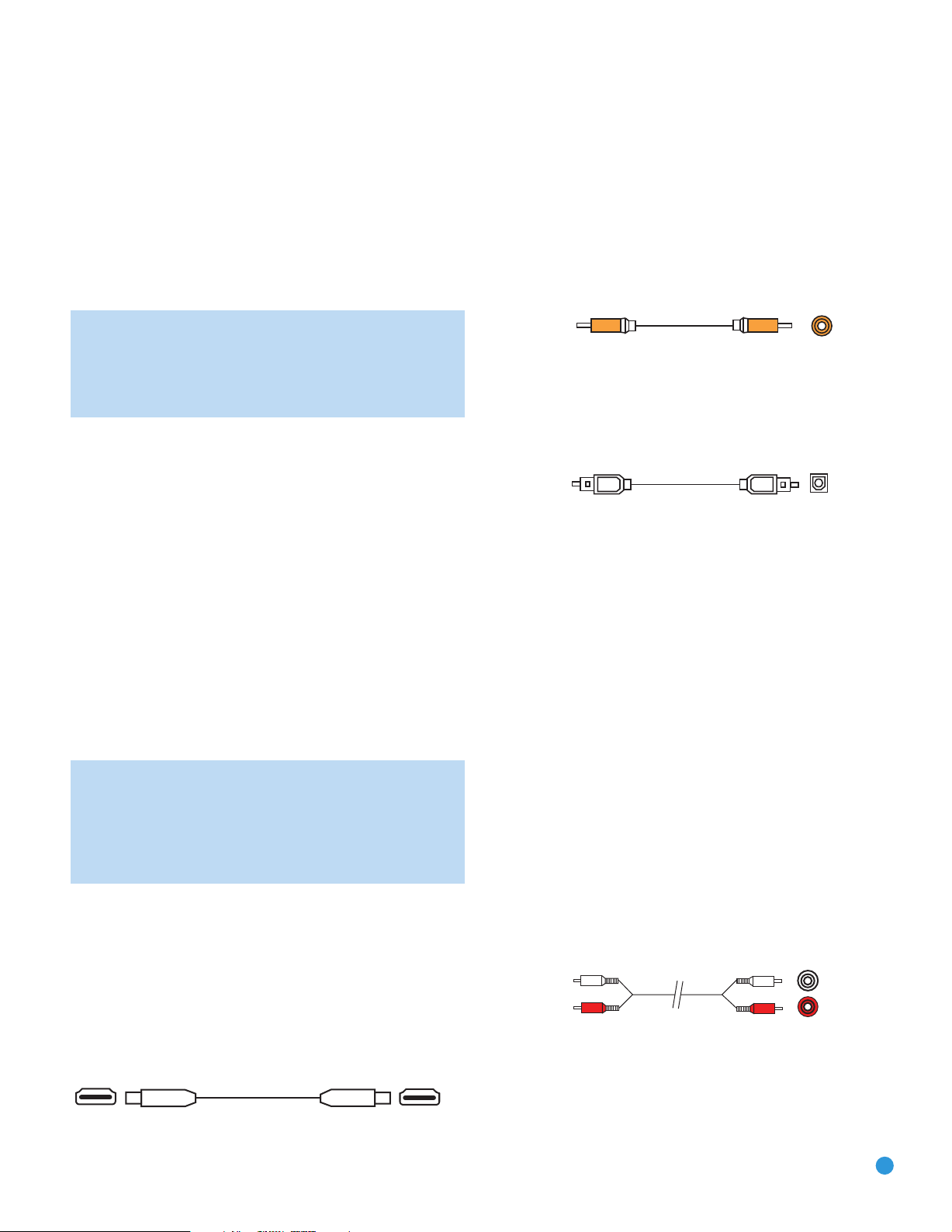
The physical HDMI connection is simple. The connector is shaped for
easy plug-in (see Figure 4). If your video display has a DVI input and is
HDCP-compliant, you may use an HDMI-to-DVI adapter (not included)
to connect it to the AVR’s HDMI Output, but a separate audio connection
is required. HDMI cable runs are usually limited to about 10 feet,
depending on the type of cable used.
Figure 4 – HDMI Connection
If your video display or source device is not HDMI-capable, use one of
the analog video connections (composite, S- or component video) and,
if available on your source device, either a coaxial or optical digital audio
connection.
Coaxial digital audio jacks are usually color-coded in orange. Although
they look similar to analog jacks, they should not be confused, and you
should not connect coaxial digital audio outputs to analog inputs or
vice versa. See Figure 5.
Figure 5 – Coaxial Digital Audio
Optical digital audio connectors are normally covered by a shutter to
protect them from dust. The shutter opens as the cable is inserted. Input
connectors are color-coded using a black shutter, while outputs use a
gray shutter. See Figure 6.
Optical digital
audio cable
Figure 6 – Optical Digital Audio
Optical
Analog Audio
Analog connections require two cables, one for the left channel (white)
and one for the right channel (red). These two cables are often attached
to each other for most of their length. See Figure 7.
Most sources that have digital audio jacks also have analog audio jacks,
although some older types of sources, such as tape decks, only have
analog jacks. For sources that are capable of both digital and analog
audio, you may make both connections.
The analog audio connection is strongly recommended if you intend to
use the source with the multizone system. It’s required if you will be
using the multizone preamp outputs with an external amplifier to power
your remote speakers, as the AVR 254’s multizone system is not capable of converting the digital signal to analog format. It’s suggested that
you also use the analog audio connections when using the Surround
Back/Zone 2 speaker outputs, in case another two-channel digital audio
source is in use in the main listening area. The AVR 254 is only capable
of processing one PCM source at a time.
You may only record materials from DVDs or other copy-protected
sources, using analog connections. Remember to comply with all copyright laws, if you choose to make a copy for your own personal use.
Analog audio
cable (RCA)
Figure 7 – Analog Audio
L
R
Multichannel analog connections are used with some high-definition
sources where the copy-protected digital content is decoded inside the
source. These types of connections are usually used with DVD-Audio,
SACD, Blu-ray Disc, HD-DVD and other multichannel players. See
Figure 8. However, the multichannel analog audio connection is not
19
19
Page 20
CONNECTIONS
S-video cable
Composite
video cable
required for DVD-Audio players compliant with HDMI version 1.1 or
better, or HD-DVD and Blu-ray Disc players that decode the digital audio
internally and output linear PCM signals in digital format. Consult the
owner’s guide for your disc player for more information.
Front Surround Center
Multichannel
analog audio
cable (RCA)
Subwoofer
Figure 8 – Multichannel Analog Audio
The AVR 254 also offers an analog audio input on the rear panel in the
form of a stereo 1/8" mini jack. Connect the headphone output of any
audio source, such as an MP3 player or portable CD player, to the
Stereo Jack input. See Figure 9.
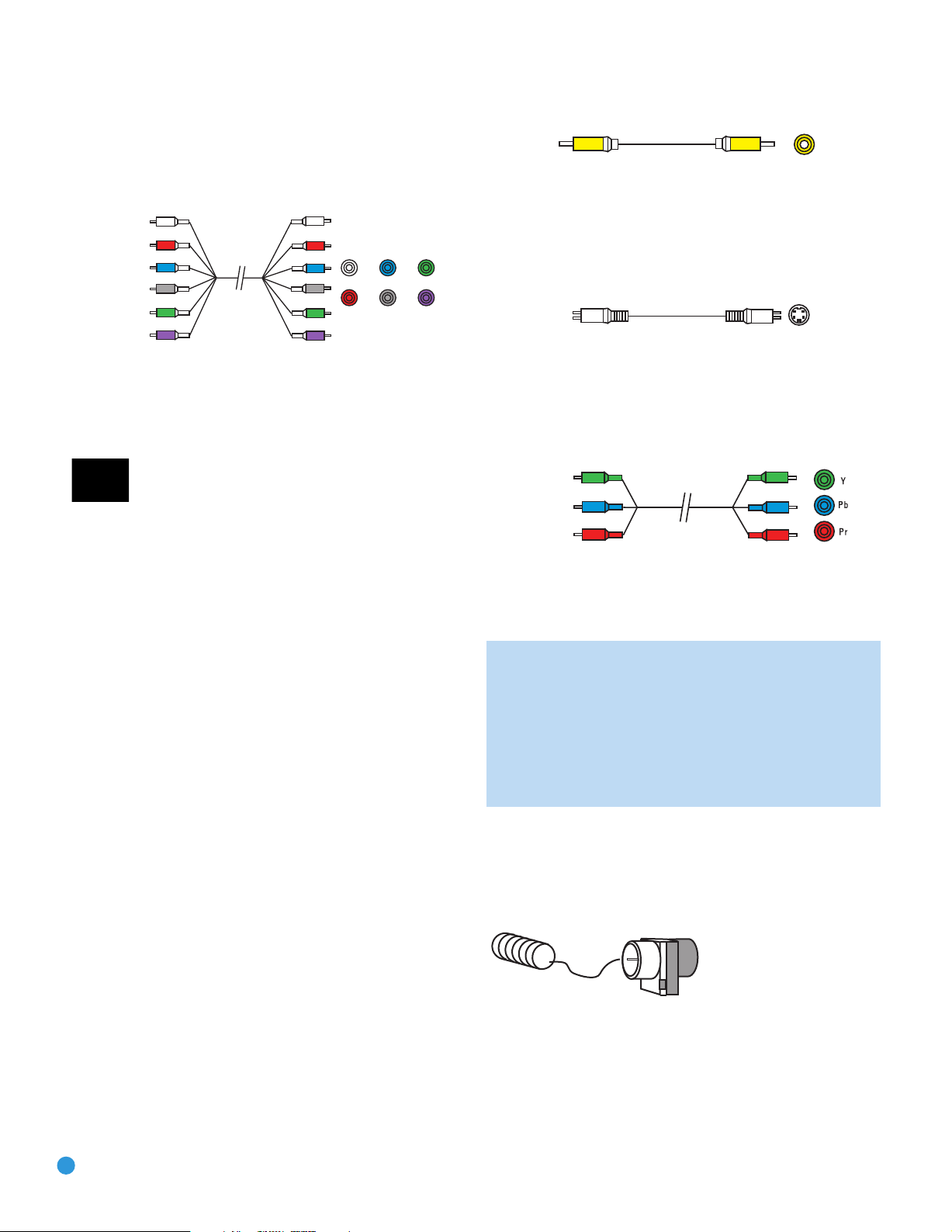
Figure 10 – Composite Video
S-video, or “separate” video, transmits the chrominance and luminance
components using separate wires contained within a single cable. The
plug on an S-video cable contains four metal pins, plus a plastic guide
pin. Be careful to line up the plug correctly when you insert it into the
jack on the receiver, source or video display. See Figure 11.
Figure 11 – S-Video
Component video separates the video signal into three components –
one luminance (“Y”) and two sub-sampled color signals (“Pb” and “Pr”) –
that are transmitted using three separate cables. The “Y” cable is colorcoded green, the “Pb” cable is colored blue and the “Pr” cable is
colored red. See Figure 12.
Figure 9 – Stereo Jack
Video Connections
Although some sources only produce an audio signal (e.g., CD player,
tape deck), many sources output both audio and video signals (e.g.,
DVD player, cable television box, HDTV tuner, satellite box, VCR, DVR).
In addition to the audio connection, make one type of video connection
for each of these sources (only one at a time for any source).
Digital Video
If you have already connected a source device to one of the HDMI
inputs as explained in the Digital Audio Connections section, you have
automatically made a video connection at the same time, as the HDMI
signal includes both digital audio and video components.
If the source device is not capable of transmitting its digital audio signal
through the HDMI connection, use one of the coaxial or optical digital
audio inputs for the source.
If a multichannel analog audio connection is required for certain lossless
formats (e.g., DVD-Audio, SACD, HD-DVD or Blu-ray Disc), you may
make both audio connections. To listen to the multichannel disc, set the
Audio Auto Polling setting to the 6/8CH inputs, and the AVR will automatically select it when no digital signal is output by the player.
Component
video cable
Figure 12 – Component Video
If it’s available on your video display, an HDMI connection is recommended as the best quality connection, followed by component video,
S-video and then composite video.
NOTES:
• Copy-protected sources are not available at the Component
Video Monitor Outputs.
• Standard and high-definition analog video signals are
upscaled to 1080i resolution for the Component Video
Monitor Outputs. For improved video performance, consider
upgrading to an HDMI-capable video display with 1080p
resolution.
Antennas
The AVR 254 uses separate terminals for the included FM and AM
antennas that provide proper reception for the tuner.
The FM antenna uses a 75-ohm F-connector. See Figure 13.
Analog Video
There are three types of analog video connections: composite video,
S-video and component video.
Composite video is the basic connection most commonly available. The
jack is usually color-coded yellow, and looks like an analog audio jack,
although it is important never to confuse the two. Do not plug a composite
video cable into an analog or coaxial digital audio jack, or vice versa.
Both the chrominance (color) and luminance (intensity) components of
the video signal are transmitted using a single cable. See Figure 10.
20
Figure 13 – FM Antenna
The AM loop antenna needs to be assembled. Connect the two leads
to the spring terminals on the receiver. As AM antenna leads have no
polarity, it doesn’t matter which of the two terminals is used for either
lead. See Figure 14.
20
Page 21
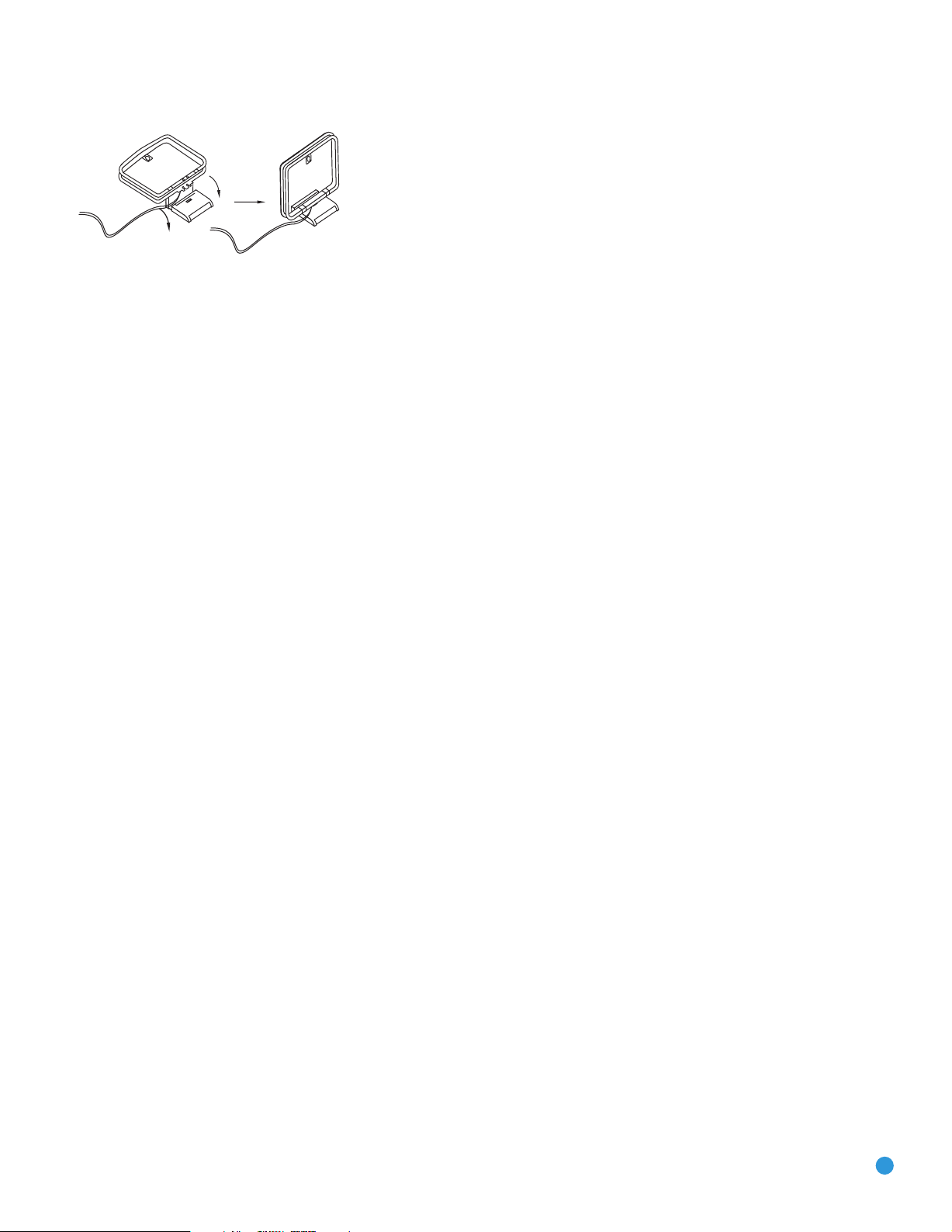
Figure 14 – AM Antenna
To enjoy XM satellite radio, purchase an XM antenna module designed
for use with XM Ready devices and a subscription to the XM service.
We recommend the XM Mini Tuner and Home Dock Bundle, available
at www.xmradio.com. The older Connect and Play module is also compatible with the AVR 254, but it may no longer be available in your area.
An XM Ready-compatible module uses the special connector on the
AVR 254’s rear panel that allows you to use the AVR’s tuner, including
its 40 preset station locations and remote control. Although you may
use a module with standard audio connections, which may be indicated
for “car and home use,” you will not be able to enjoy the AVR 254’s
ease of control.
CONNECTIONS
RS-232 Serial Port
The RS-232 serial port on the AVR 254 is used only for software
upgrades. If we release an upgrade for the receiver’s operating system
at some time in the future, it may be downloaded to the AVR using this
port. Complete instructions will be provided at that time.
21
Page 22
SPEAKER PLACEMENT
C
90°
150°
90°
150°
30° 30°
SUB
FRFL
SL
SBL SBR
SR
C
Alternate placement
for Side Surround
Left Speaker
Alternate placement
for Side Surround
Right Speaker
110°
150°
110°
150°
30° 30°
SUB
FRFL
SL SR
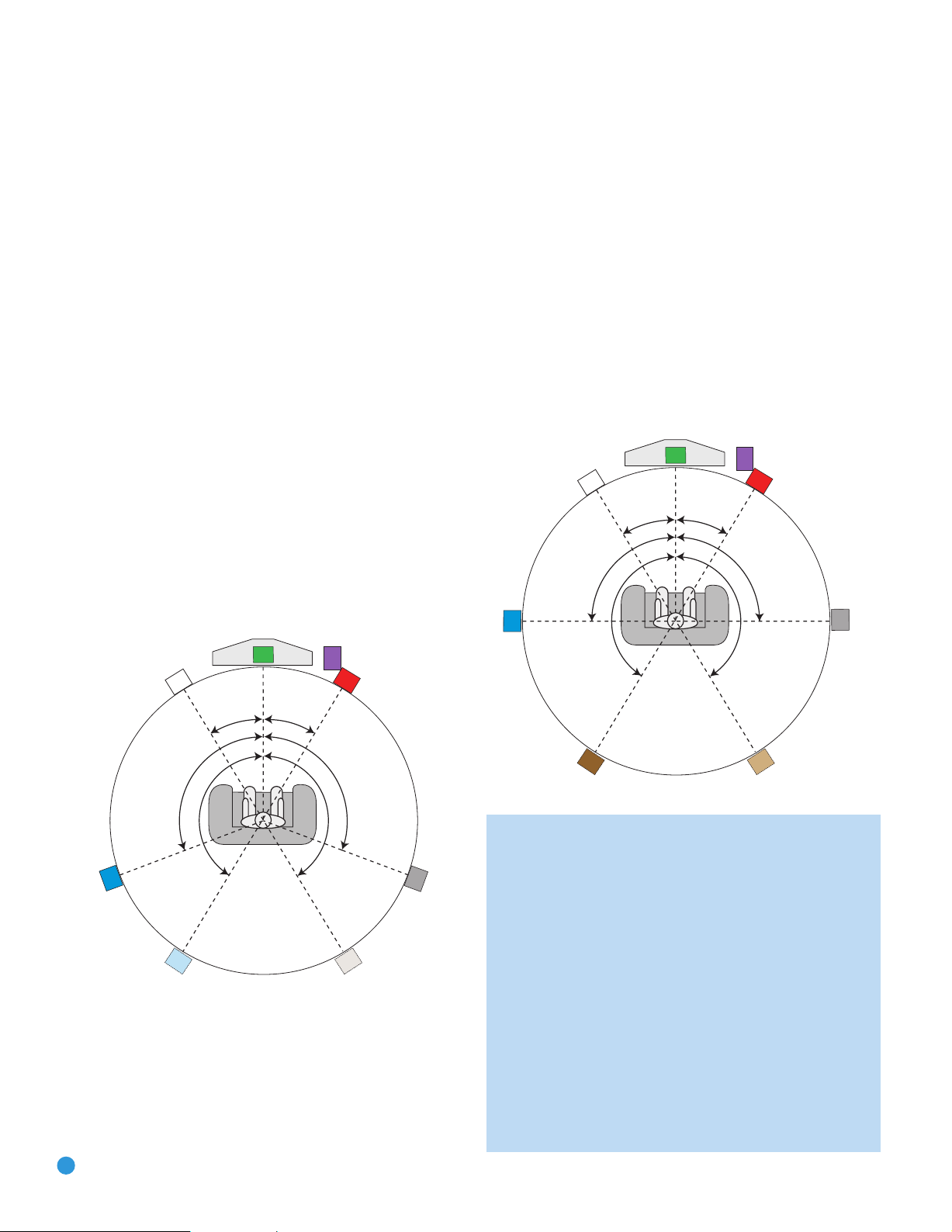
Before you begin to connect cables, it is important to place your speakers
in their correct locations in the room.
Optimally, the speakers should be placed in a circle with the listening
position at its center. The distance from the listening position to the
video display forms the radius of the circle.
The speakers should be angled so that they directly face the listening
position.
Front Speaker Placement
The center speaker is placed either on top of, below or mounted on the
wall above or below the video display screen.
The front left and right speakers are placed along the circle, about 30
degrees from the center speaker and angled toward the listener.
It is best to place the front left/right and center speakers as close to
the same height as possible, preferably at about the same height as
the listener’s ears. In any event, the center speaker should be no more
than two feet above or below the left/right speakers.
Placement of the surround speakers depends on the number of
speakers in your system. If you’re using only two speakers with the
AVR 254, place them in the front left and right positions, and skip to
the Installation section. However, we recommend using the AVR 254
in a 5.1- or 7.1-channel configuration for optimal surround sound
performance.
Placement of Surround Speakers in a 5.1-Channel
System
The side surround speakers should be placed 110 degrees from the
center speaker, that is, slightly behind and angled toward the listener.
If this isn’t feasible, place them behind the listener, with each surround
speaker facing the opposite-side front speaker. See Figure 15. The
surround speakers may be placed a little higher than the listener’s ears.
Placement of Surround Speakers in a 7.1-Channel
System
In a 7.1-channel system, the side surround speakers are placed 90 degrees
from the center speaker, directly to either side of the listening position.
The surround back left and right speakers are placed 150 degrees from
the center speaker, or directly facing the opposite-side front speaker.
See Figure 16.
Figure 15 – Speaker Placement (5.1-Channel System)
22
Figure 16 – Speaker Placement (7.1-Channel System)
NOTE: Some speaker manufacturers offer 6.1-channel speaker
systems, which are compatible with 6.1-channel surround
sound formats, such as Dolby Digital EX, DTS-ES Discrete and
Matrix modes and DTS Neo:6 mode. We do not recommend
using the AVR 254 in a 6.1-channel configuration. In fact, the
6.1-channel formats will sound better when played through
a 7.1-channel system. The same surround back channel information is played through both surround back speakers, but with
twice the power and clarity.
If you wish to use the AVR 254 with a 6.1-channel speaker
system, place the single surround back speaker directly behind
the listener, but do not connect it until after you have run the
EzSet/EQ procedure for a 5.1-channel system. After the
EzSet/EQ process finishes, connect the surround back speaker
to the Surround Back Left Speaker Output. Then follow the
directions in the Advanced Features section for manual setup
of the surround back speaker.
Page 23
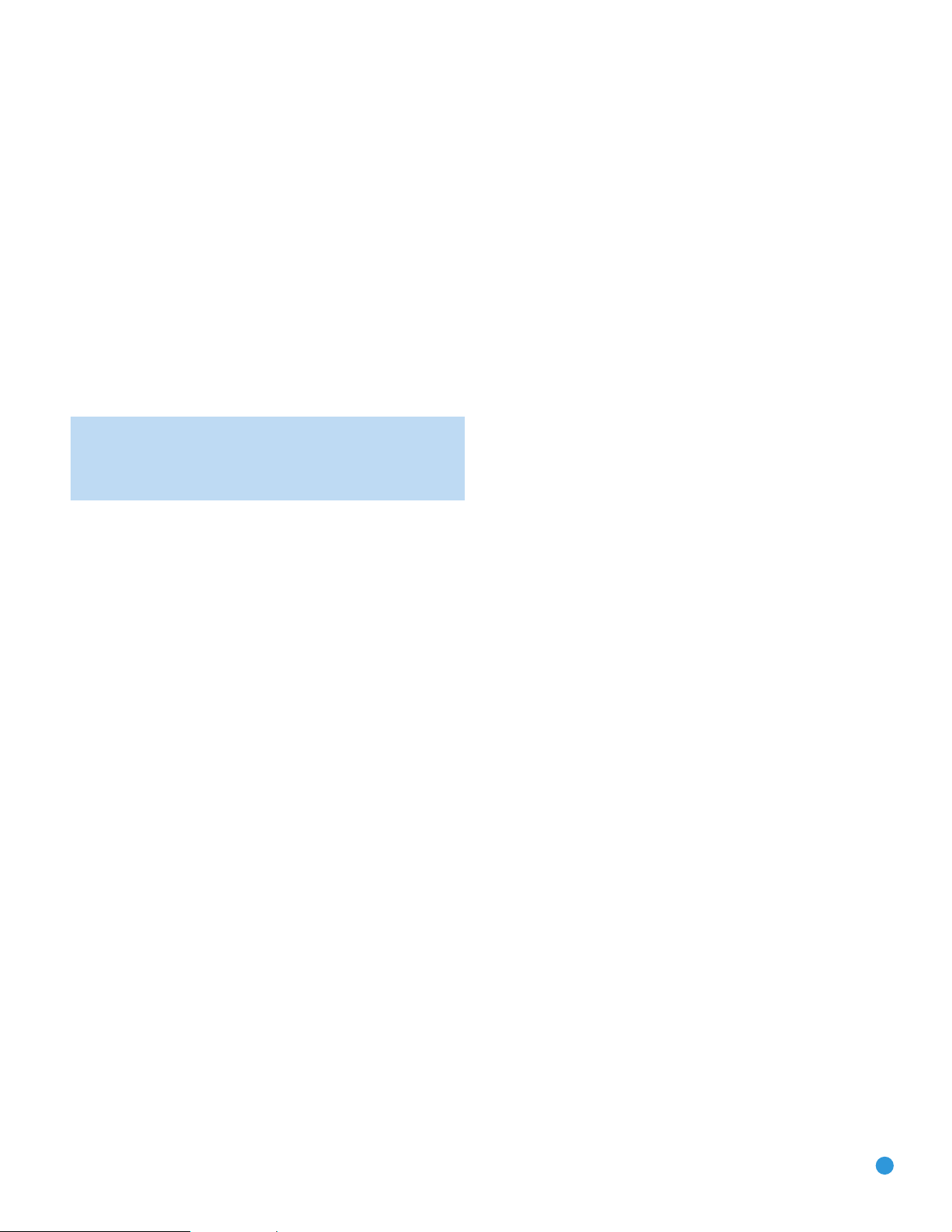
SPEAKER PLACEMENT
Subwoofer Placement
The subwoofer’s location is less critical, since low-frequency sounds
are omnidirectional. Placing the subwoofer close to a wall or in a corner
will reinforce the low frequencies, and may create a “boomy” sound.
Experiment by placing the subwoofer where the listener normally sits
and then walk around the room until the low frequencies sound best.
Place the subwoofer in that spot.
In some installations it may be desirable to use two subwoofers for
a 7.2-channel system. This is easily done by purchasing an optional
Y-Adapter with one male RCA plug and two female RCA jacks. Connect
the male jack to the Subwoofer output on the AVR’s rear panel, and
then run a standard interconnect cable from the Y-Adapter to the Line
Input of each subwoofer. You may then place the two speakers as best
suits the requirements of the room and your listening preferences.
NOTE: Your receiver will sound its best when the same model
loudspeaker is used for all positions (other than the subwoofer).
If that isn’t possible, try to use speakers made by the same
manufacturer.
23
Page 24

