Page 1

Part I
Getting Started
Part II
Learning
Part III
Macintosh
User’s Guide
for Macintosh PowerBook 145
Includes setup instructions and important health-related information
Reference
Part IV
Index
Page 2
K Apple Computer , Inc.
This manual and the software described in it are copyrighted, with all rights reserved.
Under the copyright laws, this manual or the software may not be copied, in whole or
part, without written consent of Apple, except in the normal use of the software or to
make a backup copy of the software. The same proprietary and copyright notices must
be affixed to any permitted copies as were affixed to the original. This exception does
not allow copies to be made for others, whether or not sold, but all of the material purchased (with all backup copies) may be sold, given, or loaned to another person. Under
the law, copying includes translating into another language or format.
You may use the software on any computer owned by you, but extra copies cannot be
made for this purpose.
The Apple logo is a trademark of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other
countries. Use of the “keyboard” Apple logo (Option-Shift-K) for commercial purposes
without the prior written consent of Apple may constitute trademark infringement and
unfair competition in violation of federal and state laws.
©Apple Computer, Inc., 1992
20525 Mariani Avenue
Cupertino, CA 95014-6299
(408) 996-1010
Apple, the Apple logo, APDA, AppleLink, AppleShare, AppleTalk, ImageWriter,
LaserWriter, LocalTalk, Macintosh, ProDOS, and StyleWriter are trademarks of Apple
Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
Apple Desktop Bus, Balloon Help, Chicago, Finder, Disk First Aid, Monaco, PowerBook,
System 7, and TrueType are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc.
Adobe, Adobe Illustrator, and PostScript are trademarks of Adobe Systems
Incorporated, registered in the United States. Adobe Photoshop is a trademark of
Adobe Systems Incorporated.
AGFA is a registered trademark of Agfa-Gevaert, AG.
Classic is a registered trademark licensed to Apple Computer, Inc.
Exposure is a registered trademark of Preferred Publishers, Inc.
Helvetica and Times are registered trademarks of Linotype Company.
ITC Garamond is a registered trademark of International Typeface Corporation.
MacWrite is a registered trademark of Claris Corporation.
MS-DOS is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
QMS is a registered trademark and ColorScript is a trademark of QMS, Inc.
QuarkXPress is a registered trademark of Quark, Inc.
SelectSet is a trademark of Miles, Inc., Agfa Division.
SuperPaint is a registered trademark of Aldus Corporation.
Tektronix is a registered trademark and Phaser is a trademark of Tektronix, Inc.
Simultaneously published in the United States and Canada.
Mention of third-party products is for informational purposes only and constitutes nei-
ther an endorsement nor a recommendation. Apple assumes no responsibility with
regard to the performance or use of these products.
AppleCare is a service mark of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other
countries.
Page 3
Contents
Preface How to Use This Book xiii
Radio and television interference xv
Part I Getting Started With
n
Your Computer 1
Chapter 1 Setting Up Your Macintosh
PowerBook 1
Setting up the computer 2
Step 1: Plug in the power adapter 2
Step 2: Open the display 3
Step 3: Turn on the computer 4
Trouble? 5
Installing system software 6
Continuing your work 7
What to do next 8
Learning the basics 10
Before you begin 10
Finding the tour 11
Starting the tour from the hard disk 11
Starting the tour from a floppy disk 15
Turning the Powerbook on and off 17
Off 17
Sleep 18
On 19
On/off summary 19
When you turn on your computer 20
Restarting a computer that’s already on 21
Restarting a computer that can’t be turned on normally 21
Important care and safety instructions 23
± Warning 23
s Caution 24
S Important 25
Your computer at a glance 9
Health concerns associated with computer use 26
Repetitive stress injuries 26
Arranging your work space and equipment 27
iii
Page 4

n Part II Learning Macintosh 31
Chapter 3 Creating and Changing
a Document 51
Chapter 2 Working on the Desktop 31
Use the trackball 32
Point 32
Click 33
Press 34
Drag 35
Choose a command 36
Giving orders to your computer 36
Open an icon 37
Look at the contents of a window 38
Make a window the active window 38
Make a window larger or smaller 40
Move the hidden contents of a window into view 42
Close a window 44
Move a window 45
What’s on the desktop? 46
Open a program 52
Create a document 53
Save your work 53
Switch programs 54
Close a document 56
Two types of programs 57
Open a document 57
Change a document 58
Save your work so far 61
Taking a shortcut 62
Make more changes 62
Quit a program 64
Opening and closing documents and programs 65
Make a copy of a document 65
Change the name of an icon 66
Use the Trash 67
Using the keyboard 49
iv Contents
Page 5

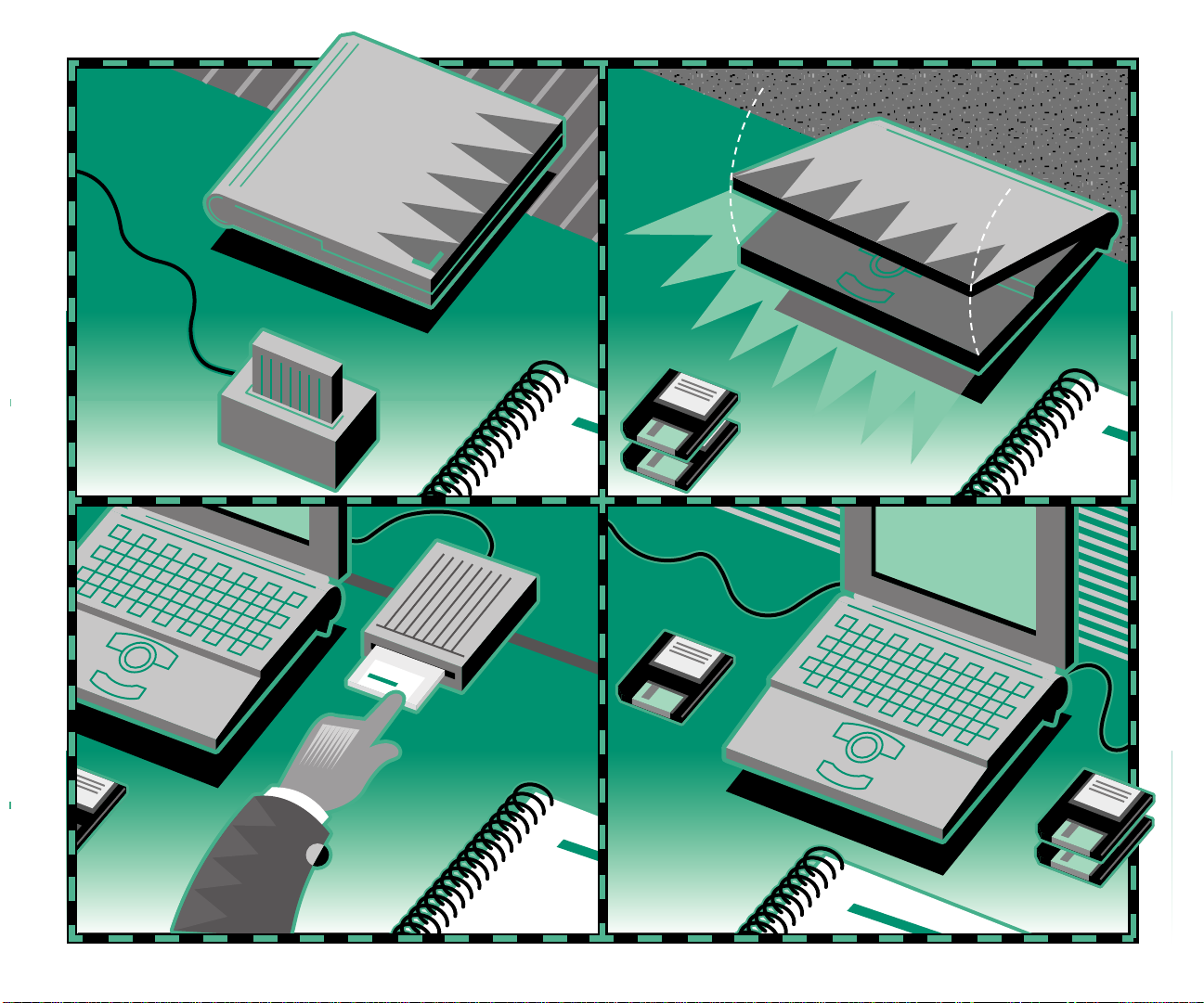
Chapter 4 Working With Disks 69
Insert a floppy disk 70
n
Part III Macintosh R eference 87
Floppy disks and hard disks 71
Initialize a disk 72
Copy the contents of a disk 74
Taking care of floppy disks 75
Take a floppy disk out of its drive 76
Protect the contents of disk 77
On your own: Install your programs 78
Throw away extra System Folders 79
Chapter 5 Learning More About
Your Computer 81
Open the Battery desk accessory 82
Open the PowerBook control panel 82
Use Balloon Help 83
Turn on Balloon Help 84
Turn off Balloon Help 84
Use Part III of this book 85
What next? 85
Chapter 6 Setting Up Your Programs 87
Installing or updating system software 87
Before you install 88
Installing system software 88
Installing customized system software 90
Starting up with a floppy disk 91
Installing your programs 92
Installing programs without a floppy disk drive 92
Checking for computer viruses 93
Working with several programs at a time 94
Finding out what programs are open 94
Switching programs 94
Hiding and showing windows on the desktop 94
Changing the amount of memory a program uses 95
Using the Scrapbook 96
Storing items in the Scrapbook 96
Copying items from the Scrapbook 96
Deleting items from the Scrapbook 96
Contents v
Page 6

Using a RAM disk 97
Creating a RAM disk 97
Erasing a RAM disk 98
Resizing or removing a RAM disk 98
Making a RAM disk the startup disk 99
Chapter 7 P ower Management 101
Monitoring the battery charge level 101
Using the battery desk accessory 101
Responding to low-power messages 102
Recharging the battery 103
Recharging with the power adapter 103
Recharging with a recharger 105
Removing or replacing the battery 106
Maximizing battery life 108
Maximizing work time 109
Ways to conserve battery power 109
Adjusting the battery conservation settings 110
Using the battery conservation options 111
Chapter 8 Using Disks 113
Preparing a new disk for use 113
Initializing a hard disk 113
Initializing a floppy disk 115
Erasing a floppy disk 116
Designating a startup disk 116
Scanning order for startup disks 117
Protecting the information on a disk 117
Locking a floppy disk 117
Locking a file 118
Backing up your files 119
If you can’t save files on a floppy disk 119
Ejecting a disk 120
If you can’t eject a floppy disk 120
Caring for disks 121
Hard disk precautions 121
Testing and repairing disks 121
If a hard disk icon doesn’t appear 121
Using Disk First Aid 122
vi Contents
Testing a hard disk 124
Page 7

Chapter 9 Organizing Your Files 125
Straightening up your files 125
Using folders to organize your files 126
Creating and naming folders 126
Filing documents when you save them 127
Making items easier to find 128
Creating an alias 128
Installing an item in the Apple menu 129
Moving an item to the desktop 129
Finding an item 130
Finding an item by name 130
Finding an item using other criteria 131
Finding items that meet two criteria 133
Ways to use the Find command 132
Creating a template or stationery 134
Getting information about your files 135
Using the Info window 135
Using the View menu 136
Assigning a label to a file 136
Tips on transferring files 137
Chapter 10 Adapting Your Computer to
Your Own Use 139
Specifying which items you want opened at startup 140
Installing an item in the Apple menu 140
Installing files in the System Folder 140
Removing files from the System Folder 141
Changing the items in the Label menu 142
Setting the time and date 142
Setting a time for the Alarm Clock to go off 143
Turning the alarm off 144
Changing time and date formats 144
Changing the date format 145
Changing the time format 146
Changing number and currency formats 147
Adjusting the way the trackball or mouse works 148
Adjusting the way the keyboard works 149
Making keyboard shortcuts easier to type 150
Adjusting the keyboard for very slow typing 150
Adjusting the blinking of a menu item 151
Adjusting the blinking of the insertion point 151
Changing the way the contents of windows appear 152
Changing an icon 153
Contents vii
Page 8

Turning off the Empty Trash warning 154
Controlling background printing 175
Managing memory 155
Checking memory use 155
Making the most of your memory 155
Adjusting the disk cache 156
Using hard disk space as memory 157
Turning on 32-bit addressing 158
Setting the beep sound 159
Installing a sound 160
Removing a sound 160
Recording sounds 161
Changing the background pattern 162
Magnifying the screen image 164
Chapter 11 Printing 167
Before you print 167
Choosing a printer 167
Selecting Page Setup options 170
Updating printer software on networked computers 171
Printing your work 172
Printing the contents of a window or the desktop 173
Solutions to common printing problems 174
Working with fonts 176
Outline fonts and bitmap fonts 176
Installing fonts 177
Removing fonts 178
Transferring fonts to a LaserWriter printer 178
Finding out about available fonts 180
Other ways to use the LaserWriter Font Utility 180
Chapter 12 Using Your Computer
on a Network 183
What networking offers 183
Setting up your computer on a network 184
Connecting to a network 185
Turning on AppleTalk 185
Naming your computer and its owner 186
Gaining access to files on shared disks 187
Before you begin 187
Connecting to a shared disk 187
Disconnecting from a shared disk 189
Connecting quickly to a shared disk 190
Connecting automatically when you start up 190
viii Contents
Page 9

Working with files and folders on other computers 191
Creating a new folder on another computer 191
Changing your password 191
Giving folder ownership to someone else 193
Sharing your own files 193
How file sharing works 193
Turning file sharing on 194
Turning on guest access 194
Selecting a folder or disk to share 195
Naming a registered user 197
Setting a registered user’s password 198
Naming a group of users 198
Seeing who’s in a group 199
Selecting a user or group to share a folder or disk 200
Preventing specific users or guests from accessing your
computer 201
Removing a user from a group 202
Disconnecting someone who is connected to
your computer 205
Gaining access to your computer from another computer 205
Changing your password 206
Using access privileges 207
Understanding access privileges 207
Setting access privileges to folders and disks 208
Access privilege strategies 209
Working with privileges others have set 211
Checking your access privileges 211
Linking programs 212
Linking to a program on another computer 212
Disconnecting a program link 213
Allowing other people to link to your programs 213
Chapter 13 Expanding Your Computer
System 217
Removing a user or group from your list of registered
users 202
Giving away ownership of a folder or disk on your
computer 203
Turning file sharing off 203
Monitoring file-sharing activity 204
Using SCSI devices 217
Installing software 218
Setting SCSI ID numbers 218
Checking that the SCSI chain is properly terminated 220
Connecting cables 221
Contents ix
Page 10

