Page 1

R
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561
Memory Interfaces
Development Board
User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 2
Xilinx is disclosing this user guide, manual, release note, and/or specification (the "Documentation") to you solely for use in the development
R
of designs to operate with Xilinx hardware devices. You may not reproduce, distribute, republish, download, display, post, or transmit the
Documentation in any form or by any means including, but not limited to, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise,
without the prior written consent of Xilinx. Xilinx expressly disclaims any liability arising out of your use of the Documentation. Xilinx reserves
the right, at its sole discretion, to change the Documentation without notice at any time. Xilinx assumes no obligation to correct any errors
contained in the Documentation, or to advise you of any corrections or updates. Xilinx expressly disclaims any liability in connection with
technical support or assistance that may be provided to you in connection with the Information.
THE DOCUMENTATION IS DISCLOSED TO YOU “AS-IS” WITH NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND. XILINX MAKES NO OTHER
WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, REGARDING THE DOCUMENTATION, INCLUDING ANY
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NONINFRINGEMENT OF THIRD-PARTY
RIGHTS. IN NO EVENT WILL XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL, INDIRECT, EXEMPLARY, SPECIAL, OR INCIDENTAL
DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY LOSS OF DATA OR LOST PROFITS, ARISING FROM YOUR USE OF THE DOCUMENTATION.
© 2007–2008 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved.
XILINX, the Xilinx logo, Virtex, Spartan, ISE, and other designated brands included herein are trademarks of Xilinx in the United States and
other countries. PCI EXPRESS is a registered trademark of PCI-SIG. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Revision History
The following table shows the revision history for this document.
Date Version Revision
02/12/07 1.0 Initial Xilinx release.
08/09/07 1.1 Revised Read and Write Strobe in Ta b le 5-4 , pag e 4 9 . Added Chapter 7, “ML561
Hardware-Simulation Correlation.”
04/19/08 1.2 Revised Figure 3-11, page 37 and Table 3-19, page 38. Corrected FPGA driver for Read
Data and Read Strobe in Ta bl e 5- 4, pa ge 49. Updated Data and Strobe entries in Ta bl e 5- 5,
page 49. Updated manufacturers and links in Appendix B, “Bill of Materials.”
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 3
Table of Contents
Preface: About This Guide
Guide Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Additional Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Additional Support Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Typographical. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Online Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chapter 1: Introduction
About the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Tool Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Development Board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Chapter 2: Getting Started
Documentation and Reference Design CD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Initial Board Check Before Applying Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Applying Power to the Board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
Hardware Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
FPGA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Memories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
DDR400 SDRAM Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
DDR2 DIMM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
DDR2 SDRAM Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
QDRII SRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
RLDRAM II Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Memory Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
DDR400 and DDR2 Component Memories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
DDR2 SDRAM DIMM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
QDRII and RLDRAM II Memories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
External Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
RS-232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
USB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Clocks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
200 MHz LVPECL Clock. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
SMA Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
33 MHz Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
33 MHz System ACE Controller Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
GTP Clocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
User I/Os. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
General-Purpose Headers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 3
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 4

R
Seven-Segment Displays. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Pushbuttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Power On or Off Slide Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Soft Touch Probe Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Power Measurement Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Liquid Crystal Display Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Power Regulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Power Distribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Voltage Regulators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Board Design Considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Chapter 4: Electrical Requirements
Power Consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
FPGA Internal Power Budget. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Chapter 5: Signal Integrity Recommendations
Termination and Transmission Line Summaries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Chapter 6: Configuration
Configuration Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
JTAG Chain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
JTAG Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Parallel IV Cable Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
System ACE Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Test Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Signal Integrity Correlation Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
DDR2 Component Write Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
DDR2 Component Read Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
DDR2 DIMM Write Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
DDR2 DIMM Read Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
QDRII Write Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
QDRII Read Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Summary and Recommendations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
How to Generate a User-Specific FPGA IBIS Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Appendix A: FPGA Pinouts
FPGA #1 Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
FPGA #2 Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
FPGA #3 Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
4 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 5

R
Appendix B: Bill of Materials
Appendix C: LCD Interface
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Display Hardware Design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Hardware Schematic Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Peripheral Device KS0713 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Controller – Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Controller – LCD Panel Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Controller – Power Supply Circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Operation Example of the 64128EFCBC-3LP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Instruction Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Read/Write Characteristics (6800 Mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Design Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
LCD Panel Used in Full Graphics Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
LCD Panel Used in Character Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Array Connector Numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 5
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 6

6 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
R
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 7
R
About This Guide
This user guide describes the Virtex®-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Development
Board. Complete and up-to-date documentation of the Virtex-5 family of FPGAs is
available on the Xilinx website at http://www.xilinx.com/virtex5
Guide Contents
This manual contains the following chapters:
• Chapter 1, “Introduction”
• Chapter 2, “Getting Started”
• Chapter 3, “Hardware Description”
• Chapter 4, “Electrical Requirements”
• Chapter 5, “Signal Integrity Recommendations”
• Chapter 6, “Configuration”
• Chapter 7, “ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation”
• Appendix A, “FPGA Pinouts”
• Appendix B, “Bill of Materials”
• Appendix C, “LCD Interface”
Preface
.
Additional Documentation
The following documents are also available for download at
http://www.xilinx.com/virtex5
• Virtex-5 Family Overview
The features and product selection of the Virtex-5 family are outlined in this overview.
• Virtex-5 FPGA Data Sheet: DC and Switching Characteristics
This data sheet contains the DC and Switching Characteristic specifications for the
Virtex-5 family.
• Virtex-5 FPGA User Guide
Chapters in this guide cover the following topics:
- Clocking Resources
- Clock Management Technology (CMT)
- Phase-Locked Loops (PLLs)
-Block RAM
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 7
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
.
Page 8

Preface: About This Guide
R
• Virtex-5 FPGA RocketIO GTP Transceiver User Guide
• Virtex-5 FPGA RocketIO GTX Transceiver User Guide
• Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Processor Block for PowerPC
• Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC User Guide
• Virtex-5 FPGA Integrated Endpoint Block User Guide for PCI Express Designs
- Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs)
-SelectIO™ Resources
- SelectIO Logic Resources
- Advanced SelectIO Logic Resources
This guide describes the RocketIO™ GTP transceivers available in the Virtex-5 LXT
and SXT platforms.
This guide describes the RocketIO GTX transceivers available in the Virtex-5 FXT
platform.
®
440 Designs
This reference guide is a description of the embedded processor block available in the
Virtex-5 FXT platform.
This guide describes the dedicated Tri-Mode Ethernet Media Access Controller
available in the Virtex-5 LXT, SXT, and FXT platforms.
This guide describes the integrated Endpoint blocks in the Virtex-5 LXT, SXT, and FXT
platforms used for PCI Express
®
designs.
• Virtex-5 FPGA XtremeDSP Design Considerations User Guide
This guide describes the XtremeDSP™ slice and includes reference designs for using
the DSP48E.
• Virtex-5 FPGA Configuration Guide
This all-encompassing configuration guide includes chapters on configuration
interfaces (serial and SelectMAP), bitstream encryption, Boundary-Scan and JTAG
configuration, reconfiguration techniques, and readback through the SelectMAP and
JTAG interfaces.
• Virtex-5 FPGA System Monitor User Guide
The System Monitor functionality available in all the Virtex-5 devices is outlined in
this guide.
• Virtex-5 FPGA Packaging and Pinout Specifications
This specification includes the tables for device/package combinations and maximum
I/Os, pin definitions, pinout tables, pinout diagrams, mechanical drawings, and
thermal specifications.
• Virtex-5 FPGA PCB Designer’s Guide
This guide provides information on PCB design for Virtex-5 devices, with a focus on
strategies for making design decisions at the PCB and interface level.
Additional Support Resources
To search the database of silicon and software questions and answers, or to create a
technical support case in WebCase, see the Xilinx website at:
http://www.xilinx.com/support
8 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
.
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 9
R
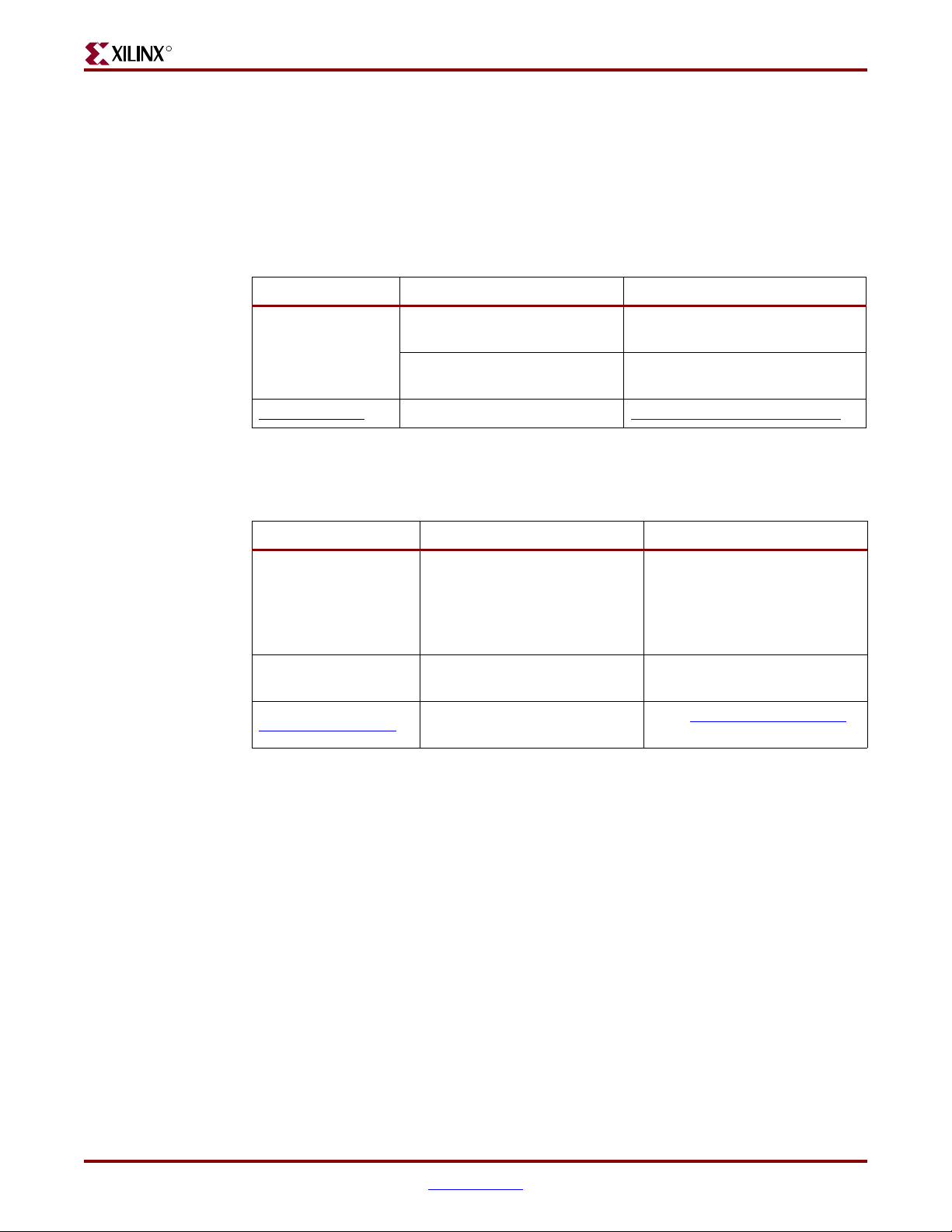
Conventions
Typographical
Conventions
This document uses the following conventions. An example illustrates each convention.
This document uses the following typographical conventions. An example illustrates each
convention.
Convention Meaning or Use Example
Italic font
Underlined Text
Online Document
The following conventions are used in this document:
Convention Meaning or Use Example
Blue text
Red text
Blue, underlined text
References to other documents
Emphasis in text
Indicates a link to a web page. http://www.xilinx.com/virtex5
Cross-reference link to a location
in the current document
Cross-reference link to a location
in another document
Hyperlink to a website (URL)
See the Virtex-5 Configuration Guide
for more information.
The address (F) is asserted after
clock event 2.
See the section “Additional
Documentation” for details.
Refer to “Clock Management
Technology (CMT)” in
Chapter 2 for details.
See Figure 5 in the Virtex-5 FPGA
Data Sheet
Go to http://www.xilinx.com
for the latest documentation.
Terminology
This section defines terms used in Chapter 7, “ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation,”
of this document.
DVW is the data valid window opening measured by the VIH and VIL masks. The
Data Valid Window (DVW)
Extrapolation
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 9
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
smaller of the two values are listed as absolute time as well as in terms of the percentage
of UI (Unit Interval), or bit time.
The ultimate goal of a design is to ascertain quality of signal at the receiver I/O Buffer
(IOB). This measurement can only be simulated. When the hardware measurements are
correlated with the simulation at the probe point, the extra probe capacitance is
removed from the IBIS schematics, and the simulation is repeated at two extreme
corners (slow-weak and fast-strong). Removal of probe capacitance is important to
represent the actual hardware. If the SI characteristics of these simulations are proved
to be within the acceptable range with sufficient margin, then the performance
requirements for data signal interface of the corresponding memory operation at the
target clock frequency are proved to have been met.
Page 10

Preface: About This Guide
R
Hardware Measurements
Inter-Symbol Interference
(ISI)
Noise Margin
These measurements are the actual real-time measurements of an eye diagram and a
segment of the test pattern (PRBS6) waveform captured on ML561 hardware at the
designated probe point using an Agilent scope.
As the frequency of operation increases, the signal delay is affected by the data pattern
that precedes the current data bit. This is called the inter-symbol interference (ISI) effect.
All testing is performed with a pseudo-random bitstream (PRBS) of order 6, that is,
PRBS6. ISI is the jitter represented by the eye at all four voltage thresholds. The worst
of the following two sum values are listed in this table:
• Sum of ISI at VIH(ac)-min and VIH(dc)-min
• Sum of ISI at VIL(ac)-max and VIL(dc)-max
This is the noise margin available at the receiver. Measurements are taken at the AC
voltage levels as the minimum vertical opening of the eye in the vicinity of the center
of the bit period. Ideally, the input voltage needs to remain above the DC voltage
specifications. However, by considering the AC voltage specifications for the nominal
voltage level for VREF, these measurements are more conservative values that also
include the effects of VREF variations.
• VIH margin: Difference between the top of the eye opening and VIH(ac)-min
• VIL margin: Difference between VIL(ac)-max and the bottom of the eye opening
These measurements are performed in stand-alone fashion for the signal under test.
Thus no consideration of crosstalk or Simultaneously Switching Output (SSO) effects
are accounted for.
Overshoot / Undershoot
Margin
Simulation Correlation
VIH(ac)-min
VIH(dc)-min
VIL(ac)-max
Overshoot margin is the difference between the maximum allowable VIH per JEDEC
specification and the maximum amplitude of the measured eye. Similarly, undershoot
margin is the difference between the minimum amplitude of the measured eye and the
minimum allowable VIL value per JEDEC specification. For both SSTL18 and 1.8V
HSTL specifications:
• VIH(max) < (VDDQ + 300 mV) = (1.8 + 0.3)V = 2.1V
• VIL(min) > -300 mV = 0.3V
The BoardSim utility of the HyperLynx simulator is used to extract the IBIS schematics
of the same signal net for which hardware measurements are made. To replicate the
hardware measurement probe set up at the probe point, a 0.5 pF probe capacitance is
added based on Agilent probe loading specifications to the extracted IBIS schematics of
the memory signal. For the FPGA devices soldered on the ML561 board under test, the
process corner (slow, typical, or fast) is not known. Thus simulation is performed for all
three corners (slow-weak, typical, and fast-strong), and the results of the case that best
fits with hardware measurement is selected for tabulation.
This term is the minimum input level at which the receiver must recognize input logic
High.
When the input signal reaches VIH(ac)-min, the receiver continues to interpret the
input as a logic High as long as the signal remains above this voltage. (This parameter
is basically the hysteresis for a logic ‘1’.)
This term is the maximum input level at which the receiver must recognize input logic
Low.
When the input signal reaches VIL(ac)-max, the receiver continues to interpret the input
VIL(dc)-max
as a logic Low as long as the signal remains below this voltage. (This parameter is
basically the hysteresis for logic ‘0’.)
10 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 11

R
Chapter 1
Introduction
This chapter introduces the Virtex®-5 FPGA ML561 reference design. It contains the
following sections:
• “About the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Tool Kit”
• “Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Development Board”
About the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Tool Kit
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Tool Kit provides a complete development
platform to interface with external memory devices for designing and verifying
applications based on the Virtex-5 LXT FPGA platform. This kit allows designers to
implement high-speed applications with extreme flexibility using IP cores and customized
modules. The Virtex-5 LXT FPGA, with its column-based architecture, makes it possible to
develop highly flexible memory interface applications.
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Tool Kit includes the following:
• Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Development Board (XC5VLX50T-FFG1136
FPGA)
• 5V/6.5 A DC power supply
• Country-specific power supply line cord
• RS-232 serial cable, DB9-F to DB9-F
• Documentation and reference design CD-ROM
Optional items that also support development efforts include:
• Xilinx
• JTAG cable
• Xilinx Parallel IV cable
For assistance with any of these items, contact your local Xilinx distributor or visit the
Xilinx online store at www.xilinx.com
The heart of the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Tool Kit is the Virtex-5 FPGA
ML561 Development Board. This manual provides comprehensive information on Rev A3
and later revisions of this board.
®
ISE® software
.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 11
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 12
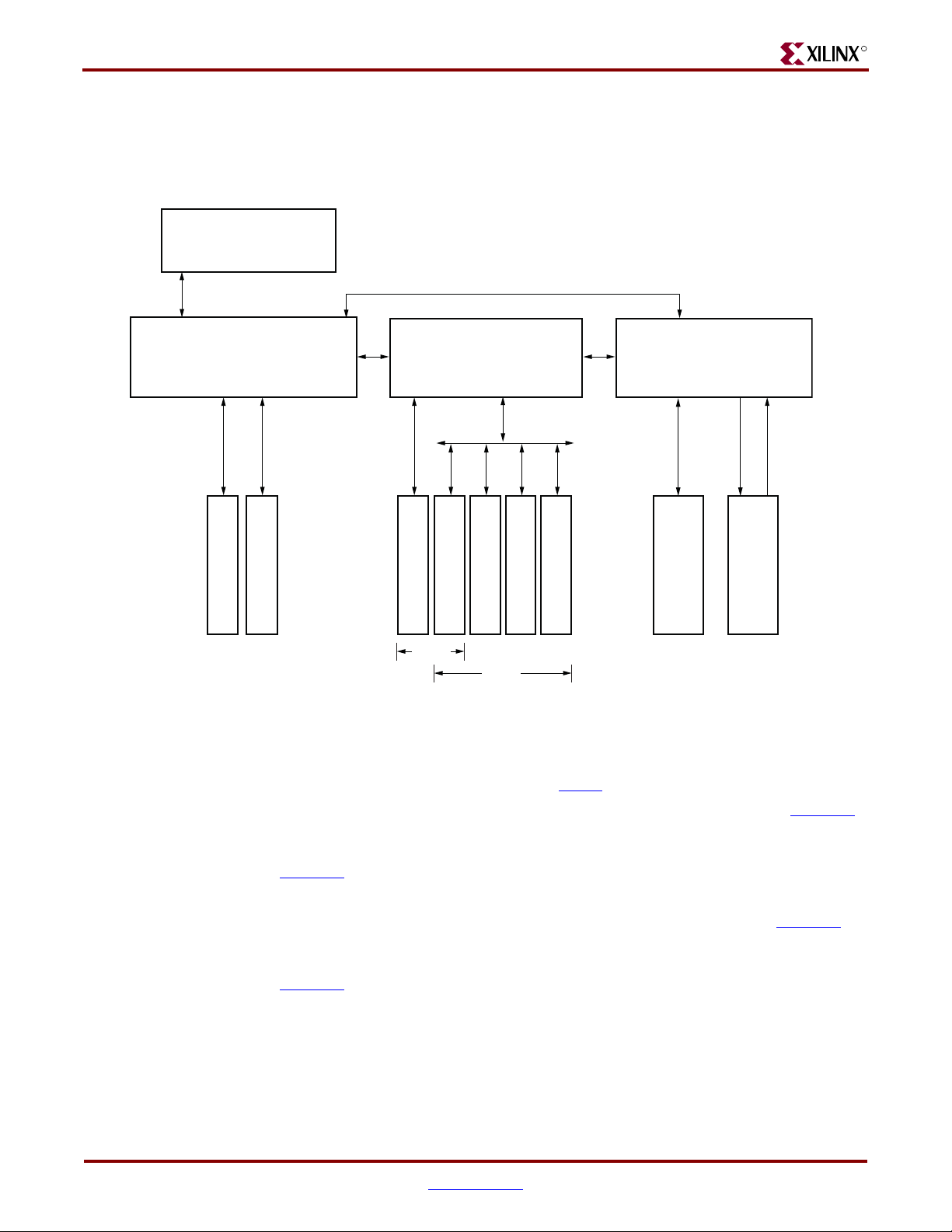
Chapter 1: Introduction
R
DDR2 DIMM
72
72
RLDRAM II
(CIO)
36
QDRII SRAM
DDR2 SDRAM
32
32
FPGA #1
XC5VLX50T/
FFG1136
FPGA #2
XC5VLX50T/
FFG1136
DDR400 SDRAM
SSTL18/SSTL2 SSTL18 HSTL
External Interfaces:
System ACE Controller,
USB, RS-232, LCD
DDR2 DIMM
DDR2 DIMM
DDR2 DIMM
DDR2 DIMM
72
72
UG191_c1_01_020807
FPGA #3
XC5VLX50T/
FFG1136
WIDE
DEEP
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Development Board
A high-level functional block diagram of the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces
Development Board is shown in Figure 1-1.
12 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
Figure 1-1: Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board Block Diagram
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board includes the following major functional
blocks:
• Three XC5VLX50T-FFG1136 FPGAs (see D
S100, Virtex-5 Family Overview)
• DDR400 components: 128 MB (32M x 32 bits) at 200 MHz clock speed. See XAPP851,
DDR SDRAM Controller Using Virtex-5 FPGA Devices.
• DDR2 DIMM: Five PC2-5300 DIMM sockets for up to 2 GB (128M x 144 bits). See
XAPP85
• DDR2-667 components: 64 MB (16M x 32 bits) at 333 MHz clock speed
• QDRII memory: 16 MB (2M x 72 bits) at up to 300 MHz clock speed. See XAPP853
QDR II SRAM Interface for Virtex-5 Devices.
• RLDRAM II memory: 64 MB (16M x 36 bits) at up to 300 MHz clock speed. See
XAPP852
• One DB9-M RS-232 port and one USB 2.0 port
8, High-Performance DDR2 SDRAM Interface in Virtex-5 Devices.
, RLDRAM II Memory Interface for Virtex-5 FPGAs.
• A System ACE™ CompactFlash (CF) Configuration Controller that allows storing
and downloading of up to eight FPGA configuration image files
• On-board power regulators with ±5% output margin test capabilities
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
,
Page 13
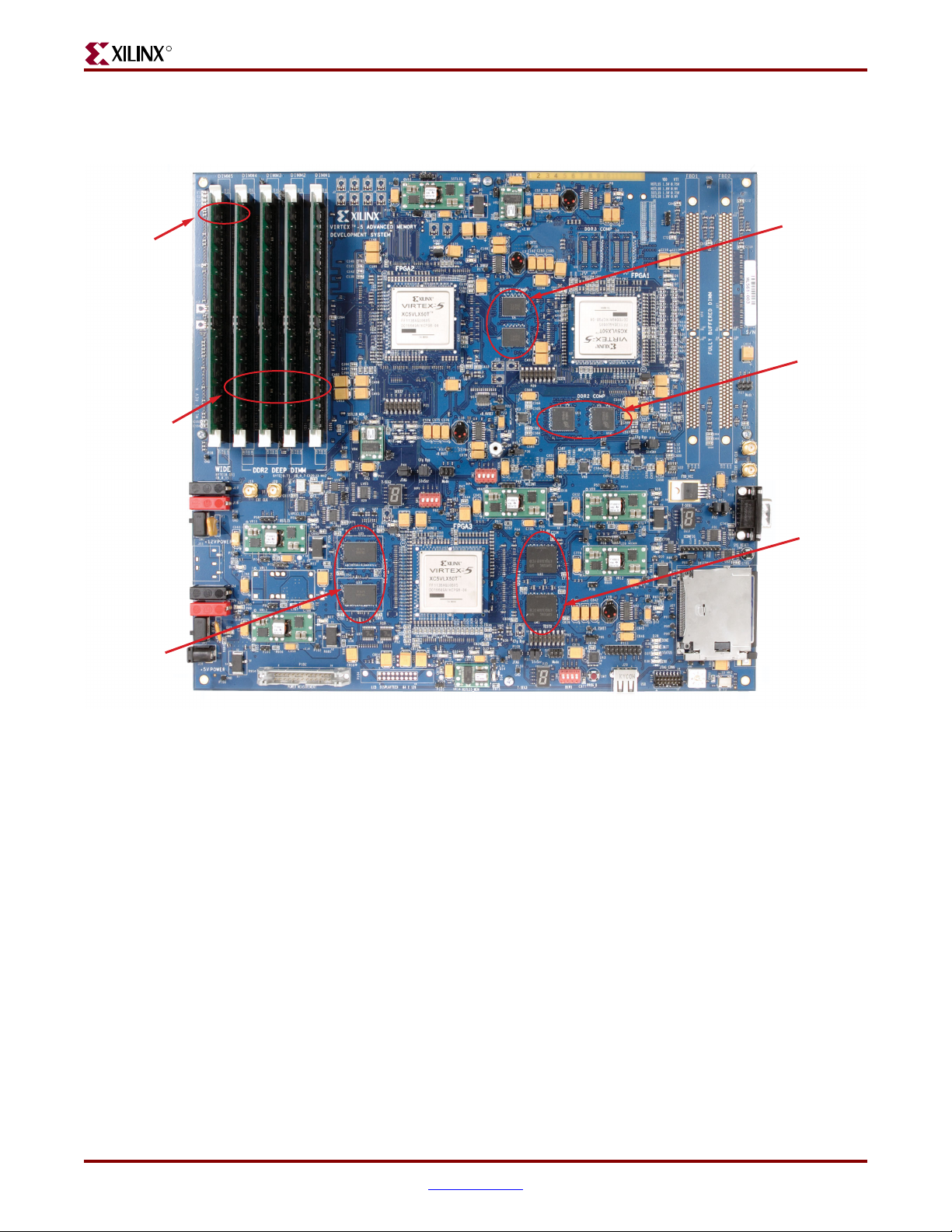
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Development Board
R
DDR2
SDRAM
DIMM
32-bit
DDR400
SDRAM
32-bit
DDR2
SDRAM
72-bit
QDRII
SRAM
36-bit
RLDRAM II
144 bits wide
72 bits wide,
up to 4 deep
UG199_c1_02_050106
Figure 1-2 shows the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board and indicates the
locations of the resident memory devices.
Figure 1-2: Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 13
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 14

