Page 1

Specifications
CONTROL BOARD FOR MLT-289
MODEL
Rev. 1.01 Issued on June 27th, 2003
BD2-2890DD
Page 2

REVISION
Rev. No. Date Content
1.00 2003.03.18 First created.
1.01 2003.06.27 Factory setting of jumper J1-2 is changed.
i
Page 3

CONTENTS
1. OUTLINE ........................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Features ............................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 Precaution .......................................................................................................................................................... 1
2. BASIC SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................... 2
3. CONNECTING CONNECTORS.................................................................................. 3
3.1 CN1 Connector for Printer Mechanism (For Print Head) ................................................................................. 3
3.2 CN2 Connector for Print Mechanism (For Motor & Sensor)............................................................................ 3
3.3 CN3 Connector for Interface ............................................................................................................................. 4
4. JUMPER SETTING ....................................................................................................... 6
5. POWER SUPPLY ........................................................................................................... 8
5.1 Specifications .................................................................................................................................................... 8
5.2 Precautions ........................................................................................................................................................ 8
6. SERIAL INTERFACE ................................................................................................... 9
6.1 Specifications .................................................................................................................................................... 9
6.2 Explanation of Input/Output Signals ............................................................................................................... 10
6.3 Error Detection ................................................................................................................................................10
6.4 Data Receiving Control ...................................................................................................................................10
6.5 Buffering.......................................................................................................................................................... 11
6.6 Electrical Characteristics ................................................................................................................................. 11
7. ERROR HANDLING ................................................................................................... 12
7.1 Peripheral Circuit Errors ................................................................................................................................. 12
7.2 Operation Errors ..............................................................................................................................................13
8. PRINTER MECHANISM CONTROL SYSTEM ..................................................... 14
8.1 Thermal Head Control System (Division Driving System)............................................................................. 14
8.1.1 Fixed Division Number System ................................................................................................................. 14
8.1.2 Variable Division Number System ............................................................................................................. 14
8.2 Motor Drive ..................................................................................................................................................... 15
8.2.1 Motor Drive Features ................................................................................................................................. 15
8.2.2 Maximum Motor Drive Speeds at Major Voltage ...................................................................................... 15
ii
Page 4

9. PRINT CONTROL FUNCTIONS ............................................................................. 16
9.1 Command List ................................................................................................................................................. 16
9.2 Command Details ............................................................................................................................................18
9.2.1 Description of Items ................................................................................................................................... 18
10. CHARACTER CODE TABLE .................................................................................. 63
10.1 International................................................................................................................................................... 63
10.2 Japanese ......................................................................................................................................................... 64
10.3 International Character Set ............................................................................................................................ 65
APPENDIX 1. BLOCK DIAGRAM ............................................................................... 66
APPENDIX 2. OUTER DIMENSION ............................................................................ 67
iii
Page 5

1. OUTLINE
This control boards is designed to be used to control our thermal printer, “MLT-289” series
through the computer etc.
As being provided with many abundant functions, it can be used widely in various applications.
Before you start using it, read this manual thoroughly and understand the content.
1.1 Features
(1) Ultra compact
(2) Input buffer incorporated.
(3) Bar code printing is available (dedicated command).
(4) User-defined character registration function (94 characters)
1.2 Precaution
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
(1) Make sure to turn OFF the power supply in case of connecting/disconnecting the connectors.
(2) Absolutely do not make a short circuit between the terminals of connectors.
(3) Use power supply, interface etc. following their specifications.
(4) Use the recommended paper shown below.
• Thermal Paper TF5KS-E2D (Nippon paper)
KF50-HDA (Shin-Oji paper)
F220VP, HP220A (Mitsubishi paper)
1
Page 6
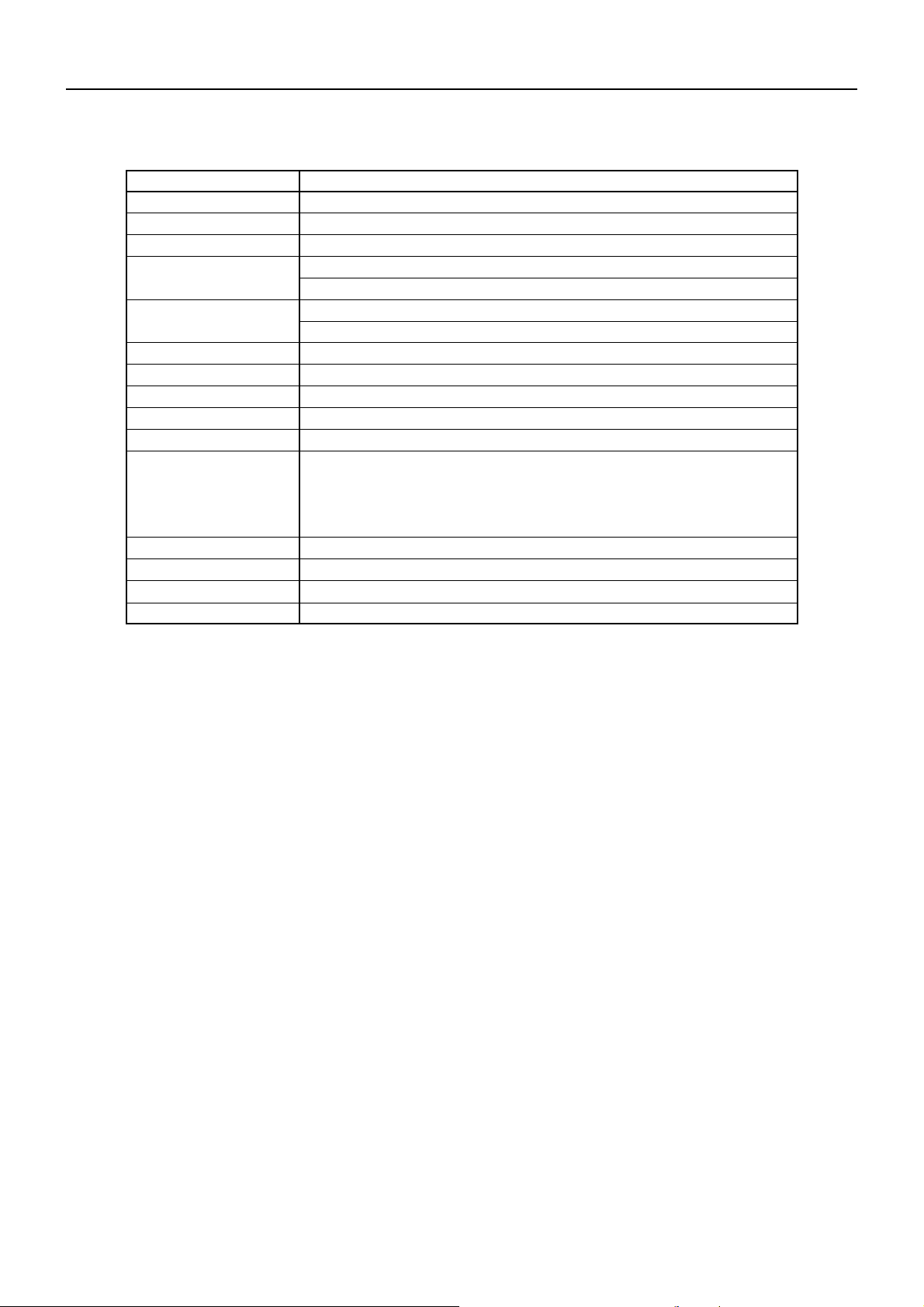
2. BASIC SPECIFICATIONS
Items Contents
Printing system
Print width
Print Speed
Number of columns
Character dimensions
Character types
Bar code type
Line pitch
Interface
Input buffer
Supply voltage
Weight
Outer Dimension
Operating Environment
Storage Environment
Thermosensitive dot-matrix printing
48 mm
420 dot line/sec
Font A : 32 columns
Font B : 42 columns
Font A : 1.25 mm × 3.00 mm
Font B : 0.88 mm × 3.00 mm
Alphanumeric, international characters
UPC-A/E, JAN (EAN) 13/8 columns, ITFCODE 39, CODE128, CODABAR
4.23 mm (Can be changed by command)
Serial (Conforms to RS-232C)
2 K bytes
VCC: 5V ± 5 % Approx. 130 mA (Self printing)
VP : 4.2V ~ 8.5V Approx. 1.5A (Ave) Approx. 4A (Peak) When 7.2V
Ordinal voltage is to be 7.2V (Max)
8.5V is a voltage, which is right after charging.
Approx. 35 g
50 mm (W) × 75 mm (D) (See outer drawing for details)
5 ~ 40˚C , 35 ~ 85% RH (with no dew condensation)
-20 ~ 60˚C , 10 ~ 90% RH (with no dew condensation)
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
2
Page 7
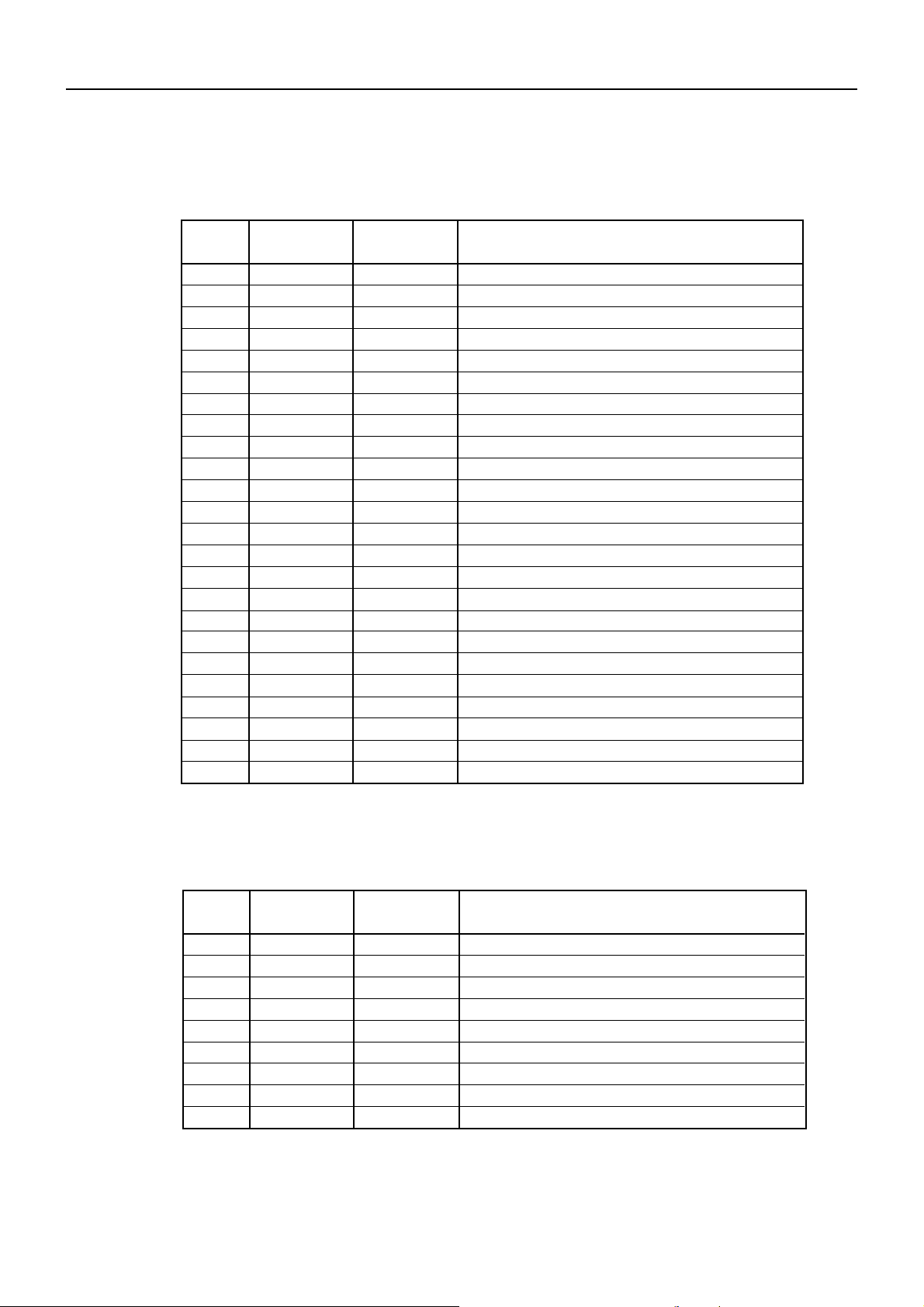
3. CONNECTING CONNECTORS
3.1 CN1 Connector for Printer Mechanism (For Print Head)
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Pin No. Signal Name I/O
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
Applicable Connector : 52806-2410 (Molex)
VH
VH
SI
GND
TM
STRB 1
STRB 2
Vdd
LATCH
GND
STRB 6
CP
GND
STRB 5
STRB 3
GND
GND
STRB 4
GND
GND
GND
VH
VH
VH
–
–
Output
–
Input
Output
Output
–
Output
–
Output
Output
–
Output
Output
–
–
Outpu
–
–
–
–
–
–
Function
Power for print head
Power for print head
Head data output signal
GND
Thermistor
Strobe 1
Strobe 2
Thermal head logics power (+5V)
Latch signal
GND
Strobe 6
Clock pulse
GND
Strobe 5
Strobe 3
GND
GND
Strobe 4
GND
GND
GND
Power for print head
Power for print head
Power for print head
3.2 CN2 Connector for Print Mechanism (For Motor & Sensor)
Pin No. Signal Name I/O
1
MOTOR B
2
MOTOR A
3
MOTOR B
4
MOTOR A
5
6
7
8
9
Applicable Connector : 53047-0910 (Molex)
PE C
GND
PE A
H-UP
GND
Output
Output
Output
Output
Input
–
–
Input
–
Operation signal for motor B
Operation signal for motor A
Operation signal for motor B
Operation signal for motor A
Photo-transistor collector (Paper sensor)
Photinterruptor emitter + cathode
Photo-LED anode (Paper sensor)
3
Function
Head-up signal
Head-up sensor GND
Page 8

