Page 1

GA500
Industrial AC Microdrive
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Catalog Code: GA50Uxxxxxxxx
240 V Single-Phase Input: 1/6 to 5 HP
240 V Three-Phase Input: 1/6 to 30 HP
480 V Three-Phase Input: 1/2 to 40 HP
Page 2

This Page Intentionally Blank
2 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. Periodic Inspection and Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.1 Section Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.2 Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Recommended Daily Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Recommended Periodic Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.3 Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
1.4 Replace Cooling Fans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Number of Cooling Fans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Replace the Cooling Fan (Procedure A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Replace the Cooling Fan (Procedure B) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.5 Replace the Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
About the Control Circuit Board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Replace the Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.6 Storage Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2. Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2.1 Section Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2.2 Types of Faults, Minor Faults, Alarms, and Errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.3 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.4 Fault . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
2.6 Parameter Setting Errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
2.7 Auto-Tuning Errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
2.8 Backup Function Operating Mode Display and Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
2.9 Diagnosing and Resetting Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Fault Occurs Without Power Loss . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Fault Occurs Without Power Loss . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Fault Reset Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Typical Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
The Parameter Settings Will Not Change. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
The Motor Does Not Rotate after You Enter a Run Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
The Motor Rotates in the Opposite Direction from the Run Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
The Motor Rotates in Only One Direction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
The Motor Is Too Hot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
The Correct Auto-Tuning Mode Is Not Available . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
The Motor Stalls during Acceleration or Accel/Decel Time Is Too Long . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 3
Page 4

The Drive Frequency Reference Is Different than the Controller Frequency Reference
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
The Motor Speed Is Not Stable When Using a PM Motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
There Is Too Much Motor Oscillation and the Rotation Is Irregular . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Deceleration Takes Longer Than Expected When Dynamic Braking Is Enabled . . . . . . . . . . 82
There Is Audible Noise from the Drive or Motor Cables When the Drive Is Energized . . . . . . 83
The Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Trips During Run . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Motor Rotation Causes Unexpected Audible Noise from Connected Machinery . . . . . . . . . . 83
Motor Rotation Causes Oscillation or Hunting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
PID Output Fault. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The Starting Torque Is Not Sufficient . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The Motor Rotates after the Drive Output Is Shut Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The Output Frequency Is Lower Than the Frequency Reference. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The Motor Will Not Restart after a Loss of Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
3. Parameter List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
3.1 Section Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
3.2 How to Read the Parameter List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Icons and Terms that Identify Parameters and Control Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
3.3 Parameter Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
3.4 A: Initialization Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
A1: Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
A2: User Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
3.5 b: Application. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
b1: Operation Mode Selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
b2: DC Injection Braking and Short Circuit Braking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
b3: Speed Search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
b4: Timer Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
b5: PID control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
b6: Dwell Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
b8: Energy Saving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
3.6 C: Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
C1: Accel & Decel Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
C2: S-Curve Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
C3: Slip Compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
C4: Torque Compensation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
C5: Automatic Speed Regulator (ASR: Automatic Speed Regulator) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
C6: Duty & Carrier Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
3.7 d: Reference Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
d1: Frequency Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
d2: Reference Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
d3: Jump Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
d4: Frequency Ref Up/Down & Hold. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
d6: Field Weakening /Forcing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
d7: Offset Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
3.8 E: Motor Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
E1: V/f Pattern for Motor 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
E2: Motor Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
E3: V/f Pattern for Motor 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
E4: Motor 2 Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
E5: PM Motor Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
E9: Motor Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
3.9 F: Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
4 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 5

F1: Fault Detection in PG Speed Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
F6: Communication Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
F7: Communication Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
3.10 H: Terminal Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
H1: Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
H2: Digital Outputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
H3: Analog Inputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
H4: Analog Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
H5: Modbus Communication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
H6: Pulse Train Input/Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
H7: Virtual MFIO selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
3.11 L: Protection Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
L1: Motor Protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
L2: Power Loss Ride Through. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
L3: Stall Prevention . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
L4: Speed Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
L5: Fault Restart. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
L6: Torque Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
L7: Torque Limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
L8: Drive Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
3.12 n: Special Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
n1: Hunting Prevention . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
n2: Auto Freq Regulator (AFR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
n3: High Slip/Overexcite Braking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
n5: Feed Forward Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
n6: Online Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
n7: EZ Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
n8: PM Motor Control Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
nA: PM Motor Control Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
3.13 o: Keypad-Related Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
o1: Keypad Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
o2: Keypad Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
o3: Copy Keypad Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
o4: Maintenance Monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
o5: Log Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
3.14 q: DriveWorksEZ Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
q1-01 to qx-xx: Reserved for DriveWorksEZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
3.15 r: DWEZ Connection 1-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
r1-01 to r1-40: DriveWorksEZ Connection Parameters 1 to 20 (Upper / Lower) . . . . . . . . . . 159
3.16 T: Motor Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
T0: Tuning Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
T1: Induction Motor Auto-Tuning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
T2: PM Motor Auto-Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
T3: ASR and Inertia Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
T4: EZ Tuning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
3.17 U: Monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
U1: Operation Status Monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
U2: Fault Trace. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
U3: Fault History. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
U4: Maintenance Monitors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
U5: PID Monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
U6: Operation Status Monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
U8: DriveWorksEZ Monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 5
Page 6

3.18 Parameters that Change from the Default Settings with A1-02 [Control Method
Selection]. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
3.19 Parameters that Change from the Default Settings with E3-01 [Motor 2 Control
Mode Selection] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
3.20 Parameters Changed by E1-03 [V/f Pattern Selection] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
3.21 Defaults by Drive Model and Duty Rating ND/HD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Single-Phase 200 V Class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Three-Phase 200 V Class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Three-Phase 400 V Class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
3.22 Parameters Changed by PM Motor Code Selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Yaskawa SMRA Series SPM Motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Yaskawa SMRD Series SPM Motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Yaskawa SSR1 Series IPM Motors (Derated Torque) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
4. Mechanical Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
4.1 Section Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
4.2 Removing/Reattaching Covers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Remove the Front Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Reattach the Front Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
4.3 Remove and Reattach the Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Remove the Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Reattach the Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
5. Electrical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
5.1 Section Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
5.2 Standard Connection Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
5.3 Main Circuit Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Motor and Main Circuit Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Main Circuit Terminal Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
5.4 Control Circuit Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
Control Circuit Connection Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
Control Circuit Terminal Block Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
Control Circuit Terminal Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Switches and Jumpers on the Terminal Board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
5.5 Control I/O Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Pulse Train Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Set Sinking Mode/Sourcing Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Set the Input Signal for the MFAI Terminal A2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Set the Output Signal for the MFAO Terminal AM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Switch ON Termination Resistor for MEMOBUS/Modbus Communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
5.6 Connect the Drive to a PC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
6. Startup Procedure and Test Run . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
6.1 Section Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
6.2 Overview of Keypad Components and Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Indicator flashing statuses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Keypad Mode and Menu Displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Set up the Drive with General-Purpose Setup Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Programming Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Change Parameter Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Verify and Set the Changed Parameters (Verify Menu). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
6 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 7

How to Switch between LOCAL and REMOTE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
6.3 Keypad Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
Digital character mapping table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
Show the Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
Check Modified Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
Set and View Necessary Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Change Parameter Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Save a Backup of Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
Write Backed-up Parameters to the Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Verify Keypad Parameters and Drive Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Delete Parameters Backed Up to the Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 244
6.4 Automatic Parameter Settings Optimized for Specific Applications (Application
Presets) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
6.5 Auto-Tuning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Auto-Tuning for Induction Motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Auto-Tuning for PM Motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
Auto-Tuning in EZ Open Loop Vector Control Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
ASR and Inertia Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
Precautions before Auto-Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
7. Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
7.1 Drive Duty Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254
7.2 Model-Specific Specifications (Single-Phase 200 V Class) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
7.3 Model Specifications (Three-Phase 200 V Class) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
7.4 Model-Specific Specifications (Three-Phase 400 V Class) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
7.5 Drive Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
7.6 Drive Derating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
Carrier Frequency Settings and Rated Current Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
Derating Depending on Ambient Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
Altitude Derating. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
8. Disposal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
8.1 Section Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
8.2 Disposal Instructions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
8.3 WEEE Directive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
9. Preface and General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
9.1 Receiving. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
About Registered Trademarks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
9.2 Using the Product Safely . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
Explanation of Signal Words . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
Section Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 7
Page 8

8 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 9

1
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
This chapter gives information about how to examine and maintain drives in use, how to replace
cooling fans and other parts, and how to store drives.
1.1 Section Safety ........................................................................................................... 10
1.2 Inspection................................................................................................................... 12
1.3 Maintenance .............................................................................................................. 15
1.4 Replace Cooling Fans ............................................................................................. 17
1.5 Replace the Drive ..................................................................................................... 23
1.6 Storage Guidelines .................................................................................................. 27
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 9
Page 10

1.1 Section Safety
1.1 Section Safety
DANGER
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not examine, connect, or disconnect wiring on an energized drive. Before servicing, disconnect
all power to the equipment and wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum. The
internal capacitor stays charged after the drive is de-energized. The charge indicator LED
extinguishes when the DC bus voltage decreases below 50 Vdc. When all indicators are OFF,
measure for dangerous voltages to make sure that the drive is safe.
If you do work on the drive when it is energized, it will cause serious injury or death from electrical shock.
Disconnect all power to the drive and wait for the time specified on the warning label before you
remove covers. Check the drive for dangerous voltages before servicing or repair work.
If you do work on the drive when it is energized and there is no cover over the electronic circuits, it will cause
serious injury or death from electrical shock. The drive has internal capacitors that stay charged after you deenergize the drive.
WARNING
Electrical Shock Hazard
The motor will run after you de-energize the drive. PM motors can generate induced voltage to the
terminal of the motor after you de-energize the drive.
If you touch a motor that is moving or energized, it can cause serious injury or death.
Do not operate the drive when covers are missing. Replace covers and shields before you operate
the drive. Use the drive only as specified by the instructions.
Some figures in this section include drives without covers or safety shields to more clearly show the inside of the
drive. If covers or safety shields are missing from the drive, it can cause serious injury or death.
Always ground the motor-side grounding terminal.
If you do not ground the equipment correctly, it can cause serious injury or death if you touch the motor case.
Only let approved personnel install, wire, maintain, examine, replace parts, and repair the drive.
If personnel are not approved, it can cause serious injury or death.
Do not wear loose clothing or jewelry when you do work on the drive. Tighten loose clothing and
remove all metal objects, for example watches or rings.
Loose clothing can catch on the drive and jewelry can conduct electricity and cause serious injury or death.
Fire Hazard
Tighten all terminal screws to the correct tightening torque.
Connections that are too loose or too tight can cause incorrect operation and damage to the drive. Incorrect
connections can also cause death or serious injury from fire.
Damage to Equipment
Do not apply incorrect voltage to the main circuit of the drive. Operate the drive in the specified
range of the input voltage on the drive nameplate.
Voltages that are higher than the permitted nameplate tolerance can cause damage to the drive.
Fire Hazard
Do not put flammable or combustible materials on top of the drive and do not install the drive near
flammable or combustible materials. Attach the drive to metal or other noncombustible material.
Flammable and combustible materials can start a fire and cause serious injury or death.
10 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 11

1.1 Section Safety
WARNING
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not modify the drive body or drive circuitry.
Modifications to drive body and circuitry can cause serious injury or death, will cause damage to the drive, and will
void the warranty. Yaskawa is not responsible for modifications of the product made by the user.
Sudden Movement Hazard
Make sure that you align the phase order for the drive and motor when you connect the motor to
drive output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3.
If the phase order is incorrect, it can cause the motor to run in reverse. If the motor accidentally runs in reverse, it
can cause serious injury or death.
CAUTION
Burn Hazard
Do not touch a hot drive heatsink. De-energize the drive, wait for a minimum of 15 minutes, then
make sure that the heatsink is cool before you replace the cooling fans.
If you touch a hot drive heatsink, it can burn you.
NOTICE
Damage to Equipment
When you touch the drive and circuit boards, make sure that you observe correct electrostatic
discharge (ESD) procedures.
If you do not follow procedures, it can cause ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
Use the instructions in this manual to replace the cooling fans. When you do maintenance on the
fans, replace all the fans to increase product life.
If you install the fans incorrectly, it can cause damage to the drive.
Make sure that all connections are correct after you install the drive and connect peripheral
devices.
Incorrect connections can cause damage to the drive.
Do not energize and de-energize the drive more frequently than one time each 30 minutes.
If you frequently energize and de-energize the drive, it can cause drive failure.
Do not operate a drive or connected equipment that has damaged or missing parts.
You can cause damage to the drive and connected equipment.
Note:
Do not use unshielded cable for control wiring. Use shielded, twisted-pair wires and ground the shield to the ground terminal of the drive.
Unshielded wire can cause electrical interference and unsatisfactory system performance.
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 11
Page 12
1.2 Inspection
1.2 Inspection
Power electronics have limited life and can show changes in performance and deterioration of performance after years
of use in usual conditions. To help prevent these problems, it is important to do preventive maintenance and regular
inspection, and replace parts on the drive.
Drives contain different types of power electronics, for example power transistors, semiconductors, capacitors,
resistors, fans, and relays. The electronics in the drive are necessary for correct motor control.
Follow the inspection lists in this chapter as a part of a regular maintenance program.
Note:
Examine the drive one time each year at a minimum.
The operating conditions, environmental conditions, and use conditions will have an effect on the examination frequency for connected
equipment.
Examine the drive more frequently if you use the drive in bad conditions or in these conditions:
• High ambient temperatures
• Frequent starting and stopping
• Changes in the AC power supply or load
• Too much vibration or shock loading
• Dust, metal dust, salt, sulfuric acid, or chlorine atmospheres
• Unsatisfactory storage conditions.
◆ Recommended Daily Inspection
Table 1.1 gives information about the recommended daily inspection for Yaskawa drives. Examine the items in Table
1.1 each day to make sure that the components do not wear out or fail. Make a copy of this checklist and put a check
mark in the “Checked” column after each inspection.
Table 1.1 Daily Inspection Checklist
Inspection Area Inspection Points Corrective Action Checked
Motor
Cooling System
Surrounding
Environment
Load
Power Supply Voltage Examine main power supply and control voltages.
Examine for unusual oscillation or noise coming from
the motor.
Examine for unusual heat from the drive or motor and
visible discoloration.
Examine the cooling fans.
Make sure that the installation environment is
applicable.
Make sure that the drive output current is not more
than the motor or drive rating for an extended period of
time.
• Check the load coupling.
• Measure motor vibration.
• Tighten all loose components.
• Check for a load that is too heavy.
• Tighten loose screws.
• Check for a dirty heatsink or motor.
• Measure the ambient temperature.
• Check for a clogged or dirty fan.
• Use the performance life monitor to check for correct fan operation.
Remove the source of contamination or correct unsatisfactory environment.
• Check for a load that is too heavy.
• Check the correct motor parameter settings.
• Correct the voltage or power supply to agree with nameplate specifications.
• Verify all main circuit phases.
◆ Recommended Periodic Inspection
Table 1.2 to Table 1.6 give information about the recommended periodic inspections for Yaskawa drives. Examine the
drive one time each year at a minimum. The operating conditions, environmental conditions, and use conditions will
have an effect on the examination frequency for connected equipment. You must use your experience with the
application to select the correct inspection frequency for each drive installation. Periodic inspections will help to
prevent performance deterioration and product failure. Make a copy of this checklist and put a check mark in the
“Checked” column after each inspection.
12 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 13

1.2 Inspection
DANGER! Electrical Shock Hazard. Do not examine, connect, or disconnect wiring on an energized drive. Before servicing,
disconnect all power to the equipment and wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum. The internal capacitor
stays charged after the drive is de-energized. The charge indicator LED extinguishes when the DC bus voltage decreases below 50
Vdc. When all indicators are OFF, measure for dangerous voltages to make sure that the drive is safe. If you do work on the drive
when it is energized, it will cause serious injury or death from electrical shock.
Table 1.2 Main Circuit Periodic Inspection Checklist
Inspection Area Inspection Points Corrective Action Checked
General
Conductors and
Wiring
Terminal Block
Electromagnetic
Contactors and
Relays
Dynamic Braking
Option
Electrolytic Capacitor
Diodes, IGBT (Power
Transistor)
• Examine equipment for discoloration from too
much heat or deterioration.
• Examine for damaged parts.
Examine for dirt, unwanted particles, or dust on
components.
• Examine wiring and connections for discoloration
or damage. Examine wiring and connections for
discoloration from too much heat.
• Examine wire insulation and shielding for
discoloration and wear.
Examine terminals for stripped, damaged, or loose
connections.
• Examine contactors and relays for too much noise
during operation.
• Examine coils for signs of too much heat, such as
melted or broken insulation.
Examine the insulation for discoloration from too
much heat.
• Examine for leaks, discoloration, or cracks.
• Examine if the cap has come off, if there is
swelling, or if there are leaks from broken sides.
Examine for dust or other unwanted material collected
on the surface.
• Replace damaged components as necessary.
• The drive does not have many serviceable parts and it could be necessary to
replace the drive.
• Examine enclosure door seal.
• Use a vacuum cleaner to remove unwanted particles and dust without touching
the components.
• If you cannot remove unwanted particles and dust with a vacuum cleaner,
replace the components.
Repair or replace damaged wiring.
• Tighten loose screws.
• Replace damaged screws.
• Check coil voltage for overvoltage or undervoltage conditions.
• Replace broken relays, contactors, or circuit boards that you can remove.
If there is discoloration in the option, check to make sure that there is not damage to
the wiring. A small quantity of discoloration is not a problem.
The drive does not have many serviceable parts and it could be necessary to replace
the drive.
Use a vacuum cleaner to remove unwanted particles and dust without touching the
components.
Table 1.3 Motor Periodic Inspection Checklist
Inspection Area Inspection Points Corrective Action Checked
Operation Check Check for increased vibration or unusual noise. Stop the motor and contact approved maintenance personnel as necessary.
Table 1.4 Control Circuit Periodic Inspection Checklist
Inspection Area Inspection Points Corrective Action Checked
• Tighten loose screws.
• Replace damaged screws or terminals.
• If terminals are integral to a circuit board, it could be necessary to replace the
control board or the drive.
• Tighten loose connections.
• Use a vacuum cleaner to remove unwanted particles and dust without touching
the components.
• If you cannot remove unwanted particles and dust with a vacuum cleaner,
replace the components.
• Do not use solvents to clean the board.
• The drive does not have many serviceable parts and it could be necessary to
replace the drive.
General
Circuit Boards
• Examine terminals for stripped, damaged, or loose
connections.
• Make sure that all terminals have been correctly
tightened.
• Check for odor, discoloration, or rust.
• Make sure that all connections are correctly
fastened.
• Make sure that the surface of the circuit board does
not have dust or oil mist.
Table 1.5 Cooling System Periodic Inspection Checklist
Inspection Area Inspection Points Corrective Action Checked
Cooling Fan
Heatsink
Air Duct
• Check for unusual oscillation or unusual noise.
• Check for damaged or missing fan blades.
• Examine for dust or other unwanted material
collected on the surface.
• Examine for dirt.
Examine air intake, exhaust openings and make sure
that there are no unwanted materials on the surface.
Clean or replace the fans as necessary.
Use a vacuum cleaner to remove unwanted particles and dust without touching the
components.
Clear blockages and clean air duct as necessary.
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 13
Page 14
1.2 Inspection
Table 1.6 Keypad Periodic Inspection Checklist
Inspection Area Inspection Points Corrective Action Checked
General
• Make sure that the keypad shows the data correctly.
• Examine for dust or other unwanted material that
collected on components in the area.
• If you have problems with the display or the keys, contact Yaskawa or your
nearest sales representative.
• Clean the keypad.
14 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 15
1.3 Maintenance
1.3 Maintenance
The drive Maintenance Monitors keep track of component wear and tell the user when the end of the estimated
performance life is approaching. The Maintenance Monitors prevent the need to shut down the full system for
unexpected problems. Users can set alarm notifications for the maintenance periods for these drive components:
• Cooling fan
• Electrolytic capacitor
• Soft charge bypass relay
• IGBT
Contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative for more information about part replacement.
◆ Replaceable Parts
You can replace these parts of the drive:
• Cooling fan
If there is a failure in the main circuit, replace the drive.
If the drive is in the warranty period, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative before you replace parts.
Yaskawa reserves the right to replace or repair the drive as specified by the Yaskawa warranty policy.
DANGER! Electrical Shock Hazard. Do not examine, connect, or disconnect wiring on an energized drive. Before servicing,
disconnect all power to the equipment and wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum. The internal capacitor
stays charged after the drive is de-energized. The charge indicator LED extinguishes when the DC bus voltage decreases below 50
Vdc. When all indicators are OFF, measure for dangerous voltages to make sure that the drive is safe. If you do work on the drive
when it is energized, it will cause serious injury or death from electrical shock.
◆ Part Replacement Guidelines
Table 1.7 shows the standard replacement period for replacement parts. When you replace these parts, make sure that
you use Yaskawa replacement parts for the applicable model and design revision number of your drive.
Table 1.7 Standard Replacement Period
Parts Standard Replacement Period
Cooling fan 10 years
Electrolytic capacitor
*1 If there is damage to parts that you cannot repair or replace, replace the drive.
Note:
Performance life estimate is based on these use conditions. These conditions are provided for the purpose of replacing parts to maintain
performance. Some parts may require more frequent replacement due to poor environments or rigorous use. Operating conditions for
performance life estimate: Ambient temperature: Yearly average of 40 °C (IP20/UL Open Type), Load factor: 80%, Operating rate: 24 hours
a day
*1
10 years
◆ Monitors that Display the Lifespan of Drive Components
The drive keypad shows percentage values for the replacement parts to help you know when you must replace those
components. Use the monitors in Table 1.8 to check replacement periods. When the monitor value is 100%, the
component is at the end of its useful life and there is an increased risk of drive malfunction. Yaskawa recommends
that you check the maintenance period regularly to make sure that you get the maximum performance life.
Table 1.8 Performance Life Monitors
Monitor No. Parts Description
U4-03
U4-04
U4-05 Electrolytic Capacitor
Cooling fan
Shows the total operation time of fans as 0 to 99999 hours. After this value is 99999, the drive automatically resets it
to 0.
Shows the total fan operation time as a percentage of the specified maintenance period.
Shows the total capacitor usage time as a percentage of the specified maintenance period.
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 15
Page 16

1.3 Maintenance
Monitor No. Parts Description
U4-06 Soft charge bypass relay
U4-07 IGBT
Shows the number of times the drive is energized as a percentage of the performance life of the inrush circuit.
Shows the percentage of the maintenance period for the IGBTs.
◆ Alarm Outputs for Maintenance Monitors
You can use H2-xx [MFDO Function Selection] to send a message that tells you when a specified component is near
the end of its performance life estimate. Set the applicable value to H2-xx as shown in Table 1.9 for your component.
When the specified component is near the end of its performance life estimate, the MFDO terminals set for H2-xx =
2F [Maintenance Notification] will activate, and the keypad will show an alarm that identifies the component to
replace.
Table 1.9 Maintenance Period Alarms
Display Alarm Name Cause Possible Solutions
LT-1
LT-2
LT-3
LT-4
TrPC
Cooling Fan
Maintenance Time
Capacitor Maintenance
Time
SoftChargeBypassRe
lay MainteTime
IGBT Maintenance
Time (50%)
IGBT Maintenance
Time (90%)
The cooling fan is at 90% of its expected
performance life.
The capacitors for the main circuit and control
circuit are at 90% of expected performance life.
The soft charge bypass relay is at 90% of its
performance life estimate.
The IGBT is at 50% of its expected performance
life.
The IGBT is at 90% of its expected performance
life.
Replace the cooling fan, then set o4-03 = 0 [Fan Operation
Time Setting = 0 h] to reset the cooling fan operation time.
Replace the board or the drive.
Contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative to
replace the board.
Replace the board or the drive.
Contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative to
replace the board.
Check the load, carrier frequency, and output frequency.
Replace the IGBT or the drive.
Digital Outputs
(Setting Value in
H2-xx)
2F
10
◆ Related Parameters
Replace the component, then set o4-03, o4-05, o4-07, and o4-09 [Maintenance Setting] = 0 to reset the Maintenance
Monitor. If these parameters are not reset after the corresponding parts have been replaced, the Maintenance Monitor
function will continue to count down the performance life from the value that was reached with the old part. If the
Maintenance Monitor is not reset, the drive will not have the correct value of the performance life for the new
component.
Note:
The maintenance period changes for different operating environments.
Table 1.10 Maintenance Setting Parameters
No. Name Function
o4-03 Fan Operation Time Setting Sets the value from which to start the cumulative drive cooling fan operation time in 10-hour units.
Note:
When o4-03 = 30 has been set, the drive will count the operation time for the cooling fan from 300 hours and
U4-03 [Cooling Fan Ope Time] will show 300 h.
o4-05
o4-07 Softcharge Relay Maintenance Set Sets as a percentage the value from which to start the count for the soft charge bypass relay maintenance time.
o4-09 IGBT Maintenance Setting Sets the value from which to start the count for the IGBT maintenance period as a percentage.
Capacitor Maintenance Setting Sets the value from which to start the count for the main circuit capacitor maintenance period as a percentage.
16 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 17

1.4 Replace Cooling Fans
1.4 Replace Cooling Fans
NOTICE: Use the instructions in this manual to replace the cooling fans. When you do maintenance on the fans, replace all the fans
to increase product life. If you install the fans incorrectly, it can cause damage to the drive.
To replace a cooling fan, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
◆ Number of Cooling Fans
Table 1.11 Single-Phase 200 V Class
Model Cooling Fans Replacement Procedure Ref.
B001 - B006 -
B010, B012 1
B018 2 B
Table 1.12 Three-Phase 200 V Class
Model Cooling Fans Replacement Procedure Ref.
2001-2004 -
2006 - 2021 1 A
2030 1 B
2042 - 2082 2 A 17
- -
A
- -
17
17
20
Table 1.13 Three-Phase 400 V Class
Model Cooling Fans Replacement Procedure Ref.
4001 - 4004 -
4005 - 4012 1
4018, 4023 1 B
4031 - 4060 2 A 17
- -
A 17
20
◆ Replace the Cooling Fan (Procedure A)
DANGER! Electrical Shock Hazard. Do not examine, connect, or disconnect wiring on an energized drive. Before servicing,
disconnect all power to the equipment and wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum. The internal capacitor
stays charged after the drive is de-energized. The charge indicator LED extinguishes when the DC bus voltage decreases below 50
Vdc. When all indicators are OFF, measure for dangerous voltages to make sure that the drive is safe. If you do work on the drive
when it is energized, it will cause serious injury or death from electrical shock.
CAUTION! Burn Hazard. Do not touch a hot drive heatsink. De-energize the drive, wait for a minimum of 15 minutes, then make
sure that the heatsink is cool before you replace the cooling fans. If you touch a hot drive heatsink, it can burn you.
NOTICE: Use the instructions in this manual to replace the cooling fans. When you do maintenance on the fans, replace all the fans
to increase product life. If you install the fans incorrectly, it can cause damage to the drive.
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 17
Page 18

1.4 Replace Cooling Fans
■ Remove a Fan
1. To remove the fan finger guard from the drive, push the hooks on the left and right sides of it and pull up.
A - Fan finger guard
Figure 1.1 Remove the Fan Finger Guard
2. Pull the cooling fan straight up from the drive. Disconnect the power supply connector and remove the fan
from the drive.
A - Cooling fan
Figure 1.2 Remove the Cooling Fan
■ Install a Fan
Reverse the removal procedure to install a cooling fan.
1. Connect the power supply connector between the drive and cooling fan.
Figure 1.3 Connect the Power Supply Connector
18 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 19

1.4 Replace Cooling Fans
2. Align the notches on the fan with the pins on the drive and install the cooling fans in the drive.
A - Alignment pins on drive
B - Front of drive
Figure 1.4 Install the Cooling Fan
Note:
When you install the cooling fan, make sure that you do not pinch cables between the cooling fan and the drive.
C - Notch on fan
3. Put the cable and connector in the recess of the drive.
A - Front of drive
Figure 1.5 Put the Cable and Connector in the Drive Recess
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 19
Page 20

