Page 1

Latitude 5491
Service Manual
Regulatory Model: P72G
Regulatory Type: P72G002
Page 2

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2018 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. Dell, EMC, and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. Other trademarks
may be trademarks of their respective owners.
2018 - 05
Rev. A00
Page 3

Contents
1 Working on your computer............................................................................................................................. 6
Safety instructions.............................................................................................................................................................6
Turning o your computer — Windows 10.....................................................................................................................6
Before working inside your computer..............................................................................................................................6
After working inside your computer.................................................................................................................................7
2 Technology and components..........................................................................................................................8
Power adapter.................................................................................................................................................................... 8
DDR4................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
DDR4 Details.................................................................................................................................................................8
Memory Errors..............................................................................................................................................................9
HDMI 1.4..............................................................................................................................................................................9
HDMI 1.4 Features...................................................................................................................................................... 10
Advantages of HDMI..................................................................................................................................................10
USB features.....................................................................................................................................................................10
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 (SuperSpeed USB)............................................................................................................10
Speed............................................................................................................................................................................ 11
Applications.................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Compatibility................................................................................................................................................................12
Advantages of Displayport over USB Type-C......................................................................................................... 12
USB Type-C.......................................................................................................................................................................12
Alternate Mode........................................................................................................................................................... 12
USB Power Delivery................................................................................................................................................... 13
USB Type-C and USB 3.1...........................................................................................................................................13
3 Disassembly and reassembly........................................................................................................................ 14
Subscriber Identity Module(SIM) board........................................................................................................................ 14
Removing the Subscriber Identication Module card............................................................................................ 14
Installing the Subscriber Identication Module card...............................................................................................14
SD card – optional............................................................................................................................................................15
Removing the SD card – WWAN models................................................................................................................15
Installing the SD card – WWAN models.................................................................................................................. 15
Base cover.........................................................................................................................................................................15
Removing the base cover..........................................................................................................................................15
Installing the base cover.............................................................................................................................................17
Battery................................................................................................................................................................................17
Removing the battery.................................................................................................................................................17
Installing the battery...................................................................................................................................................18
SSD card–optional............................................................................................................................................................18
Removing the SSD card.............................................................................................................................................18
Installing the SSD card...............................................................................................................................................19
SSD frame......................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Removing the SSD frame..........................................................................................................................................19
Contents
3
Page 4

Installing the SSD frame............................................................................................................................................20
Hard drive......................................................................................................................................................................... 20
Removing hard drive..................................................................................................................................................20
Installing hard drive ...................................................................................................................................................22
Coin-cell battery...............................................................................................................................................................22
Removing the coin cell battery.................................................................................................................................22
Installing coin cell battery..........................................................................................................................................23
WLAN card....................................................................................................................................................................... 23
Removing WLAN card...............................................................................................................................................23
Installing WLAN card................................................................................................................................................. 24
WWAN card – optional....................................................................................................................................................24
Removing the WWAN card.......................................................................................................................................24
Installing the WWAN card......................................................................................................................................... 25
Memory modules............................................................................................................................................................. 25
Removing the memory module................................................................................................................................ 25
Installing the memory module...................................................................................................................................26
Keyboard........................................................................................................................................................................... 26
Removing keyboard lattice........................................................................................................................................26
Installing keyboard lattice.......................................................................................................................................... 27
Removing the keyboard.............................................................................................................................................27
Installing the keyboard...............................................................................................................................................30
Heat sink .......................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Removing the heat sink ........................................................................................................................................... 30
Installing the heat sink ...............................................................................................................................................31
System fan.........................................................................................................................................................................31
Removing the system fan.......................................................................................................................................... 31
Installing the system fan............................................................................................................................................32
Power connector port..................................................................................................................................................... 33
Removing the power connector port...................................................................................................................... 33
Installing power connector port............................................................................................................................... 33
Chassis frame...................................................................................................................................................................34
Removing the chassis frame.................................................................................................................................... 34
Installing the chassis frame.......................................................................................................................................35
LED board......................................................................................................................................................................... 36
Removing LED board.................................................................................................................................................36
Installing LED board................................................................................................................................................... 37
SmartCard module........................................................................................................................................................... 37
Removing smart card reader board..........................................................................................................................37
Installing smart card reader board............................................................................................................................39
Touchpad panel................................................................................................................................................................ 40
Removing the touchpad............................................................................................................................................40
Installing touchpad panel...........................................................................................................................................40
System board.................................................................................................................................................................... 41
Removing system board.............................................................................................................................................41
Installing system board.............................................................................................................................................. 44
Speaker............................................................................................................................................................................. 45
Removing the speaker...............................................................................................................................................45
Contents
4
Page 5

Installing the speaker.................................................................................................................................................46
Display hinge cover..........................................................................................................................................................46
Removing display hinge cover .................................................................................................................................46
Installing display hinge cover ....................................................................................................................................47
Display assembly...............................................................................................................................................................47
Removing display assembly.......................................................................................................................................47
Installing display assembly..........................................................................................................................................51
Display bezel..................................................................................................................................................................... 52
Removing display bezel ............................................................................................................................................ 52
Installing display bezel ...............................................................................................................................................53
Display panel.....................................................................................................................................................................53
Removing display panel ............................................................................................................................................53
Installing display panel .............................................................................................................................................. 55
Display (eDP) cable..........................................................................................................................................................56
Removing display cable ............................................................................................................................................56
Installing display cable .............................................................................................................................................. 56
Camera.............................................................................................................................................................................. 57
Removing camera...................................................................................................................................................... 57
Installing camera.........................................................................................................................................................58
Display hinges...................................................................................................................................................................58
Removing display hinge ............................................................................................................................................58
Installing display hinge ..............................................................................................................................................59
Display back cover assembly..........................................................................................................................................59
Removing the display back cover assembly ..........................................................................................................59
Installing the display back cover assembly ............................................................................................................ 60
Palm rest...........................................................................................................................................................................60
Removing palm rest...................................................................................................................................................60
Installing palm rest......................................................................................................................................................61
4 Troubleshooting........................................................................................................................................... 63
Enhanced Pre-Boot System Assessment — ePSA diagnostics................................................................................63
Running the ePSA Diagnostics.................................................................................................................................63
Real Time Clock reset......................................................................................................................................................63
5 Getting help.................................................................................................................................................65
Contacting Dell.................................................................................................................................................................65
Contents
5
Page 6
Working on your computer
Safety instructions
Use the following safety guidelines to protect your computer from potential damage and to ensure your personal safety. Unless otherwise
noted, each procedure included in this document assumes that the following conditions exist:
• You have read the safety information that shipped with your computer.
• A component can be replaced or, if purchased separately, installed by performing the removal procedure in reverse order.
WARNING: Disconnect all power sources before opening the computer cover or panels. After you nish working inside the
computer, replace all covers, panels, and screws before connecting to the power source.
WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For additional
safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage at www.Dell.com/regulatory_compliance
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certied service technician. You should only perform troubleshooting and simple
repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or telephone service and support team.
Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
CAUTION: To avoid electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by using a wrist grounding strap or by periodically touching an
unpainted metal surface at the same time as touching a connector on the back of the computer.
CAUTION: Handle components and cards with care. Do not touch the components or contacts on a card. Hold a card by its
edges or by its metal mounting bracket. Hold a component such as a processor by its edges, not by its pins.
CAUTION: When you disconnect a cable, pull on its connector or on its pull-tab, not on the cable itself. Some cables have
connectors with locking tabs; if you are disconnecting this type of cable, press in on the locking tabs before you disconnect the
cable. As you pull connectors apart, keep them evenly aligned to avoid bending any connector pins. Also, before you connect a
cable, ensure that both connectors are correctly oriented and aligned.
NOTE: The color of your computer and certain components may appear dierently than shown in this document.
1
Turning o your computer — Windows 10
CAUTION
remove the side cover.
1 Click or tap .
2 Click or tap and then click or tap Shut down.
: To avoid losing data, save and close all open les and exit all open programs before you turn o your computer or
: Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned o. If your computer and attached devices did not
NOTE
automatically turn o when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the power button for about 6 seconds to
turn them o.
Before working inside your computer
1 Ensure that your work surface is at and clean to prevent the computer cover from being scratched.
2 Turn o your computer.
3 If the computer is connected to a docking device (docked), undock it.
4 Disconnect all network cables from the computer (if available).
6 Working on your computer
Page 7

