Page 1

Touchstone16xx Gateway
Router Setup - Web GUI
User’s Guide
Standard 1.0
November 2013
November 2013 Page 1 of 96
Page 2

ARRIS Trademarks, Copyright, and Other Proprietary Information
©ARRIS Enterprises, Inc. 2013 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in
any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation,
transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from ARRIS Enterprises, Inc. (“ARRIS”).
ARRIS reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes in content from time to
time without obligation on the part of ARRIS to provide notification of such revision or change.
ARRIS provides this guide without warranty of any kind, implied or expressed, including, but not
limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. ARRIS
may make improvements or changes in the product(s) described in this manual at any time. The
capabilities, system requirements and/or compatibility with third-party products described herein
are subject to change without notice.
ARRIS and the ARRIS logo are all trademarks of ARRIS Enterprises, Inc. Other trademarks and trade
names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and the
names of their products. ARRIS disclaims proprietary interest in the marks and names of others.
Page 2 of 96 November 2013
Page 3

Table of Contents
Section 1:
Configuring your Router and your Wireless LAN Connection
1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 8
1.1 Pre-Configuration Requirements ................................................................................................ 8
1.1.1 User Guides 8
2 Basic Configuration .......................................................................................................... 9
2.1 Accessing the Configuration Interface ........................................................................................ 9
2.2 Configuring Your Wireless Network .......................................................................................... 10
2.2.1 Enabling or Disabling the Wireless Network .................................................................... 10
2.2.2 Changing Your Login Password ......................................................................................... 10
2.2.3 Changing the Default Wireless Network Name (SSID) ...................................................... 11
2.2.4 Selecting the Operating Channel ...................................................................................... 12
2.2.5 Setting the Wireless Network Security Mode ................................................................... 12
2.3 Configuring Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) ................................................................................. 13
2.4 Troubleshooting Your Wireless Connection ............................................................................. 13
2.4.1 Factors Affecting Wireless Range ..................................................................................... 13
2.4.2 Interference from Other Wireless Devices ....................................................................... 14
2.4.3 Client Device Hardware/Software Configuration ............................................................. 15
2.5 Setting Up Your WAN Connection ............................................................................................ 17
3 Advanced Configuration Options .................................................................................... 18
3.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 18
3.2 WAN Setup – Configuring Dynamic Routing (RIP) - (Technician Level Only) ............................ 18
3.3 WAN Setup – Configuring Dynamic Routing (RIPng) – (Technician Level Only) ....................... 19
3.4 LAN Setup – Configuring DHCP ................................................................................................. 19
3.4.1 LAN Setup – Adding and Deleting DHCP Clients ............................................................... 20
3.5 LAN Setup – Selecting the NAT Mode ....................................................................................... 20
3.6 Wireless Setup – Setting the Wireless Mode ............................................................................ 21
3.7 2.4 GHz Wireless Setup – Setting the 802.11n Operation Mode.............................................. 21
3.8 Wireless Setup – Using MAC Address Filtering ......................................................................... 22
3.8.1 Finding the MAC Address of a Computer ......................................................................... 23
November 2013 Page 3 of 96
Page 4

3.9 Firewall – General Firewall Configuration Settings ................................................................... 24
3.10 Firewall – Configuring a Virtual Server (Port Forwarding) ........................................................ 24
3.11 Firewall – Configuring Port Triggers .......................................................................................... 25
3.12 Firewall – Configuring Client IP Filters ...................................................................................... 26
3.13 Firewall – Configuring Client IPV6 Filters .................................................................................. 27
3.14 Firewall – Configuring DMZ for Gaming or Conferencing Applications .................................... 28
3.15 Firewall – Using Parental Controls ............................................................................................ 29
3.16 Utilities – Viewing Network System Information ...................................................................... 30
3.17 Utilities – Restarting the Router ............................................................................................... 30
3.18 Utilities – Reverting to Factory Default Settings ....................................................................... 30
3.19 Utilities – Backing up your Settings ........................................................................................... 30
3.20 Utilities –Restoring your Settings .............................................................................................. 31
3.21 Utilities – Viewing the System Logs .......................................................................................... 31
3.22 Utilities – DDNS ......................................................................................................................... 31
4 Introduction .................................................................................................................. 34
5 Basic Setup .................................................................................................................... 35
5.1 BASIC SETUP – Login ................................................................................................................. 35
5.2 Basic SETUP – System Basic Setup – WPA-PSK or WPA2/PSK Security (default) ...................... 36
5.3 BASIC SETUP – Change Password.............................................................................................. 39
6 WAN Setup .................................................................................................................... 40
6.1 WAN SETUP – Dynamic Configuration Settings ........................................................................ 40
6.2 WAN SETUP – Static IP Connection Type .................................................................................. 41
6.3 WAN SETUP – Dynamic Configuration Settings (IPV6) ............................................................. 43
6.4 WAN SETUP – Static IP Connection Type (IPV6) ....................................................................... 44
6.5 WAN SETUP – Routing (Technician Level Only) ........................................................................ 46
7 LAN Setup ...................................................................................................................... 48
7.1 LAN SETUP – LAN Settings......................................................................................................... 48
7.2 LAN SETUP – LAN Settings (IPV6) .............................................................................................. 51
7.3 LAN Setup – Client List .............................................................................................................. 54
7.4 LAN Setup – Ports ..................................................................................................................... 56
Page 4 of 96 November 2013
Page 5

8 Wireless Setup ............................................................................................................... 57
8.1 Wireless 2.4 GHz – System Basic Setup .................................................................................... 57
8.2 Wireless 2.4 GHz – Advanced Settings ...................................................................................... 60
8.3 Wireless 2.4 GHz – MAC Address Control ................................................................................. 63
8.4 Wireless 2.4 GHz – Wireless Client List ..................................................................................... 65
8.5 Wireless 5 GHz – System Basic Setup ....................................................................................... 66
8.6 Wireless 5 GHz – Advanced Settings ......................................................................................... 68
8.7 Wireless 5 GHz – MAC Address Control .................................................................................... 70
8.8 Wireless 5 GHz – Wireless Client List ........................................................................................ 72
9 Firewall 73
9.1 Firewall – Firewall Settings ....................................................................................................... 73
9.2 Firewall –Virtual Servers Configuration (Port Forwarding) ....................................................... 75
9.3 Firewall – Port Triggers Configuration ...................................................................................... 76
9.4 Firewall – Client IP Filters Configuration ................................................................................... 77
9.5 Firewall – Client IP Filters (IPV6) Configuration ........................................................................ 78
9.6 Firewall – DMZ Settings ............................................................................................................ 80
9.7 Firewall – Parental Controls ...................................................................................................... 81
9.8 Firewall – ALG Settings .............................................................................................................. 83
10 Utilities 84
10.1 Utilities – System Information .................................................................................................. 84
10.2 Utilities –Restart Router............................................................................................................ 87
10.3 Utilities – Factory Defaults ........................................................................................................ 88
10.4 Utilities – Save/Backup Settings ................................................................................................ 89
10.5 Utilities – Restore Settings ........................................................................................................ 90
10.6 Utilities – System Settings ......................................................................................................... 91
10.7 Utilities – Language ................................................................................................................... 92
10.8 Utilities – System Logs .............................................................................................................. 93
10.9 Utilities –DDNS .......................................................................................................................... 94
11 MoCA Status .................................................................................................................. 95
November 2013 Page 5 of 96
Page 6

(blank page)
Page 6 of 96 November 2013
Page 7

Section 1
Configuring your Router and
your Wireless LAN Connection
Page 8

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
1 Introduction
This section explains how to set up your router and configure your wireless connection,
including:
Basic Configuration
Advanced Configuration
1.1 Pre-Configuration Requirements
IMPORTANT: In order to configure your router, you should have already
done the following:
Installed the router hardware as described in Installing and Connecting your ( Product
Name) in the User’s Guide for your specific product.
Established a wired Ethernet connection between your computer and your ARRIS
router, as follows:
- Connect an Ethernet cable to your computer and to an available Ethernet port on
the back of your router.
- Configure the Ethernet connection as explained in Configuring Your Ethernet
Connection in the User’s Guide for your specific product.
1.1.1 User Guides
If you do not have the User Guide for your product, you can download one here:
http://www.arrisi.com/support/guides/
Page 8 of 96 November 2013
Page 9

Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
2 Basic Configuration
The router ships with a basic factory default configuration that should allow you to immediately
access the Internet after installing the hardware according to your User’s Guide.
If you need to modify the routers default basic settings, or if you want to configure advanced
settings, refer to the appropriate instructions in this document.
As a minimum, it is recommended that you:
Change the default login password
Change the default wireless network name, also called the Service Set Identifier (SSID)
Wireless LAN Default Security Setting: The router ships with wireless LAN security set by
default. See the security label on your product for the factory security settings: network name
(SSID), encryption method, network key, and WPS PIN.
If you need to modify the router’s default wireless security settings, or if you want to configure
any other settings, refer to the appropriate instructions in this document.
Note: You must set up your computer and other client devices to work with the security
settings on the router. Refer to the documentation for your client device for instructions
on setting security. If your computer or client device supports WiFi Alliance WPS
(Wireless Protected Setup), activate WPS on your computer or client device and the
router simultaneously to easily set up your system security.
2.1 Accessing the Configuration Interface
Perform the following steps to access the configuration interface.
Note: You should have already performed the steps described in paragraph 1.1 PreConfiguration Requirements.
1. If security has been properly set up on your computer to access the wireless LAN on the
router, use the connection utility for your operating system to connect to the wireless LAN
using its network name (SSID), as shown on the security label.
Note: If you cannot access the wireless LAN, you must first establish a wired
Ethernet connection between your computer and the router.
2. In your web browser, open the page http://192.168.0.1/ to access the wireless router setup.
The Login screen displays.
3. Enter the user name and password and click the Apply button to log in.
November 2013 Page 9 of 96
Page 10
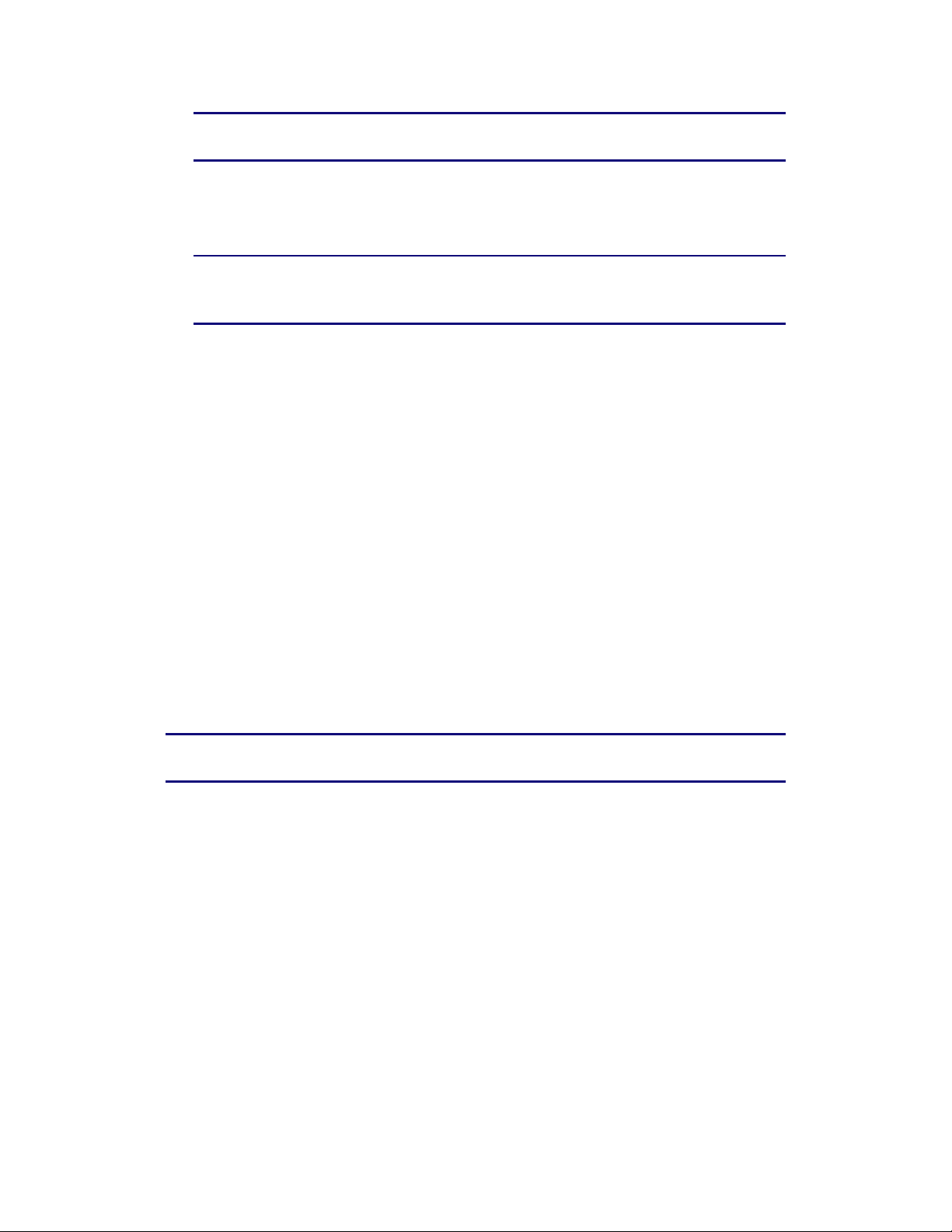
Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Note: The default user name is “admin”. The default password is “password”, in
lower case letters.
The System Basic Setup screen displays.
4. Set basic setup configuration parameters as required for your system.
Note: Most configuration parameters that you may want to set can be accessed on
the System Basic Setup screen or under the More LAN Settings or More Wireless
Settings links.
2.2 Configuring Your Wireless Network
Perform the following procedures to make the basic configuration settings for your wireless
network.
2.2.1 Enabling or Disabling the Wireless Network
Perform the following steps to enable the wireless network.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Basic Setup tab.
3. Click the Enable Wireless checkbox to enable wireless networking.
4. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
2.2.2 Changing Your Login Password
You should change your login password to something other than the default password.
Note: The default user name is “admin”. The default password is “password”, in lower
case letters.
Perform the following steps to change your password.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface via a direct wired Ethernet connection or a
wireless connection.
2. Click the Basic Setup tab.
3. Click Change Password in the side menu to display the change password screen.
Page 10 of 96 November 2013
Page 11
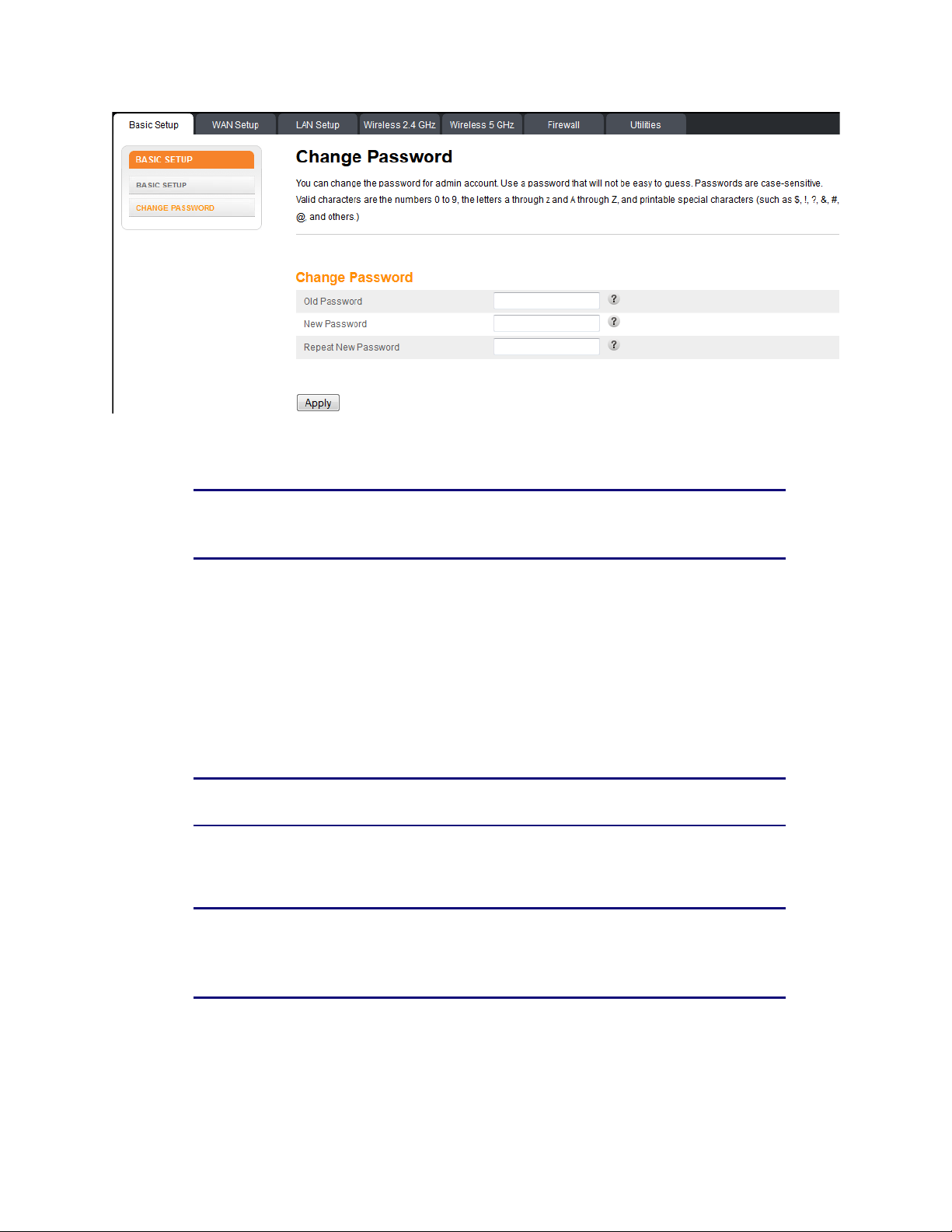
Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
4. Enter your old password.
5. Enter your new password twice.
Note: Passwords are case-sensitive. Valid characters are the numbers 0 to 9, the
letters a through z and A through Z, and printable special characters (such as $, !, ?,
&, #, @, and others.)
6. Click the Apply button.
2.2.3 Changing the Default Wireless Network Name (SSID)
While still on the Basic Setup screen, perform the following steps to change your wireless 2.4
GHz and/or wireless 5 GHz network name.
1. Enter a unique user friendly name to identify your wireless network in the Wireless
Network Name (SSID) field.
Note: This name is also referred to as the Service Set Identifier (SSID). The name can
be up to 32 characters long.
2. To set the Broadcast Network Name (SSID) option, click More Wireless Settings under
either Wireless 2.4 GHz or Wireless 5 GHz and verify the setting under Basic Setup.
Note: – Checking te Broadcast Network Name (SSID) checkbox allows the SSID to be
broadcast by the router. If enabled, your SSID could be obtained allowing
unauthorized access to your network. If you would like others not to see your access
point, uncheck the checkbox to hide the SSID.
3. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
November 2013 Page 11 of 96
Page 12
Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
2.2.4 Selecting the Operating Channel
While still on the Wireless 2.4 GHz or Wireless 5 GHZ System Basic Setup screen, perform the
following steps to select a communications channel for your router.
1. Select AUTO or a specific channel number from the Channel drop-down list.
Note: The default setting is “Auto”, in which the router selects a channel with the
least amount of interference to use. . For 2.4 GHz, if you manually select a channel,
it’s best to choose channel 1, 6, or 11, since these channels do not overlap. If
another unit is operating in the area, choose a channel that is farthest away from
the channel that unit uses. For example, if one is using channel 11, set yours to
channel 1. For 5 GHz choose a channel that is farthest away from the channel used
by any other unit operating in the area. If you experience interference or poor
performance on a particular channel, try a different channel..
2.2.5 Setting the Wireless Network Security Mode
The router ships with wireless LAN security set by default. See the security label on your
product for the factory security settings: network name (SSID), pre-shared key, security mode,
and WPS PIN.
Note: You must set up your computer and other client devices to work with the security
settings on the router. Refer to the documentation for your client device for instructions
on setting security. If your computer or client device supports WiFi Alliance WPS
(Wireless Protected Setup), activate WPS on your computer or client device and the
router simultaneously to easily set up your system security.
If you need to modify the router’s default wireless security settings perform the following steps:.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Wireless 2.4 GHz or Wireless 5 GHz tab.
3. Under Basic Setup, select the desired security mode from the Security Mode drop-down
list.
The screen will change and be populated with a section for configuring the specific security
mode that you selected.
4. Set the required configuration parameters for the security mode you selected.
Note: Refer to Wireless 2.4 GHz or Wireless 5 GHZ Setup in Section 2 - Web GUI
Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference for specific information on the
security mode configuration parameters.
5. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
Page 12 of 96 November 2013
Page 13

Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
2.3 Configuring Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
WPS is a standard method for easily configuring a secure connection between your router and
computers or other wireless devices (known as enrollees) that support WPS. When WPS is
enabled you can attach other wireless devices by pressing the WPS buttons on the device (if
equipped) and on your router, or by entering the enrollee’s PIN and then clicking the Start WPS
Association icon.
Perform the following steps to enable the wireless network.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Basic Setup tab.
3. Click the WPS Enable checkbox and click the Apply button to enable WPS on your system.
4. Select the mode from the WPS Mode drop-down menu. It can be set to PBC (Push Button
Control) or PIN Code.
If your client device has a WPS button, select PBC and go to step 5a.
If your client device has a PIN number select PIN Code and go to step 5b.
5. a) If using PBC, press the WPS buttons on the client device and on your router
simultaneously to start the WPS association.
b) If using PIN codes, enter the enrollee’s PIN in the Enrollee PIN Code field, and then click
the Start WPS Association icon. Enter the router’s PIN code in the Device PIN Code field if
requested during connection.
6. If the connection is successful, the WPS indicator light on the router stops flashing and
remains lit. If unsuccessful, the WPS light continues to flash for up to two minutes
(indicating that it’s ready to accept a client connection) and then turns off. If the WPS light
turns off, start the association process over.
2.4 Troubleshooting Your Wireless Connection
The three main factors that affect wireless network performance are:
Range from the Client Devices
Interference from other Wireless Devices
Client Device hardware/software Configuration
2.4.1 Factors Affecting Wireless Range
How close are your wireless devices to your router? The router’s wireless connection range is
typically 100 to 200 feet (30m to 65m).
Note: You should try to centralize the router in relation to where the wireless client
devices will usually be located.
A number of factors can affect the usable range for wireless connections, as described in this
table.
November 2013 Page 13 of 96
Page 14

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Affect on Range
Factor
Increases Range
•
Decreases Range
• Lowering the unit below the devices (for example, installing
Raising the unit above the devices (for example, installing
the router in the upper floor of a multi-story dwelling)
• Setting the transmit power level to High
the router in a basement)
• Metal or concrete walls between the router and client
devices
• Large metal appliances, aquariums, or metal cabinets
between the router and client devices
• Interference and RF noise (2.4 GHz cordless phones,
microwave ovens, or other wireless networks)
• Setting the transmit power level to Medium or Low
• Setting the wireless mode to 5 GHz reduces interference but
also decreases range.
Note: Decreasing the range of your wireless network may be beneficial, as long as the
decreased range is sufficient for your needs. By limiting your network’s range, you
reduce interference with other networks and make it harder for unwanted users to find
and connect to your network.
2.4.2 Interference from Other Wireless Devices
Interference from other equipment operating at 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz in the area of your wireless
network can significantly affect the range and performance of your network, such as:
Cordless phones
Wireless speakers
Microwave ovens
Baby monitors
Gaming Consoles: such as Wii™, Xbox, and PlayStation®
Any other devices operating at 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz
Page 14 of 96 November 2013
Note: If your cordless phones or other wireless devices are interfereing with your
wireless network’s performance, replace them with a similar device that operates on a
different frequency if possible. For example, change to 5.8 GHz cordless phones.
Page 15
Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
2.4.3 Client Device Hardware/Software Configuration
Client device hardware/software configuration can also affect your wireless network
performance.
For example, your computer’s operating system, network adapter, processor, and hard drive
access speed can all affect the transfer speeds that you experience across the network.
If wireless performance is slow, check the following items.
Verify which 802.11 Standard the Wireless Clients are Capable Of
If your client device network adapters use the older 802.11b or 802.11g standards, you should
upgrade them to the 802.11n standard. Network adapters using the older standards can reduce
the performance of your entire network.
802.11b (becoming more rare but not extinct yet) is much slower than 802.11g, which is slower
than 802.11n. The MAXIMUM theoretical limit for each standard is as follows.
802.11b: 11 Mbps
802.11g: 54 Mbps
802.11n: 130 Mbps to 450 Mbps (depending on the wireless router AND wireless client
hardware)
Note: Actual maximum throughput performance typically does not exceed 50% of the
above values.
Perform a Site Survey to Determine the Best Channel
Use wireless network scanning software such as MetaGeek’s free inSSIDer tool to see how many
other wireless routers and access points are broadcasting.
For wireless 2.4 GHz, try to find the cleanest channel among channels 1, 6, and 11. These are
the only three channels that do not overlap. If there are no good options among channels 1, 6
and 11, you can try channel 4 or 8. However, selecting these channels can cause degraded
throughput speeds if there is a lot of traffic on channel 1, 6, or 11. For wireless 5 GHz, choose a
channel that is farthest away from the channel used by any other unit operating in the area.
It is a trial and error process to find the best channel. The best setting may change at any time
depending on all of the other wireless routers in the environment.
Note: When Touchstone 16xx Gateways are set to Auto channel they will automatically
select the cleanest of the available channels upon boot up.
Adjust the Gateway’s Wireless Configuration Settings
Security Mode/Encryption Algorithm
- The recommended security mode/encryption algorithm is WPA2-PSK (AES) for best
performance. All other options will result in degraded throughput speeds. For
November 2013 Page 15 of 96
Page 16

