D-Link DFL-900 User Manual

D-Link DFL-900
Firewall/VPN Router
User Manual
D-Link
Building Networks for People

II
© Copyright 2003 D-Link Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication including text, examples, diagrams or illustrations may be reproduced, transmitted, or translated in any
form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, manual, optical or otherwise, for any purpose, without prior written permission of
D-Link Systems, Inc.
DFL-900 User Ma nual
Version 0.4
November 5, 2003
Trademarks
Products mentioned in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Regulatory Compliance
FCC Class A Part 15 CSA/CUS
Version 11/4/2003 6:28 PM

I
Table of Contents
Part I Basic Configuration.............................................................................................................................. 2
Chapter 1 Quick Start..................................................................... ......................................................................3
1.1 Before You Begin.......................................................................................................................................................3
1.2
Check Your Package Contents...................................................................................................................................3
1.3 Device default value...................................................................................................................................................3
1.4 Wiring the DFL-900...................................................................................................................................................4
1.5
Default Architecture of DFL-900...............................................................................................................................5
1.6 Using the Setup Wizard..............................................................................................................................................6
1.7 Internet Connectivity..................................................................................................................................................8
1.7.1
LAN1-to-WAN1 Connectivity .........................................................................................................................8
1.7.2 WAN1-to-DMZ1 Connectivity.........................................................................................................................9
Chapter 2 System Overview................................... ... ..................................... ... ................................................. 13
2.1
Topology ..................................................................................................................................................................13
2.2 Changing the LAN1 IP Address...............................................................................................................................13
2.2.1 From DMZ1 to configure DFL-900 LAN1 network settings..........................................................................14
2.2.2 From CLI (command line interface) to configure DFL-900 LAN1 network settings.....................................14
Chapter 3 Basic Setup .......................................................................... ..............................................................15
3.1 Demand....................................................................................................................................................................15
3.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................................................................15
3.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................15
3.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................15
3.4.1 Setup WAN1 IP..............................................................................................................................................16
3.4.2 Setup DMZ1, LAN1 Status.............................................................................................................................17
3.4.3 Setup WAN1 IP alias......................................................................................................................................18
Chapter 4 System Tools................................................................................................ .. ....................................21
4.1 Demand....................................................................................................................................................................21
4.2
Objectives.................................................................................................................................................................21
4.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................21
4.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................23
Chapter 5 Remote Management........................................................... .. ...................................... . ..................... 27
5.1 Demands...................................................................................................................................................................27
5.2 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................27
5.3
Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................28
Part II NAT & Firewall.................................................................................................................................. 30
Chapter 6 NAT................ ... ........................................................................ ......................................................... 31
6.1 Demands...................................................................................................................................................................31
6.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................................................................31
6.3
Methods....................................................................................................................................................................32
6.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................32
6.4.1 Setup Many-to-one NAT rules........................................................................................................................32
6.4.2
Setup Virtual Server for the FtpServer1 .........................................................................................................35
Chapter 7 Firewall..................................................................... ..................................... ....................................39

II
7.1
Demands ..................................................................................................................................................................39
7.2 Objectives ................................................................................................................................................................39
7.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................39
7.4
Steps......................................................................................................................................................................... 40
7.4.1 Block internal PC session (LAN WAN)....................................................................................................40
7.4.2 Setup Alert detected attack.............................................................................................................................41
Part III Virtual Private Network ......................................................................................................................44
Chapter 8 VPN Technical Introduction...............................................................................................................45
8.1
Terminology Explanation.........................................................................................................................................45
8.1.1 VPN................................................................................................................................................................ 45
8.1.2 IPSec............................................................................................................................................................... 45
8.1.3 Security Association.......................................................................................................................................45
8.1.4 IPSec Algorithms............................................................................................................................................45
8.1.5 Key Management............................................................................................................................................45
8.1.6 Encapsulation .................................................................................................................................................46
8.1.7 IPSec Protocols...............................................................................................................................................47
8.2 Make VPN packets pass through DFL-900..............................................................................................................47
Chapter 9 Virtual Private Network – IPSec.........................................................................................................49
9.1 Demands ..................................................................................................................................................................49
9.2 Objectives ................................................................................................................................................................49
9.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................49
9.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................50
9.4.1
DES/MD5 IPSec tunnel: the IKE way............................................................................................................50
9.4.2 DES/MD5 IPSec tunnel: the Manual-Key way..............................................................................................56
Chapter 10 Virtual Private Network – PPTP.......................................................................................................61
10.1
Demands ..................................................................................................................................................................61
10.2 Objectives ................................................................................................................................................................61
10.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................61
10.4
Steps......................................................................................................................................................................... 62
Chapter 11 Virtual Private Network – L2TP.......................................................................................................65
11.1 Demands ..................................................................................................................................................................65
11.2
Objectives ................................................................................................................................................................65
11.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................65
11.4 Steps......................................................................................................................................................................... 66
11.4.1 Setup L2TP Network Server...........................................................................................................................66
11.4.2 Setup L2TP Network Client...........................................................................................................................68
Part IV Content Filters.....................................................................................................................................70
Chapter 12 Content Filtering – Web Filters ........................................................................................................71
12.1 Demands ..................................................................................................................................................................71
12.2 Objectives ................................................................................................................................................................71
12.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................71
12.4 Steps......................................................................................................................................................................... 72
Chapter 13 Content Filtering – Mail Filters........................................................................................................77
13.1 Demands ..................................................................................................................................................................77
13.2 Objectives ................................................................................................................................................................77

III
13.3
Methods....................................................................................................................................................................77
13.4 Steps for SMTP Filters.............................................................................................................................................78
13.5 Steps for POP3 Filters..............................................................................................................................................79
Chapter 14 Content Filtering – FTP Filtering.................................................................................................... 81
14.1 Demands...................................................................................................................................................................81
14.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................................................................81
14.3
Methods....................................................................................................................................................................81
14.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................82
Part V Intrusion Detection System .......................................... .......... ........... ........... .......... .......... .................. 84
Chapter 15 Intrusion Detection Systems............................................................................................................ 85
15.1 Demands...................................................................................................................................................................85
15.2
Objectives.................................................................................................................................................................85
15.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................85
15.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................86
Part VI Bandwidth Management......................................... ........... ........... ........ .......... ........... ......................... 88
Chapter 16 Bandwidth Management.................................................................................................................. 89
16.1 Demands...................................................................................................................................................................89
16.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................................................................89
16.3 Methods....................................................................................................................................................................89
16.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................90
16.4.1 Inbound Traffic Management.........................................................................................................................90
16.4.2 Outbound Traffic Management.......................................................................................................................93
Part VII System Maintenance.................................................. ........... .......... ........... ........... ...................... 96
Chapter 17 Log System................................................ ..................................... ................................................. 97
17.1 Demands...................................................................................................................................................................97
17.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................................................................97
17.3
Methods....................................................................................................................................................................97
17.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................................................................97
Chapter 18 System Maintenance........................................................................................................................ 99
18.1
Demands...................................................................................................................................................................99
18.2 Steps for TFTP Upgrade...........................................................................................................................................99
18.3 Steps for Firmware upgrade from Web GUI..........................................................................................................100
18.4
Steps for Factory Reset...........................................................................................................................................101
18.4.1 Steps for NORMAL factory reset.................................................................................................................101
18.4.2 Steps for EMERGENT factory reset.............................................................................................................101
18.5
Steps for Backup / Restore Configurations............................................................................................................101
Appendix A Trouble Shooting...................................................................................................................... 103
Appendix B Glossary of Terms..................................................................................................................... 107