3.3 CN3 Connector for Interface
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Pin No. Signal Name I/O
1
2
3
4
A
B
C
D
Applicable Connector: Amp 178217-2
TXD
Vcc
GND
Vp
RXD
DTR
GND
Vp
Output
––
––
––
Input
Output
––
––
Function
Serial Interface TXD
Power supply for circuit (5V)
GND
Power supply for operation
Serial Interface RXD
Serial Interface DTR
GND
Power supply for circuit (5V)
1 - Txd A - Rxd
2 - Vcc B - DTR
3 - Gnd C - Gnd
4 - Vp D - Vp
A
B
C
D
4
3
2
1
4
Page 9

CAUTION:
1. Control circuit requires power supply only for one pin of each VP and GND.
However, Operation voltage is to be supplied to all of pin for safety use.
2. Serial interface equips a driver and receiver of RS-232C, make sure to use it at RS-232C
level.
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
5
Page 10
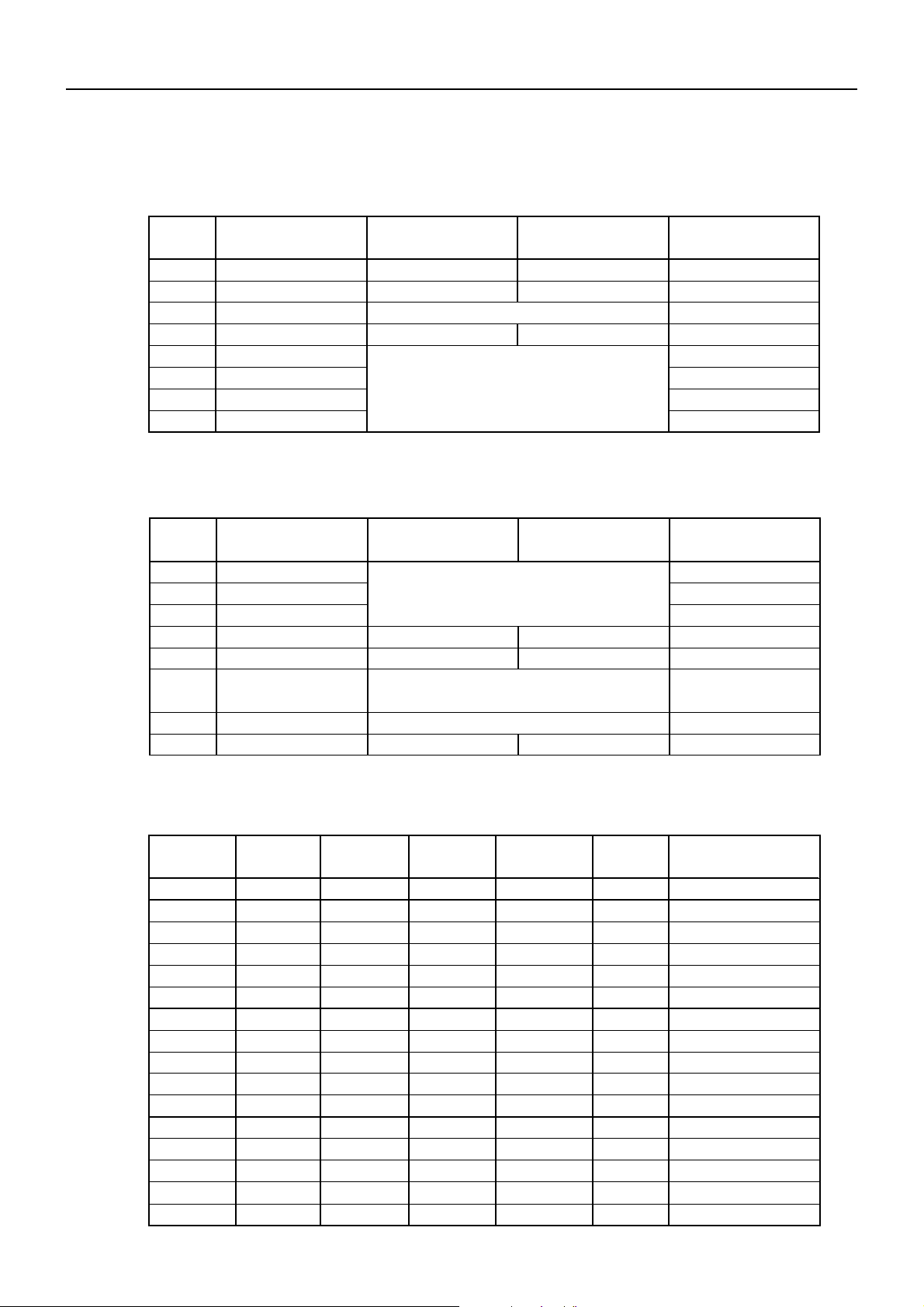
4. JUMPER SETTING
(1) JUMPER 1
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Pin No. Function Short
J1-1
J1-2
J1-3
J1-4
J1-5
J1-6
J1-7
J1-8
(2) JUMPER 2
Pin No. Function
J2-1
J2-2
J2-3
J2-4
J2-5
J2-6
J2-7
J2-8
Not used
CR Selection
Print Density
DTR/XON-XOFF
Baud Rate
"
"
"
International Character set
"
"
Not Used
Print Drive System
Print Density
(Supplementary)
Not Used
Mechanism
Open
–
LF Enable
Combination with J2-6 (See next page (5))
XON-XOFF
See below (3)
Short
See next page (4)
–
Variable division
Combination with J1-3
See next page (5)
–
MLT-288
–
LF Disable
DTR/DSR
Open
–
Fixed division
MLT-289
Factory Setting
Open
Open
Open
Short
Open
Open
Short
Open
Factory Setting
Short
Short
Short
Open
Short
Short
Short
Open
(3) INTERFACE & BAUD RATE
J1-8 J1-7
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Short
Short
Short
Short
Short
Short
Short
Short
Open
Open
Open
Open
Short
Short
Short
Short
Open
Open
Open
Open
Short
Short
Short
Short
Open
Open
Short
Short
Open
Open
Short
Short
Open
Open
Short
Short
Open
Open
Short
Short
J1-6
J1-5
Open
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
6
Input Method
–
Serial Input
"
"
"
"
"
"
"
"
"
"
"
"
"
"
Parity Baud Rate
–
None
"
"
"
"
Odd
"
"
"
"
Even
"
"
"
"
–
1200 bps
2400 bps
4800 bps
9600 bps
19200 bps
1200 bps
2400 bps
4800 bps
9600 bps
19200 bps
1200 bps
2400 bps
4800 bps
9600 bps
19200 bps
Page 11

(4) INTERNATIONAL CHARACTER SET
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
J2-3 J2-2
Open
Open
Open
Open
Short
Short
Short
Short
(5) PRINT DENSITY
J1-3 J2-6
Open
Open
Short
Short
Open
Open
Short
Short
Open
Open
Short
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
J2-1
Open
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
Open
Short
Print Density
Light
Standard
Slightly Dark
Dark
InternationalCharacter
Japan (JIS)
Japan (Shift-JIS)
Sweden
Denmark 1
Germany
Level
0
1
2
3
Print Density Rate
U.K.
France
U.S.A
80%
100%
120%
150%
Note:
1. Input Buffer is 2k byte. (Fixed)
2. Serial data length is 8 bits. (Fixed)
If print tone is set at 2 or above, printing rate tends to be lowered.
7
Page 12

5. POWER SUPPLY
5.1 Specifications
VCC : 5V ±5% Approx. 130 mA
VP : 4.2V ~ 8.5V Approx. 1.5A (Peak : Approx. 4A) when 7.2V
Ordinal Voltage is to be 7.2V (Max). 8.5V is a voltage that is right after charging.
8.5V cannot be used for ordinal voltage.
5.2 Precautions
(1) Design the product to supply power to Vcc before VP when power is supplied to this control
board.
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Design the product to turn off the power for Vcc after VP when power is turned off.
(3) Make sure to turn off the power in case of connecting/disconnecting connectors.
(4) Make sure to use Vcc and VP following their specifications.
(5) Make sure to use this control board connecting all of terminals between VP and GND.
8
Page 13

6. SERIAL INTERFACE
6.1 Specifications
(1) Data transfer system: Asynchronous
(2) Baud rates
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 bps (Selectable by user)
(3) Configuration of one word
Start bit : 1 bit
Data bit : 8 bits Fixed
Parity bit : Odd/Even or No parity (Selectable by user)
Stop bit : 1 bit or more
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
(4) Signal polarity
RS-232C
• Mark = logic “ 1” (–3V ~ –12V)
• Space = logic “ 0” (+3V ~ +12V)
(5) Receiving data (RD signal)
RS-232C
• Mark = 1
• Space = 0
(6) Receiving control (DTR signal)
RS-232C
• Mark : Data transfer is not available
• Space : Data transfer is available
(7) Transmission control (TD signal)
DC1 code (11H) X-ON : Data reception is available
DC3 code (13H) X-OFF : Data reception is not available
9
Page 14

