Page 1

Page 2

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Using Command Line Interface .................................................................................................... 1
Chapter 2 Basic Command List ..................................................................................................................... 8
Chapter 3 802.1Q VLAN Command List ..................................................................................................... 23
Chapter 4 802.1X Command List ................................................................................................................ 38
Chapter 5 Access Authentication Control Command List............................................................................ 62
Chapter 6 Access Control List (ACL) Command List ................................................................................ 103
Chapter 7 Access Control List (ACL) Egress Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ............................... 123
Chapter 8 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Command List ................................................................. 142
Chapter 9 ARP Spoofing Prevention Command List ................................................................................. 147
Chapter 10 Asymmetric VLAN Command List ............................................................................................ 149
Chapter 11 Auto-Configuration Command List ............................................................................................ 151
Chapter 12 Basic Commands Command List ............................................................................................. 153
Chapter 13 BPDU Attack Protection Command List ................................................................................... 171
Chapter 14 Cable Diagnostics Command List ............................................................................................. 176
Chapter 15 Command Logging Command List ........................................................................................... 179
Chapter 16 Compound Authentication Command List ................................................................................ 182
Chapter 17 Configuration Command List .................................................................................................... 193
Chapter 18 Configuration Trap Command List ............................................................................................ 198
Chapter 19 Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ....................... 200
Chapter 20 Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) Extension Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ...... 228
Chapter 21 CPU Interface Filtering Command List ..................................................................................... 232
Chapter 22 Debug Software Command List ................................................................................................ 243
Chapter 23 Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack Prevention Command List ...................................................... 286
Chapter 24 DHCP Local Relay Command List ............................................................................................ 290
Chapter 25 DHCP Relay Command List ..................................................................................................... 294
Chapter 26 DHCP Server Command List (RI Mode Only) .......................................................................... 318
Chapter 27 DHCP Server Screening Com mand List ................................................................................... 337
Chapter 28 DHCPv6 Relay Command List ................................................................................................. 349
Chapter 29 Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM) Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ........................... 359
Chapter 30 Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) Command List (RI Mode Only) ........... 366
Chapter 31 Domain Name System (DNS) Resolver Command List ........................................................... 373
Chapter 32 D-Link License management System (DLMS) Command List ................................................. 380
Chapter 33 D-Link Unidirectional Link Detection (DULD) Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) .............. 382
Chapter 34 Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) Command List ....................................................................... 384
I
Page 3

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Chapter 35 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) Command List (RI and EI Mode Only)................ 386
Chapter 36 FDB Command List ................................................................................................................... 396
Chapter 37 Filter Command List .................................................................................................................. 406
Chapter 38 Flash File System (FFS) Command List ................................................................................... 409
Chapter 39 Gratuitous ARP Command List ................................................................................................. 420
Chapter 40 Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Command List (RI Mode Only) ........................ 426
Chapter 41 IGMP Proxy Command List (RI Mode Only) ............................................................................. 434
Chapter 42 IGMP Snooping Command List ................................................................................................ 439
Chapter 43 IP-MAC-Port Binding (IMPB) Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ....................................... 463
Chapter 44 IP Multicast (IPMC) Command List (RI Mode Only) ................................................................. 490
Chapter 45 IP Route Filter Command List (RI Mode Only) ......................................................................... 492
Chapter 46 IP Tunnel Command List (RI Mode Only) ................................................................................. 499
Chapter 47 IPv6 Neighbor Discover Command List .................................................................................... 507
Chapter 48 IPv6 Route Command List ........................................................................................................ 514
Chapter 49 Japanese Web-Based Access Control (JWAC) Command List ............................................... 517
Chapter 50 Jumbo Frame Command List ................................................................................................... 541
Chapter 51 Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT) Command List .................................................................. 543
Chapter 52 Link Aggregation Command List ............................................................................................... 547
Chapter 53 Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Command List ............................................................. 554
Chapter 54 Loopback Detection (LBD) Command List ............................................................................... 580
Chapter 55 Loopback Interface Command List (RI Mode Only) ................................................................. 586
Chapter 56 MAC Notification Command List ............................................................................................... 589
Chapter 57 MAC-based Access Control Command List ............................................................................. 594
Chapter 58 MAC-based VLAN Command List ............................................................................................ 611
Chapter 59 MD5 Configuration Command List (RI Mode Only) .................................................................. 614
Chapter 60 Mirror Command List ................................................................................................................ 617
Chapter 61 Multicast Listener Discovery Protocol (MLD) Command List (RI Mode Only) .......................... 623
Chapter 62 MLD Proxy Command List (RI Mode Only) .............................................................................. 626
Chapter 63 MLD Snooping Command List .................................................................................................. 631
Chapter 64 MSTP debug enhancement Command List .............................................................................. 652
Chapter 65 Multicast Filter Command List................................................................................................... 659
Chapter 66 Multicast VLAN Command List ................................................................................................. 670
Chapter 67 Network Load Balancing (NLB) Command List ........................................................................ 684
Chapter 68 Network Monitoring Command List ........................................................................................... 690
Chapter 69 OAM Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ............................................................................. 696
Chapter 70 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Version 2 Command List (RI Mode Only) ........................... 704
II
Page 4

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Chapter 71 OSPF Version 3 Command List (RI Mode Only) ...................................................................... 725
Chapter 72 Password Recovery Command List .......................................................................................... 744
Chapter 73 Peripherals Command List........................................................................................................ 747
Chapter 74 Ping Command List ................................................................................................................... 754
Chapter 75 Policy Route Command List (RI Mode Only) ............................................................................ 757
Chapter 76 Port Security Command List ..................................................................................................... 760
Chapter 77 Power over Ethernet ( PoE) Com mand Lis t (DGS-3120-24PC and DGS-3120-48PC Only)
768
Chapter 78 Power Saving Command List ................................................................................................... 774
Chapter 79 PPPoE Circuit ID Insertions Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ........................................ 780
Chapter 80 Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Command List (RI Mode Only) ..................................... 784
Chapter 81 PIM for IPv6 Command List (RI Mode Only) ............................................................................ 802
Chapter 82 Protocol VLAN Command List .................................................................................................. 821
Chapter 83 QinQ Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ............................................................................ 827
Chapter 84 Quality of Service (QoS) Command List ................................................................................... 835
Chapter 85 Reboot Schedule Command List .............................................................................................. 852
Chapter 86 Remote Switched Port ANalyzer (RSPAN) Command List ...................................................... 855
Chapter 87 Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Command List (RI Mode Only) ......................................... 861
Chapter 88 RIPng Command List (RI Mode Only) ...................................................................................... 866
Chapter 89 Routing Command List ............................................................................................................. 872
Chapter 90 RPC PortMapper Command List .............................................................................................. 888
Chapter 91 Safeguard Engine Command List ............................................................................................. 890
Chapter 92 SD Card Management Command List ...................................................................................... 892
Chapter 93 Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) Command List .............................................................. 899
Chapter 94 Secure Shell (SSH) Command List .......................................................................................... 902
Chapter 95 Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Command List ............................................................................ 915
Chapter 96 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Command List ......................................................................... 922
Chapter 97 Surveillance VLAN Command List ............................................................................................ 935
Chapter 98 sFlow Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ........................................................................... 941
Chapter 99 Show Technical Support Command List ................................................................................... 953
Chapter 100 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Command List ............................................................. 956
Chapter 101 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Command List .............................................. 961
Chapter 102 Single IP Management Command List ..................................................................................... 990
Chapter 103 Stacking Command List (EI and SI Mode Only) ..................................................................... 1000
Chapter 104 Static Multicast Route Command List (RI Mode Only) ........................................................... 1008
Chapter 105 Syslog and Trap Source-interface Command List .................................................................. 1011
III
Page 5

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Chapter 106 System Log Command List ..................................................................................................... 1015
Chapter 107 System Severity Command List .............................................................................................. 1027
Chapter 108 Telnet Client Command List.................................................................................................... 1029
Chapter 109 TFTP Client Command List..................................................................................................... 1030
Chapter 110 Time and SNTP Command List .............................................................................................. 1035
Chapter 111 Trace Route Command List .................................................................................................... 1043
Chapter 112 Traffic Control Command List ................................................................................................. 1046
Chapter 113 Traffic Segmentation Command List ...................................................................................... 1052
Chapter 114 Trusted Host Command List ................................................................................................... 1054
Chapter 115 UDP Helper Command List..................................................................................................... 1058
Chapter 116 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) Command List (RI Mode Only) ....................... 1063
Chapter 117 VLAN Counter Command List (RI and EI Mode Only) ........................................................... 1071
Chapter 118 VLAN Trunking Command List ............................................................................................... 1076
Chapter 119 Voice VLAN Command List .................................................................................................... 1081
Chapter 120 Web-Based Access Control (WAC) Command List ................................................................ 1092
Chapter 121 Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) Command List .................................................. 1108
Appendix A Password Recovery Procedure .............................................................................................. 1115
Appendix B System Log Entries ................................................................................................................. 1117
Appendix C Trap Log Entries ..................................................................................................................... 1132
Appendix D RADIUS Attributes Assignment .............................................................................................. 1141
Appendix E IETF RADIUS Attributes Support ............................................................................................ 1144
IV
Page 6

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Chapter 1
Using Command Line
Interface
The Switch can be managed through the Switch’s serial port, Telnet, SNMP or the Web-based
management agent. The Command Line Interface (CLI) can be used to configure and manage the
Switch via the serial port or Telnet interfaces.
This manual provides a reference for all of the commands contained in the CLI. Every command
will be introduced in terms of purpose, format, description, parameters, and examples.
Configuration and management of the Switch via the Web-based management agent are
discussed in the Web UI Reference Guide. For detailed information on installing hardware please
also refer to the Hardware Installation Guide.
1-1 Access ing the Switch via the Serial Port
The Switch’s serial port’s default settings are as follows:
• 115200 baud
• no parity
• 8 data bits
• 1 stop bit
A computer running a terminal emulation program capable of emulating a VT-100 terminal and a
serial port configured as above are then connected to the Switch’s Console port via an included
RS-232 to RJ-45 convertor cable.
With the serial port properly connected to a management computer, the following screen should be
visible.
DGS-3120-24TC Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 4.00.015
Copyright(C) 2014 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
UserName:
PassWord:
There is no initial username or password. Just press the Enter key twice to display the CLI input
cursor − DGS-3120-24TC:admin# . This is the command line where all commands are input.
NOTE: When Switches with different modes or different firmware versions are stacked together,
the following warning message will appear after the initial login:
1
Page 7
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 4.00.015
Copyright(C) 2014 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
UserName:
PassWord:
WARNING: The stacking members are working on different firmware.
1-2 Setting the Switch’s IP Address
Each Switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communic ation with an
SNMP network manager or other TCP/IP application (for example BOOTP, TFTP). The Switch’s
default IP address is 10.90.90.90. You can change the default Switch IP address to meet the
specification of your networking address scheme.
The Switch is also assigned a unique MAC address by the factory. This MAC address cannot be
changed, and can be found on the initial boot console screen – shown below.
Boot Procedure V3.00.501
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Power On Self Test ........................................ 100 %
MAC Address : 10-BF-48-D0-E0-E0
H/W Version : B1
Please Wait, Loading V4.00.015 Runtime Image .............. 100 %
UART init ................................................. 100 %
Starting runtime image
Device Discovery .......................................... |
The Switch’s MAC address can also be found in the Web management program on the Switch
Information (Basic Settings) window on the Configuration menu.
The IP address for the S wit c h must be set before it can be managed with the Web-based manager.
The Switch IP address can be automatically set using BOOTP or DHCP protocols, in which case
the actual address assigned to the Switch must be known.
Starting at the command line prompt, enter the commands config ipif System ipaddress
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy. Where the x’s represent the IP address to be assigned to the
IP interface named System and the y’s represent the corresponding subnet mask.
Alternatively, you can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z. Where the x’s
represent the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named System and the z represents
the corresponding number of subnets in CIDR notation.
2
Page 8

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config ipif System ipaddress 10.24.22.100/255.0.0.0
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#?
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
The IP interface named System on the Switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mask
which can then be used to connect a management station to the Switch’s Telnet or Web-based
management agent.
Command: config ipif System ipaddress 10.24.22.100/8
Success.
In the above example, the Switch was assigned an IP address of 10.24.22.100 with a subnet mask
of 255.0.0.0. The system message Success indicates that the command was executed
successfully. The Switch can now be configured and managed via Telnet, SNMP MIB browser and
the CLI or via the Web-based management agent using the above IP address to connect to the
Switch.
There are a number of helpful features included in the CLI. Entering the ? command will displa y a
list of all of the top-level commands.
Command: ?
..
?
cable_diag ports
cd
cfm linktrace
cfm lock md
cfm loopback
change drive
clear
clear address_binding dhcp_snoop binding_entry ports
clear address_binding nd_snoop binding_entry ports
clear arptable
clear attack_log
clear cfm pkt_cnt
clear counters
clear dhcp binding
clear dhcp conflict_ip
clear ethernet_oam ports
clear fdb
clear igmp_snooping statistics counter
clear jwac auth_state
clear log
When entering a command without its required parameters, the CLI will prompt you with a Next
possible completions: message.
3
Page 9

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config account
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config account
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config account
Command: config account
Next possible completions:
<username 15>
In this case, the command config account was entered with the parameter <username 15>. The
CLI will then prompt to enter the <username 15> with the message, Next possible completions:.
Every command in the CLI has this feature, and complex commands have several layers of
parameter prompting.
In addition, after typing any given command plus one space, users can see all of the next possible
sub-commands, in sequential order, by repeatedly pressing the Tab key.
To re-enter the previous command at the command prompt, press the up arrow cursor key. The
previous command will appear at the command prompt.
Command: config account
Next possible completions:
<username 15>
In the above example, the command config account was entered without the required parameter
<username 15>, the CLI returned the Next possible completions: <username 15> prompt. The
up arrow cursor control key was pressed to re-enter the previous command (config account) at
the command prompt. Now the appropriate username can be entered and the config account
command re-executed.
All commands in the CLI function in this way. In addition, the syntax of the help prompts are the
same as presented in this manual − angle brackets < > indicate a numerical value or character
string, braces { } indicate optional parameters or a choice of parameters, and brackets [ ] indicate
required parameters.
If a command is entered that is unrecognized by the CLI, the top-level commands will be displayed
under the Available commands: prompt.
4
Page 10