D-Link Part I
2
Part I
Basic Configuration

Quick Start DFL-900 User Manual
3
Chapter 1
Quick Start
This chapter introduces how to quick setup the DFL-900.
DFL-900 is an integrated all-in-one solution that can facilitate the maximum security and the best resource utilization for
the enterprises. It contains a high-performance stateful packet inspection (SPI) Firewall (400Mbps at 3000 rules),
policy-based NAT, wire-speed VPN (simultaneous 2000 tunnels), upgradeable Intrusion Detection System, Dynamic
Routing, Content Filtering, Bandwidth Management, WAN Load Balancer, and other solutions in a single box. It is
one of the most cost-effective all-in-one solutions for enterprises.
1.1 Before You Begin
Prepare a computer with an Ethernet adapter for configuring the DFL-900. The default IP address for the DFL-900 is
192.168.1.254 (LAN1, Port 2) with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0. You will need to assign your computer a Static IP
address within the same range as the DFL-900’s IP address, say 192.168.1.2, to configure the DFL-900.
1.2 Check Your Package Contents
These are the items included with your DFL-900 purchase as Figure 1-1. They are the following items
1. DFL-900 Device * 1
2. Ethernet cable (RJ -45) * 1
3. RS-232 console * 1
4. CD (include User's manual and Quick Guide) * 1
5. Power code * 1
Figure 1-1 All items in the DFL-900 package
1.3 Device default value
You should have an Internet account already set up and have been given most of the following information as Table 1-1.
Fill out this table when you edit the web configuration of DFL-900.
If any of the items are
missing, please contact
your
reseller.
D-Link Part I
4
Items Default value New value
Password: admin
IP Address
____.____.____.____
Subnet Mask
____.____.____.____
Gateway IP
____.____.____.____
Primary DNS
____.____.____.____
Secondary DNS
____.____.____.____
PPPoE Username
WAN1
(Port 1)
PPPoE Password
Not initialized
IP Address
192.168.1.254 ____.____.____.____
LAN1
(Port 2)
IP Subnet Mask
255.255.255.0 ____.____.____.____
IP Address
10.1.1.254 ____.____.____.____
DMZ1
(Port 3)
IP Subnet Mask
255.255.255.0 ____.____.____.____
Table 1-1 DFL-900 related network settings
1.4 Wiring the DFL-900
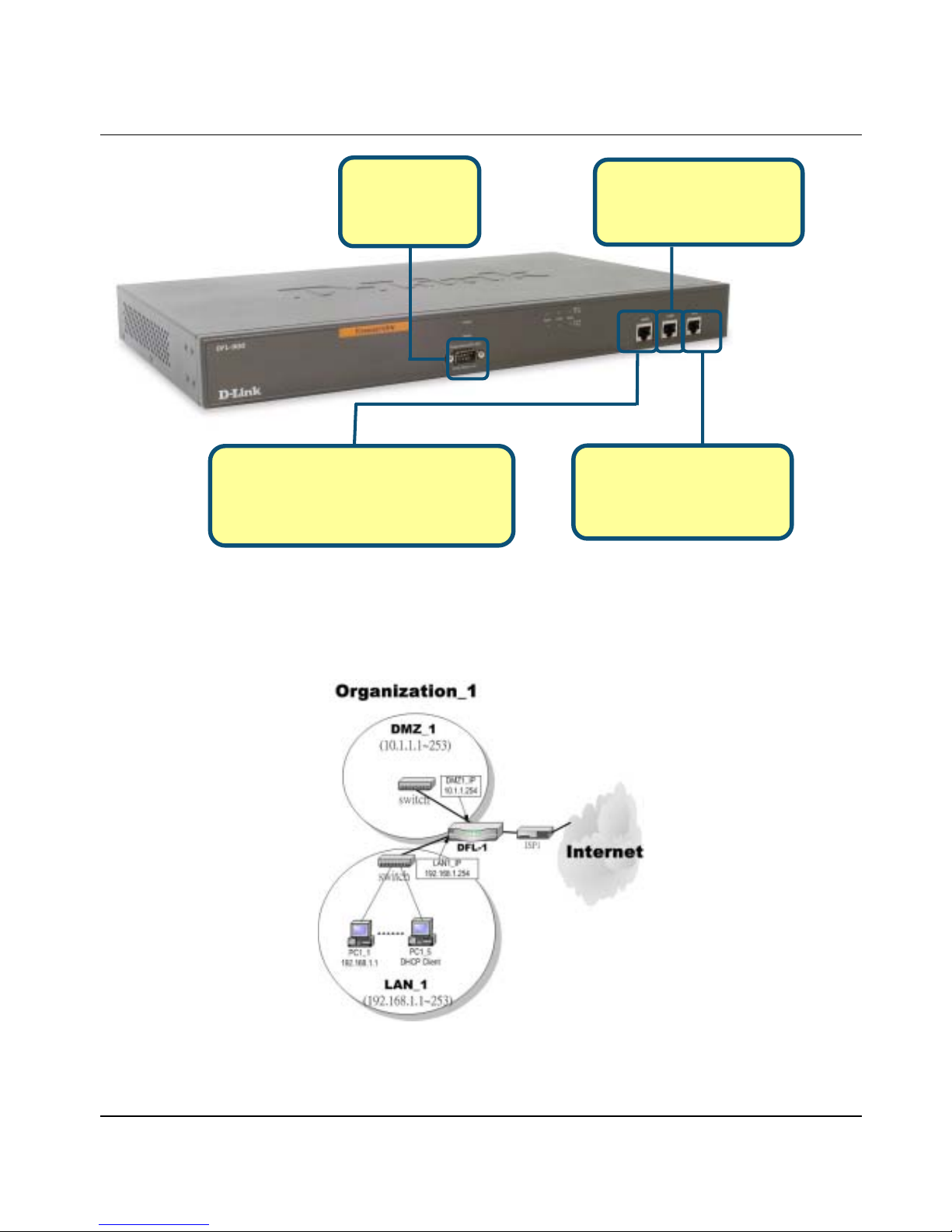
A. First, connect the power cord to the socket at the back panel of the D FL-900 as i n Figure 1-2 and then
plug the other end of the power adapter to a wall outlet or power strip. The Power LED will turn ON to
indicate proper operation.
Figure 1-2 Back panel of the DFL-900
B. Using an Ethernet cable, insert one end of the cable to the WAN port on the fron t panel of the DFL-900
and the other end of the cable to a DSL or Cable modem, as in Figure 1-3.
C. Computers with an Ethernet adapter can be directly connected to any of the LAN ports using a
cross-over Ethernet cable, as in Figure 1-3.
D. Computers that act as servers to provide Internet services should be connected to the DMZ port using an
Ethernet Cable, as in Figure 1-3.
A. Power Socket
Quick Start DFL-900 User Manual
5
Figure 1-3 Front end of the DFL-900
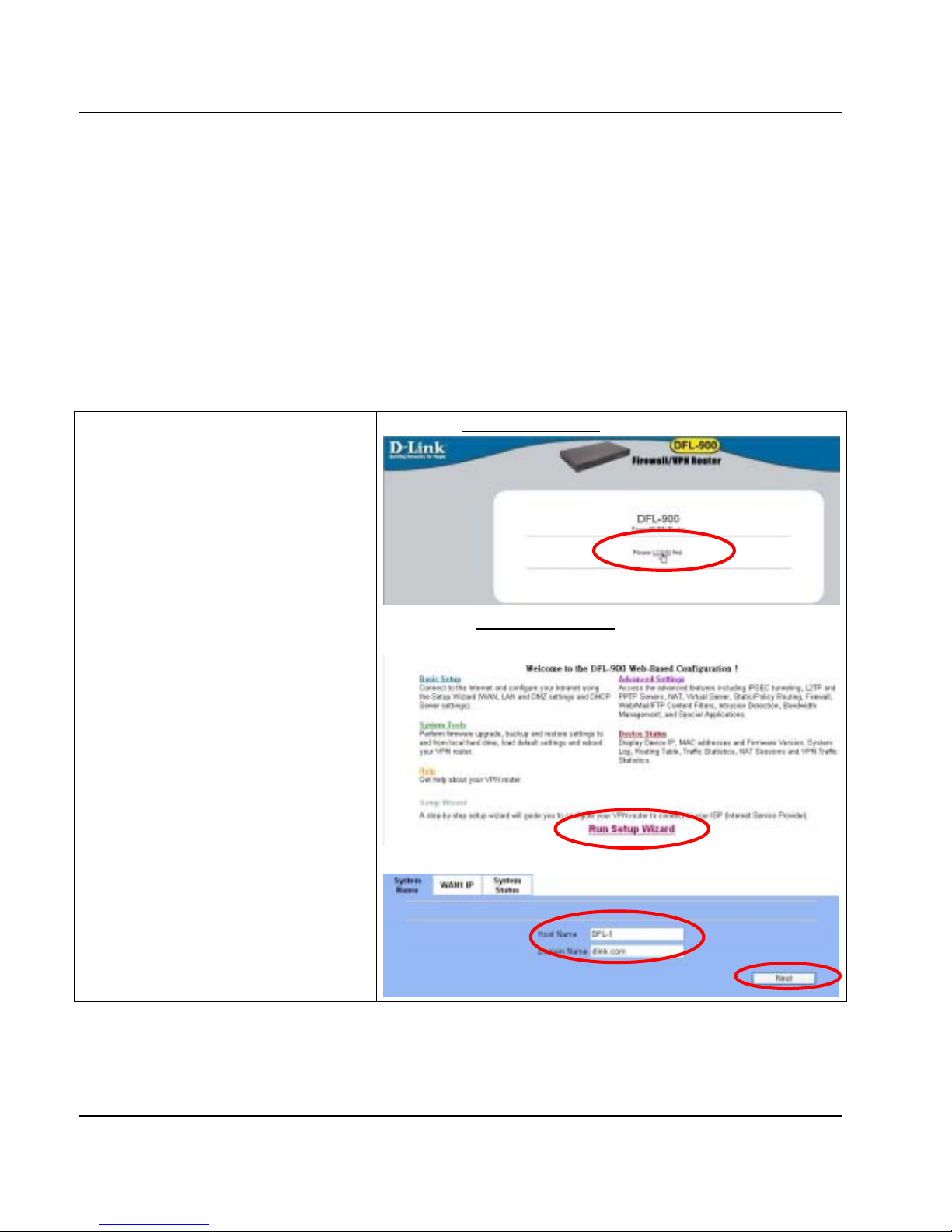
1.5 Default Architecture of DFL-900
Figure 1-4 The default settings of DFL-900
D. DMZ1 Port
For connecting computers that
act as servers for Internet users
to access.
Console Port
For managing the
DFL-900 with CLI
commands.
B. WAN1 Port
For connecting the DFL-900 to a DSL or Cable
Modem supplied by your ISP to access the
Internet.
C. LAN1 Port
For connecting computers and
network devices to your LAN.
D-Link Part I
6
The factory default settings for the DFL-900 are in the Figure 1-4 and Table 1-1. You can configure the DFL-900 by
connecting to the LAN1_IP (192.168.1.254) from the PC1_1 (192.168.1.1). The following section will teach you how to
quickly setup the DFL-900 based on Fig u re 1-4 .
1.6 Using the Setup Wizard
A computer on your LAN1 must be assigned an IP address and Subnet Mask from the same range as the IP address and
Subnet Mask assigned to the DFL-900 in order to be able to make an HTTPS connection using a web browser. The
DFL-900 is assigned an IP address of 192.168.1.254 with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0 by default. The computer that
will be used to configure the DFL-900 must b e assigned an IP add ress between 192.168.1.1 and 19 2.168.1.253 with a
Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0 to be able to connect to the DFL-900. This address range can be changed later. There are
instructions in the DFL-900 User’s Guide, if you do not know how to set the IP address and Subnet Mask for your
computer.
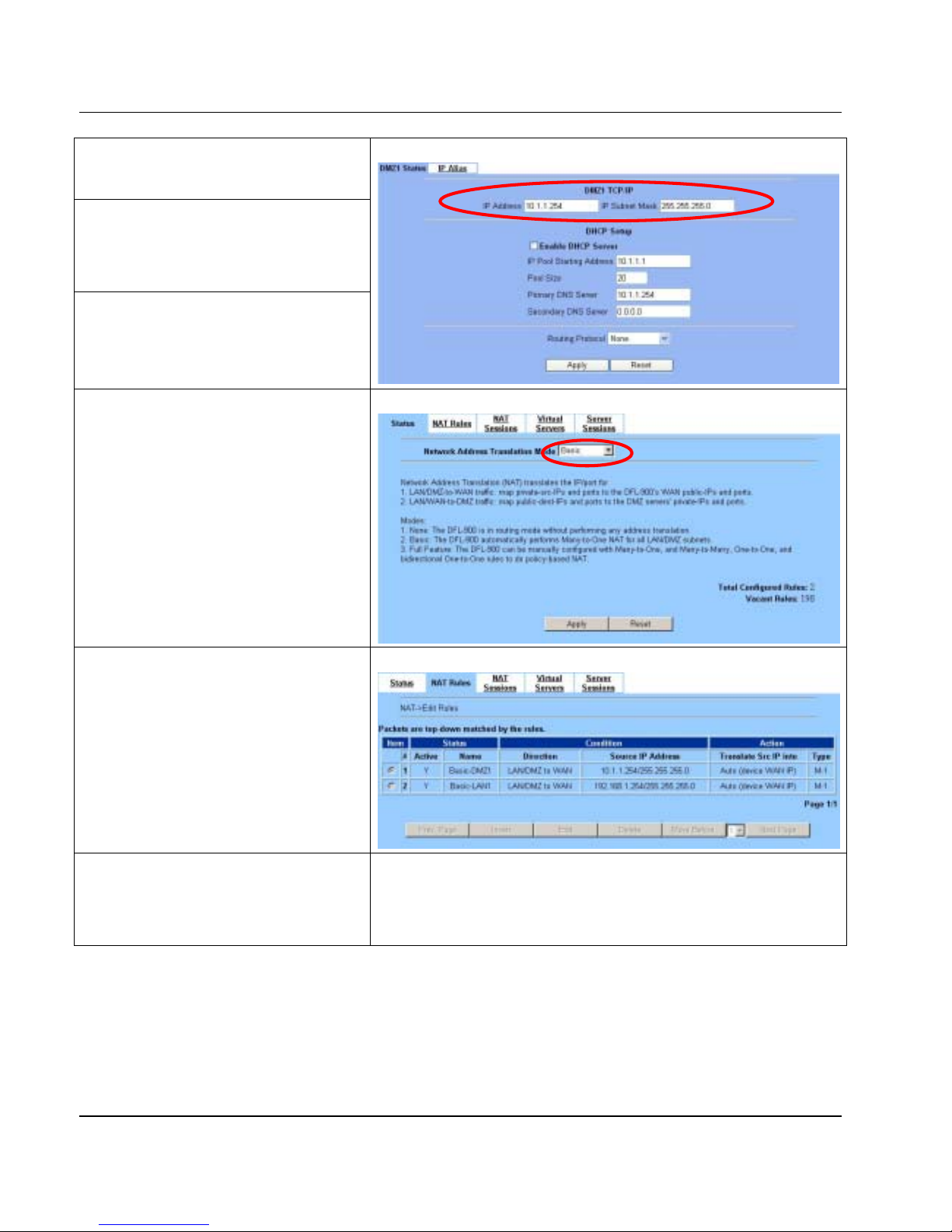
Step 1 - Login
Type “admin” in the account field, “admin” in the
Password field and click Login.
Connect to https://192.168.1.254
Step 2 - Run Setup Wizard
Click the
Run Setup Wizard
.
After login to https://192.168.1.254
BASIC SETUP > Wizard
Step 3 - System Name
Enter the Host Name and the Domain Name,
followed by clicking the Next.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard

Quick Start DFL-900 User Manual
7
Step 4 - WAN Connectivity
Choose the type of IP Address Assignment
provided by your ISP to access the Internet. Here
we have four types to select. This will determine
how the IP address of WAN1 is obtained. Click
Next
to proceed.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next
Step 4.a — DHCP client
If
Get IP Automatically (DHCP)
is selected,
DFL-900 will request for IP address, netmask, and
DNS servers from your ISP. You can use your
preferred DNS by clicking the
DNS IP Address
and then completing the
Primary DNS
and
Secondary DNS
server IP addresses. Click
Next
to proceed.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next > DHCP
Step 4.b — Fixed IP
If Fixed IP Address is selected, enter the
ISP-given
IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway
IP, Primary DNS
and
Secondary DNS
IP. Click
Next
to proceed.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next > Fixed IP

D-Link Part I
8
Step 4.c — PPPoE client
If
PPP over Ethernet
is selected, enter the
ISP-given
User Name, Password
and the optional
Service Name. Click Next to proceed.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next > PPPoE
Step 5 - System Status
Here we select
PPPoE
method in WAN1 port. Then
the DFL-900 provides a short summary of the
system. Please check if anything mentioned above
is properly set into the system. Click Finish to
close the wizard.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next > Next
1.7 Internet Connectivity
After setting up DFL-900 with the wizard, DFL-900 can connect to the ISP. In this chapter, we introduce LAN1-to-WAN1
Connectivity to explain how the computers under LAN1 can access the Internet through DFL-900. Subsequently, we introduce
WAN1-to-DMZ1 Connectivity to explain how the servers under DMZ1 can be accessed by the LAN1 users and other Internet users
on the WAN1 side.
You MUST press Apply to proceed to the next page. Once applying any changes, the settings are immediately
updated into the flash memory.
1.7.1 LAN1-to-WAN1 Connectivity
The LAN Settings page allows you to modify the IP address and Subnet Mask that will identify the DFL-900 on your LAN. This is
the IP address you will enter in the URL field of your web browser to connect to the DFL-900. It is also the IP address that all of the
computers and devices on your LAN will use as their Default Gateway.

Quick Start DFL-900 User Manual
9
Step 1 - Device IP Address
Setup the IP Address and IP Subnet Mask for
the DFL-900.
Step 2 - Client IP Range
Enable the DHCP server if you want to use
DFL-900 to assign IP addresses to the computers
under LAN1. Specify the Pool Starting
Address, Pool Size, Primary DNS, and
Secondary DNS
that will be assigned to them.
Example: in the figure, the DFL-900 will assign
one IP address from 192.168.1.100 ~
192.168.1.120, together with the DNS server
192.168.1.254, to the LAN1 PC that requests for
an IP address.
Step 3 - Apply the Changes
Click
Apply
to save. Now you can enable the
DHCP clients on your LAN1 PCs to get an IP.
BASIC SETUP > LAN Settings > LAN1 Status
Note: The
Pool Starting Address
must be on the same subnet specified in
the IP Address and the IP Subnet Mask field. For example, the addresses
given by the 192.168.1.100 with a pool size of 20 (192.168.1.100 ~
192.168.1.120) are all within the same range of 192.168.1.254 /
255.255.255.0
Step 4 - Check NAT Status
The default setting of NAT is in
Basic
Mode.
After applying the Step 3, the NAT is
automatically configured with two rules to let all
private-IP LAN1/DMZ1-to-WAN1 requests to be
translated with the public IP assigned by the ISP.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Status
Step 5 - Check NAT Rules
The DFL-900 has added two NAT rules. The rule
Basic-LAN1
(number 2) means that, when
matching the condition (requests of
LAN/DMZ-to-WAN
direction with its source IP
falling in the range of
192.168.1.254 /
255.255.255.0
), the request will be translated
into a public-source-IP requests, and then be
forwarded to the destinations.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
1.7.2 WAN1-to-DMZ1 Connectivity
This section tells you how to provide an FTP service with a server installed under your DMZ1 to the public Internet users. After
following the steps, users at the WAN side can connect to the FTP server at the DMZ1 side.
D-Link Part I
10
Step 1 - Device IP Address
Setup the
IP Address
and
IP Subnet Mask
for
the DFL-900 of the DMZ1 interface.
Step 2 - Client IP Range
Enable the
DHCP server
if you want to use
DFL-900 to assign IP addresses to the computers
under DMZ1. Here we do not want to make the
DHCP feature enable.
Step 3 - Apply the Changes
Click
Apply
to save your settings.
BASIC SETUP > DMZ Settings > DMZ1 Status
Step 4 - Check NAT Status
The default setting of NAT is in
Basic
Mode.
After applying the Step 3, the NAT is
automatically configured with two rules to let all
private-IP LAN1/DMZ1-to-WAN1 requests to be
translated with the public IP assigned by the ISP.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Status
Step 5 - Check NAT Rules
The DFL-900 has added two NAT rules. The rule
Basic-DMZ1 (number 1) means that, when
matching the condition (requests of
LAN/DMZ-to-WAN direction with its source IP
falling in the range of 10.1.1.254 /
255.255.255.0
), the request will be translated
into a public-source-IP requests, and then be
forwarded to the destinations.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
Step 6 - Setup IP for the FTP Server
Assign an IP of 10.1.1.5/255.255.255.0 to the
FTP server under DMZ1. Assume the FTP Server
is at 10.1.1.5. And it is listening on the well-known
port (21).