INSTALLATION
AVR 254
FM
AM
AVR 254
SR
SL
FR FL
SBR
SBL
C
You are now ready to connect the various components to the receiver.
Before beginning, turn off all components, including the AVR 254,
unplug their power cords.
Don’t plug in any of the power cords
until you have finished making all of your connections.
Remember that the receiver generates heat while it is on. Select a
location that leaves several inches of space on all sides of the receiver.
Avoid completely enclosing the receiver inside an unventilated cabinet.
It is preferable to place components on separate shelves rather than
stacking them directly on top of the receiver. Some surface finishes are
delicate. Try to select a location with a sturdy surface finish.
and
AVR 254
SUB
Figure 18 – Subwoofer Connection
Step Three – Connect the Antennas
Step One – Connect the Speakers
If you have not yet done so, place your speakers in the listening room,
as described in the Speaker Placement section above.
Connect the center, front left, front right, surround left, surround
right, surround back left and surround back right loudspeakers to the
corresponding speaker terminals on the AVR 254. See Figure 17.
Maintain the proper polarity by always connecting the positive and
negative terminals on each speaker to the positive and negative
terminals on the receiver. Use the Connection Color Guide on page 18
as a reference.
Figure 17 – Speaker Connections
NOTE: If you only have one surround back speaker, wait until after
you have run the EzSet/EQ process in the Initial Setup section
before connecting it to the Surround Back Left speaker outputs.
Step Two – Connect the Subwoofer
Connect the Subwoofer Output on the AVR 254 to the line-level input
on your subwoofer. See Figure 18. Consult the manufacturer’s guide for
the subwoofer for additional information.
When the system has two subwoofers for a 7.2-channel system, use a
Y-Adapter (not included) with one male RCA plug and two female RCA
jacks. Connect the male plug to the Subwoofer Output, and connect
each female jack to a cable that is then plugged into the line-level input
on each subwoofer.
Connect the FM and AM antennas to their terminals. If you have
purchased an XM antenna module designed for connection to an
XM Ready device, connect it now. To enjoy XM Radio, remember to
purchase a subscription and activate your antenna module. More
information is available at www.xmradio.com. See Figure 19.
Figure 19 – Antenna Connections
Step Four – Connect the Source Components
A source is a device where the audio and video signals originate. Some
sources, such as CD players, only offer audio, while sources used for
watching movies or broadcast-television programming deliver a video
signal as well.
Referring to the photograph of the AVR 254 remote control on page 15,
there is a section of 7 buttons near the top of the remote designated
“Source Selectors”: Cable/Sat, DVD, Media Server, Radio, TV, Game
and AUX. Each of these buttons corresponds to a “source input”. The
AVR 254’s flexible design allows you to use almost any combination
of audio and video connections for each source device. The goal of
Step Four of the Installation is to match up each of your source devices,
e.g., DVD player and cable television box, with the correct connectors
on the AVR 254.
You may connect a source device to any appropriate input connectors.
Note which audio and video inputs are used for each device in Table A5
in the appendix. Table A2 indicates the default input-connection assignments, any of which may be changed to match the actual connections
in your system.
The precise connections to be made depend on the capabilities of the
source device and your video display (TV). Select the best audio and
video connections for each source. The types of connections are listed
in order of preference:
24
Page 25

INSTALLATION
AVR 254
AVR 254
AVR 254
HDMI Connections
• Choose the HDMI connection if it’s available on your source device
and your TV. A HDMI connection carries both digital audio and video,
enabling a single-cable connection from the source device to the
AVR. Except as noted below, no other audio or video connections
are required.
NOTE: If your DVD-Audio, SACD, Blu-ray Disc or HD-DVD player
is not capable of outputting multichannel digital audio through its
HDMI output, make additional 6-/8-channel analog audio connections.
Audio Connections (for non-HDMI sources)
• Choose one digital audio connection: Optical or Coaxial
• Optional, or where digital audio is not available: Analog audio for
making recordings for personal use or as a backup. Analog audio is
required for older analog sources that don’t have digital audio outputs,
such as cassette decks.
Video Connections (for non-HDMI sources)
(choose only one, and make sure that type is available on your TV)
• Component video • Composite video
• S-video
NOTES:
• If the video display is equipped with a DVI digital video input,
make sure it is also HDCP-compliant (High-Bandwidth Digital
Content Protection) to display copy-protected materials.
outputting the multichannel audio through its HDMI output, make the
following additional connections (see Figure 21):
• Connect the DVD player’s 6-/8-channel analog audio outputs to the
6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs on the AVR.
Figure 21 – Connecting a Multichannel Audio Player
Component Video: If the DVD player or the TV does not have an
HDMI connector, but they both have component video connectors,
connect the player as follows (see Figure 22):
• Connect the DVD player’s component video output to the Component
Video 1 or 2 Input on the AVR.
• Connect one of the DVD player’s digital audio outputs to one of the
Coaxial or Optical inputs on the AVR.
• If the source or video display has a DVI input, use an HDMIto-DVI adapter (not included), and make separate audio
connections.
Connect a DVD, SACD, Blu-ray Disc or HD-DVD Player
HDMI Video:
connector, connect the player as follows (see Figure 20):
• Connect the DVD player’s HDMI output to the HDMI 1, 2 or 3 Input on
the AVR.
Figure 20 – Connecting An HDMI-Equipped Disc Player
If the player is capable of playing multichannel discs, including DVDAudio, SACD, Blu-ray Disc and HD-DVD, but it is not capable of
If the DVD player and the TV both have an HDMI
Figure 22 – Connecting a Component-Video-Equipped Disc Player
If the player is capable of playing multichannel discs, including DVD-Audio,
SACD, Blu-ray Disc and HD-DVD, make the following additional connection
(see Figure 21):
• Connect the DVD player’s 6-/8-channel analog audio outputs to the
6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs on the AVR.
Composite/S-Video: If the best video connection common to both
the DVD player and the TV is either S-video or composite video, follow
these steps (see Figure 23):
• Connect the DVD player’s S-video or composite video output (use one
connection only) to the Video 1, 2 or 3 Input on the AVR. You may also
use the Video 4 Composite or S-video Input located on the AVR’s front
panel (see Figure 31).
25
Page 26

INSTALLATION
AVR 254
AVR 254
AVR 254
• Connect the DVD player’s digital audio output to one of the Coaxial or
Optical inputs on the AVR.
If the player is capable of playing multichannel discs, including DVD-Audio,
SACD, Blu-ray Disc and HD-DVD, make the following additional connection
(see Figure 23):
• Connect the DVD player’s 6-/8-channel analog audio outputs to the
6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs on the AVR.
Figure 23 – Connecting a Composite- or S-Video-Equipped Disc Player
NOTES:
• Refer to Table A2 in the appendix for the default audio and
video input assignments for each source. Using the default
connections, if appropriate for your system, may save a few
steps during Initial Setup. However, thanks to the AVR 254’s
flexibility, you may assign any audio and any video input to
any source, as long as the assignments match the physical
connections.
Figure 24 – Connecting an HDMI-Equipped Recorder
Component Video: If the recorder or the TV does not have an
HDMI connector, but they both have component video connectors,
connect the recorder as follows (see Figure 25):
• Connect the recorder’s component video output to the Component
Video 1 or 2 Input on the AVR. This connection is for playback only,
as the AVR cannot make recordings from component video sources.
• Connect the recorder’s digital audio output to a Coaxial or Optical
Input on the AVR (if available).
• Follow the instructions in the Composite/S-Video section for making
connections required for recordings.
• If you wish to make recordings from a DVD, use an S-video or
composite video input, and an Analog Audio input in addition
to any other connections. The AVR cannot make recordings
from HDMI or component video sources, and digital audio
sources may only be recorded in two channels.
Connect an Audio/Video Recorder (PVD, DVR or TiVo®)
HDMI Video:
connect the recorder as follows (see Figure 24):
• Connect the recorder’s HDMI output to the HDMI 1, 2 or 3 Input
on the AVR. This connection is for playback only, as the AVR cannot
make recordings from HDMI sources.
• To make recordings, follow the instructions below for Composite/
S-video recorders.
26
If the recorder and the TV both have an HDMI connector,
Figure 25 – Connecting a Component-Video-Equipped Recorder
Composite/S-Video: If the best video connection common to
both the recorder and the TV is either S-video or composite video, or
to make recordings, follow these steps, using only one type of video
connection throughout (see Figure 26):
• Connect the recorder’s S-video/composite video output to the
Video 2 S-Video/Composite Video Input on the AVR.
• Connect the recorder’s S-video/composite video input to the Video 2
S-Video/Composite Video Output on the AVR.
• Connect the recorder’s analog audio outputs to the Analog 4 Audio
Inputs on the AVR.
• Connect the recorder’s analog audio inputs to the Analog 4 Audio
Outputs on the AVR.
Page 27

INSTALLATION
AVR 254
AVR 254
AVR 254
Figure 26 – Connecting a Composite or S-Video Recorder
• To make two-channel digital audio recordings, connect the recorder’s
digital audio output to one of the Optical or Coaxial Inputs, and connect the AVR’s Coaxial Digital Audio Output to the recorder’s coaxial
input. The AVR will convert an optical digital audio input signal to the
proper format for recording via the Coaxial Digital Audio Output. See
Figure 26.
Connect a Cable TV, Satellite, HDTV or Other Set-Top
Box for Broadcast Television
NOTE: If the TV has a digital audio output, connect it to one of
the digital audio inputs. If you use a direct cable connection to
your TV, or an antenna connection with the TV’s internal tuner,
connect either the TV’s digital audio output (if available) or its analog
audio outputs to the AVR. See Step Five for information on
connecting the receiver’s video monitor outputs to the television.
HDMI Video: If the set-top box and the TV both have an HDMI
connector, connect the set-top box as follows (see Figure 24):
• Connect the set-top’s HDMI output to the HDMI 1, 2 or 3 Input
on the AVR.
Component Video: If the set-top box or the TV does not have an
HDMI connector, but they both have component video connectors,
connect the set-top box as follows (see Figure 25):
• Connect the set-top’s component video output to the Component
Video 1 or 2 Input on the AVR (if available).
• Connect the set-top’s digital audio output to one of the Coaxial or
Optical Inputs on the AVR (if available).
Composite S/Video: If the best video connection common to both
the set-top box and the TV is either S-video or composite video, follow
these steps (see Figure 27):
• Connect the set-top’s S-video or composite video output (use one
connection only) to the corresponding Video 1, 2 or 3 Input on the AVR.
• Connect the set-top’s digital audio output to one of the Coaxial or
Optical Inputs on the AVR (if available). For fully analog set-top boxes,
connect the box’s analog audio outputs to the AVR’s Analog 1, 2, 3,
4 or 5 Audio Inputs.
Figure 27 – Connecting a Composite- or S-Video-Equipped Set-Top Box
Connect a CD Player or Any Audio-Only Device
If the CD player or other component has a digital audio output, connect
it to any available digital audio input on the AVR. If not, connect the CD
player’s left and right analog audio outputs to the Analog 1 or 2 Audio
Inputs. No video connection is required, although the AVR will display
any signal at the video input assigned to the same source as the audio
inputs. See Figure 28.
Figure 28 – Connecting a CD or Audio-Only Source
NOTES:
• A turntable may only be connected to the AVR if it is equipped
with an internal phono preamp, or if you supply an external
phono preamp, available at some audio specialty stores or
through the Harman Kardon Parts Dept. You may then connect
it to any set of analog audio inputs.
• Although there is no official source on the AVR 254 named
CD, Phono or Audio, you may assign the audio device to an
available source, such as TV (if the Cable/Sat source is in use
for broadcast television), Game or AUX. See the Initial Setup
section for more details on source assignment.
Connect a Tape Deck or Any Audio-Only Recorder
If the recorder has digital audio inputs and outputs, connect either its
coaxial or optical digital audio output (not both) to the corresponding
available input on the AVR, and connect the AVR’s Coaxial Digital Audio
Output to the recorder’s coaxial digital audio input.
27
Page 28

INSTALLATION
AVR 254
AVR 254
AVR 254
AVR 254
To make analog audio recordings, connect the recorder’s left and right
analog audio outputs to the Analog 2 Audio Inputs on the AVR, and the
recorder’s analog audio inputs to the AVR’s Analog 2 Audio Outputs.
No video connection is required, although the AVR will display any signal
at the video input assigned to the same source as the Analog 2 Audio
Inputs. See Figure 29.
Figure 31 – Connecting a Device to the Front-Panel Inputs
Audio Components: Connect audio-only devices, such as CD players,
to either the Coaxial or Optical Digital Audio Inputs, or the Analog Audio
Inputs (see Figure 31).
Figure 29 – Connecting an Audio Recorder
Connect a Portable Audio Player
For audio-only playback from a portable CD player, cassette deck, MP3
player or other device equipped with a 1/8-inch headphone jack, use
a stereo 1/8-inch mini-plug interconnect (not included) to connect the
device’s headphone jack to the Stereo Jack on the AVR. Use the
device’s own controls to operate it. See Figure 30.
Figure 30 – Connecting a Portable Audio Player
Alternatively, use an interconnect with a stereo 1/8-inch mini-plug at
one end and two RCA plugs at the other end to connect the player to
the Audio Inputs on the AVR’s front panel. See Figure 31.
Connecting a Game Console, Camera or Other Device
NOTE: If your video devices are equipped with HDMI or com-
ponent video outputs, you may connect them to any available
audio and video input on the AVR.
Step Five – Connect the Video Display
IMPORTANT NOTE: Do not connect any video output on the
video display (TV) to any video input on the AVR. Doing so will
cause undesirable video interference.
HDMI Video: If the display has an HDMI input, connect the HDMI
Monitor Output to the display (see Figure 32). Thanks to the AVR 254’s
sophisticated video processing and upscaling capabilities, no other video
connections are required from the AVR to the video display. Analog
video sources (composite, S-video and component) are converted to
the HDMI format and upscaled to as much as 1080p resolution,
depending on the display’s capabilities. Proceed to Step Six.
If a device will only be connected temporarily, you may use the audio/
video inputs on the front panel. When not in use, place the supplied
covers over the jacks for a cleaner appearance by snapping the covers
in place. To remove the covers, gently press on the left side of each
cover so that it pivots out.
Video Components: Install video components, e.g., game consoles
and camcorders, as follows (see Figure 31):
• Connect the component’s S-video or composite video output (use
only one connection) to the corresponding front-panel Input on the AVR.
• Connect the component’s optical or coaxial digital audio output to
either the Optical or Coaxial Input on the front panel (if available).
For fully analog devices, connect the device’s analog audio outputs
to the AVR’s front-panel Analog Audio Inputs.
28
Figure 32 – HDMI Monitor Output
Component Video: If the display does not have HDMI inputs, but
does have component video inputs, connect the Component Video
Monitor Outputs to the display (see Figure 33). As with HDMI connections, the AVR 254 is capable of converting composite and S-video
sources to the component video format, while upscaling the resolution to
as high as 1080i, depending on the display’s capabilities. Unlike HDMI
connections, component video connections do not enable the AVR 254
to detect the display’s capabilities and the appropriate resolution must
be selected manually, as described in the Initial Setup section.
Page 29

