Page 1

D-Link DGE-528T
Gigabit Ethernet PCI Adapter
Manual
Rev. 01 (Nov. 01, 2003)
Printed in Taiwan
1
Page 2

Table of Contents
Introduction ....................................................................................... 3
Contents of Package ......................................................................... 4
Technology Basics ............................................................................ 4
About Gigabit Ethernet ............................................................................... 4
About Auto-Negotiation .............................................................................. 5
About PCI Bus............................................................................................ 5
Wake On LAN ........................................................................................ 6
Connecting the WOL Cable ................................................................... 6
Flow Control ........................................................................................... 7
Networking Basics ............................................................................ 7
Troubleshooting .............................................................................. 19
Contacting Technical Support........................................................ 23
Technical Specifications ................................................................. 24
Warranty & Registration ................................................................. 27
2
Page 3

Introduction
The D-Link DGE-528T is ideal for the small office or home office environment. After completing the
steps in this manual, you will have the ability to share information and resources - such as files and
printers - and take full advantage of a “connected” environment for work and play!
The DGE-528T comes with drivers for the most popular operating systems and can be integrated
into a larger network. However, this manual is designed to help you network two computers running
Windows 95/98, Windows Me and Windows 2000 in a peer-to-peer configuration. Yet, the standards
compliant DGE-528T gives you the flexibility to expand and customize your Fast Ethernet / Gigabit Ethernet
network at will.
The Fast Ethernet standard allows you to connect computers and devices at speeds up to 100 Mbps.
Gigabit Ethernet allows speeds up to 1000 Mbps. A Dual-Speed 100/1000 Mbps Ethernet / Gigabit Ethernet
network combines both standards allowing computers and devices of different speeds to communicate
with each other. The DGE-528T is a Dual-Speed 100/1000 Mbps Fast Ethernet / Gigabit Ethernet network
card.
3
Page 4

Contents of Package
1 DGE-528T Gigabit Ethernet PCI Adapter
2 Manual on the CD-ROM
3 Quick Installation Guide
DGE-528T Gigabit Ethernet PCI Adapter
Package Contents
Technology Basics
About Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a network technology specified by IEEE Standard 802.3ab. It extends the traditional
100Mbps Fast Ethernet technology to achieve 1000Mbps transmission and reception, while retaining
the same CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol. Thus, while Gigabit Ethernet provides a tenfold increase in network
capacity, it is wholly compatible with traditional 100Mbps Fast Ethernet network facilities. This compatibility
is the key to easy and efficient upgrades to 1000Mbps in your network areas needing greater bandwidth.
Upgrading selected areas to Gigabit Ethernet does not require hardware or software changes in network
areas where traditional 100Mbps Ethernet is providing good service. For upgrading, Gigabit Ethernet is
the clear choice in terms of cost-effectiveness, as well as convenience and smoothness in transition.
4
Page 5

Category 5 cabling is required for 1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet in order to provide full duplex
operation. Full duplex 1000Base-T operation allows simultaneous transmission and reception,
both at 1000Mbps, thus providing service potentially equal to 2000Mbps full-duplex service
To provide compatibility in traditional 100Mbps Fast Ethernet environments (where, for example
DGE-528T adapters are installed anticipating upgrade of supporting switch equipment to Gigabit
Ethernet), the DGE-528T also supports traditional 100Mbps Fast Ethernet operation, in full-duplex
as well as half-duplex modes. Selection of the best operation mode in any given installation is
automatically governed by auto-negotiation.
About Auto-Negotiation
You have probably had the experience of making a dialup connection through a modem, and have
heard the sound exchange between your modem and the modem at the other end of the telephone
line. As irritating as those few seconds of noise may be, they do let you know that your modem and
the remote modem are on the job, preparing for your intended communication with the remote
computer.
When the two modems have tested the phone-line quality and settled on the combination of shared
options and parameters which will provide the best data communication over the connecting phone
line, then you are given the “connect” message which signals the end of the intermodem
negotiation and the beginning of your intended communication with the remote computer.
Auto-negotiation between devices within an Ethernet LAN is similar in concept, but much briefer.
The two devices involved in the auto-negotiation will be the DGE-528T Adapter serving your
station (installed in your computer), and the switch through which it is connected to the LAN. The
options to be negotiated between the DGE-528T and its supporting switch includes Ethernet type
(1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet or 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet) and duplex mode (half-duplex, being
one-way-at-a-time, or full duplex, being simultaneous transmit-and receive.)
Startup communication between the two devices occurs when both devices are powered up. Once
the cable connection and the Network Operating System software is satisfied, the preparatory
process of auto-negotiation between the DGE-528T and its supporting switch proceeds
automatically. If the switch has auto-negotiation functionality, it and the DGE-528T exchange a
series of messages, each device signals its capabilities and listens for corresponding information
about the other. The auto-negotiation process requires only a few milliseconds, and the two
devices select the best communication parameters supported by both.
If the switch does not support auto-negotiation, the (single capability) message will be recognized
by the DGE-528T auto-negotiation facility, which will switch to those settings of its own
capabilities, which match that of the switch.
Auto-negotiation reoccurs any time the linkage is restored, making the line ready again for optimal
data communications.
About PCI Bus
Your DGE-528T Adapter delivers outstanding performance by fully exploiting the advance
features of your computer’s PCI bus. DGE-528T Adapters utilize the Bus Master Mode of the
PCI bus, allowing direct transfers of Ethernet packet content between computer memory and the
adapter’s controller, thus minimizing network demands on the CPU. The adapter’s controller
function provides the additional benefit of reduced command processing overhead.
5
Page 6

