Page 1

VisualHub Users Guide
By Tyler Loch, Fearless Leader, Techspansion LLC
Release 1.22, 2/26/07
Page 2

This page unintentionally left blank. Whoops.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Crash Course 4
Chapter 2: iTunes 6
Chapter 3: PSP 8
Chapter 4: DV 11
Chapter 5: DVD 14
Chapter 6: AVI 17
Chapter 7: MP4 19
Chapter 8: WMV 21
Chapter 9: MPEG 23
Chapter 10: Flash 26
Chapter 11: Advanced 28
Chapter 12: Xgrid 30
Chapter 13: Tidbits 33
Chapter 14: Troubleshooting 35
Chapter 15: Appendix 37
Appendix A: Cheat Codes 39
Appendix B: Supported Codecs/Formats 41
Appendix C: Credits and Other Info 43
3
Page 4

Chapter 1:
Crash Course
"This readout tells you where you're going, this one tells you where you are, this one tells
you where you were."
- Dr. Emmett L. Brown
4
Page 5
Introduction
VisualHub was created to allow people to convert video to many popular formats with ease. Most people will figure it out
right away with no help. If you’re someone who scoffs at the notion that an “easy to use” program needs a 44 page
Users Guide, then don’t read past this page. You won’t need to learn any more than this page teaches you.
Some people will need a crash course (this section) to get jump-started.
Some people would like more in-depth information on a specific format, or on every aspect of the program.
...and a few people will just curl up in a ball and rock back and forth wishing someone else would do everything for them.
You could start a successful business catering tech support to these people since they always seem to have a lot of
extra money lying around.
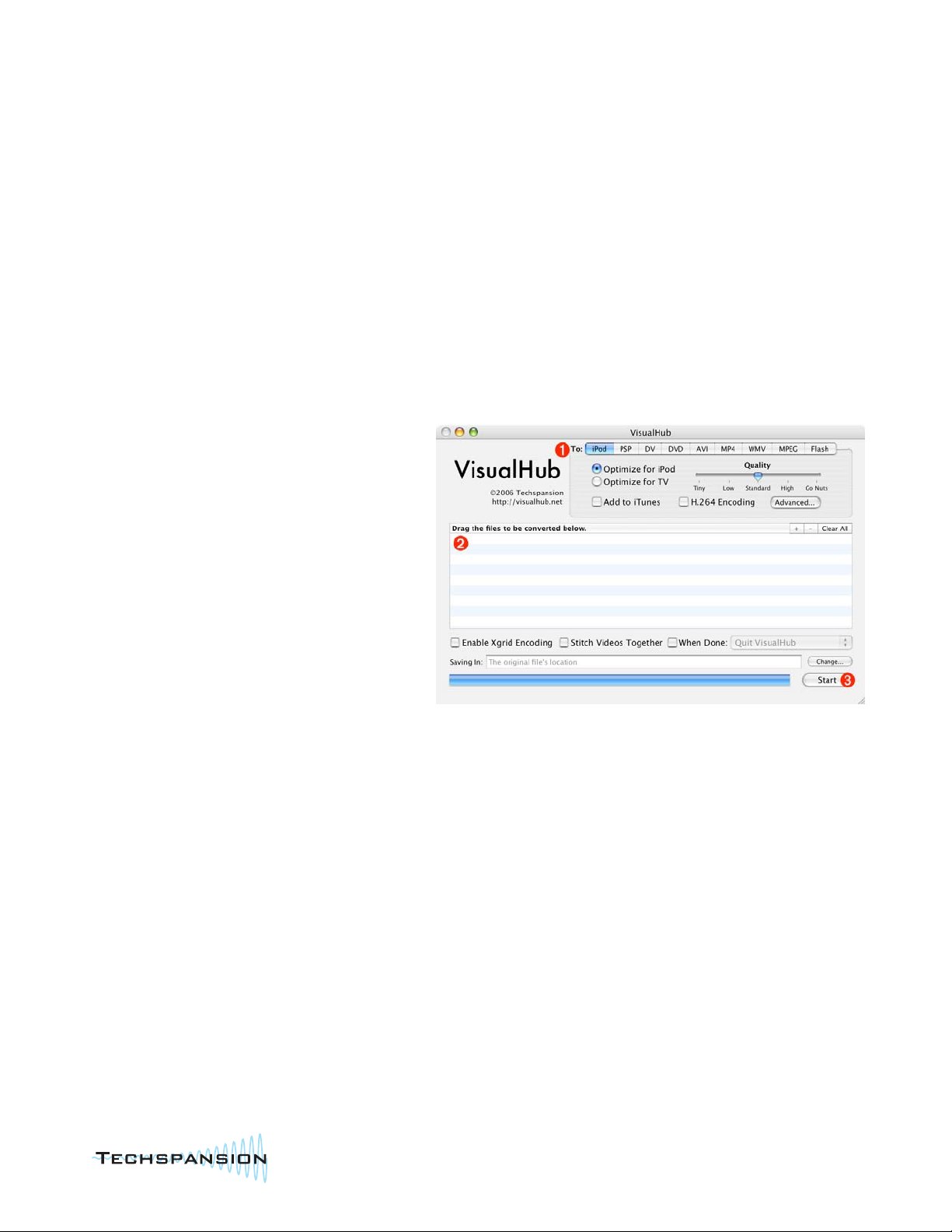
Workflow
The normal workflow of VisualHub works as
follows:
1: Choose the format you want to convert to.
2: Drag the files you want converted into VisualHub.
3: Click Start.
Easy Settings
Each format has some Easy Settings, such as
quality, TV format, etc. In many cases, the default
settings will do what you want and don't need to be
changed. There is a chapter on each video format
that explains every setting in detail. VisualHub is as
easy or complex as you want it to be. You want more control? Start changing those settings. Want total control? Click on
the "Advanced" button to tweak every aspect of your video conversion process.
Adding Files, Saved File Location
There are many ways to tell VisualHub what videos you want converted. The most popular is drag and drop. You can
drop files either into the File List in the main VisualHub window, or on top of the VisualHub icon in Finder or the Dock. The
"+" sign on top of the File List is another way.
By default, VisualHub will save each finished, converted video to the same folder that the original video came from. If
you're converting videos from multiple locations, you might find it easier to save them all to the same location. The
"Edit..." button right above "Start" will allow you to choose a folder where all converted videos will congregate after
they're completed.
Progress
Once you click Start, VisualHub will take a look at each file, figure out the best way to convert it based on the selected
settings, and start the conversion. The progress bar at the bottom of the window will keep you updated with the overall
progress and the estimated time remaining.
5
Page 6