Figure 33 – Component Video Monitor Outputs
AVR 254
AVR 254
AVR 254
Composite/S-Video: If the video display does not have HDMI or
component video inputs, connect the corresponding composite or
S-video Monitor Output to the display. If available, S-video is preferred
over composite video, and if used, the AVR 254 will convert composite
video sources to S-video. See Figure 34.
Figure 34 – Composite and S-Video Monitor Outputs
INSTALLATION
Step Seven – Insert Batteries in Remote
The AVR 254 remote control uses four AAA batteries, which are included.
To remove the battery cover located on the back of the remote,
squeeze the tab and lift the cover.
Insert the batteries, as shown in Figure 36, making sure to observe
the correct polarity.
Figure 36 – Remote Battery Compartment
When using the remote, remember to point the lens toward the front
panel of the AVR 254. Make sure no objects, such as furniture, are
blocking the remote’s path to the receiver. Bright lights, fluorescent lights
and plasma video displays may interfere with the remote’s functioning.
The remote has a range of about 20 feet, depending on the lighting
conditions. It may be used at an angle of up to 30 degrees to either
side of the AVR.
Consult the manual for your TV to make sure you understand how
to select the correct video input.
Step Six – Plug in AC Power
Having made all of your wiring connections, it is now time to plug each
component’s AC power cord into a working outlet.
You may plug one device into the AC Switched Accessory Outlet on the
rear of the AVR 254. See Figure 35. Make sure this device draws no
more than 50 watts. The device should have its mechanical or master
power switch turned on, and it will power on any time the AVR 254 is
turned on. If the device has a clock or must always be on, do not plug
it into this outlet.
Figure 35 – Switched AC Accessory Outlet
Before plugging the AVR 254’s AC Power Cord into an electrical outlet,
make sure that the Master Power Switch on the front panel is popped
out so that the word OFF appears on its top. Gently press the button to
turn the switch off. This will prevent the possibility of damaging the AVR
in case of a transient power surge.
If the remote seems to operate intermittently, or if pressing a button
on the remote does not cause the AVR Settings Button or one of the
Source Selectors to light up, then make sure the batteries have been
inserted correctly, or replace all three batteries with fresh ones.
Step Eight – Program Sources Into the Remote
The AVR 254 remote not only is capable of controlling the receiver,
but it may also be programmed to control many brands and models
of DVD players, cable boxes, satellite receivers, the Harman Kardon
DMC 1000 digital media center and TVs.
It may help to think of the remote as a book with pages. Each “page”
represents the button functions for a different device. In order to access
the functions for a particular device, first turn to its page; that is, switch
the remote’s device mode. This is done by pressing the AVR Settings
Button to access the codes that control the receiver, or the Source
Selector Buttons to access the codes for the devices programmed into
the remote.
The AVR 254’s remote is factory-programmed to control many Harman
Kardon DVD players. If you have other source devices in your system,
follow these steps to program the correct codes into the remote.
1. Using the codes in Tables A14 –A24 of the Appendix, look up the
product type (e.g., DVD, cable TV box) and the brand name of your
source. The number(s) listed is/are potential candidates for the
correct code set for your particular device.
NOTE: The AUX Source Selector is used for the CD, HDTV, PVD
recorder, TIVO and VCR device types. Select the brand code
29
Page 30

INSTALLATION
AVR 254
from the appendix table corresponding to the device and program it into the AUX Source Selector. Similarly, the CBL/SAT
Source Selector is used for either a cable or satellite television
set-top box. The first digit of the product code indicates the
device type.
2. Turn on your source device.
3. This step places the remote in program mode. Refer to Figure 37.
Press and hold the Source Selector. The button will turn red, then go
dark. Continue holding it, and when it turns red again, release the
button; the remote is now in program mode. Follow the directions in
Step 4, below.
Figure 37 – Source Selectors
Optional: To reassign a device type from one Source Selector to another
Source Selector not being used, e.g. if there are two DVD players in the
system, press the Source Selector for the new device type now. For
example, to reassign the Cable/Sat Source Selector to operate a DVD
player, first press and hold the Cable/Sat Button, and then press the
DVD Button.
If you are unable to locate a code set that correctly operates your
source device, it will not be possible to use the AVR remote to control
that device. However, you may still connect the source to the AVR 254
and operate it using the device’s original remote control.
Most of the button labels on the remote describe the button’s function
when used to control the AVR 254. However, the button may perform
a very different function when used to control another device. Refer to
the Remote Control Function List, Table A13 in the Appendix, for a list of
each button’s functions with the various product types.
If you wish, you may program Activities, which are preprogrammed code
sequences that execute many code commands with a single button
press. You may also program “punch-through” codes, which allow the
remote to operate the channel or transport controls of another device
without having to switch the remote’s device mode. See page 53 for
instructions on these advanced programming functions.
Step Nine – Remote IR Inputs and Output (Optional)
The AVR 254 is equipped with a Remote IR Input, a Zone 2 Input and
a Remote IR Output to facilitate use of your system with a remote control
in a variety of situations. See Figure 38.
4. Enter a code from Step 1, above.
a) If the device turns off, press the Source Selector again to accept
the code; it will flash. The remote will exit Program mode.
b) If the device does not turn off, try entering another code. If you
run out of codes, you may search through all of the codes in the
⁄
¤
remote’s library for that product type by pressing the
or
Button repeatedly until the device turns off. When the device turns
off, enter the code by pressing the Source Selector, which will
flash. The remote then exits Program mode.
5. Once you have programmed a code, it’s a good idea to try using
some other functions to control the device. Sometimes, manufacturers
use the same Power code for several different models, while other
codes will vary. You may wish to repeat this process until you’ve
programmed a satisfactory code set that operates most of the
functions you frequently use.
6. Find out which code number you have programmed by pressing
and holding the Source Selector to enter the Program mode. Then
press the OK Button, and the Source Selector will flash in the code
sequence. One flash represents “1”, two flashes for “2”, and so forth.
A series of many fast flashes represents “0”. Record the codes programmed for each device in Table A9 in the appendix.
Figure 38 – IR Inputs and Outputs
When the AVR 254 is placed in such a way that aiming the remote at the
front-panel IR sensor is difficult, such as inside a cabinet or facing away from
the listener, you may connect an external IR receiver, such as the optional
Harman Kardon HE 1000, to the Remote IR Input jack. When you are using
the AVR 254 in multizone mode, you may connect an optional IR receiver,
keypad or other control device to the Zone 2 IR Input for remote control
of the AVR 254 (and any sources connected to the AVR’s Remote IR
Output) from the remote zone. Any signals transmitted through the Zone 2
IR Input will only control source selection and volume for the remote zone.
If a source device is being shared with the main listening area, then any
control commands issued to that source will also affect the main room.
If any of your source devices are equipped with a compatible Remote
IR Input, use a 1/8" mini-plug interconnect cable (not included) to connect the AVR’s Remote IR Output to the source device’s Remote IR
Input, which will pass any applicable remote signals transmitted through
the AVR to the source device. This enables you to control your sources
even when the AVR itself is controlled via an external IR receiver.
Check with the manufacturer of the source device for more information
on the type of IR signal expected. The AVR 254 will output a “stripped
carrier” IR signal through the Remote IR Output.
30
Page 31

To control more than one source device using the Remote IR Output,
AVR 254
AVR 254
connect all sources in “daisy chain” fashion, with the AVR’s Remote
IR Output connected to the first device’s Remote IR Input, the second
device’s Remote IR Output connected to the next device’s Remote
IR Input, and so forth.
Step Ten – Install a Multizone System (Optional)
The AVR 254 offers several methods of distributing music to other
listening areas in your home. A multizone system is not required to enjoy
the home theater experience. If you prefer not to install a multizone
system at this time, skip to Step Eleven to turn on the AVR 254 and
configure it.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTE: Installing a multizone system typically requires running various cables inside walls. Always comply
with the appropriate safety codes when installing concealed wiring.
The AVR 254’s multizone connections should be installed per the
requirements of all applicable state and local building codes, as
well as NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements. Failure to do
so may present a potential safety hazard. If you have any doubt
about your ability to work with electrical and telecommunications
wiring, you are advised to hire a licensed electrician or custom
installer to install the multizone system.
Multizone operation uses the Surround Back/Zone 2 amplifier channels,
whether you connect the remote speakers directly to the speaker outputs, or if you connect an optional external amplifier to the preamp outputs. This limits the system in the main listening room to 5.1 channels,
which means you cannot listen to 6.1- or 7.1-channel programs in the
main room.
Select one or both:
1. Connect the remote room’s speakers directly to the Surround
Back/Zone 2 Speaker Outputs. See Figure 39.
INSTALLATION
Figure 40 – Surround Back/Multiroom Preamp Outputs
This method requires you to provide an additional component: the
amplifier. However, this method may be used to increase the number
of remote rooms in the system when you are also using the Surround
Back/Zone 2 Speaker Outputs.
Place the amplifier in the same room as the AVR 254 so that a shorter
length of interconnect cable is used with a long run of speaker wire to
the remote room. This is better than placing the amplifier in the remote
room, which necessitates a long run of interconnect cable that would
then be subject to signal degradation.
In addition to the audio signal, you may connect an IR control device to
the AVR 254’s Zone IR Input so that listeners in the remote room may
turn the multizone system on or off, select a source input, control the
source device connected to that input and adjust the volume in the
remote zone.
NOTE: Only analog audio sources are available to the multizone
system.
Step Eleven – Turn On the AVR 254
Two steps are required the first time you turn on the AVR 254.
1. Gently press the Master Power Switch until the word OFF is no longer
visible. The Power Indicator above the two power switches should
light up in amber, indicating that the AVR is in Standby mode and is
ready to be turned on. See Figure 41. Normally, you may leave the
Master Power Switch in the ON position, even when the receiver is
not being used.
Figure 39 – Surround Back/Zone 2 Speaker Outputs
If you prefer not to purchase an external amplifier to power a pair of
remote speakers, you may reassign the AVR 254’s Surround Back
amplifier channels to power the speakers.
2. Connect an external amplifier to the Surround Back/Multiroom
Preamp Outputs. See Figure 40.
Figure 41 – Power Switches
2. There are several ways in which the AVR 254 may be turned on from
Standby mode.
a) Press the Standby/On Switch on the front panel. See Figure 41.
b) Using the remote, press the AVR Power On Button or any of the
Source Selectors. See Figure 42.
31
Page 32

INSTALLATION
Figure 42 – AVR Power On and Source Selectors
NOTES:
• Any time you press one of the Source Selectors on the
remote (i.e., Cable/Sat, DVD, Media Server, Radio, TV, Game
or AUX), the remote will switch modes to transmit the codes
programmed to operate that device. To control the receiver,
press the AVR Settings Button to return the remote to AVR
mode. Some AVR functions are available in all device modes,
and you don’t have to press the AVR Settings Button first to
use them: Volume Controls (including Mute), Audio Effects,
Video Modes, Surround Modes, AVR Settings, Info Settings,
Sleep Settings and AVR Power On and Off.
• If you are not using the AVR’s HDMI Output with your display,
you may not see a picture the first time you turn on the AVR 254,
or after a system reset. To correct this, press the front-panel
Resolution Button to display the current video output resolution.
⁄
Use the
Button to change it to 480i, which should be compatible with all video displays, then press the OK Button to
select the new setting. You will be prompted to accept or cancel the change; the CANCEL message will appear on the front
¤
panel. Press the
Button to view the ACCEPT option, and
then press the OK Button to complete the change to the output
resolution. Follow the directions in the Initial Setup section to
configure the AVR to function correctly with your display and
other components.
32
Page 33

INITIAL SETUP
Before you begin enjoying your new receiver, a few adjustments should
be made to configure the AVR 254 to match your actual system.
Make sure that you have connected a video display to one of the
video
monitor outputs on the receiver. When you turn on your display and the
AVR, if the display is connected to the AVR via an analog video (composite, S-video or component) connection, you may see a plain black
screen. Press the front-panel Resolution Button, and the current video
⁄
output resolution will appear in the Message Display. Use the
Button
to change it to 480i, which should be compatible with all video displays,
then press the OK Button to select the new setting. You will be prompted
to accept or cancel the change; the CANCEL message will appear on
¤
the front panel. Press the
Button to view the ACCEPT option, and
then press the OK Button to complete the change to the output resolution.
The Main Menu should appear when you press the AVR Settings Button
on the remote, or the AVR Button on the front panel. See Figure 43.
Figure 43 – Main Menu
The current menu, setting line or setting will appear in the Message
Display as well as on screen.
To return to the previous menu or exit the menu system, press the
Back/Exit Button. Be certain all settings are correct, as any changes you
have made will be retained.
We recommend that most users follow the instructions in this INITIAL
SETUP section to configure a basic home theater system. You may
return to these menus at any time to make additional adjustments.
Thanks to the EzSet/EQ system, most of the menu adjustments may
be saved until you have become more familiar with the AVR, and are
therefore described in the Advanced Functions section.
The Initial Setup section requires that you complete all of the steps
in the Installation section that apply to your receiver. You should have
connected all of your loudspeakers and a video display, as well as your
source devices. You should be able to turn on the receiver and view
the main menu on
your video display when you press the AVR Settings
Button. If necessary, reread the Installation Section and the beginning of
this section before continuing.
Configure the AVR 254 Using EzSet/EQ Technology
One of the most important and perhaps often overlooked aspects of
setting up a home theater system is to calibrate the receiver to match
the loudspeakers, which enables the AVR to perform at its best.
Although it’s possible to configure the AVR using only the remote and
the front-panel messages, we recommend that you use the full-screen
menu system.
NOTE: When using the AVR’s on-screen menu system, we recommend selecting a video output resolution of 720p or higher for
best legibility, and to provide graphics that simplify some configuration options. Depending on the resolution selected, the menus
shown by your system may vary in appearance.
Using the On-Screen Menu System
The menu system is accessed by pressing the AVR Settings Button
on the remote. See Figure 44.
Figure 44 – Settings Buttons
The Main Menu will appear (see Figure 43), and if a video source is
playing, it will be visible behind the transparent menu.
The menu system consists of five main menus: Source Selection,
Setup Source, Speaker Setup, Zone 2 and System.
⁄/¤
Use the
the menu system, and press the OK Button to select a menu or setting
line or to enter a new setting.
/‹/›Buttons on the remote or front panel to navigate
Until recently, most receivers required the user to perform the calibration
and configuration manually, a somewhat tedious process that called for
a good ear or the purchase of an SPL (sound-pressure level) meter.
Although you may configure the AVR 254 manually, as described in
the Advanced Features section, we recommend that you take advantage
of our signature the EzSet/EQ system.
Before beginning, eliminate extraneous background noise that might
affect the results, such as noisy air conditioning. Try to avoid making
any loud noises while running EzSet/EQ setup.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTE: During the EzSet/EQ procedure,
a series of very loud test tones will be played through all of the
speakers. Avoid sitting or standing close to any one speaker
during the procedure. If you are particularly sensitive to loud
noises, you may wish to leave the room and have someone
else run the EzSet/EQ process.
Step One – Place the included EzSet/EQ microphone in the listening
position, or in the center of the room, at about the same height as the
listeners’ ears. The microphone features a threaded insert on the bottom
so that it can be mounted on a camera tripod for stability.
Step Two – Plug the EzSet/EQ microphone into the Headphone
Jack/EzSet/EQ Microphone Input Jack on the front of the receiver.
See Figure 45.
33
Page 34

INITIAL SETUP
Figure 45 – Plug EzSet/EQ microphone into receiver.
Step Three – Make sure that the AVR 254 and the video display are
turned on. Press the AVR Settings Button to display the Main Menu. See
¤
Figure 43. Use the
then press the OK Button. See Figure 46.
Figure 46 – Speaker Setup Menu Screen
Select “Automatic Setup-EzSet/EQ” and the screen shown in Figure 47
will appear to direct you to plug the EzSet/EQ microphone into the
Headphone Jack, and to set the level control on the subwoofer to the
halfway point.
Button to highlight the Speaker Setup line, and
Figure 48 – EzSet/EQ: Number of Speakers
NOTE: If you are using fewer than five main speakers in your
system, it will not be possible to configure your speakers using the
EzSet/EQ process; proceed as described in the Advanced Functions
section. If you have selected a 6.1-channel configuration, using only
a single surround back speaker, it is possible to use a combination
of EzSet/EQ automatic configuration for 5.1 speakers, connect the
left
single surround back speaker to the
Surround Back Speaker
Output, and then configure the surround back speaker manually, as
described in the Advanced Functions section. However, we do not
recommend the 6.1-channel configuration.
The test will begin, and the screen shown in Figure 49 will appear,
asking you to maintain silence during the EzSet/EQ configuration.
If possible, turn off any noisy appliances, such as air conditioners.
Avoid conversation. If unwanted sounds are inadvertently heard during
the test, such as a telephone, select Cancel to return to the Speaker
Setup menu.
Figure 47 – EzSet/EQ Screen
At any time, you may select Cancel to return to the Speaker Setup
menu without starting the EzSet/EQ process. When you are ready to
begin, select Continue and press the OK Button.
NOTE: Before running the EzSet/EQ process, the AVR 254 will
automatically set its master volume to -25dB.
Step Four – After you select “Continue”, the screen shown in Figure 48
will appear, directing you to select the number of speakers in your system.
Select 5.1 if no surround back speakers are present, or if the surround
back channels will be used for multizone operation.
34
Figure 49 – EzSet/EQ In Progress
As EzSet/EQ tests each speaker, its position will appear on screen.
Select Cancel to stop the test. If the test tone is heard from a different
speaker than the one indicated on screen, turn off the AVR and check
the speaker-wire connections, then turn the AVR back on and begin the
procedure again.
When the test is completed, the Continue option, will become available.
Select it, and a screen will appear, listing all of the speakers EzSet/EQ
detected, and offering three options:
• The Retest option reruns the EzSet/EQ process. Increasing the master
volume manually at this time may enable the EzSet/EQ process to
correctly detect some speakers.
• Selecting Cancel returns to the Speaker Setup menu.
• If the EzSet/EQ process detected the speakers correctly, select
Continue to proceed to the next test.
Page 35

INITIAL SETUP
Step Five – During the next portion of the test, the EzSet/EQ procedure
equalizes the AVR 254’s audio circuitry to compensate for the specific
room characteristics and the performance capabilities of each individual
speaker. To do this successfully, the EzSet/EQ microphone must be
placed about two feet from each speaker in the direction toward the
listening position. Wait until the on-screen instructions prompt you
before moving the microphone.
When the EzSet/EQ process has finished, a screen will appear with
its results.
See the Advanced Functions section for instructions on how to manually
configure the speakers or manually adjust the settings established by the
EzSet/EQ process.
Set Up Sources
The Source Info menu is used to assign the correct physical audio and
video connections to each source. It also provides access to a variety of
other settings, many of which may be adjusted later as you become
more familiar with the AVR.
The following settings are not optional and must be adjusted now to
enable playback of each source: Video Input from source, Audio Input
from Source and Resolution to Display.
The other settings may be adjusted at any time to improve performance.
To display the Source Info menu, press the Info Settings Button (front
panel or remote). A screen similar to the one shown in Figure 50
will appear. This screen may also be accessed from the Main Menu
by selecting the Setup Source line and selecting a source from the
slide-in menu.
Surround Modes: Select this line to display the Surround Modes submenu, where you may program the desired surround mode for various
types of analog programs, including movies, music and games. You
may also specify a stereo mode (depending on the number of channels
desired) and a virtual surround mode if your system uses fewer than
the full complement of seven main speakers (plus a subwoofer).
Digital surround signals, such as Dolby Digital and DTS, are automatically
played in their native formats, although you may change the surround
mode at any time. See the Advanced Functions section for information
on surround modes available with digital programs.
In the factory default Auto Select mode, the AVR will analyze the source
signal and select the optimum playback mode. The AVR’s default is to use
the Logic 7 Movie mode for optimal playback of movies, including television programs; the Logic 7 Music mode for music recordings, such as
CDs; and the Logic 7 Game mode when a video game console is in use.
To reprogram any of these lines in the Surround Modes menu, select it
and choose from the list of available surround modes. Whenever you
manually select the mode during playback, the AVR will use the new
surround mode.
Selecting a surround mode is a matter of taste, although the available
modes depend on the number of speakers in your system and the
format of the incoming signal. Feel free to experiment by selecting any
available mode at any time until you find a few modes that you prefer.
See the Advanced Functions section for more information.
Audio Format From Source: This line is informational only. When a
digital program is playing, its format will be identified here. When analog
audio programs are playing, this line indicates NO AUDIO INPUT, referring
to digital inputs only.
Figure 50 – Setup Source Menu
Audio Effects: Select this line to display the Audio Effects submenu,
where you may: adjust the bass and treble tone controls; adjust the
LFE trim; or adjust the Night Mode setting. It is recommended that you
leave this submenu at its default settings, and return to it later if your
system requires any fine-tuning. See the Advanced Functions section
for more information.
Video Modes: Select this line to display the Video Modes submenu,
to select from preprogrammed or custom picture settings and make
picture adjustments. It is recommended that you leave the settings at
their factory defaults. Picture adjustments should be made to your video
display first, with this menu used only for fine-tuning. See the Advanced
Functions section for more information.
Audio and Video Input Selection
Please see Table A2 in the appendix for the factory default input assignments for each source. You may assign any available input to any
source using the Source Info menu, accessible either by pressing the
AVR Settings Button and selecting the Setup Source line, or by pressing
the Info Settings Button for direct access.
When a source is selected, the AVR will check the assigned digital audio
input for a signal. If one is present, the digital input will be selected. If
not, the AVR will select the analog audio input specified at the Audio
Auto Polling line of the Setup Source menu. If you don’t want the AVR
to select an analog audio input for the source, change this setting to Off.
The AVR will also select the assigned video source. There are no “audioonly” sources on the AVR 254, other than the Radio, which uses a special
on-screen menu. If no video signal is present, the display will remain
black. You may pair an audio device with an A/V device’s video signal
using the Source Info menu. Sources may share audio or video inputs
to suit your application.
Video Input from source: Select this line to assign the correct
video input to the source. Refer to Table A5 in the appendix, where you
noted the physical video input the source is connected to, and select
the input here.
35
Page 36

