Page 1

GE Fanuc Automation
Computer Numerical Control Products
Series 30i/300i/300is-MODEL A
Series 31i/310i/310is-MODEL A5
Series 31i/310i/310is-MODEL A
Series 32i/320i/320is-MODEL A
For Machining Center System
User’s Manual
GFZ-63944EN-2/02 June 2004
Page 2

Warnings, Cautions, and Notes
as Used in this Publication
Warning notices are used in this publication to emphasize that hazardous voltages, currents,
temperatures, or other conditions that could cause personal injury exist in this equipment or
may be associated with its use.
In situations where inattention could cause either personal injury or damage to equipment, a
Warning notice is used.
Caution notices are used where equipment might be damaged if care is not taken.
GFL-001
Warning
Caution
Note
Notes merely call attention to information that is especially significant to understanding and
operating the equipment.
This document is based on information available at the time of its publication. While efforts
have been made to be accurate, the information contained herein does not purport to cover all
details or variations in hardware or software, nor to provide for every possible contingency in
connection with installation, operation, or maintenance. Features may be described herein
which are not present in all hardware and software systems. GE Fanuc Automation assumes
no obligation of notice to holders of this document with respect to changes subsequently made.
GE Fanuc Automation makes no representation or warranty, expressed, implied, or statutory
with respect to, and assumes no responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, sufficiency, or
usefulness of the information contained herein. No warranties of merchantability or fitness for
purpose shall apply.
©Copyright 2004 GE Fanuc Automation North America, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

B-63944EN-2/02 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
This section describes the safety precautions related to the use of CNC
units.
It is essential that these precautions be observed by users to ensure the
safe operation of machines equipped with a CNC unit (all descriptions
in this section assume this configuration). Note that some precautions
are related only to specific functions, and thus may not be applicable
to certain CNC units.
Users must also observe the safety precautions related to the machine,
as described in the relevant manual supplied by the machine tool
builder. Before attempting to operate the machine or create a program
to control the operation of the machine, the operator must become
fully familiar with the contents of this manual and relevant manual
supplied by the machine tool builder.
CONTENTS
1.1 DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE ........s-2
1.2 GENERAL WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS ...........................s-3
1.3 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS RELATED TO
PROGRAMMING.....................................................................s-6
1.4 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS RELATED TO HANDLINGs-9
1.5 WARNINGS RELATED TO DAILY MAINTENANCE....... s-12
s-1
Page 4

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-63944EN-2/02
1.1 DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
This manual includes safety precautions for protecting the user and
preventing damage to the machine. Precautions are classified into
Warning and Caution according to their bearing on safety. Also,
supplementary information is described as a Note. Read the
Warning, Caution, and Note thoroughly before attempting to use
the machine.
WARNING
Applied when there is a danger of the user being
injured or when there is a danger of both the user
being injured and the equipment being damaged if
the approved procedure is not observed.
CAUTION
Applied when there is a danger of the equipment
being damaged, if the approved procedure is not
observed.
NOTE
The Note is used to indicate supplementary
information other than Warning and Caution.
• Read this manual carefully, and store it in a safe place.
s-2
Page 5
B-63944EN-2/02 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.2 GENERAL WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING
1 Never attempt to machine a workpiece without first
checking the operation of the machine. Before
starting a production run, ensure that the machine
is operating correctly by performing a trial run
using, for example, the single block, feedrate
override, or machine lock function or by operating
the machine with neither a tool nor workpiece
mounted. Failure to confirm the correct operation
of the machine may result in the machine behaving
unexpectedly, possibly causing damage to the
workpiece and/or machine itself, or injury to the
user.
2 Before operating the machine, thoroughly check
the entered data.
Operating the machine with incorrectly specified
data may result in the machine behaving
unexpectedly, possibly causing damage to the
workpiece and/or machine itself, or injury to the
user.
3 Ensure that the specified feedrate is appropriate
for the intended operation. Generally, for each
machine, there is a maximum allowable feedrate.
The appropriate feedrate varies with the intended
operation. Refer to the manual provided with the
machine to determine the maximum allowable
feedrate.
If a machine is run at other than the correct speed,
it may behave unexpectedly, possibly causing
damage to the workpiece and/or machine itself, or
injury to the user.
4 When using a tool compensation function,
thoroughly check the direction and amount of
compensation.
Operating the machine with incorrectly specified
data may result in the machine behaving
unexpectedly, possibly causing damage to the
workpiece and/or machine itself, or injury to the
user.
s-3
Page 6
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-63944EN-2/02
WARNING
5 The parameters for the CNC and PMC are
factory-set. Usually, there is not need to change
them. When, however, there is not alternative other
than to change a parameter, ensure that you fully
understand the function of the parameter before
making any change.
Failure to set a parameter correctly may result in
the machine behaving unexpectedly, possibly
causing damage to the workpiece and/or machine
itself, or injury to the user.
6 Immediately after switching on the power, do not
touch any of the keys on the MDI panel until the
position display or alarm screen appears on the
CNC unit.
Some of the keys on the MDI panel are dedicated
to maintenance or other special operations.
Pressing any of these keys may place the CNC
unit in other than its normal state. Starting the
machine in this state may cause it to behave
unexpectedly.
7 The User’s Manual and programming manual
supplied with a CNC unit provide an overall
description of the machine's functions, including
any optional functions. Note that the optional
functions will vary from one machine model to
another. Therefore, some functions described in
the manuals may not actually be available for a
particular model. Check the specification of the
machine if in doubt.
8 Some functions may have been implemented at
the request of the machine-tool builder. When
using such functions, refer to the manual supplied
by the machine-tool builder for details of their use
and any related cautions.
CAUTION
The liquid-crystal display is manufactured with very
precise fabrication technology. Some pixels may
not be turned on or may remain on. This
phenomenon is a common attribute of LCDs and is
not a defect.
s-4
Page 7
B-63944EN-2/02 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
NOTE
Programs, parameters, and macro variables are
stored in nonvolatile memory in the CNC unit.
Usually, they are retained even if the power is
turned off.
Such data may be deleted inadvertently, however,
or it may prove necessary to delete all data from
nonvolatile memory as part of error recovery.
To guard against the occurrence of the above, and
assure quick restoration of deleted data, backup all
vital data, and keep the backup copy in a safe
place.
s-5
Page 8
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-63944EN-2/02
1.3 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS RELATED TO
PROGRAMMING
This section covers the major safety precautions related to
programming. Before attempting to perform programming, read the
supplied User’s Manual carefully such that you are fully familiar with
their contents.
WARNING
1 Coordinate system setting
If a coordinate system is established incorrectly,
the machine may behave unexpectedly as a result
of the program issuing an otherwise valid move
command. Such an unexpected operation may
damage the tool, the machine itself, the workpiece,
or cause injury to the user.
2 Positioning by nonlinear interpolation
When performing positioning by nonlinear
interpolation (positioning by nonlinear movement
between the start and end points), the tool path
must be carefully confirmed before performing
programming. Positioning involves rapid traverse. If
the tool collides with the workpiece, it may damage
the tool, the machine itself, the workpiece, or
cause injury to the user.
3 Function involving a rotation axis
When programming polar coordinate interpolation
or normal-direction (perpendicular) control, pay
careful attention to the speed of the rotation axis.
Incorrect programming may result in the rotation
axis speed becoming excessively high, such that
centrifugal force causes the chuck to lose its grip
on the workpiece if the latter is not mounted
securely. Such mishap is likely to damage the tool,
the machine itself, the workpiece, or cause injury to
the user.
4 Inch/metric conversion
Switching between inch and metric inputs does not
convert the measurement units of data such as the
workpiece origin offset, parameter, and current
position. Before starting the machine, therefore,
determine which measurement units are being
used. Attempting to perform an operation with
invalid data specified may damage the tool, the
machine itself, the workpiece, or cause injury to the
user.
s-6
Page 9
B-63944EN-2/02 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
5 Constant surface speed control
When an axis subject to constant surface speed
control approaches the origin of the workpiece
coordinate system, the spindle speed may become
excessively high. Therefore, it is necessary to
specify a maximum allowable speed. Specifying
the maximum allowable speed incorrectly may
damage the tool, the machine itself, the workpiece,
or cause injury to the user.
6 Stroke check
After switching on the power, perform a manual
reference position return as required. Stroke check
is not possible before manual reference position
return is performed. Note that when stroke check is
disabled, an alarm is not issued even if a stroke
limit is exceeded, possibly damaging the tool, the
machine itself, the workpiece, or causing injury to
the user.
7 Tool post interference check
A tool post interference check is performed based
on the tool data specified during automatic
operation. If the tool specification does not match
the tool actually being used, the interference check
cannot be made correctly, possibly damaging the
tool or the machine itself, or causing injury to the
user. After switching on the power, or after
selecting a tool post manually, always start
automatic operation and specify the tool number of
the tool to be used.
8 Absolute/incremental mode
If a program created with absolute values is run in
incremental mode, or vice versa, the machine may
behave unexpectedly.
9 Plane selection
If an incorrect plane is specified for circular
interpolation, helical interpolation, or a canned
cycle, the machine may behave unexpectedly.
Refer to the descriptions of the respective
functions for details.
10 Torque limit skip
Before attempting a torque limit skip, apply the
torque limit. If a torque limit skip is specified
without the torque limit actually being applied, a
move command will be executed without
performing a skip.
s-7
Page 10
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-63944EN-2/02
WARNING
11 Programmable mirror image
Note that programmed operations vary
considerably when a programmable mirror image is
enabled.
12 Compensation function
If a command based on the machine coordinate
system or a reference position return command is
issued in compensation function mode,
compensation is temporarily canceled, resulting in
the unexpected behavior of the machine.
Before issuing any of the above commands,
therefore, always cancel compensation function
mode.
s-8
Page 11
B-63944EN-2/02 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.4 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS RELATED TO
HANDLING
This section presents safety precautions related to the handling of
machine tools. Before attempting to operate your machine, read the
supplied User’s Manual carefully, such that you are fully familiar with
their contents.
WARNING
1 Manual operation
When operating the machine manually, determine
the current position of the tool and workpiece, and
ensure that the movement axis, direction, and
feedrate have been specified correctly. Incorrect
operation of the machine may damage the tool, the
machine itself, the workpiece, or cause injury to the
operator.
2 Manual reference position return
After switching on the power, perform manual
reference position return as required.
If the machine is operated without first performing
manual reference position return, it may behave
unexpectedly. Stroke check is not possible before
manual reference position return is performed.
An unexpected operation of the machine may
damage the tool, the machine itself, the workpiece,
or cause injury to the user.
3 Manual numeric command
When issuing a manual numeric command,
determine the current position of the tool and
workpiece, and ensure that the movement axis,
direction, and command have been specified
correctly, and that the entered values are valid.
Attempting to operate the machine with an invalid
command specified may damage the tool, the
machine itself, the workpiece, or cause injury to the
operator.
4 Manual handle feed
In manual handle feed, rotating the handle with a
large scale factor, such as 100, applied causes the
tool and table to move rapidly. Careless handling
may damage the tool and/or machine, or cause
injury to the user.
s-9
Page 12
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-63944EN-2/02
WARNING
5 Disabled override
If override is disabled (according to the
specification in a macro variable) during threading,
rigid tapping, or other tapping, the speed cannot be
predicted, possibly damaging the tool, the machine
itself, the workpiece, or causing injury to the
operator.
6 Origin/preset operation
Basically, never attempt an origin/preset operation
when the machine is operating under the control of
a program. Otherwise, the machine may behave
unexpectedly, possibly damaging the tool, the
machine itself, the tool, or causing injury to the
user.
7 Workpiece coordinate system shift
Manual intervention, machine lock, or mirror
imaging may shift the workpiece coordinate
system. Before attempting to operate the machine
under the control of a program, confirm the
coordinate system carefully.
If the machine is operated under the control of a
program without making allowances for any shift in
the workpiece coordinate system, the machine
may behave unexpectedly, possibly damaging the
tool, the machine itself, the workpiece, or causing
injury to the operator.
8 Software operator's panel and menu switches
Using the software operator's panel and menu
switches, in combination with the MDI panel, it is
possible to specify operations not supported by the
machine operator's panel, such as mode change,
override value change, and jog feed commands.
Note, however, that if the MDI panel keys are
operated inadvertently, the machine may behave
unexpectedly, possibly damaging the tool, the
machine itself, the workpiece, or causing injury to
the user.
9 RESET key
Pressing the RESET key stops the currently
running program. As a result, the servo axes are
stopped. However, the RESET key may fail to
function for reasons such as an MDI panel
problem. So, when the motors must be stopped,
use the emergency stop button instead of the
RESET key to ensure security.
s-10
Page 13
B-63944EN-2/02 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
10 Manual intervention
If manual intervention is performed during
programmed operation of the machine, the tool
path may vary when the machine is restarted.
Before restarting the machine after manual
intervention, therefore, confirm the settings of the
manual absolute switches, parameters, and
absolute/incremental command mode.
11 Feed hold, override, and single block
The feed hold, feedrate override, and single block
functions can be disabled using custom macro
system variable #3004. Be careful when operating
the machine in this case.
12 Dry run
Usually, a dry run is used to confirm the operation
of the machine. During a dry run, the machine
operates at dry run speed, which differs from the
corresponding programmed feedrate. Note that the
dry run speed may sometimes be higher than the
programmed feed rate.
13 Cutter and tool nose radius compensation in
MDI mode
Pay careful attention to a tool path specified by a
command in MDI mode, because cutter or tool
nose radius compensation is not applied. When a
command is entered from the MDI to interrupt in
automatic operation in cutter or tool nose radius
compensation mode, pay particular attention to the
tool path when automatic operation is subsequently
resumed. Refer to the descriptions of the
corresponding functions for details.
14 Program editing
If the machine is stopped, after which the
machining program is edited (modification,
insertion, or deletion), the machine may behave
unexpectedly if machining is resumed under the
control of that program. Basically, do not modify,
insert, or delete commands from a machining
program while it is in use.
s-11
Page 14
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-63944EN-2/02
1.5 WARNINGS RELATED TO DAILY MAINTENANCE
WARNING
1 Memory backup battery replacement
When replacing the memory backup batteries,
keep the power to the machine (CNC) turned on,
and apply an emergency stop to the machine.
Because this work is performed with the power on
and the cabinet open, only those personnel who
have received approved safety and maintenance
training may perform this work.
When replacing the batteries, be careful not to
touch the high-voltage circuits (marked
fitted with an insulating cover).
Touching the uncovered high-voltage circuits
presents an extremely dangerous electric shock
hazard.
NOTE
The CNC uses batteries to preserve the contents
of its memory, because it must retain data such as
programs, offsets, and parameters even while
external power is not applied.
If the battery voltage drops, a low battery voltage
alarm is displayed on the machine operator's panel
or screen.
When a low battery voltage alarm is displayed,
replace the batteries within a week. Otherwise, the
contents of the CNC's memory will be lost.
Refer to the Section “Method of replacing battery”
in the User’s Manual (Common to T/M series) for
details of the battery replacement procedure.
and
s-12
Page 15
B-63944EN-2/02 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
2 Absolute pulse coder battery replacement
When replacing the memory backup batteries,
keep the power to the machine (CNC) turned on,
and apply an emergency stop to the machine.
Because this work is performed with the power on
and the cabinet open, only those personnel who
have received approved safety and maintenance
training may perform this work.
When replacing the batteries, be careful not to
touch the high-voltage circuits (marked
and
fitted with an insulating cover).
Touching the uncovered high-voltage circuits
presents an extremely dangerous electric shock
hazard.
NOTE
The absolute pulse coder uses batteries to
preserve its absolute position.
If the battery voltage drops, a low battery voltage
alarm is displayed on the machine operator's panel
or screen.
When a low battery voltage alarm is displayed,
replace the batteries within a week. Otherwise, the
absolute position data held by the pulse coder will
be lost.
Refer to the FANUC SERVO MOTOR αi series
Maintenance Manual for details of the battery
replacement procedure.
s-13
Page 16
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-63944EN-2/02
WARNING
3 Fuse replacement
Before replacing a blown fuse, however, it is
necessary to locate and remove the cause of the
blown fuse.
For this reason, only those personnel who have
received approved safety and maintenance training
may perform this work.
When replacing a fuse with the cabinet open, be
careful not to touch the high-voltage circuits
(marked and fitted with an insulating cover).
Touching an uncovered high-voltage circuit
presents an extremely dangerous electric shock
hazard.
s-14
Page 17

