YAMAHA EDL13000TE SERVICE MANUAL

SERVICE MANUAL


FOREWORD
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
This manual was written by the Yamaha
Motor Company primarily for use by Yamaha
dealers and their qualified mechanics. It is
not possible to put an entire mechanic’s
education into one manual, so it is assumed
that persons using this book to perform maintenance and repairs on Yamaha generators
have a basic understanding of the mechanical precepts and procedures inherent to generator repair technology . Without such knowledge, attempted repairs or service to this
model may render it unfit for use and/or unsafe.
Yamaha Motor Company Ltd. is continually
striving to further improve all models manufactured by Yamaha. Modifications and significant changes in specifications or procedures
will be forwarded to all Authorized Yamaha
dealers and will, where applicable, appear in
future editions of this manual.
PARTICULARLY IMPORTANT
INFORMATION
This material is distinguished by the following
notation.
The Safety Alert Symbol means A TTENTION!
BECOME ALERT! YOUR SAFETY IS INVOLVED!
WARNING
Failure to follow WARNING instructions could
result in severe injury or death to the machine
operator, a bystander, or a person inspecting
or repairing the machine.
CAUTION:
A CAUTION indicates special precautions that
must be taken to avoid damage to the machine.
NOTE:
A NOTE provides key information to make procedures easier or clearer.
EDL13000TE
SERVICE MANUAL
1999 by Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
1st Edition, July 1999
All rights reserved. Any reprinting or
unauthorized use without the written
permission of Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
is expressly prohibited.
Printed in JAPAN
MANUAL FORMAT
The procedures in this manual are organized
in a sequential, step-by-step format. The information has been compiled to provide the
mechanic with an easy to read, handy reference that contains comprehensive explanations of all disassembly , repair , assembly, and
inspection operations.
In this revised format, the condition of a faulty
component will precede an arrow symbol and
the course of action required will follow the
symbol, e.g.,
Bearings
Pitting/damage Replace.
EXPLODED DIAGRAM
Each chapter provides exploded diagrams before each disassembly section for ease in
identifying the correct disassembly and assembly procedures.

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1.
GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION 1-1. . . . . . . . . . .
IMPORTANT INFORMATION 1-2. . . . . . . . .
SPECIAL TOOLS 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHAPTER 2.
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 2-1. . . . . . . .
DIMENSIONS 2-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAINTENANCE SPECIFICATIONS 2-4. . .
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS 2-10. . . .
GENERATOR SPECIFICATIONS 2-11. . . .
CHAPTER 3.
PERIODIC INSPECTIONS
AND ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE BODY 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LUBRICATION SYSTEM 3-4. . . . . . . . . . . . .
COOLING SYSTEM 3-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FUEL SYSTEM 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
STARTING SYSTEM 3-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GLOW SYSTEM 3-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
KEY SWITCH 3-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
STOP SYSTEM 3-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHARGING SYSTEM 3-23. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TIGHTNING TORQUES 3-26. . . . . . . . . . . . .
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE/
LUBRICATION INTERVALS 3-27. . . . .
DAILY CHECK POINTS 3-28. . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHECK POINTS OF EVERY
50 HOURS 3-29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHECK POINTS OF EVERY
100 HOURS 3-30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHANGING OF EVERY 200 HOURS 3-32. .
CHECK POINTS OF EVERY
500 HOURS 3-33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHECK POINTS OF EVERY
800 HOURS 3-35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHECK POINTS OF 1000 HOURS 3-35. . .
CHAPTER 4.
ENGINE
MEASURING AND ADJUSTING 4-1. . . . . .
ENGINE 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CYLINDER HEAD COVER 4-4. . . . . . . . . . .
ROCKER ARM AND PUSH ROD 4-5. . . . .
INTAKE/EXHAUST MANIFOLD 4-7. . . . . .
CYLINDER HEAD AND TAPPETS 4-8. . . .
VALVE AND VALVE SPRING 4-9. . . . . . . . .
EXTERNAL COMPONENTS/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER 4-10. . . . . . .
INJECTION PIPE/NOZZLE/
ROCKER ARM AND PUSH ROD 4-11. .
TAPPETS/CYLINDER HEAD AND
VALVES 4-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPEED CONTROL PLATE 4-15. . . . . . . . . .
GEAR CASE 4-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
INJECTION PUMP AND
CAMSHAFT 4-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TIMING GEAR AND CAMSHAFT 4-19. . . .
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD 4-23. . .
FLYWHEEL AND CRANKSHAFT 4-27. . . .
CHECK THE CYLINDER HEAD AND
VALVES 4-32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHECK THE PISTON AND
CONNECTING ROD 4-37. . . . . . . . . . . .
CHECK THE TIMING GEAR AND
CAMSHAFT 4-39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHECK THE CRANKSHAFT 4-42. . . . . . . .
CHECK THE CYLINDER 4-46. . . . . . . . . . . .
OIL PUMP 4-47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHAPTER 5.
COOLING SYSTEM
WATER PUMP/THERMOSTAT 5-1. . . . . . .
CHAPTER 6.
FUEL SYSTEM
INJECTION NOZZLE AND INJECTION
PUMP 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHAPTER 7.
ELECTRICAL
DYNAMO AND REGULATOR 7-1. . . . . . . .
STARTER AND GLOW PLUG 7-2. . . . . . . .
STARTER MOTOR 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERA TOR 7-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
POWER SOURCE 7-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERA TOR 7-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CONTROL FUNCTION 7-11. . . . . . . . . . . . .
CONTROL BOX 7-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PANEL WIRING DIAGRAM 7-15. . . . . . . . .
WIRING DIAGRAM (380/220 V) 7-16. . . . .
WIRING DIAGRAM (220/127 V) 7-17. . . . .
WIRING DIAGRAM (D.C. 12 V) 7-18. . . . . .
CHAPTER 8.
TROUBLESHOOTING
ENGINE SYSTEM 8-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .

GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
SERIAL NUMBER
When contacting the manufacturer, always
specify your engine model name and serial
number.
CYLINDER NUMBER
D722 diesel engine are designated as shown
in the figure.
The sequence of cylinder numbers is given
as No.1, No.2, No.3 starting from the gear
case side.
1
PRECAUTION AT OVERHEATING
Take the following actions in the event the
coolant temperature be nearly or more than
the boiling point, what is called “Overheating”.
(1) Stop the machine operation in a safe
place and keep the engine unloaded idling.
(2) Don’t stop the engine suddenly , but stop
it after about 5 minutes of unloaded idling.
(3) Keep yourself well away from the ma-
chine for further 10 minutes or while the
steam spout out.
(4) Checking that there gets no danger such
as burn, get rid of the causes of overheating according to the manual.
And then, start again the engine.
1-1

IMPORTANT INFORMATION
PREPARATION FOR REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
CAUTION ON SERVICE
1. Fire prevention
When servicing the engine, always keep the engine and yourself away from fire.
NOTES ON SERVICE
1. Correct tools
Be sure to use the correct special tool for the job to guard
against damage.
2. Oil, grease and seals
Be sure to use genuine Y amaha oils, grease and sealers, or the
equivalents.
3. Expendable parts
Always replace the gaskets, O-rings, cotterpins and circlips with
new parts when servicing engine.
4. Tightening torque
Be sure to follow torque specifications. When tightening bolts,
nuts or screws, start with the largest-diameter fastener and
work from an inner position to an outer position in a crisscross
pattern.
5. Notes on disassembly and assembly
a. Parts should be cleaned in solvent and blown dry with com-
pressed air after disassembly.
b. Contact surfaces of moving parts should be oiled when reas-
sembled.
c. Make sure that the parts, move smoothly after each section of
the machine is assembled.
1-2

ALL REPLACEMENT PARTS
1. We recommend the use of genuine Yamaha parts for all replacements. Use oil and/or grease, recommended by Yamaha,
for assembly and adjustment.
GASKETS, OIL SEALS AND O-RINGS
1. All gaskets, seals, and O-rings should be replaced when an engine is overhauled. All gaskets surfaces, oil seal lips, and Orings must be cleaned.
2. Properly oil all mating parts and bearings during reassembly.
Apply grease to the oil seal lips.
BEARING AND OIL SEALS
1. Install the bearing(s)
ture’s marks or numbers facing outward. (In other words, the
stamped letters must be on the side exposed to view.) When
installing oil seal(s), apply a light coating of light-weight lithium
base grease to the seal lip(s). Oil the bearings liberally when
installing.
1
and oil seal(s) 2 with their manufac-
CAUTION:
Do not use compressed air to spin the bearings dry. This
causes damage to the bearing surfaces.
1-3

