
JT922
Tier 4i
Operator’s
Manual
CMW
®
Issue 2.0
Original Instruction
053-1298

JT922 Operator’s Manual Overview - 1
Overview
Chapter Contents
Serial Number Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Intended Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Unit Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Operator Orientation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
About This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
• Bulleted Lists. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
• Numbered Lists. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
• “Continued” Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
CMW
Overview - 2 JT922 Operator’s Manual
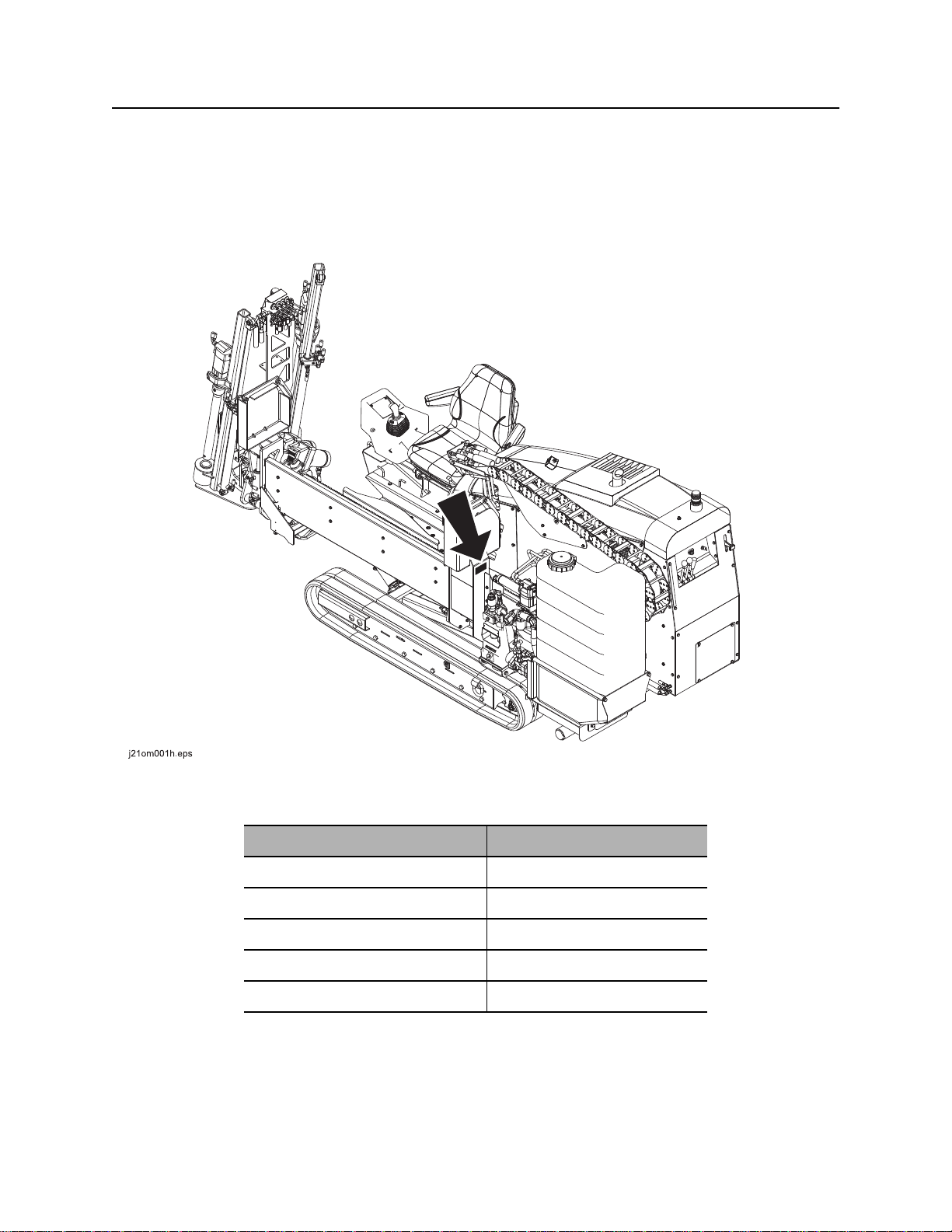
Serial Number Location
Serial Number Location
Record serial numbers and date of purchase in spaces provided. Drilling unit serial number is located as
shown.
CMW
Item
date of manufacture
date of purchase
drilling unit serial number
trailer serial number
engine serial number

JT922 Operator’s Manual Overview - 3
Intended Use
Intended Use
The JT922 Mach 1 is a self-contained horizontal directional drilling unit designed to install buried cable and
pipe at distances to 300’ (90 m) depending on soil conditions and is intended for operation in ambient
temperatures from 0° to 115°F (-18° to 46°C). Use in any other way is considered contrary to the intended
use.
The JT922 Mach 1 can be used with Ditch Witch drilling fluid units and Ditch Witch locating equipment. It
should be operated, serviced, and repaired only by persons familiar with its particular characteristics and
acquainted with the relevant safety procedures.
Equipment Modification
This equipment was designed and built in accordance with applicable standards and regulations.
Modification of equipment could mean that it will no longer meet regulations and may not function properly
or in accordance with the operating instructions. Modification of equipment should only be made by
competent personnel possessing knowledge of applicable standards, regulations, equipment design
functionality/requirements and any required specialized testing.
CMW
Overview - 4 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Unit Components
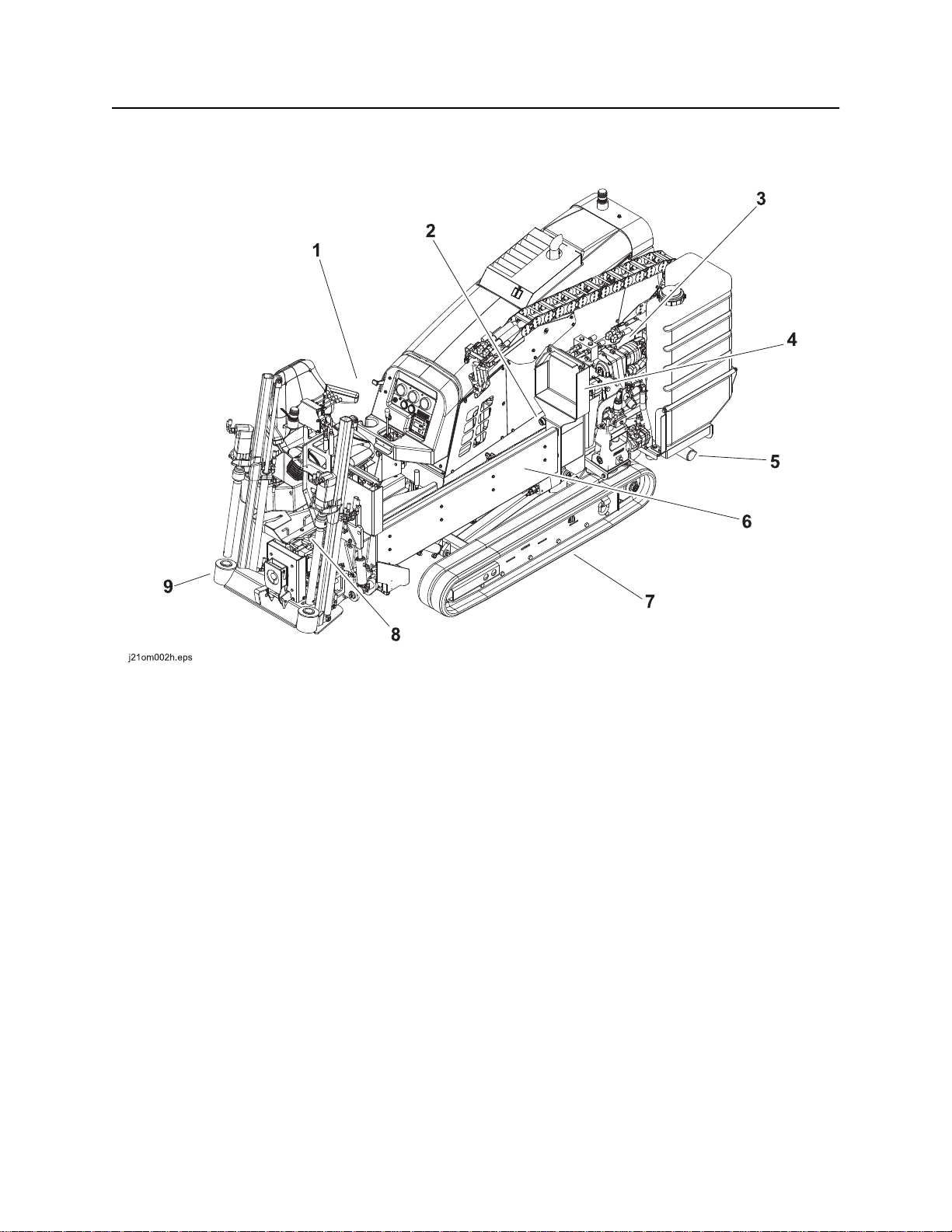
Unit Components
1. Operator’s station
2. Spindle
3. Carriage
4. Drill pipe box
5. Stabilizer
6. Drill frame
7. Tracks
8. Vise wrenches
9. Anchoring system
CMW
JT922 Operator’s Manual Overview - 5
Operator Orientation
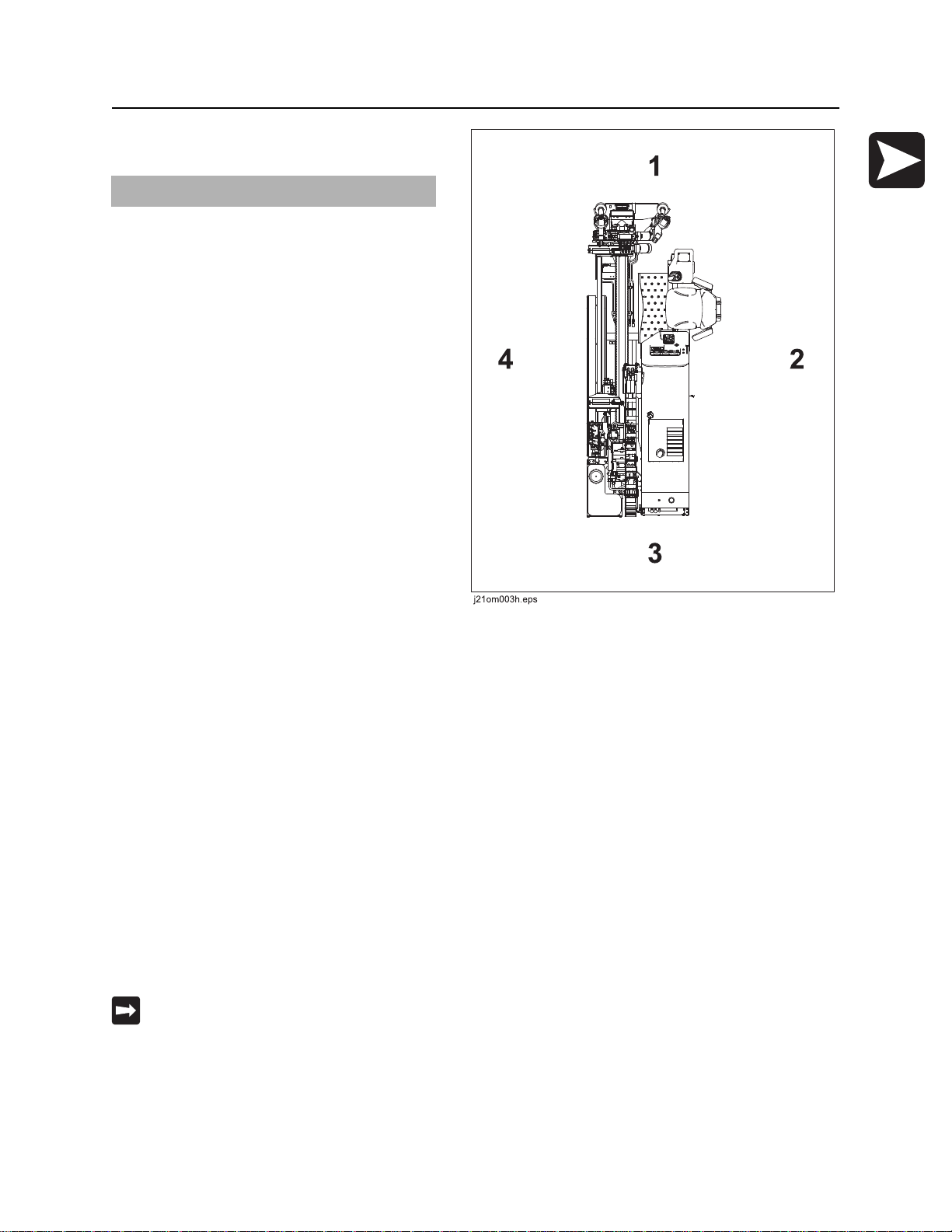
Operator Orientation
IMPORTANT: Top view of unit is shown.
1. Front of unit
2. Right side of unit
3. Rear of unit
4. Left side of unit
About This Manual
This manual contains information for the proper use of this machine. See the beige Operation Overview
pages for basic operating procedures. Cross references such as “See page 50” will direct you to detailed
procedures.
Bulleted Lists
Bulleted lists provide helpful or important information or contain procedures that do not have to be
performed in a specific order.
Numbered Lists
Numbered lists contain illustration callouts or list steps that must be performed in order.
“Continued” Indicators
indicates that a procedure is continued on the next page.
CMW