6.2 Explanation of Input/Output Signals
(1) RXD
Serial receiving data signal. On occurrence of framing error, overrun error, or parity error, the
data is printed as “?”.
(2) DTR
When this signal is READY, write data or a command. When they are written in BUSY, overrun
error is occurred and data is ignored. Data can be written into the input buffer even when the
printer is busy printing. A BUSY also occurs when the printer is powered on, in test print, in
Online mode, or being reset.
(3) TXD
If data remaining in the printer's input buffer is 256 bytes or less, the printer transfers a DC3
(13H: Data Receive Not Ready) signal to the host. If data in the input buffer exceeds 256 bytes,
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
the printer transfers a DC1 (11H: Data Receive Ready) signal to the host.
(4) GND
Common GND on the circuit.
6.3 Error Detection
Parity, framing, and overrun are detected. On detection of any error, the data are stored in the
buffer as “?”.
(1) Framing Error
With “space” state having been detected on detection of a stop bit, error takes place.
The data are stored in the buffer as “?”.
(2) Parity Error
With an error having been detected under specifying parity check, the data is stored in the buffer
as “?”.
(3) Overrun Error
On detection of an overrun error, the data are stored in the buffer as “?”.
6.4 Data Receiving Control
When DTR/DSR control having been selected, with BUSY signal at “LOW”, data from the host
side are received. With the signal at “HIGH”, they can not be received.
When DTR/DSR control not having been selected, after X-ON transmission, data is received
from the host side. No transmission of data can take place after X-OFF is transmitted.
10
Page 15
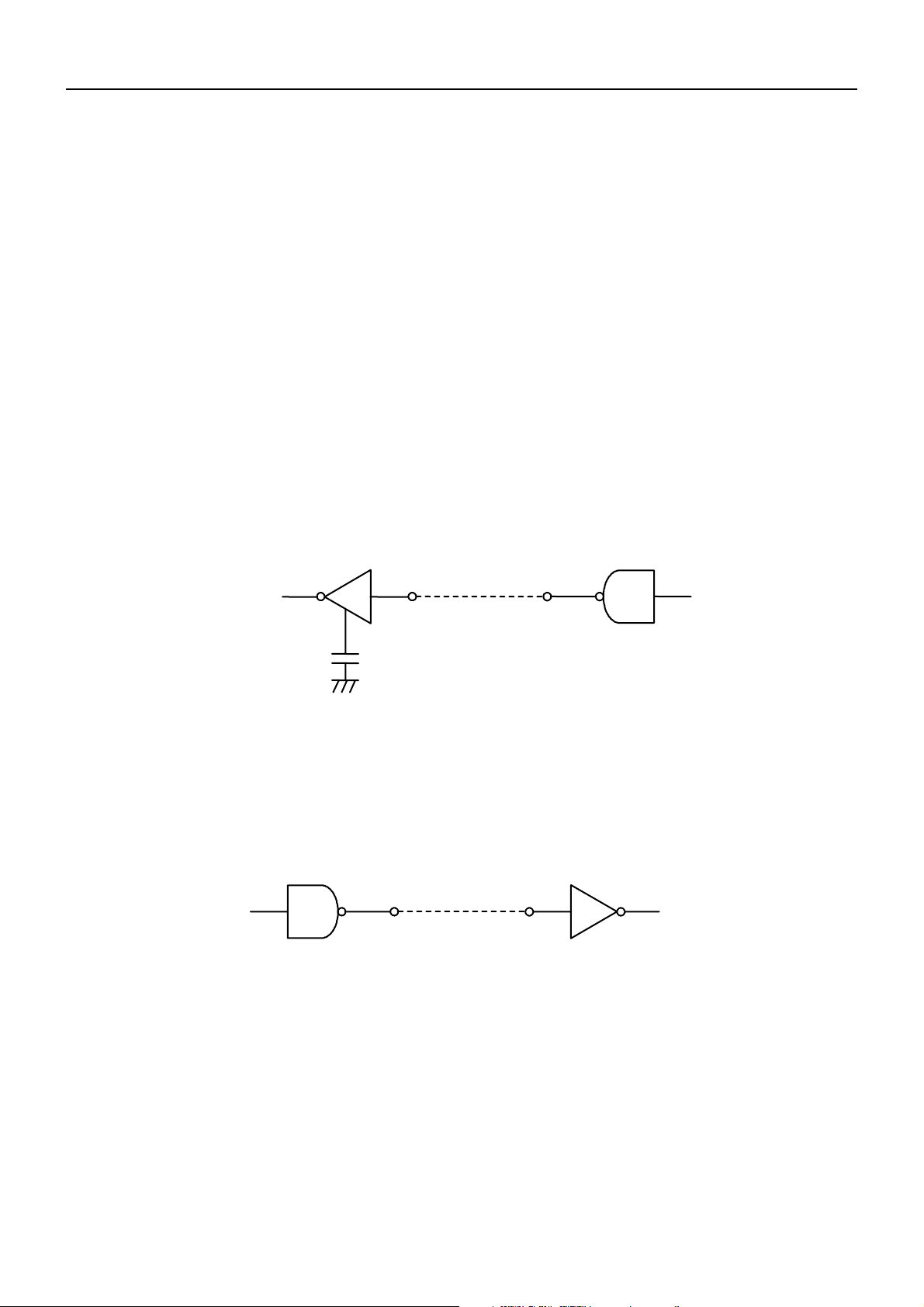
6.5 Buffering
Data transfer to the input buffer include DTR signals and TD signals as the control signals
concerned.
(1) DTR signals (See the page 7.2 (2))
(2) TXD signals (See the page 7.2 (3))
6.6 Electrical Characteristics
(1) RS-232C Circuit
Input (RXD, DSR)
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
<Printer side> <Host side>
Equivalent MAX232
Output (DTR, TXD)
<Printer side> <Host side>
Equivalent MAX232
11
Page 16
7. ERROR HANDLING
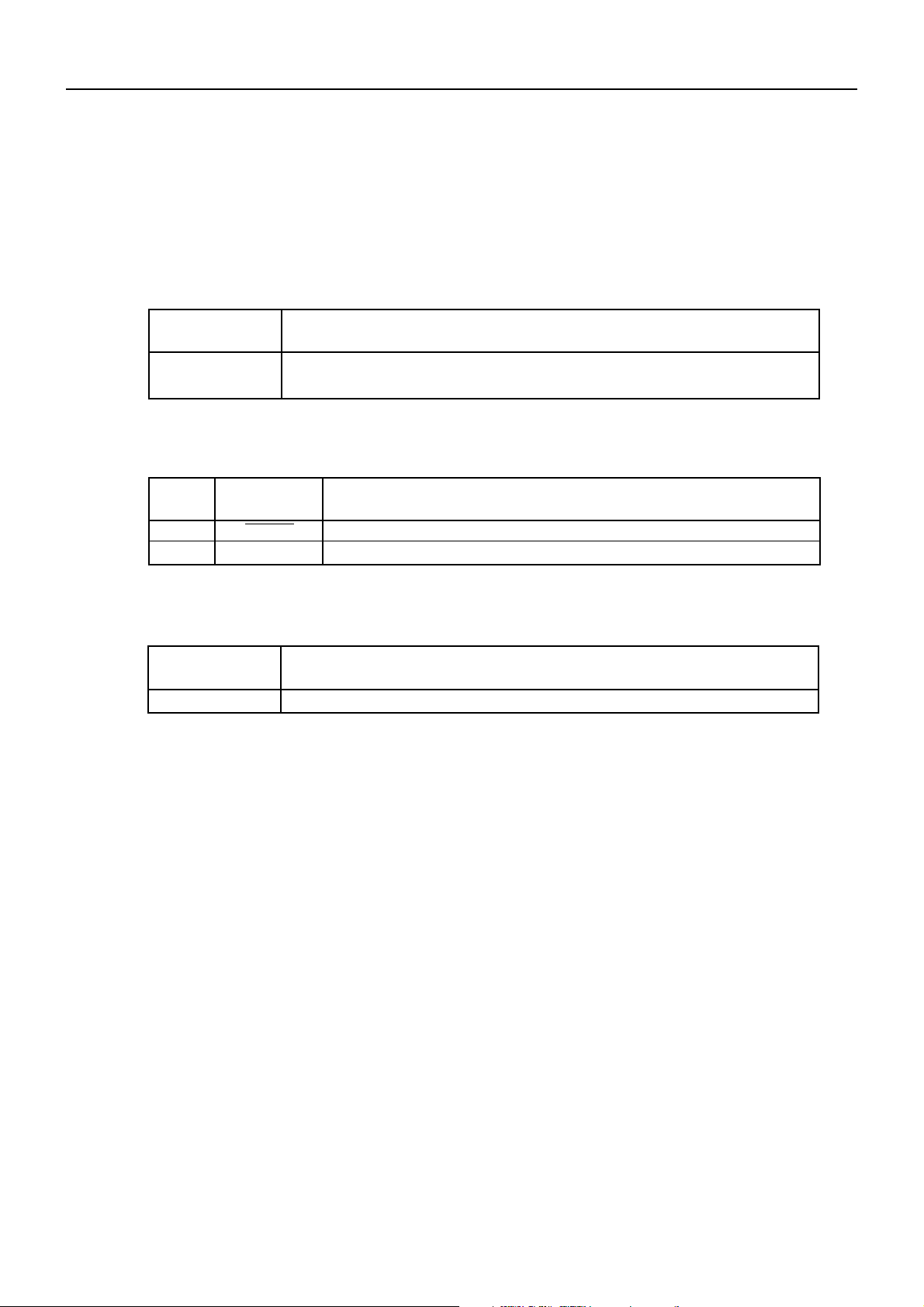
7.1 Peripheral Circuit Errors
These errors are detected at power-on or initialization just after a reset.
(1) Error types
Error Description
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Memory error
The CPU made a self-diagnosis of the circuit and detected an error with the external
RAM.
(2) External signal outputs
Pin No
20
22
Signal Name
ERROR
DTR
(3) Resetting methods
Error
Memory error
Unrecoverable
Remarks
LED output. For a blinking pattern, see 8.3 Error Indication.
Serial interface
Resetting Method
12
Page 17
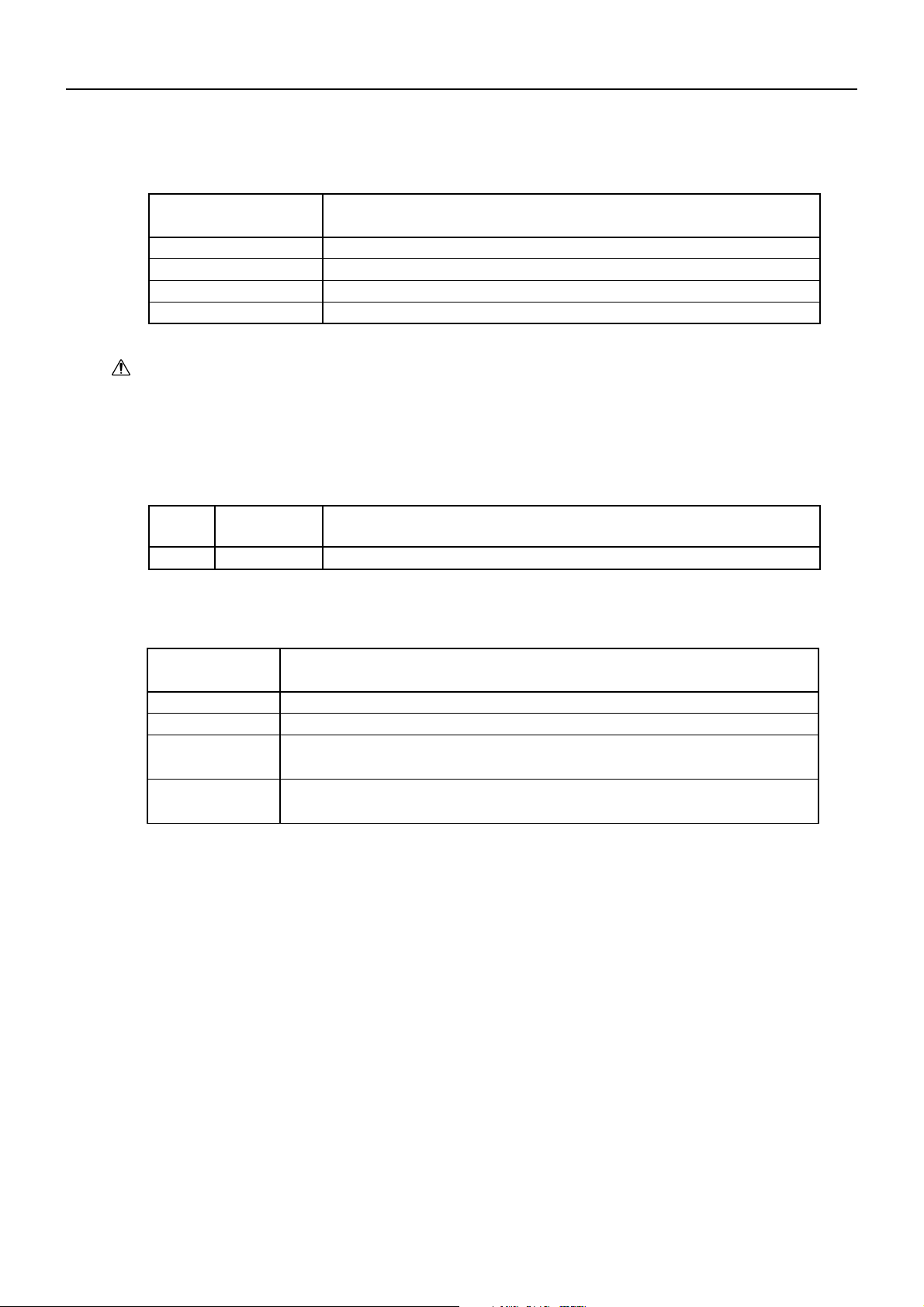
7.2 Operation Errors
(1) Error types
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Error
No paper
Head –up
VH voltage error
Head temperature error
The printing paper set is not set
The head-up lever is at its up position
A VH voltage is beyond its allowable range (4.2 to 8.5V)
A head temperature is less than 0˚C or 65 ˚C or higher.
Description
Caution: The 8.5V upper-limit voltage for VP voltage error is only an assumptive voltage just
after charging the battery when using the battery power. It cannot be normally used. A
normal maximum voltage is 7.2V.
(2) External signal outputs
Pin No
B
Signal Name
DTR
Remarks
Serial interface
(3) Resetting methods
Error
No paper
Head –up
VP voltage error
Head temperature
error
Caution:
The 8.5V upper-limit voltage for VP voltage error is only an assumptive voltage just
after charging the battery when using the battery power. It cannot be normally used. A
normal maximum voltage is 7.2V.
Resetting Method
Set the paper. See Note 1.
Bring down the head-up lever.
Set to a voltage within the allowable range (4.2 to 8.5V) and turn on the power
again.
At the lower limit (less than 0 ˚C), printing becomes operational at 0 ˚C higher.
At the upper limit (65 ˚C or higher), it become operational at 60 ˚C or lower.
13
Page 18
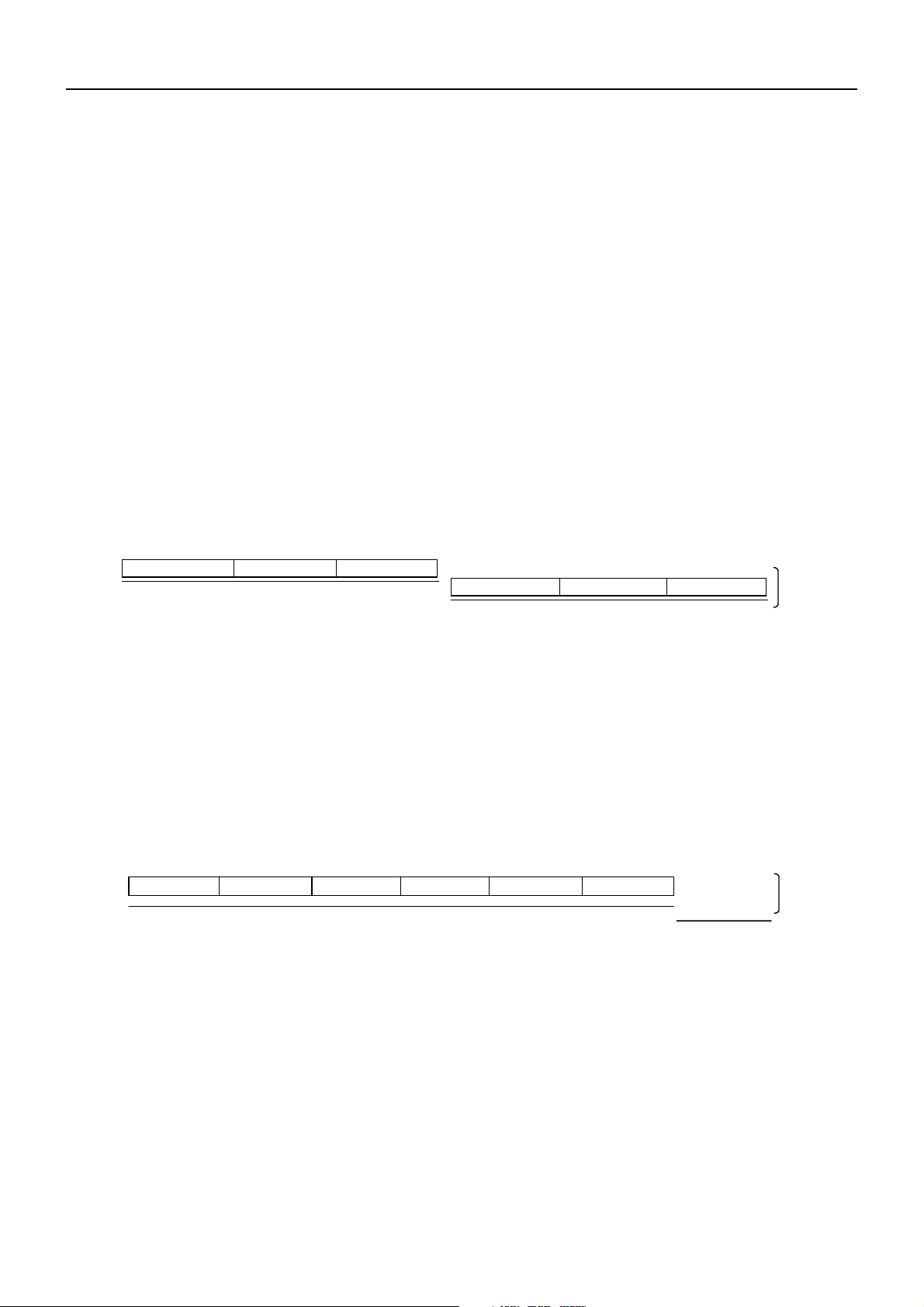
8. PRINTER MECHANISM CONTROL SYSTEM
1st Block
64 Dots
2nd Block
64 Dots
3rd Block
64 Dots
4th Block
64 Dots
5th Block
64 Dots
6th Block
64 Dots
1 Dot Line
1st Step of Motor
of Motor
2nd Step
8.1 Thermal Head Control System (Division Driving System)
The MLT-289 (Line thermal printer) is driven by this control board has a384 dots/line head
divided into 6 blocks of 64 dots each. When actually driving the head, you can select either
Fixed Division Number system, which drives the head, always dividing it into 6 blocks or
Variable Division Number system which collectively drives several blocks at the time according
to the number of activated head dots.
For selection by function selection, see 4. DIP SWITCH SETTING.
For selection by a command, see 11. PRINT CONTROL FUNCTIONS.
8.1.1 Fixed Division Number System
This system always drives each block in the same sequence.
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
1st Block
64 Dots
2nd Block
64 Dots
1st Step of Motor
3rd Block
64 Dots
4th Block
64 Dots
5th Block
64 Dots
2nd Step of Motor
6th Block
64 Dots
Note: for a stepping motor driving method, see 9.2 Motor Drive.
8.1.2 Variable Division Number System
This system counts the number of printing dots for each block of the printing dot line and drives
the blocks collective in such a manner not to exceed the maximum number of driving dots (64
dots).
1 Dot Line
14
Page 19

