Page 1

Page 2
LOG OF REVISIONS
Rev
Page
Description
FAA Approval
A
All
Complete Supplement
Seyed-Joussef Hashemi
Manager Flight Test Branch
ANM-160L
FAA, Los Angeles ACO
Transport Airplane Directorate
Date: July 15, 2008
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 2 of 52
Page 3
LOG OF REVISIONS
Rev
Page
Description
FAA Approval
B
7
Added GAD 43 to section 1.2
Seyed-Joussef Hashemi
Manager Flight Test Branch
ANM-160L
FAA, Los Angeles ACO
Transport Airplane Directorate
Date: July 17, 2009
8
Added section 1.4
11
Added GAD 43 to diagram
12
Added GAD 43 to diagram
13
Added section 1.10
14
Changed GDU s/w to 3.01, AHRS
s/w to 2.12, GNS 400W/500W
software to 3.20, and added GAD 43
to section 2.2
Updated names of charting services in
section 2.3
15
Expanded AHRS operational area in
section 2.4
Added section 2.5
16
Added section 2.6
17
Added section 2.10
18 Added section 2.13
Updated section 2.14 to account for
SVT
19
Added section 2.17
Updated section 2.18 to account for
VFR only installations
21
Added item 4 in section 3.2
22
Updated section 3.3.1 to account for
HSI track reversionary mode
25
Added ‘check attitude’ and ‘AHRS
Aligning’ alerts to table
26
Updated section 3.6 to account for
G600 internal TAWS
Updated section 4.1 for new PFD
knob mode annunciation
Added note pertinent to dual G600
installations in section 4.1
27
Added section 4.4
28
Added check boxes for FD with SVT
and GAD 43 to section 4.5
30 Updated section 4.5.7 to explain FD
behavior with SVT enabled
Added section 4.5.8
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 3 of 52
Page 4
LOG OF REVISIONS
Rev
Page
Description
FAA Approval
C
16
Added section 2.8.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: September 15, 2009
D
11
12
16
Remove requirement for standby ADI for
VFR operations/installations. Add
maximum airspeed limitation section.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: November 17, 2009
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 4 of 52
Page 5
LOG OF REVISIONS
Rev
Page
Description
FAA Approval
E
All
Changed GPS/WAAS to GPS/SBAS.
Corrected typographical errors.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: January 28, 2011
7
Updated section 1.1 for new features.
9
Added new feature descriptions to
sections 1.7, 1.8, and 1.9.
10, 11
Updated block diagrams for new
features.
13
Updated section 2.2 for applicability
to this AFMS revision. Removed
GPS navigator software table.
13
Updated section 2.3 with limitation
on use of helicopter databases and SD
card usage with GSR 56 datalink.
Added information on airport
directory database.
14
Updated section 2.8 to reflect current
airspeed tape behavior.
16
Updated sections 2.14, 2.15, and 2.16
to better describe the various terrain
awareness functions. Updated section
2.17 for GFDS weather function.
18
Corrected description of AHRS
failure.
18
Corrected description of heading
failure.
19
Corrected description of ADC failure.
21
Corrected table entry for AHRS
ALIGN.
23
Added new section 4.4 for altitude
alerter configuration.
23
Added detail to section 4.6 regarding
GAD 43 interface. Corrected
description of autopilot interfaces in
section 4.6.1.
24
Corrected altitude alerter description
in section 4.6.6.
25
Added Caution and Note regarding
GAD 43 AP TEST function in section
4.6.8.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 5 of 52
Page 6
LOG OF REVISIONS
Rev
Page
Description
FAA Approval
F
All
Changed references to GNS navigators
to GPS/SBAS navigators.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: April 01, 2011
10
Inserted new section 1.10 for HSDB
interface description.
14
Inserted new section 2.3 for moving map
limitations.
20, 21
Moved rate-of-turn failure description
from section 3.3.1 to section 3.3.2.
25
Added checkbox for disabled altitude
alerter in section 4.4.
G
All
Re-issue complete supplement.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: September 08, 2011
Revised section 2.14 limitation on
GPS/SBAS vertical coupling.
Added attitude/air data interface to
section 4.6.
Added GDU 620 as an autopilot attitude
source to section 4.6.1.
Clarified dual autopilot interface in
section 4.6.9.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 6 of 52
Page 7

LOG OF REVISIONS
Rev
Page
Description
FAA Approval
H
All
Re-issue complete supplement.
Michael Warren
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: October 25, 2012
Revised information on system power
sources in section 1.2.
Revised audio panel description in
section 1.6.
Updated block diagrams in sections 1.12
and 1.13.
Updated System Software Requirements
in section 2.2.
Revised Moving Map limitation in
Section 2.3.
Revised SafeTaxi and Airport Directory
descriptions in section 2.4.
Clarified applicability of section 2.11.
Updated autopilot interface information
in section 2.13.
Added limitation for KFC 275/325
interface in section 2.21.
Added Type Ratings limitation in section
2.22.
Added ESI-1000 limitation in section
2.23.
Added EFB limitation in Section 2.24.
Added Surface Operations limitation in
Section 2.25.
Added MFD Video limitation in Section
2.26.
Emergency Procedures reorganized into
Section 3.1.
Abnormal Procedures reorganized into
Section 3.2.
Added MISCOMP and NO AP DATA
annunciations in section 3.3.2.
Added airspeed bug description in
Section 4.1.
Removed Altitude Alerter section 4.4.
Added electric standby attitude indicator
procedure as new section 4.4.
Updated autopilot procedures throughout
section 4.6.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 7 of 52
Page 8

LOG OF REVISIONS
Rev
Page
Description
FAA Approval
J
All
Re-issue complete supplement.
Michael Warren
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: December 12, 2013
Corrected navigation radio information
in Section 1.1.
Corrected Auto Slew description in
Section 2.11.
Updated Bendix/King Altitude Preselect
functionality in Section 4.6.6.3.
K
All
Added G500 content to applicable
sections.
Michael Warren
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: April 1, 2015
Added Terrain Alerting and Terminal
Procedures to section 1.1.
Moved Traffic and Weather Systems to
separate sections, 1.7 and 1.8.
Updated software versions in section 2.2.
Moved sections 2.4 (DB Card) and 2.11
(Elec Stby) to section 7.
Added TAWS Annun from Garmin
Navigator to section 2.17.
Added Stormscope Display to
sections 2.19 and 7.6.
Revised Standby Battery preflight check
to include all. electronic indicators in
Section 2.24
Added GAD 43 AC Reference loss to
section 3.2.7.
Added TER, TAWS, NO DATA, and
A/C Ref Lost description to section 3.3
Revised sections 1.5, 2.10, 2.14, 2.18,
and 3.17 for EASA.
Added Cessna autopilots to
section 4.6.6.4.
Added detail to GAD 43 AC Ref to
section 4.6.9.
Included select systems descriptions in
section 7.
L
All
Added GSU 75(B) to applicable
sections.
See Page 1
Added reference to GTX 3X5
transponders to applicable sections.
Added limitation for database cards to
section 2.4.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 8 of 52
Page 9

Added check box for GAD 43 function
to section 4.6.
Added description of GDU control
capabilities for GWX weather radars to
section 7.9.
Edited information about obstacle and
wire depiction to section 7.10.
FAA APPROVED Page 9 of 52
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
Page 10

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1. GENERAL ................................................................................. 12
1.1 G500/G600 PRIMARY FLIGHT / MULTI-FUNCTION DISPLAY SYSTEM .. 12
1.2 SYSTEM POWER SOURCES ................................................................... 13
1.3 NAVIGATION SOURCES ........................................................................ 13
1.4 SYNTHETIC VISION TECHNOLOGY (SVT) ............................................ 14
1.5 AUTOPILOT INTERFACE ....................................................................... 15
1.6 AUDIO PANEL...................................................................................... 16
1.7 TRAFFIC DISPLAY ................................................................................ 16
1.8 WEATHER DATA ................................................................................. 16
1.9 VIDEO DISPLAY ................................................................................... 16
1.10 RADAR ALTIMETER ............................................................................. 16
1.11 HIGH SPEED DATA BUS INTERFACE .................................................... 17
1.12 SINGLE G500/G600 OPERATIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ......................... 18
1.13 DUAL G500/G600 OPERATIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................... 19
1.14 DEFINITIONS ........................................................................................ 20
SECTION 2. LIMITATIONS ......................................................................... 21
2.1 COCKPIT REFERENCE & PILOT’S GUIDE .............................................. 21
2.2 SYSTEM SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS ................................................... 21
2.3 MOVING MAP ...................................................................................... 21
2.4 DATABASE CARDS .............................................................................. 21
2.5 ADAHRS AND AHRS OPERATIONAL AREA ....................................... 21
2.6 MAGNETIC VARIATION OPERATIONAL AREA ...................................... 22
2.7 NAVIGATION ANGLE ........................................................................... 22
2.8 ADAHRS AND AHRS NORMAL OPERATING MODE ........................... 22
2.9 AIRSPEED LIMITATIONS AND INDICATOR MARKINGS .......................... 22
2.10 AEROBATIC MANEUVERS .................................................................... 23
2.11 COURSE POINTER AUTO SLEWING ....................................................... 23
2.12 SYNTHETIC VISION TECHNOLOGY ....................................................... 23
2.13 AUTOPILOT INTERFACE ....................................................................... 23
2.14 TERRAIN PROXIMITY FUNCTION ......................................................... 23
2.15 TAWS FUNCTION [GDU 620 UNITS WITH INTERNAL TAWS] ............ 24
2.16 DATALINKED WEATHER DISPLAY (XM, GFDS, FIS-B WEATHER) ...... 24
2.17 TRAFFIC DISPLAY ................................................................................ 24
2.18 ACTIVE WEATHER RADAR ................................................................ 25
2.19 STORMSCOPE
®
DISPLAY ..................................................................... 25
2.20 KINDS OF OPERATIONS ........................................................................ 26
2.21 KFC 275/325 ALTITUDE PRESELECT .................................................. 26
2.22 TYPE RATINGS .................................................................................... 26
2.23 ELECTRONIC STANDBY INSTRUMENT POWER ..................................... 27
2.24 ELECTRONIC FLIGHT BAG (EFB) APPLICATIONS ................................. 27
2.25 SURFACE OPERATIONS ........................................................................ 27
2.26 MFD VIDEO DISPLAY ......................................................................... 27
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 10 of 52
Page 11