INITIAL SETUP
Audio Input from source: Select this line to assign the correct analog
or digital audio input to the source. Refer to Table A5 in the appendix,
where you noted the physical audio input the source is connected to,
and select the input here. If both analog and digital audio connections
were made, select the digital input here, and select the analog input at
the Audio Auto Polling line below.
6-/8-Channel Direct Inputs
The 6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs are used when playing certain
multichannel discs, such as DVD-Audio, Blu-ray Discs, SACD and
HD-DVD, on a player that decodes the audio and outputs it via its
multichannel analog audio outputs but not via its HDMI output.
HDMI-equipped multichannel disc player:
• Connect the player’s HDMI output to one of the AVR’s HDMI Inputs.
No other connections are necessary.
• Assign the HDMI Input to both the Audio and Video Input from source
settings in the Source Info menu.
HDMI-equipped multichannel disc player that does not output
multichannel audio via an HDMI connection:
• Connect the player’s HDMI output and its multichannel analog
audio outputs to one of the AVR’s HDMI Inputs and to the AVR’s
6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs.
• Assign the HDMI Input to both the Audio and Video Input from source
settings in the Source Info menu.
• Assign the 6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs to the Audio Auto
Polling setting in the Source Info menu.
• When listening to DVD-Video discs, CDs or other materials outputting
standard-definition digital audio, do nothing, as long as the HDMI Input
is assigned to the Audio Input from source setting.
• When listening to high-resolution multichannel discs, the AVR’s auto
polling feature will automatically switch to the multichannel analog
audio inputs.
Multichannel disc player without HDMI output, or when video
display has no HDMI input:
• Connect the player’s component video outputs to one set of Component
Video Inputs on the AVR. Depending on the capabilities of the player
and your video display, you may need to use a composite or S-video
connection instead.
• Connect the player’s digital audio output to a corresponding available
digital audio input on the AVR.
• Connect the player’s multichannel audio outputs to the AVR’s
6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs.
• Assign the correct audio and video inputs to the Audio and Video
Input from source Settings in the Source Info menu.
• Assign the 6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs to the Audio Auto
Polling setting in the Source Info menu.
• When listening to DVD-Video discs, CDs or other materials outputting
standard-definition digital audio, do nothing, as long as the correct
digital audio input is assigned to the Audio Input From Source setting.
• When listening to high-resolution multichannel discs, the AVR’s auto
polling feature will automatically switch to the multichannel analog
audio inputs.
NOTE: The 6-/8-Channel Inputs pass the incoming signals
directly to the volume control, without digitizing or processing
them. Configure the bass management settings (i.e., speaker
size, delay and output level) on your source device to match
the settings programmed using the EzSet/EQ procedure, which
may be viewed using the Speaker Setup menu (see Advanced
Functions section). Consult the owner’s guide for your multichannel player for more information.
Resolution to Display: This setting, which may also be accessed from
the AVR Settings menu, reflects the video output resolution, which is
dependent upon the capabilities of the video display.
• If the display is connected to the AVR’s HDMI Output, the HDMI protocol enables the two devices to communicate with each other, and
the AVR will automatically select the correct video output resolution.
• If the display is connected to the AVR’s Component Video Outputs,
there is no automatic detection of the display’s capabilities, and the
video output resolution must be manually adjusted to match the
display’s capabilities (which may be obtained from the display’s
manual or its manufacturer’s Web site).
• If the display is connected to the AVR’s Composite or S-Video Monitor
Output, the video output resolution must be manually set to 480i to
view any content, including the AVR’s own menus.
Since there is no picture if the resolution is set higher than the display’s
capability, adjust the resolution by pressing the front-panel Resolution
Button repeatedly until the correct setting appears in the front-panel
Message Display. For composite and S-video, the correct setting is
480i. For component video, it is the highest resolution where a picture
is visible. You will be prompted to accept or cancel the resolution
change, as the CANCEL message will appear on the front panel.
¤
Press the
OK Button to complete the change to the output resolution.
NOTE: When the display has a DVI input which is connected
to the AVR using an HDMI-to-DVI adapter, the picture will be
distorted or blank if the display is not HDCP-compliant. In that
case, a different video connection must be used (component,
composite or S-video).
Resolution from Source: This line, which is informational only, indicates the video format (NTSC or PAL) output by the source device.
NTSC is the video format used for standard-definition television in the
U.S. and other parts of the world. The PAL format is used in parts of
Button to view the ACCEPT option, and then press the
36
Page 37

INITIAL SETUP
Europe and elsewhere. The AVR 254 is capable of detecting PAL
video sources and converting them to the NTSC format for display on
American televisions.
Adjust Lip Sync: Use this adjustment to resynchronize the audio and
video signals from a source to eliminate a “lip sync” problem. Lip sync
issues can occur when the video portion of a signal undergoes additional
processing in either the source or the video display that desynchronizes
it from the audio. Select this line to display the Lip Sync adjuster by
itself, enabling you to view the video while listening to the audio. Use the
‹/›
Buttons to delay the audio by up to 180ms. See Figure 51.
Figure 51 – Adjust Lip Sync
Change Name: Use this line to change the display name for your
source. This can be useful if your source’s device type is different from
⁄/¤
the available source names. Select this line and use the
Buttons
to scroll forward or reverse through the letters A through Z and the
numbers 0 through 9. When the desired character appears, use the
›
Button to move the cursor to the next position. Move the cursor again
to leave a blank space. When you have finished entering the new name,
press the OK Button. The name will be used on the front panel to refer
to the source, and will appear next to its original name, e.g. DVD,
throughout the on-screen menu system. To clear the entry without
making any changes, scroll to the blank character between “9” and “A”.
Use the Back/Exit Button to exit, then return to the Setup Source line of
the Main Menu and select the next source to configure. When you have
finished configuring all sources, press the Back/Exit Button to clear the
menus from view.
You are now ready to begin enjoying your new receiver!
Audio Auto Polling: Use this setting when both analog and digital audio
connections are made from the source device to the AVR. When no
digital signal is present, the AVR will automatically switch to the analog
audio input.
This can be useful for some older cable television systems that broadcast some channels in analog audio and others in digital audio. It is also
useful for making analog recordings of copy-protected digital sources,
and for multichannel disc players that decode high-resolution multichannel
audio and output it through their multichannel analog audio outputs.
However, it can be inconvenient when no analog audio connection is
made and playback is stopped, as the audio signal will be lost.
If an analog audio connection was made, select it here. If not, choose
the Off setting, and the AVR will always use the digital audio connection.
Zone 2 Audio: When a multizone system has been connected and is
in use, this setting determines the source for the remote zone. Select
the analog audio input the source is connected to. Digital audio is not
available to the multizone system, nor is any type of video.
37
Page 38

OPERATION
Now that you have installed your system components and completed
a basic configuration of your receiver, you are ready to begin enjoying
your home theater system.
Turning On the AVR 254
Gently press the Master Power Switch until the word OFF is no longer visible. The Power Indicator above the two power switches should light up in
amber. This indicates that the AVR is in Standby mode and is ready to be
turned on. Normally, you may leave the Master Power Switch in the ON
position, even when the receiver is not being used. See Figure 41.
There are several ways in which the AVR 254 may be turned on:
a) Press the Standby/On Switch on the front panel. See Figure 41.
b) Using the remote, press the AVR Power On Button or any of the
Source Selectors. See Figure 42.
To turn the receiver off, press either the Standby/On Switch on the front
panel, or press the AVR Power Off Button on the remote. Unless the
receiver will not be used for an extended period of time (for example,
when are on vacation), it is not necessary to turn off the Master Power
Switch. When the Master Power Switch is turned off, any settings you
have programmed, including system configuration and preset radio
stations, will be preserved for up to four weeks.
IMPORTANT NOTE: If the PROTECT message ever appears
in the Message Display, turn off the AVR and unplug it. Check
all speaker wires for a possible short. If none is found, bring
the unit to an authorized Harman Kardon service center for
inspection and repair before using it again.
Mute Function
To temporarily mute all speakers and the headphones, press the Mute
Button on the remote. See Figure 52. Any recording in progress will
not be affected. The MUTE message will appear in the display as a
reminder. To restore normal audio, either press the Mute Button again,
or adjust the volume. Turning off the AVR will also end muting.
Sleep Timer
You may program the AVR to play for up to 90 minutes and then turn
off automatically using the sleep timer.
Press the Sleep Settings Button on the remote, and the time until
turn-off will be displayed. See Figure 53. Each additional press of the
Sleep Button will increase the time until turn-off by 10 minutes, up
to a maximum of 90 minutes, then the SLEEP OFF setting appears,
which disables the sleep timer.
Figure 53 – Sleep Settings Button
When the sleep timer has been set, the front-panel display will automatically dim to half-brightness. If you press any button on the remote or
front panel, the display will return to full-brightness. The display will dim
again several seconds after your last command.
Volume Control
The volume may be adjusted either by turning the knob on the front
panel (clockwise to increase volume or counterclockwise to decrease
volume), or by pressing the Volume Control on the remote. See Figure 52.
The volume is displayed as a negative number of decibels (dB) below
the 0dB reference point.
Unlike the volume controls on some other products, 0dB is the maximum
volume for the AVR 254. Although it’s physically possible to turn the
volume to a higher level, doing so may damage your hearing and your
speakers. For certain more dynamic audio materials, even 0dB may be
too high, allowing for damage to equipment. We urge caution with
regard to volume levels.
You may change the volume level display from the default decibel scale
to a 0-to-100 scale by adjusting the Volume Units setting in the System
Settings menu, as described on page 52.
Figure 52 – Volume Controls
38
If you press the Sleep Button after the timer has been set, the remaining
time until turn-off will be displayed. You may press the Sleep Button to
change the time until turn-off.
Audio Effects
Depending on your preferences or the specific characteristics of your
listening room, you may wish to adjust some of the audio settings, such
as tone controls, to improve performance. Access these settings from
the Audio Effects submenu, as described in the Advanced Functions
section.
It is not necessary to adjust the Audio Effects settings to enjoy your
new AVR. We recommend leaving the settings at their default values
until you are more familiar with your system.
Video Modes
The settings in the Video Modes menu are used to fine-tune the
picture if necessary after making all adjustments on the video display.
It is recommended that you leave the settings at their defaults. See the
Advanced Functions section for detailed information.
Headphones
Plug the 1/4" plug on a pair of headphones into the headphone
jack on the front of the receiver for private listening. See Figure 54.
Page 39

OPERATION
The DOLBY H:BYPASS message indicates that Dolby Headphone
surround processing is in the default bypass mode, which delivers a
conventional 2-channel signal to the headphones.
Figure 54 – Headphone Jack
Press the Surround Modes Button on the front panel or the remote, to
switch to Dolby Headphone virtual surround processing, indicated by the
DOLBY H:DH message. Dolby Headphone delivers an enhanced sound
field that emulates a 5.1-channel speaker system. No other surround
modes are available for the headphones.
Source Selection
Press the front-panel Source List Button to scroll through the sources.
Each press of the button scrolls down the list that appears in the display
and on screen. See Figure 55.
Figure 55 – Source List Button
For direct access to any source, press its Source Selector on the remote.
Additional tips for systems using HDMI:
• Turn off all devices (including the TV, AVR and any source
components).
• Unplug the HDMI cables starting with the cable between the
TV and AVR, and continuing with the cables between the AVR
and each source device.
• Carefully reconnect the cables from the source devices to
the AVR, and connect the cable from the AVR to the TV last.
• Turn on the devices in this order: TV, then AVR, then source
devices.
Using the Tuner
To select the AVR 254’s built-in tuner:
1. Press the Source List Button on the front panel repeatedly until the
⁄/¤
desired tuner band is selected, or use the
through the source list.
2. Press the Radio Source Selector on the remote. Press this button
again to switch bands (AM, FM or XM).
A screen similar to the one shown in Figure 56 will appear, with the
band indicated in the middle of the screen. (The XM band uses a slightly
different screen.)
Buttons to scroll
The AVR 254 will switch to the audio and video inputs assigned to the
source.
The source name will appear in the upper line of the front-panel display.
If you retitled the source, the new title will appear. The audio and video
inputs assigned to the source will also appear briefly. The surround
mode will be displayed on the lower line.
Any other settings you adjusted in the Setup Source menu will also be
selected. You may view these settings in the Source Info menu at any
time by pressing the Info Settings Button.
VIDEO TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS:
If a video source is playing and there is no picture:
• Check that you have selected the source to which the
video input was assigned.
• Check the wires for a loose or incorrect connection.
• Check that you have selected the correct video input on
the display device (TV).
• Try pressing the Resolution Button on the front panel repeatedly until the correct video output resolution is selected and
a picture appears. You will be prompted to accept or cancel
the resolution change, as the CANCEL message will appear
¤
on the front panel. Press the
Button to view the ACCEPT
option, and then press the OK Button to complete the change
to the output resolution.
Figure 56 – FM Radio
Use the ⁄/¤Buttons to tune a station (or channel for XM Radio).
The frequencies will be displayed in the front panel and graphically on
screen.
The AVR defaults to automatic tuning, meaning each press of the
⁄/¤
Buttons scans through all frequencies until a station with accept-
able signal strength is found. To switch to manual tuning, in which each
⁄/¤
press of the
Buttons steps through a single frequency increment
(0.1MHz for FM, or 10kHz for AM), press the Menu Button. The Radio
Modes line will be highlighted, and each press of the OK Button toggles
between automatic and manual tuning modes.
When an FM station has been tuned, toggling the radio mode switches
between stereo and monaural play, which may improve reception of
weaker stations.
A total of 30 stations (AM and FM together) may be stored as presets.
When the desired station has been tuned, press the OK Button, and two
dashes will flash in the front-panel display. Use the Alphanumeric Keys
to enter the desired preset number.
39
Page 40

OPERATION
To tune a preset station, press the ‹/›Buttons or the Channel
Control, or press the Menu Button to view the list of programmed presets and scroll to the desired selection. Press the OK Button to tune the
station. You may also enter the preset number using the Numeric Keys.
For presets 10 through 30 press 0 before the preset number. For
example, to enter preset 21, press 0-2-1.
XM Radio Operation
XM Radio is a satellite-delivered service that offers hundreds of program
channels, as well as local traffic and weather information for select cities.
The AVR 254 is “XM Ready,” which means that it is able to receive the
XM service when a user-supplied XM antenna module is connected and
the service activated.
Select an antenna module designated for XM Ready audio components.
An XM Ready-compatible module uses the special connector on the
AVR 254’s rear panel that allows you to use the AVR’s tuner, including
its 40 preset station locations and remote control. Although you may
use a module with standard audio connections, which may be indicated
for “car and home use,” you will not be able to enjoy the AVR 254’s
ease of control.
The XM Mini-Tuner and Home Dock (Models CNP-2000 and CNP-2000H;
both pieces are required) are compatible with the AVR 254. The older
Audiovox
use is also compatible, but has been discontinued and may no longer
be available. Additional modules may become available in the future.
Modules produced for automotive, or “mobile,” use are not compatible
with the AVR 254, although if they have standard analog or digital audio
outputs, they may be connected to a compatible input and operated
using their own controls.
Plug the module into the XM Antenna Jack on the rear of the AVR 254.
Place the antenna module so that it has a clear view through a southfacing window in order to obtain reception from the XM satellite.
Select XM Radio as the source in one of these ways:
1. Press the Source List Button on the front panel repeatedly until
2. Press the Radio Source Selector on the remote repeatedly until
®
CNP 1000 “Connect and Play” module for home audio
NOTE: To listen to XM Radio using the AVR 254, you will need
to purchase an XM antenna module and subscription, and
activate your module. XM service is not available in Alaska or
Hawaii. Visit the XM Radio Web site at www.xmradio.com for
more information.
⁄/¤
XM Radio is selected, or use the
Buttons to scroll through
the source list.
XM Radio is selected..
the ⁄/¤Buttons to scan through the channel numbers within the
category.
3. After you have programmed presets, directly enter the preset number
(1 through 40) using the Alphanumeric Keys. For single-digit positions,
enter a “0” before the number.
4. Press the Menu Button to search for a channel by preset, category,
all channels (the default) or direct entry.
When you are able to hear Channel 1, you are ready to activate your
module. If you don’t hear Channel 1, make sure the module’s plug is
firmly seated in the XM Antenna jack, and that the module is near a
south-facing window. Try unfolding the module and rotating it to obtain
reception. You may need to purchase an extension cable, available on
the XM Radio site, to ensure that the module is near the window.
Tune to Channel 0 for a display of your antenna module’s Radio ID
number, required for activation.
The current channel number and preset location will appear in the upper
line of the Message Display, and the search mode (all channels, category)
will appear in the lower line. Three signal-strength bars will appear to
the right of the channel number and preset location to indicate signal
strength. The song title, artist and channel category, along with the
channel number and preset position (if programmed), will all appear
on screen when a video display is in use.
For traffic and weather channels, the current city’s name will appear
instead of the channel name, and the local weather and temperature
will be displayed on screen.
To store a channel in one of the 40 preset locations:
1. Tune to the desired channel and press the OK Button. The lowest
available preset number will flash on screen and in the front-panel
Message Display.
2. Use the Alphanumeric Keys to enter the numbered preset location
you wish to store the channel in, or do nothing if the current preset
location is acceptable.
3. Press the OK Button to store the new preset.
Recording
Two-channel analog and digital audio signals, as well as composite
and S-video signals, are normally available at the appropriate recording
outputs. Thus, to make a recording, you need only make sure to connect your audio or video recorder to the appropriate output jacks, as
described in the Installation section, insert blank media and make sure
the recorder is turned on and recording while the source is playing.
You should be able to tune in Channel 1, the Preview Channel, to
confirm that your equipment is ready for activation. There are four
ways to tune an XM Radio channel:
⁄/¤
1. Use the
2. Use the
40
Buttons to scan through the channel numbers.
‹/›
Buttons to jump to the next category, and then use
NOTES:
1. Analog audio signals are not converted to digital form, and
digital audio signals are not converted to analog audio form.
However, you may record a coaxial or optical digital audio
source using either type of digital audio output.
Page 41

OPERATION
2. Only PCM digital audio signals are available for recording.
Proprietary formats such as Dolby Digital and DTS may not
be recorded using the digital audio connections, although
if the source is connected to the AVR using analog audio
connections, an analog recording may be made.
3. HDMI and component video sources are not available for
recording.
4. Please make certain that you are aware of any copyright
restrictions on any material you record. Unauthorized duplication of copyrighted materials is prohibited by federal law.
Stereo Jack Input
Enjoy the full power and resolution of your Harman Kardon system,
including a variety of analog surround modes, while listening to content
stored on your portable device.
The Stereo Jack is provided on the AVR’s rear panel for convenient
connection of portable players, such as CD players and the iPod (iPod
and cable not included). Purchase a stereo cable with a 1/8" plug on
at least one end for connection to the Stereo Jack. Plug the other
end of the cable into the portable device’s headphone output, and
operate the device using its own controls. You may also use a cable
with separate left and right audio plugs at one end for connection to
any component equipped with analog audio outputs.
You may assign the Stereo Jack and any analog video input to the
AUX source, which uses the front-panel inputs by default.
Selecting a Surround Mode
Surround mode selection can be as simple or sophisticated as your
individual system and tastes. Feel free to experiment with the many
available surround modes on the AVR 254, and you may find a few that
become your favorites for certain sources or program types. Although
more detailed information on surround modes may be found in the
Advanced Functions section, it is easy to select any of the modes
available at a given time:
To select a surround mode, press the Surround Modes Button
(front panel or remote) repeatedly until the desired option appears:
SURR: AUTO SELECT, SURR: VIRTUAL, SURR: STEREO, SURR: MOVIE,
SURR: MUSIC or SURR: GAME. The option will be displayed in the
Lower Line of the Message Display, and the Surround Modes menu
will appear on screen (see Figure 57).
Auto Select: With this surround mode option selected, the AVR’s sophisticated circuitry will analyze the incoming audio signal, identify its type
and select an appropriate surround mode. For digital programs, such as
movies recorded with a Dolby Digital soundtrack, the AVR will automatically use the native surround format. For two-channel analog and PCM
programs, the AVR is programmed to default to Logic 7 Movie mode.
Virtual Surround: When only two main speakers are present in the
system, Dolby Virtual Surround may be used to create an enhanced
soundfield that virtualizes the missing speakers. Select between Wide
and Reference modes, depending on your preferences.
Stereo: When two-channel playback is desired, select the number of
speakers used for playback:
• 2 CH STEREO for playback through only two speakers. As described
on page 42, you may select Analog Bypass mode for a pure analog
signal when analog audio inputs are in use. Simply set the Tone
Control setting in the Audio Effects submenu to Off, and the AVR
does the rest.
• 5 CH STEREO for playing the left-channel signal through the front
and surround left speakers, the right-channel signal through the right
speakers and a summed mono signal through the center speaker
• 7 CH STEREO follows the same scheme as 5 CH STEREO, but adds
the surround back speakers to the mix. This mode is only available
when the surround back speakers are present and have not been
reassigned to multizone operation. See the Initial Setup section for
more information.
Movie: Select an analog surround mode for movie playback: Logic 7
Movie, DTS Neo:6 Cinema or Dolby Pro Logic II (IIx when seven main
speakers are present). The desired mode may also be selected when
a compatible digital surround mode is received.
Music: Select an analog surround mode for music playback: Logic 7
Music, DTS Neo:6 Music or Dolby Pro Logic II (IIx when seven main
speakers are present). The Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music mode allows
access to a submenu with some additional settings. See the Advanced
Functions section for more information.
Video Game: Select an analog surround mode for game playback:
Logic 7 Game, or Dolby Pro Logic II (IIx when seven main speakers
are present).
After you have made your selection, press the Back/Exit Button until
the screen is cleared.
Figure 57 – Surround Modes menu
See the Advanced Functions section for more information on
surround modes.
41
Page 42