B-63944EN-2/02 TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS............................................................................s-1
I. GENERAL
1 GENERAL ...............................................................................................3
1.1 NOTES ON READING THIS MANUAL.......................................................... 7
1.2 NOTES ON VARIOUS KINDS OF DATA ...................................................... 7
II. PROGRAMMING
1 GENERAL .............................................................................................11
1.1 TOOL FIGURE AND TOOL MOTION BY PROGRAM................................. 12
2 PREPARATORY FUNCTION (G FUNCTION) ...................................... 13
3 INTERPOLATION FUNCTION ..............................................................18
3.1 INVOLUTE INTERPOLATION (G02.2, G03.2) ............................................ 19
3.1.1 Automatic Speed Control for Involute Interpolation..............................................24
3.1.2 Helical Involute Interpolation (G02.2, G03.2) .......................................................26
3.1.3 Involute Interpolation on Linear Axis and Rotary Axis (G02.2, G03.2) ...............27
3.2 THREADING (G33) .....................................................................................30
4 COORDINATE VALUE AND DIMENSION ...........................................32
4.1 POLAR COORDINATE COMMAND (G15, G16) ......................................... 33
5 FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING ..................................... 37
5.1 CANNED CYCLE FOR DRILLING............................................................... 38
5.1.1 High-Speed Peck Drilling Cycle (G73)..................................................................43
5.1.2 Left-Handed Tapping Cycle (G74) ........................................................................45
5.1.3 Fine Boring Cycle (G76)........................................................................................47
5.1.4 Drilling Cycle, Spot Drilling (G81) .......................................................................49
5.1.5 Drilling Cycle Counter Boring Cycle (G82) ..........................................................51
5.1.6 Peck Drilling Cycle (G83)......................................................................................53
5.1.7 Small-Hole Peck Drilling Cycle.............................................................................55
5.1.8 Tapping Cycle (G84)..............................................................................................60
5.1.9 Boring Cycle (G85) ................................................................................................62
5.1.10 Boring Cycle (G86) ................................................................................................64
5.1.11 Back Boring Cycle (G87).......................................................................................66
5.1.12 Boring Cycle (G88) ................................................................................................69
c-1
Page 18

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-63944EN-2/02
5.1.13 Boring Cycle (G89) ................................................................................................71
5.1.14 Canned Cycle Cancel for Drilling (G80)................................................................73
5.1.15 Example for Using Canned Cycles for Drilling .....................................................74
5.2 RIGID TAPPING .......................................................................................... 76
5.2.1 Rigid Tapping (G84) ..............................................................................................77
5.2.2 Left-Handed Rigid Tapping Cycle (G74)...............................................................81
5.2.3 Peck Rigid Tapping Cycle (G84 or G74)...............................................................85
5.2.4 Canned Cycle Cancel (G80)...................................................................................89
5.2.5 Override during Rigid Tapping ..............................................................................90
5.2.5.1 Extraction override ............................................................................................ 90
5.2.5.2 Override signal .................................................................................................. 92
5.3 OPTIONAL CHAMFERING AND CORNER R .............................................93
5.4 INDEX TABLE INDEXING FUNCTION........................................................ 97
6 COMPENSATION FUNCTION ............................................................100
6.1 TOOL LENGTH COMPENSATION SHIFT TYPES ...................................101
6.2 AUTOMATIC TOOL LENGTH MEASUREMENT (G37) ............................ 106
6.3 TOOL OFFSET (G45 TO G48).................................................................. 110
6.4 OVERVIEW OF CUTTER COMPENSATION (G40-G42).......................... 115
6.5 OVERVIEW OF TOOL NOSE RADIUS COMPENSATION (G40-G42) ..... 122
6.5.1 Imaginary Tool Nose............................................................................................122
6.5.2 Direction of Imaginary Tool Nose .......................................................................124
6.5.3 Offset Number and Offset Value..........................................................................126
6.5.4 Workpiece Position and Move Command............................................................127
6.5.5 Notes on Tool Nose Radius Compensation..........................................................134
6.6 DETAILS OF CUTTER OR TOOL NOSE RADIUS COMPENSATION...... 136
6.6.1 Overview ..............................................................................................................136
6.6.2 Tool Movement in Start-up ..................................................................................140
6.6.3 Tool Movement in Offset Mode...........................................................................146
6.6.4 Tool Movement in Offset Mode Cancel...............................................................167
6.6.5 Prevention of Overcutting Due to Cutter or Tool Nose Radius Compensation ...175
6.6.6 Interference Check ...............................................................................................179
6.6.6.1 Operation to be performed if an interference is judged to occur ..................... 183
6.6.6.2 Interference check alarm function ...................................................................184
6.6.6.3 Interference check avoidance function ............................................................ 186
6.6.7 Cutter or Tool Nose Radius Compensation for Input from MDI .........................193
6.7 VECTOR RETENTION (G38) .................................................................... 195
6.8 CORNER CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION (G39) ........................................ 196
c-2
Page 19
B-63944EN-2/02 TABLE OF CONTENTS
6.9 THREE-DIMENSIONAL CUTTER COMPENSATION (G40, G41) ............198
6.10 TOOL COMPENSATION VALUES, NUMBER OF COMPENSATION
VALUES, AND ENTERING VALUES FROM THE PROGRAM (G10) ....... 203
6.11 COORDINATE SYSTEM ROTATION (G68, G69)..................................... 207
6.12 ACTIVE OFFSET VALUE CHANGE FUNCTION BASED ON MANUAL
FEED .........................................................................................................214
6.13 ROTARY TABLE DYNAMIC FIXTURE OFFSET....................................... 219
6.14 NORMAL DIRECTION CONTROL (G40.1, G41.1, G42.1)........................ 226
7 MEMORY OPERATION USING Series 15 PROGRAM FORMAT .....231
8 AXIS CONTROL FUNCTIONS............................................................232
8.1 TANDEM CONTROL ................................................................................. 233
8.2 CHOPPING FUNCTION ............................................................................ 234
III. OPERATION
1 SETTING AND DISPLAYING DATA................................................... 245
OFFSET
1.1 SCREENS DISPLAYED BY FUNCTION KEY
1.1.1 Setting and Displaying the Tool Compensation Value ........................................247
1.1.2 Tool Length Measurement ...................................................................................250
1.1.3 Tool Length/Workpiece Origin Measurement B..................................................252
1.1.4 Setting and Displaying the Rotary Table Dynamic Fixture Offset ......................271
SETTING
.................................. 246
APPENDIX
A PARAMETERS.................................................................................... 277
A.1 DESCRIPTION OF PARAMETERS........................................................... 278
A.2 DATA TYPE............................................................................................... 314
A.3 STANDARD PARAMETER SETTING TABLES......................................... 315
c-3
Page 20