Chapter 1: Introduction
R
14 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 15

R
Getting Started
This chapter describes the items needed to configure the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory
Interfaces Development Board. The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board is tested at
the factory after assembly and should be received in working condition. It is set up to load
a bitstream from the CompactFlash card at socket J27 through the System ACE controller
(U45).
This chapter contains the following sections:
• “Documentation and Reference Design CD”
• “Initial Board Check Before Applying Power”
• “Applying Power to the Board”
Documentation and Reference Design CD
Chapter 2
The CD included in the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Tool Kit contains the
design files for the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board, including schematics,
board layout, and reference design files. Open the ReadMe.rtf file on the CD to review
the list of contents.
Initial Board Check Before Applying Power
Perform these steps before applying board power:
1. Set up the Configuration Mode jumpers (P27, P46, and P112) for JTAG configuration.
See “Configuration Modes” on page 51 for all available modes for the Virtex-5 FPGA
ML561 Development Board.
2. Confirm that the JTAG chain jumpers P38, P44, and P109 are connecting pins 1 to 2 and
pins 3 to 4. This way, all three devices are in the chain. Otherwise, the ISE iMPACT
software will not find all three devices to configure. For more information see “JTAG
Chain” on page 52.
3. Make sure that no inhibit jumpers are present on any of the power supply regulator
modules. For more information, see “Voltage Regulators” on page 34.
4. The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board has a 200 MHz on-board oscillator,
which provides a copy of a differential LVPECL clock to each of the three FPGAs
through a differential clock buffer (ICS853006). There is also a connection to a pair of
SMA connectors (J19, J20) to provide a differential LVDS clock from an off-board signal
generator. Another differential clock buffer (ICS853006) provides a copy of this clock to
each of the three FPGAs. These clocks are available after configuration for the design to
use for various system clocks.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 15
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 16

Chapter 2: Getting Started
R
5. Insert the CompactFlash card included in the kit into socket J27 on the Virtex-5 FPGA
ML561 Development Board. To select the startup file, check that SW8 is set to position
0.
Applying Power to the Board
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board is now ready to power on. The Virtex-5
FPGA ML561 Development Board is shipped with a country-specific AC line cord for the
universal input 5V desktop power supply. Follow these steps to power up the Virtex-5
FPGA ML561 Development Board:
1. Confirm that the ON-OFF switch, SW5, is in the OFF position.
2. Plug the 5V desktop power supply into the 5V DC input barrel jack J28 on the Virtex-5
FPGA ML561 Development Board. Plug the desktop power supply AC line cord into
an electrical outlet supplying the appropriate voltage.
3. Turn SW5 to the ON position. The power indicators for all regulator modules should
come on, indicating output from the regulators. The System ACE status LED D37
comes on when the System ACE controller (U45) extracts the BIT configuration file
from the CompactFlash card to the FPGA. If no CompactFlash card is installed in the
card socket J27 on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board, the red System ACE
error LED D38 flashes.
4. If a CompactFlash card is not installed in socket J27, a JTAG cable must be used to
configure the FPGAs. To use a Parallel IV cable or other JTAG pod, download the
FPGA configuration bitstream into each FPGA. After the DONE LED (D28) comes on,
the FPGAs are configured and ready to use.
5. Push the reset button SW4.
16 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 17

