Page 1

ML310 User
Guide
Virtex-II Pro Embedded
Development Platform
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
R
Page 2

R
"Xilinx" and the Xilinx logo shown above are registered trademarks of Xilinx, Inc. Any rights not expressly granted herein are reserved.
CoolRunner, RocketChips, Rocket IP, Spartan, StateBENCH, StateCAD, Virtex, XACT, XC2064, XC3090, XC4005, and XC5210 are
registered trademarks of Xilinx, Inc.
The shadow X shown above is a trademark of Xilinx, Inc.
ACE Controller, ACE Flash, A.K.A. Speed, Alliance Series, AllianceCORE, Bencher, ChipScope, Configurable Logic Cell, CORE Generator,
CoreLINX, Dual Block, EZTag, Fast CLK, Fast CONNECT, Fast FLASH, FastMap, Fast Zero Power, Foundation, Gigabit Speeds...and
Beyond!, HardWire, HDL Bencher, IRL, J Drive, JBits, LCA, LogiBLOX, Logic Cell, LogiCORE, LogicProfessor, MicroBlaze, MicroVia,
MultiLINX, NanoBlaze, PicoBlaze, PLUSASM, PowerGuide, PowerMaze, QPro, Real-PCI, RocketIO, SelectIO, SelectRAM, SelectRAM+,
Silicon Xpresso, Smartguide, Smart-IP, SmartSearch, SMARTswitch, System ACE, Testbench In A Minute, TrueMap, UIM, VectorMaze,
VersaBlock, V e rsaRing, Virtex-II Pro, Virtex-II EasyPath, Wave Table, WebFITTER, WebPACK, WebPOWERED, XABEL, XACTFloorplanner, XACT-Performance, XACTstep Advanced, XACT step Foundry , XAM, XAPP, X-BLOX +, XC designated products, XChecker,
XDM, XEPLD, Xilinx Foundation Series, Xilinx XDTV, Xinfo, XSI, XtremeDSP and ZERO+ are trademarks of Xilinx, Inc.
The Programmable Logic Company is a service mark of Xilinx, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Xilinx, Inc. does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product described or shown herein; nor does it convey
any license under its patents, copyrights, or maskwork rights or any rights of others. Xilinx, Inc. reserves the right to make changes, at any
time, in order to improve reliability, function or design and to supply the best product possible. Xilinx, Inc. will not assume responsibility for
the use of any circuitry described herein other than circuitry entirely embodied in its products. Xilinx provides any design, code, or
information shown or described herein "as is." By providing the design, code, or information as one possible implementation of a feature,
application, or standard, Xilinx makes no representation that such implementation is free from any claims of infringement. You are
responsible for obtaining any rights you may require for your implementation. Xilinx expressly disclaims any warranty whatsoever with
respect to the adequacy of any such implementation, including but not limited to any warranties or representations that the implementation
is free from claims of infringement, as well as any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Xilinx, Inc. devices
and products are protected under U.S. Patents. Other U.S. and foreign patents pending. Xilinx, Inc. does not represent that devices shown
or products described herein are free from patent infringement or from any other third party right. Xilinx, Inc. assumes no obligation to
correct any errors contained herein or to advise any user of this text of any correction if such be made. Xilinx, Inc. will not assume any liability
for the accuracy or correctness of any engineering or software support or assistance provided to a user.
Xilinx products are not intended for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems. Use of a Xilinx product in such applications without
the written consent of the appropriate Xilinx officer is prohibited.
The contents of this manual are owned and copyrighted by Xilinx. Copyright 1994-2004 Xilinx, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Except as stated
herein, none of the material may be copied, reproduced, distributed, republished, downloaded, displayed, posted, or transmitted in any form
or by any means including, but not limited to, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written consent
of Xilinx. Any unauthorized use of any material contained in this manual may violate copyright laws, trademark laws, the laws of privacy and
publicity, and communications regulations and statutes.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
1-800-255-7778
Page 3
ML310 User Guide
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
The following table shows the revision history for this document..
Version Revision
08/15/04 1.0 Initial Xilinx release.
08/25/04 1.01 Added SysACE CFGADDR details.
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778
Page 4

ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
1-800-255-7778
Page 5

Table of Contents
Preface: About This Manual
Chapter 1: Introduction to Virtex-II Pro, ISE, and EDK
Virtex-II Pro . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Summary of Virtex-II Pro Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
PowerPC™ 405 Core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
RocketIO 3.125 Gb/s Transceivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Virtex-II FPGA Fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Foundation ISE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Foundation Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Design Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Synthesis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Implementation and Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Board Level Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Embedded Development Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Board Hardware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Clock Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
DDR Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
DDR DIMM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
DDR Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
DDR Memory Expansion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Serial Port FPGA UART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Introduction to Serial Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Signaling Standards of RS-232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
RS-232 on the ML310 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
System ACE CF Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Board Bring-Up. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Non-Volatile Storage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
XC2VP30 Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
JTAG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
JTAG Connection to XC2VP30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Parallel Cable IV Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
System ACE JTAG Configuration Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
GPIO LEDs and LCD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
GPIO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
GPIO LED Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
GPIO LCD Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
CPU Debug and CPU Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
CPU Debug Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
CPU Debug Connector Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
CPU Debug Connection to XC2VP30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 5
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 6

R
PCI Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
ALi South Bridge Interface, M1535D+, U15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Parallel Port Interface, connector assembly P1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Serial Port Interface, connector assembly P1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
USB, connector assembly J3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
IDE, connectors J15 and J16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
GPIO, connector J5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
System Management Bus (SMBus) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
AC97 Audio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Interface, connector P2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Flash ROM, U4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Intel GD82559, U11, 10/100 Ethernet Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Intel GD82559 Ethernet Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
IIC/SMBus Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Introduction to IIC/SMBus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
IIC/SMBus Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
IIC/SMBus on ML310 Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
SPI Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
SPI Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Push Buttons, Switches, Front Panel Interface and Jumpers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Push Buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
System ACE Configuration Dipswitch, SW3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Front Panel Interface Connector, J23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Jumpers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
ATX Power Distribution and Voltage Regulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
High-Speed I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
ML310 PM Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
PM1 Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
PM2 Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Adapter Board PM Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
ML310 PM Utility Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Contact Order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
PM1 Power and Ground. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
PM2 Power and Ground. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
ML310 PM User I/O Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
PM1 User I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
ML310 PM2 User I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
6 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 7
R
About This Manual
This manual accompanies the ML310 Embedded Development System and contains
information about the ML310 Hardware Platform and software tools.
Manual Contents
This manual contains the following chapters:
• Chapter 1, “Introduction to Virtex-II Pro, ISE, and EDK,” provides an overview of the
hardware and software features.
• Chapter 2, “ML310 Embedded Development Platform,” provides an overview of the
embedded development platform and details the components and features of the
ML310 board.
Preface
Additional Resources
For additional information, go to http://support.xilinx.com. The following table lists
some of the resources you can access from this website. You can also directly access these
resources using the provided URLs.
Resource Description/URL
Tutorials Tutorials covering Xilinx design flows, from design entry to
Answer Browser Database of Xilinx solution records
Application Notes Descriptions of device-specific design techniques and approaches
Data Sheets Device-specific information on Xilinx device characteristics,
verification and debugging
http://support.xilinx.com/support/techsup/tutorials/index.htm
http://support.xilinx.com/xlnx/xil_ans_browser.jsp
http://support.xilinx.com/apps/appsweb.htm
including readback, boundary scan, configuration, length count,
and debugging
http://support.xilinx.com/xlnx/xweb/xil_publications_index.jsp
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 7
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 8
R
Conventions
Typographical
Chapter :
Resource Description/URL
Problem Solvers Interactive tools that allow you to troubleshoot your design issues
http://support.xilinx.com/support/troubleshoot/psolvers.htm
Tech Tips Latest news, design tips, and patch information for the Xilinx
design environment
http://www.support.xilinx.com/xlnx/xil_tt_home.jsp
This document uses the following conventions. An example illustrates each convention.
The following typographical conventions are used in this document:
Convention Meaning or Use Example
Messages, prompts, and
Courier font
program files that the system
displays
speed grade: - 100
Courier bold
Helvetica bold
Italic font
Square brackets [ ]
Braces { }
Literal commands that you
enter in a syntactical statement
Commands that you select
from a menu
Keyboard shortcuts Ctrl+C
Variables in a syntax
statement for which you must
supply values
References to other manuals
Emphasis in text
An optional entry or
parameter. However, in bus
specifications, such as
bus[7:0], they are required.
A list of items from which you
must choose one or more
ngdbuild design_name
File → Open
ngdbuild design_name
See the Development System
Reference Guide for more
information.
If a wire is drawn so that it
overlaps the pin of a symbol,
the two nets are not connected.
ngdbuild [ option_name]
design_name
lowpwr ={on|off}
Vertical bar |
8 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
Separates items in a list of
choices
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
lowpwr ={on|off}
Page 9
Convention Meaning or Use Example
R
Vertical ellipsis
Horizontal ellipsis . . .
Online Document
The following conventions are used in this document:
Convention Meaning or Use Example
Blue text
Red text
Blue, underlined text
IOB #1: Name = QOUT’
.
.
Repetitive material that has
been omitted
.
Repetitive material that has
been omitted
Cross-reference link to a
location in the current file or
in another file in the current
document
Cross-reference link to a
location in another document
Hyperlink to a website (URL)
IOB #2: Name = CLKIN’
.
.
.
allow block block_name
loc1 loc2 ... locn;
See the section “Additional
Resources” for details.
Refer to “Title Formats” in
Chapter 1 for details.
See Figure 2-5 in the Virtex-II
Handbook.
Go to http://www.xilinx.com
for the latest speed files.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 9
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 10

R
Chapter :
10 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 11

R
Chapter 1
Introduction
Virtex-II Pro
The Virtex-II Pro Platform FPGA solution is the most technically sophisticated silicon and
software product development in the history of the programmable logic industry. The goal
was to revolutionize system architecture “from the ground up.” To achieve that objective,
the best circuit engineers and system architects from IBM, Mindspeed, and Xilinx codeveloped the world's most advanced Platform FPGA silicon product. Leading teams from
top embedded systems companies worked together with Xilinx software teams to develop
the systems software and IP solutions that enabled new system architecture paradigm.
The result is the first Platform FPGA solution capable of implementing high performance
system-on-a-chip designs previously the exclusive domain of custom ASICs, yet with the
flexibility and low development cost of programmable logic. The Virtex-II Pro family
marks the first paradigm change from programmable logic to programmable systems,
with profound implications for leading-edge system architectures in networking
applications, deeply embedded systems, and digital signal processing systems. It allows
custom user-defined system architectures to be synthesized, next-generation connectivity
standards to be seamlessly bridged, and complex hardware and software systems to be codeveloped rapidly with in-system debug at system speeds. Together, these capabilities
usher in the next programmable logic revolution.
to Virtex-II Pro, ISE, and EDK
Summary of Virtex-II Pro Features
The Virtex-II Pro has an impressive collection of both programmable logic and hard IP that
has historically been the domain of the ASICs.
• High-performance Platform FPGA solution including
♦ Up to twenty-four RocketIO™ embedded multi-gigabit transceiver blocks (based
on Mindspeed's SkyRail™ technology)
♦ Up to four IBM® PowerPC™ RISC processor blocks
• Based on Virtex™-II Platform FPGA technology
♦ Flexible logic resources, up to 125,136 Logic Cells
♦ SRAM-based in-system configuration
♦ Active Interconnect™ technology
♦ SelectRAM™ memory hierarchy
♦ Up to 556 Dedicated 18-bit x 18-bit multiplier blocks
♦ High-performance clock management circuitry
♦ SelectIO™-Ultra technology
♦ Digitally Controlled Impedance (DCI) I/O
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 11
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 12
R
Chapter 1: Introduction to Virtex-II Pro, ISE, and EDK
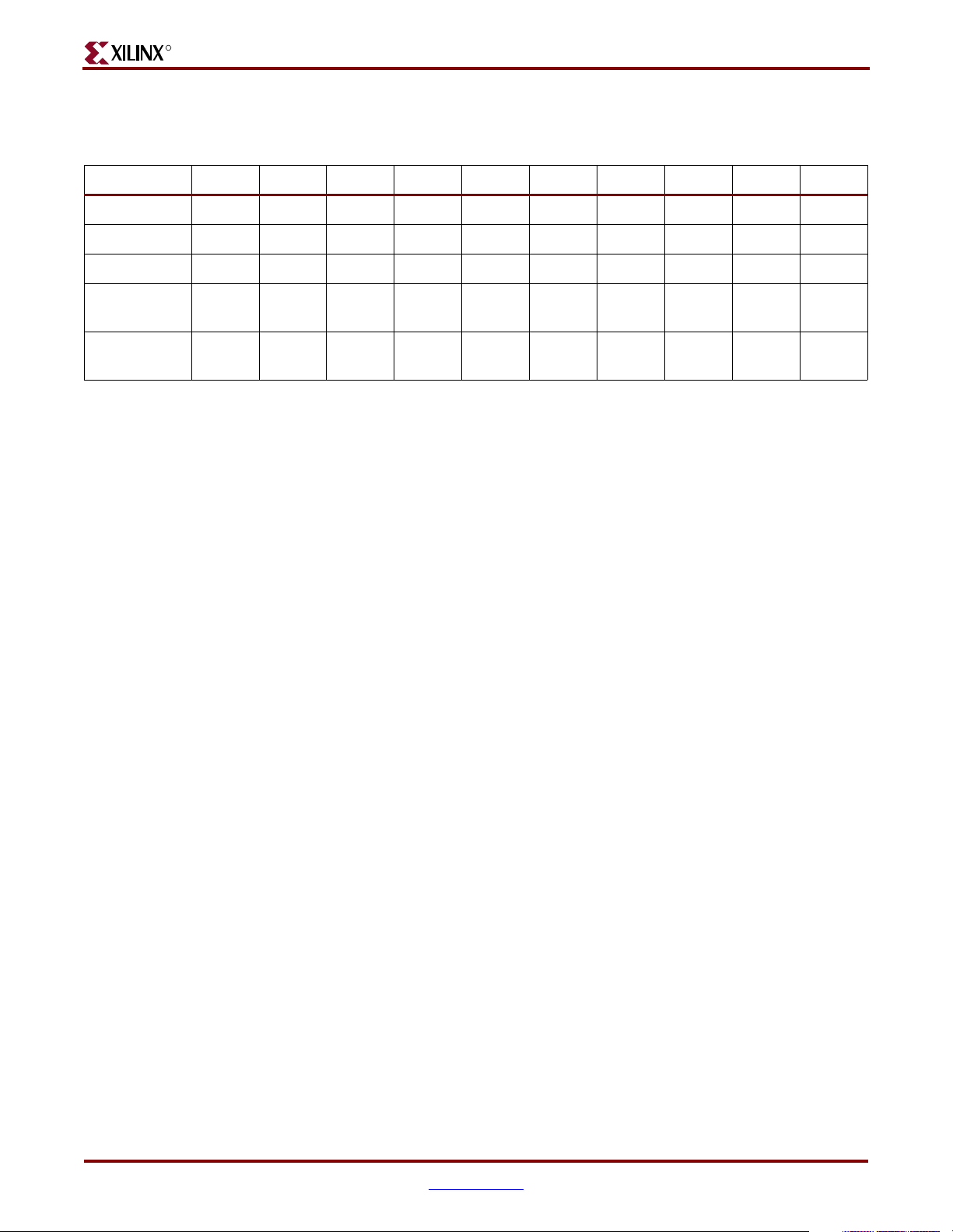
Table 1-1: Virtex-II Pro Family Members
Device 2VP2 2VP4 2VP7 2VP20 2VP30 2VP40 2VP50 2VP70 2VP100 2VP125
Logic Cells 3,168 6,768 11,088 20,880 30,816 43,632 53,136 74,448 99,216 125,136
PPC4050112222224
MGTs 448881216202024
BRAM
(Kbits)
Xtreme
Multipliers
216 504 792 1,584 2,448 3,456 4,176 5,904 7,992 10,008
12 28 44 88 136 192 232 328 444 556
PowerPC™ 405 Core
• Embedded 300+ MHz Harvard architecture core
• Low power consumption: 0.9 mW/MHz
• Five-stage data path pipeline
• Hardware multiply/divide unit
• Thirty-two 32-bit general purpose registers
• 16 KB two-way set-associative instruction cache
• 16 KB two-way set-associative data cache
• Memory Management Unit (MMU)
♦ 64-entry unified Translation Look-aside Buffers (TLB)
♦ Variable page sizes (1 KB to 16 MB)
• Dedicated on-chip memory (OCM) interface
• Supports IBM CoreConnect™ bus architecture
• Debug and trace support
• Timer facilities
RocketIO 3.125 Gb/s T r ansceivers
• Full-duplex serial transceiver (SERDES) capable of baud rates from 622 Mb/s
to 3.125 Gb/s
• 80 Gb/s duplex data rate (16 channels)
• Monolithic clock synthesis and clock recovery (CDR)
• Fibre Channel, Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gb Attachment Unit Interface (XAUI), and
Infiniband-compliant transceivers
• 8-, 16-, or 32-bit selectable internal FPGA interface
• 8B /10B encoder and decoder
• 50Ω/75Ω on-chip selectable transmit and receive terminations
• Programmable comma detection
• Channel bonding support (two to sixteen channels)
• Rate matching via insertion/deletion characters
12 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 13