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#the
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show
log_software_module loopback loopdetect
Available commands:
.. ? cable_diag cd
cfm change clear config
copy create debug del
delete dir disable download
enable erase execute format
install login logout md
move no ping ping6
rd reboot reconfig rename
reset save show smtp
telnet traceroute traceroute6 upload
The top-level commands consist of commands such as show or config. Most of these commands
require one or more param eter s to narr o w the top-level command. This is equivalent to show what?
or config what? Where the what? is the next parameter.
For example, entering the show command with no additional parameters, the CLI will then display
all of the possible next parameters.
Command: show
Next possible completions:
802.1p 802.1x aaa access_profile
account accounting acct_client address_binding
arp_spoofing_prevention arpentry asymmetric_vlan
attack_log auth_client auth_diagnostics
auth_session_statistics auth_statistics authen
authen_enable authen_login authen_policy authentication
authorization autoconfig backup bandwidth_control
boot_file bpdu_protection cfm command
command_history community_encryption config
cpu cpu_filter current_config ddm
device_status dhcp dhcp_local_relay dhcp_relay
dhcp_server dhcpv6_local_relay dhcpv6_relay
dlms dos_prevention dot1v_protocol_group
dscp duld dvmrp ecmp
eee egress_access_profile egress_flow_meter
environment erps error ethernet_oam
execute_config fdb filter flow_meter
gratuitous_arp greeting_message gvrp hol_prevention
host_name igmp igmp_proxy igmp_snooping
ip ip_tunnel ipfdb ipif
ipif_ipv6_link_local_auto ipmc ipmroute
iproute ipv6 ipv6route jumbo_frame
jwac l2protocol_tunnel lacp_port led
limited_multicast_addr link_aggregation lldp
lldp_med log log_save_timing
5
Page 11
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
mac_based_access_control mac_based_access_control_local
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
mac_based_vlan mac_notification max_mcast_group
mcast_filter_profile md5 mirror
mld mld_proxy mld_snooping multicast
multicast_fdb name_server nlb ospf
ospfv3 packet password_recovery per_queue
pim pim-ssm pim6 policy_route
port port_group port_security
port_security_entry port_vlan ports
power_saving pppoe private_vlan pvid
qinq radius reboot rip
ripng rmon route route_map
router_ports rspan safeguard_engine scheduling
scheduling_mechanism serial_port session
sflow sftp sim smtp
snmp sntp ssh ssl
stack_device stack_information stacking_mode
storage_media_info stp surveillance_vlan
switch syslog system_severity tech_support
terminal time time_range traffic
traffic_segmentation trap trusted_host
udp_helper utilization vlan vlan_counter
vlan_translation vlan_trunk voice_vlan vrrp
wac wred
In the above example, all of the possible next parameters for the show command are displayed. At
the next command prompt, the up arrow was used to re-enter the show command, followed by the
account parameter. The CLI then displays the user accounts configured on the Switch.
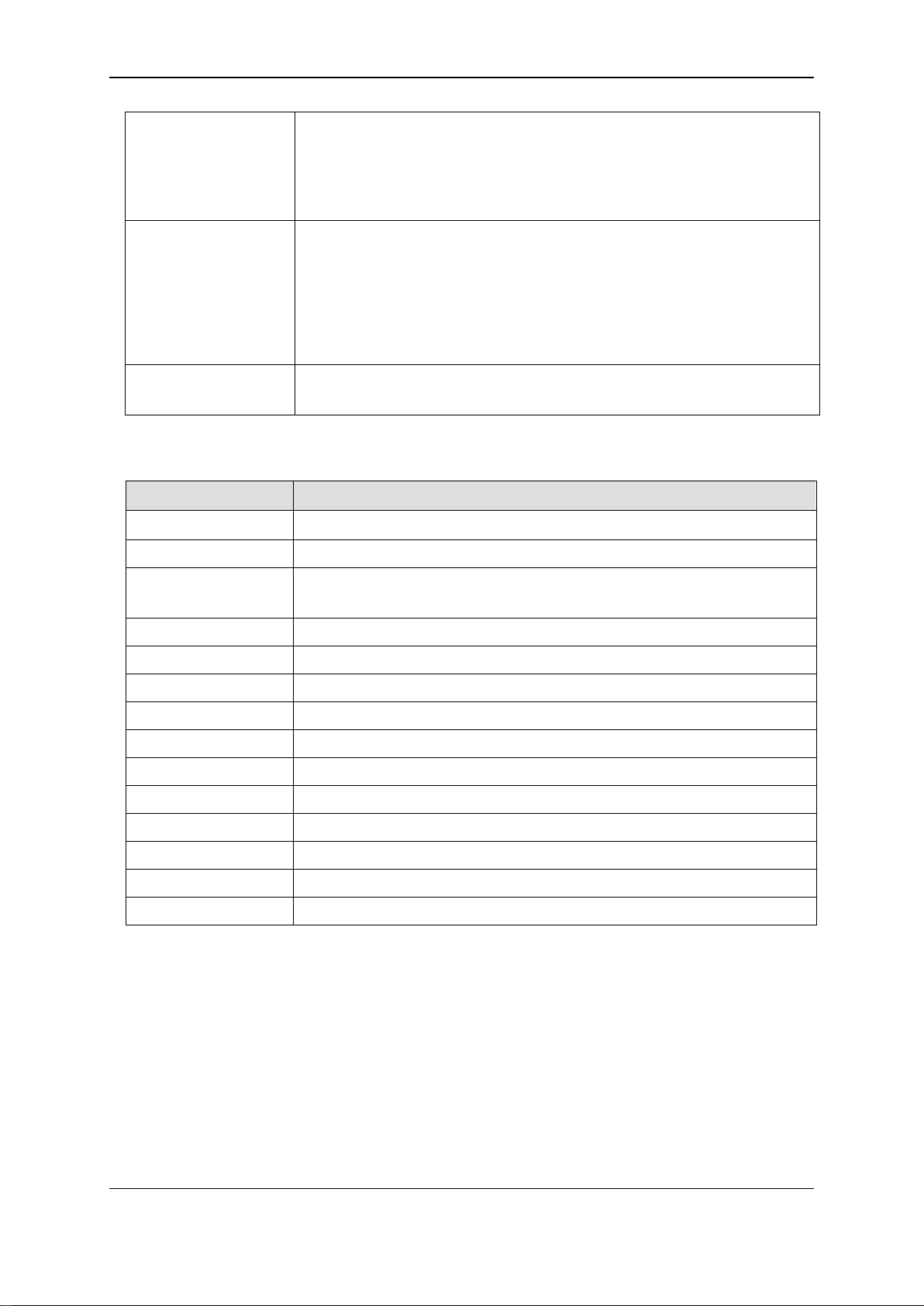
1-3 Command Syntax Symbols
Syntax Description
angle brackets < > Encloses a variable or value. Users must specify the variable or value.
For example, in the syntax
config command_history <value 1-40>
users must enter how many entries for <valu e 1-40> when entering the
command. DO NOT TYPE THE ANGLE BRACKETS.
square brackets [ ] Encloses a required value or list of required arguments. Only one value or
argument must be specified. For example, in the syntax
create account [admin | operator | power_user | user] <username 15>
{encrypt [plain_text | sha_1] <password>}
users must specify either the admin, operator, power_user or user-level
account when entering th e c ommand. DO NOT TYPE THE SQUARE
BRACKETS.
vertical bar | Separates mutually exclusive items in a list. For example, in the syntax
reset {[config | system]} {force_agree}
users must specify either the community or trap receiver in the command.
DO NOT TYPE THE VERTICAL BAR.
6
Page 12
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
braces { } Encloses an optional value or a list of optional arguments. One or more
values or arguments can be specified. For example, in the syntax
reset {[config | system]} {force_agree}
users may choose configure or system in the command. DO NOT TYPE
THE BRACES.
parentheses ( ) Indicates at least one or more of the values or arguments in the preceding
syntax enclosed by braces must be specified. For example, in the syntax
config bpdu_protection ports [<portlist> | all] {state [enable | disable] |
mode [drop | block | shutdown]}(1)
users have the option to specify hops or time or both of them. The "(1)"
following the set of braces indicates at least one argum ent or value within
the braces must be specified. DO NOT TYPE THE PARENTHESES.
ipif <ipif_name 12>
metric <value 1-31>
12 means the maximum length of the IP interface name.
1-31 means the legal range of the metric value.
1-4 Line E diting Keys
Keys Description
Delete Delete character under cursor and shift remainder of line to left.
Backspace Delete character to left of cursor and shift remainder of line to left.
CTRL+R Toggle on and off. When toggled on, inserts text and shifts previous
text to right.
Left Arrow Move cursor to left.
Right Arrow Move cursor to right
Tab Help user to select appropriate token.
P or p Display the previous page.
N, n or Space Display the next page.
CTRL+C Escape from displayed pages.
ESC Escape from displayed pages.
Q or q Escape from displayed pages.
R or r refresh the displayed pages
A or a Display the remaining pages. (The screen display will not pause again.)
Enter Display the next line.
The screen display pauses when the show command output reaches the end of the page.
In the above example, all of the possible next parameters for the show command are displayed. At
the next command prompt, the up arrow was used to re-enter the show command, followed by the
account parameter. The CLI then displays the user accounts configured on the Switch.
7
Page 13

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
show session
show serial_port
config serial_port { bau d_r at e [960 0 | 19200 | 38400 | 1152 00] | auto_l ogo ut [never | 2_minutes |
5_minutes | 10_minutes | 15_m inutes ]}
enable clipaging
disable clipaging
login
logout
?
clear
show command_history
config command_history <value 1-40>
config greeting_message {default}
show greeting_message
config command_prompt [<string 16> | username | default]
config terminal width [default | <value 80-200>]
show terminal width
config ports [<portlist> | all] {medium_type [fiber | copper]} {speed [auto {capability_advertised
clear_description] | auto_s p eed_ do wngr ad e [enab le | disabl e]}
show ports {<portlist>} {[description | err_d isab led | a uto_ neg oti ati on | details | media_type]}
Chapter 2
{10_half | 10_full | 100_half | 100_full | 1000 _f ull}} | 10_ha lf | 10_full | 100_half | 100_ful l |
1000_full {[master | slave]}] | auto_negotiation [restart_an | remote_fault_advertised [disable |
offline | link_fault | auto_negotiati on_ err or]] | flow_co nt r ol [enab le | disable] | learni ng [enab le |
disable ] | state [enable | disable] | mdix [auto | normal | cross] | [description <desc 1-32> |
Basic Command List
2-1 show session
Description
This command is used to display a list of currently users which are login to CLI sessions.
Format
show session
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable the password encryption:
8
Page 14

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show session
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show serial_port
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: show session
ID Live Time From Level User
--- ------------ --------------------------------------- ----- -------------- 8 00:04:17.870 Serial Port admin Anonymous
Total Entries: 1
2-2 show serial_port
Description
This command is used to display the current serial port settings.
Format
show serial_port
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the serial port setting:
Command: show serial_port
Baud Rate : 9600
Data Bits : 8
Parity Bits : None
Stop Bits : 1
Auto-Logout : 10 minutes
2-3 config serial_port
Description
This command is used to configure the serial bit rate that will be used to communicate with the
management host and the auto logout time for idle connections.
9
Page 15

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
baud_rate - (Optional) The serial bit rate that will be used to communicate with the management
115200 - Specify the serial bit rate to be 115200.
auto_logout - (Optional) The auto logout time out setting:
15_minutes - When idle over 15 minutes, the device will auto logout.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config serial_port baud_rate 9600
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Format
config serial_port {baud_rate [9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 115200] | auto_logout [never |
2_minutes | 5_minutes | 10_minutes | 15_minutes]}
Parameters
host. The default baud rate is 115200.
9600 - Specify the serial bit rate to be 9600.
19200 - Specify the serial bit rate to be 19200.
38400 - Specify the serial bit rate to be 38400.
never - Never timeout.
2_minutes - When idle over 2 minutes, the device will auto logout.
5_minutes - When idle over 5 minutes, the device will auto logout.
10_minutes - When idle over 10 minutes, the device will auto logout.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure baud rate:
Command: config serial_port baud_rate 9600
Success.
2-4 enable clipaging
Description
This command is used to enable the pausing of the screen display when the show command
output reaches the end of the page. For those show commands that provide the display refresh
function, the displa y will not be r ef r eshed whe n cli pag in g is dis a ble d. T he def aul t s etti ng is e nab led .
Format
enable clipaging
Parameters
None.
10
Page 16
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# enable clipaging
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# disable clipaging
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable pausing of the screen display when show command output reaches the end of the page:
Command: enable clipaging
Success.
2-5 dis able clipaging
Description
This command is used to disable the pausing of the screen display when the show command
output reaches the end of the page. The default setting is enabled.
Format
disable clipaging
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable pausing of the screen display when s ho w c om mand output reaches the end of the p ag e:
Command: disable clipaging
Success.
2-6 login
Description
This command is used to allow user login to the Switch.
11
Page 17