R
Hardware Description
This chapter describes the major hardware blocks on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561
Development Board and provides useful design consideration. It contains the following
sections:
• “Hardware Overview”
• “Memory Details”
• “External Interfaces”
• “Power Regulation”
• “Board Design Considerations”
Hardware Overview
The ML561 Development/Evaluation system reference design is implemented with three
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136 devices from the Virtex-5 FPGA family to demonstrate high-speed
external memory application interfaces. The memory technologies supported by the
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board are DDR2 SDRAM, DDR400 SDRAM, QDRII
SRAM, and RLDRAM II SDRAM.
Chapter 3
Figure 3-1 provides a view of all the major components on ML561 board. It shows the
placement of the three Virtex-5 FPGAs, and the position of the associated major interfaces
for each FPGA.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 17
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 18
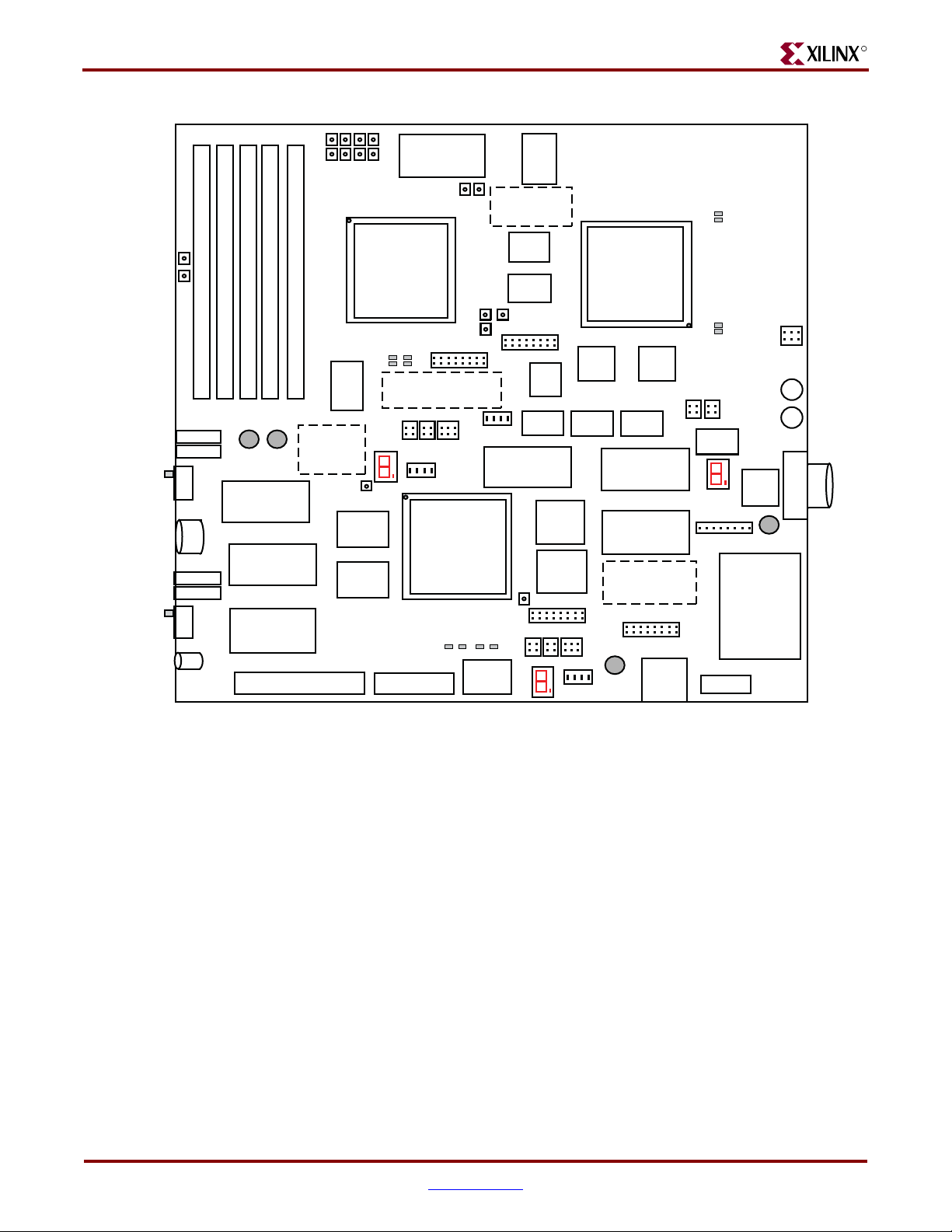
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
HSTL
FPGA #3
FPGA #1
FPGA #2
SSTL18
HSTL
V
TT
& V
REF
SSTL18
V
TT
& V
REF
SSTL2
V
TT
& V
REF
V
CCAUX
/
V
CCO
V
CCINT
USB
DIP3
DIP1
DIP2
7SEG3
7SEG2
7SEG1
Config3
PROG
External
CLK
5V Input
Jack
5V Banana
Jacks
12V Banana
Jacks
12V Input
Jack
SPY
SPY
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
RESET
SPY
Config1
Config2
SPY
SSTL2
JTAG
UG199_c3_01_050106
System ACE
Controller
FPGA #3 LEDs
FPGA #1
LEDs
FPGA #1
LEDs
FPGA #2
LEDs
JTAG Test Header
Test Header 3
A1
A1
A1
Test Header 2
Test Header 1
Serial Header
HSTL
12V -> 5V
RLDRAM II
QDRII
QDRII
DDR2
AVTRX
AVC
CPLL
AVTTX
VVTTR
XC
FBD
VCC
RS-232
Driver
DDR
DDR
DDR2
MGT
CLK
MGT Connections
RLDRAM II
Clocks &
Buffers
SSTL18
_M
DIMM1
DIMM2
DIMM3
DIMM4
DIMM5
SSTL2
_M
3.3V
LCD Connector
Pwr Measure Header
Figure 3-1: ML561 XC5VLX50T-FFG1136 Board Placement Diagram
The ML561 uses three Virtex-5 XC5VLX50T-FFG1136 devices, each in a 1136-pin,
35 mm x 35 mm BGA package. Figure 1-1, page 12 shows the memory devices associated
with the three FPGAs. Refer to Appendix A, “FPGA Pinouts,” for a complete pinout of all
FPGA
Virtex-5 devices on the board. Refer to Appendix B, “Bill of Materials,” for a list of major
components on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board, including their reference
designators and links to their corresponding data sheets.
18 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 19
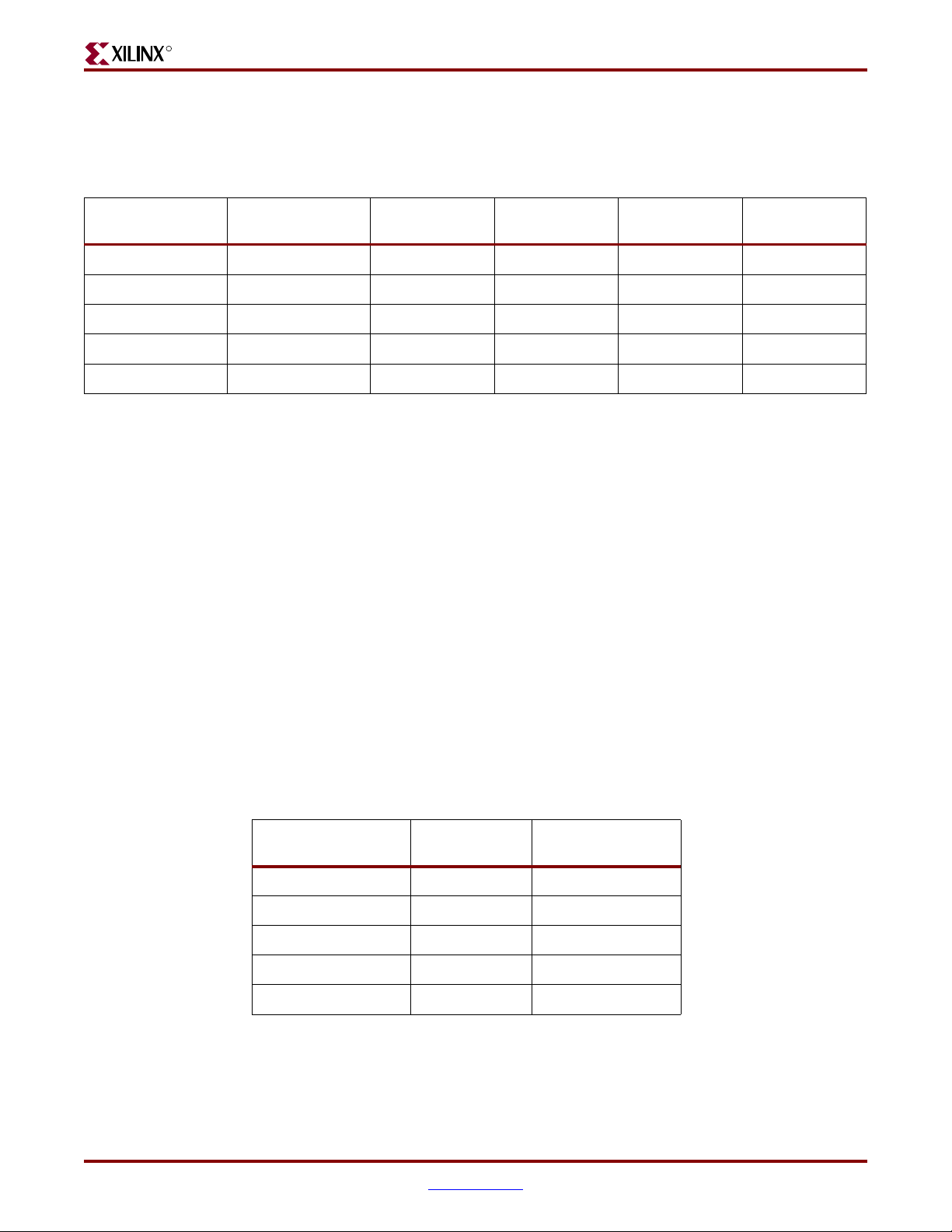
R
Memories
Tab le 3 -1 lists the types of memories that the ML561 board supports.
Table 3-1: Summary of ML561 Memory Interfaces
Hardware Overview
Memory Type Maximum Speed Data Rate Data Width I/O Standard
DDR400 SDRAM 200 MHz 400 Mbps 32 SSTL2 8:1
DDR2 DIMM 333 MHz 667 Mbps 144 SSTL18 8:1
DDR2 SDRAM 333 MHz 667 Mbps 32 SSTL18 8:1
QDRII SRAM 300 MHz 1.2 Gbps 72 HSTL18 18:1, 36:1
RLDRAM II 300 MHz 600 Mbps 36 HSTL18 9:1, 18:1
Data/Strobe
Ratios
When a larger data/strobe ratio is implemented, for example, a x36 QDRII device, the
smaller configurations can also be demonstrated by programming the FPGA for a smaller
data width, such as a 9:1 data/strobe ratio for the QDRII device.
DDR400 SDRAM Components
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board has two 200 MHz Micron
MT46V32M16BN-5B (16-bit) DDR400 SDRAM components that provide a 32-bit interface.
Each 16-bit device is packaged in a 60-ball FBGA package, with a common address and
control bus and separate clocks and DQS/DQ signals.
DDR2 DIMM
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board contains five PC-5300 240-pin DIMM
sockets for a maximum data width of 144 bits or a maximum depth of four DIMMs. The
sockets are arranged in a row leading away from the FPGA so they can share common
address and control signals. DIMM1 through DIMM4 share DQ/DQS signals to form a
deep 72-bit memory interface, while DIMM5 has separate DQ/DQS signals.
For the deep DDR2 interface, the sockets are to be populated starting at socket DIMM4.
Tab le 3 -2 illustrates how the sockets should be populated based on the interface wanted.
Table 3-2: Populating DDR2 DIMM Sockets
DIMM Interface
One Deep 5 or 4 72-bit
Two Deep 4 and 3 72-bit
Three Deep 4, 3, and 2 72-bit
Four Deep 4, 3, 2, and 1 72-bit
Two Wide 5 and 4 144-bit
DIMM Sockets
Populated
Interface Width
Populating the DIMMs in this order is necessary due to the placement of the termination
on the signals being shared. More detail on termination is given in “Board Design
Considerations,” page 36.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 19
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 20
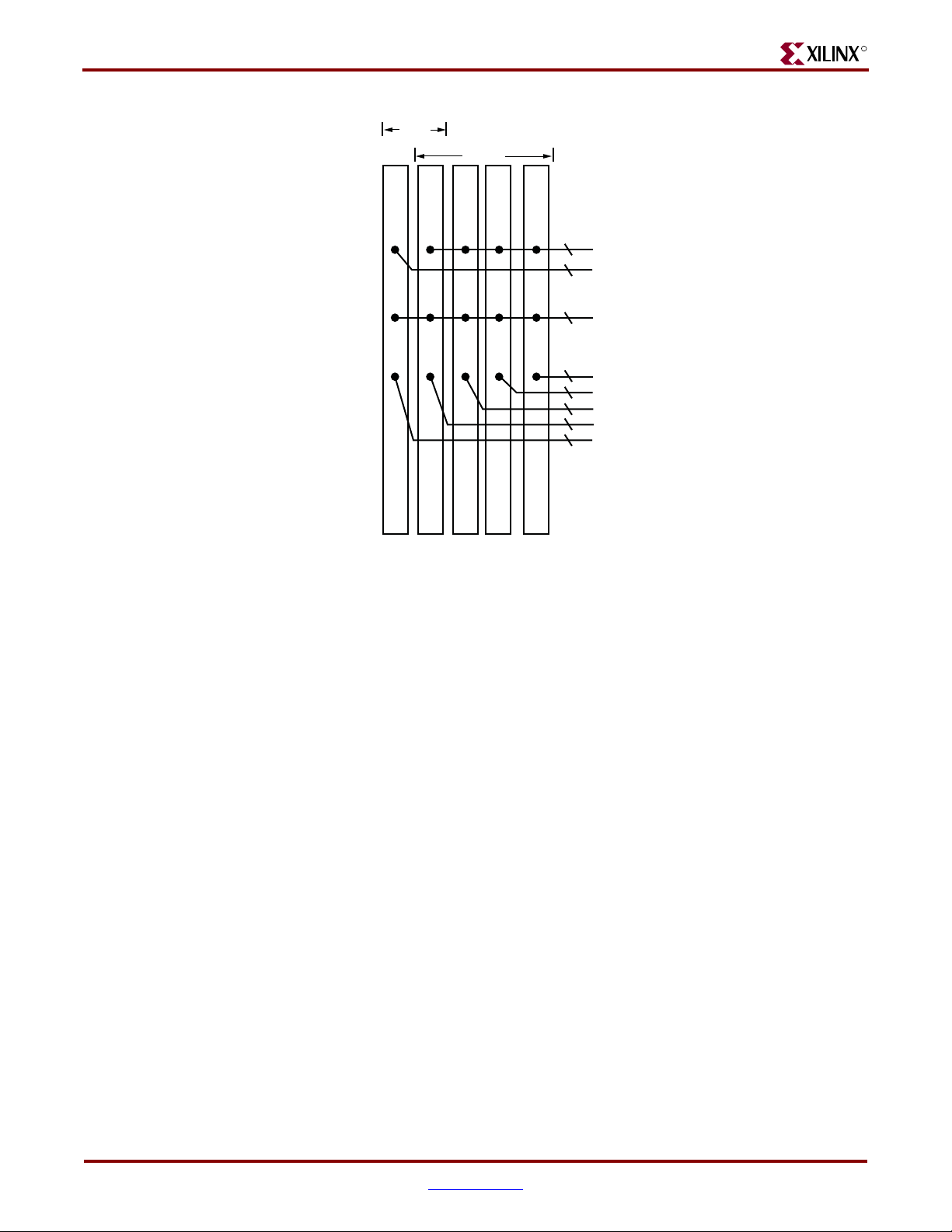
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
Wide
DIMM4 (XP2)
DIMM5 (XP1)
Deep
DIMM2 (XP4)
DIMM3 (XP3)
DIMM1 (XP5)
BY0-BY7, CB0_7
BY8-BY15, CB8_15
DQ and DQS
DQ and DQS
Address and Commands
DIMM1 Control
DIMM2 Control
DIMM3 Control
DIMM4 Control
DIMM5 Control
UG199_c3_02_050106
Figure 3-2: DDR2 Deep and Wide DIMM Sockets
DDR2 SDRAM Components
The ML561 board contains two 333 MHz Micron MT47H32M16CC-3 (16-bit) DDR2
SDRAM components that provide a 32-bit interface to FPGA #1. Each 16-bit device is
packaged in an 84-ball FBGA package, with a common address and control bus and
separate clocks and DQS/DQ signals.
QDRII SRAM
The ML561 board contains a 300 MHz QDRII SRAM interface with a 72-bit Read interface
and a 72-bit Write interface using two Samsung K7R643684M-FC30 components (x36).
They are packaged in a 165-ball FBGA package with a body size of 15 x 17 mm. These two
components share the same address/control signals but have separate clock and data
signals.
RLDRAM II Devices
The ML561 contains a 300 MHz 36-bit RLDRAM II interface using two Micron
MT49H16M18BM-25 devices (x18) packaged in a 144-ball PBGA package. They share a
common address and control bus but have separate clocks and DQS/DQ signals.
20 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 21
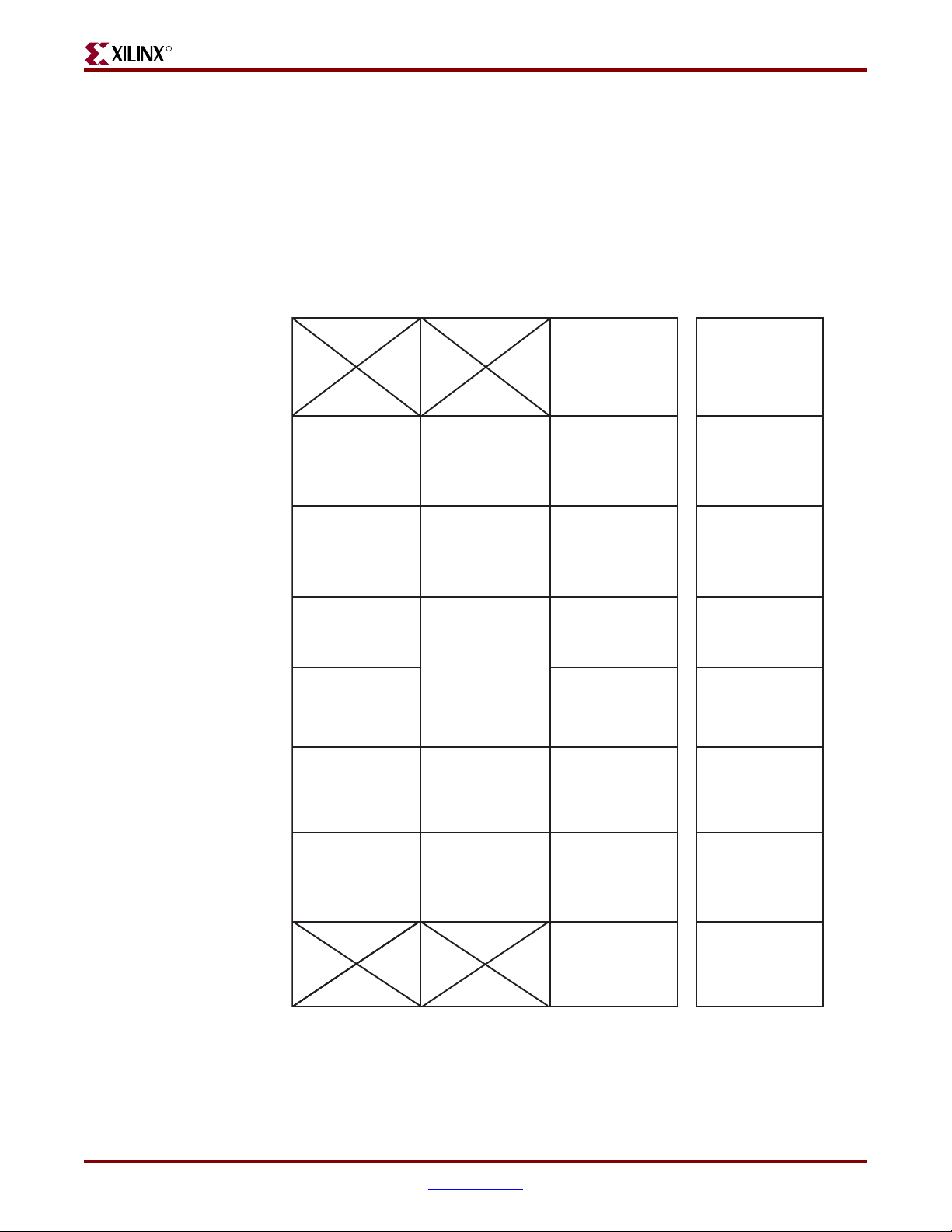
R
Memory Details
DDR400 and DDR2 Component Memories
The FPGA #1 device on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board is connected to
DDR and DDR2 component memories, as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 summarizes the distribution of DDR and DDR2 discrete component interface
signals among the different banks of the FPGA #1 device.
BANK 25 (40) BANK 6 (20)
Memory Details
GTP I/O
BANK 126
BANK 21 (40)
BANK 17 (40) BANK 18 (40) BANK 118
BANK 13 (40)
DDR Components
DQ 0, 1, 2
BANK 11 (40)
DDR Components
DQ 3 & Controls
BANK 15 (40)
DDR2 Component
DQ 0, 1
BANK 19 (40)
DDR2 Component
BANK 4 (20)
Global Clock Inputs
BANK 2 (20)
Voltage Control
(Configuration)
BANK 0
BANK 1 (20)
DDR2 Component
Address
BANK 3 (20)
DDR2 Component
BANK 22 (40) BANK 122
BANK 114
BANK 12 (40)
USB Controls
RS232
BANK 112
BANK 116
BANK 120BANK 20 (40)
DQ 2, 3
BANK 23 (40) BANK 124BANK 5 (20)
Controls
Inter-FPGA MII Links
UG199_c3_03_050106
Figure 3-3: FPGA #1 Banks for DDR400 and DDR2 Component (Top View)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 21
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 22
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
Tab le 3 -3 describes all signals associated with DDR400 Component memories.
Table 3-3: DDR400 Component Signal Summary
DDR1_A[13:0] 14 DDR400 Component Address
DDR1_CK[2:1]_[P,N] 4 DDR400 Component Differential Clock
Board Signal Name(s) Bits Description
DDR1_[RAS,CAS,WE]_N, DDR1_CKE,
12 DDR400 Component Control Signals
DDR1_BA[1:0], DDR1_BY[0_1,2_3]_CS_N,
DDR1_DM_BY[3:0]
DDR1_DQ_BY0_B[7:0], DDR1_DQS_BY0_P 9 DDR400 Data and Strobe: Byte 0
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B[7:0], DDR1_DQS_BY1_P 9 DDR400 Data and Strobe: Byte 1
DDR1_DQ_BY2_B[7:0], DDR1_DQS_BY2_P 9 DDR400 Data and Strobe: Byte 2
DDR1_DQ_BY3_B[7:0], DDR1_DQS_BY3_P 9 DDR400 Data and Strobe: Byte 3
Notes:
1. DDR1_CKE signal has a weak 4.7KΩ pull-down resistor to meet the memory power-up requirements.
Tab le 3 -4 describes all signals associated with DDR2 Component memories. For a complete
list of FPGA #1 signals and their pin locations, refer to Appendix A, “FPGA Pinouts.”
Table 3-4: DDR2 Component Signal Summary
Board Signal Name(s) Bits Description
DDR2_A[12:0] 13 DDR2 Component Address
DDR2_CK[1:0]_[P,N] 4 DDR2 Component Differential
Clock
DDR2_ODT[1:0], DDR2_[RAS,CAS,WE]_N,
14 DDR2 Component Control Signals
DDR2_CKE, DDR2_BA[1:0], DDR2_CS[1:0]_N,
DDR2_DM_BY[3:0]
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B[7:0], DDR2_DQS_BY0_[P,N] 10 DDR2 Data and Strobe: Byte 0
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B[7:0], DDR2_DQS_BY1_[P,N] 10 DDR2 Data and Strobe: Byte 1
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B[7:0], DDR2_DQS_BY2_[P,N] 10 DDR2 Data and Strobe: Byte 2
DDR2_DQ_BY3_B[7:0], DDR2_DQS_BY3_[P,N] 10 DDR2 Data and Strobe: Byte 3
Notes:
1. DDR2_CKE and DDR2_ODT[1:0] signals have a weak 4.7KΩ pull-down resistor to meet the memory
power-up requirements.
X
APP851, DDR SDRAM Controller Using Virtex-5 FPGA Devices, XAPP858, High-
Performance DDR2 SDRAM Interface in Virtex-5 Devices, and the corresponding demos are
included on the CD shipped with the ML561 Tool Kit. For a complete list of FPGA #1
signals and their pin locations, refer to Appendix A, “FPGA Pinouts.”
22 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 23
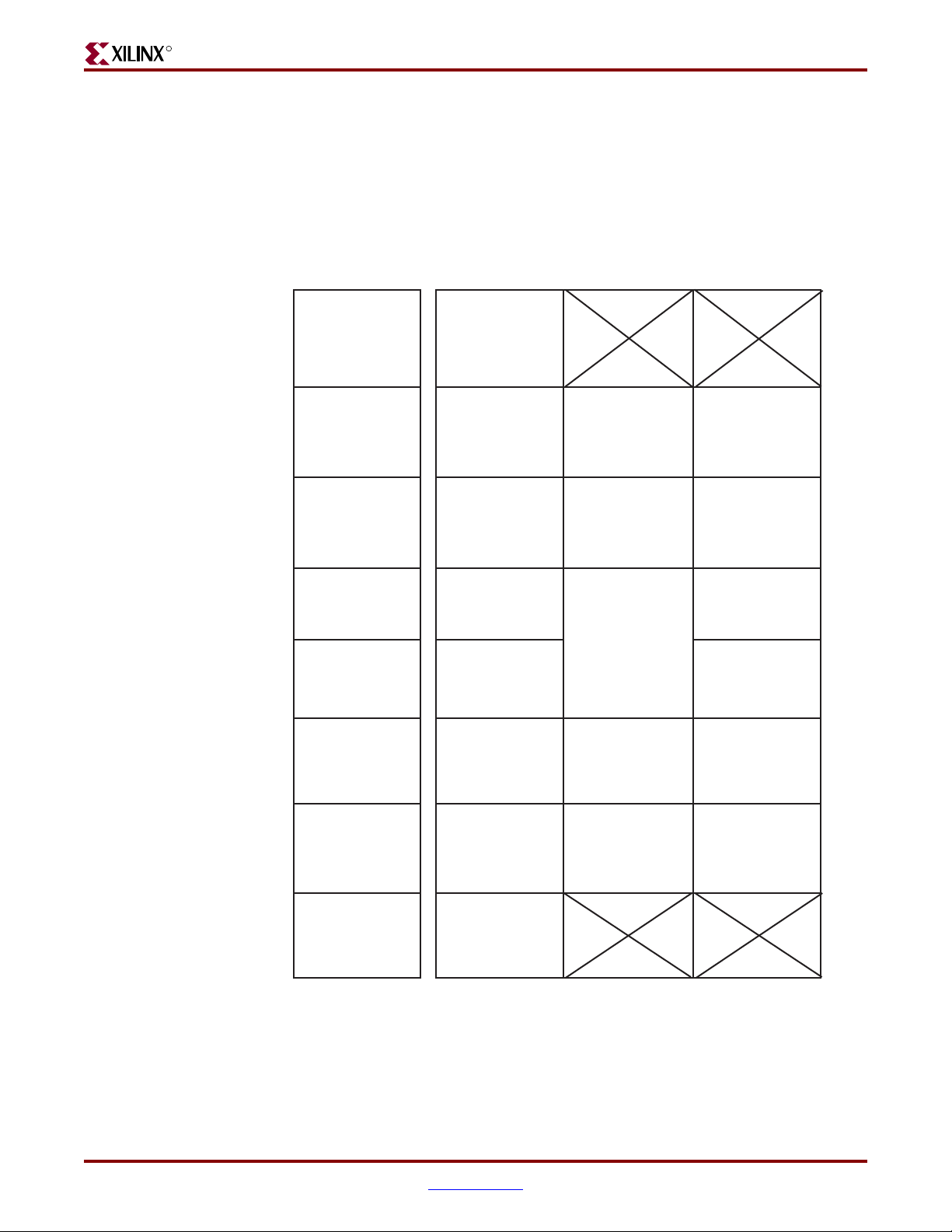
R
DDR2 SDRAM DIMM
The FPGA #2 device on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board is connected to
DDR2 memories. The DDR2 memory interface includes a 144-bit wide DIMM connection
to up to five 240-pin DDR2 DIMM sockets.
For the 144-bit wide DIMM datapath, the data bytes are spread across multiple banks of
the FPGA #2 device. Figure 3-4 summarizes the distribution of DDR2 DIMM interface
signals among the different banks of the FPGA #2 device.
TX 0, 1
Memory Details
BANK 5 (20) BANK 23 (40)BANK 124
BANK 120
RX 0, 1
BANK 116
GTP CLK
BANK 112
BANK 114
BANK 118
BANK 122 BANK 21 (40)
BANK 20 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
DQ 8, 9, 10
BANK 12 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
DQ 11, 12, CB8_15
BANK 18 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
DQ 14, 15, 13
BANK 22 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
BANK 3 (20)
General I/O
BANK 1 (20)
General I/O
(Configuration)
BANK 0
BANK 2 (20)
Inter-FPGA MII Links
BANK 4 (20)
Global Clock Inputs
BANK 19 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
Controls & DIMM1 Cntl
BANK 15 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
DQ 0, 1, 2
BANK 11 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
DQ 6, 3 CB0_7
BANK 13 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
DQ 5, 7, 4
BANK 17 (40)
DDR2 DIMM
Common Controls
DDR2 DIMM
DIMM 4 & 5 Cntl
DIMM 1, 2, 3 Cntl
BANK 25 (40)BANK 126 BANK 6 (20)
UG199_c3_04_050106
Figure 3-4: FPGA #2 Banks for DDR2 DIMM (SSTL18) Interfaces (Top View)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 23
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 24
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
Tab le 3 -5 describes all the signals associated with DDR2 DIMM component memories. For
the Deep DIMM interface to four DIMMs, the individual dedicated control signals are
listed at the bottom of Tab le 3- 5.
Table 3-5: DDR2 DIMM Signal Summary
Board Signal Name(s) Bits Description
DDR2_DIMM_A[15:0] 16 DDR2 DIMM Address
DDR2_DIMM[5:1]_CK[2:0]_[P,N] 30 DDR2 DIMM Differential Clocks: Three copies per
DIMM
DDR2_DIMM_[RAS,CAS,WE,RESET]_N,
37 DDR2 DIMM Common Control Signals
DDR2_DIMM[5:1]_CKE[1:0], DDR2_DIMM_BA[2:0],
DDR2_DIMM[5:1]_CS[1:0]_N,
DDR2_DIMM[5:1]_ODT[1:0]
DDR2_DIMM[1:5]_CS[1:0]_N,
20 DDR2 DIMM Dedicated Control Signals
DDR2_DIMM[1:5]_CKE[1:0],
DDR2_DIMM[1:5]_ODT[1:0]
DDR2_DIMM_LB_BK[11,13,15]_[IN,OUT] 6 Deep DIMMs (DIMM1 through DIMM4) Loopback
Signals
DDR2_DIMM_LB_BK[12,18,20] 3 Wide DIMM (DIMM5) Loopback Signals (Total of six
FPGA pins)
DDR2_DIMM[1:5]_CNTL_PAR,
DDR2_DIMM[1:5]_CNTL_PAR_ERR,
20 Miscellaneous Place Holder Signals to the Five
DIMMs
DDR2_DIMM[1:5]_NC_019, DDR2_DIMM[1:5]_NC_102
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY[0:15]_B[7:0],
DDR2_DIMM_DQS_BY[0:15]_L_[P,N],
176 DDR2 DIMM Data, Strobes, and Data Mask: Bytes 0
through 15
DDR2_DIMM_DM_BY[0:15]
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_CB0_7_B[7:0],
DDR2_DIMM_DQS_CB0_7_L_[P,N],
11 DDR2 DIMM Data, Strobes, and Data Mask: Check
Byte 0
DDR2_DIMM_DM_CB0_7
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_CB8_15_B[7:0],
DDR2_DIMM_DQS_CB8_15_L_[P,N],
11 DDR2 DIMM Data, Strobes, and Data Mask: Check
Byte 1
DDR2_DIMM_DM_CB8_15
DDR2_DIMM[1:5]_SA[2:0] 15 Serial PROM Address
DDR2_DIMM_[SCL,SDA]" 2 Serial PROM interface CLK and Data
Notes:
1. DDR2_DIMM_CKE and DDR2_DIMM_ODT signals are connected to a 4.7KΩ pull-down resistor to meet the memory power-up
requirements.
XAPP858
, High-Performance DDR2 SDRAM Interface in Virtex-5 Devices and its
corresponding demo are included on the CD shipped with the ML561 Tool Kit.
24 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 25
R
QDRII and RLDRAM II Memories
Figure 3-5 summarizes the distribution of QDRII and RLDRAM II component interface
signals among the different banks of the FPGA #3 device.
Memory Details
BANK 5 (20) BANK 23 (40)BANK 124
BANK 120
BANK 116
BANK 112
BANK 114
BANK 118
BANK 20 (40)
RLDII Data
DQ 0, 1 & D0
BANK 12 (40)
RLDII Data
DQ 2, 3 & D1
BANK 18 (40)
RLDII Data
D 2, 3
BANK 3 (20)
General I/O
BANK 1 (20)
System ACE Controls
(Configuration)
BANK 0
BANK 2 (20)
Inter-FPGA MII Links
BANK 19 (40)
QDRII Data
Q1, 3 & D1
BANK 15 (40)
QDRII Data
D7, 2, 3, 0
BANK 11 (40)
QDRII Data
Q0, 2 & D6
BANK 13 (40)
QDRII Data
Q4, 5, 6
BANK 17 (40)
QDRII Data
Q7 & D4, 5
BANK 122 BANK 21 (40)
BANK 22 (40)
RLDII Address
and Control
BANK 4 (20)
Global Clock Inputs
QDRII Address
and Control
BANK 25 (40)BANK 126 BANK 6 (20)
UG199_c3_05_050106
Figure 3-5: FPGA #3 Banks for QDRII SRAM and RLDRAM II Interfaces (Top View)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 25
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 26
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
Tab le 3 -6 describes all the signals associated with QDRII component memories.
Table 3-6: QDRII Component Signal Summary
Board Signal Name(s) Bits Description
QDR2_SA[18:0] 19 QDRII Address
QDR2_CK_BY0_3_[P,N],
4QDRII Differential Clock
QDR2_CK_BY4_7_[P,N]
QDR2_[R,W,DLL_OFF]_N 3 QDRII Control Signals
QDR2_D_BY[3:0]_B[8:0],
42 QDRII Write Data, Strobes, and Byte Write: Bytes 3:0
QDR2_K_BY0_3_[P,N],
QDR2_BW_BY[3:0]
QDR2_Q_BY[3:0]_B[8:0],
38 QDRII Read Data and Strobes: Bytes 3:0
QDR2_CQ_BY0_3_[P,N]
QDR2_D_BY[7:4]_B[8:0],
42 QDRII Write Data, Strobes, and Byte Write: Bytes 7:4
QDR2_K_BY4_7_[P,N],
QDR2_BW_BY[3:0]
QDR2_Q_BY[7:4]_B[8:0],
38 QDRII Read Data and Strobes: Bytes 7:4
QDR2_CQ_BY4_7_[P,N]
Notes:
1. QDR2_SA[18] is incorrectly labeled QDR2_NC_A3 in the ML561 schematics and layout file.
APP853: QDR II SRAM Interface for Virtex-5 Devices and its corresponding demo are
X
included on the CD shipped with the ML561 Tool Kit.
For a complete list of FPGA #3 signals and their pin locations, refer to Appendix A, “FPGA
Pinouts.”
Tab le 3 -7 describes all signals associated with RLDRAM II devices.
Table 3-7: RLDRAM II Component Signal Summary
Board Signal Name(s) Bits Description
RLD2_A[19:0], RLD2_BA[2:0] 23 RLDRAM II Address
RLD2_CK_BY0_1 _[P,N] 2 RLDRAM II Differential Clock
RLD2_CK_BY2_3 _[P,N] 2 RLDRAM II Differential Clock
RLD2_CS_BY[0_1,2_3]_N, RLD2_[REF,WE]_N,
8 RLDRAM II Control Signals
RLD2_DM_BY[0_1,2_3]_N, RLD2_QVLD_BY[0_1,2_3]
RLD2_DQ_BY[1:0]_B[8:0], RLD2_DK_BY0_1_[P,N],
24 RLDRAM II Data and Strobes: Bytes 1:0
RLD2_QK_BY[1:0]_[P,N]
RLD2_DQ_BY[3:2]_B[8:0], RLD2_DK_BY0_1_[P,N],
24 RLDRAM II Data and Strobes: Bytes 3:2
RLD2_QK_BY[3:2]_[P,N]
X
APP852, RLDRAM II Memory Interface for Virtex-5 FPGAs and its corresponding demo are
included on the CD shipped with the ML561 Tool Kit.
26 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 27
R
External Interfaces
The external interfaces of the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board are described in
this section.
RS-232
The ML561 board provides an RS-232 serial interface using a Maxim MAX3316ECUP
device. The maximum speed of this device is 460 Kbps.
Hooks are provided to connect and disconnect FPGAs to the RS-232 serial interface, by
placing jumpers on headers based on the FPGA involved in the communication. Only one
FPGA is allowed in the communication, and others must be dis conne cted b efore operation.
The ML561 toolkit CD contains code to implement a UART core in one FPGA for
interfacing with a host PC.
The RS-232 interface is accessible through a male DB-9 serial connector (P73).
Table 3-8: RS-232 Jumper Settings
External Interfaces
USB
To Connect FPGA # to
DB-9 (P73)
FPGA #1 P52 Pin 2 -> P52 Pin 1 P53 Pin 2 -> P53 Pin 1
FPGA #2 P52 Pin 2 -> P51 Pin 1 P53 Pin 2 -> P54 Pin 1
FPGA #3 P52 Pin 2 -> P52 Pin 3 P53 Pin 2 -> P53 Pin 3
Full-speed (12 Mbps) USB functionality is proved using a Silicon Laboratories CP2102-GM
USB to RS-232 Bridge. RS-232 and USB signals are converted between one another so a
RS-232 core needs to be implemented in the FPGA for communication. A level translator is
used to convert between the 2.5V I/O of the FPGA and the 3.3V I/O the CP2102 uses.
Hooks are provided to connect and disconnect FPGAs to the USB connection, by placing
jumpers on headers based on the FPGA involved in the communication. Only one FPGA is
allowed in the communication, and others must be disconnected before operation.
The USB interface is accessible through a female ‘A’ USB connector (J29).
Table 3-9: USB Jumper Settings
To Connect FPGA # to DB-9
(J29)
FPGA #1 P36 Pin 2 -> P36 Pin 1 P22 Pin2 -> P22 Pin 1
TX RX
TX RX
FPGA #2 P36 Pin 2 -> P35 Pin 1 P22 Pin2 -> P23 Pin 1
FPGA #3 P36 Pin 2 -> P36 Pin 3 P22 Pin2 -> P22 Pin 3
Clocks
The ML561 board contains a 200 MHz LVPECL clock oscillator and connectors for external
clock inputs for use as system clocks (J19 and J20). The GTP transceivers use their own
clock source that can be provided through SMA connectors on the board (J16 and J21).
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 27
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 28
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
200 MHz LVPECL Clock
The 200 MHz LVPECL clock source is an Epson EG-2121CA200M-PCHS oscillator (Y1)
with a differential output. The oscillator runs at 200 MHz ± 100 PPM with an operating
voltage of 2.5V ±5%. This output is fed into an ICS853006 LVPECL buffer for generating a
separate differential copy for each FPGA as well as a test point (P59).
Table 3-10: FPGA 200 MHz IDELAY Reference Clock Source
FPGA # Signal Name
1 DIRECT_CLK_TO_FPGA1_P
1 DIRECT_CLK_TO_FPGA1_N
2 DIRECT_CLK_TO_FPGA2_P
2 DIRECT_CLK_TO_FPGA2_N
3 DIRECT_CLK_TO_FPGA3_P
3 DIRECT_CLK_TO_FPGA3_N
SMA Clock
Two SMA connectors are provided for the input of an off-board differential clock (J19 and
J20). A differential clock buffer (ICS853006) is used on the board (U17 and U18) to generate
four LVPECL copies of the differential clock signal, one for each FPGA along with a probe
point (P40) for testing. The traces from the buffer are routed as a differential pair to each
FPGA where they are terminated with 100Ω differential termination.
Table 3-11: FPGA External Clock Sources
FPGA # Signal Name
1 EXT_CLK_TO_FPGA1_P
1 EXT_CLK_TO_FPGA1_N
2 EXT_CLK_TO_FPGA2_P
2 EXT_CLK_TO_FPGA2_N
3 EXT_CLK_TO_FPGA3_P
3 EXT_CLK_TO_FPGA3_N
33 MHz Clock
A single-ended 33 MHz Epson SG-8002CA oscillator is provided on the board (Y2) for
testing purposes. Four copies of this clock are generated using a clock buffer (ICS8304) on
the board, one per FPGA along with a probe point for testing (P41).
The application using this clock source as an input to the PLL on the Virtex-5 device has
not yet been fully verified.
28 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 29
External Interfaces
R
Table 3-12: FPGA Slow Clock Sources
FPGA Signal Name
1 FPGA1_LOW_FREQ_CLK
2 FPGA2_LOW_FREQ_CLK
3 FPGA3_LOW_FREQ_CLK
33 MHz System ACE Controller Oscillator
A single-ended 33 MHz Epson SG-8002CA oscillator is provided on the board (Y3) as a
clock source for System ACE functionality.
GTP Clocks
Two SMA connectors are provided for the input of an off-board differential clock (J16 and
J21). A differential clock buffer (ICS8543BG) is used on the board (U20) to generate four
LVDS copies of the differential clock signal, two for FPGA #1, one for FPGA #2, and one for
FPGA #3.
User I/Os
General-Purpose Headers
A header is used to select between a clock forwarded by the GTP or from the external clock
source used to provide a clock to the FPGA logic.
This subsection describes the devices that connect to the User I/Os of the ML561 board.
These I/Os are provided to ease hardware development using the ML561.
The 16-pin test headers are surface mounted, one per FPGA. Of the two bytes of test
signals, traces are matched for signals within a byte.
Table 3-13: Test Headers
Header Signal Description Location Header Pin #
FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B[0:7] P20 (TEST1) Odd pins: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15
FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B[0:7] P20 (TEST1) Even pins: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16
FPGA2_TEST_HDR_BY0_B[0:7] P21 (TEST2) Odd pins: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15
FPGA2_TEST_HDR_BY1_B[0:7] P21 (TEST2) Even pins: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16
FPGA3_TEST_HDR_BY0_B[0:7] P93 (TEST3) Odd pins: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15
FPGA3_TEST_HDR_BY1_B[0:7] P93 (TEST3) Even pins: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16
DIP Switch
One four-position DIP switch per FPGA (for a total of three) is available to externally pull
up or pull down a signal on the FPGA. This can be used to manually set values used by the
design running on the FPGA.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 29
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 30
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
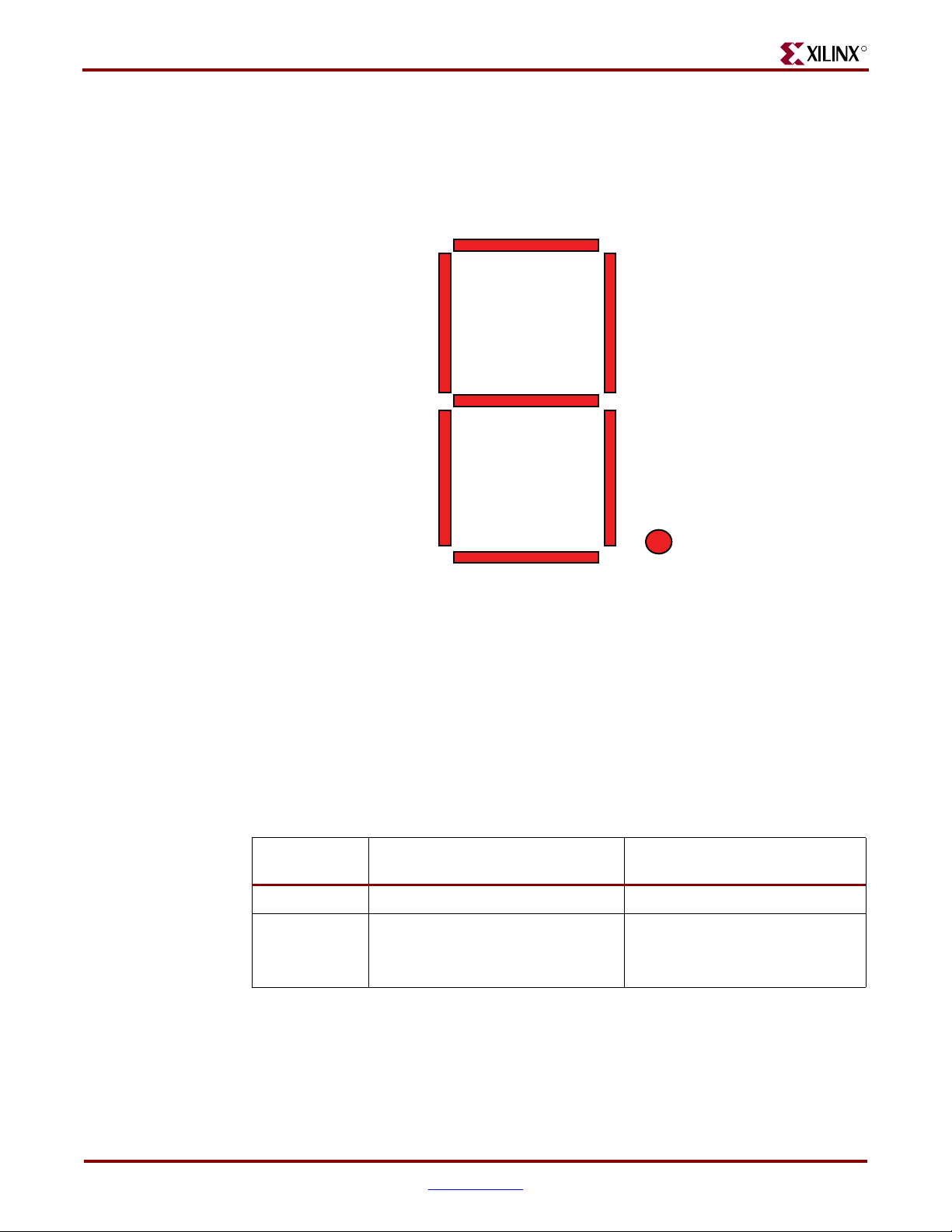
Seven-Segment Displays
One seven-segment display per FPGA (for a total of three) is available for use. The red
Stanley-Electric NAR131SB displays are active Low, using seven inputs to display a
character or number plus another input for a decimal point.
7SEG_0_N
7SEG_5_N 7SEG_1_N
7SEG_6_N
7SEG_4_N 7SEG_2_N
7SEG_3_N
7SEG_DP_N
UG199_c3_06_050106
Figure 3-6: Seven-Segment Display Signal Mapping
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Each FPGA is able to control four active-high green LEDs. The green is used to distinguish
the User LEDs from the blue system LEDs on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development
Board.
Pushbuttons
The ML561 board contains two momentary pushbuttons. Their functions and locations are
described in Tabl e 3 -1 4.
Table 3-14: User Pushbuttons
Button Description Pin Connection
SW7 PROG_B: Configure FPGA System ACE Controller: Pin 33
SW4 RESET_N: Reset the FPGA designs FPGA #1: AH14
FPGA #2: AH14
FPGA #3: AH14
The Reset signal goes to a buffer (U32) that provides a separate copy of Reset to each
FPGA.
30 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 31

External Interfaces
R
Power On or Off Slide Switch
The power on or off slide switch is a DPST slide switch used to apply input power to the
board. While the board contains two such switches, the 5V switch is primarily used to
supply 5V power to the board, whereas the 12V switch is available for testing only.
Soft Touch Probe Points
Soft Touch E5396A Probeless connection points are provided for monitoring FPGA #2 and
FPGA #3 test signals with a compatible Agilent logic analyzer. FPGA #2 uses separate test
signals for soft touch pins, while FPGA #3 shares the general-purpose test header signals
with soft touch pins due to lack of available I/O pins.
Power Measurement Header
The ML561 comes with a 3M Pak 100 power measurement header to enable easy
measurement of the power being consumed by the devices on the ML561. Each power
regulator uses an Isotek Kelvin current sense resistor (SMV-R010-0.5) in the path from the
output of the regulator to the power plane. The power can be computed by measuring the
voltage drop across each of these resistors.
+5V or +12V
MARGIN+ MARGIN-
V
IN
V
OUT
Voltage
R
SET
Regulator
R
V
CCXXPR
KELVIN
= 10 mΩ
1KΩ
V
V
CCXX
V
CCXX
CCX
V
CCXX
Sense-
Sense+
To FPGA or
Other Device
Mon
To
Monitor
Cable
UG199_c3_07_050106
Figure 3-7: Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board Power Measurement System
Table 3-15: Power Measurement Header Pins (P102)
Header Signal Power Header Pin #
VCC1V0_SENSE+ 1
VCC1V0_SENSE- 2
VCC1V0_MON 3
VCC2V5_SENSE+ 5
VCC2V5_SENSE- 6
VCC2V5_MON 7
VCC3V3_SENSE+ 9
VCC3V3_SENSE- 10
VCC3V3_MON 11
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 31
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 32

Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
Table 3-15: Power Measurement Header Pins (P102) (Continued)
Header Signal Power Header Pin #
VCC1V8_SENSE+ 13
VCC1V8_SENSE- 14
VCC1V8_MON 15
VCC1V5_SENSE+ 17
VCC1V5_SENSE- 18
VCC1V5_MON 19
VCC2V6_SENSE+ 21
VCC2V6_SENSE- 22
VCC2V6_MON 23
VCC5_SENSE+ 25
VCC5_SENSE- 26
VCC5_MON 24
VCC5 20
GND 4
GND 8
GND 12
GND 16
Liquid Crystal Display Connector
Previous memory boards such as the ML461 had a DisplaytechQ 64128E-FC-BC-3LP
64x128 LCD panel. This display was removed from the ML561, but the connection is still
available for use with embedded systems if the user connects the display to connector
(P104). The LCD panel needs to hang off the edge of the board as shown in Figure 3-8.
32 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 33

Power Regulation
R
OFF
12V Input
Jack
5V Banana
Jacks
ON
OFF
5V Input
Jack
HSTL
12V -> 5V
3.3V
Pwr Measure Header
Figure 3-8: LCD Panel Connector for Possible LCD Support
The product specification at
http://www.displaytech.com.hk/pdf/graphic/64128e%20series-v10.PDF
information. Appendix C, “LCD Interface,” describes the LCD operation in detail.
Power Regulation
SPY
RLDRAM II
RLDRAM II
A1
FPGA3
LCD Connector
LCD
FPGA3 LEDs
HSTL
SPY
Test Header 3
Config3
7SEG3
QDRII
QDRII
JTAG Test Header
DIP3
PROG
V
CCAUX
V
V
TT
CCO
HSTL
& V
USB
/
REF
7SEG1
Serial Header
System ACE
Controller
JTAG
UG199_c3_08_050106
RS232
Driver
RESET
provides more
This section describes the devices that supply power to the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561
Development Board. For electrical requirements and power consumption, see Chapter 4,
“Electrical Requirements.”
Power Distribution
The ML561 board uses +5V to drive numerous voltage regulators. Figure 3-9 shows a
general overview of the power distribution system.
+5V
Slide
Switch
+12V
Slide
Switch
Figure 3-9: Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board Power Distribution System
12V -> 5V
Board Power
3.3V
FPGA Power
or V
V
CCINT
CCAUX/VCCO
FPGA Power
SSTL18, HSTL, or SSTL2
Memory Power
SSTL18, HSTL, or SSTL2
MGT
Powe r
V
V
REF
TT
To Devices
MGT Power
To All FPGAs
To FPGAs
To Memories
V
TT
V
REF
UG199_c3_09_050106
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board is powered through the +5V input jack
(J28) from the power supply included in the ML561 Tool Kit. Alternatively, the +5V can
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 33
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 34

Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
PTH05010
Voltage Regulator
V
IN
GND
TRACK MRGN
UP
MRGN
DN
GND
C
IN
R
SET
470 μF
C
OUT
330 μF
(optional)
V
OUT
5V
+
+
1
2
3 5 4
6
7
8 9 10
Inhibit
Jumper
INHIBIT
V
O_ADJ VO_SENSE
VMARGIN_UP_xxxx_N
VMARGIN_DN_xxxx_N
TRACK
UG199_c3_10_050106
also be supplied from a bench supply using the two banana jacks: J25 (RED) for +5V and
J24 (BLACK) for GND.
The Rev-A assembly of the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board does not support
the +12V input via jack J23 or via banana jacks J18 (RED) for +12V and J17 (BLACK) for
GND.
The memory and FPGAs use separate power supplies for SSTL18, HSTL, and SSTL2,
respectively. Thus the power being consumed can be easily measured for each using the
power measurement header provided on the ML561.
Voltage Regulators
The +5V voltage source is supplied as input to nine on-board regulator modules. Six of
those modules (TI PTH05010-WAZ) are used to generate the +1.0V, +2.5V, and +1.8V for
SSTL18 at FPGA #1 and FPGA #2, +1.8V for HSTL18 at FPGA #3, +2.6V for SSTL2 at
FPGA #1, and +3.3V voltages for the GTP power supplies, LEDs, etc. The remaining three
modules (TI PTH05000-ADJ) are used to generate +1.8V for SSTL18 at the memories, +1.8V
for HSTL at the memories, and +2.6V for SSTL2 at the memories.
An additional three bulk voltage regulators (Fairchild FN6555) are used to generate
termination (V
power levels. By design, these voltage levels are half of the input reference voltage being
supplied by the memory power supplies.
) and reference (V
TT
) voltages each for the SSTL2, SSTL18, and HSTL
REF
The TI PTH05010-WAZ and TI PTH05000-ADJ regulator modules require a fixed 5V input.
The output is adjustable over a range of 0.9V to 3.6V by changing the resistor tied between
pin 4 and GND. The difference between these two modules is that the PTH05010-WAZ
output voltage can be margined up to+ 5% of the nominal value by driving pin 10 to GND
(or digital Low), or margined down to -5% of the nominal value by driving pin 9 Low. The
PTH05010-WAZ also has a tracking feature that can be used to track another voltage
source.
There are two ways to apply the digital controls to the margin input pins of the PTH05010:
either from FPGA #1 or manually with jumpers.
Figure 3-10: PTH05010 Voltage Regulator
34 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 35

Power Regulation
R
The FPGA can drive VMARGIN_DN_xxxx_N and VMARGIN_UP_xxxx_N signals, where
xxxx indicates one of the six main power regulators: SSTL2, HSTL, SSTL18, VCC1V0,
VCC2V5, and VCC3V3.
Table 3-16: Manual Voltage Margining
VMARGIN_UP_N VMARGIN_DN_N Output Voltage
High High Nominal
High Low -5%
Low High +5%
Low Low Not Applicable
If both voltage-margining inputs to the power regulator are pulled Low, the output voltage
is close to nominal but has the possibility of a slightly higher error in the output voltage.
The power modules use a low-leakage open-drain control signal to control the voltage
margining. In the FPGA, this can be approximated by using a control signal that drives the
output Low when active and does not drive the signal at all when inactive (highimpedance output).
Three-pin headers are available for performing manual voltage margining, using jumpers
to select between Nominal, -5%, and +5%. Tab le 3 -1 7 shows the jumper settings.
Table 3-17: FPGA #1 Signals and On-Board Jumpers for Voltage Margining
Power Regulator Signal Name Jumper Setting
V
(VR6) VMARGIN_UP_VCC1V0_N P48: 1 -> 2
CCINT
VMARGIN_DN_VCC1V0_N P48: 3 -> 2
SSTL18 (VR1) VMARGIN_UP_SSTL18_N P4: 1 -> 2
VMARGIN_DN_SSTL18_N P4: 3 -> 2
SSTL2 (VR9) VMARGIN_UP_SSTL2_N P450 1 -> 2
VMARGIN_DN_SSTL2_N P50: 3 -> 2
HSTL (VR10) VMARGIN_UP_HSTL_N P58: 1 -> 2
VMARGIN_DN_HSTL_N P58: 3 -> 2
V
(VR12) VMARGIN_UP_VCC2V5_N P69: 1 -> 2
CCAUX
VMARGIN_DN_VCC2V5_N P69: 3 -> 2
The TI PTH05010-WAZ and TI PTH05000-ADJ regulator outputs can be enabled or
inhibited through the use of on-board two-pin jumpers. The inhibit jumpers use the
following conventions:
• Jumper OFF = Enabled
• Jumper ON = Inhibited
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 35
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 36
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
Tab le 3 -1 8 summarizes the inhibit headers.
Table 3-18: Headers for Voltage Regulator Inhibition
Power Regulator Inhibit Header
V
SSTL18 (VR1) P11
SSTL18_M (VR4) P32
SSTL2_M (VR2) P5
HSTL (VR10) P74
HSTL_M (VR14) P105
V
VCC3V3 (VR13) P101
(VR6) P63
CCINT
SSTL2 (VR9) P68
(VR12) P79
CCAUX
Board Design Considerations
UG086, Memory Interface Generator (MIG) User Guide includes PCB implementation rules
and guidelines to be followed for designing a board for a MIG reference design.
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board design allows implementation of DCI
termination scheme at the FPGA for each of the memory interfaces on the board. A
preliminary analysis of the Weighted Average Simultaneously Switching Outputs
(WASSO) for all three Virtex-5 devices indicates that the SSO guidelines are met for the
current pinout. The following factors helped to reduce the SSO noise as compared to the
Virtex-4 FPGA ML461 board implementation:
• SparseChevron pinout resulting in larger number of Power/GND pin pairs per bank
• A revised higher SSO allowance per Power/GND pair for SparseChevron packages
• Reduced thickness of the board (74 mils vs. 98 mils) resulting in reduced via
inductance
External terminations at both the memory and FPGA are provided for data signals for
most of the memory interfaces on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board layout.
The external V
termination is implemented with a single 50Ω termination to the V
TT
REF
level. See Chapter 5, “Signal Integrity Recommendations,” for specific recommendations
and guidelines for terminations.
These are V
end terminations to the respective voltage levels for SSTL2, SSTL18, and
TT
HSTL signals. There are two topologies of end terminations for data signals:
1. Fly-by termination: The parallel termination is placed after the receiver pin.
2. Non-fly-by termination: The parallel termination is placed between the driver and the
receiver along the trace as close to the receiver pin as possible. Also the stub from
signal trace to the termination resistor is kept very short, within 0.1 inch.
For Read data, terminations at the FPGA have non-fly-by termination topology. These
terminations can be selectively depopulated on the ML561 board when DCI termination is
implemented inside FPGA for received data. Due to non-fly-by termination topology, the
result is a minimal stub for the signal, thus preserving good signal integrity for read data.
36 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 37
Board Design Considerations
R
For Write data and terminations at the memory, if the trace length from the receiver pin to
the termination resistor can be guaranteed to be within 0.3 inches, then the fly-by
termination scheme is implemented. Otherwise, the non-fly-by termination topology is
implemented for Write data at the memory end.
The physical dimensions of the raw PCB are 12.75 inches x 11.75 inches. With the
overhangs due to edge connectors, the actual size of the fully assembled board is
approximately 13 inches x 12 inches, with 1.5 inches height allowance for the DIMM
modules. This 14-layer board has 6 signal layers, 4 GND layers, and 4 power planes and
uses Polyclad 370HR material for lead-free assembly. Figure 3-11 shows a stack-up
diagram of the ML561 Revision A PCB.
Refer to UG203
, Virtex-5 PCB Designer’s Guide for more information on the PCB design
using Virtex-5 devices.
73.90 ±7 mils
1.0 oz, TOP, Z0 = 50Ω, width = 6 mils
3.8 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, 02_GND1
4 mils, Er = 4.4
0.5 oz, 03_INR1, Z
5.3 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, 04_PWR1
8 mils, Er = 4.4
0.5 oz, 05_INR2, Z
3.2 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, 06_GND2
3 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, 07_PWR2
3.3 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, 08 _PWR3
3 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, 09_GND3
3.2 mils, Er = 4.4
0.5 oz, 10_INR5, Z
8 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, 11_PWR4
5.3 mils, Er = 4.4
0.5 oz, 12_INR6, Z
4 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, 13_GND4
3.8 mils, Er = 4.4
1.0 oz, BOTTOM, Z
= 50Ω, width = 4.5 mils
0
= 50Ω, width = 4.5 mils
0
= 50Ω, width = 4.5 mils
0
= 50Ω, width = 4.5 mils
0
= 50Ω, width = 6 mils
0
UG199_c3_11_102407
Figure 3-11: ML561 Revision A PCB Stack-Up
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 37
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 38
Chapter 3: Hardware Description
R
Tab le 3 -1 9 shows the details of the dielectric material and construction for each layer and
the controlled impedance values for the signal layers.
Table 3-19: ML561 Revision A PCB Controlled Impedance
Seq #
Layer
Name
Type Usage
Cu
Weight
(oz.)
Substrate
Thickness
(mils)
Er
Test
Width
(mils)
Z
0
(ohms)
Comment
1 TOP Metal Signal 1.0 <Auto> 6 50 ±5 Microstrip Signal Top
2 Dielectric Substrate 3.8 4.4
3 02_GND1 Metal Plane 1.0 <Auto> Ground Plane #1
4 Dielectric Substrate 4 4.4
5 03_INR1 Metal Signal 0.5 <Auto> 4.5 50 ±5 Stripline Signal - Inner #1
6 Dielectric Substrate 5.3 4.4
7 04_PWR1 Metal Plane 1.0 <Auto> Split Power Plane #1
8 Dielectric Substrate 8 4.4
9 05_INR2 Metal Signal 0.5 <Auto> 4.5 50 ±5 Stripline Signal - Inner #2
10 Dielectric Substrate 3.2 4.4
11 06_GND2 Metal Plane 1.0 <Auto> Ground Plane #2
12 Dielectric Substrate 3 4.4
13 07_PWR2 Metal Plane 1.0 <Auto> Split Power Plane #2
14 Dielectric Substrate 3.3 4.4
15 08_PWR3 Metal Plane 1.0 <Auto> Split Power Plane #3
16 Dielectric Substrate 3 4.4
17 09_GND3 Metal Plane 1.0 <Auto> Ground Plane #3
18 Dielectric Substrate 3.2 4.4
19 10_INR5 Metal Signal 0.5 <Auto> 4.5 50 ±5 Stripline Signal - Inner #3
20 Dielectric Substrate 8 4.4
21 11_PWR4 Metal Plane 1.0 <Auto> Split Power Plane #4
22 Dielectric Substrate 5.3 4.4
23 12_INR6 Metal Signal 0.5 <Auto> 4.5 50 ±5 Stripline Signal - Inner #4
24 Dielectric Substrate 4 4.4
25 13_GND4 Metal Plane 1.0 <Auto> Ground Plane #4
26 Dielectric Substrate 3.8 4.4
27 BOTTOM Metal Signal 1.0 <Auto> 6 50 ±5 Microstrip Signal Bottom
38 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 39

R
Electrical Requirements
This chapter provides the electrical requirements for the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561
Development Board. It contains the following sections:
• “Power Consumption”
• “FPGA Internal Power Budget”
Power Consumption
Tab le 4 -1 lists the operating voltages, maximum currents, and power consumption used by
the ML561 board devices. The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board has provisions
for two power inputs: a 5V power supply and a 12V power supply. The maximum rating of
a commercially available 5V power supply is limited to 8A, or a 40W maximum capacity.
This power supply is similar to the 5V brick used for previous memory tool kits, for
example, ML461. This tool kit expects the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board to
exercise only one external memory interface at a time. In this case, the total power
consumption of the board stays within the 40W limit.
Chapter 4
As shown in Tab le 4 -1 , if all three FPGA devices and their associated memory devices are
activated simultaneously, then the total power consumption is approximately 57W, which
exceeds the 40W capacity of the 5V power brick. So an alternate 12V power input jack (J23)
is provided on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board to hook up a 12V power
brick, for example, CUI DTS120500U with a 60W capacity. The 12V is converted to 5V
using the TI PTH12010WAS power module (VR11), which can supply up to 12A of current
at 5V, or a 60W capacity.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 39
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 40

Chapter 4: Electrical Requirements
R
Table 4-1: ML561 Power Consumption
Device Description Quantity Voltage (V)
Current
(mA)
Power
(W)
Source
Total Available Power
5V Power Supply 1 5.0 8000 40.0 Bellus Power SPD-050-5
12V Power Supply 1 12.0 5000 60.0 CUI DTS120500U
Power Consumed
DDR400 Component Interface
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136:
FPGA #1 (DDR400)
1 1.0, 2.5, 2.6 1887 3.7
Xilinx P
ower Estimator
DDR x16 Memory 2 2.6 210 1.1 Micron DDR Component Data Sheet
DDR Comp V
Termination 60 1.2 16 1.2 All signals. ±608 mV swing around V
TT
DDR2 Component Interface
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136:
FPGA #1 (DDR2)
1
1.0, 1.8[S],
2.5
1991 3.1
Xilinx P
ower Estimator
DDR2 x16 Memory 2 1.8 250 0.9 Micron DDR2 Component Data Sheet
DDR2 Comp V
Termination 25 1.2 16 0.5 Addr/Cntl: ±603 mV swing around V
TT
DDR2 DIMM Interface
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136:
FPGA #2 (DDR2)
1
1.0, 1.8[S],
2.5
6420 10.2
Xilinx P
ower Estimator
TT
TT
DDR2 DIMM 2 1.8 1755 6.3 Micron DDR2 DIMM Data Sheet
DDR2 DIMM V
Termination 160 1.2 16 3.1 All signals: ± 603 mV swing around V
TT
QDRII Memory Interface
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136:
FPGA #3 (QDRII)
1
1.0, 1.8[H],
1.8[S], 2.5
3917 6.3
Xilinx P
ower Estimator
QDRII Memory [H] 2 1.8 950 3.4 Samsung QDRII Data Sheet
QDRII V
Termination 175 1.0 16 2.8 All signals. ±500 mV swing around V
TT
RLDRAM II Memory Interface
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136:
FPGA #3 (RLDRAM II)
1
1.0, 1.8[H],
2.5
3069 4.5
Xilinx P
ower Estimator
RLDRAM II Memory 2 1.8 920 3.3 Micron RLDRAM II Data Sheet
RLDRAM II V
Termination 60 1.0 16 1.0 All signals. ±500 mV swing around V
TT
Miscellaneous Circuit
Clock Buffer 1 3.3 23 0.1 ICS8304 Data Sheet
Differential Clock Buffer 2 3.3 115 0.8 ICS853006 Data Sheet
DS080,
System ACE Controller 1 3.3 200 0.7
System ACE CompactFlash Solution
200 MHz Oscillator 1 2.5 30 0.1 Epson EG2121CA Data Sheet
33 MHz Oscillator 2 3.3 45 0.3 Epson SG-8002CA Data Sheet
TT
TT
TT
Total Power Consumed 53.2
40 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 41

R
Table 4-1: ML561 Power Consumption (Continued)
Power Consumption
Device Description Quantity Voltage (V)
Current
(mA)
Power
(W)
Source
Power Modules Capacity
V
Power Plane (1.0V) 1 1.00 15000 15.0 TI PTH05010 15A Module Data Sheet
CCINT
HSTL FPGA Power Plane (1.8V) 1 1.80 15000 27.0
HSTL Memory Power Plane (1.8V) 1 1.80 6000 10.8 TI PTH05000 6A Module Data Sheet
HSTL _VREF Power Plane (0.9V) 1 0.90 3000 2.7 Fairchild FN6555 Data Sheet
SSTL18 FPGA Power Plane (1.8V) 1 1.80 15000 27.0 TI PTH05010 15A Module Data Sheet
SSTL18 Memory Power Plane (1.8V) 1 1.80 6000 10.8 TI PTH05000 6A Module Data Sheet
SSTL18 _VREF Power Plane (0.9V) 1 0.90 3000 2.7 Fairchild FN6555 Data Sheet
SSTL2 FPGA Power Plane (2.6V) 1 2.60 15000 39.0 TI PTH05010 15A Module Data Sheet
SSTL2 Memory Power Plane (2.6V) 1 2.60 6000 15.6 TI PTH05000 6A Module Data Sheet
SSTL2 _VREF Power Plane (1.3V) 1 1.30 3000 3.9 Fairchild FN6555 Data Sheet
2.5V Power Plane 1 2.50 15000 37.5 TI PTH05010 15A Module Data Sheet
3.3V Power Plane 1 3.30 15000 49.5
12V-to-5V Converter 1 5.00 12000 60.0 TI PTH12010 12A Module Data Sheet
Notes:
1. [S] = 1.8V power for SSTL18 plane.
2. [H] = 1.8V power for HSTL18 plane.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 41
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 42

Chapter 4: Electrical Requirements
R
Tab le 4 -2 lists the 12 different power planes on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development
Board. For the SSTL2, SSTL18, and HSTL power, separate power modules are
implemented for V
measurement for the FPGAs. The power modules for V
TI PTH05010 modules, which have provisions for ±5% voltage margining pins.
Table 4-2: Power Planes
to FPGA, and VDD to memory, allowing for ease of power
CCO
inputs are implemented with
CCO
Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) Part Power Plane VRM REFDES
V
Power Plane (1.0V) VR6 Layer 4
CCINT
SSTL18 FPGA Power Plane (1.8V) VR1 Layer 7
HSTL FPGA Power Plane (1.8V) VR10 Layer 8
TI PTH05010 15A Modules
V
Power Plane (2.5V) VR12 Layer 11
CCAUX
SSTL2 FPGA Power Plane (2.6V) VR9 Layer 8
TTL Power Plane (3.3V) VR13 Layer 11
SSTL18 Memory Power Plane (1.8V) VR4 Layer 7
TI PTH05000 6A Modules
HSTL Memory Power Plane (1.8V) VR14 Layer 8
SSTL2 Memory Power Plane (2.6V) VR2 Layer 8
SSTL18_VREF Power Plane (0.9V)
U14
SSTL18_VTT Power Plane (0.9V) Layer 8
Fairchild FN6555 3A Bus Term Regulators
(Separate outputs for V
and V
TT
REF
)
HSTL_VREF Power Plane (0.9V)
U42
HSTL_VTT Power Plane (0.9V) Layer 7
SSTL2_VREF Power Plane (1.3V)
U2
SSTL2_VTT Power Plane (1.3V) Layer 7
Stack-Up
Layer
Layer 8
Layer 7
Layer 7
Each of the three Fairchild FN6555 Bus Terminator Regulators has two voltage outputs:
one each for V
V
output and 3 mA for the V
TT
Because the V
power supply does not source any real current. Thus the 3 mA capacity for the V
and VTT. The FN6555 regulator is a push-pull device rated at ± 3A for the
REF
voltage is used by the FPGA and memory devices only as reference, the
REF
REF
output.
REF
output
is considered sufficient.
The V
regulator. The minimum driver output voltage swing around V
voltage is guaranteed to within ± 20 mV of the V
TT
output by the FN6555
REF
is specified for the
REF
SSTL18, SSTL2, and HSTL I/O standards as:
• SSTL2: ± 608 mV
• SSTL18: ± 603 mV
• HSTL: ± 500 mV (for HSTL18)
For a given memory interface, the maximum number of single-ended (non-differential)
signals that might need to be pulled up or down at a time for QDRII is 144 data bits and
approximately 30 address and control signals. The differential pair signals offset for the
sink and source of current. With a continuous current capacity of 3A for the FN6555
regulator, the regulator can supply up to (3000 / 175) = 17 mA of current per signal. The
maximum drive strength for a driver is specified at 16 mA. For a 50Ω V
42 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
termination, this
TT
Page 43

R
current can support a voltage swing of up to (16 mA * 50Ω) = 800 mV, which is sufficient to
meet the output voltage specifications for SSTL18, SSTL2, and HSTL18 I/O standards.
Tab le 4 -3 separates the power consumption information from Tab le 4 -1 according to the
nine TI power modules for the first set of nine power planes and the three Fairchild
regulators for the V
Tab le 4 -3 show that each of the 14 modules can supply the necessary power for the
corresponding power plane.
Table 4-3: ML561 Power Plane Capacities
Power Consumption
power planes. The positive values in the Excess Power column of
TT
Device Description Quantity
Volt ag e
(V)
Current
(mA)
Power
(W)
Excess
Power
(W)
Source
Total Available Power
5V Power Supply 1 5.0 8000 40.0 Bellus Power SPD-050-5
12V Power Supply 1 12.0 5000 60.0 CUI DTS120500U
Power Consumed by Power Plane
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136: FPGA #1
(DDR400, DDR2)
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136: FPGA #2
(DDR2 DIMM)
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136: FPGA #3
(QDRII and RLDRAM II)
V
Power Plane (1.0V) Capacity
CCINT
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136: FPGA #3
(QDRII and RLDRAM II)
HSTL FPGA Power Plane (1.8V)
Capacity
1 1.0 2289 2.3
1 1.0 1945 1.9
1 1.0 2675 2.7
1 1.0 15000 15.0 8.1
1 1.8 3876 7.0
1 1.8 15000 27.0 20.0
Xilinx P
Xilinx Power Estimator
Xilinx Power Estimator
TI PTH05010 15A Module Data
Sheet
Xilinx P
TI PTH05010 15A Module Data
Sheet
ower Estimator
ower Estimator
QDRII Memory [H] 2 1.8 950 3.4 Samsung QDRII Data Sheet
RLDRAM II Memory 2 1.8 920 3.3 Micron RLDRAM II Data Sheet
HSTL_Mem Power Plane (1.8V)
Capacity
QDRII V
RLDRAM II V
Termination
TT
Termi n ation
TT
1 1.8 6000 10.8 4.1
175 1.0 16 2.8
60 1.0 16 1.0
TI PTH05000 6A Module Data
Sheet
All signals. ±500 mV swing
around V
TT
.
All signals. ±500 mV swing
around V
TT
.
HSTL _VREF Power Plane (0.9V) 1 0.9 3000 2.7 -0.1 Fairchild FN6555 Data Sheet
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136:
FPGA #1 (DDR2)
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136:
FPGA #2 (DDR2 DIMM)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 43
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
1 1.8 1011 1.8
1 1.8 4258 7.7
Xilinx P
Xilinx Power Estimator
ower Estimator
Page 44