SPECIAL TOOLS
Flywheel puller (For vertical type diesel
engines)
Application: Use exclusively to take off the
flywheel of all vertical type diesel engines safely and easily.
Valve seat cutter set
Application: Use for correcting valve seats.
Special-use puller set
Application: Use for pulling out bearings,
gears and other parts.
Crank sleeve setter
Application: Use to fix the crankshaft
sleeve of the engine models.
1-4
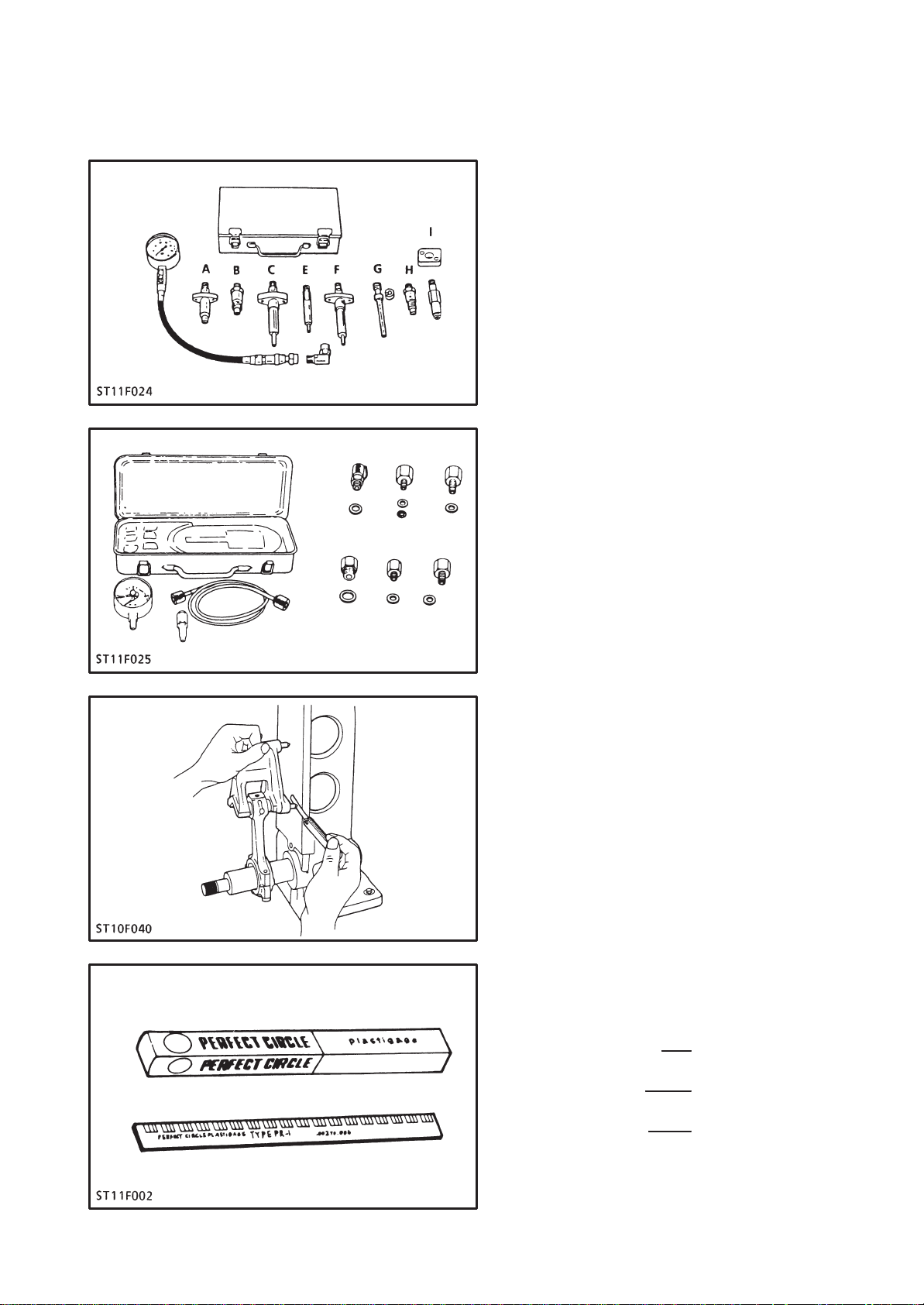
Diesel engine compression tester
Application: Use for measuring diesel en-
gine compression pressure.
Oil pressure tester
Application: Use for measuring lubricating
oil pressure.
Connecting rod alignment tool
Application: Use for checking the connect-
ing rod alignment.
Applicable: Connecting rod big end diarange meter 30 to 75 mm (1.18 to
2.95 in. dia.) Connecting rod
length 65 to 330 mm (2.56 to
12.99 in.)
Plastigage
Application: Use for checking the oil clear-
ance between crankshaft and
bearing, etc.
Measuring: Green 0.025 to 0.076 mm
range (0.001 to 0.003 in.)
Red 0.051 to 0.152 mm
(0.002 to 0.006 in.)
Blue 0.102 to 0.229 mm
(0.004 to 0.009 in.)
1-5

Unit: mm (in.)
Red check (Crack check liquid)
Application: Use for checking cracks on cyl-
inder head, cylinder block, etc.
(use the goods on the market)
NOTE:
The following special tools are not pro-
vided, so make them referring to the figures.
Valve guide replacing tool
Application: Use to press out and press fit
the valve guide.
Unit: mm (in.)
Unit: mm (in.)
Crankshaft bearing 1 replacing tool
Application: Use to press out and press fit
the crankshaft bearing 1.
(0.45)
Connecting rod small end bushing tool
Application: Use to press out and press fit
the connecting rod small end
bushing.
1-6