Page 21

I. GENERAL
Page 22

Page 23
B-63944EN-2/02 GENERAL 1.GENERAL
1 GENERAL
This manual consists of the following parts:
About this manual
I. GENERAL
Describes chapter organization, applicable models, related
manuals, and notes for reading this manual.
II. PROGRAMMING
Describes each function: Format used to program functions in the
NC language, characteristics, and restrictions.
III. OPERATION
Describes the manual operation and automatic operation of a
machine, procedures for inputting and outputting data, and
procedures for editing a program.
APPENDIX
Lists parameters.
NOTE
1 This manual describes the functions that can
operate in the machining center system path
control type. For other functions not specific to the
lathe system, refer to the User's Manual (Common
to Lathe System/Machining Center System) (B-
63944EN).
2 Some functions described in this manual may not
be applied to some products. For detail, refer to the
DESCRIPTIONS manual (B-63942EN).
3 This manual does not detail the parameters not
mentioned in the text. For details of those
parameters, refer to the parameter manual (B-
63950EN).
Parameters are used to set functions and
operating conditions of a CNC machine tool, and
frequently-used values in advance. Usually, the
machine tool builder factory-sets parameters so
that the user can use the machine tool easily.
4 This manual describes not only basic functions but
also optional functions. Look up the options
incorporated into your system in the manual written
by the machine tool builder.
- 3 -
Page 24
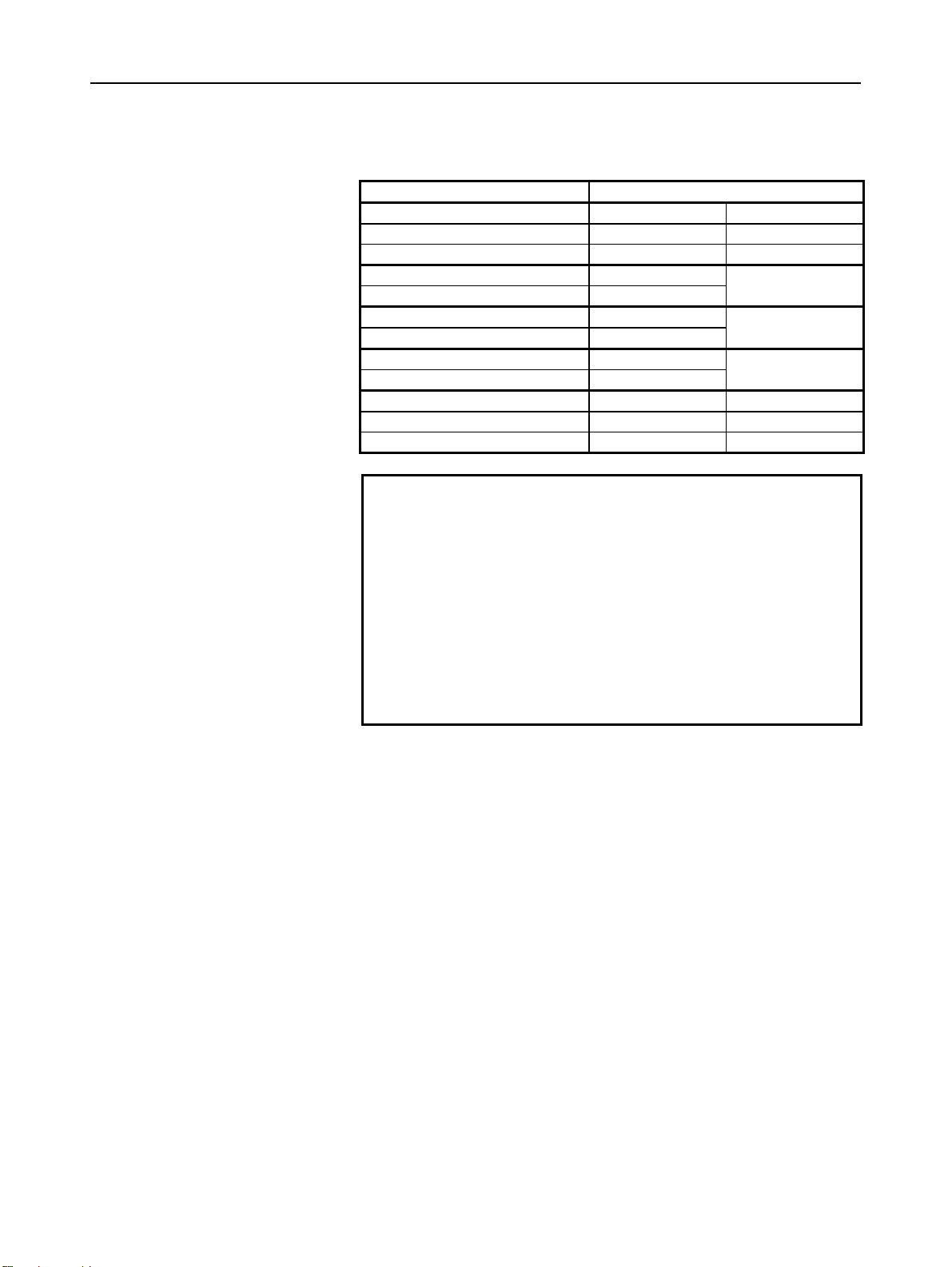
1.GENERAL GENERAL B-63944EN-2/02
Applicable models
The models covered by this manual, and their abbreviations are :
Model name Abbreviation
FANUC Series 30i-MODEL A 30i –A Series 30i
FANUC Series 300i-MODEL A 300i–A Series 300i
FANUC Series 300is-MODEL A 300is–A Series 300is
FANUC Series 31i-MODEL A 31i –A
FANUC Series 31i-MODEL A5 31i –A5
FANUC Series 310i-MODEL A 310i–A
FANUC Series 310i-MODEL A5 310i–A5
FANUC Series 310is-MODEL A 310is–A
FANUC Series 310is-MODEL A5 310is–A5
FANUC Series 32i-MODEL A 32i –A Series 32i
FANUC Series 320i-MODEL A 320i–A Series 320i
FANUC Series 320is-MODEL A 320is–A Series 320is
Series 31i
Series 310i
Series 310is
NOTE
1 Unless otherwise noted, the model names
31i/310i/310is-A, 31i/310i/310is-A5, and
32i/320i/320is-A are collectively referred to as
30i/300i/300is. However, this convention is not
necessarily observed when item 3 below is
applicable.
2 Some functions described in this manual may not
be applied to some products.
For details, refer to the DESCRIPTIONS (B-
63942EN).
Special symbols
This manual uses the following symbols:
- IP
Indicates a combination of axes such as X_ Y_ Z_
In the underlined position following each address, a numeric value
such as a coordinate value is placed (used in PROGRAMMING.).
- ;
Indicates the end of a block. It actually corresponds to the ISO code
LF or EIA code CR.
- 4 -
Page 25
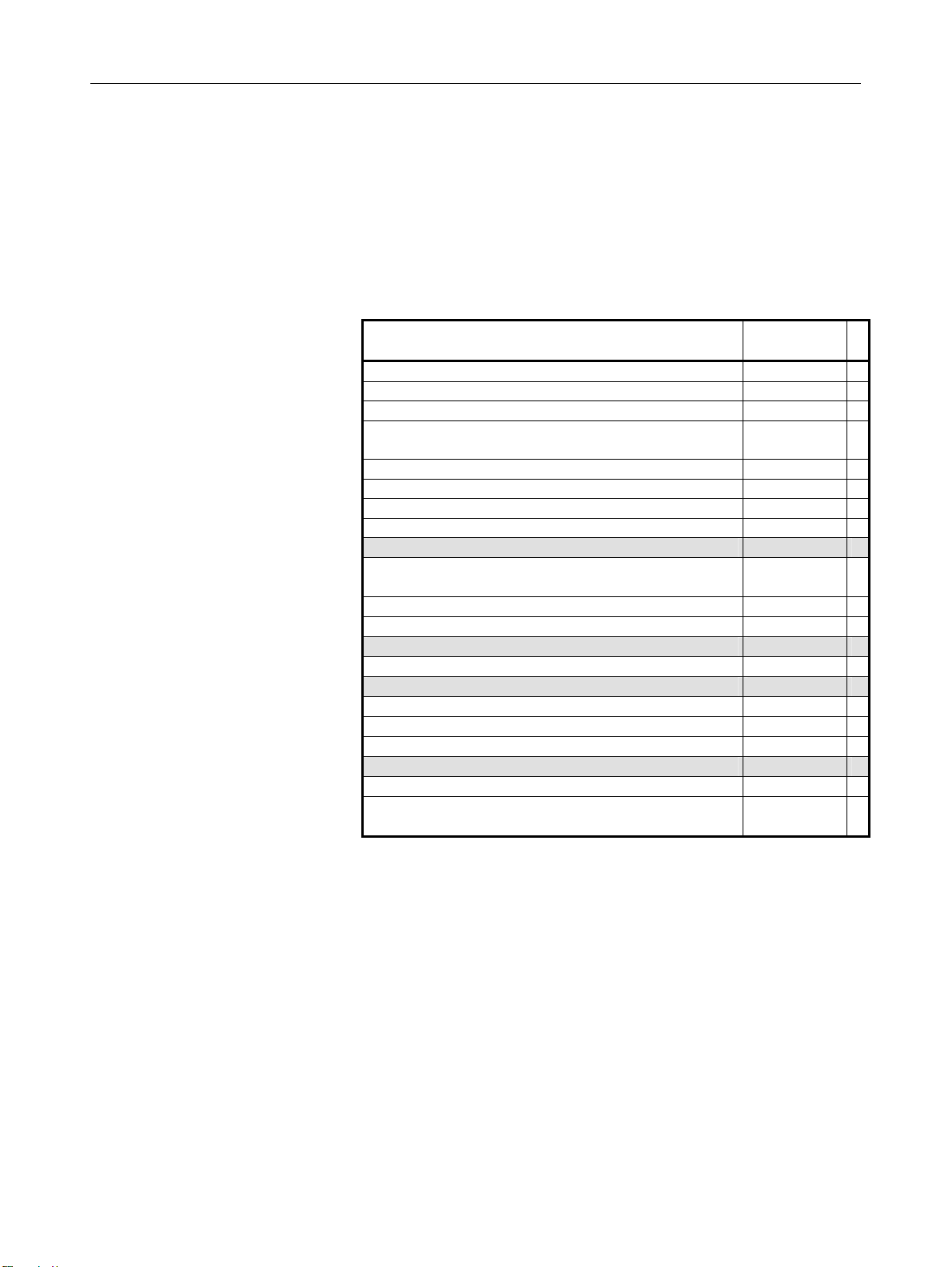
B-63944EN-2/02 GENERAL 1.GENERAL
Related manuals of
Series 30i/300i/300is- MODEL A
Series 31i/310i/310is- MODEL A
Series 31i/310i/310is- MODEL A5
Series 32i/320i/320is- MODEL A
The following table lists the manuals related to Series 30i/300i /300is-
A, Series 31i/310i /310is-A, Series 31i/310i /310is-A5, Series
32i/320i /320is-A. This manual is indicated by an asterisk(*).
Table 1 Related manuals
Manual name Specification
number
DESCRIPTIONS B-63942EN
CONNECTION MANUAL (HARDWARE) B-63943EN
CONNECTION MANUAL (FUNCTION) B-63943EN-1
USER’S MANUAL
(Common to Lathe System/Machining Center System)
USER’S MANUAL (For Lathe System) B-63944EN-1
USER’S MANUAL (For Lathe Machining Center System) B-63944EN-2 *
MAINTENANCE MANUAL B-63945EN
PARAMETER MANUAL B-65950EN
Programming
Macro Compiler / Macro Executor PROGRAMMING
MANUAL
Macro Compiler OPERATOR’S MANUAL B-66264EN
C Language Executor OPERATOR’S MANUAL B-63944EN-3
PMC
PMC PROGRAMMING MANUAL B-63983EN
Network
PROFIBUS-DP Board OPERATOR’S MANUAL B-63994EN
Fast Ethernet / Fast Data Server OPERATOR’S MANUAL B-64014EN
DeviceNet Board OPERATOR’S MANUAL B-64044EN
Operation guidance function
MANUAL GUIDE i OPERATOR’S MANUAL
MANUAL GUIDE i Set-up Guidance
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
B-63944EN
B-63943EN-2
B-63874EN
B-63874EN-1
- 5 -
Page 26
1.GENERAL GENERAL B-63944EN-2/02
Related manuals of SERVO MOTOR αis/αi/βis/βi series
The following table lists the manuals related to SERVO MOTOR
αis/αi/βis/βi series
Table 2 Related manuals
Manual name
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR αis series
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR αi series
DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR αi series
DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR βis series
DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR βi series
DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC SERVO AMPLIFIER αi series
DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC SERVO AMPLIFIER βi series
DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC SERVO MOTOR αis series
FANUC SERVO MOTOR αi series
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR αi series
FANUC SERVO AMPLIFIER αi series
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
FANUC SERVO MOTOR βis series
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR βi series
FANUC SERVO AMPLIFIER βi series
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR αis series
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR αi series
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR βis series
PARAMETER MANUAL
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR αi series
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR βi series
PARAMETER MANUAL
Any of the servo motors and spindles listed above can be connected to
the CNC described in this manual. However, αi series servo amplifiers
can only be connected to αi series SVMs (for 30i/31i/32i).
This manual mainly assumes that the FANUC SERVO MOTOR αi
series of servo motor is used. For servo motor and spindle information,
refer to the manuals for the servo motor and spindle that are actually
connected.
Specification
number
B-65262EN
B-65272EN
B-65302EN
B-65312EN
B-65282EN
B-65322EN
B-65285EN
B-65325EN
B-65270EN
B-65280EN
- 6 -
Page 27
B-63944EN-2/02 GENERAL 1.GENERAL
1.1 NOTES ON READING THIS MANUAL
CAUTION
1 The function of an CNC machine tool system
depends not only on the CNC, but on the
combination of the machine tool, its magnetic
cabinet, the servo system, the CNC, the operator's
panels, etc. It is too difficult to describe the function,
programming, and operation relating to all
combinations. This manual generally describes these
from the stand-point of the CNC. So, for details on a
particular CNC machine tool, refer to the manual
issued by the machine tool builder, which should take
precedence over this manual.
2 In the header field of each page of this manual, a
chapter title is indicated so that the reader can
reference necessary information easily.
By finding a desired title first, the reader can
reference necessary parts only.
3 This manual describes as many reasonable variations
in equipment usage as possible. It cannot address
every combination of features, options and commands
that should not be attempted.
If a particular combination of operations is not
described, it should not be attempted.
1.2 NOTES ON VARIOUS KINDS OF DATA
CAUTION
Machining programs, parameters, offset data, etc.
are stored in the CNC unit internal non-volatile
memory. In general, these contents are not lost by
the switching ON/OFF of the power. However, it is
possible that a state can occur where precious data
stored in the non-volatile memory has to be deleted,
because of deletions from a maloperation, or by a
failure restoration. In order to restore rapidly when
this kind of mishap occurs, it is recommended that
you create a copy of the various kinds of data
beforehand.
- 7 -
Page 28

Page 29

II. PROGRAMMING
Page 30

Page 31

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 1.GENERAL
1 GENERAL
- 11 -
Page 32

1.GENERAL PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
p
1.1 TOOL FIGURE AND TOOL MOTION BY PROGRAM
Explanation
- Machining using the end of cutter - Tool length compensation function
Usually, several tools are used for machining one workpiece. The
tools have different tool length. It is very troublesome to change the
program in accordance with the tools.
Therefore, the length of each tool used should be measured in advance.
By setting the difference between the length of the standard tool and
the length of each tool in the CNC (See Chapter “Setting and
Displaying Data” in User’s Manual (Common to T/M series)),
machining can be performed without altering the program even when
the tool is changed. This function is called tool length compensation
(See Section “Tool Length Compensation” in User’s Manual
(Common to T/M series)).
Standard
H1 H2
tool
Workpiece
H3 H4
- Machining using the side of cutter - Cutter compensation function
ath using cutter compensation
Cutter
Workpiece
Machined part figure
Tool
Because a cutter has a radius, the center of the cutter path goes around
the workpiece with the cutter radius deviated.
If radius of cutters are stored in the CNC (See Chapter “Setting and
Displaying Data” in User’s Manual (Common to T/M series)), the tool
can be moved by cutter radius apart from the machining part figure.
This function is called cutter compensation (See Section II-6 “Tool
Compensation Function”).
- 12 -
Page 33

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 2.PREPARATORY FUNCTION (G FUNCTION)
2 PREPARATORY FUNCTION (G
FUNCTION)
A number following address G determines the meaning of the
command for the concerned block.
G codes are divided into the following two types.
Type Meaning
One-shot G code
Modal G code
(Example)
G01 and G00 are modal G codes in group 01.
G01 X_ ;
Z_ ; G01 is effective in this range.
X_ ;
G00 Z_ ; G00 is effective in this range.
X_ ;
G01 X_ ;
:
The G code is effective only in the block in which it
is specified.
The G code is effective until another G code of the
same group is specified.
- 13 -
Page 34

2.PREPARATORY FUNCTION (G FUNCTION) PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Explanation
1. When the clear state (parameter CLR (No. 3402#6)) is set at
power-up or reset, the modal G codes are placed in the states
described below.
(1) The modal G codes are placed in the states marked with
as indicated in Table.
(2) G20 and G21 remain unchanged when the clear state is set
at power-up or reset.
(3) Which status G22 or G23 at power on is set by parameter
G23 (No. 3402#7). However, G22 and G23 remain
unchanged when the clear state is set at reset.
(4) The user can select G00 or G01 by setting parameter G01
(No. 3402#0).
(5) The user can select G90 or G91 by setting parameter G91
(No. 3402#3).
When G code system B or C is used in the lathe system,
setting parameter G91 (No. 3402#3) determines which code,
either G90 or G91, is effective.
(6) In the machining center system, the user can select G17,
G18, or G19 by setting parameters G18 and G19 (No.
3402#1 and #2).
2. G codes other than G10 and G11 are one-shot G codes.
3. When a G code not listed in the G code list is specified, or a G
code that has no corresponding option is specified, alarm PS0010
occurs.
4. Multiple G codes can be specified in the same block if each G
code belongs to a different group. If multiple G codes that belong
to the same group are specified in the same block, only the last G
code specified is valid.
5. If a G code belonging to group 01 is specified in a canned cycle
for drilling, the canned cycle for drilling is cancelled. This means
that the same state set by specifying G80 is set. Note that the G
codes in group 01 are not affected by a G code specifying a
canned cycle for drilling.
6. G codes are indicated by group.
7. The group of G60 is switched according to the setting of the
parameter MDL (No. 5431#0). (When the MDL bit is set to 0,
the 00 group is selected. When the MDL bit is set to 1, the 01
group is selected.)
- 14 -
Page 35