Chapter 2:
iTunes
"You know, our next big step is we want it to make toast. I want to brown my bagels when
I’m listening to my music. And we’re toying with refrigeration, too."
- Steve Jobs on video iPods, April 2004
6
Page 7
What Is It?
A specialized set of MPEG-4 settings that play on modern iPods, and on the Apple TV.
What Plays It?
Fifth-Generation (5G) iPods. aka "iPod with Video", released in late 2005, and Apple TV,
released in February 2007.
More Information
The 5G iPod was announced in late 2005 with video playback capabilities. Its 320x240 screen plays MPEG-4 and H.264
video at varying sizes and data rates. The iPod has the capability to hook up to a TV for higher-resolution video playback.
The Apple TV was announced in January 2007 and plays back similar formats, as well as specific high-definition formats.
Easy Settings One-by-One
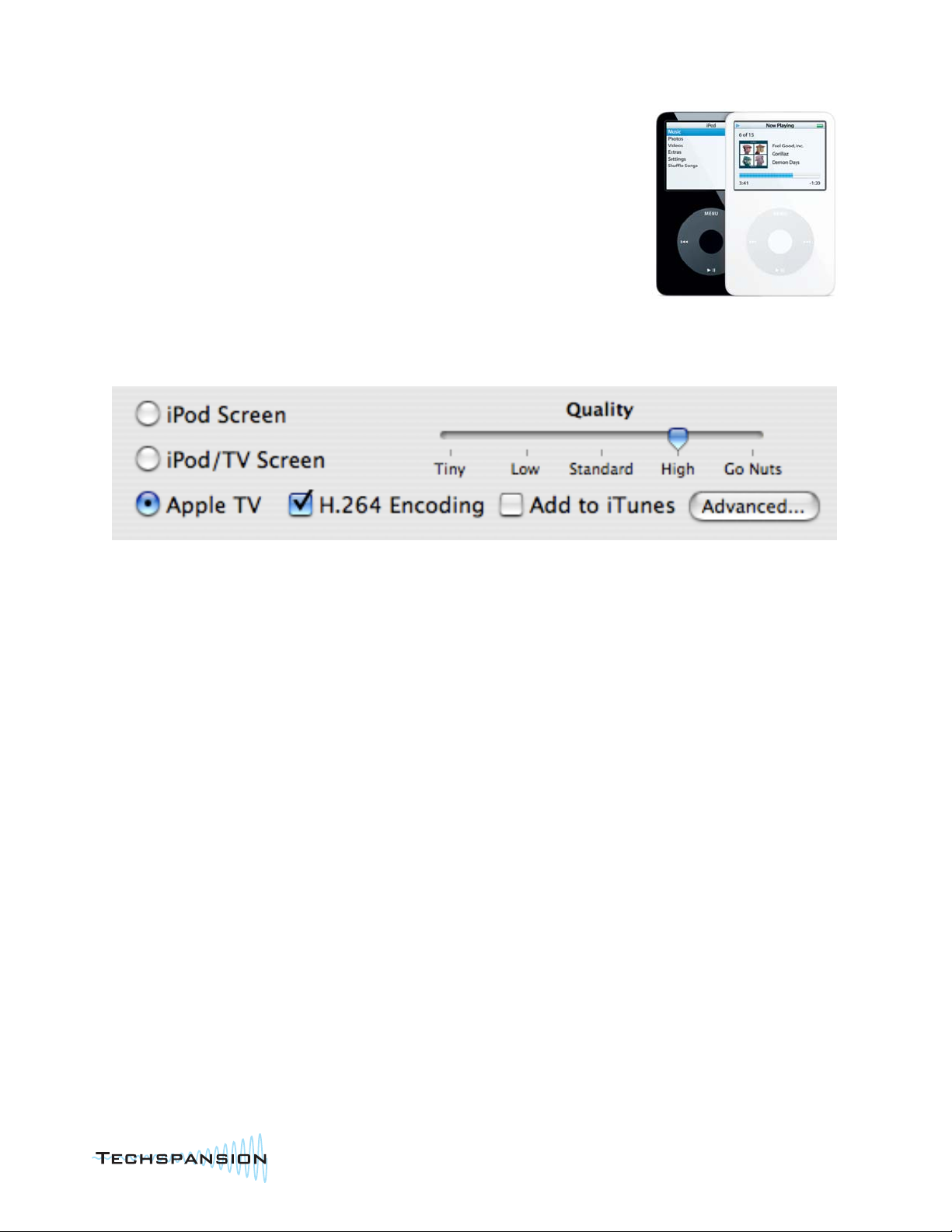
iPod Screen, iPod/TV Screen, Apple TV
Consider what screen you'll be viewing your video on.
Videos made for the iPod screen will take up less disk space, but may look blocky on a TV. Videos made for TV will look
great on a TV (and your iPod and your Apple TV), but you'll waste space if you only watch them on your iPod. Videos
made for the Apple TV will play on the Apple TV and your Mac. They are not compatible with the iPod.
Quality
If visual quality isn't as important as just getting the message across, you can set the quality slider to "Low" or "Tiny". If
the video demands the absolute best quality possible, choose "High" or "Go Nuts". "Go Nuts" Pushes Your iPod To The
Max. This setting may take over 5 times as much space as "Standard", but will look nominally better.
This is a personal preference. "Standard" is good for the majority of users and video types. The rest is up to you.
Add to iTunes
Checking this box will automatically add each video to the iTunes Videos playlist. If you have your iPod set to
automatically sync to your Music Library, this is a good setting to use.
H.264 Encoding
H.264 is a newer, more advanced video compression type. Videos compressed with H.264 will look better than the
default MPEG-4 counterparts at the same resolution, and will take up less disk space. Of course, there's a catch. It takes
much longer to compress to H.264 than MPEG-4. This is another personal preference.
After Conversion
If you checked "Add to iTunes", you're done. Otherwise, drag the completed video into your iTunes library. If you
manually manage your iPods songs/videos/playlists, drag completed videos to your iPod in iTunes' Source sidebar.
7
Page 8

Chapter 3:
PSP
"This is the design that we came up with. There may be people that complain about its
usability, but that's something which users and game software developers will have to
adapt to..."
- Ken Kutaragi
8
Page 9