Unit: mm (in.)
idle gear bushing replacing tool
Application: Use to press out and press fit
the idle gear bushing.
Unit: mm (in.)
Injection pump pressure tester
Application: Use to check the fuel tight-
ness.
Pressure gauge, full scale: more than
A
24.9 MPa (300 kgf/cm2, 4267 psi)
Copper gasket
B
Flange (material: steel)
C
Hex. nut, 27 mm (1.06 in.) across the flat
D
(material: steel)
Injection pipe
E
a
Adhesive application
Fillet welding on the enter circumference
b
1-7
SPECIFICATIONS
Starting system
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Model D722-B (YMH)
Type Vertical, liquid cooled, 4-cycle diesel engine
Number of cylinders 3
Bore Stroke mm (in.) 67 68 (2.64 2.68)
Total displacement CC (cu. in.) 719 (43.89)
SAE net
Cont. H.P.
SAE net
Intermittent H.P.
SAE gross
Intermittent H.P.
DIN 6271-NA
Brake horse power
DIN 6271-NB
DIN 70020
Maximum bare speed 3850 r/min
Minimum bare idling speed 3150 3250 r/min
Combustion chamber Spherical type
Fuel Injection pump Bosch MD mini pump
Governor Centrifugal ball mechanical governor
Direction of rotation Counter-clockwise (Viewed from flywheel)
Injection nozzle Bosch throttle type
Injection timing 0.35 to 0.38 rad. (20 to 22) before T.D.C.
Injection order 1-2-3
Injection pressure 13.73 MPa (140 kgf/cm2, 1991 psi)
Compression ratio 23 : 1
Lubricating system Forced lubrication by pump
Oil Pressure indication Electrical type switch
Lubricating filter Full flow paper filter (Cartridge type)
Cooling system Pressurized radiator, forced circulation with water pump
Starting support device by glow plug in combustion chamber
Battery 12 V, 36 AH, equivalent
Generator for charging 12 V, 150 W
Fuel Diesel fuel No.2-D (ASTM D975)
Lubricating oil API service CD or CE
Lubricating oil capacity 3.1 (3.3 U.S.qts., 2.7 Imp.qts)
Weight (Dry) 74.4 kg (164 lbs)
Application Generator
12.2 kW/3600 r/min
16.3 HP/3600 r/min
14.0 kW/3600 r/min
18.8 HP/3600 r/min
15.6 kW/3600 r/min
20.9 HP/3600 r/min
12.1 kW/3600 r/min
16.4 PS/3600 r/min
13.3 kW/3600 r/min
18.1 PS/3600 r/min
14.6 kW/3600 r/min
19.9 PS/3600 r/min
Electric starting with cell starter
12 V, 1.0 kW
2-1

D722-B (YMH)
(SAE) (DIN)
2
1 Brake horsepower
2 Engine speed
3 B.S.F.C.
4 Torque
5 Gross intermittent torque
6 Net intermittent torque
7 Net cont. torque
8 Gross intermittent B.H.P.
9 Net intermittent B.H.P.
10 Net cont. B.H.P.
11 B.S.F.C. (Net intermittent)
2-2

DIMENSIONS
D722-B (YMH)
2-3

MAINTENANCE SPECIFICATIONS
CYLINDER HEAD
Item
Cylinder head surface flatness
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
–
Top clearance 0.50 to 0.70 mm
0.0197 to 0.0276 in.
Cylinder head gasket thickness
(Grommet section)
Free
Tightened
1.15 to 1.30 mm
0.04153 to 0.0512 in.
1.05 to 1.15 mm
0.0413 to 0.0453 in.
Compression pressure 2.84 to 3.24 MPa
29 to 33 kgf/cm
412 to 469 psi
VALVES
Valve clearance (Cold)
0.145 to 0.185 mm
0.0057 to 0.0073 in.
Valve seat width 2.12 mm
0.0835 in.
Valve seat angle 0.785 rad
45
0.05 mm
0.0020 in.
–
–
–
2.26 MPa
2
23 kgf/cm
2
327 psi
–
–
–
Valve face angle 0.785 rad
45
Valve recessing –0.10 to 0.10 mm
–0.0039 to 0.0039 in.
Clearance between valve stem and valve
guide
0.030 to 0.057 mm
0.00118 to 0.00224 in.
Valve stem diameter 5.968 to 5.980 mm
0.23496 to 0.23543 in.
Valve guide inside diameter 6.010 to 6.025 mm
0.23661 to 0.23720 in.
VALVE TIMING
Inlet valve
Open 0.35 rad (20) before T.D.C.
Close 0.79 rad (45) after B.D.C.
Exhaust valve
Open 0.87 rad (50) before B.D.C.
Close 0.26 rad (15) after T.D.C.
–
0.30 mm
0.0118 in.
0.10 mm
0.0039 in.
–
–
–
–
–
–
2-4