1.4 Replace Cooling Fans
Note:
The connector installation position is different for different models.
Figure 1.6 Put the Connector in the Recess
Figure 1.7 Put the Connector in Between the Fans
Figure 1.8 Put the Connector in Between the Drive and Fan
4. Insert the fan cover straight until the hook clicks into place.
Figure 1.9 Reattach the Fan Finger Guard
5. Energize the drive and set o4-03 = 0 [Fan Operation Time Setting = 0 h] to reset the cooling fan operation
time.
◆ Replace the Cooling Fan (Procedure B)
DANGER! Electrical Shock Hazard. Do not examine, connect, or disconnect wiring on an energized drive. Before servicing,
disconnect all power to the equipment and wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum. The internal capacitor
stays charged after the drive is de-energized. The charge indicator LED extinguishes when the DC bus voltage decreases below 50
Vdc. When all indicators are OFF, measure for dangerous voltages to make sure that the drive is safe. If you do work on the drive
when it is energized, it will cause serious injury or death from electrical shock.
CAUTION! Burn Hazard. Do not touch a hot drive heatsink. De-energize the drive, wait for a minimum of 15 minutes, then make
sure that the heatsink is cool before you replace the cooling fans. If you touch a hot drive heatsink, it can burn you.
NOTICE: Use the instructions in this manual to replace the cooling fans. When you do maintenance on the fans, replace all the fans
to increase product life. If you install the fans incorrectly, it can cause damage to the drive.
20 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 21

1.4 Replace Cooling Fans
■ Remove a Fan
1. Push the tabs toward the back of the drive and pull up to remove the fan finger guard from the drive.
A - Fan finger guard
Figure 1.10 Remove the Fan Finger Guard
2. Pull the cooling fan straight up from the drive. Disconnect the power supply connector and remove the fan
from the drive.
A - Cooling fan
Figure 1.11 Remove the Cooling Fan
■ Install the Cooling Fans
Reverse the removal procedure to install a cooling fan.
1. Connect the power supply connector between the drive and cooling fan.
Figure 1.12 Connecting the power supply connector
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 21
Page 22

1.4 Replace Cooling Fans
2. Install the cooling fans so that they align with the pins on the drive.
A - Alignment pins on drive
B - Front of drive
Figure 1.13 Installing the cooling fans
Note:
When you install the cooling fan, make sure that you do not pinch cables between the cooling fan and the drive.
C - Notches
3. Put the cable and connector in the recess of the drive.
A - Front of drive
Figure 1.14 Putting the cable and connector in the recess
4. Insert the tabs of the fan cover into the holes in the drive and press in the fan cover until the hook clicks into
place.
Figure 1.15 Reattach the Fan Finger Guard
5. Energize the drive and set o4-03 = 0 [Fan Operation Time Setting = 0 h] to reset the cooling fan operation
time.
22 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 23

1.5 Replace the Drive
1.5 Replace the Drive
◆ About the Control Circuit Board
You can remove the control circuit board of the drive and install a new board. If there is a failure in the drive, you can
use this feature to easily replace the control circuit board.
A - Control circuit board
Figure 1.16 Control Circuit Terminal Block
◆ Replace the Drive
DANGER! Electrical Shock Hazard. Disconnect all power to the drive and wait for the time specified on the warning label before you
remove covers. Check the drive for dangerous voltages before servicing or repair work. If you do work on the drive when it is
energized and there is no cover over the electronic circuits, it will cause serious injury or death from electrical shock. The drive has
internal capacitors that stay charged after you de-energize the drive.
DANGER! Electrical Shock Hazard. Do not examine, connect, or disconnect wiring on an energized drive. Before servicing,
disconnect all power to the equipment and wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum. The internal capacitor
stays charged after the drive is de-energized. The charge indicator LED extinguishes when the DC bus voltage decreases below 50
Vdc. When all indicators are OFF, measure for dangerous voltages to make sure that the drive is safe. If you do work on the drive
when it is energized, it will cause serious injury or death from electrical shock.
WARNING! Electrical Shock Hazard. Only let approved personnel install, wire, maintain, examine, replace parts, and repair the
drive. If personnel are not approved, it can cause serious injury or death.
NOTICE: Damage to Equipment. When you touch the drive and circuit boards, make sure that you observe correct electrostatic
discharge (ESD) procedures. If you do not follow procedures, it can cause ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
■ Notes on Wiring the Main Circuit Terminal Block
Read these notes before you wire the main circuit terminal block.
• Use UL-Listed, vinyl-coated insulated copper wires for operation with a continuous maximum permitted
temperature of 75 °C at 600 V.
• Remove all unwanted objects that are near the terminal block connections.
• Remove the insulation from the connection wires to the wire stripping lengths shown in the manual.
• Do not use bent or crushed wires. Remove the damaged end of the wire before you use it. Incorrect connections can
cause death or serious injury from fire.
• Do not solder stranded wire. Soldered wire connections can become loose over time and cause unsatisfactory drive
performance.
• If you use stranded wire, make sure that all of the wire strands are in the connection. Also, do not twist the stranded
wire too much. Incorrect connections can cause death or serious injury from fire.
• Put the wire all the way into the terminal block. Remove the insulation from the wire to the recommended wire
stripping length to fit the wire with insulation in the plastic housing.
• Use a torque driver, torque ratchet, or torque wrench for the screws. A slotted driver or a hex tool will be necessary
to wire the screw clamp terminal. Use applicable tools as specified by the recommended conditions in the product
manual.
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 23
Page 24
1.5 Replace the Drive
• If you use power tools to tighten the terminal screws, use a low speed setting (300 to 400 r/min). Failure to obey can
cause damage to the terminal screws.
• Users can purchase wiring tools from Yaskawa. Contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative for more
information.
• Wire gauges on existing drive models to be replaced may not match wire gauge ranges on new drives. Contact
Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative for more information about the connection procedures.
• Do not tighten the terminal screws at an angle of 5 degrees or more. Failure to obey can cause damage to the
terminal screws.
If you damage a terminal screw, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
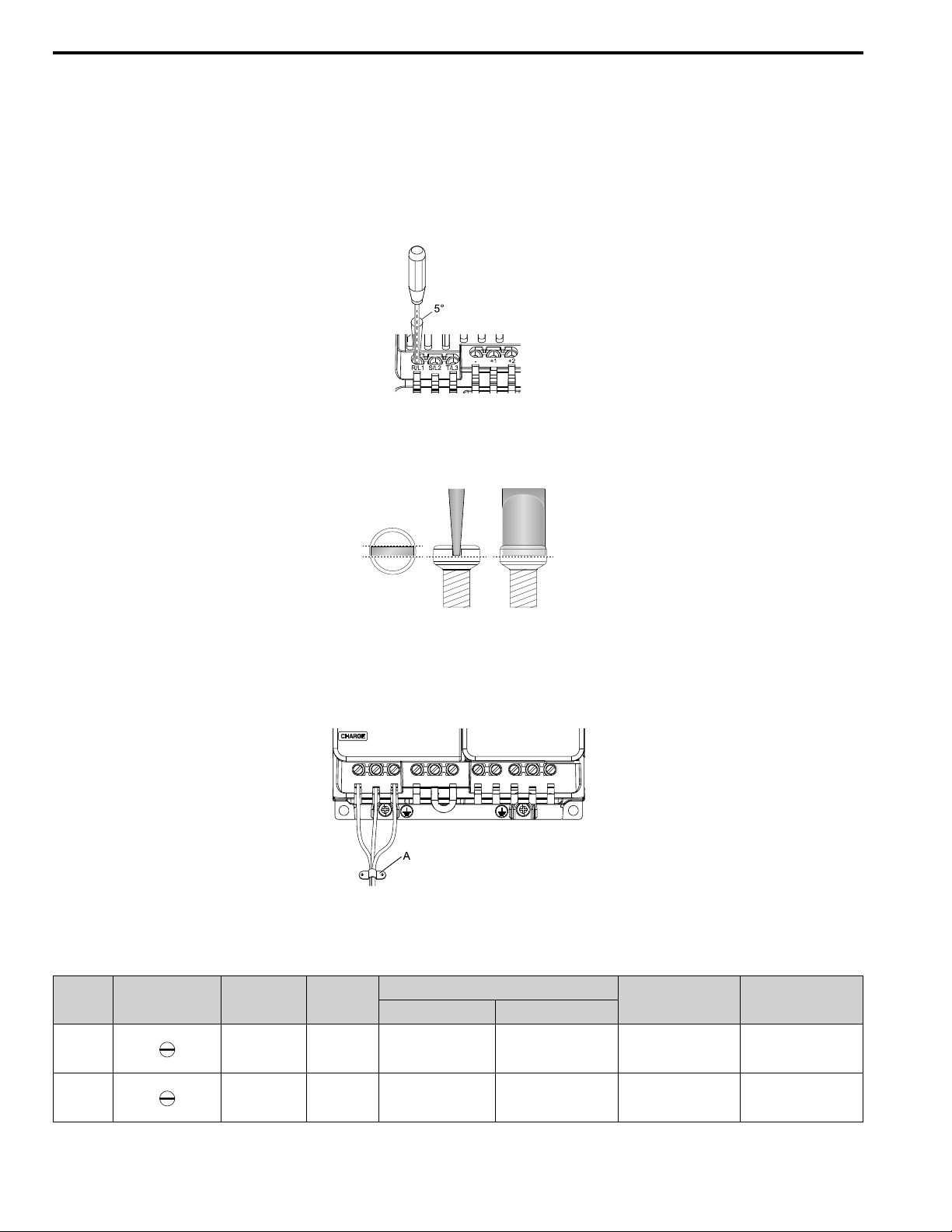
Figure 1.17 Permitted Angle
• Put the bit all the way into the hex socket to tighten the hex socket cap screw.
• When you tighten slotted screws, hold the straight-edge screwdriver perpendicularly to the screw. Make sure that
you align the end of the straight-edge screwdriver with the screw groove.
Figure 1.18 Tightening Slotted Screws
• After you connect the wires to the terminal block, lightly pull on the wires to make sure that they do not come out
of the terminals.
• Do not let strain on the wiring cause damage. Use a strain relief near the wiring to release the tension. Refer to
Figure 1.19 for an example.
A - Cable clamp
Figure 1.19 Strain Relief Example
Table 1.14 Recommended Wiring Tools
Screw
Size
M3 - Bit SF-BIT-SL 0,5X3,0-70 PHOENIX CONTACT
M4 - Bit SF-BIT-SL 1,0X4,0-70 PHOENIX CONTACT
Screw Shape Wire Gauge Adapter
Model Manufacturer
Bit
Torque Driver Model
(Tightening Torque)
TSD-M 1,2NM
(0.3 - 1.2 N∙m
(2.7 - 10.6 in∙lb))
TSD-M 3NM
(1.2 - 3.0 N∙m
(10.6 - 26.6 in∙lb))
Torque Wrench
(Tightening Torque)
-
-
24 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 25

1.5 Replace the Drive
Screw
Size
M5
M6
Screw Shape Wire Gauge Adapter
2
≤ 25 mm
*1
(WAF: 5 mm)
(AWG 10)
2
≥ 30 mm
(AWG 8)
- Bit SF-BIT-HEX 5-50 PHOENIX CONTACT -
Bit SF-BIT-SL 1,2X6,5-70 PHOENIX CONTACT
Model Manufacturer
Bit
Torque Driver Model
(Tightening Torque)
TSD-M 3NM
(1.2 - 3.0 N∙m
(10.6 - 26.6 in∙lb))
-
*1 When you wire drive models 2042, 2056, 4031, 4038, 4044, and 4060, select the correct tools for the wire gauge.
*2 Use 6.35 mm (0.25 in) bit socket holder.
*3 Use a torque wrench that can apply this torque measurement range.
■ Remove the Control Circuit Board
Remove the front cover and keypad from the drive.
1. Push the tabs to the left that hold the control board to the drive.
Torque Wrench
(Tightening Torque)
-
4.1 - 4.5 N∙m
(36.3 - 39.8 in∙lb)
5 - 9 N∙m
(44.3 - 79.7 in∙lb)
*2 *3
*2 *3
Figure 1.20 Unhook the Tabs
2. Pull the left side of the control circuit board out first.
Figure 1.21 Remove the Control Circuit Board
■ Put the Control Circuit Board in a New Drive
Remove the keypad, front cover, and control circuit board of the new drive.
Wire the main circuit terminals of the new drive, then attach the wired control circuit board.
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 25
Page 26
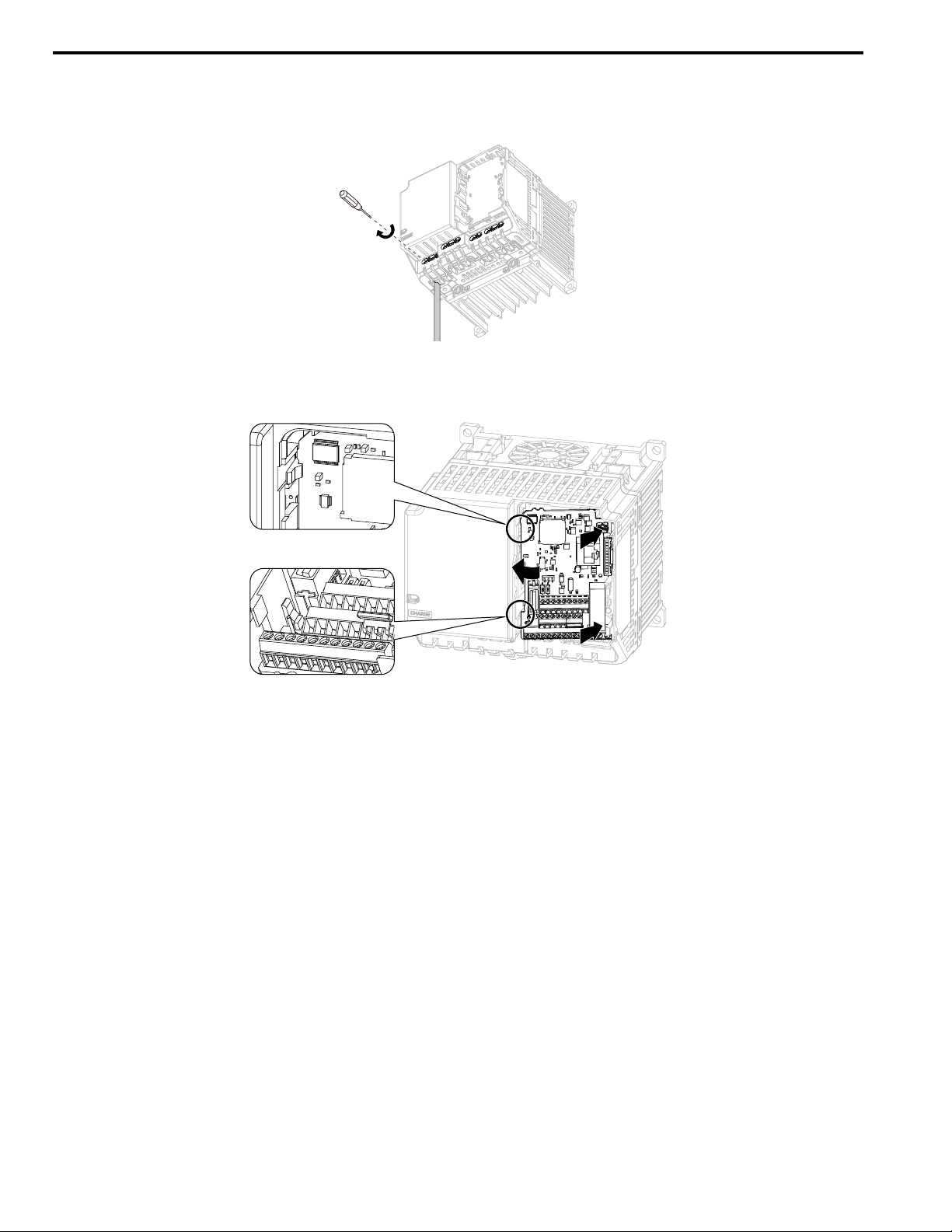
1.5 Replace the Drive
1. Wire the main circuit terminals.
Note:
To wire terminals +1 and +2, remove the jumper between terminals +1 and +2.
Figure 1.22 Wire the Main Circuit Terminals
2. Attach the wired control circuit board to the drive.
Push the control circuit board until the hooks click into place on the drive.
Figure 1.23 Attach the Control Circuit Board
3. Attach the keypad and front cover to the new drive.
4. Energize the drive and set these parameters:
• o2-04 [Drive Model (KVA) Selection]: Set this parameter to the model number of the new drive.
• o4-01 to o4-13 [Maintenance Period]: Reset the performance life monitors for the components.
26 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 27

1.6 Storage Guidelines
1.6 Storage Guidelines
The chemicals in the electrolytic capacitors and other electronic parts of the drive change over time. When you store
the drive for long periods of time, use the information in this section to help keep the performance life estimates.
◆ Storage Location
• Temperature and Humidity
When you store the drive for approximately one month, for example during shipping, you can put the drive in a
location where the temperature is -20 °C to +70 °C (-4 °F to +158 °F). Correctly package and store the drive during
shipping to prevent vibration and impact damage.
Do not put the drive in direct sunlight or where there will be condensation or ice. Put the drive in a location where
the relative humidity is 95% or less.
• Dust and Oil Mist
Do not keep the drive locations with dust or oil mist. For example, cement factories and cotton mills.
• Corrosive Gas
Do not keep the drive in locations with corrosive gas. For example, chemical plants, refineries, and sewage plants.
• Salt Damage
Do not keep the drive in salty locations. For example, locations near the ocean, and salt damage-designated
locations.
Do not keep the drive in unsatisfactory locations. Keep all drives in storage rooms that are safe from unsatisfactory
elements.
◆ Regular Application of Power
To prevent deterioration of the capacitors, Yaskawa recommends that you apply power to the drive a minimum of one
time each year for a minimum of 30 minutes.
If you store the drive for longer than two years and do not apply power, Yaskawa recommends that you use a variable
power source and gradually increase the power from 0 V to the rated drive voltage over a period of 2 to 3 minutes.
Apply power for a minimum of 1 hour with no load to reform the main circuit electrolytic capacitor. When you
operate the drive after you apply power, wire the drive correctly and check for drive faults, overcurrents, motor
vibration, motor speed differences, and other defects during operation.
A - AC power supply
B - Variable power source
Figure 1.24 Power Distribution Method
C - Drive
Periodic Inspection and Maintenance
1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 27
Page 28

1.6 Storage Guidelines
28 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 29

2
Troubleshooting
2.1 Section Safety ........................................................................................................... 30
2.2 Types of Faults, Minor Faults, Alarms, and Errors ..........................................32
2.3 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes..........................................33
2.4 Fault .............................................................................................................................38
2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms ................................................................................................55
2.6 Parameter Setting Errors........................................................................................ 65
2.7 Auto-Tuning Errors .................................................................................................. 70
2.8 Backup Function Operating Mode Display and Errors................................... 74
2.9 Diagnosing and Resetting Faults.........................................................................76
2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display..............................................................78
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 29
Page 30

2.1 Section Safety
2.1 Section Safety
DANGER
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not examine, connect, or disconnect wiring on an energized drive. Before servicing, disconnect
all power to the equipment and wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum. The
internal capacitor stays charged after the drive is de-energized. The charge indicator LED
extinguishes when the DC bus voltage decreases below 50 Vdc. When all indicators are OFF,
measure for dangerous voltages to make sure that the drive is safe.
If you do work on the drive when it is energized, it will cause serious injury or death from electrical shock.
WARNING
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not operate the drive when covers are missing. Replace covers and shields before you operate
the drive. Use the drive only as specified by the instructions.
Some figures in this section include drives without covers or safety shields to more clearly show the inside of the
drive. If covers or safety shields are missing from the drive, it can cause serious injury or death.
Always ground the motor-side grounding terminal.
If you do not ground the equipment correctly, it can cause serious injury or death if you touch the motor case.
After the drive blows a fuse or trips a GFCI, do not immediately energize the drive or operate
peripheral devices. Wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum and make sure
that all indicators are OFF. Then check the wiring and peripheral device ratings to find the cause of
the problem. If you do not know the cause of the problem, contact Yaskawa before you energize the
drive or peripheral devices.
If you do not fix the problem before you operate the drive or peripheral devices, it can cause serious injury or death.
Only let approved personnel install, wire, maintain, examine, replace parts, and repair the drive.
If personnel are not approved, it can cause serious injury or death.
Do not wear loose clothing or jewelry when you do work on the drive. Tighten loose clothing and
remove all metal objects, for example watches or rings.
Loose clothing can catch on the drive and jewelry can conduct electricity and cause serious injury or death.
Do not remove covers or touch circuit boards while the drive is energized.
If you touch the internal components of an energized drive, it can cause serious injury or death.
Do not modify the drive body or drive circuitry.
Modifications to drive body and circuitry can cause serious injury or death, will cause damage to the drive, and will
void the warranty. Yaskawa is not responsible for modifications of the product made by the user.
Fire Hazard
Tighten all terminal screws to the correct tightening torque.
Connections that are too loose or too tight can cause incorrect operation and damage to the drive. Incorrect
connections can also cause death or serious injury from fire.
Tighten screws at an angle in the specified range shown in this manual.
If you tighten the screws at an angle not in the specified range, you can have loose connections that can cause
damage to the terminal block or start a fire and cause serious injury or death.
Damage to Equipment
Do not apply incorrect voltage to the main circuit of the drive. Operate the drive in the specified
range of the input voltage on the drive nameplate.
Voltages that are higher than the permitted nameplate tolerance can cause damage to the drive.
30 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 31

2.1 Section Safety
WARNING
Fire Hazard
Do not put flammable or combustible materials on top of the drive and do not install the drive near
flammable or combustible materials. Attach the drive to metal or other noncombustible material.
Flammable and combustible materials can start a fire and cause serious injury or death.
Crush Hazard
Wear eye protection when you do work on the drive.
If you do not use correct safety equipment, it can cause serious injury or death.
Use a crane or hoist to move large drives when necessary.
If you try to move a large drive without a crane or hoist, it can cause serious injury or death.
NOTICE
Damage to Equipment
When you touch the drive and circuit boards, make sure that you observe correct electrostatic
discharge (ESD) procedures.
If you do not follow procedures, it can cause ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
Do not break the electrical connection between the drive and the motor when the drive is
outputting voltage.
Incorrect equipment sequencing can cause damage to the drive.
Make sure that all connections are correct after you install the drive and connect peripheral
devices.
Incorrect connections can cause damage to the drive.
Note:
Do not use unshielded wire for control wiring. Use shielded, twisted-pair wires and ground the shield to the ground terminal of the drive.
Unshielded wire can cause electrical interference and unsatisfactory system performance.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 31
Page 32

2.2 Types of Faults, Minor Faults, Alarms, and Errors
2.2 Types of Faults, Minor Faults, Alarms, and Errors
If the drive or motor do not operate correctly, check the drive keypad for a code or message.
If problems occur that are not identified in this manual, contact the nearest Yaskawa representative with this
information:
• Drive model
• Drive software version
• Date of purchase
• Description of the problem (for example failure conditions and modified parameters)
Table 2.1 contains descriptions of the different types of faults, minor faults, alarms, and errors that can occur during
drive operation.
Contact Yaskawa if there is damage to the drive. Contact information is on the back cover of the manual.
Table 2.1 Types of Faults, Minor Faults, Alarms, and Errors
Type Drive Response
When the drive detects a fault, it will cause these conditions:
• The keypad shows the fault code, and ALM/ERR stays illuminated.
Fault
Minor Faults/Alarms
Operation Errors
Auto-Tuning Error
Copy Function Error
• The drive shuts off output, and the motor coasts to a stop. Some faults let the user select a motor stopping method.
• The terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = E [MFDO Function Selection = Fault] will activate.
The drive will not operate until you clear the fault with a Fault Reset and the drive goes back to usual status.
When the drive detects a minor fault or an alarm, it will cause these conditions:
• The keypad shows the alarm code, and ALM/ERR flashes.
• The drive will continue to operate the motor. Some alarms let you select a motor stopping method.
• If the drive detects a minor fault, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [Alarm] will activate If you do not set parameters
H2-01 to H2-03, the drive will not trigger MFDO terminals if it detects a minor fault.
• The drive will not output a minor fault signal if it detects an alarm.
It is not necessary to do Fault Reset.
An error occurs when parameter settings do not agree or a parameter combination is incorrect. The drive will not operate until
you set the parameters correctly.
When the drive detects an operation error, these conditions will result:
• The keypad shows the error code.
• Multi-function outputs do not output an alarm signal.
Find the parameters that caused the error and correct the settings.
An error occurs during Auto-Tuning.
When the drive detects an operation error, it will cause these conditions:
• The keypad shows the error code.
• Multi-function outputs do not output an alarm signal.
• The motor coasts to stop.
Remove the cause of the error and do Auto-Tuning again.
An error occurs when you use the keypad for a backup, restore, or verify operation.
When the drive detects a copy function error, it will cause these conditions:
• The keypad shows the error code.
• Multi-function outputs do not output an alarm signal.
Push a key on the keypad to clear the error. Remove the cause of the error and try the backup, restore, or verify operation again.
32 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 33

2.3 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes
2.3 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes
Table 2.2 shows the possible fault, minor fault, alarm, and error codes.
The display codes are in alphabetical order. Search the table for the code shown on the keypad, and identify its causes
and possible solutions.
Note:
The number in parentheses adjacent to the code in the table identifies the fault code or minor fault code (hex. number) that was read during
MEMOBUS/Modbus communications.
Example: AEr (0032)
Table 2.2 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes
Display (Hex.) Name ALM LED Type Ref.
AEr (0032) Station Address Setting Error Flashing Alarm 55
bAT (0085) Keypad Battery Low Voltage Flashing Alarm 55
bAT (0402) Keypad Battery Low Voltage Illuminated Fault 38
bb (0008) Baseblock Flashing Alarm 55
bCE (008A) Bluetooth Communication Error Flashing Alarm 55
bCE (0416) Bluetooth Communication Fault Illuminated Fault 38
boL (0045) Braking Transistor Overload Flashing Alarm 55
boL (004F) BrakingTransistor Overload Fault Illuminated Fault 38
bUS (0015) Option Communication Error Flashing Alarm 55
bUS (0022) Option Communication Error Illuminated Fault 38
CALL (001D) Serial Comm Transmission Error Flashing Alarm 56
CE (0014) Modbus Communication Error Flashing Alarm 56
CE (0021) Modbus Communication Error Illuminated Fault 38
CF (0025) Control Fault Illuminated Fault 39
CoF (0046) Current Offset Fault Illuminated Fault 39
CP1 (0087) Comparator 1 Limit Error Flashing Alarm 56
CP1 (0414) Comparator 1 Limit Error Illuminated Fault 39
CP2 (0088) Comparator 2 Limit Error Flashing Alarm 56
CP2 (0415) Comparator 2 Limit Error Illuminated Fault 39
CPEr Control Mode Mismatch - Backup Function Runtime Error 74
CPF00, CPF01
CPF02, CPF03 (0083, 0084)
CPF08 (0089)
CPF11 - CPF14 (008C - 008F)
CPF16 - CPF24 (0091 - 0099)
CPF38 (00A7)
CPF06 (0087) EEPROM Memory Data Error Illuminated Fault 40
CPyE Error Writing Data - Backup Function Runtime Error 74
CrST Remove RUN Command to Reset Flashing Not an alarm. 57
CSEr Control Mode Mismatch - Backup Function Runtime Error 74
CyC (0033) MECHATROLINK CommCycleSettingErr Flashing Alarm 57
CyPo (0029) Cycle Power to Accept Changes Flashing Alarm 57
dCE1 (041A) Communication Error1 Illuminated Fault 40
dCE2 (041B) Communication Error2 Illuminated Fault 40
dEv (0011) Speed Deviation Flashing Alarm 57
dEv (0019) Speed Deviation Illuminated Fault 40
Control Circuit Error Illuminated Fault 40
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 33
Page 34