Virtex-II Pro
R
• Four levels of selectable pre-emphasis
• Five levels of output differential voltage
• Per-channel internal loopback modes
• 2.5V transceiver supply voltage
Virtex-II FPGA Fabric
Description of the Virtex-II Family fabric follows:
• SelectRAM memory hierarchy
♦ Up to 10 Mb of True Dual-Port RAM in 18 Kb block SelectRAM resources
♦ Up to 1.7 Mb of distributed SelectRAM resources
♦ High-performance interfaces to external memory
• Arithmetic functions
♦ Dedicated 18-bit x 18-bit multiplier blocks
♦ Fast look-ahead carry logic chains
• Flexible logic resources
♦ Up to 111,232 internal registers/latches with Clock Enable
♦ Up to 111,232 look-up tables (LUTs) or cascadable variable (1 to 16 bits) shift
registers
♦ Wide multiplexers and wide-input function support
♦ Horizontal cascade chain and Sum-of-Products support
♦ Internal 3-state busing
• High-performance clock management circuitry
♦ Up to eight Digital Clock Manager (DCM) modules
- Precise clock de-skew
- Flexible frequency synthesis
- High-resolution phase shifting
♦ 16 global clock multiplexer buffers in all parts
• Active Interconnect technology
♦ Fourth-generation segmented routing structure
♦ Fast, predictable routing delay, independent of fanout
♦ Deep sub-micron noise immunity benefits
• Select I/O-Ultra technology
♦ Up to 852 user I/Os
♦ Twenty two single-ended standards and five differential standards
♦ Programmable LVTTL and LVCMOS sink/source current (2 mA to 24 mA) per
I/O
♦ Digitally Controlled Impedance (DCI) I/O: on-chip termination resistors for
single-ended I/O standards
♦ PCI support(1)
♦ Differential signaling
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 13
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 14

R
Chapter 1: Introduction to Virtex-II Pro, ISE, and EDK
- 840 Mb/s Low-Voltage Differential Signaling I/O (LVDS) with current mode
drivers
- Bus LVDS I/O
- HyperTransport™ (LDT) I/O with current driver buffers
- Built-in DDR input and output registers
♦ Proprietary high-performance SelectLink technology for communications
between Xilinx devices
- High-bandwidth data path
- Double Data Rate (DDR) link
- Web-based HDL generation methodology
• SRAM-based in-system configuration
♦ Fast SelectMAP™ configuration
♦ Triple Data Encryption Standard (DES) security option (bitstream encryption)
♦ IEEE1532 support
♦ Partial reconfiguration
♦ Unlimited reprogrammability
♦ Readback capability
• Supported by Xilinx Foundation™ and Alliance™ series development systems
♦ Integrated VHDL and Verilog design flows
♦ ChipScope™ Pro Integrated Logic Analyzer
• 0.13-µm, nine-layer copper process with 90 nm high-speed transistors
• 1.5V (VCCINT) core power supply, dedicated 2.5V VCCAUX auxiliary and VCCO
I/O power supplies
• IEEE 1149.1 compatible boundary-scan logic support
• Flip-Chip and Wire-Bond Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages in standard 1.00 mm pitch
• Each device 100% factory tested
Foundation ISE
ISE Foundation is the industry's most complete programmable logic design environment.
ISE Foundation includes the industry's most advanced timing driven implementation
tools available for programmable logic design, along with design entry, synthesis and
verification capabilities. With its ultra-fast runtimes, ProActive Timing Closure
technologies, and seamless integration with the industry's most advanced verification
products, ISE Foundation offers a great design environment for anyone looking for a
complete programmable logic design solution.
Foundation Features
Design Entry
ISE greatly improves your “Time-to- Market”, productivity, and design quality with robust
design entry features.
ISE provides support for today's most popular methods for design capture including HDL
and schematic entry, integration of IP cores as well as robust support for reuse of your own
14 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 15

Foundation ISE
R
IP. ISE even includes technology called IP Builder, which allows you to capture your own
IP and reuse it in other designs.
ISE’s Architecture Wizards allow easy access to device features like the Digital Clock
Manager and Multi-Gigabit I/O technology.
ISE also includes a tool called PACE (Pinout Area Constraint Editor) which includes a
front-end pin assignment editor, a design hierarchy browser, and an area constraint editor.
By using PACE, designers are able to observe and describe information regarding the
connectivity and resource requirements of a design, resource layout of a target FPGA, and
the mapping of the design onto the FPGA via location/area.
This rich mixture of design entry capabilities provides the easiest to use design
environment available today for your logic design.
Synthesis
Synthesis is one of the most essential steps in your design methodology. It takes your
conceptual Hardware Description Language (HDL) design definition and generates the
logical or physical representation for the targeted silicon device.
A state of the art synthesis engine is required to produce highly optimized results with a
fast compile and turnaround time. To meet this requirement, the synthesis engine needs to
be tightly integrated with the physical implementation tool and have the ability to
proactively meet the design timing requirements by driving the placement in the physical
device. In addition, cross probing between the physical design report and the HDL design
code will further enhance the turnaround time.
Xilinx ISE provides the seamless integration with the leading synthesis engines from
Mentor Graphics, Synopsys, and Synplicity. You can use the synthesis engine of our choice.
In addition, ISE includes Xilinx proprietary synthesis technology, XST. You have options to
use multiple synthesis engines to obtain the best-optimized result of your programmable
logic design.
Implementation and Configuration
Programmable logic design implementation assigns the logic created during design entry
and synthesis into specific physical resources of the target device.
The term “place and route” has historically been used to describe the implementation
process for FPGA devices and “fitting” has been used for CPLDs. Implementation is
followed by device configuration, where a bitstream is generated from the physical place
and route information and downloaded into the target programmable logic device.
To ensure designers get their product to market quickly, Xilinx ISE software provides
several key technologies required for design implementation:
• Ultra-fast runtimes enable multiple “turns” per day
• ProActive™ Timing Closure drives high-performance results
• Timing-driven place and route combined with “push-button” ease
• Incremental Design
• Macro Builder
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 15
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 16

R
Board Level Integration
Xilinx understands the critical issues such as complex board layout, signal integrity, highspeed bus interface, high-performance I/O bandwidth, and electromagnetic interference
for system level designers.
To ease the system level designers’ challenge, ISE provides support to all Xilinx leading
FPGA technologies:
• System IO
• XCITE
• Digital clock management for system timing
• EMI control management for electromagnetic interference
To really help you ensure your programmable logic design works in context of your entire
system, Xilinx provides complete pin configurations, packaging information, tips on signal
integration, and various simulation models for your board level verification including:
• IBIS models
• HSPICE models
• STAMP models
Chapter 1: Introduction to Virtex-II Pro, ISE, and EDK
Embedded Development Kit
The Embedded Development Kit (EDK) is Xilinx’s solution for embedded programmable
systems design and supports designs using the Virtex-II Pro. EDK hardware and software
development tools, combined with the advanced features of Virtex-II Pro FPGA provide
you with a new level of system design.
The system design process can be loosely divided into the following tasks:
• Build the software application
• Simulate the hardware description
• Simulate the hardware with the software application
• Simulate the hardware into the FPGA using the software application in on-chip
memory
• Run timing simulation
• Configure the bitstream for the FPGA
16 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 17
R
ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Overview
The ML310 Embedded Development Platform offers designers a versatile Virtex-II Pro
XC2VP30-FF896 based platform for rapid prototyping and system verification. In addition
to the more than 30,000 logic cells, over 2,400 Kb of BRAM, dual PowerPC™ 405 processors
and RocketIO transceivers available in the FPGA, the ML310 provides an onboard
Ethernet MAC/PHY, DDR memory, multiple PCI bus slots, and standard PC I/O ports
within an ATX form factor board. An integrated System ACE CF controller is deployed to
perform board bring-up and to load applications from the included 512 MB CompactFlash
card.
The ML310 CDROM contains documentation and tutorials, along with reference designs
and data sheets. The most recent ML310 material can be found on the Xilinx web site at
http://www.xilinx.com/ml310
.
Chapter 2
The setup and quickstart documentation highlights the functionality of the ML310 using
the applications shipped on the included CompactFlash card. The reference designs were
produced using the Xilinx Embedded Development Kit (EDK), ISE and Answer Database
solution records. Tutorials in coordination with Xilinx documentation for EDK, ISE, and
the Answer Database, describe how the reference designs and applications were produced.
These tutorials may be used to re-create the applications provided and also as a basis for
the development of new designs. Xilinx EDK provides for the development of basic board
specific systems beginning with Base System Builder (BSB) to highly customized systems
leveraging the flexibility of Xilinx Platform Studio (XPS) and the EDK IP.
Documentation for Xilinx tools and solutions can be found at:
• EDK: http://www.xilinx.com/edk
• ISE: http://www.xilinx.com/ise
• Answer Database: http://www.xilinx.com/support
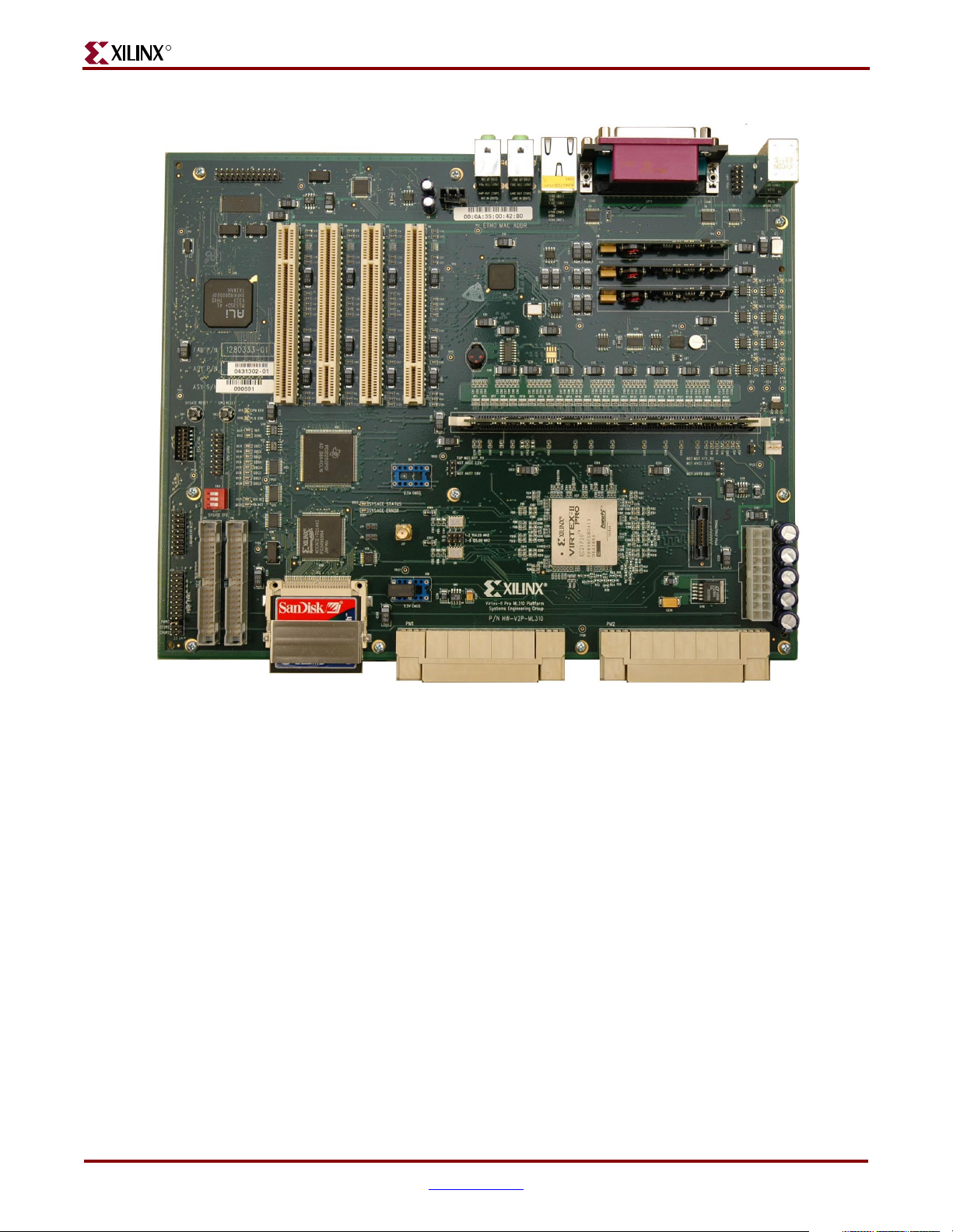
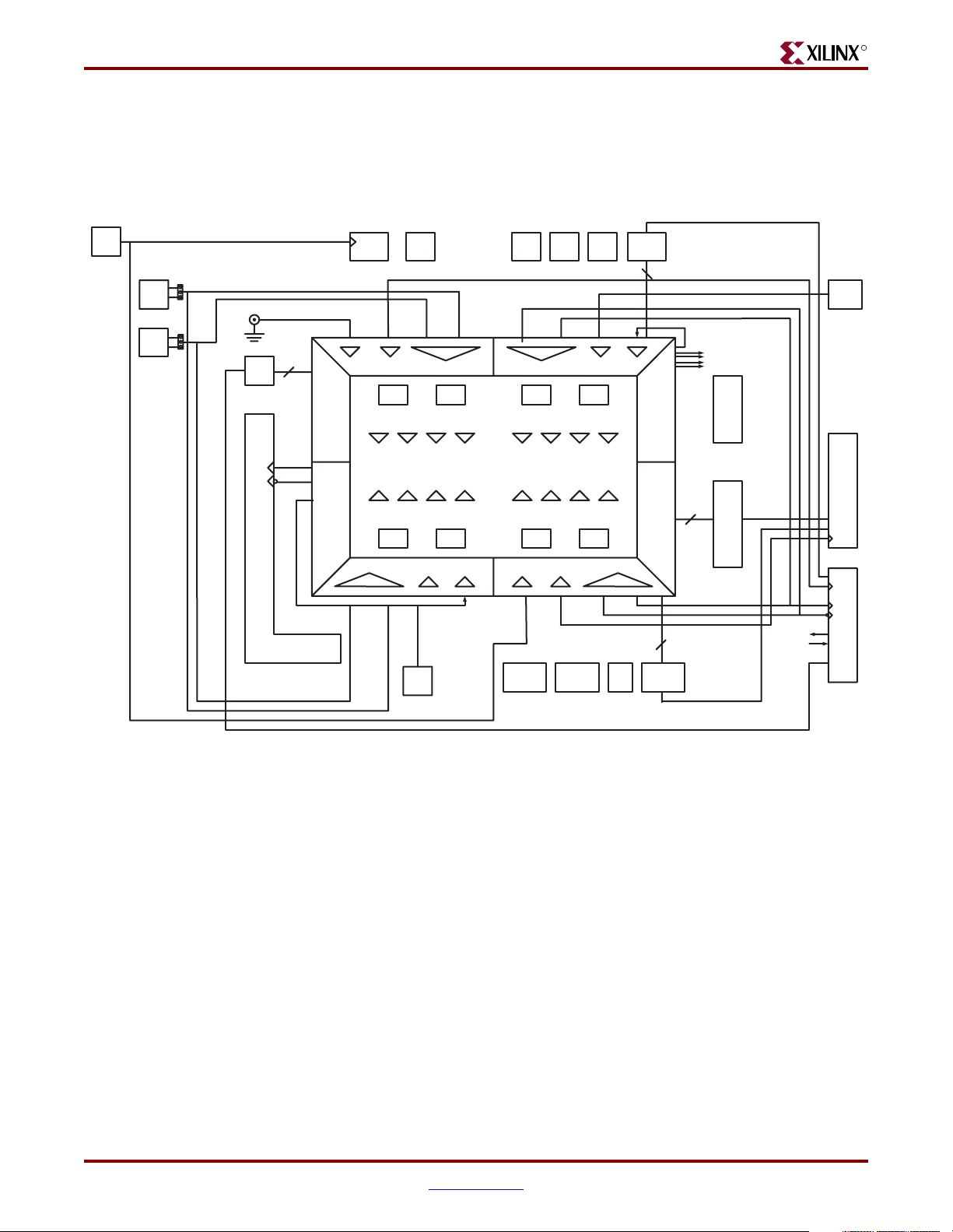
An image of the ML310 board and its corresponding block diagram are shown in,
Figure 2-1and Figure 2-2 respectively.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 17
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 18
R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Figure 2-1: ML310 Board
18 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 19
Overview
R
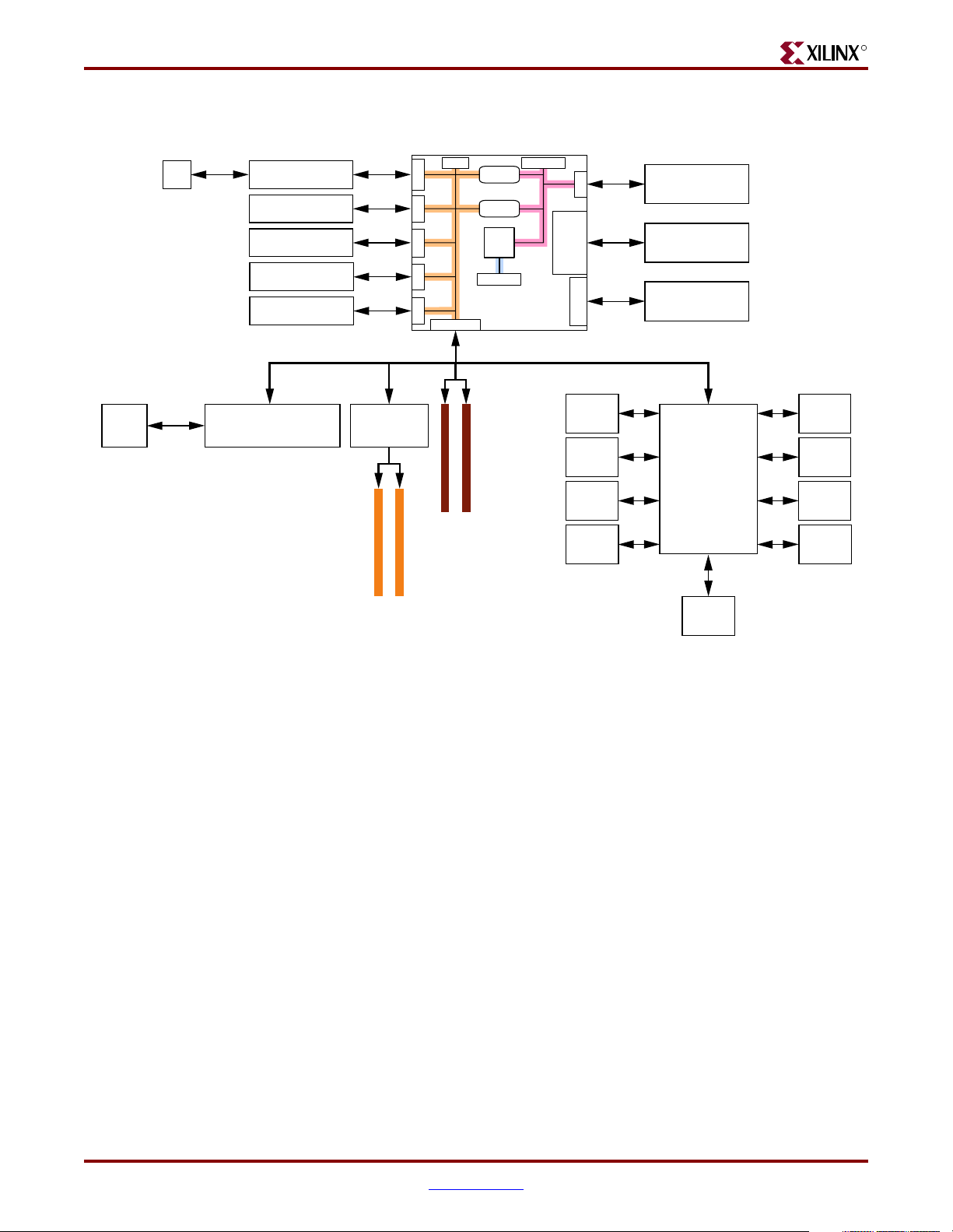
Figure 2-2 shows a high-level block diagram of the ML310 and its peripherals.
RJ45
System ACECF
RS232
SMBus
SPI
GPIO / LEDs
Intel GD82559
10/100 Ethernet NIC
5V PCI
Slots
5V PCI
3.3V PCI
TI
PCI 2250
UART SysACEGPIO SPI
SMBus
INTC
OPB
Bus
PCI Bridge
OPB2PLB
Bridge
PLB2OPB
Bridge
PPC
405
OCM
Bus
OCM BRAM
XC2VP30
FF896
3.3V PCI
Slots
PLB BRAM
PLB
Bus
DDR
8 RocketIO MGTs
3 LVDS pairs
1 LVDS Clock pair
38 Single-Ended I/O
39 LVDS Pairs
1 Clock
AMD
Flash
GPIO
IDE
(2)
USB
(2)
256 MB
DDR DIMM
High-Speed
PM1
High-Speed
PM2
ALi
M1535D+
South Bridge
RS232
(2)
PS/2
K/M
Parallel
Port
SMBus
Features
Audio
Figure 2-2: ML310 High-Level Block Diagram
In addition to the Virtex-II Pro™ FPGA with the embedded PPC405, the ML310 board
features the following:
• ATX Motherboard formfactor
• 256 MB DDR DIMM
• System ACE™ CF Controller
• 512 MB CompactFlash card
• Onboard 10/100 Ethernet NIC
• 4 PCI slots (3.3V and 5V)
• LCD character display and cable
• FPGA serial port connection
• RS-232 mini-cable
• Personality module interface for RocketIO and LVDS access
• Standard JTAG connectivity
• ALi Super I/O
♦ 1 parallel and 2 serial ports
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 19
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 20