Quick Start DFL-900 User Manual
11
Step 7 - Setup Server Rules
Insert a virtual server rule by clicking the Insert
button.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers
Step 8 - Customize the Rule
Customize the rule name as the f
tpServer
. For
any packets with its destination IP equaling to the
WAN1 IP (
61.2.1.1
) and destination port
equaling to 44444, ask DFL-900 to translate the
packet’s destination IP/port into 10.1.1.5/21.
Check the Passive FTP at this port to
maximize the compatibility of the FTP protocol.
This is useful if you want to provide connectivity to
passive FTP clients. For passive FTP clients, the
server will return them the private IP address and
the port numb er for them to connect bac k to do
data transmissions. Since the private IP from
them cannot be routed to our zone, the data
connections would fail. After enabling this feature,
the DFL-900 will translate the private IP/port into
an IP/port of its own. Thus the problem is
gracefully solved. Click
Apply
to proceed.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers > Insert
Step 9 - View the Result
Now any request towards the DFL-900’s WAN1
IP (
61.2.1.1
) with dest. port
44444
will be
translated into a request towards 10.1.1.5 with
port 21, and then be forwarded to the 10.1.1.5.
The FTP server listening at port 21 in 10.1.1.5
will pick up the request.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers

System Overview DFL-900 User Manual
13
Chapter 2
System Overview
In this chapter, we will introduce the network topology for use with later chapters.
2.1 Topology
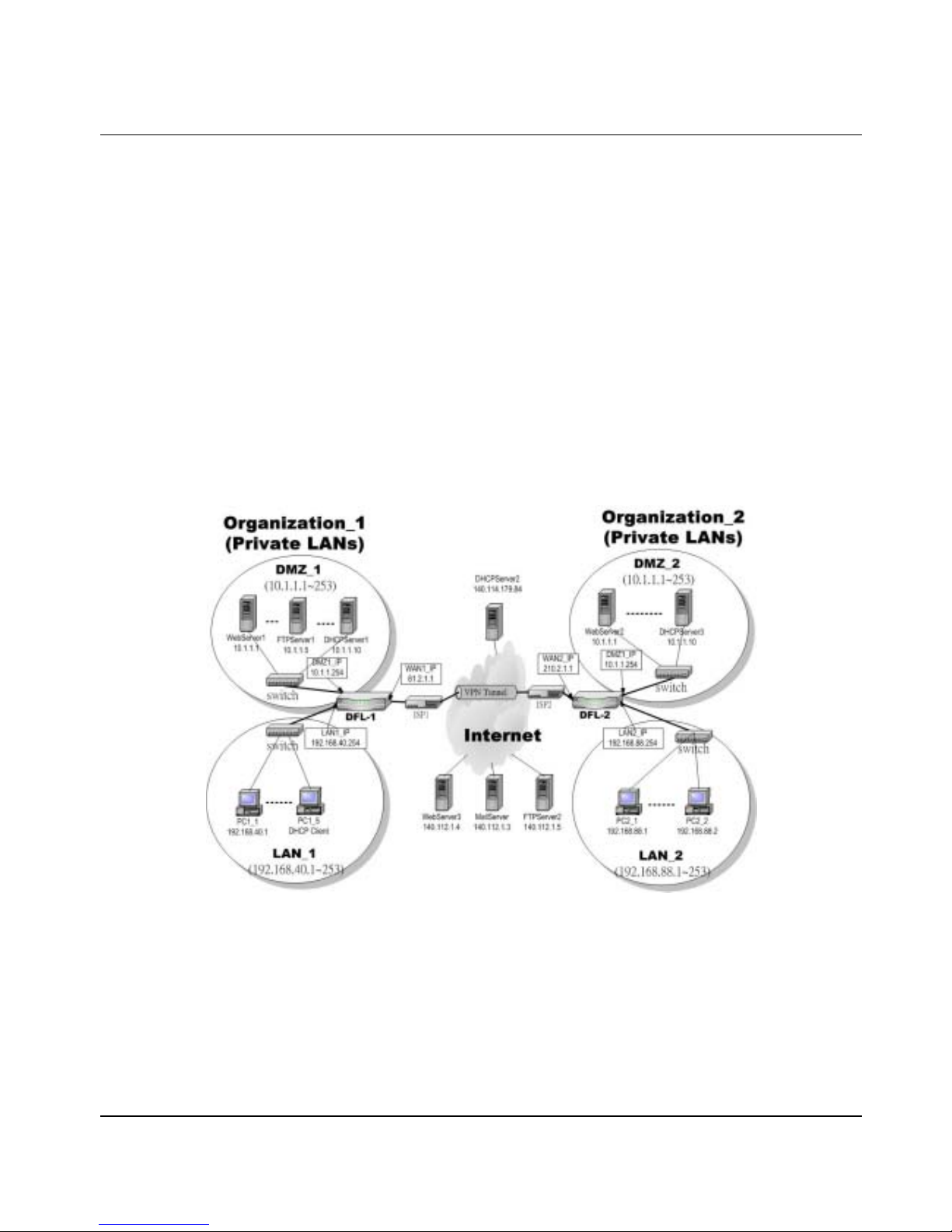
In this chapter, we introduce a typical network topology for the DFL-900. In Figure 2-1, the left half side is a DFL-900 with one
LAN, one DMZ, and one WAN links. Notice there are three ports in DFL-900. In this topology, we only use one LAN.
The right half side contains a DFL-900 connected with one LAN, one DMZ, and one WAN. In this architecture, Organization_1
communicates with Organization_2 with a VPN tunnel established by the two DFL-900 Firewall/VPN routers. The VPN tunnel
secures communications between Organizations more safely.
On the Internet side, there are web server, mail server, DHCP server, and FTP server for testing content filters and bandwidth
management.
Figure 2-1 Overview of the system architecture for DFL-900
2.2 Changing the LAN1 IP Address
The default settings of DFL-900 are listing in Table 1-1. However, the original LAN1 setting is 192.168.1.254/255.255.255.0
instead of 192.168.40.254/255.255.255.0 as in Figure 2-1. We will change the LAN1 IP of the DFL-900 to 192.168.40.254. Notice
that you cannot change the LAN1 IP from the LAN1 interface because your configuration session to LAN1 will be terminated as
long as the LAN1 IP address is changed. If you do change the IP from the LAN1 port, you will have to reboot the system, change
your computer’s IP to the new subnet, and reconnect to the new LAN1 IP address. You can also use console to login into the system
D-Link Part I
14
and then logout the system. That will clean up the zombie left in the system so you will be able to login to the DFL-900 from the
LAN1 side after your computer’s IP is changed into the new subnet.
We provide two normal ways to configure the LAN1 IP address. One is to configure the LAN1 IP from another port such as DMZ1.
The other is to configure the LAN1 IP through console. Note that when setting the IP address from console, the settings are updated
into run-time system but not stored into the flash. Namely, the settings will be lost after you reboot the system. So, it is best to use
the first method for setting the LAN1 IP address.
2.2.1 From DMZ1 to configure DFL-900 LAN1 network settings
Step 1 - Check NAT Status
In the DMZ_1 region, use a PC located 10.1.1.X
to connect DFL-900 DMZ1 port (10.1.1.254).
Type https://10.1.1.254 to configure the DFL-900
in the web browser.
Use an IE 6.0 at 10.1.1.1 to connect to
https://10.1.1.254
Step 2 - Setup LAN1 IP information
Enter the IP Address and IP Subnet Mask with
192.168.40.254 / 255.255.255.0 and click
Apply.
BASIC SETUP > LAN Settings > LAN1 Status
2.2.2 From CLI (command line interface) to configure DFL-900 LAN1 network settings
Step 1 - Use Console port to configure
DFL-900
Use the supplied console line to connect the PC
to the Diagnostic RS-232 socket of the DFL-900.
Start a new connection using the HyperTerminal
with parameters: No Parity, 8 Data bits, 1
stop bit,
and
baud rate 9600
. Enter
admin
for
user name
and
admin
for
password
to login.
After logging into DFL-900, enter the commands
“en“ to enter the privileged mode. Enter the
command “
IP ifconfig INTF1
192.168.40.254
” to change the IP of the LAN1
interface.
DFL-900> en
DFL-900# IP ifconfig INTF1 192.168.40.254 255.255.255.0
DFL-900# IP ifconfig INTF1
LAN1: flags=8843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,SIMPLEX,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
address: 00:50:fc:ba:db:fe
media: Ethernet autoselect (100baseTX full-duplex)
status: active
inet 192.168.40.254 Netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 192.168.40.255