VALVE SPRING
Item
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Free length 31.6 mm
1.244 in.
Setting load/Setting length 64.7 N/27 mm
6.6 kgf/27 mm
14.6 lbs/1.063 in.
Tilt
–
ROCKER ARM
Clearance between rocker arm shaft and
shaft hole
0.016 to 0.045 mm
0.00063 to 0.00177 in.
Rocker arm shaft diameter 10.473 to 10.484 mm
0.41232 to 0.41276 in.
Rocker arm shaft hole inside diameter 10.500 to 10.518 mm
0.41339 to 0.41410 in.
TAPPET
Clearance between tappet and guide
0.016 to 0.052 mm
0.00063 to 0.00205 in.
28.4 mm
1.118 in.
54.9 N/27 mm
5.6 kgf/27 mm
12.3 lbs/1.063 in.
1.2 mm
0.047 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
–
–
0.10 mm
0.0039 in.
Tappet diameter 17.966 to 17.984 mm
0.70732 to 0.70803 in.
Tappet guide inside diameter 18.000 to 18.018 mm
0.70866 to 0.70937 in.
CAMSHAFT
Camshaft side clearance
0.15 to 0.31 mm
0.0059 to 0.01220 in.
Camshaft alignment
–
Cam height (IN., EX.) 26.88 mm
1.0583 in.
Oil clearance of camshaft 0.050 to 0.091 mm
0.0020 to 0.0036 in.
Camshaft journal diameter 32.934 to 32.950 mm
1.2966 to 1.2972 in.
Camshaft bearing inside diameter 33.000 to 33.025 mm
1.2992 to 1.3002 in.
–
–
0.5 mm
0.020 in.
0.01 mm
0.0004 in.
26.83 mm
1.0563 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
–
–
2-5

TIMING GEAR
Item
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Timing gear backlash
Crank gear – Oil pump drive gear 0.041 to 0.123 mm
0.00161 to 0.00484 in.
Idle gear – Cam gear 0.047 to 0.123 mm
0.00185 to 0.00484 in.
Idle gear – Injection pump gear 0.046 to 0.124 mm
0.00181 to 0.00488 in.
Idle gear – Crank gear 0.043 to 0.124 mm
0.00169 to 0.00488 in.
Idle gear side clearance 0.20 to 0.51 mm
0.0079 to 0.0201 in.
Clearance between idle gear shaft and idle
gear bushing
0.020 to 0.084 mm
0.00079 to 0.00331 in.
Idle gear shaft diameter 19.967 to 19.980 mm
0.78610 to 0.78661 in.
Idle gear bushing indisde diameter 20.000 to 20.051 mm
0.78740 to 0.78941 in.
CYLINDER LINER
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.60 mm
0.0236 in.
0.10 mm
0.0039 in.
–
–
Cylinder liner inside diameter
67.000 to 67.019 mm
2.63779 to 2.63854 in.
Oversized cylinder liner inside diameter 67.250 to 67.269 mm
2.64764 to 2.64839 in.
CRANKSHAFT
Crankshaft alignment
Oil clearance between crankshaft and
crankshaft bearing 1
0.034 to 0.106 mm
0.00134 to 0.00417 in.
–
Crankshaft diameter 39.934 to 39.950 mm
1.57221 to 1.57284 in.
Crankshaft bearing 1 inside diameter 39.984 to 40.040 mm
1.57418 to 1.57638 in.
Oil clearance between crankshaft and
crankshaft bearing 2
0.034 to 0.092 mm
0.00134 to 0.00362 in.
Crankshaft diameter 43.934 to 43.950 mm
1.72969 to 1.73032 in.
Crankshaft bearing 2 inside diameter 43.984 to 44.026 mm
1.73166 to 1.73331 in.
67.169 mm
2.64444 in.
67.419 mm
2.65429 in.
0.02 mm
0.0031 in.
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
–
–
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
–
–
2-6

CRANKSHAFT
Item
Oil clearance between crankshaft and
crankshaft bearing 3
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
0.034 to 0.092 mm
0.00134 to 0.00362 in.
Crankshaft diameter 39.934 to 39.950 mm
1.57221 to 1.57284 in.
Crankshaft bearing 3 inside diameter 39.984 to 40.026 mm
1.57418 to 1.57583 in.
Oil clearance between crank pin and crank
pin bearing
0.019 to 0.081 mm
0.00075 to 0.00319 in.
Crankshaft diameter 33.959 to 33.975 mm
1.33697 to 1.33759 in.
Crank pin bearing inside diameter 33.994 to 34.040 mm
1.33835 to 1.34016 in.
Crankshaft side clearance 0.15 to 0.31 mm
0.0059 to 0.0122 in.
CONNECTING ROD
Connecting rod alignment
Clearance between piston pin and small end
bushing
0.014 to 0.038 mm
0.00055 to 0.00150 in.
–
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
–
–
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
–
–
0.5 mm
0.0197 in.
0.05 mm
0.0020 in.
0.10 mm
0.0039 in.
Piston pin diameter 20.002 to 20.011 mm
0.78748 to 0.78783 in.
Small end bushing inside diameter 20.025 to 20.040 mm
0.78839 to 0.78897 in.
PISTON/PISTON RING
Piston pin hole inside diameter
20.000 to 20.013 mm
0.78740 to 0.78791 in.
Piston ring clearance
Ring gap
Second compression
ring 2
Oil ring
Top compression
ring and oil ring
Second compression
ring
0.085 to 0.115 mm
0.0033 to 0.0045 in.
0.02 to 0.06 mm
0.0008 to 0.0024 in.
0.15 to 0.30 mm
0.0059 to 0.0118 in.
0.30 to 0.45 mm
0.0118 to 0.0177 in.
Oversize of piston rings +0.25 mm
+0.0098 in.
–
–
20.05 mm
0.7894 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
1.2 mm
0.0472 in.
1.2 mm
0.0472 in.
–
2-7