CAUTION: If your computer has an RJ45 port, disconnect the network cable by rst unplugging the cable from your
computer.
5 Disconnect your computer and all attached devices from their electrical outlets.
6 Open the display.
7 Press and hold the power button for few seconds, to ground the system board.
CAUTION: To guard against electrical shock unplug your computer from the electrical outlet before performing Step # 8.
CAUTION: To avoid electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by using a wrist grounding strap or by periodically touching an
unpainted metal surface at the same time as touching a connector on the back of the computer.
8 Remove any installed ExpressCards or Smart Cards from the appropriate slots.
After working inside your computer
After you complete any replacement procedure, ensure that you connect any external devices, cards, and cables before turning on your
computer.
CAUTION: To avoid damage to the computer, use only the battery designed for this particular Dell computer. Do not use batteries
designed for other Dell computers.
1 Replace the battery.
2 Replace the base cover.
3 Connect any external devices, such as a port replicator or media base, and replace any cards, such as an ExpressCard.
4 Connect any telephone or network cables to your computer.
CAUTION
computer.
5 Connect your computer and all attached devices to their electrical outlets.
6 Turn on your computer.
: To connect a network cable, rst plug the cable into the network device and then plug it into the
Working on your computer
7
Page 8

Technology and components
This chapter details the technology and components available in the system.
Topics:
• Power adapter
• DDR4
• HDMI 1.4
• USB features
• USB Type-C
Power adapter
This laptop is shipped with 7.4mm barrel plug on 90 W or 130 W power adapter.
2
WARNING
pull rmly but gently to avoid damaging the cable.
WARNING: The power adapter works with electrical outlets worldwide. However, power connectors and power strips vary
among countries. Using an incompatible cable or improperly connecting the cable to the power strip or electrical outlet may
cause re or equipment damage.
: When you disconnect the power adapter cable from the laptop, grasp the connector, not the cable itself, and then
DDR4
DDR4 (double data rate fourth generation) memory is a higher-speed successor to the DDR2 and DDR3 technologies and allows up to 512
GB in capacity, compared to the DDR3's maximum of 128 GB per DIMM. DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory is keyed
dierently from both SDRAM and DDR to prevent the user from installing the wrong type of memory into the system.
DDR4 needs 20 percent less or just 1.2 volts, compared to DDR3 which requires 1.5 volts of electrical power to operate. DDR4 also supports
a new, deep power-down mode that allows the host device to go into standby without needing to refresh its memory. Deep power-down
mode is expected to reduce standby power consumption by 40 to 50 percent.
DDR4 Details
There are subtle dierences between DDR3 and DDR4 memory modules, as listed below.
Key notch dierence
The key notch on a DDR4 module is in a dierent location from the key notch on a DDR3 module. Both notches are on the insertion edge
but the notch location on the DDR4 is slightly dierent, to prevent the module from being installed into an incompatible board or platform.
8 Technology and components
Page 9
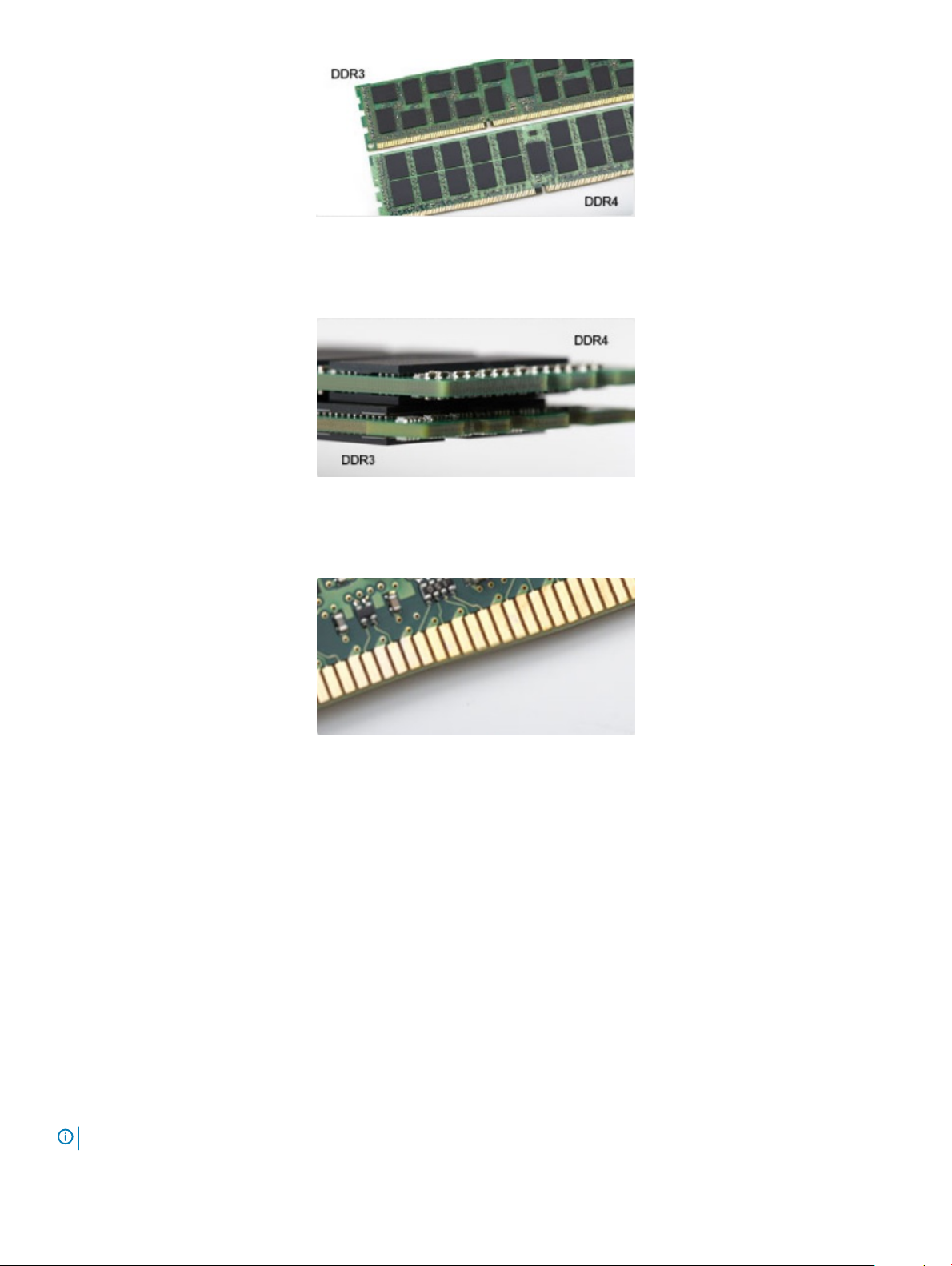
Figure 1. Notch dierence
Increased thickness
DDR4 modules are slightly thicker than DDR3, to accommodate more signal layers.
Figure 2. Thickness dierence
Curved edge
DDR4 modules feature a curved edge to help with insertion and alleviate stress on the PCB during memory installation.
Figure 3. Curved edge
Memory Errors
Memory errors on the system display the new ON-FLASH-FLASH or ON-FLASH-ON failure code. If all memory fails, the LCD does not
turn on. Troubleshoot for possible memory failure by trying known good memory modules in the memory connectors on the bottom of the
system or under the keyboard, as in some portable systems.
HDMI 1.4
This topic explains the HDMI 1.4 and its features along with the advantages.
HDMI (High-Denition Multimedia Interface) is an industry-supported, uncompressed, all-digital audio/video interface. HDMI provides an
interface between any compatible digital audio/video source, such as a DVD player, or A/V receiver and a compatible digital audio and/or
video monitor, such as a digital TV (DTV). The intended applications for HDMI TVs, and DVD players. The primary advantage is cable
reduction and content protection provisions. HDMI supports standard, enhanced, or high-denition video, plus multichannel digital audio on
a single cable.
: The HDMI 1.4 will provide 5.1 channel audio support.
NOTE
Technology and components 9
Page 10
HDMI 1.4 Features
• HDMI Ethernet Channel - Adds high-speed networking to an HDMI link, allowing users to take full advantage of their IP-enabled
devices without a separate Ethernet cable
• Audio Return Channel - Allows an HDMI-connected TV with a built-in tuner to send audio data "upstream" to a surround audio system,
eliminating the need for a separate audio cable
• 3D - Denes input/output protocols for major 3D video formats, paving the way for true 3D gaming and 3D home theater applications
• Content Type - Real-time signaling of content types between display and source devices, enabling a TV to optimize picture settings
based on content type
• Additional Color Spaces - Adds support for additional color models used in digital photography and computer graphics
• 4K Support - Enables video resolutions far beyond 1080p, supporting next-generation displays that will rival the Digital Cinema systems
used in many commercial movie theaters
• HDMI Micro Connector - A new, smaller connector for phones and other portable devices, supporting video resolutions up to 1080p
• Automotive Connection System - New cables and connectors for automotive video systems, designed to meet the unique demands of
the motoring environment while delivering true HD quality
Advantages of HDMI
• Quality HDMI transfers uncompressed digital audio and video for the highest, crispest image quality.
• Low -cost HDMI provides the quality and functionality of a digital interface while also supporting uncompressed video formats in a
simple, cost-eective manner
• Audio HDMI supports multiple audio formats from standard stereo to multichannel surround sound
• HDMI combines video and multichannel audio into a single cable, eliminating the cost, complexity, and confusion of multiple cables
currently used in A/V systems
• HDMI supports communication between the video source (such as a DVD player) and the DTV, enabling new functionality
USB features
Universal Serial Bus, or USB, was introduced in 1996. It dramatically simplied the connection between host computers and peripheral
devices like mice, keyboards, external drivers, and printers.
Let's take a quick look on the USB evolution referencing to the table below.
Table 1. USB evolution
Type Data Transfer Rate Category Introduction Year
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 5 Gbps Super Speed 2010
USB 2.0 480 Mbps High Speed 2000
USB 3.1 Gen 2 10 Gbps Super Speed 2013
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 (SuperSpeed USB)
For years, the USB 2.0 has been rmly entrenched as the de facto interface standard in the PC world with about 6 billion devices sold, and
yet the need for more speed grows by ever faster computing hardware and ever greater bandwidth demands. The USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1
nally has the answer to the consumers' demands with a theoretically 10 times faster than its predecessor. In a nutshell, USB 3.1 Gen 1
features are as follows:
• Higher transfer rates (up to 5 Gbps)
Technology and components
10
Page 11
• Increased maximum bus power and increased device current draw to better accommodate power-hungry devices
• New power management features
• Full-duplex data transfers and support for new transfer types
• Backward USB 2.0 compatibility
• New connectors and cable
The topics below cover some of the most commonly asked questions regarding USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1.
Speed
Currently, there are 3 speed modes dened by the latest USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 specication. They are Super-Speed, Hi-Speed and Full-
Speed. The new SuperSpeed mode has a transfer rate of 4.8Gbps. While the specication retains Hi-Speed, and Full-Speed USB mode,
commonly known as USB 2.0 and 1.1 respectively, the slower modes still operate at 480Mbps and 12Mbps respectively and are kept to
maintain backward compatibility.
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 achieves the much higher performance by the technical changes below:
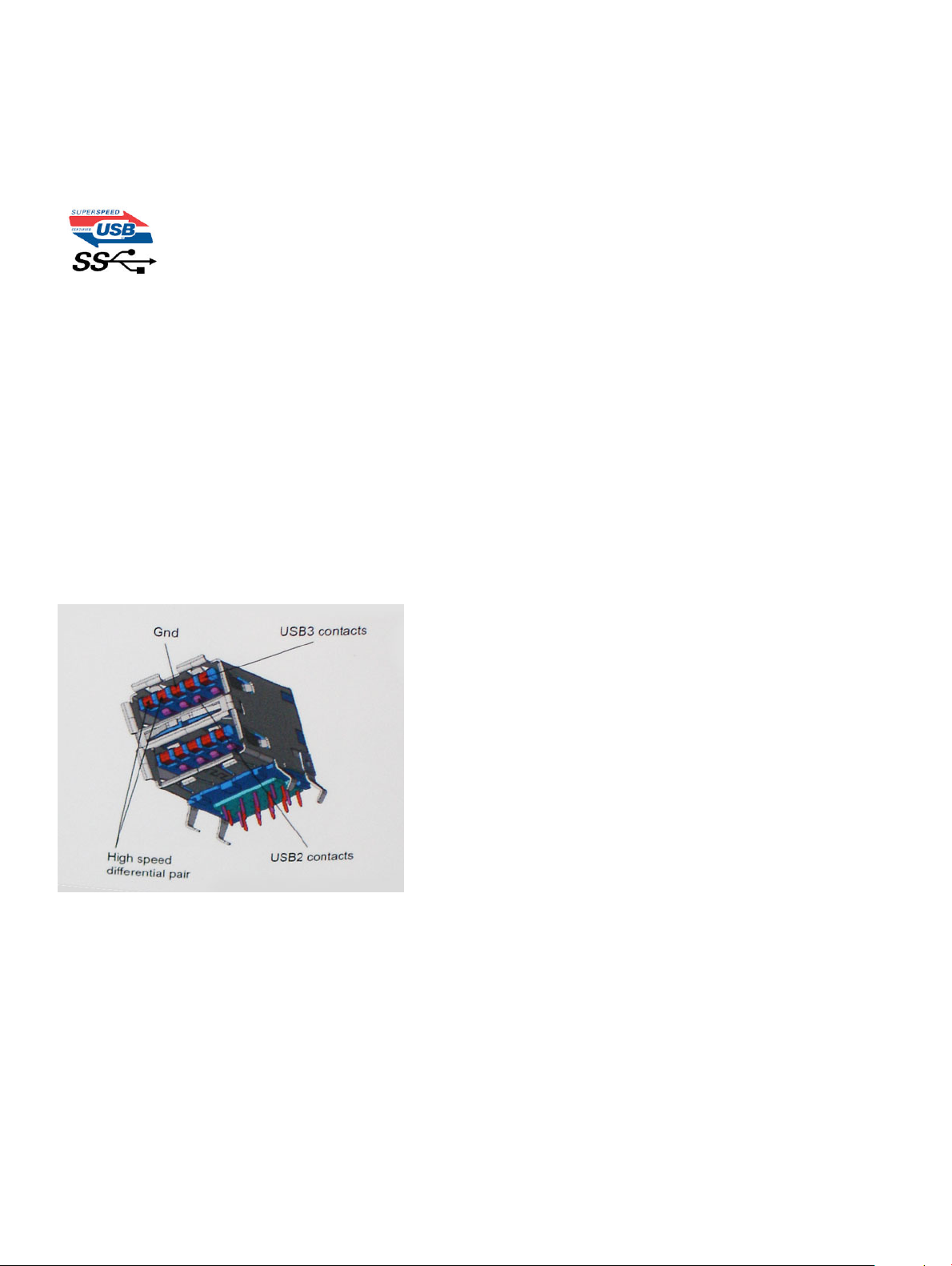
• An additional physical bus that is added in parallel with the existing USB 2.0 bus (refer to the picture below).
• USB 2.0 previously had four wires (power, ground, and a pair for dierential data); USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 adds four more for two pairs
of dierential signals (receive and transmit) for a combined total of eight connections in the connectors and cabling.
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 utilizes the bidirectional data interface, rather than USB 2.0's half-duplex arrangement. This gives a 10-fold
increase in theoretical bandwidth.
With today's ever increasing demands placed on data transfers with high-denition video content, terabyte storage devices, high megapixel
count digital cameras etc., USB 2.0 may not be fast enough. Furthermore, no USB 2.0 connection could ever come close to the 480Mbps
theoretical maximum throughput, making data transfer at around 320Mbps (40MB/s) — the actual real-world maximum. Similarly, USB
3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 connections will never achieve 4.8Gbps. We will likely see a real-world maximum rate of 400MB/s with overheads. At this
speed, USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 is a 10x improvement over USB 2.0.
Applications
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 opens up the laneways and provides more headroom for devices to deliver a better overall experience. Where USB
video was barely tolerable previously (both from a maximum resolution, latency, and video compression perspective), it's easy to imagine
Technology and components
11
Page 12