SECTION 3. EMERGENCY PROCEDURES .............................................. 28
3.1 EMERGENCY PROCEDURES ................................................................. 28
3.2 ABNORMAL PROCEDURES ................................................................... 32
3.3 WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, AND ADVISORIES ........................................... 35
SECTION 4. NORMAL PROCEDURES ...................................................... 38
4.1 PFD KNOB & PFD SOFT KEYS ........................................................... 38
4.2 MFD KNOBS & MFD SOFT KEYS ....................................................... 38
4.3 ALTITUDE SYNCHRONIZATION ............................................................ 39
4.4 ELECTRIC STANDBY ATTITUDE GYRO (MID CONTINENT 4200 AND 4300
SERIES) ........................................................................................................... 39
4.5 SYNTHETIC VISION TECHNOLOGY....................................................... 39
4.6 AUTOPILOT OPERATIONS WITH THE G500/G600 SYSTEM ................... 40
4.7 TAWS ................................................................................................ 46
4.8 RADAR ALTIMETER ............................................................................. 46
SECTION 5. PERFORMANCE ..................................................................... 47
SECTION 6. WEIGHT AND BALANCE ...................................................... 47
SECTION 7. SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONS ..................................................... 48
7.1 DATABASES ........................................................................................ 48
7.2 ELECTRIC STANDBY ATTITUDE GYRO ................................................ 49
7.3 AUTOPILOT INTERFACE ....................................................................... 49
7.4 TAWS FUNCTION [GDU 620 UNITS WITH INTERNAL TAWS] ............ 50
7.5 TAWS ANNUNCIATIONS ON THE PFD [FROM A GARMIN NAVIGATOR] 50
7.6 STORMSCOPE® .................................................................................... 50
7.7 ADS-B TRAFFIC SYSTEM INTERFACE ................................................. 51
7.8 FLIGHT PLAN ...................................................................................... 51
7.9 GWX 68 AND GWX 70 WEATHER RADAR ......................................... 51
7.10 DEPICTION OF OBSTACLES AND WIRES ............................................... 52
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 11 of 52
Page 12

Section 1. GENERAL
1.1 G500/G600 Primary Flight / Multi-Function Display System
The G500/G600 System consists of a Primary Flight Display (PFD) and MultiFunction Display (MFD) housed in a single Garmin Display Unit (GDU), plus
an Air Data Attitude and Heading Reference System (ADAHRS), and optional
signal adapter (GAD). Alternatively, the G500/G600 System may include a
separate Air Data Computer (ADC) and Attitude and Heading Reference System
(AHRS) in place of an ADAHRS.
The G500/G600 interfaces with other installed systems in the aircraft, including
Garmin GPS/SBAS navigators, VHF navigation radios, datalinks, traffic
systems, weather radars, audio panels, video sources, radar altimeters, ADF
receivers, DME receivers, and autopilots.
The G500/G600 system can optionally provide Terrain Alerting functions and
display of Terminal Procedures.
The primary function of the PFD is to provide attitude, heading, air data and
navigation information to the pilot. The primary function of the MFD is to
provide data which will facilitate the pilot’s awareness with respect to
surrounding factors that may affect the overall conduct of the flight.
The standby instruments (altimeter, airspeed, attitude, and magnetic compass)
are completely independent from the PFD and will continue to operate in the
event the PFD is not usable. These standby instruments should be included in the
pilot’s normal instrument scan and may be referenced if the PFD data is in
question. A second G500/G600 system installed on the co-pilot’s side does not
require additional standby instruments.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 12 of 52
Page 13
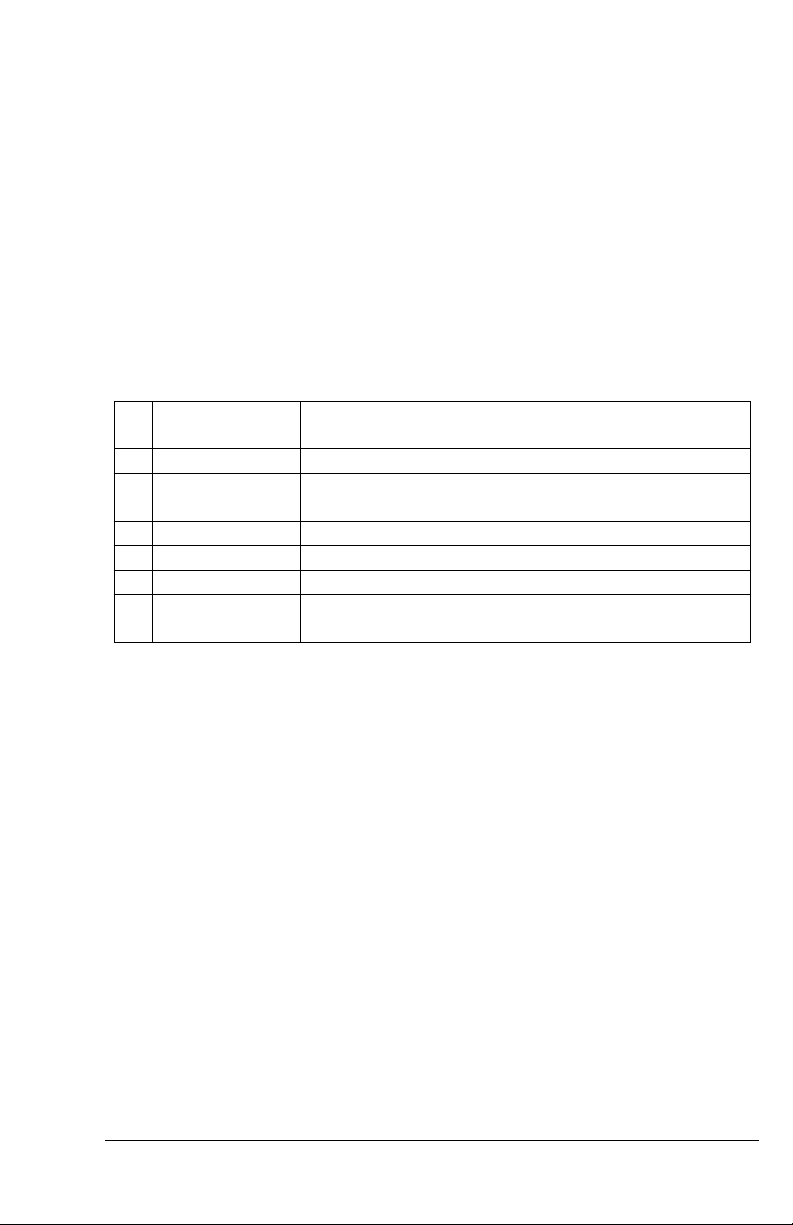
Circuit
Breaker Label
Equipment
PFD
Garmin Display Unit (PFD/MFD), GDU 620
ADAHRS
Air Data Attitude and Heading Reference System,
GSU 75(B)
AHRS
Attitude and Heading Reference System, GRS 77
ADC
Air Data Computer, GDC 74A/B
GAD
Garmin Adapter, GAD 43/43e
STBY ATT
Electric Standby Attitude Indicator (Except L-3
Trilogy and Mid Continent SAM installations)
1.2 System Power Sources
The G500/G600 system depends on electrical power to function. The Garmin
Display Unit (GDU) and Air Data Attitude and Heading Reference System
(ADAHRS) (or separate AHRS and ADC) are directly tied to the aircraft’s main
or essential bus and energized when the aircraft master switch is turned on. Other
systems, like the navigation equipment, weather datalink, autopilot and Adapter
(GAD) are typically located on the avionics bus and may not be functional when
this bus is powered off.
The major components of the G500/G600 are circuit breaker protected with
resettable type breakers available to the pilot. These breakers are located at the
main or essential bus circuit breaker panel and labeled as follows (appropriate
boxes will be checked):
In dual installations the pilot side equipment is suffixed with the number 1 and
the copilot side equipment is suffixed with the number 2. For example: PFD 1
and PFD 2.
Equipment that receives power from two different circuit breakers will be
suffixed with the letters A and B. For example: PFD 1A and PFD 1B, or
PFD 2A and PFD 2B.
1.3 Navigation Sources
The G500/G600 requires at least one Garmin GPS/SBAS navigation unit to
ensure the integrity of the Attitude and Heading Reference System. The
ADAHRS or AHRS will still operate in a reversionary mode if the GPS fails,
and the attitude display on the PFD will still be presented; see Paragraph 2.8.
The G500/G600 HSI can be selected to display course deviation information
from up to four independent sources: two GPS, and two VHF NAV. In addition,
the HSI can display two simultaneous bearing pointers sourced from GPS, VHF
NAV, or ADF. DME distances can be displayed adjacent to the HSI.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 13 of 52
Page 14

1.4 Synthetic Vision Technology (SVT)
SVT uses an internal terrain database and GPS location to present the pilot with
a synthetic view of the terrain in front of the aircraft. The purpose of the SVT
system is to assist the pilot in maintaining situational awareness with regard to
the terrain and traffic surrounding the aircraft. A typical SVT display is shown
below:
SVT provides additional features on the G500/G600 primary flight display
(PFD) which display the following information:
Synthetic Terrain; an artificial, database derived, three dimensional
view of the terrain ahead of the aircraft within a field of view of
approximately 25 degrees left and 25 degrees right of the aircraft
heading.
Obstacles; obstacles such as towers, including buildings over 200 AGL
that are within the depicted synthetic terrain field of view. Powerlines
are not depicted in synthetic vision.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 14 of 52
Page 15