Basic Setup DFL-900 User Manual
15
Chapter 3
Basic Setup
In this chapter, we will introduce how to setup network settings for each port separately
3.1 Demand
1. For the external network, suppose your company uses DSL to connect Internet via PPPoE. By this way, you should setup
WAN port of the DFL-900 in advance.
2. There are some adjustment within your company, so the original network stucture has been changed. Now, you should
modify the configuration between the internal network (DMZ, LAN).
3. Your company needs more network bandwidth if it is insufficent for your company to connect to the external network.
3.2 Objectives
1. Configure the network settings of the DFL-900 WAN1 port.
2. Configure the network settings of the DFL-900 DMZ1 and LAN1 ports.
3. Suppose your company applys another ISP, and hope that the applied Network IP can configure in the same WAN port of
DFL-900.
3.3 Methods
1. Select the PPPoE method in the DFL-900 Basic Setup/WAN settings/WAN1 IP, and then configure the related account and
password in order to connet to the internet.
2. Configure the related network settings in the pages of the DFL-900 Basic Setup / DMZ settings / DMZ1 Status and Basic
Setup / LAN settings / LAN1 Status.
3. Configure the IP alias in WAN1 port.
3.4 Steps
Notice:Do not try to configure the port network setting from the same port you login. Or the network will be terminated and system
will be locked in the original IP address.