Connecting a modem 222
Connecting a printer 223
Connecting a mouse or other ADB device 223
Using sound input and output devices 224
Connecting a microphone 224
Sound output devices 225
Adding memory to your computer 225
Chapter 14 Travel, Storage, and Service 227
Traveling with the PowerBook 227
Storing the PowerBook 228
Short-term storage (up to 2 weeks) 228
Long-term storage (more than 2 weeks) 229
Service and support 229
If the PowerBook malfunctions or is damaged 229
How to get help 230
For more information about Macintosh computers 231
Quick Reference Summary and Shortcuts 233
Shift-Click 233
Working with icons 233
Selecting icons 233
Opening an icon 234
Moving, copying, and renaming an icon 234
Working with windows 234
Making a window the active window 234
Moving a window and changing its size 234
Scrolling through the contents of a window 235
Opening higher-level folder windows 235
Using the outline form in list views 236
Working with menus 236
Choosing an item from a menu 237
Choosing an item from a submenu 237
Keyboard shortcuts in the Finder and in directory
dialog boxes 238
x Contents
Macintosh user groups 231
Technical information 231
Page 11

Troubleshooting 239
The PowerBook 239
Power 241
The Screen 243
Appendix A Keyboard and Character Sets 253
Using Caps Lock 254
Typing special characters and symbols 254
Memory 244
SCSI devices 244
Disk drives and disks 245
Modems 248
Printers 248
Networks 250
Application programs 251
Appendix B Exchanging Disks and Files with
MS-DOS Computers 257
Initializing a disk in MS-DOS format 257
Converting files to and from MS-DOS format 269
Other file-conversion options 261
Contents xi
Page 12

Appendix C Map 263
Setting your location 263
Comparing locations 264
Finding a location 265
Adding or removing a location 266
Adding a location 266
Changing or removing a location 266
n
Part IV Index 271
xii Contents
Page 13
Preface
How to Use This Book
This book has several parts.
Certain kinds of information are not included in this book.
n Information about modems. If your computer has a built-in
modem, or if you purchase one later, you receive a separate
modem manual with instructions for its use.
n Chapter 1 explains how to set up your computer and learn
how to use it.
n Chapters 2–5 are a tutorial designed for people who have not
used a Macintosh computer before. If you are new to the
Macintosh, you should read this section of the book before
you start your own work.
n Chapters 6–14 contain reference information that will help
you as you become more proficient with your computer.
Youcan turn to these chapters for information about a
particular topic.
n At the back of the book you’ll find a troubleshooting section
and an index.
n Information about application programs. Your best source of
information about a particular program is the set of books and
disks that came with that program.
n Technical specifications for your PowerBook model. These are
on a separate sheet in the box with your computer.
Turn now to Chapter 1 to set up your new PowerBook computer.
Welcome to Macintosh.
xiii
Page 14

xiv
Page 15

Radio and television interference
Important
The equipment described in this manual generates, uses, and can radiate radiofrequency energy. If it is not installed and used properly—that is, in strict accordance
with Apple’s instructions—it may cause interference with radio and television reception.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device in accordance with the specifications in Part15 of FCC rules. These specifications
are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in a residential
installation. However, there is no guarantee that the interference will not occur in a
particular installation.
You can determine whether your computer system is causing interference by turning it
off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the computer or one of the
peripheral devices.
If your computer system does cause interference to radio or television reception, try to
correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
n Turn the television or radio antenna until the interference stops.
n Move the computer to one side or the other of the television or radio.
n Move the computer farther away from the television or radio.
n Plug the computer into an outlet that is on a different circuit from the television or
radio. (That is, make certain the computer and the television or radio are on circuits
controlled by different circuit breakers or fuses.)
If necessary, consult your authorized Apple dealer or an experienced radio/television
technician for additional suggestions. You may find helpful the following booklet,
prepared by the Federal Communications Commission: Interference Handbook (stock
number 004-000-00345-4). This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing
Office, Washington, DC 20402.
S Important: Changes or modifications to this product not authorized by Apple
Computer, Inc., could void the FCC Certification and negate your authority to
operate the product.
This product was tested for FCC compliance under conditions that included the use
of shielded cables and connectors between system components. It is important that
you use shielded cables and connectors to reduce the possibility of causing
interference to radios, television sets, and other electronic devices. For Apple
peripheral devices, you can obtain the proper shielded cables from your authorized
Apple dealer. For non-Apple peripheral devices, contact the manufacturer or dealer
for assistance.
S
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device in accordance with the specifications in Part 15 of FCC rules. See
instructions if interference to radio or television reception is suspected.
DOC Class B Compliance This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits
for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus set out in the radio interference
regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Observation des normes—Classe B Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de
bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables aux appareils numériques de la
Classe B prescrites dans les règlements sur le brouillage radioélectrique édictés par le
Ministère des Communications du Canada.
xv
Page 16
Page 17

s
s
Chapter 1
Setting Up Your
Macintosh P owerBook
In this chapter
m Setting up your computer
m Installing system software
m Learning how to use your computer
m New Macintosh users:If you have never used a Macintosh
computer before, read this entire chapter. It explains how
toset up your computer, learn how to use it, and turn it on
and off.
m New PowerBook users:If you have used other Macintosh
computers but are new to the PowerBook, follow the setup
instructions that begin on the next page and then go to the
section on turning the PowerBook on and off.
m Experienced PowerBook users:Skim this chapter for
information that applies to your computer.
m Turning the computer on and off
m Important care and safety instructions
m Being comfortable while you work
Important: No matter what your level of experience, please
read the safety information in this chapter before beginning
your own work. This information can help protect you and
your computer equipment from possible harm.
1
Page 18
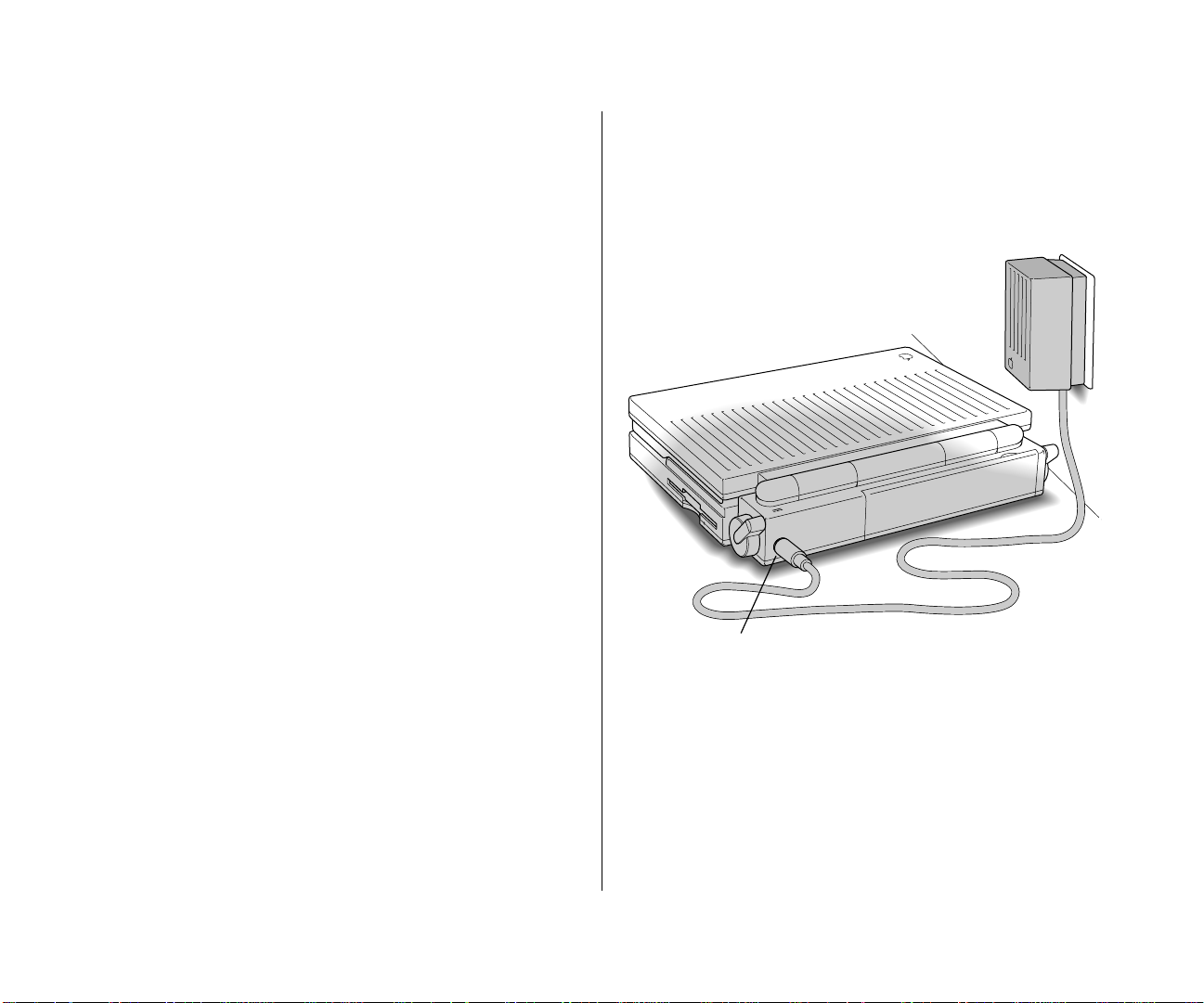
Setting up the computer
Step 1: Plug in the power adapter
Plugging in the power adapter recharges the computer’s battery
while you work. You should plug it in now in case the battery has
drained during shipping and storage.
s Warning: Use only the power adapter that came with your
PowerBook computer. Adapters for other electronic devices
(including other portable computers) may look similar, but
they may damage your computer.
s
m Plug the power adapter into a standard electrical outlet
or power strip. Then plug the power adapter cable into
the power adapter port (marked with the icon ¯) on
the back panel of the computer.
Power adapter port
2 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 19
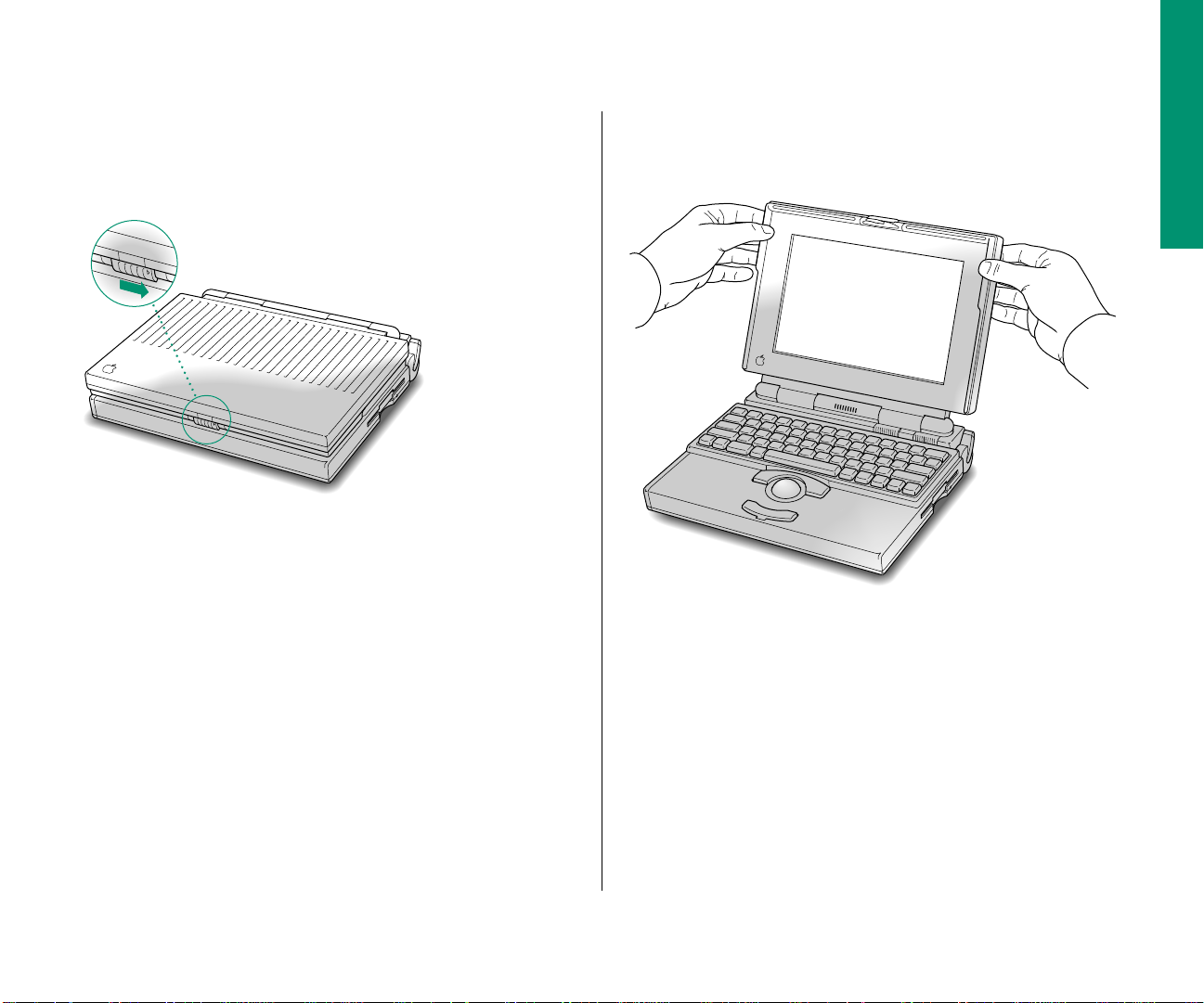
Step 2: Open the display
m Slide the latch to the right and lift up the display.
Position the display at a comfortable viewing angle. You can
adjust the angle of the display at any time.
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 3
Page 20
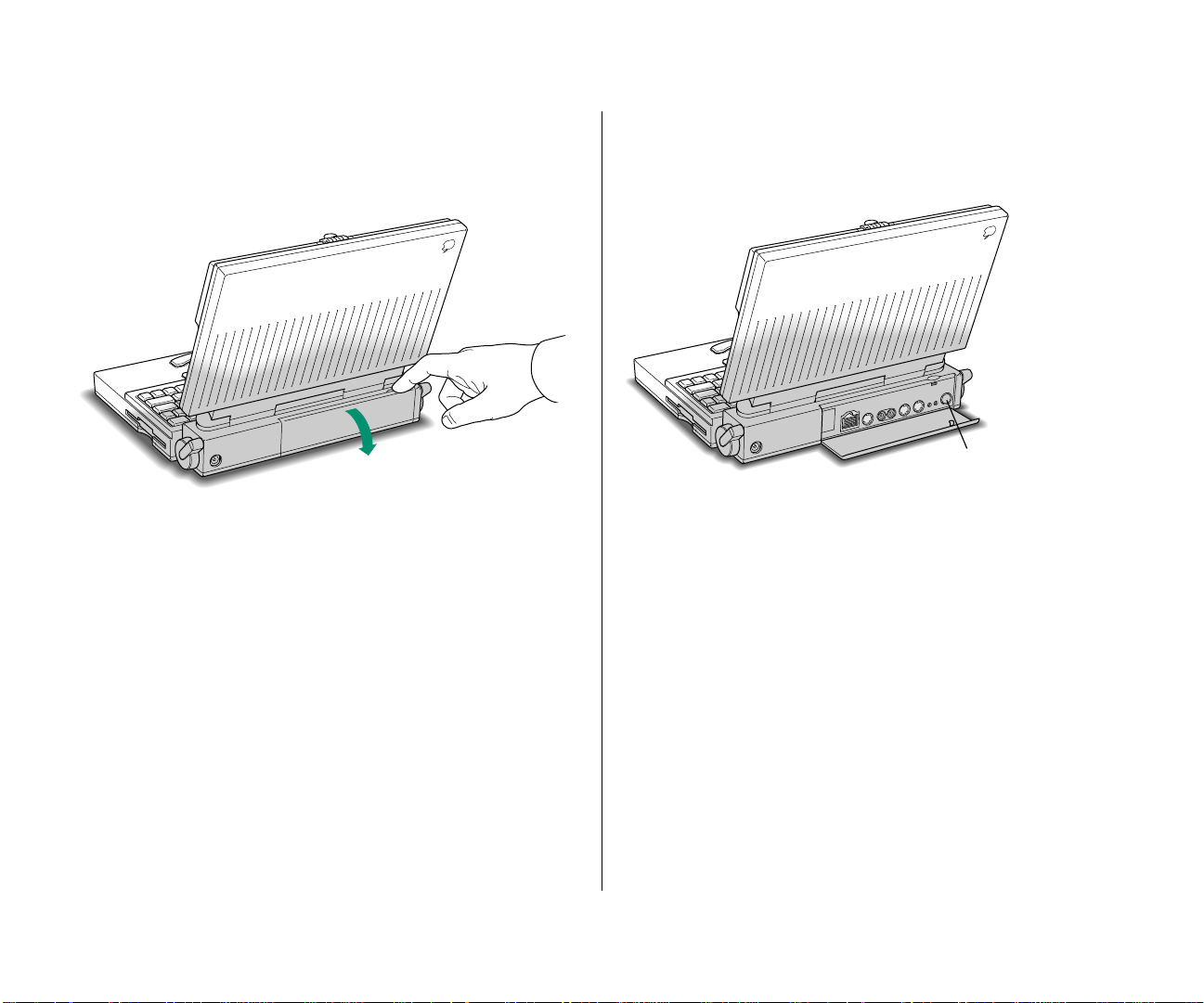
Step 3: Turn on the computer
m Open the door to the back panel of your computer.
m Press the power button to turn the computer on. The
power button has this icon: I
Power button
You hear a tone when you turn on the computer. It takes the
computer a moment to start up.
4 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 21
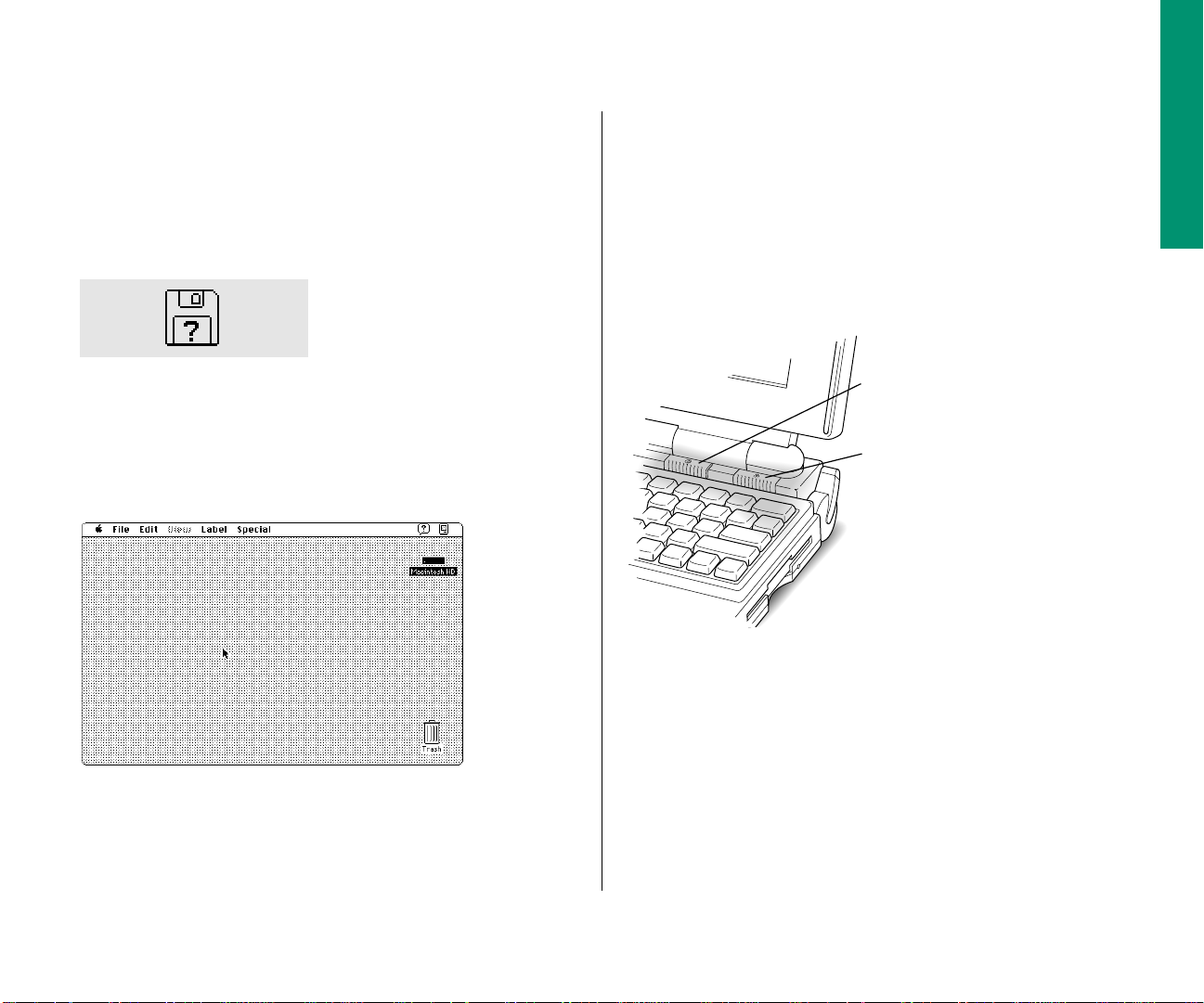
m If you see a blinking question mark on your screen, you
needto install system software on the computer’s hard disk.
System software includes the programs the computer uses to
start itself up. Continue with the section “Installing System
Software.”
m If you see the Macintosh desktop on your screen, the
computer is ready to use. You do not need to install system
software. Continue with the section “What to Do Next.”
Trouble?
m The computer made a sound, but you can’t see anything on
the screen.
Adjust the brightness control (marked with the icon ¤) and
the contrast control (O) until an image appears and the
screen is easy to read.
Contrast control
Brightness control
m Nothing happened when you pressed the power button.
Make sure the power adapter is firmly connected to both
thecomputer and a power source. If the power adapter is
plugged into a power strip, make sure the power strip is
plugged in and turned on. Then try pressing the power
button again.
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 5
Page 22
Installing system software
System software is a set of programs that your computer uses to
start up and operate. To install system software on your hard disk,
follow these steps.
You do not need to install system software if you see the
Macintosh desktop on your screen when you turn on the
computer.
1. Find the Install disk provided with your computer.
Insert the disk into the floppy disk drive (metal end
first, label side up).
2. Press the Return key on your keyboard to continue.
The Easy Install dialog box appears. Easy Install puts the
system software that you’ll need right away onto your hard
disk.
3. Press the Return key again to start installing system
software.
Messages on your screen report how installation is
progressing.
4. When the computer prompts you, remove the Install
disk and insert the next disk the computer requests.
During installation, the computer automatically ejects a disk it
has finished with and requests the next disk it needs.
Insert metal end first.
After a few moments, you’ll see the Welcome box of the
Installer, the program that installs system software on your
hard disk.
6 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
5. Insert the remaining disks as the computer
prompts you.
6. When you see a message reporting that installation was
successful, press the Return key once more to quit the
Installer program.
If you see a message saying that installation was not
successful, you need to try again. Follow the instructions on
the screen.
Page 23