Chapter 4: Electrical Requirements
R
Table 4-3: ML561 Power Plane Capacities (Continued)
Device Description Quantity
SSTL18 FPGA Power Plane (1.8V)
Capacity
DDR2 x16 Memory
Volt ag e
(V)
Current
(mA)
Power
1 1.8 15000 27.0 17.5
2 1.8 250 0.9
(W)
Excess
Power
(W)
Source
TI PTH05010 15A Module Data
Sheet
Micron DDR2 Component Data
Sheet
DDR2 DIMM 2 1.8 1755 6.3 Micron DDR2 DIMM Data Sheet
SSTL18_Mem Power Plane (1.8V)
Capacity
DDR2 Comp V
Termination
TT
DDR2 DIMM VTT Termination
1 1.8 6000 10.8 3.6
25 1.2 16 0.5
160 1.2 16 3.1
TI PTH05010 15A Module Data
Sheet
Addr/Cntl: ±603 mV swing
around V
TT
All signals: ±603 mV swing
around V
TT
SSTL18 _VREF Power Plane (0.9V) 1 0.9 3000 2.7 -0.9 Fairchild FN6555 Data Sheet
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136: FPGA #1
(DDR400, DDR2)
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136: FPGA #2
(DDR2 DIMM)
1 2.5 609 1.5
1 2.5 218 0.5
Xilinx P
Xilinx Power Estimator
ower Estimator
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136: FPGA #3
(QDRII and RLDRAM II)
1 2.5 435 1.1
Xilinx Power Estimator
Differential Clock Buffer 2 2.5 115 0.8 ICS853006 Data Sheet
200 MHz Osc 1 2.5 30 0.1 Epson EG2121CA Data Sheet
2.5V Power Plane Capacity
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136: FPGA #1
(DDR400)
SSTL2_FPGA Power Plane (2.6V)
Capacity
DDR x16 Memory
SSTL2_Mem Power Plane (2.6V)
Capacity
DDR Comp V
Termination
TT
1 2.5 15000 37.5 34.1
1 2.6 950 2.5
1 2.6 15000 39.0 36.5
2 2.6 210 1.1
1 2.6 6000 15.6 14.5
60 1.2 16 1.2
TI PTH05010 15A Module Data
Sheet
Xilinx P
ower Estimator
TI PTH05010 15A Module Data
Sheet
Micron DDR Component Data
Sheet
TI PTH05010 15A Module Data
Sheet
All signals. ±608 mV swing
around V
TT
SSTL2 _VREF Power Plane (1.3V) 1 1.3 3000 3.9 2.7 Fairchild FN6555 Data Sheet
Clock Buffer 1 3.3 23 0.1 ICS8304 Data Sheet
44 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 45

R
Table 4-3: ML561 Power Plane Capacities (Continued)
Power Consumption
Device Description Quantity
System ACE Controller
Volt ag e
(V)
Current
(mA)
Power
1 3.3 200 0.7
(W)
Excess
Power
(W)
Source
DS080, System ACE
CompactFlash Solution
33 MHz Oscillator 2 3.3 45 0.3 Epson SG-8002CA Data Sheet
3.3V Power Plane Capacity
1 3.3 15000 49.5 47.8
TI PTH05010 15A Module Data
Sheet
Total Power Consumed 53.2
12V-to-5V Power Module Capacity
Notes:
1. [S] = 1.8V power for SSTL18 plane.
2. [H] = 1.8V power for HSTL18 plane.
1 5.0 12000 60.0 6.8
TI PTH12010 12A Module Data
Sheet
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 45
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 46

Chapter 4: Electrical Requirements
R
FPGA Internal Power Budget
Tab le 4 -4 summarizes power consumption estimates by each of the three
XC5VLX50T-FFG1136 FPGAs on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board. This
estimate derives the FPGA utilization information from the respective map report of a fully
configured reference design.
Table 4-4: ML561 FPGA Power Estimate Summary
FPGA # FPGA #1 FPGA #2
(1)
FPGA #3
Interface
DDR400 Comp
(DCI)
DDR2 Comp
(DCI)
DDR2 DIMM
(DCI)
QDRII (DCI)
RLDRAM II
(DCI)
I/O Standard SSTL_18 HSTL_18 HSTL_18
Total Power (W) 3.7 3.1 10.2 6.3 4.5
V
V
SSTL_18 V
SSTL_2 V
HSTL_18 V
(1.0V) mW 763 763 1945 1160 1515
CCINT
(2.5V) mW 435 544 544 544 544
CCAUX
(1.8V) mW 1819 7664
CCO
(2.6V) mW 2469
CCO
(1.8V) mW 4571 2406
CCO
I/O Frequency (MHz) 200 400 400 400 400
Fabric Frequency (MHz) 200 200 200 200 200
Number of Slices 1500 1500 5910 2750 1951
Number of Flip-flops 2000 2000 7352 2000 1800
Number of Shift Register LUTs 50 50 143 750 400
Number of Block RAMs 5 5 17 14 21
Number of DCMs 2 2 2 2 2
Inputs 10 10 10 90 13
Outputs 50 50 90 160 52
Bidirectionals 36 40 192 0 36
Ambient Temperature (°C) 25 25 25 25 25
Airflow (LFM) 0 0 250 250 0
Heat Sink (Theta-J) n/a n/a 5 5 n/a
Junction Temperature (°C) 67 60 78 58 76
Notes:
1. For DDR2 DIMMs as well as QDRII memory interfaces with DCI, an MD35E-10B heat sink is needed. A heat sink with Theta-J = 5.0
should be okay without airflow. See http://www.alphanovatech.com/c_md35e.html
Theta-J = 5.0 might need airflow of 250 LFM.
46 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
for the heat sink profile. A heat sink with
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 47

R
Chapter 5
Signal Integrity Recommendations
Termination and Transmission Line Summaries
The following are common recommendations for the signal termination scheme to all
external memories implemented on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board:
• Single-ended signals: Simulation indicates that for a single-ended signal, there is no
significant performance difference for a signal with split termination of 100Ω + 100Ω
between V
Because the power consumption for the split termination is considerably higher than
the V
TT
is recommended for single-ended signals on the board, such as data, address, and
control. For bidirectional single-ended signals (for example, DDR2 DQ), the V
termination is provided at both ends of the signal at the FPGA as well as at the
memory.
• Differential signals: For differential pair signals, a 100Ω differential termination is
provided between the two legs of the differential pair. This termination is placed
closest to the load. For bidirectional differential signals (for example, DDR2 DQS), the
differential SelectIO™ primitives in Virtex-5 FPGAs (for example,
DIFF_SSTL_II_18_DCI), account for the differential termination within the IOB. So
external differential termination is required only at the memory.
• Multiload signals: Address and control signals are driven by the FPGA, and they
have multiple loads. The termination is placed at the end of the trace after the last
load.
and GND versus the VTT termination of 50Ω to the V
DD
termination for the SSTL2, SSTL18, and HSTL I/O standards, VTT termination
REF
voltage.
TT
Tab le 5 -1 through Tab le 5- 5 summarize the specific termination schemes used on the
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board for the following five different memory
interfaces. For each signal category, these tables include reference to the preliminary IBIS
simulation results
1. DDR400 SDRAM Components (Ta bl e 5 -1 )
2. DDR2 SDRAM DIMM (Ta bl e 5 -2 )
3. DDR2 SDRAM Components (Ta bl e 5 -3 )
4. QDRII SRAM (Ta bl e 5 -4 )
5. RLDRAM II (Tab le 5 -5 )
1. Virtex-4 device IBIS models were used during the development of the ML561 board to understand the
expected signal integrity of the memory interface signals. When the Virtex-5 device IBIS models are available,
the results of post-layout IBIS simulations and characterization results will be reported.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 47
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
(1)
.
Page 48

Chapter 5: Signal Integrity Recommendations
R
Table 5-1: DDR400 SDRAM Component Terminations
Signal FPGA Driver Termination at FPGA Termination at Memory
Data (DQ) SSTL2_II_DCI No termination 50Ω pull-up to 1.3V
Data Strobe (DQS) SSTL2_II_DCI No termination 50Ω pull-up to 1.3V
Clock (CK, CK
) SSTL2_II No termination 100Ω differential termination
between pair
Address (A, BA) SSTL2_II No termination 50Ω pull-up to 1.3V after the last
component
Control (RAS
CKE)
, CAS, WE, CS, DM, and
SSTL2_II No termination 50Ω pull-up to 1.3V after the last
component
Table 5-2: DDR2 SDRAM DIMM Terminations
Signal FPGA Driver Termination at FPGA Termination at Memory
(1)
Data (DQ) SSTL18_II_DCI No termination No termination (use 75Ω ODT
Data Strobe (DQS, DQS
) DIFF_SSTL18_II_DCI No termination No termination (use 75Ω ODT)
)
Data Mask (DM) SSTL18_II No termination No termination (use 75Ω ODT)
6 Pairs of Clocks (CK, CK
),
SSTL18_II No termination No termination
(2)
3 each per DIMM
Address (A, BA) SSTL18_II No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V after the second
DIMM
Control (RAS
, CKE, and others)
CS
Notes:
1. Due to use of DCI I/O for DQ and DQS, these signals have parallel termination at the source during Write operations. Simulation
results show that use of a weaker 75Ω ODT instead of a matching 50Ω ODT setting gives better noise margin at the memory.
2. The DIMM already contains 120Ω differential termination. A 5 pF capacitive termination is provided on the board as per Micron
TN-47-01
, CAS, WE,
.
SSTL18_II No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V after the second
DIMM
Table 5-3: DDR2 SDRAM Component Terminations
Signal FPGA Driver Termination at FPGA Termination at Memory
Data (DQ) SSTL18_II_DCI No termination No termination (use 75Ω ODT)
Data Strobe (DQS, DQS
) DIFF_SSTL18_II_DCI No termination No termination (use 75Ω ODT)
Data Mask (DM) SSTL18_II No termination No termination (use 75Ω ODT)
Clock (CK, CK
) SSTL18_II No termination 100Ω differential termination between
pair
Address (A, BA) SSTL18_II No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V after the last
component
Control (RAS
, CAS, WE, CS,
and CKE)
48 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
SSTL18_II No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V after the last
component
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 49
Termination and Transmission Line Summaries
R
Table 5-4: QDRII SRAM Terminations
Signal FPGA Driver Termination at FPGA Termination at Memory
Write Data (D) HSTL_I_18 No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V
Read Data (Q) HSTL_I_DCI_18 No termination No termination
Write Strobe (K, K
Read Strobe (CQ, CQ
Clock (CK, CK
) HSTL_I_18 No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V
) HSTL_I_DCI_18 No termination No termination
) HSTL_I_18 No termination 100Ω differential termination
between pair
Address (A, BA) HSTL_I_18 No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V after the last
component
Control (RAS
, CKE, and BW)
CS
, CAS, WE,
HSTL_I_18 No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V after the last
component
Table 5-5: RLDRAM II Terminations
Signal FPGA Driver Termination at FPGA Termination at Memory
Data (DQ for CIO) HSTL_II_DCI_18 No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V
Data (Q for SIO) HSTL_I_DCI_18 No termination No termination
Write Data (D for SIO) HSTL_I_18 No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V
Write Strobe (DK, DK
) DIFF_HSTL_I_18 No termination 100Ω differential termination
between pair
Read Strobe (QK, QK
) DIFF_HSTL_II_DCI_18 (for CIO)
No termination No termination
DIFF_HSTL_I_DCI_18 (for SIO)
Data Valid (QVLD) HSTL_II_DCI_18 (for CIO)
No termination No termination
HSTL_I_DCI_18 (for SIO)
Clock (CK, CK
) DIFF_HSTL_I_18 No termination 100Ω differential termination
between pair
Address (A, BA) HSTL_I_18 No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V after the last
component
Control (RAS
, and CKE)
CS
, CAS, WE,
HSTL_I_18 No termination 50Ω pull-up to 0.9V after the last
component
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 49
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 50

Chapter 5: Signal Integrity Recommendations
R
50 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 51

R
Configuration
This chapter provides a brief description of the FPGA configuration methods used on the
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board. This chapter contains the following sections:
• “Configuration Modes”
• “JTAG Chain”
• “JTAG Port”
• “Parallel IV Cable Port”
• “System ACE Interface”
Configuration Modes
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Memory Interfaces Development Board includes several
options to configure the Virtex-5 FPGAs. The configuration modes are:
Chapter 6
• System ACE mode
• JTAG mode
Tab le 6 -1 shows the Virtex-5 FPGA configuration modes. The Master and Slave (Parallel)
SelectMAP configuration modes are not supported on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561
Development Board. A separate 6-pin 3x2 header is provide for each FPGA to control the
Mode bits setting. The three headers are P27, P46, and P112 for FPGA #1, FPGA #2, and
FPGA #3, respectively. The even pins (# 2, 4, and 6) of the headers are tied to GND, and the
odd pins (# 1, 3, and 5) are connected to the respective Mode bit FPGA inputs (M0, M1, and
M2, respectively). A weak (4.7KΩ) pull-up is applied to each of these pins to set a logic '1'
by default.
Table 6-1: Configuration Modes
Mode
Master Serial X
Slave Serial X — 1 1 1
Master SelectMAP — — 0 1 1
Slave SelectMAP — — 1 1 0
JTAG — X 1 0 1
XCONFIG
P72
(1)
JTAG
P114
(2)
—
Mode Jumpers
5 -> 6
(M2)
3 -> 4
(M1)
000
(3,4)
1 -> 2
(M0)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 51
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 52

Chapter 6: Configuration
R
Table 6-1: Configuration Modes (Continued)
JTAG Chain
Four devices (the System ACE chip and three XC5VLX50T-FFG1136 FPGAs) are connected
via a JTAG chain on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board. The order of the four
devices in the JTAG chain is System ACE chip (U45), FPGA #1 (U7), FPGA #2 (U5), and
FPGA #3 (U34). The DONE pin of the FPGAs in the chain are tied together to a single LED
(D28). Each FPGA in the JTAG chain must be programmed for the board to be configured
properly. To program FPGAs in the JTAG chain that do not need functionality, a blank
design with no logic implementation can be used to compile to generate the corresponding
configuration bitstream.
Mode
System ACE CF Card — — 1 1 1
Notes:
1. X = Supported.
2. — = Not applicable.
3. Corresponding jumper position is Closed.
4. Corresponding jumper position is Open.
XCONFIG
P72
JTAG
P114
Mode Jumpers
5 -> 6
(M2)
3 -> 4
(M1)
(3,4)
1 -> 2
(M0)
Three different sources can be used to drive this JTAG chain:
• JTAG Port
• Xilinx Parallel IV Cable
• System ACE Controller
JTAG Port
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board provides a JTAG connector (P114) that can
be used to program the Virtex-5 FPGAs, and program and/or configure other JTAG
devices in the chain.
Parallel IV Cable Port
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board provides a Parallel IV Cable connector
(P64) to configure the Virtex-5 FPGAs and program JTAG devices located in the JTAG
chain.
System ACE Interface
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board provides a System ACE interface to
configure the Virtex-5 FPGA. The interface also gives software designers the ability to run
code (for soft processor IP within the FPGA) from removable CompactFlash cards.
Refer to the D
S080, System ACE CompactFlash Solution for detailed information on creating
System ACE compatible ACE files, formatting the CompactFlash card, and storing
multiple design images.
52 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 53
System ACE Interface
R
Tab le 6 -2 shows the System ACE interface signal names, descriptions, and pin
assignments.
Table 6-2: System ACE Interface Signal Descriptions
System ACE Pin Number Signal Name
70 SYSACE_MPA0
69 SYSACE_MPA1
68 SYSACE_MPA2
67 SYSACE_MPA3
45 SYSACE_MPA4
44 SYSACE_MPA5
43 SYSACE_MPA6
66 SYSACE_MPD0
65 SYSACE_MPD1
63 SYSACE_MPD2
62 SYSACE_MPD3
61 SYSACE_MPD4
60 SYSACE_MPD5
59 SYSACE_MPD6
58 SYSACE_MPD7
77 SYSACE_CTRL0/MPOE
76 SYSACE_CTRL1/MPWE
42 SYSACE_CTRL2/MPCE
41 SYSACE_CTRL3/MPIRQ
39 SYSACE_CTRL4/MPBRDY
93 SYSACE_CLK
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 53
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 54

Chapter 6: Configuration
R
54 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 55

R
ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
This chapter contains the following sections:
• “Introduction”
• “Test Setup”
• “Signal Integrity Correlation Results”
• “Summary and Recommendations”
• “How to Generate a User-Specific FPGA IBIS Model”
Introduction
Signal integrity (SI) simulation is a very powerful tool that predicts the quality of signal at
the receiver. The quality of signal at the I/O buffer of the receiver device is most important
to the system designer. The observation point is buried within the IC device and is not
accessible for attaching a physical probe. This signal can only be simulated. It cannot be
measured on the hardware with an oscilloscope.
Chapter 7
Signals can only be measured on hardware at the via probe points of a printed circuit board
(PCB) near the receiver device. For a high level of confidence in the SI simulation results, it
is necessary to develop and validate the simulation model to get a good correlation with
the hardware measurements at the probe points. When the correlation is obtained, the
same simulation model is used to extrapolate and accurately predict the signal quality at
the I/O buffer of the receiver device for the two significant corner driver conditions: slow-
weak and fast-strong.
The Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 Development Board implements five different memory
interfaces:
• 32-bit DDR2 component
• 144-bit DDR2 DIMM
• 72-bit QDRII SRAM
• 32-bit DDR component
• 36-bit RLDRAM II
Each of these interfaces consists address, control, clock, data, and strobe signals. The
ML561 board has over 500 unique signals.
DDR2 SDRAMs and QDRII SRAM represent the large majority of Virtex-5 FPGA memory
applications. The dual data rate (DDR) data bits are the most critical signals to analyze.
This chapter presents SI analysis for only six representative data bit signals. The procedure
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 55
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 56

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
illustrated here for these signals can be easily adopted to perform SI analysis for any other
memory interface signal on the ML561 board.
This chapter presents the SI results for the following six data bit signals:
• DDR2 component DQ bit (DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3) for write operations
• DDR2 component DQ bit (DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3) for read operations
• DDR2 DIMM DQ bit (DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3) for write operations
• DDR2 DIMM DQ bit (DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3) for read operations
• QDRII D bit (QDR2_D_BY0_B5) for write operations
• QDRII Q bit (QDR2_Q_BY0_B5) for read operations
Test Setup
Hardware measurements were performed for the six specific signal nets, and then signal
integrity (SI) simulations were performed for correlation and extrapolation. The test setup
consisted of the following hardware equipment, simulation software tools, the stimulus
test pattern, and test criteria for determining the quality of signals. The test bench is
designed so that the test pattern is applied only to the signal under test, and all other data
bits to the same memory interface are kept in a quiet Low state. This setup ensures that the
hardware measurement is not altered due to any simultaneous switching output (SSO)
effect.
• Hardware measurement equipment
♦ Agilent DSO80604B 6 GHz oscilloscope
♦ Agilent 1131A 3.5 GHz Infiniimax probe amplifier
♦ Agilent E2675A (Differential browser) or E2677A (Differential solder-in probe) or
N5425A (ZIF probe)
♦ Virtex-5 FPGA ML561, Rev B2 board: S/N 103
♦ SRS Model CG635 Synthesized Clock Generator for low jitter clock source
• Simulation software
♦ Mentor Graphics HyperLynx EXT, Version 7.5 with LineSim and BoardSim
features
♦ Xilinx Virtex-5 FPGA IBIS package file: ff1136_5vlx50t.pkg, Rev 1.0 dated
June 12, 2006
♦ ML561, Rev B layout file: ML561_B_041706.hyp
♦ Micron DDR2-667 IBIS model for output and ODT input
♦ Micron PC2-5300 RDIMM IBIS model
♦ Molex DDR2 DIMM socket specification (P/N 087705-1041)
♦ Samsung QDRII HSTL 1.8V IBIS model
♦ IBISWriter Utility of ISE software suite to create customized IBIS model of the
FPGA1 (U7) and FPGA3 (U34) devices on the ML561 board: Model files
ml561_fpga1_u7.ibs and ml561_fpga3_u34.ibs. (See “How to Generate a
User-Specific FPGA IBIS Model,” page 93 for steps on how to create a customized
IBIS model of Virtex-5 FPGA for your design.)
• Stimulus
Pseudo Random Bit Stream (PRBS) is accepted as the most effective test pattern to
measure the quality of data signals because, unlike the periodic signals like clock and
56 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 57

Test Setup
R
strobe, a random value can be applied to data bits from one cycle to another. A 63-bit
(1)
PRBS6
(PRBS of order 6) test pattern stimulus is used for this analysis. The value of
this PRBS6 string is 63’h03F5_66ED_2717_9461, that is:
63’b000001111110101011001101110110100100111000101111001010001100001.
The HyperLynx stimulus setup is for: a 2-sequence repeat, 10 bits skipped, 1 eye, and
0% jitter.
• Test c rite ria
Quality of a signal is measured in terms of the opening of the signal eye at the receiver
input for both the amplitude and the width. DDR2 SDRAM (Component and DIMM)
interfaces utilize the SSTL_18 I/O standard, and the QDRII SRAM interface utilizes
the HSTL 1.8V I/O standard. For each of these two I/O standards, the eye mask is
defined by the trapezoid enclosed by the following four voltage thresholds at the
receiver input:
♦ VIH(ac)-min at the rising edge
♦ VIH(dc)-min at the falling edge
♦ VIL(dc)-max at the rising edge
♦ VIL(ac)-max at the falling edge
Refer to Figure 7-1 for the definition of voltage levels with regard to the trapezoidal
eye mask. Refer to “Terminology,” page 9 for definitions of the voltage thresholds.
Because the HyperLynx SI simulation software does not support a trapezoidal mask
definition, two separate triangular masks for VIH and VIL are defined, as shown in
Figure 7-2, such that the third vertex of triangle falls on the VREF axis.
VDDQ
VOH(dc)
VIH(ac)
VIH(dc)
VREF
VIL(dc)
VIL(ac)
VOL(dc)
VSS
VOH(ac)
VOL(ac)
UG199_c7_01_062707
Figure 7-1: Single Trapezoid Eye Mask Definition
1. A maximal-length PRBS test sequence of order n generates all (2n – 1), n-bit combinations of test sequences
(except all 0s). Thus the test sequence contains one n-bit long consecutive string of 1s and two (n-1)-bit long
consecutive strings of 0s. With the PRBS6 test pattern, at the highest test frequency of 333 MHz (that is, the bit
time is 1.5 ns), measurements in this setup result in a maximum settling time of (1.5 ns * 5) = 7.5 ns for a logic
Low, and a maximum settling time of (1.5 ns * 6) = 9 ns for a logic High. 7.5 ns is sufficient time for the test
signal to reach a steady state before the next transition. Thus a PRBS test pattern of higher order, such as 7 or
9, does not change the eye pattern, as proven by sample simulation of one test signal with PRBS6, PRBS7, and
PRBS9 stimuli.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 57
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 58

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
VOH(dc)
VDDQ
VIH(ac)
VIH(dc)
VREF
VIL(dc)
VIL(ac)
VOL(dc)
VSS
Figure 7-2: Two Triangular Eye Mask Definitions for VIH and VIL
♦ DDR2 mask (for nominal VDDQ = 1.8V and VREF = 0.9V):
- VIH(ac)-min = VREF + 200 mV = 1.1V
- VIH(dc)-min = VREF + 125 mV = 1.025V
- VIL(ac)-max = VREF – 200 mV = 0.7V
- VIL(dc)-max = VREF – 125 mV = 0.775V
♦ QDRII mask (for nominal values of VDDQ = 1.8V and VREF = 0.9V):
- VIH(ac)-min = VREF + 200 mV = 1.1V
- VIH(dc)-min = VREF + 100 mV = 1.0V
- VIL(ac)-max = VREF – 200 mV = 0.7V
- VIL(dc)-max = VREF – 100 mV = 0.8V
VOH(ac)
VOL(ac)
UG199_c7_02_062707
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
This section presents SI results for each of the six chosen memory signals on the ML561
board. The following information is presented for each memory signal:
• A post-layout IBIS schematics of the signal under test
• A description of the major circuit elements
• A summary of four SI results: hardware measurement, correlation simulation, slow-
weak corner driver simulation extrapolation, and fast-strong corner driver simulation
extrapolation
• A set of eight figures showing eye and waveform scope shots for each of the four SI
results mentioned in the bulleted list in the previous section
For an explanation of the different terms used to present these results, refer to
“Terminology,” page 9 for some definitions and routing terminologies.
1. With regard to transmission line impedance, Ta b le 3 -1 9 in the “Board Design Considerations” section lists
controlled impedance values of all routing layers. The design goal for the ML561 board is to keep the
characteristic impedance for all routing layers as close to 50Ω as possible. Manufacturing tolerance is usually
±10%. The characteristic impedance of DIMM PCB is derived from the Micron DIMM layout file.
58 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
(1)
of this signal
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 59

R
DDR2 Component Write Operation
This subsection shows the test results for the DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3 signal from FPGA1 (U7)
to the DDR2 memory component (U12) measured at 333 MHz (667 Mb/s), where the unit
interval (UI) = 1.5 ns.
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
U12.D3
MT47H32M16CC_…
DQ11
28.5 ohms
3.579 ps
0.022 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
TL2 TL3 TL8
71.0 ohms
27.482 ps
AutoPadstk_3
DDR2_D…
22.9 fF 22.9 fF 500.0 fF
49.0 ohms
24.721 ps
0.164 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
TL4 TL6
DDR2_D…
C9
DDR2_D…
58.1 fF 140.8 fF
58.3 ohms
25.244 ps
AutoPadstk_19
49.1 ohms
47.132 ps
0.302 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
TL9 TL5
DDR2_D…
49.1 ohms
445.560 ps
2.852 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
21.2 ohms
1.000 ps
AutoPadstk_3
DDR2_D…
365.6 fF
C7
500.0 fF
28.5 ohms
4.473 ps
0.028 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
TL1
DDR2_D…
22.9 fF
UG199_c7_03_071907
Figure 7-3: Post-Layout IBIS Schematics of DDR2 Component Write Data Bit (DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3)
Table 7-1: Circuit Elements of DDR2 Component Write Data Bit
(DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3)
Element Designation Description
Driver U7.P25 FPGA SSTL18_II_DCI_O
Receiver U12.D3 DDR2 Memory, 75 Ω ODT
Probe Point C9 Via under the memory device
PCB Termination None ODT75 at load
U7.P25
Virtex-5 FPGA
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
Trace Length TL 2, 4, 9, 6, 1 3.37 inches
Table 7-2: DDR2 Component Write Operation Correlation Results
Measurement
Hardware at probe
point
Simulation correlation
slow-weak corner
Correlation Delta:
HW vs. Simulation
Extrapolation at IOB
slow-weak corner
Extrapolation at IOB
fast-strong corner
DVW
(78.7%)
(81.3%)
(%UI)
1.18 ns
1.22 ns
40 ps
(2.6%)
1.27 ns
(84%)
1.39 ns
(92%)
ISI
(% UI)
(80 + 80) = 160 ps
(10.7%)
(77 + 36) = 113 ps
(7.5%)
47 ps
(3.2%)
(91 + 36) = 127 ps
(8.5%)
(34 + 20) = 54 ps
(3.7%)
(1)
Notes:
1. DVW = Data Valid Window, ISI = Inter-Symbol Interference
Noise Margin
(VIH, + VIL) = Total
(% of VREF)
(274 + 384) = 658 mV
(73.1%)
(294 + 266) = 560 mV
(62.2%)
98 mV
(10.9%)
(300 + 270) = 570 mV
(63.3%)
(406 + 351) = 757 mV
(84.1%)
Overshoot / Undershoot
Margin
(% of VREF)
(550 + 470) = 1020 mV
(113.3%)
(461 + 490) = 951 mV
(105.7%)
69 mV
(7.6%)
(469 + 501) = 970 mV
(107.8%)
(304 + 381) = 685 mV
(76.1%)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 59
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 60