R
• ATX power supply
Board Hardware
The ML310 Virtex-II Pro FPGA is connected to several peripherals listed below. The
peripherals are either directly connected to the FPGA or in directly accessible via the PCI
Bus. The following sections describe the main features of each of the peripherals and how
they interface with the Xilinx Virtex-II Pro. The EDK Processor IP Reference Guide should be
reviewed as well as each of the data sheets corresponding to the devices listed. All device
data sheets are located on the ML310 CDROM.
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
♦ 2 USB ports
♦ 2 IDE connectors
♦ GPIO
♦ SMBus Interface
♦ AC97 Audio CODEC
♦ PS/2 keyboard and mouse ports
• DDR DIMM Memory, compatible with EDK supported IP and SW drivers
• FPGA UART, compatible with EDK supported IP and SW drivers
• System ACE, compatible with EDK supported IP and SW drivers
• GPIO- LEDs / LCD, compatible with EDK supported IP and SW drivers
• PCI Bus Interface, compatible with EDK supported IP and SW drivers
♦ ALi M1535D+ PCI Device
♦ Intel Ethernet/NIC PCI Device
• SMBus/IIC, multiple devices available, compatible with EDK supported IP and SW
drivers
♦ LTC1694 SMBUS accelerator
♦ RTC8566 Real time clock
♦ 24LC64 EEPROM 64k bits
♦ LM87 voltage/temp monitor
♦ DDR DIMM SPD EEPROM
• SPI EEPROM, compatible with EDK supported IP and SW drivers
• High speed IO through RocketIO Transceivers
Clock Generation
The ML310 board employs a Xilinx XC2VP30-FF896 FPGA. Several clocks are distributed
throughout the ML310 as can be seen in Figure 2-3. The main system clock is a 100 MHz
oscillator, X10. The system clock is typically used to generate multiple clocks with varying
frequency and phases within the FPGA fabric by using the Virtex-II Pro DMCs. The FPGA
also generates and drives clocks required by the DDR DIMM memory and PCI bus
interfaces.
The FPGA requires different banking voltages that are set based on the I/O voltage
interface requirements of each device connected directly to the FPGA. All but two of the
banks are set to 2.5V while banks 1 and 2 are set to 3.0V as shown in Figure 2-3. The Virtex-
20 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 21
Board Hardware
R
II Pro FPGA I/O can be configured to use different IO standards such as SSTL2 as required
on the DDR DIMM interface. Please review the ML310 Virtex-II Pro data sheet for more
information regarding I/O standards.
Figure 2-3 shows the top-level clocking for the ML310 board.
X8
OSC
33MHz
X7
OSC
156.25
MHz
X9
OSC
125MHz
SYACE_FPGA_CLK
J20
J21
LVDS_CLK_LOC_P
LVDS_CLK_LOC_N
J17
PM IO
12
2.5V
LVDS
(6 LVDS)
DDR
Note:
DIMM
All 3 DDR
64 bit
Clock nets
256MB
are length
matched
DDR_CLK
DDR_CLKB
USER_SMA_CLK
BANK 7
2.5V
BANK 6
2.5V
DDR_CLK_FB
7P 6S 5P 4S 3P 2S 1P 0S
7S 6P 5S 4P 3S 2P 1S 0P
LVDS_CLK_LOC_N
BANK 0
2.5V
DCM
X0Y1
DCM
X0Y0
BANK 5
2.5V
LVDS_CLK_LOC_P
OSC
PM_CLK_TOP
DCM
X1Y1
DCM
X1Y0
DDR_CLK_FB
(not used)
USER_CLKSYS
X6
SYACE_FPGA_CLK
LEDsLCDSYSACE IIC UART
LVDS_CLK_EXT_N
LVDS_CLK_EXT_P
BANK 1
3.0V
CPU
DEBUG
DCM
X2Y1
DCM
X2Y0
DCM
X03Y1
DCM
X3Y0
BANK 4
2.5V
PM_CLK_BOT
SYS_CLK
(user_clk_pci)
SPITRACE
PM IO
3V
BANK 2
3.0V
BANK 3
2.5V
26
PCI_P_CLK5
72
6
(3 LVDS)
PM IO
2.5V
PCI_P_CLK1
thru
PCI_P_CLK4
PCI
BUS
3.0V
PM IO
2.5V
(36 LVDS)
LVDS
LVDS_CLK_EXT_P
LVDS_CLK_EXT_N
Note:
All 5 PCI
Clock nets
are length
matched
(to FPGA)
8
MGTs
X10
OSC
100MHz
PM2
PM1
Figure 2-3: Top-Level Clocking
DDR Memory
DDR DIMM
The ML310 includes a registered 256MB PC3200 Double Data Rate (DDR) Dual Inline
Memory Module (DIMM) with an industry standard 184-pin count. The DDR DIMM is
commercially available from Wintec Industries as part number W4F232726HA-5Q. The
associated datasheet is provided on the ML310 CDROM. The DDR DIMM is
manufactured using nine Infineon HYB25D256800BT-5, 32Mx8 DDR SDRAM devices with
13-row address lines, 10-column address lines, and 4 bank select lines. Read and write
access to the Infineon devices is programmable in burst lengths of 2, 4, or 8 column
locations. The memory module inputs and outputs are compatible with SSTL2 signaling.
Serial Presence Detect (SPD) using an SMBus interface to the DDR DIMM is also
supported. Please refer to section “IIC/SMBus Interface” for more details on accessing the
DIMM module’s SPD EEPROM.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 21
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 22

R
DDR Signaling
The FPGA DDR DIMM interface supports SSTL2 signaling. All DDR signals are controlled
impedance and are SSTL2 terminated.
DDR Memory Expansion
The FPGA is capable of replicating up to three differential clock output pairs to the DIMM
in order to support either registered or unbuffered DIMMs. The ML310 DDR interface is
very flexible in the event different DDR memory is desired such as an unbuffered DIMM or
increased memory size. The DDR interface core delivered with EDK supports both
registered and unbuffered DRR Memory interfaces. Please review the EDK Processor IP
Reference Guide when migrating to a different DDR DIMM.
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
(U37)
IBUFG
LVCMOS
25
CLKIN
CLKFB
DCM
CLK0
CLK90
CLKIN
CLKFB
CLK90
Phase Shift
DCM
DDR_CLK_FB_in
BUFG
BUFG
CLK0
PLB_CLK
CLK90_IN
BUFG
BUFG
DDR_CLK90_in
FDDRSE
D0
D1
C0
C1
FDDRSE
D0
D1
C0
C1
FDDRSE
D0
D1
C0
C1
C
CE
Q
D
SSTL2_I
SSTL2_I
LVCMOS
SSTL2_I
DQS_i
SSTL2_II
DDR_CLK
DDR_CLK_N
DDR_CLK_FB_out
25
ADDR
DDR Control
DDR_DQ/DQS
DDR DIMM (P7)
Figure 2-4: DDR DIMM Interface Block Diagram
Ta bl e 2 -1 lists the connections from the FPGA to the DDR DIMM interface. Please note that
the DDR_DQ signal names do not correlate as the FPGA uses IBM notation, Big Endian,
while the DDR DIMMs use Intel notation, Little Endian.
Table 2-1: Connections from FPGA to DIMM Interface, P7
UCF Signal Name
XC2VP30 Pin
(U37)
Schem Signal Name
ddr_ad[0] AE23 DDR_A0 48
ddr_ad[1] AJ23 DDR_A1 43
22 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
DIMM
(P7)
Page 23

Board Hardware
R
Table 2-1: Connections from FPGA to DIMM Interface, P7
UCF Signal Name
ddr_ad[2] AG20 DDR_A2 41
ddr_ad[3] AF23 DDR_A3 130
ddr_ad[4] AH22 DDR_A4 37
ddr_ad[5] AF22 DDR_A5 32
ddr_ad[6] AF21 DDR_A6 125
ddr_ad[7] AH21 DDR_A7 29
ddr_ad[8] AG21 DDR_A8 122
ddr_ad[9] AJ21 DDR_A9 27
ddr_ad[10] AK21 DDR_A10 141
dd r_ad [11] AH 20 DD R_A 11 118
ddr_ad[12] AF20 DDR_A12 115
ddr_ba[0] AG18 DDR_BA0 59
ddr_ba[1] AF19 DDR_BA1 62
ddr_casb AF17 DDR_CAS_N 65
ddr_cke AG24 DDR_CKE0 21
ddr_csb AE17 DDR_S0_N 157
ddr_rasb AE16 DDR_RAS_N 154
XC2VP30 Pin
(U37)
Schem Signal Name
DIMM
(P7)
ddr_web AD16 DDR_WE_N 63
ddr_clk V30 DDR_CK0 137
ddr_clkb U30 DDR_CK0_N 138
ddr_clk_fb AF16 DDR_CLK_FB N/A
ddr_clk_fb_out AG25 DDR_CLK_FB N/A
ddr_dm[0] AH29 DDR_DQM07 177
ddr_dm[1] AE29 DDR_DQM06 169
ddr_dm[2] AA24 DDR_DQM05 159
ddr_dm[3] AB30 DDR_DQM04 149
ddr_dm[4] P30 DDR_DQM03 129
ddr_dm[5] M30 DDR_DQM02 119
ddr_dm[6] K24 DDR_DQM01 107
ddr_dm[7] E30 DDR_DQM00 97
ddr_dqs[0] AG30 DDR_DQS07 86
ddr_dqs[1] AF30 DDR_DQS06 78
ddr_dqs[2] AA28 DDR_DQS05 67
ddr_dqs[3] Y29 DDR_DQS04 56
ddr_dqs[4] P28 DDR_DQS03 36
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 23
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 24

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Table 2-1: Connections from FPGA to DIMM Interface, P7
UCF Signal Name
ddr_dqs[5] M29 DDR_DQS02 25
ddr_dqs[6] H29 DDR_DQS01 14
ddr_dqs[7] F29 DDR_DQS00 5
ddr_dq[0] AG28 DDR_DQ63 179
ddr_dq[1] AG26 DDR_DQ62 178
ddr_dq[2] AE26 DDR_DQ61 175
ddr_dq[3] AD26 DDR_DQ60 174
ddr_dq[4] AH27 DDR_DQ59 88
ddr_dq[5] AH26 DDR_DQ58 87
ddr_dq[6] AF25 DDR_DQ57 84
ddr_dq[7] AD25 DDR_DQ56 83
ddr_dq[8] AF28 DDR_DQ55 171
ddr_dq[9] AD28 DDR_DQ54 170
ddr_dq[10] AB25 DDR_DQ53 166
ddr_dq[11] AB26 DDR_DQ52 165
ddr_dq[12] AF27 DDR_DQ51 80
ddr_dq[13] AD27 DDR_DQ50 79
XC2VP30 Pin
(U37)
Schem Signal Name
DIMM
(P7)
ddr_dq[14] AC25 DDR_DQ49 73
ddr_dq[15] AC26 DDR_DQ48 72
ddr_dq[16] AC27 DDR_DQ47 162
ddr_dq[17] AC28 DDR_DQ46 161
ddr_dq[18] AA26 DDR_DQ45 155
ddr_dq[19] Y26 DDR_DQ44 153
ddr_dq[20] AB27 DDR_DQ43 69
ddr_dq[21] AB28 DDR_DQ42 68
ddr_dq[22] AA25 DDR_DQ41 64
ddr_dq[23] Y27 DDR_DQ40 61
ddr_dq[24] W28 DDR_DQ39 151
ddr_dq[25] W25 DDR_DQ38 150
ddr_dq[26] V27 DDR_DQ37 147
ddr_dq[27] V25 DDR_DQ36 146
ddr_dq[28] W27 DDR_DQ35 60
ddr_dq[29] W26 DDR_DQ34 57
ddr_dq[30] V28 DDR_DQ33 55
ddr_dq[31] V26 DDR_DQ32 53
24 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 25

Board Hardware
R
Table 2-1: Connections from FPGA to DIMM Interface, P7
UCF Signal Name
ddr_dq[32] N27 DDR_DQ31 133
ddr_dq[33] P26 DDR_DQ30 131
ddr_dq[34] R25 DDR_DQ29 127
ddr_dq[35] R27 DDR_DQ28 126
ddr_dq[36] N28 DDR_DQ27 40
ddr_dq[37] P27 DDR_DQ26 39
ddr_dq[38] R26 DDR_DQ25 35
ddr_dq[39] R28 DDR_DQ24 33
ddr_dq[40] K27 DDR_DQ23 123
ddr_dq[41] L26 DDR_DQ22 121
ddr_dq[42] M27 DDR_DQ21 117
ddr_dq[43] N26 DDR_DQ20 114
ddr_dq[44] K28 DDR_DQ19 31
ddr_dq[45] L27 DDR_DQ18 28
ddr_dq[46] M28 DDR_DQ17 24
ddr_dq[47] N25 DDR_DQ16 23
ddr_dq[48] K25 DDR_DQ15 110
XC2VP30 Pin
(U37)
Schem Signal Name
DIMM
(P7)
ddr_dq[49] K26 DDR_DQ14 109
ddr_dq[50] J27 DDR_DQ13 106
ddr_dq[51] J28 DDR_DQ12 105
ddr_dq[52] M25 DDR_DQ11 20
ddr_dq[53] M26 DDR_DQ10 19
ddr_dq[54] J25 DDR_DQ09 13
ddr_dq[55] J26 DDR_DQ08 12
ddr_dq[56] H28 DDR_DQ07 99
ddr_dq[57] G27 DDR_DQ06 98
ddr_dq[58] F28 DDR_DQ05 95
ddr_dq[59] E27 DDR_DQ04 94
ddr_dq[60] H27 DDR_DQ03 8
ddr_dq[61] G28 DDR_DQ02 6
ddr_dq[62] F27 DDR_DQ01 4
ddr_dq[63] E28 DDR_DQ00 2
The connections from the FPGA to the DDR DIMM support either a registered or an
unbuffered DIMM. The only difference from a connectivity perspective is that the
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 25
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 26