that with 5-10 times the bandwidth available, USB video solutions should work that much better. Single-link DVI requires almost 2Gbps
throughput. Where 480Mbps was limiting, 5Gbps is more than promising. With its promised 4.8Gbps speed, the standard will nd its way
into some products that previously weren't USB territory, like external RAID storage systems.
Listed below are some of the available SuperSpeed USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 products:
• External Desktop USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Hard Drives
• Portable USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Hard Drives
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Drive Docks & Adapters
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Flash Drives & Readers
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Solid-state Drives
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 RAIDs
• Optical Media Drives
• Multimedia Devices
• Networking
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Adapter Cards & Hubs
Compatibility
The good news is that USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 has been carefully planned from the start to peacefully co-exist with USB 2.0. First of all,
while USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 species new physical connections and thus new cables to take advantage of the higher speed capability of
the new protocol, the connector itself remains the same rectangular shape with the four USB 2.0 contacts in the exact same location as
before. Five new connections to carry receive and transmitted data independently are present on USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 cables and only
come into contact when connected to a proper SuperSpeed USB connection.
Windows 8/10 will be bringing native support for USB 3.1 Gen 1 controllers. This is in contrast to previous versions of Windows, which
continue to require separate drivers for USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 controllers.
Microsoft announced that Windows 7 would have USB 3.1 Gen 1 support, perhaps not on its immediate release, but in a subsequent Service
Pack or update. It is not out of the question to think that following a successful release of USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 support in Windows 7,
SuperSpeed support would trickle down to Vista. Microsoft has conrmed this by stating that most of their partners share the opinion that
Vista should also support USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1.
Advantages of Displayport over USB Type-C
• Full DisplayPort audio/video (A/V) performance (up to 4K at 60Hz)
• SuperSpeed USB (USB 3.1) data
• Reversible plug orientation and cable direction
• Backwards compatibility to VGA, DVI with adaptors
• Supports HDMI 2.0a and is backwards compatible with previous versions
USB Type-C
USB Type-C is a new, tiny physical connector. The connector itself can support various exciting new USB standard like USB 3.1 and USB
power delivery (USB PD).
Alternate Mode
USB Type-C is a new connector standard that's very small. It's about a third the size of an old USB Type-A plug. This is a single connector
standard that every device should be able to use. USB Type-C ports can support a variety of dierent protocols using “alternate modes,”
which allows you to have adapters that can output HDMI, VGA, DisplayPort, or other types of connections from that single USB port
Technology and components
12
Page 13