Continuing your work
2. Roll the trackball around with your fingers.
Next you see a message that asks whether you want to continue
using your Macintosh. To continue working or to learn how to use
the computer, use the trackball to choose Restart.
1. Place the index and middle fingers of your dominant
hand on the trackball and the thumb of the same
hand on the lower trackball button. Don’t press either
button yet.
Notice that the arrow (8) on the screen moves in the direction
that you roll the trackball. For example, rolling the trackball to
the right moves the arrow to the right.
3. Roll the trackball so the arrow rests over the word
Restart.
Make sure that the tip of the arrow is inside the box with the
word Restart.
continues .
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 7
Page 24
4. Press and release one of the trackball buttons.
Both buttons do the same thing.
The screen darkens, you hear a sound, and then after a
moment the Macintosh desktop appears on the screen.
If nothing happens, try clicking the word Restart again. Make sure
that the tip of the arrow is inside the box with the word Restart.
What to do next
m If you have never used a Macintosh computer before,
continue with the section “Learning the Basics.”
m Otherwise, continue with the section “Turning the PowerBook
On and Off.” This section contains information that can help
you use your computer efficiently.
m Be sure to read the safety instructions and the section on
health concerns before beginning to use your PowerBook.
8 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 25
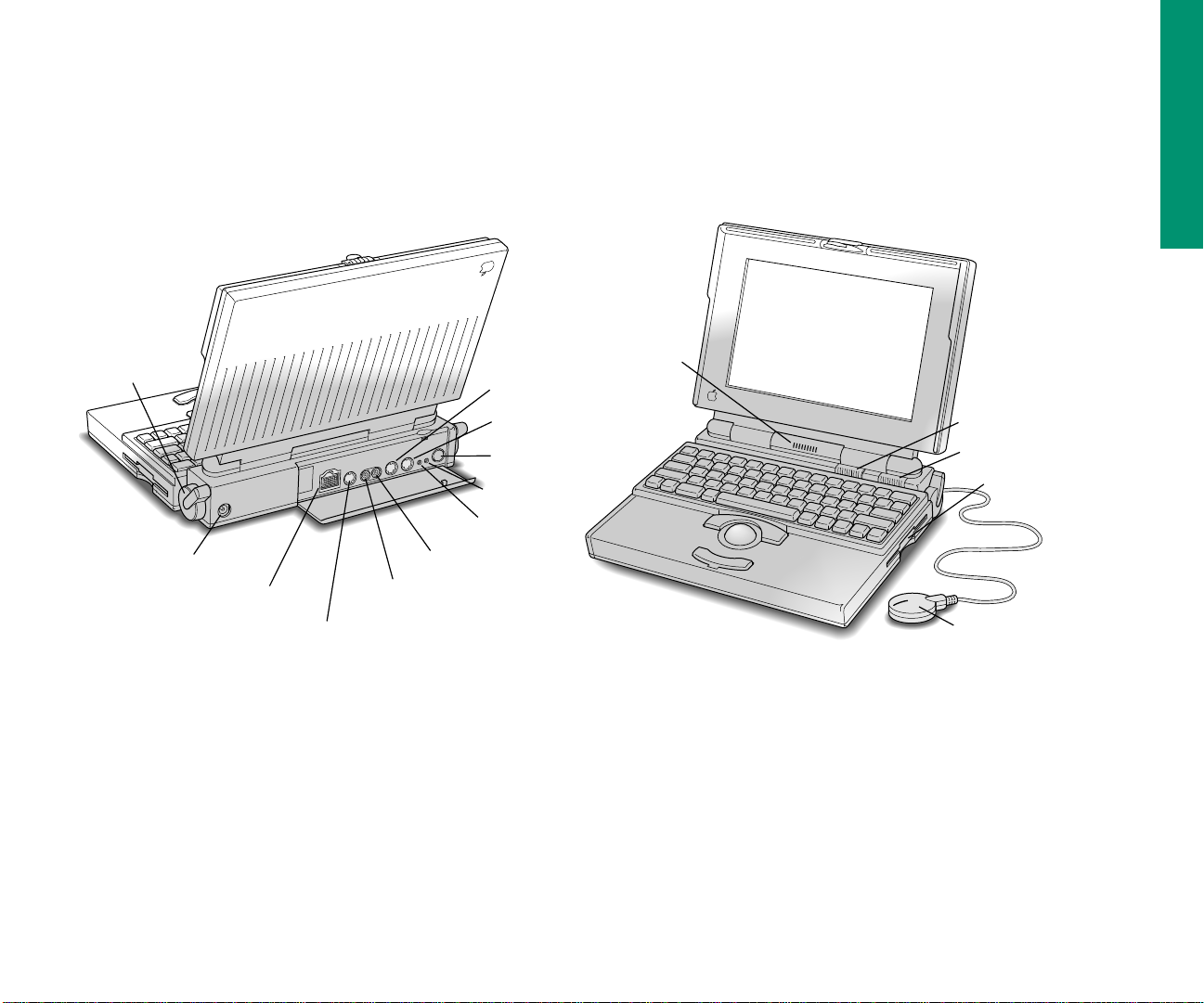
Your computer at a glance
Elevation feet
Speaker
[ Printer port
¯ Power adapter port
g SCSI port (HDI-30)
V Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) port
¥ Interrupt button
- Sound out port
≈ Sound in port
W Modem port
I Power button
P Reset button
O Contrast control
¤ Brightness control
Floppy disk drive
Microphone (optional)
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 9
Page 26