The working relationship between a DGE-528T adapter and main memory working in Bus Master
mode is powered by the Bridge/Memory Controller of the PCI bus. This reduces the CPU role in
network operations, thus freeing the CPU to service other tasks, with resulting improvement in overall
computing (multitasking) performance. At the same time, it produces superior network throughput by
reducing latency (waiting for CPU service) during transmissions and receptions.
Features
Wake On LAN
Wake On LAN (WOL) is an ACPI function allowing a powered down (sleeping) computer to be powered
ON from a remote station. To use the WOL feature, the NIC must be WOL capable and the motherboard
of the PC must be ACPI compliant. While powered-down computers Sleep, WOL enabled NICs monitor
LAN traffic for valid Wake-up frames. When one is received, the NIC will immediately wake-up and
send a signal to the motherboard to power ON the computer.
Some uses for the WOL feature include:
· Forgot a document and are out of town? Send a Wake-up signal to your computer and
retrieve the needed file.
· Initiate long routines and reports before you get to work.
· Transfer files when the network traffic is low (during late hours).
· Power ON your PC before you arrive to work.
· The MIS department can upgrade software on computers after hours from a remote station.
Connecting the WOL Cable
NOTE: If your system’s motherboard WOL Connector does not fit the WOL Cable or does not
have 3 pins, do not attempt to force a connection or alter the components to fit. Doing so could
permanently damage your computer.
The WOL function is system dependent, in addition to the following instructions, you may
need to download WOL software from INTEL or another manufacturer’s website.