OIL PUMP
Engine oil pressure
Item
At idle
speed
At rated
speed
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
98 kPa
2
1.0 kgf/cm
, 14 psi
196 to 441 kPa
2.0 to 4.5 kgf/cm
28 to 64 psi
Clearance between inner rotor and outer
rotor
Clearance between outer rotor and pump
body
0.03 to 0.14 mm
0.012 to 0.0055 in.
0.07 to 0.15 mm
0.0028 to 0.0059 in.
End clearance between inner rotor and cover 0.075 to 0.135 mm
0.0029 to 0.0053 in.
THERMOSTAT
Thermostat’s valve opening temperature
69.5 to 72.5C
157.1 to 162.5F
Temperature at which thermostat completely
opens
85C
185F
RADIATOR
–
98 kPa
2
1.0 kgf/cm
2
14 psi
–
–
–
–
–
Radiator water tightness
Water tightness at
specified pressure
157 kPa
1.6 kgf/cm
2
, 23 psi
Radiator cap air leakage 10 seconds or more
88 59 kPa
0.9 0.6 kgf/cm
13 9 psi
Fan belt tension Approx. 10 mm/10 kgf
0.39 in./10 kgf (22.1 lbs.)
INJECTION PUMP
Injection timing
0.35 to 0.38 rad before
T.D.C. (20 to 22)
Fuel tightness of pumpe element
–
Fuel tightness of delivery valve
–
–
2
–
–
–
14.71 MPa
2
150 kgf/cm
,
2133 psi
5 seconds
14.7 13.7 MPa
150 140 kgf/cm
2
2133 1990 psi
2-8

INJECTION NOZZLE
Item
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Fuel Injection pressure 13.73 to 14.71 MPa
140 to 150 kgf/cm
2
1991 to 2133 psi
Fuel tightness of nozzle valve seat When the pressure is
12.75 MPa (130 kgf/cm
1849 psi), the valve seat
must be fuel tightness
–
2
,
–
2-9

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER
Commutator diameter
Mica undercut 0.5 to 0.8 mm
Brush length 16.0 mm
DYNAMO
No-load voltage
GLOW PLUG
Glow plug resistance
28.0 mm
1.102 in.
0.020 to 0.031 in.
0.630 in.
AC20 V or more
at 5200 rpm
Approx. 0.9 Ω –
27.0 mm
1.063 in.
0.2 mm
0.008 in.
10.5 mm
0.413 in.
–
2-10

GENERATOR SPECIFICATIONS
Out ut
Max. out ut
GENERATOR
SET MODEL
Generator model PX209YK
p
p
Phases 3 Phases 4 wires
Power factor % 80
Voltage V 380/220 220/127
Current A 15.2 31.5
Frequency Hz 50 60
Insulation class F (Stator, Rotor)
Excitation Brushless
Poles 2
Engine revolution r.p.m. 3000 3600
Ambient temperature C –15 +40
Boundary dimensions (mm)
Length Width Height
kVA 10 12
kW 8 9.6
kVA 11 13
kW 8.8 10.4
1020 640 770 (Without wheels)
1020 640 928 (With wheels)
EDL13000TE
Weight kg 260
Engine model D722-B (YMH)
Engine model Vertical type water-cooled 4 cycle diesel
Number of cylinders – Bore Stroke 3 – 67 68
Rating output PS 13.8 16.3
Type 2-pole revolving-field type brushless alternator
Voltage regulating type A.V.R.
Power factor 0.8
Drive type Direct drive by engine
AC overcurrent protective device NFB
Alternating current switch capacity (A) 16 32
Output take off type Terminals
Voltage regulations (%) Less than ± 2.5
Frequency regulations (%) Less than 5
2-11

A.V.R.
Resistance (20C)
U – V
V – W
2.0 Ω 0.5 Ω
W – U
UnitEx.
3 – 4 0.51 Ω ———
J – K 8.25 Ω
U – V
V – W
0.713 Ω
W – U
F+ – F– 24.9 Ω
380 V 220 V
When the alternator is revolved at 3000
(3600) r/min. with DC12 V loaded on the EX
stator coil (F+, F–).
Generated voltage (V)
JK
U – V
V – W
W – U
O – U
O – V
O – W
About 480 V
(About 290 V)
About 277 V
(About 170 V)
NOTE:
Numerical values in ( ) are for 60 Hz, 220
V class.
CAUTION:
To perform this test, remove AVR.
When the alternator is revolved at 3000
(3600) r/min. with A VR and other lead wires
disconnected.
Generated voltage (V)
U – V
V – W
W – U
About 90 V
(About 50 V)
2-12
O – U
O – V
O – W
About 52 V
(About 29 V)