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 2.PREPARATORY FUNCTION (G FUNCTION)
Table 2(a) G code list
G code Group Function
G00 Positioning (rapid traverse)
G01 Linear interpolation (cutting feed)
G02 Circular interpolation CW or helical interpolation CW
G03 Circular interpolation CCW or helical interpolation CCW
G02.2, G03.2 Involute interpolation CW/CCW
G02.3, G03.3 Exponential interpolation CW/CCW
G02.4, G03.4
G04 Dwell
G05 AI contour control (high-precision contour control compatible command)
G05.1 AI contour control / Nano smoothing / Smooth interpolation
G05.4
G06.2 01 NURBS interpolation
G07 Hypothetical axis interpolation
G07.1 (G107) Cylindrical interpolation
G08 AI contour control (advanced preview control compatible command)
G09 Exact stop
G10 Programmable data input
G10.6 Tool retract and recover
G10.9 Programmable switching of diameter/radius specification
G11
G12.1 Polar coordinate interpolation mode
G13.1
G15 Polar coordinates command cancel
G16
G17 XpYp plane selection
G18 ZpXp plane selection
G19
G20 (G70) Input in inch
G21 (G71)
G22 Stored stroke check function on
G23
G25 Spindle speed fluctuation detection off
G26
G27 Reference position return check
G28 Automatic return to reference position
G29 Movement from reference position
G30 2nd, 3rd and 4th reference position return
G30.1 Floating reference position return
G31 Skip function
G31.8
G33 Threading
G34 Variable lead threading
G35 Circular threading CW
G36
G37 Automatic tool length measurement
G38 Cutter or tool nose radius compensation : preserve vector
G39
01
00
00
21
17
02
06
04
19
00
01
00
Three-dimensional coordinate conversion CW/CCW
HRV3,4 on/off
Programmable data input mode cancel
Polar coordinate interpolation cancel mode
Polar coordinates command
Xp: X axis or its parallel axis
Yp: Y axis or its parallel axis
YpZp plane selection
Input in mm
Stored stroke check function off
Spindle speed fluctuation detection on
EGB-axis skip
Circular threading CCW
Cutter or tool nose radius compensation : corner circular interpolation
Zp: Z axis or its parallel axis
- 15 -
Page 36

2.PREPARATORY FUNCTION (G FUNCTION) PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Table 2(a) G code list
G code Group Function
G40 Cutter or tool nose radius compensation : cancel
Three-dimensional cutter compensation : cancel
G41
G41.2 Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : left (type 1)
G41.3 Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : (leading edge offset)
G41.4 Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : left (type 1) (FS16i-compatible command)
G41.5 Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : left (type 1) (FS16i-compatible command)
G41.6 Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : left (type 2)
G42
G42.2 Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : right (type 1)
G42.4 Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : right (type 1) (FS16i-compatible command)
G42.5 Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : right (type 1) (FS16i-compatible command)
G42.6
G40.1 Normal direction control cancel mode
G41.1 Normal direction control on : right
G42.1
G43 Tool length compensation +
G44
G43.1 Tool length compensation in tool axis direction
G43.4 Tool center point control (type 1)
G43.5
G45 Tool offset increase
G46 Tool offset decrease
G47 Tool offset double increase
G48
G49 (G49.1) 08 Tool length compensation cancel
G50 Scaling cancel
G51
G50.1 Programmable mirror image cancel
G51.1
G50.2 Polygon turning cancel
G51.2
G52 Local coordinate system setting
G53 Machine coordinate system setting
G53.1
G54 (G54.1) Workpiece coordinate system 1 selection
G55 Workpiece coordinate system 2 selection
G56 Workpiece coordinate system 3 selection
G57 Workpiece coordinate system 4 selection
G58 Workpiece coordinate system 5 selection
G59
G60 00 Single direction positioning
G61 Exact stop mode
G62 Automatic corner override
G63 Tapping mode
G64
G65 00 Macro call
07
19
08
08
00
11
22
31
00
14
15
Cutter or tool nose radius compensation : left
Three-dimensional cutter compensation : left
Cutter or tool nose radius compensation : right
Three-dimensional cutter compensation : right
Cutter compensation for 5-axis machining : right (type 2)
Normal direction control on : left
Tool length compensation -
Tool center point control (type 2)
Tool offset double decrease
Scaling
Programmable mirror image
Polygon turning
Tool axis direction control
Workpiece coordinate system 6 selection
Cutting mode
- 16 -
Page 37

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 2.PREPARATORY FUNCTION (G FUNCTION)
Table 2(a) G code list
G code Group Function
G66 Macro modal call A
G66.1 Macro modal call B
G67
G68 Coordinate system rotation start or 3-dimensional coordinate conversion mode on
G69 Coordinate system rotation cancel or 3-dimensional coordinate conversion mode off
G68.2
G72.1 Figure copy (rotation copy)
G72.2
G73 Peck drilling cycle
G74 Left-handed tapping cycle
G76 Fine boring cycle
G80
G80.5 24 Electronic gear box 2 pair: synchronization cancellation
G80.8 34 Electronic gear box: synchronization cancellation
G81 09 Drilling cycle or spot boring cycle
G81.1 00 Chopping
G81.5 24 Electronic gear box 2 pair: synchronization start
G81.8 34 Electronic gear box: synchronization start
G82 Drilling cycle or counter boring cycle
G83 Peck drilling cycle
G84 Tapping cycle
G84.2 Rigid tapping cycle (FS15 format)
G84.3 Left-handed rigid tapping cycle (FS15 format)
G85 Boring cycle
G86 Boring cycle
G87 Back boring cycle
G88 Boring cycle
G89
G90 Absolute programming
G91
G91.1 Checking the maximum incremental amount specified
G92 Setting for workpiece coordinate system or clamp at maximum spindle speed
G92.1
G93 Inverse time feed
G94 Feed per minute
G95
G96 Constant surface speed control
G97
G98 Canned cycle : return to initial level
G99
G107 00 Cylindrical interpolation
G112 Polar coordinate interpolation mode
G113
12
16
00
09
09
03
00
05
13
10
21
Macro modal call A/B cancel
Feature coordinate system selection
Figure copy (linear copy)
Canned cycle cancel
Boring cycle
Incremental programming
Workpiece coordinate system preset
Feed per revolution
Constant surface speed control cancel
Canned cycle : return to R point level
Polar coordinate interpolation mode cancel
- 17 -
Page 38

3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
3 INTERPOLATION FUNCTION
- 18 -
Page 39

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION
3.1 INVOLUTE INTERPOLATION (G02.2, G03.2)
Overview
Involute curve machining can be performed by using involute
interpolation. Cutter compensation can be performed. Involute
interpolation eliminates the need for approximating an involute curve
with minute segments or arcs, and continuous pulse distribution is
ensured even in high-speed operation of small blocks. Accordingly,
high-speed operation can be performed smoothly. Moreover,
machining programs can be created more easily, and the size of
machining programs can be reduced.
In involute interpolation, the following two types of feedrate override
functions are automatically executed, and a favorable cutting surface
can be formed with high precision. (Automatic speed control
function for involute interpolation)
• Override in cutter compensation mode
• Override in the vicinity of basic circle
Format
Involute interpolation on the Xp-Yp plane
G17 G02.2 Xp_ Yp_ I_ J_ R_ F_ ;
G17 G03.2 Xp_ Yp_ I_ J_ R_ F_ ;
Involute interpolation on the Zp-Xp plane
G18 G02.2 Zp_ Xp_ K_ I_ R_ F_ ;
G18 G03.2 Zp_ Xp_ K_ I_ R_ F_ ;
Involute interpolation on the Yp-Zp plane
G19 G02.2 Yp_ Zp_ J_ K_ R_ F_ ;
G19 G03.2 Yp_ Zp_ J_ K_ R_ F_ ;
Where,
G02.2 : Involute interpolation (clockwise)
G03.2 : Involute interpolation (counterclockwise)
G17/G18/G19 : Xp-Yp/Zp-Xp/Yp-Zp plane selection
Xp_ : X-axis or an axis parallel to the X-axis
(specified in a parameter)
Yp_ : Y-axis or an axis parallel to the Y-axis
(specified in a parameter)
Zp_ : Z-axis or an axis parallel to the Z-axis
(specified in a parameter)
I_, J_, K_ : Center of the base circle for an involute curve
viewed from the start point
R_ : Base circle radius
F_ : Cutting feedrate
- 19 -
Page 40

3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Explanation
Involute curve machining can be performed by using involute
interpolation. Involute interpolation ensures continuous pulse
distribution even in high-speed operation in small blocks, thus
enabling smooth and high-speed machining. Moreover, machining
programs can be created more easily, and the size of machining
programs can be reduced.
- Involute curve
Xp
Xp
Yp
Yp
Po
Ps
I
R
Pe
I
End point
Ro
J
Start point
Ps
J
End point
Pe
0
R
0
Yp
0
I
0
R
End point
Pe
Po
R
Start point
Ps
Po
J
Start
point
Yp
End
point
Ps
Pe
J
I
Base circle
Clockwise involute interpolation (G02.2)
Counterclockwise involute interpolation (G03.2)
Fig. 3.1 (a) Actual movement
An involute curve on the X-Y plane is defined as follows ;
X (θ) = R [cos θ + (θ - θ
) sin θ] + X
O
O
Y (θ) = R [sin θ - (θ - θO) cos θ] + YO
where,
, YO : Coordinates of the center of a base circle
X
O
R : Base circle radius
: Angle of the start point of an involute curve
θ
O
θ : Angle of the point where a tangent from the current
position to the base circle contacts the base circle
X (θ), Y (θ) : Current position on the X-axis and Y-axis
Xp
Xp
- 20 -
Page 41

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION
θ
θ
Y
Start point
R
o
Involute curve
(X, Y)
- Start point and end point
- Base circle specification
(Xo, Yo)
Base circle
Fig. 3.1 (b) Involute curve
End point
X
Involute curves on the Z-X plane and Y-Z plane are defined in the
same way as an involute curve on the X-Y plane.
The end point of an involute curve is specified using address Xp, Yp,
or Zp. An absolute value or incremental value is used to specify an
Xp, Yp, or Zp value. When using an incremental value, specify the
coordinates of the end point viewed from the start point of the involute
curve.
When no end point is specified, alarm PS0241 is issued.
If the specified start point or end point lies within the base circle,
alarm PS0242 is issued. The same alarm is issued if cutter
compensation C causes the offset vector to enter the base circle. Be
particularly careful when applying an offset to the inside of an
involute curve.
The center of a base circle is specified with I, J, and K, corresponding
to X, Y, and Z. The value following I, J, or K is a vector component
defined when the center of the base circle is viewed from the start
point of the involute curve; this value must always be specified as an
incremental value, regardless of the G90/G91 setting. Assign a sign
to I, J, and K according to the direction.
If I, J, and K are all left unspecified, or I0, J0, K0 is specified, alarm
PS0241 or PS0242 is issued.
If R is not specified, or R ≤ 0, alarm PS0241 or PS0242 is issued.
- 21 -
Page 42

3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Choosing from two types of involute curves
When only a start point and I, J, and K data are given, two types of
involute curves can be created. One type of involute curve extends
towards the base circle, and the other extends away from the base
circle. When the specified end point is closer to the center of the
base circle than the start point, the involute curve extends toward the
base circle. In the opposite case, the involute curve extends away
from the base circle.
- Feedrate
The cutting feedrate specified in an F code is used as the feedrate for
involute interpolation. The feedrate along the involute curve
(feedrate along the tangent to the involute curve) is controlled to
satisfy the specified feedrate.
- Plane selection
As with circular interpolation, the plane to which to apply involute
interpolation can be selected using G17, G18, and G19.
- Cutter compensation
Cutter compensation can be applied to involute curve machining. As
with linear and circular interpolation, G40, G41, and G42 are used to
specify cutter compensation.
G40: Cutter compensation cancel
G41: Cutter compensation left
G42: Cutter compensation right
First, a point of intersection with a segment or an arc is approximated
both at the start point and at the end point of the involute curve. An
involute curve passing the two approximated points of intersection
with the start point and end pint becomes the tool center path.
Before selecting the involute interpolation mode, specify G41 or G42,
cancel involute interpolation, and then specify G40. G41, G42, and
G40 for cutter compensation cannot be specified in the involute
interpolation mode.
- Automatic speed control
Cutting precision can be improved by automatically overriding the
programmed feedrate during involute interpolation. See a
subsequent subsection, "Automatic Speed Control for Involute
Interpolation."
- 22 -
Page 43

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION
- Specifiable G codes
The following G codes can be specified in involute interpolation
mode:
G04: Dwell
G10: Programmable data input
G17: X-Y plane selection
G18: Z-X plane selection
G19: Y-Z plane selection
G65: Macro call
G66: Macro modal call
G67: Macro modal call cancel
G90: Absolute programming
G91: Incremental programming
- Modes that allow involute interpolation specification
Involute interpolation can be specified in the following G code modes:
G41 : Cutter compensation left
G42 : Cutter compensation right
G51 : Scaling
G51.1 : Programmable mirror image
G68 : Coordinate rotation
- End point error
As shown below the end point may not be located on an involute
curve that passes through the start point.
When an involute curve that passes through the start point deviates
from the involute curve that passes through the end point by more than
the value set in parameter No. 5610, alarm PS0243 is issued.
If there is an end point error, the programmed feedrate changes by the
amount of error.
X
End point
Pe
Path after correction
Deviation
Start point
Ps
Correct involute curve
Y
Fig. 3.1 (c) End point error in counterclockwise involute interpolation
(G03.2)
- 23 -
Page 44

