Page 1

Gateway 600 Notebook
user'sguide
Customizing
Troubleshooting
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
1 Checking Out Your Gateway 600. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Left side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Right side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Back . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Keyboard area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Identifying your model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Gateway model number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Gateway serial number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Internal wireless label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Finding your specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2Getting Started. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Connecting the AC adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Protecting from power source problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Starting your notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Waking up your notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Turning off your notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Restarting (rebooting) your notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Status indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Using the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Key types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
System key combinations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Multi-function buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Using the EZ Pad touchpad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Using the touchpad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Connecting the modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Connecting to a wired Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Broadband Internet connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Installing a printer, scanner, or other peripheral device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3Getting Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
HelpSpot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Searching for a topic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
HelpSpot videos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Online help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
i
Page 4

Gateway Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Using eSupport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
4 Windows Basics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
About the Windows environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Using the desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Using the Start menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Adding icons to the desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Identifying window items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Working with files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Viewing drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Creating folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Copying and moving files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Deleting files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Browsing for files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Searching for files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Using the Windows Search utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Working with documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Creating a new document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Saving a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Opening a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Printing a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Shortcuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
5 Using the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Learning about the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Setting up an Internet account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Accessing your Internet account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Using the World Wide Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Connecting to a Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Downloading files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Using e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Sending e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Checking your e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
6 Using Multimedia . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Using the diskette drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Using the DVD or recordable CD drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Identifying drive types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Inserting a CD or DVD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
Adjusting the volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Adjusting the volume in Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
ii
Page 5

Adjusting the volume in Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Using Audio DJ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Audio DJ controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Assigning music to play channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Playing your play channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Listening to CDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Listening to CDs in Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Listening to CDs in Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Recording and playing audio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Playing audio and video files with the Windows Media Player . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Using MusicMatch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Playing CDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Creating MP3 music files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Editing track information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Building a music library . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Changing the music library display settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Listening to Internet radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Using advanced features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Using a recordable CD drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Creating data CDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Creating music CDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Copying CDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Playing a DVD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Viewing the display on a television . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Capturing video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
7 Sending and Receiving Faxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Installing and configuring Fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Installing Fax in Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Configuring Fax in Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Configuring Fax in Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Sending a simple fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Setting up your cover page template . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Faxing from programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Faxing a scanned document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Receiving and viewing a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Canceling a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Automatically retry sending a fax in Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Automatically cancelling a fax in Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
8 Managing Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Monitoring the battery charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Recharging the battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
iii
Page 6

Recalibrating the battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .150
Changing batteries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
Replacing the main battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
Installing a secondary battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Extending battery life . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
Conserving battery power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
Using alternate power sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
Changing power modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .157
Changing power settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158
Changing the power scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158
Changing alarm options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .160
Changing advanced settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .161
Activating and using Hibernate mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .162
Changing SpeedStep settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .164
9 Travel Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .167
Modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Radio frequency wireless connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .168
Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .169
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
Additional tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .171
10 Customizing Your Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Adjusting the screen and desktop settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .174
Adjusting the color depth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .174
Adjusting the screen resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .176
Changing the colors on your Windows desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .177
Changing the desktop background . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .180
Selecting a screen saver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .183
Changing the touchpad settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .185
Adding and modifying user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
11 Networking Your Computer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .189
Benefits of networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190
Sharing a single Internet connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190
Sharing drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190
Sharing peripheral devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .191
Streaming audio and video files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .191
Playing multi-player games . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .191
Selecting a network connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Wired Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .192
iv
Page 7

Wireless Ethernet (IEEE 802.11a or IEEE 802.11b) network . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Using a wired Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, or Gigabit Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Example wired Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Equipment you need for a wired Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Using a wireless Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
Example access point wireless Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Equipment you need for an access point wireless Ethernet network . . . . . . 198
Example peer-to-peer wireless Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Equipment you need for a peer-to-peer wireless Ethernet network . . . . . . . 200
For more information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Using your notebook on a network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Installing and configuring your notebook for Ethernet networking . . . . . . . . . 201
Turning your wireless Ethernet on or off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
12 Moving from Your Old Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Using the Windows XP Files and Settings Transfer Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Transferring files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Finding your files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Transferring Internet settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Setting up your ISP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Transferring your e-mail and address book . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Transferring your Internet shortcuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Installing your old printer or scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Installing a USB printer or scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Installing a parallel port printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Installing your old programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
13 Maintaining Your Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Caring for your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
Creating an emergency startup diskette . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Protecting your computer from viruses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Managing hard drive space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Checking hard drive space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Using Disk Cleanup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
Checking the hard drive for errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
Defragmenting the hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Backing up files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Using the Scheduled Task Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Cleaning your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Cleaning the exterior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Cleaning the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
Cleaning the computer screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
v
Page 8

Cleaning the mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
14 Restoring Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .231
Using the Restoration CDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .232
Reinstalling device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .233
Updating device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .235
Reinstalling programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .237
Reinstalling Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .240
15 Upgrading Your Notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Adding and removing a PC Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .244
Changing drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Preventing static electricity discharge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .249
Adding or replacing memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .251
Replacing the main hard drive kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .255
16 Using the Gateway 600 Port Replicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .259
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .260
Back . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
Connecting to the port replicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .263
Attaching to the port replicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .263
Disconnecting from the port replicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
Securing your port replicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .266
17 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .267
Safety guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .268
First steps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .269
Software support tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .269
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .270
CD or DVD drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .270
Cleaning CDs or DVDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .272
Device installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .272
Diskette drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
File management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
Hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .277
Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .278
Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .279
Modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .279
Mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .284
Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .285
vi
Page 9

Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
PC Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
Sound . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
Touchpad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
Telephone support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
Before calling Gateway Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
Telephone numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
Tutoring and training . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
Self-help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
Tutoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
Training . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 294
A Safety, Regulatory, and Legal Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 307
vii
Page 10

viii
Page 11
Checking Out
Your Gateway 600
This chapter introduces you to the basic features of your
notebook. Read this chapter to learn:
■ How to identify the features of your Gateway notebook
■ How to locate your notebook’s model and serial
number
■ How to locate the Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity
■ How to locate the specifications for your notebook
■ What accessories are available for your notebook
Tips & Tricks To access the contents of this guide while you
are traveling, click Start, All Programs, then
click Gateway Utilities. You can also
download an electronic copy from
www.gateway.com/support/manlib/
.
1
www.gateway.com
1
Page 12

Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
Front
Audio DJ
controls
LCD panel
release latch
Battery
charge
indicator
Power
indicator
Component Icon Description
Audio DJ controls Control the built-in .MP3 and audio CD player. The
volume buttons control the volume level of the built-in
speakers and headphones plugged into the headphone
jack. The play/pause, back, next, and stop buttons may
control multimedia programs such as Windows Media
Player, Windows CD Player, MusicMatch, and the
InterVideo DVD Player. For more information, see “Using
Audio DJ” on page 91.
LCD panel release latch Open the LCD panel by pressing the release latch.
Battery charge indicator The LED shows the battery activity and status.
■
LED green - battery is fully charged.
■
LED orange - battery is charging.
■
LED red - battery is malfunctioning.
This LED only lights up when the notebook is plugged in.
Power indicator Lights up when the notebook is turned on and shows
notebook power status.
■
LED on - power is on.
■
LED blinking - power is in Standby mode.
■
LED off - power is off.
2
www.gateway.com
Page 13

Left side
Left side
PC Card
eject
buttons
PC Card
slots
Left-side
modular
bay
S/PDIF digital
audio jack
Microphone jack
Headphone jack
IEEE 1394 port
Line in jack
Component Icon Description
PC Card eject
buttons
PC Card slots Insert one or two Type II, or one Type III PC Card into these slots.
Left-side modular
bay
S/PDIF digital
audio jack
Microphone jack Plug a microphone into this jack. The built-in microphone is turned
Press one of the eject buttons to remove a PC Card from a
PC Card slot. For more information, see “Adding and removing a
PC Card” on page 244.
For more information, see “Adding and removing a PC Card” on
page 244.
Use this bay for a DVD, CD-RW, or combination DVD/CD-RW drive,
a diskette drive, or a second hard drive. For more information, see
“Changing drives” on page 246.
To determine the type of drive in the modular bay, examine the
drive tray’s plastic cover and compare the logo to those listed in
“Identifying drive types” on page 84.
Plug an optical (Toslink) AC-3 digital audio cable into this jack.
off when a microphone is plugged into this jack. For the location
of your built-in microphone, see “Keyboard area” on page 10.
www.gateway.com
3
Page 14

Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
Component Icon Description
Headphone jack Plug amplified speakers or headphones into this jack. The built-in
speakers are turned off when speakers or headphones are
plugged into this jack.
The headphone jack on the port replicator is turned off when
headphones are plugged into this jack.
Line in jack Connect an external audio input source (such as a stereo) to this
jack so that you can record sound on your notebook or play sound
through the notebook speakers.
IEEE 1394 port Plug an IEEE 1394 (also known as Firewire® or i.Link®) device
(such as a digital camcorder) into this 4-pin IEEE 1394 port.
4
www.gateway.com
Page 15

Right side
Right side
Ventilation fan
Right-side
modular
bay
USB ports
Kensington
lock slot
Component Icon Description
Ventilation fan Helps cool internal components. Do not block or insert
objects into these slots.
Right-side modular bay Use this bay for a secondary battery, a DVD, CD-RW, or
combination DVD/CD-RW drive, a diskette drive, or a
second hard drive. For more information, see “Changing
drives” on page 246.
To determine the type of drive in the modular bay,
examine the drive tray’s plastic cover and compare the
logo to those listed in “Identifying drive types” on
page 84.
USB ports Plug USB (Universal Serial Bus) devices (such as a USB
Iomega™ Zip™ drive, printer, scanner, camera,
keyboard, or mouse) into these ports.
Kensington™ lock slot Secure your computer to an object by connecting a
Kensington cable lock to this slot.
www.gateway.com
5
Page 16

Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
Back
TV out
jack
Monitor
port
Parallel
port
Ventilation fan
Modem jack
Ethernet jack
Serial port
Power connector
PS/2 port
Component Icon Description
TV out jack Plug a television into this jack so that you can view your display
on a television using NTSC/PAL composite video. For more
information, see “Viewing the display on a television” on page 128.
Monitor port Plug an analog VGA monitor into this port.
Parallel port Plug a parallel device (such as a printer) into this port.
Ventilation fan Cools internal components. Do not block or insert objects into
these slots.
Modem jack Plug a modem cable into this jack. For more information, see
“Connecting the modem” on page 36.
Ethernet jack Plug a 10/100 Ethernet network cable into this jack. For more
information, see “Connecting to a wired Ethernet network” on
page 37 and “Networking Your Computer” on page 189.
6
www.gateway.com
Page 17

