Garmin G 500 Airplane Flight Manual Supplement

LOG OF REVISIONS
Revision
Number
Page
Number
Description
FAA Approval
1
All
Complete Supplement
David Armstrong
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, INC
ODA-240087-CE
Date: 07/30/2009
2
9
10
14
Remove requirement for
standby ADI for VFR
operations/installations.
Add maximum airspeed
limitation section.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, INC
ODA-240087-CE
Date: 12/10/2009
3
All
Correct page numbering.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, INC
ODA-240087-CE
Date: 07/30/2010
4
None
Rerelease document.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, INC
ODA-240087-CE
Date: 08/24/2010
5
All
Changed GPS/WAAS to
GPS/SBAS. Corrected
typographical errors.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: 02/23/2011
7
Updated section 1.1 for
new features.
10
Added new feature
descriptions to
sections1.7, 1.8, and1.9.
11, 12
Updated block diagrams
for new features.
14
Updated section 2.2 for
applicability to this AFMS
revision. Removed GPS
navigator software table.
14, 15
Updated section 2.3 with
limitation on use of
helicopter databases and
SD card usage with GSR
56 datalink. Added
information on airport
directory database.
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 2 of 40
LOG OF REVISIONS
Revision
Number
Page
Number
Description
FAA Approval
16
Updated section 2.8 to
reflect current airspeed
tape behavior.
18
Updated section 2.14 to
better describe the terrain
awareness function.
Updated section 2.16 for
GFDS weather function.
23
Corrected description of
heading and AHRS
failures.
24
Corrected description of
ADC failure.
26
Corrected table entry for
AHRS ALIGN.
28
Added new section 4.4 for
altitude alerter
configuration.
29
Added detail to section 4.6
regarding GAD 43
interface. Corrected
description of autopilot
interfaces in section 4.6.1.
31
Corrected altitude alerter
description in section
4.6.6.
32
Added Caution and Note
regarding GAD 43 AP
TEST function in section
4.6.7.
6
All
Changed GNS navigator
references to GPS/SBAS
navigator references.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: 04/01/2011
11
Inserted new section 1.10
for HSDB interface
description.
15
Inserted new section 2.3
for moving map
limitations.
24
Moved rate-of-turn failure
description from section
3.3.1 to section 3.3.2.
29
Added checkbox for
disabled altitude alerter in
section 4.4.
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 3 of 40
LOG OF REVISIONS
Revision
Number
Page
Number
Description
FAA Approval
7
All
Re-issue complete
supplement.
Robert Grove
ODA STC Unit Administrator
GARMIN International, Inc
ODA-240087-CE
Date: 08-18-2011
Revised section 2.14
limitation on GPS/SBAS
vertical coupling.
Added attitude/air data
interface to section 4.6.
Added GDU 620 as an
autopilot attitude source to
section 4.6.1.
Clarified dual autopilot
interface in section 4.6.9.
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 4 of 40
LOG OF REVISIONS
Revision
Number
Page
Number
Description
FAA Approval
8
All
Re-issue complete supplement.
Michael Warren
ODA STC Unit Admin.
Garmin Int’l, Inc.
ODA-240087-CE
Date: 12/26/2012
Revised information on system
power sources in section 1.2
Revised audio panel description
in section 1.6.
Updated block diagrams in
sections 1.11 and 1.12.
Updated System Software
Requirements in section 2.2.
Revised Moving Map limitation
in Section 2.3.
Revised SafeTaxi and Airport
Directory descriptions in section
2.4.
Clarified applicability of section
2.11.
Updated autopilot interface
information in section 2.14.
Revised external TAWS
annunciation information in
section 2.16.
Added limitation for KFC
275/325 interface in section 2.21.
Added ESI-1000 limitation in
section 2.22.
Added EFB limitation in Section
2.23.
Added Surface Operations
limitation in Section 2.24.
Added MFD Video limitation in
Section 2.25.
Emergency Procedures
reorganized into Section 3.1.