What Is It?
A specialized set of MPEG-4 settings that will play on the PSP.
What Plays It?
PSP, or PlayStation Portable, released in spring 2005.
More Information
The PlayStation Portable is Sony's grand entrance into the portable gaming market. It's a "jack of all trades", competing
with both the GameBoy Advance, Nintendo DS, and iPod. Its crazy-bright and glossy 480x272 widescreen display
makes for great video playback. Sony has placed a lot of restrictions on video formats though, crippling its higher-quality
video capabilities.
Easy Settings One-by-One
Standard/Anamorphic 16:9
“Standard” is the best choice for most video types and most situations. Anamorphic allows the absolute best-possible
resolution for widescreen movies.
The PSP has a widescreen display, capable of stretching video to fit. Video in the
4:3 aspect (most traditional video) can be viewed either with black bars on the
sides of the image, or stretched to fill the entire display. Either way has its
advantages and disadvantages. Personally, I prefer black bars on the sides so the
video doesn't look "squished".
Widescreen aspects such as 16:9 (high-definition TV shows, nearly all movies) can be
displayed on the PSP with no black bars. Due to limitations in the PSP’s firmware,
widescreen video can't be played at the highest-possible resolution. “Anamorphic”
treats widescreen source video as 4:3. Playback on a computer will result in everything
looking "squished"...but the PSP will stretch the video back to its native aspect, giving
you a crisper, higher quality widescreen video. Depending on the source, you may find that Standard provides better
picture quality. Use whichever setting suits your tastes.
Quality
If visual quality isn't as important as just getting the message across, you can set the quality slider to "Low" or "Tiny". If
the video demands the absolute best quality possible, choose "High" or "Go Nuts". "Go Nuts" Pushes Your PSP To The
Max. This setting may take over 2 times as much space as "Standard", but will look nominally better.
This is a personal preference. "Standard" is good for the majority of users and video types. The rest is up to you.
9
Page 10
AVC Encoding
AVC, also known as H.264, is a newer, more advanced video compression type. Videos compressed with AVC will look
better than its default MPEG-4 counterpart and takes up less stick space. Of course, there's a catch. It takes much
longer to compress to AVC than MPEG-4. This is another personal preference.
Advanced Settings
The Advanced panel will show an extra section of you have the PSP tab selected.
Custom Title - This lets you choose your own PSP-readable title instead of VisualHub using the video file’s original
name. If you are converting a batch of files, each video will have a number placed after the name based on its order.
After Conversion
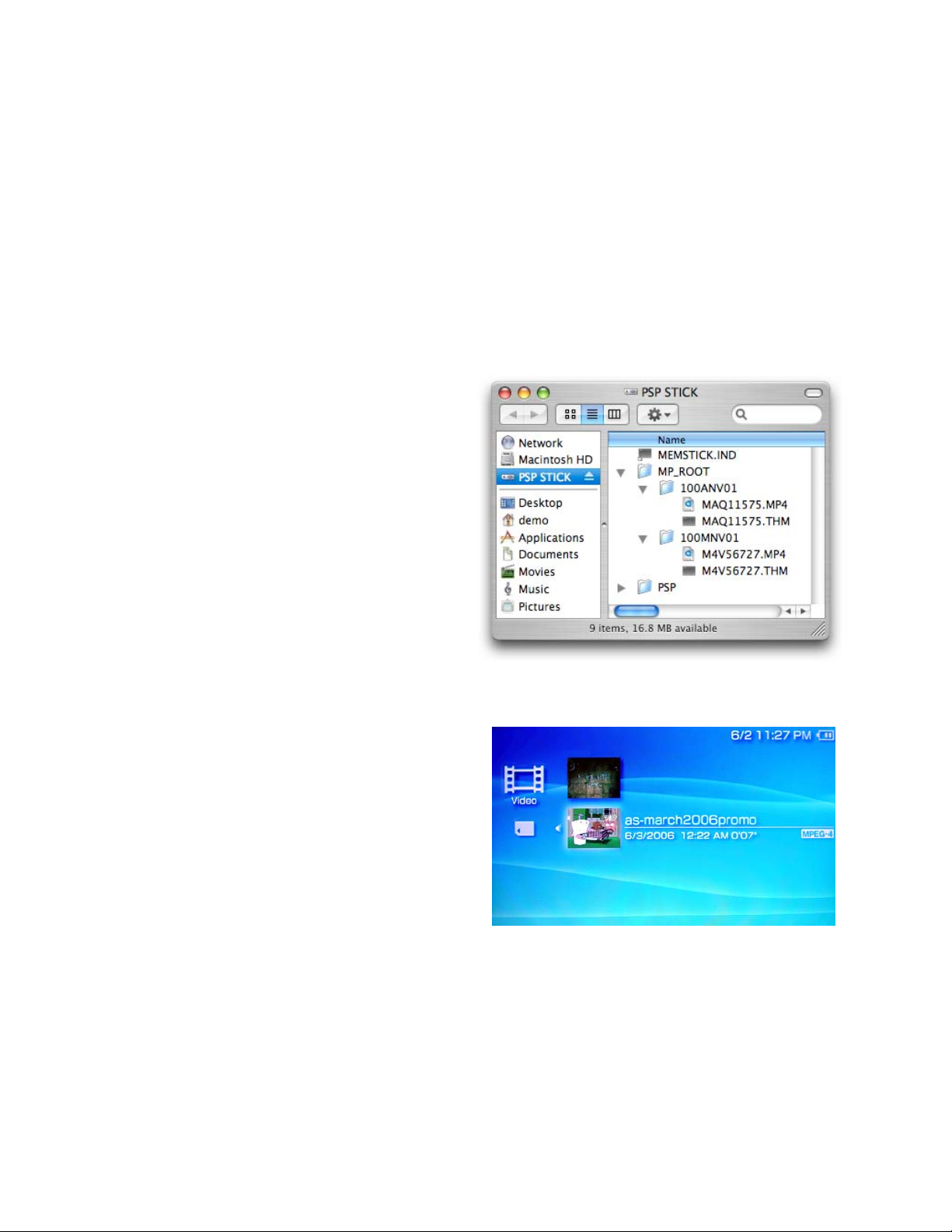
The PSP requires videos be placed in special folders on
your MemoryStick Duo for playback.
If you selected your PSP’s memory stick as the “Save To”
destination, VisualHub will automatically place your
converted file(s) in the correct location. Otherwise, follow
these steps:
1. Put your PSP into USB Connection mode and plug
it in to your Mac. Your memory stick will show up in
Finder.
2. If a folder named "MP_ROOT" does not exist on
your memory stick, create one.
3. Open the MP_ROOT folder. If folders named
"100MNV01" and “100ANV01” do not exist in this folder, create them. “100MNV01” is for MPEG-4 videos, and
“100ANV01” is for AVC videos.
4. VisualHub will name each file either “M4VXXXXX.MP4”
or “MAQXXXXX.MP4”, where “X” is a random
number. Files that begin with “M4V” are MPEG-4 files
and should be placed in the “100MNV01” folder. Files
that begin with “MAQ” are AVC files and should be
placed in the “100ANV01” folder.
5. Drop your converted videos into one of these folders
based on type. If “Make Thumbnail” was checked, you
can drag the .THM thumbnail file to the same location.
6. Eject the memory stick from Finder, and unplug your PSP.
7. When browsing videos on your PSP, you will see each video's original name, as well as a small thumbnail preview.
Note: PSP Firmwares 2.8 and up allow videos placed in a “VIDEO” folder on the main level of the Memory Stick.
Compatibility of videos placed there differ to the original placement shown above for no logical reason. It’s recommended
that you set VisualHub to save movies directly to your Memory Stick in order to guarantee playback.
10
Page 11

Chapter 4:
DV
"...and it's indestructible! [WHAM] [WHAM] [WHAM] ...aww...I broke some of the
shielding..."
- Apple Spokesperson on FireWire at MUG meeting, 1997
11
Page 12

What Is It?
A nearly-lossless format geared towards non-linear video editing.
What Plays It?
MiniDV camcorders, iMovie, Final Cut Pro.
More Information
DV video became the standard for home and prosumer video editing with the
release of iMovie in 1999. iMovie and Final Cut Pro use it as their native editing
format. Since it's a near-lossless digital format, there is no "generational loss" as experienced on analog VHS or more
primitive digital formats when copying and editing video from device to device.
Easy Settings One-by-One
NTSC/PAL
There are two major television formats in the world. NTSC and PAL.
NTSC stands for "North American Television Standards Committee", and as expected from the title, this format is used in
North America. It is also the native format of Japan and northwest South America.
PAL stands for "Phase Alternating Line", and as expected from the title, tells you absolutely nothing helpful, leaving you
lost and confused. It's the format used in the rest of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and most of
South America. People in Antarctica are too cold to watch TV.
Consult this map for more details:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:NTSC-PAL-SECAM.png
For the purpose of DV video, SECAM and PAL are identical.
Force Anamorphic 16:9
This setting allows widescreen content to be converted to DV format conserving its full
resolution without using black boxes. Viewing this video in QuickTime will result in a
squished picture, but iMovie and iDVD will play it back at its native aspect. In nearly all
cases, you will want to leave this checkbox unchecked. 16:9 DV video may not be
displayed correctly on MiniDV devices.
Ready for Final Cut
When this is selected, VisualHub will create DV-in-MOV files that Final Cut Pro/Express
can use without the need to re-render either the audio or video track.
(Continued)
12
Page 13
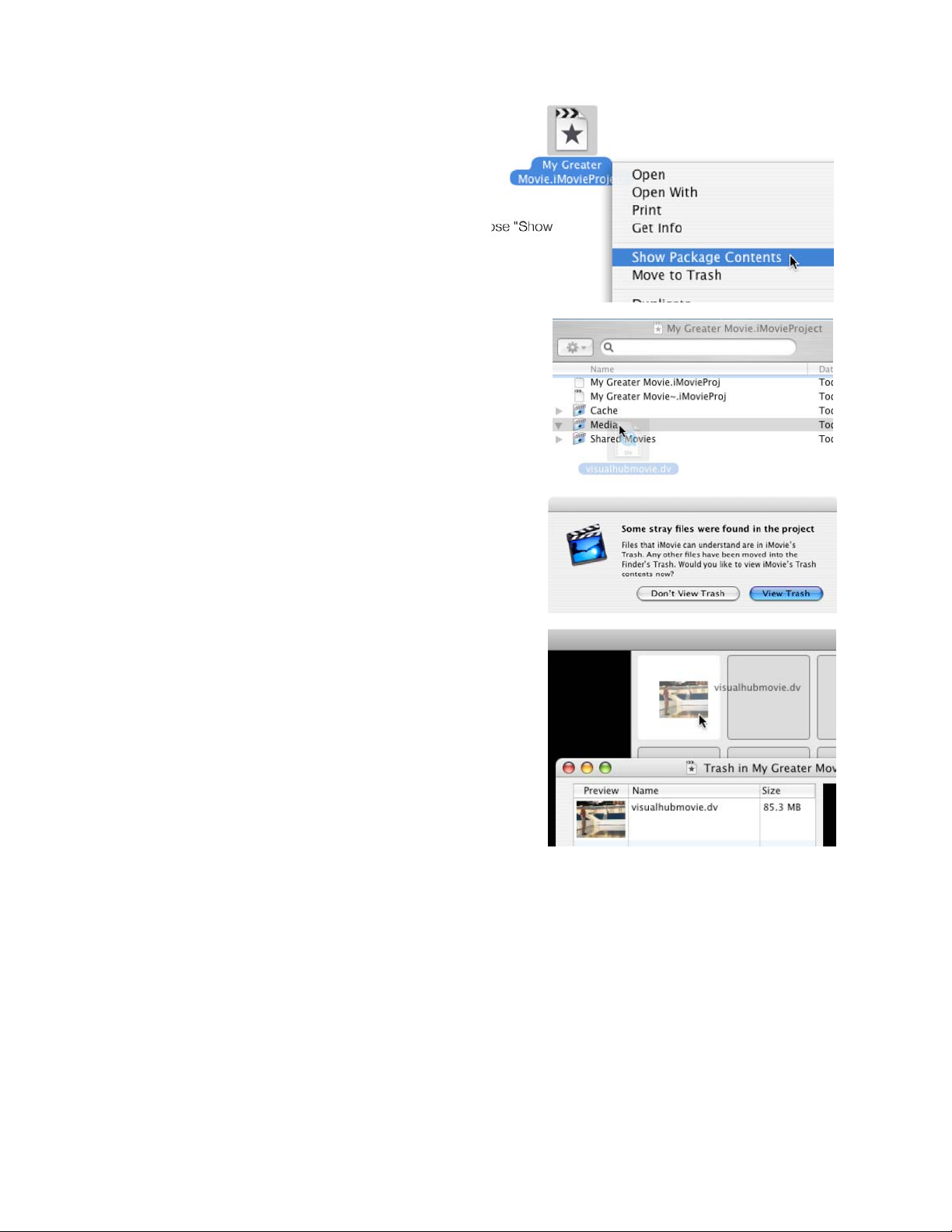
After Conversion
If you want to add your completed videos to an iMovie project,
1. Make sure iMovie is closed.
2. Locate your iMovie project file. Control-Click on it and choose "Show
Package Contents.
3. A new window will open showing you the innards of your iMovie
project. Your completed videos from VisualHub can be dropped
in the "Media" folder seen inside your iMovie project's folder.
4.
5. Open iMovie again. You will be warned about a foreign video in
the iMovie trash. View Trash to recover your new file and drag it
into the video tray.
A simpler method would be to drag the file created by VisualHub into
an open iMovie project's video tray, but this will make another copy of
your new DV file and the process may take several minutes to
complete.
13
Page 14