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# login
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Format
login
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To login the Switch with a user name dlink:
Command: login
UserName:dlink
PassWord:****
2-7 logout
Description
This command is used to logout the facility.
Format
logout
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To logout current user:
12
Page 18
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# logout
UserName:
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#? ping
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: logout
**********
* Logout *
**********
Press any key to login...
DGS-3120-24TC Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 4.00.015
Copyright(C) 2014 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
2-8 ?
Description
This command is used to display the usage description for all commands in the cuurent login
account level or the specific one.
Format
?
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To get “ping” command usage, descriptions:
Command: ? ping
Command: ping
Usage: <ipaddr> { times <value 1-255> | timeout <sec 1-99>}
Description: Used to test the connectivity between network devices.
13
Page 19
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# clear
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
2-9 clear
Description
The command is used to clear screen.
Format
clear
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To clear screen:
Command: clear
2-10 show command_history
Description
The command is used to display command history.
Format
show command_history
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display command history:
14
Page 20
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show command_history
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<value 1-40> - Enter the number of commands that the Switch can recall. This value must be
between 1 and 40.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config command_history 25
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: show command_history
? ping
login
show serial_port
show session
? config bpdu_protection ports
? reset
? create account
? create ipif
show
the
?
2-11 config command_history
Description
This command is used to configure the number of commands that the Switch can recall. The
Switch “remembers” upto the last 40 commands you entered.
Format
config command_history <value 1-40>
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To configure the number of command history:
Command: config command_history 25
Success.
2-12 config greeting_message
Description
This command is used to configure the greeting message (or banner).
15
Page 21
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
default - (Optional) Adding this parameter to the “config greeting_message” command will return
the greeting message (banner) to its original factory default entry.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config greeting_message
-
Format
config greeting_message {default}
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To edit the banner:
Command: config greeting_message
Greeting Messages Editor
===============================================================================
=
DGS-3120-24TC Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Copyright(C) 2014 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
===============================================================================
=
<Function Key> <Control Key>
Ctrl+C Quit without save left/right/
Ctrl+W Save and quit up/down Move cursor
Ctrl+D Delete line
Ctrl+X Erase all setting
Ctrl+L Reload original setting
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 4.00.015
2-13 show greeting_message
Description
The command is used to display greeting message.
Format
show greeting_message
16
Page 22
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show greeting_ message
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<string 16> - Enter the new command prompt string of no more than 16 characters.
username - Enter this command to set the login username as the command prompt.
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display greeting message:
Command: show greeting_message
==============================================================================
DGS-3120-24TC Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 4.00.015
Copyright(C) 2014 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
==============================================================================
2-14 config command_prompt
Description
This command is used to modify the command prompt.
The current command prompt consists of four parts: “product name” + “:” + ”user level” + ”#” (e.g.
“DGS-3120-24TC:admin#”). This command is used to modify the first part (1. “product name”) with
a string consisting of a maximum of 16 characters, or to be replaced with the users’ login user
name.
When users issue the “reset” command, the current command prompt will remain in tact. Yet,
issuing the “reset system” will return the command prompt to its original factory default value.
Format
config command_prompt [<stri n g 16> | username | default]
Parameters
17
Page 23
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
default - Enter this command to return the command prompt to its original factory default value.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config command_prompt Prompt#
Prompt#:admin#
default - The default setting of terminal width. The default value is 80.
<value 80-200> - The terminal width which will be configured. The widt h is betw ee n 80 and 200
characters.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To edit the command prompt:
Command: config command_prompt Prompt#
Success.
2-15 config terminal width
Description
The command is used to set current terminal width.
The usage is described as below:
1. Users login and configure the terminal width to 120, this configuration take effect on this
login section. If users implement “save” command, the configuration is saved. After users
log out and log in again, the terminal width is 120.
2. If user did not save the configuration, another user login, the term inal width is default value.
3. If at the same time, two CLI sessions are running, once section configure to 120 width and
save it, the other section will not be effected, unless it log out and then log in.
Format
config terminal width [default | <value 80-200>]
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To configure the current terminal width:
18
Page 24

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config terminal width 120
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show terminal width
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: config terminal width 120
Success.
2-16 show terminal width
Description
The command is used to display the configuration of current terminal width.
Format
show terminal width
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the configuration of current terminal width:
Command: show terminal width
Global terminal width : 80
Current terminal width : 80
2-17 config ports
Description
This command is used to configure the Switch's port settings.
Format
config ports [<portlist> | all] {medium_type [fiber | copper]} {speed [auto
{capability_advertised {10_half | 10_full | 100_half | 100_full | 1000_full}} | 10_half | 10_full |
100_half | 100_full | 1000_full {[master | slave]}] | auto_negotiation [restart_an |
remote_fault_advertised [disable | offline | link_fault | auto_negotiation_error]] |
flow_control [enable | disable] | learning [enable | disable] | state [enable | disable] | mdix
[auto | normal | cross] | [descripti o n <desc 1-32> | clear_description] |
auto_speed_downgrade [enable | disable]}
19
Page 25

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<portlist> - Enter a list of ports used here.
all - Specify that all the ports will be used for this configuration.
medium_type - (Optional) Specify the medium type while the configure ports are combo ports
copper - Specify that the medium type will be set to copper.
speed - (Optional) Specify the port speed of the specified ports .
slave - Specify that the port(s) will be set to slave.
auto_negotiation - Specify to configure the auto-negotiation method.
and link partners will be advertised at the next auto-negotiation.
flow_control - (Optional) You can turn on or turn off flow control on one or more ports. By set
disable - Specify that the flow control option will be disabled.
learning - (Optional) You can turn on or turn off MAC address learning on one or more ports.
disable - Specify that the learning option will be disabled.
state - (Optional) Enables or disables the specified port. If the specificed ports are in error-
disable - Specify that the port state will be disabled.
mdix - (Optional) The MDIX mode can be specified as auto, normal, and cross. If set to the
cross - Specify that the MDIX mode for the port will be set to cross.
description - (Optional) Specify the description of the port interface.
long.
clear_description - (Optional) Specify that the description field will be cleared.
Parameters
fiber - Specify that the medium type will be set to fiber.
auto - Set port speed to auto negotiation.
capability_advertised - (Optional) Specify that the capability will be advertised.
10_half - (Optional) Set port speed to 10_half.
10_full - (Optional) Set port speed to 10_full.
100_half - (Optional) Set port speed to 100_half.
100_full - (Optional) Set port speed to 100_full.
1000_full - (Optional) Set port speed to 1000_full.
10_half - Set port speed to 10_half.
10_full - Set port speed to 10_full.
100_half - Set port speed to 100_half.
100_full - Set port speed to 100_full.
1000_full - Set port speed to 1000_full. While set port speed to 1000_full. User should specify
master or slave mode for 1000BASE-T interface, and leave the 1000_full without any
master or slave setting for other interface.
master - Specify that the port(s) will be set to master.
restart_an - Specify to restart auto-negoti ati on proc es s.
remote_fault_advertised – Specify that the fault conditions will be remotely advertised when
the next auto-negotiation process takes place.
disable - Remote fault advertisement is disabled.
offline - Local devices that were powered off or removed from the active configuration will
be advertised at the next auto-negotiation.
link_fault - Local devices that disconnected due to link failure will be advertised at the next
auto-negotiation.
auto_negotiation_error - The resolution that precludes operatio n bet ween loc al dev ic es
flow_control to enable or disable.
enable - Specify that the flow control option will be enabled.
enable - Specify that the learning option will be enabled.
disabled status , configure their state to enable will recover these ports from disabled to
enable state.
enable - Specify that the port state will be enabled.
normal state, the port is in the MDIX mode and can be connected to PC NIC using a straight
cable. If set to cross state, the port is in mdi mode, and can be connected to a port (in mdix
mode) on another switch thru a straight cable.
auto - Specify that the MDIX mode for the port will be set to auto.
normal - Specify that the MDIX mode for the port will be set to normal.
<desc 1-32> - Enter the port interface description here. This value can be up to 32 characters
20
Page 26
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
auto_speed_downgrade - (Optional) Specify whether to automatically downgrade the advertised
disable - Disable the automatically downgrading advertised speed.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config ports all medium_type copper speed auto
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<portlist> - (Optional) Enter the list of ports to be configured here.
description - (Optional) Indicates if port description will be included in the display.
err_disabled - (Optional) Displays ports that were disabled because of an error condidtion.
auto_negotiation - (Opt ional) Displays detailed auto-negotiation information.
details - (Optional) Displays the port details.
media_type - (Optional) Displays port transceiver type.
speed when a link cannot be established at the available speed.
enable - Enable the automatically downgrading advertised speed.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the ports:
Command: config ports all medium_type copper speed auto
Success.
2-18 show ports
Description
This command is used to display the current configurations of a range of ports.
Format
show ports {<portlist>} {[description | err_disabled | auto_negotiation | details | media_type]}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the port details:
21
Page 27

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show ports details
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
Command: show ports details
Port : 1:1
-------------------Port Status : Link Down
Description :
HardWare Type : Gigabits Ethernet
MAC Address : 00-01-02-03-04-10
Bandwidth : 1000000Kbit
Auto-Negotiation : Enabled
Duplex Mode : Full Duplex
Flow Control : Disabled
MDI : Auto
Address Learning : Enabled
Last Clear of Counter : 0 hours 10 mins ago
BPDU Hardware Filtering Mode: Disabled
Queuing Strategy : FIFO
TX Load : 0/100, 0 bits/sec, 0
packets/sec
RX Load : 0/100, 0 bits/sec, 0
packets/sec
22
Page 28

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
create vlan <vlan_name 32> tag <vlanid 2-4094> {type [1q_vlan | private_vlan]} {advertisement}
create vlan vlanid <vidlist> {type [1q_vlan | private_vlan]} {advertisement}
delete vlan <vlan_name 32>
delete vlan vlanid <vidlist>
config vlan <vlan_name 32> {[add [tagged | untagge d | forbidde n] | delete] <p ortlist> |
advertisement [enable | disable]}(1)
config vlan vlanid <vidlist> {[add [tagged | untagged | forbidden] | delete] <portlist> |
advertisement [enable | disable] | name <vlan_name 32>}(1)
config port_vlan [<portlist> | all] {gvrp_state [enable | disable] | ingress _c hec k ing [enabl e |
disable] | acceptable_fr am e [tagged _on l y | admit_al l] | pvid <vla nid 1-4094>}(1)
show vlan {<vlan_name 32>}
show vlan ports {<portlist>}
show vlan vlanid <vidlist>
show port_vlan {<portlist>}
enable pvid auto_assign
disable pvid auto_assign
show pvid auto_assign
config gvrp [timer [join | leave | leaveall] < value 100-100000> | nni_bpdu_addr [dot1d | dot1ad]]
show gvrp
enable gvrp
disable gvrp
config private_vlan [<vlan_name 32> | vid <vlanid 2-4094>] [add [isolated | community] | remove]
[<vlan_name 32> | vlanid <vidlis t>]
show private_vlan {[<vlan_name 32> | vlanid<vidlist>]}
<vlan_name 32> - Enter the VLAN name to be created. The VLAN name can be up to 32
characters long.
tag - The VLAN ID of the VLAN to be created.
<vlanid 2-4094> - Enter the VLAN ID here. The VLAN ID value must be between 2 and 4094.
type - (Optional) Specify the type of VLAN here.
private_vlan – (Option al) Spec ify that the private VLAN type will be used.
advertisement - (Optional) Specify the VLAN as being able to be advertised out.
Chapter 3
802.1Q VLAN Command List
3-1 create vlan
Description
This command is used to create a VLAN on the Switch. The VLAN ID must be always specified for
creating a VLAN.
Format
create vlan <vlan_name 32> tag <vlanid 2-4094> {type [1q_vlan | private_vlan]}
{advertisement}
Parameters
1q_vlan - (Optional) Specify that the type of VLAN used is based on the 802.1Q standard.
23
Page 29
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# create vlan v2 tag 2 type 1q_vlan advertisement
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
vlanid - The VLAN ID list to be created.
<vidlist> - Enter the VLAN ID list here.
type - (Optional) Specify the type of VLAN to be created.
private_vlan – (Optional) Specify that the private VLAN type will be used.
advertisement - (Optional) Specify the VLAN as being able to be advertised out.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# create vlan vlanid 10-30
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a VLAN with name “v2” and VLAN ID 2:
Command: create vlan v2 tag 2 type 1q_vlan advertisement
Success.
3-2 create vlan vlanid
Description
This command is used to create more than one VLANs at a time. A unique VLAN name (e.g.
VLAN10) will be automatically assigned by the system. The automatic assignment of VLAN name
is based on the following rule: “VLAN”+ID. For example, for VLAN ID 100, the VLAN name will be
VLAN100. If this VLAN name is conflict with the name of an existing VLAN, then it will be renamed
based on the following rule: “VLAN”+ID+”ALT”+ collision count. For example, if this conflict is the
second collision, then the name will be VLAN100ALT2.
Format
create vlan vlanid <vidlist> {type [1q_vlan | private_vlan]} {advertisement}
Parameters
1q_vlan - (Optional) Specify that the VLAN created will be a 1Q VLAN.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To create some VLANs using VLAN ID:
Command: create vlan vlanid 10-30
Success.
24
Page 30
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
vlan - The VLAN name of the VLAN to be deleted.
<vlan_name 32> - Enter the VLAN name here. This name can be up to 32 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# delete vlan v1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
vlanid - The VLAN ID list to be deleted.
<vidlist> - Enter the VLAN ID list here.
3-3 delete vlan
Description
This command is used to delete a previously configured VLAN by the name on the Switch.
Format
delete vlan <vlan_name 32>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To remove a vlan v1:
Command: delete vlan v1
Success.
3-4 delete vlan vlanid
Description
This command is used to delete one or a number of previously configured VLAN by VID list.
Format
delete vlan vlanid <vidlist>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
25
Page 31

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# delete vlan vlanid 10-30
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<vlan_name 32> - Enter the VLAN name you want to add ports to. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
add - (Optional) Specify to add tagged, untagged or forbidden ports to the VLAN.
forbidden - Specify the additional ports as forbidden.
delete - (Optional) Specify to delete ports from the VLAN.
<portlist> - (Optional) Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
advertisement - (Optional) Specify the GVRP state of this VLAN.
disable - Specify to disable advertisement for this VLAN.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config vlan v1 add tagged 2:4-2:8
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Example
To remove VLANs from 10-30:
Command: delete vlan vlanid 10-30
Success.
3-5 config vlan
Description
This command is used to configure a VLAN based on the name.
Format
config vlan <vlan_name 32> {[add [tagged | untagged | forbidden] | delete] <portlist> |
advertisement [enable | disable]}(1)
Parameters
tagged - Specify the additional ports as tagged.
untagged - Specify the additional ports as untagged.
enable - Specify to enable advertisement for this VLAN.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To add 4 through 8 of unit 2 as tagged ports to the VLAN v1:
Command: config vlan v1 add tagged 2:4-2:8
Success.
26
Page 32