8.2 Motor Drive
The MLT-289 uses a 4-phase bipolar stepping motor. It feeds the 1 dot line worth of paper in
two steps by 2-to-2 phase excitation.
8.2.1 Motor Drive Features
1) Drive at an optimum drive speed by the VP voltage.
2) Prevents heat generation of the motor by PWM control to restrain current consumption.
3) Provides acceleration control at the time of start.
8.2.2 Maximum Motor Drive Speeds at Major Voltage
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
VH Voltage
5V
6V
7.2V
Motor Drive Speed
400pps
600pps
840pps
Caution: The maximum drive speed depends on the VH voltage.
A printing speed may slightly differ depending on a processing time or voltage
detection accuracy. During the course of printing, a motor drive speed may be slower
than the maximum drive speed, depending on what is printed or the head divided drive
system.
15
Page 20
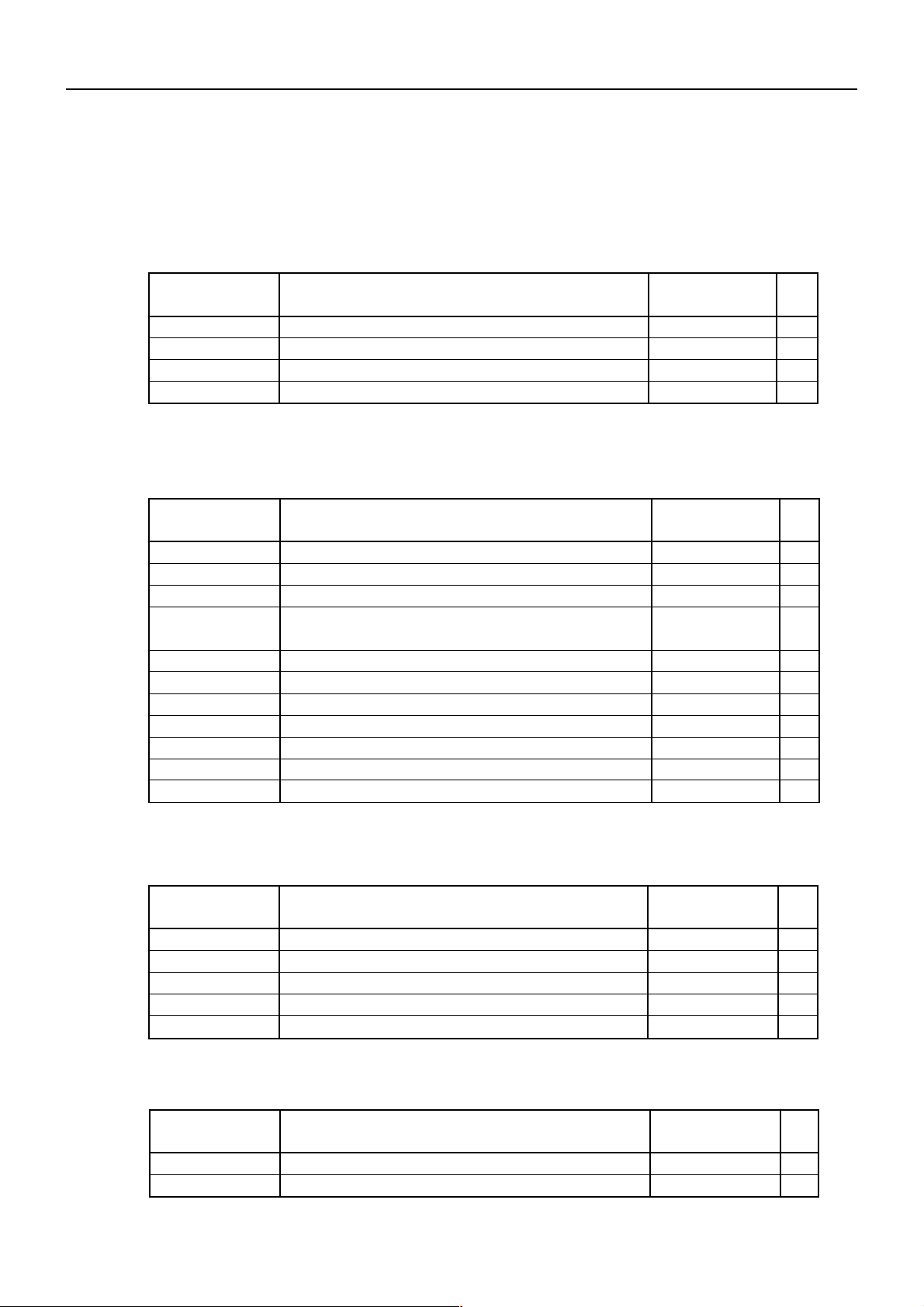
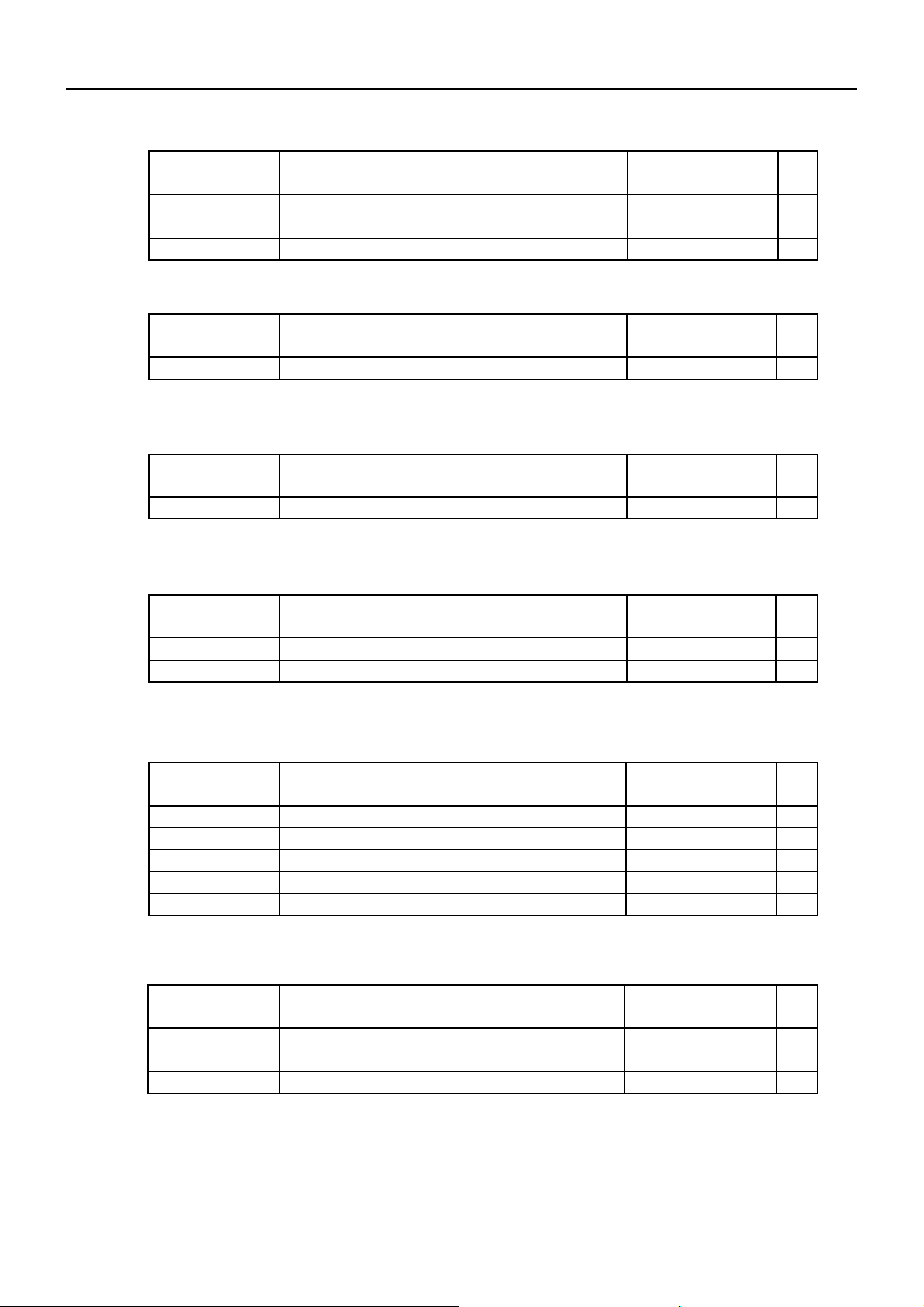
9. PRINT CONTROL FUNCTIONS
9.1 Command List
Print Control Commands
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Control Code
LF
CR
ESC J
ESC d
Printing and paper feed
Print command
Printing and feeding paper n/203 inch
Printing and feeding the paper by n lines
Print Character Commands
Control Code
ESC SP
ESC !
ESC %
ESC &
ESC –
ESC E
ESC G
ESC R
ESC V
ESC t
ESC {
Setting the right space amount of the character
Collective specifying printing mode
Specifying/canceling douwnload character set
Defining download characters
Specifying/canceling underline
Specifying/canceling highlighting
Specifying/canceling double printing
Selecting the international character set
Specifying/Canceling 90°-right- turned Characters
Selecting the character code table
Specifying/canceling the inverted characters
Function Code Page
0Ah
0Dh
1Bh4Ah n
1Bh64h n
Function Code
1Bh20h n
1Bh21h n
1Bh25h n
1Bh26h s n m
[ap1...ps×a]m–n+1
1Bh2Dh n
1Bh45h n
1Bh47h n
1Bh52h n
1Bh56h n
1Bh74h n
1Bh7Bh n
19
20
21
22
Page
23
24
26
27
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
Print Position Commands
Control Code
HT
ESC $
ESC D
ESC
ESC a
/
Horizontal tab command
Specifying the absolute positions
Setting horizontal tab position
Specifying the relative positions
Aligning the characters
Line Feed Span Commands
Control Code
ESC 2
ESC 3
Specifying 1/6-inch line feed rate
Setting line feed rate of minimum pitch
Function Code
09h
1Bh24Ah n1 n2
1Bh44[n]k 00h
1Bh 5C n1 n2
1Bh 61h n
Function Code
1Bh 32h
1Bh 33h n
16
Page
36
37
38
39
40
Page
41
42
Page 21
Bit Image Commands
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Control Code
ESC *
GS *
GS /
Specifying the bit image mode
Defining the download, bit image
Printing the download, bit image
Status Command
Control Code
ESC v 1Bh 76h
Transmitting the printer status (Serial type)
Panel Switch Command
Control Code
ESC c5 1Bh 63h 35h n
Enabling/disabling the panel switches
Macro Commands
Control Code
Function Code
1Bh 2Ah m n1 n2[d]k
1Dh 2Ah n1 n2
1Dh 2F
Function Code
Function Code
Function Code
Page
43
45
47
Page
48
Page
49
Page
GS :
GS ^
Starting/ending macro definition
Executing the macro
Bar Code Commands
Control Code
GS H
GS f
GS h
GS k
GS w
Selecting of print position of HRI code
Selecting the font of HRI code
Selecting the height of the bar code
Printing the bar code
Selecting the horizontal size (scale factor) of bar code
Other Commands
Control Code
ESC =
ESC @
DC2 A
Data input control
Initializing the Printer
Selecting the Print drive system
1Bh 63h 35h n
1Dh 5Eh n1 n2 n3
Function Code
1Dh 48H n
1Dh 66H n
1Dh 68H n
1Dh 6Bh n[‘d’]k 00h
1Dh 77H n
Function Code
1Bh 3Dh n
1Bh 40h
12h 41h n
50
51
Page
52
53
54
55
59
Page
60
61
62
17
Page 22