Chapter 5:
DVD
"I go on Kazaa every week [...] a lot of it was pornography, some of it was music, but a lot
of it was films."
- Jack Valenti, May 2003
"I say to you that the VCR is to the American film producer and the American public as the
Boston Strangler is to the woman home alone."
- Jack Valenti, 1982
"In the digital world, we don't need back-ups, because a digital copy never wears out. It is
timeless."
- Jack Valenti, 2002
14
Page 15

What Is It?
A specialized set of MPEG-2 settings and authoring utilities that are geared
towards creating discs that will play back on standalone DVD video players
as well as computers.
What Plays It?
Standalone DVD players and most computers.
More Information
DVD : VHS :: CD : Vinyl (do you remember your grade school analogies?)
DVD is the widely-used modern format for home video. Video quality is variable, allowing for very long running times.
VisualHub can fit up to 18 hours of video on one DVD. Image resolution and bitrate can be lowered to allow for the best
quality compromise.
Easy Settings One-by-One
NTSC/PAL
There are two major television formats in the world. NTSC and PAL.
NTSC stands for "North American Television Standards Committee", and as expected from the title, this format is used in
North America. It is also the native format of Japan and northwest South America.
PAL stands for "Phase Alternating Line", and as expected from the title, tells you absolutely nothing helpful, leaving you
lost and confused. It's the format used in the rest of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and most of
South America. People in Antarctica are too cold to watch TV.
Consult this map for more details: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:NTSC-PAL-SECAM.png
For the purpose of DVD video, SECAM and PAL are identical.
Quality
If visual quality isn't as important as just getting the message across, you can set the quality slider to "Low" or "Tiny". If
the video demands the absolute best quality possible, choose "Standard".
Quality settings are not available with “Author as DVD” is checked. Quality will then be automatically decided.
Author as DVD
Checking this box will tell VisualHub to create a full-fledged DVD from the input files. VisualHub will add up the running
times for each video in the File List, and choose quality and bitrate settings in order to guarantee that all files will fit on
15
Page 16

one DVD. The final result of this conversion is a disc image file named “VisualHubDVD.iso” that can be tested before
being burned at your leisure on any Mac with Disk Utility, or with any PC burning software.
Burn When Done
Does what it says. Only available when "Author as DVD" is checked, it will burn the .iso file created by VisualHub to a
recordable DVD in your default disc burner automatically. Make sure you've inserted a disc before conversion completes.
Advanced Settings
The Advanced panel will show an extra section of you have the DVD tab selected.
Custom Volume Name - This lets you pick the name used for the DVD disc and the .iso file created by VisualHub. You
must use only capital letters and underscores: THIS_IS_AN_EXAMPLE
Long names above 31 characters are not supported.
Chapters Every n Minutes - By default, VisualHub will place a chapter marker at the beginning of every video in the list.
By selecting “5”, “10”, or “15” minutes from this menu, VisualHub will also place chapter marks at those intervals.
Force
Standard/Anamorphic - This lets you decide whether a DVD should be widescreen 16:9 or not instead of letting
VisualHub choose for you based on the majority aspect of the videos in your batch.
Full Resolution - This causes VisualHub to ignore its own resolution recommendation based on video duration, and
encode at the full DVD resolution no matter how low the quality may be.
Dual Layer - This changes all the quality equations to use nearly double the bitrate in order to fill a dual layer disc. Over
36 hours of video can be fit on a single dual-layer disc with this option.
DVD Tidbits
DVD videos produced by VisualHub will play immediately when inserted in a DVD player. Each video in VisualHub’s File
•
List is a separate chapter.
When converting a batch of videos under 3 total hours, VisualHub will make a decision between anamorphic 16:9 or
•
standard 4:3 based on which format is more prevalent. The minority aspect will be letterboxed. Batches over two
hours use a different resolution and must be 4:3, with widescreen material letterboxed.
The DVD specification is limited to 99 chapters, meaning VisualHub is limited to 99 files in a batch. Some DVD players
•
will be able to cope with more, but the disc will largely be incompatible with many players.
The 18 hour limit is a soft limit. You can actually make longer DVDs, but quality will really start to suffer.
•
To play a DVD image on Mac OS X without burning it,
•
double-click on the .iso file created by VisualHub. A
disk image will appear on the Desktop, containing a
“VIDEO_TS” folder. DVD Player can play this folder by
either dragging it onto the DVD Player icon, or by
choosing “Open DVD Media...” from DVD Player’s File menu. This is a good way to preview and verify converted
DVDs before burning a disc.
16
Page 17

Chapter 6:
AVI
“Please spell DivX ;-) correctly ! Capital ‘D’ lower-case ‘iv’ capital ‘X’ and do not forget the
eye-blinking smiley ‘;-)’ !”
-Gej
17
Page 18

