Page 1
EPSON COLOR INKJET PRINTER
Stylus Pro
SERVICE MANUAL
EPSON
4004825
Page 2

NOTICE
All rights reserved. Reproduction of any part of this manual in any form whatsoever without SEIKO
EPSON’s express written permission is forbidden.
The contents of this manual are subjects to change without notice.
All efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy of the contents of this manual. However, should any
errors be detected, SEIKO EPSON would greatly appreciate being informed of them.
The above notwithstanding SEIKO EPSON can assume no responsibility for any errors in this manual or
the consequence thereof.
Epson is a registered trademark of Seiko Epson Corporation.
General Notice: Other productnamesused herein are for identication purposes only andmay be trademarks
of their respective campanies.
Copyright © 1995 by SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION Nagano, Japan
-i-
Page 3

PRECAUTIONS
Precautionary notations throughout the text are categorized relative to 1) personal injury and 2) damage to
equipment.
DANGER
WARNING
The precautionary measures itemized below should always be observed when performing repair/ maintenance procedures.
Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in serious or fatal personal injury. Great
caution should be exercised in performing procedures preceded by DANGER Headings.
Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in damage to equipment.
DANGER
1. ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE PRODUCT FROM BOTH THE POWER SOURCE AND PERIPHERAL DEVICES PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE OR REPAIR PROCEDURE.
2. NO WORK SHOULD BE PERFORMED ON THE UNIT BY PERSONS UNFAMILIAR WITH
BASIC SAFETY MEASURES AS DICTATED FOR ALL ELECTRONICS TECHNICIANS IN
THEIR LINE OF WORK.
3. WHEN PERFORMING TESTING AS DICTATED WITHIN THIS MANUAL, DO NOT CONNECT THE UNIT TO A POWER SOURCE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. WHEN THE
POWER SUPPLY CABLE MUST BE CONNECTED, USE EXTREME CAUTION IN WORKING
ON POWER SUPPLY AND OTHER ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS.
WARNING
1. REPAIRS ON EPSON PRODUCT SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY BY AN EPSON CERTIFIED REPAIR TECHNICIAN.
2. MAKE CERTAIN THAT THE SOURCE VOLTAGE IS THE SAME AS THE RATED VOLTAGE,
LISTED ON THE SERIAL NUMBER/RATING PLATE. IF THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS A
PRIMARY AC RATING DIFFERENT FROM AVAILABLE POWER SOURCE, DO NOT CONNECT IT TO THE POWER SOURCE.
3. ALWAYS VERIFY THAT THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED FROM THE
POWER SOURCE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPLACING PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS
AND/OR INDIVIDUAL CHIPS.
4. IN ORDER TO PROTECT SENSITIVE MICROPROCESSORS AND CIRCUITRY, USE STATIC
DISCHARGE EQUIPMENT, SUCH AS ANTI-STATIC WRIST STRAPS, WHEN ACCESSING
INTERNAL COMPONENTS.
5. REPLACE MALFUNCTIONING COMPONENTS ONLY WITH THOSE COMPONENTS BY
THE MANUFACTURE; INTRODUCTION OF SECOND-SOURCE ICs OR OTHER NONAPPROVED COMPONENTS MAY DAMAGE THE PRODUCT AND VOID ANY APPLICABLE
EPSON WARRANTY.
-ii-
Page 4

PREFACE
This manual describes functions, theory of electrical and mechanical operations, maintenance, and repair of
STYLUS-PRO.
The instructions and procedures included herein are intended for the experience repair technician, and attention
should be given to the precautions on the preceding page. The chapters are organized as follows:
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Provides a general product overview, lists specifications, and illustrates the main components of the printer.
CHAPTER 2. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Describes the theory of printer operation.
CHAPTER 3. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
Includes a step-by-step guide for product disassembly and assembly.
CHAPTER 4. ADJUSTMENTS
Includes a step-by-step guide for adjustment.
CHAPTER 5. TROUBLESHOOTING
Provides Epson-approved techniques for adjustment.
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
Describes preventive maintenance techniques and lists lubricants and adhesives required to service the equipment.
APPENDIX
Describes connector pin assignments, circuit diagrams, circuit board component layout and exploded diagram.
The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
-iv-
Page 5
REVISION SHEET
Revision Issue Date Revision Page
Rev. A May 30, 1995 - 1st issue
Rev. B June 5, 1995
1 - 2, 4-7
&4-10
Change Fig.1-2 and WARNINGs
-v-
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CHAPTER 2. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
CHAPTER 3. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER 4. ADJUSTMENTS
CHAPTER 5. TROUBLESHOOTING
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
APPENDIX
-vi-
Page 7

Chapter 1 Product Description
Table of Contents
1.1 FEATURES 1-1
1.2 SPECIFICATIONS 1-2
1.2.1 Printing Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.2.2 Paper Handling Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.2.3 Paper Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.2.4 Ink Cartridge Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.2.5 Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.2.6 Environmental Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.2.7 Reliability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.2.8 Safety Approvals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.2.9 Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.3 INTERFACE SPECIFICATIONS 1-9
1.3.1 Parallel Interface Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
1.3.2 Serial Interface Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
1.4 OPERATIONS 1-12
1.4.1 Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12
1.4.2 Panel Operation at Power On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-13
1.4.3 Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14
1.4.3.1 Default Setting Items. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14
1.4.3.2 Changing the Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15
1.4.4 Error Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
1.4.5 Printer Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
1.4.5.1 Hardware Initialization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
1.4.5.2 Software Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
1.4.5.3 Panel Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
1.5 MAIN COMPONENTS 1-18
1.5.1 Main Control Board (C164 MAIN Board) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-18
1.5.2 Power Supply Board (C137 PSB/PSE Board) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-19
1.5.3 Control Panel (C137 PNL Board) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-19
1.5.4 Printer Mechanism (M-4A11) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-20
1.5.5 Housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-20
Page 8