3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
3.1.1 Automatic Speed Control for Involute Interpolation
This function automatically overrides the programmed feedrate in two
different ways during involute interpolation. With this function, a
favorable cutting surface can be formed with high precision.
• Override in cutter compensation mode
• Override in the vicinity of basic circle
- Override in cutter compensation mode
When cutter compensation is applied to involute interpolation, control
is exercised in ordinary involute interpolation so that the tangential
feedrate on the tool-center path always keeps the specified feedrate.
Under the control, the actual cutting feedrate (feedrate around the
perimeter of the tool (cutting point) on the path specified in the
program) changes because the curvature of the involute curve changes
every moment.
If the tool is offset in the inward direction of the involute curve in
particular, the actual cutting feedrate becomes higher than the
specified feedrate as the tool gets nearer to the base circle.
For smooth machining, it is desirable to control the actual cutting
feedrate so that the feedrate keeps the specified feedrate. This
function calculates an appropriate override value for the
ever-changing curvature of the involute curve in the involute
interpolation mode after cutter compensation. The function also
controls the actual cutting feedrate (tangential feedrate at the cutting
point) so that it always keeps the specified feedrate.
Cutting point
Rofs
Rcp
Base
circle
Fig. 3.1 (d) Override for inward offset by cutter compensation
Path specified in
the program
- 24 -
Page 45

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION
Inward offset
OVR = Rcp/(Rcp + Rofs) × 100
Outward offset
OVR = Rcp/(Rcp - Rofs) × 100
where,
Rcp : Radius of curvature at the center of the tool of the
involute curve passing through the center of the tool
Rofs : Radius of the cutter
- Clamping the override
The lower limit of override is specified in parameter No. 5620 so that
the override for inward offset by cutter compensation or the override
in the vicinity of the basic circle will not bring the speed of the tool
center to zero in the vicinity of the basic circle.
The lower limit of override (OVR1o) is specified in parameter No.
5620 so that the inward offset will not reduce the speed of the tool
center to a very low level in the vicinity of the basic circle.
Accordingly, the feedrate is clamped but does not fall below the level
determined by the programmed feedrate and the lower limit of
override (OVR1o).
The outward offset may increase the override to a very high level, but
the feedrate will not exceed the maximum cutting feedrate.
- Clamping the acceleration in the vicinity of basic circle
If the acceleration calculated from the radius of curvature of the
involute curve exceeds a value specified in the corresponding
parameter, the tangential velocity is controlled so that the actual
acceleration will not exceed the value specified in the parameter.
Because the acceleration is always limited to a constant level, efficient
velocity control can be performed for each machine. Because
smooth velocity control can be performed continuously, impacts in
machining in the vicinity of the basic circle can be reduced.
To calculate the acceleration, the radius of curvature of the involute
curve and the tangential velocity are substituted into the following
formula of circular acceleration:
Acceleration = F × F/R
F: Tangential velocity
R: Radius of curvature
The maximum permissible acceleration is specified in parameter No.
1735.
If the calculated acceleration exceeds the maximum permissible
acceleration, the feedrate is clamped to the level calculated by the
following expression:
If the calculated clamp level falls below the lower limit of feedrate,
the lower limit of feedrate becomes the clamp level. The lower limit
of feedrate is specified in parameter No. 1732.
onaccelerati epermissibl Maximum curvature of Radius level Clamp ×=
- 25 -
Page 46

3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
3.1.2 Helical Involute Interpolation (G02.2, G03.2)
As with arc helical involute interpolation, this function performs
helical involute interpolation on the two axes involute interpolation
and on up to four other axes simultaneously.
Format
Helical involute interpolation in Xp-Yp plane
G17
Helical involute interpolation in Zp-Xp plane
G18
Helical involute interpolation in Yp-Zp plane
G19
α, β, γ, δ: Optional axis other than the axes of involute interpolation.
G02.2
G03.2
G02.2
G03.2
G02.2
G03.2
Up to four axes can be specified.
Xp Yp
Zp Xp
Yp Zp
I J R
K I R α β γ δ F ;
J K R α β γ δ F ;
β γ δ F ;
α
- 26 -
Page 47

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION
3.1.3 Involute Interpolation on Linear Axis and Rotary Axis
(G02.2, G03.2)
By performing involute interpolation in the polar coordinate
interpolation mode, involute cutting can be carried out. Cutting is
performed along an involute curve drawn in the plane formed by a
linear axis and a rotary axis.
Format
If the linear axis is the X-axis or an axis parallel to the X-axis, the
plane is considered to be the Xp-Yp plane, and I and J are used.
G02.2
G03.2
If the linear axis is the Y-axis or an axis parallel to the Y-axis, the
plane is considered to be the Yp-Zp plane, and J and K are used.
G02.2
G03.2
If the linear axis is the Z-axis or an axis parallel to the Z-axis, the
plane is considered to be the Zp-Xp plane, and K and I are used.
G02.2
G03.2
G02.2: Clockwise involute interpolation
G03.2: Counterclockwise involute interpolation
Example) If the linear axis is the X-axis
X, C : End point of the involute curve
I, J : Center of the basic circle of the involute curve, viewed from the
R : Radius of basic circle
F : Cutting feedrate
X C
Y C
Z C
start point
I J R F ;
J K R F ;
K I R F ;
- 27 -
Page 48

3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Example
C (Imaginary axis)
Path after tool
compensation
Programmed path
N202
N204
N205
N201
C-axis
Tool
X-axis
N200
N203
Fig. 3.1 (e) Involute interpolation in the polar coordinate interpolation mode
Z-axis
O0001 ;
.
.
N010 T0101 ;
.
.
N100 G90 G00 X15.0 C0 Z0 ;
N200 G12.1 ;
N201 G41 G00 X-1.0 ;
Positioning to the start point
Polar coordinate interpolation
started
N202 G01 Z-2.0 F__ ;
N203 G02.2 X1.0 C9.425 I1.0 J0 R1.0 ;
N204 G01 Z0 ;
Involute interpolation during polar
coordinate interpolation
N205 G40 G00 X15.0 C0 ;
N206 G13.1 ;
N300 Z__ ;
Polar coordinate interpolation
cancelled
N400 X__ C__ ;
.
.
M30 ;
- 28 -
Page 49

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION
Limitation
- Number of involute curve turns
Both the start point and end point must be within 100 turns from the
point where the involute curve starts. An involute curve can be
specified to make one or more turns in a single block.
If the specified start point or end point is beyond 100 turns from the
point where the involute curve starts, alarm PS0242 is issued.
- Unspecifiable functions
In involute interpolation mode, optional chamfering and corner R
cannot be specified.
- Mode that does not allow involute interpolation specification
Involute interpolation cannot be used in the following mode:
G07.1: Cylindrical interpolation
- 29 -
Page 50

3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
3.2 THREADING (G33)
Straight threads with a constant lead can be cut. The position coder
mounted on the spindle reads the spindle speed in real-time. The read
spindle speed is converted to the feedrate per minute to feed the tool.
Format
Z
G33IP_ F_ ;
F :Long axis direction lead
Workpiece
Explanation
X
In general, threading is repeated along the same tool path in rough
cutting through finish cutting for a screw. Since threading starts
when the position coder mounted on the spindle outputs a 1-turn
signal, threading is started at a fixed point and the tool path on the
workpiece is unchanged for repeated threading. Note that the spindle
speed must remain constant from rough cutting through finish cutting.
If not, incorrect thread lead will occur.
In general, the lag of the servo system, etc. will produce somewhat
incorrect leads at the starting and ending points of a thread cut. To
compensate for this, a threading length somewhat longer than required
should be specified.
Table 3.2 (a) lists the ranges for specifying the thread lead.
Table 3.2 (a) Ranges of lead sizes that can be specified
Least
Metric input
Inch input
command
increment
0.001 mm F1 to F50000 (0.01 to 500.00mm)
0.0001 mm F1 to F50000 (0.01 to 500.00mm)
0.0001 inch F1 to F99999 (0.0001 to 9.9999inch)
0.00001 inch F1 to F99999 (0.0001 to 9.9999inch)
Command value range of the lead
- 30 -
Page 51

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 3.INTERPOLATION FUNCTION
NOTE
1 The spindle speed is limited as follows :
1 ≤ spindle speed ≤ (Maximum feedrate) / (Thread
lead)
Spindle speed : min-1
Thread lead : mm or inch
Maximum feedrate : mm/min or inch/min ; maximum
command-specified feedrate for feed-per-minute
mode or maximum feedrate that is determined
based on mechanical restrictions including those
related to motors, whichever is smaller
2 Cutting feedrate override is not applied to the
converted feedrate in all machining process from
rough cutting to finish cutting. The feedrate is fixed
at 100%
3 The converted feedrate is limited by the upper
feedrate specified.
4 Feed hold is disabled during threading. Pressing the
feed hold key during threading causes the machine
to stop at the end point of the next block after
threading (that is, after the G33 mode is terminated)
Example
Threading at a pitch of 1.5mm
G33 Z10. F1.5;
- 31 -
Page 52

4.COORDINATE VALUE AND DIMENSION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
4 COORDINATE VALUE AND DIMENSION
This chapter contains the following topics.
4.1 POLAR COORDINATE COMMAND (G15, G16)
- 32 -
Page 53

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 4.COORDINATE VALUE AND DIMENSION
4.1 POLAR COORDINATE COMMAND (G15, G16)
The end point coordinate value can be input in polar coordinates
(radius and angle).
The plus direction of the angle is counterclockwise of the selected
plane first axis + direction, and the minus direction is clockwise.
Both radius and angle can be commanded in either absolute or
incremental programming (G90, G91).
Format
Gxx Gyy G16; Starting the polar coordinate
command (polar coordinate mode)
G00 IP_ ;
: Polar coordinate command
:
G15; Canceling the polar coordinate
command (polar coordinate mode)
G16 : Polar coordinate command
G15 : Polar coordinate command cancel
Gxx : Plane selection of the polar coordinate command
(G17, G18 or G19)
Gyy : Center selection of the polar coordinate command
(G90 or G91)
G90 specifies the origin of the workpiece
coordinate system as the origin of the polar
coordinate system, from which a radius is
measured.
G91 specifies the current position as the origin of
the polar coordinate system, from which a radius is
measured.
IP_ : Specifying the addresses of axes constituting the
plane selected for the polar coordinate system,
and their values
First axis : radius of polar coordinate
Second axis : angle of polar coordinate
- 33 -
Page 54

4.COORDINATE VALUE AND DIMENSION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
- Setting the origin of the workpiece coordinate system as the origin of the polar
coordinate system
Specify the radius (the distance between the origin and the point) to be
programmed with an absolute programming. The origin of the
workpiece coordinate system is set as the origin of the polar
coordinate system.
When a local coordinate system (G52) is used, the origin of the local
coordinate system becomes the center of the polar coordinates.
Command position
Radius
ngle
ctual position
Radius
Command position
ngle
ctual position
When the angle is specified with an
absolute command
When the angle is specified with an
incremental command
- Setting the current position as the origin of the polar coordinate system
Specify the radius (the distance between the current position and the
point) to be programmed with an incremental programming. The
current position is set as the origin of the polar coordinate system.
Command position
Radius
When the angle is specified with an
absolute command
ngle
ctual position
Command position
ngle
Radius
ctual position
When the angle is specified with an
incremental command
Example
Bolt hole circle
Y
- The origin of the workpiece coordinate
system is set as the origin of the polar
coordinate system.
- The XY plane is selected.
150
°
30
270
°
°
100mm
X
- 34 -
Page 55

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 4.COORDINATE VALUE AND DIMENSION
- Specifying angles and a radius with absolute programmings
N1 G17 G90 G16 ; Specifying the polar coordinate command and
selecting the XY plane
Setting the origin of the workpiece coordinate
system as the origin of the polar coordinate
system
N2 G81 X100.0 Y30.0 Z-20.0 R-5.0 F200.0 ;
Specifying a distance of 100 mm and an angle
of 30 degrees
N3 Y150.0 ; Specifying a distance of 100 mm and an angle
of 150 degrees
N4 Y270.0 ; Specifying a distance of 100 mm and an angle
of 270 degrees
N5 G15 G80 ; Canceling the polar coordinate command
- Specifying angles with incremental programmings and a radius with absolute
programmings
N1 G17 G90 G16; Specifying the polar coordinate command and
selecting the XY plane
Setting the origin of the workpiece coordinate
system as the origin of the polar coordinate
system
N2 G81 X100.0 Y30.0 Z-20.0 R-5.0 F200.0 ;
Specifying a distance of 100 mm and an angle
of 30 degrees
N3 G91 Y120.0 ; Specifying a distance of 100 mm and an angle
of +120 degrees
N4 Y120.0 ; Specifying a distance of 100 mm and an angle
of +120 degrees
N5 G15 G80 ; Canceling the polar coordinate command
Limitation
- Specifying a radius in the polar coordinate mode
In the polar coordinate mode, specify a radius for circular
interpolation or helical interpolation (G02, G03) with R.
- Axes that are not considered part of a polar coordinate command in the polar
coordinate mode
Axes specified for the following commands are not considered part of
the polar coordinate command:
• Dwell (G04)
• Programmable data input (G10)
• Local coordinate system setting (G52)
• Workpiece coordinate system setting (G92)
• Machine coordinate system setting (G53)
• Stored stroke check (G22)
• Coordinate system rotation (G68)
• Scaling (G51)
- 35 -
Page 56

4.COORDINATE VALUE AND DIMENSION PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Optional chamfering and corner R
Optional chamfering and corner R cannot be specified in polar
coordinate mode.
- 36 -
Page 57