Please consult your computer’s manual for specific BIOS settings.
The WOL Cable is an interconnect cable with standard 3-pin connectors on each end. Please follow
the procedures listed below to ensure proper installation of the WOL cable.
1. Connect either end connector of the WOL Cable to the NIC WOL Connector. Both ends of the
WOL Cable are identical, so either end may be used.
Examine the PC motherboard and/or refer to the manual for the motherboard to locate the corre-
sponding WOL Connector on the motherboard. The actual location is system dependent, but the
motherboard may have a label beside the WOL Connector. After you have located the WOL connector
on the motherboard, connect the cable.
6
Page 7
1. Power-ON the PC and press “Delete” or “F1” when prompted to enter the PCI/ISA BIOS CMOS
Setup. Enable the WOL function or the power-ON function of the PC. The name of this function
is system dependent, but may be located in a category heading titled something like Power
Management. Refer to your computer’s manual for more information regarding the CMOS
Setup Utility and BIOS settings.
Flow Control
The DGE-528T implements IEEE 802.3x compliant flow control for full-duplex, which provides traffic
management functions for full-duplex operation. Flow control allows for enhanced full-duplex operation
with switches. When operating at full-duplex (requiring a direct connection to a switch) and the switch’s
data buffer is about to overflow, a Pause frame will be transmitted to the DGE-528T. The ensuing
idle time keeps the buffer from overflowing and prevents data from being lost. This enhancement can
improve network throughput, avoid collisions and prevent lost data, helping the network achieve optimal