Abnormal Procedures reorganized
into Section 3.2.
Added MISCOMP and NO AP
DATA annunciations in section
3.3.2.
Added airspeed bug description in
Section 4.1.
Removed Altitude Alerter section
4.4.
Added electric standby attitude
indicator procedure as new
section 4.4.
Updated autopilot procedures
throughout section 4.6.
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 5 of 40
LOG OF REVISIONS
Revision
Number
Page
Number
Description
FAA Approval
9
All
Re-issue complete supplement.
See Page 1
Corrected navigation radio
information in Section 1.1.
Updated applicable system software
in Section 2.2.
Corrected Auto Slew description in
Section 2.12.
Updated Bendix/King Altitude
Preselect functionality in Section
4.6.6.3.
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 6 of 40

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION PAGE
SECTION 1. GENERAL ................................................................................... 9
1.1 GARMIN G500 PRIMARY FLIGHT / MULTI-FUNCTION DISPLAY SYSTEM ............. 9
1.2 SYSTEM POWER SOURCES .................................................................................. 9
1.3 NAVIGATION SOURCES .................................................................................... 10
1.4 SYNTHETIC VISION TECHNOLOGY .................................................................... 10
1.5 AUTOPILOT INTERFACE.................................................................................... 11
1.6 AUDIO PANEL .................................................................................................. 12
1.7 TRAFFIC AND WEATHER SYSTEMS ................................................................... 12
1.8 VIDEO SOURCES............................................................................................... 12
1.9 RADAR ALTIMETER ......................................................................................... 12
1.10 HIGH SPEED DATA BUS INTERFACE ................................................................. 12
1.11 SINGLE G500 OPERATIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................................ 13
1.12 DUAL G500 OPERATIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM .................................................. 14
1.13 DEFINITIONS .................................................................................................... 15
SECTION 2. LIMITATIONS ......................................................................... 16
2.1 COCKPIT REFERENCE & PILOT’S GUIDE ........................................................... 16
2.2 SYSTEM SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS ................................................................ 16
2.3 MOVING MAP .................................................................................................. 16
2.4 DATABASE CARDS ........................................................................................... 16
2.5 AHRS OPERATIONAL AREA ............................................................................ 17
2.6 MAGNETIC VARIATION OPERATIONAL AREA ................................................... 17
2.7 NAVIGATION ANGLE ....................................................................................... 18
2.8 AHRS NORMAL OPERATING MODE ................................................................. 18
2.9 AIRSPEED LIMITATIONS AND INDICATOR MARKINGS ........................................ 18
2.10 AEROBATIC MANEUVERS ................................................................................ 18
2.11 ELECTRIC STANDBY ATTITUDE GYRO .............................................................. 18
2.12 COURSE POINTER AUTO SLEWING ................................................................... 19
2.13 SYNTHETIC VISION TECHNOLOGY .................................................................... 19
2.14 AUTOPILOT INTERFACE.................................................................................... 19
2.15 TERRAIN PROXIMITY FUNCTION ...................................................................... 20
2.16 TAWS ANNUNCIATIONS ON THE PFD [FROM A GARMIN NAVIGATOR] ............. 20
2.17 DATALINKED WEATHER DISPLAY (XM OR GFDS WEATHER) .......................... 20
2.18 TRAFFIC DISPLAY ............................................................................................ 20
2.19 ACTIVE WEATHER RADAR ............................................................................ 21
2.20 KINDS OF OPERATIONS .................................................................................... 22
2.21 KFC 275/325 ALTITUDE PRESELECT ............................................................... 22
2.22 L-3 ESI-1000 ELECTRONIC STANDBY INSTRUMENT ......................................... 23
2.23 ELECTRONIC FLIGHT BAG (EFB) APPLICATIONS .............................................. 23