What Is It?
A legacy Windows video container resurrected by the DivX project. VisualHub creates
DivX-compatible MPEG-4 AVI files.
What Plays It?
Windows, Mac and Linux with appropriate codecs, VLC, DivX-certified DVD and
portable players.
More Information
DivX video surfaced in 1998 as a hack to allow MSMPEG4v3 video in the AVI container with MP3 audio. It quickly took
internet downloadable video by storm, becoming the preferred video format by many websites and online communities.
DivX-style MPEG-4 AVI video has changed and forked many times over the past 8 years with "DivX ;-) 3.11a", "DivX 4",
"ProjectMayo", "OpenDivx", "XviD", "DivX 5" and "DivX 6". VisualHub creates MPEG-4 Advanced Simple Profile files,
most closely related to (and recognized as) DivX 5/6 for compatibility purposes.
The AVI container can contain many different video formats. MPEG-4/DivX/XviD is(are) one of them, but is
overwhelmingly prevalent over all other types.
Easy Settings One-by-One
320 Pixels Wide
By default, VisualHub will create an AVI with the same image size as the original video. By checking this box, VisualHub
will constrain the video to 320 pixels across, scaling proportionally. 320x240 is a standard video resolution for medium-
quality Internet distribution.
Quality
If visual quality isn't as important as just getting the message across, you can set the quality slider to "Low". If the video
demands the absolute best quality possible, choose "High" or "Go Nuts". "Go Nuts" sets a data rate near the maximum
quality of the codec. This setting may take over 5 times as much space as "Standard", but will look nominally better.
Profile
A sizable number of devices, such as handheld video players and DVD players will also play AVI/DivX video. Many are
"DivX Certified" up to a certain image/file size threshold. Check the playback abilities of your device and choose
accordingly. "DivX Home Theater" reaches the full resolution of standard definition video. "DivX Portable" is meant for
handheld players and can be near standard definition quality. "Simple Profile" is compatible with nearly all devices that
play DivX. “Best Compatibility” will play on Windows with no codecs necessary. “Wii” is a special format that will play in
the Photo Channel of a Nintendo Wii. Videos are stored and played back from a SD card.
18
Page 19

Chapter 7:
MP4
"In this world of 'my codec is better than yours' -- this codec is better."
- Frank Casanova, 2004
19
Page 20

What Is It?
A modern container format, used with MPEG-4 and H.264 video.
What Plays It?
QuickTime, VLC, some portable players.
More Information
The MP4 container gets its heritage from the QuickTime .mov container. Its native video
formats are MPEG-4 and H.264 (also known as AVC), with AAC audio.
Easy Settings One-by-One
320 pixels wide
By default, VisualHub will create a MP4 file with the same image size as the original video. By checking this box,
VisualHub will constrain the video to 320 pixels across, scaling proportionally. 320x240 is a standard video resolution for
medium-quality Internet distribution.
Quality
If visual quality isn't as important as just getting the message across, you can set the quality slider to "Low". If the video
demands the absolute best quality possible, choose "High" or "Go Nuts". "Go Nuts" sets a data rate near the maximum
attainable quality of the codec. This setting may take over 5 times as much space as "Standard", but will look nominally
better.
The 56K setting will create a file that can stream in realtime over a 56K modem.
H.264 Encoding
H.264 is a newer, more advanced video compression type. Videos compressed with H.264 will look better than the
default MPEG-4 counterparts and take up less disk space. Of course, there's a catch. It takes much longer to compress
to H.264 than MPEG-4. H.264 videos compressed under the MP4 tab are "Main Profile" with one b-frame.
Hint for streaming
This option may be useful to webmasters looking to post completed videos online. Checking this box will create hinted
tracks in the finished video. Hinted tracks allow internet streaming of a video via QuickTime/Darwin Streaming Server. By
default, MP4 videos created by VisualHub are "FastStart" and will begin to play as they are downloaded from a web
server, aka, Progressive Download. Hinted streaming videos never get stored on the downloading user's computer - they
download and play back in real time with no option to save.
20
Page 21

Chapter 8:
WMV
"I've got my kids brainwashed: You don't use Google, and you don't use an iPod."
- Steve Ballmer, April 2006
21
Page 22

What Is It?
A Microsoft-created video container format.
What Plays It?
Windows Media Player on Windows, Flip4Mac and Popwire WMV decoders on Mac,
VLC, Xbox360, some portable devices.
More Information
The WMV format is Microsoft's video format for both local use and internet streaming.
The ASF and WMV formats are nearly identical, with just the file extension differentiating the two. VisualHub uses the
WMV8 video codec and WMA9 audio codec.
Easy Settings One-by-One
320 pixels wide
By default, VisualHub will create a WMV file with the same image size as the original video. By checking this box,
VisualHub will constrain the video to 320 pixels across, scaling proportionally. 320x240 is a standard video resolution for
medium-quality Internet distribution.
Quality
If visual quality isn't as important as just getting the message across, you can set the quality slider to "Low". If the video
demands the best quality possible, choose "High" or "Go Nuts". "Go Nuts" sets a data rate near the maximum attainable
quality of the codec. This setting may take over 5 times as much space as "Standard", but will look nominally better.
The 56K setting will create a file that can stream in realtime over a 56K modem.
Compatibility
WMV files created by VisualHub can be played with the following:
Mac OS X with QuickTime Windows Media plugins (Flip4Mac, Popwire). Windows Media Player 9:Mac is unsupported.
Windows 98/Me/2000/XP/Vista with Windows Media Player 7 and up.
Xbox360 with Fall 2006 Update
VLC and MPlayer-based software on any platform.
Playback compatiblity and quality on any other platforms may vary.
Xbox360 Playback
As of the 2006 Xbox fall firmware update, the Xbox360 gained the ability to play back WMV video files accessed in a
variety of different methods:
CDs/DVDs, USB Hard Drives, USB Flash Drives, Microsoft Windows Connect,and Nullriver’s Connect360.
WMVs created by VisualHub can be played back on the Xbox360 by any of these methods.
22
Page 23

Chapter 9:
MPEG
”The basic scheme is to predict motion from frame to frame in the temporal direction,
and then to use DCT's (discrete cosine transforms) to organize the redundancy in the
spatial directions.
luminance (Y) channel on 16x16 blocks
that you are trying to code, you look for a close match to that block in a previous or future frame
(there are backward prediction modes where later frames are sent first to allow interpolating
between frames).
the close match) are quantized, which means that you divide them by some value to drop bits off the bottom
end. Hopefully, many of the coefficients will then end up being zero. The quantization can change for every
"macroblock" (a macroblock is 16x16 of Y and the corresponding 8x8's in both U and V).
include the DCT coefficients, the motion vectors, and the quantization parameters (and other stuff) is Huffman coded using fixed tables.
The DCT coefficients have a special Huffman table that is two-dimensional in that one code specifies a run-length of zeros and the nonzero value that ended the run. Also, the motion vectors and the DC DCT components are DPCM, (subtracted from the last one) coded.”
The DCT's are done on 8x8 blocks, and the motion prediction is done in the
. In other words, given the 16x16 block in the current frame
The DCT coefficients (of either the actual data, or the difference between this block and
The results of all of this, which
--Berkeley Multimedia Research Center MPEG-1 Document
23
Page 24

What Is It?
A legacy format supported by virtually all computers.
What Plays It?
Some standalone devices, some DVD players, every computer after 1996.
More Information
MPEG video was created in the early 1990s as a worldwide standard for digital video. It
lives on in many forms today. MPEG video can be played by nearly every computer
without special software, plugins, or codecs needed.
Easy Settings One-by-One
NTSC/PAL
There are two major television formats in the world. NTSC and PAL.
NTSC stands for "North American Television Standards Committee", and as expected from the title, this format is used in
North America. It is also the native format of Japan and northwest South America.
PAL stands for "Phase Alternating Line", and as expected from the title, tells you absolutely nothing helpful, leaving you
lost and confused. It's the format used in the rest of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and most of
South America. People in Antarctica are too cold to watch TV.
Consult this map for more details: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:NTSC-PAL-SECAM.png
For the purpose of MPEG video, SECAM and PAL are identical.
Quality
If visual quality isn't as important as just getting the message across, you can set the quality slider to "Low" or "Tiny". If
the video demands the absolute best quality possible, choose "High" or "Go Nuts". "Go Nuts" sets a data rate near the
maximum attainable quality of the codec. This setting may take over 5 times as much space as "Standard", but will look
nominally better.
This is a personal preference. "Standard" is good for the majority of users and video types. The rest is up to you.
MPEG-2 Encoding
MPEG-2 is a revision to the MPEG format. DVDs use a specialized set of MPEG-2 settings. Don't use this unless you
know why you have to.
24
Page 25