R
unbuffered DIMM requires more than one clock input pair versus a single clock input pair
for a registered DIMM.
Ta bl e 2 -2 shows optional clocking connections that are required for interfacing the FPGA
to unbuffered DDR DIMMs.
Table 2-2: Optional DDR DIMM Clocks for use with Unbuffered DIMMs
Schem Signal XC2VP30 (U37) DIMM (P7)
DDR_CK1 K29 16
DDR_CK1_N L29 17
DDR_CK2 AD30 76
DDR_CK2_N AD25 75
Note:
All 3 DDR differential clock pairs are length matched and controlled impedance.
Serial Port FPGA UART
Introduction to Serial Ports
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Serial ports are useful as simple, low-speed interfaces between Data Terminal Equipment
(DTE) such as PCs or terminals and Data Communication Equipment (DCE) such as
modems. A DTE to DCE connection uses a "straight-through" type of cable in which the
transmit (TX) and receive (RX) lines of one end of the cable directly connect to the
corresponding TX and RX wires on the other end of the cable. In a DTE to DTE connection
a "null-modem" type of cable which cross-wires the TX and RX signals from one end of the
cable to the RX and TX signals on the other end is used. Since the ML310 is a DTE, use a
“null modem” cable when connecting to another DTE such as a PC.
Signaling Standards of RS-232
The RS-232 standard specifies output voltage levels between -5 to -15 Volts for logical 1 and
+5 to +15 Volts for logical 0. Inputs must be compatible with voltages in the range of -3V to
-15V for logical 1 and +3V to +15V for logical 0. This ensures data bits are read correctly at
the maximum cable length of 50 feet between two RS-232 connected devices.
Note: A negative voltage represents a logic level 1 while a positive voltage represents a
logic level 0. As these signaling levels are quite high compared to current signaling levels,
transceivers are often used to convert to more manageable levels.
RS-232 on the ML310
Three RS-232 ports are available on the ML310; two ports (P1) are connected to the ALi
M1535D+ South Bridge (U15) and the third (J4) is connected to the XC2VP30 FPGA (U37)
through a MAX3232 Transceiver (U7).
The two RS-232 ports connected to the ALi South Bridge(U15) are wired such that the
ML310 is a DTE device. These two ports on connector P1 are only accessible by the FPGA
through the PCI Bus. Please review section “ALi South Bridge Interface, M1535D+, U15”
for more information as well as the M1535D+ data sheet
The third RS-232 port is connected directly to the XC2VP30 FPGA and can be accessed by
simply implementing a UART in the FPGA fabric. EDK provides many IP cores, including
26 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 27

Board Hardware
XC2VP30
a UART usable with any member of the Virtex-II Pro device family. Please review the EDK
Processor IP Reference Guide for more details.
The RS-232 port directly connected to the XC2VP30 is accessible by a 10 pin header(J4). An
RS-232 mini-cable adapter included with the ML310 converts J4, 10 pin header, to a DB9
male connector. The adapter is a standard DTK/Intel IDC-10 to DB9 Male. The FPGA RS232 port on the ML310 is wired as a DTE and meets the EIA/TIA-574 standard
Figure 2-5 shows the RS-232 connectivity from the XC2VP30 to the DTK adapter.
.
USE A DTK-PINOUT IDC10
TO DB9 PLUG CABLE.
U7U37
0.1UF
0.1UF
C330
C331
11
10
12
9
1
3
DIN1
DIN2
ROUT1
ROUT2
C1+
C1-
MAX3232
UART0_TXD COM0_TXD_N
UART0_RTS_N
UART0_RXD
UART0_CTS_N
DOUT1
DOUT2
RIN1
RIN2
VCC
GNDC2-
14
7
COM0_RTS
13
COM0_RXD_N
8
COM0_CTS
VCC3V3
16
C326
0.1UF
2
V+
64
V-C2+
C327
0.1UF
155
VCC3V3
0.1UF
UG068_5_32_080204
C313
J4
12
34
56
78
910
HEADER2X5
DSR
7
RTS
CTS68
RI
9
RS232 DTE PINOUT
CONNECTS TO PC WITH
F/F NULL MODEL CABLE.
1
2
3
4
5
R
CD
RX
TX
DTR
GND
Figure 2-5: FPGA UART and RS-232 Connectivity
Ta bl e 2 -3 shows the RS-232 connections to the XCV2VP30 FPGA.
Table 2-3: FPGA RS-232 Connections
UCF Signal
XC2VP30 Pin
Name
uart1_ctsn B10 UART0_CTS 6 8
uart1_rtsn G14 UART0_RTS 4 7
uart1_sin F14 UART0_RXD 3 2
uart1_sout F12 UART0_TXD 5 3
System ACE CF Controller
Board Bring-Up
System ACE is the primary means of configuring the XC2VP30 on the ML310
board.Configuration of XC2VP30 is accomplished using the JTAG interface. System ACE
sits between the JTAG connector and the XC2VP30, and passes the JTAG signals back and
forth between the two. However, when System ACE is configuring the XC2VP30, it takes
control of the JTAG signals in order to configure the XC2VP30.
(U37)
Schem Signal
Name
10 pin Header
(J4)
DTK Adap ter
(DB9)
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 27
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 28

R
Non-Volatile Storage
In addition to programming the FPGA and storing bitstreams, System ACE can be used for
general use non-volatile storage. System ACE provides an MPU interface for allowing a
microprocessor to access the CompactFlash, allowing the use of the CompactFlash as a file
system.
XC2VP30 Connectivity
System ACE is connected to the XC2VP30 through both the JTAG chain, for configuration,
and through the MPU port of the System ACE, for allowing the XC2VP30 to control System
ACE and access the CompactFlash. Ta bl e 2 -4 shows the connection between the System
ACE and the XC2VP30. It shows the signal names with associated pins on System ACE and
the XC2VP30 for both the MPU interface.
Table 2-4: System ACE MPU Connection from FPGA to Controller
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
UCF Signal Name
XC2VP30 Pin
(U37)
Schem Signal
Name
sysace_clk_in AF15 sysace_clk_in 93
sysace_clk_oe C22 sysace_clk_oe 77
sysace_mpa[0] B22 sysace_mpa[0] 70
sysace_mpa[1] E19 sysace_mpa[1] 69
sysace_mpa[2] E18 sysace_mpa[2] 68
sysace_mpa[3] H19 sysace_mpa[3] 67
sysace_mpa[4] G19 sysace_mpa[4] 45
sysace_mpa[5] B23 sysace_mpa[5] 44
sysace_mpa[6] A23 sysace_mpa[6] 43
sysace_mpd[0] E20 sysace_mpd[0] 66
sysace_mpd[1] D20 sysace_mpd[1] 65
sysace_mpd[2] H20 sysace_mpd[2] 63
sysace_mpd[3] G20 sysace_mpd[3] 62
sysace_mpd[4] D23 sysace_mpd[4] 61
System ACE
(U38)
sysace_mpd[5] C23 sysace_mpd[5] 60
sysace_mpd[6] E21 sysace_mpd[6] 59
sysace_mpd[7] D21 sysace_mpd[7] 58
sysace_mpoe E23 sysace_mpoe 77
sysace_mpce E22 sysace_mpce 42
sysace_mpwe G23 sysace_mpwe 76
sysace_mpirq F23 sysace_mpirq 41
28 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 29

Board Hardware
0
R
JTAG
JTAG is a simple interface that provides for many uses. On the ML310 Hardware Platform,
the primary uses include configuration of the XC2VP30, debugging software (similar to
the CPU debug interface), and debugging hardware using the ChipScope™ Integrated
Logic Analyzer (ILA).
The Virtex-II Pro family is fully compliant with the IEEE Standard 1149.1 Test Access Port
and Boundary-Scan Architecture. The architecture includes all mandatory elements
defined in the IEEE 1149.1 Standard. These elements include the Test Access Port (TAP),
the TAP controller, the instruction register, the instruction decoder, the boundary-scan
register, and the bypass register. The Virtex-II Pro family also supports some optional
instructions; the 32-bit identification register, and a configuration register in full
compliance with the standard.
JTAG Connection to XC2VP30
The JTAG connector initially connects to the System ACE chip, which passes the JTAG
connections through to the XC2VP30. Figure 2-6 is a block diagram showing the
connections between the JTAG connector, System ACE, and the XC2VP30. This diagram
also shows the logic that allows the CPU JTAG debug connector (J12) to be used to access
the JTAG interface to program the XC2VP30.
J9 PC4
3.3V
J19
PC4_TCK
CPU_TCK
PC4_TMS
CPU_TMS
PC4_TDI
CPU_TDI
PC4_TDO
CPU_TDO
2.5V
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
JTAG_SRC_SEL
J14
Schem Pg. 20
U38
2.5V
2.5V
System ACE XC2VP30
U37
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
CF7
Mode
Pin
2.5V
CFG_TCK
CFG_TMS
CFG_TDI
CFG_TDO
CFG_PROG
CFG_INIT
CFGADDR
2.5V
SW3
Schem Pg. 47
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
PROG
INIT
2.5V
UG068_5_25_0805
Figure 2-6: JTAG Connections to the XC2VP30 and System ACE
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 29
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 30

R
Parallel Cable IV Interface
The Parallel Cable IV (PC IV) download cable can also be used to program the XC2VP30.
The pinout provided in Figure 2-7 is compatible with the PC IV JTAG programming
solution.
Figure 2-7 shows the pinout of the PC IV JTAG connector.
PC4_TDI
SYSACE_TSTTDO
Figure 2-7: PC4 IV JTAG Connector Pinout
System ACE JTAG Configuration Interface
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
GND
GND
GND
GND
NC
NC
13
GND
GND
GND
1
214
VCCV3
PC4_TMS
PC4_TCK
UG000_05_21_082802
The JTAG Configuration port on the System ACE device is connected directly to the JTAG
interface of the XC2VP30 device.Tabl e 2- 5 shows the JTAG connections from System ACE
to the XC2VP30.
Table 2-5: JTAG Connection from System ACE to XC2VP30
Pin Name System ACE (U38) XC2VP30 (U37)
FPGA_TCK 80 G7
FPGA_TDO 81 F5
FPGA_TDI 82 F26
FPGA_TMS 85 H8
GPIO LEDs and LCD
GPIO
The ML310 Hardware Platform provides direct GPIO access to eight LEDs for general
purpose use and provides indirect access to a 16 pin connector (J13) used to interface the
ML310 with a 2 Line by 16 character LCD Display, AND491GST. Access to the GPIO lines
is handled by a simple register interface that is connected XC2VP30 GPIO signals.
Figure 2-8 shows the connectivity of the ML310 LEDs and LCD.
The user also has an indirect access path to more GPIO capability via PCI Bus accesses
when controlling the GPIO header (J5) connected to the ALi M1535D+ South Bridge.
Please refer to section “ALi South Bridge Interface, M1535D+, U15” for more details on
programming and controlling the ALi M1535D+ GPIO port.
30 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 31

Board Hardware
DBG_LED_0
DBG_LED_1
DBG_LED_2
DBG_LED_3
DBG_LED_4
DBG_LED_5
DBG_LED_6
DBG_LED_7
OPB_BUS_ERROR
PLB_BUS_ERROR
FPGA_DONE
FPGA_INIT
FPGA_LCD_RS
FPGA_LCD_E
FPGA_LCD_RW
FPGA_LCD_DIR
FPGA_LCD_DB0
FPGA_LCD_DB1
FPGA_LCD_DB2
FPGA_LCD_DB3
FPGA_LCD_DB4
FPGA_LCD_DB5
FPGA_LCD_DB6
FPGA_LCD_DB7
VCC3V3
U36
20
VCCA
1
1OE
2
1A1
4
1A2
6
1A3
8
1A4
19
2OE
11
2A1
13
2A2
15
2A3
17 3
2A4 2Y4
BUFFER
NON-INVERTING
SN74LVC244A
R399
4.75K
VCC3V3
U33
20
VCCA
1
1OE
2
1A1
4
1A2
6
1A3
8
1A4
19
2OE
11
2A1
13
2A2
15
2A3
17 3
2A4
BUFFER
NON-INVERTING
R358
R388
0
VCC2V5 VCC3V3
SN74LVC244A
4.75K
U35
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
R373
4.75K
VCCA
DIR
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
VOLTAGE LEVEL
A8
GND1
GND2
18
1Y1
16
1Y2
14
1Y3
12
1Y4
9
2Y1
7
2Y2
5
2Y3
10
GND
18
1Y1
16
1Y2
14
1Y3
12
1Y4
9
2Y1
7
2Y2
5
2Y3
2Y4
10
GND
24
VCCB
23
NC
NC
22
OE
21
B1
20
B2
19
B3
18
B4
17
B5
16
TRANSLATOR
B6
15
B7
14
B8
1312
GND3
LCD_RS
LCD_E
LCD_RW
LED_DONE_BUF
LCD_DB0
LCD_DB1
LCD_DB2
LCD_DB3
LCD_DB4
LCD_DB5
LCD_DB6
LCD_DB7
SN74LVCC3245A
Output to Green LEDs
Output to Red/Green LEDs
LED_OPB_ERROR
LED_PLB_ERROR
LED_DONE
LED_INIT
LCD Control
LCD Data
GND
LCD_VLC
LCD_RW
LCD_DB0
LCD_DB2
LCD_DB4
LCD_DB6
LCD_BLV
LCD
J13
12
3
56
7
9
13
15
4
8
10
1211
14
16
R
VCC5V
LCD_RS
LCD_E
LCD_DB1
LCD_DB3
LCD_DB5
LCD_DB7
GND
Figure 2-8: LEDs and LCD Connectivity
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 31
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 32

R
GPIO LED Interface
All LEDs connected to the GPIO lines illuminate Green when driven with a logic zero and
extinguish with a logic one. Ta bl e 2- 6 shows the connections for the GPIO LEDs from the
FPGA to the non-inverting buffer (U36).
Table 2-6: GPIO LED Connection from FPGA to U36
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
UCF Signal Name
XC2VP30 Pin
(U37)
Schem Signal
Name
L VC244 Buffer
(U36)
DBG_LED_0 H13 DBG_LED_0 2 DBG0
DBG_LED_1 G13 DBG_LED_1 4 DBG1
DBG_LED_2 C10 DBG_LED_2 6 DBG2
DBG_LED_3 C11 DBG_LED_3 8 DBG3
DBG_LED_4 J14 DBG_LED_4 11 DBG4
DBG_LED_5 H14 DBG_LED_5 13 DBG5
DBG_LED_6 E14 DBG_LED_6 15 DBG6
DBG_LED_7 D14 DBG_LED_7 17 DBG7
GPIO LCD Interface
The GPIO signals used to connect to the 16 pin LCD header (J13) are organized into two
types of I/O, output only and input/output. There are three output only signals and eight
input/output signals. The eight input/outputs are controlled by the logic level of the
FPGA_LCD_DIR signal. Driving FPGA_LCD_DIR to a logic one configures the LVCC3245
to drive the J13 connector while a logic zero configures the LVCC3245 to drive the
XC2VP30.
LED
Ta bl e 2 -7 shows the data bus signals on the GPIO LCD interface from the FPGA to U35.
Table 2-7: GPIO LCD Data Bus Connection from FPGA to U35
L V CC3245
Translator
(U35)
LCD I/F
(J13)
UCF Signal Name
XC2VP30 Pin
(U37)
Schem Signal
Name
FPGA_LCD_DB0 F19 FPGA_LCD_DB0 3 7
FPGA_LCD_DB1 F20 FPGA_LCD_DB1 4 8
FPGA_LCD_DB2 F17 FPGA_LCD_DB2 5 9
FPGA_LCD_DB3 G17 FPGA_LCD_DB3 6 10
FPGA_LCD_DB4 B21 FPGA_LCD_DB4 7 11
FPGA_LCD_DB5 A21 FPGA_LCD_DB5 8 12
FPGA_LCD_DB6 G18 FPGA_LCD_DB6 9 13
FPGA_LCD_DB7 H18 FPGA_LCD_DB7 10 14
FPGA_LCD_DIR C20 FPGA_LCD_DIR 2 -
32 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 33