2.3 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes
Display (Hex.) Name ALM LED Type Ref.
dFPS Drive Model Mismatch - Backup Function Runtime Error 74
dnE (002A) Drive Disabled Flashing Alarm 57
dv7 (005B) Polarity Judge Timeout Illuminated Fault 40
dWA2 (004A) DriveWorksEZ Alarm 2 Flashing Alarm 57
dWA3 (004B) DriveWorksEZ Alarm 3 Flashing Alarm 57
dWAL (0049) DriveWorksEZ Alarm Flashing Alarm 57
dWF1 (004A) EEPROM Memory DWEZ Data Error Illuminated Fault 41
dWF2 (004B) DriveWorksEZ Fault 2 Illuminated Fault 41
dWF3 (004C) DriveWorksEZ Fault 3 Illuminated Fault 41
dWFL (0049) DriveWorksEZ Fault Illuminated Fault 41
E5 (0031) MECHATROLINK Watchdog Timer Err Flashing Alarm 57
E5 (0039) MECHATROLINK Watchdog Timer Err Illuminated Fault 41
EF (0007) FWD/REV Run Command Input Error Flashing Alarm 58
EF0 (001A) Option Card External Fault Flashing Alarm 58
EF0 (0027) Option Card External Fault Illuminated Fault 41
EF1 (0042) External Fault (Terminal S1) Illuminated Fault 41
EF1 (0039) External Fault (Terminal S1) Flashing Alarm 58
EF2 (003A) External Fault (Terminal S2) Flashing Alarm 58
EF2 (0043) External Fault (Terminal S2) Illuminated Fault 41
EF3 (0009) External Fault (Terminal S3) Flashing Alarm 58
EF3 (0011) External Fault (Terminal S3) Illuminated Fault 42
EF4 (000A) External Fault (Terminal S4) Flashing Alarm 58
EF4 (0012) External Fault (Terminal S4) Illuminated Fault 42
EF5 (000B) External Fault (Terminal S5) Flashing Alarm 58
EF5 (0013) External Fault (Terminal S5) Illuminated Fault 42
EF6 (000C) External Fault (Terminal S6) Flashing Alarm 59
EF6 (0014) External Fault (Terminal S6) Illuminated Fault 42
EF7 (000D) External Fault (Terminal S7) Flashing Alarm 59
EF7 (0015) External Fault (Terminal S7) Illuminated Fault 42
End1 Excessive Rated Voltage Setting Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 70
End2 Iron Core Saturation Coefficient Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 70
End3 Rated Current Setting Alarm Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 70
End4 Adjusted Slip Calculation Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 70
End5 Resistance Tuning Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 70
End6 Leakage Inductance Alarm Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 70
End7 No-Load Current Alarm Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 70
End8 HFI Alarm Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 71
End9 Initial Pole Detection Alarm Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 71
EP24v (0081) External Power 24V Supply Flashing Alarm 59
Er-01 Motor Data Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 71
Er-02 Drive in an Alarm State Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 71
Er-03 STOP Button was Pressed Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 71
Er-04 Resistance Tuning Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 72
34 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 35

2.3 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes
Display (Hex.) Name ALM LED Type Ref.
Er-05 No-Load Current Alarm Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 72
Er-08 Rated Slip Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 72
Er-09 Acceleration Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 72
Er-10 Motor Direction Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 72
Er-11 Motor Speed Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 72
Er-12 Current Detection Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-13 Leakage Inductance Alarm Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-14 Motor Speed Error 2 Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-15 Torque Saturation Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-16 Inertia ID Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-17 Reverse Prohibited Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-18 Back EMF Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-19 PM Inductance Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-20 Stator Resistance Error Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Er-25 HighFreq Inject Param Tuning Err Flashing Auto-Tuning Error 73
Err (001F) EEPROM Write Error Illuminated Fault 42
FbH (0028) Excessive PID Feedback Flashing Alarm 59
FbH (0041) Excessive PID Feedback Illuminated Fault 43
FbL (0027) PID Feedback Loss Flashing Alarm 59
FbL (0028) PID Feedback Loss Illuminated Fault 43
GF (0006) Ground Fault Illuminated Fault 43
HCA (0034) High Current Alarm Flashing Alarm 59
iFEr Communication Err - Backup Function Runtime Error 74
L24v (0021) Loss of External Power 24 Supply Flashing Alarm 60
LF (001C) Output Phase Loss Illuminated Fault 43
LF2 (0036) Output Current Imbalance Illuminated Fault 44
LoG Log Com Error Flashing Alarm 60
LSo (0051) Low Speed Motor Step-Out Illuminated Fault 44
LT-1 (0035) Cooling Fan Maintenance Time Flashing Alarm 60
LT-2 (0036) Capacitor Maintenance Time Flashing Alarm 60
LT-3 (0043) SoftChargeBypassRelay MainteTime Flashing Alarm 60
LT-4 (0044) IGBT Maintenance Time (50%) Flashing Alarm 60
ndAT Model,VolClass,Capacity Mismatch - Backup Function Runtime Error 74
nSE (0052) Node Setup Error Illuminated Fault 44
oC (0007) Overcurrent Illuminated Fault 44
oFA00 (0101) Option Not Compatible with Port Illuminated Fault 45
oFA03 - oFA06 (0104 - 0107) Option Card Error Occurred at Option Port (CN5) Illuminated Fault 46
oFA10, oFA11 (0111, 0112) Option Card Error Occurred at Option Port (CN5) Illuminated Fault 46
oFA12 - oFA17 (0113 - 0118) Option Card Connection Error (CN5) Illuminated Fault 46
oFA30 - oFA43 (0131 - 013E) Communication Option Card Connection Error (CN5) Illuminated Fault 46
oH (0003) Heatsink Overheat Flashing Alarm 60
oH (0009) Heatsink Overheat Illuminated Fault 46
oH1 (000A) Heatsink Overheat Illuminated Fault 46
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 35
Page 36

2.3 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes
Display (Hex.) Name ALM LED Type Ref.
oH2 (0004) External Overheat (H1-XX=B) Flashing Alarm 61
oH3 (001D) Motor Overheat (PTC Input) Illuminated Fault 47
oH3 (0022) Motor Overheat (PTC Input) Flashing Alarm 61
oH4 (0020) Motor Overheat Fault (PTC Input) Illuminated Fault 47
oL1 (000B) Motor Overload Illuminated Fault 47
oL2 (000C) Drive Overload Illuminated Fault 48
oL3 (0005) Overtorque 1 Flashing Alarm 61
oL3 (000D) Overtorque Detection 1 Illuminated Fault 49
oL4 (0006) Overtorque 2 Flashing Alarm 61
oL4 (000E) Overtorque Detection 2 Illuminated Fault 49
oL5 (003D) Mechanical Weakening Detection 1 Flashing Alarm 61
oL5 (0044) Mechanical Weakening Detection 1 Illuminated Fault 49
oL7 (002B) High Slip Braking Overload Illuminated Fault 49
oPE01 Drive Capacity Setting Fault Flashing Parameter Setting Error 65
oPE02 Parameter Range Setting Error Flashing Parameter Setting Error 65
oPE03 Multi-Function Input Setting Err Flashing Parameter Setting Error 65
oPE05 Run Cmd/Freq Ref Source Sel Err Flashing Parameter Setting Error 66
oPE07 Analog Input Selection Error Flashing Parameter Setting Error 67
oPE08 Parameter Selection Error Flashing Parameter Setting Error 67
oPE09 PID Control Selection Fault Flashing Parameter Setting Error 68
oPE10 V/f Data Setting Error Flashing Parameter Setting Error 68
oPE11 Carrier Frequency Setting Error Flashing Parameter Setting Error 68
oPE13 Pulse Monitor Selection Error Flashing Parameter Setting Error 68
oPE16 Energy Saving Constants Error Flashing Parameter Setting Error 68
oPE33 Digital Output Selection Error Flashing Parameter Setting Error 69
oPr (001E) Keypad Connection Fault Illuminated Fault 49
oS (0010) Overspeed Flashing Alarm 62
oS (0018) Overspeed Illuminated Fault 62
ov (0002) Overvoltage Flashing Alarm 62
ov (0008) Overvoltage Illuminated Fault 50
PASS Modbus Communication Test Flashing Not an alarm. 62
PE1 (0047)
PE2 (0048)
PF (0047) Input Phase Loss Flashing Alarm 62
PF (001B) Input Phase Loss Illuminated Fault 51
PWEr DWEZ Password Mismatch - Backup Function Runtime Error 74
rdEr Error Reading Data - Backup Function Runtime Error 75
rF (004E) Braking Resistor Fault Illuminated Fault 51
rH (0010) Braking Resistor Overheat Illuminated Fault 51
rr (000F) Dynamic Braking Transistor Fault Illuminated Fault 52
rUn (001B) Motor Switch during Run Flashing Alarm 63
SC (0005) Short Circuit/IGBT Failure Illuminated Fault 52
SCF (040F) Safety Circuit Fault Illuminated Fault 52
PLC Faults Illuminated Fault 51
36 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 37

2.3 List of Fault, Minor Fault, Alarm, and Error Codes
Display (Hex.) Name ALM LED Type Ref.
SE (0020) Modbus Test Mode Error Flashing Alarm 63
SEr (003B) Speed Search Retries Exceeded Illuminated Fault 52
SToF (003B) Safe Torque OFF Flashing Alarm 63
STPo (0037) Motor Step-Out Detected Illuminated Fault 52
TiM (0089) Keypad Time Not Set Flashing Alarm 63
TiM (0401) Keypad Time Not Set Illuminated Fault 53
TrPC (0042) IGBT Maintenance Time (90%) Flashing Alarm 63
UL3 (001E) Undertorque Detection 1 Flashing Alarm 63
UL3 (0029) Undertorque Detection 1 Illuminated Fault 53
UL4 (001F) Undertorque Detection 2 Flashing Alarm 63
UL4 (002A) Undertorque Detection 2 Illuminated Fault 53
UL5 (003E) Mechanical Weakening Detection 2 Flashing Alarm 63
UL5 (0045) Mechanical Weakening Detection 2 Illuminated Fault 53
Uv (0001) DC Bus Undervoltage Flashing Alarm 64
Uv1 (0002) DC Bus Undervoltage Illuminated Fault 53
Uv2 (0003) Control Power Undervoltage Illuminated Fault 54
Uv3 (0004) Soft Charge Answerback Fault Illuminated Fault 54
vAEr Voltage Class, Capacity Mismatch - Backup Function Runtime Error 75
vFyE Parameters do not Match - Backup Function Runtime Error 75
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 37
Troubleshooting
2
Page 38

2.4 Fault
2.4 Fault
This section gives information about some of the causes and possible solutions of faults. You must use the Fault Reset
operation to remove the fault before you can operate the drive. Use the information in this table to remove the cause
of the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
bAT Keypad Battery Low Voltage
Note:
Use o4-24 [bAT Detection Selection] to enable/disable bAT detection.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
bCE Bluetooth Communication Fault
Note:
• The drive detects this error when you use the Bluetooth LCD keypad and operate the drive with a smartphone or tablet.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Set the stopping method for this fault in o2-27 [bCE Detection Selection].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
boL BrakingTransistor Overload Fault
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
bUS Option Communication Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the Run command or frequency reference is assigned to the option card.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this error, the drive will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in F6-01 [Communication Error Selection].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CE Modbus Communication Error
The keypad battery voltage is low. Replace the keypad battery.
The smartphone or tablet with DriveWizard Mobile
installed is too far from the keypad.
Radio waves from a different device are causing
interference with communications between the
smartphone or tablet and keypad.
The duty cycle of the braking transistor is high (the
regeneration power or repetition frequency is high).
You enabled the protective function for the braking
transistor when you have a regenerative converter.
The braking transistor in the drive is broken. Replace the drive.
The drive did not receive a signal from the controller.
The communications cable wiring is incorrect.
There is a short-circuit in the communications cable
or the communications cable is not connected.
Electrical interference caused a communication data
error.
The option is incorrectly installed to the drive. Correctly install the option to the drive.
The option is damaged. If the fault continues and the wiring is correct, replace the option.
The communications cable wiring is incorrect. Correct wiring errors.
There is a short circuit in the communications cable
or the communications cable is not connected.
Use the smartphone or tablet 10 m (32.8 ft) or nearer to the keypad.
Note:
bCE can occur when the smartphone or tablet is 10 m (32.8 ft)
or nearer to the keypad depending on the specifications of the
smartphone or tablet.
Make sure that no device around the keypad uses the same radio
bandwidth (2400 MHz to 2480 MHz), and prevent radio
interference.
• Install a regenerative converter.
• Increase the deceleration time.
Set L8-55 = 0 [Internal DB TransistorProtection Selection =
Disable].
Correct wiring errors.
• Repair short circuits and connect cables.
• Replace the defective communications cable.
• Examine the control circuit lines, main circuit lines, and ground
wiring, and decrease the effects of electrical interference.
• Make sure that a magnetic contactor is not the source of the
electrical interference, then use a Surge Protective Device if
necessary.
• Use only the recommended cables or other shielded line. Ground
the shield on the controller side or the drive input power side.
• Separate the communication wiring from drive power lines, and
install a noise filter to the input side of the power supply for
communication.
• Decrease the effects of electrical interference from the controller.
• Repair short circuits and connect cables.
• Replace the defective communications cable.
38 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 39

Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Electrical interference caused a communication data
error.
Note:
• The drive detects this error if it does not correctly receive control data for the CE detection time set to H5-09 [CE Detection Time].
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this error, the drive will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in H5-04 [Communication Error Stop Method].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CF Control Fault
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the torque reference is more than the torque limit for 3 seconds or longer while the drive ramps to stop.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CoF Current Offset Fault
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the current offset value is more than the permitted setting range while the drive automatically adjusts the current offset.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CP1 Comparator 1 Limit Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error when H2-01 to H2-03 = 66 [MFDO Function Selection = Comparator1].
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Set the stopping method for this fault in H2-33 [Comparator1 Protection Selection].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CP2 Comparator 2 Limit Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error when H2-01 to H2-03 = 67 [MFDO Function Selection = Comparator2].
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Set the stopping method for this fault in H2-35 [Comparator2 Protection Selection].
Motor parameters are set incorrectly Correctly set the motor parameters and do Auto-Tuning again.
The torque limit setting is too low. Adjust L7-01 to L7-04 [Torque Limit].
The load inertia is too large. • Adjust C1-02, C1-04, C1-06, and C1-08 [Deceleration Times].
The drive is trying to ramp to stop a machine that
cannot do ramp to stop or on a machine for which
deceleration is not necessary.
The motor and drive are connected incorrectly. Correct wiring errors.
Line-to-line Resistance Tuning is not done. Do Stationary Auto-Tuning for Line-to-Line Resistance.
The drive received a Run command while the motor
was coasting.
The drive starts operation while the induced voltage
stays in the motor (during coasting to a stop or after
fast deceleration).
A drive hardware problem occurred. Replace the drive.
The monitor value set in H2-20 [Comparator 1
Monitor Selection] was in the range of H2-21
[Comparator 1 Lower Limit] and H2-22
[Comparator 1 Upper Limit].
The monitor value set in H2-26 [Comparator 2
Monitor Selection] was outside the range of H2-27
[Comparator 2 Lower Limit] and H2-28
[Comparator 2 Upper Limit].
• Examine the control circuit lines, main circuit lines, and ground
wiring, and decrease the effects of electrical interference.
• Make sure that a magnetic contactor is not the source of the
electrical interference, then use a Surge Protective Device if
necessary.
• Use only the recommended cables or other shielded line. Ground
the shield on the controller side or the drive input power side.
• Separate the communication wiring from drive power lines, and
install a noise filter to the input side of the power supply for
communication.
• Decrease the effects of electrical interference from the controller.
• Set the frequency reference to the minimum output frequency,
and stop the Run command when the drive stops deceleration.
Correctly set b1-03 [Stopping Method Selection].
• Examine the sequence and input the Run command after the
motor fully stops.
• Set b3-01 = 1 [Speed Search at Start Selection = Enabled].
• Make a sequence that does not restart operation when induced
voltage stays in the motor.
• Set b3-01 = 1 [Speed Search at Start Selection = Enabled].
• Use Speed Search from Fmax or Fref [H1-xx = 61, 62] to do a
speed search through one of the external terminals.
Note:
When controlling the PM motor, External Speed Search
commands 1 and 2 operate the same.
Examine the monitor value and remove the cause of the fault.
Examine the monitor value and remove the cause of the fault.
2.4 Fault
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 39
Page 40

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CPF00, CPF01,
CPF02, CPF03,
CPF08, CPF11
- CPF14,
CPF16 -
CPF24, CPF38
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Fault trace is not available for these faults.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CPF06 EEPROM Memory Data Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error if there is an error in the data written to the EEPROM of the drive.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Fault trace is not available for this fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CPF25 Terminal Board not Connected
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dCE1 Communication Error1
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Fault trace is not available for these faults.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dCE2 Communication Error2
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Fault trace is not available for these faults.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dEv Speed Deviation
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the difference between the detected speed and the speed reference is more than the setting of F1-10 for longer than F1-11.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this error, the drive will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in F1-04 [Speed Deviation Detection Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dv7 Polarity Judge Timeout
Note:
• The drive detects this error if it cannot detect polarity in a pre-set length of time.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Control Circuit Error
A drive hardware problem occurred. • Re-energize the drive.
The drive power supply was de-energized while a
communication option card entered a parameter Write
command.
An EEPROM peripheral circuit error occurred. • Re-energize the drive.
The terminal board is not correctly connected to the
drive.
A drive hardware problem occurred temporarily due
to noise.
A drive hardware problem occurred temporarily due
to noise.
The load is too heavy. Decrease the load.
Acceleration and deceleration times are set too short. Increase the values set in C1-01 to C1-08 [Acceleration/
The dEv detection level settings are incorrect. Adjust F1-10 [Speed Deviation Detection Level] and F1-11 [Speed
The load is locked up. Examine the machine.
The holding brake is stopping the motor. Release the holding brake.
There is a disconnection in the motor coil winding. Measure the motor line-to-line resistance and replace the motor if a
The screws on the drive output terminals are loose. Tighten the terminal screws to the correct tightening torque.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive. For
information about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa
or your nearest sales representative.
Set A1-03 = 2220, 3330 [Initialize Parameters = 2-Wire
Initialization, 3-Wire Initialization] and initialize the drive.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive. For
information about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa
or your nearest sales representative.
1. De-energize the drive.
2. Correctly connect the terminal board to the drive.
3. Re-energize the drive.
• Remove the cause of the noise.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive.
• Remove the cause of the noise.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive.
Deceleration Time].
Deviation Detect DelayTime].
coil is disconnected.
40 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 41

Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dWF1
Note:
• The drive detects this error if there is an error in the DriveWorksEZ program that was saved to EEPROM.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dWF2 DriveWorksEZ Fault 2
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dWF3 DriveWorksEZ Fault 3
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dWFL DriveWorksEZ Fault
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
E5
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the stop method set in F6-25 [MECHATROLINK Watchdog Error Sel].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF0 Option Card External Fault
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the alarm function on the external device side is operating.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the stop method set in F6-03 [Comm External Fault (EF0) Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF1 External Fault (Terminal S1)
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF2 External Fault (Terminal S2)
EEPROM Memory DWEZ Data
Error
MECHATROLINK Watchdog Timer
Err
There is an error in the EEPROM peripheral circuit. • Re-energize the drive.
There is a problem with the EEPROM data. Set A1-03 = 2220, 3330 [Initialize Parameters = 2-Wire
There was a fault in the DriveWorksEZ program. Examine the DriveWorksEZ program and remove the cause of the
There was a fault in the DriveWorksEZ program. Examine the DriveWorksEZ program and remove the cause of the
There was a fault in the DriveWorksEZ program. Examine the DriveWorksEZ program and remove the cause of the
The drive detected a watchdog circuit exception while
it received data from the controller.
The communication option received an external fault
from the controller.
A programming error occurred on the controller side. Examine the operation of the controller program.
MFDI terminal S1 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S1.
External Fault [H1-01 = 20 to 2B] is set to MFDI
terminal S1, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S2 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S2.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive. For
information about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa
or your nearest sales representative.
Initialization, 3-Wire Initialization] to initialize the drive, then
upload the DriveWorksEZ project to the drive again.
fault. This is not a drive fault.
fault. This is not a drive fault.
fault. This is not a drive fault.
Examine the MECHATROLINK cable connection. If this error
occurs frequently, examine the wiring and decrease the effects of
electrical interference as specified by these manuals:
• MECHATROLINK-II Installation Guide (MECHATROLINK
Members Association, manual number MMATDEP011)
• MECHATROLINK-III Installation Manual (MECHATROLINK
Members Association, publication number MMATDEP018)
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input from the controller.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
2.4 Fault
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 41
Page 42

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
External Fault [H1-02 = 20 to 2B] is set to MFDI
terminal S2, but the terminal is not in use.
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF3 External Fault (Terminal S3)
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF4 External Fault (Terminal S4)
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF5 External Fault (Terminal S5)
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF6 External Fault (Terminal S6)
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF7 External Fault (Terminal S7)
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Err EEPROM Write Error
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
MFDI terminal S3 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S3.
External Fault [H1-03 = 20 to 2B] is set to MFDI
terminal S3, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S4 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S4.
External Fault [H1-04 = 20 to 2B] is set to MFDI
terminal S4, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S5 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S5.
External Fault [H1-05 = 20 to 2B] is set to MFDI
terminal S5, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S6 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S6.
External Fault [H1-06 = 20 to 2B] is set to MFDI
terminal S6, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S7 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S7.
External Fault [H1-07 = 20 to 2B] is set to MFDI
terminal S7, but the terminal is not in use.
There was a problem with the EEPROM hardware. • Re-energize the drive.
Electrical interference corrupted the data while it was
writing to the EEPROM of the drive.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive. Contact
Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative to replace the
board.
• Push ENTER Key.
• Set the parameters again.
42 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 43

Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
FbH Excessive PID Feedback
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the PID feedback input is more than the level set in b5-36 for longer than b5-37.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the stop method set in b5-12 [Feedback Loss Detection Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
FbL PID Feedback Loss
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the PID feedback input is more than the level set in b5-13 for longer than b5-14.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the stop method set in b5-12 [Feedback Loss Detection Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
GF Ground Fault
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if a current short to ground was more than 50% of rated current on the output side of the drive.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• L5-08 [Fault Reset Enable Select Grp2] disables the Auto Restart function.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
LF Output Phase Loss
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if phase loss occurs on the output side of the drive.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Set L8-07 [Output Phase Loss Protection Sel] to enable and disable LF detection.
The FbH detection level is set incorrectly. Adjust b5-36 [PID High Feedback Detection Lvl] and b5-37 [PID
There is a problem with the PID feedback wiring. Correct errors with the PID control wiring.
The feedback sensor is not operating correctly. Examine the sensors on the control device side.
A fault occurred in the feedback input circuit of the
drive.
The FbL detection level is set incorrectly. Adjust b5-13 [PID Feedback Loss Detection Lvl] and b5-14 [PID
There is a problem with the PID feedback wiring. Correct errors with the PID control wiring.
The feedback sensor is not operating correctly. Examine the sensors on the control device side.
A fault occurred in the feedback input circuit of the
drive.
Overheating caused damage to the motor or the motor
insulation is not satisfactory.
The motor main circuit cable is contacting ground to
make a short circuit.
An increase in the stray capacitance of the cable and
the ground terminal caused an increase in the leakage
current.
There was a problem with the drive hardware. Replace the control board or the drive. For information about
The motor main circuit cable is disconnected. Connect motor main circuit cable wiring. Correct wiring errors in
There is a disconnection in the motor coil winding. If a coil is disconnected, measure the motor Line-to-Line Resistance
The screws on the drive output terminals are loose. Tighten the terminal screws to the correct tightening torque.
The rated output current of the motor is less than 5%
of the drive rated current.
You are trying to use a single-phase motor. The drive cannot operate a single-phase motor.
The output transistor in the drive is damaged. • Re-energize the drive.
High Feedback Detection Time].
Replace the control board or the drive. For information about
replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
Feedback Loss Detection Time].
Replace the control board or the drive. For information about
replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
Measure the motor insulation resistance, and replace the motor if
there is electrical conduction or unserviceable insulation.
• Examine the motor main circuit cable for damage, and repair
short circuits.
• Measure the resistance between the motor main circuit cable and
the ground terminal. If there is electrical conduction, replace the
cable.
• If the wiring length of the cable is more than 100 m, decrease the
carrier frequency.
• Decrease the stray capacitance.
replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
the main circuit drive input power.
and replace the motor.
Examine the drive capacity or the motor output to be applied.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive. For
information about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa
or your nearest sales representative.
2.4 Fault
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 43
Page 44

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
LF2 Output Current Imbalance
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if there is not balance between the three phases of the output current from the PM motor.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
LSo Low Speed Motor Step-Out
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if it detects step-out while running at low speed.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• LSo is a protective function that stops the motor and stops the reverse run if a motor without a motor code incorrectly detects the initial polarity. To quickly detect motor reversal,
decrease the values set in L8-93 to L8-95 to a range in which the drive does not malfunction.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
nSE Node Setup Error
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oC Overcurrent
Phase loss occurred in the wiring on the output side
of the drive.
The output terminal screws of the drive are loose. Tighten the terminal screws to the correct tightening torque.
There is not balance between the three phases of the
PM motor impedance.
The drive output circuit is broken. • Re-energize the drive.
The motor code set incorrectly. • Set E5-01 [PM Motor Code Selection] correctly as specified by
The load is too large. • Decrease the load.
An external force on the load side caused the motor to
move at start.
The drive incorrectly detected the motor magnetic
pole position.
The setting of n8-84 [Polarity Detection Current] is
too low.
Incorrect values set in L8-93 [Low Speed Pull-out
DetectionTime], L8-94 [Low Speed Pull-out Detect
Level], and L8-95 [Low Speed Pull-out Amount].
The drive incorrectly detected the motor magnetic
pole position.
The H1-xx = 47 [Node Setup (CANopen)] terminal
was activated during run.
The drive received a Run command while the Node
Setup function was active.
The load is too heavy. • Measure the current flowing into the motor.
Overheating caused damage to the motor or the motor
insulation is not satisfactory.
The motor main circuit cable is contacting ground to
make a short circuit.
A short circuit or ground fault on the drive output
side caused damage to the output transistor of the
drive.
Examine for wiring errors or disconnected wires on the output side
of the drive, and repair problems.
• Measure the Line-to-Line Resistance for each motor phase and
make sure that resistance is equal in the three phases, and that all
wires are connected correctly.
• Replace the motor.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive. For
information about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa
or your nearest sales representative.
the motor.
• For specialized motors, refer to the motor test report and set E5-
xx correctly.
• Replace the drive and motor with larger capacity models.
Find and repair problems on the load side that cause the motor to
rotate from the load side.
• Set b3-01 = 1 [Speed Search at Start Selection = Enabled].
• If the value for U6-57 [PolePolarityDeterVal] is lower than 819,
increase the value set in n8-84 [Polarity Detection Current].
Consult the motor manufacturer for information about maximum
setting values.
Increase the n8-84 setting from the default. Consult the motor
manufacturer for information about maximum setting values.
Increase the values set in L8-93 to L8-95.
If you are using an IPM motor, do High Frequency Injection AutoTuning.
Stop the drive when the Node Setup function is in use.
• Replace the drive with a larger capacity model if the current
value is more than the drive rated current.
• Decrease the load or replace with a larger drive to prevent
sudden changes in the current level.
Measure the motor insulation resistance, and replace the motor if
there is electrical conduction or unserviceable insulation.
• Examine the motor main circuit cable for damage, and repair
short circuits.
• Measure the resistance between the motor main circuit cable and
the ground terminal. If there is electrical conduction, replace the
cable.
• Make sure that there is not a short circuit in terminal B1 and
terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3. Make sure that there is not a
short circuit in terminals - and terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3.
• If there is a short circuit, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
44 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 45

Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
The acceleration time is too short. • Calculate the torque necessary during acceleration related to the
The drive is trying to operate a specialized motor or a
motor that is larger than the maximum applicable
motor output of the drive.
A magnetic contactor was switched at the output. Set the operation sequence to not turn ON or OFF the magnetic
The V/f pattern settings are incorrect. • Examine the ratios between the V/f pattern frequency and
The torque compensation gain is too large. Decrease the value set in C4-01 [Torque Compensation Gain] to
Electrical interference caused a problem. Examine the control circuit lines, main circuit lines, and ground
The gain during overexcitation operation is too large. • Find the time when the fault occurs.
The drive received a Run command while the motor
was coasting.
In PM Control Methods, the setting of the motor code
is incorrect.
If the drive detects the fault at start or in the low
speed range (10% or less) and n8-57 = 1 [HFI
Overlap Selection = Enabled] for PM Control
methods, the high frequency injection gain is too
high.
The control method is set incorrectly for the motor. Set A1-02 [Control Method Selection] correctly.
The motor main circuit cable is too long. • Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
Speed search does not complete at start when you set
A1-02 = 8 [EZ Vector Control] and use an induction
motor.
An overcurrent occurred during overexcitation
deceleration.
Note:
• This fault occurs if the drive sensors detect a drive output current more than the specified overcurrent detection level.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oC2 Overcurrent2
Note:
• This fault occurs if the drive sensors detect a drive output current more than the specified overcurrent detection level.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oFA00 Option Not Compatible with Port
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Fault trace is not available for these faults.
When A1-02 = 5, 6, 8 [Control Method Selection =
OLV/PM, AOLV/PM, or EZOLV], the output current
is more than the value set in L8-27 [Overcurrent
Detection Gain].
The option connected to connector CN5 is not
compatible.
load inertia and the specified acceleration time.
• Increase the values set in C1-01, C1-03, C1-05, or C1-07
[Acceleration Times] to get the necessary torque.
• Increase the values set in C2-01 to C2-04 [S-Curve
Characteristics] to get the necessary torque.
• Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
• Examine the motor nameplate, the motor, and the drive to make
sure that the drive rated current is larger than the motor rated
current.
• Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
contactor while the drive is outputting voltage.
voltage. Decrease the voltage if it is too high compared to the
frequency.
• Adjust E1-04 to E1-10 [V/f Pattern Parameters]. For motor 2,
adjust E3-04 to E3-10.
make sure that the motor does not stall.
wiring, and decrease the effects of electrical interference.
• If the fault occurs at the same time as an overexcitation
operation, decrease n3-13 [OverexcitationBraking (OEB) Gain]
and consider the motor flux saturation.
• Examine the sequence and input the Run command after the
motor fully stops.
• Set b3-01 = 1 [Speed Search at Start Selection = Enabled] or set
H1-xx = 61, 62 [Speed Search from Fmax or Fref] to input speed
search commands from the MFDI terminals.
• Enter the correct motor code to E5-01 [PM Motor Code
Selection] as specified by the PM motor.
• For specialized motors, refer to the motor test report and set E5-
xx [PM Motor Settings] correctly.
• Set E5-xx [PM Motor Parameters] correctly or do Rotational
Auto-Tuning.
• Decrease the value of n8-41 [HFI P Gain] in 0.5-unit
increments.
Note:
Set n8-41 > 0.0 for an ordinary IPM motor.
• Decrease C6-02 [Carrier Frequency]. Or set C6-02 = B.
When E9-01 = 0 [Motor Type Selection = Induction (IM)], set b3-
24 = 2 [Speed Search Method Selection = Current Detection Speed
Search].
• Decrease n3-13 [OverexcitationBraking (OEB) Gain].
• Decrease n3-21 [HSB Current Suppression Level].
Correct the value set in L8-27.
Connect a correct option.
2.4 Fault
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 45
Page 46

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oFA01 Option Fault/Connection Error
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oFA03 to
oFA06
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oFA10, oFA11
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oFA12 to
oFA17
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oFA30 to
oFA43
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oH Heatsink Overheat
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the heatsink temperature of the drive is more than the value set in L8-02.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L8-03 [Overheat Pre-Alarm Selection].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oH1 Heatsink Overheat
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the heatsink temperature of the drive is more than the oH1 detection level. o2-04 [Drive Model (KVA) Selection] determines the oH1 detection level.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• L5-08 [Fault Reset Enable Select Grp2] disables the Auto Restart function.
Option Card Error Occurred at
Option Port (CN5)
Option Card Error Occurred at
Option Port (CN5)
Option Card Connection Error (CN5)
Communication Option Card
Connection Error (CN5)
You changed the option card connected to connector
CN5 during operation.
A fault occurred in the option card. 1. De-energize the drive.
A fault occurred in the option card. 1. De-energize the drive.
A fault occurred in the option card. 1. De-energize the drive.
A fault occurred in the option card. 1. De-energize the drive.
The ambient temperature is high and the heatsink
temperature of the drive is more than the value set in
L8-02 [Overheat Alarm Level].
The load is too heavy. • Measure the output current.
The internal cooling fan of the drive stopped. 1. Use the procedures in this manual to replace the cooling fan.
The ambient temperature is high and the heatsink
temperature of the drive is more than the oH1
detection level.
The load is too heavy. • Measure the output current.
1. De-energize the drive.
2. Refer to the option card manual and correctly connect the
option card to the connector on the drive.
2. Make sure that the option card is correctly connected to the
connector.
3. If the problem continues, replace the option card.
2. Make sure that the option card is correctly connected to the
connector.
3. If the problem continues, replace the option card.
2. Make sure that the option card is correctly connected to the
connector.
3. If the problem continues, replace the option card.
2. Make sure that the option card is correctly connected to the
connector.
3. If the problem continues, replace the option card.
• Measure the ambient temperature.
• Increase the airflow in the control panel.
• Install a cooling device (cooling fan or air conditioner) to lower
the ambient temperature.
• Remove objects near the drive that are producing too much heat.
• Decrease the load.
• Decrease the value set in C6-02 [Carrier Frequency Selection].
2. Set o4-03 = 0 [Fan Operation Time Setting = 0 h].
• Measure the ambient temperature.
• Increase the airflow in the control panel.
• Install a cooling device (cooling fan or air conditioner) to lower
the ambient temperature.
• Remove objects near the drive that are producing too much heat.
• Decrease the load.
• Decrease the value set in C6-02 [Carrier Frequency Selection].
46 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 47

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oH3 Motor Overheat (PTC Input)
Note:
• When H3-02 or H3-10 = E [MFAI Function Select = Motor Temperature (PTC Input)], the drive detects this fault if the motor overheat signal input from analog input terminal A1
or A2 is more than the alarm detection level.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L1-03 [Motor Thermistor oH Alarm Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oH4 Motor Overheat Fault (PTC Input)
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the motor overheat signal in analog input terminals A1, or A2 is more than the Fault detection level. (If H3-02, H3-10= E [Terminal A1/A2 Function
Select = Motor Temperature (PTC Input)].)
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL1 Motor Overload
The thermistor wiring that detects motor temperature
is defective.
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: The machine is locked.
The motor has overheated. • Check the load level, acceleration/deceleration time, and motor
The motor has overheated. • Check the load level, acceleration/deceleration time, and motor
The load is too large. Decrease the load.
The acceleration/deceleration times or cycle times are
too short.
Overload occurred while running at low speed. • Decrease the load when running at low speed.
L1-01 [Motor Overload (oL1) Protection] is set
incorrectly.
The V/f pattern does not fit the motor qualities. • Examine the ratios between the V/f pattern frequency and
Correct wiring errors.
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault
start/stop frequency (cycle time).
• Decrease the load.
• Increase the values set in C1-01 to C1-08 [Acceleration/
Deceleration Times].
• Set E2-01 [Motor Rated Current (FLA)] correctly to the value
specified by the motor nameplate.
• Make sure that the motor cooling system is operating correctly,
and repair or replace it if it is damaged.
• Adjust E1-04 to E1-10 [V/f Pattern Parameters]. For motor 2,
adjust E3-04 to E3-10. Decrease the values set in E1-08 [Mid
Point A Voltage] and E1-10 [Minimum Output Voltage].
Note:
If the values set in E1-08 and E1-10 are too low, the overload
tolerance will decrease at low speeds.
start/stop frequency (cycle time).
• Decrease the load.
• Increase the values set in C1-01 to C1-08 [Acceleration/
Deceleration Times].
• Set E2-01 [Motor Rated Current (FLA)] correctly to the value
specified by the motor nameplate.
• Make sure that the motor cooling system is operating correctly,
and repair or replace it if it is damaged.
• Adjust E1-04 to E1-10 [V/f Pattern Parameters]. For motor 2,
adjust E3-04 to E3-10. Decrease the values set in E1-08 [Mid
Point A Voltage] and E1-10 [Minimum Output Voltage].
Note:
If the values set in E1-08 and E1-10 are too low, the overload
tolerance will decrease at low speeds.
Note:
Reset oL1 when U4-16 [Motor oL1 Level] < 100.
• Examine the acceleration/deceleration times and the motor start/
stop frequencies (cycle times).
• Increase the values set in C1-01 to C1-08 [Acceleration/
Deceleration Times].
• Increase the motor speed.
• If the motor is run frequently at low speeds, replace the motor
with a larger motor or use a drive-dedicated motor.
Note:
For general-purpose motors, overload can occur while running
at low speed when operating at below the rated current.
Set L1-01 in as specified by the motor qualities for a drive-dedicated
motor.
voltage. Decrease the voltage if it is too high compared to the
frequency.
• Adjust E1-04 to E1-10 [V/f Pattern Parameters]. For motor 2,
adjust E3-04 to E3-10. Decrease the values set in E1-08 [Mid
Point A Voltage] and E1-10 [Minimum Output Voltage].
Note:
If the values set in E1-08 and E1-10 are too low, the overload
tolerance will decrease at low speeds.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 47
Page 48

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
E1-06 [Base Frequency] is set incorrectly. Set E1-06 to the rated frequency shown on the motor nameplate.
One drive is operating more than one motor. Set L1-01 = 0 [Motor Overload (oL1) Protection = Disabled],
The electronic thermal protector qualities and the
motor overload properties do not match.
The electronic thermal protector is operating at an
incorrect level.
There is increased motor loss from overexcitation
operation.
The speed search-related parameters are set
incorrectly.
Phase loss in the input power supply is causing the
output current to change.
The motor main circuit cable is too long. • Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the electronic thermal protector of the drive started the motor overload protection.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• L5-07 [Fault Reset Enable Select Grp1] disables the Auto Restart function.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL2 Drive Overload
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the electronic thermal protector of the drive started the drive overload protection.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• L5-07 [Fault Reset Enable Select Grp1] disables the Auto Restart function.
The load is too large. Decrease the load.
The acceleration/deceleration times or cycle times are
too short.
The V/f pattern does not fit the motor qualities. • Examine the ratios between the V/f pattern frequency and
The drive capacity is too small. Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
Overload occurred while running at low speed. • Decrease the load when running at low speed.
The torque compensation gain is too large. Decrease the value set in C4-01 [Torque Compensation Gain] to
The speed search-related parameters are set
incorrectly.
Phase loss in the input power supply is causing the
output current to change.
Overload occurred during overexcitation deceleration. • Decrease the value set in n3-13 [OverexcitationBraking (OEB)
connect thermal overload relay to each motor to prevent damage to
the motor.
• Examine the motor qualities and set L1-01 [Motor Overload
(oL1) Protection] correctly.
• Connect a thermal overload relay to the motor.
Set E2-01 [Motor Rated Current (FLA)] correctly to the value
specified by the motor nameplate.
• Lower the value set in n3-13 [OverexcitationBraking (OEB)
Gain].
• Set L3-04 ≠ 4 [Stall Prevention during Decel ≠ Overexcitation/
High Flux].
• Set n3-23 = 0 [Overexcitation Braking Operation = Disabled].
• Examine the settings for all speed search related parameters.
• Adjust b3-03 [Speed Search Deceleration Time].
• Set b3-24 = 1 [Speed Search Method Selection = Speed
Estimation] after Auto-Tuning.
Make sure that there is no phase loss, and repair problems.
• Decrease C6-02 [Carrier Frequency]. Or set C6-02 = B.
• Examine the acceleration/deceleration times and the motor start/
stop frequencies (cycle times).
• Increase the values set in C1-01 to C1-08 [Acceleration/
Deceleration Times].
voltage. Decrease the voltage if it is too high compared to the
frequency.
• Adjust E1-04 to E1-10 [V/f Pattern Parameters]. Decrease the
values set in E1-08 [Mid Point A Voltage] and E1-10 [Minimum
Output Voltage]. For motor 2, adjust E3-04 to E3-10.
Note:
If the values set in E1-08 and E1-10 are too low, the overload
tolerance will decrease at low speeds.
• Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
• Decrease the value set in C6-02 [Carrier Frequency Selection].
make sure that the motor does not stall.
• Examine the settings for all speed search-related parameters.
• Adjust b3-03 [Speed Search Deceleration Time].
• Set b3-24 = 1 [Speed Search Method Selection = Speed
Estimation] after Auto-Tuning.
• Correct errors with the wiring for main circuit drive input power.
• Make sure that there is no phase loss, and repair problems.
Gain].
• Decrease the value set in n3-21 [HSB Current Suppression
Level].
48 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 49

Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL3 Overtorque Detection 1
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the drive output current is more than the level set in L6-02 for longer than L6-03.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L6-01 [Torque Detection Selection 1].
• L5-07 [Fault Reset Enable Select Grp1] disables the Auto Restart function.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL4 Overtorque Detection 2
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the drive output current is more than the level set in L6-05 for longer than L6-06.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L6-04 [Torque Detection Selection 2].
• L5-07 [Fault Reset Enable Select Grp1] disables the Auto Restart function.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL5 Mechanical Weakening Detection 1
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L6-08.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL7 High Slip Braking Overload
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the output frequency is constant for longer than n3-04.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPr Keypad Connection Fault
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if these conditions are correct:
–o2-06 = 1 [Keypad Disconnect Detection = Enabled].
–b1-02 = 0 [Run Command Selection 1 = Keypad], or the drive is operating in LOCAL Mode with the keypad.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oS Overspeed
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: The machine is locked.
The parameters are incorrect for the load. Adjust L6-02 [Torque Detection Level 1] and L6-03 [Torque
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: The machine is locked.
The parameters are incorrect for the load. Adjust L6-05 [Torque Detection Level 2] and L6-06 [Torque
The drive detected overtorque as specified by the
conditions for mechanical weakening detection set in
L6-08 [Mechanical Fatigue Detect Select].
The load inertia is too large.
An external force on the load side rotated the motor.
Something is preventing deceleration on the load
side.
The value set in n3-04 [HSB Overload Time] is too
small.
The keypad is not securely connected to the
connector on the drive.
The connection cable between the drive and the
keypad is disconnected.
There is overshoot. • Decrease C5-01 [ASR Proportional Gain 1] and increase C5-02
There is an incorrect number of PG pulses set in the
drive.
The oS detection level is set incorrectly. Adjust F1-08 [Overspeed Detection Level] and F1-09 [Overspeed
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault.
Detection Time 1] settings.
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault.
Detection Time 2] settings.
Do a deterioration diagnostic test on the machine side.
• Decrease deceleration times in C1-02, C1-04, C1-06, and C1-08
[Deceleration Times] for applications that do not use High Slip
Braking.
• Use a braking resistor to decrease the deceleration time.
• Increase the value set in n3-04.
• Connect a thermal overload relay to the motor, and set n3-04 =
1200 s (maximum value).
Examine the connection between the keypad and the drive.
• Remove the keypad and then reconnect it.
• Replace the cable if damaged.
[ASR Integral Time 1].
• Use H6-02 to H6-05 [Pulse Train Input Setting Parameters]to
adjust the pulse train gain.
Set H6-02 [Terminal RP Frequency Scaling] to the pulse train
frequency during 100% reference (maximum motor rotation speed).
Detection Delay Time].
2.4 Fault
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 49
Page 50

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
If the drive detects the fault at start or in the low
speed range (10% or less) and n8-57 = 1 [HFI
Overlap Selection = Enabled] for PM Control
methods, the high frequency injection gain is too
high.
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the motor speed is more than the value set in F1-08 for longer than F1-09.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this fault, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in F1-03 [Overspeed Detection Selection].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
ov Overvoltage
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the DC bus voltage is more than the ov detection level while the drive is running.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• The ov detection level is approximately 410 V with 200 V class drives. The detection level is approximately 820 V for 400 V class drives.
• L5-08 [Fault Reset Enable Select Grp2] disables the Auto Restart function.
The deceleration time is too short and too much
regenerative energy is flowing back into the drive.
The acceleration time is too short. • Make sure that sudden drive acceleration does not cause the
The braking load is too large. Connect a dynamic braking option to the drive.
There are surge voltages in the input power supply. Connect a DC link choke to the drive.
The drive output cable or motor is shorted to ground
(the current short to ground is charging the main
circuit capacitor of the drive through the power
supply).
The speed search-related parameters are set
incorrectly (this fault also occurs during recovery
from momentary power loss and after Auto Restarts).
The power supply voltage is too high. Decrease the power supply voltage to match the drive rated voltage.
The braking resistor or braking resistor unit wiring is
incorrect.
Electrical interference caused a drive malfunction. • Examine the control circuit lines, main circuit lines, and ground
The load inertia is set incorrectly. • Examine the load inertia settings with KEB, overvoltage
The Short Circuit Braking function used in OLV/PM
control method.
There is motor hunting. • Adjust n1-02 [Hunting Prevention Gain Setting].
Speed search does not complete at start when you set
A1-02 = 8 [EZOLV] and use an induction motor.
• Set E5-xx [PM Motor Parameters] correctly or do Rotational
Auto-Tuning.
• Decrease the value of n8-41 [HFI P Gain] in 0.5 unit increments.
Note:
Set n8-41 > 0.0 for IPM motors.
• Increase the values set in C1-02, C1-04, C1-06, or C1-08
[Deceleration Times].
• Connect a dynamic braking option to the drive.
• Perform Deceleration Rate Tuning.
fault.
• Increase the values set in C1-01, C1-03, C1-05, or C1-07
[Acceleration Times].
• Increase the value set in C2-02 [S-Curve Time @ End of Accel].
• Set L3-11 = 1 [Overvoltage Suppression Select = Enabled].
Note:
If you turn the phase advancing capacitors ON and OFF and use
thyristor converters in the same power supply system, there can
be surge voltages that irregularly increase the input voltage.
1. Examine the motor main circuit cable, terminals, and motor
terminal box, and then remove ground faults.
2. Re-energize the drive.
• Examine the settings for all speed search related parameters.
• Set b3-19 ≠ 0 [Speed Search Restart Attempts ≠ 0 times].
• Adjust b3-03 [Speed Search Deceleration Time].
• Do Stationary Auto-Tuning for Line-to-Line Resistance and then
set b3-24 = 1 [Speed Search Method Selection = Speed
Estimation].
Correct wiring errors in the connection to the braking resistor or
braking resistor unit.
wiring, and decrease the effects of electrical interference.
• Make sure that a magnetic contactor is not the source of the
electrical interference, then use a Surge Protective Device if
necessary.
suppression, or stall prevention during deceleration.
• Adjust L3-25 [Load Inertia Ratio] to match the qualities of the
machine.
Connect a braking resistor to the drive.
• Adjust n2-02 [Automatic Freq Regulator Time 1] and n2-03
[Automatic Freq Regulator Time 2].
• Adjust n8-45 [Speed Feedback Detection Gain] and n8-47 [Pull-
in Current Comp Filter Time].
When E9-01 = 0 [Motor Type Selection = Induction (IM)], set b324 = 2 [Speed Search Method Selection = Current Detection Speed
Search].
50 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 51

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
PE1, PE2 PLC Faults
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
PF Input Phase Loss
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the DC bus voltage changes irregularly without regeneration.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Use L8-05 to enable and disable PF detection.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
PGo Encoder (PG) Feedback Loss
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in F1-02 [PG Open Circuit Detection Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
rF Braking Resistor Fault
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
rH Braking Resistor Overheat
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the braking resistor overheat protective function is active.
• The magnitude of the braking load causes the braking resistor overheat alarm, NOT the surface temperature. If the duty cycle is higher than the braking resistor rating, the drive
will show the alarm.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Parameter L8-01 enables and disables rH detection.
The communication option detected a fault. Refer to the manual for the communication option card.
There is a phase loss in the drive input power. Correct errors with the wiring for main circuit drive input power.
There is loose wiring in the drive input power
terminals.
The drive input power voltage is changing too much. • Examine the input power for problems.
There is unsatisfactory balance between voltage
phases.
The main circuit capacitors have become
unserviceable.
The holding brake is stopping the motor. Release the holding brake.
The resistance of the dynamic braking option
connected to the drive is too low.
A regenerative converter or regenerative unit is
connected to the drive.
The deceleration time is too short and excessive
regenerative energy is flowing back into the drive.
The duty cycle is too high. Examine the duty cycle.
The braking load is too heavy. • Calculate the braking load and braking power again, and
The braking resistor is not sufficient. Use the braking resistor specifications to select a sufficient braking
Tighten the terminal screws to the correct tightening torque.
• Make the drive input power stable.
• If the input power supply is good, examine the magnetic
contactor on the main circuit side for problems.
• Examine the input power for problems.
• Make the drive input power stable.
• Set L8-05 = 0 [Input Phase Loss Protection Sel = Disabled].
• Examine the capacitor maintenance time in monitor U4-05
[CapacitorMaintenance]. If U4-05 is more than 90%, replace the
control board or the drive. For information about replacing the
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
• If drive input power is correct and the fault stays, replace the
control board or the drive. For information about replacing the
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
Use a dynamic braking option that fits the model and duty rating of
the drive.
Set L8-55 = 0 [Internal DB TransistorProtection = Disable].
• Check the load level, deceleration time, and speed.
• Decrease the load.
• Increase the values set in C1-02, C1-04, C1-06, or C1-08
[Deceleration Times].
• Use a dynamic braking option that lets you use more power.
Note:
When L8-01 = 1 [3% ERF DB Resistor Protection = Enabled],
the maximum braking duty cycle is 3%.
decrease the braking load.
• Use a braking resistor that improves braking power.
resistor.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 51
Page 52

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
rr Dynamic Braking Transistor Fault
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
SC Short Circuit/IGBT Failure
Note:
• The drive detects this error if there is a short circuit or ground fault on the drive output side, or an IGBT failure.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
SCF Safety Circuit Fault
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
SEr Speed Search Retries Exceeded
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the number of speed search restarts is more than the value set in b3-19 [Speed Search Restart Attempts].
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
STPo Motor Step-Out Detected
Note:
Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
The drive control circuit is damaged.
There is a malfunction in the internal braking
transistor of the drive.
Overheating caused damage to the motor or the motor
insulation is not satisfactory.
The motor main circuit cable is contacting ground to
make a short circuit.
A short circuit or ground fault on the drive output
side caused damage to the output transistor of the
drive.
When A1-02 = 5, 6 [Control Method Selection =
OLV/PM or AOLV/PM], the output current is more
than the value set in L8-27 [Overcurrent Detection
Gain].
The safety circuit is broken. Replace the control board or the drive. For information about
The speed search-related parameters are set
incorrectly.
The motor is coasting in the opposite direction of the
Run command.
The motor code is set incorrectly for PM Control
Methods.
The load is too large. • Increase the value set in n8-55 [Motor to Load Inertia Ratio].
The load inertia is too large. Increase the value set in n8-55.
The acceleration/deceleration times are too short. • Increase the values set in C1-01 to C1-08 [Acceleration/
Speed response is too slow. Increase the value set in n8-55.
• Re-energize the drive.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive. For
information about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa
or your nearest sales representative.
Measure the motor insulation resistance, and replace the motor if
there is electrical conduction or unserviceable insulation.
• Examine the motor main circuit cable for damage, and repair
short circuits.
• Measure the resistance between the motor main circuit cable and
the ground terminal. If there is electrical conduction, replace the
cable.
• Make sure that there is not a short circuit in terminal B1 and
terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3. Make sure that there is not a
short circuit in terminals - and terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3.
• If there is a short circuit, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
Set L8-27 correctly.
replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
• Decrease the value set in b3-10 [Speed Estimation Detection
Gain].
• Increase the value set in b3-17 [Speed Est Retry Current Level].
• Increase the value set in b3-18 [Speed Est Retry Detection Time].
• Do Auto-Tuning again.
Set b3-14 = 1 [Bi-directional Speed Search = Enabled].
• Set E5-01 [PM Motor Code Selection] correctly as specified by
the motor.
• For specialized motors, refer to the motor test report and set E5-
xx correctly.
• Increase the value set in n8-51 [Pull-in Current @ Acceleration].
If the drive detects STPo during deceleration when increasing the
value set in n8-51, set the value of n8-79 [Pull-in Current @
Deceleration] lower than n8-51.
• Decrease the load.
• Replace the drive and motor with larger capacity models.
Deceleration Times].
• Increase the value set in C2-01 [S-Curve Time @ Start of Accel].
52 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 53

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
TiM Keypad Time Not Set
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Parameter o4-24 [bAT Detection Selection] enables and disables TiM detection.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
UL3 Undertorque Detection 1
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the drive output current is less than the level set in L6-02 for longer than L6-03.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L6-01 [Torque Detection Selection 1].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
UL4 Undertorque Detection 2
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the drive output current is less than the level set in L6-05 for longer than L6-06.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L6-04 [Torque Detection Selection 2].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
UL5 Mechanical Weakening Detection 2
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L6-08.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Uv1 DC Bus Undervoltage
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the DC bus voltage decreases below the level set in L2-05 [Undervoltage Detection Lvl (Uv1)] while the drive is running.
• The Uv1 detection level is approximately 190 V for a 200 V class drives. The detection level is approximately 380 V for 400 V class drives. The detection level is approximately
350 V when E1-01 [Input AC Supply Voltage] < 400.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Fault trace is not available for this fault.
• L5-08 [Fault Reset Enable Select Grp2] disables the Auto Restart function.
There is a battery in the keypad, but the date and time
are not set.
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: There is a broken pulley belt.
The parameters are incorrect for the load. Adjust L6-02 [Torque Detection Level 1] and L6-03 [Torque
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: There is a broken pulley belt.
The parameters are incorrect for the load. Adjust L6-05 [Torque Detection Level 2] and L6-06 [Torque
The drive detected undertorque as specified by the
conditions for mechanical weakening detection set in
L6-08 [Mechanical Fatigue Detect Select].
There is a phase loss in the drive input power. Correct errors with the wiring for main circuit drive input power.
There is loose wiring in the drive input power
terminals.
The drive input power voltage is changing too much. • Examine the input power for problems.
There was a loss of power. Use a better power supply.
The main circuit capacitors have become
unserviceable.
The relay or contactor on the soft-charge bypass relay
is damaged.
Use the keypad to set the date and time.
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault.
Detection Time 1] settings.
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault.
Detection Time 2] settings.
Examine the machine for deterioration.
Tighten the terminal screws to the correct tightening torque.
• Make the drive input power stable.
• If the input power supply is good, examine the magnetic
contactor on the main circuit side for problems.
Examine the capacitor maintenance time in monitor U4-05
[CapacitorMaintenance]. If U4-05 is more than 90%, replace the
control board or the drive. For information about replacing the
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
U4-06 [PreChargeRelayMainte] shows the performance life of the
soft-charge bypass relay. If U4-06 is more than 90%, replace the
board or the drive. For information about replacing the board,
contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 53
Page 54

2.4 Fault
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Uv2 Control Power Undervoltage
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the control power supply voltage decreases.
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Fault trace is not available for this fault.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Uv3 Soft Charge Answerback Fault
Note:
• Do a Fault Reset to clear the fault.
• Fault trace is not available for these faults.
The value set in L2-02 [Power Loss Ride Through
Time] increased and the momentary power loss
recovery unit is not connected to the drive.
There was a problem with the drive hardware. • Re-energize the drive.
The relay or contactor on the soft-charge bypass relay
is damaged.
Connect the momentary power loss recovery unit to the drive.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive. For
information about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa
or your nearest sales representative.
• Re-energize the drive.
• If the fault stays, replace the control board or the drive.
• Check monitor U4-06 [PreChargeRelayMainte] shows the
performance life of the soft-charge bypass relay. If U4-06 is
more than 90%, replace the board or the drive. For information
about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa or your
nearest sales representative.
54 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 55

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
This section gives information about the causes and possible solutions when a minor fault or alarm occurs. Use the
information in this table to remove the cause of the minor fault or alarm.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
AEr Station Address Setting Error
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
bAT Keypad Battery Low Voltage
Note:
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• Parameter o4-24 [bAT Detection Selection] enables and disables bAT detection.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
bb Baseblock
Note:
The drive will not output a minor fault signal for this alarm.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
bCE Bluetooth Communication Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error when you operate the drive with a smartphone or tablet with a Bluetooth LCD Keypad.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
• Parameter o2-27 [bCE Detection selection] enables and disables bCE detection.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
boL Braking Transistor Overload
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
bUS Option Communication Error
The node address for the communication option is not
in the permitted setting range.
The keypad battery voltage is low. Replace the keypad battery.
An external baseblock command was entered through
MFDI terminal S1 to S7, and the drive output stopped
as shown by an external baseblock command.
The smartphone or tablet with DriveWizard Mobile
installed is too far from the keypad.
Radio waves from a different device are causing
interference with the communication between the
smartphone or tablet and keypad.
The duty cycle of the braking transistor is high (the
regeneration power or repetition frequency is high).
You enabled the protective function for the braking
transistor when you have a regenerative converter.
The braking transistor in the drive is broken. Replace the drive.
The communications cable wiring is incorrect. Correct wiring errors.
There is a short-circuit in the communications cable
or the communications cable is not connected.
Electrical interference caused a communication data
error.
The option card is incorrectly installed to the drive. Correctly install the option card to the drive.
• For CC-Link communication, set F6-10 [CC-Link Node Address]
correctly.
• For MECHATROLINK communication, set F6-20
[MECHATROLINK Station Address] correctly.
• For CANopen communication, set F6-35 [CANopen Node ID
Selection] correctly.
Examine the external sequence and timing of the baseblock
command input.
Use the smartphone or tablet 10 m (32.8 ft) or nearer to the keypad.
Note:
bCE can occur when the smartphone or tablet is 10 m or nearer
to the keypad depending on the specifications of the smartphone
or tablet.
Make sure that no device around the keypad uses the same radio
bandwidth (2400 MHz to 2480 MHz), and prevent radio
interference.
• Install a regenerative converter.
• Increase the deceleration time.
Set L8-55 = 0 [Internal DB TransistorProtection Selection =
Disable].
• Repair short circuits and connect cables.
• Replace the defective communications cable.
• Examine the control circuit lines, main circuit lines, and ground
wiring, and decrease the effects of electrical interference.
• Make sure that a magnetic contactor is not the source of the
electrical interference, then use a Surge Protective Device if
necessary.
• Use only the recommended cables or other shielded line. Ground
the shield on the controller side or the drive input power side.
• Separate the communication wiring from drive power lines, and
install a noise filter to the input side of the power supply for
communication.
• Decrease the effects of electrical interference from the controller.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 55
Page 56