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<vidlist> - Enter a list of VLAN IDs to configure.
add - (Optional) Specify to add tagged, untagged or forbidden ports to the VLAN.
forbidden - Specify the additional ports as forbidden.
delete - (Optional) Specify to delete ports from the VLAN.
<portlist> - (Optional) Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
advertisement - (Optional) Specify the GVRP state of this VLAN.
disable - Specify to disable advertisement for this VLAN.
name - (Optional) The new name of the VLAN.
<vlan_name 32> - Enter the VLAN name here. This name can be up to 32 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config vlan vlanid 10-20 add tagged 2:4-2:8
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
3-6 config vlan vlanid
Description
This command allows you to configure multiple VLANs at one time. But conflicts will be generated
if you configure the name of multiple VLANs at one time.
Format
config vlan vlanid <vidlist> {[add [tagged | untagged | forbidden] | delete] <portlist> |
advertisement [enable | disable] | name <vlan_name 32>}(1)
Parameters
tagged - Specify the additional ports as tagged.
untagged - Specify the additional ports as untagged.
enable - Specify to enable advertisement for this VLAN.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To add 4 through 8 of unit 2 as tagged ports to the VLAN ID from 10-20:
Command: config vlan vlanid 10-20 add tagged 2:4-2:8
Success.
3-7 config port_vlan
Description
This command is used to set the ingress checking status, the sending and receiving GVRP
information.
Format
config port_vlan [<portlist> | all] {gvrp_state [enable | disable] | ingress_checking [enable |
disable] | acceptable_frame [tagged_only | admit_all] | pvid <vlanid 1-4094>}(1)
27
Page 33

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<portlist> - A range of ports for which you want ingress checking. The port list is specified by
numerical order.
all - Specify that all the port will be used for this configuration.
gvrp_state - (Optional) Enabled or disables GVRP for the ports specified in the port list.
disable - Specify that GVRP for the specified ports will be disabled.
ingress_checking - (O pt io nal) Ena bl es or disables ingress checking for the specified portlist.
disable - Specify that ingress checking will be disabled for the specified portlist.
acceptable_frame - (Optional) The type of frame will be accepted by the port. There are two
admit_all - All packets can be accepted.
pvid - (Optional) Specify the PVID of the ports.
<vlanid 1-4094> - Enter the VLAN ID here. The VLAN ID value must be between 1 and 4094.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config port_vlan 1:1-1:5 gvrp_state enable
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<vlan_name 32> - (Optional) Enter the VLAN name to be displayed. The VLAN name can be up
to 32 characters long.
Parameters
listing the lowest switch number and the beginning port number on that switch, separated by a
colon. Then highest switch number, and the highest port number of the range (also separated
by a colon) are specified. The beginning and end of the port list range are separated by a
dash. For example, 1:3 would specify switch number 1, port 3. 2:4 specifies switch number 2,
port 4. 1:3-2:4 specifies all of the ports between switch 1, port 3 and switch 2, port 4 − in
enable - Specify that GVRP for the specified ports will be enabled.
enable - Specify that ingress checking will be enabled for the specified portlist.
types:
tagged_only - Only tagged packets can be accepted by this port.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To sets the ingress checking status, the sending and receiving GVRP information:
ingress_checking enable acceptable_frame tagged_only pvid 2
Command: config port_vlan 1:1-1:5 gvrp_state enable ingress_checking enable
acceptable_frame tagged_only pvid 2
Success
3-8 show vlan
Description
This command is used to display the vlan information including of parameters setting and
operational value.
Format
show vlan {<vlan_name 32>}
Parameters
28
Page 34

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show vlan
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<portlist> - (Optional) Enter the list of ports for which the VLAN information will be displayed.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display VLAN settings:
Command: show vlan
VLAN Trunk State : Disabled
VLAN Trunk Member Ports :
VID : 1 VLAN Name : default
VLAN Type : Static Advertisement : Enabled
Member Ports : 1:1-1:24
Static Ports : 1:1-1:24
Current Tagged Ports :
Current Untagged Ports: 1:1-1:24
Static Tagged Ports :
Static Untagged Ports : 1:1-1:24
Forbidden Ports :
Total Static VLAN Entries: 1
Total GVRP VLAN Entries: 0
3-9 show vlan ports
Description
This command is used to display the vlan information per ports.
Format
show vlan ports {<portlist>}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the VLAN configuration for port 6 of unit 1:
29
Page 35

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show vlan ports 1:6
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<vidlist> - Enter the VLAN ID to be displayed.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show vlan vlanid 1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: show vlan ports 1:6
Port VID Untagged Tagged Dynamic Forbidden
----- ---- -------- ------ ------- -------- 1:6 1 X - - -
3-10 show vlan vlanid
Description
This command is used to display the vlan information using the VLAN ID.
Format
show vlan vlanid <vidlist>
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the VLAN configuration for VLAN ID 1:
Command: show vlan vlanid 1
VID : 1 VLAN Name : default
VLAN Type : Static Advertisement : Enabled
Member Ports : 1:1-1:24
Static Ports : 1:1-1:24
Current Tagged Ports :
Current Untagged Ports: 1:1-1:24
Static Tagged Ports :
Static Untagged Ports : 1:1-1:24
Forbidden Ports :
Total Entries : 1
30
Page 36

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<portlist> - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
If no parameter specified, system will display all ports gvrp information.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show port_vlan
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
3-11 show port_vlan
Description
This command is used to display the ports’ VLAN attributes on the Switch.
Format
show port_vlan {<portlist>}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display 802.1Q port setting:
Command: show port_vlan
Port PVID GVRP Ingress Checking Acceptable Frame Type
------- ---- -------- ---------------- -------------------------- 1:1 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:2 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:3 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:4 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:5 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:6 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:7 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:8 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:9 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:10 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:11 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:12 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:13 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:14 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:15 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:16 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:17 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:18 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:19 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
1:20 1 Disabled Enabled All Frames
31
Page 37

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# enable pvid auto_assign
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
3-12 enable pvid auto assign
Description
This command is used to enable the auto-assignment of PVID.
If “Auto-assign PVID” is enabled, PV ID w ill be possi bl y changed by PVID or VLAN configuration.
When user configures a port to VLAN X’s untagged membership, this port’s PVID will be updated
with VLAN X. In the form of VLAN list command, PVID is updated with last item of VLAN list. When
user removes a port from the untagged membership of the PVID’s VLAN, the port’s PVID will be
assigned with “default VLAN” .
The default setting is enabled.
Format
enable pvid auto_assign
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable the auto-as s ig n PVID:
Command: enable pvid auto_assign
Success.
3-13 disable pvid auto assign
Description
This command is used to disable auto assignment of PVID.
Format
disable pvid auto_assign
Parameters
None.
32
Page 38

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# disable pvid auto_assign
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show pvid auto_assign
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable the auto-as s ig n PVI D:
Command: disable pvid auto_assign
Success.
3-14 show pvid auto_assign
Description
This command is used to display the PVID auto-assignment state.
Format
show pvid auto_assign
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display PVID auto-assignment state:
Command: show pvid auto_assign
PVID Auto-assignment: Enabled
3-15 config gvrp
Description
The config gvrp timer command set the GVRP timer’s value. The default value for Join time is 200
milliseconds; for Leave time is 600 milliseconds; for LeaveAll time is 10000 milliseconds.
33
Page 39

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
timer - Specify that the GVRP timer parameter will be configured.
join - (Optional) Specify the Join time will be set.
leave - (Optional) Specify the Leave time will be set.
leaveall - (Optional) Sp ecif y the Lea veA ll tim e will be set.
<value 100-100000> - Enter the time used here. This value must be between 100 and 100000.
nni_bpdu_addr - Used to determine the BPDU protocol address for GVRP in service provide
dot1ad - Specify that the NNI BPDU protocol address value will be set to Dot1ad.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config gvrp timer join 200
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Format
config gvrp [timer [join | leave | leaveall] < value 100-100000> | nni_bpdu_addr [dot1d |
dot1ad]]
Parameters
site. It can use 802.1d GVRP address, 802.1ad service provider GVRP address or a user
defined multicast address.
dot1d - Specify that the NNI BPDU protocol address value will be set to Dot1d.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To set the Join time to 200 milliseconds:
Command: config gvrp timer join 200
Success.
3-16 show gvrp
Description
This command is used to display the GVRP global setting.
Format
show gvrp
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
34
Page 40

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show gvrp
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# enable gvrp
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Example
To display the global setting of GVRP:
Command: show gvrp
Global GVRP : Disabled
Join Time : 200 Milliseconds
Leave Time : 600 Milliseconds
LeaveAll Time : 10000 Milliseconds
NNI BPDU Address: dot1d
3-17 enable gvrp
Description
This command is used to enable the Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP).
Format
enable gvrp
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable the generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP):
Command: enable gvrp
Success.
3-18 disable gvrp
Description
This command is used to disable the Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP).
Format
disable gvrp
35
Page 41

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# disable gvrp
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<vlan_name 32> - Specify the name of the private VLAN.
vid - Specify the VLAN ID of the private VLAN.
<vlanid 2-4094> - Enter the VLAN ID used here. This value must be between 2 and 4094.
add - Specify that a secondary VLAN will be added to the private VLAN.
community - Specify the secondary VLAN as community VLAN.
remove - Specify that a secondary VLAN will be removed from the private VLAN.
<vlan_name 32> - Specify the secondary VLAN name used. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
vlanid - A range of secondary VLAN to add or remove to the private VLAN.
<vidlist> - Enter the secondary VLAN ID used here.
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable the Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP):
Command: disable gvrp
Success.
3-19 config private_vlan
Description
This command is used to add or remove a secondary VLAN from a private VLAN.
Format
config private_vlan [<vlan_name 32> | vid <vlanid 2-4094>] [add [isolated | community] |
remove] [<vlan_name 32> | vlanid <vidlist>]
Parameters
isolated - Specify the secondary VLAN as isolated VLAN.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To associate secondary vlan to private v lan p1:
36
Page 42

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config private_vlan p1 add community vlanid 2-5
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<vlan_name 32> - (Optional) Specify the name of the private VLAN or its secondary VLAN. This
name can be up to 32 characters long.
vlanid - (Optional) Specif y the VLAN ID of the privat e VLAN or its second ary VLAN.
<vidlist> - Enter the VLAN ID used here.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show private_vlan
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: config private_vlan p1 add community vlanid 2-5
Success.
3-20 show private vlan
Description
This command is used to show the private VLAN information.
Format
show private_vlan {[<vlan_name 32> | vlanid<vidlist>]}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display private VLAN settings:
Command: show private_vlan
Private VLAN 100
----------------- Promiscuous Ports: 1:1
Trunk Ports : 1:2
Isolated Ports : 1:3-1:5 Isolated VLAN : 20
Community Ports : 1:6–1:8 Community VLAN: 30
Community Ports: : 1:9–1:10 Community VLAN: 40
Private VLAN 200
----------------- Promiscuous Ports: 1:11
Trunk Ports : 1:12
Isolated Ports : 1:13-1:15 Isolated VLAN : 20
Community Ports : 1:16–1:18 Community VLAN: 30
37
Page 43

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
enable 802.1x
disable 802.1x
create 802.1x user <username 15>
delete 802.1x user <username 15>
show 802.1x user
config 802.1x auth_protocol [local | radius_eap]
config 802.1x fwd_pdu system [enable | disable]
config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports [<portlist> | all] [enable | disable]
config 802.1x authorization attributes radius [enable | disable]
show 802.1x {[auth_state | auth_configuration] ports {<portlist>}}
config 802.1x capability ports [<portlist> | all] [authenticator | none]
config 802.1x max_users [<value 1–448> | no_limit]
config 802.1x auth_parameter ports [<portlist> | all] [default | {direction [both | in] | port_control
| disable]}(1)]
config 802.1x auth_mode [port_based | mac_based]
config 802.1x init [port_based ports [<portlist> | all] | mac_based ports [<portlist> | all]
{mac_address <macaddr>}]
config 802.1x reauth [port_based ports [<portlist> | all] | mac_based ports [<portlist> | all]
{mac_address <macaddr>}]
create 802.1x guest_vlan <vlan_name 32>
delete 802.1x guest_vlan <vlan_name 32>
config 802.1x guest_vlan ports [<portlist> | all] state [enable | disable]
show 802.1x guest_vlan
config 802.1x trap state [enable | disable]
config radius add <server_index 1-3> [<server_i p> | <ipv6ad dr >] [ke y <pass wor d 32> |
<udp_port_number 1-65535 > | timeout <sec 1-255> | retransmit<int 1-20>}(1)]
config radius delete <server_index 1-3>
config radius <server_index 1-3> {ipaddress [ <server_ip> | <ipv6addr>] | [key <password 32 > |
[<int 1-20> | default]}(1)
show radius
show auth_statistics {ports <portlist>}
show auth_diagnostics {ports <portlist>}
show auth_session_statistics {ports <portlist>}
show auth_client
show acct_client
Chapter 4
[force_unauth | auto | force_auth] | quiet_period <sec 0-655 35 > | tx_period <sec 1-65535> |
supp_timeout <sec 1-65535> | server_timeout <sec 1-65535> | max_req <value 1-10> |
reauth_period <sec 1-65535> | max_users [<value 1-448> | no_limit] | enable_re a ut h [ena ble
802.1X Command List
encryption_key <password 56>] [default | {auth_port <udp_port_number 1-65535 > | acct_port
encryption_key <password 56>] | auth_port [<udp_port_number 1-65535 > | default] |
acct_port [<udp_port_number 1-65535> | default] | timeout [<sec 1-255> | default] | retransmit
4-1 enable 802.1x
Description
This command is used to enable the 802.1X function.
Format
enable 802.1x
38
Page 44

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# enable 802.1x
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# disable 802.1x
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
Used to enable the 802.1X function:
Command: enable 802.1x
Success.
4-2 dis able 802.1x
Description
This command is used to disable the 802.1X function.
Format
disable 802.1x
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable the 802.1X function:
Command: disable 802.1x
Success.
39
Page 45

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<username 15> - Enter the username to be added. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#create 802.1x user test
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<username 15> - Enter the username to be deleted. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
4-3 create 802.1x user
Description
This command is used to create an 802.1X user.
Format
create 802.1x user <username 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a 802.1x user “test”:
Command: create 802.1x user test
Enter a case-sensitive new password:****
Enter the new password again for confirmation:****
Success.
4-4 delete 802.1x user
Description
This command is used to delete an 802.1X user.
Format
delete 802.1x user <username 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete user “test”:
40
Page 46