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
9.2 Command Details
9.2.1 Description of Items
XXXX ALL
[Function]
Command Function
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
[Default]
[See Also]
[Sample Program]
used, version, and so on. For details, see the ma
Describes an argument value(setting range) for the command.
Describes a command outline.
Describes a caution as required.
Describes an initial value for the command when accompanied by an argument.
Describes the associated commands for use.
A sequence of code constituting a command is represented in hexadecimal number for <
>H, binary number for < >B, and decimal number for < >, respectively; [ ]k represents a
repeat count of k-times.
Describes a coding example in the Q-BASIC sample program.
* This example is only for your reference and differs depending on the language
nual for the language used.
18
Page 23

LF
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Outline]
[See Also]
[Sample Program]
[Print Results]
Printing and Paper Feed Command
<0A>H
Prints data inside the input buffer and feeds lines based on the line feed amount having been set.
• The head of the line becomes the next print starting position.
ESC 2, ESC 3
LPRINT "AAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT "BBB" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
);
LPRINT "CCC" + CHR$ (&HA
Print and line feed
Print and line feed
Line feed only
Print and line feed
19
Page 24

CR
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Outline]
Print Command
<0D>H
1) When DS 1-2 is OFF:
This command is ignored.
2) When DS 1- 2 is ON:
With data held inside the internal print buffer, printing and line feed are performed.
Without data inside the internal print buffer, however, no printing is performed.
[See Also]
LF
[Sample Program]
LPRINT "AAA" + CHR$ (&HD);
LPRINT "BBB" + CHR$ (&HD);
LPRINT CHR$ (&HD);
LPRINT "CCC" + CHR$
[Print Results]
(&HD);
Print and line feed
Print and line feed
Line feed only
Print and line feed
20
Page 25

ESC J n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Printing and feeding paper n/203 inch
<1B>H<4A>H<n>
{0 =< n =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Prints data inside the print buffer and feeds paper by n/360 inch. Since an actual mechanical
pitch is 1/203 inch, it is internally converted approximate to the value specified with this
command.
•
•
•
[Sample Program]
See Sample Program and Print Results for ESC 2 on Page
Specified volume does not remain.
The beginning of the line is to be considered as the next printing start position.
Initial value is not defined.
[Print Results]
48.
21
Page 26

ESC d n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Printing and Feeding the paper by n lines
<1B>H<64>H<n>
* {0 =< n =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Prints data inside the buffer and feeds paper by n lines.
•
•
[Default]
[Sample Program]
•
LPRINT "AAAAA"
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "d" + CHR$ (2);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
Specified line does not remain.
The beginning of the line is to be considered as the next printing start position.
The initial value is not defined.
2/6-inch line feed
22
Page 27

ESC SP n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
[Default]
Setting the right space amount of the character
<1B>H<20>H<n>
{0 =< n=< 20} Data is described in Hex code.
The rightward space amount is set in dot unit (1/203 inch unit). In the initial value, it is n=0.
The rightward space amount in doublewide mode is made double of the set volume.
n = 0
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " " + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " " + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " " + CHR$ (12);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
0-dot space
1-dot space
12-dot space
23
Page 28