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
example, using WEP and WPA reduces throughput by approximately 80%
comparatively.
- Note that Security Mode WEP and WPA are not compatible with the 802.11n
standard. Performance would be limited to 802.11g speeds of 54mbps. Also,
802.11n requires WPA2 and AES.
Wireless Mode
- Set your wireless mode to optimize performance based on the type of network
adapters being used by your network devices, e.g., 802.11b, 820.11g, and 802.11n.
Select the proper mode to support all of the wireless devices that will connect to
your router. It’s best to have an environment with only one standard and set the
Gateway to that standard. Since this is not always feasible, ONLY include the
standards that are used in your environment.
- The presence of 802.11b devices in an active network will cause the greatest
performance degradation.
BG Protection
- This option allows you to properly operate 802.11b client devices in 802.11g
networks. These older 802.11b devices required the unit to add overhead to most
transmissions.
Operation Mode
- The options are Mixed mode or Greenfield. Select Mixed mode if you network
consists of a mix of 802.11 b, g, and n clients. Select Greenfield if your network
consists of ONLY 802.11n clients. The Greenfield mode improves efficiency of
networks using only 802.11n devices by eliminating support for the 802.11a/b/g
client devices.
Channel Bandwidth (802.11n only)
- Options are 20 MHz or 20/40 MHz . The default setting is 20 MHz. If your wireless
network is in a very clean RF environment setting the Channel Bandwidth to 20/40
will increase your throughput by “bonding” two channels. However, if there are any
other wireless routers or access points within range of the device it will stay in 20
MHz bandwidth regardless of this setting. This is a WiFi Alliance requirement. (You
can verify the channel bandwidth by using the previously mentioned wireless
network scanning software, MetaGeek’s inSSIDer.)
Guard Interval (802.11n only)
- This is the time in nanoseconds between symbols for 802.11n frames. Selecting
400ns provides higher throughput in networks where the coverage distance is small
(indoors). Selecting 800ns provides higher throughput in networks where the
coverage distance is large (outdoors).
Page 16 of 96 November 2013
Page 17
Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
2.5 Setting Up Your WAN Connection
A Dynamic or DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) connection is the most commonly
used WAN connection type.
Note: Do not change this setting unless your Internet Service Provider tells you to use
another connection type.
Perform the following steps to change your connection type.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the WAN Setup tab.
3. Click Dynamic, Dynamic (IPV6), Static, or Static (IPV6) in the side menu to display the
appropriate screen for configuring that type of WAN connection.
4. Set the required configuration parameters for the connection type you selected as provided
by your Internet Service Provider.
Note: Refer to WAN Setup in Section 2 - Web GUI Screens and Configuration
Parameter Reference for specific instructions on setting the various connection type
configuration parameters.
5. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
November 2013 Page 17 of 96
Page 18
Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
3 Advanced Configuration Options
3.1 Introduction
This section explains how to use the most common advanced configuration options for your
router in the following areas:
WAN Setup
LAN Setup
Wireless Setup
Firewall
Utilities
Note: Refer to Section 2 - Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference for
additional advanced configuration options.
3.2 WAN Setup – Configuring Dynamic Routing (RIP) - (Technician
Level Only)
Enabling Dynamic Routing or RIP (Router Information Protocol) allows your router to operate in
a network environment with other routers. This is primarily used for office environments or
multiple dwelling units where a network with existing routers already exists. Only enable
Dynamic Routing if your service provider recommends that you do so.
Requirements
To successfully configure RIP, you must have:
A static IP address assigned by our service provider.
Disabled NAT (Network Address Translation) on your router, which also means you must
either assign a static IP address to all devices on your local network or use a DHCP server
to assign addresses.
Perform the following steps to enable Dynamic Routing.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the WAN Setup tab.
3. Click Routing in the side menu to display the routing screen.
4. Click the Enable Dynamic Routing (RIP) checkbox.
Page 18 of 96 November 2013
Page 19
Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
Note: Refer to WAN Setup in Section 2 - Web GUI Screens and Configuration
Parameter Reference for specific instructions on setting the various dynamic
routingconfiguration parameters.
5. After setting the necessary configuration parameters, click the Apply button at the bottom
of the screen.
6. Set NAT Mode to Bridged on the LAN Setup – LAN Settings screen.
3.3 WAN Setup – Configuring Dynamic Routing (RIPng) – (Technician
Level Only)
Note: Not available on all models.
Enabling Dynamic Routing for IPV6 or RIPng (Router Information Protocol next generation)
allows your router to operate in a network environment with other routers. This is primarily
used for office environments or multiple dwelling units where a network with existing routers
already exists. Only enable Dynamic Routing if your service provider recommends that you do
so.
Requirements
To successfully configure RIPng, you must have:
A static IP address assigned by our service provider.
You must either assign a static IP address to all devices on your local network or use a
DHCP server to assign addresses.
Perform the following steps to enable Dynamic Routing for IPV6.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the WAN Setup tab.
3. Click Routing (RIPng) in the side menu to display the RIPng configuration screen.
4. Click the Enable Dynamic Routing checkbox.
Note: Refer to WAN Setup in Section 2 - Web GUI Screens and Configuration
Parameter Reference for specific instructions on setting the various dynamic
routingconfiguration parameters.
5. After setting the necessary configuration parameters, click the Apply button at the bottom
of the screen.
3.4 LAN Setup – Configuring DHCP
DHCP (Dynamic Host Protocol Configuration) is enabled by default on your router which allows
your router to act as a DHCP server and automatically assign an IP address to each device on
your network.
November 2013 Page 19 of 96
Page 20
Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
DHCP is a set of rules used by devices such as a computer, router, or network adapter to allow
the device to request and obtain an IP address from a server which maintains a list of addresses
available for use. The DHCP server ensures that all IP addresses are unique, e.g., no IP address is
assigned to a second device while the first device's assignment is valid (its lease has not
expired).
Without DHCP, the IP addresses must be entered manually at each computer or device and a
new IP address must be entered each time it moves to a new location on the network.
Perform the following steps to configure DHCP.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the LAN Setup tab.
3. Click LAN Settings or LAN Settings (IPV6) in the side menu to display the LAN Settings
screen.
4. Click the Enable DHCP Server checkbox under DHCP Server Settings.
5. Enter the Start IP Address and End IP Address for the range of IP addresses that the DHCP
Server will be allowed to assign to a network device.
6. Enter the Lease Time in seconds before the assigned IP address will expire. (After the lease
time is up, the user is automatically assigned a new dynamic IP address.)
Note: Refer to LAN Setup in Section 2 - Web GUI Screens and Configuration
Parameter Reference for specific instructions on setting the various DHCP
configuration parameters.
7. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
3.4.1 LAN Setup – Adding and Deleting DHCP Clients
The DHCP Client screen shows the host Name, IP address, and MAC Address of each computer
that is connected to your network. If a computer does not have a specified host name, then the
host Name field will be blank.
Perform the following steps to configure the DHCP Clients.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the LAN Setup tab.
3. Click Client List in the side menu to display the Client List screen.
4. Click the Add button to add a reserved IP client. Select an existing DHCP client and then
click the Delete button to delete the client. Click the Refresh button to update the Clients
List.
3.5 LAN Setup – Selecting the NAT Mode
NAT (Network Address Translation) allows your router to manipulate IP addresses so that just
one single IP address can represent an entire group of computers on your network and let them
Page 20 of 96 November 2013
Page 21
Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
all communicate with the Internet. This conserves IP addresses and is necessary since there are
a finite number of available IP addresses for use.
Perform the following steps to select the NAT Mode.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the LAN Setup tab.
3. Click LAN Settings in the side menu to display the LAN Settings screen.
4. Select the NAT Mode from the NAT Mode field drop-down list. The optional modes are:
Bridged - Data will pass through the device directly without any routing.
Routed with NAT - Data will be routed by the device and all the outgoing packets will be
NATed.
Routed without NAT - Data will be routed by the device but all the outgoing packets will not
be NATed.
5. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
Note: A dialog box displays “Restarting your router is recommended when NAT
settings change.” Click OK to restart.
3.6 Wireless Setup – Setting the Wireless Mode
You can set your wireless mode to optimize performance based on the type of network adapters
being used by your network devices, e.g., 802.11b, 820.11g, and 802.11n. Select the proper
mode to support all of the wireless devices that will connect to your router.
Perform the following steps to set your wireless mode.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Wireless 2.4 GHz and/or Wireless 5 GHz tab.
3. Click Advanced in the side menu to display the Advanced Settings screen.
4. Under Wireless Network Settings select the proper mode from the Wireless Mode drop-
down list.
2.4 GHz Options: B/G mixed, B only, G only, N only, G/N mixed, and B/G/N mixed.
5 GHz Options: A/N mixed, A only, and N only.
5. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
Note: Refer to the Wireless Setup – Advanced screen in Section 2 - Web GUI Screens
and Configuration Parameter Reference for instructions on setting additional
advanced wireless configuration parameters.
3.7 2.4 GHz Wireless Setup – Setting the 802.11n Operation Mode
The 802.11 operation mode must be set to work properly with the selected wireless mode
setting. The default setting, Mixed Mode, is for networks with a mix of 802.11b/g/n client
November 2013 Page 21 of 96
Page 22
Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
devices. Mixed Mode can be used with any Wireless Mode setting. If all of your network
devices are 802.11n devices, you can improve the efficiency of your network by setting the
Wireless Mode to “N only” and setting the 802.11n operation mode to Greenfield.
Perform the following steps to set your 802.11n operation mode.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Wireless 2.4 GHz tab.
3. Click Advanced in the side menu to display the Advanced Settings screen.
4. Under 802.11n Specific Settings select the proper mode from the Operation Mode drop-
down list.
Options are: Greenfield and Mixed Mode.
5. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
Note: Refer to the Wireless Setup – Advanced screen in Section 2 - Web GUI Screens
and Configuration Parameter Reference for instructions on setting additional
advanced wireless configuration parameters.
3.8 Wireless Setup – Using MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering allows you to restrict access to your wireless network to those computers
you specifically authorize to connect. This filter type is called an Allowed List. Optionally, you
can block specific computers from accessing your network. This filter type is called a Blocked
List. You have to choose one type or the other.
Perform the following steps to set up MAC address filtering.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Wireless 2.4 GHz and/or Wireless 5 GHz tab.
3. Click MAC Address Control in the side menu to display the MAC Address Control screen.
4. Under MAC Address Filtering select the proper filter type from the MAC Address Filter Type
drop-down list.
Options are: None, Allowed List, and Blocked List.
5. Under MAC Address Filter List click the Add button to display the Add MAC Address dialog
box.
6. Enter the MAC address of a computer that you want to add to the filter list, and then click
the Add MAC Address button.
Page 22 of 96 November 2013
Page 23

Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
Note: If you don’t know how to find your computer’s MAC address, see 3.8.1 Finding
the MAC Address of a Computer.
7. Repeat Step 6 for each MAC address you want to add.
Note: To delete a MAC address, first select a MAC address in the list and then click
the Delete button.
8. Click the Apply button.
3.8.1 Finding the MAC Address of a Computer
Use the specific operating system of your computer to find its MAC address, as follows.
Windows:
From the Start menu, find and select the Control Panel. Double-click Network Connections
(Windows XP), or Network & Sharing Center (Windows Vista or Windows 7). Then double-click
either “Wireless Network Connection” for a wireless connection, or “Local Area Connection” for
an Ethernet connection. Next click the Details button (Windows Vista or Windows 7), or click the
Support tab and then the Details button (Windows XP). The “Physical Address” line shows the
MAC address.
MacOS X:
Open System Preferences and click the Network icon. To find the Ethernet MAC address, select
Built-in Ethernet from the Show drop-down, then click the Ethernet tab. The “Ethernet ID” field
shows the MAC address. To find the wireless MAC address, select Airport from the Show drop-
down, then click the Airport tab. The “Airport ID” field shows the MAC address.
Linux:
Open a shell window and type /sbin/ifconfig (and press Enter). The wireless interface is eth1
(unless there is no Ethernet adapter, in which case the interface is eth0).
November 2013 Page 23 of 96
Page 24