Component Icon Description
Serial port Plug a serial device (such as a digital camera) into this port.
Power connector Plug the AC adapter cable into this connector.
PS/2 port Plug a PS/2 device (such as a keyboard or mouse) into this port.
Attaching a PS/2 mouse or keyboard to your notebook may
deactivate the touchpad or built-in keyboard.
Back
www.gateway.com
7
Page 18
Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
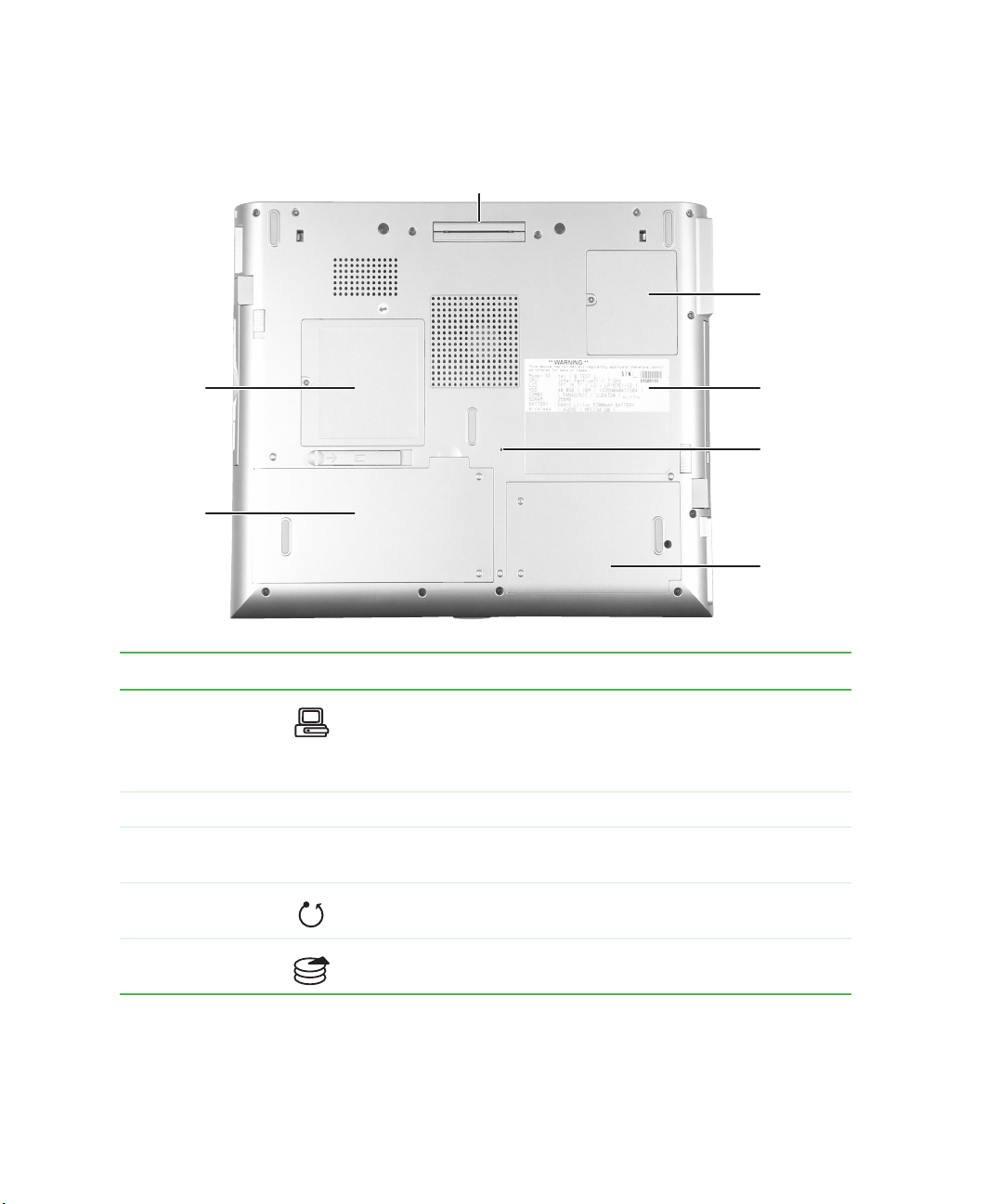
Bottom
Docking port
Mini PCI
bay
Memory
bay
Battery
bay
System
label
Reset
hole
Hard
drive bay
Component Icon Description
Docking port Connect the port replicator to this port.
Warning! Power is passed through this port. This docking
connection is certified to UL 1950 for use only with port replicators
designed for your Gateway notebook.
Mini PCI bay The optional wireless Ethernet mini PCI card is located in this bay.
System label Includes the product model number. For more information, see
“Identifying your model” on page 12.
Reset hole Insert a straightened paper clip into this hole to manually restart
the notebook.
Hard drive bay The main hard drive kit is located in this bay. For more information,
see “Replacing the main hard drive kit” on page 255.
8
www.gateway.com
Page 19

Component Icon Description
Battery bay Insert the main battery into this bay. For more information, see
“Changing batteries” on page 151.
Memory bay Install as many as two memory modules into this bay. For more
information, see “Adding or replacing memory” on page 251.
Bottom
www.gateway.com
9
Page 20
Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
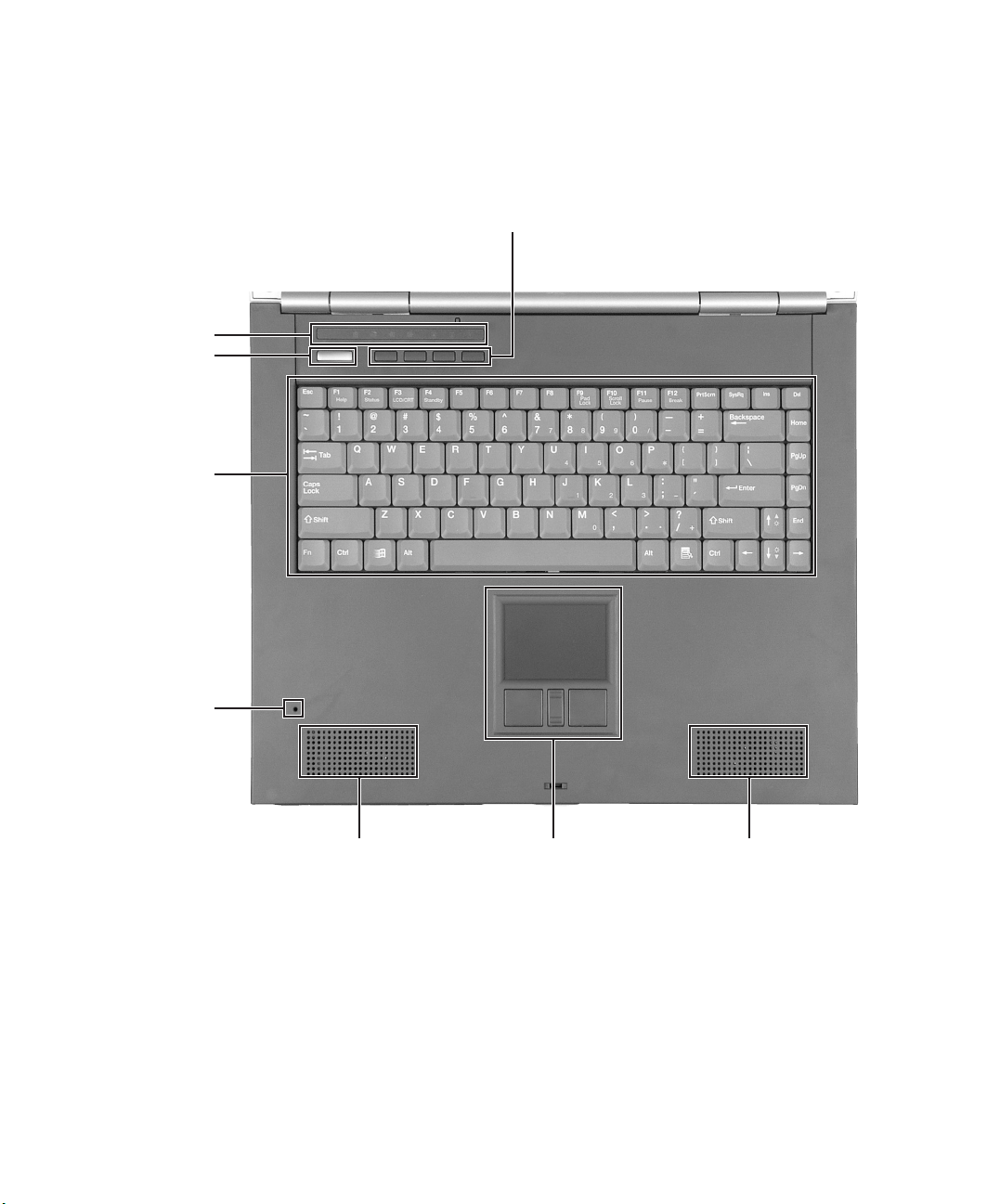
Keyboard area
For information on using your keyboard, see “Using the keyboard” on page 28.
Status
Indicators
Power
button
Keyboard
Multi-function buttons
Microphone
10
Speaker
Touchpad
www.gateway.com
Speaker
Page 21

Keyboard area
Component Icon Description
Multi-function buttons Press these buttons to open programs assigned to them.
These buttons are set to open your default e-mail
program, your default Web browser, online help, and the
My Computer window. For more information, see
“Multi-function buttons” on page 32.
Speakers Provide audio output when headphones or amplified
speakers are not plugged in.
Touchpad Provides all the functionality of a mouse. For more
information, see “Using the EZ Pad touchpad” on
page 33.
Microphone Record audio through this microphone. The built-in
microphone is turned off while an external microphone
is connected. For the location of your microphone jack,
see “Left side” on page 3.
Keyboard Provides all the features of a full-sized 86-key keyboard.
For more information, see “Using the keyboard” on
page 28.
Power button Press to turn the power on or off. You can also configure
the power button for Standby/Resume mode. For more
information on configuring the power button mode, see
“Changing power settings” on page 158.
Status indicators Inform you when a drive is in use or when a button has
been pressed that affects how the keyboard is used. For
more information, see “Status indicators” on page 26.
www.gateway.com
11
Page 22

Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
Identifying your model
Important The labels shown in this section are for informational
purposes only. Label information varies by model, features
ordered, and location.
Gateway model number
The label on the bottom of your notebook contains information that identifies
your notebook model and its features. Gateway Technical Support will need this
information if you call for assistance.
™
Gateway model
number
Gateway serial number
You can locate the Gateway serial number:
■ Printed on a white sticker on the bottom or back of your notebook.
■ Printed on the customer invoice that came with your notebook. The
invoice also contains your customer ID number.
■ Displayed in HelpSpot in Windows XP. Click Start, Help and Support, then
click
View product serial number.
12
www.gateway.com
Page 23

Identifying your model
Internal wireless label
A label similar to the following indicates your computer contains a wireless
communications device. The label is located on the bottom of your notebook.
IEEE 802.11b RLAN Approvals:
FCC ID HFS9550015318
CANADA ID 1787104509A
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity
The Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity label found on the bottom of your
notebook includes the product key code for your operating system.
www.gateway.com
13
Page 24

Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
Finding your specifications
For more information about your computer, such as memory size, memory type,
and hard drive size, go to the
eSupport page at www.gateway.com/support
additional Gateway documentation and detailed specifications.
My Computer Info link in HelpSpot or visit Gateway’s
. The eSupport page also has links to
In Windows XP, view your computer’s serial number by clicking
Support
clicking
, then clicking View system serial number. Check your specifications by
Start, Help and Support, then clicking See your PC’s configuration.
Start, Help and
14
www.gateway.com
Page 25

Finding your specifications
You can also find out more about your computer at the Gateway eSupport site.
Visit www.gateway.com/support
.
www.gateway.com
15
Page 26

Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
Accessories
Gateway offers accessories that can help you make the most of using your
notebook. To order accessories, visit the Accessories Superstore at
www.gateway.com
Batteries and automobile/airplane power adapters
If you run your notebook on battery power for extended periods, you may want
to buy an additional battery so that you can swap batteries when necessary.
See “Changing batteries” on page 151 for more information about using an
additional main battery and “Installing a secondary battery” on page 153 for
more information about using a secondary battery in your notebook.
With an automobile/airplane power adapter, you can save battery power by
plugging your notebook into an automobile cigarette lighter or an airplane
in-flight power receptacle.
Carrying cases
Gateway has large-capacity carrying cases if you need additional space for
accessories or supplies.
.
Port replicators
Although you can attach devices directly to your notebook, a port replicator
lets you make all of those connections at one time. When you travel with your
notebook, you merely disconnect from the port replicator instead of
unplugging all the devices.
A port replicator also provides additional ports and other expansion features
not included with your notebook. See “Using the Gateway 600 Port Replicator”
on page 259 for more information about using a port replicator with your
notebook.
Peripheral devices
You can attach devices (such as a keyboard, mouse, printer, or monitor) to your
notebook or port replicator.
Memory
Large programs, such as multimedia games or graphics programs, use a lot of
memory. If your programs are running more slowly than you think they should,
try adding more memory. See “Adding or replacing memory” on page 251 for
more information.
16
www.gateway.com
Page 27

Accessories
Printers
You can attach almost any type of printer to your notebook. The most common
types are inkjet and laser printers, which print in color or black and white. See
“Installing a printer, scanner, or other peripheral device” on page 38 for more
information about attaching a printer to your notebook.
Inkjet printers and cartridges are relatively inexpensive, but they are slower than
laser printers. Using an inkjet color printer, you can print pictures, banners,
and greeting cards, as well as documents.
Laser printers and cartridges are more expensive, but they print much faster
than inkjet printers. Laser printers are better than inkjet printers when you are
printing large documents.
www.gateway.com
17
Page 28

Chapter 1: Checking Out Your Gateway 600
18
www.gateway.com
Page 29

Getting Started
This chapter provides basic information about your
Gateway notebook. Read this chapter to find out how to:
■ Connect the AC adapter
■ Start and turn off your notebook
■ Identify the status indicators
■ Use the keyboard
■ Use the EZ Pad touchpad
■ Connect the modem
■ Connect to an Ethernet network
■ Install peripheral devices
2
www.gateway.com
19
Page 30
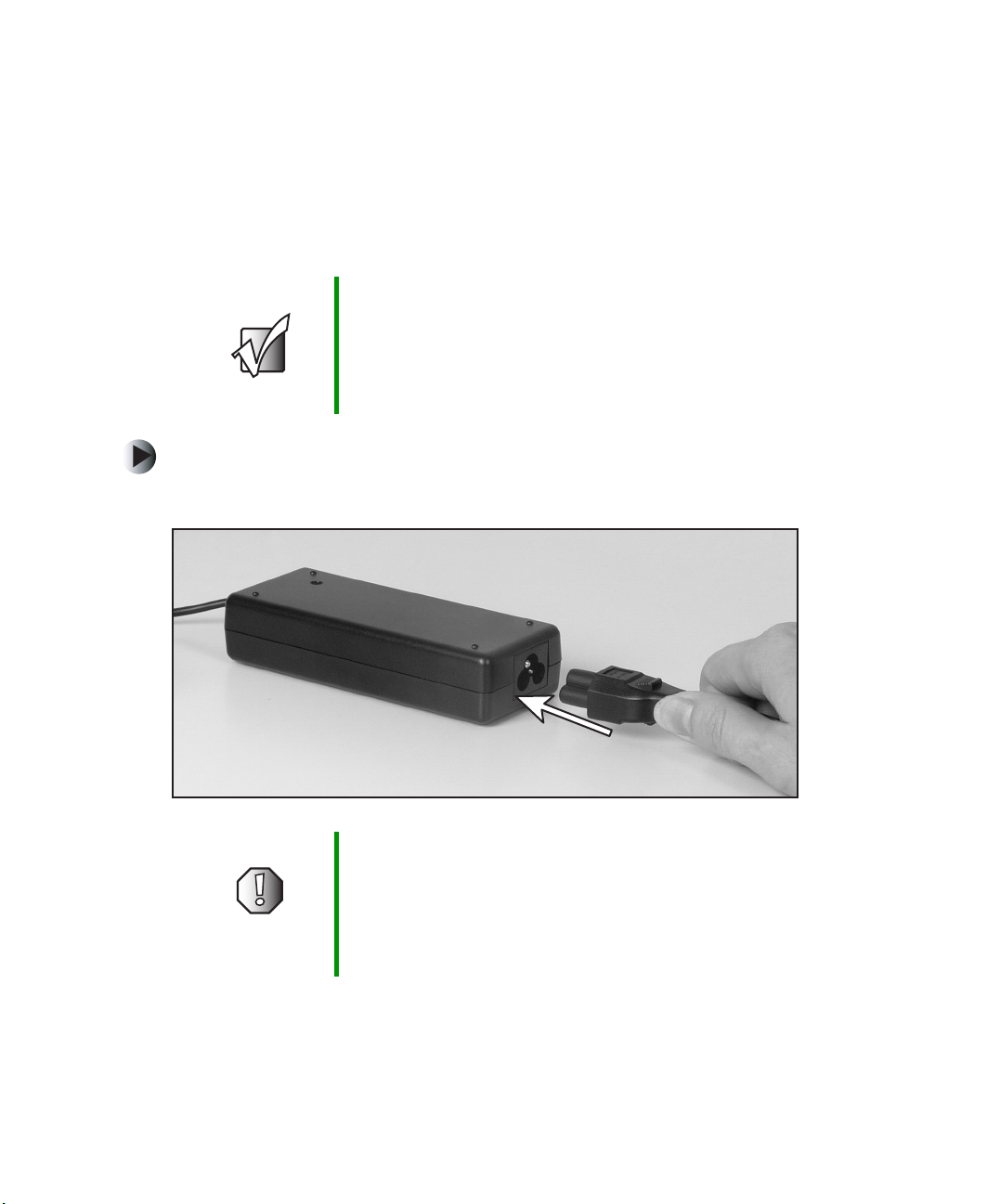
Chapter 2: Getting Started
Connecting the AC adapter
You can run your notebook using an AC adapter or the notebook battery. The
battery was shipped to you partially charged. You should use the AC adapter
right away to fully charge the battery. Allow 24 hours for the battery to fully
charge.
Important If the battery is not fully charged before you use your
notebook on battery power for the first time, the battery life
may be much shorter than you expect. If the battery life
seems short even after being charged for 24 hours, the
battery may need to be recalibrated. For information, see
“Recalibrating the battery” on page 150.
To connect the AC adapter:
1 Connect the power cord to the AC adapter.
20
Warning Make sure that you use the AC adapter that came with
your notebook.
Replace the power cord if it becomes damaged. The
replacement cord must be of the same type and voltage
rating as the original cord or your notebook may be
damaged.
www.gateway.com
Page 31

Connecting the AC adapter
2 Connect the AC adapter to your notebook’s power connector.
3 Plug the power cord into a wall outlet.
The battery charge indicator turns on (see “Front” on page 2 for the
location of the battery charge indicator). If the battery charge indicator
does not turn on, unplug the adapter from your notebook, then plug it
back in.
4 When you finish using your notebook for the first time, turn your
notebook off and leave your notebook connected to AC power for at least
24 hours. The battery charge meters may not show a charge for several
hours. For more information about the battery charge meter on your
model, see “Monitoring the battery charge” on page 148.
5 If the battery charge meters do not show a full charge after 24 hours,
contact Gateway Technical Support at www.gateway.com/support/contact
Warning Do not attempt to disassemble the AC adapter. The
AC adapter has no user-replaceable or user-serviceable
parts inside. The AC adapter has dangerous voltages that
can cause serious injury or death. Contact Gateway about
returning defective AC adapters.
www.gateway.com
.
21
Page 32

Chapter 2: Getting Started
Protecting from power source problems
During a power surge, the voltage level of electricity coming into your notebook
can increase to far above normal levels and cause data loss or system damage.
Protect your notebook and peripheral devices by connecting them to a surge
protector, which absorbs voltage surges and prevents them from reaching your
notebook.
Warning High voltages can enter your notebook through both the
power cord and the modem connection. Protect your
notebook by using a surge protector. If you have a
telephone modem, use a surge protector that has a
modem jack. If you have a cable modem, use a surge
protector that has an antenna/cable TV jack. During an
electrical storm, unplug both the surge protector and the
modem.
22
www.gateway.com
Page 33

Starting your notebook
To start your notebook:
1 Open your notebook by pressing the latch on the front of your notebook
and lifting the LCD panel.
2 Press the power button located above the keyboard.
Power bu tto n
Starting your notebook
The power button is preset to On/Off mode. However, you can also set it
to function in Standby/Resume mode. For instructions on changing the
power button mode, see “Changing power settings” on page 158.
3 If you are starting your notebook for the first time, follow the on-screen
instructions to set up your notebook.
www.gateway.com
23
Page 34

Chapter 2: Getting Started
Waking up your notebook
When you have not used your notebook for several minutes, it may enter a
power-saving mode called Standby. While in Standby, the power indicator
flas h es. I f your n oteb o ok is in S t a ndb y mode , “ w ake” it up b y pre s sing the p o we r
button. For more information on changing power-saving settings, see
“Changing power settings” on page 158.
Turning off your notebook
To turn off your notebook in Windows XP:
1 Click Start, then click Turn Off Computer. The Turn Off Computer dialog box
opens.
2 Click Turn O f f . Windows shuts down and turns off your notebook.
Important If for some reason you cannot use the Turn Off Computer
option in Windows to turn off your notebook, press and
hold the power button for about five seconds, then
release it.
To turn off your notebook in Windows 2000:
1 Click Start, then click Shut Down. The Shut Down Windows dialog box opens.
2 Click the arrow button to open the What do you want your computer to do
list, then click
Shut down.
3 Click OK. Windows shuts down and turns off your notebook.
Important If for some reason you cannot use the Shut Down option
in Windows to turn off your notebook, press and hold the
power button for about five seconds, then release it.
24
www.gateway.com
Page 35