USB Power Delivery
The USB PD specication is also closely intertwined with USB Type-C. Currently, smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices often use
a USB connection to charge. A USB 2.0 connection provides up to 2.5 watts of power — that'll charge your phone, but that's about it. A
laptop might require up to 60 watts, for example. The USB Power Delivery specication ups this power delivery to 100 watts. It's bidirectional, so a device can either send or receive power. And this power can be transferred at the same time the device is transmitting
data across the connection.
This could spell the end of all those proprietary laptop charging cables, with everything charging via a standard USB connection. You could
charge your laptop from one of those portable battery packs you charge your smartphones and other portable devices from today. You
could plug your laptop into an external display connected to a power cable, and that external display would charge your laptop as you used
it as an external display — all via the one little USB Type-C connection. To use this, the device and the cable have to support USB Power
Delivery. Just having a USB Type-C connection doesn't necessarily mean they do.
USB Type-C and USB 3.1
USB 3.1 is a new USB standard. USB 3's theoretical bandwidth is 5 Gbps, while USB 3.1 Gen2 is10Gbps . That's double the bandwidth, as
fast as a rst-generation Thunderbolt connector. USB Type-C isn't the same thing as USB 3.1. USB Type-C is just a connector shape, and
the underlying technology could just be USB 2 or USB 3.0. In fact, Nokia's N1 Android tablet uses a USB Type-C connector, but underneath
it's all USB 2.0 — not even USB 3.0. However, these technologies are closely related.
Technology and components
13
Page 14
Disassembly and reassembly
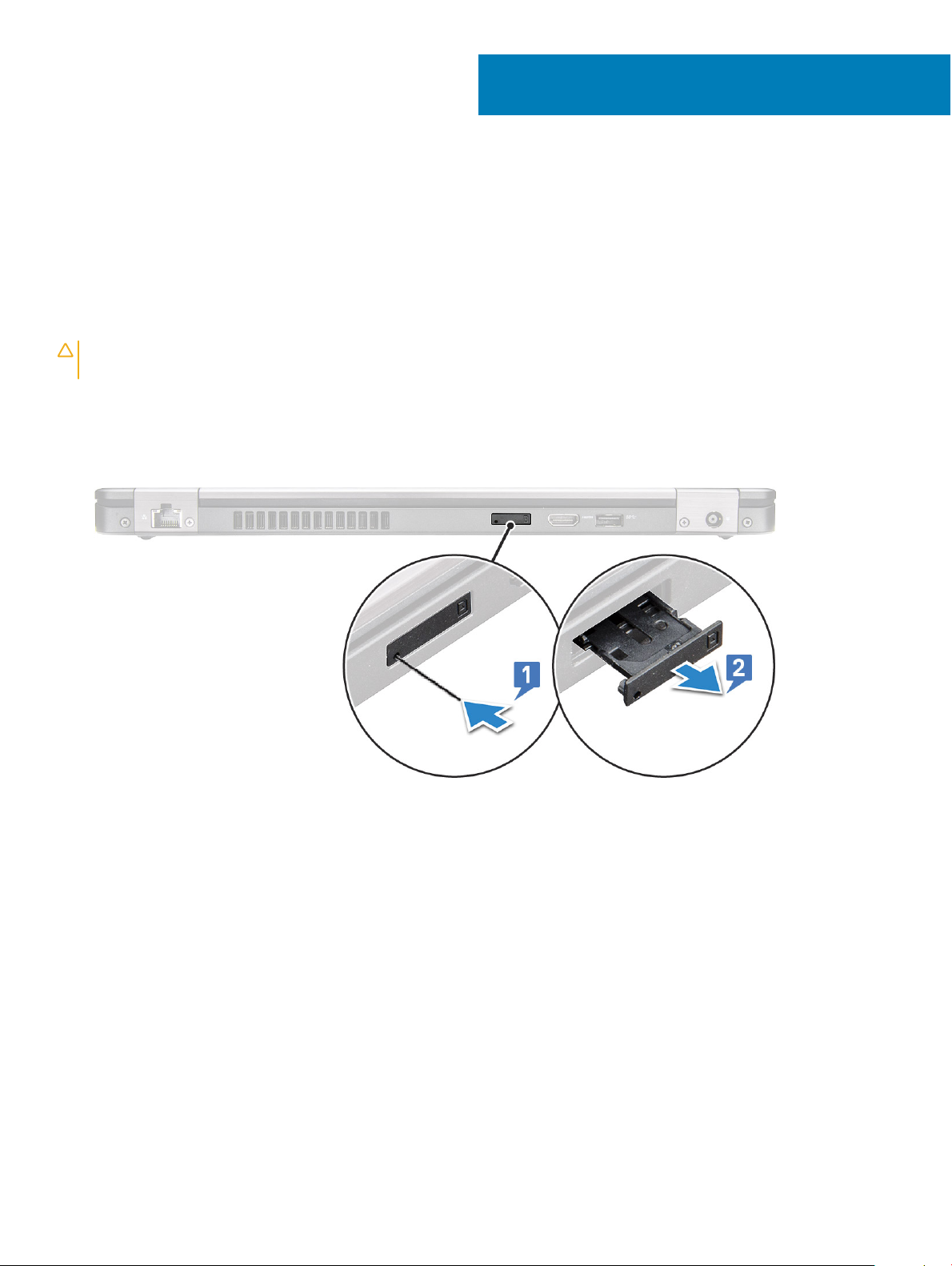
Subscriber Identity Module(SIM) board
Removing the Subscriber Identication Module card
CAUTION: Removing the SIM card when the computer is on may cause data loss or damage the card. Ensure your computer is
turned o or the network connections are disabled.
1 Insert a paperclip or a SIM card removal tool into the pinhole on the SIM card tray [1].
2 Pull the SIM card tray to remove it [2].
3 Remove the SIM card from the SIM card tray.
4 Push the SIM card tray into the slot until it clicks into place.
3
Installing the Subscriber Identication Module card
1 Insert a paperclip or a SIM card removal tool into the pinhole [1].
2 Pull the SIM card tray to remove it [2].
3 Place the SIM card on the SIM card tray.
4 Push the SIM card tray into the slot until it clicks into place .
14 Disassembly and reassembly
Page 15

SD card – optional
SD card is an optional component. You will see a SD card only in systems shipped with a WWAN card.
Removing the SD card – WWAN models
1 Follow the procedure Before working inside your computer
2 Push the SD card so that the SD card pops out from its slot [1], and then remove it from the system [2].
Installing the SD card – WWAN models
1 Push the SD card into its slot until the SD card gets secured with a click sound.
2 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer
Base cover
Removing the base cover
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 To remove the base cover:
Disassembly and reassembly
15
Page 16

a Loosen the 8 (M2.0x6) captive screws that secure the base cover to the system [1].
b Pry the base cover from the recess at the top edge [2] and continue prying throughout the outer sides of the base cover in
clockwise direction to release the base cover.
NOTE: Use a plastic scribe to pry the base cover from the edges.
c Lift the base cover from the system.
16
Disassembly and reassembly
Page 17