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5 FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY
PROGRAMMING
This chapter explains the following items:
5.1 CANNED CYCLE FOR DRILLING
5.2 RIGID TAPPING
5.3 OPTIONAL CHAMFERING AND CORNER R
5.4 INDEX TABLE INDEXING FUNCTION
- 37 -
Page 58

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
5.1 CANNED CYCLE FOR DRILLING
Overview
Canned cycles for drilling make it easier for the programmer to create
programs. With a canned cycle, a frequently-used machining
operation can be specified in a single block with a G function; without
canned cycles, normally more than one block is required. In addition,
the use of canned cycles can shorten the program to save memory.
Table 5.1 (a) lists canned cycles for drilling.
Table 5.1 (a) Canned cycles for drilling
Explanation
G code
G73
G74 Feed
G76 Feed
G80 - - - Cancel
G81 Feed - Rapid traverse
G82 Feed Dwell Rapid traverse
G83
G84 Feed
G85 Feed - Feed Boring cycle
G86 Feed Spindle stop Rapid traverse Boring cycle
G87 Feed Spindle CW Rapid traverse
G88 Feed
G89 Feed Dwell Feed Boring cycle
Drilling
(-Z direction)
Intermittent
feed
Intermittent
feed
A canned cycle for drilling consists of a sequence of six operations.
Operation 1 .........Positioning of axes X and Y (including also
Operation 2 .........Rapid traverse up to point R level
Operation 3 .........Hole machining
Operation 4 .........Operation at the bottom of a hole
Operation 5 ...........Retraction to point R level
Operation 6 ...........Rapid traverse up to the initial point
Operation at the
bottom of a hole
- Rapid traverse
Dwell →
Spindle CW
Oriented spindle
stop
- Rapid traverse
Dwell →
Spindle CCW
Dwell →
Spindle stop
another axis)
Retraction
(+Z direction)
Feed
Rapid traverse
Feed Tapping cycle
Manual Boring cycle
Application
High-speed
peck drilling
cycle
Left-hand
tapping cycle
Fine boring
cycle
Drilling cycle,
spot drilling
cycle
Drilling cycle,
counter boring
cycle
Peck drilling
cycle
Back boring
cycle
- 38 -
Page 59

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
- Positioning plane
- Drilling axis
Operation 1
Operation 2
Point R level
Operation 3
Operation 4
Fig. 5.1 (a) Operation sequence of canned cycle for drilling
Initial level
Operation 6
Operation 5
Rapid traverse
Feed
The positioning plane is determined by plane selection code G17, G18,
or G19.
The positioning axis is an axis other than the drilling axis.
Although canned cycles for drilling include tapping and boring cycles
as well as drilling cycles, in this chapter, only the term drilling will be
used to refer to operations implemented with canned cycles.
The drilling axis is a basic axis (X, Y, or Z) not used to define the
positioning plane, or any axis parallel to that basic axis.
The axis (basic axis or parallel axis) used as the drilling axis is
determined according to the axis address for the drilling axis specified
in the same block as G codes G73 to G89.
If no axis address is specified for the drilling axis, the basic axis is
assumed to be the drilling axis.
Table 5.1 (b) Positioning plane and drilling axis
G code Positioning plane Drilling axis
G17 Xp-Yp plane Zp
G18 Zp-Xp plane Yp
G19 Yp-Zp plane Xp
Xp: X axis or an axis parallel to the X axis
Yp: Y axis or an axis parallel to the Y axis
Zp: Z axis or an axis parallel to the Z axis
- 39 -
Page 60

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Example
Assume that the U, V and W axes be parallel to the X, Y, and Z axes
respectively. This condition is specified by parameter No. 1022.
G17 G81 Z _ _: The Z axis is used for drilling.
G17 G81 W _ _: The W axis is used for drilling.
G18 G81 Y _ _: The Y axis is used for drilling.
G18 G81 V _ _: The V axis is used for drilling.
G19 G81 X _ _: The X axis is used for drilling.
G19 G81 U _ _: The U axis is used for drilling.
G17 to G19 may be specified in a block in which any of G73 to G89
is not specified.
CAUTION
Switch the drilling axis after canceling a canned
cycle for drilling.
NOTE
A parameter FXY (No. 5101 #0) can be set to the Z
axis always used as the drilling axis. When
FXY=0, the Z axis is always the drilling axis.
- Travel distance along the drilling axis G90/G91
The travel distance along the drilling axis varies for G90 and G91 as
follows:
G90 (Absolute programming) G91 (Incremental programming)
- Drilling mode
R
Point R
Point Z
Fig. 5.1 (b) Absolute programming and incremental programming
R
Z = 0
Z
Point R
Point Z
Z
G73, G74, G76, and G81 to G89 are modal G codes and remain in
effect until canceled. When in effect, the current state is the drilling
mode.
Once drilling data is specified in the drilling mode, the data is retained
until modified or canceled.
Specify all necessary drilling data at the beginning of canned cycles;
when canned cycles are being performed, specify data modifications
only.
- 40 -
Page 61

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
- Return point level G98/G99
When the tool reaches the bottom of a hole, the tool may be returned
to point R or to the initial level. These operations are specified with
G98 and G99. The following illustrates how the tool moves when
G98 or G99 is specified. Generally, G99 is used for the first drilling
operation and G98 is used for the last drilling operation.
The initial level does not change even when drilling is performed in
the G99 mode.
G98 (Return to initial level) G99 (Return to point R level)
Initial level
Point R level
- Repeat
- Cancel
Fig. 5.1 (c) Initial level and point R level
To repeat drilling for equally-spaced holes, specify the number of
repeats in K_.
K is effective only within the block where it is specified.
Specify the first hole position in incremental programming (G91).
If it is specified in absolute programming (G90), drilling is repeated at
the same position.
Number of repeats K The maximum command value = 9999
If K0 is specified, drilling data is stored, but drilling is not performed.
NOTE
For K, specify an integer of 0 or 1 to 9999.
To cancel a canned cycle, use G80 or a group 01 G code.
Group 01 G codes
G00 : Positioning (rapid traverse)
G01 : Linear interpolation
G02 : Circular interpolation or helical interpolation (CW)
G03 : Circular interpolation or helical interpolation (CCW)
- 41 -
Page 62

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Symbols in figures
Subsequent sections explain the individual canned cycles. Figures in
these Explanation use the following symbols:
Positioning (rapid traverse G00)
Cutting feed (linear interpolation G01)
Manual feed
Oriented spindle stop
OSS
Shift (rapid traverse G00)
P Dwell
(The spindle stops at a fixed rotation position)
- 42 -
Page 63

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.1 High-Speed Peck Drilling Cycle (G73)
This cycle performs high-speed peck drilling. It performs
intermittent cutting feed to the bottom of a hole while removing chips
from the hole.
Format
G73 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ Q_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
Q_ : Depth of cut for each cutting feed
F_ : Cutting feedrate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G73 (G98) G73 (G99)
Initial level
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
Point R
q
q
q
d
d
Point Z
Point R
q
q
q
Point R level
d
d
Point Z
The high-speed peck drilling cycle performs intermittent feeding
along the Z-axis. When this cycle is used, chips can be removed
from the hole easily, and a smaller value can be set for retraction.
This allows, drilling to be performed efficiently. Set the clearance, d,
in parameter 5114.
The tool is retracted in rapid traverse.
Before specifying G73, rotate the spindle using an auxiliary function
(M code).
- 43 -
Page 64

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Auxiliary function
When the G73 code and an M code are specified in the same block,
the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning operation.
When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M code is
executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent holes,
the M code is not executed.
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- Q
Specify Q in blocks that perform drilling. If they are specified in a
block that does not perform drilling, they cannot be stored as modal
data.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G73 in a
single block. Otherwise, G73 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S2000 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G73 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-100. Q15. F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 44 -
Page 65

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.2 Left-Handed Tapping Cycle (G74)
This cycle performs left-handed tapping. In the left-handed tapping
cycle, when the bottom of the hole has been reached, the spindle
rotates clockwise.
Format
G74 X_ Y_ Z_ R_P_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
P_ : Dwell time
F_ : Cutting feedrate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G74 (G98) G74 (G99)
Initial level
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
Spindle
CCW
P
Point R level
Point Z
Spindle CW
Point R
Spindle
CCW
P
P
Point Z
Spindle CW
Point R
P
Tapping is performed by turning the spindle counterclockwise.
When the bottom of the hole has been reached, the spindle is rotated
clockwise for retraction. This creates a reverse thread.
CAUTION
Feedrate overrides are ignored during left-handed
tapping. A feed hold does not stop the machine
until the return operation is completed.
Before specifying G74, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle counterclockwise.
If drilling is continuously performed with a small value specified for
the distance between the hole position and point R level or between
the initial level and point R level, the normal spindle speed may not be
reached at the start of hole cutting operation. In this case, insert a
dwell before each drilling operation with G04 to delay the operation,
without specifying the number of repeats for K. For some machines,
- 45 -
Page 66

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
the above note may not be considered. Refer to the manual provided
by the machine tool builder.
- Auxiliary function
When the G74 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- P
Specify P in blocks that perform drilling. If it is specified in a
block that does not perform drilling, it cannot be stored as modal data.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G74 in a
single block. Otherwise, G74 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M4 S100 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G74 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-120. F120. ;
Position, tapping hole 1, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, tapping hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, tapping hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, tapping hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, tapping hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, tapping hole 6, then return to the initial
level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 46 -
Page 67

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.3 Fine Boring Cycle (G76)
The fine boring cycle bores a hole precisely. When the bottom of the
hole has been reached, the spindle stops, and the tool is moved away
from the machined surface of the workpiece and retracted.
Format
G76 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ Q_ P_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
Q_ : Shift amount at the bottom of a hole
P_ : Dwell time at the bottom of a hole
F_ : Cutting feedrate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G76 (G98) G76 (G99)
Spindle orientation
Shift amount q
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
- Auxiliary function
Tool
Spindle CW
Point R
P
OSS
q
Initial level
Point Z
Point R
OSS
P
Spindle CW
Point R level
Point Z
q
When the bottom of the hole has been reached, the spindle is stopped
at the fixed rotation position, and the tool is moved in the direction
opposite to the tool nose and retracted. This ensures that the
machined surface is not damaged and enables precise and efficient
boring to be performed.
Before specifying G76, use a Auxiliary function (M code) to rotate the
spindle.
When the G76 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
- 47 -
Page 68

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any additional axes,
drilling is not performed.
- P/Q
Be sure to specify a positive value in Q. If Q is specified with a
negative value, the sign is ignored. Set the direction of shift in the
parameter (No.5148).
Specify P and Q in a block that performs drilling. If they are
specified in a block that does not perform drilling, they are not stored
as modal data.
CAUTION
Q (shift at the bottom of a hole) is a modal value
retained within canned cycles for drilling. It must
be specified carefully because it is also used as the
depth of cut for G73 and G83.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G76 in a
single block. Otherwise, G76 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S500 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G76 X300. Y-250.
Position, bore hole 1, then return to point R.
Z-150. R-120. Q5. Orient at the bottom of the hole, then shift by 5
mm.
P1000 F120. ; Stop at the bottom of the hole for 1 s.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 48 -
Page 69

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.4 Drilling Cycle, Spot Drilling (G81)
This cycle is used for normal drilling. Cutting feed is performed to
the bottom of the hole. The tool is then retracted from the bottom of
the hole in rapid traverse.
Format
G81 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
F_ : Cutting feedrate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G81 (G98) G81 (G99)
Initial level
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
- Auxiliary function
- Tool length compensation
Point R
Point R
Point Z
Point R level
Point Z
After positioning along the X- and Y-axes, rapid traverse is performed
to point R.
Drilling is performed from point R to point Z.
The tool is then retracted in rapid traverse.
Before specifying G81, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
When the G81 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is performed for the first hole only; for the second and
subsequent holes, the M code is not executed.
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
- 49 -
Page 70

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G81 in a
single block. Otherwise, G81 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S2000 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G81 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-100. F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 50 -
Page 71

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.5 Drilling Cycle Counter Boring Cycle (G82)
This cycle is used for normal drilling.
Cutting feed is performed to the bottom of the hole. At the bottom, a
dwell is performed, then the tool is retracted in rapid traverse.
This cycle is used to drill holes more accurately with respect to depth.
Format
G82 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ P_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
P_ : Dwell time at the bottom of a hole
F_ : Cutting feed rate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G82 (G98) G82 (G99)
Initial level
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
- Auxiliary function
Point R
Point R
P
Point Z
P
Point R level
Point Z
After positioning along the X- and Y-axes, rapid traverse is performed
to point R.
Drilling is then performed from point R to point Z.
When the bottom of the hole has been reached, a dwell is performed.
The tool is then retracted in rapid traverse.
Before specifying G82, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
When the G82 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
- 51 -
Page 72

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- P
Specify P in blocks that perform drilling. If it is specified in a block
that does not perform drilling, it cannot be stored as modal data.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G82 in a
single block. Otherwise, G82 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S2000 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G82 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-100. P1000 F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, and dwell for 1 s at the
bottom of the hole, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 52 -
Page 73

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.6 Peck Drilling Cycle (G83)
This cycle performs peck drilling.
It performs intermittent cutting feed to the bottom of a hole while
removing shavings from the hole.
Format
G83 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ Q_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
Q_ : Depth of cut for each cutting feed
F_ : Cutting feedrate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G83 (G98) G83 (G99)
Initial level
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
- Auxiliary function
Point R
q
q
q
d
d
Point Z
Point R
q
q
q
Point R level
d
d
Point Z
Q represents the depth of cut for each cutting feed. It must always be
specified as an incremental value.
In the second and subsequent cutting feeds, rapid traverse is
performed up to a d point just before where the last drilling ended, and
cutting feed is performed again. d is set in parameter (No.5115).
Be sure to specify a positive value in Q. Negative values are
ignored.
Before specifying G83, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
When the G83 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
- 53 -
Page 74