Board Hardware
R
The three GPIO signals configured as outputs only are used as control signals that allows
the user to read/write the LCD character display in conjunction with the eight LCD data
signals defined earlier in Ta ble 2 -7 . Please review the AND491GST LCD display data sheet
located on the ML310 CDROM for more detailed information.
Ta bl e 2 -8 shows the control signal connections for the GPIO LCD from the FPGA to U33.
Table 2-8: GPIO LCD Control Signal Connections from FPGA to U33
UCF Signal Name
FPGA_LCD_E C21 FPGA_LCD_E 13 6
FPGA_LCD_RS J17 FPGA_LCD_RS 11 4
FPGA_LCD_RW H17 FPGA_LCD_RW 15 5
CPU Debug and CPU Trace
The ML310 board includes two CPU debugging interfaces, the CPU Debug (J12 header)
and the Combined CPU Trace and Debug (P8 mictor) connector.
These connectors can be used in conjunction with third party tools, or in some cases the
Xilinx Parallel Cable IV, to debug software as it runs on the processor.The PowerPC
CPU core includes dedicated debug resources that support a variety of debug modes for
debugging during hardware and software development. These debug resources include:
• Internal debug mode for use by ROM monitors and software debuggers
• External debug mode for use by JTAG debuggers
• Debug wait mode, which allows the servicing of interrupts while the processor
appears to be stopped
• Real-time trace mode, which supports event triggering for real-time tracing
Debug modes and events are controlled using debug registers in the processor. The debug
registers are accessed either through software running on the processor or through the
JTAG port. The debug modes, events, controls, and interfaces provide a powerful
combination of debug resources for hardware and software development tools. The JTAG
port interface supports the attachment of external debug tools, such as the ChipScope
Integrated Logic Analyzer, a powerful tool providing logic analyzer capabilities for signals
inside an FPGA, without the need for expensive external instrumentation. Using the JTAG
test access port, a debug tool can single-step the processor and examine the internal
processor state to facilitate software debugging. This capability complies with the IEEE
1149.1 specification for vendor-specific extensions and is, therefore, compatible with
standard JTAG hardware for boundary-scan system testing.
XC2VP30 Pin
(U37)
Schem Signal
Name
Buffer (U33)
(1)
L V C244
LCD I/F
(J13)
TM
405
TM
CPU Debug Description
External-debug mode can be used to alter normal program execution. It provides the
ability to debug system hardware as well as software. The mode supports multiple setting
breakpoints, as well as monitoring processor status. Access to processor resources is
provided through the CPU Debug port.
1. http://www.support.xilinx.com/ PowerPC Architecture - Debug (JTAG, Trace), Sept. 12, 2002
2. Virtex-II Pro Platform FPGA Documentation - Volume 2(a): PPC405 User Manual, March 2002 Release, p. 537.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 33
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
(2)
Page 34

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
The PPC405 JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) Debug port complies with IEEE standard
1149.1-1990, IEEE Standard Test Access Port and Boundary Scan Architecture. This
standard describes a method for accessing internal chip resources using a four-signal or
five-signal interface. The PPC405 JTAG Debug port supports scan-based board testing and
is further enhanced to support the attachment of debug tools. These enhancements comply
with the IEEE 1149.1 specifications for vendor-specific extensions and are compatible with
standard JTAG hardware for boundary-scan system testing.
The PPC405 JTAG debug port supports the four required JTAG signals: TCK, TMS, TDI,
and TDO. It also implements the optional TRST signal. The frequency of the JTAG clock
signal can range from 0 MHz (DC) to one-half of the processor clock frequency. The JTAG
debug port logic is reset at the same time the system is reset, using TRST. When TRST is
asserted, the JTAG TAP controller returns to the test-logic reset state.
Refer to the PPC405 Processor Block Manual for more information on the JTAG debug-port
signals. Information on JTAG is found in the IEEE standard 1149.1-1990.
(3)(3)
Figure 2-9 shows a 38-pin Mictor connector that combines the CPU Trace and the CPU
Debug interfaces for high-speed, controlled-impedance signaling. For more information
functions: starting and stopping the processor, single-stepping instruction execution on the
trace-debug capabilities, how trace-debug works, and how to connect an external trace
tool, see the RISCWatch Debugger User’s Guide.
GND, G1, G2, G3, G4, G5
MICTOR 38
037
035
033
031
029
027
025
023
021
019
017
015
013
011
009
007
005
003
001
ATD_8
ATD_9
ATD_10
ATD_11
ATD_12
ATD_13
ATD_14
ATD_15
CPU_TRST_N
CPU_TDI
CPU_TMS
CPU_TCK
CPU_TDO
CPU_HALT_N
2.5V
TRC_TS6
TRC_TS5
TRC_TS4
TRC_TS3
TRC_TS2E
TRC_TS1E
TRC_TS2O
TRC_TS1O
ATD 16
ATD 17
ATD 18
ATD 19
TRC_VSENSE
TRC_CLK
038
036
034
032
030
028
026
024
022
020
018
016
014
012
010
008
006
004
002
UG068_05_20_073004
Figure 2-9: Combined Trace/Debug Connector Pinout
3. Virtex-II Pro Platform FPGA Documentation - Volume 2(a): PPC405 User Manual, March 2002 Release, p. 557.
34 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 35

Board Hardware
R
CPU Debug Connector Pinout
Figure 2-10 shows J12, the 16 pin header used to debug the operation of software in the
CPU. This is done using debug tools such as Parallel Cable IV or third party tools. Refer to
the PPC405 Processor Block Manual for more information on the JTAG debug-port signals.
TMS
HALT_N
15
GND
TCK
TDI
TDO
1
216
TRST
VCC
UG000_05_17_082002
Figure 2-10: CPU Debug Connector (J12)
CPU Debug Connection to XC2VP30
The connection between the CPU debug connector and the XC2VP30 are shown in
Ta bl e 2 -9 . These are attached to the PowerPC™ 405 JTAG debug resources using normal
FPGA routing resources. The JTAG debug resources are not hard-wired to particular pins,
and are available for attachment in the FPGA fabric, making it possible to route these
signals to whichever FPGA pins the user prefers.
Table 2-9: CPU Debug Connection to XC2VP30
Pin Name XC2VP30 Pin (U37) Connector Pin (J12)
TDO AH19 1
PCI Bus
TDI AJ9 3
TRST_N AE12 4
TCK AC13 7
TMS AD13 9
HALT_N AE11 11
The ML310 board design provides the Xilinx Virtex-II Pro access to two 33MHz/32bit PCI
buses, Primary 3.3V PCI Bus and a Secondary 5.0V PCI Bus. The FPGA is directly
connected to the Primary 3.3V PCI bus while the 5.0V PCI Bus is connected to the Primary
PCI Bus via a PCI-to-PCI Bridge. There are several PCI devices available on the PCI Buses
as well as 4 PCI add-in card Slots. All PCI Bus signals driven by the XC2VP30 comply with
the IO requirements specified in the PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.2.
The majority of the ML310 features are accessed over the 33MHz/32 bit PCI Bus. The
Virtex-II Pro Power PC405 Processors can gain access to the Primary PCI Bus through the
EDK PCI Host Bridge IP. All PCI configuration and control can be performed via a PCI
Host Bridge implemented in the FPAG fabric. The Primary PCI Bus is wired so that the
FPGA fabric must used to provide PCI Bus arbitration logic. The EDK kit also provides PCI
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 35
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 36

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Arbiter IP. Please see the EDK Processor IP Reference Guide for more information about the
EDK IP mentioned in this section.
The FPGA is responsible generating the PCI RST signal as well as the PCI CLK signal. The
FPGA fabric is used to generate six PCI Clocks that drive each of the PCI devices/slots
shown in the Figure 2-11. All six PCI Clock outputs are length matched. Since the FPGA
generates all PCI Clocks, the downstream PCI devices have no clock input prior to or
during FPGA configuration therefore, PCI Reset should be de-asserted after the PCI CLK
has stabilized. Please review the PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.2 for more detailed
information.
The on-board 33MHz/32 bit PCI Bus is connected to three fixed PCI devices that are part of
the ML310 board. These devices are listed below and more information on the devices can
be found in the following sections as well their data sheets on the ML310 CDROM
♦ Texas Instruments, TI2250, PCI-to-PCI Bridge
♦ Intel, GD82559, 10/100 PCI Ethernet NIC.
♦ Ali, M1535D+, PCI South Bridge
In addition to the three fixed PCI devices, there are a total of four 33MHz/32 Bit PCI slots
available for use. For more information on the PCI slot pinouts, refer to the PCI Local Bus
Specification, Revision 2.2 and the ML310 schematics.
♦ 2 - 3.3V Keyed PCI Add In Card Slots (P5 and P3)
♦ 2 - 5.0V Keyed PCI Add In Card Slots (P6 and P4)
Note:
0402263) packaged with the ML310 kit before using Universal PCI add-in cards with the ML310
board.
The 5.0V PC I slots differ from the 3.3V slots. See the Important Instruc tions sheet (PN
Figure 2-11 shows the connectivity of the PCI bus and PCI devices. For more information
on the PCI slot pinouts, refer to the PCI 2.2 Specification or review the ML310 schematics.
The 5.0V PCI slots differ from the 3.3V slots. See the Important Instructions sheet
(PN 0402263) packaged with the ML310 kit before using Universal PCI add-in cards with
the ML310 board.
36 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 37

Board Hardware
U37
Virtex-II Pro
FPGA
XC2VP30
IDSEL
PCI Bus
PCI_P_CLK5
PCI_P_CLK4
PCI_P_CLK0
PCI_P_CLK1
PCI_P_CLK2
PCI_P_CLK3
R
PCI-to-PCI
3.3V
Bridge TI2250
U32
PCI_P_AD25PCI_P_AD24
0xAC23 104C
IDSEL
PCI_BUS
5.0V
PCI_S_CLK0
PCI_S_AD18
PCI_S_CLK1
PCI_S_AD19
PCI_P_AD21
5.0V PCI Slot 6
IDSEL
PCI_BUS
5.0V PCI Slot 4
IDSEL
PCI_BUS
3.3V PCI Slot 5
IDSEL
PCI_BUS
3.3V PCI Slot 3
Ethernet NIC
PCI_P_AD23
IDSEL
PCI_BUS
ALi Southbridge
U15
PCI_P_AD17
PCI_P_AD18
PCI_P_AD19
PCI_P_AD26
PCI_P_AD27
PCI_P_AD31
Audio
S. Bridge
Modem
USB#2
IDE Bus
USB#1
PCI_BUS
Dev ID Vend IDIDSEL
0x5451 10B9
0x1533 10B9
0x5457 10B9
0x5237 10B9
0x5229 10B9
0x5237 10B9
Figure 2-11: PCI Bus and Device Connectivity
Ta bl e 2 -1 0 shows the connections for the PCI controller.
Table 2-10: PCI Controller Connections
Intel 10/100
U11
0x1229 8086
PCI_P_AD22
IDSEL
PCI_BUS
UCF Signal Name XC2VP30 Pin (U37) Description
PCI_CLK0 T2 PCI_P_CLK0
PCI_CLK1 R2 PCI_P_CLK1
PCI_CLK2 R5 PCI_P_CLK2
PCI_CLK3 R6 PCI_P_CLK3
PCI_CLK4 R3 PCI_P_CLK4
PCI_CLK5 R4 PCI_P_CLK5
PCI_CLK5_FB C15 PCI_P_CLK5
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 37
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 38

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Table 2-10: PCI Controller Connections (Continued)
UCF Signal Name XC2VP30 Pin (U37) Description
PCI_INTA L5
PCI_INTB N2
PCI_INTC M2
PCI_INTD R9
PCI_INTE P9
PCI_INTF M3
PCI_REQ0_N P1
PCI_REQ1_N N1
PCI_REQ2_N P7
PCI_REQ3_N P8
PCI_REQ4_N N3
PCI_GNT0_N P2
PCI_GNT1_N P3
PCI_GNT2_N R7
PCI_GNT3_N R8
PCI_GNT4_N P4
PCI_CBE[0] J2
PCI_CBE[1] H2
PCI_CBE[2] M7
PCI_CBE[3] M8
PCI Interrupt Signals
PCI Request Signals
PCI Grant Signals
PCI Byte Enable Signals
PCI_FRAME_N K6
PCI_IRDY_N K1
PCI_TRDY_N J1
PCI_STOP_N M5
PCI_DEVSEL_N M6
PCI_PERR_N J3
PCI_SERR_N J4
PCI_LOCK L2
PCI_IDSEL K2
PCI_REQ64_N* F8 # PM_IO_3V_1
PCI_ACK64_N* E8 # PM_IO_3V_2
PCI Control Signals
38 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG0 68 (v1. 01) Augu st 25, 200 4
Page 39

Board Hardware
R
Table 2-10: PCI Controller Connections (Continued)
UCF Signal Name XC2VP30 Pin (U37) Description
PCI_AD[0] G5
PCI_AD[1] G6
PCI_AD[2] D5
PCI_AD[3] C5
PCI_AD[4] C1
PCI_AD[5] C2
PCI_AD[6] J7
PCI_AD[7] J8
PCI_AD[8] D3
PCI_AD[9] C4
PCI_AD[10] D1
PCI_AD[11] D2
PCI_AD[12] H5
PCI_AD[13] H6
PCI_AD[14] E3
PCI_AD[15] E4
PCI_AD[16] E1
PCI_AD[17] E2
PCI_AD[18] K7
PCI_AD[19] K8
PCI_AD[20] F3
PCI_AD[21] F4
PCI_AD[22] F1
PCI_AD[23] F2
PCI_AD[24] J5
PCI_AD[25] J6
PCI_AD[26] G3
PCI_AD[27] G4
PCI_AD[28] G1
PCI_AD[29] G2
PCI_AD[30] L7
PCI_AD[31] L8
PCI_PAR H3 PCI_P_PAR
PCI Address/Data Lines
PCI_RST_N N8 PCI_P_RST_N
* Note: These signals are connected, but are not required for 32 bit only PCI systems.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 39
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 40

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Ta bl e 2 -11 describes how the Primary PCI Bus interrupts are connected on the ML310
board along with each devices IDSEL, REQ/GNT, PCI Clocks and DeviceID/Vendor ID
information.
Table 2-11: 3.3V Primary PCI Bus Information
Device Name
Device IDVendor
ID
Bus DEV IDSEL
REQ
FPGA
PCI
CLK
INTR
PCI Slot 5 N/A N/A 0 5 AD21 0 0 A,B,C,D
PCI Slot 3 N/A N/A 0 6 AD22 1 1 B,C,D,A
U11, Enet Mac 0x1229 0x8086 0 7 AD23 2 2 C
U15, ALI SB 0x1533 0x10B9 0 2 AD18 3 3 INT,NMI
U15, ALi Pwr Mgt 0x7101 0x10B9 0 12 AD28 3 3 INT,NMI
U15, ALI IDE 0x5299 0x10B9 0 11 AD27 3 3 INT,NMI
U15, ALi Audio 0x5451 0x10B9 0 1 AD17 3 3 INT,NMI
U15, Ali Modem 0x5457 0x10B9 0 3 AD19 3 3 INT,NMI
U15, ALi USB#1 0x5237 0x10B9 0 15 AD31 3 3 INT,NMI
U15, ALi USB#2 0x5237 0x10B9 0 10 AD26 3 3 INT,NMI
U32, PCI-PCI Brg 0xAC23 0x104C 0 9 AD25 4 4 N/A
U37, XC2VP30 0x0300 0x10EE 0 8 AD24 Int. 5 N/A
Ta bl e 2 -1 2 describes how the Secondary PCI Bus interrupts are connected on the ML310
board along with each devices IDSEL, REQ/GNT, PCI Clocks and DeviceID/Vendor ID
information.
Table 2-12: 5.0V Secondary PCI Bus Information
Device Name
Device IDVendor
ID
Bus DEV IDSEL
PCI Slot 6 N/A N/A 1 2 AD18 0 0 A,B,C,D
PCI Slot 4 N/A N/A 1 3 AD19 1 1 B,C,D,A
U32, PCI-PCI Brg N/A N/A N/A 7 N/A Int. 4 N/A
ALi South Bridge Interface, M1535D+, U15
The ALi M1535D+ South Bridge augments the ML310 with many of the basic features
found on legacy Personal Computers (PCs). These basic PC features are only accessible
over the PCI Bus as this is the only way to access the ALI M1535D+. A brief description of
the ALi M1535D+ features employed on the ML310 board is discussed below. Please
review the ALi M1535D+ Data sheets, located on the ML310 CDROM, for more detailed
information.
REQ
Bridge
CLK
INTR
40 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 41

Board Hardware
U37
R
ALi M1535D+ supports the following features:
♦ 1 parallel and 2 serial ports
♦ 2 USB ports
♦ 2 IDE connectors
♦ GPIO
♦ SMBus Interface
♦ AC97 Audio CODEC
♦ PS/2 keyboard and mouse
PCI_BUS
FPGA
IDSEL
PCI_P_AD24
U15
PCI_P_CLK3
USB1USB
PCI_P_AD17
PCI_P_AD18
PCI_P_AD19
PCI_P_AD26
PCI_P_AD27
PCI_P_AD31
SERIAL
2
J3 P1
Parallel
Port
1
Audio
S. Bridge
Modem
USB#2
IDE Bus
PCI_BUS
SERIAL
2
ALi
South Bridge
Device ID Vendor IDIDSEL
0x5451
0x1533
0x5457
0x5237
0x5229
0x5237
PS/2
KBD
P2
0x10B9
0x10B9
0x10B9
0x10B9
0x10B9
0x10B9USB#1
Figure 2-12: ALi South Bridge Interface, M1535D+, U15
X4
OSC
32.768
MHz
X2
OSC
48MHz
X3
OSC
14.3181
MHz
U1
AC97
GPIO FLASH
J5 U4
X1
OSC
24.576
MHz
PRIMARY IDE
SECONDARY IDE
J16/J15
Parallel Port Interface, connector assembly P1
The Parallel Port interface of the ALi South Bridge is connected to a 25 Pin connector,
female DB25, which is part of the P1 connector assembly. The ALi M1535D+ supports
various Parallel Port modes such as Standard Mode (SPP), Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP)
and IEEE 1284 Compatible ECP. The P1, female DB25, connector pinout is configured as
per IEEE Std. 1284-1994. Please review the ALi M1535D+ data sheets for more detailed
information.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 41
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 42

