Anritsu wiltron 560 schematic

SERIES 560-7XXX AND 5400-71XXX RF DETECTORS OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1.INTRODUCTION
This manual provides descriptions and specifications for ANRITSU Series 560-7XXX and 5400-71XXX RF Detectors (Figure 1). It also contains procedures for field replacement of detector diodes in the model 5400-71B50 and 5400-71B75 RF detectors and most of the Series 560-7XXX RF detectors.
2.GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ANRITSU Series 560-7XXX and 5400-71XXX
RF Detectors use zero-biased Schottky diodes and have a measurement range of –55 dBm to +16 dBm.
The detectors are used with the Model 56100A and 562 Scalar Network Analyzers and with Series
541XXA, 540XXA, and 54XXA Scalar Measurement Systems for making coaxial transmission loss or gain and power measurements. The detectors are also used with the Site Master and Cable Mate Series Personal SWR/RL and Fault Location Testers for making power measurements.
NOTE: ANRITSU was formerly known as WILTRON
Figure 1. Typical Series 560-7XXX and 5400-71XXX
RF Detectors
3.PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATIONS
Performance specifications for the Series 560-7XXX and 5400-71XXX RF Detectors are listed in Table 1 on page 2.
4.PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF RF DETECTORS
ANRITSU RF Detectors are high-quality, precision laboratory instruments and should receive the same care and respect afforded such instruments. Follow the precautions listed below when handling or connecting these devices. Complying with these precautions will guarantee longer component life and less equipment downtime due to connector or device failure. Also, such compliance will ensure that RF Detector failures are not due to misuse or abuse—two failure modes not covered under the ANRITSU warranty.
a.Beware of Destructive Pin Depth of Mating Connectors. Based on RF components returned for repair, destructive pin depth of mating connectors is the major cause of failure in the field. When an RF component connector is mated with a connector having a destructive pin depth, damage will usually occur to the RF component connector. A destructive pin depth is one that is too long in respect ot the reference plane of the connector (Figure 2, page 3).
The center pin of a precision RF component connector has a precision tolerance measured in mils (1/1000 inch). The mating connectors of various RF components may not be precision types. Consequently, the center pins of these devices may not have the proper depth. The pin depth of DUT connectors should be measured to assure compatibility before attempting to mate them with RF Detector connectors. An ANRITSU Pin Depth Gauge (Figure 3, page 3), or equivalent, can be used for this purpose.
490 JARVIS DRIVE l MORGAN HILL, CA 95037-2809 |
P/N: 10100-00035 |
|
REVISION : C |
NOTE: ANRITSU Company was formerly known as WILTRON Company. |
PRINTED: MARCH 2000 |
COPYRIGHT 1997 ANRITSU CO.
Table 1. 560-7XXX and 5400-71XXX RF Detectors Performance Specifications
Model |
|
Frequency Range |
Impedance |
Return Loss |
Input Connector |
Frequency |
|
Response |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 dB, <0.04 GHz |
|
|
560-7A50 |
|
0.01 to 18 GHz |
50Ω |
22 dB, <8 GHz |
GPC-7 |
0.5 dB, 18 GHz |
|
|
|
|
17 dB, <18 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 dB, <0.04 GHz |
|
|
560-7N50B |
|
0.01 to 20 GHz |
50Ω |
22 dB, <8 GHz |
N(m) |
0.5 dB, <18 GHz |
|
17 dB, <18 GHz |
25 dB, <20 GHz |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
14 dB, <20 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 dB, <0.04 GHz |
|
|
560-7S50B |
|
0.01 to 20 GHz |
50Ω |
22 dB, <8 GHz |
WSMA(m) |
0.5 dB, <18 GHz |
|
17 dB, <18 GHz |
1.25 dB, <20 GHz |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
14 dB, <20 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 dB, <0.04 GHz |
|
|
560-7S50-2 |
|
0.01 to 26.5 GHz |
50Ω |
22 dB, <8 GHz |
WSMA(m) |
0.5 dB, <18 GHz |
|
17 dB, <18 GHz |
1.25 dB, <26.5 GHz |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