Learning the basics
Before you begin
The PowerBook comes with a tour and a tutorial to help you start
using your computer as quickly as possible.
m The Macintosh Basics tour teaches the most basic skills you
need to master before you can use your computer.
m The tutorial section of this book (Chapters 2–5) reviews the
basic skills taught in the tour, and teaches a few additional
skills you’ll find helpful as you become more proficient.
Take the Macintosh Basicstour first.
Make sure your computer is turned on. If the screen is dark, try
the following steps in order until you see the Macintosh desktop
on your screen.
1. Adjust the screen brightness and contrast controls.
If you see the Macintosh desktop, skip to “Finding the Tour.”
2. Press any key on the keyboard (except Caps Lock).
Pressing a key wakes the computer if it was in sleep (a powerconserving state described later in this chapter). If you see the
Macintosh desktop, skip to “Finding the Tour.”
3. Press the power button on the computer’s back panel.
Pressing the power button turns the computer on if it was off.
Continue with “Finding the Tour.”
10 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 27
Finding the tour
Starting the tour from the hard disk
Your Macintosh Basicstour may be on a floppy disk, or it may be
on the computer’s hard disk.
m If the Macintosh desktop appeared on the screen when you
first turned on your computer, then the system software
andthe Macintosh Basics tour were installed on your
computer’s hard disk at the factory. Continue with the section
“Starting the Tour From the Hard Disk.”
m If you needed to install system software when you set up your
computer (as described in the previous section of this
chapter), then the Macintosh Basics tour is on a floppy disk in
the box with your computer. Locate the disk and continue
with the section “Starting the Tour From a Floppy Disk.”
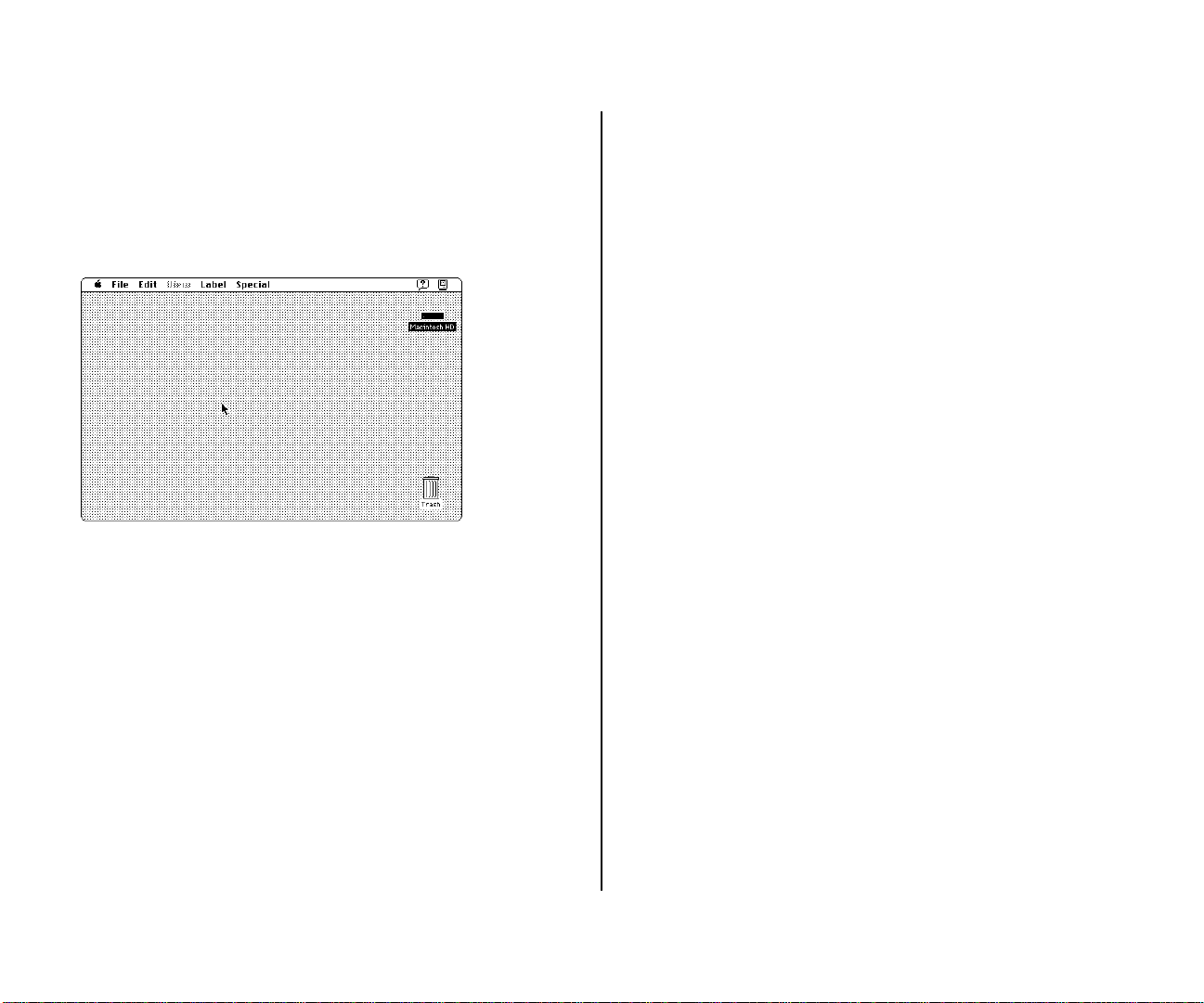
1. Roll the trackball to move the arrow over the picture
labeled “Macintosh HD.”
Make sure the tip of the arrow is over the picture, not over
the words “Macintosh HD.”
continues .
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 11
Page 28
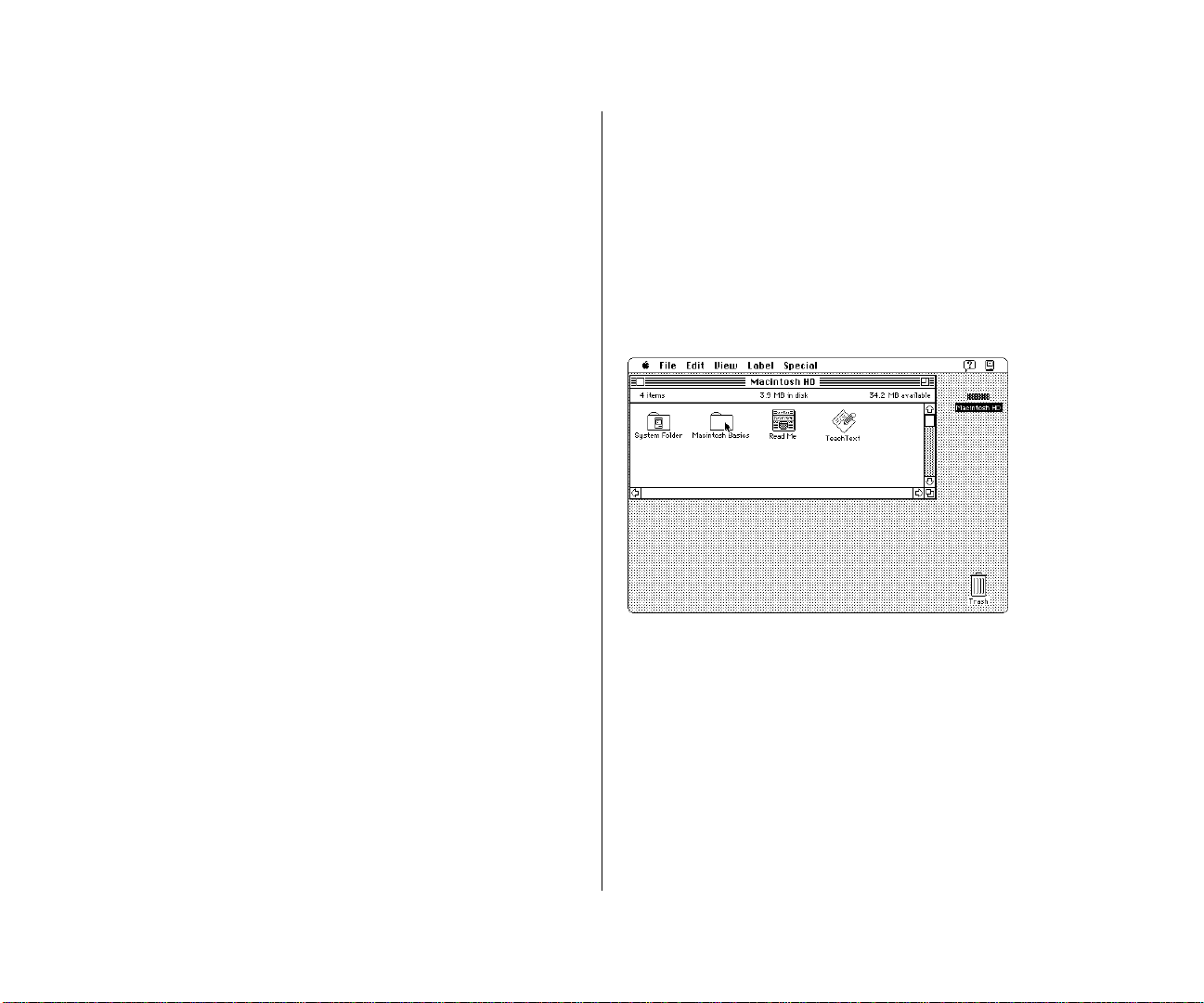
2. Being careful not to roll the trackball, press the
trackball button twice in quick succession.
3. Roll the trackball to move the arrow over the picture of
the folder labeled “Macintosh Basics.”
Now your screen should look like the picture following step 3.
If it doesn’t, try steps 1 and 2 again, paying special attention to
the following:
m Make sure the tip of the arrow is touching the picture, not
the words beneath it.
m Be sure to press the trackball button twice.
m Try pressing twice more quickly and be careful not to roll
the trackball while you press.
Make sure the tip of the arrow is over the picture, not over
the words “Macintosh Basics.”
The items in the illustration below may not exactly match
those on your screen. The only item you need right now is the
Macintosh Basics folder.
12 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 29
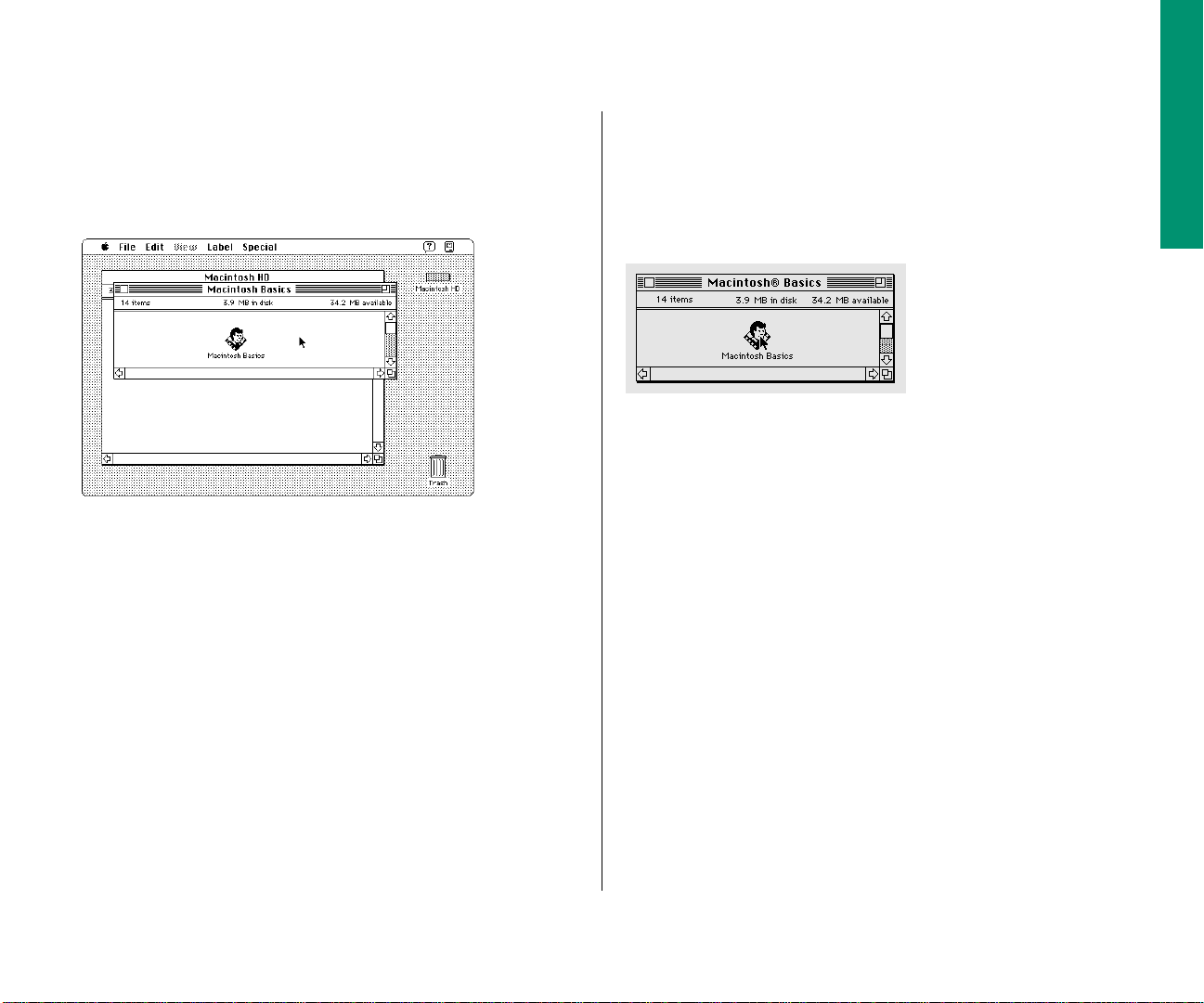
4. Being careful not to roll the trackball, press the
trackball button twice in quick succession.
5. Roll the trackball to move the arrow over the picture of
the man labeled “Macintosh Basics.”
Now your screen should look like the following illustration:
Make sure the tip of the arrow is over the picture of the man,
not over the words “Macintosh Basics.”
continues .
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 13
Page 30

6. Press the trackball button twice in quick succession.
Now your screen should look like the following picture:
If you don’t see this screen, try again, paying special attention
to the following:
m Make sure the tip of the arrow is touching the picture, not
the words beneath it.
7. Follow the instructions on the screen and work through
the tour.
When you finish the tour, continue with “Turning the PowerBook
On and Off” and read the rest of this chapter for information that
can help you use your computer safely and efficiently. Then turn
to Chapter 2 and begin the tutorial.
m Be sure to press the trackball button twice.
m Try pressing twice more quickly and be careful not to roll
the trackball while you press.
14 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 31