performance.
Networking Basics
Using the Network Setup Wizard in Windows XP
In this section you will learn how to establish a network at home or work, using Microsoft Windows
XP.
Note: Please refer to websites such as
windows2000 for information about networking computers using Windows 2000, ME or 98.
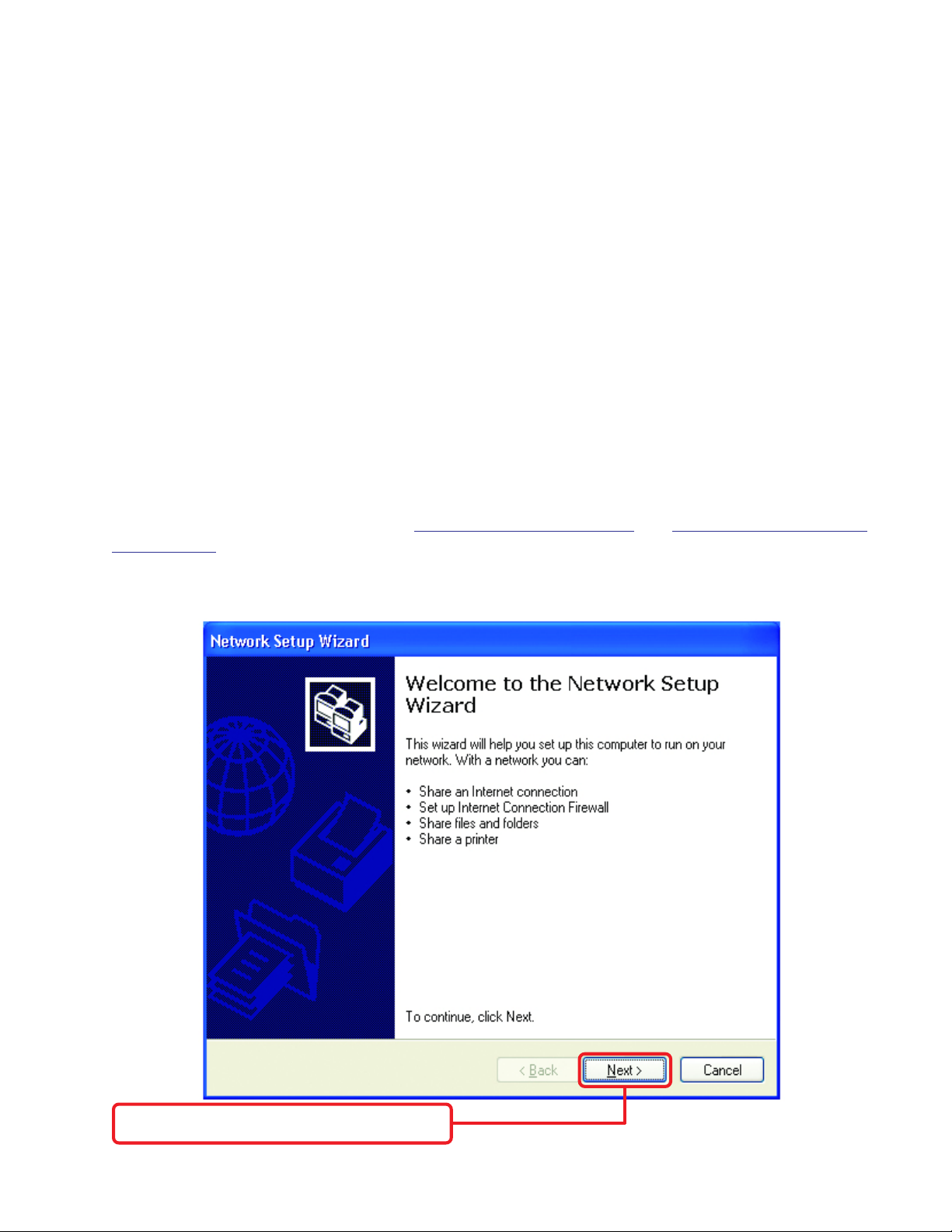
Go to Start>Control Panel>Network Connections. Select Set up a home or small office network
http://www.homenethelp.com and http://www.microsoft.com/
When this screen appears, click Next.
7
Page 8
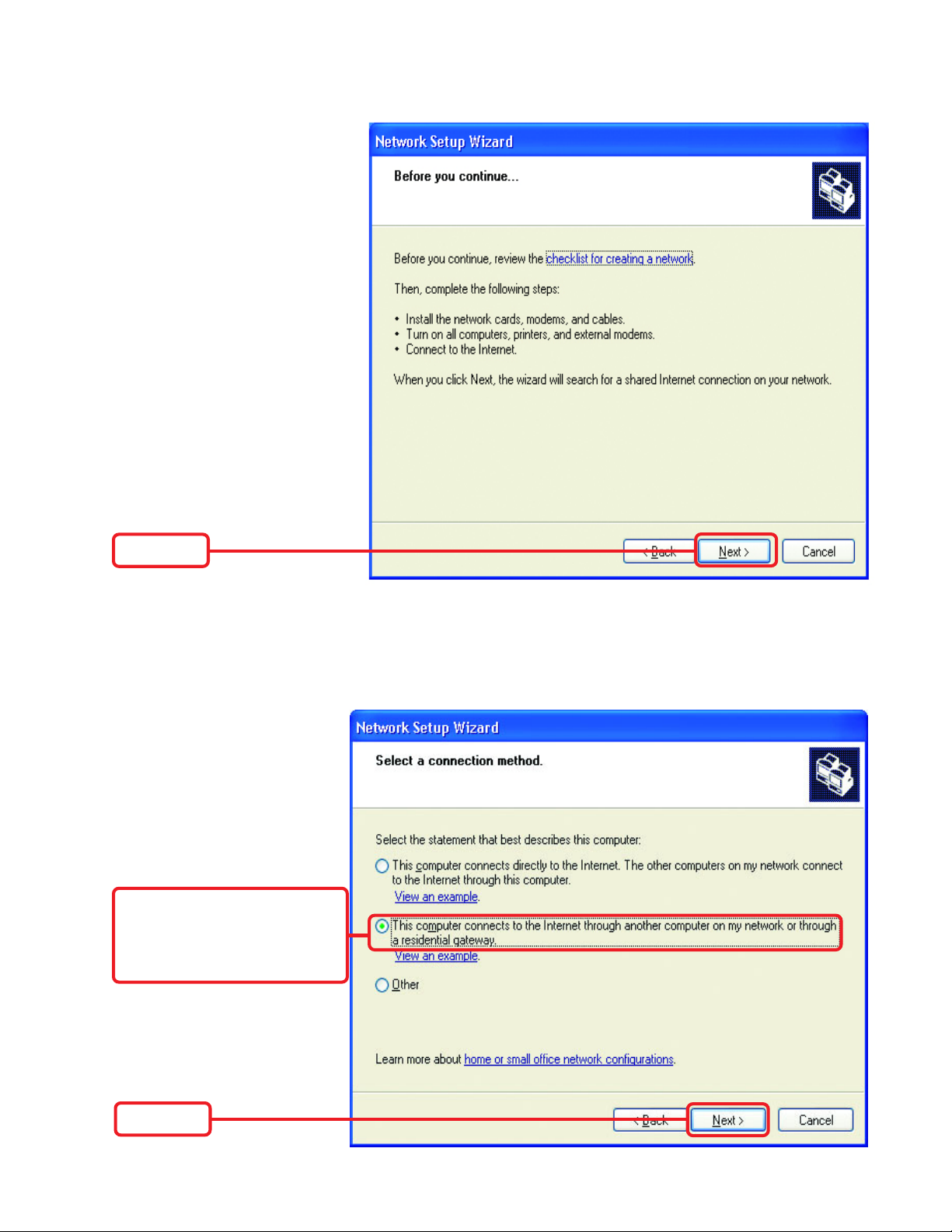
Networking Basics
Please follow all the instructions in this window:
Click Next
In the following window, select
the best description of your
computer.
If your computer connects to
the Internet through a gateway/router, select the second
option as shown.
Click Next
8
Page 9
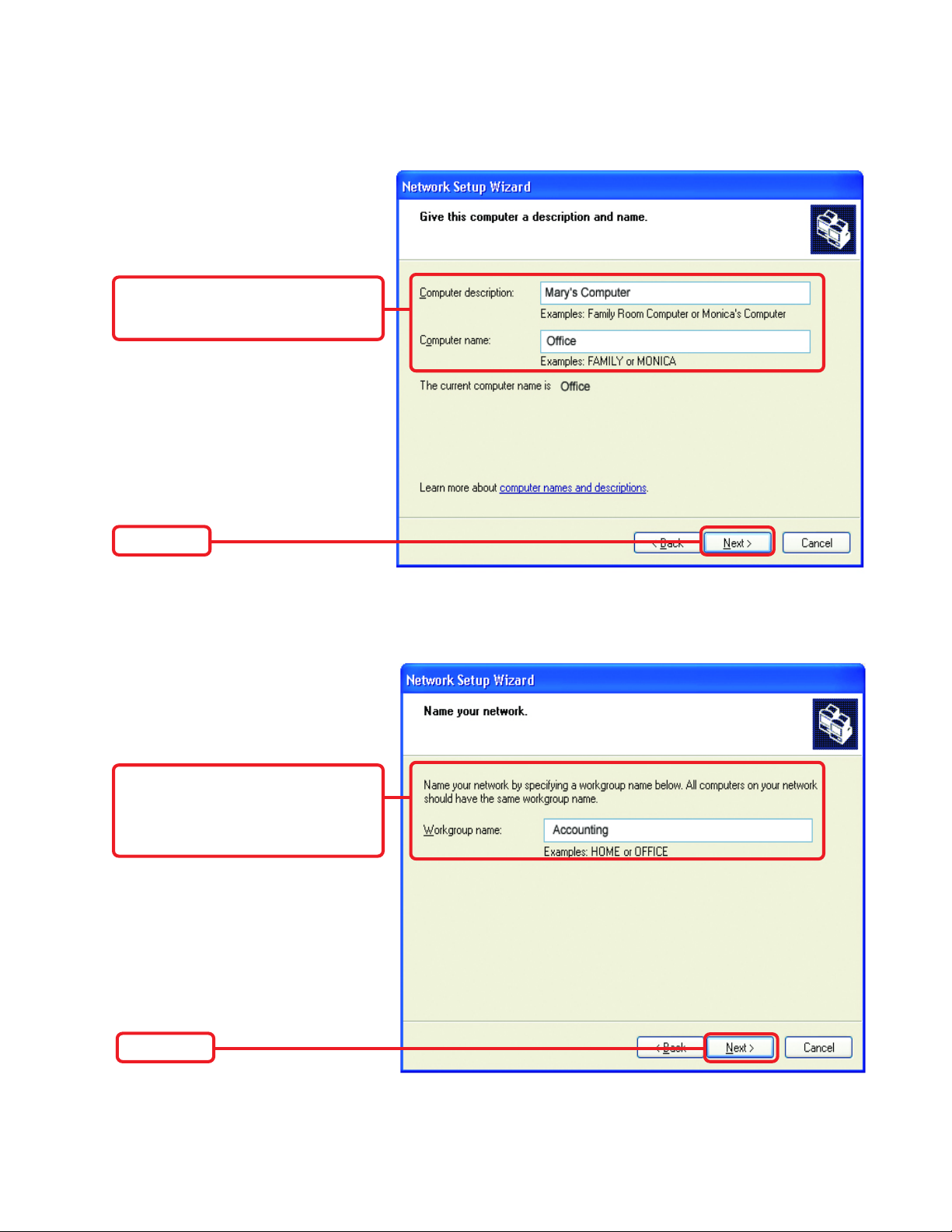
Networking Basics
Enter a Computer description and
a Computer name (optional.)
Click Next
Enter a Workgroup name.
All computers on your network
should have the same
Workgroup name.
Click Next
9
Page 10
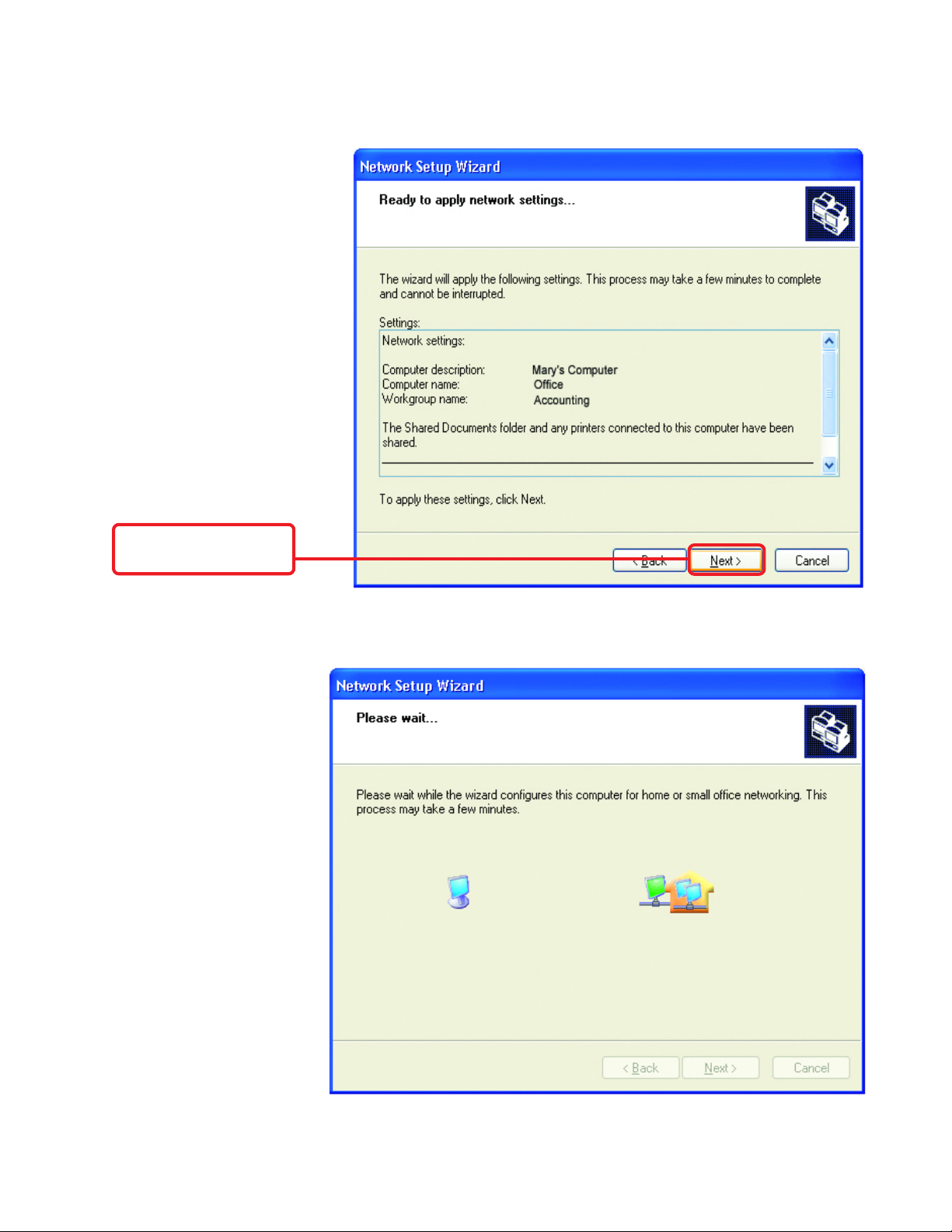
Networking Basics
Please wait while the Network
Setup Wizard applies the
changes.
When the changes are
complete, click Next
Please wait while the
Network Setup Wizard
configures the computer.
This may take a few
minutes.
10
Page 11
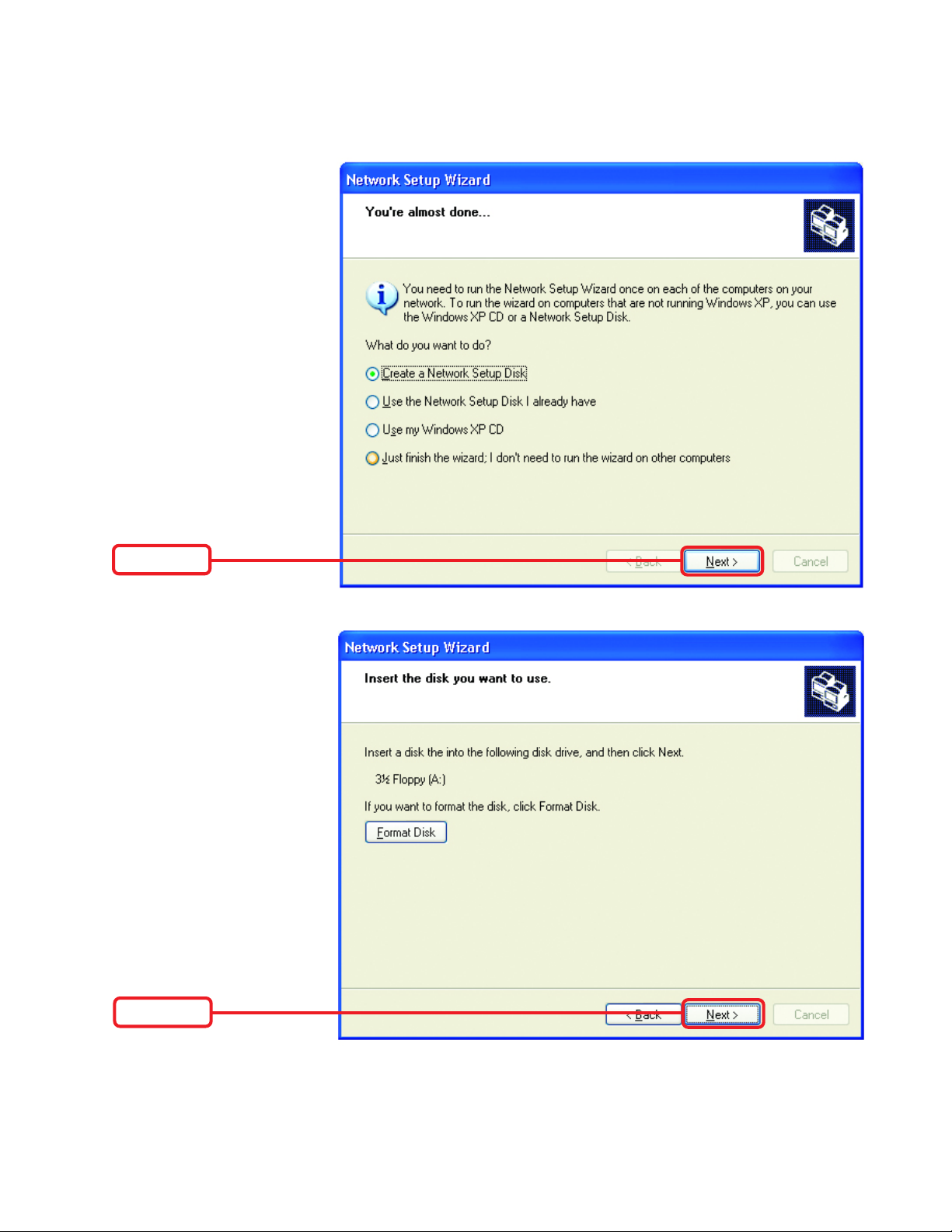
Networking Basics
In this window, select
the best option. In this
example, Create a Network
Setup Disk has been
selected. You will run this
disk on each of the
computers on your network.
Click Next
Insert a disk into the
Floppy Disk Drive, in this
case drive “A.”
Format the disk if you wish.
Click Next
11
Page 12