Overview - 6 JT922 Operator’s Manual
About This Manual
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Foreword - 7
Foreword
This manual is an important part of your equipment. It provides safety information and operation
instructions to help you use and maintain your Ditch Witch equipment.
Read this manual before using your equipment. Keep it with the equipment at all times for future reference.
If you sell your equipment, be sure to give this manual to the new owner.
If you need a replacement copy, contact your Ditch Witch dealer. If you need assistance in locating a
dealer, visit our website at www.ditchwitch.com or write to the following address:
The Charles Machine Works, Inc.
Attn: Marketing Department
PO Box 66
Perry, OK 73077-0066
USA
The descriptions and specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice. The Charles
Machine Works, Inc. reserves the right to improve equipment. Some product improvements may have
taken place after this manual was published. For the latest information on Ditch Witch equipment, see your
Ditch Witch dealer.
Thank you for buying and using Ditch Witch equipment.
CMW

Foreword - 8 JT922 Operator’s Manual
JT922 Tier 4i
Operator’s Manual
Issue number 2.0/OM-04/11
Part number 053-1298
Copyright 2008, 2011
by The Charles Machine Works, Inc.
, Ditch Witch, CMW, AutoCrowd, Jet Trac, Roto Witch, Subsite, Fluid Miser,
Power Pipe, Super Witch, Pierce Airrow, The Underground, The Underground Authority Worldwide, and
Zahn are registered trademarks of The Charles Machine Works, Inc.
This product is covered by one or more of the following patents:
U.S. B1 4,858,704; 4,953,638; 5,148,880; 5,242,026; 5,341,887; 5,490,569; 5,684,466; 5,713,423; 5,794,719; 5,880,680; 5,941,322;
6,085,852; 6,109,371; 6,179,065; 6,216,803; 6,250,403; 6,250,404; 6,290,606; 6,311,790; 6,411,094; 6,543,551; 6,550,547;
6,672,409; 6,739,413; 6,761,231; 6,776,246; 6,808,210; 6,827,158; 6,848,506; 6,871,712; RE37,450; RE37,923; RE37,975;
RE38,418; AU 689,533; 706,544; 718,034; 755,862; CA 2,156,398; 2,217,899; DE 694 17 019; 695 29 634; 297 01 406;
EP 0683845; 0674093; 0817901; 0846841; 0927892; FR 674,093; GB 2,309,239; 2,312,006; EP674,093; EP846,841; JP 3,458,247;
other U.S. and foreign patents pending.
CMW
JT922 Operator’s Manual Contents - 9
Contents
Overview
machine serial number, information about the type of work this machine is designed
to perform, basic machine components, and how to use this manual
Foreword
part number, revision level, and publication date of this manual, and factory contact
information
Safety
machine safety alerts and emergency procedures
Controls
machine controls, gauges, and indicators and how to use them
Operation Overview
an overview for completing a job with this machine: planning, setting up, installing
product, and restoring the jobsite; with cross references to detailed procedures
Prepare
procedures for inspecting and classifying the jobsite, planning the installation path,
and preparing the jobsite for work
Drive
procedures for startup, cold start, driving, and shutdown
1
7
11
21
45
49
65
Transport
procedures for lifting, hauling, and towing
Conduct a Bore
procedures for drilling and backreaming
Systems and Equipment
downhole tools and drill pipe, anchor, electric strike, tracker control, and fluid
systems
Complete the Job
procedures for restoring the jobsite and rinsing and storing equipment
Service
service intervals and instructions for this machine including lubrication, replacement
of wear items, and basic maintenance
69
75
91
121
127
CMW

Contents - 10 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Specifications
machine specifications including weights, measurements, power ratings, and fluid
capacities
Support
the warranty policy for this machine, and procedures for obtaining warranty
consideration and training
Service Record
a record of major service performed on the machine
149
153
157
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Safety - 11
Safety
Chapter Contents
Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Safety Alert Classifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Safety Alerts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Emergency Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
• Electric Strike Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
• If an Electric Line is Damaged . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
• If a Gas Line is Damaged . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
• If a Fiber Optic Cable is Damaged . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
• If Machine Catches on Fire. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CMW

Safety - 12 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Guidelines
Guidelines
Follow these guidelines before operating any jobsite equipment:
• Complete proper training and read operator’s manual before using equipment.
• Contact your local One-Call (811 in USA) or the One-Call referral number (888-258-0808 in USA and
Canada) to have underground utilities located before digging. Also contact any utilities that do not
participate in the One-Call service.
• Classify jobsite based on its hazards and use correct tools and machinery, safety equipment, and work
methods for jobsite.
• Mark jobsite clearly and keep spectators away.
• Wear personal protective equipment.
• Review jobsite hazards, safety and emergency procedures, and individual responsibilities with all
personnel before work begins. Safety videos are available from your Ditch Witch dealer.
• Replace missing or damaged safety shields and safety signs.
• Use equipment carefully. Stop operation and investigate anything that does not look or feel right.
• Do not operate unit where flammable gas may be present.
• Contact your Ditch Witch dealer if you have any question about operation, maintenance, or equipment
use.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Safety - 13
Safety Alert Classifications
Safety Alert Classifications
These classifications and the icons defined on the following pages work together to alert you to situations
which could be harmful to you, jobsite bystanders or your equipment. When you see these words and
icons in the book or on the machine, carefully read and follow all instructions. YOUR SAFETY IS AT
STAKE.
Watch for the three safety alert levels: DANGER, WARNING and CAUTION. Learn what each level
means.
indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury.
Watch for two other words: NOTICE and IMPORTANT.
NOTICE can keep you from doing something that might damage the machine or someone's property. It
can also alert you against unsafe practices.
IMPORTANT can help you do a better job or make your job easier in some way.
CMW
Safety - 14 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Safety Alerts
Safety Alerts
Turning shaft will kill you or crush arm or leg. Stay away.
Electric shock. Contacting electric lines will cause death or serious injury.
Know location of lines and stay away.
Deadly gases. Lack of oxygen or presence of gas will cause sickness or
death. Provide ventilation.
Moving tools will kill or injure. Shut off drill string power when anyone can be
struck by moving or thrown tools. Never use pipe wrenches on drill string.
Jobsite hazards could cause death or serious injury. Use
correct equipment and work methods. Use and maintain proper safety
equipment.
Crushing weight could cause death or serious injury. Use
proper procedures and equipment or stay away.
Moving parts could cut off hand or foot. Stay away.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Safety - 15
Safety Alerts
Explosion possible. Serious injury or equipment damage could occur.
Follow directions carefully.
Incorrect procedures could result in death, injury, or property damage.
Learn to use equipment correctly.
Improper control function could cause death or serious injury. If control does
not work as described in instructions, stop machine and have it serviced.
Looking into fiber optic cable could result in permanent vision damage. Do
not look into ends of fiber optic or unidentified cable.
Pressurized fluid or air could pierce skin and cause injury or
death. Stay away.
Fire or explosion possible. Fumes could ignite and cause burns. No
smoking, no flame, no spark.
Moving traffic - hazardous situation. Death or serious injury could result.
Avoid moving vehicles, wear high visibility clothing, post appropriate warning signs.
CMW

Safety - 16 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Safety Alerts
Hot pressurized cooling system fluid could cause serious burns. Allow to
cool before servicing.
Flying objects may cause injury. Wear hard hat and safety glasses.
Hot parts may cause burns. Do not touch until cool.
Exposure to high noise levels may cause hearing loss. Wear hearing
protection.
Fall possible. Slips or trips may result in injury. Keep area clean.
Battery acid may cause burns. Avoid contact.
Improper handling or use of chemicals may result in illness, injury, or
equipment damage. Follow instructions on labels and in material safety data sheets
(MSDS).
CMW
JT922 Operator’s Manual Safety - 17
Emergency Procedures
Emergency Procedures
Jobsite hazards could cause death or serious injury. Use
correct equipment and work methods. Use and maintain proper safety
equipment.
Before operating any equipment, review emergency procedures and check that all safety precautions have
been taken.
EMERGENCY SHUTDOWN - Turn ignition switch to stop position or push remote engine stop button (if
equipped).
Electric Strike Description
Electric shock. Contacting electric lines will cause death or serious injury.
Know location of lines and stay away.
When working near electric cables, remember the following:
• Electricity follows all paths to ground, not just path of least resistance.
• Pipes, hoses, and cables will conduct electricity back to all equipment.
• Low voltage current can injure or kill. Many work-related electrocutions result from contact with less
than 440 volts.
Most electric strikes are not noticeable, but indications of a strike include:
• power outage
• smoke
• explosion
• popping noises
• arcing electricity
If any of these occur, or if strike alarm sounds or flashes, assume an electric strike has occurred.
CMW

Safety - 18 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Emergency Procedures
If an Electric Line is Damaged
If you suspect an electric line has been damaged and you are on drilling unit or bonded equipment, DO
NOT MOVE. Remain on drilling machine or mats and take the following actions. The order and degree of
action will depend on the situation.
• Warn people nearby that an electric strike has occurred.
• Have someone contact electric company.
• Reverse drilling direction and try to break contact. Do not touch drill pipe with hands or hand-held
tools.
• Press electric strike system status button.
• If alarm sounds again, stay where you are and wait for electric company to shut off power.
• If alarm does not sound and there is no other indication of a strike, wait at least one full minute
before moving away from equipment. Utility might use automatic reclosers which will restart
current flow. If alarm sounds again while waiting, stay where you are until electric company shuts
off power.
• If alarm does not sound but all lights in strike indicator are on, assume strike is continuing and stay
where you are until electric company shuts off power.
• Do not resume drilling or allow anyone into area until given permission by electric company.
If you suspect an electric line has been damaged and you are off drilling unit or bonded equipment, DO
NOT TOUCH ANY EQUIPMENT connected to drilling unit. Take the following actions. The order and
degree of action will depend on the situation.
• Stay where you are unless you are wearing electric insulating boots. If you leave, do not return to area
or allow anyone into area until given permission by electric company.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Safety - 19
Emergency Procedures
If a Gas Line is Damaged
Fire or explosion possible. Fumes could ignite and cause burns. No
smoking, no flame, no spark.
Explosion possible. Serious injury or equipment damage could occur.
Follow directions carefully.
If you suspect a gas line has been damaged, take the following actions. The order and degree of action will
depend on the situation.
• Immediately shut off engine(s), if this can be done safely and quickly.
• Remove any ignition source(s), if this can be done safely and quickly.
• Warn others that a gas line has been cut and that they should leave the area.
• Leave jobsite as quickly as possible.
• Immediately call your local emergency phone number and utility company.
• If jobsite is along street, stop traffic from driving near jobsite.
• Do not return to jobsite until given permission by emergency personnel and utility company.
CMW