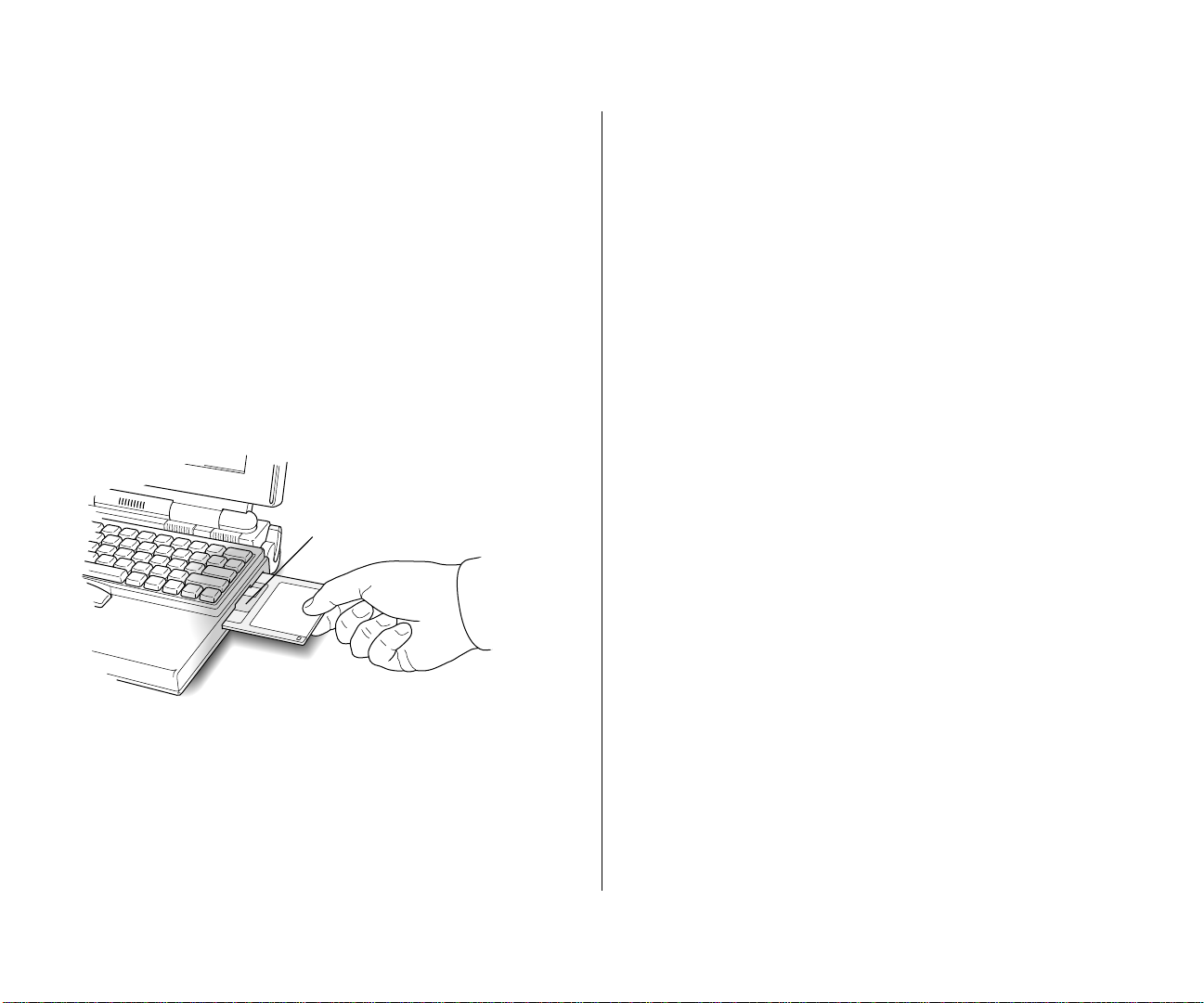
Starting the tour from a floppy disk
1. Insert the Macintosh Basicsdisk into the floppy disk
drive (metal end first, label side up).
Insert metal end first.
After a moment, your screen should look like this:
continues .
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 15
Page 32

2. Roll the trackball to move the arrow over the picture of
the man labeled “Macintosh Basics.”
If you don’t see this screen, try again, paying special attention
to the following:
Make sure the tip of the arrow is over the picture of the man,
not over the words “Macintosh Basics.”
3. Press the trackball button twice in quick succession.
Now your screen should look like the following picture:
m Make sure the tip of the arrow is touching the picture, not
the words beneath it.
m Be sure to press the trackball button twice.
m Try pressing twice more quickly and be careful not to roll
the trackball while you press.
4. Follow the instructions on the screen and work through
the tour.
When you finish the tour, read the rest of this chapter for
information that can help you use your computer safely and
efficiently. Then turn to Chapter 2 and begin the tutorial.
16 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 33

Turning the P owerBook on and off
s
s
To turn the PowerBook off
Your Macintosh PowerBook can be in one of three power states:
off, sleep, or on.
Off
When the PowerBook is off, the computer is not using any power
or doing any work. The terms shut down and offboth refer to this
state.
You should turn the computer off to
m attach other equipment to it
m replace its battery
m conserve power when you won’t be using it for several hours
m If the computer is on, choose the Shut Down command from
the Special menu. (The Macintosh Basics tour teaches how to
choose a menu command.)
m If the computer is in sleep, wake it by pressing any key on the
keyboard (except Caps Lock), and then choose Shut Down.
Important: Don’t shut down with the power button on
theback panel of the computer unless a problem prevents
you from choosing Shut Down. You will lose any work you
didnot save, and you may experience problems with your
hard disk.
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 17
Page 34

Sleep
When the PowerBook is in sleep, it draws enough power to
maintain the information in its memory (including any open
programs and documents). The computer is on, but almost
completely inactive.
You should put the computer to sleep to conserve power when
you take a work break.
To put the PowerBook to sleep
m If the computer is on, choose the Sleep command from the
Special menu.
m If the computer is off, you need to turn it on before you can
put it to sleep.
Automatic sleep
If you don’t use the computer for several minutes, it goes to sleep
automatically. This conserves battery power. You will notice that if
you spend several minutes reading without using the computer,
or if you take a break, the screen may be dark when you’re ready
to resume working.
To wake the computer, press any key on the keyboard (except
Caps Lock). The desktop reappears looking just the way it did
before the computer went to sleep.
18 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 35

On
When the PowerBook is on, you can do your work.
To turn the PowerBook on
m If the computer is off, press the power button (marked with
the icon I).
Power button
On/off summary
If the And you want it to be
power
state is Off Sleep On
Off — — Press power button
Sleep Press any key — Press any key except
to wake, and then Caps Lock (pressing
choose Shut Down the power button
also works)
On Choose Shut Down Choose Sleep —
See the chapter on power management for more information
about managing your computer’s power consumption.
m If the computer is in sleep, press any key on the keyboard
(except Caps Lock).
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 19
Page 36

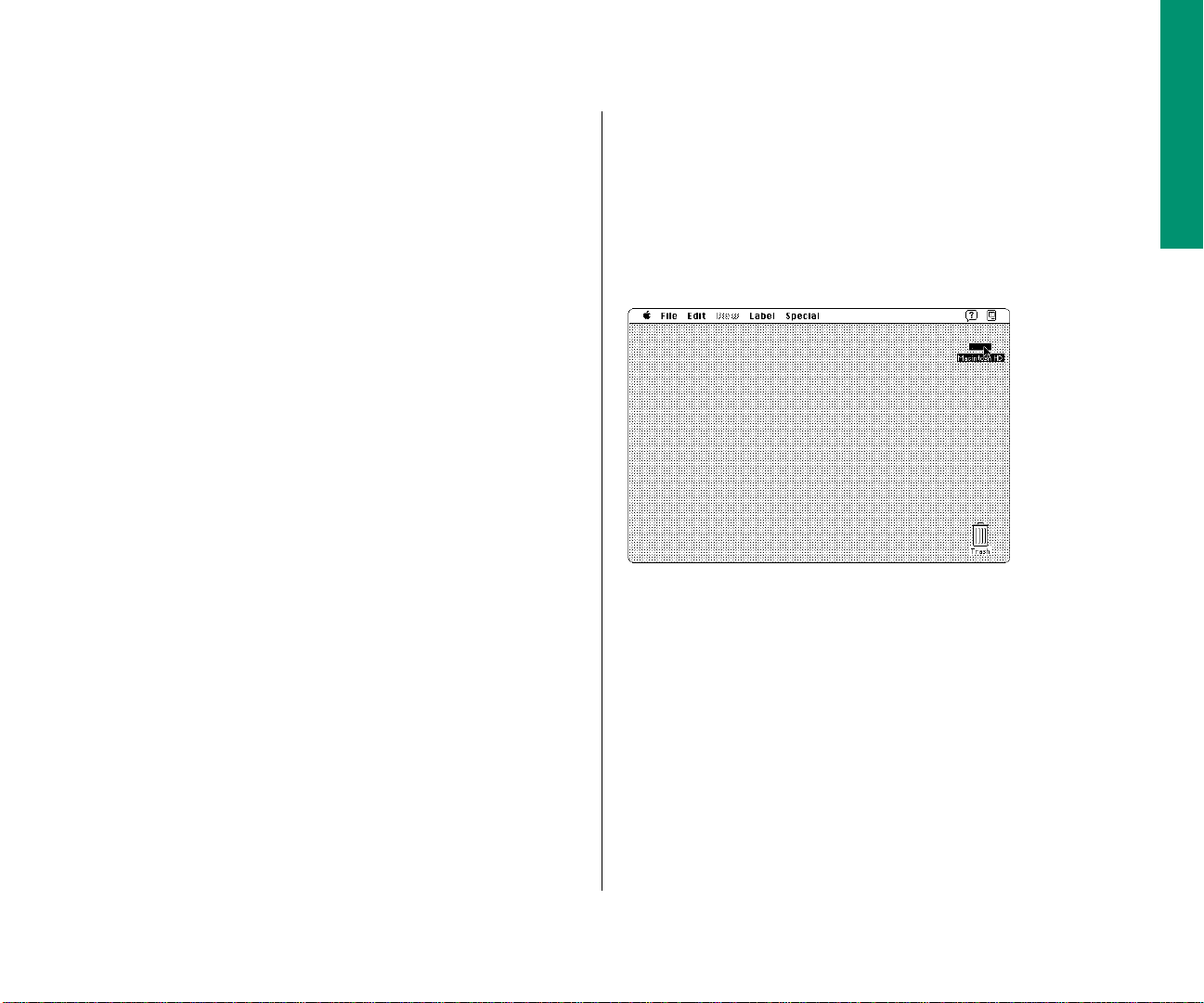
When you turn on your computer
When you turn on your PowerBook, the computer looks on the
hard disk inside the computer for the system software it uses to
start itself up. (A disk that contains the system software is called
a startup disk.) When the computer finds the system software, it
displays the icon shown and proceeds to start itself up.
When the startup process is complete, the Macintosh desktop
appears on the screen. The desktop is a gray pattern with
m a menu bar across the top (containing the names and icons
of menus)
m an icon near the upper-right corner representing the startup
disk
m an icon near the lower-right corner representing the Trash
Menu bar
Startup
disk icon
Trash icon
When you “wake” your computer from sleep, it does not go
through the startup process because it is already on (at a
reduced power level). The Macintosh desktop reappears on the
screen immediately, looking just the way it did before the
computer went to sleep.
20 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 37

Restarting a computer that’s already on
You need to restart your computer—turn it off and back on again
immediately—when you want to make certain changes to your
control panels, use a newly installed system software file, or start
up the computer from a different disk.
m Choose Restart from the Special menu.
When you choose Restart, the computer prompts you to save
your work, closes all open programs, and restarts itself.
Restarting a computer that can’t
be turned on normally
If your system crashes (a rare event resulting from temporary
software problems), or if a computer with a properly installed and
charged battery does not respond when you try to turn it on, you
should be able to restart it using one of the methods described in
this section. Try them in the order given. All these methods will
cause you to lose any work you have not saved.
m Press and release the reset button.
You can press the button with a pen, a paper clip, or a similar
object.
Restarting the computer with the reset button does not affect
your RAM disk (if you created one) or its contents.
Reset buttonInterrupt button
Choosing Restart does not affect your RAM disk (if you
created one) or its contents.
You also need to restart if you see a “system error” message on
the screen (indicating a temporary software problem). In this
case, use the trackball to click the Restart button that appears.
continues .
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 21
Page 38

m Hold down the power button for 5 seconds.
m Restart from a floppy disk.
When you let go, the computer turns itself off. Turning the
computer off with the power button erases the contents of a
RAM disk.
1. Insert the Disk Toolsdisk into the floppy disk drive.
2. Press the power button.
If the computer turns on, there may be a problem with your
hard disk. You may be able to fix the problem yourself (using
the Disk First Aid program or another disk repair program;
see the chapter on disks in the reference section). Or you can
take the computer to your authorized Apple service provider.
22 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 39

Important care and safety instructions
m Always handle batteries carefully.
For your own safety and that of your equipment, read and follow
all the instructions in this section. Keep these instructions
available for reference by you and others.
± W arning
m Electrical equipment may be hazardous if misused. Operation
of this product, or similar products, must always be
supervised by an adult. Do not allow children access to the
interior of any electrical product and do not permit them to
handle any cables.
m Do not use the computer in or near water.
m Do not use cables that are frayed or otherwise damaged. Hold
a cable by its connector (the plug, not the cord) when
connecting or disconnecting it.
m Do not drop, puncture, disassemble, mutilate, or incinerate
the battery.
m Recharge batteries only as described in this manual and only
in ventilated areas.
m Transport batteries either inside the computer or in the
protective case provided with each battery. Do not transport
unprotected batteries.
m Do not short-circuit the battery terminals (that is, do not
allow a metal object such as a paper clip or key chain to touch
the terminals). Doing so may cause an explosion or a fire.
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 23
Page 40

s Caution
m If you have a problem with your computer and nothing
presented in the manuals that came with the computer solves
the problem, take the computer to your authorized Apple
dealer or service provider. Attempting to repair the computer
yourself may void the limited warranty. Contact your
authorized Apple dealer or service provider for additional
information about this or any other warranty question.
m Do not attempt to open the computer’s case. There are no
user-serviceable parts inside. Take the computer to an
authorized Apple service provider if necessary.
m Do not drop or jar the computer.
m Do not move the computer when you can hear its hard disk
spinning. When you put the computer to sleep, wait until the
screen is blank before moving the computer.
m Use only the power adapter supplied with your computer.
Adapters designed for other electronic devices may look
similar, but they may not work with your equipment and may
damage the computer.
m Never force a connector into a port. Make sure that the
connector matches the port and that it’s right side up. If the
connector and port do not join easily, they do not match.
24 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 41

m Do not use the computer in wet or dusty environments.
s
Important
m Keep dirt and liquids away from the ports on the back panel,
the keyboard, and the trackball. If you spill any food or liquid
onto the computer, shut it down immediately and unplug it
before cleaning up the spill. Depending on what you spilled
and how much got into the computer, you may have to bring
the computer to an authorized Apple service provider for
cleaning.
m Do not touch the screen with any sharp or pointed objects.
m Use only the battery supplied with your computer. Batteries
designed for other portable computers may look similar, but
they may not work with your computer and may damage it.
m When recharging the battery, use only the power adapter
supplied with your computer. Adapters designed for other
electronic devices may not work with your equipment and
may damage the computer or the recharger.
m Do not leave batteries in hot locations (such as the trunk of a
car).
m If the computer has been in a cold place for several hours, let
it warm up to room temperature before you use it.
m Use the computer only in environments where the
temperature range is between 50°F/10°C and 104°F/40°C.
m Do not expose the computer to very low (less than
–13°F/–25°C) or very high (more than 140°F/60°C)
temperatures.
m If necessary, clean the outside surfaces of your computer
equipment with a damp (not wet) cloth or paper towel.
m Clean the screen with soft, lint-free paper or cloth and a mild
glass cleaner. Do not spray the glass cleaner (or any other
liquid) directly onto the screen.
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 25
Page 42