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
DDR2 DQ is a bidirectional signal. To perform hardware measurements for a Write
operation that is not interrupted by a Read response or a Refresh operation, the testbench
on FPGA1 is controlled by DIP switches (SW2) as indicated in Ta bl e 7 -3 .
Table 7-3: DIP[1:2] Settings
Setting Description
2’b00 or 2’b11 Normal alternating Write/Read sequence
2’b01 Write only, Refresh disabled
2’b10 Write once, then Read only, Refresh disabled
60 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 61

Signal Integrity Correlation Results
R
UG199_c7_04_071107
♦ 333 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 81.5% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.1028V, 123.6 ps
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0253V, 1.3458 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 77.5 mV, Delta Time = 1.2222 ns (81.5% UI)
Figure 7-4: DDR2 Component Write HW Measurement - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point (DDR2 Memory Via)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
0.000 400.0 800.0 1200.0 1600.0
Probe 3:C9.1 (at pin)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_05_070907
Figure 7-5: DDR2 Component Write Correlation - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 61
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 62

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
UG199_c7_06_071107
Figure 7-6: DDR2 Component Write HW Measurement - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point
(DDR2 Memory Via)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
Probe 3:C9.1 (at pin)
-200.0
65.000 75.000 85.000 95.000 105.000
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_07_070907
Figure 7-7: DDR2 Component Write Correlation - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
62 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 63

R
1800.0
♦ 333 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 84.5% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.1007V, 123.7 ps
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0253V, 1.3921 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 75.4 mV, Delta Time = 1.2684 ns (84.5% UI)
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
0.000
-200.0
-200.0 200.0 600.0
Probe 1:U12.D3 (at die)
1000.0 1400.0 1800.0
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_08_071007
Figure 7-8: DDR2 Component Write Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
65.000 75.000 85.000 95.000 105.000
Figure 7-9: DDR2 Component Write Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 63
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Probe 1:U12.D3 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_09_071007
Page 64

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
♦ 333 MHz, Fast, PRBS6, 92.5% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 701.2 mV, 1.0026 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 774.6 mV, 2.3908 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 73.4 mV, Delta Time = 1.3883 ns (92.5% UI)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
800.0 1200.0 1600.0
Probe 1:U12.D3 (at die)
Time (ps)
2000.0 2400.0 2800.0
UG199_c7_10_071007
Figure 7-10: DDR2 Component Write Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
65.000 75.000 85.000 95.000 105.000
Figure 7-11: DDR2 Component Write Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
64 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
Probe 1:U12.D3 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_11_071007
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 65
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
R
49.0 ohms
24.721 ps
0.164 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
28.5 ohms
3.579 ps
0.022 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
MT47H64M8CB-3
DQ3
TL2 TL3 TL4 TL8 TL9 TL6 TL5 TL1
U7.P25
C7
C9
U12.D3
49.1 ohms
47.132 ps
0.302 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
58.3 ohms
25.244 ps
AutoPadstk_19
21.2 ohms
1.000 ps
AutoPadstk_3
71.0 ohms
27.482 ps
AutoPadstk_3
49.1 ohms
445.560 ps
2.852 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
28.5 ohms
4.473 ps
0.028 in
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
Virtex-5 FPGA
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
22.9 fF 22.9 fF 500.0 fF
58.1 fF
140.8 fF
DDR2_D…
DDR2_D… DDR2_D…
DDR2_D…
DDR2_D…
DDR2_D…
365.6 fF
500.0 fF
22.9 fF
UG199_c7_12_071907
DDR2 Component Read Operation
This subsection shows the test results for the DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3 signal from the DDR2
memory component (U12) to FPGA1 (U7) measured at 333 MHz (667 Mb/s), where the
unit interval (UI) = 1.5 ns.
Figure 7-12: Post-Layout IBIS Schematics of the DDR2 Component Read Data Bit (DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3)
Table 7-4: Circuit Elements of DDR2 Component Read Data Bit
(DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3)
Element Designation Description
Driver U12.D3 DDR2 Memory
Receiver U7.P25 FPGA SSTL18_II_DCI_I
Probe Point C7 Via under FPGA1
PCB Termination None DCI at receiver
Trace Length TL 2, 4, 9, 6, 1 3.37 inches
Table 7-5: DDR2 Component Read Operation Correlation Results
Measurement DVW (% UI)
Hardware at probe point
Simulation correlation
slow-weak corner
Correlation Delta:
HW vs. Simulation
Extrapolation at IOB
slow-weak corner
1.28 ns
(85%)
1.28 ns
(85%)
0 ps
(0.0%)
1.29 ns
(86%)
(70 + 110) = 180 ps
(132 + 91) = 223 ps
ISI
(% UI)
(12%)
(14.9%)
43 ps
(2.9%)
(96 + 82) = 178 ps
(11.9%)
Noise Margin
(VIH + VIL) = Total
(% of VREF)
(423 + 416) = 839 mV
(83.1%)
(406 +439) = 845 mV
(83.8%)
6 mV
(0.7%)
(418 + 449) = 867 mV
(96.3%)
Overshoot /
Undershoot Margin
(% of VREF)
(400 +400) = 800 mV
(79.1%)
(279 +277) = 556 mV
(61.9%)
244 mV
(17.2%)
(304 +265) = 569 mV
(63.1%)
Extrapolation at IOB
fast-strong corner
1.32 ns
(88%)
(29 + 67) = 96 ps
(6.7%)
(455 +435) = 890 mV
(98.9%)
(167 +182) = 349 mV
(38.9%)
To perform hardware measurements for a Read operation that is not interrupted by a Write
or a Refresh operation, the testbench on FPGA1 is controlled by the following DIP switch
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 65
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
(SW2) setting:
• DIP[1:2] = 2’b10 – Write once, then Read only, Refresh disabled
Page 66

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
UG199_c7_13_071107
♦ 333 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 85.9% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 697.1 mV, 1.2345 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 774.6 mV, 2.5191 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 77.5 mV, Delta Time = 1.2846 ns (85.9% UI)
Figure 7-13: DDR2 Component Read HW Measurement - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point (FPGA1 Via)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
800.0 1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0 2800.0
Probe 3:C7.1 (at pin)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_14_071107
Figure 7-14: DDR2 Component Read Correlation - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
66 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 67

Signal Integrity Correlation Results
R
UG199_c7_15_071107
Figure 7-15: DDR2 Component Read HW Measurement - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (FPGA1
Via)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
65.000 75.000 85.000 95.000 105.000
Probe 3:C7.1 (at pin)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_16_071007
Figure 7-16: DDR2 Component Read Correlation - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 67
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 68
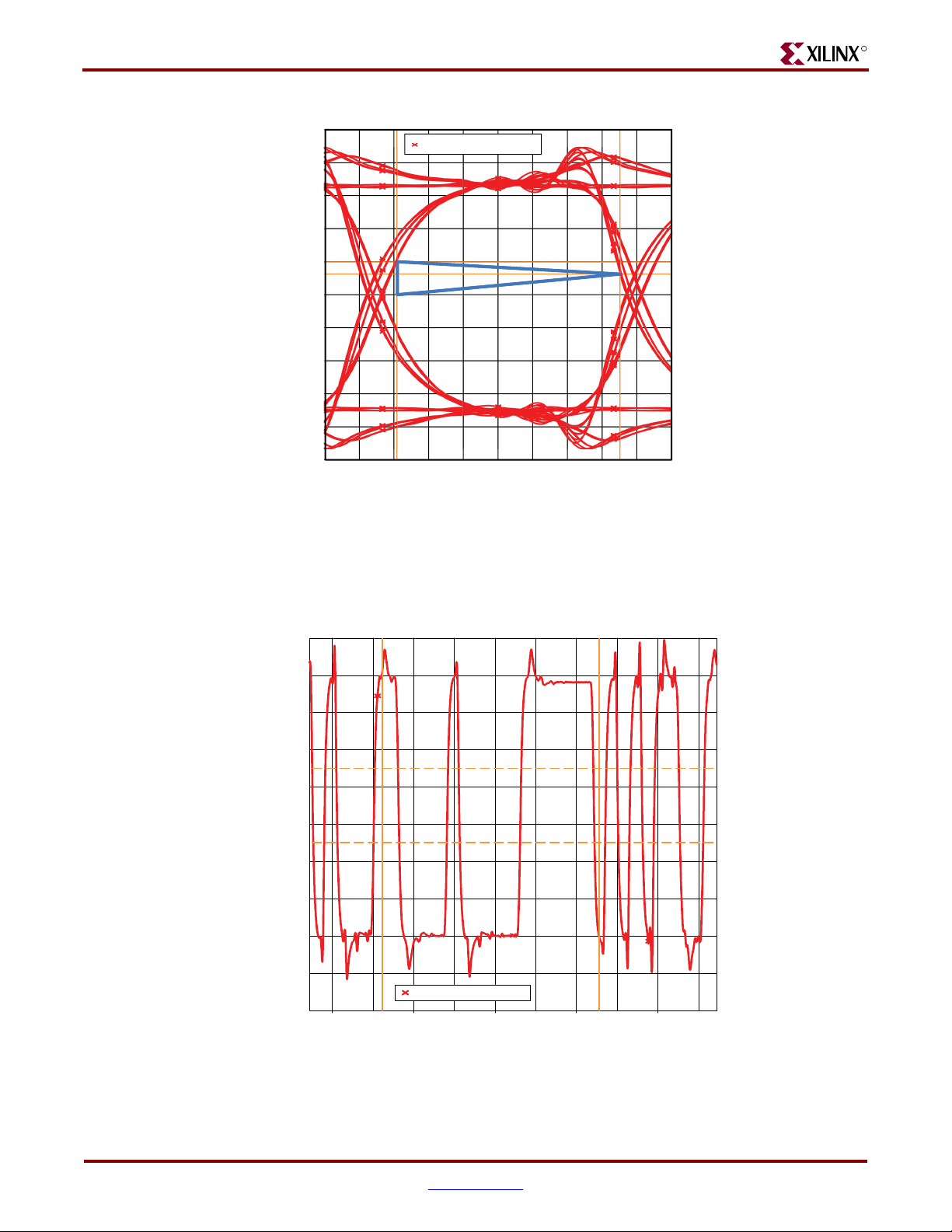
Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
♦ 333 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 85.5% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.0988V, 1.2170 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0254V, 2.5029 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 73.4 mV, Delta Time = 1.2859 ns (85.5% UI)
1900.0
Probe 1:U7.P25 (at die)
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
700.0
Voltage (mV)
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
800.0 1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0 2800.0
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_17_071007
Figure 7-17: DDR2 Component Read Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
Probe 1:U7.P25 (at die)
-200.0
65.000 75.000 85.000 95.000 105.000
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_18_071007
Figure 7-18: DDR2 Component Read Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
68 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 69
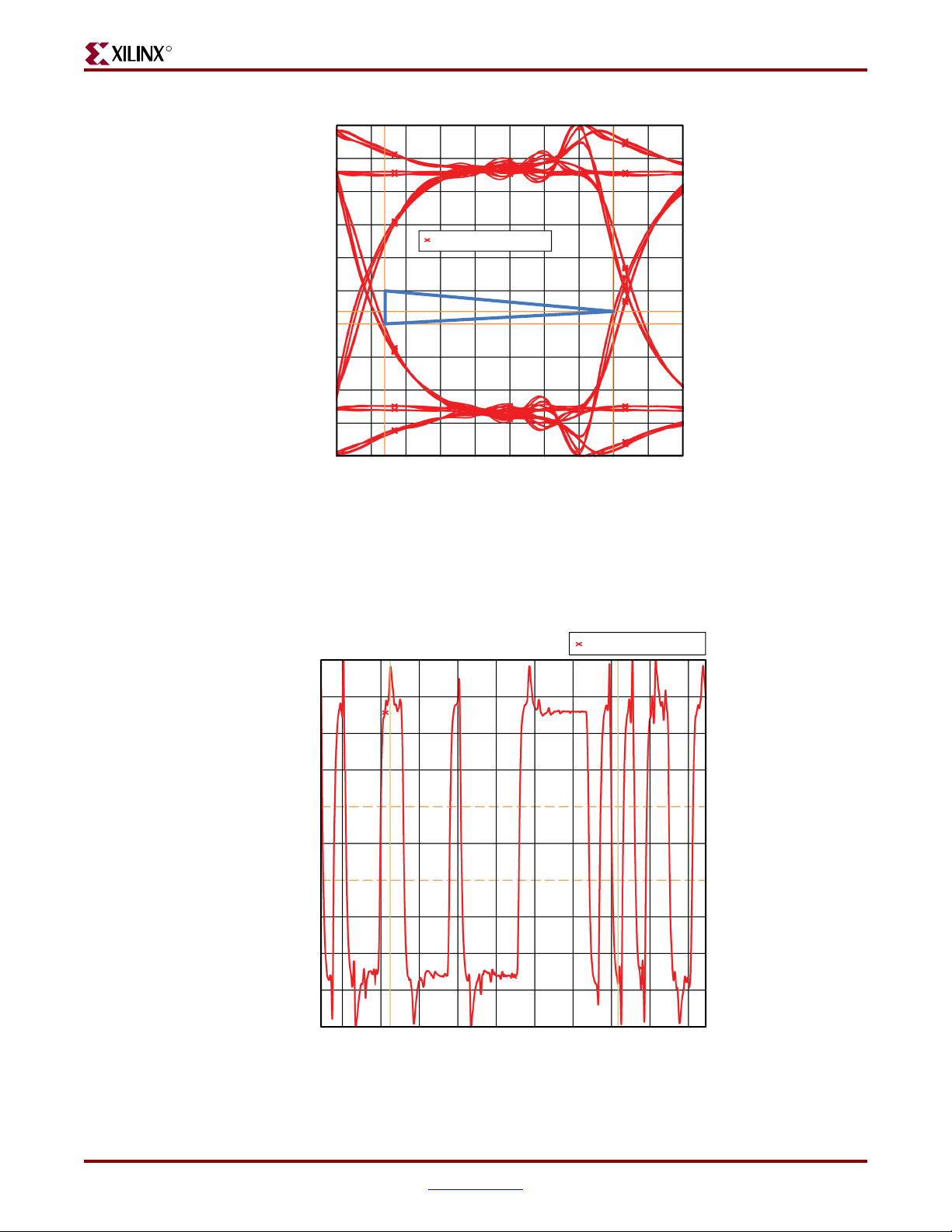
R
1900.0
♦ 333 MHz, Fast, PRBS6, 88% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 701.2 mV, 1.0772 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 774.6 mV, 2.3980 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 73.4 mV, Delta Time = 1.3208 ns (88% UI)
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
Probe 1:U7.P25 (at die)
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
800.0 1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0 2800.0
Time (ps)
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
UG199_c7_19_071007
Figure 7-19: DDR2 Component Read Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
65.000 75.000 85.000 95.000 105.000
Time (ns)
Probe 1:U7.P25 (at die)
UG199_c7_20_071007
Figure 7-20: DDR2 Component Read Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 69
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 70

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
DDR2 DIMM Write Operation
This subsection shows the test results for the DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3 signal from
FPGA2 (U5) to the DDR2 DIMM (XP2) measured at 333 MHz (667 Mb/s), where the unit
interval (UI) = 1.5 ns.
C8
500.0 fF
28.5 ohms
4.473 ps
0.028 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
TL3TL6TL7TL20TL19
DDR2_DI...
22.9 fF
UG199_c7_21_071907
U3_B01.J1
MT47H64M8CB_C...
DQ6
59.8 ohms
59.8 ohms
31.503 ps
0.195 in
MDQ19_B01
59.8 ohms
78.962 ps
0.490 in
MDQ19_B01
C13
500.0 fF
RN6_B01
3.590 ps
0.022 in
MDQ19_B01
TL1 TL5 TL11 TL1222.0 ohms
MDQ19_...
17.3 fF
59.8 ohms
10.373 ps
0.064 in
DQ19_B01
49.8 ohms
94.605 ps
0.606 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
J1_B01.31
????
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DDR2_D...
R_00179... R7 R5 R6
0.0 milliohms 0.0 milliohms 0.0 milliohms 0.0 milliohms
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DQ19_B...
49.8 ohms
90.955 ps
0.582 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
TL15 TL16 TL17 TL18
????
TL13
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DDR2_D...
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DQ19_B...
49.8 ohms
90.340 ps
0.578 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DDR2_D...
TL22TL26
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DQ19_B...
49.8 ohms
864.365 ps
5.533 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
XP5_B00.31XP4_B00.31XP3_B00.31XP2_B00.31
TL25TL23TL27TL14
????????????
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DDR2_D...
TL24
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DQ19_B...
59.1 ohms
12.486 ps
AutoPadstk_12_B...
49.1 ohms
78.216 ps
0.501 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
DDR2_DI...DDR2_DI...
46.4 fF253.0 fF
49.1 ohms
41.316 ps
0.264 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
DDR2_DI...
96.3 fF
71.6 ohms
22.319 ps
AutoPadstk_3_B00
Figure 7-21: Post-Layout IBIS Schematics of DDR2 DIMM Write Data Bit (DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3)
Table 7-6: Circuit Elements of DDR2 DIMM Write Data Bit
(DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3)
Element Designation Description
Driver U5.H29 FPGA SSTL18_II_DCI_O
Receiver XP2-U3.J1 DDR2 DIMM, 75 Ω ODT
Probe Point C13 Via under memory on DIMM
PCB Termination None ODT at load
Trace Length Multiple TLs 8.975 inches
U5_B00.H29
Virtex-5 FPGA
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3
The IBIS schematics for DDR2 DIMM interface is extracted from a multi-board project
definition of the two-board combination, which includes the ML561 motherboard and the
DDR2 DIMM at the XP2 connector of the motherboard. The impedance characteristics of
the Molex socket pin (XP2, pin 31) is also included in the IBIS model as a (TL13,
R_00179_CONN_0001, TL14) combination.
The ML561 board under test (S/N 103) is assembled with DDR2 sockets XP3, XP4, and
XP5, which can be utilized for deep DIMM interfaces as described in Tab le 3- 2, p ag e 19 and
Figure 3-2, page 20. To accurately represent the IBIS model of the
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3 signal, the IBIS schematics in Figure 7-21 have added stubs for
the three socket pins at the XP3, XP4, and XP5 connectors.
The DDR2 DIMM used for this correlation testing is a single-rank DIMM part (Micron part
number MT9HTF6472xx-667). Thus for hardware measurements closest to the load, a
probe point via on the DIMM for pin U3.J1 is available.
70 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 71
R
Table 7-7: DDR2 DIMM Write Operation Correlation Results
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
Measurement
Hardware at Probe
Point
Simulation correlation
at memory via (C13)
slow-weak corner
Correlation Delta:
HW vs. Simulation
Extrapolation at IOB
slow-weak corner
Extrapolation at IOB
fast-strong corner
DVW
(%UI)
942 ps
(62.8%)
1.16 ns
(77.3%)
218 ps
(14.5%)
1.23 ns
(82%)
1.32 ns
(88%)
ISI
(% UI)
(300 + 200) = 500 ps
(33.3%)
(80 + 54) = 134 ps
(8.9%)
366 ps
(24.4%)
(85 + 32) = 117 ps
(7.8%)
(54 + 46) = 100 ps
(6.7%)
Noise Margin
(VIH + VIL) = Total
(% of VREF)
(110 + 100) = 210 mV
(23.3%)
(172 + 150) = 322 mV
(35.9%)
112 mV
(12.6%)
(178 + 137) = 315 mV
(35.0%)
(146 + 107) = 253 mV
(28.1%)
Overshoot / Undershoot
Margin
(% of VREF)
(620 + 620) = 1240 mV
(137.7%)
(606 + 636) =1242 mV
(138%)
2 mV
(0.3%)
(604 + 632) = 1236 mV
(137.3%)
(457 + 524) = 981 mV
(109.0%)
DDR2 DQ is a bidirectional signal. To perform hardware measurements for a Write
operation that is not interrupted by a Read response or a Refresh operation, the testbench
on FPGA2 is controlled by DIP switches (SW1) as indicated in Ta bl e 7 -8 .
Table 7-8: DIP[1:2] Settings
Setting Description
2’b00 or 2’b11 Normal alternating Write/Read sequence
2’b01 Write only, Refresh disabled
2’b10 Write once, then Read only, Refresh disabled
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 71
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 72

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
UG199_c7_22_071107
♦ 333 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 77% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.1004V, 1.2553 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0253V, 2.4105 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 75.2 mV, Delta Time = 1.1582 ns (77% UI)
Figure 7-22: DDR2 DIMM Write HW Measurement - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point #1 (DDR2 Memory Via)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
800.0 1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0 2800.0
Probe 3:C13.1 (at pin)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_23_070907
Figure 7-23: DDR2 DIMM Write Correlation - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point #1 (Slow Corner)
72 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 73

Signal Integrity Correlation Results
R
UG199_c7_24_071107
Figure 7-24: DDR2 DIMM Write HW Measurement - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point #1 (DDR2 Memory
Via)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
95.000 105.000 115.000 125.000 135.000 145.000
Probe 3:C13.1 (at pin)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_23_071007
Figure 7-25: DDR2 DIMM Write Correlation - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point #1 (Slow Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 73
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 74

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
♦ 333 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 82% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.1028V, 1.2399 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0253V, 2.4671 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 77.5 mV, Delta Time = 1.2272 ns (82% UI)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
600.0
Voltage (mV)
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
1000.0 1400.0 1800.0 2200.0 2600.0
Probe 6:U3_B01.J1 (at die)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_26_071007
Figure 7-26: DDR2 DIMM Write Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
95.000 105.000 115.000 125.000 135.000 145.000
Probe 6:U3_B01.J1 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_27_071007
Figure 7-27: DDR2 DIMM Write Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
74 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 75

R
1800.0
♦ 333 MHz, Fast, PRBS6, 88% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.1004V, 646.3 ps
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0273V, 1.9659 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 73.1 mV, Delta Time = 1.3196 ns (88% UI)
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
600.0
Voltage (mV)
400.0
200.0
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
0.000
-200.0
400.0 800.0 1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0
Probe 6:U3_B01.J1 (at die)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_28_071007
Figure 7-28: DDR2 DIMM Write Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
95.000 105.000 115.000 125.000 135.000 145.000
Probe 6:U3_B01.J1 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_29_071007
Figure 7-29: DDR2 DIMM Write Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 75
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 76

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
DDR2 DIMM Read Operation
This subsection shows the test results for the DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3 signal from the
DDR2 DIMM (XP2) to FPGA2 (U5) measured at 333 MHz (667 Mb/s), where the unit
interval (UI) = 1.5 ns.
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DQ19_B...
49.8 ohms
90.340 ps
0.578 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DDR2_D...
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DQ19_B...
49.8 ohms
864.365 ps
5.533 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
XP5_B00.31XP4_B00.31XP3_B00.31XP2_B00.31
TL25TL23TL27TL14
????????????
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DDR2_D...
TL24TL22TL26
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DQ19_B...
59.1 ohms
12.486 ps
AutoPadstk_12_B...
DDR2_DI...
253.0 fF
49.1 ohms
78.216 ps
0.501 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
DDR2_DI...
46.4 fF
49.1 ohms
41.316 ps
0.264 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
DDR2_DI...
96.3 fF
71.6 ohms
22.319 ps
AutoPadstk_3_B00
C8
500.0 fF
DDR2_DI...
U3_B01.J1
MT47H64M8CB_C...
DQ6
59.8 ohms
3.590 ps
0.022 in
MDQ19_B01
59.8 ohms
59.8 ohms
78.962 ps
31.503 ps
0.490 in
0.195 in
MDQ19_B01
MDQ19_B01
TL11TL1
TL5 22.0 ohms
MDQ19_...
C13
17.3 fF
500.0 fF
RN6_B01
59.8 ohms
10.373 ps
0.064 in
DQ19_B01
TL12
49.8 ohms
94.605 ps
0.606 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
J1_B01.31
????
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DDR2_D...
R_00179... R7 R5 R6
0.0 milliohms 0.0 milliohms 0.0 milliohms 0.0 milliohms
TL13
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DQ19_B...
49.8 ohms
90.955 ps
0.582 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
TL15 TL16 TL17 TL18 TL19
????
50.3 ohms
23.650 ps
DDR2_D...
Figure 7-30: Post-Layout IBIS Schematics of the DDR2 DIMM Read Data Bit (DDR2_DIMM_DQ_B)
Table 7-9: Circuit Elements of DDR2 DIMM Read Data Bit
(DDR2_DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3)
Element Designation Description
Driver XP2-U3.J1 DDR2 DIMM
Receiver U5.H29 FPGA SSTL18_II_DCI_I
Probe Point C8 Via under FPGA2 (U5.H29)
PCB Termination None DCI at load
Trace Length Multiple TLs 8.975 inches
28.5 ohms
4.473 ps
0.028 in
DDR2_DIMM_DQ_...
TL3TL6TL7TL20
22.9 fF
UG199_c7_30_071907
U5_B00.H29
Virtex-5 FPGA
DIMM_DQ_BY2_B3
Table 7-10: DDR2 DIMM Read Operation Correlation Results
Measurement
Hardware at probe
point
Simulation correlation
slow-weak corner
Correlation Delta:
HW vs. Simulation
Extrapolation at IOB
slow-weak corner
Extrapolation at IOB
fast-strong corner
DVW (%
UI)
904 ps
(60%)
865 ps
(59%)
39 ps
(2.6%)
1.23 ns
(82%)
1.24 ns
(83%)
(107 + 62) = 169 ps
(130 + 83) = 213 ps
(139 + 75) = 224 ps
(131 + 60) = 191 ps
ISI
(% UI)
(11.2%)
(14.2%)
(VIH + VIL) = Total
(242 + 258) = 500 mV
(+292 + 298) = 590 mV
44 ps (2.9%) 90 mV (10%) 208 mV (23.1%)
(243 + 303) = 546 mV
(14.9%)
(288 + 282) = 570 mV
(12.7%)
To perform hardware measurements for a Read operation that is not interrupted by a Write
or a Refresh operation, the testbench on FPGA1 is controlled by the following DIP switch
(SW1) setting:
• DIP[1:2] = 2’b10 – Write once, then Read only, Refresh disabled
Noise Margin
(% of VREF)
(60.7%)
(63.3%)
Overshoot / Undershoot
Margin
(% of VREF)
(623 + 613) = 1236 mV
(137.3%)
(524 + 504) = 1028 mV
(114.2%)
(594 + 544) = 1138 mV
(116.5%)
(+481 + 508) = 989 mV
(109.9%)
76 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 77