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Ta bl e 2 -1 3 shows the ALi Parallel Port connections to P1, DB25.
Table 2-13: ALi South Bridge Parallel Port pinout P1 (DB25)
Signal Name
P1 (DB25)
Pin No.
Description
STROBE_N 1 Strobe
D0 2 Data Bit 0
D1 3 Data Bit 1
D2 4 Data Bit 2
D3 5 Data Bit 3
D4 6 Data Bit 4
D5 7 Data Bit 5
D6 8 Data Bit 6
D7 9 Data Bit 7
ACK_N 10 Acknowledge
BUSY 11 Busy
PEND 12 Paper End
SELECT 13 Select
AUTOFD_N 14 Autofeed
ERROR_N 15 Error
INIT_N 16 Initialize
SLCTIN_N 17 Select In
GND 18, 19, 20,
Ground
21, 22, 23,
24, 25
Serial Port Interface, connector assembly P1
In addition to the serial port accessible via the XC2VP30 FPGA, the ALi M1535D+ provides
access over the PCI Bus to two serial ports. The ALi M1535D+ employs 16450/16550
Compatible UARTs with Send/Receive16-byte FIFOs. The two Serial ports are connected
to the ALi M1535D+ device via two male DB9 connectors (P1). The DB9 connectors are
configured as DTE interfaces and meet the EIA/TIA-574 standard.
The DB9 male connectors are labeled Serial Port A and B in the ML310 schematics. The DB9
connectors are part of the P1 connector assembly. Please note that Serial Port B is located
adjacent to the PS/2 connector where COM1 in a legacy PC is traditionally located. The
two DB9 serial port connectors are labeled on the ML310 board silk-screen near the P1
connector assembly. Please review the ALi M1535D+ Data sheets for more detailed
information.
42 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 43

Board Hardware
R
Ta bl e 2 -1 4 shows the RS-232 signals connected to the two DB9 connectors, P1 A/B.
Table 2-14: ALi South Bridge DB9 Serial Port pinouts, P1 (DB9-A/B)
Signal Name
P1 (DB9-A/B)
Pin No.
Description
DCD 1 Data Carrier Detect
RD 2 Receive Data (a.k.a RxD, Rx)
TD 3 Transmit Data (a.k.a TxD, Tx)
DTR 4 Data Terminal Ready
SGND 5 Ground
DSR 6 Data Set Ready
RTS 7 Request To Send
CTS 8 Clear To Send
RI 9 Ring Indicator
USB, connector assembly J3
The M1535D+ USB is an implementation of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) 1.0a
specification that contains two (2) PCI Host Controllers and an integrated Root Hub. The
two USB connectors, A/B, are part of the J3 connector assembly and are USB Type-A plugs.
Please review the ALi M1535D+ Data sheets for more detailed information.
Ta bl e 2 -1 5 shows the ALi USB connections to the two USB Type-A plugs, J3 A/B.
Table 2-15: ALi South Bridge USB Type-A connector, J3 A/B
Signal Name
J3 (A/B)
Pin No.
Description
USB_VCC 1 USB Power, 5.0V, MOSFET Isolated
USB_DN 2 USB Data -
USB_DP 3 USB Data +
GND 4 Ground
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 43
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 44

R
IDE, connectors J15 and J16
Supports a 2-channel UltraDMA-133 IDE Master controller independently connected to a
Primary 40 Pin IDC connector (J16) and a Secondary 40 Pin IDC connector (J15). Please
review the ALi M1535D+ Data sheets for more detailed information.
Ta bl e 2 -1 6 shows the ALi Primary and Secondary IDE connections to the two 40 pin IDE
Connectors, J15 and J16.
Table 2-16: ALi South Bridge IDE connectors, J15 and J16
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
J15/J16
Pin No.
Schem Signal
J15/J16
Pin No.
Schem Signal
1 IDE_RESET_N 2 GND
3 IDE_D7 4 IDE_D8
5 IDE_D6 6 IDE_D9
7 IDE_D5 8 IDE_D10
9 IDE_D4 10 IDE_D11
11 IDE_D3 12 IDE_D12
13 IDE_D2 14 IDE_D13
15 IDE_D1 16 IDE_D14
17 IDE_D0 18 IDE_D15
19 GND 20 (KEY)
21 IDE_DMARQ 22 GND
23 IDE_DIOW_N 24 GND
25 IDE_DIOR 26 GND
27 IDE_IORDY 28 CSEL
29 IDE_DMACK_N 30 GND
31 IDE_INTRQ 32 N.C.
33 IDE_A1 34 IDE_PDIAG_N
35 IDE_A0 36 IDE_A2
37 IDE_CS1_N 38 IDE_CS3_N
39 IDE_DASP_N 40 GND
44 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 45

Board Hardware
R
GPIO, connector J5
There are 15 GPIO pins connecting the ALi M1535D+ to the J5 24 pin header. These may be
accessed via the ALi M1535D+ via the PCI Bus. Please review the ALi M1535D+ Data
sheets for more detailed information.
Ta bl e 2 -1 7 shows the types and number of GPIO signals available to the user from the ALi
South Bridge.
Table 2-17: Type of GPIO Available on Header J5
ALi GPIO Types
Number
Available
Output 5
Input 4
Input/Output 6
Ta bl e 2 -1 8 shows the connections from the ALi, M1535D+, GPIO signals available at the
GPIO header (J5). Please review the ALi M1535D+ Data sheets, located on the ML310
CDROM, for more detailed information.
Table 2-18: GPIO Connections on Header J5
Schem Net Name
GPIO Header
(J5)
M1535D+
(U15)
IO Type
GPO_35 24 P19 Output
GPO_34 22 P18 Output
GPO_30 20 N18 Output
GPO_29 23 N17 Output
GPO_10 21 T3 Output
GPI_36 7 U8 Input
GPI_34 5 W7 Input
GPI_25 3 E9 Input
GPI_24 1 M17 Input
GPIO_3 15 Y4 Input/Output
GPIO_23 19 U5 Input/Output
GPIO_22 17 U6 Input/Output
GPIO_2 13 W4 Input/Output
GPIO_1 11 V4 Input/Output
GPIO_0 9 Y3 Input/Output
System Management Bus (SMBus)
The System Management Bus (SMBus) host controller in the M1535D+ supports the ability
to communicate with power related devices using the SMBus protocol. It provides quick
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 45
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 46

R
AC97 Audio
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
send byte/receive byte/ write byte/write word/read word/block read/block write
command with clock synchronization function as well as 10-bit addressing ability. Please
see Section “IIC/SMBus Interface” for more information regarding the devices that are
connected to the SMBus. Please review the ALi M1535D+ Data sheets for more detailed
information.
The ALi South Bridge has a built-in Audio that is combined with a standard AC97 CODEC,
LM4550. Below is a list of the features available to the user. The ALi M1535D+ is used in
conjunction with an LM4550. Please review the ALi M1535D+ and LM4550 Data sheets,
located on the ML310 CDROM, for more detailed information.
♦ AC97 CODEC 2.1 Specification Compliant
♦ CODEC Variable Sample Rate Support
♦ 32-voice Hardware Wave-table Synthesis
♦ 32 Independent DMA _channels
♦ 3D Positioning Sound Acceleration
♦ Legacy Sound Blaster compatible
♦ FM OPL3 emulation
♦ MIDI Interpretation
♦ MIDI MPU-401 interface
The ML310 employs a National Semiconductor, LM4550, Audio CODEC combined with
the ALi South Bridge AC97 interface. This interface can be used to play and record audio.
The LM4550 has a left and right channel Line inputs, a microphone input, left and right
channel line outputs and an amplified version headphone output suitable for driving an 8
ohm load via LM4880 (U2). The audio jacks are available on the J1 and J2 connector
assemblies. Please consult the M1535D+, LM4550 and LM4880 data sheets in conjunction
with the ML310 schematics for more details on the ML310 Audio interface.
Ta bl e 2 -1 9 describes the audio jacks available to the user on the ML310.
Table 2-19: Audio Jacks, J1 and J2
Audio Jack Signal name Description
J1 top AC _AMP_OUTR
AC _AMP_OUTL
AC Amplified Output,
driven by U2, LM4880
J1 Bottom AC_MIC_IN Microphone Input to U1, LM4550
J2 Top AC _LINE_OUTR
AC _LINE_OUTL
J2 Bottom AC _LINE_INR
AC_LINE_INL
AC Line Output, Left and Right channels,
driven by U1, LM4550
AC Line Input, Left and Right channels,
driven by U1, LM4550
46 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 47

Board Hardware
R
PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Interface, connector P2
The ALi M1535D+ has a built-in PS2/AT Keyboard and PS/2 Mouse controller. The PS/2
Keyboard and Mouse ports are connected to the ALi M1535D+ via standard DIN
connectors contained in the P2 connector assembly. In the event of a short circuit by the
keyboard or mouse device, the 5V power provided to these devices is fuse protected by a
resettable fuse, F1. Please review the ALi M1535D+ Data sheets for more detailed
information.
Ta bl e 2 -2 0 shows the PS/2 keyboard and mouse connections to the P2 connector assembly.
Table 2-20: PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse
Signal Name Connector (P2) Description
KDAT 1 Keyboard Data
KCLK 5 Keyboard Clock
MDAT 7 Mouse Data
MCLK 11 Mouse Clock
KVCC, MVCC 4, 10 Fuse protected power to Keyboard and Mouse
Flash ROM, U4
The ALi South Bridge supports 4 Mbit Flash memory interface. The ML310 provides
connectivity to an AM29F040B 4-Megabit (512 K x 8-Bit) Flash (U4) via the ALi M1535D+
ROM interface. Please review the ALi M1535D+ Data sheets for more detailed information.
Ta bl e 2 -2 1 shows the connections between the ALi M1535D+ (U15) ROM signals to the
AM29F040B (U4) Flash Memory device. Please review the ALi M1535D+ and AM29F040B
Data sheets, located on the ML310 CDROM, for more detailed information.
Table 2-21: ALi M1535 Flash Memory Interface
Schem Net Name
M1535D+
(U15)
ROM_WE_N U14 7 Active Low Write Enable
ROM_OE_N T14 32 Active Low Output Enable
ROM_D7 W19 29
ROM_D6 Y19 28
ROM_D5 V20 27
ROM_D4 W20 26
ROM_D3 Y20 25
ROM_D2 U18 23
AM29F040B
(U4)
Description
Flash Data
ROM_D1 U19 22
ROM_D0 U20 21
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 47
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 48

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Table 2-21: ALi M1535 Flash Memory Interface
Schem Net Name
M1535D+
(U15)
ROM_A18 T15 9
ROM_A17 U15 6
ROM_A16 V15 10
ROM_A15 W15 11
ROM_A14 T16 5
ROM_A13 U16 4
ROM_A12 V16 12
ROM_A11 W16 1
ROM_A10 Y16 31
ROM_A9 R17 2
ROM_A8 T17 3
ROM_A7 U17 13
ROM_A6 V17 14
ROM_A5 W17 15
AM29F040B
(U4)
Description
Flash Addresses
ROM_A4 Y17 16
ROM_A3 V18 17
ROM_A2 W18 18
ROM_A1 Y18 19
ROM_A0 V19 20
Intel GD82559, U11, 10/100 Ethernet Controller
Intel GD82559 Ethernet Controller
The GD82559 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet controller with an integrated 10/100 Mbps
physical layer device for PCI board LAN designs. It is designed for use in Network
Interface Cards (NICs), PC LAN On Motherboard (LOM) designs, embedded systems and
networking system products. It consists of both the Media Access Controller (MAC) and
the physical layer (PHY) interface combined into a single component solution. The 82559
can operate in either full duplex or half duplex mode.The GD82559 also includes an
interface to a serial (4-pin) EEPROM and a parallel interface to a 128 Kilobyte Flash
memory. The EEPROM provides power-on initialization for hardware and software
configuration parameters.
The ML310 board utilizes the 82559 10/100 Ethernet capability via FPGA PCI host bridge
accesses over the PCI Bus. The 82559 is only accessible over the PCI bus, this includes
programming of its power-on initialization EEPROM. The GD82559’s EEPROM is pre
programmed on each ML310 with a unique MAC address. The ML310 MAC address is
identified by the mylar label near the RJ45 connector labeled "ETH0 MAC ADDR". Please
48 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 49

Board Hardware
R
review the GD82559 Data sheet, located on the ML310 CDROM, for more detailed
information.
U37
PCI_P_CLK2
FPGA
XC2VP30
PCI_BUS
Figure 2-13: Intel GD82559 Etherne t Contr oller
IIC/SMBus Interface
Introduction to IIC/SMBus
The Inter Integrated Circuit (IIC) bus provides the connection from the CPU to peripherals.
It is a serial bus with a data signal, SDA, and a clock signal, SCL, both of which are
bidirectional. The interface is designed to serve as an interface with multiple different
devices, with one master device and multiple slave devices. The interface is designed to
operate in the range of 100 KHz to 400 KHz.
PCI_P_AD23
U11
INTEL
GD82559
Ethernet MAC/PHY
Vendor ID 0x8086
Device ID 0x1229
IDSEL
PCI_BUS
X5
OSC
25MHz
U16
EEPROM
J3
RJ45
The Systems Management Bus (SMBus) also provides connectivity from the CPU to
peripherals. The SMBus is also a two wire serial bus through which simple power related
devices can communicate with the rest of the system. SMBus uses IIC as its backbone.The
EDK kit provides IP that integrates the IIC interface with a microprocessor system, please
review the EDK Processor IP reference Guide for more details.
IIC/SMBus Signaling
There are two main signals on the IIC Bus, the data signal and the clock signal. Both of
these signals operate as open-drain, by default pulled high to 5 Volts, although some
devices support lower voltages. Either the master device or a slave device can drive either
of the signals low to transmit data or clock signals.
IIC/SMBus on ML310 Board
Ta bl e 2 -2 2 provides a listing of the function, part number and addresses of the IIC devices
on the ML310. These devices include EEPROM, temperature sensors, power monitors and
Real Time Clock.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 49
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 50

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Ta bl e 2 -2 2 shows the FPGA connections to all SMBus and IIC devices.
Table 2-22: SMBus and IIC Controller Connections
UCF Signal Name XC2VP30 Pin Schem Signal Name
iic_scl C13 fpga_scl
iic_sda J15 fpga_sda
iic_irq_n E15 iic_irq_n
iic_temp_crit_n* D15 iic_therm_n
* Note: This signal connects to U20 therm_l on the LM87. See data sheet for additional details.
50 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 51

Board Hardware
R
Ta bl e 2 -1 4 shows a block diagram of the FPGA in relation to the SMBus accelerator and the
IIC bus.
Note:
U37
Virtex-II Pro
FPGA
XC2VP30
Either the XC2VP30 or the ALi M1535D+ can master the IIC bus but not simultaneously
IIC Bus
PCI Bus
U15
ALi
Southbridge
M1535 D+
U27
SMBUS
Accelerator
LTC1694
U20
Voltage
Temp
Monitor
ADDR:
0x5C
LM87
U22
RTClock
ADDR:
0xA2
RTC8566
U21
EEPROM
ADDR:
0xA0
24LC64
P7
SPD
EEPROM
Temperature
VCC12V_P
VCC5V
VCC2V5
VVCC3_PCI
VCC1V5
Note: Located on
DDR DIMM P7
Figure 2-14: SMBus and IIC Block Diagram
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 51
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 52

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Ta bl e 2 -2 3 lists the IIC devices and their associated addresses.
Table 2-23: IIC Devices and Addresses
Device
Reference
Designator
Address Description
LTC1694 U27 n/a SMBus accelerator that ensures data integrity
RTC8564 U22 0xA2 IIC bus interface real time clock module along
24LC64 U21 0xA0 EEPROM is a 64 Kb electrically erasable PROM.
LM87 U20 0x5C Voltage/Temperature monitor
* Note: The IIC bus can be controlled directly by the FPGA or indirectly by the ALi bridge over the
FPGA PCI interface.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
Introduction to SPI
Serial Peripheral Interface™ (SPI), is a serial interface much like the IIC Bus interface.
There are three primary differences; the SPI operates at a higher speed, there are separate
transmit and receive data lines, and the device access is chip-select based instead of
address based. The EDK kit provides IP that integrates the SPI interface with a
microprocessor system, please review the EDK Processor IP reference Guide for more details.
with multiple devices on the SMBus. Enhances
data transmission speed and reliability under all
specified SMBus loading conditions and is
compatible with the IIC bus.
with an external rechargeable battery and
charging circuit.
SPI Signaling
There are four main signals used in the SPI™ interface; Clock, Data In, Data Out, and Chip
Select. Signaling rates on the SPI bus range from 1 MHz to 3MHz, roughly a factor of 10
faster than the IIC bus interface. SPI continues to differ from IIC using active drivers for
driving the signal high and low, while IIC only actively drives signals low, relying on a
pull-up resistor to pull the signal high.
There are four basic signals on the SPI bus:
• Master Out Slave In (MOSI) is a data line that supplies the output data from the
master device that is shifted into a slave device
• Master In Slave Out (MISO) is a data line that supplies the output data from a slave
device that is shifted into the master device
• Serial Clock (SCK) is a control line driven by the master device to regulate the flow of
data and enable a master to transmit data at a variety of baud rates
♦ The SCK line must cycle once for each data bit that is transmitted
• Slave Select (SS) is a control line to dedicated to a specific slave device that allows the
master device to turn the slave device on and off
52 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 53