14 dB, <26.5 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 dB, <0.04 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 dB, <8 GHz |
|
0.5 dB, <18 GHz |
560-7K50 |
|
0.01 to 40 GHz |
50Ω |
17 dB, <18 GHz |
K(m) |
1.25 dB, <26.5 GHz |
|
15 dB, <26.5 GHz |
2.2 dB, <32 GHz |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
14 dB, <32 GHz |
|
2.5 dB, <40 GHz |
|
|
|
|
13 dB, <40 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 dB, <0.04 GHz |
|
0.8 dB, <20 GHz |
|
|
|
|
19 dB, <20 GHz |
|
|
560-7VA50 |
|
0.01 to 50 GHz |
50Ω |
V(m) |
2.5 dB, <40 GHz |
|
|
15 dB, <40 GHz |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
3.0 dB, <50 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
10 dB, <50 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5400-71B50 |
|
0.001 to 1.5 GHz |
50Ω |
20dB |
BNC(m) |
0.2 dB, <1.5 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5400-71B75 |
|
0.001 to 1.5 GHz |
75Ω |
20 dB |
BNC(m) |
0.2 dB, <1.5 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5400-7N50 |
|
0.001 to 3 GHz |
50Ω |
26 dB |
N(m) |
0.2 dB, <1 GHz |
|
0.3 dB, <3 GHz |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5400-71N75 |
|
0.001 to 3 GHz |
75Ω |
26 dB, <2 GHz |
N(m) |
0.2 dB, <1 GHz |
|
20 dB, <3 GHz |
0.3 dB, <3 GHz |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5400-71N75L* |
|
0.005 to 1.2 GHz |
75Ω |
24 dB |
N(m) |
0.2 dB, <1 GHz |
|
0.5 dB, <1.2 GHz |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All Models: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum Input Power: 100mW (+20 dBm) |
|
|
|
|||
Cable Length: 122 cm (4 ft) |
|
|
|
|
||
Dimensions: 7.6 x 2.9 x 2.2 cm (3 x 1-1/8 x 7/8 in.) |
|
|
|
|||
Weight: 170g (6 oz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* The input of the 5400-71N75L is limited to extend the damage level to 1W (+30 dBm) |
|
|||||
The limit begins compression at 10 dBm <0.05 GHz, 15 dBm <1 GHz, or 20 dBm <1.2 GHz |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
DET OMM |
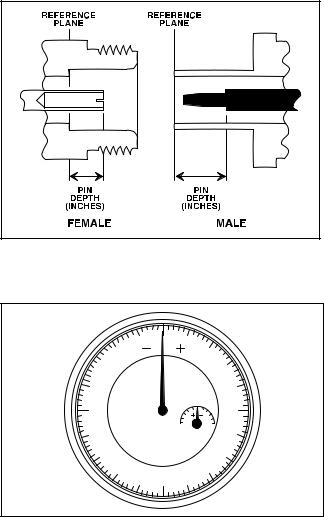
Figure 2. N Connector Pin Depth Definition
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
|
Figure 3. Pin Depth Gauge
If the measured connector is out of tolerance in the “+” region, the center pin is too long (see Table 2). Mating under this condition will likely damage the precision RF Detector connector. If the test device connector measures out of tolerance in the “–” region, the center pin is too short. This will not cause damage, but it will result in a poor connection and a consequent degradation in performance.
b.Avoid Over Torquing Connectors. O v e r torquing connectors is destructive; it may damage the connector center pin. Finger-tight is usually sufficient for Type N connectors. Always use a connector torque wrench (8 inch-pounds) when tightening GPC-7, WSMA, K, or V type connectors. Never use pliers to tighten connectors.
c.Avoid Mechanical Shock. RF Detectors are designed to withstand years of normal bench
Table 2. Allowable Device Under Test (DUT)
Connector Pin Depth
|
DUT |
|
ANRITSU |
Pin Depth |
Pin Depth |
|
|
Connector |
|
Gauging |
Gauge |
||
|
|
(inches) |
||||
|
Type |
|
Set Model |
Reading |
||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
N-Male |
|
01-163 |
.207 –0.000 |
207 +0.000 |
||
N-Female |
|
+0.030 |
–0.030 |
|||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPC-7 |
|
01-161 |
+0.000 |
Same as |
||
|
–0.030 |
Pin Depth |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
WSMA-Male |
|
01-162 |
–0.000 |
Same as |
||
WSMA-Female |
|
–0.010 |
Pin Depth |
|||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
SMA-Male, |
|
01-162 |
–0.000 |
Same as |
||
SMA-Female |
|
–0.010 |
Pin Depth |
|||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
3.5 mm-Male |
|
|
–0.000 |
Same as |
||
3 |
. |
5 |
01-162 |
–0.010 |
||
Pin Depth |
||||||
mm-Female |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
K-Male, |
|
01-162 |
+0.000 |
Same as |
||
K-Female |
|
–0.010 |
Pin Depth |
|||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
handling. However, do not drop or otherwise treat them roughly. Mechanical shock will significantly reduce their service life.