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- Q
Specify Q in blocks that perform drilling. If they are specified in a
block that does not perform drilling, they cannot be stored as modal
data.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G83 in a
single block. Otherwise, G83 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S2000 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G83 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-100. Q15. F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 54 -
Page 75

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
q
5.1.7 Small-Hole Peck Drilling Cycle
An arbor with the overload torque detection function is used to retract
the tool when the overload torque detection signal (skip signal) is
detected during drilling. Drilling is resumed after the spindle speed
and cutting feedrate are changed. These steps are repeated in this peck
drilling cycle.
The mode for the small–hole peck drilling cycle is selected when the
M code in parameter 5163 is specified. The cycle can be started by
specifying G83 in this mode. This mode is canceled when G80 is
specified or when a reset occurs.
Format
G83 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ Q_ F_I_ K_P ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : Distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : Distance from the initial level to point R
Q_ : Depth of each cut
F_ : Cutting feedrate
I_ : Forward or backward traveling speed (same format as F above)
(If this is omitted, the values in parameters No.5172 and No.5173 are
assumed as defaults.)
K_ : Number of times the operation is repeated (if required)
P_ : Dwell time at the bottom of the hole
ue
Point R level
∆
∆
Point Z
Dwell
(If this is omitted, P0 is assumed as the default.)
G83 (G98) G83 (G99)
q
Overload torque
∆: Initial clearance when the tool is retracted to point R and the clearance from the
bottom of the hole in the second or subsequent drilling (parameter 5174)
q: Depth of each cut
()
∆
Path along which the tool travels at the rapid traverse rate
Path along which the tool travels at the programmed cutting
feedrate
Path along which the tool travels at the forward or backward rate during the
cycle specified with parameters
Initial level
∆
Point Z
Dwell
Point R Point R
q
Overload tor
- 55 -
Page 76

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Explanations
- Componet operations of the cycle
* X- and Y-axis positioning
* Positioning at point R along the Z–axis
* Cutting along the Z-axis (first time, depth of cut Q, incremental)
Retracting
(bottom of hole → minimum clearance ∆, incremental)
Retraction
Repeated until
point Z is reached
( bottom of hole+∆→ to point R, absolute)
Forwarding
(point R → to point with hole bottom + clearance ∆, absolute)
Cutting
(second and subsequent times, cut of depth Q + ∆, incremental)
* Dwell
* Return to point R along the Z-axis (or initial point) = end of
cycle
Acceleration/deceleration during advancing and retraction is
controlled according to the cutting feed acceleration/deceleration time
constant.
When retraction is performed, the position is checked at point R.
- Specifying an M code
When the M code in parameter 5163 is specified, the system enters the
mode for the small–hole peck drilling cycle.
This M code does not wait for FIN. Care must be taken when this M
code is specified with another M code in the same block.
(Example) M03 M ; → Waits for FIN.
M M03 ; → Does not wait for FIN.
- Specifying a G code
When G83 is specified in the mode for the small-hole peck drilling
cycle, the cycle is started.
This continuous–state G code remains unchanged until another canned
cycle is specified or until the G code for canceling the canned cycle is
specified. This eliminates the need for specifying drilling data in each
block when identical drilling is repeated.
- Signal indicating that the cycle is in progress
In this cycle, the signal indicating that the small–hole peck drilling
cycleis in progress is output after the tool is positioned at the hole
position along the axes not used for drilling. Signal output continues
during positioning to point R along the drilling axis and terminates
upon a return to point R or the initial level. For details, refer to the
manual of the machine tool builder.
- Overload torque detection signal
A skip signal is used as the overload torque detection signal. The skip
signal is effective while the tool is advancing or drilling and the tool
- 56 -
Page 77

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
tip is between points R and Z. (The signal causes a retraction). For
details, refer to the manual of the machine tool builder.
NOTE
When receiving overload torque detect signal while the
tool is advancing, the tool will be retracted (clearance ∆
and to the point R), then advanced to the same target
point as previous advancing.
- Changing the drilling conditions
In a single G83 cycle, drilling conditions are changed for each drilling
operation (advance → drilling → retraction). Bits 1 and 2 of
parameter OLS, NOL No. 5160 can be specified to suppress the
change in drilling conditions.
1 Changing the cutting feedrate
The cutting feedrate programmed with the F code is changed for
each of the second and subsequent drilling operations. In
parameters No.5166 and No.5167, specify the respective rates of
change applied when the skip signal is detected and when it is
not detected in the previous drilling operation.
Cutting feedrate = F × α
<First drilling> α=1.0
<Second or subseqent drilling> α=α×β÷100, where β is the rate
of change for each drilling operation
When the skip signal is detected during the previous
drillingoperation: β=b1% (parameter No.5166)
When the skip signal is not detected during the previous
drillingoperation: β=b2% (parameter No.5167)
If the rate of change in cutting feedrate becomes smaller than the
rate specified in parameter 5168, the cutting feedrate is not
changed.
The cutting feedrate can be increased up to the maximum cutting
feedrate.
2 Changing the spindle speed
The spindle speed programmed with the S code is changed for
each of the second and subsequent advances. In parameters 5164
and 5165, specify the rates of change applied when the skip
signal is detected and when it is not detected in the previous
drilling operation.
Spindle speed = S × γ
<First drilling> γ=1.0
<Second or subseqent drilling> γ=γ×δ÷100, where δ is the rate of
change for each drilling operation
- 57 -
Page 78

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
When the skip signal is detected during the previous drilling
operation: δ=d1% (parameter No.5164)
When the skip signal is not detected during the previous drilling
operation: δ=d2% (parameter No.5165)
When the cutting feedrate reaches the minimum rate, the spindle
speed is not changed. The spindle speed can be increased up to a
value corresponding to the maximum value of S analog data.
- Advance and retraction
Advancing and retraction of the tool are not executed in the same
manner as rapid-traverse positioning. Like cutting feed, the two
operations are carried out as interpolated operations. Note that the tool
life management function excludes advancing and retraction from the
calculation of the tool life.
- Specifying addess I
The forward or backward traveling speed can be specified with
address I in the same format as address F, as shown below:
G83 I1000 ; (without decimal point)
G83 I1000. ; (with decimal point)
Both commands indicate a speed of 1000 mm/min.
Address I specified with G83 in the continuous-state mode continues
to be valid until G80 is specified or until a reset occurs.
NOTE
If address I is not specified and parqmeter No.5172 (for
backword) or No.5173 (for forword) is set to 0, the
forword or backword travel speed is same as the cutting
feedrate specified by F.
- Fuctions that can be specified
In this canned cycle mode, the following functions can be specified:
- Hole position on the X-axis, Y-axis, and additional axis
- Operation and branch by custom macro
- Subprogram (hole position group, etc.) calling
- Switching between absolute and incremental modes
- Coordinate system rotation
- Scaling (This command will not affect depth of cut Q or small
clearance ∆.)
- Dry run
- Feed hold
- Single block
When single-block operation is enabled, drilling is stopped after each
retraction. Also, a single block stop is performed by setting parameter
SBC (No.5105 bit 0)
- 58 -
Page 79

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
- Feedrate override
The feedrate override function works during cutting, retraction, and
advancing in the cycle.
- Custom macro interface
The number of retractions made during cutting and the number of
retractions made in response to the overload signal received during
cutting can be output to custom macro common variables (#100 to
#149) specified in parameters No.5170 and No.5171. Parameters
No.5170 and No.5171 can specify variable numbers within the range
of #100 to #149.
Parameter No.5170: Specifies the number of the common variable to
which the number of retractions made during
cutting is output.
Parameter No.5171: Specifies the number of the common variable to
which the number of retractions made in
response to the overload signal received during
cutting is output.
NOTE
The numbers of retruction output to common
valiables are cleared by G83 while small-hole peck
driling cycle mode.
Limitation
- Subprogram call
In the canned cycle mode, specify the subprogram call command
M98P_ in an independent block.
Example
M03 S_ ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
M ; Specifies the small-hole peck drilling cycle mode.
G83 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ Q_ F_ I_ K_ P_ ;
Specifies the small-hole peck drilling cycle.
X_ Y_ ; Drills at another position.
:
:
G80 ; Cancels the small-hole peck drilling cycle mode.
- 59 -
Page 80

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
5.1.8 Tapping Cycle (G84)
This cycle performs tapping.
In this tapping cycle, when the bottom of the hole has been reached,
the spindle is rotated in the reverse direction.
Format
G84 X_ Y_ Z_ R_P_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
P_ : Dwell time
F_ : Cutting feedrate
K_ : Number of repents (if required)
G84 (G98) G84 (G99)
Initial level
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
Spindle
CW
P
Point R level
Point ZP
Spindle CCW
Point R
Spindle
CW
P
Point ZP
Spindle CCW
Point R
Tapping is performed by rotating the spindle clockwise. When the
bottom of the hole has been reached, the spindle is rotated in the
reverse direction for retraction. This operation creates threads.
CAUTION
Feedrate overrides are ignored during tapping. A
feed hold does not stop the machine until the return
operation is completed.
Before specifying G84, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
If drilling is continuously performed with a small value specified for
the distance between the hole position and point R level or between
the initial level and point R level, the normal spindle speed may not be
reached at the start of hole cutting operation. In this case, insert a
dwell before each drilling operation with G04 to delay the operation,
- 60 -
Page 81

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
without specifying the number of repeats for K. For some machines,
the above note may not be considered. Refer to the manual provided
by the machine tool builder.
- Auxiliary function
When the G84 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When the K is used to specify number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- P
Specify P in blocks that perform drilling. If it is specified in a block
that does not perform drilling, it cannot be stored as modal data.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G84 in a
single block. Otherwise, G84 will be canceled.
Example
M3 S100 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G84 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-120. P300 F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial
level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 61 -
Page 82

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
5.1.9 Boring Cycle (G85)
This cycle is used to bore a hole.
Format
G85 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
F_ : Cutting feed rate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G85 (G98) G85 (G99)
Initial level
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
- Auxiliary function
- Tool length compensation
Point R
Point Z
Point R
Point R level
Point Z
After positioning along the X- and Y- axes, rapid traverse is
performed to point R.
Drilling is performed from point R to point Z.
When point Z has been reached, cutting feed is performed to return to
point R.
Before specifying G85, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
When the G85 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
- 62 -
Page 83

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G85 in a
single block. Otherwise, G85 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S100 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G85 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-120. F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the
initial level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 63 -
Page 84

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
5.1.10 Boring Cycle (G86)
This cycle is used to bore a hole.
Format
G86 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
F_ : Cutting feed rate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G86 (G98) G86 (G99)
Spindle CW
Initial level
Spindle CW
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
Point R
Point R
Point Z
Spindle stop
Point R level
Point Z
Spindle stop
After positioning along the X- and Y-axes, rapid traverse is performed
to point R.
Drilling is performed from point R to point Z.
When the spindle is stopped at the bottom of the hole, the tool is
retracted in rapid traverse.
Before specifying G86, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
If drilling is continuously performed with a small value specified for
the distance between the hole position and point R level or between
the initial level and point R level, the normal spindle speed may not be
reached at the start of hole cutting operation. In this case, insert a
dwell before each drilling operation with G04 to delay the operation,
without specifying the number of repeats for K. For some machines,
the above note may not be considered. Refer to the manual provided
by the machine tool builder.
- 64 -
Page 85

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
- Auxiliary function
When the G86 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G86 in a
single block. Otherwise, G86 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S2000 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G86 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-100. F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial
level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 65 -
Page 86

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
5.1.11 Back Boring Cycle (G87)
This cycle performs accurate boring.
Format
G87 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ Q_ P_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R
Q_ : Shift amount at the bottom of a hole
P_ : Dwell time at the bottom of a hole
F_ : Cutting feed rate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G87 (G98) G87 (G99)
Spindle orientation
Shift amount q
Explanation
- Spindle rotation
Tool
q
OSS
Spindle CW
OSS
P
Spindle CW
Initial
level
Not used
Point Z
Point R
After positioning along the X- and Y-axes, the spindle is stopped at
the fixed rotation position. The tool is moved in the direction
opposite to the tool nose, positioning (rapid traverse) is performed to
the bottom of the hole (point R).
The tool is then shifted in the direction of the tool nose and the spindle
is rotated clockwise. Boring is performed in the positive direction
along the Z-axis until point Z is reached.
At point Z, the spindle is stopped at the fixed rotation position again,
the tool is shifted in the direction opposite to the tool nose, then the
tool is returned to the initial level. The tool is then shifted in the
direction of the tool nose and the spindle is rotated clockwise to
proceed to the next block operation.
Before specifying G87, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
If drilling is continuously performed with a small value specified for
the distance between the hole position and point R level or between
the initial level and point R level, the normal spindle speed may not be
reached at the start of hole cutting operation. In this case, insert a
dwell before each drilling operation with G04 to delay the operation,
without specifying the number of repeats for K. For some machines,
the above note may not be considered. Refer to the manual provided
by the machine tool builder.
- 66 -
Page 87

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
- Auxiliary function
When the G87 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any additional axes,
drilling is not performed.
- P/Q
Be sure to specify a positive value in Q. If Q is specified with a
negative value, the sign is ignored. Set the direction of shift in the
parameter (No. 5148).
Specify P and Q in a block that performs drilling. If they are
specified in a block that does not perform drilling, they are not stored
as modal data.
CAUTION
Q (shift at the bottom of a hole) is a modal value
retained in canned cycles for drilling. It must be
specified carefully because it is also used as the
depth of cut for G73 and G83.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G87 in a
single block. Otherwise, G87 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
- 67 -
Page 88

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Example
M3 S500 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G87 X300. Y-250. Position, bore hole 1.
Z-150. R-120. Q5. Orient at the initial level, then shift by 5 mm.
P1000 F120. ; Stop at point Z for 1 s.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 68 -
Page 89