MPEG Profiles
There are hundreds of devices that use MPEG video to some extent, all with their own specific settings needs. VisualHub
has presets for some of the more popular device formats.
VCD
Creates an MPEG file conforming to the strict VCD 1.1 specifications. VCD was an MPEG-derived format popular in Asia,
and playable by many DVD players.
SVCD
Creates an MPEG file conforming to the SVCD specifications. SVCD was an MPEG2-derived format created by China as
an alternative to the DVD format. It’s playable in some DVD players.
CVD
Creates an MPEG file conforming to the CVD specifications. CVD was an MPEG2-derived format created by China along
with SVCD as an alternative to the DVD format. SVCD won. CVD is still popular with some people, as it’s very similar(and
sometimes drop-in-compatible) to the DVD format. It’s playable in some DVD players.
TiVo
Creates an MPEG file conforming to the specifications
of the TiVo Series 2 DVR. TiVos use an MPEG2-
derived format. Files created by a TiVo unit are
encrypted to only work on specific devices. Standard
MPEG-2 videos formatted specially are able to be
placed onto the TiVo using TiVo Desktop.
You must be running TiVo Desktop 1.9.3 to use this
TiVoGoBack feature.
Run the TiVoGoBack Enabler included in the VisualHub
Disk Image to turn this feature on. You can set the
folder where your TiVo will find converted videos using
the TiVo Desktop System Preferences pane. See the
TiVoGoBack ReadMe for detailed information.
Transport Stream
Creates an MPEG-2 file in a Transport Stream (.ts) container. Many digital TV decoders receive transport streams.
HDTV 720p
Creates an MPEG transport stream conforming to the ATSC HDTV 720p60/50 format. This can be fed to a FireWireequipped HDTV decoder using the freeware VirtualDVHS program.
HDTV 1080i
Creates an MPEG transport stream conforming to the ATSC HDTV 1080i30/25 format. This can be fed to a FireWire-
equipped HDTV decoder using the freeware VirtualDVHS program.
25
Page 26

Chapter 10:
Flash
"People are all the time asking me, "Mike, how do you do those stupid voices for your
dumb animal characters?", and I say, "I'm Mike. Matt does the voices."
- Mike Chapman
26
Page 27

What Is It?
A Macromedia and Sorenson-created video format commonly found in Macromedia
Flash .swf files. Used by Google Video and YouTube
What Plays It?
Macromedia/Adobe Flash web browser plugin for all formats, VLC.
More Information
Flash 6 included a video codec to go along with MP3 audio to allow simple video to be
embedded in .swf files. In recent months, its use has exploded due to its inclusion in Google Video and YouTube, among
other community video sites. It's mainly geared towards web playback, due to the limited support outside web browsers.
VisualHub supports the version of Flash video used in Flash 6 and 7.
Easy Settings One-by-One
320 pixels wide
By default, VisualHub will create a Flash .swf file with the same image size as the original video. By checking this box,
VisualHub will constrain the video to 320 pixels across, scaling proportionally. 320x240 is a standard video resolution for
medium-quality Internet distribution.
Quality
If visual quality isn't as important as just getting the message across, you can set the quality slider to "Low". If the video
demands the absolute best quality possible, choose "High" or "Go Nuts". "Go Nuts" sets a data rate near the maximum
attainable quality of the codec. This setting may take over 5 times as much space as "Standard", but will look nominally
better.
The 56K setting will create a file that can stream in realtime over a 56K modem.
Raw .flv format
The default .swf format will automatically play in a web browser as it loads. A raw .flv file is not recognized as-is by the
Flash plugin. It requires a third-party .swf wrapper for playback. Webmasters may choose a raw .flv format if they already
have a flash video-based infrastructure in place.
Specialized Controls
The .swf files outputted by VisualHub automatically play and loop. In order to provide more control, such as Play/Pause
buttons, it’s necessary to output in raw .flv format and use a FLV player solution, such as this:
http://www.jeroenwijering.com/?item=Flash_Video_Player
27
Page 28

Chapter 11:
Advanced
"We knock them into little pockets with sticks. ...and we got higher numbers too!"
- The Tick, on The Infinity Ball
28
Page 29

Warning: Certain settings used in the Advanced
drawer may create video files incompatible with
some devices.
Option Explanation
Crop
(Left,Right,Top,Bottom)
Will remove n number of pixels from a side, depending on which field a number is entered.
Crop values must be even numbers.
AutoCrop By This File: Will find video edges (black bars, etc) and automatically set Crop settings for
all videos according to the selected file only. Automatic: Will find video edges (black bars,
etc) and automatically set Crop settings for each file during their conversions.
Size Dimensions of the video in pixels. This setting will override any presets for each video type.
Framerate Video frames per second. Film: 24, NTSC: 29.97, PAL: 25. This setting will override presets.
Preview Shows a graphical preview of a frame n seconds into the video. Any settings such as Size
or Crop will be reflected here. Check “Show Compression” to view image degradation
depending on the format selected.
Bitrate Data rate for the video. Measured in kilobits per second. Dialup: 56, DSL: ~1500
“Fit each video in” Will calculate a Bitrate constrained to n megabytes based on the reported running time of
each video. Useful with the Two Pass option.
Two Pass Will take a quick overview pass at a video to determine which parts need more resources to
encode. The second pass will encode the video using information determined in the first.
Force (QuickTime/ffmpeg
Decoding)
Chooses which decoding engine to use. Left alone, VisualHub will determine by filetype
which to use. Troublesome clips may benefit by the tweaking of this setting.
Deinterlace Video from sources such as DV or DVD may demonstrate what’s commonly referred to as
“combing artifacts”. This setting will throw out every other line of video to combat that.
qmin Chooses the minimum quantizer (quality) used. A high number (8+) will mean lower quality.
Extra ffmpeg Flags Additional ffmpeg command line flags can be added here for very advanced users.
Audio Hz Audio fidelity in Hertz. DVD:48000, CD:44100. Lower levels will result in lower audio quality.
Audio Bitrate Data rate for the audio. Measured in kilobits per second. Standard MP3: 128
Audio Channels Chooses between Mono and Stereo. Mono requires only half the Audio Bitrate to encode.
Volume Amplifies or softens overall audio volume to n% of the original. A value of 0 means no audio.
29
Page 30

Chapter 12:
Xgrid
“The Xgrid Console has an intuitive Aqua interface that makes it easy to execute UNIX
commands.”
- Xgrid Technology Preview PR. January 2004
30
Page 31