d.Avoid Applying Excessive Power. The Series 560-7XXX and 5400-71XXX RF Detectors are rated at +20 dBm (100 mW) maximum input power. Exceeding this input power level, even for short durations, will permanently damage their internal components.
e.Do Not Disturb Teflon Tuning Washers on Connector Center Pins. The center conductor of many RF component connectors contains a small teflon tuning washer that is located near the point of mating (Figure 4, page 4). This washer compensates for minor impedance discontinuities at the interface. Do not disturb this washer. The location of this washer is critcal to the performance of the RF component.
f.Keep Connectors Clean. The precise geometry that makes possible the RF component’s high performance can be easily disturbed by dirt or other contamination adhering to connector interfaces. When not in use, keep the connectors covered.
To clean the connector interfaces, use a clean cotton swab that has been dampened with denatured alcohol. Figure 5, page 4 illustrates the cleaning of male and female connectors.
DET OMM |
3 |
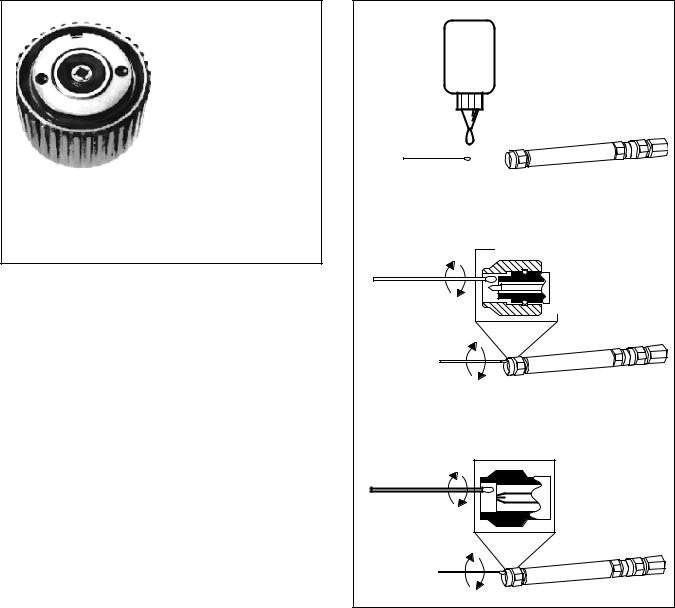
 TEFLON WASHER
TEFLON WASHER
NOTE
The teflon washer is shown on a GPC-7 connector. A similar washer may be installed on any ANRITSU precision connector.
Figure 4. Tuning Washer on GPC-7 Connector
NOTE
Most cotton swabs are too large to fit in the smaller connector types. In these cases it is necessary to peel off most of the cotton and then twist the remaining cotton tight. Be sure that the remaining cotton does not get stuck in the connector. Cotton swabs of the appropriate size can be purchased through a medi- cal-laboratory-type supply center.
The following are some important tips on cleaning connectors:
•Use only denatured alcohol as a cleaning solvent.
•Do not use excessive amounts of alcohol as prolonged drying of the connector may be required.
•Never put lateral pressure on the center pin of the connector.
•If installed, do not disturb the teflon washer on the center conductor pin.
•Verify that no cotton or other foreign material remains in the connector after cleaning it.
•If available, use compressed air to remove foreign particles and to dry the connector.
•After cleaning, verify that the center pin has not been bent or damaged.
DENATURED ALCOHOL |
DAMPEN ONLY |
DO NOT SATURATE |
MALE |
FEMALE |
Figure 5. Cleaning Male and Female Connectors
5.DETECTOR DIODE REPLACEMENT
RF Detector models 5400-71B50 and 5400-71B75 are equipped with field-replaceable detector diodes; the series 560-7XXX RF Detectors, except for model 560-7VA50, are equipped with field-replaceable detector diode modules. Paragraph 5.1 provides a procedure for replacing defective diodes in the models 5400-71B50 and 5400-71B75; paragraph 5.2 provides a procedure for replacing detector diode modules in series 560-7XXX RF Detectors.
4 |
DET OMM |
 Loading...
Loading...