D-Link Part I
16
3.4.1 Setup WAN1 IP
Step 1 - Setup WAN1 port
Here we select
PPP over Ethernet
method in
WAN1 port. Fill in the IS P-giv en
User Name
and
Password
and the optional
Service Name
. And
then check the needed field. Click
Apply
to finish
this setting.
BASIC SETUP > WAN Settings > WAN1 IP > PPPoE
IP Address
Assignment
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Service Name ISP vendor (Optional)
User Name The user name of PPPoE account 12345678@hinet.net
Password The password of PPPoE account G5468889
Get DNS Automatically /
DNS IP Address
Get DNS Automatically Get DNS related
information from PPPoE ISP
DNS IP Address manually specify these Primary
and Secondary DNS Server information
Get DNS
Automatically
PPP over
Ethernet
Disconnected
Through click Connect or Disconnect button to connect
or disconnect PPPoE line
Click Connect
IP Address / Subnet Mask Specified IP address and subnet mask
211.43.123.7
255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Default gateway IP address 211.43.123.254
DNS IP Address Specified Primary and Secondary DNS Server address
Fixed IP
Address
Routing Protocol
Determine to enable the dynamic routing protocol, to
receive RIP message, to send out the RIP message if
the RIP message is received or not.
None
Get DNS Automatically or
DNS IP Address
Get DNS Automatically Get DNS related
information from DHCP Server
DNS IP Address manually specify these Primary
and Secondary DNS Server information
Get DNS
Automatically
Get IP
Automatically
(DHCP)
Routing Protocol
Determine to enable the dynamic routing protocol, to
receive RIP message, to send out the RIP message if
the RIP message is received or not.
None
Table 3-1 Detailed information of setup WAN port configuration
Basic Setup DFL-900 User Manual
17
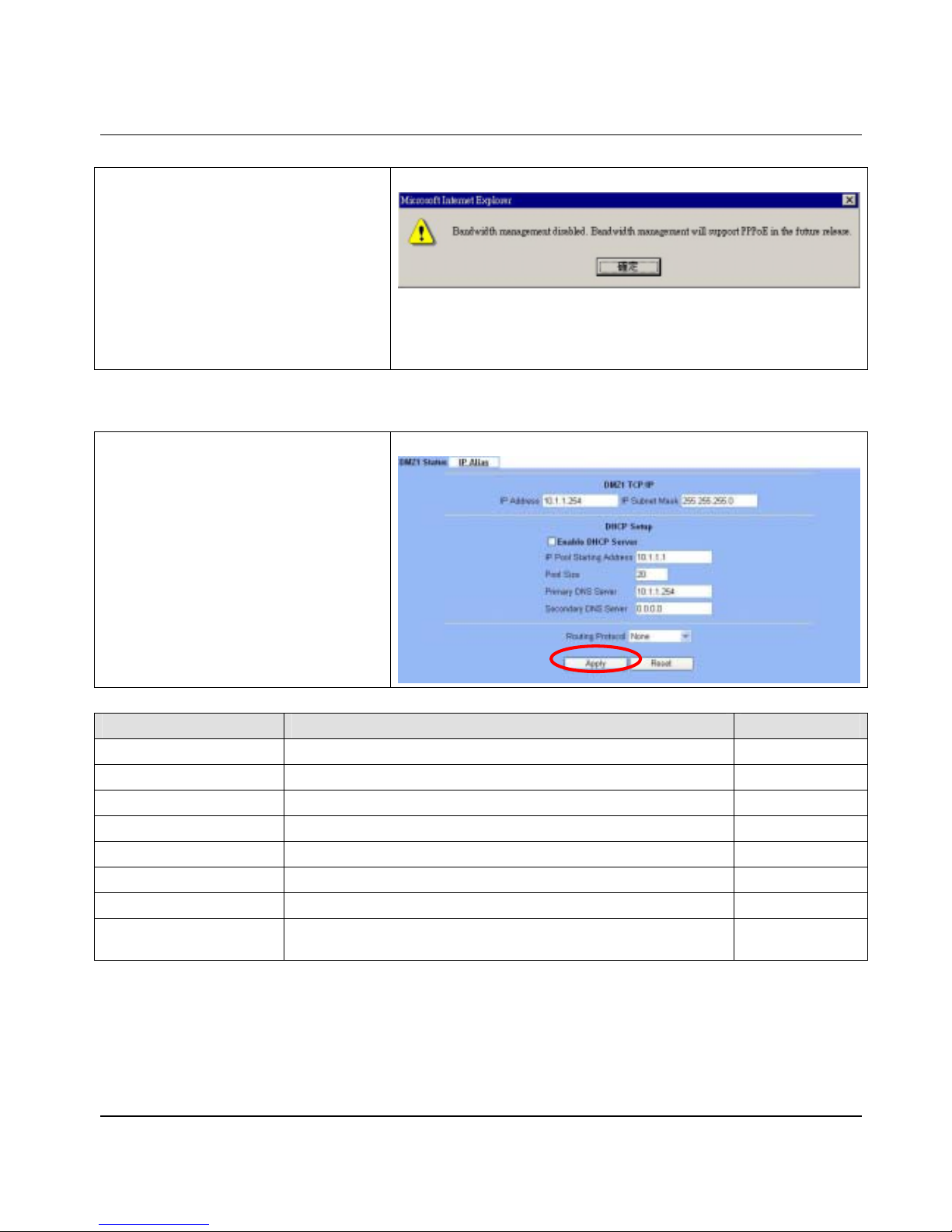
Step 2 - Show the Warning message
Note that if you have already enabled
bandwidth management (ADVANCED
SETTINGS>Bandwidth Mgt>Enable Bandwidth
Management) and then select PPPoE in BASIC
SETUP>WAN Settings>WAN1 IP>PPPoE as
your internet connection, it will show you a
message indicated as right column to tell you that
Bandwidth management will not support PPPoE
in this version. If you still like to use bandwidth
management, please try to use another method,
such as DHCP or Fixed IP, to connect Internet.
BASIC SETUP > WAN Settings > WAN1 IP > PPPoE
3.4.2 Setup DMZ1, LAN1 Status
Step 1 - Setup DMZ port
Here we are going to configure the DMZ1
settings. Setup
IP Address
and
IP Subnet
Mask
, and determine if you would like to
enable
the DHCP Server
. If yes, please check Enable
DHCP Server. And then select None for Routing
Protocol. Click
Apply
to finish this setting.
BASIC SETUP > DMZ Settings > DMZ1 Status
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
IP Address DMZ port IP address 10.1.1.254
IP Subnet Mask DMZ port IP subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Enable DHCP Server Enable DMZ port of the DHCP Sever or not
IP Pool Starting Address Specify the starting address of the DHCP IP address. 10.1.1.1
Pool Size Specify the numbers of the DHCP IP address. 20
Primary DNS Server Specify the Primary DNS Server IP address of the DHCP. 10.1.1.254
Secondary DNS Server Specify the Secondary DNS Server IP address of the DHCP.
Routing Protocol
Determine to enable the dynamic routing protocol (RIP), to receive RIP
message, to send out RIP message if the message is received or not.
None
Table 3-2 Configure DMZ network settings
D-Link Part I
18
Step 2 - Setup LAN port
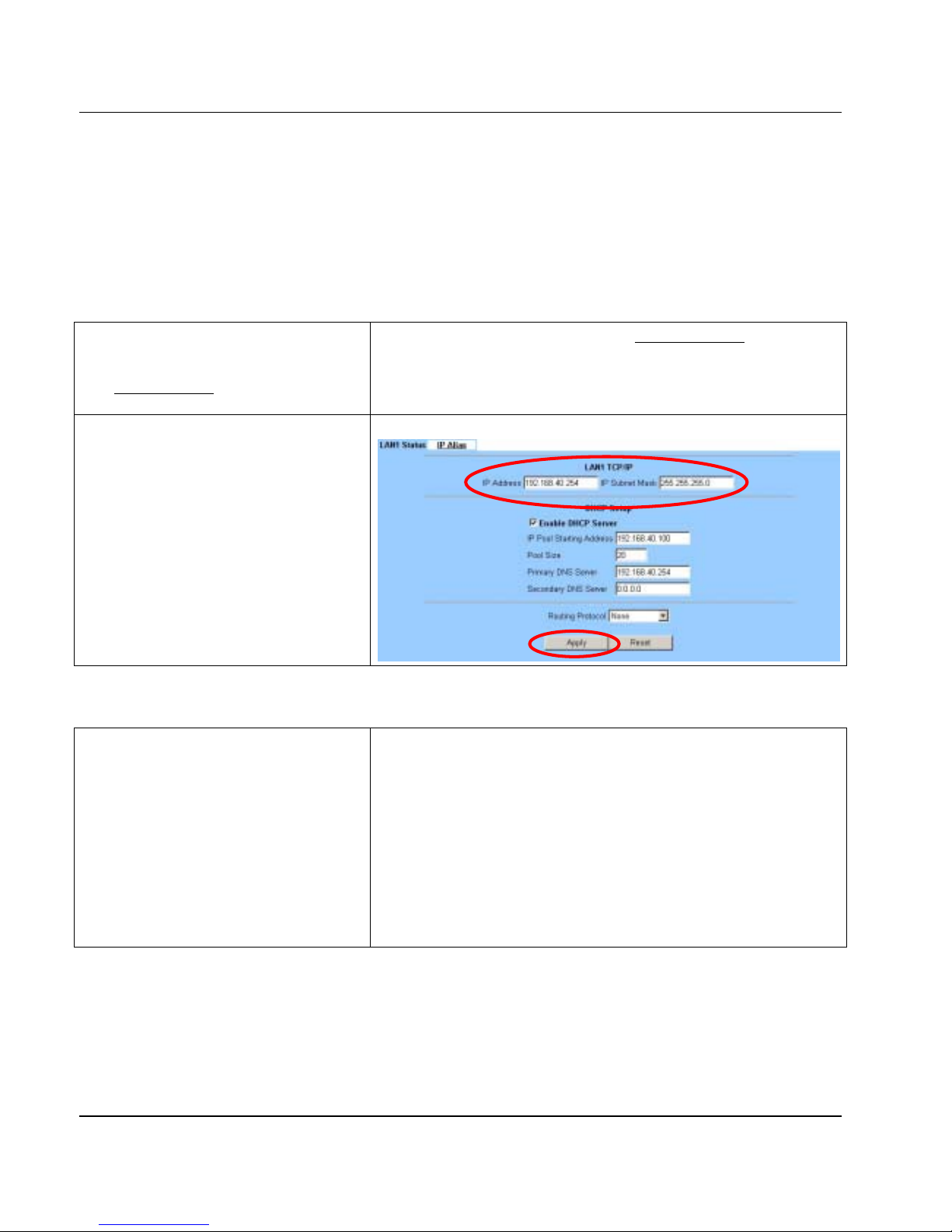
Here we are going to configure the LAN1 settings.
Setup IP Address and IP Subnet Mask, and
determine if you would li ke to enable the DHCP
Server. And then select Routing Protocol. Click
Apply to finish this setting.
BASIC SETUP > LAN Settings > LAN1 Status
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
IP Address LAN port IP address 192.168.40.254
IP Subnet Mask LAN port IP subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Enable DHCP Server Enable LAN port of the DHCP Sever or not Enabled
IP Pool Starting Address Specify the starting address of the DHCP IP address. 192.168.40.100
Pool Size Specify the numbers of the DHCP IP address. 20
Primary DNS Server Specify the Primary DNS Server IP address of the DHCP. 192.168.40.254
Secondary DNS Server Specify the Secondary DNS Server IP address of the DHCP.
Routing Protocol
Determine to enable the dynamic routing protocol (RIP), to receive RIP
message, to send out RIP message if the message is received or not.
None
Table 3-3 Configure LAN network settings
3.4.3 Setup WAN1 IP alias
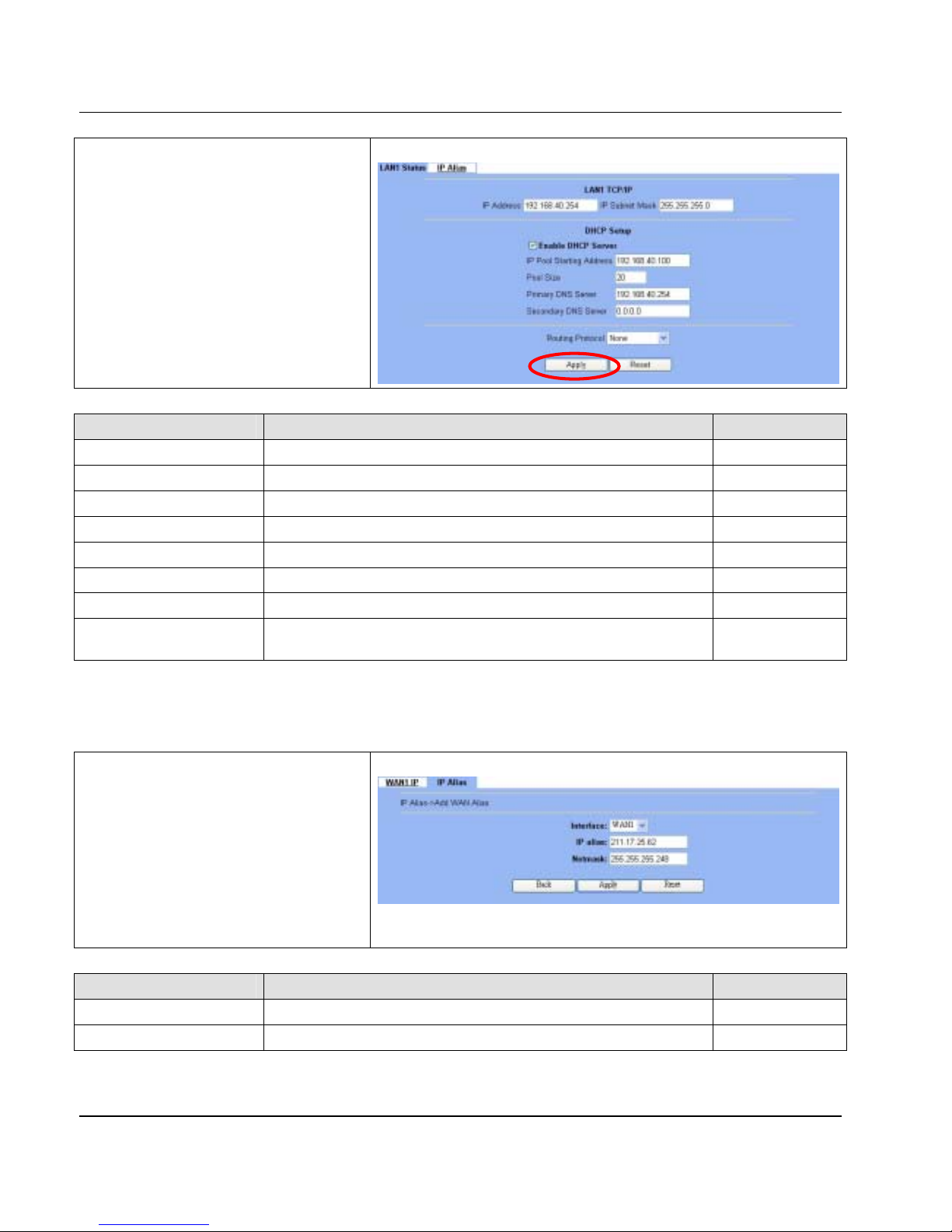
Step 1 - Add WAN1 IP alias
Suppose you apply 8 IP addresses from ISP. The
range of the ISP-given IP addresses is from
211.17.25.56 to 211.17.25.63. Now you would
like to add a WAN1 IP alias. Select WAN1 in the
Interface. Enter the IP alias and Netmask with
211.17.25.62/255.255.255.248. And then click
Apply.
Notice:It’s the same way to set IP alias in DMZ or
LAN.
BASIC SETUP > WAN Settings > IP Alias > Add
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Interface The interface which we set for the IP alias WAN1
IP alias The alias IP address
211.17.25.62