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
The option card is damaged. If the alarm continues and the wiring is correct, replace the option
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the Run command or frequency reference is assigned to the option card.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in F6-01 [Communication Error Selection].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CALL Serial Comm Transmission Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error if it does not correctly receive control data from the controller when energizing the drive.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CE Modbus Communication Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error if it does not correctly receive control data for the CE detection time set to H5-09.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in H5-04 [Communication Error Stop Method].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CP1 Comparator 1 Limit Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error when the terminal is assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 66 [MFDO Function Select = Comparator1].
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• Parameter H2-33 [Comparator1 Protection Selection] enables and disables CP1 detection.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CP2 Comparator 2 Limit Error
Note:
• The drive detects this error when the terminal is assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 67 [MFDO Function Select = Comparator2].
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• Parameter H2-35 [Comparator2 Protection Selection] enables and disables CP2 detection.
The communications cable wiring is incorrect. Correct wiring errors.
There is a short-circuit in the communications cable
or the communications cable is not connected.
A programming error occurred on the controller side. Examine communications at start-up and correct programming
The communications circuitry is damaged. • Do a self-diagnostics check.
The termination resistor setting for MEMOBUS/
Modbus communications is incorrect.
The communications cable wiring is incorrect. Correct wiring errors.
There is a short-circuit in the communications cable
or the communications cable is not connected.
Electrical interference caused a communication data
error.
The communication protocol is not compatible. • Examine the values set in H5-xx.
The value set in H5-09 [CE Detection Time] is too
small for the communications cycle.
The controller software or hardware is causing a
communication problem.
The monitor value set in H2-20 [Comparator 1
Monitor Selection] was in the range of H2-21
[Comparator 1 Lower Limit] and H2-22
[Comparator 1 Upper Limit].
The monitor value set in H2-26 [Comparator 2
Monitor Selection] was outside the range of H2-27
[Comparator 2 Lower Limit] and H2-28
[Comparator 2 Upper Limit].
card.
• Repair the short-circuited or disconnected portion of the cable.
• Replace the defective communications cable.
errors.
• If the problem continues, replace the control board or the drive.
For information about replacing the control board, contact
Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
On the last drive in a MEMOBUS/Modbus network, set DIP switch
S2 to the ON position to enable the termination resistor.
• Repair short circuits and connect cables.
• Replace the defective communications cable.
• Examine the control circuit lines, main circuit lines, and ground
wiring, and decrease the effects of electrical interference.
• Make sure that a magnetic contactor is not the source of the
electrical interference, then use a Surge Protective Device if
necessary.
• Use only the recommended cables or other shielded line. Ground
the shield on the controller side or the drive input power side.
• Separate the communication wiring from drive power lines, and
install a noise filter to the input side of the power supply for
communication.
• Decrease the effects of electrical interference from the controller.
• Examine the settings on the controller side and correct the
difference in communication conditions.
• Change the controller software settings.
• Increase the value set in H5-09.
Examine the controller and remove the cause of the problem.
Examine the monitor value and remove the cause of the fault.
Examine the monitor value and remove the cause of the fault.
56 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 57

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CrST Cannot Reset
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CyC
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CyPo Cycle Power to Accept Changes
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dEv Speed Deviation
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the difference between the detected speed and the speed reference is more than the setting of F1-10 for longer than F1-11.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in F1-04 [Speed Deviation Detection Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dnE Drive Disabled
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dWA2 DriveWorksEZ Alarm 2
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dWA3 DriveWorksEZ Alarm 3
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dWAL DriveWorksEZ Alarm
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
E5
Note:
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in F6-25 [MECHATROLINK Watchdog Error Sel].
MECHATROLINK
CommCycleSettingErr
MECHATROLINK Watchdog Timer
Err
The drive received a fault reset command when a Run
command was active.
The communications cycle setting of the controller is
not in the permitted range of the MECHATROLINK
interface option.
Although F6-15 = 1 [Comm. Option Parameters
Reload = Reload Now], the drive does not update the
communication option parameters.
The load is too large. Decrease the load.
The acceleration/deceleration times are too short. Increase the values set in C1-01 to C1-08 [Acceleration/
The dEv detection level settings are incorrect. Adjust F1-10 [Speed Deviation Detection Level] and F1-11 [Speed
The load is locked up. Examine the machine.
The holding brake is stopping the motor. Release the holding brake.
A terminal set for H1-xx = 6A [Drive Enable] turned
OFF.
There was an error in the DriveWorksEZ program. Examine the DriveWorksEZ program and remove the cause of the
There was an error in the DriveWorksEZ program. Examine the DriveWorksEZ program and remove the cause of the
There was an error in the DriveWorksEZ program. Examine the DriveWorksEZ program and remove the cause of the
The drive detected a watchdog circuit exception while
it received data from the controller.
Turn off the Run command then de-energize and re-energize the
drive.
Set the communications cycle of the controller in the permitted
range of the MECHATROLINK interface option.
Re-energize the drive to update the communication option
parameters.
Deceleration Times].
Deviation Detect DelayTime].
Examine the operation sequence.
fault. This is not a drive fault.
fault. This is not a drive fault.
fault. This is not a drive fault.
Examine the MECHATROLINK cable connection. If this error
occurs frequently, examine the wiring and decrease the effects of
electrical interference as specified by these manuals:
• MECHATROLINK-II Installation Guide (MECHATROLINK
Members Association, manual number MMATDEP011)
• MECHATROLINK-III Installation Manual (MECHATROLINK
Members Association, publication number MMATDEP018)
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 57
Page 58

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF
Note:
• If the drive detects EF, the motor will ramp to stop.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will be ON.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF0 Option Card External Fault
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the alarm function on the external device side is operating.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in F6-03 [Comm External Fault (EF0) Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF1 External Fault (Terminal S1)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF2 External Fault (Terminal S2)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF3 External Fault (Terminal S3)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF4 External Fault (Terminal S4)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF5 External Fault (Terminal S5)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
FWD/REV Run Command Input
Error
A forward command and a reverse command were
input at the same time for longer than 0.5 s.
The communication option card received an external
fault from the controller.
A programming error occurred on the controller side. Examine the operation of the controller program.
MFDI terminal S1 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S1.
External Fault [H1-01 = 2C to 2F] is set to MFDI
terminal S1, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S2 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S2.
External Fault [H1-02 = 2C to 2F] is set to MFDI
terminal S2, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S3 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S3.
External Fault [H1-03 = 2C to 2F] is set to MFDI
terminal S3, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S4 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S4.
External Fault [H1-04 = 2C to 2F] is set to MFDI
terminal S4, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S5 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S5.
External Fault [H1-05 = 2C to 2F] is set to MFDI
terminal S5, but the terminal is not in use.
Examine the forward and reverse command sequence and correct
the problem.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
caus.
2. Clear the external fault input from the controller.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
58 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 59

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF6 External Fault (Terminal S6)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EF7 External Fault (Terminal S7)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
EP24v External Power 24V Supply
Note:
• Set o2-26 [Ext. Power 24V Supply Display] to enable or disable EP24v detection.
• The drive will not output an alarm signal for this alarm.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
FbH Excessive PID Feedback
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the PID feedback input is more than the level set in b5-36 for longer than b5-37.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in b5-12 [Feedback Loss Detection Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
FbL PID Feedback Loss
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the PID feedback input is lower than the level set in b5-13 for longer than b5-14.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in b5-12 [Feedback Loss Detection Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
HCA High Current Alarm
MFDI terminal S6 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S6.
External Fault [H1-06 = 2C to 2F] is set to MFDI
terminal S6, but the terminal is not in use.
MFDI terminal S7 caused an external fault through an
external device.
The wiring is incorrect. Correctly connect the signal line to MFDI terminal S7.
External Fault [H1-07 = 2C to 2F] is set to MFDI
terminal S7, but the terminal is not in use.
The voltage of the main circuit power supply
decreased, and the 24 V power supply is supplying
power to the drive.
The FbH detection level is set incorrectly. Adjust b5-36 [PID High Feedback Detection Lvl] and b5-37 [PID
There is a problem with the PID feedback wiring. Correct errors with the PID control wiring.
The feedback sensor is not operating correctly. Examine the sensors on the control device side.
A fault occurred in the feedback input circuit of the
drive.
The FbL detection level is set incorrectly. Adjust b5-13 [PID Feedback Loss Detection Lvl] and b5-14 [PID
There is a problem with the PID feedback wiring. Correct errors with the PID control wiring.
The feedback sensor is not operating correctly. Examine the sensors on the control device side.
A fault occurred in the feedback input circuit of the
drive.
The load is too heavy. • Decrease the load for applications with repetitive starts and
The acceleration time is too short. • Calculate the torque necessary during acceleration related to the
The drive is trying to operate a specialized motor or a
motor that is larger than the maximum applicable
motor output of the drive.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
1. Find the device that caused the external fault and remove the
cause.
2. Clear the external fault input in the MFDI.
Correctly set the MFDI.
• Examine the main circuit power supply.
• Turn ON the main circuit power supply to run the drive.
High Feedback Detection Time].
Replace the board or the drive. For information about replacing the
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
Feedback Loss Detection Time].
Replace the board or the drive. For information about replacing the
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
stops.
• Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
load inertia and the specified acceleration time.
• Increase the values set in C1-01, C1-03, C1-05, or C1-07
[Acceleration Times] until you get the necessary torque.
• Increase the values set in C2-01 to C2-04 [S-Curve
Characteristics] until you get the necessary torque.
• Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
• Examine the motor nameplate, the motor, and the drive to make
sure that the drive rated current is larger than the motor rated
current.
• Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 59
Page 60

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
The current level temporarily increased because of
speed search after a momentary power loss or while
trying to Auto Restart.
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the drive output current is more than the overcurrent alarm level (150% of the rated current).
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
L24v Loss of External Power 24 Supply
Note:
• Set o2-23 [External 24V Powerloss Detection] to enable or disable L24v detection.
• The drive will not output an alarm signal for this alarm.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
LoG Log Com Error
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 6A [MFDO Function Select = Data Logger Error] will be ON.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
LT-1 Cooling Fan Maintenance Time
Note:
When the estimated performance life is expired, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 2F [MFDO Function Select = Maintenance Notification] will be ON.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
LT-2 Capacitor Maintenance Time
Note:
When the estimated performance life is expired, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 2F [MFDO Function Select = Maintenance Notification] will be ON.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
LT-3 SoftChargeBypassRelay MainteTime
Note:
When the estimated performance life is expired, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 2F [MFDO Function Select = Maintenance Notification] will be ON.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
LT-4 IGBT Maintenance Time (50%)
Note:
When the estimated performance life is expired, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 2F [MFDO Function Select = Maintenance Notification] will be ON.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oH Heatsink Overheat
The voltage of the backup 24 V power supply has
decreased. The main circuit power supply is operating
correctly.
There is not a micro SD in the keypad. Put a micro SD card in the keypad.
• The drive is connected to USB.
• The number of log communication files is more
than 1000.
• The micro SD card does not have available
memory space.
• The line number data in a log communication file
was changed.
• A communication error between the keypad and
drive occurred during a log communication.
The cooling fan is at 90% of its expected performance
life.
The capacitors for the main circuit and control circuit
are at 90% of expected performance life.
The soft charge bypass relay is at 90% of its expected
performance life.
The IGBT is at 50% of its expected performance life. Check the load, carrier frequency, and output frequency.
The ambient temperature is high and the heatsink
temperature is more than the L8-02 [Overheat Alarm
Level].
There is not sufficient airflow around the drive. • Give the drive the correct installation space as shown in the
If speed search or Auto Restart cause an increase in current, the
drive can temporarily show this alarm. The time that the drive
shows the alarm is short. No more steps are necessary to clear the
alarm.
• Examine the external 24 V power supply for disconnected wires
and wiring errors and repair the problems.
• Examine the external 24 V power supply for problems.
Set o5-01 = 0 [Log Start/Stop Selection = OFF].
1. Use the procedures in this manual to replace the cooling fan.
2. Set o4-03 = 0 [Fan Operation Time Setting = 0 h] to reset the
cooling fan operation time.
Replace the board or the drive. For information about replacing the
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
Replace the board or the drive. For information about replacing the
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
• Measure the ambient temperature.
• Increase the airflow around the drive.
• Install a cooling device (cooling fan or air conditioner) to lower
the ambient temperature.
• Remove objects near the drive that are producing too much heat.
manual.
• Make sure that there is sufficient circulation around the control
panel.
• Examine the drive for dust or other unwanted materials that
could clog the cooling fan.
• Remove unwanted materials that prevent air circulation.
60 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 61

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
The internal cooling fan or fans have stopped. 1. Use the procedures in this manual to replace the cooling fan.
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the heatsink temperature of the drive is more than L8-02.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in L8-03 [Overheat Pre-Alarm Selection].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oH2 External Overheat (H1-XX=B)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oH3 Motor Overheat (PTC Input)
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the motor overheat signal input from analog input terminal A1 or A2 is more than the fault detection level.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in L1-03 [Motor Thermistor oH Alarm Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL3 Overtorque 1
Note:
• The drive detects this fault if the drive output current is more than the level set in L6-02 for longer than L6-03.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• Set the conditions that trigger the minor fault using L6-01 [Torque Detection Selection 1].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL4 Overtorque 2
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the drive output current is more than the level set in L6-05 for longer than L6-06.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• Set the conditions that trigger the minor fault using L6-04 [Torque Detection Selection 2].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oL5 Mechanical Weakening Detection 1
Note:
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L6-08.
An external device sent an oH2. 1. Find the external device that output the overheat alarm.
The thermistor wiring that detects motor temperature
is defective.
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: The machine is locked.
The motor has overheated. • Check the load level, acceleration/deceleration time, and motor
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: The machine is locked.
The parameters are incorrect for the load. Adjust L6-02 [Torque Detection Level 1] and L6-03 [Torque
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: The machine is locked.
The parameters are incorrect for the load. Adjust L6-05 [Torque Detection Level 2] and L6-06 [Torque
The drive detected overtorque as specified by the
conditions for mechanical weakening detection set in
L6-08 [Mechanical Fatigue Detect Select].
2. Set o4-03 = 0 [Fan Operation Time Setting = 0 h].
2. Remove the cause of the problem.
3. Clear the Overheat Alarm (oH2) [H1-xx = B] set to MFDI
terminals S1 to S7.
Correct wiring errors.
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault
start/stop frequency (cycle time).
• Decrease the load.
• Increase the values set in C1-01 to C1-08 [Acceleration/
Deceleration Times].
• Set E2-01 [Motor Rated Current (FLA)] correctly to the value
specified by the motor nameplate.
• Make sure that the motor cooling system is operating correctly,
and repair or replace it if it is damaged.
• Adjust E1-04 to E1-10 [V/f Pattern Parameters]. For motor 2,
adjust E3-04 to E3-10. Decrease the values set in E1-08 [Mid
Point A Voltage] and E1-10 [Minimum Output Voltage].
Note:
If the values set in E1-08 and E1-10 are too low, the overload
tolerance will decrease at low speeds.
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault
Detection Time 1].
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault
Detection Time 2].
Do a deterioration diagnostic test on the machine side.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 61
Page 62

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oS Overspeed
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the motor speed is more than the value set in F1-08 for longer than F1-09.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in F1-03 [Overspeed Detection Selection].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
ov Overvoltage
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the DC bus voltage is more than the ov detection level when the Run command has not been input (while the drive is stopped).
• The ov detection level is approximately 410 V with 200 V class drives. The detection level is approximately 820 V for 400 V class drives.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
PASS Modbus Communication Test
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
PF Input Phase Loss
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the DC bus voltage changes irregularly without regeneration.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will be ON.
• Use L8-05 [Input Phase Loss Protection Sel] to enable and disable PF detection.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
PGo Encoder (PG) Feedback Loss
There is overshoot. • Decrease C5-01 [ASR Proportional Gain 1] and increase C5-02
There is an incorrect number of PG pulses set in the
drive.
The oS detection level is set incorrectly. Adjust F1-08 [Overspeed Detection Level] and F1-09 [Overspeed
There are surge voltages in the input power supply. Connect a DC link choke to the drive.
The drive output cable or motor is shorted to ground
(the current short to ground is charging the main
circuit capacitor of the drive through the power
supply).
The power supply voltage is too high. Decrease the power supply voltage to match the drive rated voltage.
Electrical interference caused a drive malfunction. • Examine the control circuit lines, main circuit lines, and ground
The MEMOBUS/Modbus communications test is
complete.
There is a phase loss in the drive input power. Correct all wiring errors with the main circuit power supply.
Loose wiring in the input power terminals. Tighten the screws to the correct tightening torque.
The drive input power voltage is changing too much. • Examine the supply voltage for problems.
Unsatisfactory balance between voltage phases. • Examine the supply voltage for problems.
The main circuit capacitors have become
unserviceable.
The encoder cable is disconnected or wired
incorrectly.
The encoder is not receiving power. Examine the encoder power supply.
[ASR Integral Time 1].
• Adjust the pulse train gain with H6-02 to H6-05 [Pulse Train
Input Setting Parameters].
Set H6-02 [Terminal RP Frequency Scaling] to the pulse train
frequency during 100% reference (maximum motor rotation speed).
Detection Delay Time].
Note:
If you turn the phase advancing capacitors ON and OFF and use
thyristor converters in the same power supply system, there can
be surge voltages that irregularly increase the input voltage.
1. Examine the motor main circuit cable, terminals, and motor
terminal box, and then remove ground faults.
2. Re-energize the drive.
wiring, and decrease the effects of electrical interference.
• Make sure that a magnetic contactor is not the source of the
electrical interference, then use a Surge Protective Device if
necessary.
• Set L5-01 ≠ 0 [Number of Auto-Restart Attempts ≠ 0 times].
The PASS display will turn off after communications test mode is
cleared.
• Make the drive input power stable.
• Make the drive input power stable.
• If the supply voltage is good, examine the magnetic contactor on
the main circuit side for problems.
• Examine the capacitor maintenance time in monitor U4-05
[CapacitorMaintenance].
• If U4-05 is more than 90%, replace the capacitor. Contact
Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative for more
information.
• Examine the supply voltage for problems.
• Re-energize the drive.
• If the alarm stays, replace the circuit board or the drive. For
information about replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa
or your nearest sales representative.
Examine for wiring errors or disconnected wires in the encoder
cable, and repair problems.
62 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 63

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
The holding brake is stopping the motor. Release the holding brake.
Note:
• The drive detects this error if it does not receive the speed detection pulse signal from the encoder in the detection time set in F1-14 [Encoder Open-Circuit Detect Time].
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal assigned to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Select = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the stopping method set in F1-02 [PG Open Circuit Detection Select].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
rUn Motor Switch during Run
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
SE Modbus Test Mode Error
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
SToF Safe Torque OFF Hardware
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
TiM Keypad Time Not Set
Note:
• Parameter o4-24 [bAT Detection Selection] enables and disables TiM detection.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
TrPC IGBT Maintenance Time (90%)
Note:
If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
UL3 Undertorque Detection 1
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the drive output current is less than the level set in L6-02 for longer than L6-03.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• Set the conditions that trigger the minor fault using L6-01 [Torque Detection Selection 1].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
UL4 Undertorque Detection 2
Note:
• The drive detects this error if the drive output current is less than the level set in L6-05 for longer than L6-06.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• Set the conditions that trigger the minor fault using L6-04 [Torque Detection Selection 2].
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
UL5 Mechanical Weakening Detection 2
Note:
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
• If the drive detects this error, it will operate the motor as specified by the Stopping Method set in L6-08.
The drive received a Motor 2 Selection [H1-xx = 16]
during run.
MEMOBUS/Modbus communications selfdiagnostics [H1-xx = 67] was done while the drive
was running.
One of the two terminals H1-HC and H2-HC received
the Safe Disable input signal.
The Safe Disable input signal is wired incorrectly.
There is internal damage to one Safe Disable channel. Replace the board or the drive. For information about replacing the
There is a battery in the keypad, but the date and time
are not set.
The IGBT is at 90% of its expected performance life. Replace the IGBT or the drive. For information about replacing the
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: There is a broken pulley belt.
The parameters are incorrect for the load. Adjust L6-02 [Torque Detection Level 1] and L6-03 [Torque
A fault occurred on the machine.
Example: There is a broken pulley belt.
The parameters are incorrect for the load. Adjust L6-05 [Torque Detection Level 2] and L6-06 [Torque
The drive detected undertorque as specified by the
conditions for mechanical weakening detection set in
L6-08 [Mechanical Fatigue Detect Select].
Make sure that the drive receives the Motor 2 Selection while the
drive is stopped.
Stop the drive and do MEMOBUS/Modbus communications selfdiagnostics.
• Make sure that the Safe Disable signal is input from an external
source to terminals H1-HC or H2-HC.
• When the Safe Disable function is not in use, use a jumper to
connect terminals H1-HC and H2-HC.
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
Set the date and time with the keypad.
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault
Detection Time 1].
Examine the machine and remove the cause of the fault
Detection Time 2].
Examine the machine for deterioration.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 63
Page 64

2.5 Minor Faults/Alarms
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Uv DC Bus Undervoltage
Note:
• The drive detects this error if one of these conditions is correct when the Run command has not been input (while the drive is stopped).
–The DC bus voltage < L2-05 [Undervoltage Detection Lvl (Uv1)].
–The Contactor that prevents inrush current in the drive was opened.
–There is low voltage in the control drive input power.
• If the drive detects this error, the terminal set to H2-01 to H2-03 = 10 [MFDO Function Selection = Alarm] will activate.
The drive input power voltage is changing too much. • Use a better power supply voltage to align with the drive rated
A phase loss occurred in the drive input power. Correct errors with the wiring for main circuit drive input power.
There is loose wiring in the drive input power
terminals.
There was a loss of power. Use a better power supply.
The main circuit capacitors have deteriorated. Examine the capacitor maintenance time in monitor U4-05
The drive input power transformer is too small and
voltage drops when the power is switched on.
Air inside the drive is too hot. Measure the ambient temperature of the drive.
The Charge LED is broken. Replace the board or the drive. For information about replacing the
voltage.
• Make the drive input power stable.
• If there is not a fault with the input power supply, examine the
magnetic contactor on the main circuit side for faults.
Examine for loose screws and tighten them as specified by the
tightening torque values in the manual.
[CapacitorMaintenance]. If U4-05 is more than 90%, replace the
control board or the drive. For information about replacing the
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
• Check for an alarm when a molded-case circuit breaker, Leakage
Breaker (ELCB, GFCI, or RCM/RCD) (with overcurrent
protective function), or magnetic contactor is ON.
• Check the capacity of the drive power supply transformer.
control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative.
64 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 65

2.6 Parameter Setting Errors
2.6 Parameter Setting Errors
Parameter setting errors occur when multiple parameter settings do not agree, or when parameter setting values are
not correct. Refer to the table in this section, examine the parameter setting that caused the error, and remove the
cause of the error. You must first correct the parameter setting errors before you can operate the drive. The drive will
not send notification signals for the faults and alarms when these parameter setting errors occur.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE01 Drive Capacity Setting Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE02 Parameter Range Setting Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE03 Multi-Function Input Setting Err
The value set in o2-04 [Drive Model (KVA) Selection]
does not agree with the drive model.
Parameters settings are not in the applicable setting
range.
Set E2-01 ≤ E2-03 [Motor Rated Current (FLA) ≤
Motor No-Load Current].
The settings for these parameters do not agree:
• H1-01 to H1-07 [Terminals S1 to S8 Function
Selection]
• H7-01 to H7-04 [Virtual Multi-Function Inputs 1
to 4]
The settings for MFDIs overlap.
Note:
This does not include H1-xx = 20 to 2F [MFDI
Function Select = External Fault] and
[Reserved].
You did not set these pairs of MFDI functions to
Digital Inputs (H1-xx and H7-01 to H7-04) at the
same time:
• Setting values 10 [Up Command] and 11 [Down
Command]
• Setting values 75 [Up 2 Command] and 76 [Down
2 Command]
• Setting values 42 [Run Command (2-Wire
Sequence 2)] and 43 [FWD/REV (2-Wire Sequence
2)]
You set a minimum of two of these MFDI
combinations to Digital Inputs (H1-xx and H7-01 to
H7-04) at the same time:
• Setting values 10 [Up Command] and 11 [Down
Command]
• Setting values 75 [Up 2 Command] and 76 [Down
2 Command]
• Setting value A [Accel/Decel Ramp Hold]
• Setting value 1E [Reference Sample Hold]
• Setting values 44 to 46 [Add Offset Frequency 1 to
3 (d7-01 to d7-03)]
Set o2-04 to the correct value.
1. Push to show U1-18 [oPE Fault Parameter], and find
parameters that are not in the applicable setting range.
2. Correct the parameter settings.
Note:
• If more than one error occurs at the same time, other oPExx
errors have priority over oPE02.
• If you copy the parameter settings from the drive with
software version PRG: 1021 or earlier, and then restore to the
drive with PRG: 1022 or later, the drive may detect oPE02. If
U1-18 [oPE Fault Parameter] shows n8-36 [HFI Frequency
Level for L Tuning], reset n8-36 to the default setting and do
High Frequency Injection Tuning.
The “PRG” column on the nameplate on the right side of the
drive identifies the software version. You can also use U1-25
[Software Number] to identify the software version.
Make sure that E2-01 > E2-03.
Note:
If it is necessary to set E2-01 < E2-03, first lower the value set
in E2-03, and then set E2-01.
Correct the parameter settings.
Set the parameters correctly to prevent MFDI function overlap.
Set the MFDI pairs.
Remove the function settings that are not in use.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 65
Page 66

2.6 Parameter Setting Errors
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
You set these commands in Digital Inputs (H1-xx and
H7-01 to H7-04) at the same time:
• Setting values 61 [Speed Search from Fmax] and
62 [Speed Search from Fref]
• Setting values 65, 66, 7A, 7B [KEB Ride-Thru 1 or
2 Activate] and 68 [High Slip Braking (HSB)
Activate]
• Setting values 16 [Motor 2 Selection] and 1A
[Accel/Decel Time Selection 2]
• Setting values 65, 66 [KEB Ride-Thru 1 Activate]
and 7A, 7B [KEB Ride-Thru 2 Activate]
• Setting values 40, 41 [Forward RUN (2-Wire),
Reverse RUN (2-Wire)] and 42, 43 [Run
Command (2-Wire Sequence 2), FWD/REV (2Wire Sequence 2)]
• Setting values 60 [DC Injection Braking
Command] and 6A [Drive Enable]
• Setting values 16 [Motor 2 Selection] and 75, 76
[Up 2 Command, Down 2 Command]
Settings for N.C. and N.O. input [H1-xx] for these
functions were selected at the same time:
• Setting value 15 [Fast Stop (N.O.)]
• Setting value 17 [Fast Stop (N.C.)]
You entered these settings while H1-xx = 2 [External
Reference 1/2 Selection]:
• b1-15 = 4 [Frequency Reference Selection 2 =
Pulse Train Input]
• H6-01 ≠ 0 [Terminal RP Pulse Train Function ≠
Frequency Reference]
You entered these settings while H1-xx = 2 [External
Reference 1/2 Selection]:
• b1-15 = 3 [Option PCB] or b1-16 = 3 [Run
Command Selection 2 = Option PCB]
• You did not connect an option to the drive.
You entered these settings while H1-xx = 2 [External
Reference 1/2 Selection]:
• b1-15 = 1 [Analog Input]
• H3-02 ≠ 0 [Terminal A1 Function Selection ≠
Frequency Reference] or H3-10 ≠ 0 [Terminal A2
Function Selection ≠ Frequency Reference]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• H1-xx ≠ 6A [Drive Enable]
• H2-xx = 38 [Drive Enabled]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• H6-01 ≠ 3 [PG Speed Feedback (V/F Control)]
• H1-xx = 7E [Reverse Rotation Identifier]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• H1-xx = 75/76 [Up 2 /Down 2 Command]
• H3-01, H3-09 = 1 [Terminal A1, A2 Signal Level
Select = 0 to +10V(Without Limit)]
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE05 Run Cmd/Freq Ref Source Sel Err
The setting to assign the Run command or frequency
reference to an option card or the pulse train input is
incorrect.
b1-01 = 3 [Frequency Reference Selection 1 =
Option PCB] is set, but there is no option card
connected to the drive.
b1-02 = 3 [Run Command Selection 1 = Option
PCB] is set, but there is no option card connected to
the drive.
These parameters are set at the same time:
• b1-01 = 4 [Pulse Train Input]
• H6-01 ≠ 0 [Terminal RP Pulse Train Function ≠
Frequency Reference]
Remove the function settings that are not in use.
Remove one of the function settings.
Set H6-01 = 0.
Connect an input option to the drive.
Set H3-02 = 0 or H3-10 = 0.
Correct the parameter settings.
Correct the parameter settings.
Remove one of the function settings.
Correct the parameter settings.
Connect an option card to the drive.
Set H6-01 = 0.
66 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 67