Installing the base cover
1 Place the base cover to align with the screw holders on the system and press the sides of the base cover.
2 Tighten the 8 (M2.0x6) captive screws to secure the base cover to the system.
3 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Battery
Removing the battery
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the base cover.
3 To remove the battery:
a Disconnect the battery cable from the connector on the system board [1] and unroute the cable from the routing channel.
b Loosen the M2x6 captive screw that secures the battery to the system [2].
c Lift the battery away from the system [3].
Disassembly and reassembly
17
Page 18

Installing the battery
1 Insert the battery into the slot on the system.
2 Route the battery cable through the routing channel.
3 Tighten the M2x6 captive screw to secure the battery to the system.
4 Connect the battery cable to the connector on the system board.
5 Install the base cover.
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
SSD card–optional
Removing the SSD card
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the :
a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the Solid State Drive (SSD) card:
a Peel the adhesive mylar shield that secures the SSD card [1].
: Remove the adhesive mylar carefully so that it can be reused on the replacement SSD.
NOTE
b Remove the M2x3 screw that secures the SSD to the system [2].
c Slide and lift the SSD from the system [3].
Disassembly and reassembly
18
Page 19
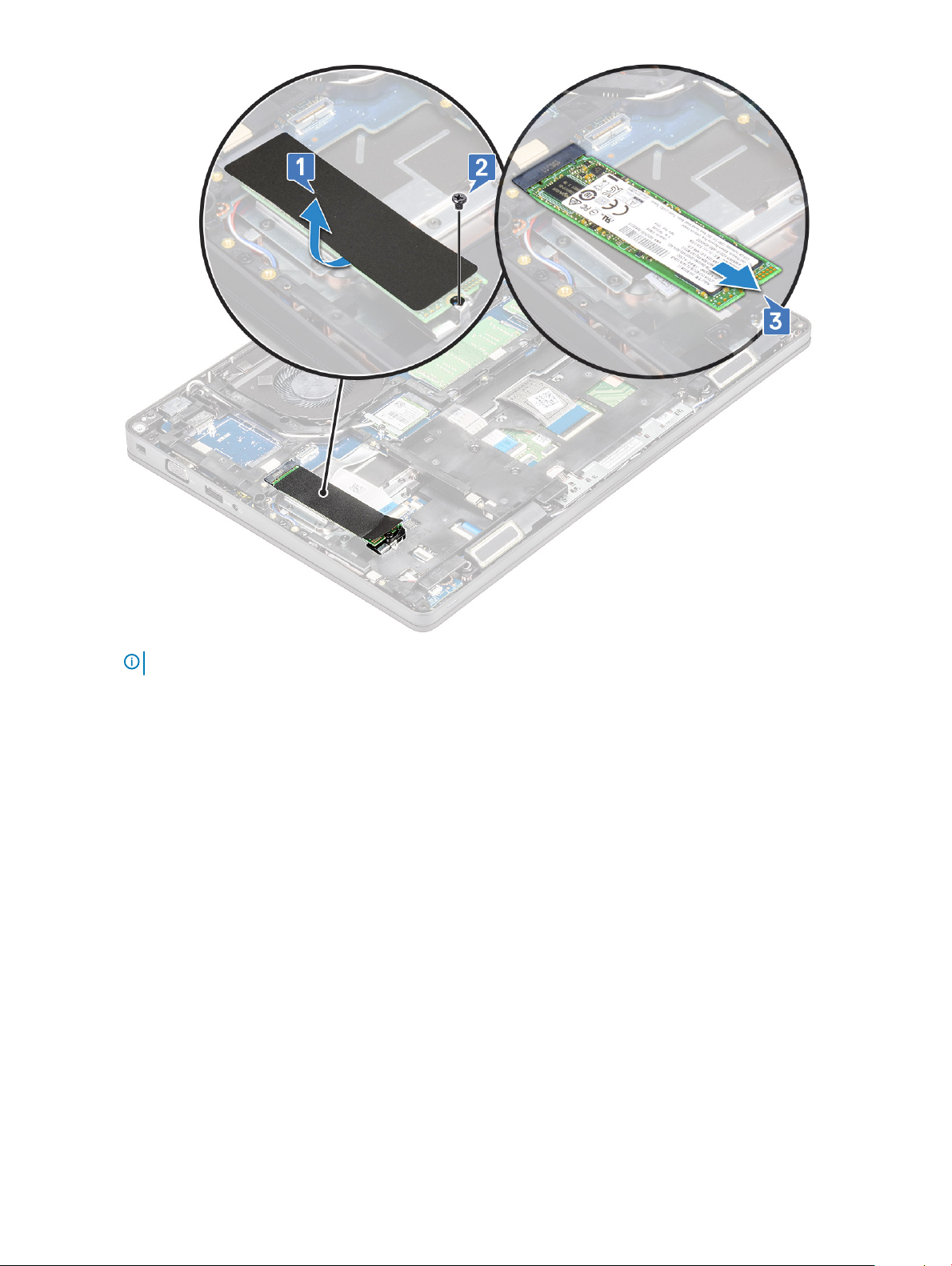
NOTE: This applies only to the SATA M.2 2280 version of the SSD
Installing the SSD card
1 Insert the SSD card into the connector on the system.
2 Replace the M2x3 screw that secures the SSD card to the system.
3 Place the Mylar shield over the SSD.
4 Install the :
a battery
b base cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
SSD frame
Removing the SSD frame
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c SSD card
Disassembly and reassembly
19
Page 20
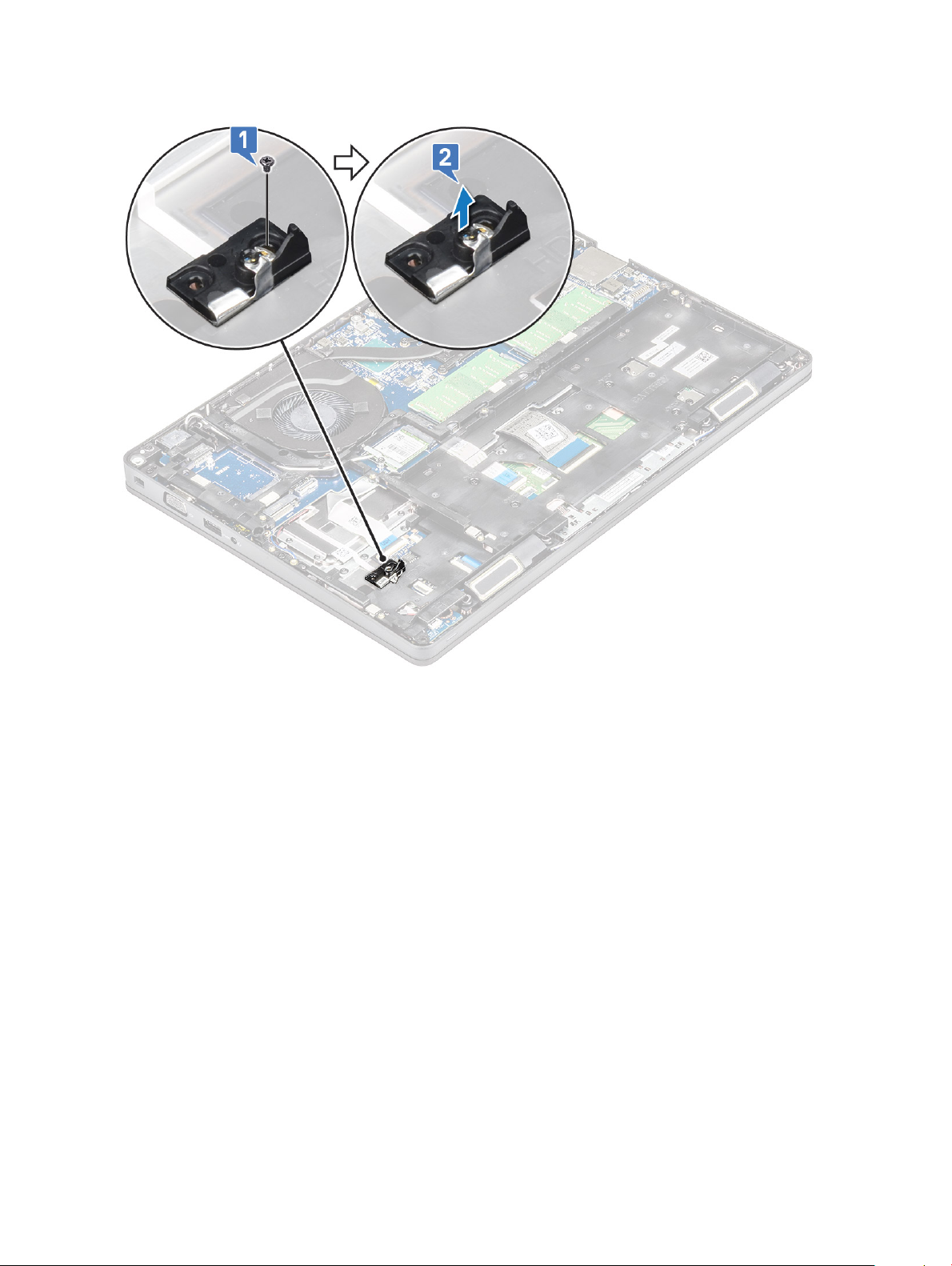
3 To remove the SSD frame:
a Remove the M2x3 screw that secures the SSD frame to the system [1].
b Lift the SSD frame from the system [2].
Installing the SSD frame
1 Place the SSD frame into the slot in the system.
2 Replace the M2x3 screw that secures the SSD frame to the system.
3 Install the:
a SSD card
b battery
c base cover
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Hard drive
Removing hard drive
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the :
a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the hard drive:
Disassembly and reassembly
20
Page 21

a Disconnect the hard drive cable from the connector on the system board [1].
b Remove the four (M2 x 2.7) screws that secure the hard drive to the system [2].
c Lift the hard drive from the system.
Disassembly and reassembly
21
Page 22