Flight Path Marker (FPM); an indication of the current lateral and
vertical path of the aircraft. The FPM is always displayed when
synthetic terrain is selected for display.
Traffic; a display on the PFD indicating the position of other aircraft
detected by a traffic system interfaced to the G500/G600 system.
Horizon Line; a white line indicating the true horizon is always
displayed on the SVT display.
Horizon Heading; a pilot selectable display of heading marks
displayed just above the horizon line on the PFD.
Airport Signs; pilot selectable “signposts” displayed on the synthetic
terrain display indicating the position of nearby airports that are in the
G500/G600 database.
Runway Highlight; a highlighted presentation of the location and
orientation of the runway(s) at the destination airport.
The synthetic terrain depiction displays an area approximating the view from the
pilot’s eye position when looking directly ahead out the windshield in front of
the pilot. Terrain features outside this field of view are not shown on the display.
The synthetic terrain display is intended to aid the pilot awareness of the terrain
and obstacles in front of the airplane. It may not provide either the accuracy or
fidelity, or both, on which to solely base decisions and plan maneuvers to avoid
terrain or obstacles. The synthetic vision elements are not intended to be used for
primary aircraft control in place of the primary flight instruments.
1.5 Autopilot Interface
The G500/G600 may optionally be interfaced to an autopilot. The G500/G600
typically provides course and heading datum to the autopilot based on the data
selected for display on the HSI. For aircraft equipped with multiple GPS/NAV
systems, the G500/G600 acts as a selection hub for the autopilot’s NAV mode,
and the G500/G600 may also provide GPS Steering (GPSS) data. Some
autopilots may have Flight Director capabilities which can be displayed on the
G500/G600 Attitude Indicator as a Single Cue Flight Director.
Optionally, the autopilot can capture the pre-selected altitude or couple to the
selected vertical speed if these capabilities are supported by the autopilot
equipment installed. Refer to the autopilot operator’s manual or autopilot
Airplane Flight Manual Supplement for the proper operation of the autopilot
system.
Not all autopilot systems are approved for coupling to vertical guidance on GPS
based approaches; consult the AFMS for the autopilot system.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 15 of 52
Page 16

1.6 Audio Panel
The G500/G600 system may be interfaced to the aircraft audio panel to provide
aural alerting generated by the G500/G600 (required for TAWS-B installations).
1.7 Traffic Display
The G500/G600 system can display traffic data from interfaced traffic systems.
Sources of traffic data include TIS-A traffic via the Garmin GTX Series Mode-S
Transponders, TAS/TCAS traffic from various active traffic awareness systems,
and ADS-B traffic from Garmin ADS-B transceivers and ADS-B In capable
Garmin transponders. The information from these systems is displayed on and
controlled using the MFD.
1.8 Weather Data
The G500/G600 system can display weather data from interfaced datalink
systems. Sources of weather data include the Garmin “GDL 69(A)” and “GDL
69(A) SXM” Sirius XM receivers, Garmin GSR 56 Iridium Transceiver, Garmin
GDL 88 ADS-B transceiver, and GTX 345 Transponder. If one of these optional
weather datalink receivers is installed, the pilot will be able to access graphical
and text weather products using the MFD.
The G500/G600 system can control various airborne weather radars and display
their data. Compatible weather radars include Garmin GWX weather radars, as
well as certain 3rd-party weather radars.
The G500/G600 system can display data from StormScope™ lightning detection
systems.
1.9 Video Display
The G500/G600 can display images from up to 2 video inputs. Video images are
displayed on the MFD. The G500/G600 does not provide a means to control the
video source; however the digital images from the video source can be adjusted
using the G500/G600.
1.10 Radar Altimeter
The G500/G600 supports the display of radar altitude on the PFD from certain
radar altimeters.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 16 of 52
Page 17

1.11 High Speed Data Bus Interface
Some Garmin equipment connected to the G500/G600 system utilizes the High
Speed Data Bus (HSDB) interface. HSDB is similar to an Ethernet bus and
provides a high-speed interface between Garmin avionics. Like Ethernet, data
between two units may be passed through intermediate “hub” units. Interfaced
equipment that uses HSDB includes the GTN 6XX/7XX navigators, GDL 69
series datalink receivers, GDL 88 ADS-B transceiver, GWX 68/70(R) weather
radars, GTS 8XX traffic systems, and GTX 3X5 Mode S/ES transponders.
The HSDB interfaces are installed to so that maximum data path redundancy is
achieved. However, depending on the number of HSDB units installed, failure of
one HSDB unit may result in loss of data on the G500/G600 from “downstream”
HSDB units. Any loss of data will be annunciated on the G500/G600.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 17 of 52
Page 18

Standby
Attitude
Standby
Airspeed
Standby
Altimeter
Magnetic
Compass
Equipment Installed per this STC
Standby Instruments
[3] [4]
PFD/MFD Display
GDU 620
[1] Alternatively, the G500/G600 system can include both the GRS 77 AHRS
and GDC 74( ) ADC in place of the GSU 75(B) ADAHRS.
[2] Audio panel connection to GDU 620 is recommended for tones and aural
alerts generated by the GDU 620. This MUST be connected if TAWS and/
or SVT is enabled.
[3] Standby instruments are not required for VFR-only operation.
[4] The requirement for standby instruments can be fulfilled using either
separate standby instruments approved under this STC (refer to Sections
2.5.2 and 3.2.2) or Electronic Standby Instruments System (ESIS) shown
to be compatible with this STC. This STC does not approve the ESIS
installation. Refer to Section E.1 for a list of ESIS that have been
determined by Garmin to be compatible.
ADAHRS
Magnetometer
GMU 44
GSU 75(B) [1]
Temperature Probe
GTP 59
No. 1 GPS/SBAS Navigator
(required)
No. 1 VOR/Localizer/GS
(optional)
No. 2 GPS/SBAS Navigator
(optional)
No. 2 VOR/Localizer/GS
(optional)
Autopilot/Flight Director
(optional)
ADF, DME
(optional)
Audio Panel
(optional) [2]
Traffic
(optional)
Datalinks
(optional)
Adapter (optional)
GAD 43/43e
to Autopilot
Weather Radar
(optional)
Radar Altimeter
(optional)
Stormscope
(optional)
Existing Equipment
(already installed in aircraft)
Video Source
(optional)
GAD 43e only
analog nav receiver, altitude
preselect, analog radar altimeter,
DME, ADF, Marker Beacon
1.12 Single G500/G600 Operational Block Diagram
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 18 of 52
Page 19

Equipment Installed per this STC
Temperature Probe
GTP
59
#
1
Pilot PFD
/
MFD Display
GDU
620
Copilot PFD
/
MFD Display
GDU
620
Audio Panel
(
optional
)
[
2
]
Datalinks
(
optional
)
Autopilot
/
Flight Director
(
optional
)
[
4
]
ADF
,
DME
(
optional
)
[
4
]
No.
1
VOR
/
Localizer
/
GS
(
optional
)
[
4
]
No.
1
GPS
/
SBAS Navigator
(
required
)
ADAHRS
Magnetometer
GMU
44
#
2
GSU
75
(
B
)
#
2
[
1
]
Temperature Probe
GTP
59
#
2
No
.
2
GPS
/
SBAS Navigator
(
required
)
No.
2
VOR
/
Localizer
/
GS
(
optional
)
[
4
]
Adapter
(
optional
)
GAD
43
/
43
e
to Autopilot
Existing Equipment
(
already installed in
aircraft
)
Weather Radar
(
optional
)
[
4
]
Traffic
(
optional
)
[
4
]
Radar Altimeter
(
optional
)
Stormscope
(
optional
)
[
4
]
Video Source
(
optional
) [
5
]
Video Source
(
optional
)
[
5
]
ARINC
708
WXR Only
GAD
43
e only
analog nav receiver, altitude
preselect
,
analog radar altimeter
,
DME,
ADF
,
Marker Beacon
Only if GDU
1 is not connected
Standby
Attitude
Standby
Airspeed
Standby
Altimeter
Magnetic
Compass
Standby Instruments
(
required on pilot side only
)
[
3
]
[
1
]
Alternatively
,
the G
500
/
G
600
system can include both the GRS
77
AHRS and GDC
74
( )
ADC in
place of the GSU
75
(
B
)
ADAHRS
.
[
2
]
Audio panel connection to GDU
620
is recommended for tones
and aural alerts generated by the
GDU
620
.
This MUST be
connected if TAWS and
/
or SVT is
enabled
.
[
3
]
Standby instruments are not
required for VFR
-
only operation
.
[
4
]
Optional Equipment
:
Connection
of optional equipment to both
GDUs is not required.
Functions
provided by the optional
equipment will only be available
on the GDU to which the optional
equipment is connected
.
ADAHRS
GSU
75
(
B
)
#
1
[
1
]
Magnetometer
GMU
44
#
2
1.13 Dual G500/G600 Operational Block Diagram
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 19 of 52
Page 20

1.14 Definitions
The following terminology is used within this document:
ADAHRS: Air Data Attitude & Heading Reference System
ADC: Air Data Computer
ADF: Automatic Direction Finder
ADS-B: Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast
AHRS: Attitude & Heading Reference System
AUX: Auxiliary
BARO: Barometric Pressure
BRG: Bearing
CDI: Course Deviation Indicator
CRS: Course
DME: Distance Measuring Equipment
FD: Flight Director
FPM: Flight Path Marker
GDU: Garmin Display Unit
GPS: Global Positioning System
GPSS: GPS Roll Steering
HDG: Heading
HSI: Horizontal Situation Indicator
IFR: Instrument Flight Rules
IMC: Instrument Meteorological Conditions
LOI: Loss of Integrity
MFD: Multi Function Display
PFD: Primary Flight Display
SBAS: Space-based Augmentation System
SD: Secure Digital
SVT: Synthetic Vision Technology
TAS: Traffic Awareness System
TAWS: Terrain Awareness and Warning System (a TSO-C151b function)
TCAS: Traffic Collision and Avoidance System
TIS: Traffic Information Service
VFR: Visual Flight Rules
VMC: Visual Meteorological Conditions
V/S: Vertical Speed
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 20 of 52
Component
Page 21