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
3.9 Firewall – General Firewall Configuration Settings
Your router is equipped with a firewall that will protect your network from a wide array of
common hacker attacks, including Ping of Death (PoD) and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. You
can also configure VPN pass-through to enable VPN tunneling using IPSec, PPTP, or L2TP
protocols to pass through the router’s firewall so that you can connect to a Virtual Private
Network at your office, for example.
You can disable the firewall function if needed. Turning off the firewall protection will not leave
your network completely vulnerable to hacker attacks, but it is recommended that you enable
the firewall whenever possible.
Perform the following steps to enable the firewall and make general firewall settings.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Firewall tab.
3. Click Firewall Settings in the side menu to display the Firewall Settings screen.
4. Check the Enable Firewall checkbox to enable the firewall on your network.
5. Check the Enable DoS Attack Protection Firewall checkbox to protect against DoS attacks.
6. Check the Enable Ping Blocking checkbox to protect against PoD attacks.
7. Check the Enable IPSec Pass Through checkbox to allow IPSec tunnels to pass through the
router.
8. Check the Enable PPTP Pass Through checkbox to allow PPTP tunnels to pass through the
router.
9. Check the Enable L2TP Pass Through checkbox to allow L2TP tunnels to pass through the
router.
10. Check the Enable Block Fragmented IP Packets checkbox to block fragmented IP packets.
11. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
3.10 Firewall – Configuring a Virtual Server (Port Forwarding)
The port forwarding function forwards inbound traffic from the Internet to a specified single
device on your network. Examples include allowing access to a web server on your network,
peer-to-peer file sharing, applications that allow remote access to your computer, some gaming
and videoconferencing applications, and others.
If you have a server in your network that you want to make available to the general Internet,
you can configure a virtual server. The firewall passes requests from the Internet to the
designated computer on your network. This function works by allowing you to route external
(Internet) calls for services such as a web server (port 80), FTP server (Port 21), or other
applications through your router to your internal network.
Perform the following steps to configure a virtual server.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Firewall tab.
Page 24 of 96 November 2013
Page 25
Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
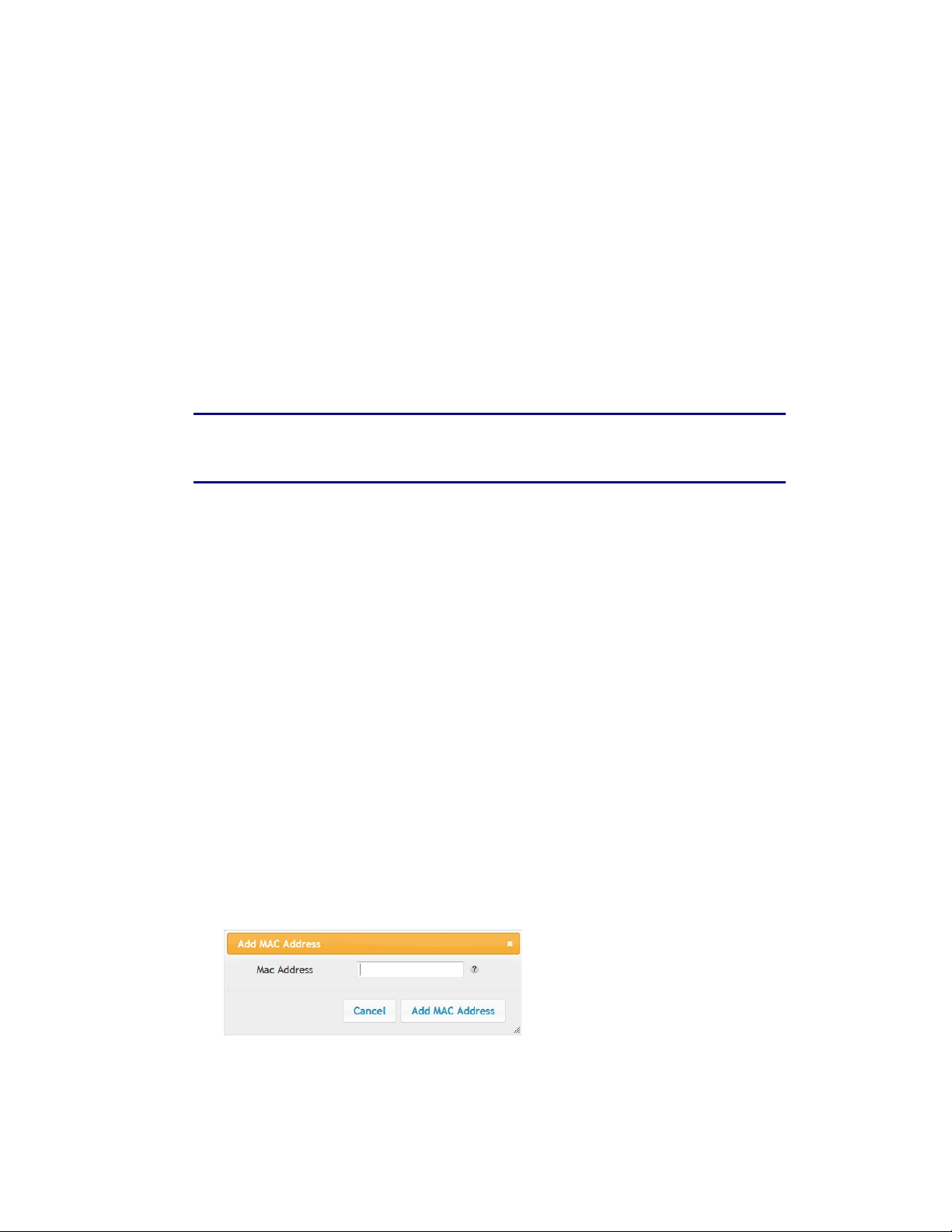
3. Click Virtual Servers in the side menu to display the Virtual Server Configuration screen.
4. Check the Add button to display the Add Virtual Server dialog box.
5. Enter the following parameters in the dialog box.
Description – Enter a name for the virtual server.
Inbound Port – Enter the inbound port range for the virtual server. It should be the same
range as the local port.
Format – Sets the format for the port. Options are TCP, UDP, or BOTH.
Private IP Address – Enter the IP address of the machine on the LAN that you want
the connections to go to.
Local Port – Enter the local port range for the virtual server. It should be the same range as
the inbound port.
6. Click the Add Virtual Server button to add the virtual server.
Note: To delete a virtual server, first select a virtual server in the list and then click
the Delete button.
3.11 Firewall – Configuring Port Triggers
Port triggering lets you set the router to watch outgoing traffic for specific port numbers,
remember the IP address of the sending computer, and then route the data back to the sending
computer when the requested data returns. This is typically used for online gaming and online
chat applications.
Perform the following steps to add a port trigger.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Firewall tab.
3. Click Port Triggers in the side menu to display the Port Triggers screen.
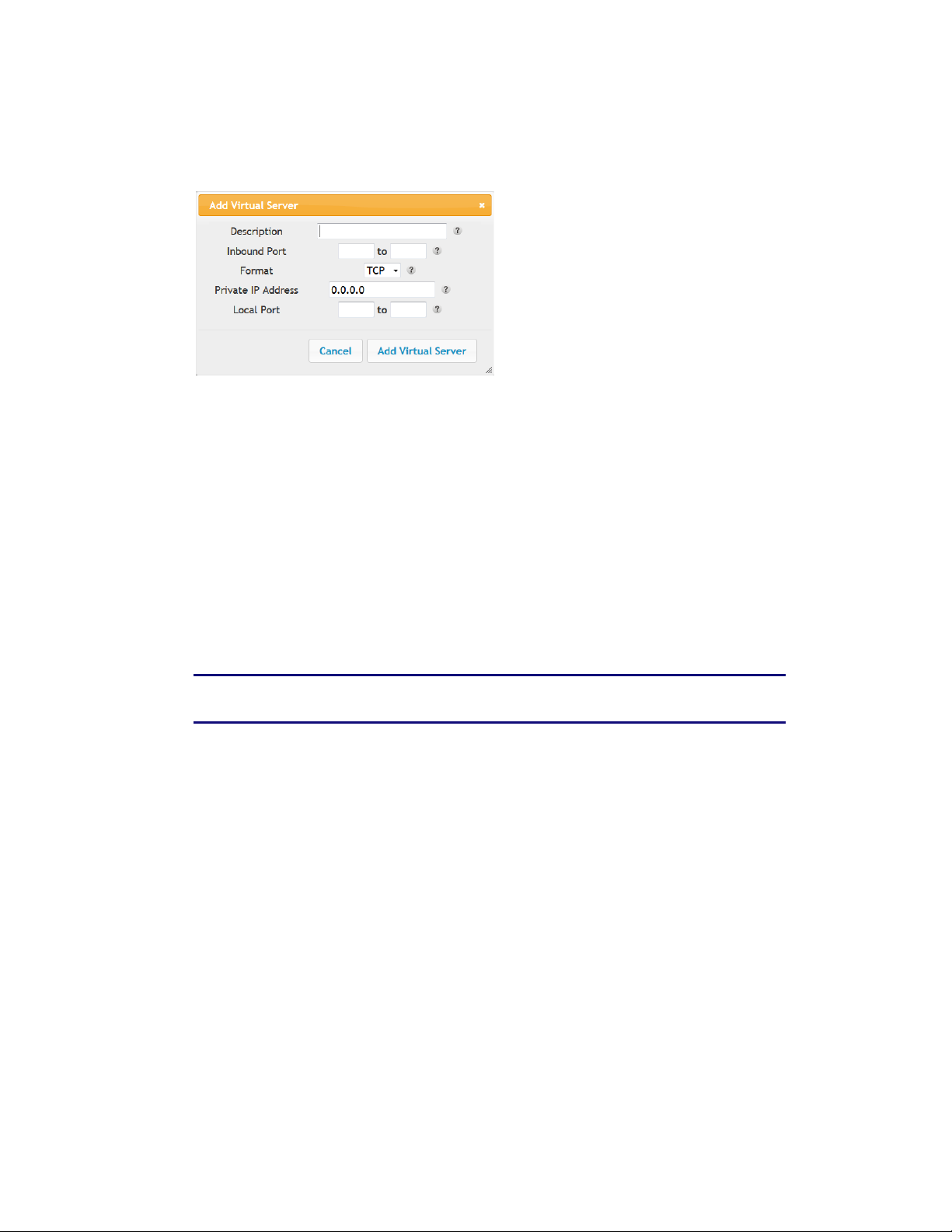
4. Check the Add button to display the Add Port Trigger dialog box.
November 2013 Page 25 of 96
Page 26
Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
5. Enter the following parameters in the dialog box.
Description – Enter a name for the port trigger.
Outbound Port – Enter the outbound port range for the port trigger. It should be the same
range as the inbound port.
Format – Sets the format for the port. Options are TCP, UDP, or BOTH.
Inbound Port – Enter the inbound port range for the port trigger. It should be the same
range as the outbound port.
6. Click the Add Port Trigger button to add the port trigger.
Note: To delete a port trigger, first select a port trigger in the list and then click the
Delete button.
3.12 Firewall – Configuring Client IP Filters
The router can be configured to restrict access to the Internet, email, or other network services
at specific days and times.
Perform the following steps to add a client IP filter.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Firewall tab.
3. Click Client IP Filters in the side menu to display the Client IP Filter Configuration screen.
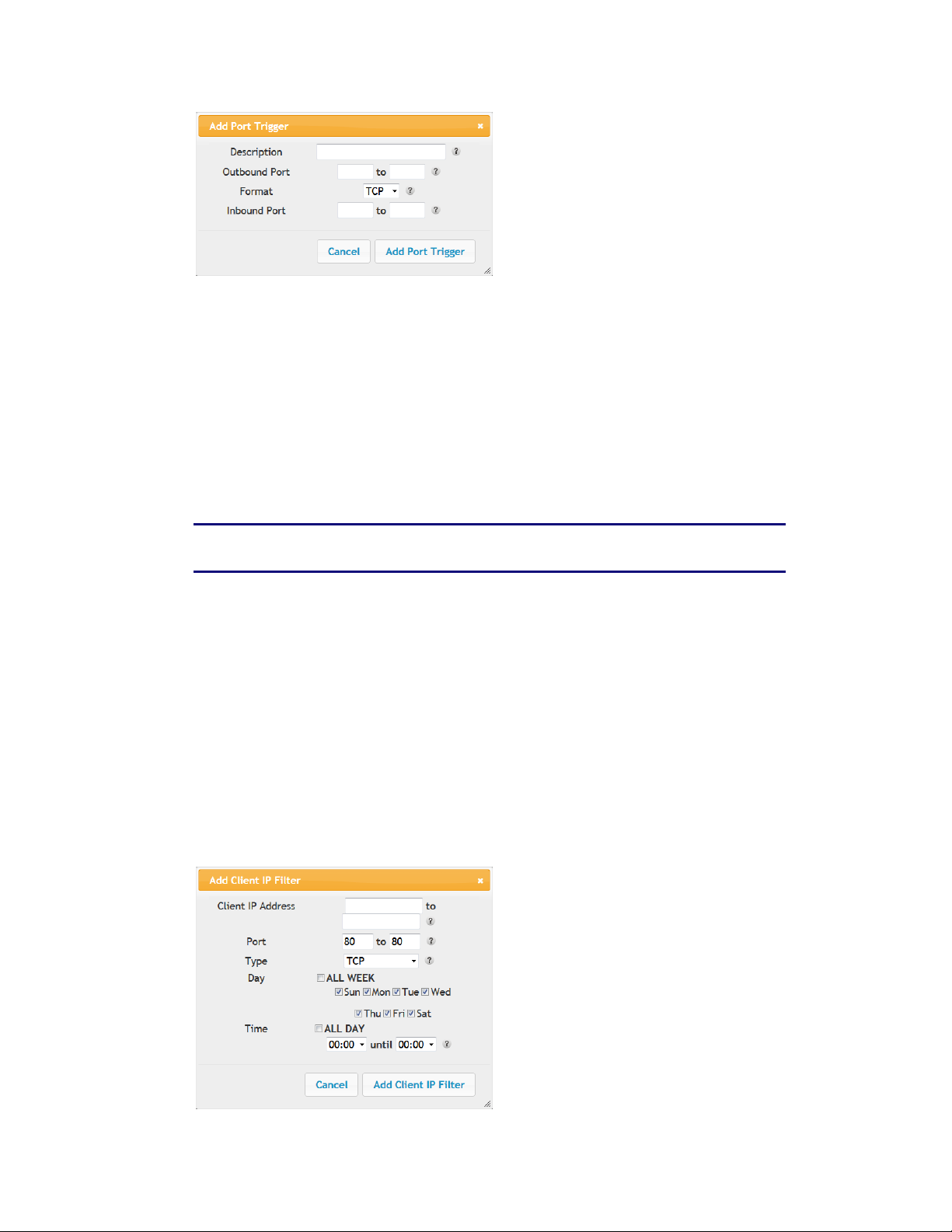
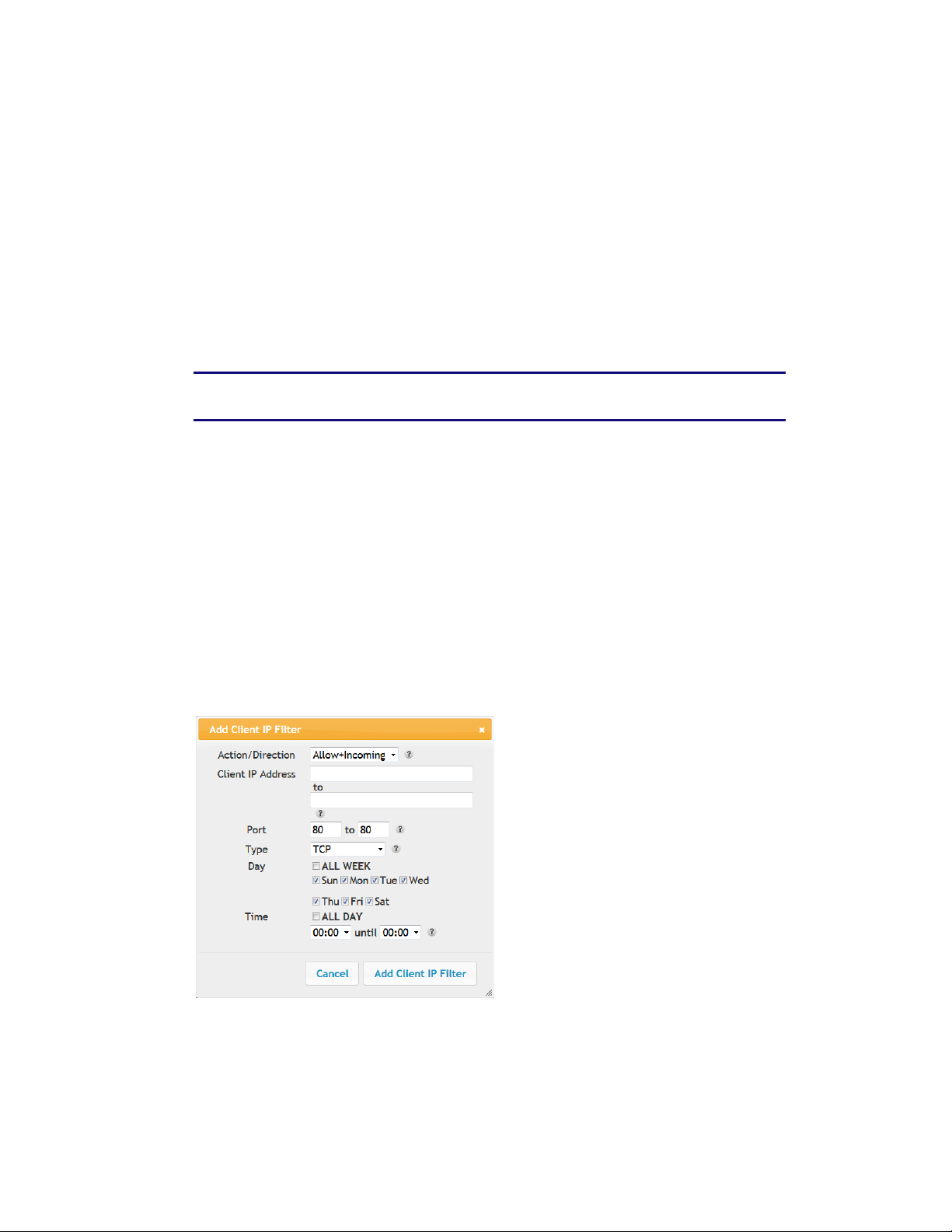
4. Check the Add button to display the Add Client IP Filter dialog box.
Page 26 of 96 November 2013
Page 27
Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
5. Enter the following parameters in the dialog box.
Client IP Address – Enter the client IP address or range to filter.
Port – Enter the outbound traffic port number range, starting and ending.
Type – Sets the port type. Options are TCP, UDP, or BOTH.
Day – Click the check boxes for the days you want access allowed, or click the All Week
checkbox for all week.
Time – Sets the start time and end time for the allowed access during the specified days (24hour clock). 00:00 to 24:00 indicates all day, or click the checkbox for All Day.
6. Click the Add Client IP Filter button to add the filter.
Note: To delete a client IP filter, first select aclient IP filter in the list and then click
the Delete button.
3.13 Firewall – Configuring Client IPV6 Filters
The router can be configured to restrict access to the Internet, email, or other network services.
Perform the following steps to add a client IPV6 filter.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Firewall tab.
3. Click Client IPV6 Filters in the side menu to display the Client IPV6 Filter Configuration
screen.
4. Check the Add button to display the Add Client IP Filter dialog box.
5. Enter the following parameters in the dialog box.
Action/Direction - Select either Allow+Incoming or Deny+Outgoing to allow data watching
this filter and watch incoming data or deny data watching and watch outgoing data.
Client IP Address – Enter the range of IPV6 addresses to filter.
November 2013 Page 27 of 96
Page 28
Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Port – Enter the outbound traffic port number range, starting and ending.
Type – Sets the port type. Options are TCP, UDP, or BOTH.
Day – Click the check boxes for the days you want access allowed, or click the All Week
checkbox for all week.
Time – Sets the start time and end time for the allowed access during the specified days (24hour clock). 00:00 to 24:00 indicates all day, or click the checkbox for All Day.
6. Click the Add Client IP Filter button to add the filter.
Note: To delete a client IP filter, first select aclient IP filter in the list and then click
the Delete button.
3.14 Firewall – Configuring DMZ for Gaming or Conferencing
Applications
The DMZ feature allows you to specify one computer on your network to be placed outside of
the NAT firewall. This may be necessary if the NAT feature is causing problems with an
application such as a game or video conferencing application.
Use this feature only on a temporary basis. The computer in the DMZ is not protected from
hacker attacks.
Perform the following steps to put a computer in the DMZ.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Firewall tab.
3. Click DMZ in the side menu to display the DMZ Settings screen.
4. Enter the following parameters.
Enable DMZ – Click this checkbox to enable DMZ on your network.
WAN IP – Displays the public IP address.
Private IP – Enter the IP address of the computer to be placed in the DMZ. Be sure that the
address is not in the range of addresses delivered by the DHCP server if enabled. After
placing the computer in the DMZ, all ports on the computer are open to the Internet and
not protected.
5. Click the Apply button at the bottom of the screen.
Note: To remove the computer from the DMZ delete the entries and uncheck the
Enable DMZ checkbox.
Page 28 of 96 November 2013
Page 29

Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
3.15 Firewall – Using Parental Controls
The Parental Control feature allows you to block specified keywords and web sites from being
accessed and also to specify trusted computers in the network. Trusted computers are not
affected by the parental control settings. You can add two trusted computers. For example,
you may want the computers of the parents to be trusted, while the childrens’ computers have
parental controls in effect.
Perform the following steps to set up your Parental Controls.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Firewall tab.
3. Click Parental Controls in the side menu to display the Parental Controls screen.
4. Check the Enable Parental Controls checkbox and click the Apply button.
5. Configure any or all of the following parental controls:
Trusted MAC Addresses - Enter the MAC addresses of any “trusted” computers on the
network and click the Apply button. Once added, these trusted computers will not be
affected by the parental control settings.
Note: Refer to 3.8.1 Finding the MAC Address of a Computer for information on
determining the MAC address of your computer.
Keyword and Web Site Filtering - You can add a list of keywords and web sites that you
want to block. To add a keyword or web site to the list, click the respective Add button. To
delete a keyword or web site from the list, first click its check box and then click the Delete
button.
6. Adding a Keyword or Web Site Filter
a) Enter the keyword in the Keyword field or web site URL address in the Web Site field.
b) Click the check boxes for the days you want access blocked, or click the All Week
checkbox for all week.
c) Set the start time and end time during the specified days (24-hour clock). (0:00 until 0:00
indicates all day, or click the All Day checkbox.)
November 2013 Page 29 of 96
Page 30

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
d) Click the Add Keyword Filter or Add Web Site Filter button respectively. Then click the
Apply button.
3.16 Utilities – Viewing Network System Information
You can view status and system information for your network on the Utilities – System
Information screen.
Perform the following steps to view system status information.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Utilities tab.
3. Click System Information in the side menu to display the System Information screen.
Note: Refer to 10.1 Utilities – Status/System Information for an explanation of the
various status information parameters.
3.17 Utilities – Restarting the Router
It may be necessary to restart (reboot) the router if it begins working improperly. Restarting the
router will not delete any of your configuration settings.
Perform the following steps to restart the router.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Utilities tab.
3. Click Restart Router in the side menu to display the Restart Router screen.
4. Click the Restart button to restart the router.
3.18 Utilities – Reverting to Factory Default Settings
This function restores all of the router’s configuration settings to the factory default setting.
Before restoring the factory defaults, you should back up your current configuration settings
using the Save/Backup Settings function.
Perform the following steps to revert to factory default settings.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Utilities tab.
3. Click Factory Defaults in the side menu to display the Factory Defaults screen.
4. Click the Factory Defaults button to reset the router to factory default settings.
3.19 Utilities – Backing up your Settings
This function saves your current configuration settings, which allows you to restore them later if
your settings are lost or changed.
Page 30 of 96 November 2013
Page 31

Section 1: Configuring Your Router and Your Wireless LAN Connection
Note: Always backup your current settings before performing a firmware update.
Perform the following steps to revert to backup your settings.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Utilities tab.
3. Click Save/Backup Settings in the side menu to display the Save/Backup Settings screen.
4. Click the Save button to backup your router’s settings.
5. Follow the “file download” and “save as” dialog box instructions for your specific browser to
select a location for and save the router.data backup file.
3.20 Utilities –Restoring your Settings
This function allows you to restore a previously saved router configuration.
Perform the following steps to restore previously saved settings.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Utilities tab.
3. Click Restore Settings in the side menu to display the Restore Settings screen.
4. Use the Browse button to locate and select the previously saved backup file.
5. Cclick the Restore Chosen File button to restore your router’s settings.
3.21 Utilities – Viewing the System Logs
The Utilities - System Logs screen displays the system logs.
Perform the following steps to configure the system logs.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Utilities tab.
3. Click System Logs in the side menu to display the System Logs.
When viewing the logs, click the Refresh button to update the list. Click the Clear Log button to
clear the list.
3.22 Utilities – DDNS
DDNS (Dynamic DNS) allows you to provide Internet users with a fixed domain name (instead of
an IP address which may periodically change). This allows your gateway and applications set up
in your gateway's virtual servers to be accessed from various locations on the Internet without
knowing your current IP address.
Requirements
In order to use DDNS you must first create an account with a DDNS provider. The DDNS
provider maps your chosen domain name to your IP address.
November 2013 Page 31 of 96
Page 32

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Once your account is established, perform the following steps to enable DDNS.
1. Access and log into the configuration interface.
2. Click the Utilities tab.
3. Click DDNS in the side menu to display the DDNS configuration screen.
4. Click the DDNS Enable checkbox.
Note: Refer to Utilities- DDNS in Section 2 - Web GUI Screens and Configuration
Parameter Reference for specific instructions on setting the various DDNS
configuration parameters.
5. After setting the necessary configuration parameters, click the Apply button at the bottom
of the screen.
Page 32 of 96 November 2013
Page 33

Section 2
Web GUI Screens and
Configuration Parameter
Reference
Page 34

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
4 Introduction
This section shows the ARRIS graphical user interface (GUI) router setup screens.
Each of the following six tabs in the GUI and their individual sub-menus and configuration
parameters are explained in detail:
Basic Setup
WAN Setup
LAN Setup
Wireless Setup
Firewall
Utilities
Page 34 of 96 November 2013
Page 35

5 Basic Setup
5.1 BASIC SETUP – Login
Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
The default user name is “admin”. Valid characters are the numbers 0 to 9, the letters a through
z, and printable special characters (such as $, !, ?, &, #, @, and others.)
Login:
User Name – Current user name.
Password – Enter a password for this user. Passwords are case-sensitive. Valid characters are
the numbers 0 to 9, the letters a through z and A through Z, and printable special characters
(such as $, !, ?, &, #, @, and others.)
November 2013 Page 35 of 96
Page 36

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
5.2 Basic SETUP – System Basic Setup – WPA-PSK or WPA2/PSK
Security (default)
While your system has many configuration options, the options on this Basic Setup page are
those required by most users. Click the tabs to access the other configuration pages to set
advanced options. Hover the mouse pointer over the question mark icon next to an option to
view a description of that option. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Page 36 of 96 November 2013
Page 37

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
Basic Setup:
Language – Sets the language for the screen display text.
Host Name – The host name of the router.
Routing Enabled – Click this checkbox to enable routing on your network.
Wireless 2.4 GHz/Wireless 5 GHz:
Enable Wireless – Click this checkbox to enable the wireless network on your system.
Wireless Network Name (SSID)– Enter a user friendly name to identify your wireless network.
This name is also referred to as the Service Set Identifier (SSID). The name can be up to 32
characters long.
Pre-Shared Key - Sets your WPA Pre-Shared Key. This text string is used to generate a unique set
of encryption keys for your network. Enter a text string in this field. The key can be either ASCII
(text) or Hex (hexadecimal). An ASCII text key can be from 8 to 63 characters long. Valid
characters are numbers “0” through “9” and letters “a” through “z”, and printable special
characters (such as $, !, ?, &, #, @, and others). A hexadecimal key must be 64 characters long.
Valid characters are numbers “0” through “9” and letters “a” through “f”.
2.4G/5G WPS Settings:
WPS Enable - Click this checkbox to enable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) on your system. WPS is
a standard method for easily configuring a secure connection between your router and
computers or other wireless devices (known as enrollees) that support WPS. When WPS is
enabled you can attach other wireless devices by pressing the WPS buttons on the device (if
equipped) and on your router, or by entering the enrollee’s PIN and then clicking the Start WPS
Association icon.
Device PIN Code: - Enter this code on your computer if requested during connection.
WPS Mode – Sets the encryption method for WPS. Can be set to PBC (Push Button Control) or
PIN Code.
If using PBC, press the WPS buttons on the client device and on your router simultaneously to
start the WPS association. If using PIN codes, enter the enrollee’s PIN in the Enrollee PIN Code
field, and then click the Start WPS Association icon.
If the connection is successful, the WPS indicator light on the router stops flashing and remains
lit. If unsuccessful, the WPS light continues to flash for up to two minutes (indicating that it’s
ready to accept a client connection) and then turns off. If the WPS light turns off, start the
association process over.
Enrollee PIN Code – If your client device has a WPS PIN number, enter it here, then click the
Start WPS Association icon.
November 2013 Page 37 of 96
Page 38

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Start WPS Association – Click the WPS icon after entering the enrollee’s PIN to configure the
network connection to the device.
Page 38 of 96 November 2013
Page 39

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
5.3 BASIC SETUP – Change Password
Click Change Password in the side menu and follow the screen instructions to change your
password. Use a password that will not be easy to guess. Passwords are case-sensitive. Valid
characters are the numbers 0 to 9, the letters a through z and A through Z, and printable special
characters (such as $, !, ?, &, #, @, and others). You must click the Apply button to save your
new password.
Note: You must be logged into the configuration interface via a direct wired Ethernet
connection to change your password.
Change Password:
Old Password – Enter your existing password.
New Password – Enter your new password.
Repeat New Password – Re-enter your new password.
November 2013 Page 39 of 96
Page 40

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
6 WAN Setup
6.1 WAN SETUP – Dynamic Configuration Settings
A dynamic connection type is the most common. The router gets its IP address from a DHCP
server at the cable company. If you are not sure of your connection type, use this type. For
changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Dynamic Configuration:
Enable DHCP – Click this checkbox to enable a DHCP connection for your system.
IP Address – This field displays the IP address.
Subnet Mask – This field displays the subnet mask.
Gateway Address – This field displays the gateway address.
Page 40 of 96 November 2013
Page 41

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
6.2 WAN SETUP – Static IP Connection Type
A static IP address connection type is less common than others and uses a permanent IP address
to connect to the Internet. If your Internet Service Provider gives you an IP address that never
changes, then use this option. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Static IP Settings:
Enable Static IP - Click this checkbox to enable a static IP address connection for your system.
IP Address – Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP or static IP operation.
Subnet Mask – Enter the subnet mask assigned for your device by your ISP or static IP operation.
Gateway Address – Enter the gateway address assigned for your device by your ISP or static IP
operation.
Primary DNS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server. Your ISP will provide
this information.
Secondary DNS Server IP - Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server. Your ISP will
provide this information.
Tertiary DNS Server IP - Enter the IP address of the tertiary DNS server. Your ISP will provide this
information.
November 2013 Page 41 of 96
Page 42

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Domain Name – The entry here will be displayed as the domain name on your client devices. It
can be specified by your ISP or by you.
MTU Size – This field displays the size of the maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the network
connection. The default value is 1500. Advanced option – do not change unless instructed by
your Service Provider.
Page 42 of 96 November 2013
Page 43

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
6.3 WAN SETUP – Dynamic Configuration Settings (IPV6)
This screen enables a DHCPv6 configured IPV6 stack. A dynamic connection type is the most
common.
The router gets its IP address from a DHCP server at the cable company. If you are not sure of
your connection type, use this type. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Dynamic Configuration (IPV6):
Enable DHCP (IPV6) – Click this checkbox to enable a DHCP (IPV6) connection for your system.
IP Address V6 – This field displays the IPV6 address automatically assigned by the MSO. An IPV6
address has eight groups of four hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f). The groups are separated by
colons (:) e.g. 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. A double colon (::) is shorthand for
an address of all zeros.
Delegated Prefix – This field displays the assigned IPV6 prefix to be used by addresses allocated
in the local network.
Delegated Prefix Length – This field displays the assigned IPV6 prefix length.
IPV6 Gateway Address – This field displays the gateway address.
November 2013 Page 43 of 96
Page 44