Installing hard drive
1 Insert the hard drive into the slot on the system.
2 Replace the four (M2 x 2.7) screws to secure the hard drive to the system.
3 Connect the hard drive cable to the connector on the system board.
4 Install the :
a battery
b base cover
5 Follow the procedures in After working inside your system.
Coin-cell battery
Removing the coin cell battery
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the :
a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the coin cell battery:
a Disconnect the coin cell battery cable from the connector on the system board [1].
b Lift the coin cell battery to release from the adhesive and lift it away from the system board [2].
22
Disassembly and reassembly
Page 23

Installing coin cell battery
1 Ax the coin cell battery on the system board.
2 Connect the coin cell battery cable to the connector on the system board.
3 Install the :
a battery
b base cover
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
WLAN card
Removing WLAN card
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the :
a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the WLAN card:
a Remove the M2x3 screw that secures the WLAN card bracket to the system [1].
b Remove the WLAN card bracket that secures the WLAN antenna cables [2].
c Disconnect the WLAN antenna cables from the connectors on the WLAN card [3].
d Lift the WLAN card away the connector as shown in the gure [4].
CAUTION
place. When removing the wireless card from the system, make sure the adhesive pad stays on the system board/
chassis frame during the prying process. If the adhesive pad is removed from the system along with the wireless card,
adhere it back to the system.
: There is an adhesive pad on the system board or chassis frame which helps secure the wireless card in
Disassembly and reassembly 23
Page 24

Installing WLAN card
1 Insert the WLAN card into the connector on the system board.
2 Connect the WLAN antenna cables to the connectors on the WLAN card.
3 Place the WLAN card bracket to secure the WLAN cables.
4 Replace the M2x3 screw to secure the WLAN card to the system.
5 Install the :
a battery
b base cover
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
WWAN card – optional
This is optional as the system might not ship with WWAN card.
Removing the WWAN card
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the :
a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the WWAN card:
Disassembly and reassembly
24
Page 25

a Disconnect the WWAN antenna cables from the connectors on the WWAN card [1].
b Remove the M2x3 screw that secures the WWAN card to the system [2]
c Slide and lift the WWAN card from the system [3].
Installing the WWAN card
1 Insert the WWAN card into the slot on the system.
2 Connect the WWAN antenna cables to the connectors on the WWAN card.
3 Replace the screw (M2X3) to secure the WWAN card to the computer.
4 Install the :
a battery
b base cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Memory modules
Removing the memory module
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the :
a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the memory module:
Disassembly and reassembly
25
Page 26

a Pry the clips securing the memory module until the memory module pops-up [1].
b Lift the memory module from the connector [2].
Installing the memory module
1 Insert the memory module into the memory connector at a 30 degree angle until the contacts are fully seated into the slot. Then, press
the module until the clips secure the memory module.
2 Install the :
a battery
b base cover
3 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Keyboard
Removing keyboard lattice
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Pry the keyboard lattice from one of the recess points [1] and continue prying the sides in clockwise or anticlockwise direction, and
then lift the keyboard lattice from the system [2]
Disassembly and reassembly
26
Page 27

Installing keyboard lattice
1 Place the keyboard lattice on the keyboard and press along the edges and in between the rows of keys until the lattice clicks in place.
2 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Removing the keyboard
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c keyboard lattice
3 To remove the keyboard:
a Lift the latch and disconnect the keyboard cable from the connector on the system.
b Lift the latch and disconnect the keyboard backlight cable from the connector on the system [2].
: This step is applicable only for models that support keyboard backlight option. Number of cables to disconnect
NOTE
is based on the keyboard type.
Disassembly and reassembly 27
Page 28

c Turn over the system and open the laptop in front view mode.
d Remove the ve (M2x2.5) screws that secure the keyboard to the system [1].
e Flip the keyboard from the bottom and lift it from the system along with the keyboard cable and the keyboard back light cable
[2].
WARNING
avoid damaging the cables.
: Gently pull the keyboard cable and the keyboard back light cable routed beneath the chassis frame to
28 Disassembly and reassembly
Page 29

Disassembly and reassembly 29
Page 30

Installing the keyboard
1 Hold the keyboard and route the keyboard cable and the keyboard backlight cables through the palmrest in the system.
2 Align the keyboard with the screw holders on the system.
3 Replace the screws to secure the keyboard to the system.
4 Turn the system over and connect the keyboard cable and the keyboard backlight cable to the connector in the system.
NOTE: When reinstalling the chassis frame ensure the keyboard cables are NOT under the lattice , but run through the
opening in the frame before connecting them to system board.
5 Install the:
a keyboard lattice
b battery
c base cover
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Heat sink
Removing the heat sink
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the :
a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the heat sink :
a Remove the four (M2x3) screws that secure the heat sink on the system board [1].
NOTE
:
• Remove the heat sink screws in sequential order as indicated on the heat-sink.
b Lift the heat sink from the system [2].
30
Disassembly and reassembly
Page 31

Installing the heat sink
1 Place the heat sink on the system board.
2 Replace the four (M2x3) screws that secure the heat sink on the system board.
NOTE
:
• Replace the heat sink screws in sequential order as indicated on the heat-sink.
3 Install the :
a battery
b base cover
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
System fan
Removing the system fan
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c hard drive
d SSD card
e SSD frame
f WLAN card
g WWAN card (optional)
Disassembly and reassembly
31
Page 32

h chassis frame
3 To remove the system fan:
a Disconnect the system fan cable from the connector on the system board [1].
b Lift the system fan away from the computer [2].
Installing the system fan
1 Place the system fan into the slot on the computer.
2 Connect the system fan cable to the connector on the system board.
3 Install the:
a chassis frame
b WWAN card (optional)
c WLAN card
d SSD frame
e SSD card
f hard drive
g battery
h base cover
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Disassembly and reassembly
32
Page 33

Power connector port
Removing the power connector port
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the :
a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the power connector port:
a Remove the M2x3 screw that secures the adhesive tape of the display cable to the power connector bracket [1], and peel o
the adhesive tape.
b Disconnect the power connector cable from the connector on the system board [2].
c Remove the M2x3 screw to release the power connector bracket that secures the power connector port to your system [3].
d Remove the power connector bracket from the system [4].
e Pull the power connector port, and lift it from the system [5].
Installing power connector port
1 Align the power connector port along the grooves on the slot and push it down.
2 Place the metal bracket on the power connector port.
3 Replace the M2x3 screw that secures one end of the power connector bracket to the power connector port.
4 Connect the power connector cable to the connector on the system board.
Disassembly and reassembly
33
Page 34

5 Ax the adhesive tape of the display cable to the power connector bracket and replace the M2x3 screw to secure another end of the
power connector bracket.
6 Install the :
a battery
b base cover
7 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Chassis frame
Removing the chassis frame
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c hard drive
d SSD card
e SSD frame
f WLAN card
g WWAN card (optional)
NOTE: There are two dierent screw sizes for chassis frame: M2x5 8ea and M2x3 5ea
3 To release the chassis frame:
a Unroute the WLAN and WWAN cables from the routing channels [1].
b Lift the latch and disconnect the keyboard backlight cable and the keyboard cable from their connectors [2] on the system.
NOTE
: There may be more than one cable to disconnect based on the keyboard type.
34 Disassembly and reassembly
Page 35