Safety - 20 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Emergency Procedures
If a Fiber Optic Cable is Damaged
Do not look into cut ends of fiber optic or unidentified cable. Vision damage can occur.
If Machine Catches on Fire
Perform emergency shutdown procedure and then take the following actions. The order and degree of
action will depend on the situation.
• Immediately move battery disconnect switch (if equipped) to disconnect position.
• If fire is small and fire extinguisher is available, attempt to extinguish fire.
• If fire cannot be extinguished, leave area as quickly as possible and contact emergency personnel.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 21
Controls
Chapter Contents
Set-Up Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Left Control Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Gauge Cluster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Right Control Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Anchoring System Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Seat/Armrest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
ESID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
750/752 Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
• Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
• Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
CMW
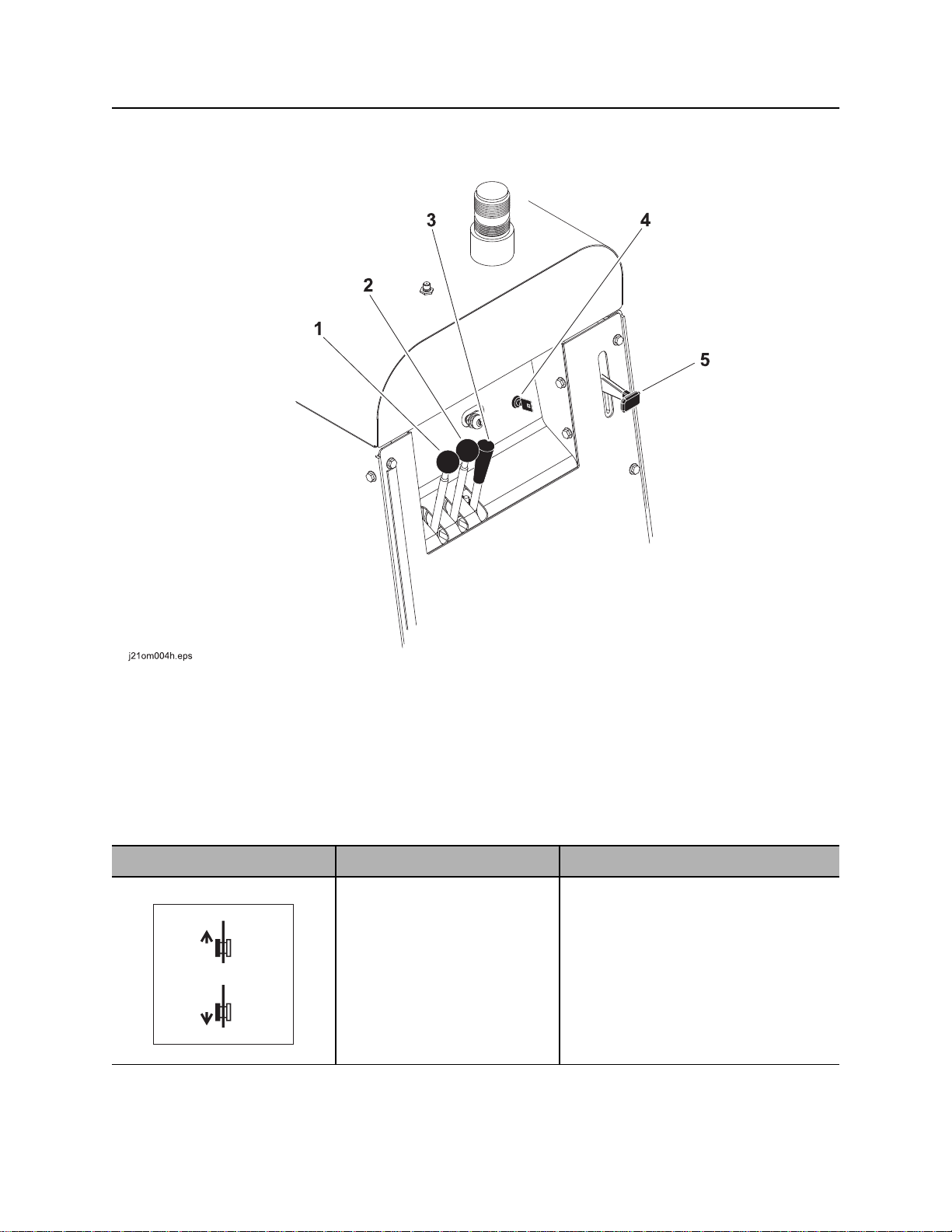
Controls - 22 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Set-Up Console
Set-Up Console
1. left track control
2. Right track control
4. Tracker control key
5. Engine throttle control
3. Stabilizer and frame tilt control
Item Description Notes
1. Left track control To move forward, push.
To move backward, pull.
To stop, move to center.
c00ic147h.eps
CMW
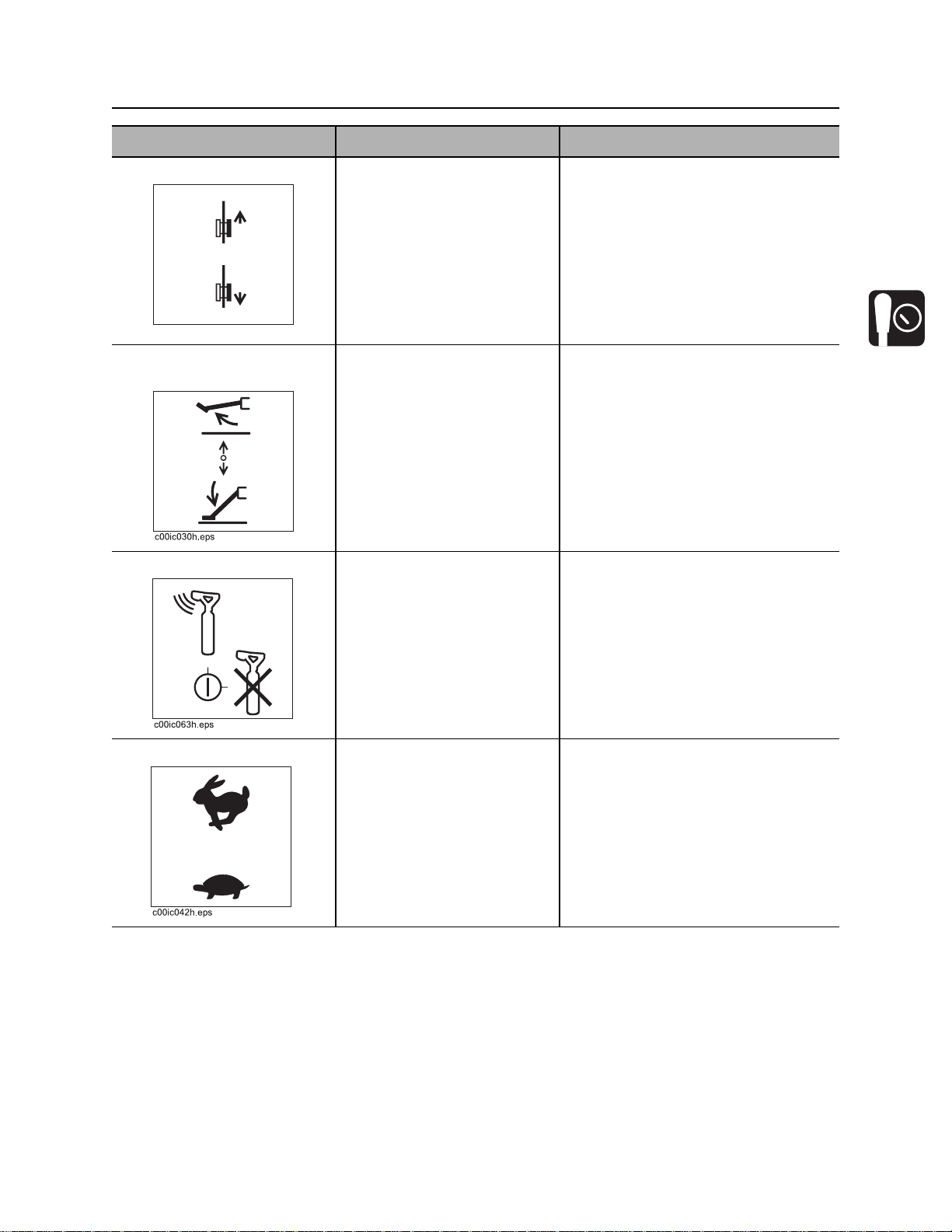
JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 23
Set-Up Console
Item Description Notes
2. Right track control To move forward, push.
To move backward, pull.
To stop, move to center.
c00ic148h.eps
3. Stabilizer and frame tilt
control
4. Tracker control key To allow tracker operator to
5. Engine throttle control To increase engine speed,
To raise stabilizer and
increase frame tilt, push.
To lower stabilizer and
decrease frame tilt, pull.
stop thrust and rotation, move
key to enable position (up).
To override tracker control
mode, move key to disable
position (right).
push up.
To decrease engine speed,
pull down.
Note: Stabilizer control lowers the
front of the drill frame along with the
stabilizer.
IMPORTANT: Remove key and keep
in tracker operator’s possession.
CMW
Controls - 24 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Left Control Console
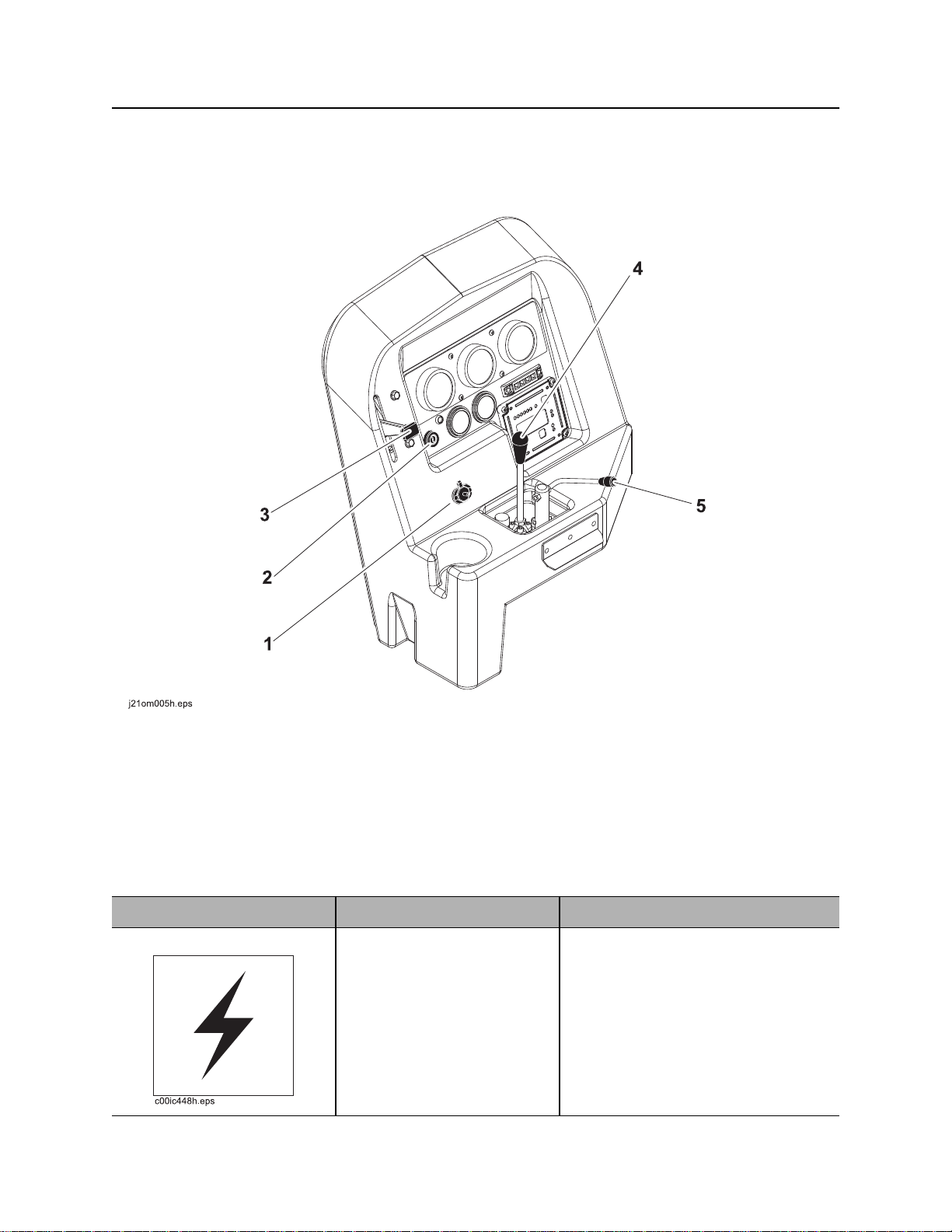
Left Control Console
Drilling/Operation Controls
1. Auxiliary outlet
2. Ignition switch
3. Engine throttle control
Item Description Notes
1. Auxiliary outlet Provides power for other
equipment.
CMW
4. Wrench control
5. Fluid flow control
Power output is 12V, 5A.
JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 25
Left Control Console
Item Description Notes
2. Ignition switch To start engine, insert key and
turn clockwise.
To stop engine, turn key
counterclockwise.
3. Engine throttle control To increase engine speed,
push up.
To decrease engine speed,
pull down.
4. Wrench control To clamp front wrench and
shut off drilling fluid, move
toward pipe box.
To unclamp front wrench,
move away from pipebox.
To clamp and rotate rear
(rotating) wrench, move
toward engine compartment.
To unclamp rear (rotating)
wrench, move toward seat.
5. Fluid flow control To increase flow, turn
counterclockwise.
To decrease flow, turn
clockwise.
To stop flow, turn all the way
clockwise.
CMW
Controls - 26 JT922 Operator’s Manual
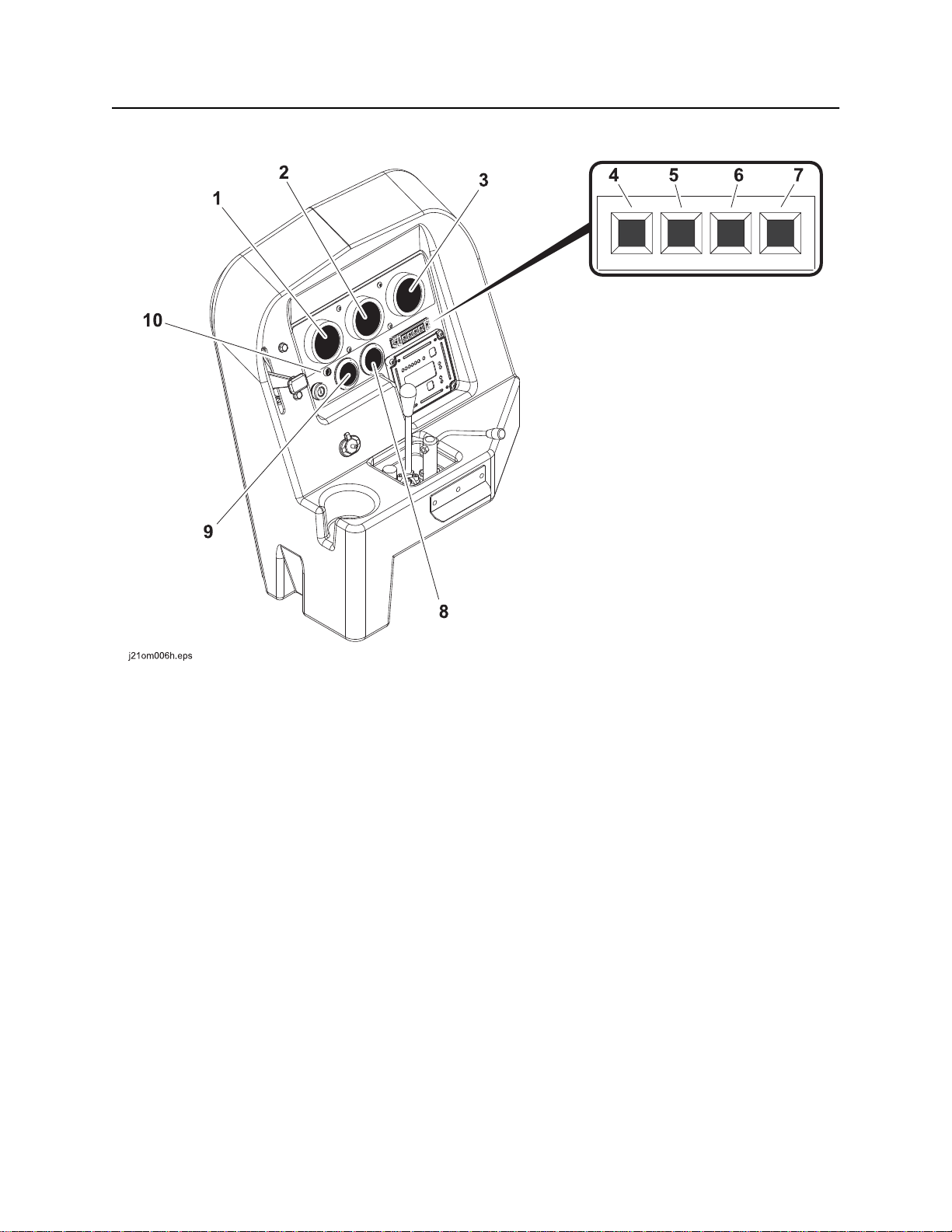
Gauge Cluster
Gauge Cluster
1. Drilling fluid pressure gauge
2. Thrust pressure gauge
3. Rotation pressure gauge
4. High temperature indicator
5. Engine oil pressure indicator
CMW
6. Hydraulic fluid temperature indicator
7. Hydraulic filter service indicator
8. Hourmeter
9. Fuel gauge
10. Cold start wait indicator
JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 27
Gauge Cluster
Item Description Notes
1. Drilling fluid pressure
gauge
Displays drilling fluid pressure
supplied by drilling fluid
pump.
c00ic157h.eps
2. Thrust pressure gauge Displays hydraulic fluid
pressure to thrust motor
during thrust and pullback.
Estimates thrust and pullback
force on lines outside gauge.
3. Rotation pressure
gauge
Displays hydraulic fluid
pressure to rotation motor
when spindle is turned
clockwise.
4. high temperature
indicator
c00ic120h.eps
Estimates rotational torque on
lines outside gauge.
Indicates engine is
overheating.
IMPORTANT: Alarms will sound when
engine overheats.
Stop engine and service unit.
CMW
Controls - 28 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Gauge Cluster
Item Description Notes
5. Engine oil pressure
indicator
6. Hydraulic fluid
temperature indicator
7. Hydraulic filter service
indicator
Indicates engine oil pressure
is too low.
Indicates hydraulic fluid is
overheating.
Indicates hydraulic fluid filter
needs replacing.
IMPORTANT: Alarms will sound when
engine oil pressure is too low.
Stop engine and check oil level.
• Check hydraulic fluid level.
• Check cooler for debris. See
page 137.
Change filter when indicator lights
continuously and as indicated on
page 142.
8. Hourmeter Displays engine operating
time.
CMW
Use engine operating times to
schedule service.
JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 29
Gauge Cluster
Item Description Notes
9. Fuel gauge Displays fuel level in tank. NOTICE: Use low sulfur or ultra low
sulfur fuel only.
Refer to engine operator’s manual for
cold weather fuel recommendations.
Tank holds 19 gal (72 L).
10. Cold start wait indicator Lights when intake air preheater is operating.
Wait until light goes off before
starting engine.
CMW