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
6.4 WAN SETUP – Static IP Connection Type (IPV6)
This screen enables a statically configured IPV6 stack. A static IP address connection type is less
common than others and uses a permanent IP address to connect to the Internet. If your
Internet Service Provider gives you an IP address that never changes, then use this option. For
changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Static IP Settings (IPV6):
Enable Static IPV6 - Click this checkbox to enable a static IPV6 address connection for your
system.
IP Address V6– Enter the IPV6 address assigned by your ISP or static IP operation. An IPV6
address has eight groups of four hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f). The groups are separated by
colons (:) e.g. 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. A double colon (::) is shorthand for
an address of all zeros.
Prefix Length (IPV6) – The length of the network portion of this address.
IPV6 Gateway Address – Enter the gateway address assigned for your device by your ISP or static
IP operation.
Page 44 of 96 November 2013
Page 45

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
Primary DNS Server (IPV6) – Enter the IPV6 address of the primary DNS server. Your ISP will
provide this information.
Secondary DNS Server (IPV6) – Enter the IPV6 address of the secondary DNS server. Your ISP
will provide this information.
Domain Name – The entry here will be displayed as the domain name on your client devices. It
can be specified by your ISP or by you.
Delegated Prefix Length – The length of the network portion of the IPV6 addresses to be
allocated to local clients.
Delegated Prefix – The network portion of the IPV6 addresses to be allocated to local clients.
November 2013 Page 45 of 96
Page 46

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
6.5 WAN SETUP – Routing (Technician Level Only)
This screen allows dynamic routing to be enabled and configured. Only change these values if
your service provider recommends that you do so.
Dynamic Routing (RIP):
Enable Dynamic Routing (RIP) - Click this checkbox to enable Dynamic Routing on your system.
RIP IP Address – Enter the router IP address.
Auth Mode – Select Disabled, Text, or MD5 as appropriate for your network.
Keychain – For MD5, enter the keychain name.
Keystring – For Text/MD5, enter the keystring name.
Key ID – For MD5, enter the RIP authentication key ID.
Routed Subnet:
Routed Subnet Enabled – Click this checkbox to route the selected subnet.
Page 46 of 96 November 2013
Page 47

Note: If enabled, the RIP routed subnet network IP address will be advertised with the
next hop as the CM IP address.
Routed Subnet DHCP Enabled – Click this checkbox to provide DHCP to devices on this network.
Note: If enabled, then a public DHCP server will be started on the device for the routed
subnet. If disabled then the public DHCP server will not be started and all LAN-based CPE
devices will need to be assigned public static IP addresses.
Routed Subnet Gateway Address – Enter the address of the router that handles traffic between
this subnet and the rest of the Internet.
Note: This is the gateway IP address for the routable subnet.
Routed Subnet Netmask – Enter the subnet mask.
Note: This is the subnet mask used for the routed subnet.
Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
November 2013 Page 47 of 96
Page 48

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
7 LAN Setup
7.1 LAN SETUP – LAN Settings
Page 48 of 96 November 2013
Page 49

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
You can make changes to the Local Area Network (LAN) configuration here. For changes to take
effect, you must click the Apply button.
LAN Segment: (Technician Level Only)
LAN – Selects the LAN index or identifier for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
LAN IP Settings:
IP Address – This field displays the IP address of your LAN.
Subnet Mask – This field displays the subnet mask of your LAN.
DHCP Server Settings:
Enable DHCP Server – Click this checkbox to enable the use of a Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) Server on your network.
DHCP is a set of rules used by devices such as a computer, router, or network adapter to allow
the device to request and obtain an IP address from a server which maintains a list of addresses
available for use.
The DHCP server ensures that all IP addresses are unique, e.g., no IP address is assigned to a
second device while the first device's assignment is valid (its lease has not expired).
Without DHCP, the IP addresses must be entered manually at each computer in an organization
and a new IP address must be entered each time a computer moves to a new location on the
network.
Start IP Address – Enter the starting address in the range of IP addresses that the DHCP Server
will be allowed to assign to a network device.
End IP Address – Enter the ending address in the range of IP addresses that the DHCP Server will
be allowed to assign to a network device.
Lease Time – Enter the lease time in seconds before the assigned IP address will expire. (After
the lease time is up, the user is automatically assigned a new dynamic IP address.)
DHCP uses the concept of a "lease" or amount of time that a given IP address will be valid for a
computer or other network device. The lease time can vary depending on how long a user is
likely to require the Internet connection at a particular location. Using very short leases, DHCP
can dynamically reconfigure networks where there are more computers than available IP
addresses, such as educational environments.
November 2013 Page 49 of 96
Page 50

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Domain Name – This field displays the domain name.
DNS Override:
Enable DNS Override – Click this checkbox to enable DNS Override and replace the DNS server
addresses provided by your service provider.
Primary DNS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server. Your ISP will provide
this information.
Secondary DNS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server. Your ISP will
provide this information.
Tertiary DNS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the tertiary DNS server. Your ISP will provide
this information.
DNS Relay:
Enable DNS Relay – Click this checkbox to enable DNS Relay and mask the DNS address.
Click this checkbox to enable Domain Name System (DNS) relay functionality on your system.
The DNS Relay feature allows the system to act as a DNS server to other IP stations, while it
simply forwards the requests to real DNS servers and then sends their responses back to the
original requesters. Your gateway basically acts as an intermediate between the requester and
the real DNS servers. When DNS Relay is enabled, the gateway will act as a DNS server, send
requests to the Internet Service Provider's DNS server, and cache the information for later
access. When DNS relay is disabled, the computer will pull domain name/IP address information
directly from the ISP's DNS server.
NAT:
NAT Mode – Select the NAT Mode. Bridged - Data will pass through the device directly without
any routing. Routed with NAT - Data will be routed by the device and all the outgoing packets
will be NATed. Routed without NAT - Data will be routed by the device but all the outgoing
packets will not be NATed.
UPnP:
Enable UPnP – Click this checkbox to enable UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) on the system.
Page 50 of 96 November 2013
Page 51

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
7.2 LAN SETUP – LAN Settings (IPV6)
This screen configures LAN side support for IPV6. You can make changes to the Local Area
Network (LAN) configuration here. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
LAN Segment: (Technician Level Only)
LAN – Selects the LAN index or identifier for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
November 2013 Page 51 of 96
Page 52

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
LAN Settings (IPV6):
IP Address (IPV6) – This field displays the IPV6 address of your LAN. An IPV6 address has eight
groups of four hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f). The groups are separated by colons (:) e.g.
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. A double colon (::) is shorthand for an address of
all zeros.
Prefix Length V6 – Length of the network portion of the IPV6 address.
Link Local Address (IPV6) – IPV6 address that can be used only on this network.
DHCP Server Settings (IPV6):
Enable DHCP Server (IPV6) – Click this checkbox to enable the use of a V6 Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server on your network.
DHCP is a set of rules used by devices such as a computer, router, or network adapter to allow
the device to request and obtain an IP address from a server which maintains a list of addresses
available for use.
The DHCP server ensures that all IP addresses are unique, e.g., no IP address is assigned to a
second device while the first device's assignment is valid (its lease has not expired).
Without DHCP, the IP addresses must be entered manually at each computer in an organization
and a new IP address must be entered each time a computer moves to a new location on the
network.
Start IP Address (IPV6) – Enter the starting address in the range of IPV6 addresses that the DHCP
Server will be allowed to assign to a network device.
End IP Address (IPV6) – Enter the ending address in the range of IPV6 addresses that the DHCP
Server will be allowed to assign to a network device.
Lease Time V6 – Enter the lease time in seconds before the assigned IPV6 address will expire.
(After the lease time is up, the user is automatically assigned a new dynamic IP address.)
DHCP uses the concept of a "lease" or amount of time that a given IP address will be valid for a
computer or other network device. The lease time can vary depending on how long a user is
likely to require the Internet connection at a particular location. Using very short leases, DHCP
can dynamically reconfigure networks where there are more computers than available IP
addresses, such as educational environments.
DNS Override:
Enable DNS Override – Click this checkbox to enable DNS Override and replace the DNS server
addresses provided by your service provider.
Primary DNS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server. Your ISP will provide
this information.
Page 52 of 96 November 2013
Page 53

Secondary DNS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server. Your ISP will
provide this information.
Tertiary DNS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the tertiary DNS server. Your ISP will provide
this information.
DNS Relay:
Enable DNS Relay – Click this checkbox to enable DNS Relay and mask the DNS address.
Click this checkbox to enable Domain Name System (DNS) relay functionality on your system.
The DNS Relay feature allows the system to act as a DNS server to other IP stations, while it
simply forwards the requests to real DNS servers and then sends their responses back to the
original requesters. Your gateway basically acts as an intermediate between the requester and
the real DNS servers. When DNS Relay is enabled, the gateway will act as a DNS server, send
requests to the Internet Service Provider's DNS server, and cache the information for later
access. When DNS relay is disabled, the computer will pull domain name/IP address information
directly from the ISP's DNS server.
Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
November 2013 Page 53 of 96
Page 54

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
7.3 LAN Setup – Client List
This page shows the host Name, IP address, and MAC Address of each computer that is
connected to your network. If a computer does not have a specified host name, then the host
Name field will be blank.
LAN Segment: (Technician Level Only)
LAN – Selects the LAN index or identifier for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
Reserved IP Client List:
Click the Add button to create a new fixed client lease.
Page 54 of 96 November 2013
Page 55

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
Name – Enter a name for the client.
IP Address – Enter the client’s IP address.
MAC Address – Enter the client’s MAC address.
Select a client and then click the Delete button to delete the client lease.
Attached Client List:
Click the Refresh button to update the client list.
November 2013 Page 55 of 96
Page 56

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
7.4 LAN Setup – Ports
This page allows the Ethernet ports to be configured. This is an advanced feature and should
not be set unless requested by your service provider.
Select Ethernet Port – Select the Ethernet port to be configured.
Ethernet Port Setup: (Technician Level Only)
Enabled – Click this checkbox to enable the selected port.
Auto – Click this checkbox to enable automatic configuration. When enabled, the port
automatically sets its duplex mode and speed.
Duplex – If Auto is not enabled, select the communication mode for the port. Can be set to Full
Duplex or Half Duplex.
Speed – If Auto is not enabled, select the speed for the port. Can be set to 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps,
or 1,000 Mbps.
Page 56 of 96 November 2013
Page 57

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
8 Wireless Setup
8.1 Wireless 2.4 GHz – System Basic Setup
While your system has many configuration options, the options on this Basic Setup page are
those required by most users. Click the tabs to access the other configuration pages to set
advanced options. Hover the mouse pointer over the question mark icon next to an option to
view a description of that option. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Wireless: (Technician Level Only)
SSID – Sets the SSID for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
November 2013 Page 57 of 96
Page 58

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Basic Setup:
Enable Wireless – Click this checkbox to enable the wireless network on your system.
Wireless Network Name – Enter a user friendly name to identify your wireless network. This
name is also referred to as the Service Set Identifier (SSID). The name can be up to 32
characters long.
Broadcast Network Name (SSID) – Click this checkbox to allow the SSID to be broadcast by the
router. If enabled, your SSID could be obtained allowing unauthorized access to your network.
If you would like others not to see your access point, uncheck the checkbox to hide the SSID.
Tx Power Level – Sets the transmit power level, which is the output power level of the wireless
radio. Can be set to High, Medium, or Low.
Channel – Sets a communications channel for your router. The default setting is “Auto”, in
which the router selects a channel with the least amount of interference to use. For 2.4 GHz, if
you manually select a channel, it’s best to choose channel 1, 6, or 11, since these channels do
not overlap. If another unit is operating in the area, choose a channel that is farthest away from
the channel that unit uses. For example, if one is using channel 11, set yours to channel 1. For 5
GHz choose a channel that is farthest away from the channel used by any other unit operating in
the area. If you experience interference or poor performance on a particular channel, try a
different channel.
AP Isolation – Click this checkbox to enable AP isolation. When enabled each of your wireless
clients will be in its own virtual network and will not be able to communicate with one another.
This may be useful if you have many quests using your network.
Enable WMM – Click this checkbox to enable Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) functionality. Enabling
WMM can help control latency and jitter when transmitting multimedia content over a wireless
connection. Disabling WMM will reduce wireless performance in 802.11n mode.
This quality of service mechanism uses four access categories, which in order of priority are:
voice, video, best effort, and background. This ensures that applications with low tolerance for
latency and jitter are treated with higher priority than less-sensitive data applications. WMM
sets different wait times for the four categories in order to provide priority network access for
applications that are less tolerant of packet delays.
Security Mode – Sets the security mode for your router. Can be set to OPEN (no security) WEP
(64/128) (Wired Equivalency Privacy – 64/128) (poor security), WPA/WPA2-PSK (TKIP/AES) (WiFi Protected Access/ Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 – Pre-Shared Key – TKIP/AES encryption) (most
compatible), WPA2-PSK (AES) (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 – Pre-Shared Key – AES encryption)
(recommended), WPA Enterprise, or WPA2 Enterprise. 802.11n performance is only available in
Open or WPA2 with AES encryption.
Pre-Shared Key - Sets your WPA Pre-Shared Key. This text string is used to generate a unique set
of encryption keys for your network. Enter a text string in this field. The key can be either ASCII
(text) or Hex (hexadecimal). An ASCII text key can be from 8 to 63 characters long. Valid
characters are numbers “0” through “9” and letters “a” through “z”, and printable special
Page 58 of 96 November 2013
Page 59

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
characters (such as $, !, ?, &, #, @, and others). A hexadecimal key must be 64 characters long.
Valid characters are numbers “0” through “9” and letters “a” through “f”.
November 2013 Page 59 of 96
Page 60

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
8.2 Wireless 2.4 GHz – Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings page is used to set up the router’s advanced wireless functions. These
settings should only be adjusted by an expert administrator since incorrect settings can reduce
wireless performance. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Wireless Network Settings:
Wireless Mode – Sets the wireless mode. Options are: B/G mixed, B only, G only, N only, G/N
mixed, and B/G/N mixed. Select the proper mode to support all of the wireless devices that will
connect to your router. 802.11b supports bandwidth up to 11 Mb/s. 802.11g supports
bandwidth up to 54 Mb/s. 802.11n supports bandwidth up to 300 Mb/s.
BG Protection – Sets the BG protection mode. Options are OFF or AUTO. Default is AUTO
(checkbox checked).
BG protection allows you to operate 802.11b client devices in 802.11g networks. Set to AUTO
(enabled) to allow 802.11b client devices to operate in the 802.11g wireless network. This will
Page 60 of 96 November 2013
Page 61