Identification
Software Version
GDU 620
PFD/MFD
7.12
GDC 74( )
ADC
3.11
GRS 77
AHRS
3.04
GSU 75(B)
ADAHRS
2.02
GMU 44
Magnetometer
011-00870-00: 2.01
011-00870-10/20: 2.05
GAD 43(e)
(optional)
Signal Adapter
2.02
Section 2. LIMITATIONS
2.1 Cockpit Reference & Pilot’s Guide
The Garmin G500/G600 Cockpit Reference Guide P/N 190-00601-03, Revision
G or later appropriate revision must be immediately available to the flight crew.
2.2 System Software Requirements
The G500/G600 must utilize the following or later FAA approved software
versions for this AFMS revision to be applicable:
2.3 Moving Map
The moving map on the MFD is advisory in nature and shall not be used for
course guidance. The moving map on the MFD must be cross checked for
correctness against the PFD HSI, published charts, or other approved sources of
navigation information.
2.4 Database Cards
The SD/database card must not be removed or inserted during flight and/or while
the GDU is powered on.
Databases identified as intended for helicopter use shall not be used. These
databases are identified by the word “HELI” or “HELICOPTER” in their title.
2.5 ADAHRS and AHRS Operational Area
The ADAHRS or AHRS used in the G500/G600 is limited in its operational
area: IFR Operations are prohibited north of 72N and south of 70S latitudes. In
addition, IFR operations are prohibited in the following four regions:
1) North of 65° North latitude between longitude 75° W and 120° W
2) North of 70° North latitude between longitude 70° W and 128° W
3) North of 70° North latitude between longitude 85° E and 114° E
4) South of 55° South latitude between longitude 120° E and 165° E
Loss of the G500/G600 heading and attitude may occur near the poles, but this
will not affect the GPS track or standby attitude indicator.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 21 of 52
Page 22

2.6 Magnetic Variation Operational Area
IFR operations are prohibited in areas where the magnetic variation is greater
than 99.9 degrees East or West.
2.7 Navigation Angle
The GDU 620 Navigation Angle, which defines whether the GDU 620 headings
are referenced to True or Magnetic North can be set to either True or Magnetic
on the AUX page. The Navigation Angle set in the GDU 620 shall be set by the
pilot to match that which is set on all GPS/SBAS navigators interfaced to the
unit.
2.8 ADAHRS and AHRS Normal Operating Mode
The Attitude and Heading Reference System integrity monitoring function
requires GPS and Air Data to be provided to the AHRS. An ADAHRS receives
Air Data internally and only requires GPS.
Note: Attitude will remain valid if either GPS or Air Data is lost.
Flight in IMC is not authorized unless the ADAHRS or AHRS is receiving valid
GPS and valid Air Data. The G500/G600 monitors these integrity systems
automatically and will alert the pilot when the ADAHRS or AHRS is not
receiving GPS or Air Data.
Note: In dual GPS installations, only one GPS needs to be available to the
ADAHRS or AHRS for IFR flight.
2.9 Airspeed Limitations and Indicator Markings
The original type design approved airspeed limitations remain in effect. The
airspeed limitations stated in the AFM/POH, standby airspeed indicator and/or
airspeed limitation placards must be observed.
The G500/G600 airspeed tape displays red/white striping to indicate the
maximum allowable airspeed (VNE/VMO/MMO). This maximum allowable
airspeed display is configured to indicate the appropriate maximum allowable
airspeed for the airplane, including variations for altitude or Mach number.
The G500/G600 airspeed tape displays a red low-speed awareness band at the
lower range of the airspeed tape. This low-speed awareness band is configured to
a fixed value. It does not indicate an actual or calculated stall speed and does not
adjust with variations in aircraft weight or other factors.
All other G600 airspeed tape indications are configured to indicate the original
type design limitations. The G500/G600 airspeed tape does not adjust these
additional markings (including VNO, landing gear, or flap speed limitations) for
variations with aircraft weight, altitude, or other factors.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 22 of 52
Page 23

2.10 Aerobatic Maneuvers
Do not conduct aerobatic maneuvers if uninterrupted attitude information is
required on the PFD.
2.11 Course Pointer Auto Slewing
The G500/G600 HSI will auto slew, i.e. automatically rotate the GPS course
pointer to the desired course defined by each GPS leg. The system will also auto
slew the VHF NAV course pointer when the CDI transitions to a LOC setting if
an ILS, LOC, LOC BC, LDA, or SDF approach is loaded in the GPS/SBAS
navigator.
The VHF NAV (green) course pointer will only auto slew if the approach is
loaded in the navigator, a LOC frequency is loaded in the active NAV frequency,
and then the HSI source is changed to the corresponding VHF NAV for the
approach. Back Course approaches will auto slew to the reciprocal course.
The system is not capable of automatically setting the inbound VHF NAV course
pointer if an approach is not loaded in the GPS/SBAS Navigation System. Auto
slewing the VHF NAV course pointer to the correct selected course is a database
dependent function.
The pilot shall confirm the inbound course pointer is set to the proper course
prior to initiating any transition on any VHF NAV approach.
2.12 Synthetic Vision Technology
The use of the synthetic vision display elements alone for aircraft control without
reference to the G500/G600 primary flight instruments or the aircraft standby
instruments is prohibited.
The use of the synthetic vision display alone for navigation, or obstacle, terrain,
or traffic avoidance is prohibited.
2.13 Autopilot Interface
Flight director commands on PFD 2 are repeated from PFD 1. When utilizing the
flight director display on PFD 2, the pilot shall ensure that the CDI source and
BARO settings on PFD 2 match those on PFD 1.
For installations where the GAD 43 provides attitude information to the
autopilot, the GAD 43 autopilot disconnect mechanism shall be tested and
operational before each flight using the autopilot.
2.14 Terrain Proximity Function
The G500/G600 terrain configuration is indicated on the dedicated terrain page
of the MAP group. “TERRAIN PROXIMITY” will be displayed as the page title
if this function is configured. Terrain information appears on the map and terrain
display pages as red and amber and is depicted for advisory use only. Obstacle
and wire information appears on the map and terrain display pages as red, amber,
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 23 of 52
Page 24

and white and is depicted for advisory use only. Aircraft maneuvers and
navigation must not be predicated upon the use of the terrain display. Terrain,
obstacle, and wire information is advisory only and is not equivalent to warnings
provided by TAWS.
The terrain display is intended to serve as a situational awareness tool only. By
itself, it may not provide either the accuracy or the fidelity on which to base
decisions and plan maneuvers to avoid terrain or obstacles.
2.15 TAWS Function [GDU 620 Units with internal TAWS]
Only the G600 system optionally contains Class B TAWS, a TSO-C151b
certified function. The G600 terrain configuration is indicated on the dedicated
terrain page of the MAP group. “TAWS-B” will be displayed as the page title if
this function is configured. Pilots are authorized to deviate from their current
ATC clearance to the extent necessary to comply with TAWS warnings.
Navigation shall not be predicated upon the use of TAWS.
To avoid unwanted alerts, TAWS shall be inhibited when landing at an airport
that is not included in the airport database.
2.16 Datalinked Weather Display (XM, GFDS, FIS-B weather)
This limitation applies to datalinked weather products from SiriusXM via a GDL
69/69A, FIS-B via a Garmin ADS-B receiver, and Connext via a GSR 56.
Do not use data link weather information for maneuvering in, near, or around
areas of hazardous weather. Information provided by data link weather products
may not accurately depict current weather conditions.
Do not use the indicated data link weather product age to determine the age of
the weather information shown by the data link weather product. Due to time
delays inherent in gathering and processing weather data for data link
transmission, the weather information shown by the data link weather product
may be significantly older than the indicated weather product age.
Do not rely solely upon data link services to provide Temporary Flight
Restriction (TFR) or Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) information. Not all TFRs and
NOTAMS may be depicted on the G500/G600.
2.17 Traffic Display
Traffic may be displayed on the G500/G600 System when connected to an
approved optional TCAS, TAS, TIS, or ADS-B traffic device. These systems are
capable of providing traffic monitoring and alerting to the pilot. Traffic shown
on the display may or may not result in traffic alerts. The display of traffic is an
aid to visual acquisition and shall not be utilized for aircraft maneuvering.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 24 of 52
Page 25

2.18 Active Weather RADAR
RADAR is broadcasting energy while in Weather or Ground mapping modes. If
the G500/G600 system is configured to control an airborne weather radar unit,
observe all safety precautions, including:
Do not operate in the vicinity of refueling operations.
Do not operate while personnel are in the vicinity (approximately 20 feet) of
the radar sweep area.
WARNING
If a radar system is installed, it generates microwave
radiation and improper use, or exposure, may cause
serious bodily injury.
DO NOT OPERATE THE RADAR EQUIPMENT
UNTIL YOU HAVE READ AND CAREFULLY
FOLLOWED THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND
INSTRUCTIONS in the USER MANUAL.
2.19 StormScope® Display
StormScope® lightning information displayed by the G500/G600 is limited to
supplemental use only. The use of the StormScope® lightning data on the display
for hazardous weather (thunderstorm) penetration is prohibited. StormScope®
lightning data on the display is intended only as an aid to enhance situational
awareness of hazardous weather, not penetration. It is the flight crew’s
responsibility to avoid hazardous weather using official weather data sources.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 25 of 52
Page 26