2.24 SURFACE OPERATIONS .................................................................................... 23
2.25 MFD VIDEO DISPLAY ..................................................................................... 23
SECTION 3. EMERGENCY PROCEDURES .............................................. 24
3.1 EMERGENCY PROCEDURES .............................................................................. 24
3.2 ABNORMAL PROCEDURES ................................................................................ 27
3.3 WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, AND ADVISORIES ................................ ........................ 29
SECTION 4. NORMAL PROCEDURES ...................................................... 32
4.1 PFD KNOB & PFD SOFT KEYS ........................................................................ 32
4.2 MFD KNOBS & MFD SOFT KEYS .................................................................... 32
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 7 of 40

4.3 ALTITUDE SYNCHRONIZATION ......................................................................... 33
4.4 ELECTRIC STANDBY ATTITUDE GYRO ............................................................. 33
4.5 SYNTHETIC VISION TECHNOLOGY ................................................................... 33
4.6 AUTOPILOT OPERATIONS WITH THE G500 SYSTEM .......................................... 34
SECTION 5. PERFORMANCE ..................................................................... 40
SECTION 6. WEIGHT AND BALANCE ...................................................... 40
SECTION 7. SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONS ..................................................... 40
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 8 of 40

Section 1. GENERAL
1.1 Garmin G500 Primary Flight / Multi-Function Display System
The G500 PFD/MFD System consists of a Primary Flight Display (PFD) and
Multi-Function Display (MFD) housed in a single Garmin Display Unit (GDU),
plus an Air Data Computer (ADC) and Attitude and Heading Reference System
(AHRS). The G500 interfaces with other installed systems in the aircraft,
including Garmin GPS/SBAS navigators, VHF navigation radios, Garmin GDL
69 data link radios, Garmin GSR 56 Iridum transceivers, and various weather
radars, audio panels, video sources, radar altimeters, traffic systems and ADF
navigators.
The primary function of the PFD is to provide attitude, heading, air data and
navigation information to the pilot. The primary function of the MFD is to
provide mapping, terrain, and flight plan information.
The standby instruments (altimeter, airspeed, attitude, and magnetic compass)
are completely independent from the PFD and will continue to operate in the
event the PFD is not usable. These standby instruments should be included in
the pilot’s normal instrument scan and may be referenced if the PFD data is in
question. A second G500 system installed on the co-pilot’s side does not require
additional standby instruments.
1.2 System Power Sources
The G500 system depends on electrical power to maintain proper operation. The
Garmin Display Unit (GDU), Attitude and Heading Reference System (AHRS),
and Air Data Computer (ADC) are directly tied to the aircraft’s main or essential
bus and energized when the aircraft master switch is turned on. Other systems,
like the navigation equipment, weather datalink, autopilot and Adapter (GAD)
are typically located on the avionics bus and may not be operable during engine
start.
The major components of the G500 are circuit breaker protected with resettable
type breakers available to the pilot. These breakers are located at the main or
essential bus circuit breaker panel and labeled as follows:
1. PFD - Garmin Display Unit (PFD/MFD), GDU 620
2. AHRS - Attitude and Heading Reference System, GRS 77
3. ADC - Air Data Computer, GDC 74A
4. GAD - Garmin Adapter, GAD 43/43e (optional)
5. STBY ATT- Electric Standby Attitude Gyro
In dual installations the pilot side equipment is suffixed with the number 1 and
the copilot side equipment is suffixed with the number 2. For example: PFD 1
and PFD 2.
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 9 of 40
Equipment that receives power from two different circuit breakers will be
suffixed with the letters A and B. For example: PFD 1A and PFD 1B, or PFD
2A and PFD 2B.
1.3 Navigation Sources
The G500 requires at least one Garmin GPS/SBAS navigation unit to ensure the
integrity of the Attitude and Heading Reference System. The AHRS will still
operate in a reversionary mode if the GPS fails, and the PFD attitude display
will still be presented, see Paragraph 2.8. The G500 HSI can be selected to
display course deviation information from up to four independent sources: two
GPS, and two VHF NAV. In addition, the HSI can display two simultaneous
bearing pointers sourced from GPS, VHF NAV, or ADF.