Networking Basics
Please wait while the Network Setup Wizard copies the files.
Please read the information under Here’s how in the screen below. After you complete the Net-
work Setup Wizard you will use the Network Setup Disk to run the Network Setup Wizard once
on each of the computers on your network. To continue click Next.
12
Page 13

Networking Basics
Please read the information on this screen, then click Finish to complete the Network Setup
Wizard.
The new settings will take effect when you restart the computer. Click Yes to restart the computer.
You have completed configuring this computer. Next, you will need to run the Network Setup Disk
on all the other computers on your network. After running the Network Setup Disk on all your
computers, your new network will be ready to use.
13
Page 14

Networking Basics
Naming your Computer
To name your computer, please follow these directions:
In Windows XP:
Click Start (in the lower left corner of
the screen)
Right-click on My Computer
Select Properties and click
Select the Computer Name Tab in the
System Properties window.
You may enter a Computer Description if you
wish, this field is optional.
To rename the computer and join the
domain, click Change.
14
Page 15

Networking Basics
Naming your Computer
In this window, enter the computer name.
All computers on your network must have the same
Workgroup name.
Select Workgroup and enter the name of the Workgroup.
Click OK
Checking the IP Address in Windows XP/2000
Go to Start >Run
15
Page 16

Networking Basics
Type in Command
Click OK
Type ipconfig /all at the prompt. Hit Enter. All the configuration settings are displayed as shown
below.
Checking the IP Address in Windows XP/2000
Type ipconfig /renew at the prompt to get a new IP Address. Hit Enter. The new IP Address is shown
below:
(Windows 98/ME users: go to Start > Run. Type Command. Type winipcfg at the prompt.
Click Release and Renew to obtain a new IP Address.)
16
Page 17

Assigning a Static IP Address
Note: Residential Gateways/Broadband Routers will automatically assign IP Addresses to the
computers on the network, using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) technology. If you
are using a DHCP-capable Gateway/Router you will not need to assign Static IP Addresses.
If you are not using a DHCP capable Gateway/Router, or you need to assign a Static IP Address,
please follow these instructions:
Go to Start
Click on Control Panel
Click on Network Connections
17
Page 18

Assigning a Static IP Address continued
Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Click Properties
Select Use the following IP Address in the Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window
Input your IP Address and subnet mask. (The IP
Addresses on your network must be within the same
range. For example, if one computer has an IP Ad
dress of 192.168.0.2, the other computers should have
IP Addresses that are sequential, like 192.168.0.3 and
192.168.0.4. The subnet mask must be the same for
all the computers on the network.)
Input your DNS server address. (Note: If you are
entering a DNS server, you must enter the IP Address
of the Default Gateway.)
The DNS server information will be provided by your
ISP (Internet Service Provider.)
Click OK
You have completed the assignment of a Static IP Address. (You do not need to assign a Static IP
Address if you have a DHCP-capable Gateway/Router.)
Other networking tasks
For help with other tasks in home or small office networking, see Using the Shared Documents
folder and Sharing files and folders in the Help and Support Center in Microsoft Windows XP.
18
Page 19

Troubleshooting
A network can be simple to install and maintain. However, occasionally something might go wrong.
The best approach to troubleshooting network problems is to start at the very simplest level and
work your way up.
Verify Each Computers Identification
If more than one computer on your network has the same Computer Name, communications may
be negatively affected. Also, each computer must have the same Workgroup name to
communicate properly. Use the steps in Networking Basics to ensure that each computer on your
network has a unique Computer Name and identical Workgroup.
Verify Network Adapter Installation
If your Network Adapters were not properly installed, including the Network System Software or
device drivers, your network will not function properly. Use these steps to verify that your Network
Adapter are properly installed:
1. Double-click the System icon in the Control Panel.
2. Select the Device manager tab on top of the System Properties dialog box.
3. Double-click Network adapters if you do not see any items branching out. You should see
D-Link DGE-528T Gigabit Ethernet PCI Adapter branching out after double-clicking Network
adapters.
19
Page 20