2.6 Parameter Setting Errors
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE07 Analog Input Selection Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE08 Parameter Selection Error
The settings for H3-02 and H3-10 [MFAI Function
Select] and H7-30 [Virtual Analog Input Selection]
overlap.
These parameters are set at the same time:
• H3-02, H3-10, H7-30 = B [PID Feedback]
• H6-01 = 1 [Terminal RP Pulse Train Function =
PID Feedback Value]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• H3-02, H3-10, H7-30 = C [PID Setpoint]
• H6-01 = 2 [PID Setpoint Value]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• H3-02, H3-10, H7-30 = C
• b5-18 = 1 [PID Setpoint Selection = Enabled]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• H6-01 = 2
• b5-18 = 1
A function was set that is not compatible with the
control method selected in A1-02 [Control Method
Selection].
When A1-02 = 2 [OLV], you used these parameter
settings:
• n2-02 > n2-03 [Automatic Freq Regulator Time 1
> Automatic Freq Regulator Time 2]
• C4-02 > C4-06 [Torque Compensation Delay
Time > Motor 2 Torque Comp Delay Time]
When A1-02 = 0 [V/f], you used these parameter
settings:
• H6-01 = 3 [Terminal RP Pulse Train Function =
Speed Feedback (V/F Control)]
• H1-xx = 16 [MFDI Function Select = Motor 2
Selection]
When A1-02 = 5 [OLV/PM], you set E5-02 to E5-07
[PM Motor Parameters] = 0.
When A1-02 = 5, 6 [OLV/PM, AOLV/PM], you used
these parameter settings:
• E5-09 = 0.0 [PM Back-EMF Vpeak (mV/(rad/s))
= 0.0 mV/(rad/s)]
• E5-24 = 0.0 [PM Back-EMF L-L Vrms (mV/rpm)
= 0.0 mV/min
When A1-02 = 5, 6, you set E5-09 ≠ 0 and E5-24 ≠ 0. Set E5-09 = 0 or E5-24 = 0.
When A1-02 = 6, you set these parameters:
• n8-57 = 0 [HFI Overlap Selection = Disabled]
• You set E1-09 [Minimum Output Frequency] < the
5% value of E1-06.
When A1-02 = 6, you set these parameters:
• n8-35 = 0 [Initial Pole Detection Method = Pull-
in]
• n8-57 = 1 [Enabled]
When A1-02 = 8 [EZOLV], you used these parameter
settings:
• E9-01 = 1, 2 [Motor Type Selection = Permanent
Magnet (PM), Synchronous Reluctance (SynRM)]
• b3-24 = 2 [Speed Search Method Selection =
Current Detection 2]
-1
]
Set H3-02, H3-10, and H7-30 correctly to prevent overlap.
Note:
It is possible to set these functions to multiple analog input
terminals at the same time:
• Setting value 0 [Frequency Reference]
• Setting values F and 1F [Not Used]
Remove the function settings that are not in use.
1. Push ENTER Key to show U1-18 [oPE Fault Parameter], and
find parameters that are not in the applicable setting range.
2. Correct the parameter settings.
Note:
If more than one error occurs at the same time, other oPExx
errors have priority over oPE02.
• Set n2-02 < n2-03.
• Set C4-02 < C4-06.
Correct the parameter settings.
Note:
You cannot use Speed Feedback (V/F Control) with the Motor
Switch function.
• Set E5-01 [PM Motor Code Selection] correctly as specified by
the motor.
• For specialized motors, refer to the motor test report and set E5-
xx correctly.
Set E5-09 or E5-24 to the correct value.
Correct the parameter settings.
Correct the parameter settings.
When E9-01 = 1 or 2, set b3-24 = 1 [Speed Estimation].
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 67
Page 68

2.6 Parameter Setting Errors
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE09 PID Control Selection Fault
Note:
The drive detects this error if the PID control function selection is incorrect.
(When b5-01 = 1 to 4 [PID Mode Setting = PID Control Enabled])
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE10 V/f Data Setting Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE11 Carrier Frequency Setting Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE13 Pulse Monitor Selection Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE16 Energy Saving Constants Error
These parameters are set at the same time:
• b5-15 ≠ 0.0 [PID Sleep Function Start Level ≠ 0.0
Hz]
• b1-03 = 2, 3 [Stopping Method Selection = DC
Injection Braking to Stop, Coast to Stop with
Timer]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• b5-01 = 1, 2 [Enabled (Standard), Enabled (D =
Feedforward)]
• d2-02 ≠ 0.0 [Frequency Reference Lower Limit ≠
0.0%]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• b5-01 = 1, 2 [Enabled (Standard), Enabled (D =
Feedforward)]
• b5-11 = 1 [PID Output Reverse Selection =
Negative Output Accepted]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• b5-01 = 3, 4 [Trim (Fref+PID Out, D = Fdbk),
Trim (Fref+PID Out, D = FeedFwd)]
• d2-02 ≠ 0.0 has been set.
The parameters that set the V/f pattern do not satisfy
these conditions:
• For motor 1: E1-09 ≤ E1-07 < E1-06 ≤ E1-11 ≤
E1-04 [Minimum Output Frequency ≤ Mid Point A
Frequency < Base Frequency ≤ Mid Point B
Frequency ≤ Maximum Output Frequency]
• For motor 2: E3-09 ≤ E3-07 < E3-06 ≤ E3-11 ≤
E3-04 [Minimum Output Frequency ≤ Mid Point A
Frequency < Base Frequency ≤ Mid Point B
Frequency ≤ Maximum Output Frequency]
These parameters are set at the same time:
• C6-05 > 6 [Carrier Freq Proportional Gain > 6]
• C6-04 > C6-03 [Carrier Frequency Lower Limit
> Carrier Frequency Upper Limit]
Note:
When C6-05 < 7, C6-04 becomes disabled. The
drive sets the carrier frequency to the value set to
C6-03.
C6-02 to C6-05 settings are not in the applicable
setting range.
H6-06 = 101, 102, 105, or 116 [Terminal MP
Monitor Selection = Frequency Reference, Output
Frequency, Motor Speed, Output Frequency after Soft
Starter] has not been set when H6-07 = 0 [Terminal
MP Frequency Scaling = 0 Hz].
The Energy Saving parameters are not set in the
applicable setting range.
• Set b5-15 ≠ 0.0.
• Set b1-03 = 0, 1 [Ramp to Stop, Coast to Stop].
Correct the parameter settings.
Correct the parameter settings.
Correct the parameter settings.
Set the parameters correctly to satisfy the conditions.
Set C6-02 to C6-05 correctly.
Set H6-06 correctly.
Make sure that E5-xx is set correctly as specified by the motor
nameplate data.
68 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 69

2.6 Parameter Setting Errors
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
oPE33 Digital Output Selection Error
These two parameters are set at the same time:
• H2-60 ≠ F [Term MA,MB,MC Secondary Function
≠ Not Used]
• H2-01 = 1xx [Term MA,MB,MC Function
Selection = Inverse output of xx]
These two parameters are set at the same time:
• H2-63 ≠ F [Terminal P1 Secondary Function ≠
Not Used]
• H2-02 = 1xx [Term P1 Function Selection =
Inverse output of xx]
These two parameters are set at the same time:
• H2-66 ≠ F [Terminal P2 Secondary Function ≠
Not Used]
• H2-03 = 1xx [Term P2 Function Selection =
Inverse output of xx]
These parameter pairs are set incorrectly:
• H2-21 [Comparator 1 Lower Limit] > H2-22
[Comparator 1 Upper Limit]
• H2-27 [Comparator 2 Lower Limit] > H2-28
[Comparator 2 Upper Limit]
Clear the H2-01 to H2-03 = 1xx [Inverse output of xx] settings.
Note:
If you use the function to output logical calculation results (H260, H2-63, H2-66 ≠ F), you cannot set H2-01 to H2-03 = 1xx.
• Set parameters H2-21 ≤ H2-22.
• Set parameters H2-27 ≤ H2-28.
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 69
Troubleshooting
2
Page 70

2.7 Auto-Tuning Errors
2.7 Auto-Tuning Errors
This table gives information about errors detected during Auto-Tuning. If the drive detects an Auto-Tuning error, the
keypad will show the error and the motor will coast to stop. The drive will not send notification signals for faults and
alarms when Auto-Tuning errors occur.
Two types of Auto-Tuning errors are: Endx and Erx. Endx identifies that Auto-Tuning has successfully completed
with calculation errors. Find and repair the cause of the error and do Auto-Tuning again, or set the motor parameters
manually. You can use the drive in the application if you cannot find the cause of the Endx error.
Erx identifies that Auto-Tuning was not successful. Find and repair the cause of the error and do Auto-Tuning again.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End1 Excessive Rated Voltage Setting
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End2 Iron Core Saturation Coefficient
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End3 Rated Current Setting Alarm
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End4 Adjusted Slip Calculation Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End5 Resistance Tuning Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End6 Leakage Inductance Alarm
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End7 No-Load Current Alarm
The torque reference was more than 20% during
Auto-Tuning or the no-load current that was
measured after Auto-Tuning is more than 80%.
The motor nameplate data entered during AutoTuning is incorrect.
Auto-Tuning results were not in the applicable
parameter setting range, and E2-07 or E2-08 [Motor
Saturation Coefficient 2] have temporary values.
The rated current value is incorrect. Do Auto-Tuning again and set the correct rated current shown on the
The Auto-Tuning results were not in the applicable
parameter setting range.
The motor rated slip that was measured after
Stationary Auto-Tuning was 0.2 Hz or lower.
The motor rated slip that was measured after
compensation with E2-08 [Motor Saturation
Coefficient 2] is not in the applicable range.
The secondary resistor measurement results were not
in the applicable range.
The Auto-Tuning results of the Line-to-Line
Resistance were not in the applicable range.
The Auto-Tuning results were not in the applicable
parameter setting range.
A1-02 [Control Method Selection] setting is not
applicable.
The Auto-Tuning results of the motor no-load current
value were not in the applicable range.
Auto-Tuning results were less than 5% of the motor
rated current.
• Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
• Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
• If you can uncouple the motor and load, remove the motor from
the machine and do Rotational Auto-Tuning again.
• If you cannot uncouple the motor and load, use the results from
Auto-Tuning.
• Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
• Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
• Examine and repair damaged motor wiring.
• If you can uncouple the motor and load, remove the motor from
the machine and do Rotational Auto-Tuning again.
motor nameplate.
• Make sure the input motor nameplate data is correct.
• Do Rotational Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor
nameplate data.
• If you cannot uncouple the motor and load, do Stationary Auto-
Tuning 2.
• Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
• Examine and repair damaged motor wiring.
Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct, and do
Auto-Tuning again.
• Examine the value set in A1-02.
• Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct, and do
Auto-Tuning again.
Examine and repair damaged motor wiring.
Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct, and do
Auto-Tuning again.
70 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 71

2.7 Auto-Tuning Errors
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End8 HFI Alarm
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
End9 Initial Pole Detection Alarm
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-01 Motor Data Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-02 Drive in an Alarm State
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-03 STOP Button was Pressed
• Inductance saliency ratio (E5-07/E5-06) is too
small.
• The drive cannot find the n8-36 [HFI Frequency
Level for L Tuning] value.
The drive cannot calculate the correct value for n8-84
[Polarity Detection Current] during High Frequency
Injection Tuning.
The motor nameplate data entered during AutoTuning is incorrect.
The combination of the motor rated power and motor
rated current do not match.
The combination of the motor rated current that was
entered during Auto-Tuning and E2-03 [Motor No-
Load Current] do not match.
The combination of the setting values of Motor Base
Frequency and Motor Base Speed do not match.
The motor nameplate data entered during AutoTuning is incorrect.
You did Auto-Tuning while the drive had a minor
fault or alarm.
There is a defective motor cable or cable connection. Examine and repair motor wiring.
The load is too large. • Decrease the load.
The drive detected a minor fault during Auto-Tuning. 1. Stop Auto-Tuning.
During Auto-Tuning, was pushed.
• Set the correct value on the motor nameplate E5-xx [PM motor
parameters] or do Stationary/Rotational Auto-Tuning, and then
do High Frequency Injection Tuning again.
• When it is necessary to set n8-35 = 1 [Initial Pole Detection
Method = High Frequency Injection] or n8-57 = 1 [HFI Overlap
Selection = Enabled], make sure that there is no unusual noise in
the low speed range (10% or less) and that the motor does not
rotate in reverse at start.
If there is unusual noise in the low speed range (10% or less),
increase the value set in n8-41 in increments of 0.5. Set n8-41 >
0.0 for IPM motors.
Note:
If the drive detects End8, it will automatically set n8-35 =0
[Pull-in] and n8-57 = 0 [Disabled]. Do not change the settings
unless necessary.
• Set the correct value on the motor nameplate E5-xx [PM motor
parameters] or do Stationary/Rotational Auto-Tuning, and then
do High Frequency Injection Tuning again.
• When n8-35 = 1 [Initial Pole Detection Method = High
Frequency Injection] or n8-57 = 1 [HFI Overlap Selection =
Enabled], make sure that the motor does not rotate in reverse at
start.
If there is unusual noise in the low speed range (10% or less),
increase the value set in n8-41 in increments of 0.5. Set n8-41 >
0.0 for IPM motors.
Note:
If the drive detects End9, it will automatically set n8-35 =0
[Pull-in] and n8-57 = 0 [Disabled]. Do not change the settings
unless necessary.
• Make sure that the motor nameplate data is correct.
• Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
• Examine the combination of drive capacity and motor output.
• Do Auto-Tuning again, and correctly set the motor rated power
and motor rated current.
• Examine the motor rated current and the no-load current.
• Set E2-03 correctly.
• Do Auto-Tuning again, and correctly set the motor rated current.
Do Auto-Tuning again, and correctly set the Motor Base Frequency
and Motor Base Speed.
• Make sure that the motor nameplate data entered in Auto-Tuning
is correct.
• Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
Clear the minor fault or alarm and do Auto-Tuning again.
• Examine the machine area to see if, for example, the motor shaft
is locked.
2. Examine the minor fault code and remove the cause of the
problem.
3. Do Auto-Tuning again.
Auto-Tuning did not complete correctly. Do Auto-Tuning again.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 71
Page 72

2.7 Auto-Tuning Errors
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-04 Line-to-Line Resistance Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-05 No-Load Current Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-08 Rated Slip Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-09 Acceleration Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-10 Motor Direction Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-11 Motor Speed Error
The Auto-Tuning results were not in the applicable
parameter setting range.
Auto-Tuning did not complete in a pre-set length of
time.
There is a defective motor cable or cable connection.
The motor nameplate data entered during AutoTuning is incorrect.
The Auto-Tuning results were not in the applicable
parameter setting range.
Auto-Tuning did not complete in a pre-set length of
time.
The motor nameplate data entered during AutoTuning is incorrect.
Rotational Auto-Tuning was done with a load that
was more than 30% of the rating connected to the
motor.
The motor nameplate data entered during AutoTuning is incorrect.
Auto-Tuning did not complete in a pre-set length of
time.
The Auto-Tuning results were not in the applicable
parameter setting range.
Rotational Auto-Tuning was done with a load that
was more than 30% of the rating connected to the
motor.
The motor did not accelerate for the specified
acceleration time.
The value of L7-01 or L7-02 [Forward/Reverse
Torque Limit] is small.
Rotational Auto-Tuning was done with a load that
was more than 30% of the rating connected to the
motor.
There is defective drive and motor wiring. Examine and repair motor wiring.
There is defective drive and encoder wiring. Examine and repair the wiring to the encoder.
The machine pulled the motor to rotate in the
opposite direction.
When the torque reference is 100% or higher, the sign
of the speed reference was opposite of the detected
speed.
The torque reference during acceleration is too high
(100%).
• Examine and repair motor wiring.
• Disconnect the machine from the motor and do Rotational Auto-
Tuning again.
• Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
• Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
• Examine and repair motor wiring.
• Disconnect the machine from the motor and do Rotational Auto-
Tuning again.
• Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
• Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
• Disconnect the machine from the motor and do Rotational Auto-
Tuning again.
• If you cannot uncouple the motor and load, make sure that the
load is less than 30% of the motor rating. If a mechanical brake
is installed in the motor, release the brake during Rotational
Auto-Tuning.
• Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
• Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
• Examine and repair the motor wiring.
• If the motor and machine are connected during Rotational Auto-
Tuning, decouple the motor from the machinery.
• Disconnect the machine from the motor and do Rotational Auto-
Tuning again.
• If you cannot uncouple the motor and load, make sure that the
load is less than 30% of the motor rating. If a mechanical brake
is installed in the motor, release the brake during Rotational
Auto-Tuning.
1. Increase the value set in C1-01 [Acceleration Time 1].
2. Disconnect the machine from the motor and do Rotational
Auto-Tuning again.
Increase the value set in L7-01 or L7-02.
• Disconnect the machine from the motor and do Rotational Auto-
Tuning again.
• If you cannot uncouple the motor and load, make sure that the
load is less than 30% of the motor rating. If a mechanical brake
is installed in the motor, release the brake during Rotational
Auto-Tuning.
Disconnect the machine from the motor and do Rotational AutoTuning again.
• Increase the value set in C1-01 [Acceleration Time 1].
• Disconnect the machine from the motor and do Rotational Auto-
Tuning again.
72 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 73

2.7 Auto-Tuning Errors
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-12 Current Detection Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-13 Leakage Inductance Alarm
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-14 Motor Speed Error 2
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-15 Torque Saturation Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-16 Inertia ID Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-17 Reverse Prohibited Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-18 Back EMF Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-19 PM Inductance Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-20 Stator Resistance Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
Er-25 HighFreq Inject Param Tuning Err
There is a phase loss in the drive input power. (U/T1,
V/T2, W/T3)
The current exceeded the current rating of the drive.
The output current is too low.
You tried Auto-Tuning without a motor connected to
the drive.
There was a current detection signal error. Replace the control board or the drive. For information about
The motor rated current value is incorrect. Correctly set the rated current indicated on the motor nameplate and
The drive could not complete tuning for leakage
inductance in fewer than 300 seconds.
The motor speed was more than two times the
amplitude of speed reference during Inertia Tuning.
During Inertia Tuning, the output torque was more
than the value set in L7-01 to L7-04 [Torque Limit].
The inertia found by the drive was too small or too
large during Inertia Tuning (10% or less, or 50000%
or more).
b1-04 = 1 [Reverse Operation Selection = Reverse
Disabled]
Note:
You cannot do Inertia Tuning if the drive cannot
rotate the motor in reverse.
The result of the induced voltage tuning was not in
the applicable range.
The Auto-Tuning results of the PM motor inductance
were not in the applicable range.
The Auto-Tuning results of the PM Motor Stator
Resistance were not in the applicable range.
The motor data is incorrect. Do Stationary Auto-Tuning again.
Examine and repair motor wiring.
• Check the motor wiring for any short circuits between the wires.
• Check and turn ON any magnetic contactors used between
motors.
• Replace the control board or the drive. For information about
replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest
sales representative.
Connect the motor and do Auto-Tuning.
replacing the control board, contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales
representative.
perform Auto-Tuning again.
Examine and repair motor wiring.
Decrease the value set in C5-01 [ASR Proportional Gain 1].
• Increase the value set in L7-01 to L7-04 [Torque Limit] as much
as possible.
• Decrease the values set for the frequency and amplitude of the
test signals used when doing inertia tuning. First, decrease the
test signal amplitude, and then do Inertia Tuning. If the error
continues, decrease the test signal frequency and do Inertia
Tuning again.
• Decrease the values set for the frequency and amplitude of the
test signals used when doing inertia tuning. First, decrease the
test signal amplitude, and then do Inertia Tuning. If the error
continues, decrease the test signal frequency and do Inertia
Tuning again
• Correctly set the motor inertia as specified by the motor, and do
Inertia Tuning again.
1. Enable reverse in the target machine.
2. Set b1-04 = 0 [Reverse Enabled].
3. Do Inertia Tuning again.
1. Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
2. Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
1. Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
2. Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
1. Make sure that the input motor nameplate data is correct.
2. Do Auto-Tuning again and correctly set the motor nameplate
data.
Note:
If the drive detects Er-25 after doing Stationary Auto-Tuning,
the motor may not be able to use high frequency injection
control. Contact Yaskawa or your nearest sales representative
for more information.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 73
Page 74

2.8 Backup Function Operating Mode Display and Errors
2.8 Backup Function Operating Mode Display and Errors
◆ Operating Mode Display
When you use the LCD keypad to do the backup function, the keypad shows the running operation on the LCD
display. These indicators do not show that an error has occurred.
Keypad Display Name Display Status
Drive and Keypad mismatch.
Should the parameters be
restored?
Restore Restore from keypad Restoring parameters Flashing The parameters stored in the keypad have
End Backup/restore/verify operation ended
Backup Backup from Drive Backing up parameters Flashing The parameters stored in the drive are being
Verify Keypad & Drive Verifying parameters Flashing The parameter settings stored in the keypad
◆ Backup Function Runtime Errors
Detection of inconsistency between the
drive and keypad
normally
Normally displayed The drive detected the connection of a
Normally displayed The parameter backup, restore, or verify
keypad from a different drive. Select [Yes]
to copy parameters backed up in the keypad
to the connected drive.
been restored to the drive.
operation ended normally.
backed up to the keypad.
and the parameter settings in the drive match
or are being compared.
When an error occurs, the keypad shows a code to identify the error.
The table in this section show the error codes. If there are errors, refer to these tables:
Note:
Push any key on the keypad to clear an error.
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CPEr Control Mode Mismatch
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CPyE Error Writing Data
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
CSEr Control Mode Mismatch
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
dFPS Drive Model Mismatch
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
iFEr Keypad Communication Error
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
ndAT Error Received Data
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
PWEr DWEZ Password Mismatch
Note:
U8-11 and U8-12 [DWEZ Versions 1 and 2] show the user ID of the DWEZ program.
The keypad setting and drive setting for A1-02
[Control Method Selection] do not agree.
Parameter restore did not end correctly. Restore the parameters.
The keypad is broken. Replace the keypad.
You tried to restore parameters to a different drive
model than the one that you backed up.
There was a communications error between the
keypad and the drive.
The parameter settings for model and specifications
(power supply voltage and capacity) are different
between the keypad and the drive.
The parameters are not stored in the keypad. 1. Connect a keypad that has the correct parameters.
The password set in the backup operation with qx-xx
[DriveWorksEZ Parameters] and rx-xx
[DriveWorksEZ Connections] is incorrect.
1. Set A1-02 on the drive to the same value that is on the keypad.
2. Restore the parameters.
1. Examine the drive model that you used to back up the
parameters.
2. Restore the parameters.
Examine the connector or cable connection.
1. Make sure that drive model and the value set in o2-04 [Drive
Model (KVA) Selection] agree.
2. Restore the parameters.
2. Restore the parameters.
Set the DWEZ PC software password supplied by Yaskawa for the
DWEZ program user ID downloaded to the drive.
74 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 75

2.8 Backup Function Operating Mode Display and Errors
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
rdEr Error Reading Data
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
vAEr Voltage Class, Capacity Mismatch
Code Name Causes Possible Solutions
vFyE Parameters do not Match
You tried to back up the data when o3-02 = 0 [Copy
Allowed Selection = Disabled].
The power supply specifications or drive capacity
parameter settings are different between the keypad
and the drive.
The parameters that are backed up in the keypad and
the parameters in the drive are not the same.
Set o3-02 = 1 [Enabled] and back up again.
1. Make sure that drive model and the value set in o2-04 [Drive
Model (KVA) Selection] agree.
2. Restore the parameters.
1. Restore or backup the parameter again.
2. Verify the parameters.
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 75
Troubleshooting
2
Page 76

2.9 Diagnosing and Resetting Faults
2.9 Diagnosing and Resetting Faults
When a fault occurs and the drive stops, do the procedures in this section to remove the cause of the fault, then reenergize the drive.
◆ Fault Occurs Without Power Loss
WARNING! Crush Hazard. Wear eye protection when you do work on the drive. If you do not use correct safety equipment, it can
cause serious injury or death.
WARNING! Electrical Shock Hazard. After the drive blows a fuse or trips a GFCI, do not immediately energize the drive or operate
peripheral devices. Wait for the time specified on the warning label at a minimum and make sure that all indicators are OFF. Then
check the wiring and peripheral device ratings to find the cause of the problem. If you do not know the cause of the problem, contact
Yaskawa before you energize the drive or peripheral devices. If you do not fix the problem before you operate the drive or peripheral
devices, it can cause serious injury or death.
1. Supply power to the control circuit from the external 24 V input.
2. Use monitor parameters U2-xx [Fault Trace] to show the fault code and data about the operating status of the
drive immediately before the fault occurred.
3. Use the information in the Troubleshooting tables to remove the fault.
Note:
1. To find the faults that were triggered, check the fault history in U2-02 [Previous Fault]. To find information about drive status (such as
frequency, current, and voltage) when the faults were triggered, check U2-03 to U2-20.
2. If the fault display stays after you re-energize the drive, remove the cause of the fault and reset.
◆ Fault Occurs Without Power Loss
1.
Examine the fault code shown on the keypad.
2. Use the information in the Troubleshooting tables to remove the fault.
3. Do a fault reset.
◆ Fault Reset Procedure
If a fault occurs, you must remove the cause of the fault and re-energize the drive. Table 2.3 lists the different
methods to reset the drive after a fault.
Table 2.3 Fault Reset Methods
Methods Description
Method 1
Method 2
While the keypad is showing the fault or alarm code, push on the keypad.
Switch ON the MFDI terminal set to H1-xx = 14 [MFDI Function Select = Fault Reset].
Note:
The default setting for H1-04 [Terminal S4 Function Selection] is 14 [Fault Reset].
1. De-energize the drive main circuit power supply.
2. Energize the drive again after the keypad display goes out.
Method 3
76 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 77

2.9 Diagnosing and Resetting Faults
Note:
If the drive receives a Run command from a communication option or control circuit terminal, the drive will not reset the fault. Turn the Run
command OFF to reset the fault. If you do a fault reset when the drive has a Run command, the keypad will show minor fault CrST [Remove
RUN Command to Reset].
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 77
Troubleshooting
2
Page 78

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
If the drive or motor operate incorrectly, but the keypad does not show a fault or error code, refer to the items this
section.
• Motor hunting and oscillation
• Unsatisfactory motor torque
• Unsatisfactory speed precision
• Unsatisfactory motor torque and speed response
• Motor noise
◆ Typical Problems
Symptom Reference
The Parameter Settings Will Not Change 78
The Motor Does Not Rotate after You Enter a Run Command 79
The Motor Rotates in the Opposite Direction from the Run Command 80
The Motor Rotates in Only One Direction 80
The Motor Is Too Hot 80
The Correct Auto-Tuning Mode Is Not Available 81
The Motor Stalls during Acceleration or Accel/Decel Time Is Too Long 81
The Drive Frequency Reference Is Different than the Controller Frequency Reference Command 82
PM Motor Speed Is Not Stable 82
There Is Too Much Motor Oscillation and the Rotation Is Irregular 82
Deceleration Takes Longer than Expected when You Enable Dynamic Braking 82
There Is Audible Noise from the Drive or Motor Cables when You Energize the Drive 83
The Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Trips During Run 83
Motor Rotation Causes Unexpected Audible Noise from Connected Machinery 83
Motor Rotation Causes Oscillation or Hunting 83
PID Output Fault 84
The Starting Torque Is Not Sufficient 84
The Motor Rotates after You Shut Off Drive Output 84
The Output Frequency Is Lower Than the Frequency Reference 84
The Motor Will Not Restart after Power Loss 85
◆ The Parameter Settings Will Not Change
Causes Possible Solutions
The drive is operating the motor (the drive is in Drive Mode). Stop the drive and change to Programming Mode.
Parameter A1-01 = 0 [Access Level Selection = Operation Only]. Set A1-01 = 2 [Access Level Selection = Advanced Level] or A1-01 = 3 [Expert Level].
Parameter H1-xx = 1B [MFDI Function Select = Programming Lockout]. Activate the terminals to which H1-xx = 1B is set, and then change the parameters.
78 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 79