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
impact the performance of the 802.11g client devices on the network. If your network consists
of ONLY 802.11g client devices, set this to OFF (disabled) for maximum performance.
Note: These older 802.11b devices required the unit to add overhead to most
transmissions. Performance will increase if no 802.11b devices are present and this
feature is disabled (OFF). The unit will auto detect 802.11b devices and set the feature
accordingly when the BG protection checkbox is checked (AUTO).
Beacon Interval – Sets the time interval between beacon transmissions in milliseconds. The
router uses these transmissions to synchronize the wireless network and its client devices. For
compliance with most client devices, the Beacon Interval should remain set at the default of
100ms. The allowable setting range is from 20 to 1024ms.
DTM Interval – Sets the DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) Interval. The DTIM Interval
informs the wireless client devices of the next available window for listening to broadcast and
multicast messages. When the router sends a DTIM beacon the client devices hear the beacon
and then listen for the messages. For compliance with most client devices, the DTIM Interval
should be left at 1 ms. The allowable setting range is from 1 to 255 ms.
RTS Threshold – Sets the packet size limit. When the threshold is passed, the ready to
send/clear to send (RTS/CTS) function is invoked. The default setting is 2347 bytes. The
allowable setting range is from 1 to 2347 bytes.
Fragment Threshold – Sets the fragmentation threshold. This threshold should be set to equal
the maximum Ethernet frame size allowable on the link including overhead. Setting a lower
threshold can damage data throughput since large frames could be fragmented and/or collisions
could occur. The default setting is 2346. The allowable setting range is from 256 to 2346 bytes.
Frame Burst – Click this checkbox to enable Frame Burst on your network. Frame Bursting is a
transmission technique that increases the throughput of point-to-point 802.11a, b, or g links by
reducing the overhead associated with the wireless transmissions. This results in the ability to
support higher data throughput in mixed and uniform networks. It can, however, result in
unfair allocation of airtime where there are a mix of client devices on the network, of which only
some support Frame-Bursting.
WMM Power Save Mode – Click this checkbox to enable WMM Power Save Mode. WMM
Power Save delivery is a more efficient power management method than legacy 802.11 power
save polling.
Enable Radio (Technician level only) – Click this checkbox to enable or disable the WiFi radio.
802.11n Specific Settings:
Operation Mode – Sets the 802.11n Operation Mode. Options are Mixed Mode or Greenfield.
The default, Mixed Mode, is for networks with a mix of 802.11a/b/g/n client devices. The
optional Greenfield mode improves efficiency of networks using only 802.11n devices by
eliminating support for the 802.11a/b/g client devices.
November 2013 Page 61 of 96
Page 62

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Channel Bandwidth – Sets the 802.11n Channel Bandwidth. Options are 20 MHz or 20/40 MHz.
The default setting is 20/40 MHz. If your wireless network is in a very clean RF environment
setting the Channel Bandwidth to 20/40 will increase your throughput by “bonding” two
channels. However, if there are any other wireless routers or access points within range of the
device it will stay in 20 MHz bandwidth regardless of this setting. This is a WiFi Alliance
requirement. (You can verify the channel bandwidth by using the previously mentioned wireless
network scanning software, MetaGeek’s inSSIDer.)
Guard Interval – The spacing between transmission of symbols in nanoseconds. Can be set to
AUTO, 400ns or 800ns. The default is AUTO. Selecting 400ns provides higher throughput in
networks where the coverage distance is small (indoors). Selecting 800ns provides higher
throughput in networks where the coverage distance is large (outdoors).
MCS – Sets the 802.11n Modulation and Coding Scheme to be used. Options are 1 through 23
Legacy and AUTO. The default is AUTO. The 802.11n standard defines a total of 77 MCS. Each
MCS specifies a certain modulation type (BPSK, QPSK, 64-QAM), coding rate (1/2, 3/4), guard
interval (800 or 400ns), and number of spatial streams. Support for MCS 0 - 15 is mandatory for
802.11n access points while support for MCS 0 - 7 is mandatory for 802.11n clients.
Page 62 of 96 November 2013
Page 63

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
8.3 Wireless 2.4 GHz – MAC Address Control
MAC Address Control allows you to restrict access to your network to only those client devices
whose MAC addresses you add to the filter list. You can make changes to the Media Access
Control (MAC) Address Filtering List on this page. For changes to take effect, you must click the
Apply button.
Wireless: (Technician Level only)
SSID – Sets the SSID for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
MAC Address Filtering:
MAC Address Filter Type – Sets the MAC address filter type. None – Allows any device to try to
connect. Allowed List – Allows any listed device to connect. Blocked List – Allows any device
not listed to connect. Note that the correct access keys must still be entered if required.
November 2013 Page 63 of 96
Page 64

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
MAC Address Filter List:
Click the Add button to add another client device’s MAC address to the filter list.
MAC Address – Enter the MAC address of the wireless client device.
Select a MAC address in the list and then click the Delete button to delete it from the filter list.
Page 64 of 96 November 2013
Page 65

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
8.4 Wireless 2.4 GHz – Wireless Client List
This page displays the Name, IP address, and MAC address of each computer or other client
device connected to your network. Click the Refresh button to update the list.
Wireless: (Technician Level only)
SSID – Sets the SSID for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
Wireless Client List:
Click the Refresh button to update the wireless client list.
November 2013 Page 65 of 96
Page 66

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
8.5 Wireless 5 GHz – System Basic Setup
While your system has many configuration options, the options on this Basic Setup page are
those required by most users. Click the tabs to access the other configuration pages to set
advanced options. Hover the mouse pointer over the question mark icon next to an option to
view a description of that option. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Wireless: (Technician Level Only)
SSID – Sets the SSID for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
Basic Setup:
Enable Wireless – Click this checkbox to enable the wireless network on your system.
Page 66 of 96 November 2013
Page 67

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
Wireless Network Name – Enter a user friendly name to identify your wireless network. This
name is also referred to as the Service Set Identifier (SSID). The name can be up to 32
characters long.
Broadcast Network Name (SSID) – Click this checkbox to allow the SSID to be broadcast by the
router. If enabled, your SSID could be obtained allowing unauthorized access to your network.
If you would like others not to see your access point, uncheck the checkbox to hide the SSID.
Tx Power Level – Sets the transmit power level, which is the output power level of the wireless
radio. Can be set to High, Medium, or Low.
Channel – Sets a communications channel for your router. The default setting is “Auto”, in
which the router selects a channel with the least amount of interference to use. If you manually
select a channel and another unit is operating in the area, choose a channel that is farthest away
from the channel that unit uses. If you experience interference or poor performance on a
particular channel, try a different channel.
AP Isolation – Click this checkbox to enable AP isolation. When enabled each of your wireless
clients will be in its own virtual network and will not be able to communicate with one another.
This may be useful if you have many quests using your network.
Enable WMM – Click this checkbox to enable Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) functionality. Enabling
WMM can help control latency and jitter when transmitting multimedia content over a wireless
connection.
This quality of service mechanism uses four access categories, which in order of priority are:
voice, video, best effort, and background. This ensures that applications with low tolerance for
latency and jitter are treated with higher priority than less-sensitive data applications. WMM
sets different wait times for the four categories in order to provide priority network access for
applications that are less tolerant of packet delays.
Security Mode – Sets the security mode for your router. Can be set to OPEN (no security) WEP
(64/128) (Wired Equivalency Privacy – 64/128) (poor security), WPA/WPA2-PSK (TKIP/AES) (WiFi Protected Access/ Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 – Pre-Shared Key – TKIP/AES encryption) (most
compatible), WPA2-PSK (AES) (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 – Pre-Shared Key – AES encryption)
(recommended), WPA Enterprise, or WPA2 Enterprise. 802.11n performance is only available in
Open or WPA2 with AES encryption.
Pre-Shared Key - Sets your WPA Pre-Shared Key. This text string is used to generate a unique set
of encryption keys for your network. Enter a text string in this field. The key can be either ASCII
(text) or Hex (hexadecimal). An ASCII text key can be from 8 to 63 characters long. Valid
characters are numbers “0” through “9” and letters “a” through “z”, and printable special
characters (such as $, !, ?, &, #, @, and others). A hexadecimal key must be 64 characters long.
Valid characters are numbers “0” through “9” and letters “a” through “f”.
November 2013 Page 67 of 96
Page 68

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
8.6 Wireless 5 GHz – Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings page is used to set up the router’s advanced wireless functions. These
settings should only be adjusted by an expert administrator since incorrect settings can reduce
wireless performance. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Wireless Network Settings:
Wireless Mode – Sets the wireless mode. Options are: A only, N only, and A/N mixed. Select
the proper mode to support all of the wireless devices that will connect to your router.
Beacon Interval – Sets the time interval between beacon transmissions in milliseconds. The
router uses these transmissions to synchronize the wireless network and its client devices. For
compliance with most client devices, the Beacon Interval should remain set at the default of
100ms. The allowable setting range is from 20 to 1024ms.
DTM Interval – Sets the DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) Interval. The DTIM Interval
informs the wireless client devices of the next available window for listening to broadcast and
multicast messages. When the router sends a DTIM beacon the client devices hear the beacon
and then listen for the messages. For compliance with most client devices, the DTIM Interval
should be left at 1 ms. The allowable setting range is from 1 to 255 ms.
Page 68 of 96 November 2013
Page 69

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
RTS Threshold – Sets the packet size limit. When the threshold is passed, the ready to
send/clear to send (RTS/CTS) function is invoked. The default setting is 2347 bytes. The
allowable setting range is from 1 to 2347 bytes.
Fragment Threshold – Sets the fragmentation threshold. This threshold should be set to equal
the maximum Ethernet frame size allowable on the link including overhead. Setting a lower
threshold can damage data throughput since large frames could be fragmented and/or collisions
could occur. The default setting is 2346. The allowable setting range is from 256 to 2346 bytes.
Frame Burst – Click this checkbox to enable Frame Burst on your network. Frame Bursting is a
transmission technique that increases the throughput of point-to-point 802.11a, b, or g links by
reducing the overhead associated with the wireless transmissions. This results in the ability to
support higher data throughput in mixed and uniform networks. It can, however, result in
unfair allocation of airtime where there are a mix of client devices on the network, of which only
some support Frame-Bursting.
WMM Power Save Mode – Click this checkbox to enable WMM Power Save Mode. WMM
Power Save delivery is a more efficient power management method than legacy 802.11 power
save polling.
Enable Radio (Technician level only) – Click this checkbox to enable or disable the WiFi radio.
802.11n Specific Settings:
Channel Bandwidth – Sets the 802.11n Channel Bandwidth. Options are 20 MHz or 20/40 MHz.
The default setting is 20/40 MHz. If your wireless network is in a very clean RF environment
setting the Channel Bandwidth to 20/40 will increase your throughput by “bonding” two
channels. However, if there are any other wireless routers or access points within range of the
device it will stay in 20 MHz bandwidth regardless of this setting. This is a WiFi Alliance
requirement. (You can verify the channel bandwidth by using the previously mentioned wireless
network scanning software, MetaGeek’s inSSIDer.)
Guard Interval – The spacing between transmission of symbols in nanoseconds. Can be set to
AUTO, 400ns or 800ns. The default is AUTO. Selecting 400ns provides higher throughput in
networks where the coverage distance is small (indoors). Selecting 800ns provides higher
throughput in networks where the coverage distance is large (outdoors).
MCS – Sets the 802.11n Modulation and Coding Scheme to be used. Options are 1 through 23
Legacy and AUTO. The default is AUTO. The 802.11n standard defines a total of 77 MCS. Each
MCS specifies a certain modulation type (BPSK, QPSK, 64-QAM), coding rate (1/2, 3/4), guard
interval (800 or 400ns), and number of spatial streams. Support for MCS 0 - 15 is mandatory for
802.11n access points while support for MCS 0 - 7 is mandatory for 802.11n clients.
November 2013 Page 69 of 96
Page 70

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
8.7 Wireless 5 GHz – MAC Address Control
MAC Address Control allows you to restrict access to your network to only those client devices
whose MAC addresses you add to the filter list. You can make changes to the Media Access
Control (MAC) Address Filtering List on this page. For changes to take effect, you must click the
Apply button.
Wireless: (Technician Level only)
SSID – Sets the SSID for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
MAC Address Filtering:
MAC Address Filter Type – Sets the MAC address filter type. None – Allows any device to try to
connect. Allowed List – Allows any listed device to connect. Blocked List – Allows any device
not listed to connect. Note that the correct access keys must still be entered if required.
Page 70 of 96 November 2013
Page 71

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
MAC Address Filter List:
Click the Add button to add another client device’s MAC address to the filter list.
MAC Address – Enter the MAC address of the wireless client device.
Select a MAC address in the list and then click the Delete button to delete it from the filter list.
November 2013 Page 71 of 96
Page 72

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
8.8 Wireless 5 GHz – Wireless Client List
This page displays the Name, IP address, and MAC address of each computer or other client
device connected to your network. Click the Refresh button to update the list.
Wireless: (Technician Level only)
SSID – Sets the SSID for each individual LAN on your network.
Note: You can optionally set up the system so that there is more than one LAN in your
network. This is most useful for commercial applications not home use. All of the “LAN
Setup” and “Wireless Setup” configuration parameters can be set independently for each
individual LAN.
Wireless Client List:
Click the Refresh button to update the wireless client list.
Page 72 of 96 November 2013
Page 73

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
9 Firewall
9.1 Firewall – Firewall Settings
Your router is equipped with a firewall that will protect your network from a wide array of
common hacker attacks, including Ping of Death (PoD) and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. You
can also configure VPN pass-through to enable VPN tunneling using IPSec, PPTP, or L2TP
protocols to pass through the router’s firewall so that you can connect to a Virtual Private
Network at your office, for example.
November 2013 Page 73 of 96
Page 74