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#delete 802.1x user test
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show 802.1x user
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: delete 802.1x user test
Success.
4-5 show 802.1x user
Description
This command is used to display the 802.1X user.
Format
show 802.1x user
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the 802.1X user information:
Command: show 802.1x user
Current Accounts:
Username Password
--------------- -------------- test test
Total Entries:1
4-6 config 802.1x auth_protocol
Description
This command is used to configure the 802.1X authentication protocol.
Format
config 802.1x auth_protocol [l o cal | radius_eap]
41
Page 47

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
local - Specify the authenti c ation protocol as local.
radius_eap - Specify the authentication protocol as RADIUS EAP.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config 802.1x auth_protocol radius_eap
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
enable - Enable the forwarding of EAPOL PDU.
disable - Disable the forwarding of EAPOL PDU.
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the 802.1X authentication protocol to RADIUS EAP:
Command: config 802.1x auth_protocol radius_eap
Success.
4-7 config 802.1x fwd_pdu system
Description
This command is used to globally control the forwarding of EAPOL PDU. When 802.1X
functionality is disabled globally or for a port, and if 802.1X fwd_pdu is enabled both globally and
for the port, a received EAPOL packet on the port will be flooded in the same VLAN to those ports
for which 802.1X fwd_pdu is enabled and 802.1X is disabled (globally or just for the port). The
default state is disabled.
Format
config 802.1x fwd_pdu system [enable | disable]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure forwarding of EAPOL PDU system state enable:
42
Page 48

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config 802.1x fwd_pdu system enable
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration.
all - Specify that all the ports will be used.
enable - Enable forwarding EAPOL PDU receive on the ports.
disable - Disable forwarding EAPOL PDU receive on the ports.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports 1:1-1:2 enable
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: config 802.1x fwd_pdu system enable
Success.
4-8 config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports
Description
This command is used to control the forwarding of EAPOL PDU. When 802.1X functionality is
disabled globally or for a port, and if 802.1X fwd_pdu is enabled both globally and for the port, a
received EAPOL packet on the port will be flooded in the same VLAN to those ports for which
802.1X fwd_pdu is enabled and 802.1X is disabled (globally or just for the port). The default state
is disabled.
Format
config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports [<portlist> | all] [enable | disable]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure 802.1X fwd_pdu for ports:
Command: config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports 1:1-1:2 enable
Success.
4-9 config 802.1x authorization attributes
Description
This command is used to enable or disable acception of authorized configuration.
When the authorization is enabled for 802.1X’s RADIUS authentication, the authorized attributes
(for example VLAN, 802.1p default priority, and ACL) assigned by the RADUIS server will be
accepted if the global authorization status is enabled.
43
Page 49

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
radius - If specified to enable, the authorization attributes (for example VLAN, 802.1p default
disable - Specify to disable the authorization attributes.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config 802.1x authorization attributes radius disable
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
auth_state - (Optional) Used to display 802.1X authentication state machine of some or all ports
auth_configuration - (Optional) Used to display 802.1X configurations of some or all ports.
port - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed. If no port is specified, all ports will be
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
If no parameter is specified, the 802.1X system configurations will be displayed.
Format
config 802.1x authorization attributes radius [enable | disable]
Parameters
priority, and ACL) assigned by the RADUIS server will be accepted if the global authorization
status is enabled. The default state is enabled.
enable - Specif y to enable the authorization attributes.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
The following exam ple w ill dis ab le t o acc ept t he a uthorized data assigned fr om the RADIUS server:
Command: config 802.1x authorization attributes radius disable
Success.
4-10 show 802.1x
Description
This command is used to display the 802.1X state or configurations.
Format
show 802.1x {[auth_state | auth_configuration] ports {<portlist>}}
Parameters
displayed.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the 802.1X port level configurations:
44
Page 50

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show 802.1x auth_configuration ports 1:1
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
ports - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
all - Specify all ports to be configured.
authenticator - Specify the port that will enforce authentication before allowing access to
services that are accessible from that port. This port will adopt the authenticator role.
none - Disable authentication on the specified ports.
Command: show 802.1x auth_configuration ports 1:1
Port Number : 1:1
Capability : None
AdminCrlDir : Both
OpenCrlDir : Both
Port Control : Auto
QuietPeriod : 60 sec
TxPeriod : 30 sec
SuppTimeout : 30 sec
ServerTimeout : 30 sec
MaxReq : 2 times
ReAuthPeriod : 3600 sec
ReAuthenticate : Disabled
Forward EAPOL PDU On Port : Enabled
Max User On Port : 16
4-11 config 802.1x capability
Description
This command is used to configure the port capability.
Format
config 802.1x capability ports [< p o rtlist> | all] [authenticator | none]
Parameters
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
45
Page 51

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config 802.1x capability ports 1:1-1:10 authenticator
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<value 1-448> - Enter the maximum number of users. This value must be between 1 and 448.
no_limit – Specify that the maximum user limit will be set to 448.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config 802.1x max_users 200
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Example
To configure the port capability:
Command: config 802.1x capability ports 1:1-1:10 authenticator
Success.
4-12 config 802.1x max_users
Description
This command is used to limit the maximum number of users that can be learned via 802.1X
authentication. In addition to the global limitation, maximum user for per port is also limited. It is
specified by config 802.1x auth_parameter command.
Format
config 802.1x max_users [<value 1–448> | no_limit]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure 802.1X number of users to be limited to 200:
Command: config 802.1x max_users 200
Success.
4-13 config 802.1x auth_parameter
Description
This command is used to configure the parameters that control the operation of the authenticator
associated with a port.
46
Page 52

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
ports - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
all - Specify that all the ports will be used.
default - Sets all parameter to be default value.
direction - (Optional) Sets the direction of access control.
in - For unidirectional access control.
port_control - (Optional) You can force a specific port to be unconditionally authorized or
force_auth - Force a specific port to be unconditionally authorized.
quiet_period - (Optional) It is the initialization value of the quietWhile timer. The default value is
seconds.
tx_period - (Optional) It is the initialization value of the transmit timer period. The default value is
seconds.
supp_timeout - (Optional) The initialization value of the aWhile timer when timing out the
65535 seconds.
server_timeout - (Optional) The initialization value of the aWhile timer when timing out the
65535 seconds.
max_req - (Optional) The maximum number of times that the authentication PAE state machine
10.
reauth_period - (Optional) It’s a nonzero number of seconds, which is used to be the re-
and 65535 seconds.
enable_reauth - (Optional) You can enable or disable the re-authentication mechanism for a
disable - Specify to disable the re-authentication mechanism for a specific port.
max_users - (Optional) Specify per port maximum number of users. The default value is 16.
no_limit - Specify that no limit is enforced on the maximum users used.
Format
config 802.1x auth_parameter ports [<portlist> | all] [default | {direction [both | in] |
port_control [force_unauth | auto | force_auth] | quiet_period <sec 0-65535> | tx_period
<sec 1-65535> | supp_timeout <sec 1-65535> | server_timeout <sec 1-65535> | max_req
<value 1-10> | reauth_period <sec 1-65535> | max_users [<value 1-448> | no_limit] |
enable_reauth [enable | disable]}(1)]
Parameters
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
both - For bidirectional access control.
unauthorized by setting the parameter of port_control to be force_authorized or
force_unauthorized. Besides, the controlled port will reflect the outcome of authentication if
port_control is auto.
force_unauth - Force a specific port to be unconditionally unauthorized.
auto - The controlled port will reflect the outcome of authentication.
60 seconds and can be any value among 0 to 65535.
<sec 0-65535> - Enter the quiet period value here. This value must be between 0 and 65535
30 seconds and can be any integer value among 1 to 65535.
<sec 1-65535> - Enter the tx period value here. This value must be between 1 and 65535
supplicant. Its default value is 30 seconds and can be any integer value among 1 to 65535.
<sec 1-65535> - Enter the supplicant timeout value here. This value must be between 1 and
authentication server. Its default value is 30 seconds and can be any integer value among 1 to
65535.
<sec 1-65535> - Enter the server timeout value here. This value must be between 1 and
will retransmit an EAP Request packet to the supplicant. Its default value is 2 and can be any
integer number among 1 to 10.
<value 1-10> - Enter the maximum required value here. This value must be between 1 and
authentication timer. The default value is 3600.
<sec 1-65535> - Enter the re-authentication period value here. This value must be between 1
specific port.
enable - Specify to enable the re-authentication mechanism for a specific port.
<value 1-448> - Enter the maximum users value here. This value must be between 1 and
448.
47
Page 53

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config 802.1x auth_parameter ports 1:1-1:20 direction
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
port_based - Configure the authentication as port based mode.
mac_based - Configure the authentication as MAC based mode.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config 802.1x auth_mode port_based
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the parameters that control the operation of the authenticator associated with a port:
both
Command: config 802.1x auth_parameter ports 1:1-1:20 direction both
Success.
4-14 config 802.1x auth_mode
Description
This command is used to configure 802.1X authentication mode.
Format
config 802.1x auth_mode [port_based | mac_based]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the authentication mode:
Command: config 802.1x auth_mode port_based
Success.
4-15 config 802.1x init
Description
This command is used to initialize the authentication state machine of some or all ports.
48
Page 54

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
port_based ports- Configure the authentication as port based mode.
all - Specify that all ports will be used.
mac_based ports - Configure the authentication as MAC based mode.
all - Specify that all ports will be used.
mac_address - (Optional) Specify the MAC address of client.
<macaddr> - Enter the MAC address used here.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config 802.1x init port_based ports all
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
port_based ports - Configure the authentication as port based mode.
all - Specify that all ports will be used.
mac_based ports - Configure the authentication as MAC based mode.
all - Specify that all ports will be used.
mac_address - (Optional) Specify the MAC address of client.
<macaddr> - Enter the MAC address used here.
Format
config 802.1x init [port_based ports [<portlist> | all] | mac_based ports [<portlist> | all]
{mac_address <macaddr >}]
Parameters
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To initialize the authentication state machine of some or all:
Command: config 802.1x init port_based ports all
Success.
4-16 config 802.1x reauth
Description
This command is used to re-authenticate the device connected to the port. During the reauthentication period, the port status remains authorized until failed re-authentication.
Format
config 802.1x reauth [port_based ports [<portlist> | all] | mac_based ports [<portlist> | all]
{mac_address <macaddr >}]
Parameters
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
49
Page 55

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config 802.1x reauth port_based ports all
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<vlan_name 32> - Specify the VLAN to be guest VLAN. The VLAN name can be up to 32
characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# create 802.1x guest_vlan guestVLAN
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To re-authenticate the device connected to the port:
Command: config 802.1x reauth port_based ports all
Success.
4-17 create 802.1x guest_vlan
Description
This command is used to assign a static VLAN to be guest VLAN. The specific VLAN which
assigned to guest VLAN must be existed. The specific VLAN which assigned to guest VLAN can’t
be deleting.
Format
create 802.1x guest_vlan <vlan_name 32>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a VLAN named “guestVLAN” as 802.1X guest VLAN:
Command: create 802.1x guest_vlan guestVLAN
Success.
4-18 delete 802.1x guest_vlan
Description
This command is used to delete guest VLAN setting, but not delete the static VLAN. All ports
which enabled guest VLAN will remove to original VLAN after deleted guest VLAN.
50
Page 56

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<vlan_name 32> - Enter the VLAN name here. The VLAN name can be up to 32 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# delete 802.1x guest_vlan guestVLAN
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
ports - A range of ports enable or disable guest VLAN function.
all - Specify that all the port will be included in this configuration.
state - Specify the guest VLAN port state of the configured ports.
disable - Specify to be removed from the guest VLAN.
Format
delete 802.1x guest_vlan <vlan_name 32>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete the guest VLAN named “guestVLAN”:
Command: delete 802.1x guest_vlan guestVLAN
Success.
4-19 config 802.1x guest_vlan
Description
This command is used to configure guest VLAN setting. If the specific port state is changed from
enabled state to disable state, this port will move to its original VLAN.
Format
config 802.1x guest_vlan ports [<po rtlist> | all] state [enable | disable]
Parameters
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports used for the configuration here.
enable - Specify to join the guest VLAN.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable from port 1:2 to 1:8 to configure 802.1X guest VLAN:
51
Page 57

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config 802.1x guest_vlan ports 1:2-1:8 state enable
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show 802.1x guest_vlan
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: config 802.1x guest_vlan ports 1:2-1:8 state enable
Warning, The ports are moved to Guest VLAN.
Success.
4-20 show 802.1x guest_vlan
Description
This command is used to show the information of guest VLANs.
Format
show 802.1x guest_vlan
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To show 802.1X guest VLAN on the Switch:
Command: show 802.1x guest_vlan
Guest VLAN Setting
----------------------------------------------------------Guest VLAN : guestVLAN
Enabled Guest VLAN Ports : 1:2-1:8
4-21 config 802.1x trap state
Description
This command is used to enable or disable the sending of 802.1X traps.
Format
config 802.1x trap state [enable | disable]
52
Page 58

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
enable - Specify to enable the sending of 802.1X traps.
disable - Specify to disable the sending of 802.1X traps.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config 802.1x trap state enable
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<server_index 1-3> - Enter the RADIUS server index. This value must be between 1 and 3.
<server_ip> - Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server here.
<ipv6addr> - Enter the IPv6 address of the RADIUS server here.
key - The key pre-negotiated between switch and the RADIUS server. It is used to encrypt user’s
<password 32> - Enter the password here. The password can be up to 32 characters long.
encryption_key - The key pre-negotiated between the Switch and the RADIUS server. It is used
bytes. The encryption algorithm is based on DES.
default - Sets the authentication UDP port number to 1812 accounting UDP port number to 1813,
timeout to 5 seconds and retransmit to 2.
auth_port - Specify the UDP port number which is used to transmit RADIUS authentication data
be between 1 and 65535.
acct_port - Specify the UDP port number which is used to transmit RADIUS accounting statistics
between the Switch and the RADIUS server. The range is 1 to 65535.
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
This example shows how to enable the trap state for 802.1X.
Command: config 802.1x trap state enable
Success.
4-22 config radius add
Description
This command is used to add a new RADIUS server. The server with lower index has higher
authenticative priorit y.
Format
config radius add <server_index 1-3> [<server_ip> | <ipv6addr>] [key <password 32> |
encryption_key <password 56>] [default | {auth_port <udp_port_number 1-65535 > |
acct_port <udp_port_number 1-65535 > | timeout <sec 1-255> | retransmit<int 1-20>}(1)]
Parameters
authentication data before being transmitted over internet. The maximum length of the key is
32.
to encrypt user’s authentication data before being transmitted over the Internet. The maximum
length of the key is 32.
<password 56> - The encrypted key string. The maximum length of the plain text key is 56
between the Switch and the RADIUS server. The range is 1 to 65535.
<udp_port_number 1-65535> - Enter the authentication port number here. This value must
53
Page 59