PERIODIC INSPECTIONS AND ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER BLOCK
The engine has a high durability tunnel-type
cylinder block in which the crank bearing
component is a constructed body. Furthermore, liner less type, allow effective cooling,
less distortion, and greater wear-resistance.
The noise level is reduced to a minimum because each cylinder has its own chamber.
CYLINDER HEAD
The cross-flow type intake/exhaust ports in
this engine have their openings at both sides
of the cylinder head. Because overlaps of intake/exhaust ports are smaller than in ports
of other types which have openings on one
side, the suction air can be protected from
being heated and expanded by heated exhaust air. The cool, high density suction air
has high volume efficiency and raises the
power of the engine. Furthermore, distortion
of the cylinder head by heated exhaust gas
is reduced because intake ports are arranged alternately. The combustion chamber is exclusive New TVCS combustion
chamber type. Suction air is whirled to be
mixed effectively with fuel, prompting combustion and reducing fuel consumption.
In the combustion chamber are installed
throttle type injection nozzle and rapid heating sheathed type glow plug. This glow plug
assures easier than ever engine starts even
at – 15C (5°F).
Combustion chamber
1
Intake port
2
Exhaust port
3
Nozzle assembly
4
Glow plug
5
Cylinder head
6
Fan-shaped concave
7
Stream
8
Air inlet
9
3-1
Combustion system
These engine use the “NTVCS” (New Three
Vortex Combustion System) to achieve perfect combustion for maximum power. The
NTVCS combustion system provides unique
9
shape of throat in the air inlet
tion chamber, to produce three streams
1
air in the chamber
when compressing, giv-
for combus-
8
of
ing an ideal mixture of air and fuel.
7
In addition, a fan-shaped concave
is provided on top of the piston to allow a smooth
ejection of the exhaust gas, offering highly
efficient combustion.

CRANKSHAFT
The crankshaft with the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston
into the rotating motion.
The crankshaft is made of tough special alloy
steel, and the journals, pins and oil seal sliding
portions are induction hardened to increase
the hardness for higher wear resistance.
The front journal is supported by a solid type
bearing, the intermediate journal by a split
type, and the rear journal by a split type with
thrust bearings.
The crankshaft is provided with an oil gallery ,
through which engine oil is fed to the crank
pin portion, and lubricate it.
PISTON AND PISTON RINGS
The piston is made of aluminum alloy.
Two recesses for the valves are provided on
top of the piston. A fan-shaped depression is
also given stop the piston in order to allow
combustion gas to jet smoothly. The piston
pin is slightly out of the center of the piston.
In this design, the run-out of the piston at the
top and bottom dead points can be reduced,
thereby resulting in lower operating noise.
The piston has a slightly oval shape when
cold (in consideration of thermal expansion)
and a concave head.
Three rings are installed in grooves in the
piston.
1
The top ring
stand against heavy loads, and the barrel face
on the ring fits well to the cylinder wall.
The second ring
effectively prevents the oil from being carried
up.
The oil ring
and an expander ring, which increase the pressure of the oil ring against the cylinder wall.
Several grooves are cut on the topland to
help heat dissipate and to prevent scuffing.
Fan-shaped concave
4
Valve recess
5
is a keystone type, which can
2
is an undercut type, which
3
has chamfered contact faces
3
3-2
CONNECTING ROD
2
Connecting rod
piston with the crankshaft. The big end of the
connecting rod has a crank pin bearing
(split type) and the small end has a small end
1
bushing
(solid type).
is used to connect the
3

CAMSHAFT
3
The camshaft
is made of special cast iron
and the journal and cam sections are chilled to
resist wear. The journal sections are force-lu-
5
bricated. The fuel camshaft
controls the reciprocating movement of the injection pump.
The fuel camshaft is made of carbon steel and
the cam sections are quenched and tempered
to provide greater wear resistance.
1 Cam gear
2 Camshaft stopper
3 Camshaft
4 Injection pump gear
5 Fuel camshaft
FLYWHEEL
The flywheel stores the rotating force in the
combustion stroke as inertial energy , reduces
crankshaft rotating speed fluctuation and
maintains the smooth rotating conditions.
The flywheel periphery is inscribed with the
marks showing top dead center mark TC.
The flywheel periphery is inscribed with the
fuel injection period mark FI.
The flywheel has gear teeth around its outer
rim, which mesh with the drive pinion of the
starter.
1 Crankshaft
2 Flywheel
3 Flywheel screw
ROCKER ARM
The rocker arm assembly includes the rock-
1
er arms
er arm shaft
, rocker arm brackets 4 and rock-
5
and converts the reciprocating movement of the push rods to an
open/ close movement of the inlet and exhaust valves.
Lubricating oil is pressurized through the
bracket to the rocker arm shaft, which serves
as a fulcrum so that the rocker arm and the
entire system are lubricated sufficiently.
1 Rocker arm
2 Lock nut
3 Adjusting screw
4 Rocker arm bracket
5 Rocker arm shaft
VALVE TIMING
The timing for opening and closing the valve
is extremely important to achieve effective
air intake and sufficient gas exhaust.
The appropriate timing can be obtained by
aligning the marks on the crank gear and the
cam gear when assembling.
Inlet valve open 0.35 rad. (20) before T.D.C.
Inlet valve close 0.79 rad. (45) after B.D.C.
Exhaust valve open 0.87 rad. (50) before B.D.C.
Exhaust valve close 0.26 rad. (15) after T.D.C.
1
2
3
4
T.D.C. TOP DEAD CENTER. .
B.D.C. BOTTOM DEAD CENTER. .
3-3