Equipment
Number
installed
VFR
IFR
Primary/Multi Flight Display
1 or 2
1a* 1 Garmin GPS/SBAS Navigator
1 or 2
-
1
OR
Air data and Attitude / Heading Unit (ADAHRS)
1 or 2
1a* 1 Attitude / Heading Unit (AHRS)
1 or 2
- 1 Air data computer (ADC)
1 or 2
1a* 1 Magnetometer (GMU)
1 or 2
-
1
Standby Attitude Indicator
1 - 1
Standby Airspeed Indicator
1
1b 1 Standby Altimeter
1
1b 1 Magnetic Compass
1 1 1
2.20 Kinds of Operations
Unless placarded as limited to VFR only operations, G500/G600 equipment
installed in a certified aircraft is approved for Day and Night / VFR and IFR
operations in accordance with 14 Code of Federal Regulations Part 91, Part 121,
and Part 135 when appropriately maintained.
The table below lists the minimum fully functional G500/G600 System
Equipment ** required for IFR flight operations:
* For VFR operations under 14 CFR Part 91, the aircraft shall have one source
of altitude and airspeed information. This may be from either the PFD or the
standby instruments. (i.e. all “1a” items or all “1b” items from the table above)
** For IFR flight a fully functional G500/G600 system shall not generate system
alerts, which indicate faults within the system or any interfaced equipment.
2.21 KFC 275/325 Altitude Preselect
When the altitude preselect option is installed with KFC 275/325 autopilots,
SOFT RIDE (SR) mode shall be disengaged during altitude capture mode
(ALTC). The following placard must be installed near the autopilot mode
controller or above PFD 1:
“DISENGAGE SOFT RIDE DURING ALTITUDE CAPTURE (ALTC)”
2.22 Type Ratings
Unless otherwise authorized by this section, operations are prohibited in aircraft
that require a type rating under 14 CFR 61.31(a).
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 26 of 52
Page 27

2.23 Electronic Standby Instrument Power
The independent power source for the electronic standby instrument(s) shall be
verified to be operational before flight, or the electronic standby(s) must be
considered inoperative. For the verification procedure, refer to the approved
Airplane Flight Manual and/or Instructions for Continued Airworthiness for the
independent power source.
2.24 Electronic Flight Bag (EFB) Applications
Class 3 EFB applications have not been evaluated as part of this STC. Use of the
system for EFB applications (such as the moving map or electronic charts) is not
authorized if additional evaluation or operational approval is required unless that
approval has been obtained.
2.25 Surface Operations
SafeTaxi or Chartview functions shall not be used as the basis for ground
maneuvering. SafeTaxi and Chartview functions do not comply with the
requirements of AC 20-159 and are not qualified to be used as an airport moving
map display (AMMD). SafeTaxi and Chartview use is limited to airport surface
orientation to improve flight crew situational awareness during ground
operations.
2.26 MFD Video Display
Video images displayed on the MFD are intended for use as an aid to situational
awareness only. Aircraft maneuvering based solely on the MFD video display is
prohibited.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 27 of 52
Page 28

Section 3. EMERGENCY PROCEDURES
3.1 Emergency Procedures
3.1.1 PFD 1 Failure
PFD 1 failure is indicated by the loss of displayed information on the PFD,
including blank, frozen, or unresponsive display.
1. Use standby flight instruments for attitude, airspeed, altitude, and
heading reference.
2. Refer directly to navigation source for navigation information (such as
GPS).
3. Seek VFR conditions or land as soon as practical.
If autopilot is engaged:
4. Verify autopilot mode and cross check against standby flight and
navigation data.
3.1.2 ADAHRS Failure
Failure of a combined Air Data Attitude and Heading Reference System
(ADAHRS) may result in either individual or simultaneous AHRS and/or ADC
failure. AHRS and ADC failures are described in sections 3.1.3 and 3.1.4.
3.1.3 AHRS Failure
Attitude and Heading Reference System (AHRS) failure is indicated by removal
of the sky/ground presentation, a red X, and a yellow “ATTITUDE FAIL” on the
PFD. Rate-of-turn information (heading trend vector) will not be available. A
heading failure will also occur as described in Section 3.2.1.
1. Use Standby Attitude Indicator.
2. Seek VFR conditions or land as soon as practical.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 28 of 52
Page 29

3.1.4 Air Data Computer (ADC) Failure
Air Data Computer failure is indicated by a red X and yellow text over the
airspeed, altimeter, vertical speed, TAS and OAT displays. Some derived
functions, such as true airspeed and wind calculations will also be lost. If valid
GPS data is available, the PFD will automatically revert to display GPS
calculated altitude relative to mean sea level. This GPS altitude is displayed
above the altitude tape.
1. Use Standby Airspeed Indicator and Altimeter
2. Seek VFR conditions or land as soon as practical
If ADC 1 has failed and PFD 1 AIR DATA switch is installed:
3. PFD 1 AIR DATA switch – Select ADC 2
NOTE
ALT NO COMP and IAS NO COMP alerts will be present.
3.1.5 Loss of Electrical Power
In the event of a total loss of electrical power, the G500/G600 system will cease
to operate and the pilot must utilize the standby instruments to fly the aircraft.
3.1.6 Loss of Electrical Power to 3-inch Electric Standby Attitude
Indicator (flashing amber STBY PWR light) (MidContinent 4300 Series)
When a 3-inch electric standby attitude indicator is installed, loss of primary
electrical power to the attitude indicator is annunciated by a flashing amber light
on the indicator. The attitude indicator is operating on backup battery power, and
pilot action is required for the gyro to continue operating.
1. Press STBY PWR button on the indicator one time.
2. Verify that the flashing amber light extinguishes.
3. Verify that the red gyro warning flag is not displayed.
4. Seek visual meteorological conditions (VMC) or land as soon as
practical (operation of standby attitude indicator is limited by battery
life).
WARNING
Do not press the STBY PWR button a second time after the
flashing amber light extinguishes. This will turn off the backup
battery and the red gyro warning flag will be displayed. If the
STBY PWR button is inadvertently pressed and the red gyro
warning flag is displayed, press the STBY PWR button again
to return to battery power operation (red gyro warning flag
should not be displayed).
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 29 of 52
Page 30

3.1.7 Loss of Electrical Power to 2-inch Electric Standby Attitude
Indicator (flashing or steady amber STBY text) (MidContinent 4200 Series)
When a 2-inch electric standby attitude indicator is installed, loss of primary
electrical power to the attitude indicator is annunciated by amber STBY text on
the Annunciation Control Unit. The attitude indicator is operating on backup
battery power, and pilot action may be required for the gyro to continue
operating.
If the amber STBY text is flashing (manual operation):
1. Press the STBY PWR button one time.
2. Verify that the amber STBY text is steadily illuminated.
3. Verify that the red gyro warning flag is not displayed.
4. Seek visual meteorological conditions (VMC) or land as soon
as practical (operation of standby attitude indicator is limited
by battery life).
If the amber STBY text is steadily illuminated (automatic operation):
1. Verify that the red gyro warning flag is not displayed.
2. Seek visual meteorological conditions (VMC) or land as soon
as practical (operation of standby attitude indicator is limited
by battery life).
WARNING
Do not press the STBY PWR when the amber STBY text is
steadily illuminated. This will turn off the backup battery and
the red gyro warning flag will be displayed. If the STBY PWR
button is inadvertently pressed and the red gyro warning flag is
displayed, press the STBY PWR button again to return to
battery power operation (red gyro warning flag should not be
displayed).
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 30 of 52
Page 31

3.1.8 TAWS WARNING
Red annunciator on PFD and aural “PULL UP”:
1. Disconnect Autopilot.
2. Initiate maximum power climb at best angle of climb airspeed (VX).
After warning ceases:
3. Climb and maintain safe altitude.
4. Advise ATC of altitude deviation, if appropriate.
NOTE
Only vertical maneuvers are recommended, unless either
operating in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), or the
flight crew determines, based on all available information, that
turning in addition to the vertical escape maneuver is the safest
course of action, or both.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 31 of 52
Page 32

3.2 Abnormal Procedures
3.2.1 Heading Failure
Heading failure is indicated by replacement of the digital heading display with
amber “HDG” text and a red X.
If valid GPS ground track is available, it will automatically be displayed in place
of heading. The HSI heading bug and course pointer will continue to function
normally, using GPS ground track as a reference instead of magnetic heading.
If GPS track is not available:
1. Use standby compass for heading reference.
2. Verify selected course using “CRS” button and PFD knob.
CAUTION
No directional references will be displayed on HSI. The
heading bug will be removed, and the course pointer will
remain fixed at the top of the HSI regardless of aircraft
heading. Course deviation indications will behave similar to a
traditional CDI. VOR deviations will be relative the selected
course with a TO/FROM indication. Localizer deviations will
not be affected by the selected course, and reverse sensing will
occur when tracking inbound on a localizer back course.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 32 of 52
Page 33

3.2.2 GPS Data Failure
GPS data failure may be indicated by any or all of following:
Loss of GPS course deviation information on HSI
Amber “LOI” text on the HSI
Amber “NO GPS POSITION” text on the MFD moving map
Loss of waypoint bearing or distance information
1. Select alternate GPS source, if available, by pressing “1-2” softkey on
PFD.
If alternate GPS source is not available:
2. Select alternate navigation source using “CDI,” “1-2,” or “BRG”
softkeys on PFD, or refer directly to external navigation data.
3.2.3 Navigation Data Failure (VOR/LOC/GS/ADF)
Navigation data failure may be indicated by any or all of following:
Loss of course deviation information on HSI
Loss of glideslope/glidepath information on PFD
Loss of bearing pointer on HSI
1. Select alternate navigation source using “CDI,” “1-2,” or “BRG”
softkeys on PFD, or refer directly to external navigation data.
3.2.4 Synthetic Vision (SVT) Failure
Several data sources are required to display SVT on the PFD (GPS, terrain
database, attitude information, etc.). If any of these required data sources
become unreliable or unavailable, SVT will automatically be removed, and the
PFD will revert to the standard display of blue sky over brown ground. If there is
a discrepancy between the SVT display and the actual terrain around the aircraft,
SVT should be turned off manually.
To turn off SVT:
1. Press the “PFD” softkey on the PFD.
2. Press the “SYN VIS” softkey to turn off SVT.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 33 of 52
Page 34