Board Hardware
R
SPI Addressing
The SPI does not use an addressed based system like the IIC Bus Interface uses. Instead,
devices are selected by dedicated Slave Select signals, comparable to a Chip Select signal.
Each SPI Slave device needs its own Slave Select signal driven from the SPI master. This
increases the total pin count, but decreases overhead and complexity, which increases the
available bandwidth and decreases bus contention.
The ML310 employs a single SPI device which is a 25LC640, 64k bits EEPROM. For more
details on this device, please review the data sheet available on the ML310 CDROM.
Ta bl e 2 -1 5 shows the FPGA and the EEPROM connected by the SPI bus.
U37
SPI Bus
Virtex-II Pro
FPGA
XC2VP30
EEPROM
25LC640
Figure 2-15: SPI EEPROM Device Interface
Ta bl e 2 -2 4 shows the connections between the SMBus/IIC controller. and the XC2VP30.
Table 2-24: SMBus and IIC Controller Connections
UCF Signal Name XC2VP30 Pin (U37) Schem Signal Name
spi_miso AJ10 SPI_DATA_OUT
spi_mosi AK10 SPI_DATA_IN
spi_sck AF12 SPI_CLK
spi_ss[0] AF13 SPI_DATA_CS_N
* Note: This signal connects to U20 therm_l on the LM87. See data sheet for additional details.
Push Buttons, Switches, Front Panel Interface and Jumpers
U19
SPI
Push Buttons
System ACE Reset, SW1
SW1 provides a way to manually reset the System ACE CF (U38) device. When SW1 is
actuated it drives the signal PB_SYSTEM_ACE_RESET low which causes the LTC1326
(U31) to generate a 100us active low pulse. The active low output of the LTC1326 drives the
reset input of the System ACE CF (U38) device via signal SYSTEMACE_RESET_N.
When the System ACE CF device is reset, it causes a re-configuration of the XC2VP30
FPGA. The ace file used to program the device is selected via dipswitch, SW3, settings.
Please review the System ACE CF data sheet for more details, as it is located on the ML310
CDROM and also available on http://www.xilinx.com
The front panel interface header (J23) can also drive the PB_SYSTEM_ACE_RESET signal.
For more details on J23, please review section “Front Panel Interface Connector, J23”.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 53
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 54

R
CPU Reset, SW2
SW2 provides a way to manually reset the powerpc system implemented in the XC2VP30.
The user is responsible for connecting this signal to the PPC405 system implemented in the
FPGA fabric. The EDK kit provides IP to perform this task, please review the EDK Processor
IP reference Guide for more details. When SW2 is actuated it drives the signal
PB_FPGA_CPU_RESET low which causes the LTC1326 (U30) to generate a 100us active
low pulse. The active low output of the LTC1326 pin E16 on the XC2VP30 (U38) device via
signal FPGA_CPU_RESET_N. In addition to resetting the CPU, SW2 can also perform a
System ACE CF reset as described in the above section. This can be accomplished by
simply holding down the SW2 push button for longer than 2 seconds. This action performs
a CPU reset followed by a System ACE CF reset. Please review the ML310 schematics and
the LTC1236 data sheet found on the ML310 CDROM for more details.
The front panel interface header (J23) can also drive the PB_ FPGA_CPU_RESET signal.
For more details on J23, please review section “Front Panel Interface Connector, J23”
System ACE Configuration Dipswitch, SW3
The System ACE configuration dipswitch is a three position dipswitch that controls the
three configuration address pins on the System ACE CF controller. The three configuration
address lines are; CFGADDR0, CFGADDR1 and CFGADDR2 and are marked as positions
1, 2 and 3 respectively on the dipswitch (SW3) plastic housing. Dipswitch SW3 is also
marked with an "on" indicator that is etched onto the plastic housing of SW3 as well as an
arrow head on the board silk-screen for SW3. When any of the three switches are moved to
the "on" position then the associated CFGADDR bit is set to a logic zero. When any of the
three switches are moved opposite of the "on" position then the associated CFGADDR bit
is set to a logic one via a pull-up resistor.
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Ta bl e 2 -1 6 depicts the SW3 dipswitch connections to the System ACE device. One side of
the dipswitch is tied to pull-ups that are connected to each of the CFGADDR lines while
the other side of the dipswitch is connected to ground. The configuration address lines are
also connected to the Front Panel Interface, see “Front Panel Interface Connector, J23” for
more details. This allows the user to manually select one of eight configurations stored on
the CompactFlash that is connected to the System ACE device. Once the user makes a valid
selection on SW3 the user can then depress push button SW1 to command the System ACE
device to reset and configure the FPGA using the configuration selected by dipswitch SW3.
Please review the System ACE CF data sheet which is available at http://www.xilinx.com
or on the ML310 CDROM.
54 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 55

Board Hardware
SW3 = 0 0 0 (default)
321
R
2.5V
System ACE
U38
SW3
210
ON
SYSACE CFG
Shown here with
CFGADDR[2:0]
set to "000".
ON => SW Closed
CFGADDR[2:0] =
0x0
0x1 0x2 0x3
Default
0x4 0x5 0x6 0x7
Figure 2-16: SW3 - SysACE CFG Switch Detail
Front Panel Interface Connector, J23
RESET
SYSACE_
RESET_N
CFGADDR
U31
Debounce
SW1
SYSACE
Reset
The Front panel Interface connector (J23) is a 24-pin header that accepts a standard IDC 24
pin connector (0.1inch pitch). J23 provides an optional means to control and gather status
information from the ML310 board if it were to be enclosed similar to that of a desktop PC.
The functionality listed below can easily be connected via a user build cable that connects
to some collection of user created logic the could be used to control/monitor the
functionality available via the Front Panel Interface.
The front panel interface provides the following control capability available through the
J23 header.
♦ Power on/off the ML310
- ML310 board is delivered with a jumper installed on J23
♦ Select any of the eight System ACE configuration
- Connects to the 3 System ACE configuration address lines
♦ System ACE Reset
- Active low input
♦ CPU Reset
- Active low input
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 55
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 56

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
The front panel interface provides the following status information available at the J23
header.
♦ FPGA Configuration DONE
- Output intended for driving an LED
♦ IDE Disk access
- Output intended for driving an LED
♦ ATX Power
- Output intended for driving an LED
♦ 2 FPGA User Defined Signals
- Outputs intended for driving LEDs
♦ ATX Speaker
- Output, see Ali M1535D+ data sheet for more details
♦ Keyboard Inhibit (active low input)
Ta bl e 2 -2 5 shows the signals available at the Front Panel Interface header, J23.
Table 2-25: Front Panel Interface connector, J23
J23
Pin
Schem Signal Description
1 SYACE_CFGA0 Used to select System ACE configuration,
CFGADDR0
2 FPGA_USER_LED1 User Defined function, Connects to XC2VP30, U37-
AH10, (2.5V Bank)
3 SYACE_CFGA1 Used to select System ACE configuration,
CFGADDR1
4 FPGA_USER_LED2 User Defined function, Connects to XC2VP30, U37-
AC14, (2.5V Bank)
5 SYACE_CFGA2 Used to select System ACE configuration,
CFGADDR2
6NC No Connect
7 LED_DONE_R Remote FPGA DONE indicator, Tie this pin to Anode
of user’s LED and Cathode to GND
8GND Ground
9 ATX_PWRLED ATX 3.3V power indicator, Tie this pin to Anode of
user’s LED and Cathode to GND
10 ATX_SPKR Used to drive user defined ATX Speaker input
11 NC No Connect
12 NC No Connect
13 GND Ground
14 GND Ground
56 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 57

Board Hardware
R
Table 2-25: Front Panel Interface connector, J23
J23
Pin
Schem Signal Description
15 KBINH Tie this pin to GND to activate Keyboard inhibit, see
ALi M1536D+ data sheet for more details
16 VCC5V 5V ATX power available to user
17 ATX_IDELED_R ATX IDE access indicator, Tie this pin to Anode of
user’s LED and Cathode to GND
18 VCC5V 5V ATX power available to user
19 PWR_SUPPLY_ON Short this pin to GND to enable the ATX power
supply. Note: This pin cannot be controlled by a
momentary pulse.
20 GND Ground
21 PB_SYSACE_RESET Used to reset System ACE when driven low, as
described earlier, “System ACE Reset, SW1”
22 GND Ground
23 PB_FPGA_CPU_RESET Used to reset CPU when driven low, as described
earlier, “CPU Reset, SW2”
24 GND Ground
Jumpers
MGT VTRX Termination Voltage Jumpers, J10 and J11
The MGT receive termination voltage, VTRX, on the top and bottom MGTs are jumper
selectable via jumpers J10 (top) and J11 (bottom). The onboard regulated VTRX
termination voltage can be configured for AC or DC coupling, 1.8V or 2.5V respectively.
Ta bl e 2 -2 6 shows the MGT VTRX voltage selections available on the ML310 board.
Table 2-26: Jumper Selection for Top and Bottom MGT VTRX Voltages,J10/J11
MGTs VTRX Voltage
Jumper
(J10)
All Top MGT_VTT 1.8V Shunt 2 - 3 Open AC
MGT_AVCC 2.5V Shunt 1 - 2 Open DC
All Bottom MGT_VTT 1.8V Open Shunt 2 - 3 AC
MGT_AVCC 2.5V Open Shunt 1- 2 DC
All MGT_VTT 1.8V Open Open Default
MGT_AVCC 2.5V Open Open Default
Jumper
(J11)
MGT RX
Coupling
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 57
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 58

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
MGT BREF Clock Selection Jumpers, J20 and J21
One of two onboard LVDS BREF clock sources, X7 or X9, can be selected via jumpers, J20
and J21. The selected clock source drives both top and bottom LVDS BREF Clock input
pairs to the XC2VP30 FPGA.
Ta bl e 2 -2 7 shows the MGT BREF clock selections available on the ML310 board.
Table 2-27: Jumper Selection for MGT BREF clocks,J20/J21
BREF Clock Freq.
Jumper
(J10)
Jumper
(J11)
Description
156.25MHz Shunt 1 - 2 Shunt 1 - 2 LVDS Oscillator, X7, 156.25MHz
125.00MHz Shunt 2 - 3 Shunt 2 - 3 LVDS Oscillator, X9, 125.00MHz
Note:
BREF Clock Pins driven on the XC2VP30 FPGA are:
LVDS_CLKLOC_P (U37-F16/AH16)
LVDS_CLKLOC_N (U37-G16/AJ16)
System ACE Configuration Mode Jumper, J14
Selects the System ACE configuration mode behavior after reset or power up.
J14 = Open (default)
♦ Allows System ACE CF to configure immediately after reset or power up
J14 = Shorted
♦ Inhibits the System ACE from configuring after reset or power up and can only be
commanded by the MPU control to do so. Please review section “System ACE CF
Controller” and the System ACE data sheet for more details on the System ACE
device operation, which can be found on the ML310 CDROM
JTAG Source Select Jumper, J19
The JTAG Source Select jumper (J19) enables the use of either the Parallel Cable IV
connector (J9) or the CPU_DEBUG/Trace Port connectors, J12/P8, to source the XC2VP30
JTAG pins. This is available for third party tool support. The muxing is performed by an
external device, 74LVC157A (U39), as shown earlier in Figure 2-6. The data sheet for this
device is available on the ML310 CDROM.
Note:
DEBUG connector (J12) as contention may result after the FPGA is configured.
This functionality should not be used if the user implements logic that also drives the CPU
J19 = Open (default, use the Parallel Cable IV connector, J9)
ATX Power Distribution and Voltage Regulation
The ML310 board is shipped with a commercially available 250W ATX Power supply. All
voltages required by the ML310 logic devices are derived from the 5.0V supply, except the
+/- 12V supplies, as shown in Figure 2-17. The ML310 ATX power supply can easily be
mounted in a standard ATX Chassis along with the ML310 board.
58 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 59

Board Hardware
R
Note: An Antec, mo del SL250S, ATX Power Supply is del ivered with y our ML310. The Antec User’s
Manual is provided in the Data sheets section on the ML310 CDROM. Prior to installation please read
the Installation section of the Antec User’s Manual which describes the red voltage switch power
setting on your Antec SL250S supply.
Check the red power supply voltage switch setting before installation. It should be the
same as your local power voltage (115V for North America, Japan, etc. and 230V for
Europe and many other countries). Change the voltage setting if necessary. Failure to take
this precaution could result in damage to your equipment and could void your warranty.
The ML310 requires a variety of voltages as is required by the different logic devices used
in the ML310 board design. The varieties of voltages are derived from the 5.0V supply and
regulated on board as shown in Figure 2-17.
Figure 2-17 shows the power distribution and regulation for the ATX-compatible power
supply.
J18
VCC5V
Pin 1 Pin 11
3.3-A
3.3-B
COM-A
5V-A
COM-B
5V-B
COM-C
PW-OK
5VSB
12V
3.3-C
-12V
COM-D
PS-ON
COM-G
-5V
5V-C
5V-D
U9
MIC2076-2
U41
LT1763CS8
U8
SC10A-DAC
COM-E
COM-F
VCC5V
VCC12V_N
VCC12V_P
VCC3V3_ATX
R185-188
Nostuff
USB_AVC
(5V @ 500 mA)
VCC3_PCI
(3.0V @
500mA)
VCC1V5
(1.5V @
10A)
NOTE: Typical ATX power supplies may not
produce a well-regulated 3.3V supply unless
there is a minimum load on the 5V output.
Therefore 3.3V is regulated separately for
on-board use.
VCC3V3
NOTE: These resistors (R185-188) allow the 3.3v regulator
to be nostuffed and 3.3v power taken directly from the ATX
supply in the case where it is well-behaved given the load
on the other outputs.
U14
SC10A-DAC
U10
SC10A-DAC
VCC12V_P
VCC3V3
VCC3V3
(3.3V @ 10A)
VCC2V5
(2.5V @ 10A)
U3
LT1763CS8
U40
LT1764AEQ
U34
LT1763CS8
U25
ML655460
AC_AVDD
(5.0V @ 500mA)
MGT_AVCC
(2.5V @ 3A)
MGT_VTT
(1.8V @ 500 mA)
DDR_VTT
(1.25 V @ 3A)
VREF_DDR
Figure 2-17: ATX Power Distribution and Voltage Regulation
Several voltage monitors, MC34161D, monitor all regulated power on the ML310 board.
Each of the voltage monitors is connected to power indicator LEDs as shown in
Figure 2-18. The indicator LEDs will illuminate RED if a regulated supply voltage is out of
spec and will illuminate Green if the regulated supply voltage is nominal. Each regulated
supply voltage has a corresponding test point located near its indicator LED. Please review
the ML310 schematics and the MC34161D data sheet for more detailed information.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 59
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 60

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
In addition to the MC34161D voltage monitors, the ML310 employs a SMBus device,
LM87, which samples several of the same supply voltages when accessed over the System
Management Bus or SMBus. More information on the SMBus features of the ML310 can be
found in section “IIC/SMBus Interface”.
TP17
TP14
TP10
VCC1V5 VCC5V
1.5V 5.0V
VCC2V5 VCC5V
2.5V
VCC3_PCI VCC5V
3.0V
U29
MC34161D
U24
MC34161D
U18
MC34161D
RED = Fault
GRN = Nominal
DS8
RED = Fault
GRN = Nominal
DS6
RED = Fault
GRN = Nominal
DS4
TP16
TP13
1.25V
VCC5V VCC5V
U28
MC34161D
VTT_DDR VCC5V
U23
MC34161D
MGT_AVCC VCC5V
2.5V
U17
MC34161D
DS7
DS5
DS3
RED = Fault
GRN = Nominal
RED = Fault
GRN = Nominal
RED = Fault
GRN = Nominal
VCC3V3 VCC5V
TP8
3.3V
U13
MC34161D
RED = Fault
GRN = Nominal
DS2
MGT_VTT VCC5V
1.8V
U12
MC34161D
DS1
RED = Fault
GRN = Nominal
Figure 2-18: Voltage Monitor
60 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 61

High-Speed I/O
Ta bl e 2 -2 8 Shows the various Voltage monitor information.
Table 2-28: Voltage Monitor Information
R
Schem Name Voltage Testpoint
*Indicator
LED
Notes
VCC1V5 1.5V TP17 DS8 Regulated FPGA Core voltage
VCC2V5 2.5V TP14 DS6 Regulated FPGA / Board Logic
VCC3_PCI 3.0V TP10 DS4 Regulated FPGA PCI Bank 1-2 Voltage
VCC3V3 3.3V TP8 DS2 Regulated PCI/Misc Logic
VCC5V 5.0V TP16 DS7 From ATX Supply, All Regulators Derive Power
VTT_DDR 1.25V TP13 DS5 Regulated DDR Termination (SSTL2)
MGT_AVCC 2.5V N/A DS3 Regulated MGT Power
MGT_VTT 1.8V N/A DS1 Regulated MGT Power
VCC3V3_ATX 3.3V TP20 N/A Not used
VCC12V_P +12V TP18 N/A Direct from ATX Supply
VCC12V_N -12V TP19 N/A Direct from ATX Supply
* Green = Voltage Nominal
* Red = Voltage Fault
High-Speed I/O
Xilinx Virtex-II Pro FPGAs offer a variety of high-speed I/O solutions. The ML310
Embedded Development Platform’s high-speed I/O is based on the XC2VP30-FF896
FPGA’s RocketIO multi-gigabit transceivers (MGTs) and LVDS capability. The high-speed
I/O signals on the FPGA are accessible through two personality module (PM) connectors,
PM1 and PM2, on the ML310 board. The ML310 is the host board, functioning as the
development platform for Virtex-II Pro FPGA. The PM connectors on the ML310 board
provide a means for extending the functionality of the board through high-speed I/O pins.
Personality modules connect to the ML310 board using Tyco Z-Dok+ docking connectors,
PM1 and PM2. In addition to having differential pairs and shielding ground connections,
Z-Dok+ connectors include utility connections for power, ground, and sensing. Tyco ZDok+ high-speed connectors are rated to 6.25 Gb/s.
Figure 2-19 shows a personality module connected to the ML310 board through the PM1
and PM2 connectors. The plug, located on the ML310 board, is referred to as the host board
connector; the receptacle, located on the personality module, is referred to as the adapter
board connector.
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 61
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 62