1.4 Synthetic Vision Technology
SVT uses an internal terrain database and GPS location to present the pilot with
a synthetic view of the terrain in front of the aircraft. The purpose of the SVT
system is to assist the pilot in maintaining situational awareness with regard to
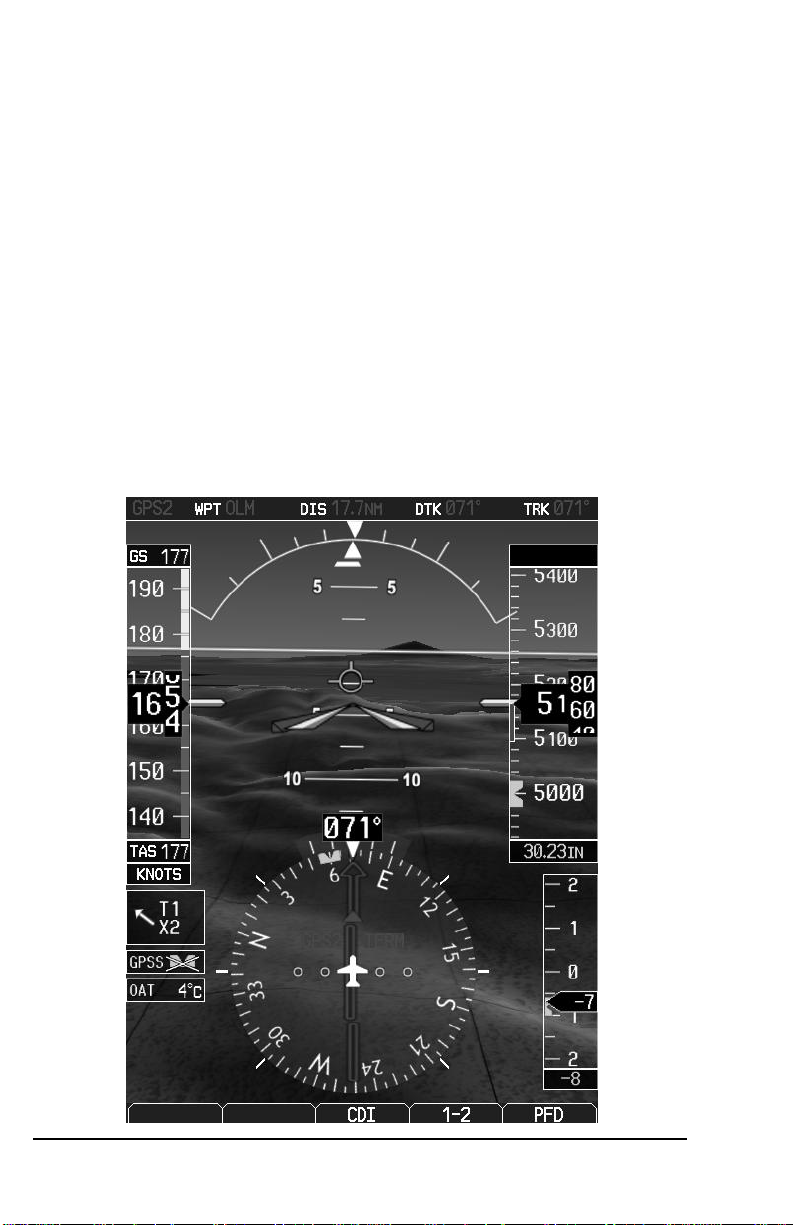
the terrain and traffic surrounding the aircraft. A typical SVT display is shown
below:
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 10 of 40

SVT provides additional features on the G500 primary flight display (PFD)
which display the following information:
Synthetic Terrain; an artificial, database derived, three dimensional
view of the terrain ahead of the aircraft within a field of view of
approximately 25 degrees left and 25 degrees right of the aircraft
heading.
Obstacles; obstacles such as towers, including buildings over 200 AGL
that are within the depicted synthetic terrain field of view.