ESC ! n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
Collective Specifying Printing Mode
<1B>H<21>H<n>
{0 =< n=< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Printing mode is assigned. Each n bit indicates the following:
Va l ue
Bit Function 0 1
0 Character Font Font A Font B
1 Undefined
2 Undefined
3 High-lighting Canceled Specified
4 Double height Canceled Specified
5 Double width Canceled Specified
6 Undefined
7 Underline Canceled Specified
• With double height and double width being specified simultaneously, double wide and
[Default]
[See Also]
double high characters are consisted.
• An underline is attached to the full character width, which, however, is not attached to
the part having been skipped by the horizontal tab.
Neither is it attached to 90°-right-turned characters.
• The underline width is as having been specified by <ESC ->.
(The default setting is 1 dot width. )
• Specification with this command is invalid to Kanji, except specification and cancellation
of highlighting
• In case that double wide character and normal character exist in same one line, the layout
of underline is consistent one.
n = 0
ESC E,ESC
–
24
Page 29

[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " ! " + CHR$ (&H00) + "H" ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " ! " + CHR$ (&H01) + "H";
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " ! " + CHR$ (&H08) + "H";
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " ! " + CHR$ (&H10) + "H";
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " ! " + CHR$ (&H20) + "H";
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " ! " + CHR$ (&H80) + "H";
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " ! " + CHR$ (&HB9) + "H";
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Font A
Font B
Font A + Highlighting
Font B + Highlighting + Quadruple + Underline
Font A + Underline
Font A + Double Width
Font A + Double Height
25
Page 30

ESC % n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Specifying/Canceling Download Character Set
<1B>H<25>H<n>
{0 =< n =< FF} data is described in Hex code.
Specifying/canceling download characters.
Further, only the lowest bit (n0) is valid for n.
The lowest bit (n0) indicates the following.
[Caution]
[Default]
[See Also]
Download characters and download bit images cannot be defined simultaneously.
n = 0
ESC &
[Sample Program]
GOSUB SETCHR DATA 6
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "%" + CHR$ (0); DATA &HFF, &H80, &H00
LPRINT "@A" + CHR$ (&HA); DATA &H80, &H80, &H00
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "%" + CHR$ (1); DATA &H80, &H80, &H00
LPRINT "@A" + CHR$ (&HA); DATA &H80, &H80, &H00
END DATA &HFF, &HFF, &HFF
SETCHR: DATA &HFF, &HFF, &HFF
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "&”; DATA 12
LPRINT CHR$ (3) + "@" + "A”; DATA &HFF, &HFF, &HFF
FOR J=1 TO 2 DATA &H80, &H07, &HF9
READ REP DATA &H80, &HFF, &HF9
LPRINT CHR$ (REP); DATA &H87, &HFE, &H01
FOR I=1 TO REP*3 DATA &H9F, &H06, &H01
READ D DATA &HF8, &H06, &H01
LPRINTCHR$ (D); DATA &HF8, &H06, &H01
NEXT I DATA &H9F, &H06, &H01
NEXT J DATA &H87, &HFE, &H01
RETURN DATA &H80, &HFF, &HF9
[Print Results]
n0 Function
0 Canceling download character set
1 Specifying download character set
DATA &H80, &H07, &HF9
DATA &HFF, &HFF, &HFF
Internal Character Set
Download Character
26
Page 31

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
ESC & s n m [a [p] s a] m – n +1
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Defining Download Character
<1B>H<26>H<s><n><m> [<a><p1><p2><ps a>]m-n+1
{s = 03}
{20 (Hex) =< n =< m =< 7E (Hex)}
{0 =< a =< 0C(Hex)} (Font A)
{0 =< a =< 0A(Hex)} (Font B)
Defines the font of download characters of alphanumeric characters.
• "s" indicates the number of bytes in vertical direction.
• "n" indicates the start character code and m the end character code. To define only one character,
set n=m.
• Character codes definable includes 95 ASCII codes in total between <20>H~<7E>H.
• "a" indicates the number of dots in horizontal direction for definition.
• "p" is the data to be defined, which indicate a pattern equal to "a" dot in horizontal direction from
×
×
[Caution]
[Default]
the left end. The rest of the pattern on the right side is filled with space.
The rest of data to be defined is s x a.
• Download characters thus defined remain valid until redefinition, ESC @ execution,
GS * execution, or power OFF is practiced.
Download characters and download bit images can not be defined simultaneously.
Running this command clears the definition of the download bit image.
Same
as the internal character set
27
Page 32

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Example]
Create each data bit by setting "1" for a printed dot and "0" for an unprinted dot.
[Sample Program]
See Sample Program and Print Results for ESC % on Pa
[Print Results]
ge 33.
28
Page 33

ESC – n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
[See Also]
Specifying/ Canceling Underline
<1B>H<2D>H<n>
{0 =< n =< 02} data is described in Hex code.
Specifying/canceling an underline.
• Types of underlines by n value are shown below:
n (Hex) Type
0 Canceling an underline.
1 Specifying an underline for 1-dot width.
2 Specifying an underline for 2-dots width.
• An underline is attached to the full character width. It is, however, not attached to
the part having been skipped by horizontal tab command.
• An underline is not attached to a 90 °- right-turned characters.
• Specification/cancellation with this command is invalid to Kanji.
ESC !, FS
–
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "–" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "AAAAA" ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Re
sults]
Underline Canceled
Underline Specified
–
" + CHR$ (1);
29
Page 34

ESC E n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
[See Also]
Specifying/canceling highlighting
<1B>H<45>H<n>
{0 =< n =<FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Specifying/canceling the highlighting characters.
"n" is valid only for the lowest bit (n0).
•
Control by the lowest bit (n0) is shown as follows:
•
n0 Type
0 Canceling highlighting.
1 Specifying highlighting.
This is effective to all characters.
•
Dot configuration of a highlighted character includes one extra dot added at its side.
•
The print result of Double printing and highlight character printing is completely same.
•
ESC !
[Example]
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "E" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "AAABBB" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "E" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT "AAABBB" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
Highlighting canceled
Highlighting canceled
30
Page 35

ESC G n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
[See Also]
Specifying/canceling Double Printing
<1B>H<47>H<n>
{0 =< n =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Specifying/canceling the double printing.
"n" is valid only for the lowest bit (n0).
•
Control by n is shown as follows.
•
n0 Type
0 Canceling double printing.
1 Specifying double printing.
This is effective to all characters.
•
The print result of Double printing and highlight character printing is completely same.
•
ESC E
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "G" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "AAABBB" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "G" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT "AAABBB" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
Highlighting canceled
Highlighting canceled
31
Page 36

ESC R n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Selecting the International Character set
<1B>H<52>H<n>
{0 =< n =< 0A) Data is described in Hex code.
Depending on the value of n, following character sets are specified.
n(Hex) Character Set
0 U.S.A.
1 France
2 Germany
3 U.K.
4 DenmarkI
5 Sweden
6 Italy
7 Spain
8 Japan
9 Norway
A DenmarkII
[Default]
[See Also]
•
Character Code Table (International Character Set)
[Sample Program]
FOR I=0 TO 10
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "R" + CHR$ (I);
LPRINT " #$@[¥]^”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H60) + "{¥} ˜";
LPRINT "n=" + STR$ (I);
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
NEXT
The initial value of n indicates the character set specified by Jumper (J1~J3).
[Print Results]
I
32
Page 37

ESC V n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Specifying/Canceling 90°-right- turned Characters
<1B>H<56>H<n>
{0 =< n =< 1} Data is described in Hex code.
Specifying/canceling characters 90°-right- turned character.
•
[Caution]
[Default]
•
•
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "V" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "AAAAA”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "V" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
90° Rotation Canceled
"n" means the followings.
n (Hex) Condition
0
1
Canceling
Specifying
90°-right- turned Characters
90°-right- turned Characters
No underlines are attached to 90°-right- turned characters.
The initial value of n is "0".
90° Rotation Specified
33
Page 38

ESC t n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Default]
[See Also]
Selecting Character Code Table
<1B>H<74>H<n>
{0 =< n =< 1} Data is described in Hex code.
Selecting Page n on the character code table:
The character code table is selected depending on the value of n.
"n" means the followings.
n (Hex) Condition
0 Page0(IBM Character #2)
1 Page1(Domestic Character)
The initial value of n is subject to the character set for the country specified
by the Jumper(J1~J3).
When Japan is selected: Domestic characters
•
When non-Japan is selected: IBM characters #2
•
Character Code Table
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "t" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT " n=0 “;
FOR C=&HB1 TO &HB5
LPRINT CHR$ (C);
NEXT C
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "t" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT " n=1 “;
FOR C=&HB1 TO &HB5
LPRINT CHR$ (C);
NEXT C
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
Page 0
Page 1
34
Page 39

ESC { n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Specifying/Canceling the Inverted Characters
<1B>H<7B>H<n>
{0 =< n =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Specifying/canceling inverted characters.
•
•
[Caution]
•
•
[Default]
•
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "{" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT "BBBBB" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "{" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT "BBBBB" + CHR$ (&HA);
"n" is valid only for the lowest bit (n0).
Bit n (n0) means the followings.
n0 Condition
0 Canceling inv rted characters.
1 Specifying inverted characters.
Inverted-printing means printing the line at 180°turned.
This is valid only when this is specified at the beginning of a line.
The initial value of n is "0".
[Print Results]
Inversion Canceled
Paper Feed Direction
Inversion Specified
35
Page 40

HT
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Outline]
Horizontal Tab Command
<09>H
Shifts the printing position to the next horizontal tab position.
• Ignored when the next horizontal tab position has not been set.
[Caution]
• The horizontal tab position is set by ESC D.
• Initial setting of the horizontal tab position is each 8 characters in 9th, 17th,
25th,columns.
[See Also]
ESC D
[Sample Program]
LPRINT "0123456789012345678901”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H9) + "AAA”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H9) + "BBB”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "D”;
LPRINT CHR$ (3) + CHR$ (7) + CHR$ (14) + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H9) + "AAA”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H9) + "BBB”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H9) + "CCC" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
Initially set horizontal tab
When set to the 4th, 8th, and 15th digits
36
Page 41

ESC $ n1 n2
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
Specifying the Absolute Positions
<1B>H<24>H<n1><n2>
{0 =< n1 =< FF}
{0 =< n2 =< 1} Data is described in Hex code.
[Outline]
The printing start position is specified in the number of dots (1/203 inch unit) from
the beginning of line.
•
•
[Caution]
[Default]
[See Also]
•
•
ESC \
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "$”;
LPRINT CHR$ (0) + CHR$ (0) + "A”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "$”;
LPRINT CHR$ (50) + CHR$ (0) + "B”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "$”;
LPRINT CHR$ (0) + CHR$ (1) + "C”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "$”;
LPRINT CHR$ (100) + CHR$ (0) + "A”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "¥”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HC2) + CHR$ (&HFF) + "B”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
The number of dots is divided by 256, whose quotient is taken as n2 and the residual as n1.
Therefore, the printing start position is equal to n1+n2 x 256 from the beginning of line.
Specifying beyond the line end is ignored.
The initial value is not specified.
[Print Results]
Absolute Position Specified
Relative Position Specified – 62
37
Page 42

ESC D [ n ] k NUL
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Setting Horizontal Tab Position
<1B>H<44>H [ <n> ] k<00>H
{0 =< n =< FFH} Data is described in Hex code.
{0 =< k =< 20H} Data is described in Hex code.
Specifying a horizontal tab position.
"n" indicates the no. of columns from the beginning to the horizontal tab position.
•
At this time, n= set position
–
1 is to be specified. For example, to set the position at 9th
column, n=8 is to be specified.
k denotes the number of horizontal tab positions you want to set.
•
The tab position is set at position where it is "character width x n" from the line beginning.
•
The character width, at this time, includes the rightward space amount.
In double wide characters, it is made double of the ordinary case.
Tab positions can be specified are maximum 32. Specifying exceeding this is ignored.
•
<n> k, which denotes a setting position, is input in the increasing order and ends at <00> H.
•
ESC D NUL clears all the set tab positions. Following clearing, horizontal tab command is
•
ignored.
[Caution]
When the data, <n> k, is equal to or smaller than its preceding data, <n> k-1, it is assumed
that tab setting is finished. If this is the case, the next data onward will be processed as normal
data.
When the data, <n> k, exceeds a 1-line print area, set the horizontal tab position, assuming
"Set digit position = Maximum print digits + 1." The horizontal tab position does not
change even if the character width is altered after setting the horizontal tab position.
[Default]
[See Also]
[Sample Program]
•
HT
See Sample Program and Print Results for HT on Page
Initial value is specified for each eight characters(9th.17th.25th column) of ANK characters.
[Print Results]
43.
38
Page 43