If you do not see any items branching out after double-clicking “Network adapters,” your Network
Adapter has not been properly installed. Start at the beginning of the guide and follow all the steps
for this computer.
If you see symbols such as a yellow exclamation point or red “X” over the icon adjacent to “D-Link
DGE-528T Gigabit Ethernet PCI Adapter,” your adapter is not installed properly or may have a
problem. Double-click the “D-LinkDGE-528T Gigabit Ethernet PCI Adapter” to read the explanation
of the problem. This information will be helpful if you require technical support from D-Link.
Verify Cable Connections
Check to see that the computer(s) you are troubleshooting are properly connected. Each computer
must be connected from its DGE-528T with Category 5 UTP cables. Examine the Network cables
and ensure that they have not been damaged by walking-on, rolling over with chairs, or closed in
doors. Additionally, make note of and alleviate any possible electromagnetic interference that may
be affecting your network.
Your network cables can be plugged into any port on your hub except the “Uplink” port. The
“Uplink” port is only used when connecting your hub to another hub or switch.
Understanding Indicators
Your DGE-528T has indicators or lights that can give you information about your network traffic
and help you determine problems when troubleshooting.
Your DGE-528T have two indicators labeled “ACT” and “LINK” on their back panels. A steady
green “LINK” light indicates a good connection with the switch. A flashing green “ACT” light
indicates that the Network Adapter is sending or receiving data.
Pinging your DGE-528T Card
Follow these steps to Ping a device:
Ping is the acronym for Packet Internet Groper (PING), a utility to determine if a specific IP address
is accessible. It works by sending a packet to the specified address and waiting for a reply. Ping is
primarily used to troubleshoot Internet connections. By sending out a ping, you are verifying that a
specific computer is available. Since all computers on the network must have a unique IP address,
getting a reply means that a computer is on the network and that they can communicate. If they can
communicate, then the hardware and cabling is probably okay. If you cannot ping another
computer, then there is probably a problem with the hardware. Check the cabling and adapter
installation. If you are unable to network, even when you receive a reply to your ping, it is probably
a software configuration issue. Verify that all the settings are correct.
20
Page 21

Pinging your DGE-528T Card continued
Go to Start> Run.
Type Command
Click OK
Type in the following: ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address to be
pinged (i.e. 192.168.0.1). In this case, computer B with the IP address=192.168.0.1 is being
pinged from computer A. Press Enter to begin pinging.
21
Page 22

If the connection is good, you will receive four “Reply from” messages. Type exit at the prompt
to return to Windows.
22
Page 23

Technical Support
23
23
You can find software updates and user documentation on the D-Link website.
D-Link provides free technical support for customers within the United States and
within Canada for the duration of the warranty period on this product.
U.S. and Canadian customers can contact D-Link technical support through our
website, or by phone.
Tech Support for customers within the United States:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(877) 453-5465
24 hours a day, seven days a week.
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.com
email:support@dlink.com
Tech Support for customers within Canada:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(800) 361-5265
Monday to Friday 8:30am to 9:00pm EST
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.ca
email:support@dlink.ca
Page 24

Technical Specifications
24
Network Type:
Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-T
IEEE 802.3ab standard for 1000 Mbps baseband CSMA/CD local area network
Fast Ethernet 100Base-TX
IEEE 802.3u standard for 100Mbps baseband CSMA/CD local area network
Jumperless Hardware
Auto-negotiation functionality
ACPI PCI power management support
Remote Wake up of ACPI/APM system support
With AMD magic packet,
Link Chg.
Microsoft wake-up frame
Media interface: RJ-45
EMI Compatibility:
FCC Class B
VCCI Class B
CISPR B
CE Certification, Class B
C-Tick
Page 25

Host Interface: PCI 2.1 and PCI 2.2 Bus (Bus Master)
I/O & IRQ base address: assigned by Plug and Play system
Physical Dimensions: 14 cm x 5.9 cm
Environment:
Storage: -10° to 70°C, (14° to 158°F)
Operating: 0° to 55°C, (32° to 131° F)
Humidity: 10% to 90% RH, non-condensing
Power Consumption: 4.5W max.
Software drivers for:
• Microsoft Windows XP
• Microsoft Windows 98
• Microsoft Windows Me
• Microsoft Windows 2000
• Microsoft Window NT4.0
• Novell Netware Server 5.x
• Novell Netware Server 6.x
• Linux driver for kernel 2.2.x
• Linux driver for kernel 2.4.x
• Macintosh OS X (10.2.x)
25
Page 26