Basic Setup DFL-900 User Manual
19
Netmask The netmask of the IP alias 255.255.255.248
Table 3-4 Add a IP alias record
Step 2 - Edit, Delete IP alias record
You can easily add, edit, or delete IP alias
records by the Add, Edit, or Delete button.
BASIC SETUP > WAN Settings > IP Alias


System Tools DFL-900 User Manual
21
Chapter 4
System Tools
This chapter introduces System Management and explains how to implement it.
4.1 Demand
1. Basic configurations for domain name, password, system time, and management timeout.
2. DDNS: Suppose the DFL-900’s WAN uses dynamic IP but needs a fixed host name. When the IP is changed, it is
necessary to have the DNS record updated accordingly. To use this service, one has to register the account, password, and
the wanted host name with the service provider.
3. DNS Proxy: Shorten the time of DNS lookup performed by applications.
4. DHCP Relay: It is to solve the problem that when the DHCP client is not in the same domain with the DHCP server, the
DHCP broadcast will not be received by the server. If the client is in the LAN (192.168.40.X) while the server is located in
the DMZ (10.1.1.10), the server will not receive any broadcast packet from the client.
4.2 Objectives
1. Configure the domain name, password, system time, and connection timeout.
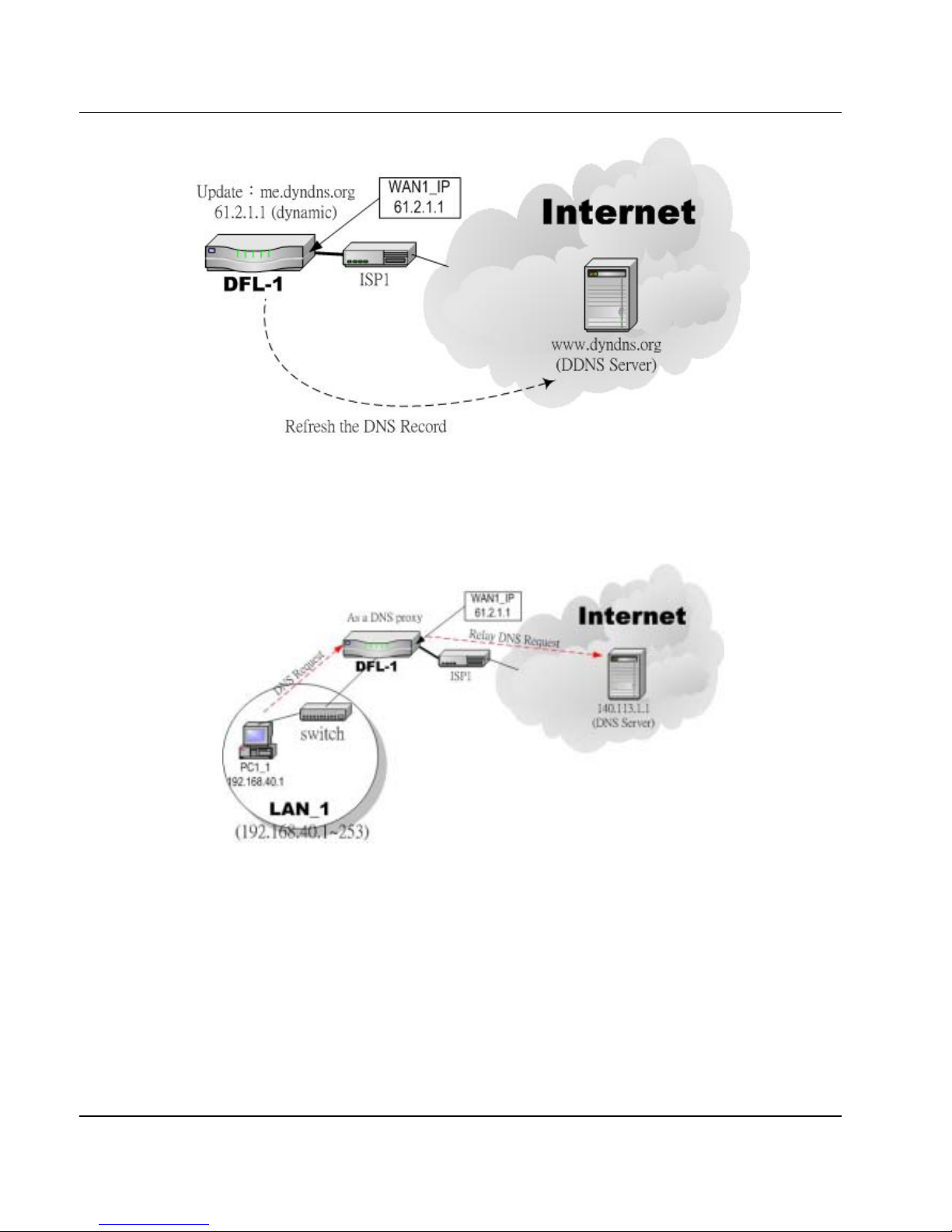
2. DDNS: By using the DDNS (Dynamic DNS), the DFL-900 will send the request for modification of the corresponding
DNS record to the DDNS server after the IP is changed.
3. DNS Proxy: Reduce the number of DNS requests and the time for DNS lookup.
4. DHCP Relay: Enable the DHCP client to contact with the DHCP server located in different domain and get the required IP.
4.3 Methods
1. Configure the domain name, password, system time, and connection timeout.
2. DDNS: Configure the DFL-900 so that whenever the IP of the DFL-900 is changed, it will send requests to the DDNS
server to refresh the DNS record.
D-Link Part I
22
Figure 4-1 DDNS mechanism chart
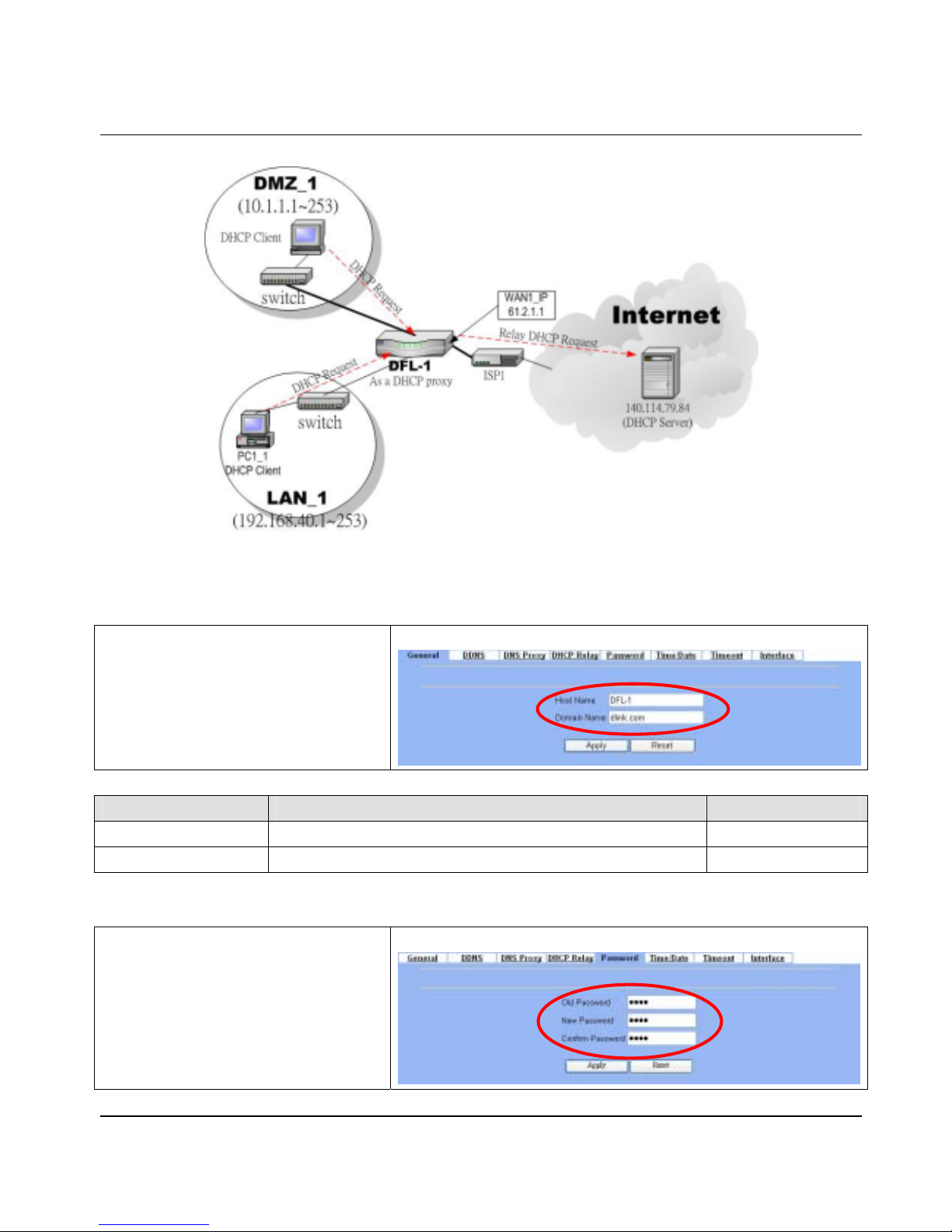
3. DNS Proxy: After activating the DNS proxy mode, the client can set its DNS server to the DFL-900 (that is, send the DNS
requests to the DFL-900). The DFL-900 will then make the enquiry to the DNS server and return the result to the client.
Besides, the caching mechanism performed by the DNS proxy can also help reduce possible duplicate DNS lookups.
Figure 4-2 DNS Proxy mechanism chart
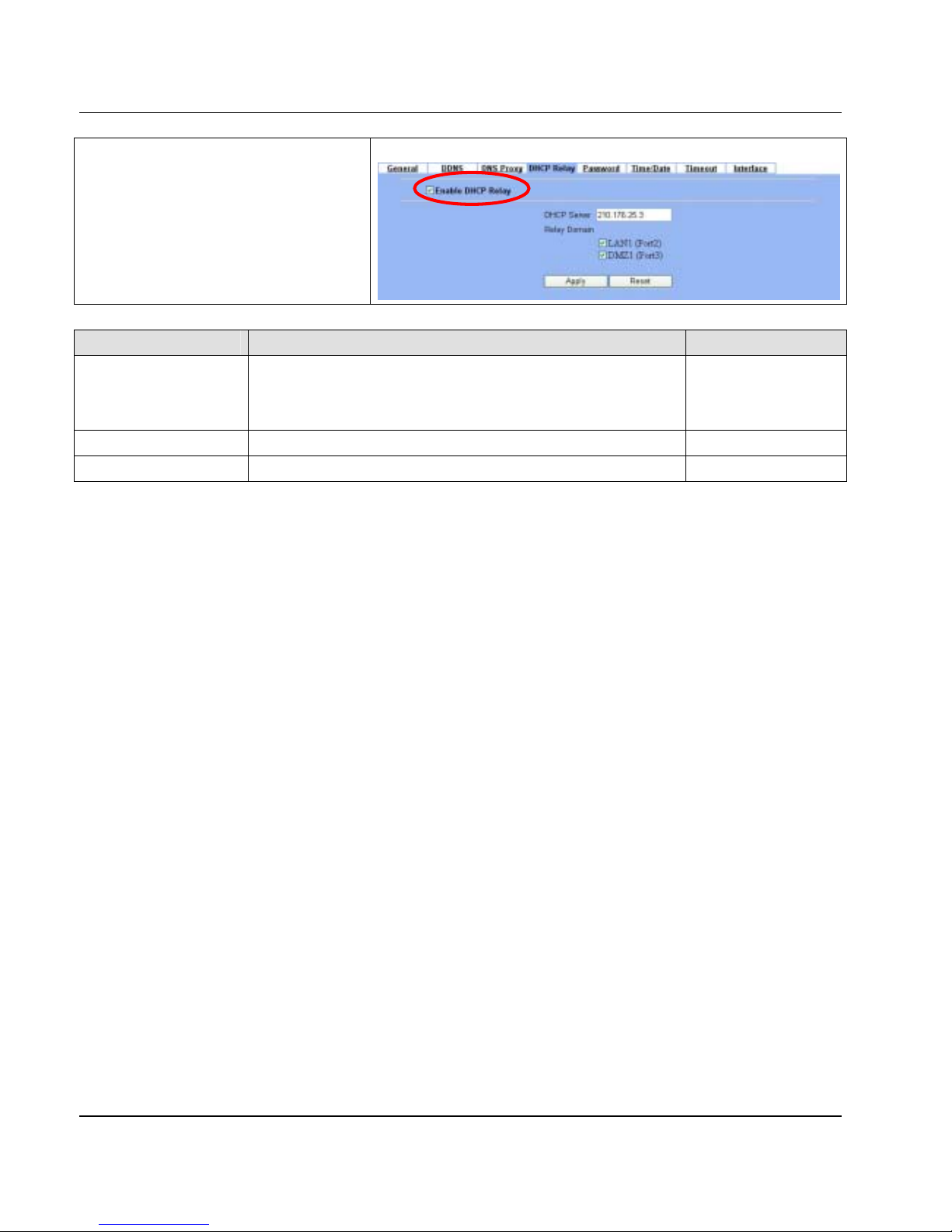
4. DHCP Relay: Activate the DHCP relay mode of DFL-900 so that the DFL-900 will become the relay agent and relay the
DHCP broadcast to the configured DHCP server.
System Tools DFL-900 User Manual
23
Figure 4-3 DHCP Relay mechanism chart
4.4 Steps
Step 1 - General Setup
Enter the
Host Name
as
DFL-1, Domain Name
as the domain name of your company Click
Apply.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > General
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Host Name the host name of the DFL-900 device DFL-1
Domain Name Fill in the domain name of company dlink.com
Table 4-1 System Tools - General Setup menu
Step 2 - Change Password
Enter the current password in the Old Password
field. Enter the new password in the New
Password
and retype it in the
Retype to
Confirm
field. Click
Apply
.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Password