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
Much of the AVR 254’s performance is handled automatically, with little
intervention required on your part. However, the AVR 254 is a sophisticated component, and is capable of being customized to suit your
particular system and your tastes. In this section we describe some of
the more advanced adjustments available on the AVR 254. You may
return to this section later, when you have become more familiar with
your receiver.
Audio Processing and Surround Sound
Audio signals output by sources are encoded in a variety of formats that
can affect not only the quality of the sound but the number of speaker
channels and the surround mode. You may also manually select a
different surround mode, although for certain types of audio signals,
the modes available will be limited in certain ways, as described below.
Analog Audio Signals
Analog audio signals usually consist of two channels – left and right.
The AVR 254 offers three basic options for playback of analog audio:
Analog Bypass Mode: In this mode, the 2-channel signal is passed
1.
directly from the input to the volume control, without being digitized
or undergoing any processing for bass management or surround
sound. The requirements for selecting analog bypass mode are:
a) The analog audio inputs for the source must be selected. If neces-
sary, press the Info Button on the remote and use the
Buttons to scroll to the Audio Source setting, then select an
analog input.
b) The tone controls must be disabled by setting Tone Control to Off.
Press the Audio Effects Button to access the Tone Control setting
in the Audio Effects submenu.
c) The 2-channel Stereo mode must be selected. Press the Surround
Modes Button to access the STEREO line of the Surround Modes
submenu.
When the Tone Control setting is Off, the front speakers will be set to
Large automatically, as indicated by the double boxes in their positions
in the Speaker/Channel Input Indicators on the front panel. That indicates that Analog Bypass mode is active. When the Tone Control setting
is turned On, if you have set the front speaker crossover to a numeric
setting, the front speakers will return to the Small setting, as indicated by
single boxes in the Speaker/Channel Input Indicators. When the front
speakers are Small and 2-Channel Stereo mode has been selected in
the Surround Modes submenu, DSP Surround Off mode is active.
DSP Surround Off Mode: The DSP Surround Off mode digitizes the
2.
incoming signal and applies the bass management settings, including
speaker configuration, delay times and output levels. This mode is
desirable when your front speakers are small, limited-range satellites
and you are using a subwoofer. To select this mode, use a digital
audio input, or turn the Tone Control setting off.
Analog Surround Modes: One of the main benefits of a surround
3.
receiver such as the AVR 254 is its ability to process 2-channel
⁄/¤
audio signals to produce multichannel surround sound in a variety
of modes, even when no surround sound has been encoded in the
recording. Among the available modes are the Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx
modes, the Dolby Virtual Speaker modes, the DTS Neo:6 modes, the
Logic 7 modes, and the Stereo modes.
Digital Audio Signals
Digital audio signals offer the benefit of greater capacity, which allows
recording artists to encode center and surround channel information
directly into the signal. The result is improved sound quality and startling
directionality, since each of these channels is reproduced discretely.
Alternatively, the artist may encode only two channels, but the digital
signal allows for a higher sampling rate that delivers greater detail.
High-resolution recordings usually sound extraordinarily distortion-free
at all frequencies, but especially at high frequencies.
Multichannel digital recordings usually are found in the 5.1-, 6.1- or
7.1-channel formats. The channels included in a 5.1-channel recording
are front left, front right, center, surround left, surround right and LFE.
The LFE channel is denoted as “.1” to represent the fact that it is not
full-range, being limited to the low frequencies.
6.1-Channel recordings add a single surround back channel, and
7.1-channel recordings add surround back left and surround back
right channels to the 5.1-channel configuration. New formats, such
as Dolby TrueHD, Dolby Digital Plus, DTS-HD and DTS-HD Master
Audio, are available in 7.1-channel configurations. The AVR 254 is
able to play the new audio formats, delivering a more exciting home
theater experience.
NOTE: To use the 6.1- and 7.1-channel surround modes, the
AVR 254 must be configured so that the Surround Back channels
are enabled. See the Manual Setup section on page 46 of the
Advanced Functions section for more information.
Digital formats include Dolby Digital 2.0 (two channels only), Dolby
Digital 5.1, Dolby Digital EX, Dolby Digital Plus, Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD,
DTS-HD Master Audio, DTS 5.1, DTS-ES (6.1 Matrix and Discrete),
DTS 96/24, 2-channel PCM modes in 32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz
or 96kHz, and 5.1 or 7.1 multichannel PCM.
When a digital signal is received, the AVR 254 detects the encoding
method and the number of channels. The number of channels encoded
will appear briefly in the front-panel display as three numbers, separated
by slashes (e.g., “3/2/.1”).
The first number indicates the number of front channels in the signal:
“1” represents a monophonic recording, usually an older program that
has been digitally remastered or, more rarely, a modern program
for which the director has chosen a special effect.
“2” indicates the presence of the left and right channels, but no
center channel.
“3” indicates that all three front channels (left, right and center)
are present.
42
Page 43

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
The second number indicates whether any surround channels are present:
“0” indicates that no surround information is present.
“1” indicates that a matrixed surround signal is present.
“2” indicates discrete left and right surround channels.
“3” is used with DTS-ES bitstreams to represent the presence of the
discrete surround back channel in addition to the side surround left and
right channels.
“4” is used with 7.1-channel digital formats, including Dolby TrueHD, Dolby
Digital Plus, DTS-HD and DTS-HD Master Audio, to indicate the presence of
two discrete side surround channels and two discrete back surround channels.
The third number is used for the LFE channel:
“0” indicates no LFE channel.
“.1” indicates that an LFE channel is present.
The 6.1-channel signals – Dolby Digital EX and DTS-ES Matrix and
Discrete – each include a flag meant to signal the receiver to decode
the surround back channel.
For Dolby Digital EX materials, the incoming bitstream will be displayed
as 3/2/.1 EX-ON. For older discs, the display may show EX-OFF, but
you will still be able to select the Dolby Digital EX mode manually.
For DTS-ES materials, the incoming bitstream will be displayed as
3/3/.1 ES-ON.
When a PCM signal is received, the PCM message, followed by the
sampling rate of the signal (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz or 96kHz), will
appear in the front-panel display.
In addition, the Speaker/Channel Input Indicators will indicate the
number of channels discretely encoded in the signal by displaying a
letter inside that channel’s speaker box. A line will connect the SBL and
SBR boxes when a 6.1-channel signal is detected, indicating that the
same signal is playing through both speakers. The letters flash when
no signal is present, such as when a DVD is paused. See Figure 58.
C
L
R
LFE
SL
SBL
SR
SBR
Figure 58 – Speaker/Channel Input Indicators
When only two channels – left and right – are present, the analog
surround modes may be used to decode the signal into the remaining
channels.
Each line is set to a default surround mode:
Virtual Surround: Dolby Virtual Speaker Reference
•
Stereo: 7-channel stereo
•
Movie: Logic 7 Movie
•
Music: Logic 7 Music
•
Video Game: Logic 7 Game
•
You may change each line’s setting to a different surround mode.
The choice of new modes depends on the number of speakers in
your system.
Virtual Surround: Dolby Virtual Speaker Reference or Wide
•
Stereo: 2-channel stereo, 5-channel stereo or 7-channel stereo
•
Movie: Logic 7 Movie, DTS Neo 6:Cinema, Dolby Pro Logic II Movie,
•
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie
Music: Logic 7 Music, DTS Neo 6:Music, Dolby Pro Logic II Music,
•
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music
Video Game: Logic 7 Game, Dolby Pro Logic II Game, Dolby Pro
•
Logic IIx Game
When one of the Dolby Pro Logic II Music modes is selected, access
to the Edit submenu becomes available. This submenu may be used
to adjust special settings available only in Music mode: Center Width,
Dimension and Panorama.
Once you have programmed the default surround mode for each type
of program, simply select the line from the Surround Modes menu any
time you wish to override the AVR’s automatic surround mode selection.
The AVR will use the same surround mode the next time the source
input is selected.
Please refer to Table A12 in the appendix for more information on which
surround modes are available with different bitstreams.
NOTE: Dolby Digital 2.0 signals may also include a Dolby
Surround flag indicating DS-ON or DS-OFF, depending on
whether the 2-channel bitstream contains only stereo information, or a downmix of a multichannel program that can be
decoded by the Dolby Pro Logic decoder in the AVR. By default,
these signals are played in Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie mode, but
you may select another Dolby surround mode manually.
If you would prefer a different surround format than the native signal’s
digital encoding, press the Surround Modes Button to display the
Surround Modes menu (see Figure 57).
The Auto Select option (the first line) uses the native signal’s digital
encoding, e.g. Dolby Digital or DTS. For two-channel materials, the
AVR defaults to Logic 7 Movie mode. If you prefer a different surround
processing mode, select the appropriate line from the menu: Virtual
Surround, Stereo, Movie, Music or Video Game.
Surround Modes
Surround mode selection is dependent upon the format of the incoming
audio signal, as well as personal taste. There is no harm in experimenting with all of the modes available with any given source material. Table
A12 offers a brief description of each mode the AVR 254 is capable of
using, and also indicates the types of incoming signals or digital bitstreams the mode may be used with. Additional information about the
Dolby and DTS modes is available on the companies’ Web sites:
www.dolby.com and www.dtsonline.com.
43
Page 44

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
When in doubt, check the jacket of your DVD for more information on
which surround modes are available on the disc. Usually, nonessential
sections of the disc, such as trailers, extra materials or the disc menu,
are only available in Dolby Digital 2.0 (2-channel) or PCM 2-channel
mode. If the main title is playing and the letters in the Speaker/Channel
Input Indicators are not lit for all speaker locations, look for an audio or
language setup section in the disc’s menu. Also, make sure your DVD
player’s audio output is set to the original bitstream rather than just
PCM. Check the DVD player’s output setting by stopping play of the
disc and checking the DVD player’s menu system.
As indicated in Table A12, different surround modes may only be
available with certain input signals or bitstream formats. For any incoming signal, only a limited number of surround modes are available.
Although there is never a time when all of the AVR 254’s surround
modes are available, there is usually a wide variety of modes available
for a given input.
To select a surround mode, press the Surround Modes Button
(front panel or remote) repeatedly until the desired option appears:
SURR: AUTO SELECT, SURR: VIRTUAL, SURR: STEREO, SURR: MOVIE,
SURR: MUSIC or SURR: GAME. The option will be displayed in the
Lower Line of the Message Display, and the Surround Modes menu
will appear on screen (see Figure 57). Press the OK Button, and the
menu option will move to the Upper Line, while the Lower Line indicates
⁄/¤
the current mode. Use the
press the OK Button, then press the Back/Exit Button to return to the
previous menu.
Buttons to select a new mode and
Dolby Surround Settings
Some additional settings are available for Dolby modes. Three settings
are active only when the Dolby Pro Logic II or IIx Music modes have
been selected. See Figure 59.
Panorama: With the Panorama mode turned ON, some of the sound
from the front speakers is moved to the surround speakers, creating an
enveloping “wraparound” type of effect. Each press of the OK Button
toggles the setting on or off.
Night Mode
Night mode is available with some Dolby Digital programs, if it has been
encoded in the material. It compresses the peak sound levels, maintaining the intelligibility of the dialogue and quieter passages, while reducing
the loudness of special effects and louder passages to avoid disturbing
others. Night Mode is accessed from the Audio Effects menu. Press
the Audio Effects Button and scroll down to the Night Mode line. Three
levels of compression are available:
Off: At this setting, there is no compression, as the Night mode is
deactivated.
Half: A mild compression is applied.
Full: More compression is applied.
Table A12 provides descriptions of all surround modes available on the
AVR 254, along with the incoming bitstreams or signals that the particular
mode may be used with. Feel free to experiment and simply cycle
through all of the available modes at any time; you cannot cause any
problems for the AVR 254 by doing so.
NOTE: To access 6.1- and 7.1-channel modes, such as
Dolby Digital EX, DTS-ES, Logic 7 (7.1 modes), DTS Neo:6
(6.1 modes), and 7-channel Stereo, you must enable the
surround back channels as explained in the Manual Setup
section. You should not enable these channels if you don’t
have surround back speakers in your system.
Figure 59 – Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music Mode Settings
Center Width: This setting affects how vocals sound through the three
front speakers. A higher number (up to 7) focuses the vocal information
tightly on the center channel. Lower numbers broaden the vocal sound-
‹/›
stage across the three speakers. Use the
setting.
Dimension: This setting affects the depth of the surround presentation,
allowing you to “move” the sound toward the front or rear of the room.
The setting of “0” is a neutral default. Setting “F-3” moves the sound
mostly toward the front of the room, while setting “R-3” moves the sound
‹/›
mostly toward the rear. Use the
44
Buttons to change the setting.
Buttons to change the
Page 45

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
Manual Setup
The AVR 254 is flexibly designed to be used with almost any loudspeakers available. The flexibility comes from the AVR 254’s capability to
be configured to match the characteristics of your particular speakers,
and to compensate for the acoustic characteristics of your room.
The EzSet/EQ process automatically detects the capabilities of each
speaker, and optimizes the AVR 254’s performance in your system.
However, if for some reason you are unable to run EzSet/EQ calibration,
e.g., you have misplaced the microphone, or if you wish to make further
adjustments to the settings made by the EzSet/EQ process, you may
use the Manual Setup on-screen menus as described in this section.
Before beginning manual setup place your loudspeakers in their correct
locations within the room (see Speaker Placement section), and connect
them to the AVR. You will need the specifications for each of your speakers,
which may usually be found in the owner’s guide for the speakers or
on the manufacturer’s Web site. If necessary, contact the manufacturer
to obtain the frequency range specification. Although the output-level
setting portion of manual setup may be performed “by ear,” we recommend that you purchase an SPL (sound-pressure level) meter at a local
electronics store.
We suggest that you record your configuration settings in the appropriate places in Tables A3 through A11 in the appendix in case you need
to reenter them after a system reset, or if the AVR’s Master Power
Switch is turned off or the unit is unplugged for more than four weeks.
NOTE: When using the AVR’s Speaker Setup menus, we recommend selecting a video output resolution of 720p or higher
to provide graphics that simplify configuration. Those menus will
vary in appearance from the ones shown here.
Step One – Determine Speaker Crossover
Without using the EzSet/EQ process, the AVR 254 can’t detect how
many speakers you’ve connected to it; nor can it determine their capabilities. For this part of the system setup consult the speaker’s technical
specifications.
Locate the frequency response, which is usually given as a range, e.g.,
100Hz – 20kHz (±3dB). This specification tells you whether the speaker
is able to play sounds that are very high- or low-pitched, represented
by the high and low frequencies. We are concerned here with the lowest
frequency that each of your main speakers is capable of playing, which
is 100Hz in this example. Use the Table A3 worksheet in the appendix
to note this number as the crossover for that speaker (not the same as
the crossover frequency listed in the speaker’s specifications).
If you send the lowest notes to small satellite speakers, you won’t hear
these notes very well, and you may even damage the speaker by
exceeding its capabilities. If you send the highest notes to the specialpurpose subwoofer, you may not hear them at all.
With proper bass management, the AVR 254 divides the source signal
at a crossover point. All information above the crossover point is played
through the satellite speaker (front left/right, center, surround left/right, or
surround back left/right), and all information below the crossover point is
played through the subwoofer. This enables each loudspeaker in your
system to perform at its best, delivering an enjoyable sound experience.
Step Two – Measure Speaker Distances
Ideally, all of your speakers would be placed in a circle, each at the
same distance from the listening position. However, your room may not
be ideal, and you may have had to place some speakers a little further
away than others. This could affect the overall sound of the receiver,
as sounds that are supposed to arrive simultaneously from different
speakers blur due to different arrival times.
The AVR 254 has a delay adjustment that enables the receiver to
compensate for real-world speaker placements.
Before you begin making adjustments, measure the distance from each
speaker to the listening position, and note it in the Table A4 worksheet
in the appendix. Even if all of your speakers are the same distance from
the listening position, you should enter your speaker distances as
described in Step Three.
Step Three – Manual Setup Menu
Now you are ready to program these adjustments into the receiver. It’s
best to sit in the usual listening position and make the room as quiet
as possible.
With the receiver and video display turned on, press the AVR Button to
¤
display the menu system. Use the
Speaker Setup line, and press the Set Button to display the Speaker
Setup menu. See Figure 46.
If you have run the EzSet/EQ process, those results were saved. To
tweak the EzSet/EQ results, or to configure the AVR from scratch, select
Manual Setup. The screen shown in Figure 60 will appear.
Button to move the cursor to the
The subwoofer’s frequency response will include only the very lowest
frequencies, since the subwoofer is designed to play only bass materials.
A typical frequency response for a subwoofer is 25Hz – 150Hz. In this
case, the higher number should be noted in the worksheet.
This information is required to program the receiver’s bass management, which determines which speakers the receiver will use to play
back the low-frequency (bass) portion of the source program.
Figure 60 – Manual Speaker Setup Menu
45
Page 46

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
NOTE: All of the speaker setup submenus include the Exit and
Back options as shown at the bottom of Figure 58. To return
to a previous menu without making any changes, select Exit.
To save the current settings, select the Back option.
If you previously saved EzSet/EQ results in this setup position and you
wish to reconfigure the speakers from scratch, select the Reset option.
For best results, we recommend configuring the speakers in this order,
although it may differ from the order in which the submenus appear in
the Manual Speaker Setup menu: Number of Speakers, Crossover
(Size), Sub Mode, Distance and Level Adjust.
Number of Speakers
Move the cursor to the Number of Speakers line and press the Set
Button. See Figure 61.
Figure 61 – Number of Speakers Menu
The Number of Speakers menu lists each of the speaker groups.
Program the correct setting for each group: ON when the speakers are
present in the system, and OFF for positions where no speakers have
been installed. The Front Left & Right speakers are always ON and may
not be disabled. Any changes made to the system configuration will be
reflected in the total number of speakers displayed at the top of the
screen.
The setting for the surround back speakers includes a third option:
Zone 2. The AVR 254 is capable of multizone operation, allowing placement of a pair of speakers in another room. Listeners in the remote room
may enjoy either the same program as in the main room or a different
source. The AVR 254’s assignable surround back amplifier channels make
multizone operation easier than ever, since an external power amplifier is
not required. Simply select the Zone 2 option at this line, and connect the
Surround Back Speaker Outputs to loudspeakers located in the remote
room. The main room will be configured automatically for up to 5.1
channels. See the Multizone Operation section for more information.
The settings in this menu affect a number of aspects of the AVR’s
operation, including the remainder of the speaker setup process and
the availability of various surround modes at any time.
When you have finished programming the number of speakers in the
system, select the Back option to insure the settings are saved correctly.
You may use the Back/Exit Button, and the settings will be saved.
Adjust Crossover Frequencies Menu
After you have programmed the number of speakers in the system, the
AVR will return to the Manual Speaker Setup menu, similar to the one
shown in Figure 46. Navigate to the Crossover (Size) line and press
the OK Button to display the Adjust Crossover Frequencies menu (see
Figure 62).
Figure 62 – Adjust Crossover Frequencies Menu
The AVR will only display those speaker groups which you programmed
in the Number of Speakers menu.
Refer back to Step One, where you determined each speaker’s
crossover. For the main speakers, this is the lowest frequency the
speaker reproduces well; and for the subwoofer, it’s the highest.
For each main speaker, select one of the seven crossover frequencies:
40Hz, 60Hz, 80Hz, 100Hz, 120Hz, 150Hz or 200Hz. If the crossover
frequency you determined in Step One is below 40Hz, select the first
option, “Large”. This setting doesn’t refer to the speaker’s physical size,
but to its frequency response, which is also called “full range”. This means
the speaker is capable of playing sounds throughout the frequency
spectrum, from the high pitches to the bass.
Specify the size of the subwoofer’s transducer as 8, 10, 12 or 15 inches.
Make a note of each speaker group’s crossover setting in Table A3 in
the appendix.
When you have finished entering the settings, remember to select Back,
not Exit.
Sub Mode
Move the cursor to the Sub Mode line to program bass management
for the subwoofer. The subwoofer’s setting depends upon how you
programmed the front left and right speakers.
• If you set the front speakers to a numeric crossover frequency, the
subwoofer setting will be LFE, and you won’t be able to change it.
All low-frequency information will always be sent to the subwoofer.
If you don’t have a subwoofer, we recommend that you either
upgrade to full-range speakers or add a subwoofer to your system
at the earliest opportunity.
• If you set the front speakers to LARGE, you may select between
two possible settings for the subwoofer.
46
L/R+LFE: This setting sends all low-frequency information to
the subwoofer, including both information that would normally be
Page 47

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
played through the front left and right speakers and the special
low-frequency effects (LFE) channel information.
LFE: This setting plays low-frequency information contained in the
left and right program channels to the front speakers, and directs
only the LFE channel information to the subwoofer.
NOTE: If you are using a Harman Kardon HKTS Series speaker
system, select the appropriate numeric crossover frequency for
the Left/Right, Center, Surround and Surr Back lines, and the
subwoofer will automatically be set to LFE.
The Speaker/Channel Indicators on the front panel of the receiver (see
Figure 58) will display the speaker size settings as follows. For each
speaker configured numerically, a single box will appear in the position
for that speaker. For each speaker configured as LARGE, a double box
will appear in its position. If a speaker is configured as OFF, no box will
appear. The subwoofer will be indicated by a single box, or no box if
no subwoofer has been configured. The letters inside the boxes appear
when a digital
encoded.
a DVD is paused. A line will connect the SBL and SBR boxes when a
6.1-channel signal is detected, indicating that the same signal is playing
through both speakers.
signal is being received that has that channel discretely
The letters flash when the signal is not present, such as when
Adjust Speaker Distance Menu
As explained above in Step Two – Measure Speaker Distances, sometimes the speakers are placed at different distances from the listening
position, which can muddy the sound, as sounds are heard earlier or
later than desired.
Even if all of your speakers are placed the same distance from the
listening position, do not skip this menu.
On the Manual Speaker Setup menu, move the cursor to the Distance
line and press the Set Button to display the Adjust Speaker Distance
menu. See Figure 63.
section, and select the Unit of Measure line. Press the OK Button to
change the setting from Feet to Meters.
⁄/¤
Use the
the OK Button then use the
as needed. The values vary between 0 and 30 feet, with a default of
10 feet for all speakers. Use the
speaker in turn – Center, Front Right, Surround Right, Surround Back
Right, Surround Back Left, Surround Left and Subwoofer, if present in
your system.
NOTE: When the multiroom system is in use, the surround back
channels are automatically assigned to the multiroom system, as
mentioned earlier. You will not be able to adjust the delay settings
for these channels, and the cursor will skip past them.
Buttons to move the cursor to the Front Left line, press
‹/›
Buttons to change the measurement
⁄/¤
Buttons to move to each
Step Four – Setting Channel Output Levels
Manually
For a conventional 2-channel receiver, the balance control enables the
user to control the stereo imaging by adjusting the relative loudness of
the left and right channels, as heard at the listening position.
With up to seven main channels plus a subwoofer, imaging becomes
both more critical and more complex. Unlike the rotary balance control,
the goal of the AVR 254’s channel output adjustment process is to
examine the output level of each channel independently and ensure
that each is heard at the listening position with equal loudness.
If you followed the instructions in the Initial Setup section, then you
let EzSet/EQ calibration handle this critical task for you, simply and
automatically.
However, if you prefer to make these adjustments manually, the
AVR 254’s Adjust Speaker Levels menu allows you to do so, either
using the system’s test tone or while playing source material. In addition,
this is the only method for adjusting the level of the subwoofer.
If you use a handheld SPL meter (available at many electronics stores),
set it to the C-Weighting, Slow scale.
Figure 63 – Adjust Speaker Distance Menu
This menu requires you to enter the distance from each speaker to the
listening position, which you measured in Step Two – Measure Speaker
Distances and noted in Table A4 in the appendix.
The default unit of measurement is feet. If you wish to change the unit
to meters, press the Back/Exit Button until you return to the main AVR
menu. Scroll down to the System line, and select it to view the System
Settings menu. Scroll down this menu to the General AVR Settings
1. Make sure all speakers have been connected correctly.
2. Adjust the number of speakers, crossover, distance and sub mode
for each speaker in your system as described in Step Three.
3. If you are using a handheld SPL meter with source material, such
as a test disc or another audio selection, play it now and adjust the
AVR’s master volume control until the meter measures 75dB.
4. There are several methods of adjusting the channel output levels,
using either the test tone or source materials. In all cases, you may
measure the channel levels in one of two ways:
a) By ear. Try to adjust the levels so that all channels sound equally loud.
b) Using a handheld SPL meter set to the C-Weighting, Slow scale.
Try to adjust each channel so that the meter reads 75dB.
47
Page 48