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<udp_port_number 1-65535> - Enter the accounting port number here. This value must be
between 1 and 65535.
timeout - The time in second for waiting server reply. The default value is 5 seconds.
<sec 1-255> - Enter the timeout value here. This value must be between 1 and 255 seconds.
retransmit - The count for re-transmitting. The default value is 2.
<int 1-20> - Enter the re-transmit value here. This value must be between 1 and 20.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config radius add 1 10.48.74.121 key dlink default
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<server_index 1-3> - Specify to delete a RADIUS server.Enter the RADIUS server index.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config radius delete 1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To add a new RADIUS server:
Command: config radius add 1 10.48.74.121 key dlink default
Success.
4-23 config radius delete
Description
This command is used to delete a RADIUS server.
Format
config radius delete <server_index 1-3>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete a radius server:
Command: config radius delete 1
Success.
54
Page 60

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<server_index 1-3> - Enter the RADIUS server index here. This value must be between 1 and 3.
ipaddress - The IP address of the RADIUS server.
<ipv6addr> - Enter the RADIUS server IPv6 address used here.
key - The key pre-negotiated between switch and RADIUS server. It is used to encrypt user’s
<password 32> - Enter the key here. The key can be up to 32 characters long.
encryption_key - The key pre-negotiated between the Switch and the RADIUS server. It is used
bytes. The encryption algorithm is based on DES.
auth_port - Specify the UDP port number which is used to transmit RADIUS authentication data
default - Specify that the default port number will be used.
acct_port - Specify the UDP port number which is used to transmit RADIUS accounting statistics
default - Specify that the default port number will be used.
timeout - The time in second for waiting server reply. The default value is 5 seconds.
default - Specify that the default timeout value will be used.
retransmit - The count f or re-transmitting. The default value is 2.
default - Specify that the default re-transmit value will be used.
4-24 config radius
Description
This command is used to configure a RADIUS server.
Format
config radius <server_index 1-3> {ipaddress [<server_ip> | <ipv6addr>] | [key <password
32> | encryption_key <password 56>] | auth_port [<udp_port_number 1-65535 > | default] |
acct_port [<udp_port_number 1-65535> | default] | timeout [<sec 1-255> | default] |
retransmit [<int 1-20> | default]}(1)
Parameters
<server_ip> - Enter the RADIUS server IP address here.
authentication data before being transmitted over internet. The maximum length of the key is
32.
to encrypt user’s authentication data before being transmitted over the Internet. The maximum
length of the key is 32.
<password 56> - The encrypted key string. The maximum length of the plain text key is 56
between the Switch and the RADIUS server. The range is 1 to 65535. The default value is
1812.
<udp_port_number 1-65535> - Enter the authentication port number here. This value must
be between 1 and 65535.
between the Switch and the RADIUS server. The range is 1 to 65535. The default value is
1813.
<udp_port_number 1-65535> - Enter the accounting port number here. This value must be
between 1 and 65535.
<sec 1-255> - Enter the timeout value here. This value must be between 1 and 255 seconds.
<int 1-20> - Enter the re-transmit value here. This value must be between 1 and 20.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a radius server:
55
Page 61

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config radius 1 auth_port 60
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show radius
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: config radius 1 auth_port 60
Success.
4-25 show radius
Description
This command is used to display RADIUS server configurations.
Format
show radius
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display RADIUS server configurations:
Command: show radius
Index 1
IP Address : 172.18.211.71
Auth-Port : 1812
Acct-Port : 1813
Timeout : 5 sec
Retransmit : 2
Key : 1234567
Index 2
IP Address : 172.18.211.108
Auth-Port : 1812
Acct-Port : 1813
Timeout : 5 sec
Retransmit : 2
Key : adfdslkfjefiefdkgjdassdwtgjk6y1w
Total Entries : 2
56
Page 62

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
ports - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports that will be displayed here.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show auth_statistics ports 1:1
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
4-26 show auth_statistics
Description
This command is used to display information of authenticator statistics.
Format
show auth_statistics {ports <por tlist>}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display authenticator statistics information for port 1:1:
Command: show auth_statistics ports 1:1
Port Number : 1:1
EapolFramesRx 0
EapolFramesTx 9
EapolStartFramesRx 0
EapolReqIdFramesTx 6
EapolLogoffFramesRx 0
EapolReqFramesTx 0
EapolRespIdFramesRx 0
EapolRespFramesRx 0
InvalidEapolFramesRx 0
EapLengthErrorFramesRx 0
LastEapolFrameVersion 0
LastEapolFrameSource 00-00-00-00-00-00
57
Page 63

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
ports - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports that will be displayed here.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show auth_diagnostics ports 1:1
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
4-27 show auth_diagnostics
Description
This command is used to display information of authenticator diagnostics.
Format
show auth_diagnostics {ports <portlist>}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display authenticator diagnostics information for port 1:1:
Command: show auth_diagnostics ports 1:1
Port Number : 1:1
EntersConnecting 11
EapLogoffsWhileConnecting 0
EntersAuthenticating 0
SuccessWhileAuthenticating 0
TimeoutsWhileAuthenticating 0
FailWhileAuthenticating 0
ReauthsWhileAuthenticating 0
EapStartsWhileAuthenticating 0
EapLogoffWhileAuthenticating 0
ReauthsWhileAuthenticated 0
EapStartsWhileAuthenticated 0
EapLogoffWhileAuthenticated 0
BackendResponses 0
BackendAccessChallenges 0
BackendOtherRequestsToSupplicant 0
BackendNonNakResponsesFromSupplicant 0
BackendAuthSuccesses 0
BackendAuthFails 0
58
Page 64

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
ports - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
<portlist> - Enter the list of ports that will be displayed here.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show auth_session_statistics ports 1:1
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
4-28 show auth_session_statistics
Description
This command is used to display information of authenticator session statistics.
Format
show auth_session_stat istics {p ort s <portl ist >}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display authenticator session statistics information for port 1:1:
Command: show auth_session_statistics ports 1:1
Port Number : 1:1
SessionOctetsRx 0
SessionOctetsTx 0
SessionFramesRx 0
SessionFramesTx 0
SessionId
SessionAuthenticMethod Remote Authentication Server
SessionTime 0
SessionTerminateCause SupplicantLogoff
SessionUserName
4-29 show auth_client
Description
This command is used to display information of RADIUS authentication client.
Format
show auth_client
Parameters
None.
59
Page 65

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show auth_client
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display authentication client information:
Command: show auth_client
radiusAuthClient ==>
radiusAuthClientInvalidServerAddresses 0
radiusAuthClientIdentifier D-Link
radiusAuthServerEntry ==>
radiusAuthServerIndex :3
radiusAuthServerAddress 0.0.0.0
radiusAuthClientServerPortNumber 0
radiusAuthClientRoundTripTime 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRequests 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRetransmissions 0
radiusAuthClientAccessAccepts 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRejects 0
radiusAuthClientAccessChallenges 0
radiusAuthClientMalformedAccessResponses 0
radiusAuthClientBadAuthenticators 0
radiusAuthClientPendingRequests 0
radiusAuthClientTimeouts 0
radiusAuthClientUnknownTypes 0
radiusAuthClientPacketsDropped 0
4-30 show acct_client
Description
This command is used to display information of RADIUS accounting client.
Format
show acct_client
Parameters
None.
60
Page 66

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show acct_client
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display information of RADIUS accounting client:
Command: show acct_client
radiusAcctClient ==>
radiusAcctClientInvalidServerAddresses 0
radiusAcctClientIdentifier D-Link
radiusAuthServerEntry ==>
radiusAccServerIndex : 1
radiusAccServerAddress 0.0.0.0
radiusAccClientServerPortNumber 0
radiusAccClientRoundTripTime 0
radiusAccClientRequests 0
radiusAccClientRetransmissions 0
radiusAccClientResponses 0
radiusAccClientMalformedResponses 0
radiusAccClientBadAuthenticators 0
radiusAccClientPendingRequests 0
radiusAccClientTimeouts 0
radiusAccClientUnknownTypes 0
radiusAccClientPacketsDropped 0
61
Page 67

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
enable authen_policy_en cryption
disable authen_policy_en cryption
enable password encryption
disable password encryption
enable authen_policy
disable authen_policy
show authen_policy
create authen_login method_list_name <string 15>
config authen_login [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+
| radius | server_group <string 15> | local | none}
delete authen_login method_list_name <string 15>
show authen_login [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
create authen_enable method_list_name <string 15>
config authen_enable [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs | xtacacs |
tacacs+ | radius | server_group <string 15> | loca l _en abl e | none}
delete authen_enable method_list_name <string 15>
show authen_enable [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
config authen application [console | telnet | ssh | http | all] [login | enable] [default |
method_list_name <string 15>]
show authen application
create authen server_group <string 15>
config authen server_group [tacac s | xtacacs | tacac s + | radius | <string 15>] [add | delet e]
server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius]
delete authen server_group <string 15>
show authen server_group {<string 15>}
create authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius] {port <int 1-
255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}
config authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius] {port <int 1-
255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}
delete authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius]
show authen server_host
config authen parameter response_ti m eout <int 0-255>
config authen parameter attempt <int 1-255>
show authen parameter
enable admin
config admin local_enable {encrypt [plain_text | sha_1] <password>}
create aaa server_group <string 15>
config aaa server_group [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius | group_name <string 15>] [add | de
lete] server_host <ipaddr> protoc ol [tacacs | xtacac s | tacacs + | radius]
delete aaa server_group <string 15>
show aaa server_group {<string 15>}
create accounting method_list_name <string 15>
config accounting [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs+ | radius |
server_group <string 15> | none}
delete accounting method_list_ n ame <string 15>
show accounting [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
config accounting service command {administrator | operator | power_user | user}
[method_list_name <string> | none]
Chapter 5
Access Authentication
Control Command List
65535> | [key [<key_string 254> | none] | encr yption_key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int 1-
65535> | [key [<key_string 254> | none] | encr yption_key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int 1-
62
Page 68

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
create radius server_host <ipaddr> {auth _port < int 1-65535> | acct_port <int 1-65535> | [key
retransmit <int 1-20>}
config radius server_host <ipaddr> {auth_port <int 1-65535> | acct_port <int 1-65535> | [key
retransmit <int 1-20>}
delete aaa server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+| radius]
show aaa server_host
create tacacs server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-
20>}
config tacacs server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-
20>}
create xtacacs server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-
20>}
config xtacacs server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-
20>}
create tacacs+ server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | [key [<key_string 254> | none] |
encryption_key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int 1-255>}
config tacacs+ server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | [key [<key_string 254> | none] |
encryption_key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int 1-255>}
enable aaa_server_pass word_encryption
disable aaa_server_pass word_encryption
show aaa
config accounting service [network | shell | system] state [enable {[radius_only |
method_list_name <strin g 15> | default_method_list]} | disable]
show accounting service
[<key_string 254> | none] | encryption_key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int 1-255> |
[<key_string 254> | none] | encryptio n_k ey <key_string 344>] | timeout <int 1-255> |
5-1 enable authen_policy_encryption
Description
This command is used to enable the authentication policy encryption. When enabled, TACACS+
and RADIUS key will be in the encrypted form.
Format
enable authen_policy_en cryption
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable the authentication policy encryption:
63
Page 69

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#enable authen_policy_encryption
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#disable authen_policy_encryption
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: enable authen_policy_encryption
Success.
5-2 dis able authen_policy_encryption
Description
This command is used to disable the authentication policy encryption. When disabled, TACACS+
and RADIUS key will be in the plain text form.
Format
disable authen_policy_en cryption
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable the authentication policy encryption:
Command: disable authen_policy_encryption
Success.
5-3 enable pas s word encryption
Description
This command is used to enable password encryption. The user account configuration information
will be stored in the configuration file, and can be applied to the system later.
If the password encryption is enabled, the password will be in encrypted form.
Format
enable password encryption
64
Page 70

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#enable password encryption
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#disable password encryption
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable the password encryption:
Command: enable password encryption
Success.
5-4 dis able password encryption
Description
This command is used to disable password encryption. The user account configuration information
will be stored in the configuration file, and can be applied to the system later.
When password encryption is disabled, if the user specifies the password in plain text form, the
password will be in plan text form. However, if the user specifies the password in encrypted form,
or if the password has been converted to encrypted form by the last enable password encryption
command, the password will still be in the encrypted form. It can not be reverted to the plaintext.
Format
disable password encryption
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable the password encryption:
Command: disable password encryption
Success.
65
Page 71

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# enable authen_policy
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
5-5 enable authen_policy
Description
This command is used to enable system access authentication policy.
Enable system access authentication policy. When authentication is enabled, the device will adopt
the login authentication method list to authenticate the user for login, and adopt the enable
authentication method list to authenticate the enable password for promoting the user‘s privilege to
Admin level.
Format
enable authen_policy
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable system access authentication policy:
Command: enable authen_policy
Success.
5-6 dis able authen_policy
Description
This command is used to disable system access authentication policy.
Disable system access authentication policy. When authentication is disabled, the device will
adopt the local user account database to authenticate the user for login, and adopt the local
enable password to authenticate the enable password for promoting the user‘s privilege to Admin
level.
Format
disable authen_policy
Parameters
None.
66
Page 72

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# disable authen_policy
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show authen_policy
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable system access authentication policy:
Command: disable authen_policy
Success.
5-7 show authen_policy
Description
This command is used to display that system access authentication policy is enabled or disabled.
Format
show authen_policy
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display system access authentication policy:
Command: show authen_policy
Authentication Policy : Enabled
Authentication Policy Encryption: Enabled
5-8 create authen_login
Description
This command is used to create a user-defined method list of authentication methods for user
login. The maximum supported number of the login method lists is 8.
67
Page 73