List of Figures
Figure 1-1. Exterior View of the Stylus Color Pro . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Figure 1-2. Nozzle Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Figure 1-3. Printable Area for Cut Sheets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Figure 1-4. Printable Area for Envelopes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Figure 1-5. Adjustment Lever Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Figure 1-6. Temperature/Humidity Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Figure 1-7. Data Transmission Timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
Figure 1-8. Control Panel Appearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12
Figure 1-9. C164 MAIN Board Component Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-18
Figure 1-10. C137 PSB/PSE Component Layout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-19
Figure 1-11. C137 PNL Board Component Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-19
List of Tables
Table 1-1. Print Speed and Printable Columns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Table 1-2. Character Tables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Table 1-3. Cut Sheet Paper Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Table 1-4. Envelope Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Table 1-5. Adjust Lever Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Table 1-6. Rated Electrical Ranges. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Table 1-7. Acceptable Environmental Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Table 1-8. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments for Parallel Interface 1-10
Table 1-9. DTR and X-ON/X-OFF Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
Table 1-10. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments for Serial Interface . 1-11
Table 1-11. Default Setting Items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14
Table 1-12. Characteristics of Print Direction Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14
Table 1-13. Printing Direction and ESC U Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14
Table 1-14. Language Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15
Table 1-15. Feature Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15
Table 1-16. Character Table Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-16
Table 1-17. Error Indications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
Table 1-18. The Comparison between C164 MAIN and C162 MAIN . . . . . . 1-18
Page 9
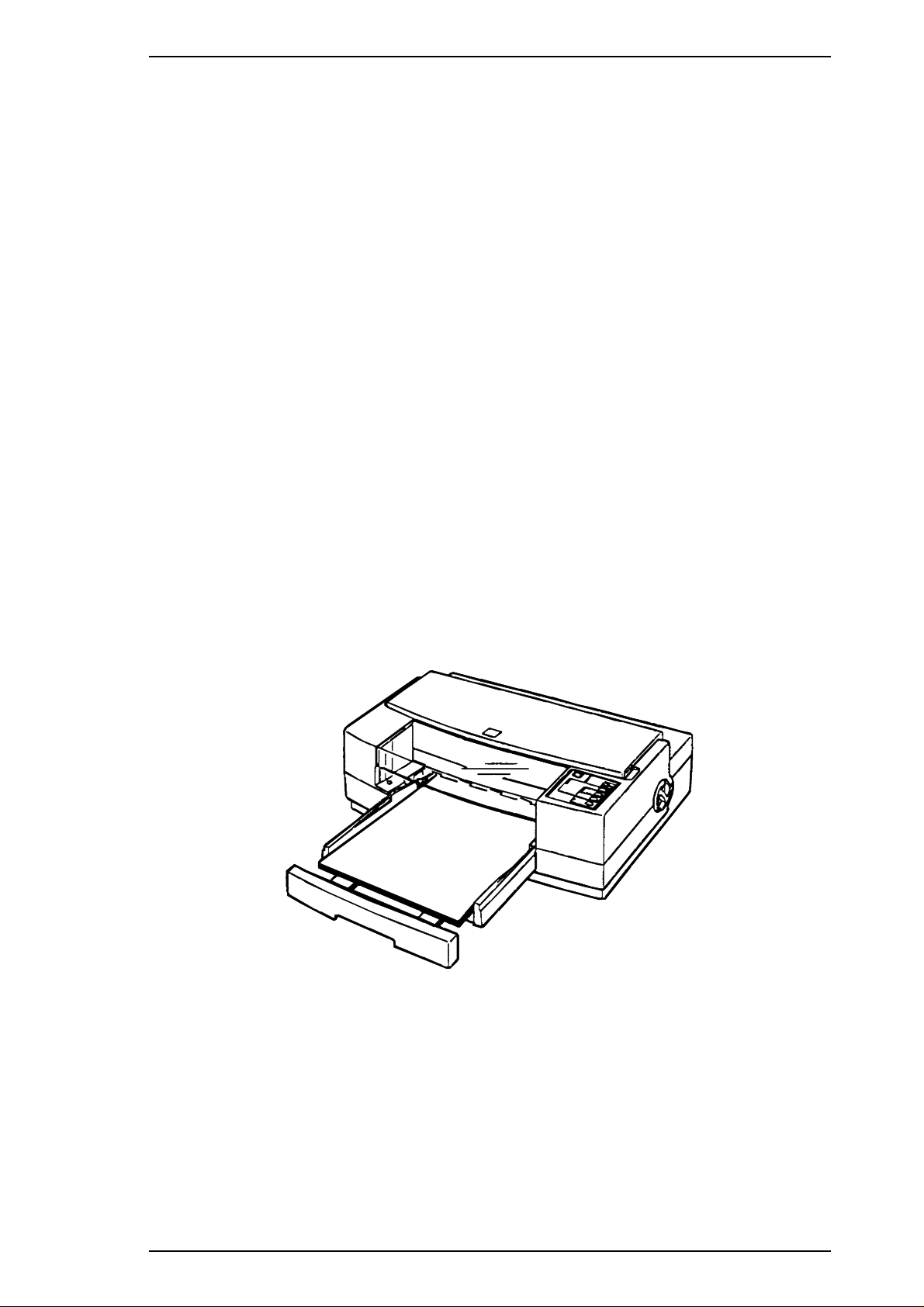
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
1.1 FEATURE
The Stylus Pro is a high-performance color ink jet printer with a small footprint and low cost. The main
components of this printer are similar to the Stylus Color. The main features are:
r High quality color print Super dot 720 dpi printing
Plain paper 720 dpi printing
Special coated paper for 720 dpi printing
r High print speed LQ printing at 200 cps
2
r Built-in auto sheet feeder Holds 100 cut sheets (55 g/m
Holds 10 envelopes
Holds 50 transparency film sheets
Holds 70 sheets of special paper
r Three built-in I/F types Macintosh Serial interface
Parallel interface (I-EEE 1284-compatible)
Type-B interface (optional)
Note :
Type-B interfaces are available, except C82324*(ETHERNET I/F CARD for NETWARE).
* The asterisk represents the last digit, which varies by country.
r Easy to set up No DIP switches
Multilingual setting messages (5 languages)
r 4 scalable fonts,
5 LQ fonts
Roman T, Sans Serif H, Roman, Sans Serif (scalable), Roman, Sans Serif,
Courier, Prestige, Script (LQ)
)
r Character Tables Italic, PC437, PC850, PC860, PC863, PC865, PC437 Greek, PC852,
PC853, PC855, PC857, PC866, PC869, PC861, BRASCII, Abicomp,
MAZOWIA, Code MJK, ISO 8859-7, ISO Latin 1T, Bulgaria
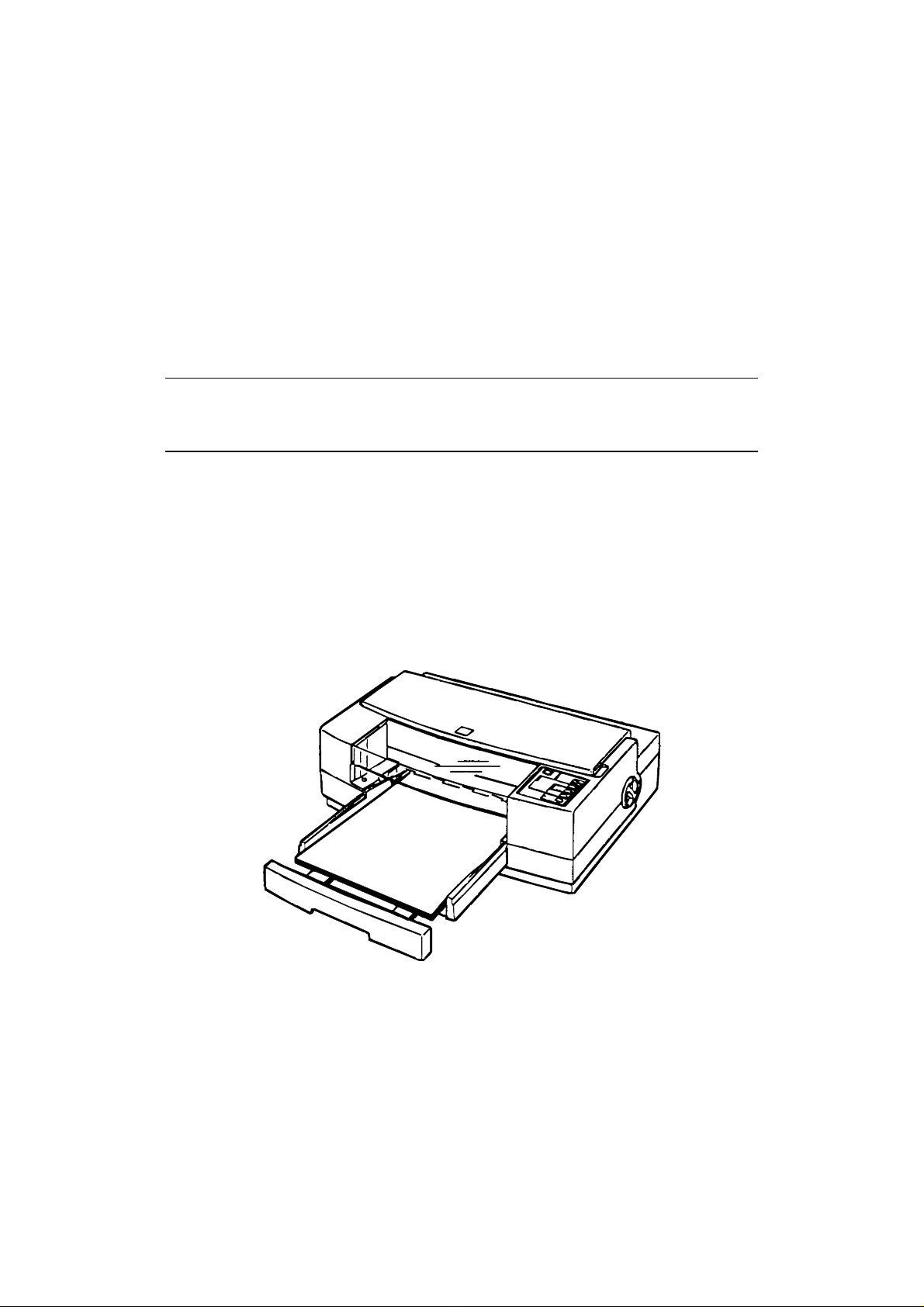
The figure below shows the Stylus Pro.
Figure 1-1. Exterior View of Stylus Pro
Rev.B 1-1
Page 10
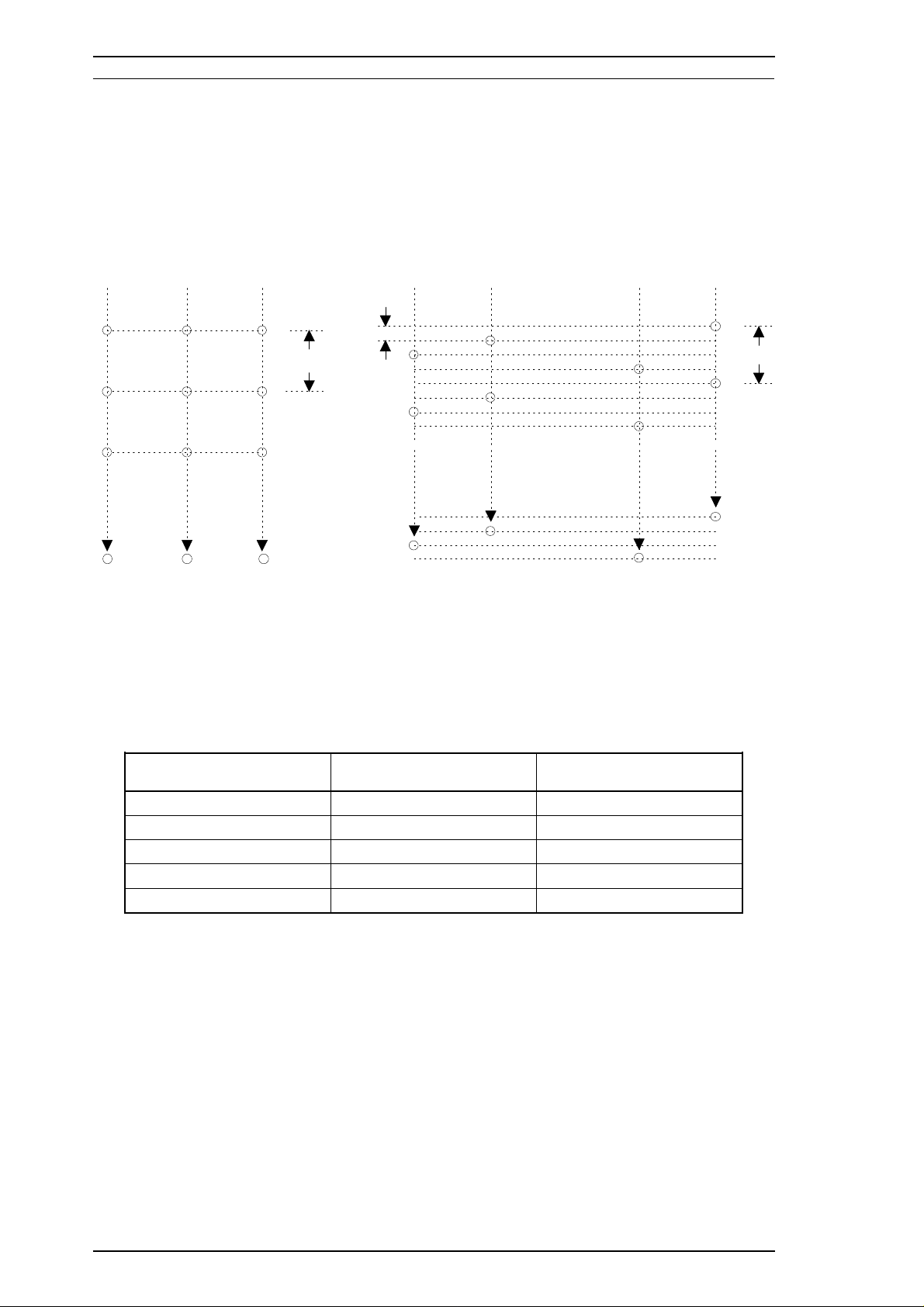
Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
1.2 SPECIFICATIONS
This section provides statistical facts and other detailed information for the printer.
1.2.1 Printing Specifications
Print system: On demand ink jet system
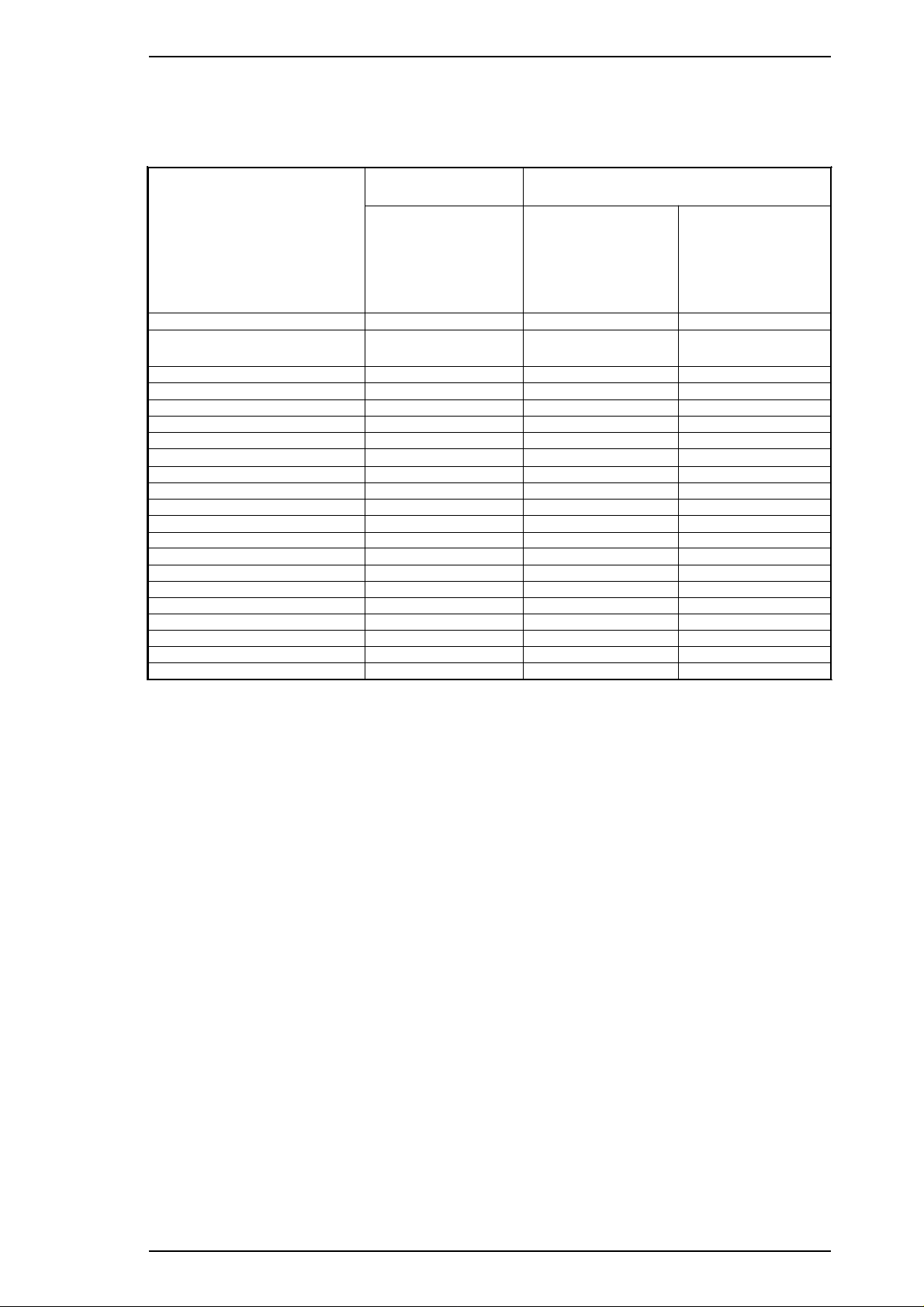
Nozzle configuration: 64 nozzles (16 × 4 staggered): monochrome
48 nozzles (16 × 3 staggered): color
Row CRow D
#1
#2
#3
#16
#1
#2
#3
#16
MagentaCyanYellow
#1
1/360"
1/90"
#2
#3
#16
#3
#7
#63
Figure 1-2. Nozzle Configuration
Printing direction: Bidirectional with logic-seeking
The table below shows print speed and printable columns.
Table 1-1. Print Speed and Printable Columns
#2
#6
#62
Row B
#4
#8
#64
Row A
#1
1/90"
#5
#61
Character Pitch Printable Columns Print Speed (LQ)
10 cpi (pica) 80 200 cps
12 cpi (elite) 96 240 cps
15 cpi 120 300 cps
17 cpi (pica condensed) 137 340 cps
20 cpi (elite condensed) 160 400 cps
1-2 Rev.B
Page 11
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
Character sets: Legal and 21 international character sets.
Character tables: See Table 1-2.
Table 1-2. Character Tables
Bitmap Fonts Scalable Fonts
EPSON Roman
Character Tables
Italic table mmm
PC437
(U.S./Standard Europe)
PC850 (Multilingual) mmm
PC860 (Portuguese) mmm
PC861 (Iceland) mmm
PC863 (Canadian-French) mmm
PC865 (Nordic) mmm
Abicomp
BRASCII mmm
PC437 (Greek) mm×
PC852 (East Europe) mm×
PC853 (Turkish) mm×
PC855 (Cyrillic) mm×
PC857 (Turkish) mm×
PC866 (Russian) mm×
PC869 (Greek) mm×
MAZOWIA (Poland) mm×
Code MJK (Czecho/Slovakia) mm×
ISO 8859-7 (Greek) mm×
ISO Latin 1T (Turkish) mm×
Bulgaria (Bulgaria) mm×
mSupported ×
EPSON Sans Serif
EPSON Courier
EPSON Prestige
EPSON Script
Not supported
EPSON Roman
EPSON Sans Serif
mmm
mmm
EPSON Roman T
EPSON Sans Serif H
Note: These character tables are not supported for EPSON Roman T and EPSON Sans Serif H
scalable fonts.
Fonts: Bitmap LQ fonts
r EPSON Roman (10 cpi/12 cpi/15 cpi/Proportional)
r EPSON Sans Serif (10/12/15/Proportional)
r EPSON Courier (10/12/15)
r EPSON Prestige (10/12/15)
r EPSON Script (10/12/15)
Scalable fonts
r EPSON Roman 10.5 points, 8 ∼ 32 points (in units of 2 points)
r EPSON Sans Serif 10.5 points, 8 ∼ 32 points (in units of 2 points)
r EPSON Roman T 10.5 points, 8 ∼ 32 points (in units of 2 points)
r EPSON Sans Serif H 10.5 points, 8 ∼ 32 points (in units of 2 points)
Control codes: ESC/P 2 and expanded raster graphics codes
Input data buffer: 64K bytes
Rev.B 1-3
Page 12
Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
1.2.2 Paper Handling Specifications
Feeding method: Friction feed paper is fed from the built-in auto sheet feeder (ASF).
Notes: The following operations are not allowed:
1. Reverse feeding within 3 mm (0.12 in.) from the top edge of the paper or 16 mm
(0.63 in.) from the bottom edge of the paper.
2. Reverse feeding beyond 7.9 mm (0.3 in.).
Line spacing:
1
⁄6-inch feed,1⁄8-inch feed, or programmable in1⁄
-inch minimum increments.
360
Paper path: Cut sheets: Built-in auto sheet feeder (ASF). Front entry.
Feeding speed:
89 msec. (at
1
⁄6-inch feed pitch).
1.2.3 Paper Specifications
Table 1-3. Cut Sheet Paper Specifications
Legal: 216 mm (8.5 in.) × 356 mm (14.0 in.)
Letter: 216 mm (8.5 in.) × 279 mm (11.0 in.)
Size (W × L)
Thickness 0.08 mm (0.003 in.) ∼ 0.11 mm (0.004 in.)
Weight 55 g/m
Quality
Note : Printing on special coated paper for 720 dpi, special coated paper for 360 dpi,
transparency film, and high-quality glossy paper is only available at normal temperatures.
A4: 210 mm (8.3 in.) × 297 mm (11.7 in.)
Executive: 184 mm (7.25 in.) × 267 mm (10.5 in.)
Statement :140 mm (5.5 in.) × 216 mm (8.5 in.)
2
(17 lb) ∼ 90 g/m2(24 lb)
Plain paper, special coated paper for 720 dpi, special coated paper for
360 dpi, transparency film, high-quality glossy paper
Table 1-4. Envelope Specifications
C5: 229 mm (9 in.) × 162 mm (6.4 in.)
Size (W × L)
No. 10: 240 mm (9
DL: 220 mm (8.7 in.) × 110 mm (4.3 in.)
Thickness Less than 0.52 mm (0.020 in.)
Weight 75 g/m
2
(20 lb) ∼ 90 g/m2(24 lb)
Quality Plain paper
Note: Printing of envelopes is supported only at room temperature. When inserting envelopes,
keep the longer side horizontal.
1
⁄2in.) × 104 mm (41⁄8in.)
1-4 Rev.B
Page 13
Top mar gin
3 mm (0.12 in.)
Left margin
3 mm (0.12 in.)
Right margin
3 mm (0.12 in.)
Bottom margin
14 mm (0.55 in.)
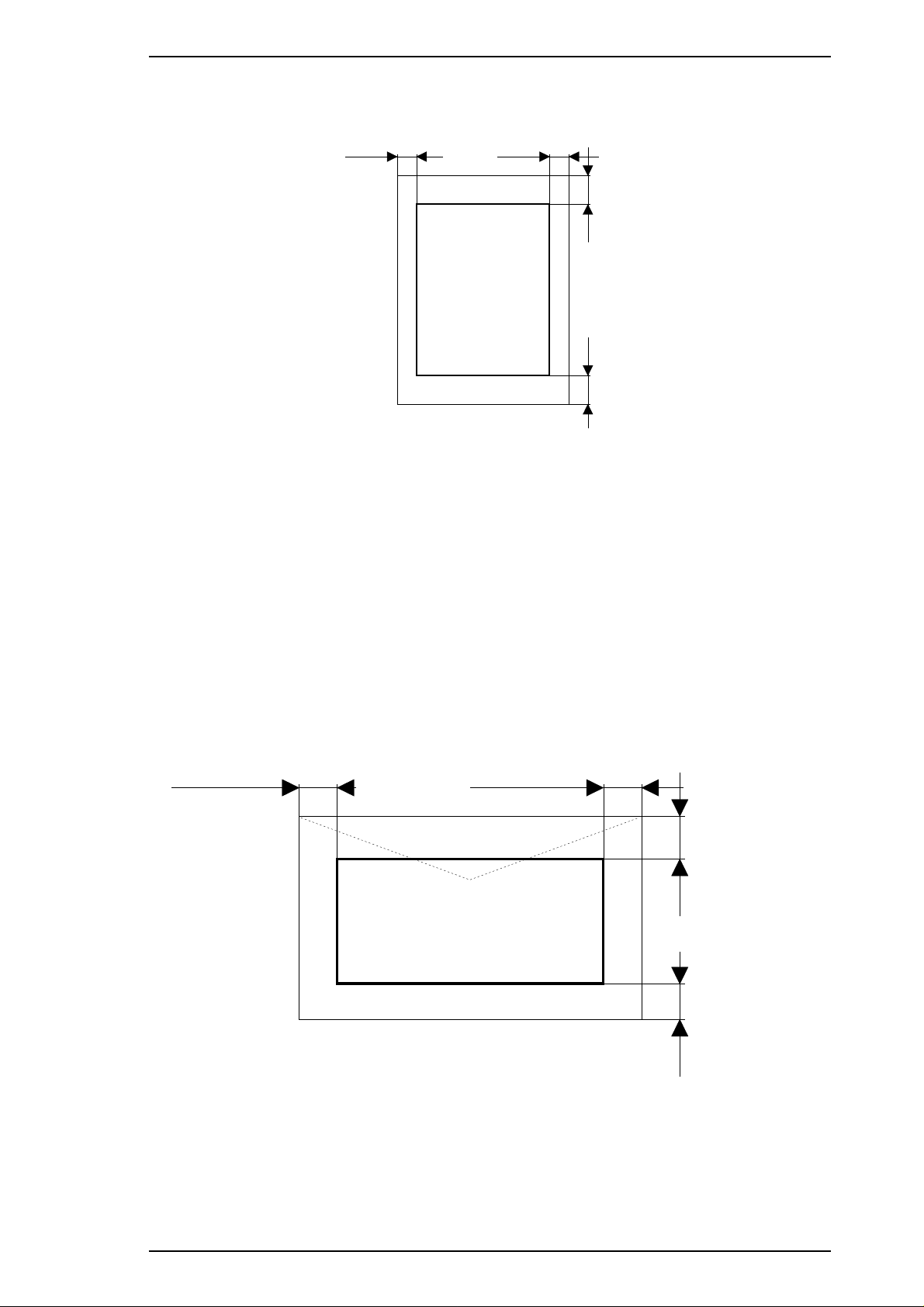
Printable area
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
Printable area:
Cut sheets
B
(Left margin)
C
(Right margin)
Printable area
A
(Top margin)
D
(Bottom margin)
Figure 1-3. Printable Area for Cut Sheets
Note: A: Mnimum top margin = 3 mm (0.12 in.)
B: Minimum left margin = 3 mm (0.12 in.)
C:Minimum right margin is:
A4 size: 3 mm (0.12 in.)
Letter size: 9 mm (0.35 in.)
Legal size: 9 mm (0.35 in.)
Envelopes: 3 mm (0.12 in.)
D:Minimum bottom margin = 14 mm (0.55 in.)
Envelopes
Figure 1-4. Printable Area for Envelopes
Rev.B 1-5
Page 14
Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
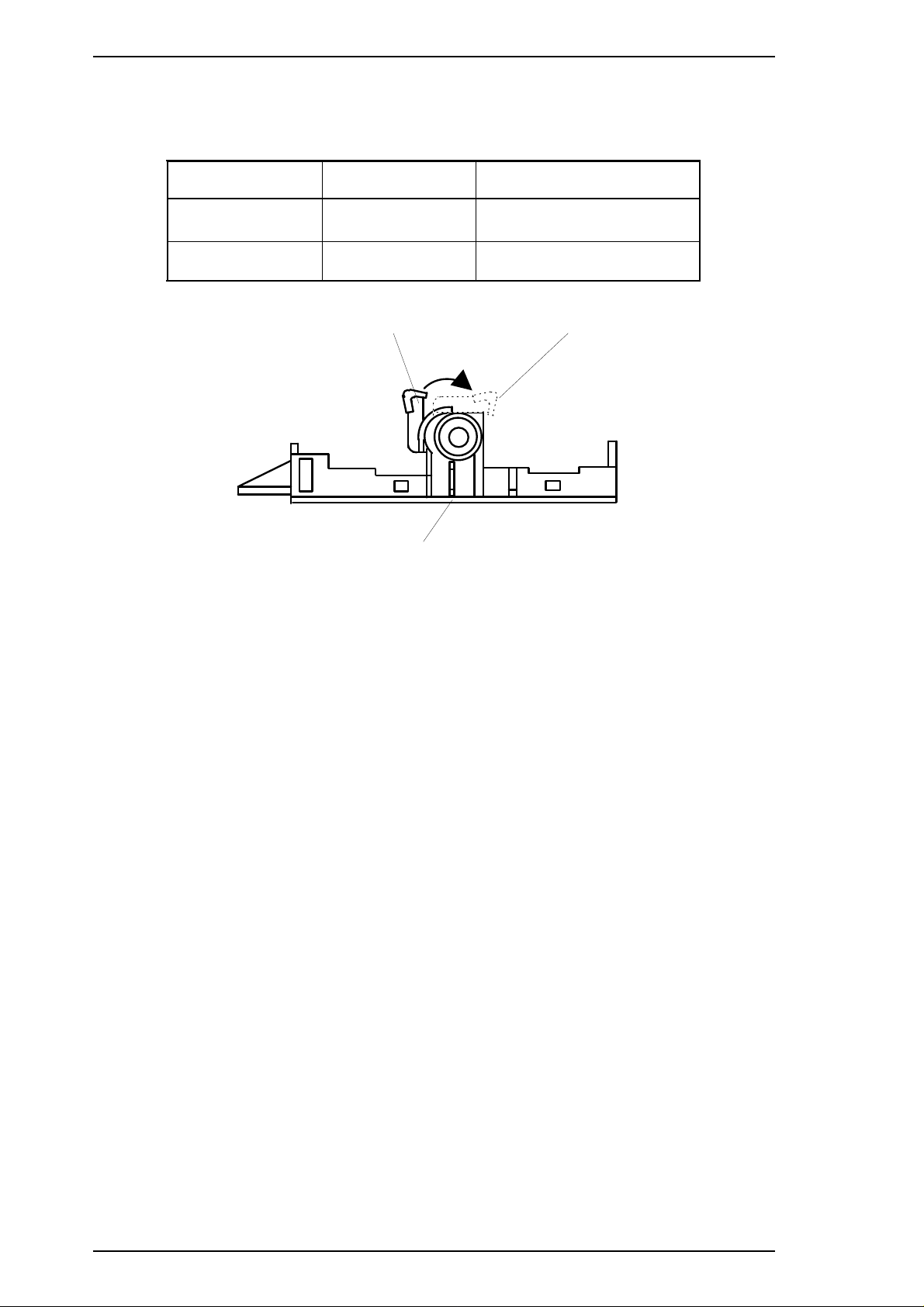
Adjust lever settings: The adjust lever on the carriage unit must be set to the proper position for the
paper thickness, as shown in Table 1-5.
Table 1-5. Adjust Lever Setting
Lever Position
LEFT
(Vertical)
RIGHT
(Horizontal)
1.2.4 Ink Cartridge Specifications
Paper Paper Thickness
Cut Sheets
Envelopes Less than 0.5 mm (0.020 in.)
Cut Sheets
Carriage Unit
Figure 1-5. Adjustment Lever Settings
Black
0.08 ∼
(0.003
0.11 mm
∼
0.004 in.)
Envelopes
Type: Exclusive cartridge
Color: Black
Print capacity: 1.2 million characters (315 dots/character, Roman 10 cpi)
Life: The effective life from the indicated production date is 2 years.
Storage temperature:
Dimension (W × D × H): 26.9 × 67.4 × 41.8 mm (1.06 × 2.65 × 1.65 in.)
–30 ∼ 40° C (−22 ∼ 104° F) Storage under a month at 40° C (104° F)
−30 ∼ 60° C(−22 ∼ 140° F) Transit under a month at 40° C (104° F)
−30 ∼ 60° C(−22 ∼ 140° F) Transit under 120 hours at 60° C (140° F)
Color
Type: Exclusive cartridge
Color: Cyan, magenta, yellow
Print capacity:
Life: The effective life from the indicated production date is 2 years.
Storage Temperature:
Dimension (W × D × H): 54.0 × 67.4 × 41.8 mm (2.13 × 2.65 × 1.65 in.)
Notes:
r
Ink cartridge cannot be refilled; it is the only consumable article.
r
Do not use an ink cartridge that has exceeded the ink life.
r
Ink freezes below−3°C; however, it can be used after it returns to room
temperature.
28 sheets/color (A4, full image printing at 360 dpi)
–30 ∼ 40° C (−22 ∼ 104° F) Storage under a month at 40° C (104° F)
−30 ∼ 60° C(−22 ∼ 140° F) Transit under a month at 40° C (104° F)
−30 ∼ 60° C(−22 ∼ 140° F) Transit under 120 hours at 60° C (140° F)
1.2.5 Electrical Specifications
Table 1-6. Rated Electrical Ranges
1-6 Rev.B
Page 15
Humidity
(% RH)
˚C
(˚F)
80%
55%
20%
10˚C
(50˚F)
27˚C
(80˚F)
35˚C
(95˚F)
Guaranteed range
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
Item
Rated voltage
Input voltage range
Rated frequency range
Input frequency range
Rated current
Power consumption
Insulation resistance
120 VAC 220 - 240 VAC
103.5 ∼
50 ∼
49.5 ∼
0.6 A 0.4 A
Approx. 20 W
(self-test with 10-cpi LQ characters)
10 MΩ,
(applying 500 VDC between
120 V Version 220 - 240 V Version
132 V
60 Hz
60.5 Hz
minimum
AC line and chassis)
1000 VAC rms - 1 minute or
Dielectric strength
1200 VAC rms - 1 second
(between AC line and chassis)
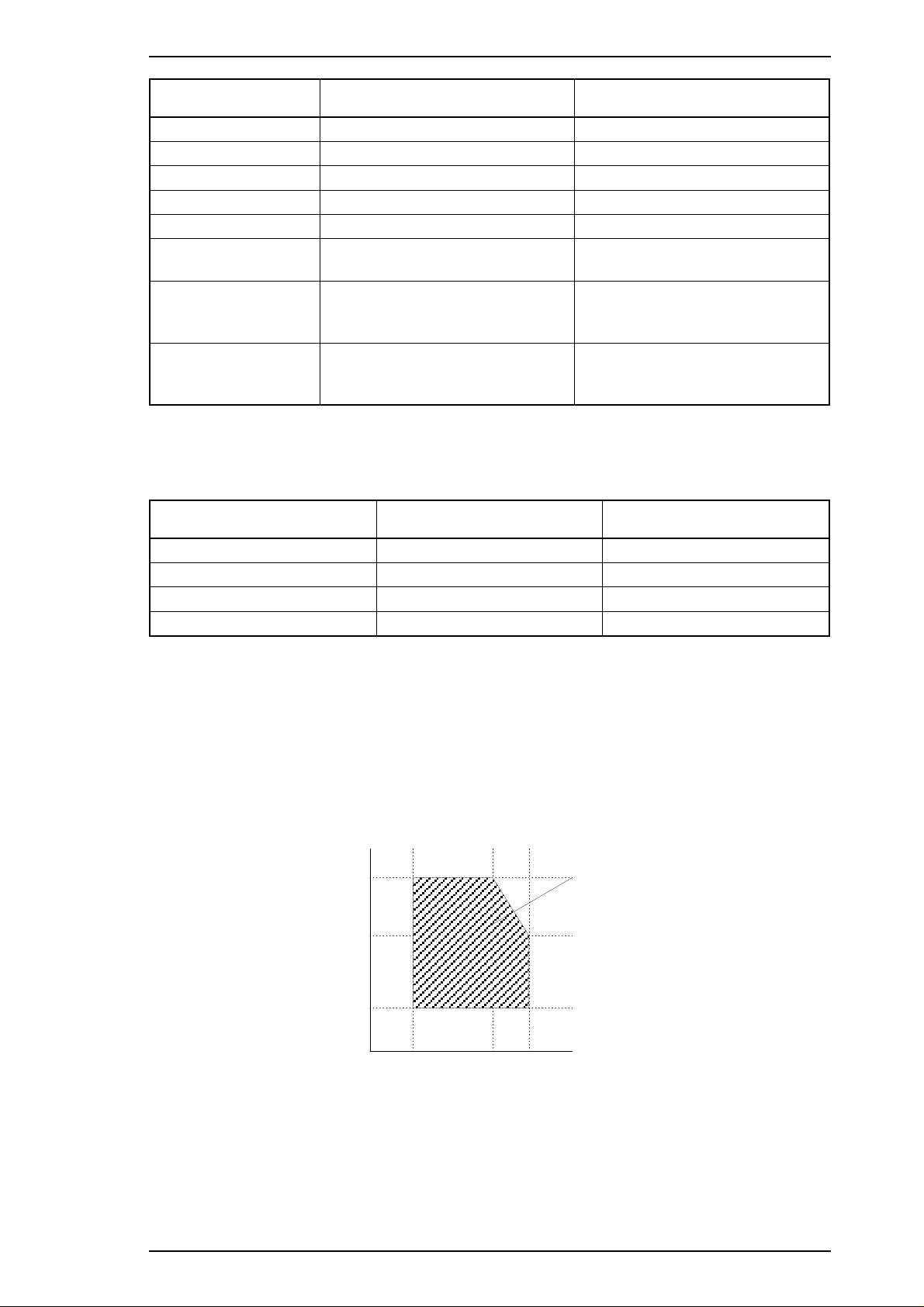
1.2.6 Environmental Conditions
Table 1-7. Acceptable Environmental Conditions
Description
Temperature
Humidity
Shock resistance
Vibration resistance
10 ∼
35°C (50∼95°F)
20 ∼
80% RH
1G (within 1 msec.) 2G (within 2 msec.)
0.15 G 0.50 G
198 ∼
264 V
50 ∼
60 Hz
49.5 ∼
60.5 Hz
Approx. 20 W
(self-test with 10-cpi LQ characters)
10 MΩ
, minimum
(applying 500 VDC between
AC line and chassis)
1500 VAC rms - 1 minute
(between AC line and chassis)
Operating Non Operating
*1
*1,3
−20∼60°
5 ∼
C (−4∼122°F)
85% RH
*2,3
2
*2
*2
*1 : For operating the printer, conditions must be in the range shown in the figure below.
2
*
: These conditions are acceptable when the printer is in its shipping container.
3
: Without condensation.
*
Figure 1-6. Temperature/Humidity Range
Rev.B 1-7
Page 16

Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
1.2.7 Reliability
Total print volume: 75,000 pages (A4, letter)
Printhead life: 1,000 million dots/nozzle
1.2.8 Safety Approvals
Safety standards: 120V version: UL1950 with D3,
CSA22.2 # 950 with D3
220-240 V version: EN 60950 (TÜV, SEMKO, DEMKO,
NEMKO, SETI)
Radio frequency interference (RFI): 120 V version: FCC part 15 subpart B class B
220-240 V version: Vfg.243 (VDE0878 part 3, part 30)
EN55022 (CISPR PUB. 22) class B
1.2.9 Physical Specifications
Dimension (W × D × H): 482 × 530 × 192 mm (18.5 × 20.7 × 7.56 in.)
Weight: Approximately 7.5 kg (16.5 lb)
1-8 Rev.B
Page 17
Approx. 5 µs
Approx. 5 µs
0.5 µs (minimum)
0.5 µs (minimum)
0.5 µs (minimum)
BUSY
ACKNLG
DATA
STROBE
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
1.3 INTERFACE SPECIFICATIONS
The Stylus Pro is standard-equipped with an 8-bit parallel and serial interface.
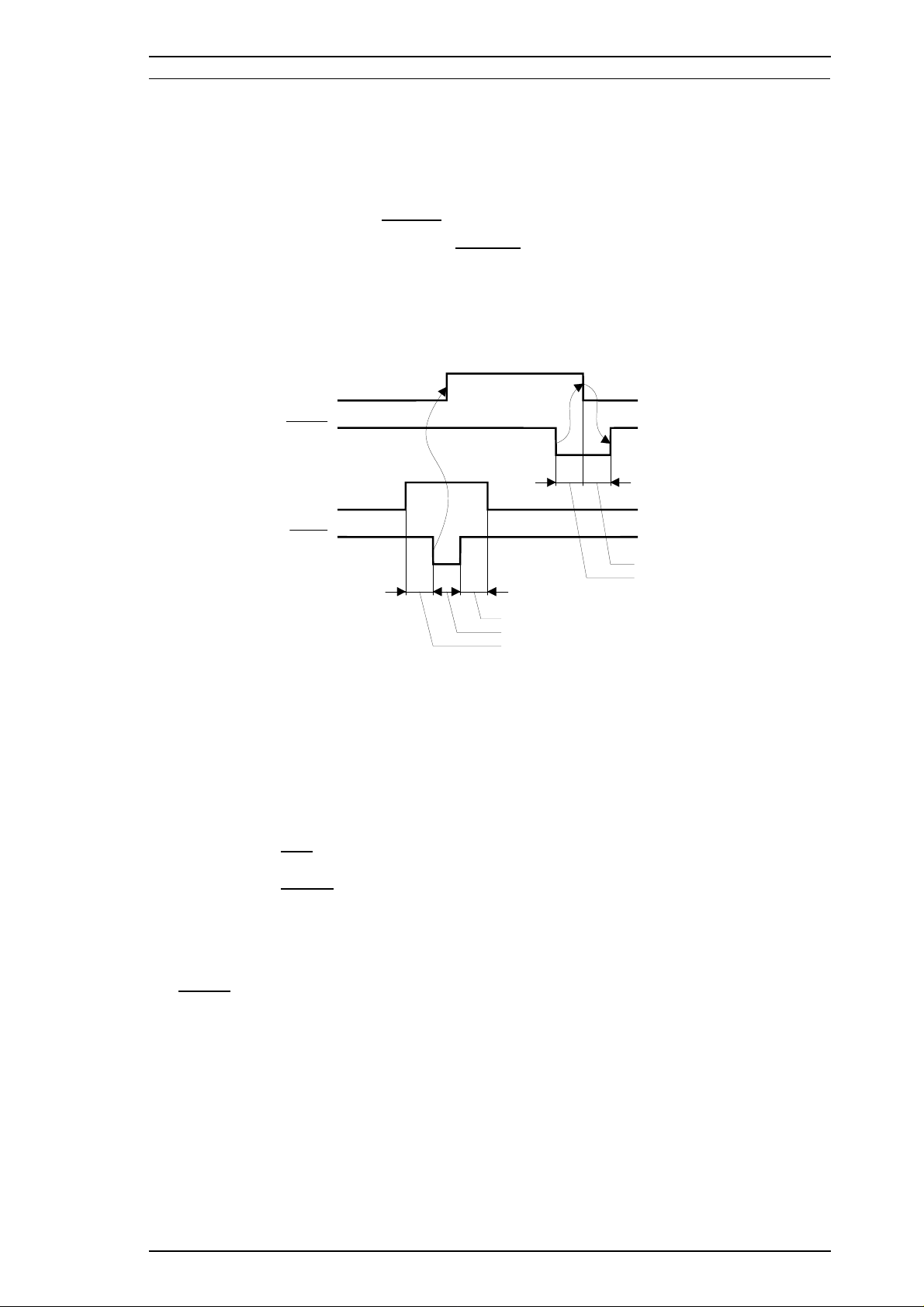
1.3.1 Parallel Interface Specifications
Data format: 8-bit parallel
Synchronization: By
Handshaking: By BUSY and
STROBE pulse synchronization
ACKNLG signals
Signal level: TTL compatible level
Adaptable connector: 36-pin 57-30360 (Amphenol or equivalent)
Data transmission timing: See Figure 1-7.
Figure 1-7. Data Transmission Timing
Note: Transition time (rise time and fall time) of every input signal must be less than 0.2
µ
s.
The Busy signal is active (HIGH) under the following conditions:
r During data reception (See Figure 1-7.)
r When the input buffer is full
r When the
INIT input signal is active
r During initialization
r When the
ERROR or PE signal is active
r During the self-test mode
r During the demonstration mode
r During the default setting mode
r When a fatal error occurs
The
ERROR signal is active (LOW) under the following conditions:
r When a paper-out error occurs
r When a no ink cartridge error occurs
r When a fatal error occurs
The PE signal is active (HIGH) under the following conditions:
r When a paper-out error occurs
r When a fatal error occurs
Rev.B 1-9
Page 18
Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
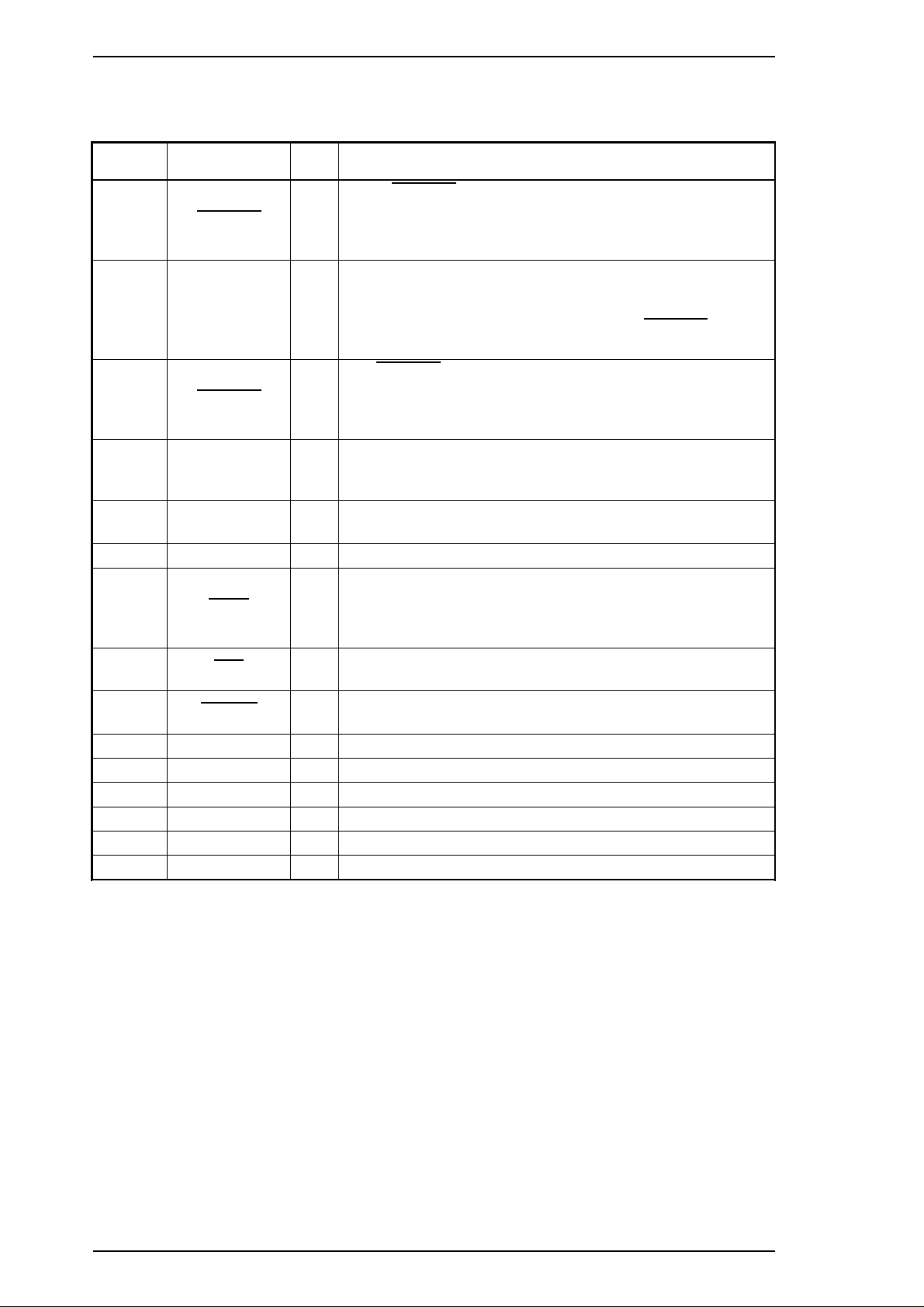
Table 1-8 shows connector pin assignments and signal functions of the 8-bit parallel interface.
Table 1-8. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments for Parallel Interface
Pin No.
1
2-9
10
11
12
13
14
31
32
35
17
16
19-30
33,36
15,18,34
Signal Name I/O* Description
The
STROBE pulse is used to read data from the host
STROBE I
DATA 1-8 I
ACKNLG O
BUSY O
PE O
SLCT O Pulled up to +5 V through a 1.0 KΩ resistor in the printer.
AFXT I
INIT I
ERROR O
+5 V — Pulled up to +5 V through 1.0 KΩ resistor in the printer.
CHASSIS — Chassis ground.
GND — Signal ground.
—— —
— — Not used.
—— —
computer. Pulse width must be 0.5 µs or more. Normally, it
is HIGH, and data is latched with the rising edge of this
signal.
DATA 1-8 are parallel data bits. When one of these signals is
HIGH, the data bit is 1; when LOW, the data bit is 0. The most
significant bit (MSB) is DATA 8. The signal state must be
maintained for 0.5 µs on either side of the
active edge.
ACKNLG is an acknowledge pulse with a width of
approximately 10 µs. This signal goes LOW upon
completion of data reception to indicate that the printer is
ready to receive further data.
The BUSY signal informs the host computer of the printer’s
status. When this signal is HIGH, the printer cannot accept any
more data.
This signal indicates whether paper is available in the printer or
not. A HIGH level indicates no paper.
If this signal is set to LOW, the printer automatically performs
one line feed upon receipt of a CR (carriage return) code. The
status of this signal is checked only at power on and
initialization.
If this signal goes LOW, the printer is initialized. The pulse
width of this signal must be 50 µs or more.
This signal goes LOW if the printer has a fatal error or runs out
of paper.
STROBE signal’s
* The I/O column indicates the direction of the signal as viewed from the printer.
1-10 Rev.B
Page 19
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
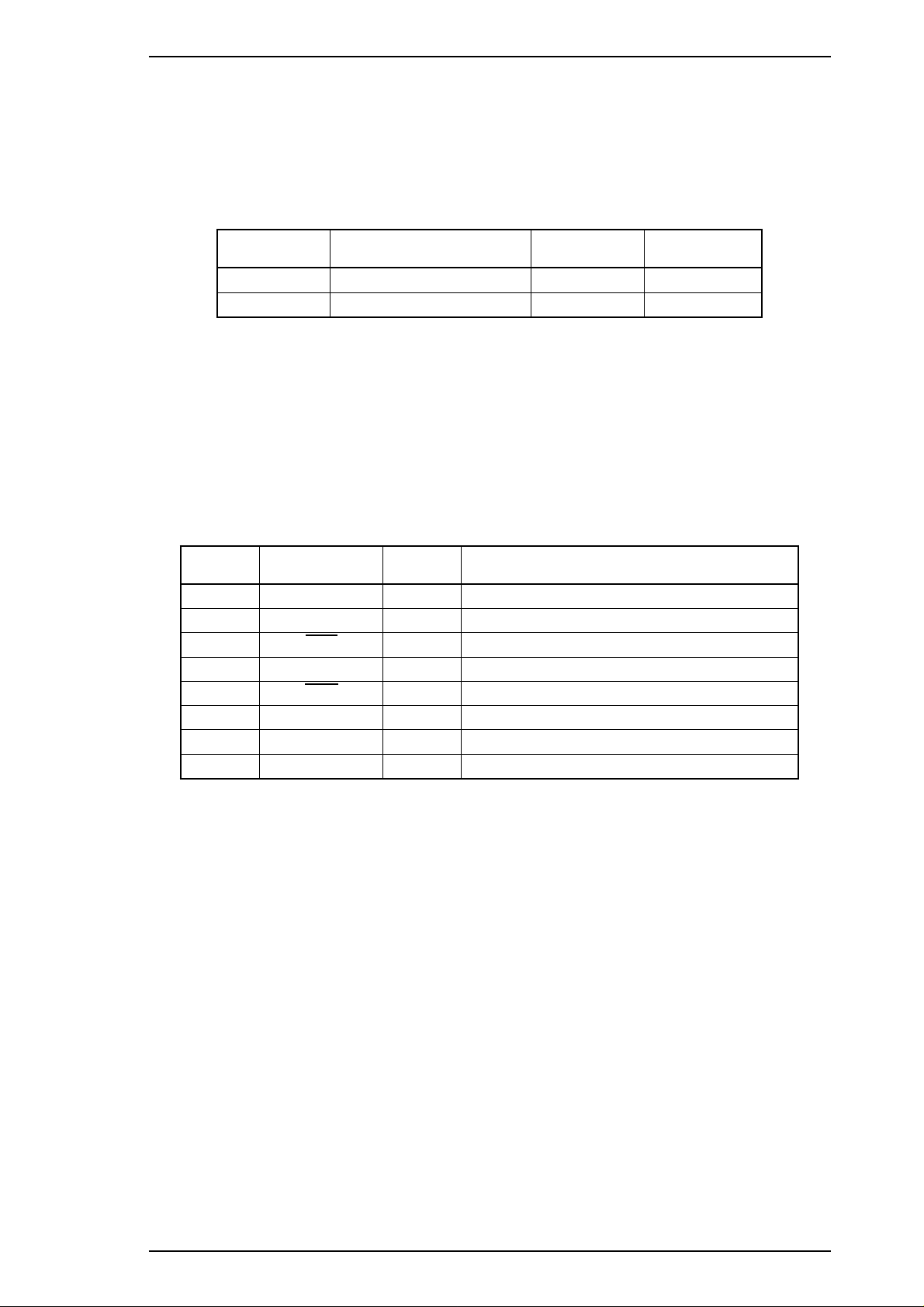
1.3.2 Serial Interface Specifications
Data format: RS-422 serial
Synchronization: Asynchronous
Handshaking: By DTR signal and X-ON/X-OFF protocol
Table 1-9. DTR and X-ON/X-OFF Protocol
State
Busy
Ready
Word length
Start bits:
Data bits:
Parity bits:
Stop bits:
Bit rate: 57.6K / 230.4K bps
Adaptable connector: 8-pin mini-circular connector
Recommended I/F cable: Apple
Buffer Space DTR X-ON/X-OFF
Less than 512 bytes Off X-OFF
More than 1,024 bytes On X-ON
1 bit
8 bit
none
1 bit
®
System peripheral-8 cable
Table 1-10. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments for Serial Interface
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Signal Name I/O* Description
DTR Out Data terminal ready
NC — No connection
TXD Out Transmit data
SG In Signal ground
RXD In Receive data
TXD Out Balanced transmit
NC — No connection
RXD In Balanced receive
* The I/O column indicates the data flow as viewed from the printer.
Rev.B 1-11
Page 20
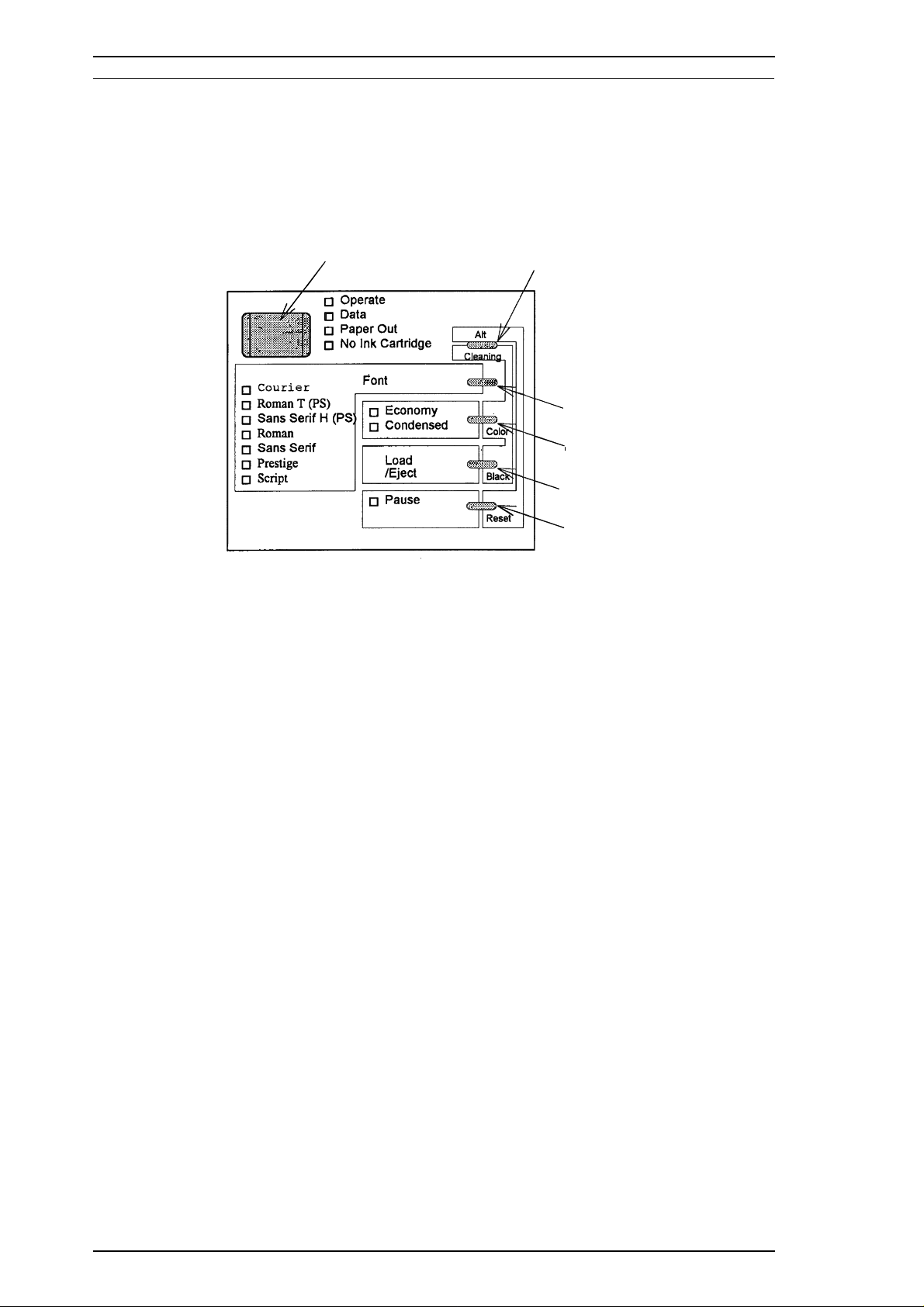
Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
1.4 OPERATIONS
This section describes the basic operations of the printer.
1.4.1 Control Panel
The control panel for this printer has 1 lock-type and 5 non lock-type pushbuttons, and 15 LED
indicators for easy operation of the various printer functions.
Operate Alt
Font
Economy/
Condensed
Load/Eject
Pause
Figure 1-8. Control Panel Appearance
Buttons
Operate Turns the printer on or off.
Alt Modifies the function of other buttons. Holding down this button for
3 seconds turns the Pause light to come on, and causes the printer to
move the carriage to the ink cartridge installation position. Pressing Alt
again causes the carriage to return to the home position.
Font Cycles through the font choices. Pressing the Font button, while holding
down the Alt button in pause mode causes the carriage to move to the
gap adjustment position. Pressing the Alt button again causes the
carriage to return to the home position.
Economy/Condensed Selects either economy printing or condensed printing mode. Pressing
the Economy/Condensed button while holding down the Alt button turns
the Pause light on and starts the color printhead cleaning cycle.
Load/Eject Either loads a new sheet into the printer or ejects paper currently in
the paper path. Pressing the Load/Eject button while holding down the
Alt button starts the black printhead cleaning cycle.
Pause Stops printing temporarily or resumes printing if it has been stopped
temporarily. Pressing Pause while holding down the Alt button for
about three seconds, or until all LEDs light, resets the printer.
1-12 Rev.B
Page 21

Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
Indicators
Operate On when the printer is on. Blinks during power on and off.
Data On when print data is in the input buffer. Data and Pause lights blink if
an error occurs.
Paper Out On when the printer is out of paper. Blinks when a paper jam occurs.
No Ink Cartridge Onwhen the ink is out.
Economy Onwhen economy printing mode is selected.
Condensed On when condensed printing mode is selected.
Font These LEDs indicate the selected font.
Pause On when printing is paused.
1.4.2 Panel Operation at Power On
You can activate the modes below by doing the following:
Self-test mode Turn on the printer while holding down the Load/Eject button.
Hex dump mode Turn on the printer while holding down the Font and Load/Eject
buttons. Once this mode is selected, the printer prints all received data
in hexadecimal format.
Default setting mode Turn on the printer while holding down the Economy/ Condensed
button. For more information about the mode, see Section 1.4.3.
Initialize EEPROM Turn on the printer while holding the Alt, Font, Load/Eject, and Pause
buttons.
Rev.B 1-13
Page 22
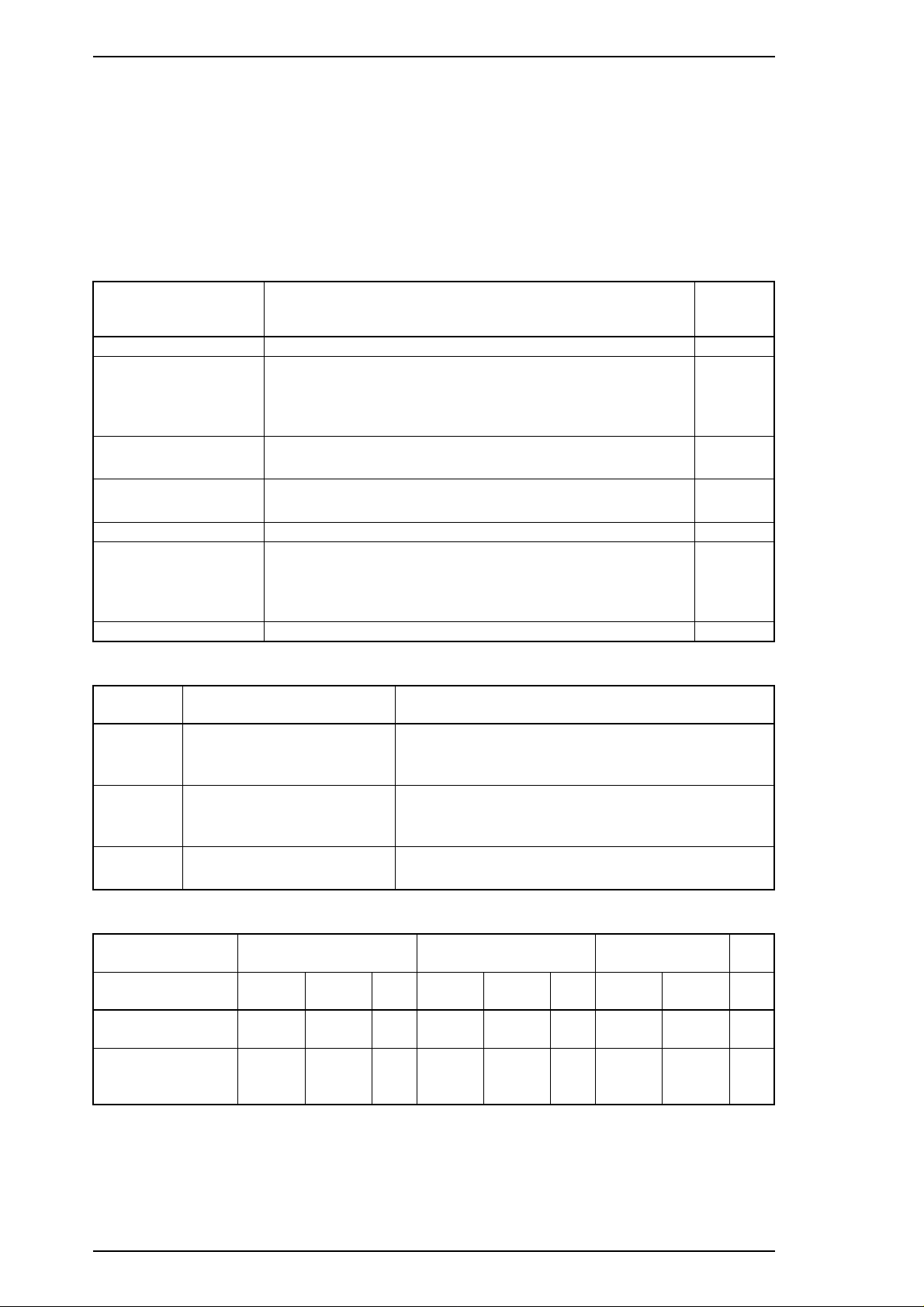
Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
1.4.3 Default Settings
The printer can save some printer setting parameters that define its functions at initialization. You can
change these parameters using the printer’s default-setting mode.
1.4.3.1 Default Setting Items
In default-setting mode, you can change settings listed in the table below. Activate default-setting mode
by holding down the Economy/Condensed button while turning on the printer.
Table 1-11. Default Setting Items
Menu
Contents
Character table
Print direction
Network I/F mode
Auto line feed
Loading position
Interface mode
Auto I/F wait mode
Table 1-12. Characteristics of Print Direction Mode
Item
Auto
Bi-D
Uni-D
Black and White Printing Color (CMYK) Printing
Throughput and quality is
Print quality may be down.
Selects the character table —
Controls the print direction. (See Tables 1-12 and 1-13)
Auto
Bi-D
Uni-D
Off: For normal environments.
On: For network environments.
On: Valid
Off: Invalid
3.0/8.5 mm (0.12/0.33 in.) 3.0 mm
Auto I/F mode
Parallel I/F mode
Serial I/F mode
Optional I/F mode
10/30 seconds 10 sec.
better.
Throughput is best.
Throughput is worse.
Print quality is better.
Description
Throughput is better.
Color quality with special paper is worse.
(Color correction depends on the printing direction.)
Throughput is better.
Color quality with special paper is worse.
(Color correction depends on the printing direction.)
Throughput is worse.
Color quality is best.
Factory
Setting
—
Off
—
—
Table 1-13. Printing Direction and ESC U Command
Default Setting
Mode
^
Character mode
(for MS-DOS
Raster graphics
mode (for
Windows
®
™
)
)
ESC U0 ESC U1 None ESC U0 ESC U1 None ESC U0 ESC U1 None
Auto Auto Auto Bi-D Uni-D Bi-D Uni-D Uni-D Uni-D
Bi-D Uni-D Auto Bi-D Uni-D Bi-D Bi-D Uni-D Uni-D
Note: Printing direction is controlled by driver in Windows environment.
1.4.3.2 Changing the Default Settings
To change the printer’s default settings:
1-14 Rev.B
Auto Bi-D Uni-D +
Page 23
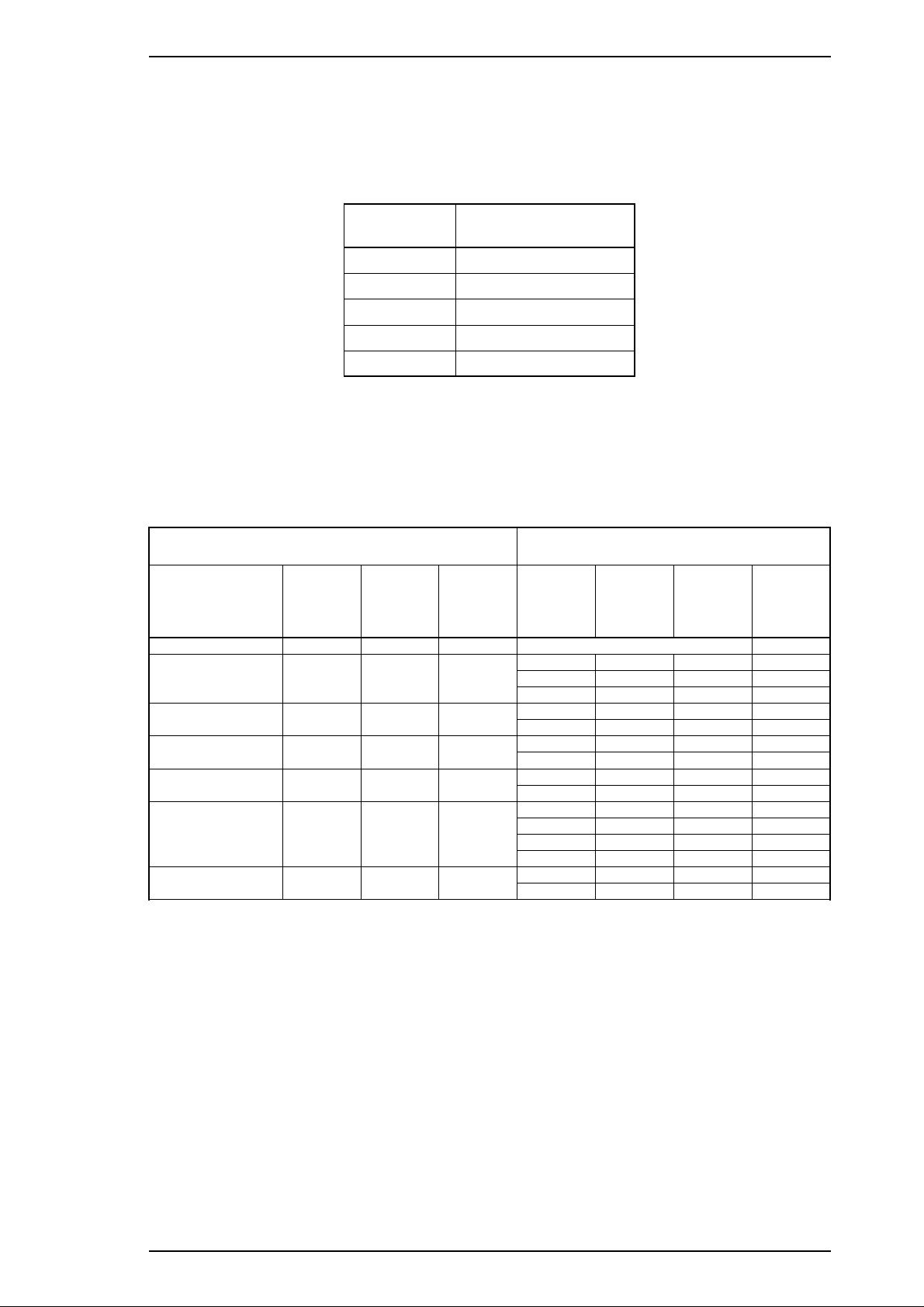
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
a. Hold down the Economy/Condensed button and turn on the printer. The printer prints a sheet that
shows the firmware version and describes how to select the language used to print messages.
b. Press the Font button until the appropriate font LED is selected. The following table shows which
language corresponds to which font LED.
Table 1-14. Language Selection
Language
English
Français
Deutsch
Italiana
Español
c. Press the Alt button. The printer prints the current settings using the selected language. It also
prints a table showing how to change the printer settings.
d. Press the Font button to advance through the setting menu. The current printer settings are
indicated by the Courier, Roman T (PS), and San Serif H (PS) LEDs. Each time you press the Font
button, you adance to the next setting, and the three font LEDs change according to the selection.
Font LED
Courier
Roman T (PS)
Sans Serif H (PS)
Roman
Sans Serif
Table 1-15. Feature Selection
Menu
Feature/Menu
Character table On On On See Table 1-16 +
Print direction
Network I/F mode
Auto line feed
Loading position
Interface mode
Auto I/F wait time
e. Change the setting value by pressing Alt button. Pressing the Alt button changes the setting for the
current menu. The status of the LEDs will be changed as the button is pressed.
Courier
LED
On Off Off
Off On Off
On On Off
Off Off On
On Off On
Off On On
Roman T
(PS) LED
Sans
Serif H
(PS) LED
Setting
Auto On Off Off
Bi-D Off On Off
Uni-D On On Off
Off Off Off Off
On On Off Off
Off Off Off Off
On On Off Off
3 mm Off Off Off
8.5 mm On Off Off
Auto On Off Off
Parallel Off On Off
Serial On On Off
Option Off Off On
10 sec. Off Off Off
30 sec. On Off Off
Setting Value
Operate
LED
Data
LED
Paper Out
LED
Rev.B 1-15
Page 24
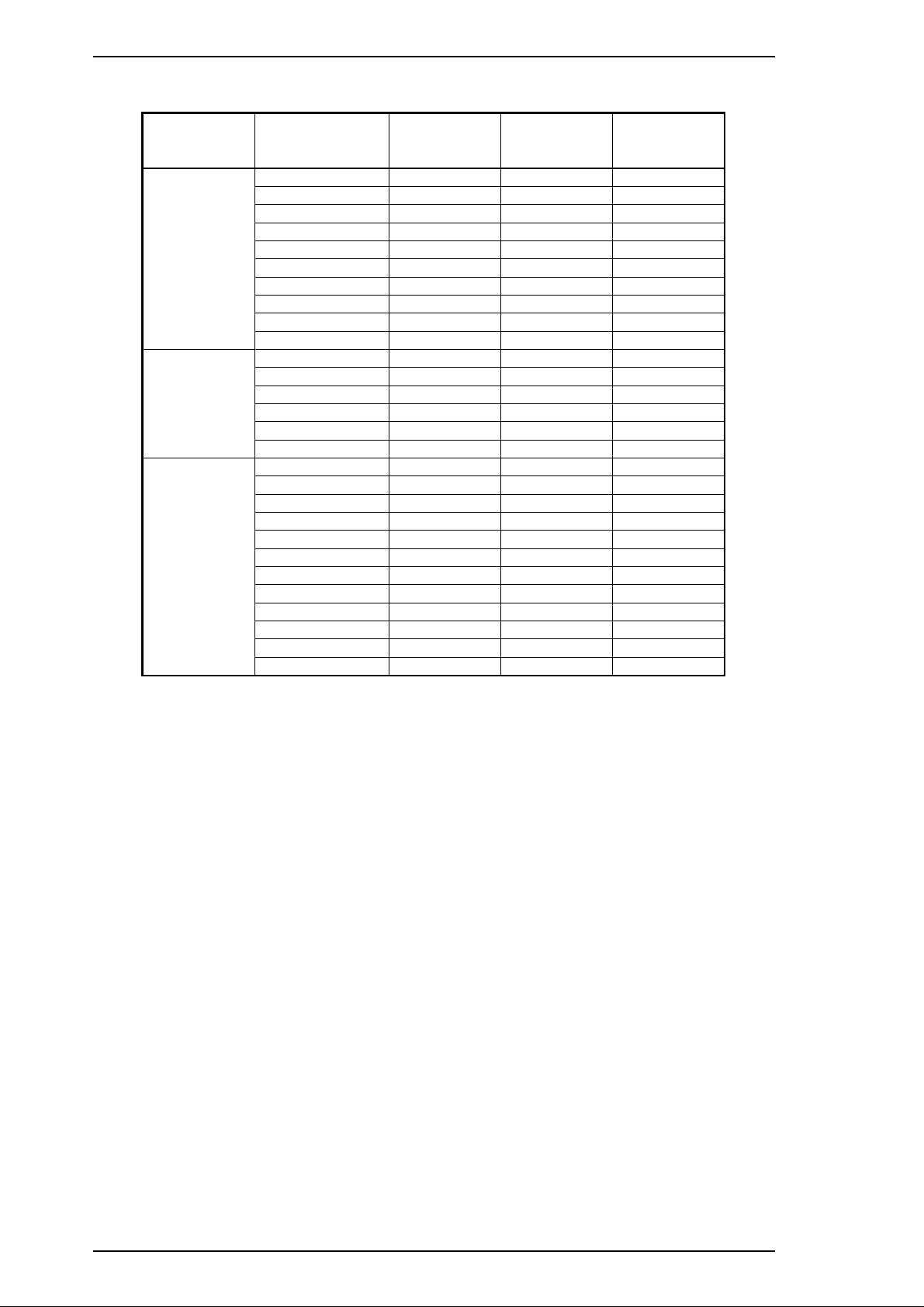
Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
Table 1-16. Character Table Selection
Version Settings Operate LED Data LED
Italic U.S.A. Off Off Off
Italic France On Off Off
Italic Germany Blinks Off Off
Italic U.K. Off On Off
Common
Standard
NLSP
f. Repeat d and e to change other printer settings. The setting menu selection will return to the first menu
after the last menu selection is over.
g. Turn off the printer. The setting is stored into non-volatile memory.
Italic Denmark 1 On On Off
Italic Sweden Blinks On Off
Italic Italy Off Blinks Off
Italic Spain 1 On Blinks Off
PC437 Blinks Blinks Off
PC850 Off Off On
PC860 On Off On
PC863 Blinks Off On
PC865 Off On On
PC861 On On On
BRASCII Blinks On On
Abicomp Off Blinks On
PC437 Greek Off Off On
PC853 Blinks Off On
PC855 Off On On
PC852 On On On
PC857 Blinks On On
PC866 Off Blinks On
PC869 On Blinks On
MAZOWIA Blinks Blinks On
Code MJK Off Off Blinks
ISO 8859-7 On Off Blinks
ISO Latin 1T Blinks Off Blinks
Bulgaria Off On Blinks
Paper Out
LED
1-16 Rev.B
Page 25
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
1.4.4 Error Conditions
The printer can detect the various errors and indicate them with LEDs.
Table 1-17. Error Indications
Error Data LED
Paper out Off On Off Off Off Off
No ink cartridge Off Off On Off Off Off
Paper jam Off Blinks Off Off Off Off
Maintenance request Blinks Blinks Blinks Blinks Blinks Blinks
Carriage error Blinks Off Off Off Off Blinks
Paper Out
LED
No Ink
Cartridge
LED
Economy
LED
Condensed
LED
Pause
LED
1.4.5 Printer Initialization
There are three initialization methods: hardware initialization, software initialization, and panel initialization.
1.4.5.1 Hardware Initialization
Hardware initialization is performed by:
r Turning on the printer.
r Sending the parallel interface
(If the
INIT signal is active when the printer is turned on, hardware initialization is started when the INIT
signal becomes inactive.)
When the hardware initialization is performed:
r The printer mechanism is initialized.
r Input data buffer is cleared.
r Downloaded character definitions are cleared.
r Print buffer is cleared.
r Default values are set.
INIT signal.
1.4.5.2 Software Initialization
Software initialization is performed upon receipt of the control code ESC @.
When the software initialization is performed:
r Print buffer is cleared.
r Default values are set.
The last panel settings are kept.
1.4.5.3 Panel Initialization
This printer is initialized by pressing the Load/Eject button while pressing the Alt button.
When the panel initialization is performed:
r Input data buffer is cleared.
r Print buffer is cleared.
r Default values are set.
The last panel settings are kept.
Rev.B 1-17
Page 26
Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
1.5 MAIN COMPONENTS
The main components of the Stylus Pro are:
o Main control board (C164 MAIN Board)
o Power supply unit (C137 PSB/PSE Board)
o Control panel board (C137 PNL Board)
o Printer mechanism (M-4A10)
o Housing
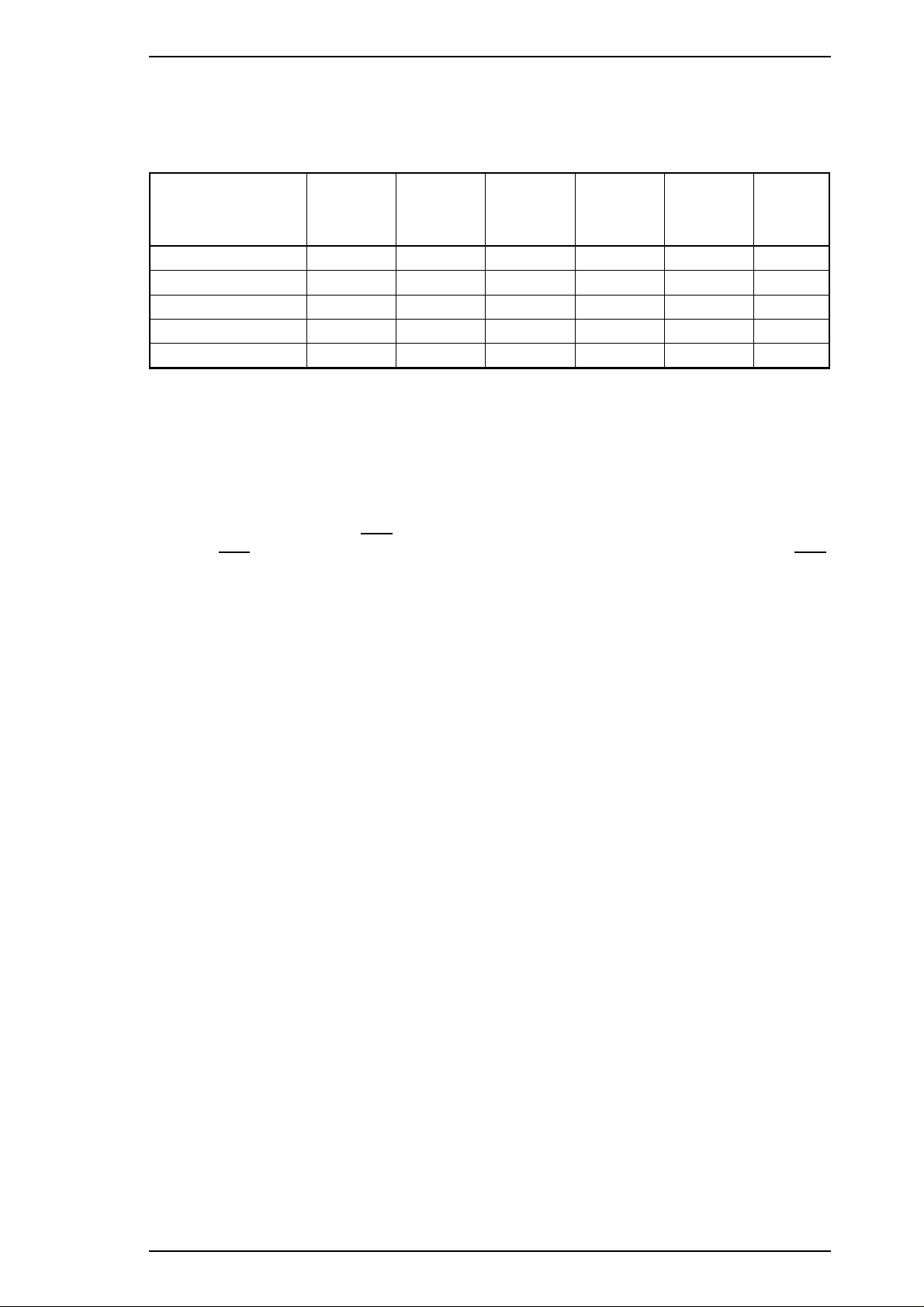
1.5.1 Main Control Board (C164 MAIN Board)
The main control board (C164 MAIN Board) consists of an H8/3003 16-bit CPU, E05A09 gate array, a
program ROM (1/2/4Mb), a program/CG ROM (1/2/4/8Mb), 1 DRAM (4Mb), a mask ROM (4/8Mb), an
EEPROM (1Kb), and a lithium battery for powering the protect counters. The reset IC (M51955 and PST 592)
is equipped with both a logic system and a power system. The C164 MAIN Board is almost the same as the
C162 MAIN Board, except that the C164 board has no solenoid driving circuit for the ADF. (The C162
MAIN Board has a solenoid driver to operate the document feeder. )
Table 1-18. Comparison between C164 MAIN and C162 MAIN
Main Board C164 MAIN Board C162 MAIN Board
DRAMs 1 2
ADF Plunger
Driving Circuit *
None Equipped
* The ADF plunger switches the PF motor operation from paper feed to paper pickup.
CPU (H8/3003)
RAM
Program ROM
Head Common Drive Tansistors
Lithium Battery
164
Gate Array (E05B09)
EEPROM
PF Motor Driver IC
CR Motor Driver IC
CG ROM
Figure 1-9. C164 MAIN Board Component Layout
1-18 Rev.B
Page 27
L1
C1
R2
CN1
CN2
F1
IC51 (TL494)
T1
Q1
C11
C51
C82
PC1
C3
Q51
DB1
D51
SW6
LED1
/
LED4
LED8
/
LED14
LED5
LED6
LED7
SW4
/
SW0
Stylus Pro Service Manual Product Description
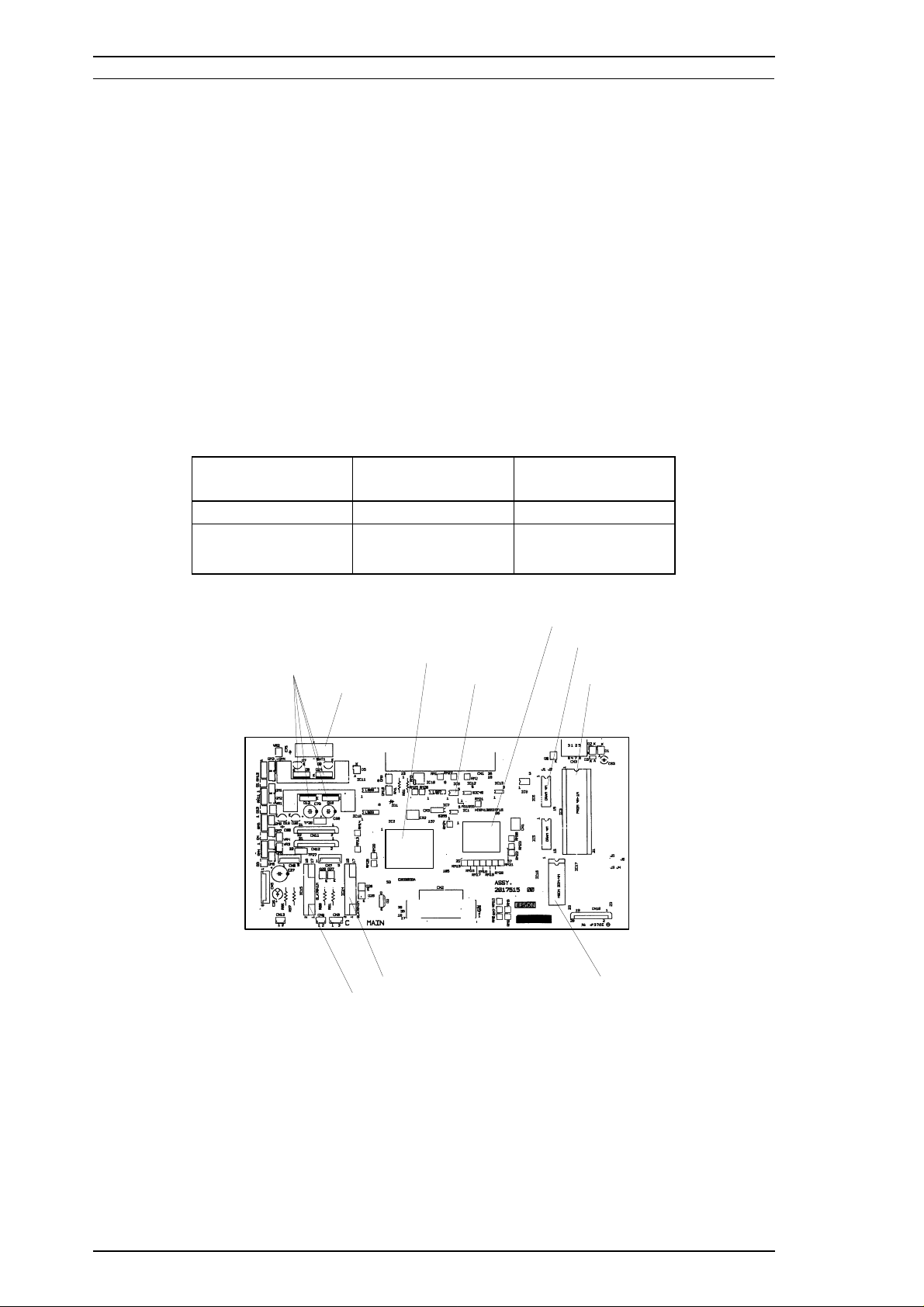
1.5.2 Power Supply Board (C137 PSB/PSE Board)
The power supply board (C137 PSB/PSE Board) consists of an RCC switching regulator circuit. This board is
equipped with a power switch, connected to the secondary circuit. Thus, if the printer is turned off, it can
continue to operate to eject the paper and perform the head-capping operation. The power on/off signal is
always monitored by the E05A09 gate array on the C164 MAIN Board, and the logic system recognizes the
power switch status.
Figure 1-10. C137 PSB/PSE Component Layout
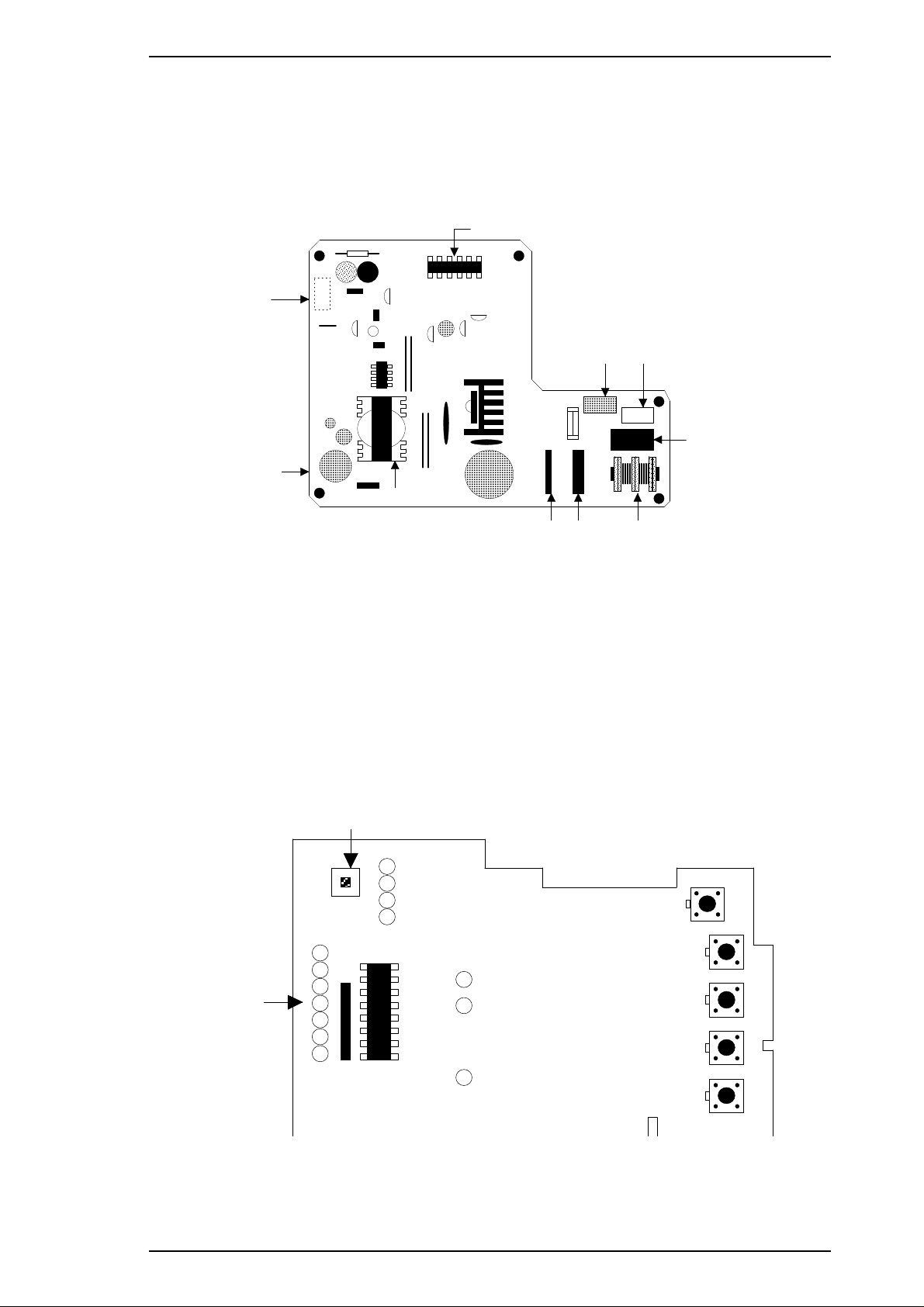
1.5.3 Control Panel (C137 PNL Board)
The 15 LEDs on this board indicate error status (there is no buzzer system). By using the 6 buttons in
combination with one another, you can operate the printer in each protected mode (cleaning color or black ink
systems, exchanging ink cartridges, running a self-test, setting default values, resetting the printer, and
EEPROM clearing).
Figure 1-11. C137 PNL Board Component Layout
Rev.B 1-19
Page 28