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
The best method of setting the output levels is by running the EzSet/EQ
process, as described in the Initial Setup section. If any finer adjustments
are desired, we recommend using the menu system to make the adjustments while playing the AVR’s built-in test tone and measuring the output
using an SPL meter. Less effective would be to measure the output by ear.
Press the AVR Button to display the menu system, and then navigate
to the Speaker Setup line. Press the OK Button to display the Speaker
Setup menu. Select Manual Speaker Setup, press the OK Button, and
then navigate to the Level Adjust line. Press the OK Button to display
the Adjust Speaker Levels menu. See Figure 64.
Figure 64 – Adjust Speaker Levels Menu
All of the speaker channels will appear with their current level settings.
Reset Levels: If you wish to start by resetting all of the levels to their
factory defaults of 0dB, scroll down to this line and press the OK Button.
The levels will be reset.
you may either copy the settings you obtained (as a short cut),
or redo the procedure to determine the correct settings.
When you have finished adjusting the speaker levels, select the SAVE
option so that the settings will not be lost. Record the level settings in
Table A3 in the appendix for future reference.
Audio Effects
Depending on the specific characteristics of your listening room, you
may wish to adjust some of the audio settings, such as tone controls,
to improve performance. Access these settings from the Audio Effects
menu. Press the Audio Effects Button on the front panel or remote,
and the screen shown in Figure 65 will appear. The menu may also be
accessed from the Setup Source menu by pressing the Info Settings
Button and selecting the Audio Effects line.
NOTE: The settings in the Audio Effects menu affect each
source independently.
If you are using an external source to set your output levels, simply
‹/›
navigate to each channel, press the Set Button and use the
Buttons
to adjust the level as desired between –10dB and +10dB.
If you would like to set your levels using the AVR 254’s internal test
tone, adjust the TEST TONE line as follows.
Test Tone: This line determines whether the test tone is active. To begin
the process of setting the levels, press the OK Button repeatedly to
select the OFF, AUTO or MANUAL setting. Any time you manually move
the cursor out of the channel listings area of the screen, this
setting will automatically change to OFF, stopping the test tone.
When this setting reads AUTO, the test tone will automatically circulate
to all channels, pausing for a few moments at each channel and then
moving to the next channel several seconds later, as indicated by the
highlight bar. You may adjust the level for any channel when the test
‹/›
tone is paused there by using the
⁄/¤
Buttons at any time to move the cursor to another line, and the
Buttons. You may also use the
test tone will follow the cursor.
When this setting reads MANUAL, the test tone will not move to the
⁄/¤
next channel until you use the
Buttons to move it.
NOTE: Setting the channel levels while one surround mode is
active does not carry over to other mode groups. We recommend that after you have set the levels satisfactorily in one
mode, you note the results and change to other surround
modes. For those modes that don’t reflect your level settings,
Figure 65 – Audio Effects Menu
Tone Control: This setting determines whether the treble and bass
controls are active. When it’s off, the tone controls are “flat”, with no
changes. When it’s on, the bass and treble frequencies are boosted
or cut depending upon the tone-control settings. When an analog audio
source is in use and the 2-Channel Stereo surround mode is selected,
setting the Tone Control to “Off” places the unit in analog bypass mode,
with no digital processing of the analog signal.
Treble: Boost or cut the high frequencies by up to 10dB by using the
‹/›
Buttons to change the temperature bar setting. The default setting
is 0dB, at the center of the temperature bar.
Bass: Boost or cut the low frequencies by up to 10dB by using the
‹/›
Buttons to change the temperature bar setting. The default setting
is 0dB, at the center of the temperature bar.
LFE Trim: This setting may be used to attenuate the loudness of the
subwoofer. The setting defaults to 0dB, which is the maximum. Press the
‹/›
Buttons to reduce the level by up to 10dB; the setting will appear
as a negative number.
Night Mode: This setting is used with specially encoded Dolby Digital
programs to compress the signal so that louder passages do not disturb
others, while dialogue remains intelligible.
Off: For normal listening.
•
48
48
Page 49

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
• Half: Applies moderate compression.
Full: Applies the most compression.
•
When you have finished making adjustments in the Audio Effects menu,
press the Audio Effects Button or the Back/Exit Button to clear the screen.
Video Adjustments
The AVR 254 uses leading-edge Faroudja DCDi Cinema video processing technology, with incoming video upscaled to 1080p (up to 1080i
when component video outputs are used) for outstanding video quality,
even with older analog video sources. Faroudja DCDi Cinema’s Dual 3D
comb filters and 10-bit video processing eliminates the jagged edges
and moiré patterns seen with less advanced processing. Thanks to this
“Torino” video processing chip, on-screen graphics may be generated
in high definition, and blended with the incoming video. This not only
delivers crisp, clear information messages, it allows you to continue to
watch a program while making system adjustments.
The video processor automatically provides the best picture based on
the capabilities of your video display and the incoming source video
signals. However, you may experiment with the Video Modes menu
adjustments to try to improve the picture further.
Video Modes
screen as sliders with values ranging from 0 to 100. The default
‹/›
setting for each adjustment is 50. Use the
each setting’s value.
Picture Adjust: Use this setting to change the aspect ratio of the
displayed image.
When displaying widescreen (16:9) images on a full screen (4:3)
device, letterbox format will be used, in which black bars may appear
above and below the image (pillarboxing).
When displaying full screen images on a widescreen device, black or
gray bars may appear to the left and right of the image.
Some displays, especially plasma and CRT monitors, may suffer from
“burn-in” when the same image, such as the horizontal or vertical bars,
is left on screen for a long period of time. Use this setting to adjust the
picture so that it fills the display’s screen. The options are:
Auto Fit: The AVR automatically adjusts the image as required to
•
fit the display’s capabilities.
Height Fit: Adjusts the image to eliminate any bars above or below
•
it. Bars may remain at the sides.
Width Fit: Adjusts the image to eliminate any bars on the sides.
•
Bars may remain above and below the image.
Buttons to change
After you have adjusted the picture settings on your video display, additional adjustments may be made to the AVR, if necessary, to further
improve the picture. Access these settings from the Video Modes menu.
Press the Video Modes Button on the front panel or remote, and the
screen shown in Figure 66 will appear. The menu may also be accessed
from the Setup Source menu by pressing the Info Settings Button and
selecting the Video Modes line.
Figure 66 – Video Modes Menu
Video Mode: The default setting of Processor Off passes the video
signal through to the display without any processing. Select one of these
processing options to optimize the picture for the current program by
applying adjustments to the brightness, contrast, color and sharpness:
Sports: For sporting events.
•
Nature: For programs shot outdoors, in a natural setting.
•
Movie: For movies and many television broadcasts.
•
Custom: Allows manual adjustment of the picture settings. The
•
Brightness, Contrast, Color and Sharpness settings will appear on
Zoom 1x: Displays the image as received from the source. If the
•
image is in the 4:3 aspect ratio, on widescreen displays pillarbox
format may be used. If the image is in the 16:9 aspect ratio, on full
screen (4:3) displays letterbox format may be used.
Zoom 2x: Stretches the image evenly to completely fill the screen.
•
The outer portions of the image may be cropped.
Feel free to experiment with this setting for each source until you find
a pleasing display format for each program.
Advanced Video Settings: Press the ›or OK Button to display the
Advanced Video Modes submenu (see Figure 67).
Figure 67 – Advanced Video Modes Menu
Noise Reduction: Change this setting from its default of Off to Low,
Medium or High to filter out signal noise.
MPEG Noise Reduction: This setting is designed to address two
specific types of video distortion, mosquito noise and blocking artifacts.
If you see haziness or shimmering around the edges of objects or the
scrolling credits in a film, or if the image appears to “pixellate” into
49
Page 50

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
blocks, change the MPEG Noise Reduction setting from its default of
Off to the Low, Medium or High setting to improve the picture.
Cross Color Suppressor: Turn this setting on to remove cross color
artifacts, which can occur when high-frequency luminance (brightness)
signals are misinterpreted as chroma (color) signals, which can cause
unwanted flickering, flashing colors or rainbow patterns.
Film Mode Detect: While normally left off, turn this setting on to compensate for authoring errors in the process of converting film programs
to video.
How to Adjust the Custom Picture Settings
Set the Video Mode to Custom to display the picture settings as shown
in Figure 68.
Figure 68 – Video Modes Custom Processing
With a color bar test pattern screen from a test disc or other source
showing on your video display, the following adjustments may be made:
• The proper color intensity setting on your TV.
• Proper color adjustments using the color bars, which should be (left
to right) black, white, yellow, cyan (turquoise), green, magenta, red,
blue, black.
• The proper color transition, seen as sharp separation of the bars.
• The performance of the color circuits in your TV (with “Video” signals);
bar edges should show no vertical crawling dots.
With the gray scale and the black/white fields below the color bars, the
brightness and contrast of your screen can be adjusted.
Brightness Adjustment
1. Turn down the color control on your TV until the color bars appear
in black and white.
2. Adjust the contrast to the lowest level where you still can see all gray
scale bars separately and clearly.
3. Adjust the brightness so that the bars in the gray scale are all visible.
The bar farthest to the left has to be as black as possible rather than
gray but the next gradation must clearly be distinct from it. All the
bars in the gray scale should be gradually and evenly changing from
black to white, left to right.
Contrast Adjustment
1. Adjust the contrast on your TV until you see a bright white bar in the
lower right corner of the screen and a deep-dark-black bar to the
left. The optimal contrast setting will depend on your preference and
the surrounding light in the TV room.
2. If the brightness of the white bar no longer increases when the contrast is turned up or the borders of white letters bloom (overlight) into
the black areas (drastically decreasing the sharpness of the type), the
contrast has been turned up too much. Reduce the contrast until
these effects disappear and the video still looks realistic.
3. If you are watching TV with ambient daylight, adjust the contrast so
that a normal video picture has about the same look as the surroundings in your room. That way the eye is relaxed when watching the TV
picture. This contrast setting may be reduced when the surrounding
light is dimmed, thereby usually improving the sharpness of a video
significantly.
4. The gray scale in the middle line needs to have the same clear
difference between each bar as before the contrast adjustment. If
not, go back to “Brightness Adjustment” and repeat Step 3 and then
“Contrast Adjustment,” making only minor adjustments each time for
optimization.
Color Adjustment
1. When the brightness and contrast are set optimally, adjust the color
control to the level of your preference. Set the level so that the colors
look strong but still natural, not overdone. If the color level is too
high, depending on the TV, some of the bars will seem wider or the
color intensity will not increase when the control is turned up. Then
the color control must be reduced again. Ultimately, you also should
test the color intensity with a video – e.g., pictures of natural faces,
flowers, fruit and vegetables, and other common natural articles for
an optimal setting of the color intensity.
2. Refer to the large white bar below the gray scale to tweak the
warmth of the picture. Every viewer has a preference as to how the
glow of the picture should be. Some prefer a colder picture, some
a warmer glow. The Tint function on your TV and the white bar can
be used to control this. Adjust the Tint to the level where you feel
the white color has the tone you prefer.
Sharpness Adjustment
Contrary to intuition, the picture will appear sharper and clearer with the
sharpness backed off from the maximum setting. Reduce the sharpness
setting on your television, and the setting on the AVR 254 if necessary,
to minimize the appearance of any white lines between the bars in the
gray scale portion of the test screen.
Convergence and Edge Focus
The crosshatch pattern that surrounds the test screen may be used to
evaluate edge focus and convergence in front- or rear-projection video
displays. However, the controls used to adjust these parameters are
often not user-accessible. In any event, these adjustments are extremely
50
50
Page 51

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
complex, and require proper training and experience to avoid worsening
the situation. Therefore, it is recommended that if you are unable to
improve the picture using the available controls, contact the video display
manufacturer’s authorized service representative for assistance.
When you have finished making any video adjustments, press the
Back/Exit Button to back out of the menu system.
Multizone Operation
The AVR 254 offers the benefits of multizone operation, a rarity in a
receiver this affordable. With the multizone system in use, you may enjoy
an exciting 5.1-channel home theater presentation in the main listening
area, while others listen to the same materials or an entirely different
presentation in another room.
Although installation of a multizone system is not complicated, it requires
running wires inside walls. We urge you to check your local building
codes and comply with the requirements for in-wall wiring systems to
prevent the possibility of a dangerous situation. If you have any questions about installing a multiroom system, we strongly recommend that
you contact a professional custom installer.
Installing a Multizone System
A typical multizone system consists of only one remote room in the
remote zone. That is, you connect only one pair of loudspeakers to the
AVR 254, placing those speakers in the remote room the same way
you would place the front left and right speakers in the main listening
room. It is not recommended that you place the left and right
multizone speakers in different rooms.
However, when the multizone system is turned off, you may reassign your
remote speakers to the main listening room for 7.1-channel operation.
You may install an optional remote infrared (IR) receiver in the remote
room and connect it to the Zone 2 IR Input on the back of the receiver.
This lets you use an optional second-zone remote, a keypad or another
control device to turn the multizone system on or off, select a source
input, and operate any source devices that are connected in daisychain
fashion to the AVR 254’s Remote IR Output. You may use the main
AVR 254 remote control in the remote zone, or you may purchase a
second-zone remote by contacting Harman Kardon customer service
through our Web site.
You may use the above connection methods simultaneously to increase
the total number of remote rooms in your system. Remember that
sending control commands from one room in the system will affect
the entire remote zone of the multizone system.
Operating the Multizone System
The AVR 254’s multizone system is accessed using the on-screen
Zone 2 menu. Press the AVR Button to display the menu System, and
⁄/¤
use the
OK Button to display the Zone Control menu. See Figure 69.
Buttons to navigate to the Zone 2 line. Press the
To use the AVR 254 with more than one remote room, purchase a
multichannel external amplifier that enables you to connect several pairs
of loudspeakers. However, the AVR 254 only outputs one remote zone,
meaning that only one signal is sent through the multizone system.
All remote rooms will hear the same source, even when a multichannel
amplifier is used.
There are two ways of connecting the remote speakers to the AVR 254:
a) Connect the speakers to the left and right SB/Zone 2 Speaker
Outputs on the rear panel of the AVR 254. This is the simplest
type of multizone system. However, it is not recommended for long
speaker-wire runs (e.g., more than 25 feet), as the audio signal tends
to degrade over long distances. If your application would require a
long speaker-wire run, consider option b) below.
b) Purchase an external amplifier. Connect the SB/Zone 2 Preamp
Outputs to the amplifier’s inputs. You may place the amplifier either in
the main listening room or the remote room. Placing the amplifier in
the main listening room would require the use of long speaker wires
to reach the remote room, while placing the amplifier in the remote
room calls for the opposite – long interconnect cables and short
speaker wires.
When you use either the SB/Zone 2 Speaker Outputs or the Preamp Outputs
for a multizone system, you will not be able to use the surround back
speakers with your main system, which will then be limited to 5.1channels.
Figure 69 – Zone 2 Menu
Status: This line is used to turn the multizone system on or off. When
no one is listening in the remote room, leave this setting at the default
of OFF.
Source: This line indicates the source input selected for the remote
zone. You may select any source input for which a device has been
connected to the AVR 254, even when a different source is being
enjoyed in the main listening area. However, if the tuner has been
selected for simultaneous operation in both the main listening area and
the remote zone, listeners in both areas will hear the same radio station.
NOTE: Only analog audio sources are available to the multizone
system. To hear digital devices, such as a CD player, in the
remote zone, follow these steps:
1. In addition to a digital audio connection, connect the source
device’s analog audio outputs to any available analog audio
inputs on the AVR, noting in Table A5 in the appendix which
set of inputs was used.
2. In the Setup Source menu, leave the Audio Source setting at
the digital audio input. However, scroll down to the Zone 2 Audio
setting and select the analog audio source used in step 1.
51
Page 52

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
Volume: The volume is controlled separately for the remote zone.
To operate the multizone system using the remote, slide the Zone Select
Switch at the bottom of the remote to the “2” position (see Figure 70).
Press a Source Selector to select a source input for the remote zone.
Adjusting the volume or mute controls will only affect the volume in the
remote zone. The on-screen menu functions will not be operative. The
remote will operate source devices that have been programmed into it
as explained in the Initial Setup section.
Figure 70 – Zone Select Switch
System Settings
The AVR 254 offers system settings that allow you to make the receiver
easier to use rather than directly affecting performance. These settings
may be accessed from the System Settings menu, which is selected
by pressing the AVR Button and navigating to the System line. Press the
OK Button to display the System Settings menu. See Figure 71.
when turned on. This feature avoids discomfort for listeners in case the
last user turned the volume very high.
Turn Volume Default on, and then set the Volume Default Level to the
desired turn-on volume.
Unit of Measure: This setting only affects the speaker-distance settings
when performing Manual Speaker Setup. Select between meters and feet.
Language: Select the preferred language for the AVR’s on-screen
menus and displays: English, French, Spanish or German.
HDMI Audio to TV: This setting determines whether audio signals
received through any of the HDMI Inputs are passed through the HDMI
Output to the video display. In normal operation, leave this setting Off,
as audio will be played through the AVR rather than the video display’s
built-in speakers. However, sometimes you may wish to use the TV by
itself, without using the complete home theater system. For those occasions change this setting to On. You may always mute the TV’s speakers
when using the AVR for audio.
Resolution to Display: This setting reflects the video output resolution.
See page 36 in the Initial Setup section for more information.
Menu Appearance
OSD Transparency: This setting allows you to select whether video
programs will be visible when the menu system is in use. Select Normal
for a fully-transparent background, Medium for the menu background to
be partially visible or Opaque to block the view of any video programs
while the menus are on screen.
Figure 71 – Systems Settings Screen
Front Panel Dimmer: Some people find the front-panel messages
distracting while watching a movie. The AVR 254 allows you to dim the
front-panel lighting or turn it off altogether. When the display is partly or
fully dimmed, it will return to full brightness for five seconds whenever a
command is entered, and then it will dim again. Select On 100% for full
brightness, dim to 50% or 25% of full brightness or select Off to fully
darken the display. The light inside the Volume Control will go out when
the display is partly or fully dimmed, but the Power Indicator will always
remain lit to remind you that the AVR is powered on.
General AVR Settings
Volume Units: Select whether volume is displayed in the conventional
decibel scale or on a numeric scale from 0 to 100. When the decibel
scale is used, 0dB is the maximum volume, with lower volumes measured
as negative values.
Volume Default and Volume Default Level: These two settings are
used together to program a volume level the AVR will always switch to
Volume Status Messages: When the AVR is turned on, the volume is
adjusted or the source is changed, or if a change in the input signal is
detected, a status message will be displayed on screen. Use this setting
to select how long the message remains visible. The setting varies from
2 to 10 seconds, with a default of 3 seconds.
Menus: Some menu settings only remain in effect during the current
listening session, including the settings in the Surround Modes, Video
Modes and Audio Effects menus. This setting governs how long these
menus will remain visible after your last adjustment, varying from 2 to
10 seconds, with a default of 3 seconds.
Setup and Slide-In Menus: This setting determines how long the
setup menus (Main Menu, Speaker Setup Menu, Zone 2 Menu,
all slide-in menus) remain visible after your last adjustment. Select
a timeout period of 5, 10 or 15 (the default) minutes, or no timeout,
which leaves the menus on screen until you manually clear them.
We recommend setting some timeout period to avoid the possibility
of burn-in damage to plasma or CRT displays.
Screen Saver: Use this setting to program a timeout period for no
activity (with no menus displayed) before the AVR’s built-in screen saver
begins. Select a period of 5 (the default), 10 or 20 minutes, or turn off
the screen saver. We recommend setting some timeout period to avoid
the possibility of burn-in damage to plasma or CRT displays.
52
52
Page 53

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
Advanced Remote Control Functions
The AVR 254 remote control not only operates the AVR 254, but it also
serves as a universal remote that may be programmed to operate many
other home theater components, as described in the Installation section.
Each time you select one of your other components, the AVR remote
switches to the control functions for that component. Since many buttons
have unique functions for each component, refer to the Function List
(Table A13 in the appendix) for assistance in operating your other components. The function of each button will not necessarily correspond to
the label printed on the button.
Punch-Through Programming
The AVR 254 remote’s punch-through feature allows you to select
one component for the remote to operate, while simultaneously setting
certain groups of controls to operate another component. For example,
while using the AVR to control surround modes and other audio functions, you may operate the transport controls of your DVD player. Or while
using the remote to control video functions on your TV, you may use your
cable box to change channels.
To program punch-through control while operating any device:
1. Press and hold the Source Selector (or AVR selector) for the main
device the remote will be operating. The Source Selector will light,
go dark and then light up again, indicating the remote is in Program
mode and that you may release the button.
2. Select the type of punch-through programming.
a) To program channel control punch-through, press the Channel
Up Button.
device, but with more flexibility than the built-in punch-through controls.
Up to eleven activities may be programmed.
NOTE: Use caution when programming complicated activities. It
isn’t possible to program a pause or delay before sending commands after Power On, and the component may not be ready
to respond to commands instantaneously after powering on.
To program, or “record” an activity, follow these steps:
1. To enter Program mode, simultaneously press and hold the Activity
Button and the Alphanumeric Key or AVR Power On Button to which
the activity will be assigned.
2. Press the Input (or AVR) Selector for each device before you enter
commands to be transmitted to that device. This step counts as one
of the 19 commands allowed for each macro.
3. For the Power On command, press the AVR or Device Power On
Button as appropriate.
4. Press the AVR or Device Power Off Button to program the Power
Off command.
5. Press the Activity Button to end the programming process, and the
last Source Selector (or the AVR Settings Button) will flash 3 times
to indicate that the activity has been programmed.
It isn’t possible to “edit” a command within a macro. However, you may
erase the macro as follows:
1. Simultaneously press and hold the Activity Button and the Numeric
Key or AVR Power On Button assigned to the activity until the Source
Selector or AVR Settings Button lights.
b) To program transport control punch-through, press the Play Button.
3. Press the Source Selector for the device whose channel or transport
controls you would like to be active while operating the device you
selected in the first step. The Source Selector will flash to confirm the
programming.
For example, if you wish to watch your TV while changing channels
using your cable box, first press and hold the TV Button until it lights.
Then press the Channel Up Button, followed by the CBL/SAT Button.
To undo punch-through programming, follow the same steps as above,
but press the same Source Selector in Steps 1 and 3.
NOTE: The remote always allows volume-control punchthrough, since the Volume and Mute controls are dedicated
to the AVR.
Activities (Macros)
Activities are used to program sequences of up to 19 commands that
are executed with a single button press. Activities are well suited for
power on and off commands, or to send out a favorite multidigit channel
number with one button press, or to have the ability to send out a code
sequence to control another device while the remote is operating one
2. Press the Activity Button to erase the macro.
Resetting the Remote
To reset the remote to its factory defaults, simultaneously press and
hold the TV Source Selector and the “0” Alphanumeric Key. When the
TV Button re-lights, enter the code “333”. When the TV Button goes
out, and all of the Source Selectors flash, the remote will have been
fully reset.
Processor Reset
There may be instances when you wish to fully reset the AVR 254 to its
factory defaults, or the unit may behave erratically after a power surge.
To correct erratic behavior, first try turning the Master Power Switch off
and unplugging the AC power cord for at least three minutes. Plug
the cord back in and turn the receiver back on. If this doesn’t help,
try a system reset.
NOTES:
• A system reset erases all user configurations, including video
resolution, speaker and level settings, and tuner presets. After
a reset, you will need to reenter all of these settings.
53
Page 54