Restarting (rebooting) your notebook
Restarting (rebooting) your
notebook
If your notebook does not respond to keyboard or touchpad input, you may
have to close programs that are not responding. If closing unresponsive
programs does not restore your notebook to normal operation, you may have
to restart (reboot) your notebook.
To close unresponsive programs and restart your notebook:
1 Press CTRL+ALT+DEL. A window opens that lets you close a program that
is not responding.
2 Click the program that is not responding.
3 Close the program by clicking End Task.
4 If your notebook does not respond, turn it off, wait ten seconds and turn
it on again.
Important If your notebook does not turn off immediately, complete
the following steps until the notebook turns off:
1 Press and hold the power button for about five seconds,
then release it.
2 Insert a straightened paper clip into the reset hole on
the bottom of your notebook.
3 Remove AC power and the batteries for more than
10 seconds.
As a part of the regular startup process, a program to check the disk status
runs automatically. When the checks are finished, Windows starts.
www.gateway.com
25
Page 36

Chapter 2: Getting Started
Status indicators
Status indicators inform you when a drive is being used or when a button has
been pressed that affects how the keyboard is used.
Right-side modular drive
Left-side modular drive
Hard drive
Caps lock
Scroll lock
Pad lock
Indicator Icon Description
Hard drive The hard drive is in use.
Left-side
modular drive
26
■
Indicator Blinking Green - The modular drive is in use.
■
Indicator Solid Green - The module is ready to swap.
www.gateway.com
Page 37

Indicator Icon Description
Status indicators
Right-side
modular drive
■
Indicator Blinking Green - The modular drive is in use.
■
Indicator Solid Green - The module is ready to swap.
Caps Lock Caps Lock is turned on.
Scroll Lock Scroll Lock is turned on. For more information, see “System key
combinations” on page 30.
Pad Lock Numeric keypad is turned on. For more information, see “System
key combinations” on page 30.
1
www.gateway.com
27
Page 38

Chapter 2: Getting Started
Using the keyboard
Your notebook features a full-size keyboard that functions the same as a desktop
computer keyboard. Many of the keys have been assigned alternate functions,
including shortcut keys for Windows, function keys for specific system
operations, and the Pad Lock keys for the numeric keypad.
You can attach an external keyboard to the notebook using a USB or PS/2 port.
You do not need to shut down the notebook to connect a USB keyboard.
Attaching a PS/2 keyboard to your notebook or port replicator may turn off
the built-in keyboard.
Function keys/System keys Navigation keys
28
FN key Windows
key
Numeric
keypad
www.gateway.com
Application
key
Arrow keys/LCD
brightness keys
Page 39

Using the keyboard
Key types
The keyboard has several different types of keys. Some keys perform specific
actions when pressed alone and other actions when pressed in combination
with another key.
Key type Icon Description
Function keys Press these keys labeled F1 to F12 to perform actions in
programs. For example, pressing
Each program uses different function keys for different purposes.
See the program documentation to find out more about the
function key actions.
F1 may open help.
System keys Press these colored keys in combination with the
perform specific actions.
Navigation keys Press these keys to move the cursor to the beginning of a line,
to the end of a line, up the page, down the page, to the beginning
of a document, or to the end of a document.
FN key to
FN key Press the FN key in combination with a colored system key (such
as
STATUS, STANDBY, or PAUSE) to perform a specific action.
Windows key Press this key to open the Windows Start menu. This key can
also be used in combination with other keys to open utilities like
F (Search utility), R (Run utility), and E (Explorer utility).
Numeric keypad Use these keys to type numbers when the numeric keypad is
turned on. Press
Application key Press this key for quick access to shortcut menus and help
assistants in Windows.
Arrow keys Press these keys to move the cursor up, down, right, or left.
LCD brightness
keys
Press these colored keys in combination with the
control the screen brightness.
FN+PAD LOCK to turn on the numeric keypad.
FN key to
www.gateway.com
29
Page 40

Chapter 2: Getting Started
System key combinations
When you press an FN key and a system key at the same time, your notebook
performs the action identified by the colored text or icon on the key.
N
Press and hold F
while pressing
this system key...
To...
Display the power status box in the upper-left corner of your display. The
box shows the battery charge level, the BIOS version, and whether the
AC adapter is being used. Press the key combination again to close this box.
Toggle the notebook display between the LCD, an external monitor, or both
displays at the same time. A monitor must be plugged into the monitor port
on your notebook or port replicator.
Enter Standby mode. Press the power button to leave Standby mode. For
more information, see “Changing power modes” on page 157.
Turn on Pad Lock so you can use the numeric keypad. Press this key
combination again to turn off Pad Lock. The Pad Lock status indicator
appears when this function is turned on.
30
Pause the text scrolling in a DOS screen. Press this key combination again
to continue scrolling. The Scroll Lock status indicator appears when this
function is turned on. (This function is only available in some programs.)
Pause execution of a DOS program. (This function is only available in some
programs.)
Stop the currently running DOS program. (This function is only available in
some programs.)
www.gateway.com
Page 41

Using the keyboard
Press and hold FN
while pressing
this system key...
To...
Increase the brightness of the display.
Decrease the brightness of the display.
www.gateway.com
31
Page 42

Chapter 2: Getting Started
Multi-function buttons
Press the multi-function buttons to open the programs associated with them.
Internet
E-mail
Help
My Computer
Button Icon Press to...
E-mail Open your default e-mail program.
Internet Open your default Web browser.
Help Open online help.
My Computer Open the My Computer window.
32
www.gateway.com
Page 43

Using the EZ Pad touchpad
Using the EZ Pad touchpad
The EZ Pad™ consists of a touchpad, two buttons, and a rocker switch.
Touchpad
Left
touchpad
button
Rocker
switch
www.gateway.com
Right
touchpad
button
33
Page 44

Chapter 2: Getting Started
When you move your finger on the touchpad, the pointer (arrow) on the screen
moves in the same direction.
You can use the EZ-Pad left and right buttons below the touchpad to select
objects.
You can assign a function to the rocker switch between the touchpad buttons.
This function can be to scroll up or down, maximize or minimize the active
window, or open and close the Start menu. For more information about
programming the rocker switch, see “Changing the touchpad settings” on
page 185.
Important Attaching a PS/2 mouse to your notebook or port replicator
may turn off the touchpad.
Using the touchpad
To... Do this...
Move the pointer
on the screen.
34
Move your finger around on the
touchpad. If you run out of space
and need to move the pointer
farther, lift your finger, move it to
the middle of the touchpad, then
continue moving your finger.
www.gateway.com
Page 45
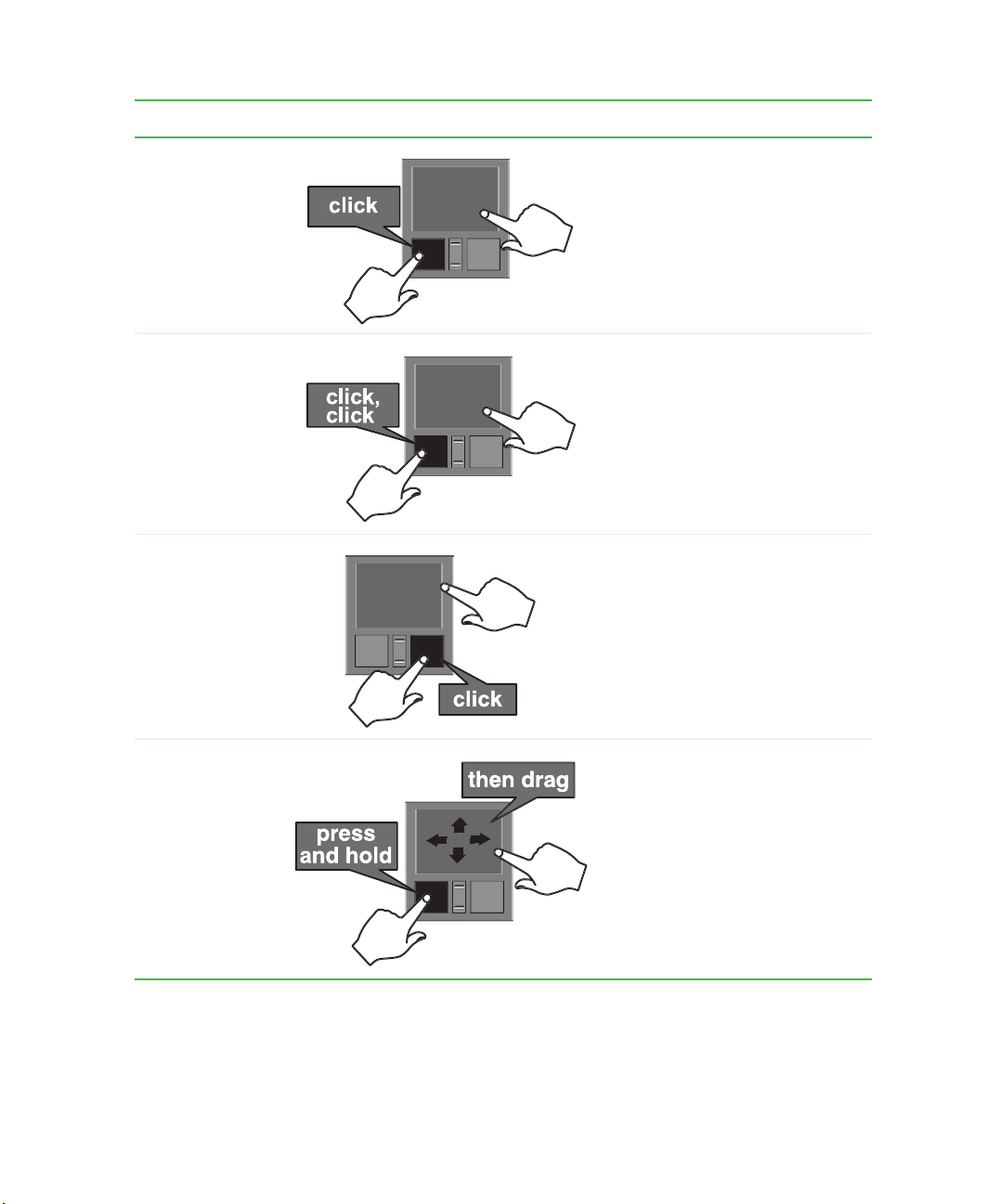
To... Do t his . ..
Using the EZ Pad touchpad
Select an object
on the screen.
Start a program
or open a file or
folder.
Access a shortcut
menu or find
more information
about an object
on the screen.
Position the pointer over the object.
Quickly press and release the left
button once. This action is called
clicking.
Position the pointer over the object.
Press the left button twice in rapid
succession. This action is called
double-clicking.
Position the pointer over the object.
Quickly press and release the right
button once. This action is called
right-clicking.
Move an object
on the screen.
Position the pointer over the object.
Press the left button and hold it
down, then use the touchpad to
move (drag) the object to the
appropriate part of the screen.
Release the button to drop the
object where you want it.
For instructions on how to adjust the double-click speed, pointer speed,
right-hand or left-hand configuration, and other touchpad settings, see
“Changing the touchpad settings” on page 185.
www.gateway.com
35
Page 46