Product Description Stylus Pro Service Manual
1.5.4 Printer Mechanism (M-4A11)
The M-4A11 printer mechanism is equipped with a 64-nozzle black printhead and 48-nozzle color (CMY)
printhead on the carriage unit. A resolution of 720 dpi is possible with special (non-absorbent) paper.
The ink system has both a black pump unit and a color pump unit. Waste ink from each printhead flows into
individual caps. Power for the pump system and paper feed system is supplied by the paper feed motor. This
printer mechanism is based on Stylus Color’s (M-4A10).
1.5.5 Housing
The Stylus Pro’s housing consists of the printer cover, upper case, and the lower case.
Attached to the housing is the front paper tray, with paper separator.
1-20 Rev.B
Page 29

Chapter 2 Operating Principles
Table of Contents
2.1 OVERVIEW 2-1
2.2 OPERATING PRINCIPLES OF THE PRINTER MECHANISM 2-1
2.2.1 Printer Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.2.2 Principles of the Printing Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2.2.3 Carriage Drive Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.2.3.1 Platen Gap Adjust Lever . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.2.4 Paper Feed Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.2.5 Ink System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2.2.6 Pump Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
2.2.7 Cap Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
2.2.8 Wiping Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
2.3 OPERATING PRINCIPLES OF THE ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 2-13
2.3.1 Operating Principles of the Power Supply Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
2.3.2 Operating Principles of the Main Control Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
2.3.2.1 Reset Circuits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
2.3.2.2 Sensor Circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
2.3.2.3 Carriage Motor Drive Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
2.3.2.4 Paper Feed Motor Drive Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
2.3.2.5 Printhead Drive Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
2.3.2.6 DMA Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
2.3.2.7 DRAM Refresh Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
2.4 INK SYSTEM MANAGEMENT 2-21
2.4.1 Ink Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
2.4.2 Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
2.4.2.1 Protect Counter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
Page 30

List of Figures
Figure 2-1. Printer Mechanism Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Figure 2-2. Structure of Printhead. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Figure 2-3. Principles of the Printing Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Figure 2-4. Platen Gap Lever Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Figure 2-5. Platen Gap Lever Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Figure 2-6. Paper Feed Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Figure 2-7. Ink System Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Figure 2-8. Pump Mechanism Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Figure 2-9. Switch Lever Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Figure 2-10. Paper Feed Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
Figure 2-11. Switch Lever Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
Figure 2-12. Pump Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Figure 2-13. Cap Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Figure 2-14. Wiping Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Figure 2-15. Block Diagram of the Electrical Circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Figure 2-16. Power Supply Circuit Block Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Figure 2-17. Main Control Circuit Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Figure 2-18. Reset Circuit Block Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Figure 2-19. Sensor Circuit Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Figure 2-20. Carriage Motor Circuit Block Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Figure 2-21. Serial Data Transfer Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Figure 2-22. Paper Feed Motor Drive Circuit Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Figure 2-23. Normal/EPSON Micro Dot Switching Block Diagram. . . . . . . 2-19
Figure 2-24. Trapezoidal Drive Waveform. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
Figure 2-25. Printhead Drive Circuit Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
Figure 2-26. DMA Controller Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
Figure 2-27. Junction Method (CPU-DRAM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
List of Tables
Table 2-1. Carriage Drive Motor Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Table 2-2. Drive Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Table 2-3. Platen Gap Adjust Lever Position. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Table 2-4. Paper Feed Drive Motor Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Table 2-5. Drive Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Table 2-6. Pump Mechanism Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Table 2-7. DC Voltage Distribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Table 2-8. Serial Data Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Table 2-9. Paper Feed Motor Drive Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Page 31

Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
2.1 OVERVIEW
This section describes the operating principles of the printer mechanism and the electrical circuits of the
Stylus Pro.
2.2 OPERATING PRINCIPLES OF THE PRINTER MECHANISM
2.2.1 Printer Mechanism
The Stylus Pro is based on the Stylus Color printer. The Stylus Pro printer mechanism is composed of the
printhead unit, paper feed mechanism, carriage drive mechanism, pump mechanism, and various sensors such
as the Stylus Color’s. The figure below shows a functional block diagram of the printer mechanism.
Pickup Re lease Lever
ASF Mechanism
Pa per Feed Moto r
Carriage Motor
Figure 2-1. Printer Mechanism Block
Disengage Lev er
Paper Feed Mechanism
Pump Unit Drive Mechanism
Carriage Unit
Color Black
Rev.A 2-1
Page 32

Cartridg e Needle
Piezo
Printhead Driver Board
Nozzle
Nozzle Plate
Piezo
Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.2.2 Principles of the Printing Operation
The printing mechanism of this printer uses a drop-on-demand ink jet system similar to the system used on all
other EPSON ink jet printers. However, the printhead in this system is completely redesigned to make it more
compact and ensure a high level of reliability, just as with the Stylus Color. The figure below shows the
structure of the printhead and ink supply system.
Figure 2-2. Structure of Printhead
2-2 Rev.A
Page 33

Normal
State
Ejection
State
Vibration PlateNozzle
Vibration Plate
Cavit y
Nozzle
Piezo
Piezo
Cavit y
Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
The printhead operates in one of two modes to eject ink from each nozzle:
r Normal state
No electrical charge is applied to the piezoelectric element attached to the back of the cavity, and
pressure inside the cavity is kept at a constant level.
r Ejecting state
The head data signal is applied to the specific nozzle control line to select the active nozzle for printing,
and the piezoelectric element is gradually charged by the drive voltage. By charging the piezoelectric
element, the vibration plate is bent to compress the cavity. Then, ink is ejected from the nozzle.
Figure 2-3. Principles of the Printing Operation
When the ink charge or printhead cleaning operation is performed, the ink in the cavity is vacuumed out with
the pump mechanism. During printing, on the other hand, the ink is simultaneously supplied from the ink
cartridge and ejected from the nozzle, according to the changes in the volume of the cavity.
A thermistor is attached to the side of the color printhead drive board to monitor the temperature, because the
viscosity of the ink varies, depending on the temperature. The detected temperature level is fed back to the
printhead drive voltage control circuit to change the time of the Tc pulse. (The Tc pulse is shown in Section
2.3.2.5.)
EPSON Micro Dot Printing Mode (Super 720 dpi Printing Mode)
The Stylus Pro printer has a special printing mode, called the EPSON Micro Dot Printing mode. This printing
mode can be selected on command from the host computer. Using this printing mode can improve the quality
of output because it eliminates the banding that can sometimes occur in normal mode. In EPSON Micro Dot
Printing mode, the ink dot size becomes smaller than the normal dot size.
Rev.A 2-3
Page 34

Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.2.3 Carriage Drive Mechanism
The timing belt attached to the base of the carriage unit is driven by the carriage motor, causing the carriage
unit to move along the carriage guide shaft from left to right, or vice versa. The carriage drive motor on this
printer is a 4-phase, 200-pole, hybrid-type stepping motor mechanism, allowing the printer to stop the carriage
or change the carriage movement at any position. The position of the carriage is recognized by the home
position sensor, and position information is fed back to the carriage drive control circuit. This carriage motor
is driven by motor driver IC SLA7041 (see Section 2.3.2.3 for more information).
Table 2-1. Carriage Drive Motor Specifications
Item Description
Motor Type 4-phase / 200-pole hybrid-type stepping motor
Drive Voltage +35 VDC ± 5%
Coil Resistance 10.0 Ω ± 7%
Drive Frequency 960 ~ 4800 PPS
Excitation Mode Constant current unipolar drive, micro step driving
Table 2-2. Drive Terms
Acceleration/
CR Speed Frequency Phase Drive Method
Deceleration
Steps
Mode 1
(200 CPS)
Mode 2
(100 CPS)
Mode 3
(40 CPS)
4800
(2400)
2400
(1200)
960
(480)
r Acceleration/Deceleration Area:
2W1-2 phase + 1-2 phase
r Constant Area: 1-2 phase
r Acceleration/Deceleration Area:
2W1-2 phase + 1-2 phase
r Constant Area: 1-2 phase
r Acceleration/Deceleration Area:
2W1-2 phase
r Constant Area: 2W1-2 phase
Notes: 2W1-2 phase means the 1/8 2-2 phase drive control.
Values in parentheses ( ) are values of the 2-2 phase.
2.2.3.1 Platen Gap Adjust Lever
<Plain Paper>
(A)
Platen Gap Adjust Lever
Acceleration
40 (5)+110 (55)
Deceleration
32( 4)+112 (56)
40 (5)+40 (20)
16 (2)
<Envelopes>
(B)
0.6 mm
Eject Frame
Platen
Printhead
Carriage Slide r
Figure 2-4. Carriage Drive Mechanism
2-4 Rev.A
Page 35

Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
The platen gap adjust lever, which is attached to the carriage unit, needs to be set to the appropriate position
for the paper thickness. To change the platen gap, put the printer in the PAUSE state, then press the Font
button while holding down the Alt button. The carriage unit moves the platen gap adjustment position
automatically. The platen gap adjustment mechanism consists of platen gap lever, carriage slider, and eject
frame. When you set the lever for vertical or horizontal position, the carriage slider either pushes against the
eject frame or does not push it. Then the platen gap is changed because of the up and down motion of
carriage.
Table 2-3. Platen Gap Adjust Lever Position
Paper Type Lever Position
Cut sheets Horizontal (A) (± 0 mm)
Envelopes Vertical (B) (+0.6 mm)
CR HP Sensor
CR Motor
Carriage Guide Shaft
Belt Pul ley
Car riag e Unit
Figure 2-5. Platen Gap Lever Operation
2.2.4 Paper Feed Mechanism
This printer’s paper feed mechanism can feed paper only from the built-in ASF (auto sheet feeder). The paper
feed drive motor is a 4-phase, 96-pole, hybrid-type stepping motor that directly drives the paper feed
mechanism (paper advancing operation, paper pickup operation). This motor also drives the pump
mechanism, but only when the printer is in the cleaning state. The paper feed motor uses 2-2 phase excitation,
except for the paper feed drive sequence (which is 2W1-2 phase).
Table 2-4. Paper Feed Drive Motor Specification
Item Description
Motor Type 4-phase, 96-pole, hybrid-type
Drive Voltage +35 VDC ± 5%
Coil Resistance 11.5 Ω ± 1.1Ω
Drive Frequency 300 ~ 1800 PPS
Excitation Mode Paper feed / pump drive: 2-2 phase, 2W1-2 phase
Rev.A 2-5
Page 36

Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
Table 2-5. Drive Terms
Current Value (mA)
Mode
Paper loading 1600 970/750 750 750 240
ASF feed 1600 970/750 750 750 240
Paper feed 391 — / — 970 — 240
Pump Drive 1 1800 1380/1380 1380 750 240
Pump Drive 2 300 — / — 1380 — 240
PF Transmission Ge ar
Frequency
(pps)
Quenchi ng Roller
Acceleration/
Deceleration
PF Pinch Roller Unit
Constant Rush Hold
PF Motor
Pinion Gear
Paper Pickup Lever
Pickup Roller
Platen Drive Gear
Carr iag e
Lever
Tension Spring
Cam Roller
Hopper Frame
Figure 2-6. Paper Feed Mechanism
2-6 Rev.A
Page 37

Air Valve
Black HeadColor Head
Pump 1
Pump 2
Ink Absorber
Waste In k Dra in Ta nk
Cleani ng B la de
(for Color / Bla ck Head )
Pump Unit
Friction Clutch
Disengage Unit
Platen Roller
PF Motor
Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
2.2.5 Ink System
This printer’s ink system is composed of the following mechanisms:
r Ink cartridge
r Pump mechanism
r Cap mechanism
r Waste ink drain tank
r Wiping mechanism
The figure below shows a diagram of the ink system.
Figure 2-7. Ink System Block Diagram
Rev.A 2-7
Page 38

D/E Lever
D/E Set L ever
D/E Reset Le ver
Carria g e
Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.2.6 Pump Mechanism
The paper feed motor drives the pump mechanism when the transmission gear is moved to the position where
the paper feed motor engages the pump mechanism gear trains, when the carriage unit is at the ink system
home position. The figure below shows a block diagram of the pump mechanism. Pump system operation
depends on the rotational direction of the paper feed drive motor, as shown in Table 2-6.
Drive: Pump Mechanism
Carriage
Left Frame
Platen D rive Gear
PF Motor
Figure 2-8. Pump Mechanism Block Diagram
Drive: Switch Lever Set
Hook
Platen
Spring
Sub Frame
Disengage
Lever
Release
Clutch
Pump
Drive Gear
Pump Unit
Right Frame
2-8 Rev.A
Figure 2-9. Switch Lever Set
Page 39

Carriage
Carriage
D/E Reset Lever
D/E Lever
Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
Drive: Pump Mechanism
Figure 2-10. Paper Feed Mechanism
Drive: Switch Lever Set
Figure2-11. Switch Lever Reset
Rev.A 2-9
Page 40

Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
Table 2-6. Pump Mechanism Operation
PF Motor Rotational Direction Operation
Clockwise (CW)
forward rotation
Counterclockwise (CCW)
backward rotation
r Color absorption
r Wiper reset
r Carriage lock reset
r Monochrome absorption
r Wiper set
r Carriage lock set
The pump draws ink from the printhead nozzles and drains it into the waste ink drain tank. The printer
performs this operation to eliminate dust or bubbles within the nozzles. The figure below illustrates pump
operation. When the paper feed drive motor rotates CW (forward), the color pulley pumps in the wheel pump
unit rotate in the direction of the arrow while squeezing the ink tube to push the ink inside the tube out to the
waste ink drain tank. When the motor rotates CCW (backward), the black pulley pumps in the wheel pump
unit rotate in the direction of the arrow while squeezing the ink tube to push the ink inside the tube out to the
waste ink drain tank. There are 2 pump rollers in the pump unit, and the drive power is supplied from the
paper feed motor via the pump drive gear (D/E gear), which is moved by carriage operation. In the pump
unit, the transmission gear supplies both the black and color pulley, which are rotated by the rotation of each
other.
Ink Draining
Ink Draining
Vacuuming
Pump Motor (CW) : Color Pumping
No ink draining
No vacuuming
Pump Motor (CW): Black No Pump in g
Figure 2-12. Pump Operation
Vacuuming
Pump Motor (CC W) : Bla ck Pu mpin g
No ink draining
No vacuuming
Pump Motor (CCW): Color No Pumping
2-10 Rev.A
Page 41

1
Color Cartridge Black Cartridge
Carriage
Air Tube
Cap Holder
Cap 1 Cap 2
Air Valve
Valve Spring
1'
Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
2.2.7 Cap Mechanism
The cap mechanism prevents printhead nozzles from drying and keeps bubbles from forming inside the nozzle
while the printer is not in use. The printer performs this operation automatically when print data is not
received, when printer power is turned off, and during printing or ink system operations. (The power switch
uses a secondary circuit that allows this operation to be performed.) Also this printer has 2 caps, 1 for the
black head and 1 for the color head.
2.2.8 Wiping Mechanism
The wiping mechanism cleans the surface of the printhead nose when the printer is in the ink system
sequence. The wiper drive gear transmits power from the paper feed motor via the clutch gear. When the
wiper is raised up against the printhead surface, the hook for securing the carriage to the home position is
raised, too. When the wiper goes down toward the bottom frame, the hook goes down, too. Both the black
head and the color head are cleaned by this wiper.
Platen
Figure 2-13. Cap Mechanism
Hook
Hook Lever
Wiper (Cleaning Blade)
Wiper Drive Gear
Clutch
Rev.A 2-11
Wipe r Drive Ge ar Frame
Figure 2-14. Wiping Mechanism
Page 42

Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.3 OPERATING PRINCIPLES OF THE ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
The Stylus Color Pro contains the following circuit board units:
r C164 MAIN Board (main control circuit board).
r C137 PSB/PSE Board (power supply circuit board). This board is the same as Stylus Color’s
r C137 PNL (control panel board). This board is the same as Stylus Color’s.
In addition to the circuit boards above, part of the printhead drive circuit is built on a separate circuit board
installed in the carriage unit; the printhead is attached directly to this board. The figure below shows a block
diagram of the electrical circuits.
C137 PNL
C137 PSB/PSE
+5 VDC
+35 VDC
C164 MAIN
M-4A11 PRINTER MECHANISM
CR/PF Motor
Carriage Unit
YMC Head
Driver
R-T02 Head R-T01 Head
Black Head
Driver
Figure 2-15. Block Diagram of the Electrical Circuits
2.3.1 Operating Principles of the Power Supply Circuit
The power supply circuitry for this printer is provided either by the C137 PSB board (120 VAC) or the C137
PSE board (220-240 VAC). Both boards are identical in design and functionality, except for the components
in the primary circuit that accommodate the specified input voltage. The input voltage and the application of
output voltages are summarized in the table below.
Table 2-7. DC Voltage Distribution
Voltage Application
+35 VDC
+5 VDC
2-12 Rev.A
Motor drive (carriage and paper feed)
Printhead (through the drive voltage generation circuit)
C164 MAIN Board
Sensors (home position, paper end, no ink cartridge, head thermistor)
Control panel, head nozzle selector
Page 43

Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
The figure below shows a block diagram of the power supply circuit (C137 PSB/PSE). The power switch is
equipped with a secondary circuit that allows the CPU to remain active for a while after the printer is turned
off. This allows the printhead to return to the capping position after power has been turned off. The CPU,
which is mounted on the C164 MAIN Board, always monitors the PSC (Power On/Off) signal. If this signal
goes LOW, the CPU resets each device after performing the head-capping sequence. Also, this board
employs the RCC (Ringing Choke Converter) switching system. The AC voltage is first input to the filter
circuit for higher harmonics absorption, and then input to the rectification and smoothing circuit, converting it
into DC voltage. This DC voltage is then input to the switching circuit for the switching operation. Along
with the switching operation on the primary side, +35 VDC is generated after passing through the +35 V line
voltage detection circuit. This +35 VDC output level is stabilized. This +35 VDC is also input to the +5 VDC
generation circuit to generate a stable +5 VDC.
DB1 C11
Full-wave
Rectifie r Circuit
L1,R1
C1-C4
Filter Circuit
F1
Fuse
Smoothing
Circuit
Q1
Main Switching
Circuit
Feedback
Circuit
C51
T1
Smoothing
Circuit
ZD51, 81-84
Transformer
P-OFF De te ctio n
and Delay Circuit
ZD86,
C82
Drop Protection
Circuit
Over Voltage
Protection Circuit
Photo
Coupler
PC1
TL 494
ZD52
P-OFF Signal
Figure 2-16. Cap Mechanism
+35 VDC
ZD53
Over Voltage
Protection
Circu i t
C164 MAIN
+5 VDC
Power SW
on Panel
1. +5 VDC line over voltage protection circuit
The output voltage level of +5 V line is monitored by Zener diode ZD53. If the voltage level exceeds +7 V,
the status is fed back to the primary switching circuit through a photocoupler (PC1) to stop the +35 V
generation.
2. +5 VDC line over current / over voltage control circuit
The output current is monitored by detection resistor R53 and fed back to +5 VDC generation switching
control IC51, which monitors the output voltage. This information is input to the internal comparator, which
outputs a HIGH signal to turn off transistor Q51 when the voltage or current becomes abnormal.
3. +35 VDC line over voltage protection circuit
The output level is monitored by Zener diode ZD36. If the voltage level exceeds +36 V, photocoupler PC1 is
activated. This stops primary switching circuit operation.
4. +35 VDC line drop protection circuit
The output level of +35 VDC line is monitored by a detection circuit that consists of Zener diodes ZD51 and
ZD81 to 84. This circuit feeds back the output voltage level status through a photo- coupler to the primary
switching circuit to control the ON/OFF time of the switching transistor for constant output voltage.
Rev.A 2-13
Page 44

Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.3.2 Operating Principles of the Main Control Circuit
The main control circuit for this printer is the C164 MAIN Board. This circuit is controlled by a 16-bit
H8/3003 CPU (IC1), running at 14.7456 MHz. The CPU has a unique architecture, capable of handling data
on the data bus at either an 8-bit or 16-bit bus width. Because of this, a 16-bit or 8-bit data bus width-type
ROM is used on this board, increasing the internal processing speed. Also, the CPU’s unique architecture is
capable of the refresh control function. A 4M DRAM (2 CAS method) on the main board is controlled by the
CPU itself. In addition, the CPU controls the serial interface control (RS-422 for Mac).
®
Gate array E05B06 (IC2) manages printhead drive control, the external Centronics
CG board and the control panel, and the controls that create the 4-bit signal for the carriage or the paper feed
motor. (The carriage and paper feed motor are controlled by the current duty data.)
This board also is equipped with EEPROM 93C46 (IC12) to store certain parameters, such as the printer
mechanism control parameter, default setting parameters, as well as a special counter value used for printhead
(ink management) protection.
The timer IC NJU6355E (IC7) counts each time the printer is cleaned and keeps track of how long the printer
is not used, thereby allowing the printer to be cleared only when necessary.
parallel I/F, extension
Type B I/F
EEPROM
Reset
(Power)
RS-422 Serial I/F
(IC12)
93C46
(IC8)
M51955B
C164 MAIN Board
PROM (4M)
(IC3)
Note:1
Refresh
CPU
H8/3003
(IC1)
SD I/O
(IC7)
NJU6355E
(Timer
Counter)
CG-ROM
(IC4)
CLK
Carriage
DRAM
(IC5 )
DMAREQ
Vx
Battery
Note:2
CG-ROM (IC1 6)
(8M or16M)
Address Bus
E05B09
(IC2)
To B
Pa ralle l I/F
(Centronics)
Drive S ignal
Carriage/Paper Feed
CG-ROM (IC 17)
Data Bus
(IC13)
PST592D
Panel
To A
Black/Color H ead
Com mon and Nozz le
Selector D rive Signal
(8M )
Reset
(Logic)
From A
From B
Notes 1: 32-pin IC socket only
2: IC 17 is socket only.
16M (IC16), IC1 7 are only in stalled in JAPAN version .
Black/Color Head
Common Driver Circuit
SLA7041MS (IC14,15)
Carriage/Paper Feed
Motor Driver
SED5620
(U1,U2)
Black 64 Nozzles
Color 48 Nozzles
Figure 2-17. Main Control Circuit Block Diagram
2-14 Rev.A
Page 45

+35 V
+5 V
NMI
P62
CPU (IC1)
+5 V
PST592D
(IC13)
E05B09 (IC2)
RES
RES ET
135
71
1
6
72
68
RST
Type B
55
PA8
M51955B
(IC8)
1
2
1
2
3
TH
10
9
+5 V
AN3
89
86
(CN12)
CCO
7
AN5
91
CPU (IC1)
AN1
AN0
HP
PE
+5 V
(CN8)
(CN9)
AN4
8
90
BCO
(CN11)
87
Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
2.3.2.1 Reset Circuits
The C164 MAIN Board contains 2 reset circuits: the +5 V monitor reset circuit and the +35 V monitor reset
circuit. The +5 V monitor reset circuit monitors the voltage level of the +5 V line (logic line), using reset IC
PST592D (IC13), and outputs a reset signal to the CPU (IC1) and the E05E09 gate array (IC2) when the
voltage level drops below +4.2 V. The +35 V monitor reset circuit monitors the voltage level of the +35 V
line, using reset IC M51955B (IC8), and outputs a reset signal to the CPU. The reset signal is generated when
the voltage level drops below +28 V, and this causes a non-maskable interrupt (NMI).
Figure 2-18. Reset Circuit Block Diagram
2.3.2.2 Sensor Circuits
The following sensor circuits enable the C164 MAIN Board to monitor printer mechanism status:
HP sensor A photocoupler-type HP (home position) sensor is attached to the surface of the printer
mechanism to detect the carriage home position. A HIGH level from the signal indicates
that the carriage is in home position.
PE sensor A mechanical switch PE (paper end) sensor is built into the printer mechanism to determine
whether there is paper in the printer or not. A LOW level from the signal indicates that no
paper is loaded.
BCO sensor,
CCO sensor
Thermistor A thermistor is attached to the color printhead driver board to monitor its temperature by
Micro switches (BCO sensor for the monochrome ink cartridge, CCO sensor for the color
ink cartridge) are attached to the bottom of monochrome ink cartridge holder in the carriage
unit. When the ink cartridge is installed, these switches are pressed and a LOW level from
the signal indicates that the ink cartridge is installed into the ink cartridge holder.
thermistor’s resistance value (at 25° C (77° F) , approximately 10 KΩ ). The CPU changes
the printhead drive signal’s pulse width (charge pulse width) based on the temperature level.
Rev.A 2-15
Figure 2-19. Sensor Circuit Block Diagram
Page 46

NPN Tr
(Q27, 28)
E05B09
(IC2)
25
29
28
CRB
CRSTB
CLKA
5
16
2
13
CRA
SLA7041MS
(IC15)
CLKB
STBA
STBB
DATA A
DATA B
6
17
CRVRF
REF A
REF B
CRHLD
(PA6)
RSA
RSB
3
14
9
10
CRCLK
(PB0-PB7)
BE
CC
A
A
B
B
1
8
11
18
1
2
3
4
+35V
5
(CN6)
30
31-38
56
Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.3.2.3 Carriage Motor Drive Circuit
The carriage motor drive IC SLA7041MS (IC15) outputs a constant current to drive the carriage motor for the
printer mechanism. Gate array E05B09 (IC2) decides the motor phase and speed and then sends a signal to the
carriage motor driver IC (SLA7041MS) using the 4-bit serial transmission line.
The first bit indicates the direction of motor rotation. The other three bits are current duty data for the motor
speed of each printing sequence. SLA7041MS can select the reference voltage itself based on these three
current duty data bits. Also, it receives these signals by two serial transmission lines for the two motor phases
(phase A and phase B). Due to this, the carriage motor can drive micro step sequence (
1
⁄
inches, minimum).
720
Figure 2-20. Carriage Motor Circuit Block Diagram
The SLA7041MS motor driver reads four-bit serial data using four clock counts from the E05B06 (IC2)
clock. Each bit is read at the falling edges of these clock pulses. As a result of this, received serial data is set
into the shift register and then shifts the latch register. When the strobe pulse becomes active from the E05B06
(IC2), serial data is moved into the reference voltage selection circuit and the voltage is changed. Therefore,
when the printer is in the constant speed mode, this strobe pulse becomes inactive. The following table
indicates the current duty of each carriage motor speed mode.
Table 2-8. Serial Data Contents
Mode c b a Vref (typical)
0 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 × 20%
2 0 1 0 × 40 %
3 0 1 1 × 55.5%
4 1 0 0 × 71.4%
5 1 0 1 × 83%
6 1 1 0 × 91%
2-16 Rev.A
7 1 1 1 × 100%
Vref × 1/3
(Vref = +5V)
× 0%
Page 47

Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
The following figure shows 4-bit serial data and how this data is transferred by the SLA7041MS driver. The
step time of the reference voltage is determined by the interval time of the strobe pulse.
Vref
+5 V
SLA7041
Vref
To Motor
(Phase Signal)
STRB
4-bit Serial Data
CLK
CLK
STRB
At this time, the reference voltage selection
circuit checks phase signal outputs
Vref Voltage Selection
Circuit
1-bit 2-bit 3-bit 4-bit
Phase a b c
1-bit 2-bit 3-bit 4-bit
Phase a b c
Reading of serial data from the
phase signal in order
Latch
4-bit Shift Register
Figure 2-21. Serial Data Transfer Procedure
Rev.A 2-17
Page 48

E05A96
(IC2)
41
40
43
42
PFB
PFSTB
CLKA
5
16
2
13
PFA
SLA7041MS
(IC14)
CLKB
STBA
STBB
DATA A
DATA B
6
17
PFVRF
REF A
REF B
PFHLD
RSA
RSB
3
14
9
10
PFCLK
(PB8-PB13)
BE
C
A
A
B
B
1
8
11
18
1
2
3
4
+35V
5
(CN7)
57
NPN Tr
(Q25, 26)
Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.3.2.4 Paper Feed Motor Drive Circuit
The paper feed motor for this printer drives the following mechanisms:
r Paper feed mechanism
r Paper pickup mechanism
r Pump mechanism
Driver IC SLA7041MS (IC14) drives the paper feed motor by a constant current. The operation principle is
same as for the carriage motor drive circuit. But the paper feed motor drives not only the paper feed
mechanism but also the pump unit. (Refer to Section 2.2.4.)
Table 2-9. Paper Feed Motor Drive Modes
Mode Phase Excitation Drive Frequency
Paper feed 2-2 phase or 2W1-2 phase 391 or 1600 pps
Pump drive 2-2 phase 300 or 1800 pps
Figure 2-22. Paper Feed Motor Drive Circuit Diagram
2-18 Rev.A
Page 49

Micro Dot
Charge/Discharge
Circuit
SELM
SELN
Normal Dot
Micro Do t
Resistor A rra y
Common Drive
Signal
Printhead
Normal Dot
Charge/Discharge
Circuit
RM12, RM5
RM11, RM4
COM
GND
BPWC
CPEC
Pc
Tc
Th
Td
VH
Ph
Pd
BPWD
CPED
Tc: Charge time
Th: Idle time
Td: Discharge time
Pc: Charge pulse
Ph: Idle pulse
Pd: Discharge pu lse
Head drive volt age (VH)
Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
2.3.2.5 Printhead Drive Circuit
The printhead drive circuit for this printer is composed of the following two parts:
r Common drive circuit (trapezoidal drive pulse generation)
r Head drive circuit (nozzle control built on the printhead)
The 64-bit thermal head driver SED5620D in the head drive circuit on the carriage is used as a nozzle selector
to selectively drive the printhead nozzles. Print data is converted into serial data by gate array E05B09 (IC2)
and is output from port BSO (pin 20) to the black head drive circuit or output from port CSO (pin 24) to the
color head drive circuit. Then, head driver SED5620D latches the head data when gate array E05B09 outputs
the BLAT or CLAT signal, and the latched data becomes 64-bit parallel data for the black head, or 48-bit
parallel data for the color head. One bit corresponds to each nozzle.
When data transfer and nozzle selection are complete, gate array E05B09 outputs the common drive pulse
BPWC or CPWC (charge pulse) and BPWD or CPWD (discharge pulse) to the common drive circuit. The
common drive circuit then generates the trapezoidal pulse and applies it to the printhead as a common drive
pulse. After this, the nozzle selected by the head data is activated to eject ink.
Normal Dot / EPSON Micro Dot Printing Mode
The Stylus Color Pro produces two types of ink ejection (normal print mode and EPSON Micro Dot Mode).
The signals for switching ink ejection modes are “SELM” (for normal dot printing) and “SELN” (for EPSON
Micro Dot printing). These signals are output from pin 49 and pin 50 of gate array E05B09 to IC11 and IC18.
In normal dot print mode, the common drive signals (BPWC, CPWC and BPWD, CPWD) are output to the
register arrays (RM12 for black, RM5 for color). In the Micro Dot Mode, the signals (BPWC, CPWC and
BPWD, CPWD) are output to the register arrays (RM11 for black, RM4 for color). The signals through the
resistor array are output to the charge / discharge circuit that consists of Darlington connected transistors.
Then the circuit generates printhead drive pulses.
Figure 2-23. Normal / EPSON Micro Dot Switching
Figure 2-24. Trapezoidal Drive Waveform
Rev.A 2-19
Page 50

Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
E05B09 (IC2)
BPWC
BPWD
BLAT
BCLK
BCLKIN
BSO
CPWC
CPWD
CLAT
CCLK
CCLKIN
CSO
13
14
19
18
17
20
15
16
23
22
21
24
Common Driver
CN11
Common Driver
CN11
C164 MAIN
COM1-8
SED5620D (U1)
68
LAT
DO64-49
69
CN1
67
CLK
SI
COM1-6
DO48-33
DO32-1 7
DO16-1
SED56 20D (U2)
68
69
CN1
67
On Carriag e (Head Driver B oard)
LAT
CLK
SI
DO64-49
DO48-3 3
DO32-1 7
DO16-1
Row A
Row B
Row C
Row D
Not Connected
Row R (Magenta)
Row S (Cyan)
Row T (Yellow)
Figure 2-25. Printhead Drive Circuit Block Diagram
2.3.2.6 DMA Controller
Data from the host computer is received automatically by the STB signal via the external Centronics interface.
The data is input to the input buffer on the DRAM (IC5). At this time, E05B09 detects the rising edge of the
external
detects this signal, the DMA controller in the CPU sends a bus request to the bus controller in the CPU, and
then the CPU releases the bus line. Because of this, the external data is transported into the memory,
bypassing the CPU.
STB signal and outputs the STBDMA (strobe DMA request) signal to the CPU. When the CPU
STB
ACK
BUSY
E05B09 (IC2)
STBDMA
DMARQ
Figure 2-26. DMA Controller Operation
128 14
CPU H8 (IC1)
9129
DREQ1
DREQ2
BAREQ
BACDMAC
Memory
2-20 Rev.A
Page 51

Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
2.3.2.7 DRAM Refresh Controller
The CPU is equipped with a refresh controller in its internal controller. This CPU controller can contact the
16-bit length IC5 DRAM, which is a 2 CAS type. The following table lists the junction method between the
H8 CPU and the 2 CAS DRAM.
Table 2-10. Junction Method (CPU - 2 CAS DRAM)
CPU 2 CAS DRAM
HWR
LWR
CS3
RD
UCAS
LCAS
RAS
WR
This method of the DRAM refresh is only used for the CAS-before-RAS cycle method. The following figure
shows the timing of each cycle.
UCAS
LCAS
RAS
Read Cycle
WR
Writ e Cycle
AS
(Read / Write Cycle)
UCAS
LCAS
RAS
WR
AS
(Refresh Cycle)
Figure 2-27. Junction Method (CPU - DRAM)
Rev.A 2-21
Page 52

Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.4 INK SYSTEM MANAGEMENT
This section explains how the ink system is controlled to protect the printhead and the ink supply system and
to ensure high-quality output. Ink system control is composed of the following operations:
r Power On r Wiping Operation 1
r Cleaning Selection r Wiping Operation 2
r Micro Absorbing Cleaning r Rubbing Operation
r Power Off r Disengage On
r Print Start r Disengage Off
r Refresh r Micro Absorbing
r Standby r Carriage Lock Set
r False Absorbing r Carriage Lock Reset
r Ink Cartridge Replacement r Refresh (When loading or ejecting paper)
r Adjust Lever Operation Position Moving Sequence
r Transportation Sequence
These ink system operations are controlled by the following counter:
r Protect counter
2.4.1 Ink Operations
The various ink operations that can be performed selectively by the printer are described below:
1. Power On Operation
This operation is performed when power is turned on.
2. Cleaning Selection Mode
This operation cleans each nozzle to ensure that the nozzle fires and that no dots are skipped during printing.
This operation is performed by pressing the cleaning switch (Alt + Load/Eject or Economy/Condensed) while
the printer is in PAUSE status.
3. Micro Absorbing Cleaning Operation
This operation prevents an increase in the viscosity of ink in the printhead using ink absorbing discharge.
4. Power Off Operation
This operation ensures that the carriage is in the home position when the printer turns off, and prevents the
disengage gear from turning continuously when the printer turns off. This operation is performed when the
switch on the secondary side is turned off.
5. Print Start Operation
This operation eliminates ink from the nozzle surface, and is performed when the printer receives print data
while in the standby state.
6. Refresh Operation
This operation prevents an increase in the viscosity of the head ink.
7. Standby Operation
This operation also prevents an increase in the viscosity of the head ink.
8. False Absorbing Operation
This operation absorbs ink inside the cap, and eliminates ink from the nozzle plate.
9. Ink Cartridge Replacement Operation
2-22 Rev.A
Page 53

Stylus Pro Service Manual Operating Principles
This operation is performed when the Alt button is held down for more than 3 seconds (the Pause LED lights);
the carriage then moves to the ink cartridge replacement position.
10. Wiping Operation 1
This operation eliminates dust from the nozzle plate before performing ink absorption.
11. Wiping Operation 2
This operation eliminates dust or ink from the nozzle plate after performing ink absorption.
12. Rubbing Operation
This operation removes dust or ink that adheres to the head surface.
13. Disengage ON Operation
This operation sets the switch lever to the position where it transmits the PF motor drive to the pump
mechanism. It also moves the carriage to the home position, where the lever is set to the specified position.
14. Disengage OFF Operation
This operation resets the switch lever to the position where it transmits the PF motor drive to the pump
mechanism. It also moves the carriage to the flushing position, where the lever is reset to the specified
position.
15. Micro Absorbing Operation
When the cartridge is removed, it is possible for a small amount of air to form small air bubbles that can block
the ink from the nozzle. This operation eliminates small air bubbles from the cavity of the printhead.
16. Carriage Lock Set
This operation prevents the carriage from moving out of the home position if the printer is turned off or is
paused. This operation is performed when the carriage is in the ink system home position and no paper is
loaded.
17. Carriage Lock Reset
This operation resets the carriage lock lever.
18. Refresh Operation (Performed when Loading or Ejecting Paper)
This operation prevents an increase in the viscosity of ink inside the black head surface when paper is being
loaded or ejected. When just the black head is on, the color head is capped as paper is loaded or ejected. The
printer performs the flushing operation for the black head only.
19. Adjust Lever Operate Position Moving Sequence
This operation is performed when the Alt and Font buttons are pressed simultaneously while the printer is
paused.
20. Transportation Sequence
This sequence is performed to clean the printhead when the printer is transported to the market.
Rev.A 2-23
Page 54

Operating Principles Stylus Pro Service Manual
2.4.2 Counter
EEPROM LE93C46 (IC12) on the main board stores certain counter and timer values that are used for
controlling the ink system operation.
2.4.2.1 Protect Counter
The value of protect counter A is stored into the EEPROM on the main board, and while the printer is on, this
data is stored in the RAM on the main board.
n Protect counter A This counter is used to manage the total amount of drained ink. If the
counter value is equal to or exceeds 40000, the printer indicates an error on
the control panel that maintenance is required.
Notes for Service
Protect counter A is reset:
1. Upon shipment from the factory.
2. After maintenance is performed (when the ink drain tank is replaced).
2-24 Rev.A
Page 55

Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
Table of Contents
3.1 OVERVIEW 3-1
3.1.1 Precautions for Disassembling the Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY 3-2
3.2.1 Upper Case Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.2.2 Power Supply Unit (C137 PSB/PSE Board) Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3.2.3 Main Controller (C164 MAIN Board) Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.2.4 Printer Mechanism (M-4A11) Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
3.2.5 Printer Mechanism Disassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.2.5.1 Printhead Unit Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.2.5.2 Carriage Unit Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
3.2.5.3 Pump Unit Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
3.2.5.4 Cleaner Head Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
3.2.5.5 CR Motor Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
3.2.5.6 PF Motor Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
3.2.5.7 Carriage Home Position Sensor Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
3.2.5.8 PE Sensor Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
3.2.5.9 Paper Feed Roller Assembly Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
3.2.5.10 Upper Frame Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
3.2.6 Drain Ink Pad Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 3-1. Disassembly Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Figure 3-2. C137 Control Panel Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Figure 3-3. Upper Case Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Figure 3-4. Power Supply Unit Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Figure 3-5. Main Controller Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Figure 3-6. Printer Mechanism (M-4A11) Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Figure 3-7. Ink Cartridge Clamp Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Figure 3-8. Ink Carriage Holder Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Figure 3-10. Printhead Resistance Value. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Figure 3-11. Head Spacer Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Figure 3-12. Front Frame Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Figure 3-13. Carriage Unit Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Figure 3-14. Pump Unit Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Figure 3-15. Cleaner Head Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Figure 3-16. CR Motor Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
Figure 3-17. PF Motor Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
Figure 3-18. Carriage Home Position Sensor removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Figure 3-19. PE Sensor Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Figure 3-20. Tension Roller Assembly Removal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Figure 3-21. Paper Feed Roller Assembly Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Figure 3-22. Upper Frame Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Figure 3-23. Attaching the Torsion Spring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Page 56

Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.1 OVERVIEW
This section describes procedures for disassembling the main components of this printer. Unless otherwise
specified, the disassembled unit or components can be reassembled by reversing the disassembly procedure.
Therefore no assembly procedures are included. Precautions for any disassembly or assembly procedure are
described under the heading “Disassembly/Assembly Points.” Adjustments required after assembling the unit
are described under the heading “Required Adjustments.”
3.1.1 Precautions for Disassembling the Printer
See the precautions below when disassembling the printer.
WARNING
r Disconnect the power cable before disassembling or assembling the printer.
r Wear protective goggles to protect your eyes from ink. If ink gets in your eye, flush it with fresh
water and see a doctor immediately. If ink comes into contact with your skin, wash it off with
soap and water. If irritation occurs, contact a physician.
r A lithium battery is installed on the C164 MAIN Board of this printer. Be sure to observe
the following instructions when servicing the battery:
1. Keep the battery away from any metal or other batteries so that electrodes of opposite polarity
do not come in contact with each other.
2. Do not heat the battery or put it near fire.
3. Do not solder on any part of the battery. (Doing so may result in leakage of electrolyte
from the battery, burning, or explosion. The leakage may affect other devices close to the battery.)
4. Do not charge the battery. (An explosive gas may be generated inside the battery, and
cause burning or explosion.)
5. Do not dismantle the battery. (The gas inside the battery may hurt your throat. Leakage,
burning, or explosion may also result.)
6. Do not install the battery in the wrong direction. (This may cause burning or explosion.)
CAUTION
There is danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or
equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to
government’s laws and regulations.
ATTENTION
Risque d’explosion si la pile est remplacée incorrectement. Ne remplacer que par une pile du
même type ou d’un type équivalent recommandé par le fabricant. Elminer les piles déchargées
selon les lois et les règles de sécurité en vigueur.
CAUTION
r Never remove the ink cartridge from the carriage unless specified to do so.
r When transporting the printer after installing the ink cartridge, be sure to pack the printer for
transportation without removing the ink cartridge.
r Use only recommended tools for disassembling, assembling, or adjusting the printer.
r Apply lubricants and adhesives as specified. (See Chapter 6.)
r Make specified adjustments when you disassemble the printer. (See Chapter 4.)
Rev.A 3-1
Page 57

Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
3.2 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
WARNING
Follow the precautions in Section 3.1.1 when disassembling the printer.
This section consists of the subheads shown in the diagram below. See the exploded view of the printer in the
Appendix, if necessary.
START
Upper Case Removal
3.2.1
Power Supply Unit
(C137 PSB/PSE) Removal
3.2.2
Main Controller
(C137 MAI N) Remo val
3.2.3
Printer Mechanism
(M-4A10) Remo val
3.2.4
Page 3-3
Page 3-4
Page 3-5
Page 3-7
A
Pump Unit Removal
3.2.5. 3
PF Roller Assembly
Removal
3.2.5. 9
Page 3-11
Page 3-15
Drain Ink Pad Rem oval
3.2.6
Printhead Unit Removal
3.2.5.1
Carriage Unit Removal
3.2.5.2
Page 3-18
Page 3-8
Page 3-10
A
A
Cleaner Head
Removal
3.2.5.4
CR Motor Remova l
3.2.5. 5
Page 3-12
A
Page 3-13
B
B
Carriage Home Position
Sensor Removal
3.2.5.7
PE Sensor Removal
3.2.5. 8
Page 3-14
B
Page 3-14
A
Upp er Fra me
Removal
3.2.5.10
Page 3-16
A
PF Motor Removal
3.2.5.6
Page 3-
Figure 3-1. Disassembly Flowchart
3-2 Rev.A
Page 58

CBB(M3x11)
Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.1 Upper Case Removal
1.1. Remove the printer cover by releasing the 2 tabs holding it to the upper case.
2. Remove the paper support by releasing the 2 tabs holding it to the lower case.
3. Move the carriage to the center while pressing the carriage lock lever.
4. Remove the control panel. (Release the tab by inserting a screwdriver into the hole in the upper case, as
shown in the figure below.) At this time, disconnect the connector on the C137 PNL Board.
Carriage Lock Lever
1. Press
2. Move
Prin te r Co ver
Control Pa nel
Figure 3-2. C137 Control Panel Removal
5.
Remove 2 CBB (M3×11) screws securing the upper case to the lower case.
6. Release 2 tabs by inserting a flathead screwdriver into the holes at the bottom of the lower case, as
shown in the figure below.
7. Remove the upper case by lifting the front side.
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY POINT
Hold the upper case firmly and pull it to remove it, while you release the tabs.
Figure 3-3. Upper Case Removal
Rev.A 3-3
Page 59