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
PM1
Host Board ConnectorAdapter Board Connector
PM2
Personality Module ML310 Board
Figure 2-19: Personality Module Connected to ML310 Board
ML310 PM Connectors
The ML310 PM connectors are Tyco Z-Dok+ connectors, part number 1367550-5. The "-5"
suffix indicates a 40 pair connector. Each connector has 40 differential pairs and several
power and ground pins.
Together, the two PM connectors on the ML310 support 158 high-speed I/O pins that can
be user defined. The PM1 and PM2 signals are as follows:
• 8 RocketIO MGT pairs (32 pins total)
• 42 LVDS pairs (can be used as 84 single-ended I/O at 2.5V)
• 1 LVDS clock pair
• 38 single-ended I/O
♦ 12 at 2.5V
♦ 26 at 3.3V
• 2 single-ended 2.5V clocks
• 2 pins not connected
The Tyco data sheet for part number 1367550-5 is available at
http://www.z-dok.com/documents/1367550.pdf
62 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
.
Page 63

High-Speed I/O
R
Figure 2-20 shows an edge view of the PM host board connectors on the ML310 board.
PM1 Host Board Connector
PM2 Host Board Connector
Figure 2-20: Edge View of Host Board Connectors on ML310
Each signal pair on the PM1 and PM2 host board connectors has a wide ground pin on the
opposite side of the plastic divider, as shown in Figure 2-21. The signal pairs alternate from
side to side along the length of the divider. All of the "B" and "E" pins are grounded on the
ML310. The "A", "C", "D", and "F" pins are signal pins.
Copper Pins
Plastic Divider
E1 F2F1 E3 F4F3
A1
B1
D2D1
A2
E2
C2C1
B2
D3 E4
D4
B3
A4A3
Figure 2-21: Host Board Connector Pin Detail
PM1 Connector
The PM1 connector on the ML310 board provides the following signals:
• 8 RocketIO 3.125 Gb/s MGTs
• 3 LVDS pairs at 2.5V (can be used as 6 single-ended I/O at 2.5V)
• 1 LVDS clock pair at 2.5V
• 12 single- ended I/O at 2.5V
• 26 single-ended I/O at 3.3V
• 1 single-ended clock at 2.5V
• 1 pin not connected
C4C3
B4
PM2 Connector
The PM2 connector on the ML310 board provides the following signals:
• 39 LVDS pairs at 2.5V (can be used as 78 single-ended I/O at 2.5V)
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 63
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 64

R
• 1 single-ended clock at 2.5V
• 1 pin not connected
Adapter Board PM Connectors
Tyco Z-Dok+ adapter board connectors, part number 1367555-1 are the receptacle
connectors on the personality modules that mate to the ML310 Tyco Z-Dok+ host board
connectors, part number 1367550-5. The Tyco data sheet for part number 1367555-1 is
available at http://www.z-dok.com/documents/1367555.pdf
On the adapter board connectors, located on the personality module, each signal pair has
a pair of ground pins on the opposite side of the open space, as shown in Figure 2-22. The
signal pairs alternate from side to side along the length of the open space. All of the "B" and
"E" pins are two contacts tied together and grounded on the personality module. The "A",
"C", "D", and "F" pins are signal pins.
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
.
ML310 PM Utility Pins
Contact Order
Copper Pins
Plastic Housing
F4
C4
E4
B4
F3
C3
D4
A4
E3
B3
F2
D3
C2
A3
E2
B2
F1
C1
E1
D2
B1
A2
Figure 2-22: Adapter Board Connector Pin Detail
D1
A1
The Z-Dok+ power and ground pins contact in the following order:
• 1 and 6;
• then 2 and 5;
• then 3 and 4
64 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 65

High-Speed I/O
R
PM1 Power and Ground
Ta bl e 2 -2 9 shows the power and ground pins for the PM1 connector on the ML310.
Table 2-29: PM1 Power and Ground Pins
Pin Number Description Length Contact Order
1, 6 Ground Level 4 First
2, 5 2.5V Level 3 Second
3 3.3V Level 2 Third
4 1.5V Level 2 Third
PM2 Power and Ground
Ta bl e 2 -3 0 shows the power and ground pins for the PM2 connector on the ML310.
Table 2-30: PM2 Power and Ground Pins
Pin Number Description Length Contact Order
1, 6 Ground Level 4 First
2, 5 5V Level 3 Second
3, 4 12V Level 2 Third
ML310 PM User I/O Pins
PM1 User I/O
The PM1 connector makes the MGT signals from the eight RocketIO transceivers available
to the user, along with LVDS pairs and single-ended signals. Tab le 2 - 31 shows the pinout
for the PM1 connector on the ML310.
Table 2-31: PM1 Pinout
PM1 Pin FPGA Pin Pin Description ML310 Schematic Net
A1 H26 IO_L32P_7 PM_IO_94 2.5V
A2 H25 IO_L32N_7 PM_IO_95 2.5V
A3 D26 IO_L03P_7 PM_IO_86 2.5V
A4 C26 IO_L03N_7 PM_IO_87 2.5V
A5 E13 IO_L46N_1 PM_IO_3V_25 3V
FPGA Bank
V
CCO
A6 E11 IO_L43P_1 PM_IO_3V_18 3V
A7 F10 IO_L07N_1 PM_IO_3V_7 3V
A8 H12 IO_L45P_1 PM_IO_3V_22 3V
A9 C7 IO_L08N_1 PM_IO_3V_9 3V
A10 D10 IO_L37N_1 PM_IO_3V_13 3V
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 65
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 66

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Table 2-31: PM1 Pinout (Continued)
PM1 Pin FPGA Pin Pin Description ML310 Schematic Net
FPGA Bank
V
CCO
A11 H16 IO_L69P_0 PM_IO_82 2.5V
A12 J16 IO_L69N_0 PM_IO_83 2.5V
A13 A25 RXPPAD4 RXPPAD4_A25
A14 A24 RXNPAD4 RXNPAD4_A24
A15 A12 RXPPAD7 RXPPAD7_A12
A16 A11 RXNPAD7 RXNPAD7_A11
A17 AK6 TXPPAD16 TXPPAD16_AK6
A18 AK7 TXNPAD16 TXNPAD16_AK7
A19 AK19 TXPPAD19 TXPPAD19_AK19
A20 AK20 TXNPAD19 TXNPAD19_AK20
C1 D28 IO_L06P_7 PM_IO_90 2.5V
C2 C27 IO_L06N_7 PM_IO_91 2.5V
C3 H11 IO_L39P_1 PM_IO_3V_16 3V
C4 E10 IO_L37P_1 PM_IO_3V_12 3V
C5 F8 IO_L02N_1 PM_IO_3V_1 3V
C6 E9 IO_L03N_1 PM_IO_3V_3 3V
C7 G11 IO_L39N_1 PM_IO_3V_17 3V
C8 G9 IO_L06N_1 PM_IO_3V_5 3V
C9 C18 IO_L68P_0 PM_IO_80 2.5V
C10 D18 IO_L68N_0 PM_IO_81 2.5V
C11 D11 IO_L43N_1 PM_IO_3V_19 3V
C12 E12 IO_L46P_1 PM_IO_3V_24 3V
C13 A18 RXPPAD6 RXPPAD6_A18
C14 A17 RXNPAD6 RXNPAD6_A17
C15 A5 RXPPAD9 RXPPAD9_A5
C16 A4 RXNPAD9 RXNPAD9_A4
C17 AK13 TXPPAD18 TXPPAD18_AK13
C18 AK14 TXNPAD18 TXNPAD18_AK14
C19 AK26 TXPPAD21 TXPPAD21_AK26
C20 AK27 TXNPAD21 TXNPAD21_AK27
D1 D30 IO_L31P_7 PM_IO_92 2.5V
D2 D29 IO_L31N_7 PM_IO_93 2.5V
D3 G26 IO_L02P_7 PM_IO_84 2.5V
66 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 67

High-Speed I/O
R
Table 2-31: PM1 Pinout (Continued)
PM1 Pin FPGA Pin Pin Description ML310 Schematic Net
FPGA Bank
V
CCO
D4 G25 IO_L02N_7 PM_IO_85 2.5V
D5 A8 IO_L44N_1 PM_IO_3V_21 3V
D6 B8 IO_L44P_1 PM_IO_3V_20 3V
D7 D7 IO_L08P_1 PM_IO_3V_8 3V
D8 F9 IO_L07P_1 PM_IO_3V_6 3V
D9 E8 IO_L03P_1 PM_IO_3V_2 3V
D10 D8 IO_L38P_1 PM_IO_3V_14 3V
D11 D17 IO_L67P_0 PM_IO_78 2.5V
D12 E17 IO_L67N_0 PM_IO_79 2.5V
D13 A27 TXNPAD4 TXNPAD4_A27
D14 A26 TXPPAD4 TXPPAD4_A26
D15 A14 TXNPAD7 TXNPAD7_A14
D16 A13 TXPPAD7 TXPPAD7_A13
D17 AK4 RXNPAD16 RXNPAD16_AK4
D18 AK5 RXPPAD16 RXPPAD16_AK5
D19 AK17 RXNPAD19 RXNPAD19_AK17
D20 AK18 RXPPAD19 RXPPAD19_AK18
F1 J24 IO_L05P_7 PM_IO_88 2.5V
F2 J23 IO_L05N_7 PM_IO_89 2.5V
F3 H10 IO_L09P_1 PM_IO_3V_10 3V
F4 H9 IO_L06P_1 PM_IO_3V_4 3V
F5 C8 IO_L38N_1 PM_IO_3V_15 3V
F6 F7 IO_L02P_1 PM_IO_3V_0 3V
F7 G12 IO_L45N_1 PM_IO_3V_23 3V
F8 G10 IO_L09N_1 PM_IO_3V_11 3V
F9 B16 GCLK6S PM_CLK_TOP 2.5V
F10 NC NC NC NC
F11 F15/AH15 GCLK3P/1S LVDS_CLKEXT_N 2.5V
F12 G15/AJ15 GCLK2S/0P LVDS_CLKEXT_P 2.5V
F13 A20 TXNPAD6 TXNPAD6_A20
F14 A19 TXPPAD6 TXPPAD6_A19
F15 A7 TXNPAD9 TXNPAD9_A7
F16 A6 TXPPAD9 TXPPAD9_A6
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 67
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 68

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Table 2-31: PM1 Pinout (Continued)
PM1 Pin FPGA Pin Pin Description ML310 Schematic Net
F17 AK11 RXNPAD18 RXNPAD18_AK11
F18 AK12 RXPPAD18 RXPPAD18_AK12
F19 AK24 RXNPAD21 RXNPAD21_AK24
F20 AK25 RXPPAD21 RXPPAD21_AK25
Notes:
1. LVDS pairs are shown shaded; all other signals are single-ended.
2. LVDS pairs can also be used as single-ended I/O at 2.5V
3. NC indicates a “no connect” signal.
ML310 PM2 User I/O
The PM2 connector makes most of the LVDS pairs available to the user, along with singleended signals. Tab l e 2- 32 shows the pinout for the PM2 connector on the ML310.
Table 2-32: PM2 Pinout
PM2 Pin FPGA Pin Pin Description ML310 Schematic Net
A1 T5 IO_L89N_3 PM_IO_69 2.5V
A2 T6 IO_L89P_3 PM_IO_68 2.5V
FPGA Bank
V
CCO
FPGA Bank
V
CCO
A3 T3 IO_L88N_3 PM_IO_67 2.5V
A4 T4 IO_L88P_3 PM_IO_66 2.5V
A5 V3 IO_L58N_3 PM_IO_55 2.5V
A6 V4 IO_L58P_3 PM_IO_54 2.5V
A7 U7 IO_L56N_3 PM_IO_51 2.5V
A8 U8 IO_L56P_3 PM_IO_50 2.5V
A9 V7 IO_L53N_3 PM_IO_45 2.5V
A10 V8 IO_L53P_3 PM_IO_44 2.5V
A11 AC15 IO_L67P_4 PM_IO_72 2.5V
A12 AB15 IO_L67N_4 PM_IO_73 2.5V
A13 AA4 IO_L48P_3 PM_IO_34 2.5V
A14 AA3 IO_L48N_3 PM_IO_35 2.5V
A15 AD2 IO_L42P_3 PM_IO_22 2.5V
A16 AD1 IO_L42N_3 PM_IO_23 2.5V
A17 AG2 IO_L06P_3 PM_IO_6 2.5V
A18 AG1 IO_L06N_3 PM_IO_7 2.5V
A19 AH5 IO_L02P_3 PM_IO_0 2.5V
A20 AG5 IO_L02N_3 PM_IO_1 2.5V
68 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
Page 69

High-Speed I/O
R
Table 2-32: PM2 Pinout (Continued)
PM2 Pin FPGA Pin Pin Description ML310 Schematic Net
FPGA Bank
C1 W1 IO_L57N_3 PM_IO_53 2.5V
C2 Y1 IO_L57P_3 PM_IO_52 2.5V
C3 U4 IO_L85N_3 PM_IO_61 2.5V
C4 U5 IO_L85P_3 PM_IO_60 2.5V
C5 W5 IO_L50N_3 PM_IO_39 2.5V
C6 W6 IO_L50P_3 PM_IO_38 2.5V
C7 V5 IO_L55N_3 PM_IO_49 2.5V
C8 V6 IO_L55P_3 PM_IO_48 2.5V
C9 AE14 IO_L68P_4 PM_IO_74 2.5V
C10 AD14 IO_L68N_4 PM_IO_75 2.5V
C11 AB6 IO_L40P_3 PM_IO_20 2.5V
C12 AB5 IO_L40N_3 PM_IO_21 2.5V
C13 AC2 IO_L45P_3 PM_IO_28 2.5V
C14 AB2 IO_L45N_3 PM_IO_29 2.5V
C15 AD2 IO_L42P_3 PM_IO_14 2.5V
V
CCO
C16 AD1 IO_L42N_3 PM_IO_15 2.5V
C17 AH4 IO_L04P_3 PM_IO_4 2.5V
C18 AG3 IO_L04N_3 PM_IO_5 2.5V
C19 AF6 IO_L31P_3 PM_IO_8 2.5V
C20 AE5 IO_L31N_3 PM_IO_9 2.5V
D1 U1 IO_L90N_3 PM_IO_71 2.5V
D2 V1 IO_L90P_3 PM_IO_70 2.5V
D3 T7 IO_L86N_3 PM_IO_63 2.5V
D4 T8 IO_L86P_3 PM_IO_62 2.5V
D5 V2 IO_L60N_3 PM_IO_59 2.5V
D6 W2 IO_L60P_3 PM_IO_58 2.5V
D7 W3 IO_L52N_3 PM_IO_43 2.5V
D8 W4 IO_L52P_3 PM_IO_42 2.5V
D9 T9 IO_L59N_3 PM_IO_57 2.5V
D10 U9 IO_L59P_3 PM_IO_56 2.5V
D11 AG14 IO_L69P_4 PM_IO_76 2.5V
D12 AF14 IO_L69N_4 PM_IO_77 2.5V
D13 AA6 IO_L44P_3 PM_IO_26 2.5V
ML310 User Guide www.xilinx.com 69
UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004 1-800-255-7778
Page 70

R
Chapter 2: ML310 Embedded Development Platform
Table 2-32: PM2 Pinout (Continued)
PM2 Pin FPGA Pin Pin Description ML310 Schematic Net
FPGA Bank
D14 AA5 IO_L44N_3 PM_IO_27 2.5V
D15 AC4 IO_L43P_3 PM_IO_24 2.5V
D16 AC3 IO_L43N_3 PM_IO_25 2.5V
D17 AE4 IO_L33P_3 PM_IO_10 2.5V
D18 AE3 IO_L33N_3 PM_IO_11 2.5V
D19 AF4 IO_L34P_3 PM_IO_12 2.5V
D20 AF3 IO_L34N_3 PM_IO_13 2.5V
F1 AA1 IO_L51N_3 PM_IO_41 2.5V
F2 AB1 IO_L51P_3 PM_IO_40 2.5V
F3 U2 IO_L87N_3 PM_IO_65 2.5V
F4 U3 IO_L87P_3 PM_IO_64 2.5V
F5 Y2 IO_L54N_3 PM_IO_47 2.5V
F6 AA2 IO_L54P_3 PM_IO_46 2.5V
F7 Y4 IO_L49N_3 PM_IO_37 2.5V
F8 Y5 IO_L49P_3 PM_IO_36 2.5V
V
CCO
F9 NC NC NC 2.5V
F10 AG15 IO_L74P_4 PM_CLK_BOT 2.5V
F11 W8 IO_L47P_3 PM_IO_32 2.5V
F12 W7 IO_L47N_3 PM_IO_33 2.5V
F13 AB4 IO_L46P_3 PM_IO_30 2.5V
F14 AB3 IO_L46N_3 PM_IO_31 2.5V
F15 AE2 IO_L39P_3 PM_IO_18 2.5V
F16 AE1 IO_L39N_3 PM_IO_19 2.5V
F17 AH2 IO_L03P_3 PM_IO_2 2.5V
F18 AH1 IO_L03N_3 PM_IO_3 2.5V
F19 AD4 IO_L37P_3 PM_IO_16 2.5V
F20 AD3 IO_L37N_3 PM_IO_17 2.5V
Notes:
1. LVDS pairs are shown shaded; all other signals are single-ended.
2. LVDS pairs can also be used as single-ended I/O at 2.5V
3. NC indicates a “no connect” signal.
70 www.xilinx.com ML310 User Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG068 (v1.01) August 25, 2004
 Loading...
Loading...