Health concerns associated with
Repetitive stress injuries
computeruse
Muscle soreness, eye fatigue, and other discomforts and injuries
sometimes associated with computer use can result from
performing any number of activities. Misuse of the same muscles
during multiple activities can create a problem that might not
otherwise exist. For example, if you engage in nonwork activities
that involve repetitive stress on the wrist—such as bicycling—and
also use your computer’s keyboard improperly, you may increase
your likelihood of developing wrist problems. Preventing health
problems requires careful attention to the way you use your body
at all times.
The most common health effects associated with using a
computer are musculoskeletal discomfort and eye fatigue. Any
activity that involves sitting for long periods of time, including
using a computer, can make your muscles sore and stiff.
To prevent discomfort and fatigue:
m Arrange your work space so the furniture is properly adjusted
for you and doesn’t contribute to an awkward, inappropriate
working posture.
m Take frequent short breaks to give your muscles and eyes a
chance to rest and refresh.
Repetitive stress injuries (RSIs) can occur when a certain muscle
or tendon is repeatedly overused and forced into an unnatural
position. The exact causes of RSIs are not understood, but it is
thought that awkward posture, the amount of repetition, the
force used in the activity, and your physiology and lifestyle may all
contribute to their occurrence.
One RSI often discussed in connection with computer use is a
wrist problem called carpal tunnel syndrome, which may be
aggravated by improper use of computer keyboards. This nerve
disorder results from excessive pressure on the median nerve as it
passes through the wrist to the hand. The information on the next
few pages can help you recognize hand positions that may cause
discomfort.
Since the effects of repetitive movement associated with
computer use can be compounded by those of other work and
leisure activities to produce or aggravate physical problems,
proper use of your computer system must be considered just one
element of a healthy lifestyle. No one can guarantee that you
won’t have problems even when you follow the most expert
advice on using computer equipment. You should always check
with a qualified health specialist if muscle, joint, or eye problems
occur.
26 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
Page 43

Arranging your work space and equipment
Keyboard and trackball
The suggestions in this section can help you work more
comfortably with your computer.
Chair
Whenever possible, use an adjustable chair that provides firm,
comfortable support.
m Adjust the height of the chair so your thighs are horizontal,
your feet flat on the floor, and the backs of your knees slightly
higher than the seat of your chair.
m The chair should support your lower back. Follow the
manufacturer’s instructions for adjusting the backrest.
m When you use the keyboard and trackball, your shoulders
should be relaxed. Your upper arm and forearm should
form aright angle, with your wrist and hand in roughly a
straight line.
Not thisThis
m Use a soft touch on the keyboard and keep your hands
andfingers relaxed. Avoid rolling your thumbs under
yourpalms.
This Not this
m Change hand positions often to avoid fatigue.
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 27
Page 44

m If you prefer, you can adjust the angle of the keyboard by
rotating the elevation feet at both ends of the back panel until
they snap into position.
The back of the keyboard is slightly elevated when the feet are
in use. Otherwise, the keyboard is level.
Mouse
Built-in display
m Adjust the angle of the display to minimize glare and
reflections from lights and windows. Make sure there is
enough light to read the screen easily.
m You may need to adjust the brightness and contrast of the
screen when you take the computer from one work location
to another, or if the lighting in your work area changes.
Contrast control
Brightness control
If you use a mouse, position it at the same height as your
keyboard. When you slide the mouse, move your entire arm.
Avoid resting your arm on the desk and bending your wrist as you
move the mouse.
28 Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook
m Clean the screen regularly (see “Important Care and Safety
Instructions”).
Page 45

General suggestions
m Wherever you’re working, take a moment to think about
whether you feel comfortable, and change position if
necessary.
m Occasionally rest your eyes. From time to time focus your eyes
on a distant object, and blink often while you work.
m Some computer users may develop discomfort in their arms,
wrists, or hands if they do intensive work without breaks. If
you begin to develop chronic pain or discomfort in your arms,
wrists, or hands, consult your health specialist.
Chapter 1: Setting Up Your Macintosh PowerBook 29
Page 46

Page 47

Chapter 2
Working on the Desktop
Before you begin
You should have already
In this chapter
Review basic trackball skills:
m Moving the pointer
m Choosing a command
m Opening an icon
m Looking at the contents of a window
And learn:
m How to close a window
m How to move a window
m What the icons on your desktop represent
m set up your computer according to the instructions in
Chapter1
m gone through the Macintosh Basics tour supplied with your
computer
Make sure your computer is on.
31
Page 48

Use the trackball
Point
Your computer has a two-button trackball. You use the ball itself to
control the movements of a pointer on the screen. The pointer
you’ll see most often is an arrow (8).
You use the buttons to initiate actions that you want the computer
to perform. Both trackball buttons do the same thing. You can
always use whichever one you prefer.
Much of the work you do on the Macintosh uses four trackball
actions: pointing, clicking, pressing, and dragging.
You point to an object on the screen by rolling the trackball so the
pointer is positioned over that object. When the pointer is an
arrow, the tipof the arrow must be exactly over the object.
Practice pointing to different objects on the Macintosh desktop,
such as the startup hard disk icon near the upper-right corner, the
Trash icon near the lower-right corner, and the Help menu icon
near the right end of the menu bar.
(If you want to return to the Macintosh Basics tour for more
practice with the trackball, see Chapter 1 for instructions.)
32 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
Page 49

Click
You click an object on the screen by pressing and quickly releasing
a trackball button while the pointer is over that object.
Practice clicking different objects on the Macintosh desktop, such
as the startup hard disk icon near the upper-right corner and the
Trash icon near the lower-right corner.
When you click an icon, it becomes highlighted(the icon is
darkened).A highlighted icon is said to be selected. A selected
icon is the object of whatever action you choose next.
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 33
Page 50

Press
You press by holding down a trackball button without moving the
trackball.
Practice pressing the menu names and icons in the menu bar—
start with the Apple (K) menu icon at the left side, through the
menu names, and across to the Help and Application menu icons
at the right side. Pressing a menu name or icon “pulls down” the
menu. Read the items in each menu you pull down.
34 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
Page 51

Drag
You drag an object on the screen by pointing to that object and
holding down a trackball button while you roll the trackball.
Practice dragging the startup hard disk icon and the Trash icon
around the Macintosh desktop. When you drag an icon, an outline
of the icon follows the pointer on the screen. When you release
the trackball button, the icon itself moves.
When you’re finished practicing, drag the icons back to their
original positions. Then click once in the middle of the desktop.
(Clicking anywhere outside a selected icon returns that icon to its
original “unselected” state.)
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 35
Page 52

Choose a command
Choosing a command involves using a combination of the
trackball actions you’ve reviewed.
1. Point to the Special menu title in the menu bar.
2. Press to pull down the Special menu.
3. Drag to the first item in the menu (the Clean Up
Desktop command) so it becomes highlighted,
and then release the trackball button.
Giving orders to your computer
Telling the Macintosh to do something involves two steps:
1. selecting an object on the screen, and
2. choosing the action you want to perform on that
object.
When you select an object, you’re telling the Macintosh toact
upon that object.
The objects you can select include an icon on the Macintosh
desktop, a sentence in a word-processing program, and a
picture in a graphics program—to give just three examples.
Most of the actions you can perform on the selected object
are listed in the menus at the top of the screen. The items, or
actions, in the menus are called commands. When you
choose a command, you are telling the computer to take
theaction you’ve chosen on the selected object.
So—you tell your Macintosh what to do by using a very simple
“language” with only two kinds of words:
When you choose Clean Up Desktop, the hard disk icon and the
Trash return to their original positions (as long as they’re already
close).
36 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
n nouns (the objects), and
n verbs (the actions)
and with only one rule:
n First the noun, then the verb (to this object, do that
action). In Macintosh terms: select an object, then choose
a command.
Page 53

Open an icon
Opening an icon is your first exercise in telling the computer
what you want it to do.
1. Click the startup hard disk icon to select it.
The icon is in the upper-right corner of the screen.
Unlesssomeone has changed its name, the icon is called
“Macintosh HD.” Make sure that the icon is highlighted
(darkened), which means that it’s selected.
2. Point to the File menu title in the menu bar.
3. Press to pull down the File menu.
4. Drag to the Open command (the second item in the
File menu) so it becomes highlighted, and then release
the trackball button.
When you choose the Open command, the selected icon
opens into a window (in this case, the Macintosh HD
window). The icon becomes filled in with a pattern
ofdots, indicating that it has been opened.
v Different icons? The Macintosh HD window on your screen
may contain items not shown above. The differences are not
important; you can still do the exercises in this chapter and
the next. v
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 37
Page 54

Look at the contents of a window
Every window has several features that help you view the
window’s contents. But before you can work with the contents of
a window, you need to make that window the active window.
Make a window the active window
You can have several windows open on your screen at one
time,but only one window can be the active window. An active
window is one in which you can select objects and choose actions
to perform on those objects.
The Macintosh HD window is currently on your Macintosh
desktop. (The window appeared when you opened the Macintosh
HD icon.) You’re going to open another window now.
1. Click the Trash icon near the lower-right corner of the
screen to select it.
Make sure that the icon is highlighted, which means that
it’sselected to be the object you’ll act upon next.
2. Point to the File menu title in the menu bar.
3. Press to pull down the File menu.
38 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
Page 55

4. Drag to the Open command so it becomes highlighted,
and then release the trackball button.
When you choose the Open command, the Trash icon opens
into a window (the Trash window). The Trash icon becomes
filled in with a pattern of dots, indicating that it has been
opened.
Active window
You should now have two windows on your Macintosh
desktop: the Macintosh HD window and the Trash window.
The Trash window is the active window. An active window has
a series of solid lines at the top of the window.
continues .
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 39
Page 56

5. Click anywhere in the Macintosh HD window to make
it the active window.
Notice that the solid lines now appear at the top of the
Macintosh HD window. (The area containing the window title
and the solid lines is called the title bar.) When windows
overlap, the active window is the one that’s on top.
Active window
Make a window larger or smaller
Sometimes you want to make a window larger, so you can see
more of its contents, or smaller, so it takes up less space on your
screen. You can change a window’s size by dragging its size box
orby clicking its zoom box.
1. Point to the size box in the lower-right corner of the
(active) Macintosh HD window.
Size box
40 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
Page 57

2. Drag the size box in any direction, and then release the
trackball button.
3. Click the zoom box near the right end of the title bar.
While you drag, an outline follows the pointer to indicate the
window’s new size. The new size takes effect when you
release the trackball button.
Zoom box
The window “zooms” to a size that shows all the items in
thewindow.
4. Click the zoom box again.
The window zooms back to its previous size (the size that you
chose in step 2).
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 41
Page 58

Move the hidden contents of a window into view
2. Point to the File menu title in the menu bar.
As you work with your computer, you’ll encounter windows
containing more than you can view on the screen at one time. You
can view contents that are out of sight, as described in the
following steps.
1. Check that the Macintosh HD window is active, then
click the System Folder to select it.
Make sure that the icon is highlighted, which means that
it’sselected.
3. Press to pull down the File menu.
4. Drag to the Open command so it becomes highlighted,
and then release the trackball button.
When you choose the Open command, the System Folder
icon opens into a window (the System Folder window).
You should now have three windows on your Macintosh
desktop: the Macintosh HD window, the Trash window, and
the System Folder window. (One or more of these windows
may be covered by the others.) The System Folder window is
the active window because you opened the System Folder
most recently.
5. Point to the size box in the lower-right corner of the
System Folder window.
42 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
Page 59

6. Drag the size box diagonally (up and to the left) to
make the window about half its current size, and then
release the trackball button.
Vertical
scroll bar
7. Press the scroll arrow at the right end of the horizontal
scroll bar.
Scroll arrow
The contents of the window scroll past, bringing into view the
icons that were out of sight on the right.
8. Press the scroll arrow at the left end of the horizontal
scroll bar.
The contents of the window scroll past, bringing back into
view the icons that were out of sight on the left.
Horizontal scroll bar
The bars across the bottom and along the right side of the
System Folder window should now be gray, indicating that the
window has contents that are not currently visible. The gray
bars are called scroll bars.
continues .
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 43
Page 60

9. Drag the scroll box toward the middle of the horizontal
scroll bar, and then release the trackball button.
Scroll box
Now you see the icons near the middle of the window.
The vertical scroll bar, scroll box, and scroll arrows work the same
way. Try them.
Close a window
When you no longer need to see the contents of a window,
youcan close it by clicking the close box.
1. In the (active) System Folder window, point to the close
box near the left end of the title bar.
Close box
2. Click the close box.
The window closes, and the System Folder icon no longer has
a pattern of dots in it.
44 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
There are now two windows on the desktop: the Macintosh
HD window and the Trash window. (One may be hidden by
the other.)
Page 61

Move a window
You can move a window anywhere on the screen by dragging its
title bar. By changing the position and size of windows, you can
arrange your Macintosh desktop in whatever way is best for you.
1. Point to the title bar of the (active) Macintosh HD
window.
Position the pointer anywhere on the title bar except over the
close box or the zoom box.
Title bar
Notice how the Macintosh HD window, because it is the active
window, stays on top of the Trash window if and when the two
windows overlap.
3. Close the Macintosh HD window by clicking the close
box near the left end of the window’s title bar.
If you can’t see the close box, drag the window until you can.
2. Drag in any direction, and then release the trackball
button.
When you drag, an outline of the window follows the pointer
on the screen. When you release the trackball button, the
window moves to the position you’ve chosen.
continues .
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 45
Page 62

The window closes, and the Macintosh HD icon reappears in
its previous form.
What’s on the desktop?
The Trash window (the remaining window on the Macintosh
desktop) becomes the active window.
4. Close the Trash window by choosing Close Window
from the File menu.
You choose Close Window by pointing to the File menu
title,pressing to pull down the menu, dragging to the Close
Window command, and, with the command highlighted,
releasing the trackball button.
Of course, you can also close the window by clicking its
closebox.
Just as a desk’s large flat surface is its work space, the Macintosh
“desktop” is the work space on your computer. The desktop
metaphor gives you a familiar way of thinking about how to use
the Macintosh.
Aside from the field of gray that represents the “surface” of your
work space, the Macintosh desktop has icons, windows, and
menus.
n Icons represent containers.
n Windows let you view what’s inside the containers.
n Menus list actions that you can apply to selected containers
or their contents.
Icons represent containers
Icons can contain other icons, or they can contain information.
For example, the startup hard disk icon contains the System
Folder icon. The System Folder icon contains the programs (also
represented by icons) that in turn contain the information the
Macintosh needs to start itself up and work properly.
46 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
Page 63

Different types of icons represent different types of containers.
Hard disks and floppy disks are like filing cabinets. You use disks
to store files—your programs and the documents you create
with them.
Shared disks are like filing cabinets containing office supplies or
information that you share with others in your work group. Your
Macintosh needs to be connected to a network before you can
use shared disks.
Folders are like folders in a file drawer. You use folders to
organize your files.
Programs are files containing instructions to the computer that
let you do certain types of work.
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 47
Page 64

Documents are files containing words, pictures, numbers,
sounds—whatever you create with your programs.
The Trash is a container for files that you no longer want.
Windows let you see what’s inside containers
Windows let you see what’s inside all these containers.
Whenyou open a disk icon, the window that appears shows you
what’s on the disk. When you open the document icon
representing a memo, the window that appears shows you
thememo.
Changing the size of a window or viewing its contents does
notchange the contents. The contents remain the same; only
your view changes.
Menus offer you choices
Like the menus in a restaurant, Macintosh menus let you
choose. You choose among different actions that the computer
can perform on containers (icons), or on their contents (such as
words in a memo).
48 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
Page 65