Flight Path Marker (FPM); an indication of the current lateral and
vertical path of the aircraft. The FPM is always displayed when
synthetic terrain is selected for display.
Traffic; a display on the PFD indicating the position of other aircraft
detected by a traffic system interfaced to the G500 system.
Horizon Line; a white line indicating the true horizon is always
displayed on the SVT display.
Horizon Heading; a pilot selectable display of heading marks
displayed just above the horizon line on the PFD.
Airport Signs; pilot selectable “signposts” displayed on the synthetic
terrain display indicating the position of nearby airports that are in the
G500 database.
Runway Highlight; a highlighted presentation of the location and
orientation of the runway(s) at the destination airport.
The synthetic terrain depiction displays an area approximating the view from the
pilot’s eye position when looking directly ahead out the windshield in front of
the pilot. Terrain features outside this field of view are not shown on the display.
The synthetic terrain display is intended to aid the pilot awareness of the terrain
and obstacles in front of the airplane. It may not provide either the accuracy or
fidelity, or both, on which to solely base decisions and plan maneuvers to avoid
terrain or obstacles. The synthetic vision elements are not intended to be used
for primary aircraft control in place of the primary flight instruments.
1.5 Autopilot Interface
The G500 may be interfaced to an optional autopilot. The G500 typically
provides course and heading datum to the autopilot based on the data selected
for display on the HSI. For multiple GPS/NAV systems, the G500 acts as a
selection hub for the autopilot’s NAV mode, and the G500 may also provide
GPS Steering data. Some autopilots may provide Flight Director capabilities
which can be displayed on the G500 Attitude Indicator as a Single Cue Flight
Director.
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 11 of 40

1.6 Audio Panel
The G500 PFD/MFD system should be interfaced into the aircraft audio panel to
provide aural altering generated by the G500 (required for SVT installations).
1.7 Traffic and Weather Systems
The G500 PFD/MFD system supports TIS traffic via the Garmin GTX Series
Mode-S Transponders. The system also supports TAS/TCAS/TIS traffic from
various active traffic awareness systems. The information from these systems is
available and controllable on the MFD.
The G500 PFD/MFD system supports XM datalink weather via the Garmin
GDL69 and GDL69A receivers. If an optional XM datalink receiver is installed,
the pilot will be able to access graphical and text weather products on the MFD
and control the audio entertainment data from the MFD while listening via an
appropriately installed audio panel.
Datalink weather is also available via the Garmin GSR 56 Iridium Transceiver.
The control and display of Iridium satellite weather on the MFD is similar to
XM weather.
Control and display of various airborne weather radars is optionally available on
the MFD. The G500 supports Garmin GWX weather radar, as well as certain
3rd-party weather radars.
1.8 Video sources
The G500 Avionics Display System can display images from up to 2 video
inputs. Video images are displayed on the MFD. The G500 does not provide a
means to control the video source; however the digital images from the video
source can be adjusted using the G500.
1.9 Radar Altimeter
The G500 supports the display of radar altitude on the PFD from supported
radar altimeters.
1.10 High Speed Data Bus Interface
Some Garmin equipment connected to the G500 system utilizes the High Speed
Data Bus (HSDB) interface. HSDB is similar to an Ethernet bus and provides a
high-speed interface between Garmin avionics. Like Ethernet, data between two
units may be passed through intermediate “hub” units. Interfaced equipment
that uses HSDB includes the GTN 6XX/7XX navigators, GDL 69 datalink
receiver, GWX 68, and GTS 8XX traffic systems.
The HSDB interfaces are installed to so that maximum data path redundancy is
achieved. However, depending on the number of HSDB units installed, failure
of one HSDB unit may result in loss of data on the G500 from “downstream”
HSDB units. Any loss of data will be annunciated on the G500.
AFMS, GARMIN G500 PFD/MFD SYSTEM 190-01102-01 Rev. 9
FAA APPROVED Page 12 of 40
 Loading...
Loading...