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<string 15> - The user-defined method list name. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# create authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
default - The default method list of authentication methods.
method_list_name - The user-defined method list of authentication methods.
<string 15> - Enter the method list name here. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
method - Specify the authentication method used.
Format
create authen_login method_list_name <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a user-defined method list for user login:
Command: create authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
Success.
5-9 config authen_login
Description
Configure a user-defined or default method list of authentication methods for user login. The
sequence of methods will effect the altercation result. For example, if the sequence is tacacs+ first,
then tacacs and local, when user trys to login, the authentication request will be sent to the first
server host in tacacs+ built-in server group. If the first server host in tacacs+ group is missing, the
authentication request will be sent to the second server host in tacacs+ group, and so on. If all
server hosts in tacacs+ group are missing, the authentication request will be sent to the first server
host in tacacs group…If all server hosts in tacacs group are missing, the local account database in
the device is used to authenticate this user. When user logins the device success full y while us ing
methods like tacacs/xtacacs/tacacs+/radius built-in or user-defined server groups or none, the
“user” privilege level is assigned only. If user wants to get admin privilege level, user must use the
“enable admin” command to promote his privilege level. But when local method is used, the
privilege level will depend on this account privilege level stored in the local device.
Format
config authen_login [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs | xtacacs |
tacacs+ | radius | server_group <string 15> | local | none}
Parameters
68
Page 74

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
tacacs - (Optional) Specify to authenticate by using the built-in server group called “tacacs”.
none - (Optional) No authentication.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config authen_login method_list_name login_list_1 method
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<string 15> - The user-defined method list name. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# delete authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
xtacacs - (Optional) Specify to authenticate by using the built-in server group called “xtacacs”.
tacacs+ - (Optional) Specify to authenticate by using the built-in server group called “tacacs+”.
radius - (Optional) Specify to authenticate by using the built-in server group called “radius”.
server_group - (Optional) Specify to authenticat e b y the user-defined server group.
<string 15> - Enter the server group value here. This value can be up 15 characters long.
local - (Optional) Specify to authenticate by local user account database in device.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a user-defined method list for user login:
tacacs+ tacacs local
Command: config authen_login method_list_name login_list_1 method tacacs+
tacacs local
Success.
5-10 delete authen_login
Description
This command is used to delete a user-defined method list of authentication methods for user login.
Format
delete authen_login method_list_name <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete a user-defined method list for user login:
Command: delete authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
Success.
69
Page 75

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
default - Display default user-defined method list for user login.
method_list_name - Display the specific user-defined method list for user login.
<string 15> - Enter the method list name here. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
all - Display all method lists for user login.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<string 15> - The user-defined method list name. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
5-11 show authen_login
Description
This command is used to display the method list of authentication methods for user login.
Format
show authen_login [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display a user-defined method list for user login:
Command: show authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
Method List Name Priority Method Name Comment
---------------- -------- --------------- -----------------login_list_1 1 tacacs+ Built-in Group
2 tacacs Built-in Group
3 mix_1 User-defined Group
4 local Keyword
5-12 create authen_enable
Description
This command is used to create a user-defined method list of authentication methods for
promoting user's privilege to Admin level.
Format
create authen_enable method_list_name <string 15>
Parameters
70
Page 76

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# create authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
default - The default method list of authentication methods.
method_list_name - The user-defined method list of authentication methods.
<string 15> Enter the method list name here. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
method - Specify the authentication method used.
none - (Optional) No authentication.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a user-defined method list for promoting user's privilege to Admin level:
Command: create authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
Success.
5-13 config authen_enable
Description
This command is used to configure a user-defined or default method list of authentication methods
for promoting user's privilege to Admin level. The sequence of methods will affect the altercation
result. For example, if the sequence is tacacs+ first, then tacacs and local_enable, when user try
to promote user's privilege to Admin level, the authentication request will be sent to the first server
host in tacacs+ built-in server group. If the first server host in tacacs+ group is missing, the
authentication request will be sent to the second server host in tacacs+ group, and so on. If all
server hosts in tacacs+ group are missing, the authentication request will be sent to the first server
host in tacacs group…If all server hosts in tacacs group are missing, the local enable password in
the device is used to authenticate this user’s password.
Format
config authen_enable [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs | xtacacs |
tacacs+ | radius | server_group <string 15> | local _enable | none}
Parameters
tacacs - (Optional) Authentication by the built-in server group “tacacs”.
xtacacs - (Optional) Authentication by the built-in server group “xtacacs”.
tacacs+ - (Optional) Authentication by the built-in server group “tacacs+”.
radius - (Optional) Authentication by the built-in server group “radius”.
server_group - (Opti ona l) Auth ent ic ati on b y the user-defined server group.
<string 15> - Enter the server group name here. This value can be up to 15 characters
long.
local_enable - (Optional) Authentication by local enable password in device.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
71
Page 77

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1 method
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<string 15> - The user-defined method list name. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# delete authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Example
To configure a user-defined method list for promoting user's privilege to Admin level:
tacacs+ tacacs local_enable
Command: config authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1 method tacacs+
tacacs local_enable
Success.
5-14 delete authen_enable
Description
This command is used to delete a user-defined method list of authentication methods for
promoting user's privilege to Admin level.
Format
delete authen_enable method_list_name <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete a user-defined method list for promoting user's privilege to Admin level:
Command: delete authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
Success.
5-15 show authen_enable
Description
This command is used to display the method list of authentication methods for promoting user's
privilege to Admin level.
72
Page 78

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
default - Display default user-defined method list for promoting user's privilege to Admin level.
method_list_name - Display the specific user-defined method list for promoting user's privilege
<string 15> - Enter the method list name here. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
all - Display all method lists for promoting user's privilege to Admin level.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
console - Application: console.
telnet - Application: telnet.
ssh - Application: SSH.
http - Application: web.
all - Application: console, telnet, SSH, and web.
login - Select the method list of authentication methods for user login.
enable - Select the method list of authentication methods for promoting user's privilege to Admin
level.
default - Default method list.
method_list_name - The user-defined method list nam e.
<string> - Enter the method list name here. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
Format
show authen_enable [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
Parameters
to Admin level.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display all method lists for promoting user's privilege to Admin level:
Command: show authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
Method List Name Priority Method Name Comment
---------------- -------- --------------- -----------------enable_list_1 1 local_enable Keyword
5-16 config authen application
Description
This command is used to configure login or enable method list for all or the specified application.
Format
config authen application [console | telnet | ssh | http | all] [login | enable] [default |
method_list_name <string 15>]
Parameters
73
Page 79

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config authen application telnet login method_list_name
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show authen application
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the login method list for telnet:
login_list_1
Command: config authen application telnet login method_list_name login_list_1
Success.
5-17 show authen application
Description
This command is used to display the login/enable method list for all applications.
Format
show authen application
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display the login/enable method list for all applications:
Command: show authen application
Application Login Method List Enable Method List
----------- ----------------- -----------------Console default default
Telnet login_list_1 default
SSH default default
HTTP default default
74
Page 80

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<string 15> - The user-defined server group name. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# create authen server_group mix_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
server_group - User-defined server group.
<string 15> - Enter the server group name here. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
5-18 create authen server_group
Description
This command is used to create a user-defined authentication server group. The maximum
supported number of server groups including built-in server groups is 8. Each group consists of 8
server hosts as maximum.
Format
create authen server_group <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a user-defined authentication server group:
Command: create authen server_group mix_1
Success.
5-19 config authen server_group
Description
This command is used to add or remove an authentication server host to or from the specified
server group. Built-in server group “tacacs”, “xtacacs”, “tacacs+”, “radius” accepts the server host
with the same protocol only, but user-defined server group can accept server hosts with different
protocols.
Format
config authen server_group [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius | <string 15>] [add | delete]
server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius]
Parameters
tacacs - Built-in server group “tacacs”.
xtacacs - Built-in server group “xtacacs”.
tacacs+ - Built-in server group “tacacs+”.
radius - Built-in server group “radius”.
75
Page 81

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
add - Add a server host to a server group.
delete - Remove a server host from a server group.
server_host - Server host’s IP address.
<ipaddr> - Enter the server host IP address here.
protocol - Specify the authentication protocol used.
radius - Specify that the radius authentication protocol will be used.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config authen server_group mix_1 add server_host
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<string 15> - The user-defined server group name. This value can be up to 15 characters long.
tacacs - Specify that the TACACS authentication protocol will be used.
xtacacs - Specify that the XTACACS authentication protocol will be used.
tacacs+ - Specify that the TACACS+ authentication protocol will be used.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To add an authentication server host to an server group:
10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+
Command: config authen server_group mix_1 add server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol
tacacs+
Success.
5-20 delete authen server_group
Description
This command is used to delete a user-defined authentication server group.
Format
delete authen server_group <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete a user-defined authentication server group:
76
Page 82

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# delete authen server_group mix_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<string 15> - (Optional) The built-in or user-defined server group name. This value can be up to
15 characters long.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show authen server_group
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: delete authen server_group mix_1
Success.
5-21 show authen server_group
Description
This command is used to display the authentication server groups.
Format
show authen server_group {<stri n g 15>}
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display all authentication server groups:
Command: show authen server_group
Group Name IP Address Protocol
--------------- --------------- -------mix_1 10.1.1.222 TACACS+
10.1.1.223 TACACS
radius 10.1.1.224 RADIUS
tacacs 10.1.1.225 TACACS
tacacs+ 10.1.1.226 TACACS+
xtacacs 10.1.1.227 XTACACS
Total Entries : 5
5-22 create authen server_host
Description
This command is used to create an authentication server host. When an authentication server host
is created, IP address and protocol are the index. That means over 1 authentication protocol
77
Page 83

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<ipaddr> - Enter the server host IP address.
protocol - Specify the host's authentication protocol.
radius - Server host’s authentication protocol.
port - (Optional) The port number of authentication protocol for server host. Default value for
between 1 and 65535.
key - (Optional) The key for TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication. If the value is null, no
for TACACS and XTACACS.
encryption_key - (Optional) Specify the encryption key string for TACACS+ and RADIUS
<key_string 344> - Enter the encryption key string.
timeout - (Optional) The time in second for waiting server reply. Default value is 5 seconds.
<int 1-255> - Enter the timeout value here. This value must be between 1 and 255 seconds.
retransmit - (Optional) The count for re-transmit. This value is meaningless for TACACS+.
<int 1-20> - Enter the re-transmit value here. This value must be between 1 and 20.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#create authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+ port
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
services can be run on the same physical host. The maximum supported number of server hosts is
16.
Format
create authen server_host <ipaddr> p rotocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius] {port <int
1-65535> | [key [<key_string 254> | none] | en cryption_key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int
1-255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}
Parameters
tacacs - Server host’s authentication protocol.
xtacacs - Server host’s authentication protocol.
tacacs+ - Server host’s authentication protocol.
TACACS/XTACACS/TACACS+ is 49. Default value for RADIUS is 1812.
<int 1-65535> - Enter the authentication protocol port number here. This value must be
encryption will apply. This value is meaningless for TACACS and XTACACS.
<key_string 254> - Enter the TACACS+ or the RADIUS key here. This key can be up to 254
characters long.
none - No encryption for TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication. This value is meaningless
authentication.
Default value is 2.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a TACACS+ authentication server host, its listening port number is 15555 and timeout
value is 10 seconds:
15555 timeout 10
Command: create authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+ port 15555
timeout 10
Key is empty for TACACS+ or RADIUS.
Success.
78
Page 84

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<ipaddr> - Enter the server host IP address.
protocol - Specify the server host's authentication protocol.
radius - Server host’s authentication protocol.
port - (Optional) The port number of authentication protocol for server host. Default value for
<int 1-65535> - Enter the port number here. This value must be between 1 and 65535.
key - (Optional) The key for TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication. If the value is null, no
for TACACS and XTACACS.
encryption_key - (Optional) Specify the encryption key string for TACACS+ and RADIUS
<key_string 344> - Enter the encryption key string.
timeout - (Optional) The time in second for waiting server reply. Default value is 5 seconds.
<int 1-255> - Enter the timeout value here. This value must be between 1 and 255 seconds.
retransmit - (Optional) The count for re-transmit. This value is meaningless for TACACS+.
<int 1-20> - Enter the re-transmit value here. This value must be between 1 and 20.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+ key
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
5-23 config authen server_host
Description
This command is used to configure an authenticati on s erver host.
Format
config authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius] {port <int
1-65535> | [key [<key_string 254> | none] | en cryption_key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int
1-255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}
Parameters
tacacs - Server host’s authentication protocol.
xtacacs - Server host’s authentication protocol.
tacacs+ - Server host’s authentication protocol.
TACACS/XTACACS/TACACS+ is 49. Default value for RADIUS is 1812.
encryption will apply. This value is meaningless for TACACS and XTACACS.
<key_string 254> - Enter the TACACS+ key here. This value can be up to 254 characters
long.
none - No encryption for TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication. This value is meaningless
authentication.
Default value is 2.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a TACACS+ authentication server host’s key value:
"This is a secret."
Command: config authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+ key "This is a
secret."
Success.
79
Page 85

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<ipaddr> - Enter the server host's IP address.
protocol - Specify that server host's authentication protocol.
radius - Server host’s authentication protocol.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# delete authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
5-24 delete authen server_host
Description
This command is used to delete an authentication server host.
Format
delete authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius]
Parameters
tacacs - Server host’s authentication protocol.
xtacacs - Server host’s authentication protocol.
tacacs+ - Server host’s authentication protocol.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete an authentication server host:
Command: delete authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+
Success.
5-25 show authen server_host
Description
This command is used to display the authentication server hosts.
Format
show authen server_host
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
80
Page 86

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show authen server_host
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<int 0-255> - The amount of time for user input on console or telnet or SSH. 0 means there is no
time out. This value must be between 0 and 255. Default value is 30 seconds.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config authen parameter response_timeout 60
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Example
To display all authentication server hosts:
Command: show authen server_host
IP Address Protocol Port Timeout Retransmit Key
-------------------- -------- ----- ------- ---------- -----------------------
10.1.1.222 TACACS+ 15555 10 - This is a secret.
Total Entries : 1
5-26 config authen parameter response_timeout
Description
This command is used to configure the amount of time waiting or user input on console, telnet,
SSH application.
Format
config authen parameter response_ti m eout <int 0-255>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the amount of time waiting or user input to be 60 seconds:
Command: config authen parameter response_timeout 60
Success.
5-27 config authen parameter attempt
Description
This command is used to configure the maximum attempts for user's trying to login or promote the
privilege on console, telnet, SSH application.
81
Page 87