Using the keyboard
Arrow keys
You use the keyboard to type text and numbers, just as you
would on a typewriter. (For touch typists, your keyboard has
raised dots in the middle of the D key and the K key to help
position your fingers on the home row.)
Depending on the program you’re using, you can use special
keys on the keyboard to give commands to the computer and to
modify certain things that you do with the trackball. Macintosh
PowerBook computer keyboards have two types of special keys:
modifier keys and arrow keys.
Modifier keys
All Macintosh keyboards have four modifier keys: Shift,
x (Command), Option, and Control.
Pressed by itself, a modifier key does nothing. You need to press
it in combination with another key (or while using the trackball).
The modifier key causes the other key or trackball to give a
different (“modified”) result.
You type a capital letter, for example, by pressing the Shift key
with a letter key. Most programs let you choose commands by
pressing the x key with certain letter keys.
All Macintosh keyboards have four arrow keys: Up Arrow, Down
Arrow, Left Arrow, and Right Arrow.
Many programs let you use the arrow keys as well as the
trackball to move the pointer on the screen.
shift
ctrl option
Modifier keys Arrow keys
shift
Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop 49
Page 66

50 Chapter 2: Working on the Desktop
Page 67

Chapter 3
Creating and Changing
n What “keyboard shortcuts” are and how to use them
n How to quit a program
a Document
In this chapter
n How to open a program
n How to use a program to create a document
n Why it’s important to save your work, and how to save it
n How to switch between programs
n How programs and system software differ from each other
n How to close a document
n How to open a document
n How to change a document
n How to make a copy of a document
n How to change the name of a document
n How to use the Trash
Before you begin
Make sure that your computer is on.
51
Page 68

Open a program
Your computer comes with a simple word-processing program
called TeachText. You’re going to use this program to create a
document.
When you open the TeachText program, there is one dramatic
change on your desktop:
n A window called “Untitled” appears.
There are also two subtle changes:
1. Open the Macintosh HD icon.
(Click the icon to select it, and then choose Open from the
File menu.)
The Macintosh HD window appears, showing you the
contents of your hard disk. The contents include the
TeachText program.
2. Open the TeachText icon.
If you can’t find the TeachText icon, use the scroll bars to bring
it into view.
To open the icon, click the icon to select it, and then choose
Open from the File menu.
n The menu bar shows the menu names for the TeachText
program.
n The Application menu icon in the right corner of the menu
bar becomes the TeachText icon.
TeachText iconTeachText menus
The untitled window is empty because you haven’t put anything
in it. In the next few sections, you’re going to write a short
document, save it, and give it a name.
52 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
Page 69

Create a document
Save your work
The untitled window is like a blank sheet of paper. In the
upper-left corner of the empty document is a blinking vertical
line (|). This line is called the insertion point,because it marks
theplace where the text you type will be inserted.
As you type, use your computer keyboard as you would a
typewriter keyboard, except:
n If you make a mistake, press the Delete key to backspace
overit.
n Don’t press the Return key when you get to the end of a line.
Keep typing, and words will move to the next line
automatically.
Type the following text:
All people are born free and equal.
Endowed with reason and conscience, they
should act towards each other in a spirit
of togetherness.
You will be changing this text later in this chapter.
Work that you do in a program exists only in the computer’s
memory until you save it onto a disk. Since work that exists only
in memory is lost when you shut down the computer, you need
to save your work so you can come back to it later. If you don’t
save your work, it disappears—like thoughts that are lost unless
you write them down.
1. Choose Save from the File menu.
The box that appears (called a dialog box) lets you name the
document and save it on your hard disk.
continues .
Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document 53
Page 70

2. Type “Opening Lines”.
Because the word “Untitled” is selected (highlighted) when
the dialog box appears, all you have to do to name your
document is start typing. Whatever you type replaces the
selected text.
3. Click Save.
Switch programs
You can have several programs open on your Macintosh desktop
at one time (how many depends on how much memory your
computer has and how much memory the programs use). But
only one program at a time can be the active program. The active
program is the one that’s “on top of” other open programs—in
the same way that the active window is on top of other windows.
The Opening Lines window is now the active window, and
TeachText is the active program. But TeachText is not the only
program that’s open.
Since you turned on your computer, you’ve been working with
the Finder program. The Finder displays the Macintosh desktop.
The Finder is always open when your Macintosh is on, so right
now it is open but not active.
1. If the Opening Lines window covers most of your
screen, make the window smaller by dragging its size
box up and to the left, and then release the trackball
button.
The window is now titled “Opening Lines” and the document
has been stored on your hard disk.
54 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
After you resize the window, you should be able to see your
hard disk icon in the upper-right corner of the desktop.
Page 71

2. Make the Finder the active program by clicking the
Macintosh HD icon, or clicking anywhere on the
desktop outside the Opening Lines window.
The Finder becomes the active program. Notice:
3. Make the Opening Lines window active by clicking
anywhere inside it.
(Part of the window may be hidden by the Macintosh HD
window.)
n The Macintosh HD window appears on top of the
Opening Lines window.
n The menu bar shows the Finder’s menu titles.
n The Application menu icon at the right end of the
menubar becomes the Finder icon.
You may also notice the Opening Lines icon in the
MacintoshHD window, representing the document you
justcreated and saved.
When you click, the Opening Lines window comes back to the
top. It’s now the active window again, and TeachText is the
active program.
You make a window active by clicking any visible part of it.
The program that “owns” the window becomes active when
the window becomes active.
Here is another way to make a program active:
4. Make the Finder the active program by choosing Finder
from the Application menu at the right end of the
menu bar.
continues .
Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document 55
Page 72

You choose Finder by pointing to the Application menu icon,
pressing to pull down the menu, dragging to highlight the
name Finder, and then releasing the trackball button.
The Finder becomes the active program, and the
MacintoshHD window becomes the active window.
5. Make TeachText the active program by choosing
TeachText from the Application menu.
TeachText becomes the active program, and the Opening
Lines window becomes the active window.
Close a document
When you close a document, you do not close the program that
you used to create it. (Closing a program is called quitting.) The
program remains open and active until you quit the program or
make another program active.
1. If the Opening Lines window is not the active window,
click anywhere inside it to make it active.
2. Close the Opening Lines window.
You can either click the close box near the left end of the title
bar, or choose Close from the File menu.
The Opening Lines window closes but TeachText is still the active
program. Notice:
n The menu bar still shows the TeachText menu titles.
n The Application menu icon at the right end of the menu bar
is still the TeachText icon.
All open programs are listed in the Application menu. You can
use the Application menu to choose which program to make
active. The icon in the menu bar is always the icon of the
currently active program.
56 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
Page 73

Two types of programs
Programs that you use to do your work on the computer are
called application programs,or applications,because they’re
ways of applying computer technology to the work that you do.
Word-processing programs, for example, are applications that
enable you to write memos, novels, or whatever you need to
write. And if your work involves creating illustrations,
designing buildings, composing music, or keeping track of
large amounts of data, there are application programs for
those kinds of work, too.
Because most Macintosh programs work in similar ways,
youcan transfer much of what you learn in one application to
other applications.
Programs that the computer uses to do its work (in contrast to
your work) are called system software, or sometimes the
operating system.
Between you and the system software is a program called the
Finder,which displays the Macintosh desktop. It’s called the
Finder because, like the viewfinder in a camera, it gives you a
view of all the objects— disks, programs, folders, and
documents—on your desktop.
Open a document
When you open a document, the program you used to create that
document becomes the active program.
1. If you closed the Macintosh HD window, open the
Macintosh HD icon now.
(Click the icon to select it, and then choose Open from the
File menu.)
The Macintosh HD window appears, showing you the
contents of your hard disk. The contents include the
TeachText program and the TeachText document you created
called Opening Lines.
The next step describes a different way to open an icon.
continues .
You use the Finder to tell the system software what you want it
to do for you: which disks you want to use, which documents
and programs you want to open, and where you want files to be
stored.
Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document 57
Page 74

2. Open the Opening Lines icon by double-clicking it.
To double-click an icon, you click it twice in rapid succession
without moving the pointer. (Use the trackball to position the
pointer over the icon, and then click one of the trackball
buttons twice.) Double-clicking an icon has the same effect as
selecting the icon and then choosing the Open command.
Change a document
The Opening Lines window shows you the text you typed. In this
section you’ll make some changes to the text using techniques
that work in most Macintosh programs.
Keep two things in mind:
n The insertion point—the blinking vertical line—marks the
place where text will appear.
n A pointer called an I-beam (it looks like this: 9) replaces the
arrow pointer (8) when you’re working with text. You control
the I-beam pointer with the trackball in the same way that you
control thearrow pointer.
When you open Opening Lines, TeachText becomes the active
program. Notice that:
n the Opening Lines window appears
n the menu bar shows the TeachText menu titles
n the Application icon at the right end of the menu bar is the
TeachText icon
58 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
1. Locate the insertion point. It should be in the upperleft corner of the document.
2. Locate the I-beam pointer (9). If you don’t see it, roll
the trackball slightly. The pointer moves as the
trackball moves.
Now you’re ready to change the text.
Page 75

3. Move the I-beam pointer to the immediate left of the
word “people” (after “All”).
4. Drag horizontally, selecting the word “people”, and
then release the trackball button.
To drag, hold the trackball button down while you roll the
trackball. The selected word is highlighted (surrounded by
black).
If you select more or less than you intended to, go back to
step 3 and try again.
5. With “people” selected, type the words “human beings”.
The words you type replace the word you selected. (Press the
Delete key to backspace over any typing errors.)
6. Move the I-beam pointer between the word “equal” and
the period (to the immediate left of the period).
7. Click the trackball button once.
Clicking moves the insertion point to the spot where you
positioned the I-beam. Whatever you type next is inserted
atthat point.
8. Press the space bar once, and then type the words “in
dignity and rights”.
continues .
Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document 59
Page 76

Now you’ll rearrange some text.
9.Move the I-beam pointer to the immediate left of the
word “they” (after “conscience,”).
10.Drag horizontally, selecting the word “they”, and then
release the trackball button.
11.With “they” selected, choose Cut from the Edit menu.
Choosing Cut removes the selected material from the
document and stores it in a temporary file called the
Clipboard.
12.Move the I-beam pointer to the immediate left of the
word “Endowed”.
13.Click to place the insertion point.
14.Choose Paste from the Edit menu.
60 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
When you choose Paste, your computer takes whatever’s in
the Clipboard and puts it into the document at the location of
the insertion point.
Page 77

15.Press the space bar once, type “are”, and then press the
space bar once again.
16.Move the I-beam pointer between the letters t and h in
the word “they”.
17.Click the trackball button to place the insertion point.
18.Press the Delete key once and then type a capital T.
Save your work so far
The changes you’ve made so far are not part of Opening Lines
until you save them. You save them by telling the computer to
record them in the Opening Lines document that’s stored on your
hard disk.
It’s important to remember that no change is “official” until
yousave it onto a disk. Your work could be lost if power to
thecomputer were interrupted or if a problem caused the
computer to stop working properly.
Choose Save from the File menu.
Save regularly, and save often.
Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document 61
Page 78

Taking a shortcut
You can choose some menu commands by using the
keyboard instead of the trackball. A keyboard shortcutis a
combination of keys that you press at the same time to get
the same result as choosing a command from a menu. One of
the keys you press is always the x key or another modifier
key.
For example, instead of choosing Save from the File menu,
you can hold down the x (Command) key on the keyboard
while you press the S key. Pressing x-S is a keyboard shortcut
equivalent to choosing Save from the File menu.
Make more changes
The changes you’ve made so far are now part of the document
that’s stored on your hard disk.
1. Move the I-beam pointer (9) between the letters E and
n in the word “Endowed”.
You can see the available keyboard shortcuts by pressing a
menu title and looking at the commands in the menu. The
keyboard shortcuts are listed next to the commands.
62 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
2. Click once to place the insertion point.
3. Press the Delete key once and then type a lowercasee.
4. Move the I-beam pointer to the immediate right of the
comma after the word “conscience”.
Page 79

5. Press the Delete key once, press the space bar once,
and then type “and”.
6. Move the I-beam pointer to the immediate left of “each
other”.
7. Click the trackball button once.
Clicking moves the insertion point to the place where you
positioned the I-beam.
8.Move the I-beam pointer to the immediate right of the
“each other”. Do not drag. Do not click the trackball
button yet.
9.Hold down the Shift key on your keyboard and click to
select the words “each other”.
Holding down the Shift key while you click selects the text
between the insertion point and wherever you click.
10.With “each other” selected, type “one another”.
continues .
Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document 63
Page 80

11.Select the word “togetherness” by double-clicking it.
Quit a program
Quitting a program closes the program as well as any open
documents that were created using that program. (Simply closing
a document leaves the program open and active.)
1. Make sure that the Opening Lines window is active.
2. Quit the TeachText program.
To select a word by double-clicking it, position the I-beam
pointer over the word and then click twice in rapid
succession, without moving the pointer.
12.With “togetherness” selected, type “brotherhood”.
You may now have extra spaces or no spaces between words.
If so, position the I-beam pointer where you need to delete or
add a space, click to place the insertion point, and press the
Delete key or the Space bar as necessary.
13.Choose Save from the File menu.
You can either choose Quit from the File menu, or press
thex key and the Q key together.
If a message asks whether you want to save any changes, click
Save.
The Opening Lines document and the TeachText program are
closed, and the Finder becomes the active program.
64 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
Page 81

Opening and closing documents and programs
Doing this Also causes this
Opening a document Opens the program that created
that document
Making a document Makes the program that “owns”
window active that document active
Closing a document Simply closes that document;does
notclose the program that created
that document (the program continues
to use memory)
Quitting a program Prompts you to save your work,
then closes the program that created
the active document (memory becomes
available for other programs)
Make a copy of a document
You’ll often want to make a copy of a document so you can
preserve the original and modify the copy. To practice making a
copy of a document, you’ll use the “Opening Lines” document
you created.
1. If you closed the Macintosh HD window, open the
Macintosh HD icon now.
(Click the icon to select it, and then choose Open from the
File menu.)
The Macintosh HD window appears, showing you the
contents of your hard disk. The contents include the
TeachText program and the TeachText document you created
called Opening Lines.
2. Click the Opening Lines icon to select it.
continues .
Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document 65
Page 82

3. Choose Duplicate from the File menu.
A new icon, labeled “Opening Lines copy”, appears in the hard
disk window. Notice that the icon is selected.
Change the name of an icon
You can change the name of any icon, using any characters except
a colon (:). If you change an icon’s name and then open it, you’ll
see that the name of its window has also changed.
1. Drag the “Opening Lines copy” icon away from the
original icon so that the two icons do not overlap.
2. Click the name (not the icon) “Opening Lines copy.”
Do this even if the icon is already selected.
When the name is selected, it is highlighted and a box appears
around it. Notice that when you point to the selected name,
the arrow pointer becomes an I-beam.
Other ways to make a copy of a file are outlined in the summary
chapter in the reference section of this book.
66 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
Page 83