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
Causes Possible Solutions
You entered an incorrect password in A1-04 [Password]. • Enter the correct password to A1-04 again.
The drive detected Uv [Undervoltage]. • View U1-07 [DC Bus Voltage] to see the power supply voltage.
• If you forgot the password, set the password again with A1-04 and A1-05 [Password Setting].
Note:
If you set the password, you cannot change these parameters until the password aligns:
• A1-01 [Access Level Selection]
• A1-02 [Control Method Selection]
• A1-03 [Initialize Parameters]
• A1-06 [Application Preset]
• A1-07 [DriveWorksEZ Function Selection]
• A2-01 to A2-32 [User Parameter 1 to User Parameter 32]
• Examine the main circuit wiring.
◆ The Motor Does Not Rotate after You Enter a Run Command
Causes Possible Solutions
The drive is not in Drive Mode. 1. Make sure that the READY LED on the keypad is ON.
The drive stopped and you pushed to transfer the Run command source
to the keypad.
Auto-Tuning completed. Push and hold the ESC Key to go back to the frequency reference screen (the initial screen).
The drive received a Fast Stop command. Turn off the fast stop input signal.
The settings for the source that supplies the Run command are incorrect. Set b1-02 [Run Command Selection 1] correctly.
The frequency reference source is not set correctly. Set b1-01 [Frequency Reference Selection 1] correctly.
There is defective wiring in the control circuit terminals. • Correctly wire the drive control circuit terminals.
The settings for voltage input and current input of the master frequency
reference are incorrect.
The selection for the sinking/sourcing mode and the internal/external power
supply is incorrect.
The frequency reference is too low. • View U1-01 [Freq Reference].
The MFAI setting is incorrect. • Make sure that the functions set to the MFAI are correct. The frequency reference is 0 when H3-
You pushed .
2. If the READY LED is OFF, push and hold the ESC Key to go back to the frequency reference
screen (the initial screen).
Do one of these two:
• Push .
• Re-energize the drive.
Note:
When must not change the Run command source, set o2-01 = 0 [LO/RE Key Function
Selection = Disabled].
Note:
When Auto-Tuning completes, the drive changes to Programming Mode. The drive will not
accept a Run command unless the drive is in Drive Mode.
• View U1-10 [Input Terminal Status] for input terminal status.
Examine these analog input terminal signal level settings:
• Terminal A1: H3-01 [Terminal A1 Signal Level Select]
• Terminal A2: DIP switch S1 and H3-09 [Terminal A2 Signal Level Select]
• For sinking mode, close the circuit between terminals SC-SP with a wire jumper.
• For sourcing mode, close the circuit between terminals SC-SN with a wire jumper.
• For external power supply, remove the wire jumper.
• Increase the frequency reference to a value higher than E1-09 [Minimum Output Frequency].
02, H3-10 = 1 [MFAI Function Select = Frequency Gain] and voltage (current) is not input.
• Use U1-13, U1-14 [Terminal A1, A2 Input Voltage] to make sure that the analog input values set
to terminals A1 and A2 are applicable.
Turn the Run command OFF then ON from an external input.
Note:
Troubleshooting
2
When you push during operation, the drive will ramp to stop. Set o2-02 = 0 [STOP Key
Function Selection = Disabled] to disable the function.
The 2-wire sequence and 3-wire sequence are not set correctly. • Set one of the parameters H1-03 to H1-07 [Terminals S3 to S7 Function Select] to 0 [3-Wire
Sequence] to enable the 3-wire sequence.
• If a 2-wire sequence is necessary, make sure that H1-03 to H1-07 ≠ 0.
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 79
Page 80

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
◆ The Motor Rotates in the Opposite Direction from the Run Command
Causes Possible Solutions
The phase wiring between the drive and motor is incorrect. • Examine the wiring between the drive and motor.
• Connect drive output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3 in the correct sequence to agree with
motor terminals U, V, and W.
• Switch two motor cables U, V, and W to reverse motor direction.
The forward direction for the motor is set incorrectly. • Connect drive output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3 in the correct sequence to agree with
The signal connections for forward run and reverse run on the drive control
circuit terminals and control panel side are incorrect.
The motor is running at almost 0 Hz and the Speed Search estimated the speed
to be in the opposite direction.
motor terminals U, V, and W.
• Switch two motor cables U, V, and W to reverse motor direction.
Figure 2.1 Forward Rotating Motor
Note:
• For Yaskawa motors, the forward direction is counterclockwise when looking from the motor
shaft side.
• Refer to the motor specifications, and make sure that the forward rotation direction is correct
for the application. The forward rotation direction of motors can be different for different motor
manufacturers and types.
Correctly wire the control circuit.
Set b3-14 = 0 [Bi-directional Speed Search = Disabled], then the drive will only do speed search in
the specified direction.
◆ The Motor Rotates in Only One Direction
Causes Possible Solutions
The drive will not let the motor rotate in reverse. Set b1-04 = 0 [Reverse Operation Selection = Reverse Enabled].
The drive did not receive a Reverse run signal and 3-Wire sequence is selected. Activate the terminals to which H1-xx = 0 [3-Wire Sequence] is set, and then enable reverse
operation.
◆ The Motor Is Too Hot
Causes Possible Solutions
The load is too heavy. • Decrease the load.
The motor is running continuously at a very low speed. • Change the run speed.
The drive is operating in a vector control mode, but Auto-Tuning has not been
done.
The voltage insulation between motor phases is not sufficient. • Use a motor with a voltage tolerance that is higher than the maximum voltage surge.
The air around the motor is too hot. • Measure the ambient temperature.
The motor fan stopped or is clogged. • Clean the motor fan.
• Increase the acceleration and deceleration times.
• Examine the values set in L1-01 [Motor Overload (oL1) Protection], L1-02 [Motor Overload
Protection Time], and E2-01 [Motor Rated Current (FLA)].
• Use a larger motor.
Note:
The motor also has a short-term overload rating. Examine this rating carefully before setting
drive parameters.
• Use a drive-dedicated motor.
• Do Auto-Tuning.
• Calculate motor parameter and set motor parameters.
• Set A1-02 = 0 [Control Method Selection = V/f Control].
• Use a drive-dedicated motor that is rated for use with AC drives for applications that use a motor
on drives rated higher than 400 V class.
• Install an AC reactor on the output side of the drive and set C6-02 = 1 [Carrier Frequency
Selection = 2.0 kHz].
Note:
When the motor is connected to the drive output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3, surges occur
between the drive switching and the motor coils. These surges can be three times the drive input
power supply voltage (600 V for a 200 V class drive, 1200 V for a 400 V class drive).
• Decrease the temperature in the area until it is in the specified temperature range.
• Make the drive environment better.
80 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 81

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
◆ The Correct Auto-Tuning Mode Is Not Available
Causes Possible Solutions
The desired Auto-Tuning mode is not available for the selected control mode. Change the motor control method with parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection].
◆ The Motor Stalls during Acceleration or Accel/Decel Time Is Too Long
Causes Possible Solutions
The drive and motor system are at the torque limit or current suppression will
not let the drive accelerate.
Torque limit is set incorrectly. Set the torque limit correctly.
The acceleration time setting is too short. Examine the values set in C1-01, C1-03, C1-05, or C1-07 [Acceleration Time] and set them to
The load is too large. • Increase the acceleration time.
The frequency reference is low. • Examine E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency] and increase the setting if it is set too low.
The frequency reference is set incorrectly. When H3-10 = 1 Terminal A2 Function Selection = Frequency Gain], see if the drive is set for
The motor characteristics and drive parameter settings are not compatible. • Set the correct V/f pattern to agree with the characteristics of the motor.
The drive is operating in vector control mode, but you did not complete AutoTuning.
The Stall Prevention level during acceleration setting is too low. Increase the value set in L3-02 [Stall Prevent Level during Accel].
The Stall Prevention level during run setting is too low. Increase the value set in L3-06 [Stall Prevent Level during Run].
The drive is at the limit of the V/f motor control method. • When the motor cable is longer than 50 m (164 ft), do Auto-Tuning for line-to-line resistance.
• Decrease the load.
• Use a larger motor.
Note:
Although the drive has a Stall Prevention function and a Torque Compensation Limit function, if
you try to accelerate too fast or try to drive a load that is too large, it can be too much for the
limits of the motor.
applicable values.
• Examine the mechanical brake and make sure that it is fully releasing.
• Decrease the load to make sure that the output current stays less than the motor rated current.
• Use a larger motor.
Note:
• In extruder and mixer applications, the load can increase as the temperature decreases.
• Although the drive has a Stall Prevention function and a Torque Compensation Limit function,
if you try to accelerate too fast or try to drive a load that is too large, it can be too much for the
limits of the motor.
• Examine U1-01 [Frequency Reference] for the correct frequency reference.
• Examine the multi-function input terminals to see if a frequency reference signal switch is set.
• When you use an MFAI, examine the low gain level set in H3-03, H3-11 [Terminal A1, A2 Gain
Setting].
voltage (current).
• Examine the value set in H3-10.
• Use U1-14 [Terminal A2 Input Voltage] to make sure that the analog input value set to terminal
A2 is applicable.
• Examine the V/f pattern set in E1-03 [V/f Pattern Selection].
• Do Rotational Auto-Tuning.
• Do Auto-Tuning.
• Calculate motor data and reset motor parameters.
• Set A1-02 = 0 [Control Method Selection = V/f Control].
Note:
If the L3-02 value is too low, the acceleration time can be unsatisfactorily long.
Note:
If the L3-06 value is too low, speed will decrease before the drive outputs torque.
• Set the V/f pattern to “High Starting Torque”.
• Use a Vector Control method.
Note:
V/f control method does not supply high torque at low speeds.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 81
Page 82

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
◆ The Drive Frequency Reference Is Different than the Controller Frequency
Reference Command
Causes Possible Solutions
The analog input gain and bias for the frequency reference input are set
incorrectly.
The drive is receiving frequency bias signals from analog input terminals A1
and A2 and the sum of all signals makes the frequency reference.
PID control is enabled. If PID control is not necessary, set b5-01 = 0 [PID Mode Setting = Disabled].
Examine the gain and bias settings for the analog inputs that set the frequency reference.
• Terminal A1: H3-03 [Terminal A1 Gain Setting], H3-04 [Terminal A1 Bias Setting]
• Terminal A2: H3-11 [Terminal A2 Gain Setting], H3-12 [Terminal A2 Bias Setting]
• Examine parameters H3-02, H3-10 [MFAI Function Select]. If both of these parameters = 0,
change the settings.
• Use U1-13, U1-14 [Terminal A1, A2 Input Voltage] to make sure that the analog input values set
to terminals A1 and A2 are applicable.
Note:
When PID control is enabled, the drive adjusts the output frequency as specified by the target
value. The drive will only accelerate to the maximum output frequency set in E1-04 [Maximum
Output Frequency] while PID control is active.
◆ The Motor Speed Is Not Stable When Using a PM Motor
Causes Possible Solutions
E5-01 [PM Motor Code Selection] is set incorrectly. Refer to “Motor Performance Fine-Tuning” in the technical manual.
The drive is operating the motor at more than the specified speed control range. Examine the speed control range and adjust the speed.
The motor is hunting. Adjust these parameters to have the largest effect:
Hunting occurs at start. Increase the value set in C2-01 [S-Curve Time @ Start of Accel].
Too much current is flowing through the drive. Set E5-01 [PM Motor Code Selection] correctly as specified by the motor. For special-purpose
Operation is not stable when n8-57 = 1 [HFI Overlap Selection = Enabled]. • Do High Frequency Injection Auto-Tuning.
• n8-55 [Motor to Load Inertia Ratio]
• n8-45 [Speed Feedback Detection Gain]
• C4-02 [Torque Compensation Delay Time]
motors, enter the correct value to E5-xx as specified by the motor test report.
• Decrease the value set in n8-41 [HFI P Gain] in increments of 0.5.
Note:
Set n8-41 > 0.0 for IPM motors.
◆ There Is Too Much Motor Oscillation and the Rotation Is Irregular
Causes Possible Solutions
Unsatisfactory balance of motor phases. • Make sure that the drive input power voltage supplies stable power.
• Set L8-05 = 0 [Input Phase Loss Protect Select = Disabled].
The motor is hunting. • Set n1-01 = 1 [Hunting Prevention Selection = Enabled].
• Increase the value of n2-01 [SpdFeedbackDetectCtr (AFR) Gain] or n2-02 [SpdFeedbackDetCtr
(AFR)TimeConst1].
◆ Deceleration Takes Longer Than Expected When Dynamic Braking Is Enabled
Causes Possible Solutions
The stall prevention during deceleration setting is incorrect. • Examine the setting for L3-04 [Decel Stall Prevention Selection].
The deceleration time setting is too long. Set C1-02, C1-04, C1-06, or C1-08 [Deceleration Times] to applicable values.
The motor torque is not sufficient. Use a larger motor.
• When the drive has a dynamic braking option installed, set L3-04 = 0 [Disabled].
• If the drive detects ov [Overvoltage], set L3-04 = 3 [General Purpose w/ DB resistor].
Note:
If these items are correct, the demand on the motor is more than the motor capacity:
• Parameter settings are correct.
• The drive does not detect ov [Overvoltage].
82 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 83

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
Causes Possible Solutions
The drive and motor system reached the torque limit. • Examine the values set in L7-01 to L7-04 [Torque Limit] and increase them if necessary.
The load is more than the internal torque limit as specified by the drive rated
current.
Note:
If the torque limit is enabled, deceleration time can increase because the drive cannot output
more torque than the limit.
• If H3-02, H3-10 = 10, 11, 12, 15 [MFAI Function Select = Torque Limit], examine the settings
for the MFAIs.
• Examine the values set in H3-02 and H3-10.
• Use U1-13, U1-14 [Terminal A1, A2 Input Voltage] to make sure that the analog input values
set to terminals A1 and A2 are applicable.
Replace the drive with a larger capacity model.
◆ There Is Audible Noise from the Drive or Motor Cables When the Drive Is
Energized
Causes Possible Solutions
The relay switching in the drive is making too much noise. • Use C6-02 [Carrier Frequency Selection] to decrease the carrier frequency.
• Connect a noise filter to the input side of the drive power supply.
• Connect a noise filter to the output side of the drive.
• Isolate the control circuit wiring from the main circuit wiring.
• Use a metal cable gland to wire the drive.
• Shield the periphery of the drive with metal.
• Make sure that the drive and motor are grounded correctly.
• Make sure that ground faults have not occurred in the wiring or motor.
◆ The Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Trips During Run
Causes Possible Solutions
There is too much leakage current from the drive. • Increase the GFCI sensitivity or use GFCI with a higher threshold.
• Use C6-02 [Carrier Frequency Selection] to decrease the carrier frequency.
• Decrease the length of the cable used between the drive and the motor.
• Install a noise filter or AC reactor on the output side of the drive. Set C6-02 = 1 [2.0 kHz] when
connecting an AC reactor.
• Disable the internal EMC filter.
◆ Motor Rotation Causes Unexpected Audible Noise from Connected Machinery
Causes Possible Solutions
The carrier frequency and the resonant frequency of the connected machinery
are the same.
The drive output frequency and the resonant frequency of the connected
machinery are the same.
• Adjust C6-02 to C6-05 [Carrier Frequency].
• Set C6-02 = 1 to 6 [Carrier Frequency Selection = Frequency other than Swing PWM].
Note:
If C6-02 = 7 to A [Carrier Frequency Selection = Swing PWM], the drive will not know if the
noise comes from the drive or the machine.
• Adjust d3-01 to d3-04 [Jump Frequency].
• Put the motor on a rubber pad to decrease vibration.
◆ Motor Rotation Causes Oscillation or Hunting
Causes Possible Solutions
The frequency reference is assigned to an external source, and there is electrical
interference in the signal.
The cable between the drive and motor is too long. • Do Auto-Tuning.
The PID parameters are not sufficiently adjusted. Adjust b5-xx [PID control].
Make sure that electrical interference does not have an effect on the signal lines.
• Isolate control circuit wiring from main circuit wiring.
• Use twisted-pair cables or shielded wiring for the control circuit.
• Increase the value of H3-13 [Analog Input FilterTime Constant].
• Make the wiring as short as possible.
Troubleshooting
2
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 83
Page 84

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
◆ PID Output Fault
Causes Possible Solutions
There is no PID feedback input. • Examine the MFAI terminal settings.
• Make sure that H3-02, H3-10 = B [MFAI Function Select = PID Feedback].
• Make sure that the MFAI terminal settings agree with the signal inputs.
• Examine the connection of the feedback signal.
• Make sure that you set b5-xx [PID Control] correctly.
Note:
If there is no PID feedback input to the terminal, the detected value is 0, which causes a PID
fault and also causes the drive to operate at maximum frequency.
The detection level and the target value do not align. Use H3-03, H3-11 [Terminal A1 and A2 Gain Setting] to adjust PID target and feedback signal
Reverse drive output frequency and speed detection. When output frequency
increases, the sensor detects a speed decrease.
scaling.
Note:
PID control keeps the difference between the target value and detection value at 0. Set the input
level for the values relative to each other.
Set b5-09 = 1 [PID Output Level Selection = Reverse output (reverse acting)].
◆ The Starting Torque Is Not Sufficient
Causes Possible Solutions
Auto-Tuning has not been done in vector control method. Do Auto-Tuning.
The control method was changed after doing Auto-Tuning. Do Auto-Tuning again.
Stationary Auto-Tuning for Line-to-Line Resistance was done. Do Rotational Auto-Tuning.
◆ The Motor Rotates after the Drive Output Is Shut Off
Causes Possible Solutions
DC Injection Braking is too low and the drive cannot decelerate correctly. • Increase the value set in b2-02 [DC Injection Braking Current].
The stopping method makes the drive coast to stop. Set b1-03 = 0 or 2 [Stopping Method Selection = Ramp to Stop, DC Injection Braking to Stop].
• Increase the value set in b2-04 [DC Inject Braking Time at Stop].
◆ The Output Frequency Is Lower Than the Frequency Reference
Causes Possible Solutions
The frequency reference is in the Jump frequency range. Adjust d3-01 to d3-03 [Jump Frequency 1 to 3] and d3-04 [Jump Frequency Width].
The upper limit for the frequency reference has been exceeded. Set E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency] and d2-01 [Frequency Reference Upper Limit] to the best
A large load triggered Stall Prevention function during acceleration. • Decrease the load.
L3-01 = 3 [Stall Prevent Select duringAccel = ILim Mode] has been set. 1. Check whether the V/f pattern and motor parameter settings are appropriate, and set them
The motor is rotating at this speed:
b2-01 [DC Injection/Zero SpeedThreshold] ≤ Motor Speed < E1-09 [Minimum
Output Frequency]
Note:
Enabling the Jump frequency prevents the drive from outputting the frequencies specified in the
Jump range.
values for the application.
Note:
This calculation supplies the upper value for the output frequency:
E1-04 × d2-01 / 100
• Adjust L3-02 [Stall Prevent Level during Accel].
correctly.
2. If this does not solve the problem, and it is not necessary to limit the current level of stall during
acceleration, adjust L3-02.
3. If this does not solve the problem, set L3-01 = 1 [Enabled].
Set E1-09 < b2-01.
84 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 85

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
◆ The Motor Will Not Restart after a Loss of Power
Causes Possible Solutions
The drive did not receive a Run command after applying power. • Examine the sequence and wiring that enters the Run command.
• Set up a relay to make sure that the Run command stays enabled during a loss of power.
For applications that use 3-wire sequence, the momentary power loss continued
for a long time, and the relay that keeps the Run command has been switched
off.
Examine the wiring and circuitry for the relay that keeps the Run command enabled during the
momentary power loss ride-thru time.
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 85
Troubleshooting
2
Page 86

2.10 Troubleshooting Without Fault Display
86 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 87

3
Parameter List
3.1 Section Safety ........................................................................................................... 88
3.2 How to Read the Parameter List ...........................................................................89
3.3 Parameter Groups.................................................................................................... 90
3.4 A: Initialization Parameters.................................................................................... 91
3.5 b: Application ............................................................................................................ 93
3.6 C: Tuning ..................................................................................................................102
3.7 d: Reference Settings............................................................................................106
3.8 E: Motor Parameters..............................................................................................110
3.9 F: Options................................................................................................................. 114
3.10 H: Terminal Functions ...........................................................................................122
3.11 L: Protection Functions ........................................................................................137
3.12 n: Special Adjustment...........................................................................................147
3.13 o: Keypad-Related Settings .................................................................................153
3.14 q: DriveWorksEZ Parameters..............................................................................158
3.15 r: DWEZ Connection 1-20 .....................................................................................159
3.16 T: Motor Tuning .......................................................................................................160
3.17 U: Monitors...............................................................................................................163
3.18 Parameters that Change from the Default Settings with A1-02 [Control
Method Selection] ..................................................................................................175
3.19 Parameters that Change from the Default Settings with E3-01 [Motor 2
Control Mode Selection].......................................................................................179
3.20 Parameters Changed by E1-03 [V/f Pattern Selection] .................................180
3.21 Defaults by Drive Model and Duty Rating ND/HD...........................................181
3.22 Parameters Changed by PM Motor Code Selection ......................................194
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 87
Page 88

3.1 Section Safety
3.1 Section Safety
DANGER
Do not ignore the safety messages in this manual.
If you ignore the safety messages in this manual, it will cause serious injury or death. The manufacturer is not
responsible for injuries or damage to equipment.
88 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 89

3.2 How to Read the Parameter List
3.2 How to Read the Parameter List
◆ Icons and Terms that Identify Parameters and Control Modes
Icon Description
The parameter is available when operating the drive with V/f Control.
The parameter is available when operating the drive with Open Loop Vector Control.
The parameter is available when operating the drive with Open Loop Vector Control for PM.
The parameter is available when operating the drive with Advanced Open Loop Vector Control for PM.
The parameter is available when operating the drive with EZ Open Loop Vector Control.
Hex. Hexadecimal numbers that represent MEMOBUS addresses to change parameters over network communication.
RUN The parameter can be changed settings during run.
Expert The parameter that is available in Expert Mode only.
*1 Set A1-01 = 3 [Access Level Selection = Expert Level] to display and set Expert Mode parameters on the keypad.
Note:
Gray icons identify parameters that are not available in the specified control method.
*1
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 89
Parameter List
3
Page 90

3.3 Parameter Groups
3.3 Parameter Groups
Represents the type of product parameters.
Parameter Name
A1 Initialization
A2 User Parameters
b1 Operation Mode Selection
b2 DC Injection Braking and Short Circuit Braking
b3 Speed Search
b4 Timer Function
b5 PID control
b6 Dwell Function
b8 Energy Saving
C1 Accel & Decel Time
C2 S-Curve Characteristics
C3 Slip Compensation
C4 Torque Compensation
C5
C6 Carrier Frequency
d1 Frequency Reference
d2 Reference Limits
d3 Jump Frequency
d4 Frequency Ref Up/Down & Hold
d6 Field Weakening /Forcing
d7 Offset Frequency
E1 V/f Pattern for Motor 1
E2 Motor Parameters
E3 V/f Pattern for Motor 2
E4 Motor 2 Parameters
E5 PM Motor Settings
E9 Motor Setting
F1 Fault Detection during PG Speed Control
F6 Communication Options
F7 Communication Options
H1 Digital Inputs
H2 Digital Outputs
H3 Analog Inputs
H4 Analog Outputs
H5 Modbus Communication
H6 Pulse Train Input/Output
Automatic Speed Regulator (ASR: Automatic Speed
Regulator)
Parameter Name
H7 Virtual MFIO selection
L1 Motor Protection
L2 Power Loss Ride Through
L3 Stall Prevention
L4 Speed Detection
L5 Fault Restart
L6 Torque Detection
L7 Torque Limit
L8 Drive Protection
n1 Hunting Prevention
n2 Auto Freq Regulator (AFR)
n3 High Slip/Overexcite Braking
n5 Feed Forward Control
n6 Online Tuning
n7 EZ Drive
n8 PM Motor Control Tuning
nA PM Motor Control Tuning
o1 Keypad Display
o2 Keypad Operation
o3 Copy Keypad Function
o4 Maintenance Monitors
o5 Log Function
q DriveWorksEZ Parameters
r DWEZ Connection 1-20
T0 Tuning Mode Selection
T1 Induction Motor Auto-Tuning
T2 PM Motor Auto-Tuning
T3 ASR and Inertia Tuning
T4 EZ Tuning
U1 Operation Status Monitors
U2 Fault Trace
U3 Fault History
U4 Maintenance Monitors
U5 PID Monitors
U6 Operation Status Monitors
U8 DriveWorksEZ Monitors
90 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 91

3.4 A: Initialization Parameters
◆ A1: Initialization
3.4 A: Initialization Parameters
No.
(Hex.)
A1-00
(0100)
RUN
A1-01
(0101)
RUN
A1-02
(0102)
A1-03
(0103)
A1-04
(0104)
A1-05
(0105)
A1-06
(0127)
A1-07
(0128)
A1-11
(111D)
Expert
A1-12
(1564)
Name Description
Language Selection Sets the language for the LCD keypad.
Note:
When you use A1-03 [Initialize Parameters] to initialize the drive, the drive will not reset this
parameter.
0 : English
1 : Japanese
2 : German
3 : French
4 : Italian
5 : Spanish
6 : Portuguese
7 : Chinese
8 : Czech
9 : Russian
10 : Turkish
11 : Polish
12 : Greek
Access Level Selection Sets user access to parameters. The access level controls which parameters the keypad will display,
Control Method Selection Sets the control method for the drive application and the motor.
Initialize Parameters Sets parameters to default values.
Password Entry point for the password set in A1-05 [Password Setting]. The user can view the settings of
Password Setting Set the password to lock parameters and prevent changes to parameter settings. Enter the correct
Application Preset Sets the drive to operate in selected application conditions.
DriveWorksEZ Function
Selection
Firmware Update Lock Protects the drive firmware. When you enable the protection, you cannot update the drive firmware.
Bluetooth ID Sets the password necessary to use Bluetooth to control the drive with a smartphone or tablet. -
and which parameters the user can set.
0 : Operation Only
1 : User Parameters
2 : Advanced Level
3 : Expert Level
0 : V/f Control
2 : Open Loop Vector
5 : PM Open Loop Vector
6 : PM Advanced Open Loop Vector
8 : EZ Vector Control
0 : No Initialization
1110 : User Initialization
2220 : 2-Wire Initialization
3330 : 3-Wire Initialization
parameters that are locked without entering the password. Enter the correct password in this
parameter to change parameter settings.
password in A1-04 [Password] to unlock parameters and accept changes.
0 : General-purpose
1 : Water Supply Pump 2
2 : Conveyor
3 : Exhaust Fan
4 : HVAC Fan
5 : Air Compressor
8 : Conveyor 2
Sets the drive to operate with DriveWorksEZ.
0 : DWEZ Disabled
1 : DWEZ Enabled
2 : Enabled/Disabled wDigital Input
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
Default
(Range)
(0 - 12)
(0 - 3)
(0, 2, 5, 6, 8)
(0 - 3330)
0000
(0000 - 9999)
0000
(0000 - 9999)
(0 - 5, 8)
(0 - 2)
(0, 1)
(0000 - 9999)
0
2
2
0
0
Parameter List
3
0
0
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 91
Page 92