4 To remove the chassis frame:
a Remove the ve (M2x3) screws and eight (M2x5) screws that secure the chassis frame to the system [1].
b Lift the chassis frame from the system [2].
Installing the chassis frame
1 Place the chassis frame into the slot on the system.
NOTE
: Gently pull the keyboard cable and keyboard back light cables through the spacing in the chassis frame before
placing the chassis frame in the slot on the system.
2 Replace the ve (M2x3) screws and eight (M2x5) screws to secure the chassis frame to the system.
3 Connect the keyboard cable and the keyboard backlight cable to their connectors on the system.
NOTE
: There may be more than one cable to connect based on keyboard types.
4 Route the WLAN and WWAN (optional) cables through the routing channels.
5 Install the:
a WWAN card (optional)
b WLAN card
c SSD frame
d SSD card
e hard drive
f battery
g base cover
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your system.
Disassembly and reassembly
35
Page 36

LED board
Removing LED board
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the .
a base cover
b battery
c hard drive
d SSD card
e SSD frame
f WLAN card
g WWAN card (optional)
h chassis frame
3 To remove the LED board:
a Lift the latch and remove the LED cable connected to the connector on the LED board [1]
b Remove the (M2.0x2.0) screw that secures the LED board to the system [2].
c Lift the LED board from the connector [3].
36 Disassembly and reassembly
Page 37

Installing LED board
1 Place the LED board in its slot on the system.
2 Replace the M2.0x2.0 screw to secure the LED board to the system.
3 Connect the LED cable to its connector on the LED board.
4 Install the:
a chassis frame
b WWAN card (optional)
c WLAN card
d SSD frame
e SSD card
f hard drive
g battery
h base cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
SmartCard module
Removing smart card reader board
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c hard drive
d SSD card
e SSD frame
f WLAN card
g WWAN card (optional)
h chassis frame
3 To release the smart card reader board:
a Lift the latch and disconnect the smart card reader board cable from the connector [1].
b Peel the cable from the palmrest [2].
Disassembly and reassembly
37
Page 38

4 To remove the smart card reader board:
a Remove the 2 (M2x3) screws that secure the smart card reader board to the palmrest [1].
b Slide and lift the smart card reader from the slot in the system [2].
38
Disassembly and reassembly
Page 39

Installing smart card reader board
1 Insert the smart card reader board to align with the tabs on the chassis.
2 Replace the 2 (M2x3) screws to secure the smart card reader board to the system.
3 Ax the smart card reader board cable and connect the cable to the connector.
4 Install the:
a chassis frame
b WWAN card (optional)
c WLAN card
d SSD frame
e SSD card
f hard drive
g battery
h base cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Disassembly and reassembly
39
Page 40

Touchpad panel
Removing the touchpad
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c SSD card
d SSD frame
e WLAN card
f WWAN card
g chassis frame
3 To remove the touchpad panel:
a Disconnect the touchpad panel cable from the connector on the system board [1].
b Remove the two M2x3 screws that secure the touchpad panel to the system. [2].
c Lift the touchpad panel from the system [3].
Installing touchpad panel
1 Place the touchpad panel into its slot on the chassis.
2 Tighten the two screws to secure the touchpad panel to your system.
Disassembly and reassembly
40
Page 41

3 Connect the touchpad panel cable to the connector on the system board.
4 Install the:
a chassis frame
b SSD frame
c SSD card
d WWAN
e WLAN card
f battery
g base cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
System board
Removing system board
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a SIM card
b base cover
c battery
d memory module
e hard drive
f SSD card
g SSD frame
h WLAN card
i WWAN card (optional)
j keyboard lattice
k keyboard
l heat sink
m chassis frame
n system fan
3 Disconnect the following cables from the system board:
a Touchpad cable [1]
b USH cable [2]
c LED board cable [3]
d Speaker cable [4]
Disassembly and reassembly
41
Page 42

4 To release the system board:
a Flip over the system and remove the two M2x3 screw that secure the display cable bracket in place [1].
b Lift the metal display cable bracket from the system [2].
c Disconnect the display cables from the connectors on the system board [3,4] and peel the adhesive tape securing the display
cable to the system.
d Disconnect the power connector port cable from the connector on the system board [5].
e Remove the two M2x5 screws that secure the Type-C USB bracket in place [6].
NOTE
: The metal bracket secures the DisplayPort over USB Type-C.
f Lift the metal bracket away from the system [7].
42
Disassembly and reassembly
Page 43

5 To remove the system board:
NOTE
: Ensure SIM card tray is removed
a Remove the four (M2x3) screws that secure the system board in place [1].
b Lift the system board away from the system [2].
Disassembly and reassembly
43
Page 44

Installing system board
1 Align the system board with the screw holders on the computer.
NOTE
: Insert the cables through the openings in the keyboard area while placing the system board in the computer.
2 Replace the four (M2x3) screws to secure the system board to the system.
3 Place the metal bracket to secure the DisplayPort over USB Type-C.
4 Replace the two (M2x3) screws to secure the metal bracket on the DisplayPort over USB Type-C.
5 Connect the power connector port cable to the connector on the system board.
6 Connect the display cables to the connectors on the system board and ax the tape that secures the display cable to the system.
7 Place the display cable metal bracket over the display cable.
8 Replace the two M2x3 screws to secure the metal bracket.
9 Flip over the system and open the system in working mode.
10 Connect the following cables:
a Touchpad cable
b LED board cable
c USH board cable
d speaker cable
11 Install the:
a system fan
b chassis frame
c heat sink
d keyboard
e keyboard lattice
f WWAN card (optional)
Disassembly and reassembly
44
Page 45

g WLAN card
h SSD frame
i SSD card
j hard drive
k memory module
l battery
m base cover
n SIM card
12 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Speaker
Removing the speaker
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c memory module
d hard drive
e SSD card
f SSD frame
g WLAN card
h WWAN card (optional)
i keyboard lattice
j keyboard
k chassis frame
l system board
3 To remove the speakers:
a Release the speaker cable through the routing channels [1].
b Lift the speaker away from the computer [2].
Disassembly and reassembly
45
Page 46

Installing the speaker
1 Insert the speaker module aligning it with the nodes on the chassis.
2 Route the speaker cable through the routing channels.
3 Install the:
a system board
b chassis frame
c keyboard
d keyboard lattice
e WLAN card
f SSD frame
g SSD card
h hard drive
i memory module
j battery
k base cover
l SIM card
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Display hinge cover
Removing display hinge cover
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
Disassembly and reassembly
46
Page 47

a base cover
b battery
3 To remove the display hinge cover:
a Remove the M2x3 screw that secures the display hinge cover to the chassis [1].
b Lift the display hinge cover away from the display hinge [2].
c Repeat step a and step b to remove the other display hinge cover.
Installing display hinge cover
1 Place the display hinge cover on the display hinge.
2 Replace the M2x3 screw to secure the display hinge cover to the display hinge.
3 Repeat step 1 and step 2 to install the other display hinge cover.
4 Install the:
a battery
b base cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Display assembly
Removing display assembly
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
Disassembly and reassembly
47
Page 48

a base cover
b battery
c WLAN card
d WWAN card (optional)
e display hinge cover
3 To disconnect the display cable:
a Release the WLAN and WWAN cables from the routing channels [1].
b Remove the two (M2x3) screws that secure the display cable bracket in place [2].
c Remove the display cable bracket that secures the display cable from the system [3].
d Disconnect the display cables from their respective connectors on the system board [4,5].
e Remove the single screw that secure the power connector bracket and also the display cable to the system [6].
4 To release the display assembly:
a Remove the two M2x5 screws that secure the display assembly to the computer [1].
b Release the WLAN cable and display cable through the routing channels [2] [3].
Disassembly and reassembly
48
Page 49

5 Turn over the computer.
6 To remove the display assembly:
a Remove the two M2x5 screws that secure the display assembly to the computer [1].
b Open the display [2].
Disassembly and reassembly
49
Page 50

c Lift the display assembly from the computer.
50
Disassembly and reassembly
Page 51

Installing display assembly
1 Place the chassis on a plane surface.
2 Align the display assembly with the screw holders on the system and place it on the chassis.
3 Close the display.
4 Replace the two screws that secure the display assembly.
5 Flip over the system and replace two screws to secure the display assembly to the system.
6 Replace the single screw that secure the power connector bracket and the display cable to the system.
7 Connect the display cables to the connectors on the system board.
8 Place the metal bracket to secure the display cable.
9 Replace the (M2x3) screws to secure the metal bracket to the system.
10 Route the WLAN and WWAN cables through the routing channels.
11 Install the:
a hinge cover
b WWAN card (optional)
c WLAN card
d battery
e base cover
12 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Disassembly and reassembly
51
Page 52