Signal Integrity Correlation Results
R
UG199_c7_31_071107
♦ 333 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 59% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.0988V, 2.5207 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0254V, 3.3859 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 73.4 mV, Delta Time = 865.2 ps (59% UI)
Figure 7-31: DDR2 DIMM Read HW Measurement - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point (FPGA1 Via)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
700.0
Voltage (mV)
500.0
300.0
100.0
Probe 3:C8.1 (at pin)
-100.0
2000.0 2400.0 2800.0 3200.0 3600.0
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_32_071107
Figure 7-32: DDR2 DIMM Read Correlation - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 77
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 78

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
UG199_c7_33_071107
Figure 7-33: DDR2 DIMM Read HW Measurement - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (FPGA1 Via)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
25.000 35.000 45.000 55.000 65.000 75.000
Probe 3:C8.1 (at pin)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_34_071007
Figure 7-34: DDR2 DIMM Read Correlation - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
78 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 79

R
1800.0
♦ 333 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 82% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.1007V, 2.3997 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0232V, 3.6257 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 77.5 mV, Delta Time = 1.2260 ns (82% UI)
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
600.0
Voltage (mV)
400.0
200.0
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
0.000
-200.0
2000.0 2400.0 2800.0 3200.0 3600.0 4000.0
Probe 6:U5_B00.H29 (at die)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_35_071007
Figure 7-35: DDR2 DIMM Read Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
30.000 40.000 50.000 60.000 70.000
Probe 6:U5_B00.H29 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_36_071007
Figure 7-36: DDR2 DIMM Read Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 79
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 80
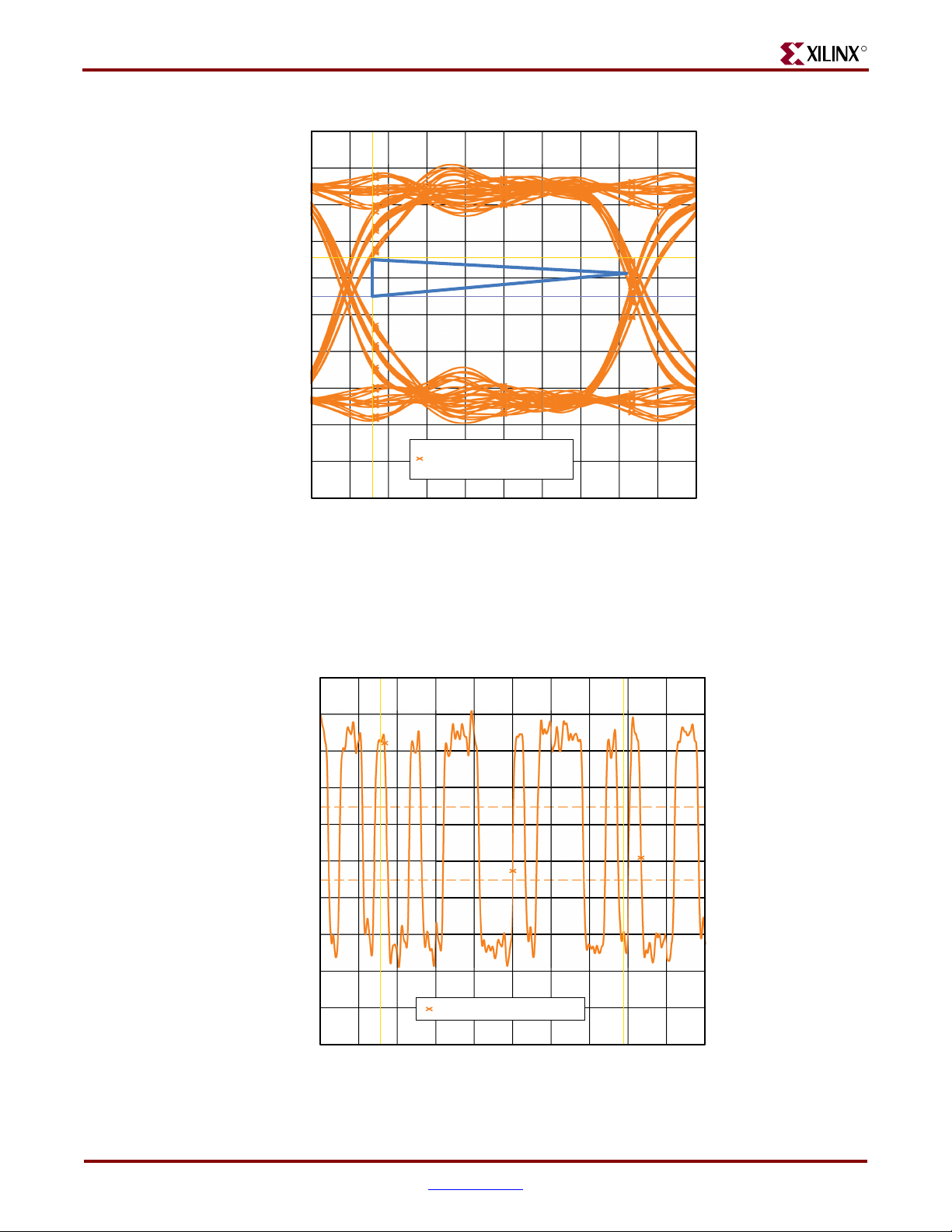
Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
♦ 333 MHz, Fast, PRBS6, 83% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 697.0 mV, 763.0 ps
♦ Cursor 2: 776.6 mV, 2.0052 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 79.5 mV, Delta Time = 1.2422 ns (83% UI)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
400.0 800.0 1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0
Probe 6:U5_B00.H29 (at die)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_37_071007
Figure 7-37: DDR2 DIMM Read Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
30.000 40.000 50.000 60.000 70.000
Figure 7-38: DDR2 DIMM Read Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
80 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
Probe 6:U5_B00.H29 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_38_071007
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 81

R
U35.G11
QDRII Write Operation
This subsection shows the test results for the QDR2_D_BY0_B5 signal from FPGA3 (U34)
to QDRII memory (U35) measured at 300 MHz (600 Mb/s), where the unit interval
(UI) = 167 ns.
49.0 ohms
VCC0V7…
0.9V
28.5 ohms
4.404 ps
0.027 in
QDR2_D_BY0_B5
R1586
49.9 ohms
71.0 ohms
27.482 ps
AutoPadstk_3
5.283 ps
0.035 in
QDR2_D_BY0_B5
TL6
49.0 ohms
11.902 ps
0.079 in
QDR2_D_BY0_B5
45.1 ohms
7.862 ps
AutoPadstk_19
49.8 ohms
520.665 ps
3.333 in
QDR2_D_BY0_B5
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
70.8 ohms
16.339 ps
AutoPadstk_3
28.5 ohms
4.473 ps
0.028 in
QDR2_D_BY0_B5
U34.M31
K7R323684M_1.8V
D5
TL2 TL4 TL5
QDR2_D... QDR2_D... QDR2_D...
22.9 fF22.9 fF
C7
500.0 fF
QDR2_D...
58.1 fF
Figure 7-39: Post-Layout IBIS Schematics of QDRII Write Data Bit (QDR2_D_BY0_B5)
Table 7-11: Circuit Elements of QDRII Write Data bit (QDR2_D_BY0_B5)
Element Designation Description
Driver U34.M31 FPGA HSTL_I_18
Receiver U35.G11 QDRII memory
Probe Point C7 Via under Memory
PCB Termination R1586 External termination at memory
Trace Length TL 2, 5, 8, 1 3.46 inches
Table 7-12: QDRII Write Operation Correlation Results
Measurement
DVW
(% UI)
ISI
(% UI)
TL7 TL8 TL3 TL1
QDR2_D...
22.9 fF
Overshoot / Undershoot
399.1 fF
Noise Margin
QDR2_D...
177.3 fF
(VIH + VIL) = Total
(% of VREF)
(% of VREF)
UG199_c7_39_070907
Margin
Virtex-5 FPGA
QDR2_D_BY0_B5
Hardware at probe
point
Simulation correlation
slow-weak corner
Correlation Delta:
HW vs. Simulation
Extrapolation at IOB
slow-weak corner
Extrapolation at IOB
fast-strong corner
1.40 ns
(84.1%)
1.39 ns
(83.5%)
10 ps
(0.6%)
1.38 ns
(83%)
1.49 ns
(89%)
(50 + 70) = 120 ps (7.2%)
(136 + 91) = 227 ps (13.6%)
(340 + 400) = 740 mV
(82.2%)
(344 + 398) = 742 mV
(82.5%)
(450 + 400) = 850 mV
(483 + 452) = 935 mV
107 ps (6.4%) 2 mV (0.3%) 85 mV (9.4%)
(172 + 141) = 313 ps
(18.8%)
(126 + 91) = 217 ps (13.0%)
(329 + 358) = 687 mV
(76.3%)
(353 + 376) = 729 mV
(81.0%)
(400 + 361) = 761 mV
(156 + 30) = 186 mV
(94.5%)
(103.9%)
(84.5%)
(20.7%)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 81
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 82
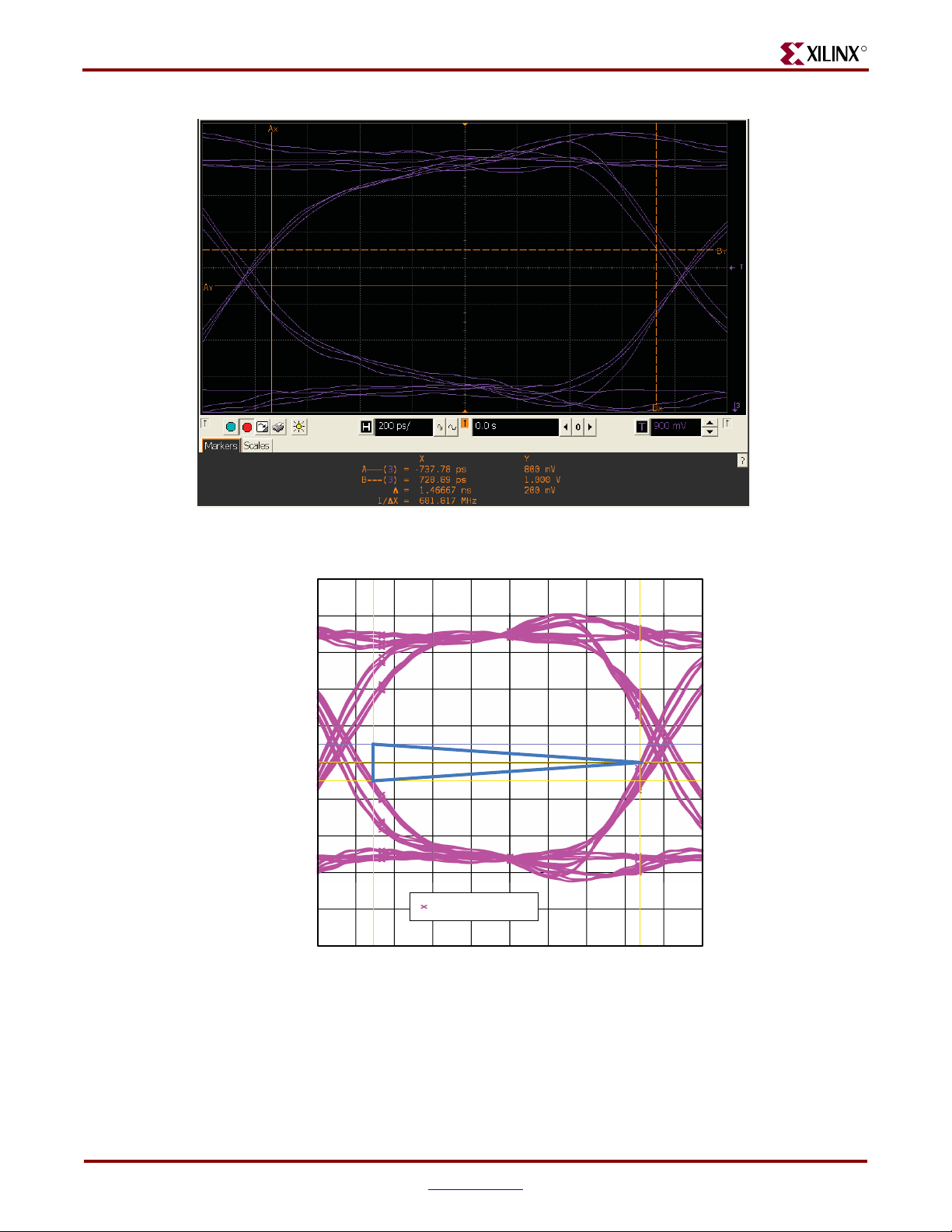
Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
UG199_c7_40_071107
♦ 300 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 83.5% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 699.1 mV, 90.0 ps
♦ Cursor 2: 801.0 mV, 1.4770 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 101.9 mV, Delta Time = 1.3870 ns (83.5% UI)
Figure 7-40: QDRII Write HW Measurement - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point (QDRII Memory Via)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
0.000 400.0 800.0 1200.0 1600.0
Probe 3:C7.1 (at pin)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_41_070907
Figure 7-41: QDRII Write Correlation - Eye Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
82 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 83

Signal Integrity Correlation Results
R
UG199_c7_42_071107
Figure 7-42: QDRII Write HW Measurement - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (QDRII Memory Via)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
Probe 3:C7.1 (at pin)
-100.0
110.000 120.000 130.000 140.000 150.000 160.000
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_43_071007
Figure 7-43: QDRII Write Correlation - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 83
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 84
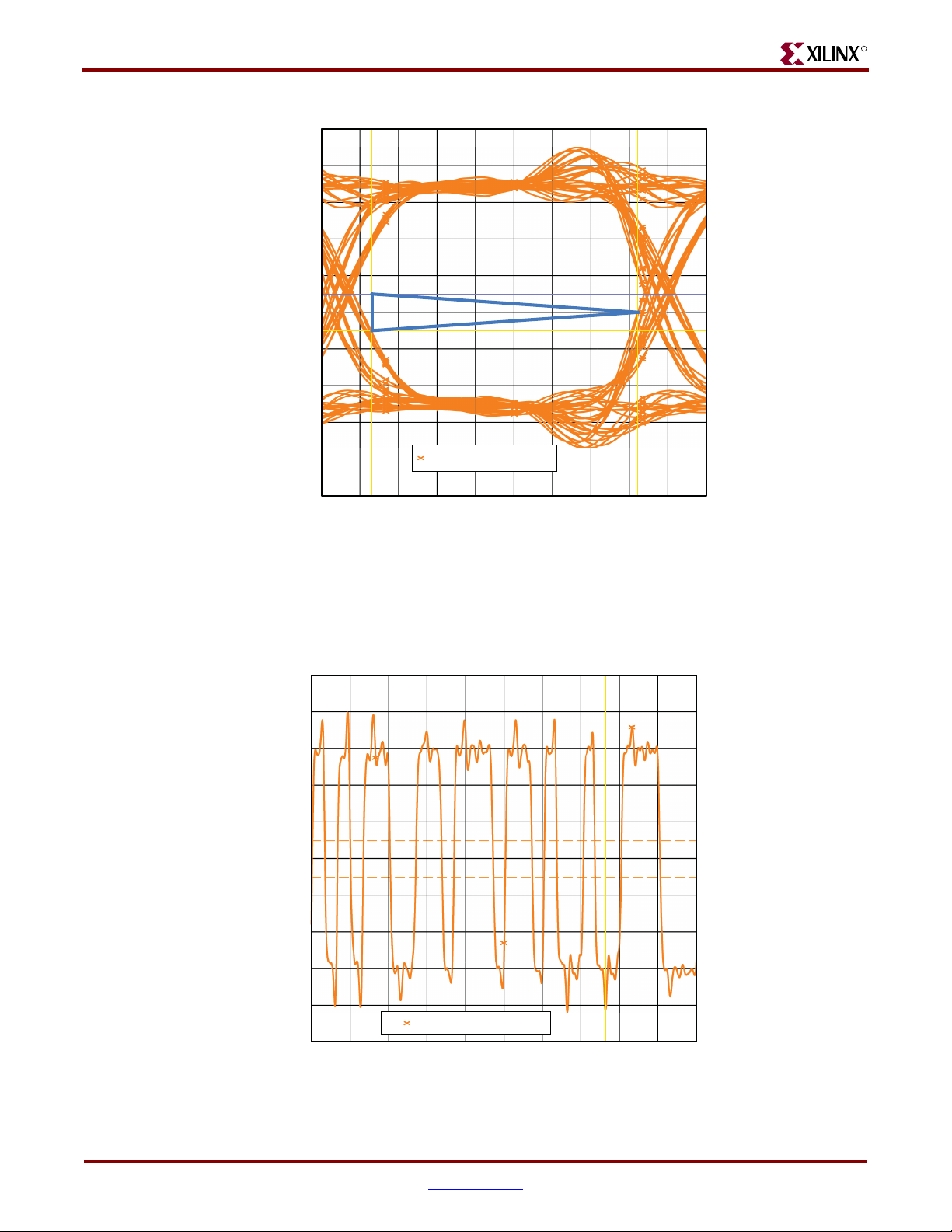
Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
♦ 300 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 83% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 699.1 mV, 61.3 ps
♦ Cursor 2: 801.0 mV, 1.4433 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 101.9 mV, Delta Time = 1.3820 ns (83% UI)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
0.000 400.0 800.0 1200.0 1600.0
Probe 6:U35.G11 (at die)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_44_070907
Figure 7-44: QDRII Write Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
110.000 120.000 130.000 140.000 150.000 160.000
Figure 7-45: QDRII Write Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
84 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
Probe 6:U35.G11 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_45_071007
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 85

R
3100.0
♦ 300 MHz, Fast, PRBS6, 89% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 699.1 mV, 1.1440 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 801.0 mV, 2.6334 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 101.9 mV, Delta Time = 1.4894 ns (89% UI)
2600.0
2100.0
1600.0
1100.0
600.0
Voltage (mV)
100.0
-400.0
-900.0
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
-1400.0
-1900.0
800.0 1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0 2800.0
Probe 6:U35.G11 (at die)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_46_070907
Figure 7-46: QDRII Write Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
3400.0
2900.0
2400.0
1900.0
1400.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
400.0
-100.0
-600.0
-1100.0
-1600.0
110.000 120.000 130.000 140.000 150.000 160.000
Figure 7-47: QDRII Write Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 85
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Probe 6:U35.G11 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_47_070907
Page 86

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
Virtex-5 FPGA
QDR2_Q_BY0_B5
U34.G33
28.5 ohms
4.473 ps
0.028 in
QDR2_Q_BY0_B5
49.1 ohms
95.834 ps
0.613 in
QDR2_Q_BY0_B5
28.5 ohms
4.404 ps
0.027 in
QDR2_Q_BY0_B5
49.1 ohms
427.654 ps
2.737 in
QDR2_Q_BY0_B5
71.6 ohms
22.319 ps
AutoPadstk_3
71.8 ohms
22.319 ps
AutoPad...
TL1 TL2
TL3
TL6 TL7 TL8
22.9 fF
96.3 fF 500.0 fF
513.2 fF
C7
QDR2_Q...
QDR2_Q...
QDR2_Q...
96.3 fF
QDR2_Q...
22.9 fF
QDR2_Q...
U35.F11
UG199_c7_48_071907
K7R323684M_1.8V
C5
QDRII Read Operation
This subsection shows the test results for the QDR2_Q_BY0_B5 signal from QDRII
memory (U35) to FPGA3 (U34) measured at 300 MHz (600 Mb/s), where the unit interval
(UI) = 1.67 ns.
Figure 7-48: Post-Layout IBIS Schematics of QDRII Read Data Bit (QDR2_Q_BY0_B5)
Table 7-13: Circuit Elements of QDRII Read Data Bit (QDR2_Q_BY0_B5)
Element Designation Description
Driver U36.F11 QDRII memory
Receiver U34.G33 FPGA HSTL_I_DCI_18
Probe Point C7 Via under FPGA3 (U34)
PCB Termination None DCI at FPGA
Trace Length TL 1, 3, 6, 8 3.41 inches
Table 7-14: QDRII Read Operation Correlation Results
Measurement
Hardware at probe point
Simulation correlation
slow-weak corner
Correlation Delta:
HW vs. Simulation
Extrapolation at IOB
slow-weak corner
DVW
(% UI)
1.09 ns
(65.4%)
984 ps
(59.0%)
106 ps
(6.4%)
1.46 ns
(88%)
(70 + 50) = 120 ps (7.2%)
(72 + 75) = 147 ps (8.8%)
(49 + 36) = 85 ps (5.1%)
ISI
(% UI)
27 ps (1.6%) 386 mV (31.8%) 50 mV (5.6%)
Noise Margin
(VIH + VIL) = Total
(% of VREF)
(400 + 400) = 800 mV
(88.9%)
(250 + 264) = 514 mV
(57.1%)
(237 + 272) = 509 mV
(56.5%)
Overshoot / Undershoot
Margin
(% of VREF)
(500 + 500) = 1000 mV
(111.1%)
(532 + 518) = 1050 mV
(105.5%)
(608 + 575) = 1183 mV
(131.5%)
Extrapolation at IOB
fast-strong corner
86 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
1.45 ns
(87%)
(27 + 39) = 66 ps (4.0%)
(341 +201) = 542 mV
(60.3%)
(532 + 661) = 1193 mV
(132.6%)
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 87
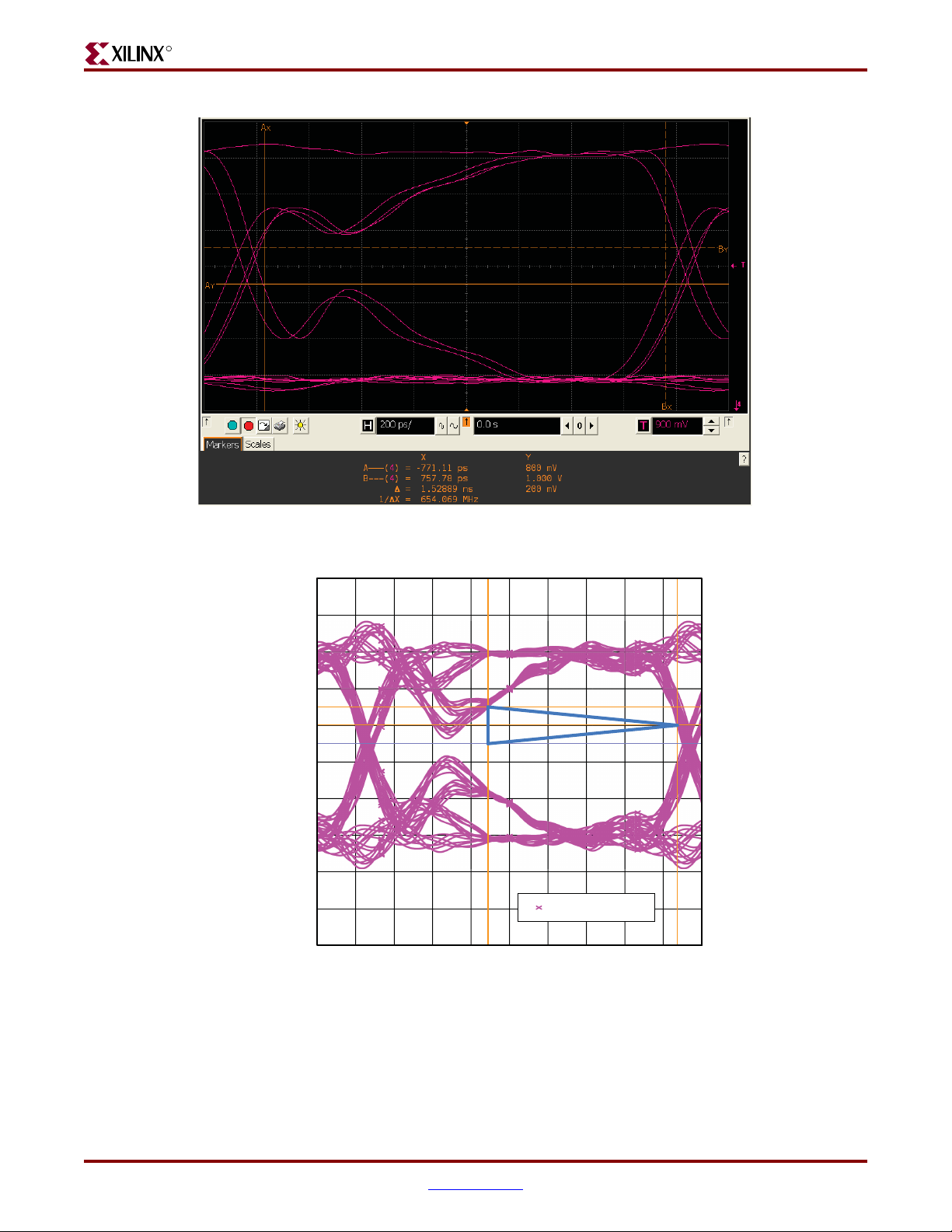
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
R
UG199_c7_49_071107
♦ 300 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 59% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.1007V, 1.4881 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 1.0029V, 2.4719 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 97.9 mV, Delta Time = 983.8 ps (59% UI)
Figure 7-49: QDRII Read HW Measurement - Eye Diagram Scope Shot at Probe Point (FPGA3 Via)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
800.0 1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0
Time (ps)
Probe 3:C7.1 (at pin)
UG199_c7_50_070907
Figure 7-50: QDRII Read Correlation - Eye Diagram Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 87
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 88
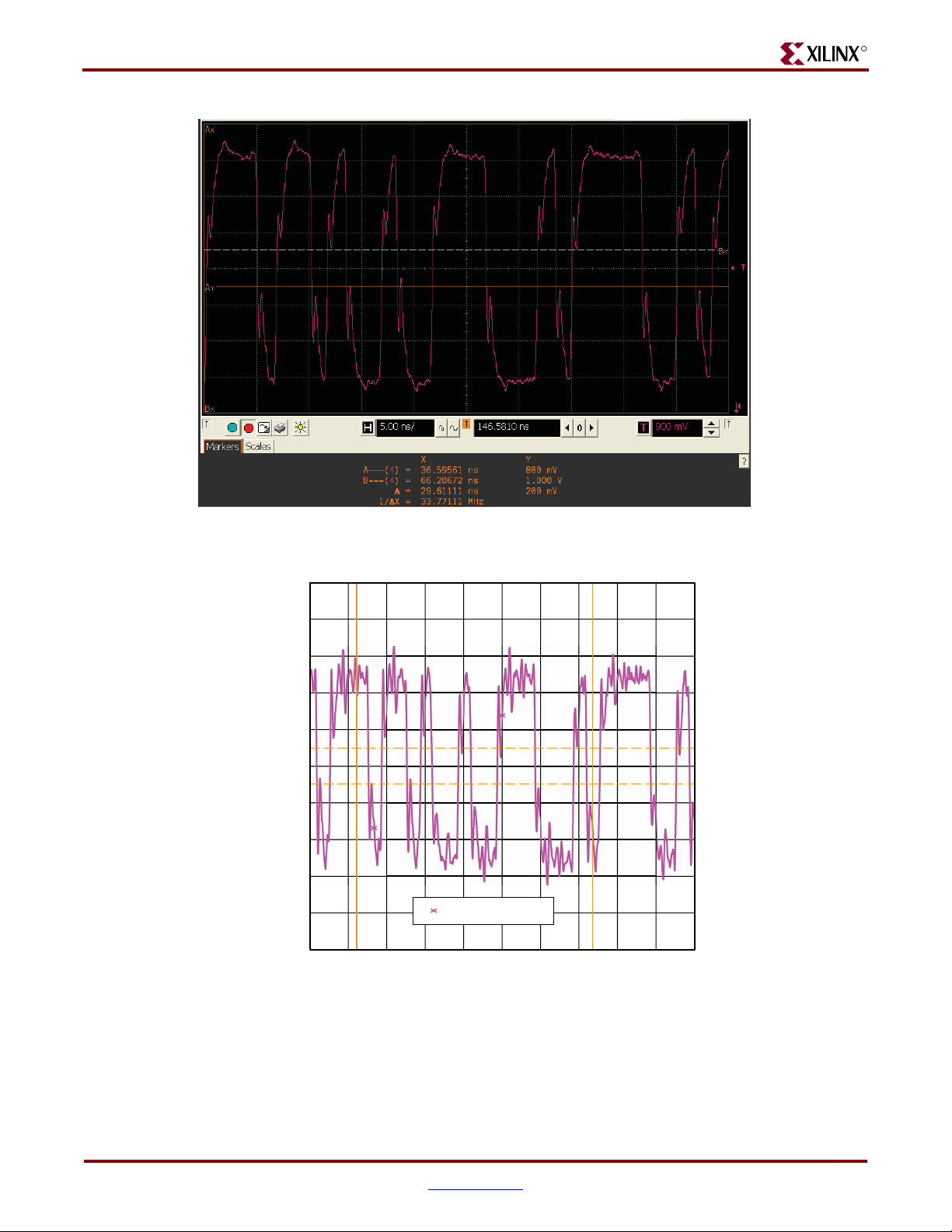
Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
UG199_c7_51_071107
Figure 7-51: QDRII Read HW Measurement - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (FPGA3 Via)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
20.000 30.000 40.000 50.000 60.000 70.000
Probe 3:C7.1 (at pin)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_52_071007
Figure 7-52: QDRII Read Correlation - Waveform Scope Shot at Probe Point (Slow Corner)
88 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 89