3.4 A: Initialization Parameters
◆ A2: User Parameters
No.
(Hex.)
A2-01 to A2-32
(0106 - 0125)
A2-33
(0126)
Name Description
User Parameters 1 to 32 You can select a maximum of 32 parameters for the drive and save the values to parameters A2-01 to
User Parameter Auto
Selection
A2-32. Use Setup Mode to show the saved parameters. You can immediately access these saved
parameters.
Note:
When the A1-06 [Application Preset] value changes, the settings for A2-01 to A2-32 change.
Sets the automatic save feature for changes to parameters A2-17 to A2-32 [User Parameters 17 to
32].
0 : Disabled: Manual Entry Required
1 : Enabled: Auto Save Recent Parms
Default
(Range)
Parameters in General-
Purpose Setup Mode
(Determined by A1-06)
Determined by A1-06
(0, 1)
92 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 93

3.5 b: Application
◆ b1: Operation Mode Selection
3.5 b: Application
No.
(Hex.)
b1-01
(0180)
b1-02
(0181)
b1-03
(0182)
b1-04
(0183)
b1-06
(0185)
b1-07
(0186)
b1-08
(0187)
b1-14
(01C3)
b1-15
(01C4)
b1-16
(01C5)
Name Description
Frequency Reference
Selection 1
Run Command Selection 1 Sets the input method for the Run command.
Stopping Method Selection Sets the method to stop the motor after removing a Run command or entering a Stop command.
Reverse Operation Selection Sets the reverse operation function. Disable reverse operation in fan or pump applications where
Digital Input Reading Sets the number of times that the drive reads the sequence input command to prevent malfunction
LOCAL/REMOTE Run
Selection
Run Command Select in
PRG Mode
Phase Order Selection Sets the phase order for output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3. This parameter can align the
Frequency Reference
Selection 2
Run Command Selection 2 Sets the input method for Run Command 2 when the user switches the control circuit terminals ON/
Sets the input method for the frequency reference.
0 : Keypad
1 : Analog Input
2 : Memobus/Modbus Communications
3 : Option PCB
4 : Pulse Train Input
0 : Keypad
1 : Digital Input
2 : Memobus/Modbus Communications
3 : Option PCB
Note:
When A1-02 = 5, 6, 8 [Control Method Selection = OLV/PM, AOLV/PM, EZOLV], the setting
range is 0, 1, 3.
0 : Ramp to Stop
1 : Coast to Stop
2 : DC Injection Braking to Stop
3 : Coast to Stop with Timer
reverse rotation is dangerous.
0 : Reverse Enabled
1 : Reverse Disabled
because of electrical interference.
0 : Single Scan
1 : Double Scan
Sets drive response to an existing Run command when the drive receives a second Run command
from a different location.
0 : Disregard Existing RUN Command
1 : Accept Existing RUN Command
Sets the conditions for the drive to accept a Run command entered from an external source when
using the keypad to set parameters.
0 : Disregard RUN while Programming
1 : Accept RUN while Programming
2 : Allow Programming Only at Stop
Forward Run command from the drive and the forward direction of the motor without changing
wiring.
0 : Standard
1 : Switch Phase Order
Sets the input method for frequency reference 2.
0 : Keypad
1 : Analog Input
2 : Memobus/Modbus Communications
3 : Option PCB
4 : Pulse Train Input
OFF to change the Run command source.
0 : Keypad
1 : Digital Input
2 : Memobus/Modbus Communications
3 : Option PCB
Default
(Setting Range)
1
(0 - 4)
1
(0 - 3)
0
(0 - 3)
0
(0, 1)
1
(0, 1)
0
(0, 1)
0
(0 - 2)
0
(0, 1)
0
(0 - 4)
0
(0 - 3)
Parameter List
3
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 93
Page 94

3.5 b: Application
No.
(Hex.)
b1-17
(01C6)
b1-35
(1117)
Expert
Run Command at Power Up Sets drive response when energizing a drive that has an external Run command. Set this parameter in
Digital Input Deadband
Time
Name Description
applications where energizing or de-energizing the drive enables the Run command.
0 : Disregard Existing RUN Command
1 : Accept Existing RUN Command
Sets the deadband time for MFDIs. 0.0 ms
◆ b2: DC Injection Braking and Short Circuit Braking
No.
(Hex.)
b2-01
(0189)
b2-02
(018A)
b2-03
(018B)
b2-04
(018C)
b2-08
(0190)
b2-12
(01BA)
b2-13
(01BB)
b2-18
(0177)
DC Injection/Zero
SpeedThreshold
DC Injection Braking
Current
DC Inject Braking Time at
Start
DC Inject Braking Time at
Stop
Magnetic Flux
Compensation Value
Short Circuit Brake Time @
Start
Short Circuit Brake Time @
Stop
Short Circuit Braking
Current
Name Description
Sets the frequency to start DC Injection Braking or Short Circuit Braking.
Note:
This parameter is available when b1-03 = 0 [Stopping Method Selection = Ramp to Stop].
Sets the DC Injection Braking current as a percentage of the drive rated current. 50%
Sets the DC Injection Braking Time at stop. 0.00 s
Sets the DC Injection Braking Time at stop. Determined by A1-02
Sets how much current the drive injects when DC Injection Braking at Start starts (Initial Excitation)
as a percentage of E2-03 [Motor No-Load Current].
Sets the Short Circuit Braking time at start. 0.00 s
Sets the Short Circuit Braking time at stop. A1-02 = 8: 0.00 s
Sets the Short Circuit Braking Current as a percentage of the motor rated current.
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the motor rated current.
• A1-02 = 5, 6 [OLV/PM, AOLV/PM]: E5-03 [PM Motor Rated Current (FLA)]
• A1-02 = 8 [EZOLV]: E9-06 [Motor Rated Current (FLA)]
Default
(Setting Range)
0
(0, 1)
(0.0 to 100.0 ms)
Default
(Range)
Determined by A1-02
(0.0 - 10.0 Hz)
(0 - 75%)
(0.00 - 10.00 s)
(0.00 - 10.00 s)
0%
(0 - 1000%)
(0.00 - 25.50 s)
Other than A1-02 = 8: 0.50 s
(0.00 - 25.50 s)
100.0%
(0.0 - 200.0%)
◆ b3: Speed Search
No.
(Hex.)
b3-01
(0191)
b3-02
(0192)
b3-03
(0193)
b3-04
(0194)
b3-05
(0195)
b3-06
(0196)
Expert
Speed Search at Start
Selection
SpeedSearch Deactivation
Current
Speed Search Deceleration
Time
V/f Gain during Speed
Search
Speed Search Delay Time Sets the Speed Search delay time to activate a magnetic contactor installed between the drive and
Speed Estimation Current
Level 1
Name Description
Sets the Speed Search at Start function where the drive will perform Speed Search with each Run
command.
0 : Disable
1 : Enabled
Sets the current level that stops Speed Search as a percentage of the drive rated output current.
Usually it is not necessary to change this setting.
Sets the deceleration time during Speed Search operation. Set the length of time to decelerate from
the maximum output frequency to the minimum output frequency.
Note:
When A1-02 = 8 [Control Method Selection = EZOLV], this parameter takes effect only in
Expert Mode.
Sets the ratio used to reduce the V/f during searches to reduce the output current during speed
searches.
motor.
Sets the level of current that flows to the motor during Speed Estimation Speed Search as a
coefficient of the motor rated current. Usually it is not necessary to change this setting.
Default
(Range)
Determined by A1-02
(0, 1)
Determined by A1-02
(0 - 200%)
2.0 s
(0.1 - 10.0 s)
Determined by o2-04
(10 - 100)
0.2 s
(0.0 - 100.0 s)
Determined by o2-04
(0.0 - 2.0)
94 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 95

3.5 b: Application
No.
(Hex.)
b3-07
(0197)
Expert
b3-08
(0198)
b3-09
(0199)
b3-10
(019A)
Expert
b3-14
(019E)
b3-17
(01F0)
Expert
b3-18
(01F1)
Expert
b3-19
(01F2)
b3-24
(01C0)
b3-25
(01C8)
Expert
b3-26
(01C7)
Expert
b3-29
(077C)
Expert
b3-31
(0BC0)
Expert
b3-32
(0BC1)
Expert
b3-33
(0B3F)
Expert
Name Description
Speed Estimation Current
Level 2
Speed Estimation ACR P
Gain
Speed Estimation ACR I
Time
Speed Estimation Detection
Gain
Bi-directional Speed Search Sets the direction of Speed Search to the direction of the frequency reference or in the motor rotation
Speed Est Retry Current
Level
Speed Est Retry Detection
Time
Speed Search Restart
Attempts
Speed Search Method
Selection
Speed Search Wait Time Sets the length of time the drive will wait to start the Speed Search Retry function. 0.5 s
Direction Determination
Level
Speed Search Back-EMF
Threshold
Spd Search Current
Reference Lvl
Spd Search Current
Complete Lvl
Speed Search during Uv
Selection
Sets the level of current that flows to the motor during Speed Estimation Speed Search as a
coefficient of E2-03 [Motor No-Load Current] or E4-03 [Motor 2 Rated No-Load Current]. Usually
it is not necessary to change this setting.
Sets the proportional gain for the automatic current regulator during Speed Estimation Speed Search.
Also adjusts speed search responsiveness. Usually it is not necessary to change this setting.
Sets the integral time for the automatic current regulator during Speed Estimation Speed Search. Also
adjusts speed search responsiveness. Usually it is not necessary to change this setting.
Sets the gain to correct estimated frequencies from Speed Estimation Speed Search. 1.05
direction as detected by the drive.
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
Note:
• When E9-01 = 0 [Motor Type Selection = Induction (IM)] and A1-02 = 0, 2, or 8 [Control
Method Selection = V/f, OLV, or EZOLV], the default settings change when the setting of b3-24
[Speed Search Method Selection] changes.
–b3-24 = 1 [Speed Estimation]: Refer to 175.
–b3-24 = 2 [Current Detection 2]: 0
• When E9-01 = 1 or 2 [Permanent Magnet (PM), Synchronous Reluctance (SynRM)] and A1-02
= 0 or 8 [V/f, EZOLV], refer to 175.
When you set A1-02, b3-24, and E9-01, set b3-14.
Sets the current level for the search retry function in Speed Estimation Speed Search as a percentage
where drive rated current is a setting value of 100%.
Sets the length of time that the drive will wait to retry Speed Estimation Speed Search when too
much current flow stopped the Speed Search.
Sets the number of times to restart Speed Search if Speed Search does not complete. 3 times
Sets the Speed Search method when you start the motor or when you restore power after a
momentary power loss.
Note:
• When A1-02 = 8 [Control Method Selection = EZOLV], the default setting changes when the
setting for E9-01 [Motor Type Selection] changes.
–E9-01 = 0 [Induction (IM)]: 2
–E9-01 = 1, 2 [Permanent Magnet (PM), Synchronous Reluctance (SynRM)]: 1
• When you set b3-24, it will trigger the drive to initialize b3-14 [Bi-directional Speed Search].
After you set b3-24, set b3-14.
1 : Speed Estimation
2 : Current Detection 2
Sets the level to find the motor rotation direction. Increase the value if the drive cannot find the
direction.
Sets the induced voltage for motors that use Speed Search. The drive will start Speed Search when
the motor induced voltage level is the same as the setting value. Usually it is not necessary to change
this setting.
Sets the current level that decreases the output current during Current Detection Speed Search. 1.50
Sets the current level that completes Speed Search. 1.20
Sets the function that starts Speed Search at start-up if the drive detects a Uv [Undervoltage] when it
receives a Run command.
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
Default
(Range)
1.0
(0.0 - 3.0)
Determined by A1-02 and
o2-04
(0.00 - 6.00)
Determined by A1-02 when
A1-02 ≠ 5
20.0 when A1-02 = 5
(0.0 - 1000.0 ms)
(1.00 - 1.20)
Determined by A1-02 and
b3-24
(0, 1)
150%
(0 - 200%)
0.10 s
(0.00 - 1.00 s)
(0 - 10 times)
2
(1, 2)
(0.0 - 30.0 s)
1000
(40 to 60000)
10%
(0 - 10%)
(1.50 - 3.50)
(0.00 - 1.49)
1
(0, 1)
Parameter List
3
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 95
Page 96

3.5 b: Application
No.
(Hex.)
b3-54
(3123)
b3-55
(3124)
Expert
b3-56
(3126)
b3-61
(1B96)
Expert
Search Time Sets the length of time that the drive will run Speed Search. 400 ms
Current Increment Time Sets the length of time that the drive will increase the current from zero current to the setting value of
InverseRotationSearch
WaitTime
Initial Pole Detection
Response Gain
Name Description
◆ b4: Timer Function
No.
(Hex.)
b4-01
(01A3)
b4-02
(01A4)
b4-03
(0B30)
Expert
b4-04
(0B31)
Expert
b4-05
(0B32)
Expert
b4-06
(0B33)
Expert
b4-07
(0B34)
Expert
b4-08
(0B35)
Expert
Timer Function ON-Delay
Time
Timer Function OFF-Delay
Time
Terminal M1-M2 ON-Delay
Time
Terminal M1-M2 OFF-Delay
Time
Terminal M3-M4 ON-Delay
Time
Terminal M3-M4 OFF-Delay
Time
Terminal P2 ON-Delay Time Sets the delay time until the contact is turned ON after the function set with H2-03 turns ON. 0 ms
Terminal P2 OFF-Delay
Time
Name Description
Default
(Range)
(10 - 2000 ms)
b3-06 [Speed Estimation Current Level 1].
Sets the wait time until the drive starts inverse rotation search after it completes forward search when
you do inverse rotation search during Current Detection Speed Search.
Sets the responsiveness for initial motor magnetic pole calculation when A1-02 = 6 [Control Method
Selection = AOLV/PM]. Set b3-61 > 0.0 for an ordinary IPM motor.
It is automatically set if High Frequency Injection Tuning is used.
Note:
• Set n8-35 = 1 [Initial Pole Calculation Method = High Frequency Injection] to enable this
parameter.
• Set n8-41 [HFI P Gain] to adjust the responsiveness for initial motor magnetic pole calculation
when A1-02 = 5 [OLV/PM].
Sets the ON-delay time for the timer input. 0.0 s
Sets the OFF-delay time for the timer input. 0.0 s
Sets the delay time until the contact is turned ON after the function set with H2-01 turns ON. 0 ms
Sets the delay time to deactivate the contact after the function set in H2-01 deactivates. 0 ms
Sets the delay time to activate the contact after the function set in H2-02 activates. 0 ms
Sets the delay time to deactivate the contact after the function set in H2-02 deactivates. 0 ms
Sets the delay time to deactivate the contact after the function set in H2-03 deactivates. 0 ms
10 ms
(10 - 2000 ms)
Determined by o2-04
(0.1 - 5.0 s)
5.0
(-20.0 - +20.0)
Default
(Range)
(0.0 - 3000.0 s)
(0.0 - 3000.0 s)
(0 - 65000 ms)
(0 - 65000 ms)
(0 - 65000 ms)
(0 - 65000 ms)
(0 - 65000 ms)
(0 - 65000 ms)
96 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 97

◆ b5: PID control
3.5 b: Application
No.
(Hex.)
b5-01
(01A5)
b5-02
(01A6)
RUN
b5-03
(01A7)
RUN
b5-04
(01A8)
RUN
b5-05
(01A9)
RUN
b5-06
(01AA)
RUN
b5-07
(01AB)
RUN
b5-08
(01AC)
RUN
Expert
b5-09
(01AD)
b5-10
(01AE)
RUN
b5-11
(01AF)
Name Description
PID Mode Setting Sets the type of PID control.
0 : Disabled
1 : Standard
2 : Standard (D on feedback)
3 : Fref + PID Trim
4 : Fref + PID Trim (D on feedback)
5 : Same as 7series & prior, b5-01=1
6 : Same as 7series & prior, b5-01=2
7 : Same as 7series & prior, b5-01=3
8 : Same as 7series & prior, b5-01=4
Note:
Use settings 5 to 8 when the drive is a replacement for a previous generation drive.
Proportional Gain (P) Sets the proportional gain (P) that is applied to PID input. 1.00
Integral Time (I) Sets the integral time (I) that is applied to PID input. 1.0 s
Integral Limit Sets the upper limit for integral control (I) as a percentage of the Maximum Output Frequency.
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Derivative Time (D) Sets the derivative time (D) for PID control. This parameter adjusts system responsiveness. 0.00 s
PID Output Limit Sets the maximum possible output from the PID controller as a percentage of the Maximum Output
PID Offset Adjustment Sets the offset for the PID control output as a percentage of the Maximum Output Frequency.
PID Primary Delay Time
Constant
PID Output Level Selection Sets the polarity of the PID output.
PID Output Gain Setting Sets the amount of gain to apply to the PID output. 1.00
PID Output Reverse
Selection
Frequency.
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Sets the primary delay time constant for the PID control output. Usually it is not necessary to change
this setting.
0 : Normal Output (Direct Acting)
1 : Reverse Output (Reverse Acting)
Sets the function that enables and disables reverse motor rotation for negative PID control output.
0 : Lower Limit is Zero
1 : Negative Output Accepted
Default
(Range)
0
(0 - 8)
(0.00 - 25.00)
(0.0 - 360.0 s)
100.0%
(0.0 - 100.0%)
(0.00 - 10.00 s)
100.0%
(0.0 - 100.0%)
0.0%
(-100.0 - +100.0%)
0.00 s
(0.00 - 10.00 s)
0
(0, 1)
(0.00 - 25.00)
0
(0, 1)
Parameter List
3
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 97
Page 98

3.5 b: Application
No.
(Hex.)
b5-12
(01B0)
b5-13
(01B1)
b5-14
(01B2)
b5-15
(01B3)
b5-16
(01B4)
b5-17
(01B5)
RUN
b5-18
(01DC)
b5-19
(01DD)
RUN
b5-20
(01E2)
b5-34
(019F)
RUN
b5-35
(01A0)
RUN
b5-36
(01A1)
b5-37
(01A2)
b5-38
(01FE)
b5-39
(01FF)
Name Description
Feedback Loss Detection
Select
PID Feedback Loss
Detection Lvl
PID Feedback Loss
Detection Time
PID Sleep Function Start
Level
PID Sleep Delay Time Sets a delay time to start or stop the PID Sleep function. 0.0 s
PID Accel/Decel Time Raises or lowers the PID setpoint using the acceleration and deceleration times set to the drive. This
b5-19 PID Setpoint Selection Sets the function that enables and disables b5-19 [PID Setpoint Value].
PID Setpoint Value Sets the PID setpoint when b5-18 = 1 [b5-19 PID Setpoint Selection = Enabled]. 0.00%
PID Unit Selection Sets the number of digits to set and show the PID setpoint.
PID Output Lower Limit
Level
PID Input Limit Level Sets the output upper limit for the PID control as a percentage of the Maximum Output Frequency.
PID High Feedback
Detection Lvl
PID High Feedback
Detection Time
PID User Unit Display
Scaling
PID User Unit Display
Digits
Sets the drive response to PID feedback loss/excess. Sets drive operation after the drive detects PID
feedback loss/excess.
0 : Digital Out Only, Always Detect
1 : Alarm + Digital Out, Always Det
2 : Fault + Digital Out, Always Det
3 : Digital Out Only, @ PID Enable
4 : Alarm + Digital Out, @PID Enable
5 : Fault + Digital Out, @PID Enable
Sets the level that triggers PID Feedback Loss [FbL] detection as a percentage of the Maximum
Output Frequency.
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Sets the length of time that PID Feedback must be less than b5-13 [PID Feedback Loss Detection
Lvl] to detect PID Feedback Loss [FbL].
Sets the output level that triggers the PID Sleep function. Determined by A1-02
is a soft-starter for the PID setpoint.
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
0 : 0.01Hz units
1 : 0.01% units
2 : rev/min
3 : User Units
Sets the output lower limit for the PID control as a percentage of the Maximum Output Frequency.
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Sets the level that triggers Excessive PID Feedback [FbH] as a percentage of the Maximum Output
Frequency.
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Sets the length of time that the PID feedback signal must be more than the level set in b5-36 [PID
Feedback High Detection Lvl] to cause Excessive PID Feedback [FbH].
Sets the value that the drive sets or shows as the PID setpoint when at the maximum output
frequency.
Sets the number of digits to set and show the PID setpoint.
0 : No Decimal Places (XXXXX)
1 : One Decimal Places (XXXX.X)
2 : Two Decimal Places (XXX.XX)
3 : Three Decimal Places (XX.XXX)
Default
(Range)
0
(0 - 5)
0%
(0 - 100%)
1.0 s
(0.0 - 25.5 s)
(0.0 - 590.0)
(0.0 - 25.5 s)
0.0 s
(0.0 - 6000.0 s)
0
(0, 1)
(0.00 - 100.00%)
1
(0 - 3)
0.0%
(-100.0 - +100.0%)
1000.0%
(0.0 - 1000.0%)
100%
(0 - 100%)
1.0 s
(0.0 - 25.5 s)
Determined by b5-20
(1 - 60000)
Determined by b5-20
(0 - 3)
98 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Page 99

3.5 b: Application
No.
(Hex.)
b5-40
(017F)
b5-47
(017D)
b5-53
(0B8F)
RUN
b5-55
(0BE1)
b5-56
(0BE2)
b5-57
(11DD)
b5-58 to b5-60:
(1182 - 1184)
RUN
b5-61
(119A)
b5-62
(119B)
b5-63
(119C)
b5-64
(119D)
b5-65
(119F)
b5-66
(11DE)
b5-67
(11DF)
b5-89
(0B89)
RUN
b5-90
(0B90)
b5-91
(0B91)
RUN
b5-92
(0B92)
RUN
b5-93
(0B93)
RUN
Name Description
Frequency Reference
Monitor @PID
PID Trim Mode Output
Reverse Sel
PID Integrator Ramp Limit Sets the responsiveness of PID control when the PID feedback changes quickly. 0.0 Hz
PID Feedback Monitor
Selection
PID Feedback Monitor Gain Sets the gain for the monitor set in b5-55 [PID Feedback Monitor Selection]. 1.00
PID Feedback Monitor Bias Sets the bias for the monitor specified in b5-55 [PID Feedback Monitor Selection]. 0.00
PID Setpoints 2 to 4 Sets the PID setpoint when H1-xx = 3E or 3F [MFDI Function Selection = PID Setpoint Selection 1/
PID Trim Mode Lower Limit
Sel
PID Trim Mode Lower Limit
Value
PID Differential FB Monitor
Sel
PID Differential FB Monitor
Gain
PID Differential FB Monitor
Bias
PID Feedback Monitor Level Sets the signal level for the monitor specified in b5-55 [PID Feedback Monitor Selection].
PID Differential FB Monitor
Lvl
Sleep Method Selection Sets sleep and wake up operation when using PID.
EZ Sleep Unit Sets the measurement units for b5-91 [EZ Sleep Minimum Speed] and b5-92 [EZ Sleep Level].
EZ Sleep Minimum Speed Sets the minimum speed for the EZ Sleep/Wakeup function. This parameter uses the largest value
EZ Sleep Level Sets the value that the output frequency or motor speed must be less than for longer than b5-93 [EZ
EZ Sleep Time Sets the length of time that the output frequency or motor speed must be less than b5-92 [EZ Sleep
Sets the contents for monitor U1-01 [Frequency Reference] in PID control.
0 : U1-01 Includes PID Output
1 : U1-01 Excludes PID Output
Sets reverse motor rotation when the PID control output is negative.
0 : Lower Limit is Zero
1 : Negative Output Accepted
Sets the monitor (Ux-xx) used as the PID Feedback. Set the x-xx part of the Ux-xx [Monitor]. 000
2]. This value is a percentage of the maximum output frequency.
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Sets the function that adjusts the PID output in relation to the frequency reference.
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
Sets the PID Trim Mode Lower Limit Value as a percentage of the maximum output frequency.
Note:
Parameter A1-02 [Control Method Selection] selects which parameter is the maximum output
frequency.
• A1-02 ≠ 8 [EZOLV]: E1-04 [Maximum Output Frequency]
• A1-02 = 8: E9-02 [Maximum Speed]
Selects the monitor (Ux-xx) used as the PID Differential Feedback. Set the x-xx part of the Ux-xx
[Monitor].
Sets the gain for the monitor specified in b5-63 [PID Differential FB Monitor Sel]. 1.00
Sets the bias for the monitor specified in b5-63 [PID Differential FB Monitor Sel]. 0.00
0 : Absolute
1 : Bi-directional (+/-)
Sets the signal level for the monitor specified in b5-63 [PID Differential FB Monitor Sel].
0 : Absolute
1 : Bi-directional (+/-)
0 : Standard
1 : EZ Sleep/Wake-up
0 : 0.1Hz units
1 : rev/min
from b5-91, b5-34 [PID Output Lower Limit Level], and d2-02 [Frequency Reference Lower Limit].
Sleep Time] to enter Sleep Mode.
Level] to enter Sleep Mode.
Default
(Range)
0
(0, 1)
1
(0, 1)
(0.0 - 10.0 Hz)
(000 - 999)
(0.00 - 10.00)
(-10.00 - +10.00)
0.00%
(0.00 - 100.00%)
0
(0, 1)
0.00%
(0.00 - 100.00%)
000
(000 - 999)
(0.00 - 10.00)
(-10.00 - +10.00)
0
(0, 1)
0
(0, 1)
0
(0, 1)
0
(0, 1)
0.0 Hz or 0 min
(0.0 to 590.0 Hz or 0 to
35400 min
0.0 Hz or 0 min
(0.0 to 590.0 Hz or 0 to
35400 min
-1
-1
5.0 s
(0.0 - 1000.0 s)
-1
(r/min)
(r/min))
-1
(r/min)
(r/min))
Parameter List
3
YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting 99
Page 100

3.5 b: Application
No.
(Hex.)
b5-94
(0B94)
RUN
b5-95
(0B95)
b5-96
(0B96)
RUN
EZ Sleep Wake-up Level Sets the level at which the drive resumes operation when exiting Sleep Mode. 0.00%
EZ Sleep Wake-up Mode Sets the wake-up mode to use when exiting Sleep Mode.
EZ Sleep Wake-up Time Sets the EZ Wake-up time. 1.0 s
Name Description
◆ b6: Dwell Function
No.
(Hex.)
b6-01
(01B6)
b6-02
(01B7)
b6-03
(01B8)
b6-04
(01B9)
Dwell Reference at Start Sets the output frequency that the drive will hold momentarily when the motor starts. 0.0
Dwell Time at Start Sets the length of time that the drive will hold the output frequency when the motor starts. 0.0 s
Dwell Reference at Stop Sets the output frequency that the drive will hold momentarily when ramping to stop the motor. 0.0
Dwell Time at Stop Sets the length of time for the drive to hold the output frequency when ramping to stop the motor. 0.0 s
Name Description
0 : Absolute
1 : Setpoint Delta
Default
(Range)
(0.00 - 600.00%)
0
(0, 1)
(0.0 - 1000.0 s)
Default
(Range)
(Determined by A1-02)
(0.0 - 10.0 s)
(Determined by A1-02)
(0.0 - 10.0 s)
◆ b8: Energy Saving
No.
(Hex.)
b8-01
(01CC)
b8-02
(01CD)
RUN
Expert
b8-03
(01CE)
RUN
Expert
b8-04
(01CF)
Expert
b8-05
(01D0)
Expert
b8-06
(01D1)
Expert
b8-16
(01F8)
Expert
b8-17
(01F9)
Expert
Energy Saving Control
Selection
Energy Saving Gain Sets the gain for Energy-saving control. Determined by A1-02
Energy Saving Filter Time Sets the responsiveness for Energy-saving control. Determined by A1-02,C6-
Energy Saving Coefficient
Value
Power Detection Filter Time Sets the time constant to measure output power. 20 ms
Search Operation Voltage
Limit
PM E-Save Coefficient Ki Sets torque linearity. This parameter uses the Ki value from the motor nameplate. Usually it is not
PM E-Save Coefficient Kt Sets torque linearity. This parameter uses the Kt value from the motor nameplate. Usually it is not
Name Description
Default
(Range)
Sets the Energy-saving control function.
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
2 : Automatic Optimization
Note:
When A1-02 = 6 [Control Method Selection = AOLV/PM], you can only select setting 2 in
Expert Mode.
Sets the Energy-saving control coefficient to maintain maximum motor efficiency. The default setting
is for Yaskawa motors.
Sets the voltage limit for Search Operation as a percentage of the motor rated voltage. 0%
necessary to change this setting.
necessary to change this setting.
(0 - 2)
(0.0 - 10.0)
01 and o2-04
(0.00 - 10.00 s)
Determined by C6-01, E2-
11, and o2-04
(0.00 - 655.00)
(0 - 2000 ms)
(0 - 100%)
1.00
(0.00 - 3.00)
1.00
(0.00 - 3.00)
0
100 YASKAWA TOEPYAIGA5001A GA500 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
 Loading...
Loading...