Chapter 2: Getting Started
Connecting the modem
Your notebook has a built-in 56K modem that you can use to connect to a
standard telephone line.
Caution To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger
telecommunications line cord.
To connect the modem:
1 Insert one end of the modem cable into the modem jack on the back
of your notebook.
36
2 Insert the other end of the modem cable into a telephone wall jack. The
modem will not work with digital or PBX telephone lines.
3 Start your notebook, then start your communications program.
www.gateway.com
Page 47

Connecting to a wired Ethernet network
Connecting to a wired Ethernet
network
Your notebook has a network jack that you can use to connect to a 10/100 wired
Ethernet network.
Important Your notebook may be equipped with built-in wireless
Ethernet or you may have a wireless Ethernet PC Card.
For information about connecting to a wired or wireless
Ethernet network, see “Networking Your Computer” on
page 189. For information about installing a wireless
Ethernet PC Card, see “Adding and removing a PC Card”
on page 244.
To connect to a wired Ethernet network:
1 Insert one end of the network cable into the network jack on the back
of your notebook.
2 Insert the other end of the network cable into a network jack. Ask your
network administrator to help you select the correct network jack.
www.gateway.com
37
Page 48

Chapter 2: Getting Started
Broadband Internet connections
You can use your notebook’s Ethernet jack for more than just networking. Many
broadband Internet connections, such as cable modems and DSL modems,
connect to your notebook’s Ethernet jack. For more information, see “Using
the Internet” on page 71 and “Networking Your Computer” on page 189.
Installing a printer, scanner, or other peripheral device
Important Before you install a printer, scanner, or other peripheral
device, see the device documentation and installation
instructions.
Your computer has one or more of the following ports: IEEE 1394 (also known
as Firewire
these ports to connect peripheral devices such as printers, scanners, and digital
cameras to your computer. For more information about port locations, see
“Checking Out Your Gateway 600” on page 1 and “Using the Gateway 600 Port
Replicator” on page 259.
IEEE 1394 and USB ports support plug-and-play and hot swapping, which means
that your computer will usually recognize such a device whenever you plug it
into the appropriate port. When you use an IEEE 1394 or USB device for the
first time, your computer will prompt you to install any software the device
needs. After doing this, you can disconnect and reconnect the device at any
time.
Parallel and serial port devices are not plug-and-play. See the device
documentation for detailed information and installation instructions.
®
or i.Link®), Universal Serial Bus (USB), serial, and parallel. You use
Help and
Support
For more information about installing peripheral devices in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword installing devices in the HelpSpot
Search box , then click the arrow.
38
www.gateway.com
Page 49

Getting Help
This chapter tells you about additional information
resources available to help you use your computer. Read this
chapter to learn how to access:
■ HelpSpot™
■ Online help
■ Gateway Web site
3
www.gateway.com
39
Page 50

Chapter 3: Getting Help
HelpSpot
Your computer may include HelpSpot, an easily accessible collection of help
information, troubleshooters, instructional videos, and automated support. Use
HelpSpot to answer questions about Windows and to help you quickly discover
and use the many features of your Gateway computer. HelpSpot also has an
area called Contact Gateway that helps you find the right resource at Gateway
to answer your questions or help solve your problems.
To start HelpSpot:
■ Click Start, then click Help and Support. HelpSpot opens.
40
If this is the first time you have started HelpSpot, you may experience a
brief wait while HelpSpot builds the help database, then HelpSpot displays
an introductory video.
www.gateway.com
Page 51

You can find help information by clicking a link, performing a search, or
browsing the index. To learn about using your Gateway computer, your
touchpad, and other tasks, click the
Using your computer link on the HelpSpot
main page.
HelpSpot
www.gateway.com
41
Page 52

Chapter 3: Getting Help
Searching for a topic
To search for a topic in HelpSpot, type a word or phrase (keyword) in the Search
box located at the top of any HelpSpot screen, then click the arrow button.
Search box
Search results
header
Search results
headers
For each search, you receive the following search result types:
■ Suggested Topics - These topics are located in HelpSpot and are relevant
to your search topic.
■ Full-text Search Matches - These topics are located in HelpSpot and contain
the words you entered in the
■ Microsoft Knowledge Base - These topics are located on the Microsoft Web
site and contain the words you entered in the
Search box.
Search box. You must be
connected to the Internet to search for and access these topics.
■ Gateway.com Search - These topics are located on the Gateway Web site
and contain the words you entered in the
Search box. You must be
connected to the Internet to search for and access these topics.
To view a list of your search results, click the results header for the type of results
you want to view.
To view a topic, click the topic name in the
42
www.gateway.com
Search Results list.
Page 53

HelpSpot videos
HelpSpot contains several short videos to help introduce you to new concepts
or show you how to perform various tasks.
To play a HelpSpot video:
■ To watch a video in HelpSpot, click Video Tutorials on the HelpSpot home
page, then click a video title. The video plays.
HelpSpot
www.gateway.com
43
Page 54

Chapter 3: Getting Help
Online help
Many programs provide information online so you can research a topic or learn
how to perform a task while you are using the program. You can access most
online help information by selecting a topic from a
a
Help button.
You can search for information by viewing the help contents, checking the
index, searching for a topic or keyword, or browsing through the online help.
Help menu or by clicking
44
www.gateway.com
Page 55

Gateway Web site
Gateway's online support is available 24 hours per day, 7 days per week and
provides the most current drivers, product specifications, tutorials and
personalized information about your system. Visit the Gateway eSupport
Web site at www.
to the Internet, see “Using the Internet” on page 71.
gateway.com/support. For more information about connecting
Gateway Web site
www.gateway.com
45
Page 56

Chapter 3: Getting Help
Using eSupport
The eSupport site is divided into four major areas:
■ Support Home
■ Downloads
■ Contact Us
■ Account Info
Each of these areas is represented by a tab across the top of the Web page.
Support Home tab
To get specific information about your computer, type your serial number into
the My System Information box, then click
for me
. For more information, see “Finding your specifications” on page 14.
The Support Information link lets you access product documentation,
specifications, and manuals. By entering your serial number, you get specific
documents related to your system. You can also browse through the reference
area to locate an article specific to the question you have.
GO, or click Look up my serial number
The Tutorials link lets you access an extensive library of how-to articles and
videos on topics such as making audio CDs and installing a hard drive.
Downloads tab
The Downloads tab provides the latest software updates for BIOS and driver
upgrades. By entering your serial number you get drivers specific to your system.
Click
All Downloads to walk through a step-by-step wizard to locate your drivers.
For more information, see “Updating device drivers” on page 235.
Contact Us tab
The Contact Us tab contains links to technical support with a live technician,
including chat and e-mail. Click
numbers for both sales and support. For more information, see “Telephone
support” on page 291.
Call Us to get a list of Gateway telephone
Account Info tab
The Account Info tab contains support for non-technical issues, like the status
of your order or changing your account address.
46
www.gateway.com
Page 57

Windows Basics
Read this chapter to learn how to:
■ Use the Windows desktop
■ Manage files and folders
■ Work w i th d o cu me n ts
■ Use shortcuts
4
www.gateway.com
47
Page 58
Chapter 4: Windows Basics
About the Windows environment
After your computer starts, the first screen you see is the Windows desktop. The
desktop is like the top of a real desk. Think of the desktop as your personalized
work space where you open programs and perform other tasks.
Your desktop may be different from this example, depending on how your
computer is set up.
Help and
Support
For more information about the Windows XP desktop, click
Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword Windows desktop in the HelpSpot
Search box , then click the arrow.
48
www.gateway.com
Page 59

Using the desktop
The desktop contains the taskbar, the Start button, and the Recycle Bin icon.
Desktop elements Description
The taskbar is the bar at the bottom of the computer display containing the
Start button on the left and a clock on the right. Other buttons on the taskbar
represent programs that are running.
Click a program’s button on the taskbar to open the program’s window.
The Start button provides access to programs, files, help for Windows and
other programs, and computer tools and utilities.
Click the Start button, then open a file or program by clicking an item on
the menu that opens.
The Recycle Bin is where files, folders, and programs that you discarded
are stored. You must empty the Recycle Bin to permanently delete them from
your computer. For instructions on how to use the Recycle Bin, see “Deleting
files and folders” on page 59.
Using the desktop
Using the Start menu
You can start programs, open files, customize your system, get help, search for
files and folders, and more using the Start menu.
To use the Start menu:
1 Click the Start button on the lower left of the Windows desktop. The Start
menu opens showing you the first level of menu items.
2 Click All Programs or Programs to see all programs and files in the Start
menu. When you move the mouse pointer over any menu item that has
an arrow next to it, another menu, called a submenu, opens and reveals
related files, programs, or commands.
www.gateway.com
49
Page 60

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
3 Click a file or program to open it.
50
Help and
Support
For more information about the Windows XP Start menu,
click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword Windows Start menu in the HelpSpot
Search box , then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
Page 61

Adding icons to the desktop
You may want to add an icon (shortcut) to the desktop for a program that you
use frequently.
To add icons to the desktop:
1 Click Start, then click All Programs.
2 Right-click (press the right touchpad button) the program that you want
to add to the desktop.
3 Click Send To, then click Desktop (create shortcut). A shortcut icon for that
program appears on the desktop.
Using the desktop
Help and
Support
For more information about desktop icons in Windows XP,
click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword desktop icons in the HelpSpot Search
box , then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
51
Page 62

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
Identifying window items
When you double-click the icon for a drive, folder, file, or program, a window
opens on the desktop. This example shows the Local Disk (C:) window, which
opens after you double-click the
Local Disk (C:) icon in the My Computer window.
Title bar
Menu bar
Every program window looks a little different because each has its own menus,
icons, and controls. Most windows include these items:
Window item Description
The title bar is the horizontal bar at the top
of a window that shows the window title.
Close
Maximize
Minimize
52
Clicking the minimize button reduces the
active window to a button on the taskbar.
Clicking the program button in the taskbar
opens the window again.
Clicking the maximize button expands the
active window to fit the entire computer
display. Clicking the maximize button again
restores the window to its former size.
www.gateway.com
Page 63
Window item Description
Clicking the close button closes the active
window or program.
Clicking an item on the menu bar starts an
action such as Print or Save.
Identifying window items
Help and
Support
For more information about windows in Windows XP, click
Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword window in the HelpSpot Search box
, then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
53
Page 64

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
Working with files and folders
You can organize your files and programs to suit your preferences much like
you would store information in a file cabinet. You can store these files in folders
and copy, move, and delete the information just as you would reorganize and
throw away information in a file cabinet.
Viewing drives
Drives are like file cabinets because they hold files and folders. A computer
almost always has more than one drive. Each drive has a letter, usually Local
Disk (C:) for the hard drive and 3½ Floppy (A:) for the diskette drive. You may
also have more drives such as a DVD or recordable CD drive.
To view the drives on your computer:
■ In Windows XP, click Start, then click My Computer on the Start menu.
- OR -
In Windows 2000, double-click the
Drives
My Computer icon on the desktop.
54
www.gateway.com
Page 65