Controls - 30 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Right Control Console
Right Control Console
1. Carriage control 2. Pipe lubricator button (optional)
Item Description Notes
1. Carriage control To move carriage forward,
push.
To move carriage backward,
pull.
To rotate spindle
counterclockwise (breakout),
move right.
To rotate spindle clockwise
(makeup), move left.
2. Pipe lubricator button
(optional)
CMW
To apply joint compound to
threads at wrenches, press
button.

JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 31
Anchoring System Console
Anchoring System Console
1. Left rotation control
2. Left thrust control
Item Description Notes
1. Left rotation control To drive anchor, push down.
To remove anchor, pull up.
3. Right rotation control
4. Right thrust control
IMPORTANT: Stand on platform when
operating anchor controls.
CMW

Controls - 32 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Anchoring System Console
Item Description Notes
2. Left thrust control To move anchor down, push
down.
To move anchor up, pull up.
3. Right rotation control To drive anchor, push down.
To remove anchor, pull up.
4. Right thrust control To move anchor down, push
down.
IMPORTANT: Stand on platform when
operating anchor controls.
IMPORTANT: Stand on platform when
operating anchor controls.
IMPORTANT: Stand on platform when
operating anchor controls.
To move anchor up, pull up.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 33
Seat/Armrest
Seat/Armrest
1. Seat tilt latch 2. Seat leveling wheel
Item Description Notes
1. Seat tilt latch To tilt seat forward for
transport, push knob.
To lower seat for operation,
pull knob.
2. Seat leveling wheel To level seat when the unit is
set up on a side slope, turn
wheel.
CMW

Controls - 34 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Battery
Battery
1. Battery disconnect switch
Item Description Notes
1. Battery disconnect
switch
To disable battery power,
move switch to the
disconnect position.
To enable battery power,
move switch to the connect
position.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 35
ESID
ESID
23
1
j07om042h.eps
1. Alphanumeric display
2. Strike indicator
3. Alarm interrupt button
4. Voltage problem indicator
Item Description Notes
1. Alphanumeric display Display amount of current
and voltage being detected
as a percentage of strike
condition.
5. Current problem indicator
6. OK indicator
7. Electrical power supply indicator
8. Self test button
4
5
6
7
8
The line with the “V” shows
voltage reading and the line
with the “A” shows current
reading.
2. Strike indicator Red lights come on as values
in display increase.
Light in triangle represents
strike warning condition and
will trigger alarm(s) and
strobe(s).
Remember that system can
go from one or two lights to
an electric strike immediately.
NOTICE: The ESID does not indicate
proximity to electric lines. System will
activate only when voltage and/or
amperage detected at the drilling unit
are above threshold minimum limits.
CMW

Controls - 36 JT922 Operator’s Manual
ESID
Item Description Notes
3. Alarm interrupt button To turn off strike alarm at
drilling unit, press.
4. Voltage problem
indicator
5. Current problem
indicator
6. OK indicator Green light means system
Blinking red light indicates a
voltage indicator problem.
Blinking red light indicates a
current indicator problem.
self test detected no
problems.
See “Troubleshoot Strike System” on
page 97.
See “Troubleshoot Strike System” on
page 97.
CMW
Strike system is ready to
operate.

JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 37
ESID
Item Description Notes
7. Electrical power supply
indicator
8. Self test button To start manual self test,
Green light means control
box has sufficient electrical
power for operation.
Strike system is ready to
operate if OK indicator is also
on.
press.
To reset system after a strike
has been detected, press.
Checks all systems and circuits.
NOTICE: See “If an Electric Line is
Damaged” on page 18.
CMW

Controls - 38 JT922 Operator’s Manual
750/752 Display
750/752 Display
Indicators
1. Beacon temperature display
2. Pitch/slope indicator and percentage indicator
3. Roll indicator
4. Target indentifier indicator
IMPORTANT: Some items operate differently depending where data is being saved. Internal refers to
pipe data being saved to 750 Display memory. External refers to pipe data being sent to a properly
connected laptop computer running a version of Trac Management System software.
Item Description Notes
1. Beacon temperature
display
Shows beacon temperature
readings in degrees Farenheit
and degrees Centigrade.
5. Depth estimate
6. Display battery status indicator
7. Beacon battery status indicator
8. Beacon temperature indicator
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 39
750/752 Display
Item Description Notes
2. Pitch/slope indicator
and percentage
indicator
3. Roll indicator Indicates beacon roll angle.
4. Target identifier
indicator
Indicates pitch beacon
percent of grade.
Indicates approximate
beacon location.
Internal: shows pipe label and stored
pitch.
External: shows desired pitch.
Only one set of arrows is active at a
time.
5. Depth estimate Indicates beacon depth
estimate.
Internal: shows job number and
stored depth.
External: shows desired depth.
CMW

Controls - 40 JT922 Operator’s Manual
750/752 Display
Item Description Notes
6. Display battery status
indicator
7. Beacon battery status
indicator
8. Beacon temperature
indicator
Indicates display power from
drilling unit.
Indicates beacon battery
status.
Indicates beacon
temperature.
If all bars are not showing, check
display power connections.
See beacon instruction sheet.
See beacon instruction sheet.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 41
750/752 Display
Controls
1. Delete button
2. On/Off button
3. Channel select button
IMPORTANT: Some items operate differently depending where data is being saved. Internal refers to
pipe data being saved to 750 Display memory. External refers to pipe data being sent to a properly
connected laptop computer running a version of Trac Management System software.
Item Description Notes
1. Delete button To delete current pipe, press.
Second function:
To delete all jobs in internal
logging memory, press with
Recall button.
4. Roll stop button
5. Recall button
6. Store button
Previous pipe number will appear in
numeric display when data is deleted.
CMW

Controls - 42 JT922 Operator’s Manual
750/752 Display
Item Description Notes
2. On/Off button To turn on, press.
To turn off, press again.
3. Channel select button To display current channel,
press and release.
To switch channels, press
and hold.
Second function:
To start a new job, press with
Recall button.
“Init” and job number will be
displayed.
4. Roll stop button This feature is not yet
available.
Unit defaults to last channel used
each time unit is turned on.
IMPORTANT: Make sure display and
tracker are set to the same channel.
5. Recall button To see data about pipe, press
and release.
Second function:
To access second functions,
press with other buttons.
CMW
Internal: shows data about previous
pipe.
External: shows data about next pipe.

JT922 Operator’s Manual Controls - 43
750/752 Display
Item Description Notes
6. Store button To display serial number,
press and hold while pressing
on/off button.
To store current pipe data,
press.
Second function:
To download all jobs stored in
internal logging memory:
• Press with Recall button
• Connect display to PC
running Trac
Management System
software.
Pipe number will appear in numeric
display when data is stored.
IMPORTANT: Pipe data cannot be
stored without a valid depth estimate.
CMW

Controls - 44 JT922 Operator’s Manual
750/752 Display
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Operation Overview - 45
Operation Overview
Chapter Contents
Planning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Setting Up at Jobsite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Drilling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Backreaming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Leaving Jobsite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Storing Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
CMW

Operation Overview - 46 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Planning
Planning
1. Gather information about jobsite. See page 51.
2. Inspect jobsite. See page 52.
3. Classify jobsite. See page 54.
4. Plan bore path. See page 57.
5. Check supplies and prepare equipment. See page 63.
6. Load equipment. See page 70.
Setting Up at Jobsite
1. Prepare jobsite. See page 62.
2. Unload drilling unit from trailer. See page 73.
3. Position drilling unit and frame. See page 77.
4. Assemble strike system. See page 95.
5. Anchor drilling unit. See page 93.
6. Calibrate tracker with beacon that will be installed in beacon housing. See tracker operator’s manual.
Drilling
1. Start system. See page 77.
2. Prime drilling fluid pump. See page 77.
3. Engage tracker control if desired. See page 106.
4. Assemble drill string. See page 80.
5. Drill first pipe. See page 82.
6. Record bore path. See page 85.
7. Add pipe. See page 83.
8. Drill remaining pipes in pipe box.
• Correct direction. See page 84.
9. Surface drill head. See page 86.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Operation Overview - 47
Backreaming
Backreaming
1. Assemble backream string. See page 87.
2. Start drilling unit and adjust throttle.
3. Set drilling fluid flow. Check that fluid flows through all nozzles.
4. Remove pipe from bore. See page 89.
5. Remove pullback device. See page 90.
Backreaming Tips
• Plan backreaming job before drilling. Plan bore path as straight as possible. Check bend limits of
pullback material. Check that appropriate pullback devices are on hand.
• Keep all bends as gradual as possible.
• Drilling fluid quality is a key factor in backreaming success. Contact your Ditch Witch dealer for
information on testing water, selecting additives, and mixing drilling fluid.
• Backreaming requires more fluid than drilling. Make sure enough fluid is used.
Leaving Jobsite
1. Remove downhole tools. See page 90.
2. Remove anchors. See page 94.
3. Rinse unit and downhole tools. See page 124.
4. Disassemble strike system and disconnect from fluid system. See page 125.
5. Stow tools. See page 125.
6. Load unit onto trailer. See page 70.
Storing Equipment
1. For cold weather storage, antifreeze drilling unit. See page 122.
2. For long-term storage, disconnect battery disconnect switch.
CMW

Operation Overview - 48 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Storing Equipment
CMW

Manual Prepare - 49
Prepare
Chapter Contents
Gather Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
• Review Job Plan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
• Notify One-Call Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
• Examine Pullback Material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
• Arrange for Traffic Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
• Plan for Emergency Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Inspect Site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
• Identify Hazards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
• Select Start and End Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Classify Jobsite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
• Inspect Jobsite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
• Select a Classification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
• Apply Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Plan Bore Path . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
• Recommended Bend Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
• Entry Pitch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
• Minimum Setback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
• Minimum Depth. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
• Bore Path Calculator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
CMW

Prepare - 50 Manual
Prepare Jobsite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
• Mark Bore Path. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
• Prepare Entry Point. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Check Supplies and Prepare Equipment . . . . . . . 63
• Check Supplies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
• Prepare Equipment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
• Assemble Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
CMW

Manual Prepare - 51
Gather Information
Gather Information
A successful job begins before the bore. The first step in planning is reviewing information already
available about the job and jobsite.
Review Job Plan
Review blueprints or other plans and make sure you have taken bore enlargement during backreaming
and pullback into account. Check for information about existing or planned structures, elevations, or
proposed work that may be taking place at the same time.
Notify One-Call Services
Contact your local One-Call (811 in USA) or the One-Call referral number (888-258-0808 in USA and
Canada) to have underground utilities located before digging. Also contact any utilities that do not
participate in the One-Call service.
Examine Pullback Material
Ask for a sample of the material you will be pulling back. Check its weight and stiffness. Contact the
manufacturer for bend radius information. Check that you have appropriate pullback devices.
Arrange for Traffic Control
If working near a road or other traffic area, contact local authorities about safety procedures and
regulations.
Plan for Emergency Services
Have the telephone numbers for local emergency and medical facilities on hand. Check that you will have
access to a telephone.
CMW

Prepare - 52 Manual
Inspect Site
Inspect Site
Inspect jobsite before transporting equipment. Check for the following:
• overall grade or slope
• changes in elevation such as hills or open trenches
• obstacles such as buildings, railroad crossings, or streams
• signs of utilities (See “Inspect Jobsite” on page 54.)
• traffic
• access
• soil type and condition
• water supply
• sources of locator interference (rebar, railroad tracks, etc.)
Take soil samples from several locations along bore path to determine best bit and backreamer
combinations.
Identify Hazards
Identify safety hazards and classify jobsite. See “Classify Jobsite” on page 54.
Jobsite hazards could cause death or serious injury. Use
correct equipment and work methods. Use and maintain proper safety
equipment.
NOTICE:
• Wear personal protective equipment including hard hat, safety eye wear, and hearing protection.
• Do not wear jewelry or loose clothing.
• Notify One-Call and companies which do not subscribe to One-Call.
• Comply with all utility notification regulations before digging or drilling.
• Verify location of previously marked underground hazards.
• Mark jobsite clearly and keep spectators away.
Remember, jobsite is classified by hazards in place -- not by line being installed.
CMW

Manual Prepare - 53
Inspect Site
Select Start and End Points
Select one end to use as a starting point. Consider the following when selecting a starting point:
Slope
Fluid system should be parked on a level site. Consider how slope will affect drilling unit setup, bending
pipe, and fluid flow out of hole.
Traffic
Vehicle and pedestrian traffic must be a safe distance from drilling equipment. Allow at least 10’ (3 m)
buffer zone around equipment.
Space
Check that starting and ending points allow enough space for gradual pipe bending. See “Minimum
Setback” on page 60.
Check that there is enough space to work and to set up electric strike system.
Comfort
Consider shade, wind, fumes, and other site features.
Drill downhill when possible so fluid will flow away from drilling unit.
CMW

Prepare - 54 Manual
Classify Jobsite
Classify Jobsite
Inspect Jobsite
• Follow U.S. Department of Labor regulations on excavating and trenching (Part 1926, Subpart P) and
other similar regulations.
• Contact your local One-Call (811 in USA) or the One-Call referral number (888-258-0808 in USA and
Canada) to have underground utilities located before digging. Also contact any utilities that do not
participate in the One-Call service.
• Inspect jobsite and perimeter for evidence of underground hazards, such as:
– “buried utility” notices
– utility facilities without overhead lines
– gas or water meters
– junction boxes
– drop boxes
– light poles
– manhole covers
– sunken ground
• Have an experienced locating equipment operator sweep area within 20’ (6 m) to each side of bore
path. Verify previously marked line and cable locations.
• Mark location of all buried utilities and obstructions.
• Classify jobsite.
Select a Classification
Jobsites are classified according to underground hazards present.
If working . . . then classify jobsite as . . .
within 10’ (3 m) of a buried electric line electric
within 10’ (3 m) of a natural gas line natural gas
in concrete, sand or granite which is capable of producing
crystalline silica (quartz) dust
within 10’ (3 m) of any other hazard other
NOTICE: If you have any doubt about jobsite classification, or if jobsite might contain unmarked
hazards, take steps outlined previously to identify hazards and classify jobsite before working.
crystalline silica (quartz) dust
CMW

Manual Prepare - 55
Classify Jobsite
Apply Precautions
Once classified, precautions appropriate for jobsite must be taken.
Electric Jobsite Precautions
Electric shock. Contacting electric lines will cause death or serious injury.
Know location of lines and stay away.
In addition to using a directional drilling system with an electric strike system, use one or both of these
methods.
• Expose line by careful hand digging or soft excavation. Use beacon to track bore path. Have someone
observe clearance between drill head and backreamer when crossing a line.
• Have service shut down while work is in progress. Have electric company test lines before returning
them to service.
Natural Gas Jobsite Precautions
Fire or explosion possible. Fumes could ignite and cause burns. No
smoking, no flame, no spark.
Explosion possible. Serious injury or equipment damage could occur.
Follow directions carefully.
In addition to using a directional drilling system and positioning equipment upwind from gas lines, use one
or both of these methods.
• Expose lines by careful hand digging or soft excavation. Use beacon to track bore path. Have
someone observe clearance between drill head and backreamer when crossing a line.
• Have gas shut off while work is in progress. Have gas company test lines before returning them to
service.
CMW

Prepare - 56 Manual
Classify Jobsite
Crystalline Silica (Quartz) Dust Precautions
Jobsite hazards could cause death or serious injury. Use correct
equipment and work methods. Use and maintain proper safety equipment.
NOTICE: Cutting, drilling, or working materials such as concrete, sand, or rock containing quartz may
result in exposure to silica dust. Use water spray or other means to control dust. If workers are exposed
to dust they must wear appropriate breathing protection. Silica dust may cause lung disease and is
known to the State of California to cause cancer.
Follow OSHA or other guidelines for exposure to crystalline silica when trenching, sawing or drilling
through material that might produce dust containing crystalline silica (quartz).
Other Jobsite Precautions
You may need to use different methods to safely avoid other underground hazards. Talk with those
knowledgeable about hazards present at each site to determine which precautions should be taken or if
job should be attempted.
CMW