3.2.5 Electrical Load Shedding
The following equipment is considered non-essential. If it becomes necessary to
reduce electrical load (for example, during loss of generators or alternators),
power to these units may be removed in the order listed.
1. PFD 2 circuit breaker(s) [if installed] – PULL
2. ADAHRS 2 circuit breaker(s) [if installed] – PULL
3. AHRS 2 circuit breaker(s) [if installed] – PULL
4. ADC 2 circuit breaker(s) [if installed] – PULL
5. GAD circuit breaker(s) [if installed] – PULL
3.2.6 TAWS Caution
TAWS Cautions include an amber or or
annunciator on the PFD and one of the following aural messages:
“Terrain Ahead” or “Caution Terrain”
“Obstacle Ahead” or “Caution Obstacle”
“Wire Ahead” or “Caution Wire”
“Too Low, Terrain”
“Sink Rate”
“Don’t Sink”
If a TAWS Caution occurs, take corrective action until the alert ceases. Stop
descending or initiate either a climb or a turn, or both as necessary, based on
analysis of all available instruments and information.
3.2.7 GAD 43 AC Reference Lost of Reference Timeout Fault
If “AC Reference Lost” or “Reference Timeout Fault” message is present the
reference signal used by the autopilot is unavailable and the autopilot may
deviate from the intended path or may disconnect.
1. Immediately disengage the autopilot and do not re-engage.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 34 of 52
Page 35

3.3.1 Warning annunciations – Red
Annunciation
Pilot Action
Cause
ATTITUDE
FAIL
Use
Standby
Attitude.
Display system is not receiving attitude
reference information from the ADAHRS or
AHRS; accompanied by the removal of
sky/ground presentation and a red X over the
attitude area.
AIRSPEED
FAIL
Use
Standby
Airspeed.
Display system is not receiving airspeed input
from the ADAHRS or ADC; accompanied by a
red X through the airspeed display.
ALTITUDE
FAIL
Use
Standby
Altitude.
Display system is not receiving altitude input
from the ADAHRS or ADC; accompanied by a
red X through the altimeter display.
VERT SPD
FAIL
Cross check
instruments.
Display system is not receiving vertical speed
input from the ADAHRS or ADC; accompanied
by a red X through the vertical speed display.
HDG
Use
Standby
Magnetic
Compass or
GPS track
information.
Display system is not receiving valid heading
input from the ADAHRS or AHRS;
accompanied by a red X through the digital
heading display.
Red X
Reference
the data
source or
alternate
equipment.
A red X through any display field, indicates that
display field is not receiving data or is
corrupted.
3.3 Warnings, Cautions, and Advisories
The following tables show the color and significance of the warning, caution,
and advisory messages which may appear on the G500/G600 displays.
NOTE
The G500/G600 Cockpit Reference Guide and the
G500/G600 Pilot’s Guide contain detailed descriptions of the
annunciator system and all warnings, cautions and advisories.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 35 of 52
Page 36

3.3.2 Caution annunciations – Yellow
Annunciation
Pilot Action
Cause
CHECK
ATTITUDE
Autopilot will
automatically
disconnect.
Note: Only
appears with the
installation of an
optional GAD 43
adapter
Fly the aircraft
manually and
crosscheck GDU 620
attitude indication
with standby attitude
indicator and other
sources of attitude
information
(airspeed, heading,
altitude, etc.)
The GDU 620 attitude monitors have
detected an ADAHRS or AHRS
malfunction, or the inability to actively
monitor the ADAHRS or AHRS
output.
MISCOMP
(flag displayed
on PFD
attitude,
airspeed, or
altitude
indicators)
Cross-check the
flagged information
against other sources
to identify erroneous
information.
Difference detected between displayed
attitude, airspeed, or altitude (dual
installations only).
AHRS ALIGN
– Keep Wings
Level
Limit aircraft attitude
to ±10º bank and ±5º
pitch as AHRS
Aligns - OK to taxi.
Attitude and Heading Reference
System is aligning. ADAHRS or
AHRS may not align with excessive
pitch/bank angles.
AHRS ALIGN
– Remain
Stationary
Note: Only
appears with GSU
75 ADAHRS
Remain stationary
and allow AHRS to
finish initialization
and allow navigators
to acquire sufficient
GPS position.
Attitude and Heading Reference
System is aligning on the ground.
Additionally, the interfaced navigator
does not have sufficient GPS position.
NO GPS
POSITION
If the system is
configured with dual
GPS, press the 1-2
button.
GPS data on the selected system is no
longer valid. The Moving Map and
associated data are not updating.
TRAFFIC
Visually acquire the
traffic to see and
avoid.
The interfaced traffic system has
determined that nearby traffic may be
a threat to the aircraft.
No Traffic
Data
Use vigilance, as the
traffic sensor is not
able to detect traffic.
The configured traffic system is not
able to detect traffic and / or provide
the pilot with any traffic awareness.
NO AP DATA
Verify autopilot
mode of operation
using alternate
means.
Autopilot mode of operation is not
available.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 36 of 52
Page 37

TER N/A,
TER FAIL
Use vigilance, terrain
depiction is no
longer provided.
Database errors or lack of required
GPS position.
TAWS N/A,
TAWS FAIL
Use vigilance, terrain
depiction and TAWS
alerting is no longer
provided.
Database errors or lack of required
GPS position.
NO DATA
Displayed on
dedicated display
pages. Indicates that
data from the
interfaced sensor is
not available
Loss of connection or failure of
interfaced sensor.
3.3.3 Advisories – White
Annunciation
Pilot Action
Various Alert
Messages may
appear under the
MFD ALERTS soft
key.
View and understand all advisory messages. Typically, they
indicate communication issues within the G500/G600
System. Refer to the G500/G600 Cockpit Reference for
appropriate pilot or service action.
A/C Reference
Lost or
Reference
Timeout Fault
The A/C reference signal used for attitude provided to the
autopilot has been lost. Disconnect the autopilot and do not
re-engage.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 37 of 52
Page 38

Section 4. NORMAL PROCEDURES
Refer to the Garmin G500/G600 PFD/MFD System Cockpit Reference Guide
P/N 190-00601-03 or G500/G600 Pilot’s Guide P/N 190-00601-02 for normal
operating procedures. This includes all Primary Flight Display and MultiFunction Display information.
Although intuitive and user friendly, the G500/G600 System requires a
reasonable degree of familiarity to avoid becoming too engrossed at the expense
of basic instrument flying in IMC and basic see-and-avoid procedures in VMC.
Pilot workload will be higher for pilots with limited familiarity in using the unit
in an IFR environment, particularly without the autopilot engaged. Garmin
provides training material with the Cockpit Reference Guide and the detailed
Pilot’s Guide. Pilots should take full advantage of these training tools to enhance
system familiarization.
4.1 PFD Knob & PFD Soft Keys
The basic PFD controls are on the side and bottom of the PFD, next to and
beneath the PFD display. The rotary knob performs the function annunciated on
the display just to the upper left of the HSI: HDG, CRS, ALT, V/S, or BARO. If
no function is annunciated then the knob is providing a HDG function. Assigning
the function of the knob is done by pressing/releasing one of the dedicated
function buttons to the left of the display. The knob defaults back to HDG if it is
not rotated for a period of 10 seconds. The Garmin G500/G600 PFD/MFD
System Cockpit Reference Guide describes each function and its operation.
The soft keys at the bottom of the PFD display are used to configure the course
data displayed in the HSI (CDI button, 1-2 button) and select the optional
bearing pointers (BRG1 and BRG2 button) which may be overlaid in the HSI
presentation on the PFD. The soft keys operate by press and release. Note: In
dual G500/G600 installations, the CDI key located on the GNS units is not
operational. Consult the Garmin G500/G600 PFD/MFD System Cockpit
Reference Guide for a complete description.
The units and markings on the PFD are not user configurable. They match the
units as specified in the aircraft’s FAA approved Airplane Flight Manual and
standby instruments. Display and control of the airspeed references (VR, VX, VY,
and GLIDE) are made via the AUX page of the MFD; consult the Garmin
G500/G600 Cockpit Reference Guide for description and operation of these
references.
4.2 MFD Knobs & MFD Soft Keys
The MFD controls are on the side and bottom of the MFD, next to and beneath
the MFD display. The rotary knobs scroll through various page groups and pages
of the MFD and manipulate data and settings by pressing the knob to activate a
cursor.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 38 of 52
Page 39

Soft keys at the bottom of the display allow for some quick functions to be
performed on each page. The soft keys operate by press and release. More
detailed configuration is typically available by pressing the MENU button, which
is on the right side of the display.
Pressing and holding down the CLR key is a shortcut to get back to the main
map page on the MFD. This can be used as a quick way back, or when the pilot
has selected a submenu within the system. The functions available under the
MFD are explained in the Garmin G500/G600 Cockpit Reference Guide.
4.3 Altitude Synchronization
The pilot must synchronize the PFD BARO setting and the Standby Altimeter
Kollsman window with the local altimeter setting as appropriate. In dual
installations if synchronization between the units is enabled, setting either PFD
will adjust both PFDs, but the standby must still be set by the pilot. Reference
the Garmin G500/G600 Cockpit Reference Guide for a complete description and
the usage of synchronization in dual installations.
4.4 Electric Standby Attitude Gyro (Mid Continent 4200 and 4300 Series)
When an electric standby attitude gyro is installed, test the backup battery before
takeoff.
1. Apply power to electric standby attitude gyro and allow the gyro to
reach operating speed (approximately 5 minutes).
2. Verify that the red gyro flag is not in view.
3. Press and hold the STBY PWR button until the amber annunciator
begins to flash.
4. Verify that the green annunciator is displayed continuously and the red
annunciator is not displayed for the duration of the test (approximately
1 minute).
CAUTION
The standby attitude gyro must be considered inoperative if the
red annunciator is displayed during the test.
4.5 Synthetic Vision Technology
The SVT system may be turned on or off, as desired. To access the synthetic
vision system softkey menu, press the PFD softkey on the GDU 620, followed
by the SYN VIS softkey. Synthetic vision terrain, horizon headings, and airport
signs can be toggled on and off from this menu. Press the BACK softkey to
return to the root PFD menu.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 39 of 52
Page 40