Working with files and folders
To see the files and folders on a drive:
■ Double-click the drive icon. If you do not see the contents of a drive after
you double-click its icon, click
Show the contents of this drive.
Help and
Support
For more information about files and folders in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword files and folders in the HelpSpot
Search box , then click the arrow.
Creating folders
Folders are much like the folders in a file cabinet. They can contain files and
other folders.
Files are much like paper documents—letters, spreadsheets, and pictures—that
you keep on your computer. In fact, all information on a computer is stored
in files.
Folders
Files
www.gateway.com
55
Page 66

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
To create a folder:
1 In Windows XP, click Start, then click My Computer on the Start menu.
- OR -
In Windows 2000, double-click the
My Computer icon on the desktop.
2 Double-click the drive where you want to put the new folder. Typically,
Local Disk (C:) is your hard drive and 3½ Floppy (A:) is your diskette drive.
If you do not see the contents of the drive, click
drive
.
Show the contents of this
3 If you want to create a new folder inside an existing folder, double-click
the existing folder. If you do not see the contents of the folder, click
the contents of this drive
or Show the contents of this folder.
Show
4 Click File, New, then click Folder. The new folder is created.
5 Type a name for the folder, then press ENTER. The new folder name appears
by the folder icon.
Help and
Support
For information about renaming folders, see “Shortcuts” on page 69.
For more information about creating files and folders in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword creating files and folders in the
HelpSpot Search box , then click
the arrow.
56
www.gateway.com
Page 67

Working with files and folders
Copying and moving files and folders
The skills you need to copy and move files are called copying, cutting, and pasting.
When you copy and paste a file or folder, you place a copy of the file or folder
on the Windows clipboard, which temporarily stores it. Then, when you decide
what folder you want the copy to go in (t he destination folder), you paste it there.
When you cut and paste a file or folder, you remove the file or folder from its
original location and place the file or folder on the Windows clipboard. When
you decide where you want the file or folder to go, you paste it there.
Important The clipboard stores whatever you cut or copy until you cut
or copy again. Then the clipboard contains the new
information only. Therefore, you can paste copies of a file
or folder into more than one place, but as soon as you copy
or cut a different file or folder, the original file or folder is
deleted from the clipboard.
To copy a file or folder to another folder:
1 Locate the file or folder you want to copy. For more information, see
“Viewing drives” on page 54 and “Searching for files” on page 62.
2 Right-click (press the right touchpad button) the file or folder that you
want to copy. A pop-up menu opens on the desktop.
3 Click Copy on the pop-up menu.
4 Open the destination folder.
5 With the pointer inside the destination folder, right-click.
6 Click Paste. A copy of the file or folder appears in the new location.
www.gateway.com
57
Page 68

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
To move a file or folder to another folder:
1 Locate the file or folder you want to move. For more information, see
“Viewing drives” on page 54 and “Searching for files” on page 62.
2 Right-click (press the right touchpad button) the file or folder that you
want to move. A pop-up menu opens on the desktop.
3 Click Cut on the pop-up menu.
4 Open the destination folder.
5 With the pointer inside the destination folder, right-click.
6 Click Paste. The file or folder you moved appears in its new location and
is removed from its old location.
Help and
Support
For more information about copying files and folders or
moving files and folders in Windows XP, click Start, then
click Help and Support.
Type the keyword copying files and folders or moving
files and folders in the HelpSpot Search box
, then click the arrow.
58
www.gateway.com
Page 69
Working with files and folders
Deleting files and folders
When you throw away paper files and folders, you take them from the file
cabinet and put them in a trash can. Eventually the trash can is emptied.
In Windows, you throw away files and folders by first moving them to the
Windows trash can, called the Recycle Bin, where they remain until you decide
to empty the bin.
You can recover any file in the Recycle Bin as long as the bin has not been
emptied.
To delete files or folders:
1 In My Computer or Windows Explorer, click the files or folders that you
want to delete. For instructions on how to select multiple files and folders,
see “Shortcuts” on page 69.
If you cannot find the file you want to delete, see “Searching for files” on
page 62.
2 Click File, then click Delete. Windows moves the files and folders to the
Recycle Bin.
Help and
Support
For more information about deleting files and folders in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword deleting files and folders in the
HelpSpot Search box , then click
the arrow.
To recover files or folders from the Recycle Bin:
1 Double-click the Recycle Bin icon. The Recycle Bin window opens and lists
the files and folders you have thrown away since you last emptied it.
2 Click the files or folders that you want to restore. For instructions on how
to select multiple files and folders, see “Shortcuts” on page 69.
3 Click File, then click Restore. Windows returns the deleted files or folders
to their original locations.
www.gateway.com
59
Page 70

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
To empty the Recycle Bin:
Caution Emptying the Recycle Bin permanently erases any files or
1 Double-click the Recycle Bin icon on the desktop. The Recycle Bin window
opens.
2 Click File, then click Empty Recycle Bin. Windows asks you if you are sure
that you want to empty the bin.
3 Click Yes. Windows permanently deletes all files in the Recycle Bin.
folders in the bin. These files cannot be restored.
Help and
Support
For more information about emptying the Recycle Bin in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword emptying Recycle Bin in the HelpSpot
Search box , then click the arrow.
Browsing for files and folders
A file or folder that you need is rarely right on top of your Windows desktop.
It is usually on a drive inside a folder that may be inside yet another folder,
and so on.
Windows drives, folders, and files are organized in the same way as a real file
cabinet in that they may have many levels (usually many more levels than a
file cabinet, in fact). So you usually will have to search through levels of folders
to find the file or folder that you need. This is called browsing.
To browse for a file:
1 In Windows XP, click Start, then click My Computer. The My Computer
window opens.
- OR -
In Windows 2000, double-click the
My Computer window opens.
My Computer icon on the desktop. The
60
www.gateway.com
Page 71

Working with files and folders
2 Double-click the drive or folder that you think contains the file or folder
that you want to find. If you do not see the contents of a folder, click
the contents of this drive
or Show the contents of this folder.
Show
3 Continue double-clicking folders and their subfolders until you find the
file or folder you want.
Help and
Support
For more information about browsing for files and folders
in Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword files and folders in the HelpSpot
Search box , then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
61
Page 72

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
Searching for files
If you are looking for a particular file or folder or a set of files or folders that
have characteristics in common, but you do not remember where they are
stored on your hard drive, you can use the Search utility to search by:
■ Name or part of a name
■ Creation date
■ Modification date
■ File type
■ Text contained in the file
■ Time period in which it was created or modified
You can also combine search criteria to refine searches.
Files and folders found using this utility can be opened, copied, cut, renamed,
or deleted directly from the list in the results window.
62
www.gateway.com
Page 73

Using the Windows Search utility
To find files and folders using the Search utility:
1 In Windows XP, click Start, then click Search. The Search Results window
opens. Click
- OR -
All files and folders.
Searching for files
In Windows 2000, click
Search Results window opens.
Start, Search, then click For Files or Folders. The
2 If you want to search by file or folder name, type in all or part of the file
or folder name in the name box in the left pane of the window.
■ If you type all of the name, Search will list all files and folders of that
name.
■ If you type part of the name, Search will list all of the file and folder
names containing the letters you typed.
www.gateway.com
63
Page 74
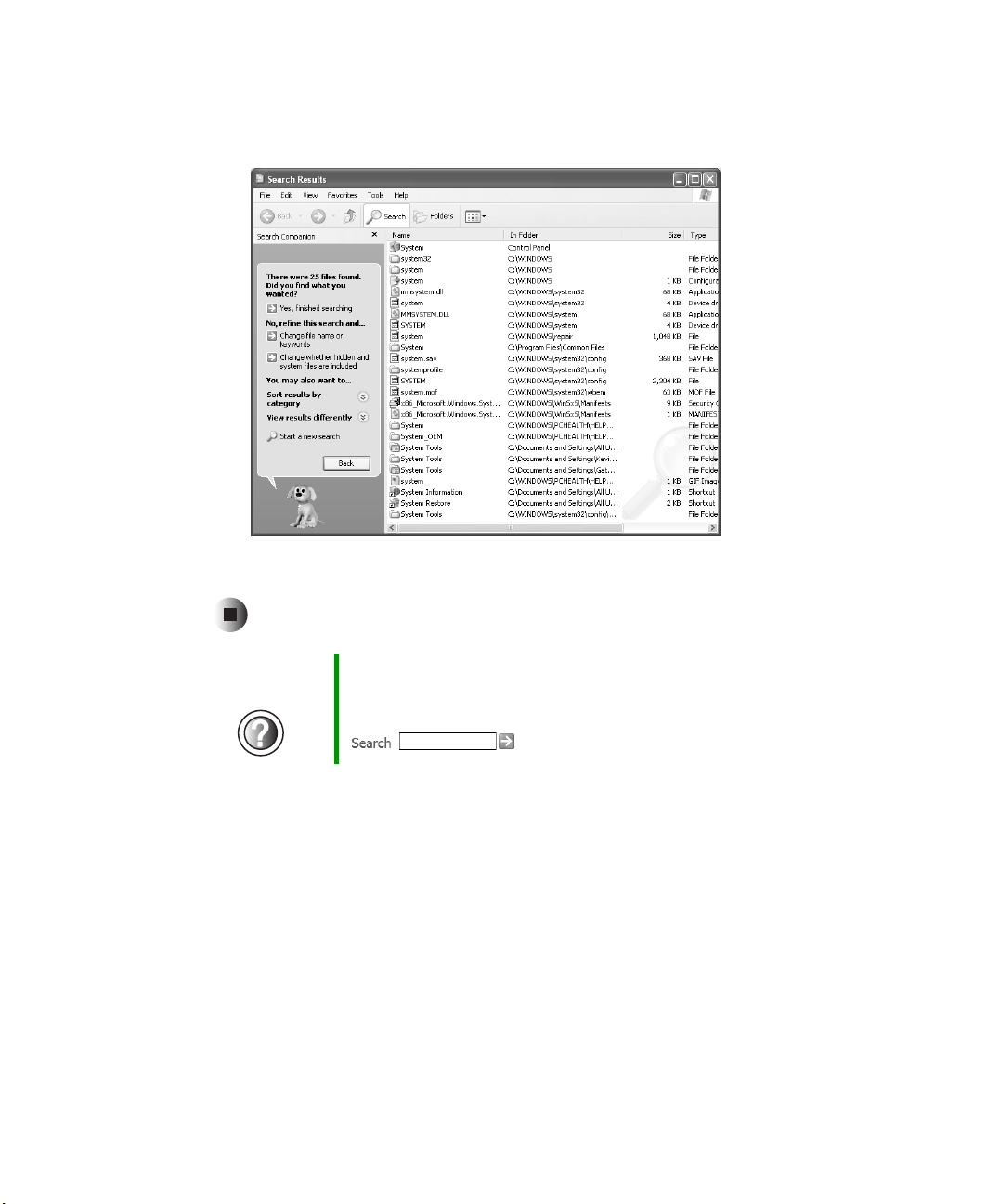
Chapter 4: Windows Basics
3 Click Search or Search Now. When the search is completed, Windows lists
the files and folders whose names contain the text that you searched for.
4 Open a file, folder, or program by double-clicking the name in the list.
Help and
Support
For more information about searching for files and folders
in Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword searching in the HelpSpot Search box
, then click the arrow.
Using advanced search options
Search can find files meeting more criteria than file name. You can narrow your
search by selecting the search options that you want. You can search by the:
■ Date the file was created or modified.
■ Size of the file.
■ Type of file, such as a program or a text document.
64
www.gateway.com
Page 75