Manual Prepare - 57
Plan Bore Path
Plan Bore Path
Plan the bore path, from entry to end, before drilling begins. The Ditch Witch Trac Management System
Plus is available for planning your bore path. This special software can be run in the field using a laptop
computer equipped with Windows
If not using Trac Management System Plus, mark the bore path on the ground with spray paint or flags, or
record it on paper for operator reference.
For complicated bores, consult an engineer. Have the jobsite surveyed and bore path calculated. Be sure
the engineer knows minimum entry pitch, bend limits of drill pipe, bend and tension limits of pullback
material, pipe lengths, and location of all underground utilities.
For less complicated bores, plan the bore based on four measurements:
• recommended bend limit
• entry pitch
• minimum setback
• minimum depth
®
95 or higher operating system. See your Ditch Witch dealer for details.
IMPORTANT: See the following pages for more information about these measurements. If not using
Trac Management System Plus, see “Bore Path Calculator” on page 61 and use these measurements to
help plan your bore.
CMW

Prepare - 58 Manual
Plan Bore Path
Recommended Bend Limits
Ditch Witch drill pipes are designed to bend slightly during operation. Slight bending allows for steering and
correcting direction. Bending beyond recommended limits will cause damage that might not be visible. This
damage adds up and will later lead to sudden drill pipe failure.
IMPORTANT: Consider recommended bend limits during any bend, not just during bore entry.
Pipe Pitch
Ditch Witch drill pipe is tested to bend at a maximum
percent pitch. For JT922 drill pipe, make sure pitch (A)
changes no more than 6% over the full length of each
pipe.
NOTICE: Bending drill pipe more sharply than
recommended will damage pipe and cause failure
over time. Changes in pitch must be equally
distributed over the length of a pipe. Maximum
changes in pitch within 1-2’ (300-600 mm) of pipe
create sharp bends that will damage pipe.
Monitor the pitch of each pipe with the remote display
on the operator’s console. See page 38.
Bend Radius
JT922 drill pipes have a tested minimum bend radius
of 105’ (32 m). This means that a 90-degree bend in
the bore path:
• has a radius (A) of 105’ (32 m)
• requires approximately 165’ (50 m) of drill pipe
(B).
NOTICE: Bending drill pipe more sharply than
recommended will damage the pipe and cause
failure over time.
• If bend radius is reduced, drill pipe life is
reduced.
• If bend radius is increased, drill pipe life is
increased.
IMPORTANT: Use the charts on the next page to keep bends within safe limits.
CMW

Manual Prepare - 59
Plan Bore Path
Pipe-By-Pipe Bend Limits
Pipe
(C)
1 6 ft 0 in (1.8 m) 0 ft 2 in (0.1 m) 15 79 ft 5 in (24.3 m) 36 ft 3 in (11.1 m)
2 12 ft 0 in (3.7 m) 0 ft 8 in (0.2 m) 16 83 ft 2 in (25.4 m) 40 ft 11 in (12.5 m)
3 17 ft 11 in (5.5 m) 1 ft 6 in (0.5 m) 17 86 ft 8 in (26.2m) 45 ft 9 in (13.9 m)
4 23 ft 9 in (7.2 m) 2 ft 9 in (0.8 m) 18 89 ft 11 in (27.4m) 50 ft 10 in (15.5 m)
5 29 ft 7 in (9 m) 4 ft 3 in (1.3 m) 19 92 ft 11 in (28.3m) 56 ft 0 in (17 m)
6 35 ft 4 in (10.8 m) 6 ft 1 in (1.8 m) 20 95 ft 6 in (29.2m) 61 ft 5 in (18.7 m)
7 40 ft 11 in (12.5 m) 8 ft 3 in (2.5 m) 21 97 ft 10 in (29.9m) 66 ft 11 in (20.4 m)
8 46 ft 4 in (14.1 m) 10 ft 9 in (3.2 m) 22 99 ft 11 in (30.5m) 72 ft 7 in (22.2 m)
9 51 ft 8 in (15.7 m) 13 ft 7 in (4.2 m) 23 101 ft 7 in (31m) 78 ft 4 in (23.9 m)
10 56 ft 9 in (17.3 m) 16 ft 8 in (5.1 m) 24 102 ft 11 in (31.4m) 84 ft 2 in (25.7 m)
11 61 ft 9 in (18.8 m) 20 ft 1 in (6.2 m) 25 103 ft 11 in (31.7m) 90 ft 1 in (27.5 m)
12 66 ft 6 in (20.3 m) 23 ft 9 in (7.2 m) 26 104 ft 7 in (31.9m) 96 ft 1 in (29.4 m)
13 71 ft 0 in (21.6 m) 27 ft 8 in (8.4 m) 27 105 ft 0 in (32m) 102 ft 1 in (31.2 m)
14 75 ft 4 in (23 m) 31 ft 10 in (9.8 m) 27.5 105 ft 0 in (32m) 105 ft 0 in (32 m)
Forward (B) Deflection (A) Pipe
(C)
Forward (B) Deflection (A)
Pipe 14 is illustrated.
CMW

Prepare - 60 Manual
Plan Bore Path
Entry Pitch
Entry pitch is the slope of the drill frame compared with the slope of the ground. Determine entry pitch one
of two ways:
1. With Pitch Beacon
• Lay pitch beacon on the ground and read
pitch.
• Lay pitch beacon on drill frame and read pitch.
• Subtract ground pitch from drilling unit pitch.
2. With Measurements
• Measure from the ground to front end of drill
frame (H1).
• Measure from the ground to back end of frame
(H2).
• Subtract (H1) from (H2). Record this number.
• Measure the distance between front and back
points (C).
• Divide (H2-H1) by (C), then multiply by 100.
This is your pitch.
IMPORTANT: A shallow entry pitch (A1) allows you
to reach horizontal sooner and with less bending.
Increasing entry pitch (A2) makes bore path longer
and deeper.
Minimum Setback
Setback is the distance from the entry point to where
pipe becomes horizontal (B1).
NOTICE: If setback is too small (B2), you will
exceed bend limits and damage the pipe.
CMW

Manual Prepare - 61
Plan Bore Path
Minimum Depth
Because you must bend pipe gradually, entry pitch and
bend limits determine how deep the pipe will be when
it becomes horizontal. This is called the minimum
depth.
• To reduce minimum depth (D1), reduce entry
pitch. This also decreases setback.
• To increase minimum depth (D2), increase
entry pitch. This also increases setback.
Bore Path Calculator
Entry pitch, setback, and minimum depth work together with bend limits to determine the bore path. To find
the setback (B) and entry pitch (A) that will take you to the desired minimum depth (D), use the chart
below.
Minimum depth (D) Entry pitch (A) Setback (B) Depth to begin steering (S)
2 ft 9 in (0.8 m) -18% 24 ft 6 in (7.5 m) 1 ft 1 in (0.33 m)
3 ft 3 in (1.0 m) -20% 26 ft 6 in (8.1 m) 1 ft 2 in (0.36 m)
3 ft 9 in (1.1 m) -22% 28 ft 5 in (8.7 m) 1 ft 3 in (0.38 m)
4 ft 4 in (1.3 m) -24% 30 ft 4 in (9.2 m) 1 ft 5 in (0.43 m)
4 ft 7 in (1.4 m) -25% 31 ft 3 in (9.5 m) 1 ft 5 in (0.43 m)
IMPORTANT: Numbers in table based on 105’ (32 m) minimum bend radius, beacon housing, EZ-
Connect, connector, transition sub, and 1/3 of first drill pipe (L, totalling 8’ [2.4 m]) in the ground before
steering.
CMW

Prepare - 62 Manual
Prepare Jobsite
Prepare Jobsite
Jobsite hazards could cause death or serious injury. Use
correct equipment and work methods. Use and maintain proper safety
equipment.
NOTICE:
• If jobsite classification is in question or if the possibility of unmarked electric utilities exists, classify
jobsite as electric.
• Cutting high voltage cable can cause electrocution. Expose lines by hand before digging.
• All vegetation near operator’s station must be removed. Contact with trees, shrubs, or weeds during
electrical strike could result in electrocution.
Mark Bore Path
Mark your planned bore path and all located utility lines with flags or paint.
Prepare Entry Point
For bore to be successful, first pipe must be straight as
it enters the ground.
To help ensure that the first pipe does not bend, dig a
small starting hole so that the first pipe is drilled into a
vertical surface.
To prevent bending or straining pipe, position drilling
unit for straight entry.
CMW

Manual Prepare - 63
Check Supplies and Prepare Equipment
Check Supplies and Prepare Equipment
Check Supplies
• receiver/transmitter or tracker with spare batteries
• beacons with new and spare batteries
• two-way radios with new and spare batteries
• quick wrench (see page 114)
• transition sub
• anchoring equipment and accessories
• bits, screens, nozzles (see page 109)
• adapters, pipe, beacon housings
• marking flags or paint
• water and additional hoses
• fuel (Use low sulfur or ultra low sulfur fuel only.)
• drilling fluid additives (see page 101)
• spare fuses
• keys
• backreamers, swivels, pulling devices (see page 109)
• wash down hose and spray gun
• duct tape
• spray lubricant
• tool joint compound (see page 130)
• electrically insulating boots and gloves
• personal protective equipment, such as hard hat and safety glasses
• notepad and pencil
CMW

Prepare - 64 Manual
Prepare Equipment
Fluid Levels
• fuel (Use low sulfur or ultra low sulfur fuel only.)
• hydraulic fluid
• battery charge
• engine oil
Condition and Function
• filters (air, oil, hydraulic)
• fluid pump
• couplers
• tires and tracks
• pumps and motors
• drilling fluid mixer
• hoses and valves
• water tanks
Assemble Accessories
Fire Extinguisher
If required, mount a fire extinguisher near the power unit but away from possible points of ignition. The fire
extinguisher should always be classified for both oil and electric fires. It should meet legal and regulatory
requirements.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Drive - 65
Drive
Chapter Contents
Start Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Steer Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Shut Down Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
CMW

Drive - 66 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Start Unit
Start Unit
1. Insert key.
2. Turn key clockwise. See page 25 for more information.
3. Run engine at low throttle for 5 minutes.
Steer Unit
To steer drilling unit, follow instructions for type of steering desired. See page 22 for more information.
To steer while moving forward, move one control slightly more than the other to turn in the desired
direction. Drilling unit will gradually turn to left or right.
To steer while moving backward, move one control slightly more than the other to turn in the desired
direction. Drilling unit will gradually turn to left or right.
For tight steering at low speed, one control to reverse and one control to forward to turn in the desired
direction. Tracks will counter-rotate and turn drilling unit in a tight circle.
Tips to Reduce Track Wear
Rubber tracks are best suited at soil-based job sites with minimal rock and debris. Sharp objects such as
gravel, steel shards, and broken concrete will damage rubber tracks and undercarriage components.
Excessive operation on concrete or asphalt will shorten track life. When storing your machine, keep tracks
away from rain and direct sunlight.
Wash tracks daily to remove foreign objects and abrasive soil from sprockets and idler rollers. Drive slowly
and make wide turns when possible. Regularly check undercarriage components (sprocket, rollers, idler)
for wear and damage. Maintain proper track tension. (See “Check Track Tension and Condition” on
page 147.)
To prevent premature wear, avoid the following:
• Spinning tracks under heavy load.
• Turning on sharp objects such as stones, stumps and debris.
• Quick turns or “spin” turns on asphalt or concrete.
• Driving over curbs, ledges, and sharp objects.
• Driving with sidewall edges pressed against hard walls, curbs or other objects.
• Driving on slopes.
• Operating on corrosive materials such as salt or fertilizer. Wash immediately.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Drive - 67
Shut Down Unit
Shut Down Unit
1. Stop track movement.
2. Lower drill frame and stabilizer to the ground.
IMPORTANT: If frame and stabilizer cannot be lowered, use cylinder locks or other suitable
material to block the tracks. Remove cylinder locks or chocks before driving unit.
3. Run engine at low throttle for 3 minutes to cool.
4. Turn key to STOP.
5. Remove key.
CMW

Drive - 68 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Shut Down Unit
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Transport - 69
Transport
Chapter Contents
Lift . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Haul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
• Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
• Tie Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
• Unload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Tow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
CMW