4.6 Autopilot Operations with the G500/G600 System
The G500/G600 System offers various integration capabilities dependent mainly
upon the type of autopilot installed in a particular aircraft.
The G500/G600 installation in this aircraft provides the following autopilot
functions (appropriate boxes will be checked):
This installation does not interface with the autopilot (basic wing
leveling autopilot or no autopilot is installed in the aircraft).
Course / NAV Selection coupling to the autopilot.
Heading Bug coupling capability to the autopilot.
Roll Steering emulated via heading mode.
Roll Steering capable autopilot.
Altitude Pre-Selector integrated with the autopilot.
Vertical speed bug integrated with the autopilot
Flight Director display driven from external autopilot or FD computer.
Flight Director is not available with Synthetic Vision enabled.
A GAD 43 Adapter is installed in this aircraft
GAD 43 provides attitude to the autopilot
GAD 43 provides yaw rate to the yaw damper
GAD 43 provides baro correction to the altitude preselector
GAD 43 provides altitude preselect and/or vertical speed
GDU 620 provides attitude / air data to autopilot
4.6.1 Attitude and Rate Based Autopilots
Attitude-based autopilots may be driven by the standby gyro, a remote mounted
gyro, the GDU 620, or the GAD 43 adapter. If the GDU 620 or GAD 43 is
providing attitude to the autopilot, it will be indicated in section 4.6 above.
Otherwise, if the attitude-based autopilot is receiving attitude from the standby
or a remote gyro, the autopilot attitude input is independent of the attitude
displayed on the PFD.
Rate-based autopilots are driven by a turn coordinator gyro which may be
mounted in the instrument panel or remotely mounted. The autopilot rate input is
independent of the G500/G600 system.
The pilot must understand the autopilot system inputs to detect faults and
capabilities with inoperative equipment. Refer to the autopilot flight manual for
operational information.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 40 of 52
Page 41

GPSS
HDG
(toggle switch)
AP HDG
DATUM
GPSS
HDG
(push-button)
AP HDG
DATUM
4.6.2 Course / NAV Selection coupling to the autopilot
When operating the autopilot in NAV mode, the deviation information from the
installed navigation sources (i.e. GPS1, GPS2, NAV1, NAV2) is switched via
the G500/G600 PFD display. Whatever is displayed on the HSI is the NAV
source the autopilot is following. Most autopilots also use the course datum to
determine the best intercept angles when operating in NAV mode.
4.6.3 Heading Bug coupling capability to the autopilot
When operating the autopilot in HDG mode, the difference between the HDG
bug location on the HSI and the actual aircraft heading creates an error signal
which the autopilot will minimize by turning in the direction of the bug. If the
bug is turned more than 180 degrees, the autopilot may turn the airplane in the
opposite direction of the desired turn.
4.6.4 GPSS emulated via HDG mode
For autopilots that do not support digital GPSS signals, GPSS functionality may
be emulated by operating the autopilot in HDG mode and selecting GPSS on the
PFD. Depending on the installation, GPSS mode may be toggled via an external
switch located near the autopilot control panel, or by pressing and holding the
HDG button on the PFD. If an external switch is installed, it will be either a
toggle or push-button switch as depicted below.
OR
If the installation uses the HDG button on the PFD, the PFD Knob Mode
Indicator is expanded to label the button function.
GPSS OFF GPSS ON
When GPSS is selected on the PFD, the heading bug on the HSI changes to a
hollow outline and a crossed-out heading bug appears in the PFD Knob Mode
Indicator, indicating that the autopilot is not coupled to the heading bug. The bug
is still controllable and may still be used by the pilot for reference.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 41 of 52
Page 42

When GPSS is selected on the PFD, GPSS is annunciated in the lower left
portion of the PFD. The GPSS mode annunciation depends on the location of the
NAV STATUS information, as shown below.
NAV STATUS STYLE 1 NAV STATUS STYLE 2
NOTE
GPSS mode is selectable from PFD 2, but GPSS is not
annunciated on PFD 2. The GPSS commands to the autopilot
are based on the GPS source displayed on PFD 1.
When GPSS is selected on the PFD, GPSS turn commands are converted into a
heading error signal to the autopilot. When the autopilot is operated in HDG
mode, the autopilot will fly the turn commands from the GPS navigator selected
on PFD 1.
If the GPSS data is invalid (for example, if there is no active GPS leg) or the
selected HSI source on PFD 1 is not GPS, the annunciated GPSS text will be
yellow and a zero turn command will be sent to the autopilot.
4.6.5 Roll Steering capable autopilots
If the autopilot is already designed to receive Roll Steering information, the data
is transmitted via a digital communications bus from the G500/G600 to the
autopilot. The G500/G600 receives this data from the GPS. In dual GPS
installations, the G500/G600 sends Roll Steering information for the GPS which
is currently selected for use via the PFD 1-2 button.
4.6.6 Selected Altitude Bug Coupling
When installed appropriately, certain autopilots may be coupled to the PFD
selected altitude bug for altitude preselect and capture. Except as described in
this section, refer to the autopilot AFMS and/or Pilot’s Guide for autopilot
system operation.
4.6.6.1 S-Tec Autopilots
To preselect and capture a selected altitude:
1. Select the desired altitude with the PFD selected altitude bug.
2. Press/hold VS then press ALT on the autopilot programmer computer
to arm altitude hold mode.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 42 of 52
Page 43

4.6.6.2 Collins Autopilots
To preselect and capture a selected altitude:
1. Select the desired altitude with the PFD selected altitude bug.
2. Select ALT SEL mode on the autopilot flight control panel.
CAUTION
Changing the selected altitude bug while ALT SEL mode is
selected may result in autopilot mode changes. Verify the
autopilot mode after changing the selected altitude.
4.6.6.3 Bendix/King Autopilots
To preselect and capture a selected altitude:
1. Select the desired altitude with the PFD selected altitude bug.
2. Press and hold the ALT button on the PFD to arm or disarm the
selected altitude.
NOTE
When the selected altitude is armed for capture, ALT is
displayed in white text in the upper right corner of the PFD.
When altitude capture mode is active, ALTC is displayed in
green text in the upper right corner of the PFD. When a
KA 315 annunciator panel is installed, the “ALT ARM”
annunciator on this panel will not be operative.
NOTE
KFC 200/250 autopilots will inhibit glideslope (GS) mode if
altitude capture (ALTC) mode is engaged during glideslope
intercept.
CAUTION
Changing the selected altitude bug while ALTC mode is active
will result in cancellation of ALTC mode. Verify the autopilot
mode after changing the selected altitude.
4.6.6.4 Cessna Autopilots
To preselect and capture a selected altitude:
1. Select the desired altitude with the PFD selected altitude bug.
2. Press and hold the ALT button on the PFD to arm or disarm the
selected altitude.
NOTE
When the selected altitude is armed for capture, ARMED is
displayed in white text next to the selected altitude.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 43 of 52
Page 44

4.6.7 Vertical Speed Bug Coupling
Certain autopilots may be coupled to the PFD vertical speed bug for maintaining
a selected vertical speed. Except as described in this section, refer to the
autopilot AFMS and/or Pilot’s Guide for autopilot system operation.
4.6.7.1 S-Tec Autopilots
To select and maintain a vertical speed:
1. Select the desired vertical speed with the PFD vertical speed bug.
2. Press VS on the autopilot programmer computer to engage vertical
speed mode.
NOTE
The selected vertical speed will automatically be reduced
towards zero when approaching the selected altitude bug.
AUTO will appear in the vertical speed PFD knob mode
indicator when vertical speed is being reduced automatically.
Manually changing the selected vertical speed while AUTO is
displayed will cancel automatic vertical speed reduction.
4.6.7.2 Bendix/King Autopilots
To select and maintain a vertical speed:
1. Press and hold the VS button on the PFD to synch the VS to current
vertical speed and engage vertical speed mode.
2. Select the desired vertical speed with the PFD vertical speed bug.
NOTE
When VS mode is engaged, the VS bug will be synced to the
aircraft’s current vertical speed and the selected VS with flash
momentarily. VS is displayed in green text in the upper right
corner of the PFD to indicate that VS mode is engaged.
While VS mode is engaged, the vertical speed bug may be changed by:
Adjust the vertical speed bug with the PFD knob, or
Press and hold the vertical trim rocker switch on the autopilot in the
desired direction, or
Press the CWS button on the control wheel to synchronize the vertical
speed bug to the current vertical speed.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 44 of 52
Page 45

4.6.8 Flight Director Display
If autopilot flight director commands are interfaced to the G500/G600, they will
be presented as a single cue flight director on the PFD. Control of the flight
director is accomplished via the autopilot/flight director controller; there are no
pilot controls or adjustments for the flight director on the G500/G600.
The G500/G600 system limits the distance the flight director pitch commands
may deviate from the aircraft attitude icon. In the event that the pitch command
provided by the autopilot flight director is greater than the distance allowed by
the G500/G600, the command bars will be displayed at the maximum distance
allowed by the G500/G600. As the aircraft pitch changes to satisfy the command
bars, the bars will continue to be displayed at the maximum distance from the
aircraft attitude icon until the aircraft pitch deviation is within the command
display limit. In both examples below, the flight director is commanding
approximately 7 degrees pitch up. With SVT turned off, the 7 degree pitch up
command is displayed with the command bar at 7 degrees pitch up. With SVT
turned on, the G500/G600 limits the command bar shown as 4.5 degrees pitch
up, which is the maximum deviation that can be displayed. The G500/G600
system will hold the command bars at the same distance from the aircraft icon
until the aircraft pitch attitude is within 4.5 degrees of the command.
SVT Off SVT On
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 45 of 52
Page 46