D-Link Part I
24
Step 3 - Setup Time/Date
Select the
Time Zone
where you are located.
Enter the nearest NTP time server in the
NTP
time server address. Note that your DNS
must be set if the entered address requires
domain name lookup. You can also enter an IP
address instead. Check the Continuously
(every 3 min) update system clock and
click
Apply
. The DFL-900 will immediately
update the system time and will periodically
update it. Check the
Update system clock
using the time server at boot time
and
click
Apply
if you want to update the clock at
each boot. If you want to manually change the
system time, uncheck the
Continuously
(every 3 min) update system clock and
proceed by entering the target date.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Time/Date
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Time zone the time zone of your area
NTP time server address Use NTP time server to auto update date/time value tock.usno.navy.mil
Continuously (every 3 min)
update system clock
System will update system date/time value every 3 minutes to NTP time
sever.
Enabled
Update system clock using
the time server at boot time
System will update system date/time value to the NTP time server at boot
time.
Manual Time Setup Manual setting Time & Date value.
Table 4-2 System Tools – Time Data menu
Step 4 - Setup Timeout
Select the target timeout (e.g. 1
0 min
) from the
System Auto Timeout Lifetime
. Click the
Apply button. Now the browser will not timeout
for the following 10 minutes after your last
touching of it.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Timeout
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
System Auto Timeout
Lifetime
When system is idle for a specified time, system will force the people
who logins into the system will logout automatically.
10
Table 4-3 System Tools – Timeout menu

System Tools DFL-900 User Manual
25
Step 5 - Setup DDNS
If the IP address of DFL-900 WAN port is dynamic
allocated. You may want to have the Dynamic
DNS mechanism to make your partner always
use the same domain name (like xxx.com) to
connect to you. Select a WAN
interface
to
update the DDNS record. Here we supply two
DDNS
Service Providers
. Fill in the H
ost
Name
, U
sername
, P
assword
supplied by the
DDNS web site. Please refer to the DDNS web
site for the detail information. Click
Apply
to
activate the settings.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > DDNS
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Enable DDNS for WAN1 Enable DDNS feature of DFL-900 Enabled
Interface Assign which public IP address of interface to the DDNS server. WAN1
Service Provide
The domain address of DDNS server. In the DFL-900, we provide
www.DYNDNS.org
and www.DHS.org two websites for choice.
WWW.DYNDNS.ORG
Hostname The registered Hostname in the DDNS server. abc.com
Username The registered username in the DDNS server. user
Password The registered password in the DDNS server. 1234567
Table 4-4 System Tools – DDNS setting page
Step 6 - Setup DNS Proxy
Check the
Enable DNS Proxy
and click the
Apply
to store the settings. From now on, your
LAN/DMZ PCs can use DFL-900 as their DNS
server, as long as the DNS server for DFL-900
has been set in its WAN settings.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > DNS Proxy
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Enable DNS Proxy
When the host of the LAN/DMZ sends a DNS Request, DFL-900 will
request for forwarding it to the DNS server of the WAN link. When there
is a response from DNS, DFL-900 will forward it back to the host of the
LAN/DMZ.
Enabled
Table 4-5 System Tools – DNS Proxy menu
D-Link Part I
26
Step 7 - Setup DHCP Relay
Check the
Enable DHCP Relay.
Enter the IP
address of your
DHCP server
. Check the
relay
domain of DFL-900 that needs to be relayed.
Namely, check the one where the DHCP server
resides and the one where DHCP clients are
located. Click the Apply button.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > DHCP Relay
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Enable DHCP Relay
When the host of the LAN/DMZ in the DFL-900 internal network sends a
DHCP request, DFL-900 will forward it automatically to the specified
DHCP server (different subnet from the network segment of the DHCP
client).
Enabled
DHCP Server Current location of the DHCP server. 210.176.25.3
Relay Domain The locations of the DHCP clients.
Table 4-6 System Tools – DHCP Relay menu
 Loading...
Loading...