Display bezel
Removing display bezel
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c WLAN card
d WWAN card (optional)
e Display hinge cover
f display assembly
3 To remove the display bezel:
a Pry the display bezel at the base of the display [1].
NOTE: When removing or reinstalling the display bezel from the display assembly, technicians should note that the
display bezel is secured to the LCD panel with a strong adhesive and care must be taken to avoid damage to LCD.
b Lift the display bezel to release it [2].
c Pry the edges on the side of the display to release the display bezel [3, 4,,5].
CAUTION
adhesive is very strong and tends to stay stuck to the LCD portion and can peel the layers up or crack the glass when
trying to pry the two items apart.
: The adhesive used on the LCD bezel to seal it with the LCD itself, makes it hard to remove the bezel as the
52 Disassembly and reassembly
Page 53

Installing display bezel
1 Place the display bezel on the display assembly.
NOTE: Remove the protective covering on the adhesive on the LCD bezel before placing on the display assembly.
Starting from a top corner, press on the display bezel and work around the entire bezel until it clicks on to the display assembly.
2
3 Install the:
a display assembly
b display hinge cover
c WWAN card (optional)
d WLAN card
e battery
f base cover
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Display panel
Removing display panel
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c WLAN card
d WWAN card (optional)
e display hinge cover
f display assembly
g display bezel
3 Remove the four M2x3 screws that secure the display panel to the display assembly [1] and lift to turn over the display panel to access
the display cable [2].
Disassembly and reassembly
53
Page 54

4 To remove the display panel:
a Peel the conductive tape [1].
b Remove the adhesive strip that secures the display cable [2].
c Lift the latch and disconnect the display cable from the connector on the display panel [3] [4].
54
Disassembly and reassembly
Page 55

Installing display panel
1 Connect the display cable to the connector and ax the adhesive strip.
2 Ax the conductive tape to secure the display cable.
3 Replace the display panel to align with the screw holders on the display assembly.
4 Replace the four M2x3 screws to secure the display panel to the display back cover.
5 Install the:
a display bezel
b display assembly
c display hinge cover
d WLAN card
e WWAN card (optional)
f battery
g base cover
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Disassembly and reassembly
55
Page 56

Display (eDP) cable
Removing display cable
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c WLAN card
d WWAN card (optional)
e display hinge cover
f display assembly
g display bezel
h display panel
3 Disconnect the camera cable from the connector on the camera module [1].
4 Peel the display cable to release it from adhesive and lift the display cable from the display back cover [2].
Installing display cable
1 Ax the display cable to the display back cover.
2 Connect the camera cable to the connector on camera module.
3 Install the:
a display panel
b display bezel
c display assembly
d display hinge cover
Disassembly and reassembly
56
Page 57

e WLAN card
f WWAN card (optional)
g battery
h base cover
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Camera
Removing camera
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c WLAN card
d WWAN card (optional)
e display hinge cover
f display assembly
g display bezel
h display panel
3 To remove the camera:
a Disconnect the camera cable from the connector on the camera module [1].
b Carefully pry and lift the camera module from the display back cover [2].
Disassembly and reassembly
57
Page 58

Installing camera
1 Insert the camera into the slot on the display back cover.
2 Connect the camera cable to the connector on the camera module.
3 Install the :
a display panel
b display bezel
c display assembly
d display hinge cover
e WLAN card
f WWAN card (optional)
g memory module
h battery
i base cover
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Display hinges
Removing display hinge
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
a base cover
b battery
c WLAN card
d WWAN card (optional)
e display hinge cover
f display assembly
g display bezel
3 To remove the display hinge:
a Remove the 3 (M2.5x3) screws that secure the display hinge to the display assembly [1].
b Lift the display hinge from the display assembly [2].
c Repeat step a and step b to remove the other display hinge.
58
Disassembly and reassembly
Page 59

Installing display hinge
1 Place the display hinge on the display assembly.
2 Replace the 3 (M2.5x3) screws to secure the display hinge to the display assembly.
3 Repeat step 1 and step 2 to install the other display hinge.
4 Install the:
a display bezel
b display assembly
c display hinge cover
d WLAN card
e WWAN card (optional)
f battery
g base cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Display back cover assembly
Removing the display back cover assembly
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
Disassembly and reassembly
59
Page 60

a base cover
b battery
c WLAN card
d WWAN card (optional)
e display hinge cover
f display assembly
g display bezel
h display panel
i display hinge
j display cable
k camera
The display back cover assembly is the remaining component, after removing all the components.
Installing the display back cover assembly
1 Place the display back cover assembly on a at surface.
2 Install the:
a camera
b display cable
c display hinge
d display panel
e display bezel
f display assembly
g display hinge cover
h WLAN card
i WWAN card (optional)
j battery
k base cover
3 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Palm rest
Removing palm rest
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
Disassembly and reassembly
60
Page 61

a SIM card
b base cover
c battery
d memory module
e hard drive
f SSD card
g SSD frame
h WLAN card
i WWAN card (optional)
j keyboard lattice
k keyboard
l heat sink
m chassis frame
n system fan
o system board
p display hinge cover
q display assembly
3 The palm rest is the remaining component after removing all the components.
Installing palm rest
1 Place the palm rest on a at surface.
2 Install the:
a display assembly
b display hinge cover
c system board
d system fan
e chassis frame
Disassembly and reassembly
61
Page 62

f heat sink assembly
g keyboard
h keyboard lattice
i WWAN card (optional)
j WLAN card
k SSD frame
l SSD card
m hard drive
n memory module
o battery
p base cover
q SIM card
3 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
62 Disassembly and reassembly
Page 63

4
Troubleshooting
Enhanced Pre-Boot System Assessment — ePSA diagnostics
The ePSA diagnostics (also known as system diagnostics) performs a complete check of your hardware. The ePSA is embedded with the
BIOS and is launched by the BIOS internally. The embedded system diagnostics provides a set of options for particular devices or device
groups allowing you to:
• Run tests automatically or in an interactive mode
• Repeat tests
• Display or save test results
• Run thorough tests to introduce additional test options to provide extra information about the failed device(s)
• View status messages that inform you if tests are completed successfully
• View error messages that inform you of problems encountered during testing
CAUTION
results or error messages.
NOTE: Some tests for specic devices require user interaction. Always ensure that you are present at the computer terminal
when the diagnostic tests are performed.
: Use the system diagnostics to test only your computer. Using this program with other computers may cause invalid
Running the ePSA Diagnostics
1 Invoke diagnostics boot by either of the methods suggested above
2 Once on one time boot menu use up/down arrow key to navigate to ePSA or diagnostics and press <return> key to launch
Fn+PWR will ash diagnostics boot selected on screen and launch ePSA/diagnostics directly.
3 On the boot menu screen, select the Diagnostics option.
4 Press the arrow in the lower-right corner to go to the page listing.
The items detected are listed and will be tested
5 If there are any issues, error codes are displayed.
Note the error code and validation number and contact Dell.
To run a diagnostic test on a specic device
1 Press Esc and click Yes to stop the diagnostic test.
2 Select the device from the left pane and click Run Tests.
3 If there are any issues, error codes are displayed.
Note the error code and validation number and contact Dell.
Real Time Clock reset
The Real Time Clock (RTC) reset function allows you to recover your Dell system from No POST/No Boot/No Power situations. To initiate
the RTC reset on the system make sure system is in a power-o state and is connected to power source . Press and hold the power button
for 25 seconds and then release the power button.
Troubleshooting 63
Page 64

NOTE: If AC power is disconnected from the system during the process or the power button is held longer than 40 seconds, the
RTC reset process is aborted.
The RTC reset will reset the BIOS to Defaults, un-provision Intel vPro and reset the system date and time. The following items are
unaected by the RTC reset:
• Service Tag
• Asset Tag
• Ownership Tag
• Admin Password
• System Password
• HDD Password
• Key Databases
• System Logs
The following items may or may not reset based on your custom BIOS setting selections:
• The Boot List
• Enable Legacy OROMs
• Secure Boot Enable
• Allow BIOS Downgrade
64 Troubleshooting
Page 65

5
Getting help
Contacting Dell
NOTE: If you do not have an active Internet connection, you can nd contact information on your purchase invoice, packing slip,
bill, or Dell product catalog.
Dell provides several online and telephone-based support and service options. Availability varies by country and product, and some services
may not be available in your area. To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer service issues:
1 Go to Dell.com/support.
2 Select your support category.
3 Verify your country or region in the Choose a Country/Region drop-down list at the bottom of the page.
4 Select the appropriate service or support link based on your need.
Getting help 65
 Loading...
Loading...