R
1800.0
♦ 300 MHz, Slow, PRBS6, 88% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 1.1008V, 1.2758 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 998.9 mV, 2.7352 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 101.9 mV, Delta Time = 1.4594 ns (88% UI)
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
Signal Integrity Correlation Results
0.000
-200.0
1000.0 1400.0 1800.0 2200.0 2600.0
Probe 6:U34.G33 (at die)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_53_070907
Figure 7-53: QDRII Read Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
30.000 40.000 50.000 60.000 70.000
Figure 7-54: QDRII Read Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Slow Corner
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 89
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Probe 6:U34.G33 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_54_071007
Page 90

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
♦ 300 MHz, Fast, PRBS6, 87% UI
♦ Cursor 1: 801 mV, 2.7263 ns
♦ Cursor 2: 697.0 mV, 1.2744 ns
♦ Delta Voltage = 104.0 mV, Delta Time = 1.4519 ns (87% UI)
1800.0
1600.0
1400.0
1200.0
1000.0
800.0
Voltage (mV)
600.0
400.0
200.0
0.000
-200.0
1200.0 1600.0 2000.0 2400.0 2800.0
Probe 6:U34.G33 (at die)
Time (ps)
UG199_c7_55_070907
Figure 7-55: QDRII Read Extrapolation - Eye Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
1900.0
1700.0
1500.0
1300.0
1100.0
900.0
Voltage (mV)
700.0
500.0
300.0
100.0
-100.0
25.000 35.000 45.000 55.000 65.000 75.000
Probe 6:U34.G33 (at die)
Time (ns)
UG199_c7_56_071007
Figure 7-56: QDRII Read Extrapolation - Waveform Scope Shot at Receiver IOB (Fast Corner)
90 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 91

R
Summary and Recommendations
The first objective of this exercise is to establish correlation between hardware
measurements and the simulation at the probe point. The intention was to validate the
simulation model for the targeted signal. The degree of correlation achieved is looked at in
terms of absolute difference as well as relative percentage. The relative percentage
differences are presented in terms of unit interval (UI) for timing characteristics and in
terms of VREF voltage for the voltage margin characteristics.
Correlation simulation is performed under ideal conditions, that is, the stimulus is
generated without any jitter. On the other hand, the hardware measurements are subject to
jitter (which tends to increase ISI), board-level power fluctuation (which can affect the eye
amplitude), and stability of the probing station. Thus some correlation differences are
expected. The user ultimately uses his or her own judgment to account for these
differences, and adjusts the values extrapolated for quality of signal at the receiver IOB.
Tab le 7 -1 5 contains this information for all six test signals.
Table 7-15: Summary of Correlation Differences: Hardware vs. Simulation
Summary and Recommendations
Overshoot /
Undershoot Margin
(% VREF)
69 mV
(7.6%)
244 mV
(17.2%)
2 mV
(0.3%)
208 mV
(23.1%)
85 mV
(9.4%)
50 mV
(5.6%)
)
ΔISI
(% UI)
47 ps
(3.2%)
43 ps
(2.9%)
366 ps
(24.5%)
44 ps
(2.9%)
107 ps
(6.4%)
27 ps
(1.6%)
Operation
DDR2 Component Write
DDR2 Component Read
DDR2 DIMM Write
DDR2 DIMM Read
QDRII Write
QDRII Read
Notes:
1. Unit Interval (UI): 1.5 ns for DDR2 and 1.67 ns for QDRII. VREF = 0.9V for DDR2 and QDRII.
ΔDVW
(% UI
40 ps
(2.6%)
0 ps
(0%)
218 ps
(14.5%)
39 ps
(2.6%)
10 ps
(0.6%)
106 ps
(6.4%)
(1)
Noise Margin
(% VREF)
98 mV
(10.9%)
6 mV
(0.7%)
112 mV
(12.6%)
90 mV
(10.0%)
2 mV
(0.3%)
386 mV
(31.8%)
There are varying degrees of correlation differences among the six test signals. In general,
there is a good match between hardware measurements and the correlation simulation,
except for some yet-to-be analyzed differences, for example, DDR2 DIMM Write DVW and
QDRII read noise margin.
The remainder of this section summarizes the extrapolation results of the data bit interface
for all six memory operations on the ML561 board. The measure of SI characteristics of
each signal is determined by the worst-case extrapolation measurement from among the
simulations with drivers at slow-weak and fast-strong corners. The values chosen between
these two corner cases are:
• Minimum of DVW, noise margin, and overshoot/undershoot margin
• Maximum of ISI
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 91
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 92

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
Tab le 7 -1 6 summarizes the extrapolated SI characteristics of all six test signals.
Table 7-16: Summary of Worst-Case SI Characteristics
Overshoot /
Undershoot Margin
(% VREF)
685 mV
(76.1%)
349 mV
(38.9%)
981 mV
(109.0%)
989 mV
(109.9%)
186 mV
(20.7%)
1183 mV
(131.5%)
Operation
DDR2 Component Write
DDR2 Component Read
DDR2 DIMM Write
DDR2 DIMM Read
QDRII Write
QDRII Read
ΔDVW
(% UI)
1.27 ns
(84%)
1.29 ns
(86%)
1.23 ns
(82%)
1.23 ns
(82%)
1.38 ns
(83%)
1.45 ns
(87%)
ΔISI
(% UI)
127 ps
(8.5%)
178 ps
(11.9%)
117 ps
(7.8%)
224 ps
(14.9%)
313 ps
(18.8%)
85 ps
(5.1%)
Noise Margin
(% VREF)
570 mV
(63.3%)
867 mV
(96.3%)
253 mV
(28.1%)
546 mV
(60.7%)
687 mV
(76.3%)
509 mV
(56.5%)
Here are some observations about extrapolated SI characteristics among these test signals:
• The Data Valid Window (DVW) values already account for the degradation caused by
ISI due to the PRBS6 test pattern. For timing analysis, two values need to be taken into
consideration appropriately. For a PRBS6 test pattern, the worst-case DVW value
(after discounting for ISI) is 82% UI for DDR2 DIMM operations.
• DDR2 write operations, as compared to QDRII write operations, have a lower noise
margin due to the always on nature of the DCI termination on the DQ signal for the
SSTL18_II_DCI I/O standard at the FPGA. Consequently, the overshoot/undershoot
margin for DDR2 write operations is higher than for QDRII write operations. The
DDR2 DIMM write operation has the lowest VIL noise margin of 107 mV.
• For read operations, the sum of VIH and VIL noise margins beyond the AC value
specifications is at least 509 mV (56.6% of VREF). QDRII read operations have the
lowest VIL noise margin of 201 mV.
• All six signals have positive values for overshoot and undershoot margins. QDRII
write operations have the lowest undershoot margin value of 30 mV.
(For Tabl e 5 -1, p age 48 through Ta ble 5- 5 , pa g e 49, the recommendations remain the same
except for a clarification for DDR2 ODT as “75 ohm ODT”.)
92 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 93

How to Generate a User-Specific FPGA IBIS Model
R
How to Generate a User-Specific FPGA IBIS Model
The following steps indicate how to generate an IBIS model:
1. Under ISE, open your fully compiled project.
2. Go to the Tcl S he l l tab, and issue an ibiswriter command as:
ibiswriter –allmodels <your top level project design file>.ncd <name up
to 24 lowercase characters>.ibs ;
For example, ibiswriter –allmodels mem_interface_top.ncd
ml561_fpga3_u34.ibs
3. Unzip the Virtex-5 FPGA IBIS models ZIP file located at the Xilinx
Download Center
(under the “Device Models” sidebar link). Then unzip the ZIP file containing the
device package files and extract a package file for your device, for example,
ff1136_5vlx50t.pkg. Place this file in the same directory as the FPGA IBIS file (for
example, ml561_fpga3_u34.ibs).
4. Open the ml561_fpga3_u34.ibs file generated by ibiswriter in HyperLynx Visual
IBIS Editor. Check the file for correctness by clicking on the check (9) button in the top
toolbar. Warnings are okay.
5. Open the ff1136_5vlx50t.pkg file using a text editor and locate the [Define
Package Model] line. Copy and paste this line into the ml561_fpga3_u34.ibs file
just above the line with the [Package] declaration. Edit the copied line to change
[Define Package Model] to [Package Model].
6. Again, check the file for correctness by clicking on the check (9) button in the top
toolbar. Multiple errors will appear. The package model file defines I/O definitions for
all usable pins, but now ibiswriter only declares pins defined under the UCF. Thus
errors are displayed for all the undefined pins, for example:
ERROR - Pin 'AK9' found in Package_Model 'ff1136_xc5vlx50t_fga0106_dc' Pin_Numbers
list not found in Component 'VIRTEX-5' Pin list.
7. Copy all these errors into a text file with a .txt file type.
♦ Open this text file with Excel and provide the delimiter as (‘), which puts all the
unused pin names in one column. Delete all other columns before and after the
one with the pin names.
♦ In column 2, fill in Unused_IO for all pins.
♦ In column 3, fill in the name of one of the I/O standards defined under the
[Model] section of the ml561_fpga3_u34.ibs file, for example,
LVCMOS25_S_12. Choose a name that is not an output only standard, because it
might conflict with other outputs in the same bank.
♦ Right-justify the indentation for all three columns and make sure that each
column is wider by a few spaces than the longest string in that column.
♦ Save this file with the Save As command in Excel using the Formatted Text (space
delimited) (*.prn) option to create a text file with text columns separated by
spaces. (The IBIS checker gives a warning if the .ibs file contains tabs.)
8. Open the .prn file with a text editor and copy all these lines to the .ibs file at the end
of the [Pin] definitions section (just above the [Diff Pin] declarations).
9. Check (9) the .ibs file again. There should not be any errors. Again, warnings are
okay.
10. The result is an accurate custom-made IBIS model of a Virtex-5 device specific to your
design.
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 93
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 94

Chapter 7: ML561 Hardware-Simulation Correlation
R
94 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 95

R
FPGA Pinouts
This appendix provides the pinouts for the three FPGAs on the Virtex-5 FPGA ML561
Development Board. The toolkit CD shipped with every ML561 contains sample UCFs for
each memory interface. These UCFs are for pinout reference only and do not include other
constraints, like I/O standards.
FPGA #1 Pinout
Tab le A -1 lists the connections for FPGA #1 (U7).
Table A-1: FPGA #1 Pinout
Signal Name Pin Signal Name Pin
DDR1_A0 M32 DDR1_CK1_N AJ34
Appendix A
DDR400 Component Interface
DDR1_A1 L33 DDR1_CK1_P AH34
DDR1_A10 E33 DDR1_CK2_N AE34
DDR1_A11 E32 DDR1_CK2_P AF34
DDR1_A12 E34 DDR1_CKE AC34
DDR1_A13 F33 DDR1_LB_BK11 N32
DDR1_A2 K32 DDR1_LB_BK11 P32
DDR1_A3 K34 DDR1_LB_BK13 AJ32
DDR1_A4 L34 DDR1_LB_BK13 AK32
DDR1_A5 J34 DDR1_RAS_N AB32
DDR1_A6 H34 DDR1_WE_N AD34
DDR1_A7 H33 DDR1_DM_BY0 AG32
DDR1_A8 F34 DDR1_DM_BY1 Y32
DDR1_A9 G33 DDR1_DM_BY2 P34
DDR1_BA0 AK33 DDR1_DM_BY3 G32
DDR1_BA1 AK34 DDR1_DQ_BY0_B0 AP32
DDR1_BY0_1_CS_N AB33 DDR1_DQ_BY0_B1 AN32
DDR1_BY2_3_CS_N AC33 DDR1_DQ_BY0_B2 AN33
DDR1_CAS_N AC32 DDR1_DQ_BY0_B3 AN34
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 95
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 96
Appendix A: FPGA Pinouts
R
Table A-1: FPGA #1 Pinout (Continued)
Signal Name Pin Signal Name Pin
DDR400 Component Interface (cont.)
DDR1_DQ_BY0_B4 AM32 DDR1_DQ_BY2_B4 R32
DDR1_DQ_BY0_B5 AM33 DDR1_DQ_BY2_B5 R33
DDR1_DQ_BY0_B6 AL33 DDR1_DQ_BY2_B6 R34
DDR1_DQ_BY0_B7 AL34 DDR1_DQ_BY2_B7 T33
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B0 Y34 DDR1_DQ_BY3_B0 D34
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B1 AA34 DDR1_DQ_BY3_B1 C34
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B2 AA33 DDR1_DQ_BY3_B2 D32
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B3 Y33 DDR1_DQ_BY3_B3 C32
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B4 V34 DDR1_DQ_BY3_B4 C33
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B5 W34 DDR1_DQ_BY3_B5 B33
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B6 V33 DDR1_DQ_BY3_B6 A33
DDR1_DQ_BY1_B7 V32 DDR1_DQ_BY3_B7 B32
DDR1_DQ_BY2_B0 U31 DDR1_DQS_BY0_P AD32
DDR1_DQ_BY2_B1 U32 DDR1_DQS_BY1_P AF33
DDR1_DQ_BY2_B2 T34 DDR1_DQS_BY2_P K33
DDR1_DQ_BY2_B3 U33 DDR1_DQS_BY3_P J32
DDR2 Component Interface
DDR2_A0 K12 DDR2_CAS_N J14
DDR2_A1 K13 DDR2_CK0_N K19
DDR2_A10 G22 DDR2_CK0_P L19
DDR2_A11 J15 DDR2_CK1_N J19
DDR2_A12 K16 DDR2_CK1_P K18
DDR2_A2 H23 DDR2_CKE K17
DDR2_A3 G23 DDR2_CS0_N H20
DDR2_A4 H12 DDR2_CS1_N H19
DDR2_A5 J12 DDR2_LB_BK15 T28
DDR2_A6 K22 DDR2_LB_BK15 T29
DDR2_A7 K23 DDR2_LB_BK19 M28
DDR2_A8 K14 DDR2_LB_BK19 N28
DDR2_A9 L14 DDR2_ODT0 H18
DDR2_BA0 K21 DDR2_ODT1 H17
DDR2_BA1 J22 DDR2_RAS_N H13
96 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 97

R
Table A-1: FPGA #1 Pinout (Continued)
Signal Name Pin Signal Name Pin
DDR2 Component Interface (cont.)
DDR2_WE_N J21 DDR2_DQ_BY2_B2 N25
DDR2_DM_BY0 U30 DDR2_DQ_BY2_B3 P25
DDR2_DM_BY1 L29 DDR2_DQ_BY2_B4 P24
DDR2_DM_BY2 K27 DDR2_DQ_BY2_B5 N24
DDR2_DM_BY3 J27 DDR2_DQ_BY2_B6 P27
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B0 T25 DDR2_DQ_BY2_B7 P26
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B1 U25 DDR2_DQ_BY3_B0 M26
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B2 T26 DDR2_DQ_BY3_B1 M25
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B3 U26 DDR2_DQ_BY3_B2 J25
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B4 R27 DDR2_DQ_BY3_B3 J24
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B5 R26 DDR2_DQ_BY3_B4 L26
FPGA #1 Pinout
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B6 U28 DDR2_DQ_BY3_B5 L25
DDR2_DQ_BY0_B7 U27 DDR2_DQ_BY3_B6 L24
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B0 E31 DDR2_DQ_BY3_B7 K24
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B1 F31 DDR2_DQS_BY0_N N30
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B2 J29 DDR2_DQS_BY0_P M31
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B3 H29 DDR2_DQS_BY1_N P29
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B4 F30 DDR2_DQS_BY1_P N29
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B5 G30 DDR2_DQS_BY2_N E27
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B6 F29 DDR2_DQS_BY2_P E26
DDR2_DQ_BY1_B7 E29 DDR2_DQS_BY3_N H27
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B0 T24 DDR2_DQS_BY3_P G27
DDR2_DQ_BY2_B1 23 R24
FPGA #1 Clock and Reset Signals
CLK_TO_FPGA1_MGT_116_N H3 DIRECT_CLK_TO_FPGA1_P AG22
CLK_TO_FPGA1_MGT_116_P H4 EXT_CLK_TO_FPGA1_N AG13
CLK_TO_FPGA1_MGT_118_N AF3 EXT_CLK_TO_FPGA1_P AH12
CLK_TO_FPGA1_MGT_118_P AF4 FPGA1_LOW_FREQ_CLK AH20
DIRECT_CLK_TO_FPGA1_N AH22 FPGA1_RESET_N AH14
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 97
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 98

Appendix A: FPGA Pinouts
R
Table A-1: FPGA #1 Pinout (Continued)
Signal Name Pin Signal Name Pin
FPGA #1 MII Link Interface
FPGA2_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_CLK J10 FPGA3_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_CLK D10
FPGA2_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_DATA0 C13 FPGA3_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_DATA0 H10
FPGA2_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_DATA1 B13 FPGA3_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_DATA1 C12
FPGA2_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_DATA2 K9 FPGA3_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_DATA2 D12
FPGA2_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_DATA3 K8 FPGA3_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_DATA3 J11
FPGA2_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_EN L11 FPGA3_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_EN A13
FPGA2_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_ERR L10 FPGA3_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_ERR H9
FPGA2_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_SPARE J9 FPGA3_TO_FPGA1_MII_TX_SPARE K11
FPGA #1 Configuration Signals
FPGA_INIT N14 FPGA1_D_IN P15
FPGA_PROGB M22 FPGA1_DONE M15
FPGA_TMS AC14 FPGA1_DOUT_B AD15
FPGA_VBATT L23 FPGA1_HSWAPEN M23
FPGA1_CCLK N15 FPGA1_TCK AB15
FPGA1_CNFG_M0 AD21 FPGA1_TDI_IN AC15
FPGA1_CNFG_M1 AC22 FPGA1_TDO 15 AD14
FPGA1_CNFG_M2 AD22
FPGA #1 Test and Debug Signals
FPGA1_DIP0 AG18 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B6 E8
FPGA1_DIP1 AG15 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B7 E9
FPGA1_DIP2 AH15 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B0 E12
FPGA1_DIP3 AG20 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B1 L9
FPGA1_SPYHOLE_BK21 AF26 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B2 M10
FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B0 H8 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B3 E11
FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B1 G8 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B4 F11
FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B2 G10 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B5 L8
FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B3 F10 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B6 M8
FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B4 F8 FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY1_B7 G12
FPGA1_TEST_HDR_BY0_B5 F9
98 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 99

R
Table A-1: FPGA #1 Pinout (Continued)
Signal Name Pin Signal Name Pin
FPGA1_7SEG_0_N AG17 FPGA1_7SEG_6_N AF19
FPGA1_7SEG_1_N AH18 FPGA1_7SEG_DP_N AG21
FPGA1_7SEG_2_N AE18 FPGA1_LED0 AD19
FPGA1_7SEG_3_N AF18 FPGA1_LED1 AE19
FPGA1_7SEG_4_N AG16 FPGA1_LED2 AE17
FPGA1_7SEG_5_N AH17 FPGA1_LED3 AF16
FPGA1_LCD_BL_ON M6 FPGA1_LCD_E M5
FPGA1_LCD_CSB M7 FPGA1_LCD_R_WB N8
FPGA1_LCD_DB0 K6 FPGA1_LCD_RESET_N L6
FPGA1_LCD_DB1 K7 FPGA1_LCD_RS N7
FPGA #1 Pinout
FPGA #1 Test Display Signals
FPGA #1 External Interfaces
FPGA1_LCD_DB2 P6 FPGA1_RS232_CTS R11
FPGA1_LCD_DB3 P7 FPGA1_RS232_RTS G5
FPGA1_LCD_DB4 L5 FPGA1_RS232_RX P9
FPGA1_LCD_DB5 L4 FPGA1_RS232_TX H5
FPGA1_LCD_DB6 P5 FPGA1_TXN0_BK124 B9
FPGA1_LCD_DB7 N5 FPGA1_TXP0_BK124 B10
FPGA1_USB_CTS_N G6 FPGA1_USB_RTS_N G7
FPGA1_USB_DSR_N E6 FPGA1_USB_RX T9
FPGA1_USB_DTR_N E7 FPGA1_USB_SUSPEND T11
FPGA1_USB_RST_N T10 FPGA1_USB_TX U10
FPGA #1 Voltage Margining Interface
VMARGIN_DN_3V3_N AE22 VMARGIN_UP_3V3_N AE23
VMARGIN_DN_HSTL_N AE13 VMARGIN_UP_HSTL_N AE12
VMARGIN_DN_SSTL18_N AF13 VMARGIN_UP_SSTL18_N AG12
VMARGIN_DN_SSTL2_N AF23 VMARGIN_UP_SSTL2_N AG23
VMARGIN_DN_VCC1V0_N AF20 VMARGIN_UP_VCC1V0_N AF21
VMARGIN_DN_VCC2V5_N AE14 VMARGIN_UP_VCC2V5_N AF14
Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide www.xilinx.com 99
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
Page 100

Appendix A: FPGA Pinouts
R
FPGA #2 Pinout
Tab le A -2 lists the connections for FPGA #2 (U5).
Table A-2: FPGA #2 Pinout
Signal Name Pin Signal Name Pin
DDR2_DIMM_A0 AG30 DDR2_DIMM1_CK0_N M26
DDR2_DIMM_A1 AH29 DDR2_DIMM1_CK0_P M25
DDR2_DIMM_A10 AF31 DDR2_DIMM1_CK1_N J25
DDR2_DIMM_A11 AC29 DDR2_DIMM1_CK1_P J24
DDR2_DIMM_A12 AD30 DDR2_DIMM1_CK2_N L26
DDR2_DIMM_A13 AA30 DDR2_DIMM1_CK2_P L25
DDR2_DIMM_A14 AA29 DDR2_DIMM1_CKE0 G28
DDR2_DIMM_A15 AC30 DDR2_DIMM1_CKE1 H28
DDR2_DIMM_A2 AH30 DDR2_DIMM1_CS0_N V27
DDR2 DIMM Deep Interface
DDR2_DIMM_A3 AJ30 DDR2_DIMM1_CS1_N V28
DDR2_DIMM_A4 AF30 DDR2_DIMM1_ODT0 H24
DDR2_DIMM_A5 AF29 DDR2_DIMM1_ODT1 H25
DDR2_DIMM_A6 AK31 DDR2_DIMM2_CK0_N AF26
DDR2_DIMM_A7 AJ31 DDR2_DIMM2_CK0_P AF25
DDR2_DIMM_A8 AD29 DDR2_DIMM2_CK1_N AG25
DDR2_DIMM_A9 AE29 DDR2_DIMM2_CK1_P AF24
DDR2_DIMM_BA0 AB30 DDR2_DIMM2_CK2_N AJ26
DDR2_DIMM_BA1 AA31 DDR2_DIMM2_CK2_P AH27
DDR2_DIMM_BA2 AB31 DDR2_DIMM2_CKE0 AE24
DDR2_DIMM_CAS_N V29 DDR2_DIMM2_CKE1 AD24
DDR2_DIMM_LB_BK11_IN P32 DDR2_DIMM2_CS0_N W27
DDR2_DIMM_LB_BK11_OUT H33 DDR2_DIMM2_CS1_N Y27
DDR2_DIMM_LB_BK13_IN AJ32 DDR2_DIMM2_ODT0 AE26
DDR2_DIMM_LB_BK13_OUT AK32 DDR2_DIMM2_ODT1 AE27
DDR2_DIMM_LB_BK15_IN T28 DDR2_DIMM3_CK0_N AA24
DDR2_DIMM_LB_BK15_OUT T29 DDR2_DIMM3_CK0_P Y24
DDR2_DIMM_RAS_N Y28 DDR2_DIMM3_CK1_N AC27
DDR2_DIMM_RESET_N Y29 DDR2_DIMM3_CK1_P AB27
DDR2_DIMM_WE_N W29 DDR2_DIMM3_CK2_N AA26
100 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA ML561 User Guide
UG199 (v1.2) April 19, 2008
 Loading...
Loading...