3. With the name selected, type “Article 1”.
Whatever you type replaces the selected text.
4. Press the Return key.
Pressing Return saves the new name.
Now you have two identical documents with different names.
You can revise one without changing the other.
Use the Trash
When you no longer need a file or a folder, you can throw it away
by dragging its icon to the Trash. Practice using the Trash by
throwing away the “Article 1” document, which you created when
you made a copy of the “Opening Lines” document.
1. If you closed the Macintosh HD window, open the
Macintosh HD icon now.
(Click the icon to select it, and then choose Open from the
File menu.)
The Macintosh HD window appears, showing you the
contents of your hard disk. The contents include the
TeachText program and two documents, one called Opening
Lines and the other called Article 1 (you may have to use the
window’s scroll bars to see them).
continues .
Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document 67
Page 84

2. Drag the Article 1 icon to the Trash icon until both
icons are highlighted, and then release the trackball
button.
If the Macintosh HD window is blocking the Trash icon, move
the window by dragging its title bar.
Both icons are highlighted when the tip of the arrow pointer
reaches the Trash icon.
3. Open the Trash icon.
(Click to select the icon, and then choose Open from theFile
menu, or click the Trash twice in quick succession.)
The Trash window appears. Anything you drag to the Trash
stays there until you empty the Trash.
You can retrieve items from the Trash by clicking to select
them and then choosing Put Away from the File menu.
(Oryou can drag the items back to where they were.)
4. Choose Empty Trash from the Special menu.
A message appears asking you to confirm that you want to
permanently remove the contents of the Trash.
5. Click OK.
Clicking OK empties the Trash—in other words, its contents
are erased from the disk.
Notice that the Trash icon no longer bulges, indicating that
itis empty.
6. Close the Trash window by clicking its close box.
When you release the trackball button, the Article 1 icon
“disappears” into the Trash. When you put an object in the
Trash, the Trash icon bulges to indicate that it is no longer
empty.
68 Chapter 3: Creating and Changing a Document
Page 85

Chapter 4
Working With Disks
In this chapter
Before you begin
You need a new floppy disk to follow the steps in this chapter.
Youshould be able to get floppy disks from wherever you got
your computer.
m What hard disks and floppy disks are for, and how they differ
m How to insert and remove a floppy disk
m How to prepare a disk for use
m How to copy the contents of a disk
m How to protect a floppy disk and its contents
m How to put programs onto your computer
Make sure that your computer is on.
69
Page 86

Insert a floppy disk
Your computer’s floppy disk drive can accommodate 3.5-inch
(89-millimeter) floppy disks of two types:
Follow these steps to insert your new disk into the disk drive.
1. W rite “Practice” on a blank disk label.
2. Attach the label to your new floppy disk.
m high-density disks, which can hold up to 1.4 megabytes (MB)
of information
m double-sided disks, which can hold up to 800 kilobytes (K)
ofinformation
(The next page explains kilobytes and megabytes.)
Double-sided (800K) disk
Second hole
High-density
disk symbol
High-density (1.4 MB) disk
The molding of the disk’s plastic case indicates where the
label goes. Do not affix the label over the metal shutter.
3. Hold the disk with your thumb on the label and the
metal shutter pointing away from you.
4. Push the disk into the floppy disk drive, label side up
and metal shutter first.
Insert metal end first.
The next section, “Initialize a Disk,” explains what to do about
the message that appears on your screen.
70 Chapter 4: Working With Disks
Page 87

Floppy disks and hard disks
Both floppy disks and hard disks function like filing cabinets:
you use them to store information. You can store much more on
a hard disk than on a floppy disk, however, and the computer
can retrieve information from a hard disk much faster.
Floppy disks and hard disks are represented by different icons.
10,000 pages
5,000 pages
The disk whose icon is closest to the upper-right corner of your
desktop is the startup disk,which contains the information the
Macintosh uses to operate.
Your hard disk is sealed into the hard disk drive inside your
computer. Floppy disks, in contrast, can be taken in and out of
floppy disk drives so you can easily transfer information from
one computer to another.
A floppy disk is made of thin, flexible material with a magnetic
coating. To protect it and make it easier to handle, the floppy
disk itself is enclosed in a rigid plastic case, which gives the
floppy disk its “non-floppy” character. Floppy disks are
sometimes called diskettes.
200 pages
300 pages
1 page
40 MB20 MB1.4 MB800K4K
Floppy disks Hard disks
Even the smallest hard disks can hold the equivalent of a few
thousand pages of information. High-density floppy disks can
hold 1.4 megabytes (MB) of information—about 300 typewritten
pages. Double-sided floppy disks can hold 800 kilobytes (K) of
information—about 200 typewritten pages. (A megabyte is about
1,000 kilobytes.)
Chapter 4: Working With Disks 71
Page 88

Initialize a disk
Every new disk needs to be prepared for use. Preparing a new
disk is called initializing it. In the same way that lines are drawn on
a newly paved parking lot to mark off parking spaces, the
initializing process creates organized areas on the disk where the
computer can store information. Your computer’s hard disk was
initialized at the factory, but you need to initialize any new floppy
disks you want to use.
If you inserted a double-sided disk, this dialog box appears:
1. Read the message on your screen.
The computer requests information from you or warns you
about the consequences of an action by presenting a message
in the form of a dialog box.
If you inserted a high-density disk, this dialog box appears:
2. If you inserted a high-density disk, click Initialize.
If you inserted a double-sided disk, click Two-Sided.
Another dialog box appears:
This dialog box appears because you can initialize old disks as
well as new ones—and the computer doesn’t know whether
the disk in the drive is old or new. Initializing erases all
information on a disk. In this case, because the floppy disk is
new, there is no information on it to erase.
72 Chapter 4: Working With Disks
Page 89

3. Click Erase.
5. Click OK.
A third dialog box appears:
4. Type “Practice”.
If you make any typing errors, press the Delete key to
backspace over them.
The computer takes about a minute to initialize the disk.
Messages appear on the screen to let you know how the
process is going.
When initialization is finished, the disk’s icon appears directly
below the Macintosh HD icon (the startup hard disk icon)
near the upper-right corner of the desktop.
Chapter 4: Working With Disks 73
Page 90

Copy the contents of a disk
Most programs you’ll use with your Macintosh are supplied on
floppy disks. You can use a program more efficiently if you first
install it on your hard disk. You install most programs by copying
them from the floppy disk to your hard disk.
To practice copying the contents of a floppy disk to your hard
disk, use your practice disk (even though there’s nothing on it).
1. Drag the Practice floppy disk icon to the Macintosh HD
icon until both icons are highlighted, and then release
the trackball button.
Both icons are highlighted when the tip of the arrow pointer
reaches the Macintosh HD icon.
When you release the trackball button, the Macintosh copies
the contents of the Practice disk onto Macintosh HD (your
hard disk). Because there is nothing on the Practice disk, the
copying happens very quickly.
Now, find the copy of Practice you just created.
2. Open the Macintosh HD icon.
To open the icon, click the icon to select it and then choose
Open from the File menu. (You choose Open by pointing to
the File menu title, pressing to pull down the menu, dragging
to the Open command, and then releasing the trackball
button.)
The Macintosh HD window appears, showing you the
contents of the hard disk. The contents should include a new
folder called Practice, which the computer created when it
copied the contents of the Practice disk to Macintosh HD.
You may have to make the window larger or use the scroll bars
to see the Practice folder.
74 Chapter 4: Working With Disks
Page 91

3. Open the Practice folder icon.
To open the icon, click the icon to select it and then choose
Open from the File menu.
The folder holds the contents of the floppy disk you’ve
copied. In this case, the folder is empty because there’s
nothing on the Practice disk.
4. Close all the windows on the Macintosh desktop.
You close a window (when it’s the active window) by either
clicking its close box or choosing Close Window from the
File menu.
Taking care of floppy disks
Follow the care instructions that came with your disks, and
remember three key points:
n Keep floppy disks away from magnets. Because
information is stored on the disk in the form of magnetic
signals, a magnetic field can destroy that information.
Televisions and monitors, telephones, loudspeakers, and
certain kinds of lighting fixtures all contain magnets.
n Protect disks from extremes of temperature and humidity.
n Do not open the disk’s metal shutter. Touching the disk
inside the shutter could damage it.
Chapter 4: Working With Disks 75
Page 92

Take a floppy disk out of its drive
You take a floppy disk out of its drive when you no longer need to
get information from or store information on that disk.
1. Click the Practice floppy disk icon to select it.
Click the icon, not its name.
2. Eject the floppy disk by choosing Put Away from the
File menu.
You choose Put Away by pointing to the File menu title,
pressing to pull down the menu, dragging to the Put Away
command, and releasing the trackball button.
76 Chapter 4: Working With Disks
Put Away returns the object you’ve selected to its original
place. In this case, it ejects the floppy disk from the disk drive
so you can put it away.
Page 93

Protect the contents of a disk
You can lock a floppy disk so its contents cannot be changed in
any way. When a disk is locked, you can look at the files it
contains, but you cannot modify the files on it, delete them, or
store any new files.
Use your practice disk to practice locking and unlocking a
floppydisk.
1. Hold the practice disk with your thumb on the label
and the metal shutter pointing away from you, as
though you were going to insert the disk into a drive.
3. Turn the disk over and lock it by sliding the tab so that
the square hole is open.
2. Find the square hole in the near-left corner of the
floppy disk.
A moveable tab on the back side of the disk should be
blocking the hole, indicating that the disk is unlocked.
If you’re using a high-density disk, you’ll notice an additional
square hole, across the label from the first hole. This second
hole has no tab and is always open.
Locked
Use your thumbnail or a push pin to move the tab.
4. Unlock the disk by sliding the tab back so that the
square hole is blocked.
You are unlocking your practice disk now so you can use it to
store files in the next chapter.
Chapter 4: Working With Disks 77
Unlocked
Page 94

On your own: Install your programs
s
s
If you have a floppy disk drive and disks containing programs that
you plan to use with your Macintosh, you can install the programs
on your hard disk now (or you can wait until later and continue
with the next chapter).
The general instructions in this section describe how to copy the
contents of a program disk to your hard disk.
Important: Some programs need to be installed in a
particular way. If your programs came with specific
instructions, follow them instead of the instructions in this
section.
1. Lock the program disk.
The program disk contains your master copy of the program.
Locking the disk protects its contents but doesn’t keep you
from copying the contents onto another disk.
2. Insert the program disk into your floppy disk drive.
3. Drag the program disk icon to the Macintosh HD icon
(your hard disk icon) until both icons are highlighted,
and then release the trackball button.
Both icons are highlighted when the tip of the arrow pointer
reaches the Macintosh HD icon.
When you release the trackball button, messages appear on
the screen to let you know that the computer is copying the
contents of the program disk onto your hard disk.
When copying is finished, the contents of the program disk
appear on your hard disk in a folder that has the same name
as the program disk.
4. Eject the program disk by selecting it and choosing Put
Away from the File menu.
5. Open the Macintosh HD icon.
The Macintosh HD window shows you the contents of your
hard disk. Among its contents is the program folder, which
contains the same items as the original disk.
78 Chapter 4: Working With Disks
Page 95

6. Click the program folder to select it.
Throw away extra System Folders
7. Choose Open from the File menu.
The folder window appears, showing you the contents of
the program folder. The folder has the same contents as the
program disk.
8. Look for a System Folder in the program folder.
Some program disks contain a System Folder so they can be
used as startup disks. (A startup disk, by definition, is a disk
that has a System Folder on it.) If the program disk you’ve
copied has a System Folder, you now have two System Folders
on your hard disk. For the computer to work properly, you
must throw away any extra System Folders.
Your startup disk must have only one System Folder on it.
Whenever you copy the contents of a program disk to your hard
disk, make sure that you have not copied an extra System Folder.
If you have, throw the extra System Folder away.
1. Drag the extra System Folder from the program folder
to the Trash.
2. Choose Empty Trash from the Special menu.
A message alerts you that you’re about to throw away the
contents of the Trash (in this case, the extra System Folder).
3. Click OK to confirm that you want to throw away the
contents of the Trash.
4. Close the window by clicking its close box.
Chapter 4: Working With Disks 79
Page 96

Page 97

Chapter 5
Learning More
Before you begin
Make sure that your computer is on.
About Your Computer
In this chapter
m How to open the Battery desk accessory
m How to open the PowerBook control panel
m How to use the Balloon Help system
m Where to look for information about your computer and
its software
This short chapter introduces you to the Battery desk accessory
and the PowerBook control panel, with which you can monitor
and control your computer’s power consumption.
This chapter also tells you where to find answers to other
questions you may have about your computer.
81
Page 98

Open the Battery desk accessory
Open the PowerBook control panel
The Battery desk accessory tells you approximately how much
power is left in the battery as you use the computer.
To open the Battery desk accessory:
m Choose Battery from the Apple (K) menu.
You can leave the Battery desk accessory open to keep track of
the battery charge while you work. The desk accessory works like
a fuel gauge (the solid bars indicate how much power is left).
The PowerBook control panel lets you control the balance
between power consumption and system performance (it also lets
you control other PowerBook features).
To open the PowerBook control panel:
1. Choose Control Panels from the Apple (K) menu.
For more information on how to use the Battery desk accessory,
go to the power management chapter in Part III of this book.
82 Chapter 5: Learning More About Your Computer
Page 99

2. Open the PowerBook icon.
Use Balloon Help
Balloon Help explains icons, menus, commands, and other
objects on the Macintosh screen, using balloons similar to those
in comic strips. Each balloon points to the object it explains.
Many Macintosh programs also have Balloon Help.
(Click the icon once to select it, then choose Open from the
File menu. Or double-click the icon.)
The PowerBook control panel appears. You drag the Battery
Conservation slider to the left to improve performance (but
battery power is used up more quickly) or to the right to
conserve power (but the computer may work more slowly).
For more information on how to use the PowerBook control
panel, go to the power management chapter in Part III of this
book.
Turn on Balloon Help
1. Point to the Help icon near the right end of the
menu bar.
2. Press to pull down the Help menu.
3. Drag to highlight the Show Balloons command,
then release the trackball button.
When Balloon Help is turned on, balloons containing
explanatory text appear next to objects that you point to
onthe screen.
continues .
Chapter 5: Learning More About Your Computer 83
Page 100

4. To show a balloon describing your startup hard disk,
point to the hard disk icon.
A balloon appears next to the icon. Balloons do not affect how
you work with your computer. You still select icons, choose
commands, and so on.
5. Click your hard disk icon to select it.
You can select the icon even with the balloon showing.
6. Point to the File menu.
A balloon appears next to the menu title.
7. Press to pull down the File menu.
Turn off Balloon Help
Balloons can block items on the screen as you work, so you may
wish to turn them off when you're finished reading.
m Choose Hide Balloons from the Help menu.
The balloon disappears when you pull down the menu.
8. Slowly drag to highlight the Open command, and then
release the trackball button.
Notice that a balloon appears next to a command if you pause
briefly as you drag past it.
The hard disk window becomes the active window. To see
more balloons, you can point to different parts of the window
and to different icons in the window.
84 Chapter 5: Learning More About Your Computer
(Point to the Help icon in the menu bar, press to pull down
the Help menu, drag to highlight the Hide Balloons
command, and then release the trackball button.)
 Loading...
Loading...