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
• The RS-232 Reset Button on the rear panel of the AVR 254
does not perform a system reset. DO NOT press the RS-232
Reset Button.
To reset the AVR 254, place the receiver in Standby mode (press the
front-panel Standby/On Switch so that the Power Indicator turns amber).
Then press and hold the front-panel OK Button for at least five seconds
until the RESET message appears in the display.
Follow the directions in the note on page 32 to restore the picture
if necessary.
If the receiver still does not function correctly after a processor reset,
contact an authorized Harman Kardon service center for assistance.
Authorized service centers may be located by visiting our Web site
at www.harmankardon.com.
Memory
If the AVR 254 is unplugged or experiences a power outage, it will
retain user settings for up to four weeks.
54
54
Page 55

TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
SYMPTOM CAUSE SOLUTION
Unit does not function when Main • No AC Power • Make certain AC power cord is plugged into
Power Switch is pushed a live outlet
• Check to see whether outlet is switch-controlled
Display lights, but no sound • Intermittent input connections • Make certain that all input and speaker connections
or picture are secure
Mute is on • Press Mute Button
•
• Volume control is down • Turn up volume control
No sound from any speaker; • Amplifier is in protection mode • Check speaker wire connections for shorts at receiver and
light around power switch is red due to possible short speaker ends
• Amplifier is in protection mode • Contact your local Harman Kardon service center
due to internal problems
No sound from surround or • Incorrect surround mode • Select a mode other than Stereo
center speakers • Input is monaural • There is no surround information from mono sources
• Incorrect configuration • Check speaker mode configuration
• Stereo or Mono program material • The surround decoder may not create center- or rear-channel
information from nonencoded programs
Unit does not respond to • Weak batteries in remote • Change remote batteries
remote commands • Wrong device selected • Press the AVR selector
• Remote sensor is obscured • Make certain front-panel sensor is in line of sight of remote
or connect an optional remote sensor
Intermittent buzzing in tuner • Local interference • Move unit or antenna away from computers, fluorescent
lights, motors or other electrical appliances
Letters flash in the channel indicator • Digital audio feed paused • Resume play for DVD
display and digital audio stops • Check that the correct digital input is selected
Surround Back Speaker settings • Multizone system has been turned • Use the menu system to access the Zone 2 menu and turn
cannot be accessed, and test tone on, and the surround back channels off the multizone system.
does not play through Surround were reassigned to multizone operation
Back Speakers
The XM Preview Channel (001) • XM antenna is not plugged in • Make sure you are using a home audio XM antenna module
is silent designed for use with XM Ready home audio equipment,
and that the module is plugged into the XM Radio Jack
on the rear panel of the receiver.
• XM antenna is not located in such • The XM Antenna module needs to be placed with an
a way as to enable reception unobstructed view of the southern sky, or within range of an
XM terrestrial repeater. If necessary, purchase an extension
cable from your XM Radio dealer.
Unable to activate Program mode • Source Selector not held for at least • The selector will light as you initially press it, and go dark as you
on remote 3 seconds hold it down. Wait at least 3 seconds for the selector to light
up again.
Remote behaves erratically • Buttons are pressed too hard • Always press remote control buttons as gently as possible.
Remote buttons light, but AVR does • Remote is in Zone 2 mode • Slide the Zone Switch at the bottom of the remote to the
not respond Zone 1 position
Additional information on troubleshooting possible problems with your AVR 254, or installation-related issues, may be found in the list of “Frequently
Asked Questions”, which is located in the Product Support section of our Web site at www.harmankardon.com.
55
Page 56

APPENDIX
Appendix – Default settings, worksheets, remote product codes
Table A1 – Recommended Source Component Connections
Device Type AVR 254 Source Digital Audio Connection Analog Audio Connection Video Connections
Cable TV, satellite TV, HDTV CBL/SAT HDMI 2 Analog 1 HDMI 2
or other device that delivers
television programs
DVD Audio/Video, SACD, DVD HDMI 1 Analog 2 HDMI 1
Blu-ray Disc, HD-DVD player
Media Server, including Media Server Optical 2 Analog 5 S-Video 1
Harman Kardon DMC 1000
TV TV Optical 1 Analog 3 Component 1
Video game console Game Coaxial 1 Analog 4 Composite 1
Any audio or video device, AUX Coax Front Analog Front Composite Front (not used for
e.g. CD player, camcorder, audio-only devices)
cassette deck
Recorder Any Coaxial 1 or 2 input and Analog 4 inputs and outputs Composite OR S-Video 2 input
Coaxial Output and output
Portable audio player AUX Any Stereo Jack (use mini-plug Not required.
cable, not included)
Make this connection only when using the TV source for a non-display device. Do not connect your television’s or video display’s video output to the AVR at any time.
*
*
Table A2 – Source Setting Defaults
Cable/Sat DVD Media Server Radio TV Game AUX
Surround Modes (Auto Select) Logic 7 Movie Logic 7 Movie Logic 7 Movie Logic 7 Movie Logic 7 Movie Logic 7 Movie Logic 7 Movie
Video Input HDMI 2 HDMI 1 S-Video 1 N/A Component 1 Composite 1 Composite Front
Audio Input HDMI 2 HDMI 1 Optical 2 N/A Optical 1 Coaxial 1 Coaxial Front
Resolution to Display 720p 720p 720p 720p 720p 720p 720p
Audio Auto Polling Analog 1 Analog 2 Analog 5 N/A Analog 3 Analog 4 Analog Front
Zone 2 Audio Analog 1 Analog 2 Analog 5 N/A Analog 3 Analog 4 Analog Front
56
56
Page 57

APPENDIX
Table A3 – Speaker/Channel Setting Defaults
Audio Input All Digital and 2-Channel Analog Audio Inputs 6-/8-Channel Analog Audio Inputs* Your Settings
Left/Right Speakers ON ON
Center Speaker ON ON
Left/Right Surround Speakers ON ON
Left/Right Surround Back Speakers ON ON
Subwoofer ON ON
Left/Right Speakers Crossover 100Hz Large
Center Speaker Crossover 100Hz Large
Left/Right Surround Speakers Crossover 100Hz Large
Left/Right Surround Back Speakers Crossover 100Hz Large
Subwoofer Mode LFE N/A
Subwoofer Size 8 inch N/A
Front Left Level 0dB 0dB
Center Level 0dB 0dB
Front Right Level 0dB 0dB
Surround Right Level 0dB 0dB
Surround Back Right Level 0dB 0dB
Surround Back Left Level 0dB 0dB
Surround Left Level 0dB 0dB
Sub Level 0dB 0dB
Note: The 6-/8-Channel Inputs are “direct” inputs whose signals are passed directly to the volume control without any bass management processing. Thus, the speakers are always full-range
*
and cannot be adjusted. The settings are global for the remaining audio inputs.
*
*
*
*
*
*
Table A4 – Delay Setting Defaults
Speaker Position Distance From Speaker to Listening Position Your Delay Settings
Front Left 10 feet
Center 10 feet
Front Right 10 feet
Surround Right 10 feet
Surround Left 10 feet
Surround Back Right 10 feet
Surround Back Left 10 feet
Subwoofer 10 feet
A/V Sync Delay 0mS
57
Page 58

APPENDIX
Table A5 – Source Settings
Cable/Sat DVD Media Server Radio TV Game AUX
Surround Modes
Video Input
Audio Input
Resolution to Display
Adjust Lip Sync
Change Name
Audio Auto Polling
Zone 2 Audio
Table A6 – Audio Effects Settings
Default Cable/Sat DVD Media Server Radio TV Game AUX
Tone Control Off
Treble 0dB
Bass 0dB
LFE Trim Off
Night Mode Off
Table A7 – Video Modes Settings
Default Cable/Sat DVD Media Server Radio TV Game AUX
Video Mode Processor Off
Brightness
Contrast
Color
Sharpness
Picture Adjust Auto Fit
Noise Reduction
*
*
*
*
**
50
50
50
50
0ff
MPEG Noise Reduction**0ff
Cross Color Suppressor**Off
Film Mode Detect
Note: These settings are only available when the Video Mode is set to Custom.
*
Note: These settings are only displayed when Advanced Video Settings is selected.
**
58
**
Off
58
Page 59

Table A8 – Surround Modes
Default Cable/Sat DVD Media Server Radio TV Game AUX
Auto Select Logic 7 Movie or
native digital format
Virtual Surround Dolby Virtual
Speaker Reference
Stereo 7 CH Stereo
Movie Logic 7 Movie
Music Logic 7 Music
Game Logic 7 Game
APPENDIX
Center Width
Dimension
Panorama
Note: These settings are only available when Dolby Pro Logic II or IIx Music mode has been selected. Access these settings by selecting the Edit option.
*
*
*
*
0
0
Off
Table A9 – Remote Control Codes
Source Input Device Type (if changed) Product Code
Cable/Sat
DVD
Media Server
TV
Game
AUX
Table A10 – System Settings
Feature Default Your Setting
Front Panel Dimmer On 100%
Volume Units dB
Volume Default Off
Volume Default Level -25dB
Unit of Measure Feet
Language English
HDMI Audio to TV Off
OSD Transparency Normal
Volume/Status Messages 3 seconds
Menus 5 seconds
Setup and Slide-In Menus 15 minutes
Screen Saver 5 minutes
59
Page 60

APPENDIX
Table A11 – Zone 2 Settings
Source Input Device Type (if changed) Your Settings
Status Off
Source Cable/Sat
Volume -25dB
Surround Back Amps Main Room
Table A12 – Surround Modes
Surround Mode Description Incoming Bitstream or Signal
Dolby Digital Provides up to five separate main audio channels and a dedicated • Dolby Digital 1/0/.0 or .1, 2/0/.0 or .1,
low-frequency effects (LFE) channel. May be encoded for Night mode, 3/0/.0 or .1, 2/1/.0 or .1, 2/2/.0 or .1,
which allows the user to apply a compression setting that maintains 3/2/.0 or .1
intelligibility of softer passages while reducing the loudness of dynamic • Dolby Digital EX (played as 5.1)
passages to avoid disturbing others. • Dolby Digital Plus decoded and delivered
via coax or optical connection.
Dolby Digital EX An expansion of Dolby Digital 5.1 that adds a surround back channel • Dolby Digital EX
which may be played through one or two surround back speakers. May • Dolby Digital 2/2/.0 or .1, 3/2/.0 or .1
be manually selected when a non-EX Dolby Digital stream is detected.
Dolby Digital Plus An enhanced version of Dolby Digital encoded more efficiently, Dolby • Dolby Digital Plus via HDMI connection
Digital Plus has the capacity for additional discrete channels and for (source device decodes to Dolby Digital
streaming audio from the internet, all with enhanced audio quality. Source when a coax or optical connection is used).
material may be delivered via an HDMI connection, or decoded to Dolby
Digital or PCM and transmitted via S/P-DIF coaxial or optical digital audio.
Dolby TrueHD Dolby TrueHD is an expansion of MLP Lossless™audio, the same format • Blu-ray Disc or HD-DVD encoded with
used on DVD Audio discs. Dolby TrueHD adds the features found in Dolby TrueHD, delivered via HDMI or
Dolby Digital, such as night mode settings, while delivering fully lossless multichannel analog connection.
audio that is a true reproduction of the studio master recording.
Dolby Digital Stereo Delivers a 2-channel downmix of Dolby Digital materials. • Dolby Digital 1/0/.0 or .1, 2/0/.0 or .1,
3/0/.0 or .1, 2/1/.0 or .1, 2/2/.0 or .1,
3/2/.0 or .1
• Dolby Digital EX
Dolby Pro Logic II Analog decoder that derives five full-range, discrete main audio channels See below.
Mode Group from matrix surround-encoded or 2-channel analog sources. Four variants
are available.
Dolby Pro Logic II Variant of Dolby Pro Logic II that is optimized for movie and • Dolby Digital 2.0 or 2.1
Movie television programs. • Analog (2-channel)
• Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
Dolby Pro Logic II Variant of Dolby Pro Logic II that is optimized for music selections. • Dolby Digital 2.0 or 2.1
Music Allows adjustment of sound field presentation in three dimensions: • Analog (2-channel)
• Center Width (adjusts width of vocal soundstage) • Tuner
• Dimension (adjusts depth of soundstage) • PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
• Panorama (adjusts wraparound surround effect)
60
60
Page 61

APPENDIX
Surround Mode Description Incoming Bitstream or Signal
Dolby Pro Logic II Variant of Dolby Pro Logic II that emphasizes use of the surround • Dolby Digital 2.0 or 2.1
Game channels and subwoofer for total immersion in the video gaming • Analog (2-channel)
experience. • Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
Dolby Pro Logic Original version of Dolby Pro Logic that steered a mono signal • Dolby Digital 2.0 or 2.1
containing information below 7kHz to the surround channels. • Analog (2-channel)
• Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
Dolby Pro Logic IIx An expansion of Dolby Pro Logic II that adds a surround back channel
Mode Group
Dolby Pro Logic IIx This mode is similar to Dolby Pro Logic II Movie, with an added surround • Dolby Digital 2/0/.0 or .1, 2/2/.0 or .1,
Movie back channel. 3/2/.0 or .1, EX
which may be played through one or two surround back speakers. The
Dolby
Pro Logic IIx modes may be selected not only with Dolby Digital bitstreams, but thanks to the AVR 254’s post-processor, they may also be used
with some DTS bitstreams to add a surround back channel to 5.1 modes.
• Analog (2-channel)
• Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
Dolby Pro Logic IIx This mode is similar to Dolby Pro Logic II Music, including the availability • Dolby Digital 2/0/.0 or .1, 2/2/.0 or .1,
Music of center width, dimension and panorama adjustments. Dolby Pro Logic IIx 3/2/.0 or .1, EX
Music adds a surround back channel. • Analog (2-channel)
• Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
Dolby Pro Logic IIx This mode is similar to Dolby Pro Logic II Game, with the added benefit • Dolby Digital 2/0/.0 or .1
Game of a surround back channel. • Analog (2-channel)
• Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz or 48kHz)
Dolby Virtual Speaker Simulates 5.1 channels when only two speakers are present, or a more See below.
Mode Group enveloping sound field is desired.
Dolby Virtual Speaker When only two main speakers are present, the Reference mode virtualizes • Dolby Digital (uses only two-speaker mode
Reference a full surround presentation with accurate localization. when s
• Analog (2-channel)
• Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz or 48kHz)
Dolby Virtual Speaker Wide mode may be used with two main speakers to widen the front • Dolby Digital (number of channels available
Wide soundstage by virtualizing the locations of the left and right speakers. varies by number of channels in signal)
• Analog (2-channel)
• Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz or 48kHz)
ignal does not contain center channel
information)
DTS Digital Using a different encoding/decoding method than Dolby Digital, it also • DTS 1/0/.0 or .1, 2/0/.0 or .1, 3/0/.0 or .1,
provides up to five discrete main channels, plus an LFE channel. 3/1/.0 or .1, 2/2/.0 or .1, 3/2/.0 or .1
• DTS-ES Matrix (played as 5.1)
• DTS-ES Discrete (played as 5.1)
61
Page 62

APPENDIX
Surround Mode Description Incoming Bitstream or Signal
DTS-HD DTS-HD is a new high-definition audio format that complements the • Blu-ray Discs or HD-DVD discs encoded
high-definition video found on Blu-ray Discs and HD-DVD discs. It is transmitted with DTS-HD modes, delivered via HDMI or
using a DTS core with high-resolution extensions. Even when only DTS 5.1 multichannel analog connection.
surround sound is desired (or available, if the multizone system is in use),
the higher capacity of high-resolution discs serves up DTS at twice the bit
rate used on DVD-Video discs.
DTS-HD Master Audio DTS-HD Master Audio technology delivers bit-for-bit reproductions of the • Blu-ray Discs or HD-DVD discs encoded with
studio master recording in up to 7.1 channels, for an incredibly accurate DTS-HD Master Audio technology, delivered
performance. via HDMI or multichannel analog connection.
DTS-ES Matrix DTS Extended Surround adds a single surround back channel to DTS 5.1 • DTS-ES Matrix
digital surround sound. The Matrix version includes the surround back
channel information “matrixed” into the left and right (side) surround
channels, for compatibility with 5.1-channel systems.
DTS-ES Discrete DTS-ES Discrete is another Extended Surround mode that adds a surround • DTS-ES Discrete
back channel, but this information is encoded discretely on the disc, and
is not derived from information contained in the surround channels.
DTS Stereo Delivers a 2-channel downmix of DTS Digital materials, or presents • DTS 1/0/.0 or .1, 2/0/.0 or .1, 3/0/.0 or .1,
a matrix-encoded surround presentation. 3/1/.0 or .1, 2/2/.0 or .1, 3/2/.0 or .1
• DTS 96/24
• DTS-ES Matrix
• DTS-ES Discrete
DTS Neo:6 DTS Neo:6 analog processing is available with DTS and DTS 96/24 See below.
Mode Group
DTS Neo:6 Depending on the number of speakers in your system, select 3-, 5- or • DTS 2/2/.0 or .1, 3/2/.0 or .1
Cinema 6-channel modes, enhanced for movie or video presentations. • DTS 96/24
DTS Neo:6 Available only in 5- and 6-channel modes, creates a surround presentation • DTS 2/2/.0 or .1, 3/2/.0 or .1
Music suitable for music recordings. • DTS 96/24
Logic 7 A Harman International proprietary technology, Logic 7 technology enhances See below.
Mode Group 2-channel and matrix-encoded recordings by deriving separate information
Logic 7 Especially suited to 2-channel sources containing Dolby Surround or matrix • Analog (2-channel)
Movie encoding, Logic 7 Movie mode increases center channel intelligibility. • Tuner
Logic 7 The AVR 254 is programmed at the factory to default to this mode for • Analog (2-channel)
Music 2-channel signals. Logic 7 Music mode is well suited to conventional • Tuner
signals and 2-channel analog or PCM signals to create a 3-, 5- or 6-channel
presentation.
• Analog (2-channel)
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz or 48kHz)
• Analog (2-channel)
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz or 48kHz)
for the surround back channels. This provides more accurate placement of
sound, improves panning and expands the sound field, even when used
with 5.1-channel systems. Logic 7 technology uses 96kHz processing, and is
available in 5.1- or 7.1-channel modes. Three variants are available.
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
2-channel music recordings. • PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
62
Page 63

APPENDIX
Surround Mode Description Incoming Bitstream or Signal
Logic 7 Game Use Logic 7 Game mode to enhance enjoyment of video game consoles. • Analog (2-channel)
• Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
5-Channel Stereo Useful for parties, the left- and right-channel information is played through • Analog (2-channel)
both the front and surround speakers on each side, while the center speaker • Tuner
plays a summed mono mix. • PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz or 48kHz)
7-Channel Stereo Expands the 5-Channel Stereo presentation to include the surround back • Analog (2-channel)
channels. • Tuner
• PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz or 48kHz)
2-Channel Stereo Turns off all surround processing and plays a pure 2-channel signal. • Analog (2-channel)
The signal is digitized and bass management settings are applied, making it • Tuner
appropriate when a subwoofer is used. • PCM (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz)
2-Channel Stereo Maintains an analog input signal in that form, bypassing all digital processing • Analog (2-channel)
(Analog Bypass) (i.e., surround and bass management). Requires Tone Control setting to be off. • Tuner
Copyright (c) 2003 by Bitstream, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Bitstream Vera is a trademark of Bitstream, Inc.
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of the fonts accompanying this license (“Fonts”) and associated documentation files (the “Font Software”),
to reproduce and distribute the Font Software, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, merge, publish, distribute, and/or sell copies of the Font Software, and to permit persons
to whom the Font Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright and trademark notices and this permission notice shall be included in all copies of one or more of the Font Software typefaces.
The Font Software may be modified, altered, or added to, and in particular the designs of glyphs or characters in the Fonts may be modified and additional glyphs or characters
may be added to the Fonts, only if the fonts are renamed to names not containing either the words “Bitstream” or the word “Vera”.
This License becomes null and void to the extent applicable to Fonts or Font Software that has been modified and is distributed under the “Bitstream Vera” names.
The Font Software may be sold as part of a larger software package but no copy of one or more of the Font Software typefaces may be sold by itself.
THE FONT SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OF COPYRIGHT, PATENT, TRADEMARK, OR OTHER RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL BITSTREAM OR THE GNOME FOUNDATION
BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF
CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE FONT SOFTWARE OR FROM OTHER DEALINGS IN THE FONT SOFTWARE.
Except as contained in this notice, the names of Gnome, the Gnome Foundation, and Bitstream Inc., shall not be used in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings
in this Font Software without prior written authorization from the Gnome Foundation or Bitstream Inc., respectively. For further information, contact: fonts at gnome dot org.
This product incorporates copyright protection technology that is protected by method claims of certain U.S. patents and other intellectual property rights owned by Macrovision Corporation
and other rights owners. Use of this copyright protection technology must be authorized by Macrovision Corporation, and is intended for home and other limited viewing uses only unless
otherwise authorized by Macrovision Corporation. Reverse engineering or disassembly is prohibited.
63
Page 64

1 2
3
15 16 17
18 19 20
21
22 23
24
35 36 37 38
25
26
27 28
29
33
30 31 32
34
4
5678 9
10 11
12 13 14
39 40 41
42 43 44
45 46
48 49
50 51 525453
47
APPENDIX
Refer to the numbered buttons in Figure 72 when using the Function List.
64
Figure 72 – Remote Control Function List Reference
64
Page 65