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
ESC n1 n2
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
[Default]
\
Specifying the Relative Positions
<1B>H<5C>H<n1>< n2>
{0 =< n1 =< FF}
{0 =< n2 =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
The printing start position is specified in the number of dots(1/203 inch unit) from
the current position.
Rightward direction is taken as plus and leftward direction as minus.
•
To specify N dot in minus (left) direction, use a complement of N for assignment.
•
–
N dots = 65536 – N
The number of dots is divided by 256, whose quotient is taken as n2 and the residual as n1.
•
Specifying exceeding the top of line or the end of line is ignored.
•
The initial value is not specified.
•
[See Also]
[Sample Program]
ESC $
See Sample Program and Print Results for ESC $ on Page
[Print Results]
44.
39
Page 44

ESC a n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Aligning the characters
<1B>H<61>H<n>
{0 =< n =< 2} Data is described in Hex code.
All the printed data within one line are aligned in the specified position.
•
[Caution]
•
•
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "a" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "a" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "a" + CHR$ (2);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
Depending on n value, positional alignment is carried out as in the table below:
n (Hex) Position
0 Left end alignment
1 Centering
2 Right end alignment
This is valid only when n is inputted at the beginning of line.
The initial value of n is "0".
[Print Results]
Paper Feed Direction
Left-justified Centered Right-justified
40
Page 45

ESC 2
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
Specifying 1/6-inch line feed rate
[Code] <1B>H<32>H
[Code]
[Outline]
[Sample Program]
The line feed rate per line is specified by 1/6 inch.
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "3" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "3" + CHR$ (50);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "2”;
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT "AAAAA”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "J" + CHR$ (100);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
1/6-inch line feed
0/360-inch line feed
50/360-inch line feed
1/6-inch line feed
100/360-inch line feed
1/6-inch line feed
41
Page 46

ESC 3 n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Default]
[Sample Program]
Setting line feed rate of minimum pitch
<1B>H<33>H<n>
{0 =< n =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
The line feed rate per line is specified by n/360 inch.
Since an actual mechanical pitch is 1/203 inch, it is internally converted approximate
to the value specified with this command.
• The initial value is n = 60 (1/6 inch) (18H), being 4.23 mm line feed rate.
See Sample Program and Print Results for ESC 2 on Pa
[Print Results]
ge 48.
42
Page 47

ESC * m n1 n2 [ d ] k
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
m(Hex) Mode
0 8-dot single density 8 67 DPI 101 DPI 192
1 8-dot double density 8 67 DPI 203 DPI 384
32 24-dot single density 24 203 DPI 101 DPI 192
33 24-dot double density 24 203 DPI 203 DPI 384
Specifying the Bit Image Mode
<1B>H<2A>H<m><n1><n2> [ <d> ] k
{m= 0, 1, 32, 33 bit image mode (See the table below.)}
{0 =< n1 =< FF(Hex)}
{0 =< n2 =< 03(Hex)}
{0 =< d =< FF(Hex)}
{k = n1 + FF(Hex) n2 (m = 0, 1)
{k = (n1+ FF(Hex) n2) 3} (m = 32, 33)
According to the number of dots specified in n1, n2, specify the bit image of mode n.
• The No. of dots printed is divided by 256, whose quotient is taken as n2 and residual as n1.
• The total no. of dots printed in the bit image is equal to n1 + (256 x n2).
• When bit image data have been input in excess of dot position of one line (448 dots) ,
the excess data are discarded.
• d is bit image data, the bits subject to printing are taken as "1" and those not as "0".
• The bit image modes specified by m are shown as follows:
×
××
Vertical Direction Horizontal Direction
No. of Dots Dot Density Dot Density Max. No. of Dots
[Caution]
[Examp
le]
• When the values set in m (bit image mode) are out of the above range, the data
following after n1 is processed as normal printing data.
• After completion of bit image printing, printer returns to normal data processing mode.
Single Density Double Density Single Density Double Density
43
Page 48

[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "*”;
LPRINT CHR$ (0) + CHR$ (20) + CHR$ (0); IMG1 :
GOSUB IMG1 LPRINT CHR$ (&HFF) ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA); FOR I=1 TO 18
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "*”; LPRINT CHR$ (&H85) ;
LPRINT CHR$ (1) + CHR$ (20) + CHR$ (0); NEXT I
GOSUB IMG1 LPRINT CHR$ (&HFF) ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA); RETURN
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "*”; IMG2 ;
LPRINT CHR$ (32) + CHR$ (20) + CHR$ (0); LPRINT CHR$ (&HFF) ;
GOSUB IMG2 LPRINT CHR$ (&HFF) ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA); LPRINT CHR$ (&HFF) ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "*”; FOR I=1 TO 18
LPRINT CHR$ (33) + CHR$ (20) + CHR$ (0); LPRINTCHR$ (&H80) ;
GOSUB IMG2 LPRINTCHR$ (&H00) ;
LPRINT CHR& (&HA); LPRINTCHR$ (&H05) ;
END NEXT I
[Print Results]
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
LPRINT CHR$ (&HFF) ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HFF) ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&HFF) ;
RETURN
44
Page 49

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
GS * n1 n2 [ d ] n1 n2 8
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
Defining the Download Bit Image
<1D>H<2A>H<n1><n2> [ < d > ] n1 n2 8
{1 =< n1 =< FF}
{1 =< n2 =< 30}
{n1 n2 =< 51F} Data is described in Hex code.
Defines downloading bit images of the number of dots specified by n1/n2.
The numbers of dots are n1 x 8 in horizontal direction and n2 x 8 in vertical direction.
•
d indicates bit image data.
•
The download bit image thus defined remains effective until redefinition,
•
ESC @ execution, ESC &, or power OFF takes place.
A download character and a download bit image can not be defined simultaneously.
•
With this command executed, defined content of a download character is cleared.
Relations between the bit image data and the dot defined are shown below:
•
•
If a download bit image is defined with this command while it is being printed (GS/) ,
printing operation may become unstable (fluctuating print pitch).
××
××
[See Also]
GS
/
45
Page 50

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Sample Program]
GOSUB IMG
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "/" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "/" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "/" + CHR$ (2);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "/" + CHR$ (3);
END
IMG:
n 1 = 10 : n 2= 5
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "*”;
LPRINT CHR$ (n1) + CHR$ (n2);
FOR J=1 TO n1*8
FOR I=1 TO n2
LPRINT CHR$ (J);
NEXT I
NEXT J
RETURN
[Print Results]
Nomal Mode
Double Width Mode
Double Height Mode
Quadruple Mode
46
Page 51

GS / m
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
Printing the Download, Bit Image
<1D>H<2F>H<m>
{0 =< m =< 03} Data is described in Hex code.
Prints download bit image in a mode specified by m.
Modes can be selected by m are shown below.
•
m Mode Name Dot Density in
Vertical Direction
0 Normal mode 203 DPI 203 DPI
1 Double wide mode 203 DPI 101 DPI
2 Double high mode 101 DPI 203 DPI
3 Double wide/double high mode 101 DPI 101 DPI
When data exist inside the print buffer, this command is ignored.
•
When a download bit image has not been defined, this command is ignored.
•
Dot Density in
Horizontal Direction
•
•
[Default]
[See Also]
•
•
GS *
[Sample Program]
See Sample Program and Print Results for GS * on Page
A portion of a download bit image exceeding one line length is not printed.
A download character and a download bit image cannot be defined simultaneously.
If a download bit image data is defined while it is being printed with this command,
printing operation may become unstable (fluctuating print pitch).
The initial value is not specified.
[Print Results]
52.
47
Page 52

ESC v (Serial Interface Only)
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Outline]
[Caution]
Transmitting the printer status (Serial Type)
<1B>H<76>H
Current printer status is transmitted.
Status sent out consists of 1 byte whose content is as in the table below.
•
In DTR/DSR control, after revertible state of the host (DSR signal being in SPACE
•
state) is confirmed, only 1 byte is transmitted. In XON/XOFF control, DSR signal state
not being confirmed, only 1 byte is transmitted.
In DTR/DSR control, when the host is in unrespectable state (DSR signal being in
•
MARK state), it waits until receptacle state is created.
In paper end (paper near end) status, this command may be unrespectable state due to
•
BUSY state.
Remarks. This command is valid only for serial interface model.
Va l u e Bit Function
0 1
0 Not defined
1 Not defined
2 Paper end With paper Without paper
3 Not defined
4 Not used Fixed to 0
5 Not defined
6 Not defined
7 Not defined
–
[Sample Program]
OPEN "COM1: N81NN" AS #1;
PRINT #1, CHR$ (&H1B) + "v”;
A$ = INPUT$ (1, #1);
CLOS
E #1
48
Page 53

ESC c5 n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
Enabling/Disabling Panel Switches
<1B>H<63>H<35>H<n>
{0 =< n =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Selecting the LF switch valid/invalid.
"n" is valid only in the lowest bit (n0).
•
"n" bit means the followings.
•
n0
Condition
0 LFSW valid.
1 LFSW invalid.
When the panel switch is disabled with this command, the LF switch is disabled. Therefore,
the paper cannot be fed by operating the LF switch.
[Default]
The initial value of n is "0".
•
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "c5" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "c5" + CHR$ (1);
When enabling the LF switch
………
………
When disabling the LF switch
49
Page 54

GS :
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Outline]
Starting / Ending Macro Definition
<1D>H<3A>H
Specifying starting / ending macro definition.
Means termination when received while defining a macro.
[Caution]
Maximum content available for macro definition is 2048 bytes.
A portion exceeding 2048 bytes is not defined.
•
cleared. Therefore, it is possible to include ESC @ into the content of macro definition.
•
[Default]
[See Also]
•
GS ^
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + “: " ;
LPRINT "+
LPRINT " | | " + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT "+
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + “: “;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + " ^ “;
LPRINT CHR$ (2) + CHR$ (10);
LPRINT CHR$ (0);
[Print Results]
Even with ESC @ (initialization of the printer) having been executed, defined content is not
Normal printing operation is carried out even while in macro definition
Initially, Macro is not specified.
–––
+" + CHR$ (&HA);
–––
+" + CHR$ (&HA);
Nomal Printing during
Macro Definition
Printing during Macro Execution
50
Page 55

GS ^ n1 n2 n3
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Executing the Macro
<1D>H<5E>H<n1><n2><n3>
{0 =< n1 =< FF}
{0 =< n2 =< FF}
{0 =< 3 =< 1} Data is described in Hex code.
Executing contents defined in macro.
"n1~ n3" indicate as follows:
•
n1 : The number of times of macro execution
n2 : Waiting time on macro execution
Waiting time of n2 x 100msec is given for every execution.
n3 : Macro execution mode
n3 Mode
0 Continuous execution
1 Execution by LFSW
Continuous execution: The Macro is executed n1 times continuously at the time
Execution by FEED S: After waiting for lapse of time specified by n2, the ALAME
[Caution]
•
indicated. At this time, the defined content is cleared.
•
•
[Default]
[See Also]
[Sample Program]
•
GS :
intervals specified by n2.
LED flickers and the LF switch is waited to be pressed. When
it is pressed, the macro is executed once.
This action is repeated n1 times.
When this command is received while in macro definition, suspension of macro definition is
No execution takes place when macro is held undefined or n1=0.
While in macro execution with n3=1, paper feed with the LF SW is not available.
Initially, this command is not specified.
[Print Results]
See Sample Program and Print Results for GS : on Page
57.
51
Page 56