What is it and what does it do?
Xgrid is Apple’s clustering technology built into Mac OS X.
Xgrid can speed up a batch conversion by dealing out a video to each available CPU on
your network for conversion.
When you have more than one video in the file list and then check the "Enable Xgrid
Encoding" checkbox, VisualHub will enlist the help of any Macs on your local network that
have Xgrid enabled to distribute the load of batch encoding. If you have a multi-processor Mac,
Xgrid may also speed up the encoding process, with each processor working on a different video.
For example, a PowerMac G5 Quad under normal circumstances will only convert one video at a time, leaving anywhere
from 2.5 to 3 of its processors idle. With Xgrid, the same computer can utilize all 4 processors to their highest capacity.
How does it work?
There are two different types of Xgrid-enabled computers: Controllers and Agents.
The Controller is the computer responsible for telling the Agents what to do and to collect completed files. The
computer running VisualHub is the Controller. Controllers must be running 10.4 (Tiger) or higher and connected to a
network.
Agents take orders from the Controller and do the grunt work of video compression. Agents must be running 10.3.9
(Panther) or later and connected to the same network as the Controller. An Xgrid process running on an Agent will not
adversely affect the use of that computer; Xgrid processes always run at very low priority.
A Controller can also be an Agent to itself. You’ll see later how that can be a very good thing.
When you start an Xgrid-enabled batch, the Controller will do all the necessary detection and decision of settings for
each video, one by one. That information is sent to the Xgrid to await assignment. When an Agent is available, the Xgrid
will submit that information along with the video to be converted over the network to an Agent. Once all videos are sent
to the Xgrid, VisualHub will wait to hear back from Agents with completed videos. The progress bar will update for every
completed video. Once all videos are received, VisualHub will execute any post-conversion routines it normally does.
How do I set it up?
When Xgrid is enabled for the first time (by clicking on the
“Enable Xgrid Encoding” checkbox in the main window,
you will be prompted to start the Xgrid Controller. This is a
one-time action requiring an administrator’s password. A
tweak is also made to the number of processes that can run
at any given time, as Xgrid may spawn more than 100
background processes.
You will also have to set up each Xgrid Agent.
Tiger Agents: Go to the Sharing Preference Pane in System
Preferences. You will see a checkbox labeled Xgrid. If you
select the checkbox, the system will prompt you to edit the Xgrid settings. Click the “Configure” button to make these
changes. Use the settings in the screenshot to set up your Agent. For added security, you can have the Agents only
accept orders from a specific controller.
31
Page 32

Panther Agents: You will need to download the Xgrid Agent for Panther from Apple’s website:
http://www.apple.com/support/downloads/xgridagentformacosx103.html
Once installed, there will be a new Xgrid option in System Preferences. It has a similar window as shown above and
should be filled out in the same manner.
Note: VisualHub does not need to be installed on an Agent. All necessary files are sent to the Agent prior to conversion.
Important notes on Xgrid
Number of files
Xgrid jobs are granular to the file-level. Meaning, each file to be converted becomes its own job. If you only convert one
video at a time, only one processor of one agent will be working on the video - potentially negating the entire reasoning
behind batch processing. Xgrid Encoding is best left for when you are converting multiple videos at a time.
Running the Controller as an Agent
If you have a fast single processor Mac or any dual processor Mac, it will be beneficial to use your Controller computer as
an agent as well. Also, a multi-processor Mac with no other Agents will still convert video faster than it would with Xgrid
off, since both processors will be utilized up to 100%.
If your Controller is a single-processor Mac and you have a large number of Agents on the network (10 or more), the
Controller computer will spend most of its time dealing with organizing the Agents, and very little processing power will
be left over for video conversion
Network Throughput
It’s strongly recommended that the Controller and all Agents be connected via a wired network. Each Agent must receive
the entire file it’s meant to convert before conversion begins. On a wireless network, throughput can be 1/20th that of a
standard wired network. Creating a network bottleneck like that may eliminate any benefit of running Xgrid in the first
place. Gigabit ethernet would sure be nice if you had it, but it’s in no way a requirement.
Network Ports
VisualHub needs ports 8264-8267 open for file transport. Ports 4111-4120 are used for regular Xgrid Controller/Agent
communication. Make sure your software firewall is off or has these ports open.
Xgrid Management
Apple makes available an Xgrid management program called Xgrid Admin included in the Tiger Server Admin Tools
software package. The Admin Tools are a free download from Apple and can be used with a standard Mac OS X
computer too. http://www.apple.com/support/downloads/serveradmintools1047.html
Xgrid Admin can be used to monitor the activity of your Xgrid cluster.
What Xgrid can’t do
Xgrid Encoding in VisualHub can’t convert QuickTime reference movies. Reference movies use video resources from
•
many locations on a hard drive and can’t be transferred.
Files over 4GB will not be correctly converted.
•
The TwoPass option is ignored.
•
Any packages for video files, such as .iMovieProject and .eyetv files aren’t supported.
•
Conversion from DVD discs or VIDEO_TS folders either won’t work, work slowly, or wear down your DVD drive.
•
32
Page 33

Chapter 13:
Tidbits
"But the most important rule, the rule you can never forget, no matter how much he cries
or how much he begs...never, never feed him after midnight. Got it?"
- Gremlins, 1984
33
Page 34

Video Stitching
Video Stitching = Combining all the files in the video list into one massive file big enough to tell your grandkids about.
Stiching is available for the iPod, DV, MP4, AVI, and MPEG formats, and is enabled by selecting the “Stitch Videos
Together” checkbox in the main window.
Important: Every file that is going to be stitched together must have the SAME characteristics as all the other files. This
means the same resolution, framerate and audio quality. To ensure this, it’s best to set these characteristics manually in
the Advanced drawer.
Conversion from DVD
VisualHub is able to read and convert the Main Title from either a VIDEO_TS folder or a non-protected DVD. DVDs that
you’d buy at the store are more likely to be protected - meaning they block regular attempts at copying. You will need to
use DVD ripping software to pull the entire VIDEO_TS folder (or one big .vob file) before VisualHub is able to convert the
video. If the DVD has multiple audio tracks, VisualHub will prompt you with a list as it’s preparing for conversion.
Post-Conversion Actions
VisualHub can perform a few tasks after conversion completes to help people automate things (a little) better. These
actions are located in the “When Done:” pulldown menu on the main window.
Open Enclosing Folder
This will open a new Finder window with the contents of the folder listed in the “Save To” field. If blank, this will open the
folder containing the last-converted file.
Quit VisualHub
Self-explanatory.
Set Computer to Sleep
Will put the computer into Sleep/Suspend mode. Tapping a key on the keyboard or clicking the mouse will wake it up.
Shut Down Computer
Will initiate a shutdown. If there are any unsaved documents open in other applications, the shutdown will cancel.
Pause/Resume Conversion
You may want to pause conversion in VisualHub if you’re running other CPU-intensive programs, or if your laptop starts
burning your crotch. This can be accomplished through the File menu.
You shouldn’t quit VisualHub if you’ve paused conversions until you resume and complete/cancel them. Also, the Time
Remaining indicator will show an inaccurate estimate for the remainder of the file you’re currently converting.
Preferences
Under the VisualHub menu, click “Preferences...”
Low CPU Priority
By default, VisualHub's processing is no more and no less important than every other task on your computer.
Checking this box will make VisualHub "nice", and only use resources that would otherwise be idle.
Default Save Location
Changing this will change the “Save To” field on launch. Leave it blank to use the converted file’s original location.
Turn off Xgrid Controller
This will deactivate the Xgrid Controller process and disable its launch on startup.
Play Sound When Complete
Normally, VisualHub plays a “ding” sound when conversion completes. Uncheck this box to effectively silence VisualHub.
34
Page 35

Chapter 14:
Troubleshooting
"Son, you tried your hardest and failed miserably. The lesson is: Never try."
- Homer J. Simpson
35
Page 36