D-Link Offices
AUSTRALIA D-LINK AUSTRALIA
Unit 16, 390 Eastern Valley Way, Roseville, NSW 2069, Australia TEL: 61-2-9417-7100 FAX: 61-2-9417-1077
TOLL FREE: 1800-177-100 (Australia), 0800-900900 (New Zealand)
URL: www.dlink.com.au E-MAIL: support@dlink.com.au, info@dlink.com.au
CANADA D-LINK CANADA
#2180 Winston Park Drive, Oakville, Ontario, L6H 5W1 Canada
CHILE D-LINK SOUTH AMERICA
Isidora Goyeechea 2934 of 702, Las Condes, Santiago – Chile S.A.
TEL: 56-2-232-3185 FAX: 56-2-232-0923 URL: www.dlink.cl
E-MAIL: ccasassu@dlink.cl, tsilva@dlink.cl
CHINA
2F., Sigma Building, 49 Zhichun Road, Haidian District, 100080 Beijing, China
TEL: 86-10-88097777 FAX: 86-10-88096789
URL: www.dlink.com.cn
DENMARK D-LINK DENMARK
Naverland 2, DK-2600 Glostrup, Copenhagen, Denmark
TEL:45-43-969040 FAX:45-43-424347 URL: www.dlink.dk
E-MAIL: info@dlink.dk
EGYPT D-LINK MIDDLE EAST
7 Assem Ebn Sabet Street, Heliopolis Cairo, Egypt
TEL: 202-2456176 FAX: 202-2456192 URL: www.dlink-me.com
E-MAIL: support@dlink-me.com
FRANCE D-LINK FRANCE
Le Florilege #2, Allee de la Fresnerie , 78330 Fontenay le Fleury France
TEL: 33-1-302-38688 FAX: 33-1-3023-8689 URL: www.dlink-france.fr
E-MAIL: info@dlink-france.fr
GERMANY D-LINK Central Europe/D-Link Deutschland GmbH
Schwalbacher Strasse 74, D-65760 Eschborn, Germany . TEL: 49-6196-77990 FAX: 49-6196-7799300
URL: www.dlink.de BBS: 49-(0)6192-971199 (Analog) 49-(0)6192-971198 (ISDN)
INFO LINE: 00800-7250-0000 (toll free) HELP LINE: 00800-7250-4000 (toll free)
REPAIR LINE: 00800-7250-8000 E-MAIL: info@dlink.de
INDIA D-LINK INDIA
Plot No.5, Kurla-Bandra Complex Road, Off Cst Road, Santacruz (E), Bombay - 400 098 India
TEL: 91-22-652-6696 FAX: 91-22-652-8914 URL: www.dlink-india.com
E-MAIL: service@dlink.india.com
ITALY D-LINK ITALIA
Via Nino Bonnet No. 6/b, 20154 Milano, Italy
TEL: 39-02-2900-0676 FAX: 39-02-2900-1723 URL: www.dlink.it
JAPAN D-LINK JAPAN
10F, 8-8-15 Nishi-Gotanda, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo 141, Japan
TEL: 81-3-5434-9678 FAX: 81-3-5434-9868 URL: www.d-link.co.jp
E-MAIL: kida@d-link.co.jp
RUSSIA D-LINK RUSSIA
Michurinski Prospekt 49, 117607 Moscow, Russia
TEL: 7-095-737-3389, 7-095-737-3492 FAX: 7-095-737-3390
URL: www.dlink.ru
SINGAPORE D-LINK INTERNATIONAL
1 International Business Park, #03-12 The Synergy, Singapore 609917
TEL: 65-774-6233 FAX: 65-774-6322 URL: www.dlink-intl.com E-MAIL: info@dlink.com.sg
S. AFRICA D-LINK SOUTH AFRICA
102-106 Witchhazel Avenue, Einetein Park 2, Block B,
Highveld Technopark Centurion, South Africa
TEL: 27(0)126652165 FAX: 27(0)126652186
URL: www.d-link.co.za
SWEDEN D-LINK SWEDEN
P.O. Box 15036, S-167 15 Bromma Sweden
TEL: 46-(0)8564-61900 FAX: 46-(0)8564-61901 E-MAIL: info@dlink.se
TAIWAN D-LINK TAIWAN
2F, No. 119 Pao-Chung Road, Hsin-Tien, Taipei, Taiwan
TEL: 886-2-2910-2626 FAX: 886-2-2910-1515 URL: www.dlinktw.com.tw
U.K. D-LINK EUROPE
4
TEL: 44-20-8731-5555 FAX: 44-20-8731-5511
URL: www.dlink.co.uk E-MAIL: info@dlink.co.uk
U.S.A.
TEL: 1-714-855-6000 FAX: 1-866-743-4905 INFO LINE: 1-877-453-5465
E-MAIL: tech@dlink.com, support@dlink.com URL: www.dlink.com
TEL: 1-905-829-5033 FAX: 1-905-829-5095 BBS: 1-965-279-8732 FREE CALL: 1-800-354-6522
URL: www.dlink.ca E-MAIL: techsup@dlink.ca FTP: ftp.dlinknet.com
D-LINK CHINA
, fateen@dlink-me.com
E-MAIL: vl@dlink.ru
E-MAIL: attie@d-link.co.za
th
Floor, Merit House, Edgware Road, Colindale, London, NW9 5AB, U.K.
-LINK U.S.A.
D
17595 Mt. Hermann Street, Fountain Valley, CA 92708, USA
, E-MAIL: info@dlink.it
, URL: www.dlink.se
, E-MAIL: dssqa@tsc.dlinktw.com.tw
26
Page 27

LIMITED WARRANTY (excluding USA)
D-Link provides this limited warranty for its product only to the person or entity who
originally purchased the product from D-Link or its authorized reseller or distributor.
Limited Hardware Warranty:
D-Link products described below (“Hardware”) will be free from material defects in
workmanship and materials from the date of original retail purchase of the Hardware,
for the period set forth below applicable to the product type (“Warranty Period”) if the
Hardware is used and serviced in accordance with applicable documentation; provided
that a completed Registration Card is returned to an Authorized D-Link Service Office
within ninety (90) days after the date of original retail purchase of the Hardware. If a
completed Registration Card is not received by an authorized D-Link Service Office
within such ninety (90) period, then the Warranty Period shall be ninety (90) days from
the date of purchase.
Product Type Warranty Period
Product (excluding power supplies and fans) One (1) Year
Power Supplies and Fans One (1) Year
D-Link warrants that the hardware portion of the
Spare parts and spare kits Ninety (90) days
D-Link’s sole obligation shall be to repair or replace the defective Hardware at no charge
to the original owner. Such repair or replacement will be rendered by D-Link at an
Authorized D-Link Service Office. The replacement Hardware need not be new or of an
identical make, model or part; D-Link may in its discretion may replace the defective
Hardware (or any part thereof) with any reconditioned product that D-Link reasonably
determines is substantially equivalent (or superior) in all material respects to the
defective Hardware. The Warranty Period shall extend for an additional ninety (90)
days after any repaired or replaced Hardware is delivered. If a material defect is
incapable of correction, or if D-Link determines in its sole discretion that it is not
practical to repair or replace the defective Hardware, the price paid by the original
purchaser for the defective Hardware will be refunded by D-Link upon return to
27
Page 28

D-Link of the defective Hardware. All Hardware (or part thereof) that is replaced by D-
Link, or for which the purchase price is refunded, shall become the property of D-Link
upon replacement or refund.
Limited Software Warranty:
product (“Software”) will substantially conform to D-Link’s then current functional
specifications for the Software, as set forth in the applicable documentation, from the
date of original delivery of the Software for a period of ninety (90) days (“Warranty
Period”), if the Software is properly installed on approved hardware and operated as
contemplated in its documentation. D-Link further warrants that, during the Warranty
Period, the magnetic media on which D-Link delivers the Software will be free of
physical defects. D-Link’s sole obligation shall be to replace the non-conforming
Software (or defective media) with software that substantially conforms to D-Link’s
functional specifications for the Software. Except as otherwise agreed by D-Link in
writing, the replacement Software is provided only to the original licensee, and is subject
to the terms and conditions of the license granted by D-Link for the Software. The
D-Link warrants that the software portion of the
Warranty Period shall extend for an additional ninety (90) days after any replacement
Software is delivered. If a material non-conformance is incapable of correction, or if D-
Link determines in its sole discretion that it is not practical to replace the non-
conforming Software, the price paid by the original licensee for the non-conforming
Software will be refunded by D-Link; provided that the non-conforming Software (and all
copies thereof) is first returned to D-Link. The license granted respecting any Software
for which a refund is given automatically terminates.
What You Must Do For Warranty Service:
Registration Card. The Registration Card provided at the back of this manual must be
completed and returned to an Authorized D-Link Service Office for each D-Link product
within ninety (90) days after the product is purchased and/or licensed. The
addresses/telephone/fax list of the nearest Authorized D-Link Service Office is provided
in the back of this manual. FAILURE TO PROPERLY COMPLETE AND TIMELY
28
Page 29