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.12 Boring Cycle (G88)
This cycle is used to bore a hole.
Format
G88 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ P_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
P_ : Dwell time at the bottom of a hole
F_ : Cutting feed rate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G88 (G98) G88 (G99)
Spindle CW
Initial level
Spindle CW
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
Point R
Point Z
P
Spindle stop
after dwell
Point R
Point Z
P
Point R level
Spindle stop
after dwell
After positioning along the X- and Y-axes, rapid traverse is performed
to point R. Boring is performed from point R to point Z.
When boring is completed, a dwell is performed at the bottom of the
hole, then the spindle is stopped and enters the hold state. At this
time, you can switch to the manual mode and move the tool manually.
Any manual operations are available; it is desirable to finally retract
the tool from the hole for safety, though.
At the restart of machining in the DNC operation or memory mode,
the tool returns to the initial level or point R level according to G98 or
G99 and the spindle rotates clockwise. Then, operation is restarted
according to the programmed commands in the next block.
Before specifying G88, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
- 69 -
Page 90

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Auxiliary function
When the G88 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
- Tool length compensation
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- P
Specify P in blocks that perform drilling. If it is specified in a block
that does not perform drilling, it cannot be stored as modal data.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G88 in a
single block. Otherwise, G88 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S2000 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G88 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-100. P1000 F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, return to point R then stop
at the bottom of the hole for 1 s.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial
level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 70 -
Page 91

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.13 Boring Cycle (G89)
This cycle is used to bore a hole.
Format
G89 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ P_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
P_ : Dwell time at the bottom of a hole
F_ : Cutting feed rate
K_ : Number of repeats (if required)
G89 (G98) G89 (G99)
Initial level
Explanation
- Operations
- Spindle rotation
- Auxiliary function
- Tool length compensation
Point R
Point Z
P
Point R
Point R level
Point Z
P
This cycle is almost the same as G85. The difference is that this
cycle performs a dwell at the bottom of the hole.
Before specifying G89, use an auxiliary function (M code) to rotate
the spindle.
When the G89 command and an M code are specified in the same
block, the M code is executed at the time of the first positioning
operation. When K is used to specify the number of repeats, the M
code is executed for the first hole only; for the second and subsequent
holes, the M code is not executed.
When a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in
the canned cycle for drilling, the offset is applied after the time of
positioning to point R.
- 71 -
Page 92

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle for drilling
must be canceled.
- Drilling
In a block that does not contain X, Y, Z, R, or any other axes, drilling
is not performed.
- P
Specify P in blocks that perform drilling. If it is specified in a block
that does not perform drilling, it cannot be stored as modal data.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03) and G89 in a
single block. Otherwise, G89 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode for drilling, tool offsets are ignored.
Example
M3 S100 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G89 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-120. P1000 F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, return to point R then stop
at the bottom of the hole for 1 s.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial
level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 72 -
Page 93

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.1.14 Canned Cycle Cancel for Drilling (G80)
G80 cancels canned cycles for drilling.
Format
G80 ;
Explanation
All canned cycles for drilling are canceled to perform normal
operation. Point R and point Z are cleared.
Other drilling data is also canceled (cleared).
Example
M3 S100 ; Cause the spindle to start rotating.
G90 G99 G88 X300. Y-250. Z-150. R-120. F120. ;
Position, drill hole 1, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 2, then return to point R.
Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 3, then return to point R.
X1000. ; Position, drill hole 4, then return to point R.
Y-550. ; Position, drill hole 5, then return to point R.
G98 Y-750. ; Position, drill hole 6, then return to the initial
level.
G80 G28 G91 X0 Y0 Z0 ; Return to the reference position, canned cycle
cancel
M5 ; Cause the spindle to stop rotating.
- 73 -
Page 94

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
5.1.15 Example for Using Canned Cycles for Drilling
Offset value +200.0 is set in offset No.11, +190.0 is set in offset No.15, and +150.0 is set in offset No.31
Program example
;
N001 G92 X0 Y0 Z0; Coordinate setting at reference position
N002 G90 G00 Z250.0 T11 M6; Tool change
N003 G43 Z0 H11; Initial level, tool length compensation
N004 S30 M3; Spindle start
N005 G99 G81 X400.0 Y-350.0 Z-153.0 R-97.0 F120; Positioning, then #1 drilling
N006 Y-550.0; Positioning, then #2 drilling and point R level return
N007 G98 Y-750.0; Positioning, then #3 drilling and initial level return
N008 G99 X1200.0; Positioning, then #4 drilling and point R level return
N009 Y-550.0; Positioning, then #5 drilling and point R level return
N010 G98 Y-350.0; Positioning, then #6 drilling and initial level return
N011 G00 X0 Y0 M5; Reference position return, spindle stop
N012 G49 Z250.0 T15 M6; Tool length compensation cancel, tool change
N013 G43 Z0 H15; Initial level, tool length compensation
N014 S20 M3; Spindle start
N015 G99 G82 X550.0 Y-450.0 Z-130.0 R-97.0 P300 F70; Positioning, then #7 drilling, point R level return
N016 G98 Y-650.0; Positioning, then #8 drilling, initial level return
N017 G99 X1050.0; Positioning, then #9 drilling, point R level return
N018 G98 Y-450.0; Positioning, then #10 drilling, initial level return
N019 G00 X0 Y0 M5; Reference position return, spindle stop
N020 G49 Z250.0 T31 M6; Tool length compensation cancel, tool change
N021 G43 Z0 H31; Initial level, tool length compensation
N022 S10 M3; Spindle start
N023 G85 G99 X800.0 Y-350.0 Z-153.0 R47.0 F50; Positioning, then #11 drilling, point R level return
N024 G91 Y-200.0 K2; Positioning, then #12, 13 drilling, point R level return
N025 G28 X0 Y0 M5; Reference position return, spindle stop
N026 G49 Z0; Tool length compensation cancel
N027 M0; Program stop
- 74 -
Page 95

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
Program using tool length offset and canned cycles
Reference position
350
#1 #11
100
100
100
Y
100
X
400 150 250 250 150
#1 to 6 Drilling of a 10 mm diameter hole
#7 to 10 Drilling of a 20 mm diameter hole
#11 to 13 Boring of a 95 mm diameter hole (depth 50 mm)
Z
X
Retract position
250
50
50
30
20
T 11 T 15 T 31
#2
#3
#7
#8
200
#12
200
#13
#6
#10
#5
#9
#4
Initial level
190200 150
Fig. 5.1.15 (a) Example for using canned cycles for drilling
- 75 -
Page 96

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
5.2 RIGID TAPPING
The tapping cycle (G84) and left-handed tapping cycle (G74) may be
performed in standard mode or rigid tapping mode.
In standard mode, the spindle is rotated and stopped along with a
movement along the tapping axis using auxiliary functions M03
(rotating the spindle clockwise), M04 (rotating the spindle
counterclockwise), and M05 (stopping the spindle) to perform
tapping.
In rigid mode, tapping is performed by controlling the spindle motor
as if it were a servo motor and by interpolating between the tapping
axis and spindle.
When tapping is performed in rigid mode, the spindle rotates one turn
every time a certain feed (thread lead) which takes place along the
tapping axis. This operation does not vary even during acceleration
or deceleration.
Rigid mode eliminates the need to use a floating tap required in the
standard tapping mode, thus allowing faster and more precise tapping.
- 76 -
Page 97

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
5.2.1 Rigid Tapping (G84)
When the spindle motor is controlled in rigid mode as if it were a
servo motor, a tapping cycle can be sped up.
Format
G84 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ P_ F_ K_ ;
X_ Y_ : Hole position data
Z_ : The distance from point R to the bottom of the hole and the
position of the bottom of the hole
R_ : The distance from the initial level to point R level
P_ : Dwell time at the bottom of the hole and at point R when a return
is made
F_ : Cutting feedrate
K_ : Number of repeats (Only for necessity of repeat)
G84.2 X_ Y_ Z_ R_ P_ F_ L_ ;
(Series 15 format)
L_ : Number of repeats (only for necessity of repeat)
G84 (G98) G84 (G99)
Explanation
Spindle stop
Initial level
Operation 1
Operation 2
Spindle CW
Point R
Operation 3
Spindle stop Spindle CCW
Operation 4
Operation 6
P
P
Spindle
stop
Point R level
Operation 5
Point Z
After positioning along the X- and Y-axes, rapid traverse is performed
to point R.
Tapping is performed from point R to point Z. When tapping is
completed, the spindle is stopped and a dwell is performed. The
spindle is then rotated in the reverse direction, the tool is retracted to
point R, then the spindle is stopped. Rapid traverse to initial level is
then performed.
While tapping is being performed, the feedrate override and spindle
override are assumed to be 100%. Feedrate override can be enabled
by setting, however.
Spindle stop
Spindle stop
Spindle CW
Point R
Spindle stop Spindle CCW
P
Point R level
Point Z
P
- 77 -
Page 98

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Rigid mode
Rigid mode can be specified using any of the following methods:
• Specify M29 S***** before a tapping command.
• Specify M29 S***** in a block which contains a tapping command.
• Specify G84 for rigid tapping (parameter G84 No. 5200 #0 set to 1).
- Thread lead
In feed-per-minute mode, the thread lead is obtained from the
expression, feedrate ÷ spindle speed. In feed-per-revolution mode,
the thread lead equals the feedrate speed.
- Tool length compensation
If a tool length compensation (G43, G44, or G49) is specified in the
canned cycle, the offset is applied at the time of positioning to point
R.
- Series 15 format command
Rigid tapping can be performed using Series 15 format commands.
The rigid tapping sequence (including data transfer to and from the
PMC), Limitation, and the like are the same as described in this
chapter.
- Acceleration/deceleration after interpolation
Linear or bell-shaped acceleration/deceleration can be applied.
- Look-ahead acceleration/deceleration before interpolation
Look-ahead acceleration/deceleration before interpolation is invalid.
- Override
Various types of override functions are invalid. The following
override functions can be enabled by setting corresponding
parameters:
• Extraction override
• Override signal
Details are given later.
- Dry run
Dry run can be executed also in G84 (G74). When dry run is
executed at the feedrate for the drilling axis in G84 (G74), tapping is
performed according to the feedrate. Note that the spindle speed
becomes faster at a higher dry run feedrate.
- Machine lock
Machine lock can be executed also in G84 (G74).
When G84 (G74) is executed in the machine lock state, the tool does
not move along the drilling axis. Therefore, the spindle does not also
rotate.
- 78 -
Page 99

B-63944EN-2/02 PROGRAMMING 5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING
- Reset
When a reset is performed during rigid tapping, the rigid tapping
mode is canceled and the spindle motor enters the normal mode.
Note that the G84 (G74) mode is not canceled in this case when bit 6
(CLR) of parameter No. 3402 is set.
- Interlock
Interlock can also be applied in G84 (G74).
- Feed hold and single block
When bit 6 (FHD) of parameter No. 5200 is set to 0, feed hold and
single block are invalid in the G84 (G74) mode. When this bit is set
to 1, they are valid.
- Manual feed
For rigid tapping by manual handle feed, see the section "Rigid
Tapping by Manual Handle."
With other manual operations, rigid tapping cannot be performed.
- Backlash compensation
In the rigid tapping mode, backlash compensation is applied to
compensate the lost motion when the spindle rotates clockwise or
counterclockwise. Set the amount of backlash in parameters Nos.
5321 to 5324.
Along the drilling axis, backlash compensation has been applied.
Limitation
- Axis switching
Before the drilling axis can be changed, the canned cycle must be
canceled. If the drilling axis is changed in rigid mode, alarm PS0206
is issued.
- S command
• If a speed higher than the maximum speed for the gear being used
is specified, alarm PS0200 is issued.
• When the rigid tapping canned cycle is cancelled, the S command
used for rigid tapping is cleared to S0.
- Distribution amount for the spindle
The maximum distribution amount is as follows (displayed on
diagnostic screen No. 451):
• For a serial spindle: 32,767 pulses per 8 ms
This amount is changed according to the gear ratio setting for the
position coder or rigid tapping command. If a setting is made to
exceed the upper limit, alarm PS0202 is issued.
- F command
If a value exceeding the upper limit of cutting feedrate is specified,
alarm PS0011 is issued.
- 79 -
Page 100

5.FUNCTIONS TO SIMPLIFY PROGRAMMING PROGRAMMING B-63944EN-2/02
- Unit of F command
Metric input Inch input Remarks
G94 1 mm/min 0.01 inch/min
G95 0.01 mm/rev 0.0001 inch/rev
Decimal point programming
allowed
Decimal point programming
allowed
- M29
If an S command and axis movement are specified between M29 and
G84, alarm PS0203 is issued. If M29 is specified in a tapping cycle,
alarm PS0204 is issued.
- P
Specify P in a block that performs drilling. If P is specified in a
non-drilling block, it is not stored as modal data.
- Cancel
Do not specify a G code of the 01 group (G00 to G03 or G60 (when
the MDL bit (bit 0 of parameter 5431) is set to 1)) and G74 in a single
block. Otherwise, G74 will be canceled.
- Tool offset
In the canned cycle mode, tool offsets are ignored.
- Program restart
A program cannot be restarted during rigid tapping.
- Subprogram call
In the canned cycle mode, specify the subprogram call command
M98P_ in an independent block.
Example
Z-axis feedrate 1000 mm/min
Spindle speed 1000 min
Thread lead 1.0 mm
<Programming of feed per minute>
G94; Specify a feed-per-minute command.
G00 X120.0 Y100.0 ; Positioning
M29 S1000 ; Rigid mode specification
G84 Z-100.0 R-20.0 F1000 ; Rigid tapping
<Programming of feed per revolution>
G95 ; Specify a feed-per-revolution command.
G00 X120.0 Y100.0 ; Positioning
M29 S1000 ; Rigid mode specification
G84 Z-100.0 R-20.0 F1.0 ; Rigid tapping
-1
- 80 -
 Loading...
Loading...