APPENDIX
Table A13 – Remote Control Function List
Radio Media Server
No. Button Name AVR FM AM XM DVD DMC1000 TV
01 AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On
02 AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off
03 Device Power On Power On On Power On
04 Device Power Off Power Off Off Power Off
05 CBL/SAT Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
06 DVD Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
07 Media Server Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
08 Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio
09 TV Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
10 Game Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
11 AUX Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
12 Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects
13 Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes
14 Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes
15 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
16 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
17 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
18 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
19 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
20 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
21 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7
22 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8
23 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
24 Last Last Last Last Last Prev. Ch
25 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
26 Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity
27 Back/Exit Back/Exit Back/Exit Back/Exit Back/Exit Clear Back
28 Menu Menu Menu Menu Menu Menu Menu Menu
29 Up Up Tune Up Tune Up Channel/Preset Up Up Up Up
30 Left Left Preset/Down Preset/Down
31 OK OK OK OK OK Enter Enter OK
32 Right Right Preset/Up Preset/Up
33 Down Down Tune Down Tune Down
34 Disc Menu Disc Menu Disc Menu OSD
35 Red Angle Angle
36 Green Subtitle Subtitle
37 Yellow Audio Audio
38 Blue Zoom Zoom
39
40 Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute
41
42 Previous Prev. Step Previous
43 Pause Pause Pause
44 Next Next Step Next Step
45 Rew 77 Rew 77 Rew 77
46 Play 3 Play 3 Play 3
47 FF 33 FF 33 FF 33
48 Record Record
49 Stop Stop Stop
50 AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings
51 Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings
52 Source Settings Setup Setup TV/VCR
53 Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep
54 Zone Select Zone Select
Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume +
Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume –
Channel/Page Up Channel/Preset Up Preset Up Preset Up Preset Up Page Up Channel Up
Channel/Page Down Channel/
Preset
Down
Preset
Down
Preset
Down
Preset/Category Down
Preset/Category Up
Channel/Preset Down
Preset
Down
Left Left Left
Right Right Right
Down Down Down
Page Down Channel Down
65
Page 66

APPENDIX
Table A13 – continued
AUX
No. Button Name CBL/SAT Game CD HDTV PVD TiVO VCR
01 AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On AVR Power On
02 AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off AVR Power Off
03 Device Power On Power On Play Power On Power On Power On Power On Power On
04 Device Power Off Power Off Stop Power Off Power Off Power Off Power Off Power Off
05 CBL/SAT Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
06 DVD Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
07 Media Server Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
08 Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio
09 TV Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
10 Game Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
11 AUX Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel Input Sel
12 Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects Audio Effects
13 Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes Video Modes
14 Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes Surround Modes
15 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
16 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
17 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
18 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
19 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
20 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
21 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7
22 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8
23 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
24 Last Prev. Ch Enter Prev. Ch Instant Replay Enter/Last
25 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
26 Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity
27 Back/Exit Bypass Clear Exit/Cancel Exit Exit Cancel
28 Menu Menu Start Menu Menu Menu Menu
29 Up Up Up Up Up Up Up
30 Left Left Left Left Left Left Left
31 OK OK Select Enter Setup Select Enter
32 Right Right Right Right Right Right Right
33 Down Down Down Down Down Down Down
34 Disc Menu OSD DVD Menu OSD AV TiVo OSD
35 Red Guide • Open/Close Caption Mark Window
36 Green PPV
37 Yellow Fav. Ch
38 Blue Music X Intro Scan Aspect Jump Down Skip
39
40 Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute AVR Mute
41
42 Previous Slow Down Skip Down Back Last Clip Thumb Down Scan Down
43 Pause Pause Pause Pause Pause Pause Pause
44 Next Slow Up Skip Up Replay Next Clip Thumb Up Scan Up
45 Rew 77 Prev. R. Search Rew 77 Rew 77 Rew 77 Rew 77
46 Play 3 Play 3 Play 3 Play 3 Play 3 Play 3 Play 3
47 FF 33 Next F. Search FF 33 FF 33 FF 33 FF 33
48 Record Subtitle Time Record Record Record Record
49 Stop Stop Stop Stop Stop Stop Stop
50 AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings AVR Settings
51 Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings Info Settings
52 Source Settings TV/CATV Program TV/VCR TV/DVR TV Input TV/VCR
53 Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep Sleep
54 Zone Select
Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume + AVR Volume +
Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume – AVR Volume –
Channel/Page Up Channel Up Scan Up (+10) Channel Up Channel Up Channel Up Channel Up
Channel/Page Down Channel Down Scan Down Disc Skip Channel Down
■
▲
Random Play Fav. Ch Repeat Live TV
Repeat MTS Jump Up Slow
Channel Down Channel Down Channel Down
66
66
Page 67

APPENDIX
Refer to Tables A14 through A24 when programming the codes for your components into the remote.
Table A14 – Remote Control Product Codes:
TV Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
AIWA 027
A MARK 122 132
ADMIRAL 192
AKAI 123 160
AMPRO 164
ANAM 045 106 109 112 122
AOC 122 123 128
BLAUPUNKT 084
BROKSONIC 205 206
CANDLE 123 128
CAPEHART 059
CENTURION 123 171
CENTRONIC 045
CITIZEN 045 123 128 132
CLASSIC 045
CONCERTO 128
CONTEC 045
CORANDO 172
CORONADO 132
CRAIG 045 157 158 159
CROWN 045 132
CURTIS MATHES 123 128 132
CXC 045
DAEWOO 045 087 102 105 106 108 111
114 116 119 127 128 132
DAYTRON 128 132
DIGI LINK 200
DYNASTY 045
DYNATECH 063
ELECTROHOME 115 132
EMERSON 045 123 128 132 139 157 158
159 162 205
FUNAI 045
FUTURETECH 045
GE 029 087 121 123 128 133 145
159 163
GRUNDIG 193
HALL MARK 128
HARMAN KARDON 201
HITACHI 123 128 132 144 147
INFINITY 148
INKEL 120
JBL 148
JC PENNEY 115 123 128 132 145
JENSEN 019
JVC 079 087 134
KAWASHO 173
KEC 045
KENWOOD 123 204
KMC 132
KTV 045 123 132 162
TV
TV Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
LG/GOLDSTAR 101 110 122 128 132
LLOYTRON 172 173
LODGENET 069
LOGIK 069
LUXMAN 128
LXI 077 145 148
MAGNAVOX 030 123 128 132 145 148
MARANTZ 115 123 148
MATSUI 148
MEMOREX 069 128
METZ 084
MGA 115 123 128
MINERVA 084
MITSUBISHI 077 115 123 128 160 167 168
MTC 175 176
NATIONAL 148 177 179 180 181 182
NEC 115 121 123 125
NIKEI 045
ONKING 045
ONWA 045
OPTONICA 077
ORION 207 208 209 210 211
PANASONIC 087 148 169
PHILCO 045 115 123 128 132 148
PHILIPS 033 034 035 036 123 128 132
145 148
PIONEER 024 123 128
PORTLAND 128 132
PROSCAN 133
PROTON 059 122 128 132 165
QUASAR 032 087
RADIO SHACK 045 128 132 180 196 197
RCA 021 115 123 128 133 145 161 163
REALISTIC 045 167 196
RUNCO 152 153
SAA 183
SAMPO 059 123 128
SAMSUNG 020 022 124 128 132 145
SANYO 026 054
SCOTT 045 128 132
SEARS 128 132 145
SHARP 077 128 132
SIEMENS 084
SIGNATURE 069
SONY 028 031 117 130 136 194 212
SOUNDESIGN 045 128
SPECTRICON 122
SSS 045
SYLVANIA 025 123 128 145 148
SYMPHONIC 184
TANDY 077
67
Page 68

APPENDIX
Table A14 – continued
TV Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
TATUNG 063
TECHNICS 181
TECHWOOD 128
TEKNIKA 045 069 115 123 128 132
TELERENT 069
TERA 156
THOMSON 190 191
TMK 128
TOSHIBA 063 129 202
TOTEVISION 132
VIDEO CONCEPTS 160
VIDTECH 128
WARDS 069 128 132 148
YAMAHA 123 128
YORK 128
YUPITERU 045
ZENITH 069 090
ZONDA 122
Table A15 – Remote Control Product Codes: AUX-HDTV
TV Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
LG 604
MOTOROLA 605
RCA 601
SAMSUNG 603
ZENITH 602
68
68
Page 69

Table A16 – Remote Control Product Codes: AUX-VCR
VCR Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
AIWA 340
AKAI 348 408 409 426
AMPRO 376
ASA 434
AUDIO DYNAMICS 318 348
BROKSONIC 410 447
CANDLE 434 435
CANON 435 440
CAPEHART 394
CITIZEN 434
CRAIG 345 416
DAEWOO 317 394 404
DAYTRON 394
DBX 318 348
DIRECTV 314 315
DYNATECH 340
EMERSON 313 340 342 410 412
FISHER 317
FUNAI 340
GE 376 395 424
GO VIDEO 413
HARMAN KARDON 302 303 318 349
HITACHI 340 348
JC PENNEY 318 345
JENSEN 348
JVC 318 348 411 432
KENWOOD 320 348
LG/GOLDSTAR 318 407
LLOYD 340
LXI 320 340
MAGIN 345
MAGNAVOX 340
MARANTZ 318
MEMOREX 317 320 340 352 353 354 376
MGA 349
MITSUBISHI 349 431
MULTITECH 340
NAD 439
NATIONAL 440
NEC 318 348
NORDMENDE 348
OPTIMUS 459
ORION 447
PANASONIC 425 450 467 472
PHILCO 340
PHILIPS 340 375
PORTLAND 394
PULSAR 376
QUASAR 301 425
RADIO SHACK 355 434 440 442 458 459
RCA 395 424 425 457 472
REALISTIC 317 320 340 345 459
APPENDIX
VCR Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
SALORA 320
SAMSUNG 345 351 395 405 409
SANSUI 348 416 447
SANYO 317 320
SCOTT 410 412
SEARS 317 320
SHARP 429 456
SONY 380 429
SOUNDESIGN 340
SYLVANIA 340
SYMPHONIC 340
TANDY 317 340
TASHICO 434
TATUNG 348
TEAC 340 348
TEKNIKA 340
THOMAS 340
TiVo 304 305 306 307 308 309 310
311 312
TMK 313
TOSHIBA 412 455
TOTEVISION 345
UNITECH 345
VECTOR RESEARCH 318
VIDEO CONCEPTS 318 340
VIDEOSONIC 345
WARDS 340 345 412
YAMAHA 318 340 348
ZENITH 340 350 376 383
69
Page 70

APPENDIX
Table A17 – Remote Control Product Codes: AUX-CD
CD Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
ADCOM 063 069
AIWA 072 111 118 156 170
AKAI 050 177 184
AUDIO TECHNICA 053
AUDIOACCESS 125
AUDIOFILE 211
BSR 044
CALIFORNIA AUDIO 109
CAPETRONIC 070
CARRERA 087
CARVER 136 140 141 143 144 145 185 186
CASIO 117 166
CLARINETTE 166
DENON 187 188 213
EMERSON 052 093 108
FISHER 055 095
FRABA 117
FUNAI 126
GE 164
GENEXXA 108
HAITAI 099 214
HARMAN KARDON 001 002 025 054 190
HITACHI 093
INKEL 216
JC PENNEY 098 147
JENSEN 153
JVC 176 195 196
KENWOOD 030 062 078 079 148 151 176
178 181
LG/GOLDSTAR 016 087
LOTTE 108
LUXMAN 077 102
LXI 164
MAGNAVOX 039 113
MARANTZ 058 084 191 192 193
MCINTOSH 194
MCS 080 098
MITSUMI 152
MODULAIRE 166
NAD 013 074 197 198
NAKAMICHI 199 200 201
NEC 069
NIKKO 053 055
ONKYO 037 038 045 046 171 175 202 203
OPTIMUS 065 089 091 092 099 104 212
PANASONIC 075 109 119 158 183 204
PHILIPS 039 138 149 209
PIONEER 071 094 100 112 123 131 161
162 215
PROTON 210
QUASAR 109
RADIO SHACK 126 166 213
CD Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
RCA 024 081 093 150
RCX 169
REALISTIC 058 093 095 104 105 108 164 166
SANSUI 047 081 134 157 172
SANYO 033 082 095
SCOTT 108
SHARP 058 105 114 151 159 167 180 181
SHERWOOD 003 041 058 105 133
SONY 103 115 116 118 132 139 163 205
206 207 208 212 217
SOUNDSTREAM 124
SYMPHONIC 059 110
TAEKWANG 177
TEAC 011 058 085 086 106 107 110 121
137 146 154
THETA DIGITAL 039
TOSHIBA 013 074 097 151 155 173
VECTOR RESEARCH 087
VICTOR 120 130
WARDS 095
YAMAHA 019 031 053 061 135 169
YORK 166
70
70
Page 71

APPENDIX
Table A18 – Remote Control Product Codes: DVD
DVD Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
APEX DIGITAL 061
DENON 019 051
GE 003 004
HARMAN KARDON 001 002 007 068 201 202
JVC 006
LG/GOLDSTAR 005 055 064 066
MAGNAVOX 056
MARANTZ 059
MITSUBISHI 023
NAD 062
ONKYO 009 048
PANASONIC 024 030 044
PHILIPS 056
PIONEER 041 065
PROCEED 060
PROSCAN 003 004
RCA 003 004
SAMSUNG 053 054
SHARP 028
SONY 043 045
THOMSON 003 004
TOSHIBA 009 058 067
YAMAHA 030 063
ZENITH 005 055 064
Table A19 – Remote Control Product Codes: SAT
SAT Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
ALPHASTAR 472
ALPHASTAR DBS 450
ALPHASTAR DSR 442
BIRDVIEW 425
CHANNEL MASTER 320 321 325 361
CHAPARRAL 315 316 451
CITOH 360
DRAKE 313 317 318 413 481
DX ANTENNA 331 352 379 483
ECHOSTAR 395 397 452 453 463 477 478
484 485
ELECTRO HOME 392
FUJITSU 324 329 334
GENERAL INSTRUMENT 303 311 323 365 403 454 468 474
HITACHI DBS 455
HOUSTON TRACKER 463
HUGHES 437 489
JANIEL 366
JERROLD 454 468 484
KATHREIN 410
LEGEND 453
MACOM 317 365 369 370 371
MAGNAVOX 461 473
MEMOREX 453
NEXTWAVE 423
NORSAT 373
OPTIMUS 466
PACE DSS 487
PANASONIC 366 469
PANASONIC DBS 457
PANSAT 420
PERSONAL CABLE 418
PHILIPS 375
PICO 407
PRESIDENT 381 404
PRIMESTAR 412 454 468 475
RCA 301 439 465 490
RCA DSS 458
REALISTIC 349 480
SAMSUNG 442
SATELLITE SERVICE CO 335 388
SCIENTIFIC ATLANTA 339
SONY 405
STAR CHOICE DBS 459
STARCAST 347
SUPER GUIDE 327 423
TELECOM 330 333 390 391 393 409
TOSHIBA 302 426 460 461 462 470
UNIDEN 323 332 348 349 350 351 354 355
381 383 389 403 466 479 480
ZENITH 384 385 387 394 419 488
71
Page 72

APPENDIX
Table A20 – Remote Control Product Codes: GAME
Game Manufacturer/Brand
MICROSOFT (XBOX) 001
SONY (PLAYSTATION 2) 002
Setup Code Number
Table A21 – Remote Control Product Codes: CBL
CBL Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
ABC 001 011
ALLEGRO 111
AMERICAST 212
ARCHER 112
BELCOR 113
CABLE STAR 033 113
CITIZEN 111
COLOUR VOICE 085 090
DIGI 114
EAGLE 186
EASTERN 066 070
ELECTRICORD 039
EMERSON 112
FOCUS 116
G.I. 001 011 017 096 097
GC ELECTRONICS 113
GEMINI 032 060
GENERAL 210
GENERAL INSTRUMENT 210
GOODMIND 112
HAMLIN 056 099 100 101 117 175 208
HITACHI 001 188
JASCO 111
JERROLD 001 002 011 017 073 096 097 162
188 210
LINDSAY 118
MACOM 191
MAGNAVOX 017 019 068
MOVIE TIME 035 039
NSC 035 190
OAK 197 220
PACE 179
PANASONIC 053 176 177 189 214
PANTHER 114
PHILIPS 013 019 020 085 090
PIONEER 001 041 119 171 209 215 216
POPULAR MECHANICS 116
PRELUDE 120
PRIMESTAR 162
RADIO SHACK 111 112 213
RCA 053 214
RECOTON 116
REGAL 056 099 100 101 208
REMBRANT 032
SAMSUNG 003 072 186
Table A21 – continued
CBL Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
SCIENTIFIC ATLANTA 183 203 221 222
SEAM 121
SIGNATURE 001 188
SPRUCER 053 081 177 189
STARCOM 002 011 163
STARGATE 120
TANDY 024
TELECAPATION 028
TEXSCAN 036
TFC 122
TIMELESS 123
TOCOM 170 205
UNITED CABLE 011
UNIVERSAL 033 034 039 042 113
VIDEOWAY 124 211
VIEWSTAR 019 025 086 089 190
ZENITH 065 125 211 219
ZENTEK 116
Table A22 – Remote Control Product Codes:
AUX-MEDIA SERVER
Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
HARMAN KARDON 002
Table A23 – Remote Control Product Codes:
AUX-CBL/SAT RECORDER (PVD)
Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
DAEWOO 701 704
ECHOSTAR 714 715 716
EXPRESSVU 714
HUGHES 717 727
HYUNDAI 718
KEEN 709
PANASONIC 710 723
PHILIPS 711 717 724 727
PROSCAN 719
RCA 719 727
REPLAYTV 708 710 712 725 726
SONICBLUE 710 712
SONY 707 713 720 721 722 723 724
Table A24 – Remote Control Product Codes: AUX- TiVO
Manufacturer/Brand Setup Code Number
DIRECTV 806 (See also Table A16)
PIONEER 801
SERIES 2 DVR 802 809
TOSHIBA 803
OTHER TiV
o
804 805 807 808 810
72
72
Page 73

NOTES
73
Page 74

NOTES
74
74
Page 75

AVR 254 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Audio Section
Stereo Mode
Continuous Average Power (FTC)
65 Watts per channel, 20Hz–20kHz,
@ <0.07% THD, both channels driven into 8 ohms
Seven-Channel Surround Modes
Power per Individual Channel
Front L & R channels:
50 Watts per channel
@ <0.07% THD, 20Hz–20kHz into 8 ohms
Center channel:
50 Watts @ <0.07% THD, 20Hz–20kHz into 8 ohms
Surround (L & R Side, L & R Back) channels:
50 Watts per channel
@ <0.07% THD, 20Hz–20kHz into 8 ohms
Input Sensitivity/Impedance
Linear (High-Level) 200mV/47k ohms
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (IHF-A) 100dB
Surround System Adjacent Channel Separation
Pro Logic I/II 40dB
Dolby Digital (AC-3) 55dB
DTS 55dB
Frequency Response
@ 1W (+0dB, –3dB) 10Hz –130kHz
High Instantaneous
Current Capability (HCC) ±35 Amps
Transient Intermodulation
Distortion (TIM) Unmeasurable
Slew Rate 40V/µsec
FM Tuner Section
Frequency Range 87.5–108.0MHz
Usable Sensitivity IHF 1.3µV/13.2dBf
Signal-to-Noise Ratio Mono/Stereo 70/68dB
Distortion Mono/Stereo 0.2/0.3%
Stereo Separation 40dB @ 1kHz
Selectivity ±400kHz, 70dB
Image Rejection 80dB
IF Rejection 90dB
Please register your AVR 254 on our Web site at
www.harmankardon.com.
NOTE:
You’ll need the product’s serial number.
At the same time, you can choose to be notified about
our new products and/or special promotions.
AM Tuner Section
Frequency Range 520–1720 kHz
Signal-to-Noise Ratio 45dB
Usable Sensitivity Loop 500 µV
Distortion 1kHz, 50% Mod 0.8%
Selectivity ±10kHz, 30dB
Video Section
Television Format NTSC
Input Level/Impedance 1Vp-p /75 ohms
Output Level/Impedance 1Vp-p / 75 ohms
Video Frequency Response
(Composite and S-Video) 10Hz–8MHz (–3dB)
Video Frequency Response
(Component Video) 10Hz–100MHz (–3dB)
™
HDMI
Version 1.3a with 10-bit Deep Color
General
Power Requirement AC 120V/60Hz
Power Consumption 65W idle, 540W maximum
(7 channels driven)
Dimensions (Product) (Shipping)
Width 17-5/16 inches (440mm) 21-7/8 inches (555mm)
Height 6-1/2 inches (165mm) 10-1/2 inches (266mm)
Depth 15 inches (382mm) 18-5/16 inches (465mm)
(Product) (Shipping)
Weight 27.1 lb (12.3kg) 32.8 lb (14.9kg)
Depth measurement includes knobs, buttons and terminal connections.
Height measurement includes feet and chassis.
All features and specifications are subject to change without notice.
Harman Kardon and Logic 7 are trademarks of Harman International Industries, Incorporated, registered
in the United States and/or other countries. EzSet/EQ, Designed to Entertain and The Bridge logo are trademarks
of Harman International Industries, Incorporated.
iPod is a trademark of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
Audiovox is a registered trademark of Audiovox Corporation.
Blu-ray Disc is a trademark of the Blu-ray Disc Association.
CEA is a registered trademark of the Consumer Electronics Association.
Cirrus Logic is a registered trademark of Cirrus Logic, Inc.
Dolby and Pro Logic are registered trademarks, and MLP Lossless is a trademark, of Dolby Laboratories.
Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories. Dolby and the double-D symbol are trademarks of
Dolby Laboratories. Copyright 1999-2004 Dolby Laboratories. All rights reserved.
DTS, DTS-ES and DTS Neo:6 are registered trademarks, and DTS 96/24, DTS-HD and
DTS-HD Master Audio are trademarks, of DTS, Inc. Manufactured under license under U.S. Patent #’s:
5,451,942; 5,956,674; 5,974,380; 5,978,762; 6,226,616; 6,487,535; 7,003,467 and other
U.S. and worldwide patents issued and pending. © 1996-2007 DTS, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Faroudja DCDi Cinema is a registered trademark of Genesis Microchip Inc.
HD-DVD is a trademark of the DVD Format/Logo Licensing Corporation (DVD FLLC).
HDMI is a trademark or registered trademark of HDMI Licensing LLC.
SACD is a trademark of Sony Corporation.
TiVo is a registered trademark of TiVo Inc.
XM and XM Ready are registered trademarks of XM Satellite Radio.
75
Page 76

®
250 Crossways Park Drive, Woodbury, New York 11797
www.harmankardon.com
© 2008 Harman International Industries, Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Part No. CQX1A1310Z
 Loading...
Loading...