Transport - 70 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Lift
Lift
This machine is not configured for lifting. If the machine must be lifted, load machine into a container or
onto a platform appropriate for lifting. See “Specifications” for weight of machine.
Haul
Load
Crushing weight. If load falls or moves it could kill or crush you. Use
proper procedures and equipment or stay away.
NOTICE:
• Load and unload trailer on level ground.
• Verify that trailer wheels are blocked.
• Incorrect loading can cause trailer swaying.
• Attach trailer to vehicle before loading or unloading.
• Ten to fifteen percent of total vehicle weight (equipment plus trailer) must be on tongue to help
prevent trailer sway.
1. Start drilling unit engine.
2. Move drilling unit to rear of trailer and align with ramps.
3. Slow engine to low throttle and slowly drive unit onto trailer.
4. Lower stabilizer and drill frame to trailer floor.
5. Stop engine when unit is safely positioned on trailer bed.
6. Attach tiedowns to drilling unit where indicated on page 71.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Transport - 71
Haul
Tie Down
Points
Tiedown points are identified by tiedown decals. Securing to trailer at other
points is unsafe and can damage machinery.
Procedure
Incorrect procedures could result in death, injury, or property damage.
Learn to use equipment correctly.
NOTICE: Wrenches can open after engine shutdown. Ensure that any downhole tool or pipe in tool joint
vises is attached to spindle or removed before transport.
CMW

Transport - 72 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Haul
Attach chains at front and rear tie-down points (shown). Make sure chains are tight before transporting
unit.
IMPORTANT: Drill frame must be lowered to trailer floor before attaching chains.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Transport - 73
Haul
Unload
Crushing weight. If load falls or moves it could kill or crush you. Use
proper procedures and equipment or stay away.
NOTICE:
• Load and unload trailer on level ground.
• Ensure trailer wheels are blocked.
• Attach trailer to vehicle before loading or unloading.
1. Lower ramps.
2. Remove tiedowns.
3. Start drilling unit engine.
4. Raise stabilizers.
5. Raise drill frame.
6. Slow engine to low throttle and slowly back unit down trailer or ramps.
CMW

Transport - 74 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Tow
Tow
Under normal conditions, drilling unit should not be towed. If unit breaks down and towing is necessary:
• Tow for short distances at less than 1 mph (1.6 kph).
• Attach chains to indicated tow points facing towing vehicle.
• Use maximum towing force of 1.5 times unit weight.
• disengage power to tracks.
IMPORTANT: When hydraulics are disengaged, unit has no brakes.
To disengage track hydraulics:
1. Loosen locknut (B).
2. Turn screw (A) on each counterbalance valve
clockwise until it stops.
IMPORTANT: Be sure to count number of
turns.
3. Repeat on other track.
To engage track hydraulics:
1. Turn screw (A) on counterbalance exactly
same number of turns counterclockwise.
2. Tighten locknut (B).
3. Repeat on other track.
To attach chains to tow points, determine which points are facing towing vehicle.
Loop chains around crossmember (either front or
back) on drill frame.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Conduct a Bore - 75
Conduct a Bore
Chapter Contents
Position Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Start System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Prime Drilling Fluid Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Operate Carriage Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Clamp Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Assemble Drill String . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
• Prepare Beacon Housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
• Attach Transition Sub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
• Connect Drill Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Drill First Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Add Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Correct Direction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
• Basic Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
• Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
• Drill Head Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
CMW

Conduct a Bore - 76 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Record Bore Path . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Surface Drill Head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Assemble Backream String . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Remove Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Remove Pullback Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Conduct a Bore - 77
Position Equipment
Position Equipment
1. Review bore plan and select drilling unit position and fluid unit position. See “Select Start and End
Points” on page 53.
2. Move equipment into selected positions.
Start System
1. Start drilling unit and remote fluid unit. Allow both engines to warm up.
IMPORTANT: Ensure that mixture of drilling fluid matches drilling conditions.
2. Enable tracker control mode if desired. See “Tracker Control” on page 106.
3. Set engine to full throttle.
4. Press and hold quick fill fluid pump switch until pipe fills and fluid pressure begins to rise.
Prime Drilling Fluid Pump
Incorrect procedures could result in death, injury, or property damage.
Learn to use equipment correctly.
NOTICE: Failure to prime the drilling fluid pump will cause flow fluctuations, which will
make it difficult to control the washwand.
Pressurized fluid or air could pierce skin and cause injury
or death. Stay away.
Prime drilling fluid pump each time tank is changed. To prime the pump:
1. Fill drilling fluid hose and connect hose to unit.
2. Operate mixing/transfer pump at full speed for 1 - 3 minutes to discharge air from system.
3. Return mixing/transfer pump to normal operating speed and continue the bore.
4. If drilling fluid pressure surges are observed, repeat step 2.
CMW

Conduct a Bore - 78 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Operate Carriage Control
Operate Carriage Control
The thrust/rotation control has eight positions which allow the four basic
functions to be combined. The chart below summarizes functions that occur
when control is put at a combined position. Operator must be in seat for
control to function.
Carriage Movement Rotation Direction
forward clockwise (makeup)
reverse counterclockwise (breakout)
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Conduct a Bore - 79
Clamp Pipe
Clamp Pipe
Turning shaft can kill you or crush arm or leg. Stay away.
NOTICE: Clamping anywhere else on the pipe will weaken the pipe. Pipe can later break,
even when operating under normal loads.
Incorrect procedures could result in death, injury, or property damage.
Learn to use equipment correctly.
NOTICE: Wrenches can open after engine shutdown. Ensure that any downhole tool or pipe in tool joint
vises is attached to spindle or removed before transport.
Clamp on pipe when joint is centered between
wrenches (1 and 2). Always clamp on the larger
diameter areas on either side of the tool joint face.
CMW

Conduct a Bore - 80 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Assemble Drill String
Assemble Drill String
Prepare Beacon Housing
1. Select nozzles and bit.
IMPORTANT: A variety of nozzles and bits
are available to suit your particular job
conditions. See “Downhole Tools” on
page 109 for more information, or contact
your Ditch Witch dealer.
2. Insert nozzle into beacon housing.
3. Attach bit (2) to beacon housing (1).
4. Install beacon, following beacon instructions for:
• battery replacement
• beacon positioning
5. Install beacon housing lid. See “Beacon Housings”
on page 110.
6. Follow beacon instructions to check beacon operation.
7. Follow tracker instructions to calibrate beacon.
Attach Transition Sub
Use either machine torque or quick wrench to attach transition sub (3) to beacon housing (1).
Machine Torque
1. Pull transition sub into front wrench.
2. Close wrench.
3. Lube joints.
4. Slowly make up joint.
5. Use full machine torque to tighten joint fully.
Quick Wrench
1. Lube joints with TJC.
2. Attach quick wrench to the joint in the join position and tighten joint. See “Quick Wrench” on page 114.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Conduct a Bore - 81
Assemble Drill String
Connect Drill Pipe
1. Start drilling unit engine.
2. Align transition sub (3) in front wrench.
3. Clamp tool in front wrench. See “Clamp Pipe” on page 79.
4. Lift pipe box latches.
NOTICE: If drilling unit is set up in a side-slope,
the rear pipe box latch should be left latched to
help ensure that upper rows of drill pipe do not
fall.
5. Load pipe (4).
• Lubricate upper pipe threads.
• Move pipe to spindle. Move pin end of pipe into saver sub and release pipe to rest rear wrench.
Lubricate lower threads.
6. Connect pipe.
• Move carriage forward until saver sub nears male pipe thread.
• Slowly rotate spindle clockwise. Carriage will move forward as threads screw together.
• Slowly move carriage forward until pipe end touches end of transition sub.
• To screw pipes together and fully torque joint, slowly rotate drill pipe until spindle stops turning.
• Open wrench.
7. Close guides.
CMW

Conduct a Bore - 82 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Drill First Pipe
Drill First Pipe
Turning shaft can kill you or crush arm or leg. Stay away.
NOTICE:
• Keep everyone at least 10’ (3 m) away from turning drill string.
• Push rod or pipe slowly. Forcing can bend string. Do not use bent rod or pipe.
Jobsite hazards could cause death or serious injury. Use
correct equipment and work methods. Use and maintain proper safety
equipment.
1. Turn on drilling fluid.
2. Visually check for drilling fluid flow.
3. Turn drill bit to starting position. See “Prepare Entry Point” on page 62.
4. Slowly move carriage forward. See “Prepare Entry Point” on page 62. Take care to steer to drill
straight in line with drilling unit. Drill in downhole tools and 1/3 of first pipe before steering.
5. Monitor gauges.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Conduct a Bore - 83
Add Pipe
Add Pipe
1. Set engine throttle to full speed.
2. Clamp pipe joint. See “Clamp Pipe” on page 79.
3. Locate drill head.
4. Engage front wrench until pipe is clamped and pressure develops.
5. Slowly rotate spindle counterclockwise. Move carriage back as threads unscrew.
6. After threads are fully unscrewed, stop rotation and move carriage to back of frame, slowing down as
carriage approaches rear end.
7. Connect Pipe. See “Connect Drill Pipe” on page 81.
8. Ensure that pipe fills and fluid pressure begins to rise.
9. Rotate spindle.
10. Slowly move carriage forward. Adjust rotation speed control according to bit size and soil conditions.
11. Monitor gauges.
12. Locate drill head with tracker at least every half-length of pipe.
CMW

Conduct a Bore - 84 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Correct Direction
Correct Direction
Correcting direction is a skill operators gain with experience and knowledge of equipment and soil
conditions. These instructions cover only basic procedures. For information about specific equipment or
jobsites, contact your Ditch Witch dealer.
To track progress and make corrections, one crew member locates the drill head and sends instructions to
the operator. Corrections are made by tracking the drill head, comparing current position to bore plan, and
steering drill head as needed.
Basic Rules
• Steering ability depends on soil condition; bit, drill head, and nozzle used; roll of drill head; and
distance pushed without outer rotation.
• All corrections should be made as gradually as possible. See “Recommended Bend Limits” on
page 58.
• Over correcting will cause “snaking.” This can damage pipe and will make drilling and pullback more
difficult. Begin to straighten out of each correction as early as possible.
• Do not push an entire piece of drill pipe into ground without rotation. This can exceed bend radius and
cause pipe failure.
Procedure
1. Locate drill head. Take readings available with your beacon and locating equipment such as:
• depth
• pitch
• left/right information
• temperature
• beacon roll
2. Compare position to bore plan. Determine direction drilling should go.
3. Position drill head.
4. Push in drill pipe as needed to change direction.
5. Rotate in remaining length of drill pipe.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Conduct a Bore - 85
Record Bore Path
Drill Head Position
The drill head position is determined by reading
beacon roll. Roll is displayed as a clock face
position.
1. Read beacon roll.
2. Slowly rotate pipe until locator displays desired
beacon roll.
To change direction:
1. Rotate pipe to clock position you intend to travel.
2. Push pipe into ground.
To move forward without changing direction:
Rotate pipe into ground.
Record Bore Path
Locate drill head every half-length of pipe. As the job is completed, record the actual data for each drill
pipe. List pitch and depth of each joint and a brief description of the procedure. In addition, draw a simple
sketch of the site and record depth and rough location of pullback.
The Trac Management System Plus is also available for plotting and tracking your bore path. It utilizes the
750 Tracker, 750 Display, a tracking beacon, and special software. The display can store jobs in its
memory or the system can be run in the field using a laptop computer equipped with the Windows® 95 or
higher operating system. See your Ditch Witch dealer for details.
CMW