Locking Tab
CBS (M3x8)
C164 MAIN Board
C137 PSB/PSE Board
CN5
Shield Plate for
C137 PSB/PSE
Board
CBS(O) (M4x8)
CBB (M3x12)
CN1
Harnesses for Motors
Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
3.2.2 Power Supply Unit (C137 PSB/PSE Board) Removal
1. Remove the upper case. (See Section 3.2.1.)
2. Disconnect the cables from connector CN1 on the C137 PSB/PSE Board and from CN5 on the C164
MAIN Board.
3.
Remove 1 CBS (M3×8) screw and remove 4 CBB (M3×12) screws securing the shield plate to the lower
case via the C137 PSB/PSE Board.
4.
Remove 2 CBB (M3×12) screws and 1 CBS (M3×8) screw securing the C137 PSB/PSE Board to the
lower case. Then remove 1 CBS (O) (M4×8) screw fixing the earth line from the AC cable to the earth
plate.
5. Remove the wire harness for the motors in the locking tab on the shield plate and take the shield plate out
by pulling upward toward the back of the printer.
6. Remove the power supply unit by pulling it upward toward the back of the printer.
CAUTION
As the shield plates of C164 MAIN and C137 PSB/PSE have sharp edges, so take care in
handling them.
3-4 Rev.A
Figure 3-4. Power Supply Unit Removal
Page 60

Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.3 Main Controller (C164 MAIN Board) Removal
1. Remove the upper case. (See Section 3.2.1.)
2. Remove the P/S shield plate from the upper shield plate.
3.
Remove 2 CBS (M3×8) screws securing the upper cover connector to the I/F grounding plate and remove
the upper cover connector (Type-B interface cover).
4.
Insert a screwdriver into the printer mechanism to remove the CBS (M3×8) screw securing the C164
MAIN Board and the printer mechanism to the lower shield plate.
5.
Remove 4 CBB (M3×12) screws securing the upper shield plate to the lower case.
6.
Remove 2 CBB (M3×12) screws securing the main controller (C164 MAIN Board) to the lower case and
remove it by pulling it upward, toward the back of the printer.
7. Disconnect the cables from the connectors CN5, CN6, CN7, CN8, CN9, CN10, CN11, and CN12 of the
C164 MAIN board.
Lower G rounding Pl ate
CBB (M3x12)
CBB (M3x12)
CBS (M3x8)
Black Head
Color He ad
P/S Shield Plate
CBB ( M3x12)
FFC Form Black Head
Upper Shield Plate
Upper Connector Cover
CBS ( M3x12)
Figure 3-5. Main Controller Removal
Rev.A 3-5
Page 61

Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
ASSEMBLY POINT
r When you replace the main board, initialize the EEPROM contents as follows;
1) Reassemble the printer.
2) Turn the printer ON while hold down [Alt], [Font], [Load/Eject] and [Pause] buttons on the
control panel.
r It is possible to misconnect the cables. When reconnecting the cables from the connectors CN6,
CN7 and connectors CN11, CN12 of the C164 MAIN board, see the following instructions.
1. CN11 : Printhead FFC cable (white color mark)
CN12 : Printhead FFC cable (blue color mark)
2. CN6 : Carriage motor cable (red color mark : Also the red color indicates the 1-pin of the
CN6.)
CN7 : Paper feed motor cable (black color mark : Also the black color indicates the
1-pin of the CN7.)
r When you replace the main board, block resistances RM4, RM5, RM11 and RM12 must be
re-installed at same position on new board.
REQUIRED ADJUSTMENT
r When replacing the main controller board, adjust both the head gap and the Bi-D adjustment
alignment, and input the destination parameter into the EEPROM on the C164 MAIN Board.
(See Chapter 4.)
r When you replace the main board, the parameters in the internal timer are all reset. Therefore,
it is possible that printing becomes abnormally. At this time, perform the cleaning operation by
the control panel on command (Refer to Chapter 4) until the printing becomes normally.
CAUTION
As the shield plates of C164 MAIN and C137 PSB/PSE have sharp edge, take care of handling
them.
3-6 Rev.A
Page 62

CBS (M4x14)
Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.4 Printer Mechanism (M-4A11) Removal
1. Remove the upper case. (See Section 3.2.1.)
2. Remove the power supply unit. (See Section 3.2.2.)
3. Remove the main controller. (See Section 3.2.3.)
4.
Remove the 4 CBS (M4×14) screws and take out the printer mechanism.
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY POINT
r Wipe off any ink around the end of the ink drain tube when you remove the printer
mechanism.
r When reinstalling the printer mechanism, check that the waste ink drain tube is properly
inserted between the lower case and the waste ink absorbing material.
Figure 3-6. Printer Mechanism (M-4A11) Removal
r When the printhead or the printer mechanism is replaced, the block resistor must be replaced at
locations RM4, RM5, RM11 and RM12 on the C164 MAIN Board. (Every spare printhead or spare
printer mechanism comes with a block resistor that is specifically selected for each printhead.)
r Adjust both the head gap and the Bi-D alignment when replacing the printer mechanism.
CAUTION
Rev.A 3-7
Page 63

Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
3.2.5 Printer Mechanism Disassembly
The procedures described in this section explain how to remove the components within the printer
mechanism.
3.2.5.1 Printhead Unit Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Move the carriage to the middle of the printer while pressing the hook that fixes the carriage unit to the
home position.
3. Pull the ink cartridge clamp toward you and remove the ink cartridge.
CAUTION
r When removing the ink cartridge, always install a new cartridge immediately after removing the
old one.
r When the ink cartridge is replaced, the printer performs the ink cartridge replacement
operation automatically.
Exclusive cartridge is as follows; Monochrome : 1020626
YMC: 1020627
r Ink cartridges should never be kept longer than 6 months.
4.
Ink Cartridge Clamp (Monochrome)
Tweezers
Ink Cartridge Clamp (Color)
Ink Cartridge Holder
Carriage Base
Figure 3-7. Ink Cartridge Clamp Removal
Push the 2 hooks from the inside of ink carriage holder with tweezers, push the ink cartridge clamp
(monochrome/color) to remove the clamps from ink carriage holder.
5.
Remove the 3 CBB (M3×11) screws and 3 plain washers securing the ink cartridge holder to the carriage
base, and then lift the ink cartridge holder out of the carriage base sliding a little toward left.
Note : As the head FFC cables are secured to the ink cartridge holder with the adhesive tape,
tear off the cables from the ink cartridge holder before removing the ink cartridge holder
from the carriage base.
3-8 Rev.A
Page 64

Ink Cart ridge Holder
CR Cap Cover
CBB (M3x11)
CBB (M3x11)
Carriage Base
CBB (M3x11)
PRINTH EAD I J48- 0C 0
(COLOR)
PRINTH EAD I J48- 0A 0
(MONOCHROME)
Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
6.
Remove the CBB (M3×11) screw (under CR cap cover) and a plain washer securing the monochrome
and color printheads to the carriage base.
Figure 3-8. Ink Carriage Holder Removal
7. Pull the black or color head toward you and disconnect the head flexible flat cable (FFC) on the head
driver board (nozzle selector). Then remove the black or color head.
Figure 3-9. Printhead Removal
CAUTION
r Take proper measures to protect the printhead unit from static electricity, because the driver IC
is directly attached to the printhead unit.
r Never touch the metallic nozzle surface cover of the printhead. Handle it only by holding the
edges of the printhead.
r When the printhead or the printer mechanism is replaced, the block resistor must be replaced at
location RM4 (for Normal Dot R), RM5(for Micro Dot M), RM11 (for Normal Dot R), and RM12
(for Micro Dot M) on the C164 MAIN Board. (Every spare printhead or spare printer mechanism
comes with a block resistor that is specifically selected for each printhead. And the resistance
value of block resistor are written on the nozzle face of printhead. (Refer to Figure 3-10.)
Rev.A 3-9
Page 65

Black Head
Head Nose
Spacer
Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
Printhead Nozzles
R, M
Color Printhead
R: Normal Dot Res istance Val ue
M: Micro Dot Resistance Value
R, M
Monochrome Printhead
Figure 3-10. Printhead Resistance Value
REQUIRED ADJUSTMENT
r When removing or changing the black head, you need to make the following adjustments:
1. Black head angle adjustment (See Section 4.1.4)
2. Black - Color head vertical adjustment (See Section 4.1.5)
3. Head gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.3)
4. Bi-D alignment adjustment (See Section 4.1.2)
r When removing or changing the color head, you need to make the following adjustments:
1. Color head angle adjustment (See Section 4.1.6)
2. Black - Color head vertical adjustment (See Section 4.1.5)
3. Head gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.3)
4. Bi-D alignment adjustment (See Section 4.1.2)
r When removing or changing both heads, the following adjustments are needed.
1. Color head angle adjustment (See Section 4.1.6)
2. Black head angle adjustment (See Section 4.1.4)
3. Black - Color head vertical adjustment (See Section 4.1.5)
4. Head gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.3)
5. Bi-D alignment adjustment (See Section 4.1.2)
WARNING
r When removing the color or black head, do not lose the spacer that is fixed to each head. This
spacer modifies the angle error that occurs during manufacturing. Also, this spacer is different
from the linear spacer or angular spacer. (See Chapter 4.)
Figure 3-11. Head Spacer Position
3-10 Rev.A
Page 66

Grounding Wire
Parallelis m
Adjustment Bushing
Parallelis m
Adjustment Bushing
Pulley Lever
Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.5.2 Carriage Unit Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Move the carriage to the left side of the printer while pressing the hook that fixes the carriage to the
home position.
3.
Remove the 2 CBS (O) (M3× 6) screws securing the front frame to both side frames.
CBS(O) (M3x6)
Front Fra me
Hook
CBS(O) (M3x6)
Figure 3-12. Front Frame Removal
4. Remove the cartridge holder with from the carriage unit. (See Section 3.2.5.1.)
5. Release the carriage timing belt from the belt pulley while pressing the pulley lever.
6. Remove the grounding wire from the left side frame.
7. Remove 2 parallelism adjustment bushings from both side frames.
8. Lift the carriage unit with the carriage guide shaft out of the printer mechanism.
Rev.A 3-11
Figure 3-13. Carriage Unit Removal
CAUTION
r Take proper measures to protect the printhead unit from static electricity, because the driver IC
is directly attached to the printhead unit.
r Never touch the metallic nozzle surface cover of the printhead. Handle it only by holding the
edges of the printhead.
r When the printhead or the printer mechanism is replaced, the block resistor must be replaced at
locations RM4, RM5, RM11 and RM12 on the C164 MAIN Board.
ADJUSTMENT REQUIRED
r Platen gap adjustment (See Chapter 4.)
Page 67

CBS (M3x6)
Bottom F rame
Pump Unit
(1)
(2)
(2)
Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
3.2.5.3 Pump Unit Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Remove the carriage unit. (See Section 3.2.5.2.)
3. Remove the CBS (M3×6) screw securing the pump unit to the bottom frame.
4. Push the pump unit outward while releasing the tab at the bottom side of the pump unit, and then lift
up the pump unit.
Figure 3-14. Pump Unit Removal
3-12 Rev.A
Page 68

Cleaner Head
Hook
Cleaning Lever
Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.5.4 Cleaner Head Replacement
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Use tweezers to unhook the cleaner head from the hook on the cleaning lever.
CAUTION
Keeping the cleaner head clean is extremely important to keep the ink injection system working
properly in the printhead, and it directly affects printing quality.
Therefore, handle the cleaner head very carefully, and observe the following precautions.
r Never touch the cleaner head with your bare hands.
r When attaching the cleaner head to the pump unit, wear gloves and use clean tweezers to
handle it.
Figure 3-15. Cleaner Head Replacement
Rev.A 3-13
Page 69

Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
3.2.5.5 CR Motor Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Release the timing belt. (See Section 3.2.5.2.)
3. Remove the 3 screws securing the CR motor to the upper frame, and then remove the CR motor.
3.2.5.6 PF Motor Removal
Screws
CR Mo tor
Figure 3-16. CR Motor Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2.
Remove the 2 CBS (M3×6) screws and then remove the PF motor.
CBS (M3x6)
PF Mo tor
Figure 3-17. PF Motor Removal
3-14 Rev.A
Page 70

Sensor Cable
Carriage Home
Position Sensor
Sensor Cable
PE Sensor
Botto m Frame
Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.5.7 Carriage Home Position Sensor Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Disconnect the sensor cable from the carriage home position sensor.
3. Unhook the 3 notches securing the carriage home position sensor to the upper frame. Then remove
the carriage home position sensor.
Figure 3-18. Carriage Home Position Sensor Removal
3.2.5.8 PE Sensor Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Disconnect the connector for the PE sensor.
3. Rotate the printer mechanism upside down; use tweezers to release the 2 hooks securing the PE sensor
to the paper feed roller assembly. Then remove the PE sensor.
Figure 3-19. PE Sensor Removal
Rev.A 3-15
Page 71

Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
3.2.5.9 Paper Feed Roller Assembly Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Remove the carriage unit. (See Section 3.2.5.2.)
3. Remove the tension spring holding the tension roller assembly to the sub frame.
4. Remove the torsion spring on the side frame (L) holding the tension roller assembly to the left side
frame.
5.
Remove 1 CBS (M3×6) screw securing the tension roller assembly to the sub frame and remove the
tension roller assembly.
CBS (M3x6)
Tosion Spring
Tension Spring
Tens ion Rolle r Asse mbly
Figure 3-20. Tension Roller Assembly Removal
6. Release the 2 bushings securing the paper feed roller assembly to both the left side frame and the sub
frame. Then remove the paper feed roller assembly.
Paper Feed Roller Assembly
Figure 3-21. Paper Feed Roller Assembly Removal
3-16 Rev.A
Page 72

CBS (M3x6)
E-ring
Tension Spring
Knob
CBS (M3x6)
Upper Frame
Driven Roller Support
Upper Frame
Torsion Spring 6700
Stylus Pro Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.5.10 Upper Frame Removal
1. Remove the printer mechanism. (See Section 3.2.4.)
2. Remove the carriage unit. (See Section 3.2.5.2.)
3. Remove the E-ring securing the knob shaft to the sub frame; then remove the knob with the knob
shaft from the right side frame.
4.
Remove the 5 CBS (M3×6) screws securing the upper frame to both side frames and the sub frame.
5. Remove the upper frame with 4 PF support rollers.
Figure 3-22. Upper Frame Removal
ASSEMBLY POINT
Assemble each straight end of the torsion spring 6700s to attach them to the center of the driven
roller support.
Figure 3-23. Attaching the Torsion Spring
Rev.A 3-17
Page 73

Disassembly and Assembly Stylus Pro Service Manual
3.2.6 Drain Ink Pad Removal
The procedures described in this section explain how to remove the drain ink pad when the protect counter
value reaches its maximum, and the printer displays a maintenance request error. (Refer to Section 2.4.2.)
1. Remove the upper case. (See Section 3.2.1.)
2. Remove the drain ink pad.
ASSEMBLY POINTS
r After reassembling the printer, power it on while holding down the ALT, Font, Load/Eject and
Pause buttons to reset the protect counter.(Refer to Section 2.4.2.)
o The protect counter value is shown in the first line of printing in the default setting mode.
The first line consists of the ROM version number, the protect counter value, and nozzle check
patterns.
o At any time, if the protect counter value is more than 32000, replace the drain ink pad.
CAUTION
After resetting the protect counter, perform the destination data writing operation (Refer to
Section 4.1.1.), the Bi-D alignment adjustment (Refer to Section 4.1.2.) and the Head Gap
Adjustment. (Refer to Section 4.1.3.)
3-18 Rev.A
Page 74

Chapter 4 Adjustment
Table of Contents
4.1 OVERVIEW 4-1
4.1.1 Destination Data Writing Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.1.2 Bi-D (Bidirectional Printing) Alignment Adjustment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.1.3 Head Gap Adjustment (Black and Color Head). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.1.4 Black Head Angle Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4.1.5 Black - Color Head Vertical Adjustment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4.1.6 Color Head Angle Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
4.1.7 Platen Gap Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
4.1.8 Internal Timer Reset Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-16
List of Figures
Figure 4-1. Head Gap Adjustment Sample. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Figure 4-2. B-Head Angle and Linear, Angular Spacer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Figure 4-3. Spacer Kinds and Relationship of the Shape and Thickness . . 4-5
Figure 4-4. Black Head Angle Adjustment Sample . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Figure 4-5. Head Gap Adjustment Sample. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Figure 4-6. Removing the Rubber Cap. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Figure 4-7. Spacer Angular Replacement Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Figure 4-8. Black-Color Head Vertical Adjust Conception. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Figure 4-9. Spacer Linear Selection Sample . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Figure 4-10. Spacer Linear Replacement Method. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
Figure 4-11. C-Head Angle and Spacer Angular Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
Figure 4-12. Color Head Angle Confirmation Sample. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
Figure 4-13. Relationship of the Shape and Thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
Figure 4-14. Spacer Select Judgment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
Figure 4-15. Spacer Angular Replacement Method (YMC). . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
Figure 4-16. Adjusting the Paper Gap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
Figure 4-17. Confirming the Gap. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
List of Tables
Table 4-1. Required Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Table 4-2. Gap and Adjustment Direction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
Page 75

Stylus Pro Service Manual Adjustment
4.1 OVERVIEW
This section describes adjustments required when the printer is disassembled and assembled after repair.
Since this printer has both black and color heads, it needs new adjustments not required for previous printers.
Refer to the following table to perform the appropriate adjustments.
WARNING
r Always perform adjustments in the order indicated.
r After performing destination setting, head angle adjustment, head vertical position adjustment,
head gap adjustment, or bidirectional adjustment, perform the cleaning
operation for the black and color printheads. The cleaning operation is necessary because
printing sample patterns for these adjustments increases the viscosity of the ink and the
printer will not print the correct value. For instance if you replace the black head, you
must perform the following adjustments in the order shown:
(1) black head angle, (2) black-color head vertical, (3) head gap, (4) Bi-D alignment.
r After removing an ink cartridge, always install a new cartridge immediately. During
adjustments and testing, use the cartridges designed exclusively for service:
Monochrome: 1020626, CMY: 1020627.
Table 4-1. Required Adjustments
Work Contents Adjustment Contents
When replacing the M-4A11
printer mechanism
When replacing or
disassembling the
C164 MAIN board or
printer mechanism
When replacing or
disassembling the
black head (board)
When replacing or
disassembling
the color head (board)
When replacing or
disassembling both the
color and black head
1. Bi-D alignment adjustment (See Section 4.1.2)
2. Head gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.3)
3. Internal timer reset operation (See Section 4.1.8)
1. Destination data writing operation (See Section 4.1.1)
2. Bi-D alignment adjustment (See Section 4.1.2)
3. Head gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.3)
1. Black head angle adjustment (See Section 4.1.4)
2. Black - Color head vertical adjustment (See Section 4.1.5)
3. Head gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.3)
4. Bi-D alignment adjustment (See Section 4.1.2)
1. Color head angle adjustment (See Section 4.1.6)
2. Black - Color head vertical adjustment (See Section 4.1.5)
3. Head gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.3)
4. Bi-D alignment adjustment (See Section 4.1.2)
1. Color head angle adjustment (See Section 4.1.6)
2. Black head angle adjustment (See Section 4.1.4)
3. Black - Color head vertical adjustment (See Section 4.1.5)
4. Head gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.3)
5. Bi-D alignment adjustment (See Section 4.1.2)
When replacing or
disassembling
the carriage unit
Rev.B 4-1
1. Platen gap adjustment (See Section 4.1.7)
Page 76

Adjustment Stylus Pro Service Manual
4.1.1 Destination Data Writing Operation
The setup value that specifies the destination setting is stored in the EEPROM on the C164 MAIN board.
This setup value must be rewritten to the EEPROM when the main board or the EEPROM chip is replaced.
CAUTION
Before writing destination data, set the interface setting to the parallel interface•or the auto select
setting.
1. Connect the PC to the target printer with a parallel interface cable, and turn the printer on.
2. Execute BASIC on the PC and run the program “VERPxxx.BAS.”
1. Destination Setting
2. Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing
(Black Head Spacer Selection)
3. Head Vertical Position Confirmation
4. Head Gap Adjustment
5. Bi-D Adjustment
6. Internal Timer Reset
7. END
3.
When the main menu appears, choose “Destination Setting” by typing
4. The main menu immediately disappears briefly and then reappears. (At this time, specific destination
parameters, including the destination, interface mode, TOF value, economy/condensed, are
automatically written to the EEPROM.)
5.
Choose “END” by typing
6. Turn off the printer.
7 and Enter. The following message appears on the display.
All parameters that you have specified so far
are written to EEPROM upon power off.
Turn the printer OFF, Now!
1 and Enter.
4-2 Rev.B
Page 77

Stylus Pro Service Manual Adjustment
4.1.2 Bi-D (Bidirectional Printing) Alignment Adjustment
The bidirectional alignment is required when the printer mechanism, main board, or the printhead (board) is
replaced. Performing this adjustment determines a compensation value to rectify any deviation in the print
position. This deviation could be caused by the different print speeds, which are due to tolerances in the
mechanical components, or to the differences in print timing between odd-numbered lines and even-numbered
lines in bidirectional printing. The printer stores the compensation data in the EEPROM on the C164 MAIN
Board and refers to this data when performing bidirectional printing.
1. Connect the PC to the target printer and turn the printer on.
2. Execute BASIC on the PC and run the program “VERPxxx.BAS.”
1. Destination Setting
2. Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing
(Black Head Spacer Selection)
3. Head Vertical Position Confirmation
4. Head Gap Adjustment
5. Bi-D Adjustment
6. Internal Timer Reset
7. END
3.
When the main menu appears, choose “Bi-D Adjustment” by typing
the check pattern with a sample compensation value.)
4. The following menu appears on the display.
Input Bi-D value No. (If OK, input [Y] key.)? _
5. If the sample printing is not vertically aligned for both the odd-numbered lines and even- numbered
lines, enter a compensation value in the range from −30 to +30.
r Positive compensation value: Shifts the 2nd line to the left
r Negative compensation value: Shifts the 2nd line to the right
When the sample printing becomes vertically aligned in both lines, press
you to the main menu.
6.
Choose “END” by typing
7 and Enter. The following message appears on the display.
All parameters that you have specified so far
are written to EEPROM upon power off.
Turn the printer OFF, Now!
5 and Enter. (The printer prints
Y and Enter; this returns
7. Turn off the printer.
Rev.B 4-3
Page 78

Adjustments Stylus Pro XL
4.1.3 Head Gap Adjustment (Black and Color Head)
The head gap adjustment is required when the printer mechanism, main board, or printhead
(board) is replaced or diassembled. This adjustment calibrates the head drive timing between the
black and color head. If this adjustment is not made, the vertical alignment will not be completed.
1. Connect the PC to the target printer, and turn the printer on.
2. Execute BASIC on the PC and run the program “VERxxx.BAS.”
1. Destination Setting
2. Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing
(Black Head Spacer Selection)
3. Head Vertical Position Confirmation
4. Head Gap Adjustment
5. Bi-D Adjustment
6. Internal Timer Reset
7. END
3. When the main menu appears, choose “Head Gap Adjustment” by typing 4 and ENTER.(The
printer prints a check pattern with a sample compensation value.)
4. The printer prints a sample like the one shown in Figure 4-1.
5. If the sample print is not vertically aligned for both odd-numbered lines (black lines) and
even-numbered lines (magenta lines), enter a compensation value in the range from −16 to
+16.
❏ Positive compensation value: Shifts the 2nd line to the left
❏ Negative compensation value: Shifts the 2nd line to the right
When both the black and magenta lines are vertically aligned, press Y and ENTER; this returns
you to the main menu.
6.6. Choose “END” by typing 7 and ENTER. The next message appears on the display.
All parameters that you have specified so far
arewrittentoEEPROMuponpoweroff.
7. Turn off the printer.
Head Gap Adjustment No. 0
Color (Magenta ) Line
Turn the printer OFF, Now!
Black Line
Figure 4-1. Head Gap Adjustment Sample
4-4 Rev. A
Page 79