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<int 1-255> - The amount of attempts for user's trying to login or promote the privilege on console
or telnet or SSH. This value must be between 1 and 255. Default value is 3.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config authen parameter attempt 9
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Format
config authen parameter attempt <int 1-255>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the maximum attempts for user's trying to login or promote the privilege to be 9:
Command: config authen parameter attempt 9
Success.
5-28 show authen parameter
Description
This command is used to display the parameters of authentication.
Format
show authen parameter
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display the parameters of authentication:
82
Page 88

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# show authen parameter
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
DGS-3120-24TC:oper#enable admin
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: show authen parameter
Response Timeout : 60 seconds
User Attempts : 9
5-29 enable admin
Description
This command is used to enter the administrator level privilege. Promote the "user" privilege level
to "admin" level. When the user enters this command, the authentication method tacacs, xtacacs,
tacacs+, user-defined server groups, local_enable or none will be used to aut he n ticate the us er .
Because TACACS, XTACACS and RADIUS don't support "enable" function in itself, if user wants
to use either one of these 3 protocols to do enable authentication, user must create a special
account on the server host first, which has a username "enable" and then configure its password
as the enable password to support "enab le" func tio n.
This command can not be used when auth ent ic at ion p olicy is disabled.
Format
enable admin
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To enable administrator lever privilege:
Command: enable admin
PassWord:*****
Success.
5-30 config admin local_enable
Description
This command is used to config the local enable password of administrator level privilege. When
the user chooses the “local_enable” method to promote the privilege level, the enable password of
local device is needed. When the password information is not specified in the command, the
83
Page 89

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
encrypt - (Optional) Specify the password form.
sha_1 - Specify the password in SHA-1 encrypted form.
<password> - (Optional) The password for promoting the privilege level. The length for a
sensitive.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config admin local_enable
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
system will prompt the user to input the password interactively. For this case, the user can only
input the plain text password. If the password is present in the command, the user can select to
input the password in the plain text form or in the encrypted form. The encryption algorithm is
based on SHA-I.
Format
config admin local_enable {encrypt [plain_text | sha_1] <password>}
Parameters
plain_text - Specify the password in plain text form.
password in plain-text form and SHA-1 encrypted form are different.
plain-text: Passwords can be from a minimum of 0 to a maximum of 15 characters.
SHA-1: The length of Encrypted passwords is fixed to 35 bytes longand the password is case-
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the administrator password:
Command: config admin local_enable
Enter the old password:
Enter the case-sensitive new password:*****
Enter the new password again for confirmation:*****
Success.
5-31 create aaa server_group
Description
This command is used to create a group of user-defined AAA servers. The maximum number of
supported server groups, including the built-in server groups, is 8. Each group can have a
maximum of 8 server hosts.
Format
create aaa server_group <string 15>
84
Page 90

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined server group name.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#create aaa server_group mix_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
tacacs - Specify the built-in TACACS server group.
xtacacs - Specify the built-in XTACACS server group.
tacacs+ - Specify the built-in TACACS+ server group.
radius - Specify the built-in RADIUS server group.
group_name - Specify a user-defined server group.
<string 15> - Enter the name of the server group.
add - Add a server host to the server group.
delete - Remove a server host to the server group.
server_host - Specify the server host.
radius - Specify the server host using RADIUS protocol.
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a user-defined AAA server group called “mix_1”:
Command: create aaa server_group mix_1
Success.
5-32 config aaa server_group
Description
This command is used to add or remove an AAA server host to or from the specified server group.
The built-in TACACS, XTACACS, TACACS+, and RADIUS server groups only accept server hosts
with the same protocol, but a user-defined server group can accept server hosts with different
protocols.
Format
config aaa server_group [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius | group_name <string 15>] [add
| delete] server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+| radius]
Parameters
<ipaddr> - Enter the IP address of the server host.
protocol - Specify the server host protocol.
tacacs - Specify the server host using TACACS protocol.
xtacacs - Specify the server host using XTACACS protocol.
tacacs+ - Specify the server host using TACACS+ protocol.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
85
Page 91

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin# config aaa server_group group_name mix_1 add server_host
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<string 15> - Specify the server group name to be deleted.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#delete aaa server_group mix_1
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Example
To add an AAA server host with an IP address of 10.1.1.222 to server group “mix_1”, specifying
the TACACS+ protocol:
10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+
Command: config aaa server_group group_name mix_1 add server_host 10.1.1.222
protocol tacacs+
Success.
5-33 delete aaa server_group
Description
This command is used to delete a group of user-defined AAA servers.
Format
delete aaa server_group <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete a user-defined AAA server group called “mix_1”:
Command: delete aaa server_group mix_1
Success.
5-34 show aaa server_group
Description
This command is used to display the groups of AAA servers groups.
Format
show aaa server_group {<string 15>}
86
Page 92

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<string 15> - (Optional) Specify the built-in or user-defined server group name.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show aaa server_group
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<string 15> - Specify the built-in or user-defined method list.
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display all AAA server groups:
Command: show aaa server_group
Group Name IP Address Protocol
--------------- --------------------------------------- -------mix_1 --------------------------------------- --------
radius --------------------------------------- --------
tacacs --------------------------------------- --------
tacacs+ --------------------------------------- --------
xtacacs --------------------------------------- --------
Total Entries : 5
5-35 create accounting method_list_name
Description
This command is used to create a user-defined list of accounting methods for accounting services
on the Switch. The maximum supported number of accounting method lists is 8.
Format
create accounting method_lis t_name <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
87
Page 93

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#create accounting method_list_name shell_acct
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
default - Specify the default method list of accounting methods.
method_list_name - Specify the user-defined method list of accounting methods.
<string 15> - Enter the name of the method list.
method - Specify the protocol.
none - Specify no accounting.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config accounting method_list_name shell_acct method
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Example
To create a user-defined accounting method list called “shell_acct”:
Command: create accounting method_list_name shell_acct
Success.
5-36 config accounting
Description
This command is used to a user-defined or default method list of accounting methods.
Format
config accounting [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs+ | radius |
server_group <string 15> | none}
Parameters
tacacs+ - Specify the built-in TACACS+ server group.
radius – Specify the built-in RADIUS server group.
server_group - Specify the user-defined server group. If the group contains TACACS and
XTACACS server, it will be skipped in account in g.
<string 15> - Enter the name of server group.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a user-defined method list called “shell_acct”, that specifies a sequence of the built-in
TACACS+ server group, followed by the RADIUS server group for accounting service on the
Switch:
tacacs+ radius
Command: config accounting method_list_name shell_acct method tacacs+ radius
Success.
88
Page 94

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<string 15> - Specify the built-in or user-defined method list.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#delete accounting method_list_name shell_acct
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
default - Display the user-def ined list of default acc oun ting m ethods .
method_list_name - Specify the user-defined list of specific accounting methods.
<string 15> - Enter the name of the method list.
all - Display all accounting method lists on the Switch.
5-37 delete accounting method_list_name
Description
This command is used to delete a user-defined method list of accounting methods.
Format
delete accounting method_list_ n ame <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete the user-defined accounting method list called “shell_acct” from switch:
Command: delete accounting method_list_name shell_acct
Success.
5-38 show accounting
Description
This command is used to display the list of accounting methods on the Switch.
Format
show accounting [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
89
Page 95

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show accounting method_list_name shell_acct
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
administrator - Accounting service for all administrator level commands.
operator - Accounting service for all operator level commands.
power_user - Accounting service for all power-user level commands.
user - Accounting service for all user level commands.
method_list_name - Specify accounting service by the AAA user-defined method list specified
<string> - Enter the name of the method list.
none - Disable AAA command accounting services by specified command level.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config accounting service command method_list_name
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Example
To display the user-defined accounting method list called “shell_acct”:
Command: show accounting method_list_name shell_acct
Method List Name Priority Method Name Comment
---------------- -------- --------------- -----------------shell_acct 1 tacacs+ Built-in Group
2 radius Built-in Group
5-39 config accounting service command
Description
This command is used to confiugre the state of the specified accounting service.
Format
config accounting service command {a d ministrator | operator | power_user | user}
[method_list_name <string> | none]
Parameters
by the “create accounting method_list_name <string 15>” command.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable AAA accounting methodlist “shell_acct” to configure accounting shell state:
shell_acct
Command: config accounting service command method_list_name shell_acct
Success.
90
Page 96

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<ipaddr> - Enter the IP address of the server host.
auth_port - (Optional) Specify the port of the RADIUS authentication.
<int 1-65535> - Enter the value between 1 and 65535. The default value is 1812.
acct_port - (Optional) Specify the port of the RAIDUS accounting.
<int 1-65535> - Enter the value between 1 and 65535. The default value is 1813.
key - (Optional) Specify the key for RADIUS.
none - No encryption for RADIUS.
encryption_key - (Optional) The encrypted form key string for RADIUS. The encryption
<key_string 344> - Etner the string with maximum 344 characters.
timeout - (Optional) Specify the time in second to wait for the server to reply.
<int 1-255> - Enter the value between 1 and 255. The default value is 5.
retransmit - (Optional) Specify the count for re-transmissions.
<int 1-20> - Enter the value between 1 and 20. The default value is 2.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#create radius server_host 10.1.1.222 auth_port 15555
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
5-40 create radius server_host
Description
This command is used to create an RADIUS server host.
Format
create radius server_host <ipaddr> {auth_port <int 1-65535> | acct_port <int 1-65535> | [key
[<key_string 254> | none] | encryption _key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int 1-255> |
retransmit <int 1-20>}
Parameters
<key_string 254> - Enter the plain text key string for RADIUS.
algorithm is based on DES.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create an RADIUS server host:
timeout 10
Command: create radius server_host 10.1.1.222 auth_port 15555 timeout 10
Key is empty for TACACS+ or RADIUS.
Success.
5-41 config radius server_host
Description
This command is used to
91
Page 97

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<ipaddr> - Enter the IP address of the server host.
auth_port - (Optional) Specify the port of the RADIUS authentication.
<int 1-65535> - Enter the value between 1 and 65535. The default value is 1812.
acct_port - (Optional) Specify the port of the RAIDUS accounting.
<int 1-65535> - Enter the value between 1 and 65535. The default value is 1813.
key - (Optional) Specify the key for RADIUS.
none - No encryption for RADIUS.
encryption_key - (Optional) The encrypted form key string for RADIUS. The encryption
<key_string 344> - Etner the string with maximum 344 characters.
timeout - (Optional) Specify the time in second to wait for the server to reply.
<int 1-255> - Enter the value between 1 and 255. The default value is 5.
retransmit - (Optional) Specify the count for re-transmissions.
<int 1-20> - Enter the value between 1 and 20. The default value is 2.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config radius server_host 10.1.1.222 key "abc123"
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<ipaddr> - Enter the IP address of the server host.
protocol – Specify the protocol.
tacacs – Specify TACACS server host.
Format
config radius server_host <ipaddr> {auth_port <int 1-65535> | acct_port <int 1-65535> | [key
[<key_string 254> | none] | encryption _key <key_string 344>] | timeout <int 1-255> |
retransmit <int 1-20>}
Parameters
<key_string 254> - Enter the plain text key string for RADIUS.
algorithm is based on DES.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the RADIUS server host:
Command: config radius server_host 10.1.1.222 key "abc123"
Success.
5-42 delete aaa server_host
Description
This command is used to delete an AAA server host.
Format
delete aaa server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+| radius]
Parameters
92
Page 98

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
xtacacs - Specify XTACACS server host.
radius - Specify RADIUS server host.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#delete aaa server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
tacacs+ - Specify TACACS+ server host.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+| delete an AAA server host, with an IP address of 10.1.1.222, that is
running the TACACS+ protocol:
Command: delete aaa server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+
Success.
5-43 show aaa server_host
Description
This command is used to display the AAA server hosts.
Format
show aaa server_host
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display all AAA server hosts:
93
Page 99

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#show aaa server_host
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<ipaddr> - Enter the IP address of the server host.
port - (Optional) The port number of the TACACS server host.
<int 1-65535> - Enter the value between 1 and 65535. The default value is 49.
timeout - (Optional) Specify the time in second to wait for the server to reply.
<int 1-255> - Enter the value between 1 and 255. The default value is 5.
retransmit - (Optional) Specify the count for re-transmissions.
<int 1-20> - Enter the value between 1 and 20. The default value is 2.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#create tacacs server_host 10.1.1.223 port 15555 timeout 10
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
Command: show aaa server_host
IP Address Protocl Port Acct Time Retry Key
Port out
-------------------- ------- ----- ----- ---- ----- ---------------------------
10.1.1.222 RADIUS 15555 1813 10 2 abc123
Total Entries : 1
5-44 create tacacs server_host
Description
This command is used to create a TACACS server host.
Format
create tacacs server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit
<int 1-20>}
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a TACACS server host:
Command: create tacacs server_host 10.1.1.223 port 15555 timeout 10
Success.
94
Page 100

xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
<ipaddr> - Enter the IP address of the server host.
port - (Optional) The port number of the TACACS server host.
<int 1-65535> - Enter the value between 1 and 65535. The default value is 49.
timeout - (Optional) Specify the time in second to wait for the server to reply.
<int 1-255> - Enter the value between 1 and 255. The default value is 5.
retransmit - (Optional) Specify the count for re-transmissions.
<int 1-20> - Enter the value between 1 and 20. The default value is 2.
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#config tacacs server_host 10.1.1.223 retransmit 5
DGS-3120-24TC:admin#
<ipaddr> - Enter the IP address of the server host.
port - (Optional) The port number of the XTACACS server host.
5-45 config tacacs server_host
Description
This command is used to configure a TACACS server host.
Format
config tacacs server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit
<int 1-20>}
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the TACACS server host:
Command: config tacacs server_host 10.1.1.223 retransmit 5
Key is meaningless for TACACS and XTACACS.
Success.
5-46 create xtacacs server_host
Description
This command is used to
Format
create xtacacs server_host <ipaddr> {port <int 1-65535> | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit
<int 1-20>}
Parameters
95
 Loading...
Loading...