Conduct a Bore - 86 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Surface Drill Head
Surface Drill Head
Moving tools will kill or injure. Shut off drill string power when anyone can
be struck by moving or thrown tools. Never use pipe wrenches on drill string.
Turning shaft will kill you or crush arm or leg. Stay away.
NOTICE:
• Tracker operator and drill operator should maintain two-way communication.
• Keep everyone clear of the exposed drill string.
• No one should enter pit until clear communication is given by the drill operator that the drill unit is
shut down. If using tracker control, do not enter pit until tracker control is turned off and green light
on drill unit is lit.
• Drill operator should be instructed to discontinue drill string rotation as soon as drill bit exits the
bore. Use thrust only to extend drill string beyond exit hole.
1. Guide drill head to target pit or up through surface. Make all bends gradual. See “Recommended
Bend Limits” on page 58.
2. Clean area around exit point.
3. If using tracker control mode, tracker operator turns off tracker to disable drilling unit thrust/pullback
and rotation hydraulics. Tracker operator waits for green light to enter pit and change tools.
If not using tracker control mode, tracker operator signals to drilling unit operator to stop engine before
changing downhole tools.
4. Turn fluid flow control to off position as soon as drill head emerges.
5. Clean drill head especially around threads.
6. Disconnect EZ-Connect joint or use quick wrench to remove drill head. Keep threads clean. See
“Quick Wrench” on page 114.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Conduct a Bore - 87
Assemble Backream String
Assemble Backream String
Sometimes it is necessary to enlarge the pilot hole to accommodate larger product. As a general rule, the
final hole should be 1.5 times larger than the diameter of the product being installed. The number of
passes needed depends on soil conditions. Do not try to increase hole size too much in one pass. Several
passes using successively larger reamers will save wear on machine.
Moving tools will kill or injure. Shut off drill string power when anyone can
be struck by moving or thrown tools. Never use pipe wrenches on drill string.
Jobsite hazards could cause death or serious injury. Use
correct equipment and work methods. Use and maintain proper safety
equipment.
NOTICE: Continue to use strike system during backreaming.
Turning shaft will kill you or crush arm or leg. Stay away.
NOTICE:
• Maintain two-way communication with tracker operator.
• Begin backream only when tracker operator has communicated that everyone is clear of the
exposed backream string or has disabled thrust and rotation hydraulics using tracker control.
• Do not allow anyone to stand to the side of the exposed drill string. Drill string and backreamer can
move sideways suddenly if rotated while away from the exit hole.
CMW

Conduct a Bore - 88 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Assemble Backream String
1. Select backreaming devices. See “Backreamers” on page 111.
2. Determine fluid rate requirements and install appropriate nozzles to provide sufficient flow. See
“Backream Fluid Requirements” on page 112 and “Nozzles” on page 109.
3. Attach backreamer to backream beacon housing if tracking backream.
4. Install beacon, following beacon instructions for:
• battery replacement
• beacon positioning
5. Install beacon housing lid. See “Beacon Housings” on page 110.
6. Follow beacon instructions to check beacon operation.
7. Follow tracker instructions to calibrate beacon.
8. Connect EZ-Connect joint or use quick wrench to attach backreamer/beacon housing assembly to
transition sub. See “Quick Wrench” on page 114.
9. Attach swivel and additional pullback devices or product to end of backreamer/beacon housing
assembly.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Conduct a Bore - 89
Remove Pipe
Remove Pipe
NOTICE: If engine is shut off during backreaming, drill pipe clamped by wrenches but not connected to
saver sub can be pulled downhole as vise wrenches loosen.
1. Stop carriage when pipes are aligned in wrenches.
2. Clamp pipe in front wrench. See page 79.
3. Clamp and rotate rear wrench to break front joint. See “Wrench control” on page 25.
4. Disengage rear wrench.
5. Unscrew front joint.
• Slowly rotate spindle counterclockwise to unscrew pipe. Move carriage back slowly until threads
unscrew.
• Move carriage back until pipe is properly positioned in rear wrench.
6. Break rear joint.
• Engage rear wrench.
• Slowly rotate spindle counterclockwise until joint is loosened. Do not fully unscrew joint.
• Disengage rear wrench.
• Move carriage back, move seat toward pipe and grip pipe with both hands.
• Pull pin end of pipe clear of saver sub, lift pipe and stow it in box.
7. Lube front threads.
8. Attach saver sub to next pipe.
• Move carriage forward until saver sub touches pipe.
• Rotate spindle to screw onto pipe. Slowly tighten joint to full machine torque.
9. Disengage front wrench to release pipe.
CMW

Conduct a Bore - 90 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Remove Pullback Device
Remove Pullback Device
The pullback device can be removed when the last pipe is on the frame. It can also be removed when a
target pit along the bore path has been reached. Remaining pipe is then pulled back and removed.
Moving tools will kill or injure. Shut off drill string power when anyone can
be struck by moving or thrown tools. Never use pipe wrenches on drill string.
1. Turn off drilling fluid.
2. Move engine throttle to low speed.
3. Turn drilling unit engine off.
4. Use tracker control to verify that unit is turned off.
5. Clean pullback device.
6. Use quick wrench to remove pullback device. See “Quick Wrench” on page 114.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Systems and Equipment - 91
Systems and Equipment
Chapter Contents
Anchor System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
• Drive Anchors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
• Remove Anchors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Electric Strike System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
• FCC Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
• Assemble Voltage Detector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
• Test Strike System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
• Troubleshoot Strike System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
• Use Electric Strike Simulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Drilling Fluid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
• Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
• Polymer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
• Bentonite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
• Mixtures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
• Basic Fluid Recipes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
• Drilling Fluid Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
• Funnel Viscosity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Tracker Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
• Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
• Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
CMW

Systems and Equipment - 92 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Downhole Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
• Nozzles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
• Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
• Beacon Housings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
• Backreamers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
• Backream Fluid Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Quick Wrench . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Drill Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
• Perform Regular Drill Pipe Care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
• Use Drill Pipe Correctly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Systems and Equipment - 93
Anchor System
Anchor System
Crushing weight. If load falls or moves, it could kill or crush
you. Use proper procedures and equipment or stay away.
NOTICE:
• Drive anchors properly before drilling.
• Stand on platform when operating anchor controls.
• Wear high-top protective boots with legs of pants completely tucked inside.
• Wear protective gloves.
• If you are not driving two anchors to full depth, drive optional ground rod into soil away from drilling
unit and connect ground rod to drilling unit.
Turning shaft can kill you or crush arm or leg. Stay away.
NOTICE: Do not replace anchor collar bolt with one longer than original. Clothing could
catch on turning shaft.
CMW

Systems and Equipment - 94 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Anchor System
Drive Anchors
IMPORTANT: Carefully time anchor rotation
with anchor movement. Properly driven
anchors should thread into soil and should
not auger up soil.
1. Use anchor rotation and thrust controls to
drive anchor into ground.
2. Anchor is set when cap top plate (1) rests
firmly on centering tube (2).
3. Repeat process for other anchor.
Remove Anchors
1. Use anchor rotation and thrust controls to
slowly remove anchor shaft from ground.
2. Repeat process for other anchor.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Systems and Equipment - 95
Electric Strike System
Electric Strike System
Any time you drill in an electric jobsite, electric strike system must be properly set up, tested, and used.
You must wear protective boots and gloves meeting the following standards:
• Boots must have high tops and meet the electric hazard protection requirements of ASTM F2413 when
tested at 14,000 volts. Tuck legs of pants completely inside boots.
• Gloves must have 17,000 AC maximum use voltage, according to ASTM specification D120-87.
If working around higher voltage, use gloves and boots with appropriately higher ratings.
NOTICE: The strike system does not prevent electric strikes or detect strikes before they occur. If
alarms are activated, a strike has already occurred and equipment is electrified.
Read and follow “Electric Jobsite Precautions” on page 55. Review safety procedures before each job.
FCC Statement
The Electric Strike System has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated
in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with the instructions, can cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area could cause harmful interference which the user will be required to correct at his own expense.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved in writing by The Charles Machine Works, Inc. may void the user's authority to
operate this equipment.
CMW

Systems and Equipment - 96 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Electric Strike System
Assemble Voltage Detector
1. Drive voltage stake into ground at least 6’
(2 m) away from any part of system.
2. Clip voltage limiter to voltage stake.
Test Strike System
If system fails any part of this test, see “Troubleshoot Strike System” on page 97 on the following page. Do
not drill until test is completed successfully.
1. Turn on drilling unit.
2. ESID control module will perform internal tests which check everything but alarms and strobe.
3. If green OK indicator and electrical power supply indicator lights remain on, press self test button to
perform total test of strike system. During this test:
• All lights should glow.
• Alphanumeric readout should display numbers.
• Alarms and strobes on all connected units should sound.
4. If this test is successful, OK indicator and electrical power supply indicator lights will remain on.
5. Use Electric Strike Simulator to test voltage and current sensors. See page 99.
CMW

JT922 Operator’s Manual Systems and Equipment - 97
Electric Strike System
Troubleshoot Strike System
When strike system detects a problem, an error code will be displayed. Anytime this happens, press self
test button to retest. If error code is still displayed and does not appear in this chart, have control module
checked or replaced.
Other problem situations and their possible causes and solutions are listed in the chart below.
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
No lights or readings
showing after drilling unit
key has been on at least
one minute
Screen is blank Strike system is not getting
Information on screen is
visible during self test but
not after test is complete
Problems in startup Push self test button. If problem goes
No power to strike system
control module
Defective control module Have control module checked or
adequate power from drilling
unit
Defective control module Have control module checked or
LCD contrast is not set properly Contact your Ditch Witch dealer to
away, retest strike system
Check drilling unit electric system
Check that harness from drilling unit
to control module is connected
Check that cable from drilling unit
carries more than 10V
replaced
Check drilling unit electric system
Check that harness from drilling unit
to control module is connected
Check that harness from drilling unit
carries more than 10V
replaced
adjust contrast
OK indicator is on, but
electrical power supply
indicator is off
Electrical power supply
indicator is on, but OK
indicator is off
Strike system is not getting
adequate power from drilling
unit
Defective control module Have control module checked or
Problem detected during test Check for error code and have control
Defective control module Have control module checked or
Check drilling unit electric system
Check that harness from drilling unit
to control module is connected
Check that harness from drilling unit
carries more than 10V
replaced
module checked or replaced
replaced
CMW

Systems and Equipment - 98 JT922 Operator’s Manual
Electric Strike System
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
Strobe light on drilling unit
does not work during total
test
Alarm on drilling unit does
not work during total test
Strobe light and alarm on
drilling unit do not work
during total test
Improper connections with
control module
Defective strobe light 1. Disconnect strobe and connect to
Defective control module Have control module checked or
Improper connections with
control module
Defective alarm 1. Disconnect strobe and connect to
Defective control module Have control module checked or
Improper connections with
control module
Defective control module Have control module checked or
Check connections and wiring
harness
external 12V power source.
2. If strobe does not work, replace it.
replaced
Check connections and wiring
harness
external 12V power source.
2. If strobe does not work, replace it.
replaced
Check connections and wiring
harness
replaced
EC2 code displays and
current problem indicator is
on
EV1 code displays and
voltage problem indicator is
on
Improper connections with
control module
Defective current transformer 1. Disconnect current transformer.
Defective current transformer
cable
Defective control module Have control module checked or
Improper connection of voltage
limiter to ground stake
Defective voltage limiter Have voltage limiter checked or
Check cable connections on control
module and current transformer
2. Check for 20-40 ohms from pin 1
to pin 4, 20-40 ohms from pin 1 to
pin 2, and less than 1 ohm from
pin 2 to pin 4.
1. Disconnect cable from
transformer and control module.
2. Check continuity of cable.
3. If continuity is zero or cable is
damaged, replace.
replaced
Check voltage limiter connection to
ground stake and verify that ground
stake is driven into the ground
replaced
CMW
Defective control module Have control module checked or
replaced

JT922 Operator’s Manual Systems and Equipment - 99
Electric Strike System
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
EV2 code displays and
voltage problem indicator is
on
Improper connections with
control module
Defective voltage limiter Have voltage limiter checked or
Defective control module Have control module checked or
Check cable connection on control
module
replaced
replaced
Use Electric Strike Simulator
Use the Electric Strike Simulator (p/n 259-506) to test voltage and current sensors on ESID. If readings are
less than indicated here, replace 9V battery in simulator and retest.
Current Test
To test for current at normal levels:
1. Thread one lead wire through current transformer.
2. Clip ends of lead wires together to make one loop.
3. Move simulator switch to "current" and press test button.
4. Watch screen and lights above display on strike system.
• Three or four lights should turn on.
• Current "A" should show 30-50% in display.
CMW
 Loading...
Loading...