Black Head
(Angle Adjustment Concept)
Black Head
(Reverse Side)
Head Base
Carriage
Angular Spacer
Linear Spacer
(Spacer Setting Position)
Stylus Pro XL Adjustments
4.1.4 Black Head Angle Adjustment
The black head angle adjustment is required when the black head is replaced or disassembled. If
this adjustment is not correct, a white banding problem may occur, or the color head timing may
not match the black head timing. The following figure illustrates the black head angle adjustment.
The black head angle is adjusted with linear and angular spacers. A linear spacer is attached to both
sides of the head base, and an angular spacer is attached only to the right side of the head base.
Spacers for the black head come in different shapes for the thickness needed. The following figure
shows the relationship between the shape and thickness.
Figure 4-2. Black Head Angular and Linear Spacers
Angular Spacers (For Black Head)
Spacer Name Spacer NameThickness Thickness
angular spacer BK
angular spacer BK:B
angular spacer BK:C
angular spacer BK:D
angular spacer BK:E
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
Shape
Linear Spacers (Only Use for Black Head)
linear spacer K
linear spacer J
linear spacer I
linear spacer
linear spacer B
linear spacer C
linear spacer D
linear spacer E
linear spacer F
Shape
0.05
0.12
0.19
0.26
0.33
0.40
0.47
0.54
0.61
Rev. A 4-5
linear spacer G
linear spacer H
0.68
0.75
Figure 4-3. Types of Spacers and Relationship between
Shape and Thickness
Page 80

AB
Black Head Angle Adjustment
Adjustments Stylus Pro XL
1. Connect the PC to the target printer, and turn the printer on.
2. Execute BASIC on the PC and run the program “VERxxx.BAS.”
1. Destination Setting
2. Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing
(Black Head Spacer Selection)
3. Head Vertical Position Confirmation
4. Head Gap Adjustment
5. Bi-D Adjustment
6. Internal Timer Reset
7. END
3. When the main menu appears, choose “Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing” by typing
2 and ENTER. (The printer prints the check pattern, along with the sample name. )
WARNING
❏ When replacing both the black and color heads, always adjust the color head angle first.
The black head angle is based on the color head angle.
❏ After you replace the black head and print the black head angle pattern, you only have
to insert an angular spacer if the pattern is incorrect.
4. The printer prints a pattern like one in the following sample. Only the nozzles in rows A and
D are fired (making it is easy to see the angle of the black head).
Figure 4-4. Black Head Angle Adjustment Sample
5. In the figure above, pay attention to position A. (Do not look at position B.)
6. Using the following flowchart, replace the angular spacer for the black head, which is under
the right linear spacer. The procedure for this replacement is explained beginning with step 7.
Check p osit ion A.
Position A Position A
4-6 Rev. A
Replace the right
angular spacer with
a thinner one.
Figure 4-5. Spacer Selection
Replace the right
angular spacer with
a thicker one.
Page 81

1: Push
Carriage Unit
Platen Gap
Adjust Lev er
Linear Spac er
Black Head
Head Ba se
Angular Spacer
2: Replace
(Angular Spacer
Replacement Position)
Stylus Pro XL Adjustments
7. Turn the printer power off now.
8. Manually move the carriage to the center while pressing the carriage lock lever, and remove
the two ink cartridges.
9. Remove the rubber cap covering the head screw at the side of color ink cartridge. Then loosen
(but do not remove) 3 screws. (Refer to Figure 4-6.)
Figure 4-6. Removing the Rubber Cap
WARNING
After replacing the spacer, always install new ink cartridges before returning the printer to
the user. During this adjustment, use ink cartridges exclusively for service (Monochrome:
1020626, CMY: 1020627). You can reuse old ink cartridges for other purposes.
10. Replace the angular spacer for the black head with a new one, referring Figure 4-7.
(Replace the angular spacer by using tweezers to push the head base toward the rear.)
Rev. A 4-7
Page 82

1: Push
Carriage Unit
Platen Gap
Adjust Lev er
Linear Spac er
Black Head
Head Ba se
Angular Spacer
2: Replace
(Angular Spacer
Replacement Position)
Adjustments Stylus Pro XL
11. After replacing the angular spacer, reassemble the ink cartridge holder and reinstall the ink
cartridges. Use the BASIC program to verify the angle of the black head. Confirm the angle by
performing the steps 1 to 6 again, and if the angle is wrong, perform the adjustment again
until the head angle is correct.
WARNING
❏ The angular spacer comes in five thicknesses. Continue performing this adjustment, by
changing the black head angle is correct.
❏ When inserting an angular spacer, always place the angular spacer on the linear spacer.
Figure 4-7. Angular Spacer Replacement Method
4-8 Rev. A
Page 83

#1
#2
#16
#1#2
#4
#5
#6
#3
#8
#9
#61
#62
#63
#64
#7
Carriage Unit
Adjust
Color Head
Black Head
Vertical Position
Vertical Position
Magenta
Cyan
Yellow
Stylus Pro XL Adjustments
4.1.5 Black - Color Head Vertical Adjustment
This adjustment calibrates the vertical position between the black head and the color head. Align
the top nozzles (both nozzle #1 on the black head and nozzle #1 on the color head). You can make
this adjustment by using only the linear spacers for the black head. This adjustment is required
when the black head or the color head is replaced or disassembled. The following figure illustrates
this adjustment.
Figure 4-8. Black-Color Head Vertical Adjustment Concept
1. Connect the PC to the target printer, and turn the printer on.
2. Execute BASIC on the PC and run the program “VERxxx.BAS”.
1. Destination Setting
2. Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing
(Black Head Spacer Selection)
3. Head Vertical Position Confirmation
4. Head Gap Adjustment
5. Bi-D Adjustment
6. Internal Timer Reset
7. END
3. When the main menu appears, choose “Head Vertical Position Confirmation” by typing 3 and
ENTER. (The printer prints the check pattern, along with the sample name.)
WARNING
When replacing the black head, always adjust the black head angle first, because the blackcolor head vertical adjustment is based upon the black head angle.
2-3 BLACK HEAD SPACER SELECTION
Magenta
-5 -4
-3 -2
-1
OK (0)
Black
+1 +2 +3 +4
Figure 4-9. Linear Spacer Selection Sample
Rev. A 4-9
+5
Page 84

Adjustments Stylus Pro XL
4. In Figure 4-10, the vertical position is correct when both the magenta line and the black line
are aligned (as shown in position OK (0)). If the vertical position is correct, turn off the
printer. If the black and magenta lines are not aligned, perform the vertical adjustment as
described in steps 5-10.
WARNING
❏ The number shown in the sample indicates the thickness level compared to the current
linear spacer. (See * .) There are 11 linear spacers with 11 different thicknesses.
❏ The linear spacer is attached by two pieces, one on each side of the head base. Therefore,
when you need to replace one linear spacer, always replace both linear spacers at the
same time.
❏ When replacing the linear spacer, place it under the angular spacer.
* If necessary, replace the linear spacer. For instance, if your pattern is similar to the pattern
shown under –2, replace the linear spacer with a thinner linear spacer. If your pattern is similar
to the pattern shown under 2, replace the linear spacer with a thicker spacer.
5. Turn the printer off.
6. Move the carriage to the center while pressing the carriage lock lever, and remove the two ink
cartridges.
Rubber Cap
Screw 1
Screw 2
Screw 3
Figure 4-10. Removing the Rubber Cap
7. Remove the rubber cap that covering a head screw at the side of color ink cartridge and then
loosen (but do not remove) 3 screws. (Refer to the figure below.)
WARNING
After replacing the spacer, always install new ink cartridges before returning the printer to
the user. During adjustment, use the ink cartridges exclusively for service (Monochrome:
1020626, CMY: 1020627). You can reuse the old ink cartridges for other purposes.
4-10 Rev. A
Page 85

1: Push
Carriage Un it
Platen G ap
Adjust Lever
2: Replace
Black Head
Head Base
Linear Spacer x 2
(Linear Spacer
Replacement Position)
Angular Spacer
Stylus Pro XL Adjustments
8. Change the linear spacers (2 spacers for the monochrome head only) with new ones, referring
the figure below. (Replace linear spacers using tweezers to push the head base toward the
rear.)
Figure 4-11. Linear Spacer Replacement Method
9. Rerun the BASIC program, and choose the “Head Vertical Position Confirmation” by typing 3
and ENTER; then confirm that the sample print is correct. If the sample is incorrect, change the
thickness of the linear spacer and perform this adjustment again until the two black and
magenta lines are aligned at the position “OK (0).”
10. When you complete this adjustment, exit the BASIC program and turn off the printer.
Rev. A 4-11
Page 86

4.1.6 Color Head Angle Adjustment
The color head angle adjustment is required when the color head is replaced or disassembled.
If this adjustment is not correct, a white banding problem may occur, or the black head timing may
not match the color head timing. The following figure illustrates the color head angle adjustment.
The color head angle is adjusted by the angular spacer. The angular spacer is attached only to the
left side of the head base.
1. Connect the PC to the target printer, and turn the printer on.
2. Execute BASIC on the PC and run the program “VERxxx.BAS”.
1. Destination Setting
2. Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing
(Black Head Spacer Selection)
3. Head Vertical Position Confirmation
4. Head Gap Adjustment
5. Bi-D Adjustment
6. Internal Timer Reset
7. END
3. When the main menu appears, choose “Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing” by typing
2 and ENTER. (The printer prints the check pattern with the sample name.)
WARNING
When replacing both the black head and color head, always adjust the color head angle
first. The black head angle and the black-color head vertical position adjustments are based
on the color head angle adjustment.
Page 87

0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
0.50
Angular Spacer (for Color Head)
Spacer Name
Thickness
Shape
angular spacer YMC
angular spacer YMC-B
angular spac er YM C-C
angular spacer YMC-D
angular spacer YMC-E
(A) (B ) (A) (B )
Check
positions A, B
Positio n A, B
Position A, B
Replace the right
angular spacer
with a thicker one.
Replace the right
angular spacer
with a thinner one
Magenta
Cyan
Magenta
Cyan
Stylus Pro XL Adjustments
Angular spacers for the color head come in five thicknesses, each having its own shape. The
following figure shows the relationship between the shape and thickness. Since the color head is
not equipped with a linear spacer, the angle adjustment is decided only by the angular spacer
(specifically designed for the color head), which is placed under the left side of the head base.
Figure 4-14. Relationship between the Shape and Thickness
4. In Figure 4-13, pay attention to the position of A and B while you reset the left angular spacer.
The replacement procedure is explained beginning in step 5.
5. Turn off the printer now.
6. Move the carriage to the center manually, and loosen (but do not remove) the screw securing
the color head to the carriage.
Rev. A 4-13
Figure 4-15. Spacer Selection
Page 88

Adjustments Stylus Pro XL
7.
Rubber Cap
Screw 1
Screw 2
Screw 3
Figure 4-16. Removing the Rubber Cap
Remove the rubber cap covering the head screw at one side of color ink cartridge. Then loosen
(but do not remove) 3 screws. (Refer to the figure below.)
8. Replace the angular spacer on the left side with a new one, referring the figure below. (Replace
the angular spacer using tweezers to push the head base toward the rear.)
4-14 Rev. A
Page 89

Stylus Pro XL Adjustments
9. Rerun the BASIC program and choose “Head Angle Confirmation Pattern” again by typing 2
and ENTER. Then verify that the confirmation sample is correct.
Carriage Unit
1: Push
Head Base
Color H ead
Angular Spacer
(one side on ly)
Platen Gap Adjust Lever
2: Replace
Figure 4-17. YMC Angular Spacer Replacement
10. If the sample is incorrect, repeat steps 5-9 until the upper lines in the sample are aligned with
one another and the lower lines in the sample are exactly equidistant to one another (as shown
at B in Figure 4-15).
11. When you complete this adjustment, turn off the printer.
Rev. A 4-15
Page 90

Attach the thickness gauge
under the PF pinch roller unit.
Left Adjustment Position
Right Adjustment Position
Paper Guide P late
Bushing
Pump Un it
Eject Frame
Thickness Gau ge
Thickness Gauge
Front
Fron t Frame
PF Pinch Roller
Unit
Attach ment Point
Tension Roller
Thickness Gau ge
Paper G uide
Platen
Adjustments Stylus Pro XL
4.1.7 Platen Gap Adjustment
This adjustment is required when the carriage unit is replaced or removed from the printer
mechanism. Adjust the distance between the printhead nose and the paper surface to 1.1 mm.
1. Attach a thickness gauge (commercially available) to the left side adjustment position on the
paper guide plate, as shown in the figure below, so that one side hooks the paper feed pinch
roller unit.
2. Move the carriage unit manually onto the thickness gauge.
Table 4-2. Gap and Adjustment Direction
Gap between Head Nose and Gauge Surface Left Bushing Right Bushing
Narrow CW CCW
Spread CCW CW
3. Rotate the parallelism adjustment bushing, attached to the left and right ends of the carriage
guide shaft, when the black and color printheads contact the thickness gauge.
4. After attaching the printheads to the gauge surface, verify that the gap between the carriage
roller and the front frame is less than 0.04 mm. (See Figure 4-16.)
5. Attach the 1.1 mm thickness gauge to the right side adjustment position on the paper guide
plate, as shown below, so that one side hooks the paper feed pinch roller unit.
Note: When checking the gap between the carriage roller and the front frame, use the thickness
gauge or the paper guide plate. If the gap is correct the gauge cannot be installed into the
gap. If the gap is incorrect, the gauge can be inserted in the gap.
4-16 Rev. A
Figure 4-18. Adjusting the Platen Gap
Page 91

0.04 mm
Carriage Roller
Thickness
Gauge
Gap
Eject Frame
Stylus Pro XL Adjustments
6. Move the carriage manually to the right adjustment position and repeat steps 3 and 4,
referring to Figures 4-18 and 4-19.
Figure 4-19. Confirming the Gap
4.1.8 Internal Timer Reset Operation
This operation is required when the M-4A60 printer mechanism is replaced. There are 6 timers in
this printer:
1. Refresh timer
2. Timer (monochrome and CMY)
3. Flushing level decision timer
4. False absorbing timer
5. Total print timer
6. PAUSE timer
When the printer mechanism is replaced, reset the timers as described here:
1. Connect the PC to the target printer, and turn on the printer.
2. Execute BASIC on the PC and run the VERxxx.BAS program.
1. Destination Setting
2. Head Angle Confirmation Pattern Printing
(Black Head Spacer Selection)
3. Head Vertical Position Confirmation
4. Head Gap Adjustment
5. Bi-D Adjustment
6. Internal Timer Reset
7. END
3. When the main menu appears, choose “Internal timer reset” by typing 6 and ENTER.This
resets the internal timer. The following message then appears.
All parameters of the internal timer
are now reset. Press Y and ENTER
to return to the main menu.
4. Press Y and ENTER.
5. Press 7 and ENTER.
6. Turn off the printer.
Rev. A 4-17
Page 92

Chapter 5 Troubleshooting
Table of Contents
5.1 OVERVIEW 5-1
5.2 UNIT LEVEL TROUBLESHOOTING 5-3
5.2.1 Printer Does Not Operate at Power on. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.2.2 Error is Detected. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
5.2.3 Failure Occurs During Printing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
5.2.4 Printer Does Not Feed the Paper Correctly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
5.2.5 Control Panel Operation is Abnormal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
5.3 UNIT REPAIR - C137 PSB/PSE BOARD 5-9
5.4 UNIT REPAIR - C164 MAIN BOARD 5-10
5.5 UNIT REPAIR - PRINTER MECHANISM (M-4A11) 5-12
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 5-1. Troubleshooting Process Flowchart. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
LIST OF TABLES
Table 5-1. Motor Coil Resistance Test Points. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Table 5-2. Sensor Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Table 5-3. Sensor Test Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Table 5-4. Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Table 5-5. Symptoms and Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Table 5-6. Repair of the C137 PSB/PSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
Table 5-7. Repair of the C164 MAIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
Table 5-8. Repair of the Printer Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
Page 93

Stylus Pro Service Manual Troubleshooting
5.1 OVERVIEW
The printer may exhibit different symptoms for the same problem, which makes troubleshooting more
difficult. This section, however, provides simple and effective ways to facilitate troubleshooting. The
following flowchart illustrates the main steps in the troubleshooting process.
START
UNIT LEVEL TROUBLESHOOTING
UNIT REPAIR OF
C137 PSB/PSE BOARD
Motor
Connector
Number
UNIT REPAIR OF
C164 MAIN B OAR D
ASSEMBLY
AND
ADJUSTMENT
END
UNIT REPAIR OF
M-4A11 Mechanism
Figure 5-1. Troubleshooting Process Flowchart
Table 5-1. Motor Coil Resistance Test Points
Common
Pin
Number
Test Pin
Number
(Set Meter to Ohms. Disconnect
Motor from Main Board and Check it
Test Method
with Printer Power Off.)
Meter Reading
CR Motor
(CN6)
PF Motor
(CN7)
5 1, 2, 3, 4
5 1, 2, 3, 4
Place one lead on pin 5 and the other
lead on each of the 4 test pins to
check the two motor phases.
Place one lead on pin 5 and the other
lead on each of the 4 test pins to
check the two motor phases.
10.0Ω±
10%(At 25 °C,
77 °F)
11.5 Ω±
10%(At 25 °C,
77 °F)
Rev.A 5-1
Page 94

Troubleshooting Stylus Pro Service Manual
Table 5-2. Sensor Status
Sensor Point Signal Level Status
PE Sensor
BCO Sensor
CCO Sensor
HP Sensor
TH Sensor
Sensor
connector
Number
PE Sensor
(CN8)
BCO Sensor
(CN11)
CCO Sensor
(CN12)
CN8 /
Pin 1 to Pin 2
CN11 /
Pin 8 to Pin 7
CN12 /
Pin 8 to Pin 7
CN9 /
Pin 3 to Pin 2
CN12/
Pin 10 to Pin 11
H (5 V) Paper exists
L (GND) No paper (paper end)
L (GND) Black cartridge exists
H (5 V) No black cartridge
L (GND) Color cartridge exists
H (5 V) No color cartridge
L At home position (HP)
H Away from HP
Analog data
Table 5-3. Sensor Test Points
Test Method
(Set Meter to Ohms. Check Printer with
Power Off.)
Place one lead on pin 1 and the other lead
on pin 2. Toggle the sensor by inserting
and removing a sheet of paper.
Place one lead on pin 8 and the other lead
on pin 1. Toggle the sensor by inserting
and removing a monochrome ink cartridge.
Place one lead on pin 8 and the other lead
on pin 1. Toggle the sensor by inserting
and removing a color ink cartridge.
Change the pulse width of the charge
pulse for the common driver circuit
Method Reading
Meter should toggle between open
and short (open = active).
Meter should toggle between open
and short.
Meter should toggle between open
and short.
Table 5-4. Error Codes
Error
Status
Paper out
No ink
cartridge
Paper jam — Blinks — — — —
Maintenance
request
Carriage
error
Data
Blinks Blinks Blinks Blinks Blinks Blinks
Blinks — — — — Blinks
Paper
Out
—On — — — —
— — On — — —
No Ink
Cartridge
LED
Economy Condensed Pause
Recovery
Load paper and press
Pause and Load/Eject
buttons.
Install the new ink
cartridge and press the
Pause button.
Load paper and press
Pause and Load/Eject
Buttons.
Service maintenance
request. (Change the
waste ink drain tank
and reset the counter.)
Turn off the printer and
turn it on again.
5-2 Rev.A
Page 95

Stylus Pro Service Manual Troubleshooting
5.2 UNIT LEVEL TROUBLESHOOTING
When a problem occurs, you can identify the defective unit by the symptoms exhibited. The table below lists
the symptoms of certain problems. Once the problem is identified, refer to the flowchart that corresponds to
the problem.
Table 5-5. Symptom and Problem
Symptom Problem Flowchart No.
Printer does not operate at
power on
Error is detected
Failure occurs during printing
Printer does not feed the
paper correctly
Control panel operation is
abnormal
❒ LEDs do not light up.
❒ Printer mechanism does not operate.
❒ Error is indicated by LED indication.
❒ Printing is not performed.
❒ Abnormal printing (missing dots, etc.)
❒ Print quality is poor
❒ No paper is fed.
❒ Paper feed is irregular.
❒ Paper jam occurs.
❒ No response to button access.
1
2
3
4
5
Rev.A 5-3
Page 96

START
Is the AC
input voltage
correct ?
Has fuse
(F1) on the C137
PSB/PSE
blown ?
Check the output
voltage of the C137
PSB/PSE at CN2.
Is the output
voltage correct ?
Replace the C137
MAIN board.
Is the problem
corrected ?
END
Use the correct
input voltage.
Replace the fuse
and disconnect
CN5 on the C164
MAIN board .
Replace the
C137 PSB/PSE
board.
Does the
fuse blow again
at power on ?
Check motors and drivers.
Refer to the section describing
repair of the printer mechanism.
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
Troubleshooting Stylus Pro Service Manual
5.2.1 Printer Does Not Operate at Power On
5-4 Rev.A
Flowchart - 1
Page 97

Stylus Pro Service Manual Troubleshooting
5.2.2 Error is Detected
START
Identify the type
of error indicated.
(See Table 5-3.)
Carriage error
NO
No ink cartridge
NO
Waste ink drain
tank overflow
Replace the waste
ink absorbing
material, and reset
the protect counter.
(See Chapter 6.)
YES
YES
YES
Turn the printer
off and try to
move the carriage
manually.
Replace the ink
cartridge with a
new one.
Does error
occur again ?
NO
YES
Does the
carriage move
smoothly ?
YES
Check CR moto r
and drivers. If they
are OK, replace the
C164 MAIN bo ard.
Is the
problem
corrected ?
NO
NO
Check ink cartridge
sensor and, if bad,
replace.
END
Refer to the se ction
describing repair of
the printer mechanism.
END
Flowchart - 2
Rev.A 5-5
Page 98

Troubleshooting Stylus Pro Service Manual
5.2.3 Failure Occurs During Printing
START
Run the
self-test.
Does the self-
test print?
YES
Is print
quality bad ?
YES
Perform the
cleaning.
Is the problem
corrected ?
YES
NO
NO
Adjust the
bidirectional
print alignment or
readjust the head
arrangement
adjustment.
(See Chapter 4.)
NO
See the section
describing repair of
the printer mechanism.
YES
Are all cables
connected to C164
MAIN firmly ?
NO
Connect the cables
correctly.
Is the problem
corrected ?
NO
Check all motors,
drivers, and printhead
for shorts . If th ey are
OK, replace the C164
MAIN board.
YES
Is the problem
corrected ?
YES
Check all motors,
END END
drivers, and printhead
for shorts . If th ey are
OK, replace the C164
MAIN board.
NO
Flowchart - 3
5-6 Rev.A
Page 99

Stylus Pro Service Manual Troubleshooting
5.2.4 Printer Does Not Feed the Paper Correctly
START
Is paper loaded
in the sheet feeder
correctly ?
YES
Does a
paper jam
occur ?
NO
Check the PF motor
and drivers. If OK,
replace the C164
MAIN board.
Is the problem
corrected ?
YES
END
NO
YES
NO
Load the paper
correctly.
Verify that the
paper path is clear.
Also confirm that
there are no foreign
objects that may
interfere with paper
movement.
See the section
describing
repair of the
printer mechanism.
Is the problem
corrected ?
NO
YES
END
Flowchart - 4
Rev.A 5-7
Page 100

Troubleshooting Stylus Pro Service Manual
5.2.5 Control Panel Operation is Abnormal
START
Is the control
panel connected
properly ?
YES
Replace the
control panel.
NO
Connect the control
panel correctly.
Is the problem
corrected ?
NO
YES
END
Is the problem
corrected ?
YES
NO
Replace the C164
MAIN board.
END
Flowchart - 5
5-8 Rev.A
 Loading...
Loading...