4.6.9 GAD 43 Operation
The GAD 43 Adapter may provide attitude, heading, and barometric correction
information from the G500/G600 System to the autopilot. The GAD 43 can also
be configured to provide synchro heading output to other systems and its attitude
output can be used for RADAR stabilization. The GAD 43 has the ability to
disconnect the autopilot if an error in the GAD 43 output or the ADAHRS or
AHRS is detected. This disconnect mechanism must be tested prior to each flight
in the following manner:
1. Upon startup, an AP TEST soft key will be available on the PFD side of
the display.
2. Engage the AP while on the ground.
3. Press the AP TEST soft key and verify that the autopilot disconnects.
CAUTION
Do not use the autopilot if the AP TEST key fails to disengage
the autopilot normally.
NOTE
Pressing and holding the AP TEST key for longer than 1
second will prevent the test from running and the AP TEST
key will remain displayed.
Do not engage the autopilot if advisory “AC Reference Lost” or “Reference
Timeout Fault” is present.
4.6.10 Dual G500/G600 Autopilot Interface
If the installation has dual G500/G600 systems installed, control of navigation
course, heading, or altitude data affecting the autopilot from the co-pilot side can
only be made if the systems are synchronized with each other. Refer to the
Garmin G500/G600 Cockpit Reference Guide for additional information.
4.7 TAWS
At system startup verify that the TAWS SYSTEM TEST audio message is loud
and compelling. Adjust headset volumes as necessary.
4.8 Radar Altimeter
If the installation of the G500/G600 is interfaced to a radar altimeter the radar
altitude can be displayed on the PFD. If the installed radar altimeter includes
self-test capability the Test controls are provided on the AUX/System Setup age.
Refer to the Radar Altimeter user documentation for information about values
displayed during Test. Note, for KRA 405 Radar Altimeters the displayed Test
value will be between 25 and 50ft.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 46 of 52
Page 47

Section 5. PERFORMANCE
No change.
Section 6. WEIGHT AND BALANCE
See current weight and balance data.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
FAA APPROVED Page 47 of 52
Page 48

Section 7. SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONS
Garmin also provides a detailed G500/G600 Pilot’s Guide P/N 190-00601-02.
This reference material is not required to be on board the aircraft but does
contain a more in depth description of all the functions and capabilities of the
G500/G600.
7.1 Databases
The G500/G600 utilizes several databases. Database titles display in yellow if
expired or in question (Note: the G500/G600 receives the calendar date from the
GPS, but only after acquiring a position fix). Database cycle information is
displayed at power up on the MFD screen, but more detailed information is
available on the AUX pages. Internal database validation prevents incorrect data
from being displayed.
The upper Secure Digital (SD) data card slot should be vacant as it is used for
software maintenance and aviation database updates only. The lower data card
slot should contain a data card with the system’s aviation and terrain / obstacle
information and optional data including Safe Taxi, FliteCharts and ChartView
electronic charts.
The terrain databases are updated periodically, have no expiration date, and
provide worldwide coverage.
The obstacle database contains data for obstacles and wires that pose a potential
hazard to aircraft. Obstacles 200 feet and higher are included in the obstacle
database. Wires which have been identified as a hazard to fixed wing aircraft are
included in the database. It is very important to note that not all obstacles or
wires are necessarily charted and therefore may not be contained in the obstacle
database. Coverage of the obstacle database includes the United States and
Europe. Wire coverage is limited to the United States. This database is updated
on a 56-day cycle.
The Garmin SafeTaxi database contains airport diagrams for selected airports.
This database is updated on a 56-day cycle.
The Garmin FliteCharts or Jeppesen ChartView electronic charts database
contains procedure charts for the coverage area purchased. An own-ship position
icon will be displayed on these charts when the aircraft icon on the chart page is
not X’d. This database is updated on a 28-day cycle. If not updated within 180
days of the expiration date, FliteCharts or ChartView will no longer function.
The airport directory database contains information on landing facilities, such as
operating hours, services available, and transportation/lodging resources. Airport
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
Page 48 of 52
Page 49

directory information may be available from multiple sources and coverage
areas. This database is updated on a 56-day cycle.
7.2 Electric Standby Attitude Gyro
If an electric standby attitude gyro is installed, the gyro operates from the aircraft
electrical system with a dedicated emergency battery specific to the electric gyro.
The electric attitude gyro battery capacity may vary considerably depending on
temperature, charge status, and battery life condition. Low temperatures below
32°F will temporarily degrade battery capacity. Internal chemistry will slowly
degrade battery capacity over several years of operation even when correctly
maintained. A poorly maintained battery will suffer accelerated degradation.
Extended storage in a discharged state and over-charging will permanently
damage the battery. Complete charging is required to bring the battery up to full
capacity if it has been unused for more than four months or partially discharged.
7.3 Autopilot Interface
The G500/G600 acts as a navigation source switching hub to an interfaced
autopilot when multiple navigation sources are available. The autopilot will only
couple to the heading, navigation, altitude, and vertical speed selections on PFD
1. Some autopilots may have navigation source selection integral to their system;
this feature is overridden by the G500/G600 navigation source selection
described herein. Changing the navigation sources displayed on the HSI (by
pressing the CDI button or the 1-2 button) may result in some autopilots
disconnecting or entering a wings level mode.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
Page 49 of 52
Page 50

7.4 TAWS Function [GDU 620 Units with internal TAWS]
In Dual G600 installations, TAWS audio is only provided by the Pilot side GDU.
If the Pilot side GDU TAWS becomes inoperative, the Co-Pilot side GDU
TAWS visual annunciations may still function, but the aural TAWS alerts will
not be heard.
7.5 TAWS Annunciations on the PFD [from a Garmin navigator]
The G500/G600 will display TAWS (Terrain Awareness and Warning System)
annunciations on the PFD if the G500/G600 is interfaced to a Garmin navigator
with integrated TAWS on GPS 1. The required TAWS annunciations appear in
the upper right of the PFD. These annunciations include PULL UP (red),
TERRAIN (yellow), TER N/A (yellow), TER INHB (white). These
annunciations are not relative to the terrain displayed on the MFD or the
yellow/red terrain shading of the Synthetic Vision displayed on the PFD of the
G500/G600 system. Refer to the Garmin navigator Airplane Flight Manual
Supplement for proper pilot action and information on these alerts.
TAWS alerts on the PFD of the G500/G600 System are only displayed from the
GPS/TAWS navigator interfaced as GPS 1 and are displayed regardless of the
system 1-2 setting, which drives all other PFD and MFD data used by the
G500/G600.
7.6 StormScope®
When optionally interfaced to a StormScope® weather detection system, the
G500/G600 may be used to display the StormScope® information. Weather
information supplied by the StormScope® will be displayed on the StormScope®
page of the G500/G600 system and may be overlaid on the map page. For
detailed information about the capabilities and limitations of the StormScope®
system, refer to the documentation provided with that system.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
Page 50 of 52
Page 51

7.7 ADS-B Traffic System Interface
The G500/G600 system can be interfaced to sources of ADS-B traffic. The nose
of the ownship symbol on both the G500/G600 main map page and dedicated
traffic page serves as the actual location of your aircraft. The center of the traffic
target icon serves as the reported location for the target aircraft. Motion vectors
for traffic may be displayed in either absolute or relative motion. The location of
the traffic targets relative to the ownship are the same, regardless of the selected
motion vector.
Absolute motion vectors are colored white and depict the reported track of the
traffic target referenced to the ground. An absolute motion vector pointed
towards your ownship symbol does not necessarily mean the traffic target is
getting closer to your aircraft.
Relative motion vectors are colored green and depict the motion of the traffic
target relative to your ownship symbol. The direction the traffic target is pointed
may vary greatly from the motion vector and a target may be getting closer to
your aircraft independent of the direction the target is pointed. A green relative
motion vector pointed towards your ownship indicates that the traffic target is
converging on your aircraft.
Traffic targets displayed on the dedicated traffic page may be selected using the
MFD knobs in order to obtain additional information about a traffic target.
7.8 Flight Plan
The Flight Plan shown on the GDU 620 is the same as that provided by the GPS
navigation source selected on the PFD. When waypoints are removed from the
Flight Plan on the GPS navigator or when the entire flight plan is deleted it may
take as long as 20 seconds for the change to be reflected on the G500/600 Flight
Plan page and map.
7.9 GWX 68 and GWX 70 Weather Radar
The GDU 620 controls the mode and sweep settings of the GWX 68 and GWX
70 Weather Radars as well as the display of the radar returns. The GWX 70
Weather Radar uses Doppler technology to provide advanced features to the
flight crew such as turbulence detection and ground clutter suppression. The
turbulence detection function can only detect turbulence between 2.5 nautical
miles and 40 nautical miles ahead of the aircraft. The display of turbulence is
only provided when the radar range is set to 160 nautical miles or less.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
Page 51 of 52
Page 52

NOTE
Turbulence detection does not detect all turbulence
especially that which is occurring in clear air. The display of
turbulence indicates the possibility of Severe or greater
turbulence, as defined in the Aeronautical Information
Manual.
7.10 Depiction of Obstacles and Wires
NOTE
Only obstacles and wires within 2,000 ft vertically of the
aircraft will be drawn on the Map and Terrain pages.
Obstacle Overlay Icon (Left), Wire Overlay Icon (Right)
7.10.1 Dedicated Terrain Page
The dedicated Terrain page will always depict point obstacles at zoom scales of
10 nautical miles or less and depict wire obstacles at zoom scales of 5 nautical
miles or less. The obstacle or wire overlay icon will be shown near the bottom of
the display when the obstacle or wire depiction is active based on the zoom
scale.
7.10.2 Map Page
The Map page may be configured to depict point obstacles and wire obstacles at
various zoom scales, or to not depict point obstacles or wire obstacles at all, by
the pilot by using the Map page menu. The obstacle or wire overlay icon will be
shown near the bottom of the display when the obstacle or wire overlay is active
based on the current zoom scale and setting selected by the pilot.
The settings chosen by the pilot on the Map page menu (including obstacle and
wire display ranges) are saved over a power cycle.
AFMS, GARMIN G500/G600 SYSTEM 190-00601-01 Rev. L
Page 52 of 52
 Loading...
Loading...