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
You can disable the firewall function if needed. Turning off the firewall protection will not leave
your network completely vulnerable to hacker attacks, but it is recommended that you enable
the firewall whenever possible. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Firewall Enable/Disable
Enable Firewall – Click this checkbox to enable the firewall on your system.
DoS Attack Protection:
Enable DoS Attack Protection Firewall – Click this checkbox to enable DoS attack protection.
Block Pings:
Enable Block Pings – Click this checkbox to enable ping blocking.
IPSec Pass Through:
Enable IPSec Pass Through – Click this checkbox to enable IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) pass
through. This allows IPSec tunnels to pass through the firewall.
PPTP Pass Through:
Enable PPTP Pass Through – Click this checkbox to enable PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling
Protocol) pass through. This allows PPTP tunnels to pass through the firewall.
L2TP Pass Through:
Enable L2TP Pass Through – Click this checkbox to enable L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) pass
through. This allows L2TP tunnels to pass through the firewall.
Block Fragmented IP Packets:
Enable Block Fragmented IP Packets – Click this checkbox to enable fragmented IP packet
blocking.
Page 74 of 96 November 2013
Page 75

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
9.2 Firewall –Virtual Servers Configuration (Port Forwarding)
The port forwarding function forwards inbound traffic from the Internet to a specified single
device on your network. Examples include allowing access to a web server on your network,
peer-to-peer file sharing, some gaming and videoconferencing applications, and others. This
function allows you to route external (Internet) calls for services such as a web server (port 80),
FTP server (Port 21), or other applications through your router to your internal network.
Click the Add button to add a virtual server. Select a virtual server from the list and click the
Delete button to delete a virtual server.
Virtual Servers:
Description – Enter a name for the virtual server.
Inbound Port – Enter the inbound port range for the virtual server. It should be the same range
as the local port.
Format – Sets the format for the port. Options are TCP, UDP, or BOTH.
Private IP Address – Enter the IP address of the machine on the LAN that you want
the connections to go to.
Local Port – Enter the local port range for the virtual server. It should be the same range as the
inbound port.
November 2013 Page 75 of 96
Page 76

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
9.3 Firewall – Port Triggers Configuration
Port triggering lets you set the router to watch outgoing traffic for specific port numbers,
remember the IP address of the sending computer, and then route the data back to the sending
computer when the requested data returns. This is typically used for online gaming and online
chat applications.
Port triggers allow virtual servers to be allowed when an outbound port is accessed.
Click the Add button to add a port trigger. Select a port trigger from the list and click the Delete
button to delete a port trigger.
Port Triggers:
Description – Enter a name for the port trigger.
Outbound Port – Enter the outbound port range for the port trigger. It should be the same
range as the inbound port.
Format – Sets the format for the port. Options are TCP, UDP, or BOTH.
Inbound Port – Enter the inbound port range for the port trigger. It should be the same range as
the outbound port.
Page 76 of 96 November 2013
Page 77

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
9.4 Firewall – Client IP Filters Configuration
The router can be configured to restrict access to the Internet, email, or other network services
at specific days and times.
Client IP Filters:
Client IP Address – Enter the client IP address or range to filter.
Port – Enter the outbound traffic port number range, starting and ending.
Type – Sets the port type. Options are TCP, UDP, or BOTH.
Day – Click the check boxes for the days you want access allowed, or click the All Week checkbox
for all week.
Time – Sets the start time and end time for the allowed access during the specified days (24hour clock). 00:00 to 24:00 indicates all day, or click the checkbox for All Day.
November 2013 Page 77 of 96
Page 78

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
9.5 Firewall – Client IP Filters (IPV6) Configuration
The router can be configured to restrict access to the Internet, email, or other network services.
This screen adds and deletes filters for IPV6.
Client IP Filters:
Action/Direction - Select either Allow+Incoming or Deny+Outgoing to allow data watching this
filter and watch incoming data or deny data watching and watch outgoing data.
Client IP Address – Enter the range of IPV6 addresses to filter.
Port – Enter the outbound traffic port number range, starting and ending.
Type – Sets the port type. Options are TCP, UDP, or BOTH.
Day – Click the check boxes for the days you want access allowed, or click the All Week checkbox
for all week.
Page 78 of 96 November 2013
Page 79

Time – Sets the start time and end time for the allowed access during the specified days (24hour clock). 00:00 to 24:00 indicates all day, or click the checkbox for All Day.
Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
November 2013 Page 79 of 96
Page 80

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
9.6 Firewall – DMZ Settings
The DMZ feature allows you to specify one computer on your network to be placed outside of
the NAT firewall. This may be necessary if the NAT feature is causing problems with an
application such as a game or video conferencing application.
Use this feature only on a temporary basis. The computer in the DMZ is not protected from
hacker attacks.
To put a computer in the DMZ, click the Enable DMZ checkbox enter its IP address, and click the
Apply button.
IP Address Of Virtual DMZ Host:
Enable DMZ – Click this checkbox to enable DMZ on your network.
WAN IP – Displays the public IP address.
Private IP – Enter the IP address of the computer to be placed in the DMZ. Be sure that the
address is not in the range of addresses delivered by the DHCP server if enabled. After placing
the computer in the DMZ, all ports on the computer are open to the Internet and not protected.
Page 80 of 96 November 2013
Page 81

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
9.7 Firewall – Parental Controls
Parental Controls:
To enable Parental Controls on your network, check the Enable Parental Controls checkbox and
then click the Apply button. Parental Controls consist of Trusted MAC Addresses, Keyword
Filtering and Web Site Filtering. Enter any Trusted MAC Addresses and click the Apply button.
To add a Keyword or Web Site filter to the list, click the respective Add button. To delete a
Keyword or Web Site from the list, first click its checkbox and then click the Delete button.
Trusted MAC:
Trusted MAC Addresses – Enter the trusted MAC addresses. These MAC addresses will not be
affected by Parental Control settings. You can add a total of two trusted MAC addresses. If the
Trusted MAC Addresses fields are left empty, all source MAC addresses are trusted.
November 2013 Page 81 of 96
Page 82

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Keyword Filtering:
Keyword – Enter a keyword that you want to filter out.
Day – Click the check boxes for the days you want access blocked, or click the All Week checkbox
for all week.
Time – Sets the start time and end time for the blocked access during the specified days (24hour clock). 00:00 to 24:00 indicates all day, or click the checkbox for All Day.
Web Site Filtering:
Web Site – Enter the domain name of a web site that you want to filter out.
Day – Click the check boxes for the days you want access blocked, or click the All Week checkbox
for all week.
Time – Sets the start time and end time for the blocked access during the specified days (24hour clock). 00:00 to 24:00 indicates all day, or click the checkbox for All Day.
Page 82 of 96 November 2013
Page 83

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
9.8 Firewall – ALG Settings
Note: This screen is not used on all models.
Application layer gateway settings allow the router to recognize and treat certain network
protocols specially.
Application Layer Gateway:
Click the checkbox for each network protocol for which you want special handling.
November 2013 Page 83 of 96
Page 84

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
10 Utilities
10.1 Utilities – System Information
This page shows a summary of your system’s status.
Page 84 of 96 November 2013
Page 85

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
Hardware Software Version:
Serial Number – This field displays the product serial number.
Bootcode Version – This field displays the bootcode version.
Hardware Version – This field displays the hardware version.
Firmware Version – This field displays the firmware version.
WAN Status Summary:
WAN MAC Address – This field displays the WAN MAC address.
Connection Setup – This field displays the connection type: Dynamic or Static
IP Address – This field displays the WAN IP address.
Subnet Mask – This field displays the WAN subnet mask.
Domain Name – This field displays the domain name.
Primary DNS – This field displays the Primary DNS IP address.
Secondary DNS – This field displays the Secondary DNS IP address.
Tertiary DNS – This field displays the Tertiary DNS IP address.
Gateway – This field displays the gateway IP address.
Wireless 2.4 GHz Status Summary:
Wireless SSID – This field displays the Service Set Identifier (SSID), which is the wireless network
name.
Wireless Channel – This field displays the communications channel for your router.
Wireless Mode – This field displays the wireless mode: B/G mixed, B only, G only, N only, A only,
G/N mixed, A/N mixed, or B/G/N mixed.
SSID Broadcast – This field displays the status of the SSID Broadcast function: Enabled or
Disabled.
WMM – This field displays the status of the Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) function: Enabled or
Disabled.
MAC Address – This field displays the wireless adapter MAC Address.
Number of WiFi Clients – This field displays the number of wireless client devices connected to
the router.
November 2013 Page 85 of 96
Page 86

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Radio Status – This field displays the status of the wireless radio: Enabled or Disabled.
WPS Status - This field displays the status of the WPS function: Enabled or Disabled.
Wireless 5 GHz Status Summary:
Wireless SSID – This field displays the Service Set Identifier (SSID), which is the wireless network
name.
Wireless Channel – This field displays the communications channel for your router.
Wireless Mode – This field displays the wireless mode: A/N mixed, A only, or N only.
SSID Broadcast – This field displays the status of the SSID Broadcast function: Enabled or
Disabled.
WMM – This field displays the status of the Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) function: Enabled or
Disabled.
MAC Address – This field displays the wireless adapter MAC Address.
Number of WiFi Clients – This field displays the number of wireless client devices connected to
the router.
Radio Status – This field displays the status of the wireless radio: Enabled or Disabled.
WPS Status - This field displays the status of the WPS function: Enabled or Disabled.
LAN Status Summary:
IP Address – This field displays the IP Address of your LAN.
DHCP Server – This field displays the status of the DHCP Server: Enabled or Disabled.
DNS Relay – This field displays the status of the DNS Relay function: Enabled or Disabled.
Subnet Mask – This field displays the subnet mask of your LAN.
UPnP – This field displays the status of the UPnP feature: Enabled or Disabled.
Number of LAN Clients – This field displays the number of LAN client devices connected to the
gateway.
Page 86 of 96 November 2013
Page 87

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
10.2 Utilities –Restart Router
It may be necessary to restart (reboot) the router if it begins working improperly. Restarting the
router will not delete any of your configuration settings.
To restart the router, click the Restart button.
Note: A dialog box displays “This will restart your router. Current connections and
telephony may be interrupted.” Click OK to restart now or click Cancel to restart later.
November 2013 Page 87 of 96
Page 88

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
10.3 Utilities – Factory Defaults
This function restores all of the router’s configuration settings to the factory default setting.
Before restoring the factory defaults, you should back up your current configuration settings
using the Save/Backup Settings page.
Click the Factory Defaults button to restore the factory default configuration settings.
Note: A dialog box displays “This will restore your router to its factory state. Any
customizations you have made will be lost. Current connections and telephony may be
interrupted.” Click OK to restore now or click Cancel to restore later.
Page 88 of 96 November 2013
Page 89

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
10.4 Utilities – Save/Backup Settings
This function saves your current configuration settings, which allows you to restore them later if
your settings are lost or changed. Click the Save button to backup your current settings.
Note: A dialog box displays “This will take a few minutes. Continue? Click OK to save
settings now or click Cancel to save later.
When saving, follow the “file download” and “save as” dialog box instructions for your
specific browser to select a location to save the router.data backup file.
Important: Always backup your current settings before performing a firmware update.
November 2013 Page 89 of 96
Page 90

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
10.5 Utilities – Restore Settings
This function allows you to restore a previously saved configuration.
To restore a previous configuration: Use the Browse button to locate and select the previously
saved backup file. Then click the Restore Chosen File button.
Note: A dialog box displays “This will restore your router’s saved state. Current
connections, recordings, and telephony may be interrupted.” Click OK to restore now or
click Cancel to restore later.
Page 90 of 96 November 2013
Page 91

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
10.6 Utilities – System Settings
This page allows you to make certain system settings. For changes to take effect, you must click
the Apply button.
Login:
- (Technician Level Only) Click this button to change your login password. Enter
your old password and then your new password twice in the Set Password dialog box.
Login Timeout – Number of seconds before web page logs out.
Router Time:
Router Time – Date and time on the router. (yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss.ss)
Time Server:
Enable Time Server – Click this checkbox to set the time via these servers.
Time Server – The host name or IP address of the time server.
November 2013 Page 91 of 96
Page 92

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
10.7 Utilities – Language
This page allows you to select a language for the screen display text. Click the arrow to display
the drop-down list.
For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Language – Sets the language for the screen display text.
Page 92 of 96 November 2013
Page 93

Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
10.8 Utilities – System Logs
Utilities – System Logs
Log:
This page displays the system logs. Click the Refresh button to update the list. Click the Clear
Log button to clear the list.
November 2013 Page 93 of 96
Page 94

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
10.9 Utilities –DDNS
DDNS (Dynamic DNS) allows you to provide Internet users with a fixed domain name (instead of
an IP address which may periodically change). This allows your gateway and applications set up
in your gateway's virtual servers to be accessed from various locations on the Internet without
knowing your current IP address. For changes to take effect, you must click the Apply button.
Note: You must first create an account with a DDNS provider in order to use DDNS. The DDNS
provider maps your chosen domain name to your IP address.
DDNS Setting:
DDNS Enable – Click this checkbox to enable DDNS on your system.
DDNS Service – Sets the DDNS provider that our account is with. The options are DynDNS and
TZO.
User Name – Enter the user name for your DDNS account.
Password Key – Enter the password for your DDNS account. (Provided by your DDNS provider.)
Domain Name – Enter the domain name you selected to use with your DDNS account.
Page 94 of 96 November 2013
Page 95

11 MoCA Status
Section 2: Web GUI Screens and Configuration Parameter Reference
MoCA Settins:
MoCA Enabled – Click this checkbox to enable MoCA on your system.
Note: This parameter may be set to a default by your service provider and not be user
configurable.
MoCA Status:
Status – Displays the status of MoCA, either noLink, linkUp, or disable.
Node Count – Displays the number of nodes that this device communicates with in the MoCA
network.
Node Coordinator – Displays the node ID of the network coordinator.
November 2013 Page 95 of 96
Page 96

Touchstone 16xx Gateway Router Setup – Web GUI User’s Guide
Channel – Displays the MoCA channel in MHz this interface is tuned to when part of a MoCA
network. When not part of a MoCA network, this value may not indicate the actual tuned
channel.
Last Good Channel – Displays the MoCA channel this interface was tuned to when it was last in
the linkUp state.
Link Up Time – Displays the total time in seconds this interface is part of a MoCA network.
MoCA Node List:
The devices table lists the ID, node type, MAC address, and performance data (if any is available)
of the nodes.
Page 96 of 96 November 2013
 Loading...
Loading...