LUBRICATING SYSTEM
GENERAL, LUBRICATING SYSTEM
This engine’s lubricating system consists of oil strainer, oil pump, relief
valve, oil filter cartridge and oil
switch. The oil pump sucks lubricating oil from the oil pan through the oil
strainer and the oil flows down to the
filter cartridge, where it is further filtered. Then the oil is forced to crankshaft, connecting rods, idle gear,
camshaft and rocker arm shaft to lubricate each part.
Some part of oil, splashed by the
crankshaft or leaking and dropping
from gaps of each part, lubricates
these parts: pistons, cylinders, small
ends of connecting rods, tappets,
pushrods, inlet and exhaust valves
and timing gears.
3-4
Engine oil flow
1 Oil pan
2 Oil strainer
3 Oil pump
4 Relief valve
5 Oil filter cartridge
6 Idle gear
7 Main oil gallery
8 Main bearing
9 Big end
10 Timing gear
11 Splash
12 Bore
13 Small end
14 Piston
15 Fuel camshaft
16 Tappets
17 Camshaft bearing
18 Camshaft
19 Drain
20 Rocker arm
21 Oil switch
22 Rocker arm shaft
[A]Oil pump
[B]Oil strainer
[C]Rocker arm and rocker
arm shaft
[D]Piston
[E]Camshaft
[F] Oil filter cartridge and
relief valve

OIL PUMP
The oil pump is a trochoid pump, whose rotors have trochoid lobes. The inner rotor
3
has 4 lobes and the outer rotor 4 has 5
lobes, and they are eccentrically engaged
with each other. The inner rotor, which is
driven by the crankshaft through the gears,
rotates the outer rotor in the same direction,
varying the space between the lobes.
While the rotors rotate from
A
to B, the
space leading to the inlet port increases,
which causes the vacuum to suck in the oil
from the inlet port
When the rotors rotate to
1
.
C
, the space between both rotors switches from the inlet port
to the outlet port.
D
At
, the space decreases and the sucked
2
oil is discharged from the outlet port
.
RELIEF VALVE
The relief valve prevents the damage to the
lubricating system due to the high pressure
of the oil.
The relief valve is ball direct acting type, and
is best suited for low pressures.
When the pressure of the oil, forced by the
pump, exceeds the specified value, the oil
pushes back the ball
2
and escapes to the
oil pan.
1 Spring
2 Ball
3 Valve seat
3-5
OIL FILTER CARTRIDGE
After lubricating, the lubricating oil brings back
various particles of grit and dirt to the oil pan.
Those particles and the impurities in the lubricating oil can cause wear or seizure of the engine parts. It may also impair the physical and
chemical properties of the oil itself.
The lubricating oil which is force-fed by the
pump, is filtered by the filter cartridge with
the filter element
2
. When the filter element
accumulates on excessive amount of dirt
and the oil pressure in the inlet line builds up
by 98 kPa (1.0 kgf / cm
the outlet line, the bypass valve
2
, 14 psi) more than
1
opens to
allow the oil to flow from the inlet into the outlet line, bypassing the filter element.

OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
The oil pressure switch is mounted on the
cylinder block and is led to the lubricating oil
passage.
When the oil pressure falls below the specified value, the oil pressure warning lamp
lights.
[A]At the proper oil
pressure
1 Terminal
2 Insulator
3 Spring
4 Rubber gasket
[B]At lower oil pressure,
49 kPa (0.5 kgf/cm2,
7 psi) or less
5 Contact rivet
6 Contact
7 Oil switch body
3-6

COOLING SYSTEM
GENERAL, COOLING SYSTEM
1 Radiator
2 Suction fan
3 Water pump
4 Thermostat
5 Cylinder head
6 Cylinder block
The cooling system consists of a radiator , centrifugal water pump , suction fan and thermostat .
4
3
1
2
The water is cooled through the radiator core, and
the fan set behind the radiator pushs cooling air
through the core to improve cooling.
The water pump sucks the cooled water, forces it
into the cylinder block and draws out the hot water.
Then the cooling is repeated. Furthermore, to
control temperature of water, a thermostat is provided in the system. When the thermostat opens,
the water moves directly to radiator, but when it
closes, the water moves toward the water pump
through the bypass between thermostat and water pump. The opening temperature of thermostat
is approx. 71C (160F).
WATER PUMP
The water pump is driven by the crankshaft
via a V-belt. Water cooled in the radiator is
sucked into the water pump from its lower
portion and is sent from the center of the wa-
4
ter pump impeller
radially outward into
the water jacket in the crankcase.
The special mechanical seal is installed as a
seal between bearing and pump chamber,
which is effective to water and heat.
1 Bearing unit
2 Water pump body
3 Mechanical seal
4 Water pump impeller
3-7
 Loading...
Loading...