Working with documents
Working with documents
Computer documents include word processing files, spreadsheet files, or other
similar files. The basic methods of creating, saving, opening, and printing a
document apply to most of these types of files.
The following examples show how to create, save, open, and print a document
using Microsoft
as WordPerfect, Microsoft Word, and Microsoft Excel.
For more information about using a program, click
®
WordPad. Similar procedures apply to other programs such
Help on its menu bar.
Creating a new document
To create a new document:
1 Click Start, All Programs, Accessories, then click WordPad. Microsoft
WordPad starts and a blank document opens.
2 Begin composing your document. Use the menus and toolbar buttons at
the top of the window to format the document.
www.gateway.com
65
Page 76

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
Saving a document
After you create a document, you need to save it if you want to use it later.
To save a document:
1 Click File, then click Save. The Save As dialog box opens.
Save in
list
66
File
name
2 Click the arrow button to open the Save in list, then click the folder where
you want to save the file. If you do not see the folder you want, browse
through the folders listed below the Save in list.
3 Type a new file name in the File name box.
4 Click Save.
Help and
Support
For more information about saving documents in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword saving in the HelpSpot Search box
, then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
Page 77

Working with documents
Opening a document
To view, revise, or print an existing document, first you need to open it. Open
the document in the program that it was created in.
To open a document:
1 Start the program.
2 Click File, then click Open.
3 Click the arrow button to open the Look in list, then click the folder you
want to open. If you do not see the folder you want, browse through the
folders listed below the Look in list.
Look in
list
4 Double-click the document file name. The document opens.
Help and
Support
For more information about opening documents in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword opening files in the HelpSpot Search
box , then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
67
Page 78

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
Printing a document
To print a document, you must have a printer connected to your computer or
have access to a network printer. For more information about installing or using
your printer, see the printer documentation.
To print a document:
1 Make sure that the printer is turned on and loaded with paper.
2 Start the program and open the document.
3 Click File, then click Print. The Print dialog box opens.
4 Set the print options, then click OK. The document prints.
Help and
Support
For more information about printing documents in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword printing in the HelpSpot Search box
, then click the arrow.
68
www.gateway.com
Page 79
Shortcuts
The following table shows a few shortcuts that you can use in Windows and
almost all programs that run in Windows. For more information on Windows
shortcuts, see your Windows or program documentation.
To... Do this...
Copy a file, folder, text, or graphic Click the item, then press CTRL + C.
Cut a file, folder, text, or graphic Click the item, then press CTRL + X.
Paste a file, folder, text, or graphic Click inside the folder or window where you want to paste
the object, then press
CTRL + V.
Shortcuts
Select multiple items in a list or window Click the first item, press and hold down the
then click each of the remaining items.
Select multiple adjacent items in a list
or window
Permanently delete a file or folder Click the file or folder, then press
Rename a file or folder Click the file or folder, press F2, type the new name, then
Close the active window or program Press ALT + F4.
Switch to a different file, folder, or
running program
Help and
Support
For more information about Windows keyboard shortcuts
in Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword Windows keyboard shortcuts in the
HelpSpot Search box , then click
the arrow.
Click the first item in the list, press and hold down the
SHIFT key, then click the last item in the list.
SHIFT + DELETE. The
file or folder is permanently deleted. The file or folder is
not stored in the Recycle Bin.
press
ENTER.
ALT +TAB.
Press
CTRL key,
www.gateway.com
69
Page 80

Chapter 4: Windows Basics
70
www.gateway.com
Page 81

Using the Internet
This chapter provides information about the Internet and
the World Wide Web. Read this chapter to learn how to:
5
■ Set up and access an Internet account using
America Online
■
Connect to a Web site using a browser
■ Download files from the Internet
■ Send and receive e-mail using America Online
®
www.gateway.com
71
Page 82

Chapter 5: Using the Internet
Learning about the Internet
The Internet is a worldwide network of computers linked together to provide
information to people everywhere. The two most popular services on the
Internet are e-mail and the World Wide Web. You can access this network by
connecting your computer to a telephone, DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), or
cable line and signing up with an Internet service provider (ISP).
Cable and DSL modems, a connection known as broadband, use your TV cable
or special telephone lines to connect to your ISP and access the Internet. Cable
and DSL modems connect to your computer through an Ethernet jack and
provide a faster connection speed than a standard telephone modem.
Important For the location of your modem and Ethernet jacks, see
“Back” on page 6 and “Back” on page 261.
Internet Servers
store information so other
computers can access it
from the Internet.
Your computer
connects to the
Internet through
an ISP.
72
ISP Servers
let you connect to
the Internet and
access your e-mail
messages.
www.gateway.com
Page 83

Setting up an Internet account
If you want to access the Internet you need:
■ A modem – a device that connects your computer to other computers or
servers using a telephone, DSL, or cable line.
■ An Internet service provider – a company that provides access to the
Internet through an ISP server. When you connect to an ISP, the ISP server
lets you access the Internet and your e-mail messages.
■ A Web browser – a program that displays information from the World Wide
Web.
■ An e-mail program – a program that lets you create, send, and receive
e-mail messages over the Internet.
Setting up an Internet account
Before you can view the information on the World Wide Web, you need to set
up an Internet account with an Internet service provider (ISP). If you have
chosen America Online as an ISP, follow these instructions to set up and connect
to your account. To set up a different ISP service or to transfer an existing
account to this computer, contact the ISP directly.
If you set up an account with America Online, an Internet e-mail address is
created for you. After completing the setup, you are ready to access the Internet.
To set up an Internet account with America Online:
1 Click Start, All Programs, then click America Online.
2 Follow the on-screen instructions. After setting up your account, you can
connect to the Internet and access your e-mail services.
www.gateway.com
73
Page 84

Chapter 5: Using the Internet
Accessing your Internet account
To connect to your America Online Internet account:
1 Click Start, All Programs, then click America Online.
2 Complete the member name and password information, then click
Connect. Your computer dials the Internet account telephone number. After
connecting, the Wel com e window opens.
If you are using a service other than America Online, check with your ISP for
the correct procedure for connecting.
To disconnect from your America Online Internet account:
■ Click X in the top-right corner of the America Online window. Your
computer disconnects from the Internet.
Important Make sure that your computer disconnects correctly from
your Internet account. If you do not have an “unlimited
hours” ISP account, you may have to pay for the time that
you are connected, even if you are not at your computer.
If you are using a service other than America Online, check with your ISP for
the correct procedure for disconnecting.
Help and
Support
74
For general information about using Internet accounts in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword ISP in the HelpSpot Search box
, then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
Page 85

Using the World Wide Web
Using the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a multimedia window to the Internet that gives you
access to millions of information sources.
Information on the Web comes to you on Web p a ge s, which are electronic
documents that you view using a Web page display program called a browser.
You can use any of the commercially available Web browsers, like Microsoft
Internet Explorer (which comes installed on your new computer), Netscape
Navigator, or the browser built into America Online.
Web pages can contain text, animations, music, and other multimedia features.
A group of related Web pages is called a Web site. You can access Web sites to
shop, track investments, read the news, download programs, and much more.
You can explore a Web site or visit other Web sites by clicking areas on a Web
page called links or hyperlinks. A link may be colored or underlined text, a
picture, or an animated image. You can identify a link by moving the mouse
pointer over it. If the pointer changes to a hand, the item is a link.
To learn more about using the Web browser features, click
Link
Web
page
Linked Web
page
Help in the menu bar.
www.gateway.com
75
Page 86

Chapter 5: Using the Internet
Connecting to a Web site
After you set up an account with an Internet service provider (ISP) such as
America Online, you can access the many information sources on the World
Wide Web.
To connect to a Web site:
1 Connect to your Internet account. After your computer connects, a default
opening page or welcome screen opens.
2 To go to a different Web site, type the address (called a URL for “Universal
Resource Locator”) in the browser address bar (for example
www.gateway.com), then click
- OR -
On the current Web page, click a link to a Web site.
The Web browser locates the server computer on the Internet, downloads
(transfers) data to your computer, and displays the page on the site that
you requested.
GO on the browser address bar.
Help and
Support
Sometimes Web pages display slowly. The speed that a Web page displays on
your screen depends on the complexity of the Web page and other Internet
conditions. Additionally, the speed of your connection will determine how fast
Web pages display.
76
For more information about connecting to a Web site in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword connecting to Web site in the
HelpSpot Search box , then click
the arrow.
www.gateway.com
Page 87

Using the World Wide Web
Downloading files
Downloading is the process of transferring files from a computer on the Internet
to your computer.
To protect your computer against viruses, make sure that you scan the files you
download. For more information, see “Protecting your computer from viruses”
on page 216.
To download files or programs from a Web site:
1 Connect to your Internet account.
2 In the address bar, type the address of the Web site that contains the file
or program you want to download, then click
bar.
- OR -
Click a link on a Web page to navigate to the Web site containing the file
that you want to download.
3 Create or locate the folder where you want to store the file on your
computer. For more information, see “Working with files and folders” on
page 54.
GO on the browser address
4 Click the link on the Web page for the file that you want to download.
5 Follow the on-screen instructions for saving the file in the folder that you
want. A copy of the file is downloaded to your computer. The time that
it takes to transfer the file to your computer depends on file size and
Internet conditions.
6 Open the folder that you created.
7 Install or view the downloaded file by double-clicking it. If applicable,
follow the instructions provided on the Web site to run or install the
program.
Help and
Support
For more information about downloading files in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword downloading files in the HelpSpot
Search box , then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
77
Page 88

Chapter 5: Using the Internet
Using e-mail
E-mail (electronic mail) lets you send messages to anyone who has an Internet
connection and e-mail address. E-mail is usually a free service of your Internet
account.
The Internet never closes, so you can send e-mail messages at any time. Your
e-mail messages arrive at most e-mail addresses in minutes.
An e-mail address consists of a user name, the @ symbol, and the Internet domain
name of the Internet service provider (ISP) or company that “hosts” that user.
Your e-mail address is assigned when you sign up for an account with an ISP.
For example, a person with an account with America Online might have an
e-mail address that is similar to this one:
jdoe@aol.com
User name Internet domain name
Sending e-mail
To send e-mail using America Online:
1 Connect to your America Online account.
2 Click Write.
3 Type the e-mail address of the recipient you want to send e-mail to in the
Send To box.
4 Type the subject of your e-mail in the Subject box.
5 Type the e-mail message.
6 When finished, click Send Now. Your e-mail is sent over the Internet to the
e-mail address you specified.
78
www.gateway.com
Page 89