RETURN THE REGISTRATION CARD MAY AFFECT THE WARRANTY FOR THIS
PRODUCT.
Submitting A Claim
writing before the end of the Warranty Period to an Authorized D-Link Service Office.
The claim must include a written description of the Hardware defect or Software
nonconformance in sufficient detail to allow D-Link to confirm the same. The original
product owner must obtain a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number from the
Authorized D-Link Service Office and, if requested, provide written proof of purchase of
the product (such as a copy of the dated purchase invoice for the product) before the
warranty service is provided. After an RMA number is issued, the defective product
must be packaged securely in the original or other suitable shipping package to ensure
that it will not be damaged in transit, and the RMA number must be prominently
marked on the outside of the package. The packaged product shall be insured and
shipped to D-Link, 17595 Mt. Hermann Street, Fountain Valley, CA92708, with all shipping costs
. Any claim under this limited warranty must be submitted in
prepaid. D-Link may reject or return any product that is not packaged and shipped in
strict compliance with the foregoing requirements, or for which an RMA number is not visible from
the outside of the package. The product owner agrees to pay D-Link’s reasonable handling
and return shipping charges for any product that is not packaged and shipped in accordance with the
foregoing requirements, or that is determined by D-Link not to be defective or non-conforming.
What Is Not Covered:
This limited warranty provided by D-Link does not cover:
Products that have been subjected to abuse, accident, alteration, modification, tampering,
negligence, misuse, faulty installation, lack of reasonable care, repair or service in any
way that is not contemplated in the documentation for the product, or if the model or
serial number has been altered, tampered with, defaced or removed;
Initial installation, installation and removal of the product for repair, and shipping costs;
29
Page 30

Operational adjustments covered in the operating manual for the product, and normal
maintenance;
Damage that occurs in shipment, due to act of God, failures due to power surge, and
cosmetic damage; and
Any hardware, software, firmware or other products or services provided by anyone other
than D-Link.
Disclaimer of Other Warranties: EXCEPT FOR THE LIMITED WARRANTY
SPECIFIED HEREIN, THE PRODUCT IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” WITHOUT ANY
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. IF ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY CANNOT BE
DISCLAIMED IN ANY TERRITORY WHERE A PRODUCT IS SOLD, THE DURATION
OF SUCH IMPLIED WARRANTY SHALL BE LIMITED TO NINETY (90) DAYS.
EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY COVERED UNDER THE LIMITED WARRANTY
PROVIDED HEREIN, THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY, SELECTION AND
PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT IS WITH THE PURCHASER OF THE PRODUCT.
Limitation of Liability:
IS NOT LIABLE UNDER ANY CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY OR OTHER
LEGAL OR EQUITABLE THEORY FOR ANY LOSS OF USE OF THE PRODUCT,
INCONVENIENCE OR DAMAGES OF ANY CHARACTER, WHETHER DIRECT, SPECIAL,
TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, D-LINK
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES
FOR LOSS OF GOODWILL, WORK STOPPAGE, COMPUTER FAILURE OR
MALFUNCTION, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATA CONTAINED IN, STORED ON, OR
INTEGRATED WITH ANY PRODUCT RETURNED TO D-LINK FOR WARRANTY
SERVICE) RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, RELATING TO WARRANTY
SERVICE, OR ARISING OUT OF ANY BREACH OF THIS LIMITED WARRANTY, EVEN IF
D-LINK HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. THE SOLE
30
Page 31

REMEDY FOR A BREACH OF THE FOREGOING LIMITED WARRANTY IS REPAIR,
REPLACEMENT OR REFUND OF THE DEFECTIVE OR NON-CONFORMING PRODUCT.
GOVERNING LAW: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the
state of California.
Some states do not allow exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, or
limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the foregoing limitations and
exclusions may not apply. This limited warranty provides specific legal rights and the
product owner may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
31
Page 32

FCC Certifications
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with emission limits. You are
cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void your authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) This device must
accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
32
Page 33

CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
VCCI Warning
Trademarks
Copyright 1999 D-Link Corporation. Contents subject to change without prior notice. D-Link is a
registered trademark of D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc. All other trademarks belong to their
respective proprietors.
Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to
make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without
permission from D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems Inc., as stipulated by the United
States Copyright Act of 1976.
33
Page 34

Registration Card (excluding USA)
Print, type or use block letters.
Your name: Mr./Ms _____________________________________________________________________________
Organization: ________________________________________________ Dept. ____________________________
Your title at organization: ________________________________________________________________________
Telephone: _______________________________________ Fax:________________________________________
Organization's full address: ______________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Country: _____________________________________________________________________________________
Date of purchase (Month/Day/Year): _______________________________________________________________
Product Model Product Serial No. * Product installed in type of
* Product installed in
computer (e.g., Compaq 486)
(* Applies to adapters only)
Product was purchased from:
Reseller's name: ______________________________________________________________________________
Telephone: _______________________________________ Fax:________________________________________
Reseller's full address: _________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
Answers to the following questions help us to support your product:
1. Where and how will the product primarily be used?
Home Office Travel Company Business Home Business Personal Use
2. How many employees work at installation site?
1 employee 2-9 10-49 50-99 100-499 500-999 1000 or more
3. What network protocol(s) does your organization use ?
XNS/IPX TCP/IP DECnet Others_____________________________
4. What network operating system(s) does your organization use ?
D-Link LANsmart Novell NetWare NetWare Lite SCO Unix/Xenix PC NFS 3Com 3+Open
Banyan Vines DECnet Pathwork Windows NT Windows NTAS Windows '95
Others__________________________________________
5. What network management program does your organization use ?
D-View HP OpenView/Windows HP OpenView/Unix SunNet Manager Novell NMS
NetView 6000 Others________________________________________
6. What network medium/media does your organization use ?
Fiber-optics Thick coax Ethernet Thin coax Ethernet 10BASE-T UTP/STP
100BASE-TX 100BASE-T4 100VGAnyLAN Others_________________
7. What applications are used on your network?
Desktop publishing Spreadsheet Word processing CAD/CAM
Database management Accounting Others_____________________
8. What category best describes your company?
Aerospace Engineering Education Finance Hospital Legal Insurance/Real Estate Manufacturing
Retail/Chainstore/Wholesale Government Transportation/Utilities/Communication VAR
System house/company Other________________________________
9. Would you recommend your D-Link product to a friend?
Yes No Don't know yet
10.Your comments on this product?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
computer serial No.
34
 Loading...
Loading...