GS H n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Caution]
[Default]
Selecting of Printing Position of HRI Code
<1D>H<48>H<n>
{0 =< n =< 3} Data is described in Hex code.
Selecting printing position of HRI code in printing bar codes.
"n" means the followings.
•
n (Hex) Printing Position
0 No printing
1 Above the bar code
2 Below the bar code
3 Both above and below the bar code
The HRI code refers to the bar code-turned characters so that you can read them.
The HRI code is printed in the font selected with GS f. Specify before the GS k command.
The initial value of n is "0".
•
[See Also]
GS f
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "3" + CHR$ (5);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "h" + CHR$ (50);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "H" + CHR$ (0);
GOSUB BC
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "H" + CHR$ (1);
GOSUB BC
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "H" + CHR$ (2);
GOSUB BC
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "H" + CHR$ (3);
GOSUB BC
END
BC:
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "k”;
LPRINT CHR$ (4);
LPRINT "12" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
RETU
[Print Results]
No Visible Code
Printed above
Printed below
Printed above
and below
RN
52
Page 57

GS f n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Selecting the font of HRI code
<1D>H<66>H<n>
n = 0, 1
Selecting the font of HRI code in printing bar code.
The type of font can be printed by selecting n is as follows.
The HRI code refers to the bar code-turned characters so that you can read them.
[Caution]
[Default]
[See Also]
The HRI code is printed at the position specified with GS h on page 63.
The initial value of n is “0”.
GS H
[Sample Program]
L
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "H" + CHR$ (2);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "f" + CHR$ (0);
GOSUB BC
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "f" + CHR$ (1);
GOSUB BC
END
BC:
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "k”;
LPRINT CHR$ (4);
LPRINT "123" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT CHR$ (&HA);
RETURN
n Font
0 Font A
1 Font B
PRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "h" + CHR$ (50);
[Print Results]
FONT A
FONT B
53
Page 58

GS h n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Selecting the height of the Bar Code
<1D>H<68>H<n>
{1 =< n =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Selecting bar code height.
n denotes the number of dots in the vertical direction.
[Default]
[Sample Program]
•
See Sample Program and Print Results for GS w on page
The initial value of n is "162".
[Print Results]
68.
54
Page 59

GS k n [ d ] k NUL
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Printing the Bar Code
<1D>H<6B>H<n> [ < d> ] k <00>H
{0 =< n =< 7} Data are described in Hex code.
Specifying a type of bar code and printing bar codes.
The beginning of line is considered as the next printing start position.
•
Depending on the value of n, the following bar code can be selected.
•
d indicates a character code to be printed and k indicates the number of character to be
printed.
n (Hex) Bar Code System Maximum Columns
0 UPC-A --1 UPC-E --2 JAN13 (EAN) --3 JAN 8 (EAN) --4 CODE 39 13
5 ITF 22
6 CODABAR (NW-7) 17
7 CODE 128 15
[Caution]
[Default]
When data being held in the print buffer, this command is ignored.
•
Regardless of the specified feed pitch, this command feeds the paper to be required to
•
print a bar code.
If the character code d cannot be printed in the respective bar code system, the bar
•
code so far will be printed, processing the subsequent data as normal data.
When a bar code whose number of characters to be printed is fixed has been selected,
•
the number of characters k have to be always made equal to the number of characters
to be printed. (The bar code is not printed when not matching.)
When the horizontal direction exceeds one line length, the excess part is not printed.
•
The initial va
•
lue is not specified.
55
Page 60

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Description of Bar Codes] <For print examples, see Page 67. >
UPC-A This bar code, consisting of numerals only, has a fixed length of 12 column; a 11-columns
number entered from the host or application software plus a check column(12th column)
automatically calculated inside the printer. If the 12th-column numeral is sent from the host,
the entire bar code will be printed as it is.
UPC-E This bar code, consisting of numerals only, has a fixed length of 8 column; the first
number system character is "0" stationary. A 12-column numeral entered from the host or
application software is compressed to 8 columns with a check column and printed. The 12thcolumn check column is automatically calculated inside the printer and sent from the host, the
entire bar code will be printed, compressed to 8 columns.
JAN-13(EAN) This bar code, consisting of numerals only, has a fixed length of 13 column; a 12-column
number entered from the host or application software plus a check column(13th column)
automatically calculated inside the printer. If the 13th-column numeral is sent from the host,
the entire bar code will be printed as it is.
JAN-8(EAN) This bar code, consisting of numerals only, has a fixed length of 8 column; a 7-column number
entered from the host or application software plus a check column(8th column) automatically
calculated inside the printer. If the 8th-column numeral is sent from the host, the entire bar
code will be printed as it is.
CODE39 This bar code, consisting of uppercase alphabets and numerals, has a variable length of column.
A start/stop code "*" is automatically added by the printer. Available characters include a
space and "$, %, *, +, -, · , /, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9," and uppercase alphabets.
ITF This bar code, consisting of numerals only, has a variable length of even column. If an odd-
column code is transferred, nothing will be printed.
CODABAR (NW-7)
This bar code, consisting of alpha numerals, has a variable length of column. Available
characters include "0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, D, D, $, +, -,., /, :." A start/stop code is
required; any one of A, B, C, and D is used.
CODE128 • This bar code consists of all of 128 ASCII code characters and has a variable length of
column. This printer supports the code subsets A, B, and C. By prefixing a transfer
code with any one character of A, B, and C, you can select the code subset to start from.
If not prefixed with A, B, or C, the code subset B will be selected.
The code subset A is the bar code consisting of standard uppercase alphabets, numerals,
•
symbols, and special codes.
The code subset B is the bar code consisting of standard uppercase/lowercase alphabets,
•
numerals, symbols, control codes, and special codes.
The code subset C is the bar code consisting of special characters and 100 kinds of
•
numbers ranging from 00 to 99.
The check column automatically calculated inside the printer is added to the end of the
•
entered column
to be printed.
56
Page 61

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Processing of the special characters
•
The characters above the ASCII code number 96 are considered special characters. The
following lists the converted characters for entering these characters.
ASCII Code Converted Character Subset Code Subset Code B Subset Code C
96 80h FNC 3 FNC 3 -N/A-
97 81h FNC 2 FNC 2 -N/A-
98 82h SHIFT SHIFT -N/A-
99 83h CODE C CODE C -N/A-
100 84h CODE B FNC 4 CODE B
101 85h FNC 4 CODE A CODE A
102 86h FNC 1 FNC 1 FNC 1
The following exemplifies a selection of the code subset as a method to utilize the special
characters.
<Selection of Code Subset>
Initial selection: Enter any one character of A, B, and C.
•
Conversion on the way: Enter any one character of 82h through 85h
•
Example) When initially testing with the code subset B, and then, printing the bar code,
"123," with the code subset A
Input code : B TEST <85> 123
•
Bar code data : <CODE B>TEST<CODE A>123
•
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "H" + CHR$ (2);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "k”;
LPRINT CHR$ (4);
LPRINT "123" + CHR$ (0);
[Print Results]
When the data "123" is printed with the code 39
57
Page 62

BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Description of Bar Codes]
UPC-A, UPC-E, JAN-13 (EAN), JAN-8 (EAN), CODE39, ITF, CODABAR, CODE128
Type Print Sample Outline of Symbol Max. column
12-column fixed-length bar code consisting
UPC-A
UPC-E
JAN-13
JAN-8
CODE39
ITF
CODABAR
(NW-7)
CODE128
of numerals only
8-column fixed-length bar code consisting
of numerals only. Abbreviated version of
UPC-A
13-column fixed-length bar code consisting
of numerals only
8-column fixed-length bar code consisting
of numerals only
Variable-length bar code consisting of
alphabets and numerals. The start/stop code
"*" is automatically added.
Even-column variable-length bar code
consisting of numerals only
Variable-length bar code consisting of
alpha numerals. Any one of A, B, C, and D
is required as the start/stop code.
Variable-length bar code consisting of all
128 ASCII code characters.
–
–
–
–
13
22
17
15
Printing is done depending on bar code specification type, number of print column, bar code
height, width (Magnification), vi
sible code presence, and bar code data specification.
58
Page 63

GS w n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Selecting the horizontal size (Scale factor) of the Bar Code
<1D>H <77>H<n>
{2 =< n =< 4} Data is described in Hex code.
Selecting bar code width.
n denotes the number of dots in fine element width.
[Default]
•
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "h" + CHR$ (30);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "w" + CHR$ (2);
GOSUB BC
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "h" + CHR$ (50);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "w" + CHR$ (3);
GOSUB BC
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "h" + CHR$ (80);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "w" + CHR$ (4);
GOSUB BC
END
BC:
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1D) + "k”;
LPRINT CHR$ (4);
LPRINT "12" + CHR$ (0);
RETURN
[Print Results]
The initial value of this width is "3".
Height 30,
Magnification 2
Height 50,
Magnification 3
Height 80,
Magnification 4
59
Page 64

ESC = n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
Data Input Control
<1B>H<3D>H<n>
{0 =< n =< FF} Data is described in Hex code.
Selecting equipment in which data input from the host is effective.
• Each bit of n indicates as follows:
Va l u e Bit Equipment
0 1
0 Printer Invalid Valid
1 Not defined
2 Not defined
3 Not defined
4 Not defined
5 Not defined
6 Not defined
7 Not defined
• When the printer has not been selected, this printer abandons all the received data
until it is selected by this command.
[Caution]
• Even when the printer has not been selected, it can become BUSY state through
printer operation.
• When the printer is deselected, this printer discards all the data until it is selected
with this command.
[Default]
• The initial value of n is "1".
[Sample Program]
LPRINT "AAAAA”;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "=" + CHR$ (0);
LPRINT "aaaaa" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "=" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT "AAAAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
is not printed
60
Page 65

ESC @
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Caution]
Initializing the Printer
<1B>H<40>H
Clears data stored in the print buffer and brings various settings to the initial state (Default state).
•
•
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + " ! " + CHR$ (&H30) ;
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "V" + CHR$ (1);
LPRINT "AAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
LPRINT CHR$ (&H1B) + "@”;
LPRINT "AAA" + CHR$ (&HA);
[Print Results]
Data inside the internal input buffer are not cleared.
Dip switches setting are red once again.
61
Page 66

DC2 A n
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
[Function]
[Code]
[Range]
[Outline]
[Default]
Selecting the Print drive system
<12>H<41>H<n>
{0 =< n =< FF}
Selecting the Fixed division system or the Variable division system.
"n" is valid only for the lowest bit (n0).
•
n0 Print Drive System
0 Fixed division number system
1 Variable division number system
The initial value of n is specified by Jumper (J
5).
62
Page 67

10. CHARACTER CODE TABLE
10.1 International
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
63
Page 68

10.2 Japanese
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
64
Page 69

10.3 International Character Set
COUNTRY
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
65
Page 70

APPENDIX 1. BLOCK DIAGRAM
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
Driver
Timing
CN3
OSC 16.0MH
CPU
Reset
FLASH
MEMORY
Driver
RAM
G/A
Print Head
Operation Panel
Serial
(RS-232C)
Power Supply
Stepping
Moter
Paper End
Head Up
66
Page 71

APPENDIX 2. OUTER DIMENSION
BD2-2890DD SPECIFICATIONS
67
 Loading...
Loading...