Checking your e-mail
To check your e-mail using America Online:
1 Connect to your America Online account.
2 Click Read.
3 Double-click the message you want to read.
For more information about managing and organizing your e-mail messages,
see the online help in your e-mail program.
Using e-mail
Help and
Support
For general information about using e-mail in Windows XP,
click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword e-mail in the HelpSpot Search box
, then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
79
Page 90

Chapter 5: Using the Internet
80
www.gateway.com
Page 91

Using Multimedia
This chapter provides information on using the multimedia
capabilities of your notebook. Read this chapter to learn
how to:
■ Use the diskette drive
■ Use a DVD or recordable CD drive
■ Adjust the volume
■ Use Audio DJ
■ Play CDs
■ Record and play audio files
■ Use Windows Media Player
■ Use MusicMatch
■ Use a recordable CD drive to create CDs
■ Play DVDs
■ View the display on a television
6
■ Capture video using the IEEE 1394 (also known as
Firewire or i.Link) port
www.gateway.com
81
Page 92

Chapter 6: Using Multimedia
Using the diskette drive
The diskette drive uses 3.5-inch diskettes (sometimes called floppy disks).
Diskettes are useful for storing files or transferring files to another computer.
Warning Do not expose diskettes to water or magnetic fields.
Exposure could damage the data on the diskette.
Diskette slot Diskette eject button
To use a diskette:
1 Insert the diskette into the diskette drive with the label facing up.
82
Important If the diskette drive is not in the right-side modular bay, you
need to swap modules. For more information about
swapping modules, see “Changing drives” on page 246.
The diskette drive will not work in the left-side modular bay.
www.gateway.com
Page 93

Using the diskette drive
2 To access a file on the diskette in Windows XP, click Start, then click My
Computer
double-click the file name.
- OR -
. Double-click the drive letter (for example, the A: drive), then
To access a file on the diskette in Windows 2000, double-click the
Computer
the file name.
icon, the drive letter (for example, the A: drive), then double-click
My
3 To remove the diskette, make sure that the modular drive status indicator
is off (see “Status indicators” on page 26), then press the diskette eject
button.
www.gateway.com
83
Page 94

Chapter 6: Using Multimedia
Using the DVD or recordable CD drive
You can use your computer to enjoy a wide variety of multimedia features.
Identifying drive types
Your Gateway computer may contain one of the following drive types. Look
on the front of the drive for one of the following logos:
CD-RW drive
DVD drive
Combination
DVD/CD-RW drive
Use a CD-RW drive for installing programs, playing
audio CDs, accessing data, and creating CDs.
You cannot use this drive to play DVDs.
You can only write to a CD-R disc once. You can
write to and erase CD-RW discs multiple times.
For more information, see “Using a recordable CD
drive” on page 112.
Use a DVD drive for installing programs, playing
audio CDs, playing DVDs, and accessing data.
You cannot use this drive to create CDs.
Use a combination DVD/CD-RW drive for installing
programs, playing audio CDs, playing DVDs,
accessing data, and recording music and data to
CD-R or CD-RW discs. For more information, see
“Using a recordable CD drive” on page 112.
84
www.gateway.com
Page 95
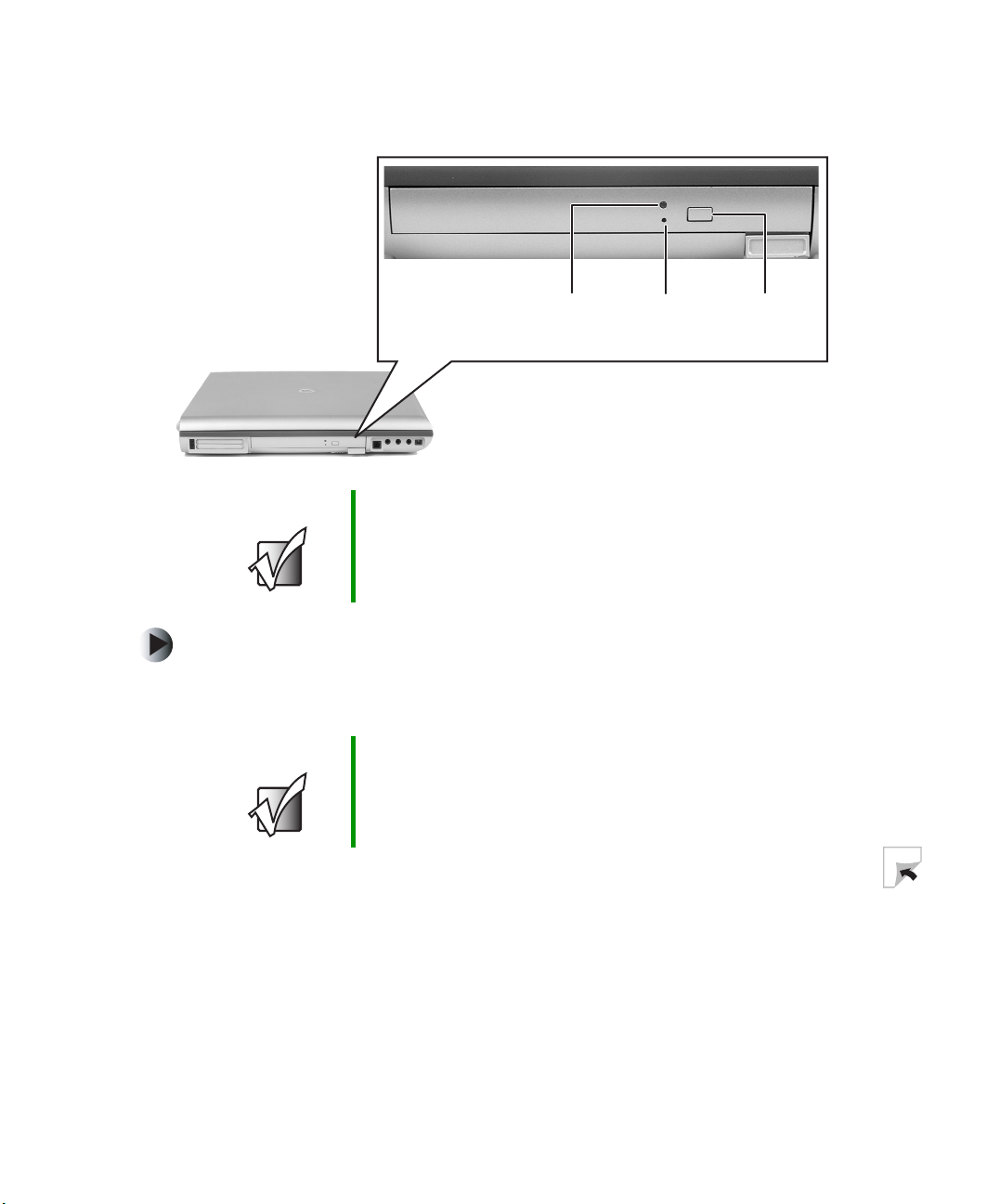
Inserting a CD or DVD
Using the DVD or recordable CD drive
Activity
indicator
Important Some music CDs have copy protection software. You may
not be able to play these CDs on your computer.
Manual
eject hole
Eject
button
To insert a CD or DVD:
1 Press the eject button on the DVD or recordable CD drive. After the tray
opens slightly, pull the disc tray completely open.
Important If the drive you want to use is not in the modular bay, you
need to swap modules. For more information about
swapping modules, see “Changing drives” on page 246.
www.gateway.com
85
Page 96

Chapter 6: Using Multimedia
2 Place the disc in the tray with the label facing up, then press down carefully
on the disc until it snaps into place.
Important When you place a single-sided disc in the tray, make sure
that the label side is facing up. If the disc has two playable
sides, place the disc so that the name of the side you want
to play is facing up.
3 Push the tray in until it is closed.
Adjusting the volume
Adjusting the volume in Windows XP
You can use the volume controls to adjust the overall volume and the volume
of specific sound devices in your computer.
To adjust the overall volume level using hardware controls:
■ If you are using external speakers, turn the knob on the front of the
speakers.
-OR-
Use the mute and volume control buttons on the Audio DJ control panel.
For more information, see “Audio DJ controls” on page 92.
86
www.gateway.com
Page 97

Adjusting the volume
To adjust the overall volume level from Windows:
1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel win dow o p ens . I f you r
Control Panel is in Category View, click
Sounds, Speech, and Audio Devices.
2 Click/Double-click the Adjust the system volume or Sounds and Audio
Devices
. The Sounds and Audio Devices Properties dialog box opens.
3 Click the Vol ume tab.
4 Drag the Device Volume slider to change the volume or click to select the
Mute check box, then click OK.
Help and
Support
For more information about adjusting volume in
Windows XP, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type the keyword adjusting volume in the HelpSpot
Search box , then click the arrow.
www.gateway.com
87
Page 98

Chapter 6: Using Multimedia
To adjust specific volume levels:
1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel win dow o p ens . I f you r
Control Panel is in Category View, click
2 Click/Double-click the Adjust the system volume or Sounds and Audio
Devices
. The Sounds and Audio Devices Properties dialog box opens.
3 Click the Vol ume tab.
Sounds, Speech, and Audio Devices.
88
4 Click Advanced in the Device volume area.
If the device you want to adjust does not appear in the window, click
Options, Properties, the check box next to the audio device you want to
adjust, then click
OK.
www.gateway.com
Page 99

Adjusting the volume
5 Drag the volume level and balance sliders for the device you want to adjust.
For more information about the volume controls, click
Help in the window.
6 Click X in the top-right corner of the window to close it.
Adjusting the volume in Windows 2000
You can use the volume controls to adjust the overall volume and the volume
of specific sound devices in your computer.
To adjust overall volume level using hardware controls:
■ If you are using external speakers, turn the knob on the front of the
speakers.
-OR-
Use the mute and volume control buttons on the Audio DJ control panel.
For more information, see “Audio DJ controls” on page 92.
To adjust overall volume level from Windows:
■ Click the speaker icon on the taskbar, then drag the slider to change
the volume or click to select the
www.gateway.com
Mute check box.
89
Page 100

Chapter 6: Using Multimedia
To adjust specific volume levels:
1 Double-click the speaker icon on the taskbar. The Vol ume Cont rol
window opens.
If the device you want to adjust does not appear in the Vol ume Co ntr o l
window, click
click
OK.
Options, Properties, the audio device you want to adjust, then
90
2 Drag the volume level and balance sliders for the device you want to adjust.
For more information about the volume controls, click
Control window.
Help in the Volu me
3 Click X in the top-right corner of the window to close it.
www.gateway.com
 Loading...
Loading...