Hey, my video’s out of sync. What gives?
Sometimes, a video file will get out of sync during conversion. It’s usually more noticeable near the end of the video. Two
possible ways to solve this:
1. Switch decoding methods. In the Advanced panel, check the “Force” box and try converting with QuickTime or
ffmpeg Decoding. If your file is a QuickTime movie, try ffmpeg Decoding. if not, try QuickTime Decoding. Both
methods have a different way to keep audio sync and one may work better than the other.
Type “-async 1” into the “Extra ffmpeg Flags” text field in the Advanced panel’s video section. This is yet another
sync method that may work better on some files.
I want to convert a DVD I bought.
That’s not a question.
Converting straight from most purchased DVDs is an entirely different beast. VisualHub can convert unencrypted, or
unprotected DVDs. Files on most store-bought DVD are encrypted (protected). You would need a program to break
through the encryption before the DVD files could be read by VisualHub.
What’s with all these lines in my converted video?
Those are “interlacing” artifacts. Interlacing, in 10 words or less, was a good idea in 1940,
but a horrible idea now. Home movies from a DV camera, or certain DVD footage may
demonstrate interlacing. If your video has these lines, Click the “Deinterlace” checkbox on
the Advanced panel.
How can I speed up VisualHub?
1. Hide the VisualHub window. Progress bars in Mac OS X can use a surprising amount of CPU. Hiding or
minimizing the VisualHub window will prevent the bar from updating.
2. Check for other programs hogging up the processor. Open Activity Monitor in /Applications/Utilities/. There,
you can sort by “% CPU” to see what programs are the most active. VisualHub’s main conversion process is
“ffmpeg” (movtoy4m helps for QuickTime files).
Quit open programs that aren’t vital.
3. For QuickTime files, force ffmpeg Decoding.
QuickTime files use a different decoding method that’s slower, but provides maximum compatibility. Try checking the
“Force” box in the Advanced panel and choose “ffmpeg Decoding” for a potential speed boost. It won’t work well on
all files though.
None of this is helping! What do I do?
Take it easy. Help is a few clicks and some panicked typing away.
Go to the Techspansion Forums and check the Knowledge Base
for some frequently-asked questions. If that doesn’t help, post a
topic in the Support forum.
The log VisualHub offers at the end of encoding is very helpful when solving problems.
Archived log files are available at ~/Library/Logs/Techspansion in your home folder.
http://www.techspansion.com/forums/
36
Page 37

Chapter 15:
Appendix
"...But what I'd really like to do is drive a flaming bus through a wall of TVs with a stick of
dynamite strapped to my head."
- Pinky, Rocko’s Modern Life
37
Page 38

(vermiform appendix)
38
Page 39

Appendix A:
Cheat Codes
"The arcade version of Gradius is really difficult, right? I never played it that much, and
there was no way I could finish the game, so I inserted the so-called Konami code
(laughs)."
- Kazuhisa Hashimoto
39
Page 40

What in the world is a “cheat code”? How do I rescue the princess?
A “cheat code” in this sense is a very advanced setting for people who want to go above and beyond the GUI. A cheat
code could also be a way to use VisualHub in strange, horrible ways.
Many Cheat Codes are selectable from the Advanced panel. All cheat codes should go in the “Extra ffmpeg Flags”
section in the Advanced drawer unless otherwise noted.
Explanation String
Best possible H.264/AVC
(much slower):
Best possible H.264/AVC for
animation (much slower):
-refs 5 -me umh -subq 6 -me_range 21 -me_threshold 6 -i_qfactor 0.71428572
-refs 5 -me umh -subq 6 -me_range 21 -me_threshold 6 -i_qfactor 0.71428572
-deblockalpha 1 -deblockbeta 1
Encode only a specific
duration (in seconds):
Start encoding n seconds
into the video file:
Make a .mp4 file compatible
with both the iPod AND PSP
Mid-batch settings change: Did you know you can change settings during a batch encode? The next file in line will
Copy original video track
(passthrough):
Copy original audio track
(passthrough):
Best possible MPEG-4
(much slower):
Use n keyframes: -g n
Konami Code:
-t n
-ss n
For MPEG-4: Use any PSP setting
For H.264/AVC: Check PSP’s AVC setting and type “-level 13” into Extra ffmpeg Flags
get the new settings. You really shouldn’t do this, but you can if you live dangerously.
-vcodec copy
-acodec copy
-mbd 2 -flags +4mv+trell -aic 2 -cmp 2 -subcmp 2
ⒷⒶ
Add your own
Have any Cheat Codes of your own? Submit them to the VisualHub Forum! http://www.techspansion.com/forums/
40
Page 41

Appendix B:
Supported Codecs/Formats
“Note, the names of encoders and decoders dont always match, so there are several
cases where the above table shows encoder only or decoder only entries even though
both encoding and decoding are supported for example, the h263 decoder corresponds
to the h263 and h263p encoders, for file formats its even worse”
- ffmpeg Source
41
Page 42

Extra Information
What follows are charts of supported video/audio codecs and container formats for import into VisualHub. Supported
output formats are the selection tabs in the main interface. “Partial” means not all files in that format/container are
supported - it’s hit or miss depending on container/codec-specific information. VisualHub cannot convert protected files,
as found on the iTunes Music Store or Windows-based audio/video stores.
Video Codecs
All QuickTime Codecs
MPEG-1
MPEG-2
MPEG-4 (DivX, XviD, etc)
MSMPEG4
WMV7
WMV8 (partial)
WMV9
H.263
H.264
Flash Video 6/7 (Sorenson Spark)
Flash Video 8 (VP62)
MotionJPEG
DV
HDV
Cinepak
Legacy RealVideo (RV20)
Ogg Theora
Snow
Indeo 2/3
Many other specialized codecs
Audio Codecs
All QuickTime Codecs
MP3
AAC
WAV
AIFF
PCM
AC3
MP2
Ogg Vorbis
WMA (non-specialized, unencrypted)
Legacy RealAudio
Many other specialized codecs
Container Formats
QuickTime: .mov
MPEG-4: .mp4 .m4v (unprotected)
AVI: .avi
MPEG: .mpg .mpeg .m1v .m2v .vob .ts .m2t
WMV: .asf .wmv (unprotected)
DV: .dv
3GPP: .3gp
Flash Video: .flv .swf
Notable Unsupported Exceptions
Modern RealVideo (RV40/RMVB)
Indeo Video 4/5
Ogg Media Container: .ogm (partial)
Matroska: .mkv (partial)
Legacy RealMedia: .rm (partial)
42
Page 43

Appendix C:
Credits and Other Info
43
Page 44

Credits
License Information
ffmpeg
©2006 ffmpeg Contributors.
ffmpeg is a trademark of Fabrice Bellard.
http://ffmpeg.sourceforge.net
FAAC, FAAD
©2004 AudioCoding - http://www.audiocoding.com
libvorbis, libogg
© 1994-2006 Xiph.org - http://xiph.org
liba52
http://liba52.sourceforge.net
LAME
http://www.mp3dev.org/
x264, libdca
http://developers.videolan.org
movtoy4m, movtowav, movinfo
©2002-2005 Johan Lindström
http://homepage.mac.com/johan/
dvb-mpegtools
libdvb - http://www.metzlerbros.org/dvb/index.html
qt_export
@2003-2004 David Van Brink
http://www.omino.com/~poly/software/qt_tools/
yuvcorrect, y4mtoppm, ppmtoy4m
MJPEG Tools - http://mjpeg.sourceforge.net/
pnmcrop
Netpbm - http://netpbm.sourceforge.net/
mkisofs
CDRecord
http://cdrecord.berlios.de/old/private/cdrecord.html
dvdauthor
http://dvdauthor.sourceforge.net/
catMovies
http://www8.atwiki.jp/quicktimeprogramer/pages/5.html
Installing and using the software indicates your
agreement to the terms of this license. If you do not
agree to the terms of this license you must uninstall and
delete the software from your computer.
All rights and privileges are reserved except as explicitly
defined in this document.
VisualHub's license allows household use. Any
computers within or controlled by the members of a
standard household are allowed to share the same
license. A user may install the software and license on
their home and personal work computer. Your uncle Phil
from Oregon is not in the same household as you. The
cute girl in Accounting’s computer is not your work
computer. She wouldn’t go out with you anyway.
Commercial use of single license on multiple computers
is prohibited without a separate commercial license.
Contact techspansion@mac.com
licenses.
You may not share your Registration Code with persons
outside your immediate family or household.
You may not redistribute the software.
You may not alter or reverse engineer the software.
for details on volume
Warranty
This program is provided as-is without warranty. Limited
technical support is provided through e-mail and support
forums. No software program will be perfect until robots
start writing them. No promises are made that VisualHub
is error-free. Techspansion LLC and its members will not
be liable for damages or losses, tangible or intangible,
arising out of use of this software.
play_title
libdvdread - http://www.dtek.chalmers.se/groups/dvd/
development.shtml
lsdvd
acidrip - http://untrepid.com/acidrip/lsdvd.html
AtomicParsley - http://atomicparsley.sf.net
44
 Loading...
Loading...